Yadava Dynasty
- 02 Mar 2026
In News:
- Recently, remains of a 12th-century Mandir-style stone pillar associated with the Seuna (Yadava) dynasty were discovered along the Vena River in Hinganghat, Wardha district, Maharashtra.
- The find highlights the architectural and cultural legacy of the Yadavas in the Deccan region and provides material evidence of medieval temple construction traditions in central India.
About the Yadava (Seuna) Dynasty
The Yadava Dynasty, also known as the Seuna Dynasty, ruled a powerful Hindu kingdom in the Deccan between the 12th and 14th centuries CE.
Territorial Extent
At its peak, the Yadava kingdom extended:
- From the River Tungabhadra in the south
- To the River Narmada in the north
- Covering present-day Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, and parts of Madhya Pradesh
Political Evolution
Early Phase
- Initially feudatories of the Western Chalukyas of Kalyani.
- Rose to prominence under Bhillama V (c. 1187–1191 CE).
- Founded Devagiri (later Daulatabad) as the capital.
Zenith under Singhana (c. 1210–1247 CE)
- Grandson of Bhillama.
- Declared independence.
- Conducted military campaigns against:
- Hoysalas (South)
- Kakatiyas (East)
- Paramaras and Chalukyas (North)
This period marked the territorial and political high point of the dynasty.
Decline and Annexation
- During the reign of Ramachandra (1271–c. 1309 CE):
- In 1294, Alauddin Khalji invaded Devagiri.
- The Yadava kingdom was reduced to tributary status under the Delhi Sultanate.
- A later attempt to assert independence failed.
- In 1317, the kingdom was fully annexed by the Khalji Empire.
This marked the beginning of stronger Delhi Sultanate penetration into the Deccan.
Cultural and Architectural Contributions
1. Foundations of Marathi Culture
- The Yadavas played a crucial role in shaping early Marathi language and literature.
- Social and cultural institutions of Maharashtra evolved significantly during their rule.
2. Hemadpanti Architecture: The dynasty is closely associated with the Hemadpanti style, attributed to minister Hemadri (Hemadpant).
Key Features:
- Construction using large blocks of black stone
- Dry masonry technique (without mortar)
- Massive, durable structures
- Temple-oriented architectural designs
Numerous temples in Maharashtra are built in this style.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- 24 Feb 2026
In News:
India has recorded unprecedented progress in organ donation and transplantation:
- Transplants increased fourfold:
- < 5,000 (2013) → ~20,000 (2025)
- 18% of transplants now from deceased donors.
- 1,200 families donated organs of loved ones in 2025.
- 4.8 lakh citizens registered for posthumous organ donation via Aadhaar-based verification system (since 17 September 2023).
- India leads globally in hand transplants and performs the highest number worldwide.
- High competence in complex transplants: Heart, Lung, Pancreas.
About NOTTO
Establishment
- Set up under the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS).
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Located in New Delhi.
- Mandated by the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues (Amendment) Act, 2011.
Organizational Structure
NOTTO comprises two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network
- National Biomaterial Centre
It functions as the apex coordinating centre for organ procurement, allocation, and data registry across India.
Core Functions
1. Coordination & Allocation
- National-level coordination of organ procurement and distribution.
- Facilitates inter-state sharing of organs.
- Ensures equitable and transparent allocation.
2. National Registry
- Maintains and publishes the National Organ & Tissue Transplant Registry.
- Compiles data from States and Regions.
- Maintains transplant surveillance and databank.
3. Policy & Protocols
- Frames guidelines and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
- Aligns transplant systems with global best practices.
4. Capacity Building
- Strengthens:
- SOTTOs (State Organ & Tissue Transplant Organizations)
- ROTTOs (Regional Organ & Tissue Transplant Organizations)
- Assists States in data management and transplant monitoring.
5. Public Awareness
- Promotes deceased organ donation.
- Engages youth, institutions, Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Encourages multiorgan donation as a family choice.
Government Reforms Strengthening NOTTO
- Real-time digital organ allocation system.
- Expansion & modernization of National Registry.
- Promotion of Green Corridors for rapid organ transport.
- Aadhaar-based donor registration.
- Enhanced hospital connectivity and digital integration.
These measures have reduced logistical barriers and improved clinical outcomes.
Titanidiops Kolhapurensis

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A new species of trapdoor spider, Titanidiops kolhapurensis, has been discovered in the grasslands of Kolhapur district.
About Titanidiops kolhapurensis
- Habitat: Flat or gently sloping grassy meadows.
- Burrow structure: Constructs vertical or slanted burrows with entrances expertly camouflaged to blend with surrounding soil, making them nearly invisible.
- Distribution pattern: Found in native grasslands and natural forests, but absent in areas dominated by exotic plantations such as Gliricidia sepium (Undirmari).
- Conservation concern: On the verge of local extinction due to rapid habitat degradation and land-use change.
What are Trapdoor Spiders?
- A group of large-bodied, burrowing spiders found across several taxonomic families.
- Burrowing behaviour: Dig burrows up to 15 cm (6 inches) deep, sealed with a silken-hinged trapdoor.
- Feeding strategy: Ambush predators—rapidly open the door to seize passing insects or arthropods.
- Behaviour: Reclusive and timid; retreat quickly into burrows when disturbed.
- Human impact: Bite not medically significant to humans.
- Climate preference: Tropical, subtropical and warm regions.
- Size: Typically ~2.5 cm (1 inch) long; some species up to 4 cm (1.5 inches).
- Threats: Predation by spider-hunting wasps; low dispersal ability (juveniles remain close to maternal burrows), making populations highly vulnerable to habitat loss.
Why this discovery matters
- Highlights the ecological importance of native grasslands, often overlooked in conservation.
- Demonstrates the negative impact of exotic tree plantations on indigenous fauna.
- Strengthens the case for habitat-specific conservation planning in the Western India landscape.
Border Roads Organisation (BRO)

- 11 Dec 2025
In News:
The Defence Minister recently dedicated 125 infrastructure projects worth about ?5,000 crore built by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO). This marks the largest single-day inauguration of projects in BRO’s history. The projects include roads, bridges, tunnels, and other strategic works in border areas such as Ladakh, Jammu & Kashmir, and other frontier states.
What is BRO?
BRO is India’s premier road construction force responsible for developing and maintaining strategic infrastructure in border areas and also in certain friendly foreign countries.
- Established: 7 May 1960
- Administrative Control: Ministry of Defence (fully under MoD since 2015)
- Parent Body: Border Roads Development Board (BRDB)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Motto:Shramena Sarvam Sadhyam (Everything is achievable through hard work)
Organisational Setup
The organisation is headed by the Director General Border Roads (DGBR), an officer of Lieutenant General rank.
Its workforce includes:
- Personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF)
- Officers and troops from the Indian Army Corps of Engineers on deputation
- Over 2 lakh local workers, providing employment in remote and border regions
Key Roles of BRO
Peace-Time Role
BRO constructs and maintains:
- Strategic border roads
- Bridges, tunnels, airfields, and other infrastructure
It plays a major role in socio-economic development by improving connectivity in remote and backward regions.
War-Time Role
During hostilities, BRO:
- Maintains and repairs roads used for troop movement
- Clears snow, landslides, and avalanches to keep supply lines open
- Supports operational requirements of the armed forces, including forward airfields
International Projects
BRO undertakes infrastructure projects in friendly countries such as:Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan, and Sri Lanka — strengthening India’s regional connectivity and diplomatic outreach.
Engineering Specialisation
BRO is known for working in extreme terrains, including:
- High-altitude Himalayan regions
- Snow-bound and glaciated zones
- Deserts and marshlands
- Seismically active areas
It uses advanced and indigenous technologies such as Class-70 modular bridges, capable of carrying heavy military equipment.
Strategic Importance
BRO is crucial for national security, as border roads enable rapid troop mobilisation along sensitive frontiers, particularly with China and Pakistan.
It also promotes:
- Economic development and tourism in border regions
- Better access to remote villages
- Disaster response during floods, earthquakes, and landslides
Shani Shingnapur Temple
- 10 Dec 2025
In News:
Two employees of the Shani Shingnapur Temple Trust were recently arrested for allegedly diverting funds by manipulating online applications used for booking pooja services, bringing the temple into the news.
Location
- Situated in Shingnapur village, Ahilyanagar (formerly Ahmednagar) district, Maharashtra
- The village itself is culturally famous for its doorless houses
Deity and Religious Significance
- Dedicated to Lord Shanidev (Shani), the Hindu deity associated with the planet Saturn
- The idol is a five-and-a-half-foot-high black stone slab
- Believed to be Swayambhu (self-manifested), not sculpted by humans
- Devotees worship Shani for relief from malefic planetary effects and life hardships
Unique Traditions of Shingnapur Village
- The village is widely known for houses without doors or locks
- The belief is that Lord Shani protects the village, and theft does not occur due to divine fear
- This tradition has made Shingnapur a symbol of faith-based social trust
Temple Architecture and Features
The Shani Shingnapur Temple is architecturally distinct:
- The idol is placed in the open, under the sky
- There is no enclosed sanctum (garbhagriha) with roof or walls over the main deity
- Devotees traditionally offer mustard oil to Lord Shani, poured over the idol from a suspended copper vessel
Other features within the temple complex include:
- A Trishul (trident) near the idol
- A Nandi statue located to the south of the idol
- Small images of Lord Shiva and Hanuman in front of the Shani idol
- A later-built east-facing multi-deity temple situated west of the Shani stone
- A samadhi (tomb) of Saint Udasi Baba
- A temple dedicated to Lord Dattatreya
Cultural and Pilgrimage Importance
- One of the most important Shani temples in India
- Attracts thousands of devotees, especially on Shani Amavasya and Saturdays
- Reflects a blend of folk belief, astrology, and devotional Hindu practices
Significance
- Represents a unique open-sky form of deity worship
- Illustrates strong links between faith and social customs (doorless homes tradition)
- An important religious and cultural landmark in Maharashtra
PM-WANI Scheme

- 08 Dec 2025
In News:
The PM-WANI Scheme, approved on 9 December 2020, is a national framework to expand public Wi-Fi access across India. It is implemented by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications, and aligns with the goals of the National Digital Communications Policy (NDCP) 2018 to create robust digital infrastructure and promote affordable broadband access.
As of November 2025, over 3.9 lakh PM-WANI Wi-Fi hotspots (Public Data Offices – PDOs) have been deployed across the country, reflecting rapid expansion of decentralized public internet access.
Objective
PM-WANI aims to:
- Democratize internet access
- Bridge the digital divide, especially in rural and underserved areas
- Encourage local entrepreneurship through small-scale Wi-Fi providers
- Support digital services such as e-governance, digital payments, telemedicine, and online education
Key Concept
PM-WANI allows small shopkeepers, entrepreneurs, and establishments to provide public Wi-Fi without needing a telecom licence, spectrum, or heavy regulatory compliance. This low-entry model makes broadband delivery affordable and scalable.
Four-Tier Architecture
- Public Data Offices (PDOs):Local entities that set up and operate Wi-Fi hotspots to provide internet access to users.
- Public Data Office Aggregators (PDOAs):They manage authentication, authorization, and accounting functions for PDOs.
- App Providers:Provide mobile/web applications through which users discover hotspots, authenticate, and access services.
- Central Registry (maintained by C-DoT):Stores details of PDOs, PDOAs, and App Providers to ensure interoperability.
Major Reforms and Features
1. Use of FTTH Connections:PDOs can now use regular Fibre-to-the-Home (FTTH) broadband connections, reducing deployment costs.
2. Aggregation of Access Points:Multiple Wi-Fi access points can share a single backhaul connection, enabling wider hotspot coverage.
3. Integration of Existing Wi-Fi Routers:Existing home and business Wi-Fi access points can join the PM-WANI ecosystem, creating additional income streams.
4. Roaming Across Networks:Users can seamlessly switch between hotspots of different PDOAs, similar to mobile network roaming.
5. Mobile Data Offload:PDOs can collaborate with telecom service providers to offload mobile data traffic onto Wi-Fi, improving network efficiency.
6. Consent-Based Communication:PDOAs and App Providers may send promotional or informational content to users only with explicit user consent, ensuring privacy safeguards.
Affordable Broadband for PDOs (TRAI Provision)
The Telecommunication Tariff (71st Amendment) Order, 2025 mandates that retail FTTH broadband plans up to 200 Mbps must be offered to PDOs at not more than twice the tariff of equivalent consumer plans, ensuring cost-effective operations.
Technology and Compliance
Hardware and software are procured by stakeholders (PDOs, PDOAs, App Providers), but all solutions must be PM-WANI compliant and certified by C-DoT as per scheme guidelines.
Significance
PM-WANI strengthens India’s Digital Public Infrastructure ecosystem alongside Aadhaar and UPI. By enabling community-based broadband delivery, it promotes digital inclusion, entrepreneurship, and last-mile connectivity, especially in remote and low-income regions.
Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2025
- 30 Nov 2025
In News:
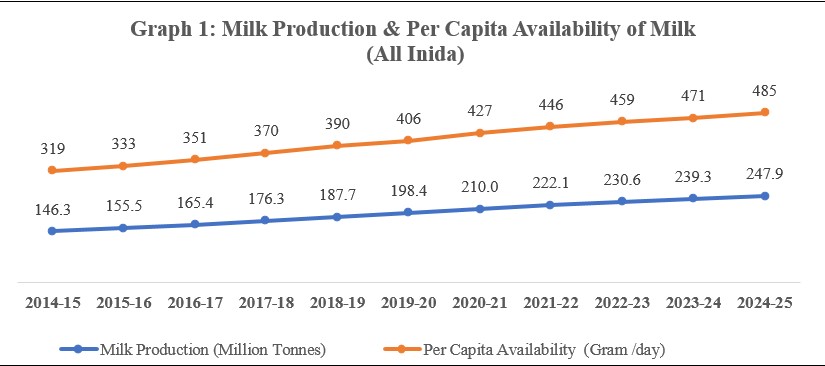
The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, in coordination with the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, released the annual publication Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics (BAHS) 2025 on National Milk Day (26 November 2025). The report presents comprehensive, state-wise data on production and per-capita availability of milk, eggs, meat and wool, based on the Integrated Sample Survey (ISS) conducted from 1 March 2024 to 29 February 2025 across three seasons—summer, rainy and winter.
Key Findings
Milk Production
- Global Rank: 1st
- Output (2024–25): 247.87 million tonnes, a 3.58% increase over 2023–24.
- Per Capita Availability: 485 g/day (up from 319 g/day in 2014–15).
- Top Producers: Uttar Pradesh (15.66%), Rajasthan (14.82%), Madhya Pradesh (9.12%), Gujarat (7.78%), Maharashtra (6.71%)—54.09% combined share.
- Growth by Source: Crossbred cattle (+4.97%), Indigenous cattle (+3.51%), Buffaloes (+2.45%).
Egg Production
- Global Rank: 2nd
- Output (2024–25): 149.11 billion eggs, 4.44% growth.
- Per Capita Availability: 106 eggs/year (up from 62 in 2014–15).
- Major Contributors: Andhra Pradesh (18.37%), Tamil Nadu (15.63%), Telangana (12.98%), West Bengal (10.72%), Karnataka (6.67%)—64.37% combined.
- Production Mix: Commercial poultry 84.49%; Backyard poultry 15.51%.
Meat Production
- Global Rank: 4th
- Output (2024–25): 10.50 million tonnes, 2.46% growth.
- Poultry Share: ~50% (5.18 million tonnes).
- Top States: West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana—57.55% combined.
Wool Production
- Output (2024–25): 34.57 million kg, 2.63% growth.
- Leading States: Rajasthan (47.85%), Jammu & Kashmir (22.88%), Gujarat, Maharashtra, Himachal Pradesh—85.98% combined.
GeM–UN Women MoU & Womaniya Initiative

- 25 Nov 2025
In News:
The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) and UN Women signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to enhance the participation of women entrepreneurs, especially from the informal sector, in India’s public procurement system under the Womaniya initiative.
About the GeM–UN Women MoU
- Purpose: Promote gender-responsive public procurement by increasing sourcing from women-led businesses.
- Focus Areas:
- Expanding market access for women entrepreneurs on GeM
- Capacity building, training, and onboarding of women-led MSEs, SHGs, artisans, and informal-sector enterprises
- Strengthening hyper-local and forward market linkages
- Implementation:
- UN Women:
- Design training modules
- Share global best practices and success stories
- Develop validation criteria for women-led businesses
- Support Womaniya – #VocalForLocal outlet, Udyam registration, and mentoring linkages
- GeM:
- Conduct training and onboarding workshops
- Sensitise government buyers
- Develop vernacular learning material
- Connect women entrepreneurs with R&D institutions and Government Labs for product development
- UN Women:
- Outcome Alignment: Contributes to Sustainable Development Goal 5 (Gender Equality).
Womaniya Initiative
- Launch: 2019 (on GeM platform)
- Aim: Enable women-led MSEs, SHGs, artisans, and marginalised women to sell directly to government buyers.
- Key Objective: Address the triple challenge faced by women entrepreneurs:
- Access to markets
- Access to finance
- Access to value addition
- Policy Linkage: Supports the objective of 3% reservation in government procurement for women-owned enterprises.
- Impact (Udyam Data):
- Women-owned MSMEs: 20.5% of total MSMEs
- Employment contribution: 18.73%
- Share in total investment: 11.15%
Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
- Launched: 2016
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Nature: One-stop online public procurement portal for Central & State Ministries, Departments, PSUs, and autonomous bodies
- Operator: GeM Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) – fully government-owned, not-for-profit entity
- Coverage: Adopted across all 36 States and UTs (with several states mandating its use)
- Objectives: Transparency, efficiency, cost savings, and reduced corruption
- Independent assessments (e.g., World Bank) note ~10% cost savings
- Inclusivity Footprint:
- 10+ lakh MSEs
- 1.3 lakh artisans & weavers
- 1.84 lakh women entrepreneurs
- 31,000+ startups
- Innovation: GeMAI – India’s first generative AI-powered public sector chatbot, supporting voice and text in 10 Indian languages.
VrindavaniVastra

- 19 Nov 2025
In News:
The Government of Assam has initiated formal discussions with the British Museum to facilitate the return of the VrindavaniVastra, a priceless 16th–17th century Assamese textile that holds immense cultural, historical, and religious significance. The move is part of broader efforts to reclaim India’s cultural artefacts preserved abroad.
What is VrindavaniVastra?
- A 400-year-old traditional textile originating from Assam.
- The word Vrindavani refers to Vrindavan, the sacred land of Lord Krishna’s childhood; Vastra means cloth.
- The textile depicts:
- Scenes from Lord Krishna’s childhood.
- His lilas (divine exploits).
- Various events of Vaishnav devotional narratives.
Origin & Patronage
- Created during the rule of Koch King Nara Narayan (16th century).
- Produced under the guidance of SrimantaSankardeva, the founder of Assamese Neo-Vaishnavism.
- Sankardeva took refuge under Nara Narayan after he faced hostility from sections of Ahom-era Brahmin priests.
Weaving Technique
- Made of woven silk using the complex lampas technique.
- Lampas weaving requires:Two weavers working simultaneously, making it a technically demanding process.
- Uses a rich palette of colours:Red, yellow, green, black, white, and others.
- Combines artistic traditions from:
- Assam
- Bengal
- Tibetan and broader Himalayan influences
Historical Journey
- The textile originally consisted of 15 separate silk panels, later stitched into a continuous piece.
- The specimen held in the British Museum is:
- Nine and a half metres long
- Assembled from several draped silk sections
- It travelled from Assam to Tibet through ancient cultural exchanges.
- Acquired by the British Museum in 1904, where it remains one of the most significant exhibits from South Asia.
Cultural Significance
- A masterpiece of Assamese Vaishnavite art and a visual representation of Sankardeva’s devotional philosophy.
- Reflects a synthesis of:
- Textile craftsmanship
- Storytelling
- Religious aesthetics
- Represents the rich heritage of Sattriya tradition, associated with monasteries (sattras) founded by Sankardeva.
Empowered Committee for Animal Health (ECAH)
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The Empowered Committee for Animal Health (ECAH) is India’s apex, evidence-driven policy body guiding animal health governance. Established in 2021, it functions as the think tank of the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) under the aegis of the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India.
Composition and Mandate
- Chair: Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India
- Vice-Chair: Secretary, DAHD
- Members: Experts from Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Veterinary Council of India (VCI), academia, and industry.
- Core Role: Provide strategic guidance on national animal health programmes, emerging disease threats, One Health initiatives, and regulatory frameworks for veterinary vaccines, drugs, and biologicals.
Functions
- Act as a national think tank for animal health programmes of importance.
- Streamline regulatory approvals by assessing safety, efficacy, and quality of veterinary products.
- Promote innovation uptake and resilient, farmer-centric animal health systems.
- Assess and advise on emerging animal diseases with epidemic/pandemic potential.
9th ECAH Meeting (July 2025): Key Outcomes
Held in New Delhi under DAHD, the meeting-chaired by the PSA-reviewed progress and charted the roadmap for animal health strengthening. Emphasis areas included farmer awareness, vaccination coverage, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and regulatory reforms to improve access to quality veterinary products.
Major Milestones Reported
National Disease Control Programmes (Vaccination):
- FMD: 124.10 crore doses
- PPR: 28.89 crore doses
- Brucellosis: 4.77 crore doses
- Classical Swine Fever: 0.88 crore doses
- Vaccination records digitised via Bharat Pashudhan app.
- Animal Vaccine Intelligence Network (AVIN) pilots for real-time cold-chain monitoring.
- All programme vaccines are indigenously developed, reinforcing Atmanirbhar Bharat; India also exports vaccines.
Disease-Free Compartments & International Recognition:
- India’s first Equine Disease-Free Compartment (EDFC) endorsed by World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) (July 2025), enabling global movement of Indian sport horses.
- 44 HPAI (Avian Influenza) compartments approved for biosecure, export-ready poultry systems.
- ICAR–NIHSAD, Bhopal recognised as a Category A Rinderpest Holding Facility by WOAH and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)-placing India among a small global cohort.
- Additional WOAH reference labs recognised for Equine Piroplasmosis (Hisar) and Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome in fish (Lucknow).
Laboratory & Surveillance Capacity:
- Under the Pandemic Fund Project:
- Indian Network of Genomic Surveillance (INGeS): 11 labs
- Indian Network on Transboundary Animal Diseases & EIDs: 19 labs
- Push for NABL accreditation of CDDLs/RDDLs and State ADLs; launch of “Rate My Lab” for transparency and benchmarking.
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) Block Mechanism
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) block mechanism is an emerging reform in India’s capital markets aimed at enhancing investor protection and fund safety in secondary market trading. Recently, the market regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed making this facility mandatory for Qualified Stock Brokers (QSBs), drawing parallels with the well-established Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA) system used in the primary market.
What is the UPI Block Mechanism?
- It allows investors to trade in the secondary market using funds blocked in their bank accounts, rather than transferring money upfront to the trading member.
- The actual debit occurs only when a trade is executed, while the remaining funds stay safely in the investor’s bank account.
- The mechanism is conceptually similar to ASBA, but extended to secondary market transactions.
Key Features
- Funds remain in the investor’s bank account, with only a lien/block created.
- Reduces the risk of misuse or diversion of client funds by intermediaries.
- Currently optional for investors and not mandatory for trading members, though SEBI has proposed mandatory adoption for QSBs.
- SEBI has also sought feedback on whether a “3-in-1 trading account” (bank + demat + trading) can be allowed as an alternative.
Role of Qualified Stock Brokers (QSBs)
- Trading members are classified as QSBs based on:
- Number of active clients
- Total client assets held
- Trading volumes
- End-of-day margins
- Being a QSB entails higher regulatory responsibilities and compliance standards.
- SEBI’s proposal targets QSBs first due to their scale and systemic importance.
Link with ASBA
Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA):
- Introduced by SEBI in 2008.
- Mandatory for IPOs and rights issues.
- Allows investors to apply for issues by blocking funds in their bank account, with debit only after allotment.
- Prevents premature transfer of investor money and improves transparency.
The UPI block mechanism mirrors this principle but applies it to secondary market trading.
Regulatory Background
- UPI, developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), was launched in 2016.
- SEBI mandated UPI-based payments with fund blocking for IPO applications in 2019.
- In January 2024, SEBI introduced a single-block, multiple-debits UPI mechanism for secondary market use, paving the way for the current proposal.
Significance
- Enhanced investor protection by keeping funds under the investor’s control.
- Improves trust and transparency in secondary market operations.
- Aligns with SEBI’s broader objective of segregation and safety of client funds.
- Reduces settlement risk and strengthens market integrity.
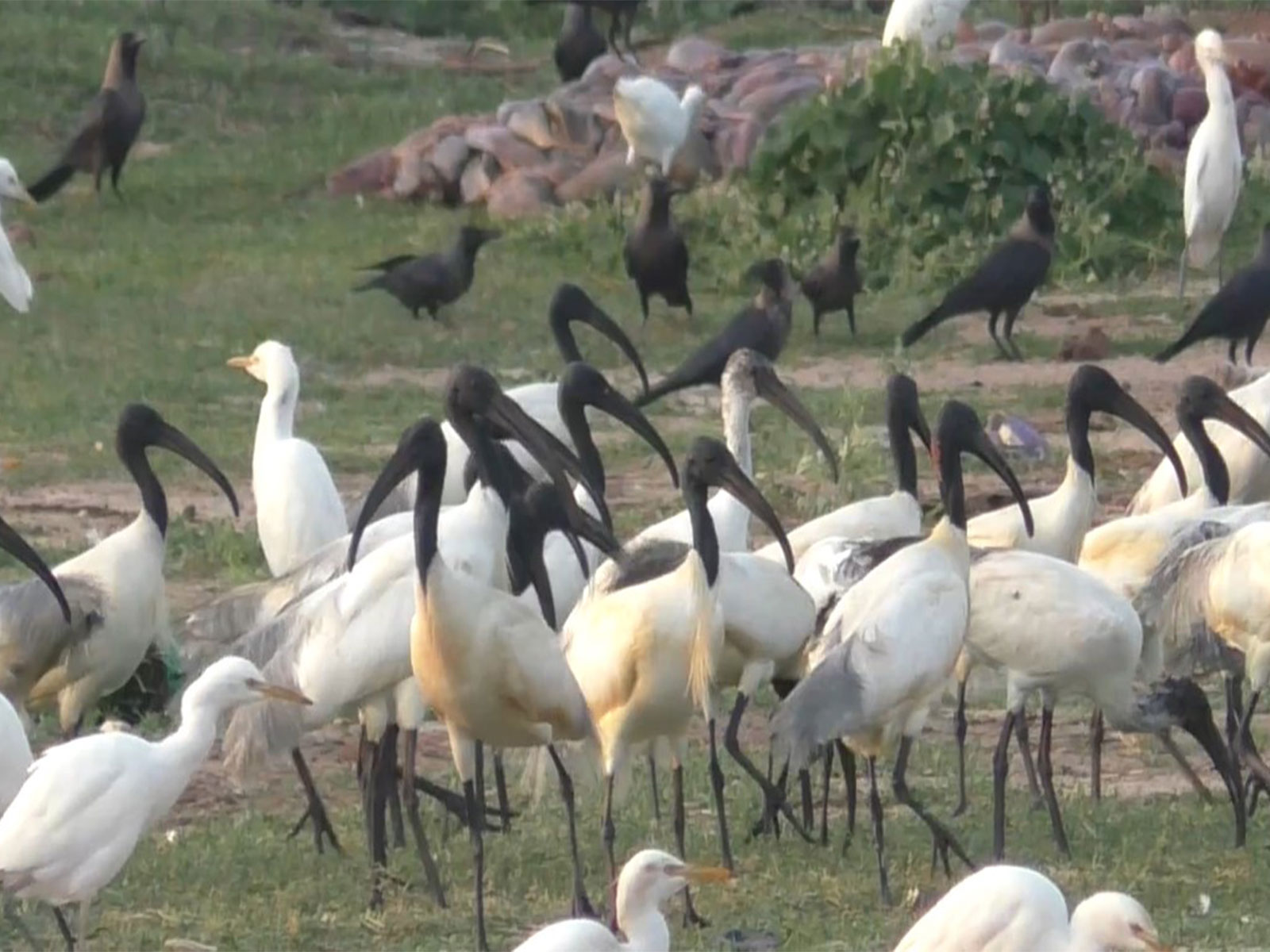
Black-Headed Ibis

- 10 Nov 2025
In News:
Recent sightings of a flock of Black-headed Ibis (Oriental White Ibis) in the salt pan regions of Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu, have drawn the attention of bird enthusiasts, ecologists, and conservationists. Such observations are significant not only for avifaunal studies but also as indicators of wetland health and ecological recovery, especially in coastal and human-modified landscapes.
About the Black-Headed Ibis
The Black-headed Ibis (Threskiornis melanocephalus), also known as the Oriental white ibis, Indian white ibis, or black-necked ibis, belongs to the family Threskiornithidae. It is a large wading bird, measuring about 65–76 cm in length, adapted to a wide variety of aquatic environments, which is why it is classified as a wader bird.
Morphologically, it is distinctive as the only native ibis species in its range with an overall white plumage combined with a black head and neck. Both males and females appear similar. Adults have greyish tail feathers, which turn jet black during the breeding season, adding to their ornamental appearance. The species is characterised by a long, curved bill, suited for probing mud and shallow water in search of food.
Habitat, Distribution and Ecology
The Black-headed Ibis is widely distributed across South and Southeast Asia, ranging from India westwards to Sri Lanka and eastwards up to Japan. It primarily inhabits wetlands, including lakes, marshes, riverbanks, and flooded agricultural fields. Notably, it is also found in coastal areas such as salt pans, as seen in Thoothukudi, and occasionally forages in dry fields and human-modified landscapes.
Its diet mainly consists of fish, insects, crustaceans, and other small aquatic organisms, making it an important component of wetland food webs. The presence of ibises, along with species such as flamingos, pelicans, and rosy starlings, reflects adequate food availability and suitable habitat conditions.
Conservation Status and Significance
At the global level, the Black-headed Ibis is classified as ‘Least Concern’ under the IUCN Red List. However, in parts of Asia, it is sometimes regarded as ‘Near Threatened’, owing to wetland degradation, pollution, altered hydrology, and habitat loss. This highlights the importance of regional conservation perspectives even when a species is not globally threatened.
The recent sightings in the salt pans of Thoothukudi are seen by experts as a positive ecological signal, suggesting improved habitat conditions following seasonal changes, particularly after the northeast monsoon (October–January), which replenishes wetlands and associated ecosystems.
Migratory Birds and Conservation Measures
The Thoothukudi observation also fits into a broader national context of avian conservation and migratory bird protection. Across India, wetlands and coastal regions act as crucial stopovers and wintering grounds for both resident and migratory birds. In this regard, proactive conservation measures, such as the declaration of a temporary ‘Silence Zone’ around Pangti village in Wokha district, Nagaland, to protect the globally significant congregation of Amur Falcons, demonstrate growing administrative and community awareness. Scientific studies have shown that excessive noise can disturb birds, disrupt breeding behaviour, and lead to habitat abandonment, underlining the need for habitat-sensitive governance.
Second World Summit for Social Development (WSSD-2), 2025

- 07 Nov 2025
In News:
The Second World Summit for Social Development (WSSD-2) is being held Doha, Qatar, under the aegis of the United Nations. India is represented at the summit by the Minister for Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, underscoring India’s commitment to global social development and social justice.
Background and Evolution
The first World Summit for Social Development was held in Copenhagen in 1995, marking a watershed moment in global consensus on placing people-centric development at the heart of economic policy. It resulted in the Copenhagen Declaration, which laid down 10 commitments focused on poverty eradication, employment generation, and social inclusion.
Three decades later, WSSD-2 seeks to reassess global progress, address emerging challenges, and reinvigorate global solidarity in the context of widening inequalities, technological disruption, climate stress, and demographic transitions.
Objectives of WSSD-2
The summit aims to:
- Reaffirm commitment to poverty eradication, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
- Promote social inclusion, equality, and well-being, particularly for vulnerable and marginalized groups.
- Assess gaps in implementation of social development commitments since 1995.
- Strengthen the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reaffirm the 10 commitments of the Copenhagen Declaration.
- Enhance global cooperation and solidarity in social development.
Importantly, WSSD-2 is aligned with other key global processes, including the 2023 SDG Summit Political Declaration, the Pact of the Future, and the forthcoming Fourth International Conference on Financing for Development (FfD4), ensuring policy coherence across global development frameworks.
India’s Participation and Contributions
At the summit, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya is participating in the Opening Plenary, delivering India’s National Statement, and joining global leaders in adopting the Doha Political Declaration, which will guide future international action on social development.
India is actively contributing to the High-Level Round Table on the Three Pillars of Social Development:
- Poverty Eradication
- Full and Productive Employment and Decent Work for All
- Social Inclusion
In this forum, India is showcasing its inclusive and digitally enabled growth model, highlighting how digital public infrastructure, financial inclusion, and targeted welfare delivery have strengthened social protection and employment outcomes.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements
On the sidelines of WSSD-2, India is strengthening international cooperation through bilateral meetings with representatives from Qatar, Romania, Mauritius, and the European Union, as well as interactions with the Director-General of the International Labour Organization (ILO) and senior UN officials. These engagements focus on:
- Labour mobility
- Skilling and workforce development
- Social protection frameworks
- Employment generation
Additionally, India is highlighting institutional innovations such as the National Career Service (NCS) Portal, which connects job seekers and employers, improving transparency and inclusivity in labour markets.
Employee’s Enrolment Scheme 2025

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
- The Ministry of Labour and Employment has launched the Employee’s Enrolment Scheme 2025 (EES-2025) to widen the social security net by bringing excluded employees into the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) fold.
- Implemented by the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO), the scheme provides a single, time-bound opportunity for employers to voluntarily regularise workers who should have been covered under the EPF Act but were not enrolled earlier.
About the Scheme
- Type: One-time voluntary compliance window.
- Implementing Agency: EPFO, Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Coverage Period for Eligible Employees: 1 July 2017 to 31 October 2025.
- Operational Window: 1 November 2025 – 30 April 2026 (six months).
The scheme allows employers to declare and enrol employees who were omitted—intentionally or inadvertently—from EPF coverage during the above period.
Objectives
- To expand EPF coverage under the EPF & MP Act, 1952.
- To promote voluntary compliance and foster trust between employers and regulators.
- To support workforce formalisation and ensure financial protection for previously unregistered workers.
- To reduce litigation and compliance burden by providing a simplified remedial mechanism.
Key Features
- Employers may enrol all eligible employees engaged between July 2017 and October 2025 who were not covered earlier.
- Waiver of employee contribution for the past period if it was not deducted earlier.
- Employers are required to pay:
- Employer’s share of EPF contribution, and
- A nominal penalty of ?100 per establishment.
- Applicable even to establishments under inquiry under:
- Section 7A of the EPF Act, or
- Paragraph 26B of the EPF Scheme.
- EPFO will not initiate suo motu action for earlier non-compliance once the employer makes full voluntary disclosure under the scheme.
Significance
- Strengthens social security by widening EPF coverage for millions of workers.
- Boosts ease of doing business by reducing penalties and enabling smooth compliance.
- Encourages formalisation, aligning with India's goal of universal social protection.
- Helps reduce disputes, improve employer-employee relations, and enhance long-term financial safety for the workforce.
Dhvani Hypersonic Missile
- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is preparing for the first test of Dhvani, India’s next-generation hypersonic missile system. Its development marks a major advancement in India’s indigenous strategic and aerospace capabilities, placing the country among a select group working on Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) technology.
What is Dhvani?
- Dhvani is an upcoming hypersonic missile being developed by DRDO.
- It is designed as a Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV), enabling high-speed, maneuverable flight at hypersonic speed (greater than Mach 5 or approx. 7,400 km/h).
- The system departs from conventional ballistic or cruise missile trajectories by:
- Being launched to very high altitudes, and
- Then gliding at hypersonic speeds toward the target with significant maneuvering capability.
This flight profile complicates detection and interception by most existing missile defence systems.
Key Technical Features
1. Speed & Range
- Expected to fly at Mach 5–6+.
- Estimated operating range: 6,000–10,000 km (long-range strategic class).
2. Hypersonic Glide Vehicle Design
- Blended wing–body configuration
- Approx. 9 m length
- Approx. 2.5 m width
- Optimized for lift generation and maneuverability during hypersonic glide.
3. Thermal Protection System
- Uses ultra-high-temperature ceramic composites.
- Can withstand 2,000–3,000°C generated during atmospheric re-entry and sustained hypersonic flight.
4. Stealth Features
- Stealth-shaped geometry with:
- Angled surfaces
- Smooth contours
- Intended to reduce radar cross-section (RCS) and enhance survivability against surveillance systems.
5. Guidance & Precision: Designed to strike both land and maritime targets with high accuracy.
Technology Background
- Dhvani builds on technologies proven in the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV), including:
- Scramjet propulsion research
- Thermal shielding systems
- High-temperature material development
The success of HSTDV provided DRDO the platform to develop operational HGV systems such as Dhvani.
Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–31)

- 31 Oct 2025
In News:
- India, the world’s largest producer and consumer of pulses, continues to face a structural gap between domestic production and rising demand. Lower productivity levels, yield gaps, and increasing import dependence have highlighted the need for a targeted national strategy.
- To address these concerns, the Government of India has launched the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–31)—a six-year initiative aimed at transforming India into a self-reliant pulses-producing nation through scientific, institutional, and market reforms.
Overview of the Mission
Formally launched by the Prime Minister on 11 October 2025, the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses was first announced in the Union Budget 2024–25. The programme is implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, with collaborative support from NAFED, NCCF, and state governments.
Mission Duration and Financial Outlay
- Implementation period: 2025–26 to 2030–31
- Total outlay: ?11,440 crore
- Targets:
- Raise production by 45%—from 242 lakh MT (2023–24) to 350 lakh MT (2030–31)
- Expand cultivated area by 13%—from 275 lakh ha to 310 lakh ha
- Improve average yield by 28%—from 881 kg/ha to 1,130 kg/ha
Rationale: Current Status and Challenges
India cultivates a wide variety of pulses across agro-climatic zones. Major pulse-growing states include:
- Area (2023–24): Rajasthan (54.67 lakh ha), Madhya Pradesh (51 lakh ha), Maharashtra (44 lakh ha), Uttar Pradesh (30 lakh ha)
- Production (2023–24): Madhya Pradesh (59.74 lakh MT), Maharashtra (40 lakh MT), Rajasthan (33 lakh MT), Uttar Pradesh (31 lakh MT)
Gram dominates both area and output, followed by moong, tur (arhar), urad, and masoor. Over 60% of pulses production occurs during the rabi season.
Despite being the largest pulses producer, India remains dependent on imports from Myanmar, Tanzania, Mozambique, Canada, Australia, among others. Demand is projected to reach 268 lakh MT by 2030 and 293 lakh MT by 2047 (NITI Aayog), far exceeding current production levels. Productivity remains significantly lower than global benchmarks—Canada (2200 kg/ha) and China (1815 kg/ha).
Why Focus on Tur, Urad, and Masoor?
These three pulses account for 34% of total pulses area and contribute significantly to national output. They also exhibit high yield gaps and are crucial for nutritional security. The Mission plans:
- 9 lakh ha expansion in tur—across Karnataka, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Jharkhand and non-traditional areas like the Northeast.
- Utilisation of rice fallows for expanding urad in Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Promotion of masoor in rice fallow areas of West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh.
Key Components and Features of the Mission
1. Development of Climate-Resilient Seeds: Focus on high-yielding, drought-tolerant, pest-resistant, and protein-enriched varieties.
2. Higher Productivity through Technological Adoption
- Enhanced support of ?10,000/ha for Front Line Demonstrations (FLDs) of improved technologies (higher than ?9,000 under NFSM).
- Strengthening post-harvest storage, grading, and processing infrastructure.
3. 100% Assured Procurement
A major innovation in the mission framework:
- NAFED and NCCF will undertake 100% procurement of tur, urad and masoor for four years under PM-AASHA’s Price Support Scheme (PSS).
- Aadhaar-enabled biometric/facial authentication will ensure transparency and eliminate leakages.
4. Cluster-Based Approach
Each cluster will include minimum 10 ha (2 ha in hilly/Northeast region). Cluster selection based on:
- Four-fold district classification: HA-HY, HA-LY, LA-HY, LA-LY
- Rice fallow, rainfed, and watershed areas
- Aspirational districts, border/LWE districts
- Regions under PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, Adarsh Gram Yojana, and Northeast/Himalayan areas
5. Value-Chain Strengthening: Interventions span input supply, extension, mechanisation, processing, market linkages and digital traceability.
Comparative Advantage over Previous Schemes
The Mission subsumes the pulses component of National Food Security and Nutrition Mission (NFSNM) but provides:
- Higher financial support
- Wider geographical coverage
- Expanded interventions (seed hubs, storage, procurement)
- Stronger digital governance
- Guaranteed procurement for three major pulses
National Significance
- Food and Nutritional Security: Pulses are key protein sources in Indian diets.
- Import Substitution: Reduces dependency on global markets and price volatility.
- Farmer Income Stability: Guaranteed procurement and improved yields boost profitability.
- Climate Resilience: Promotes drought-friendly crops, diversifies cropping patterns, and utilises rice fallows.
- Balanced Regional Development: Targets backward, rainfed, aspirational and border districts.
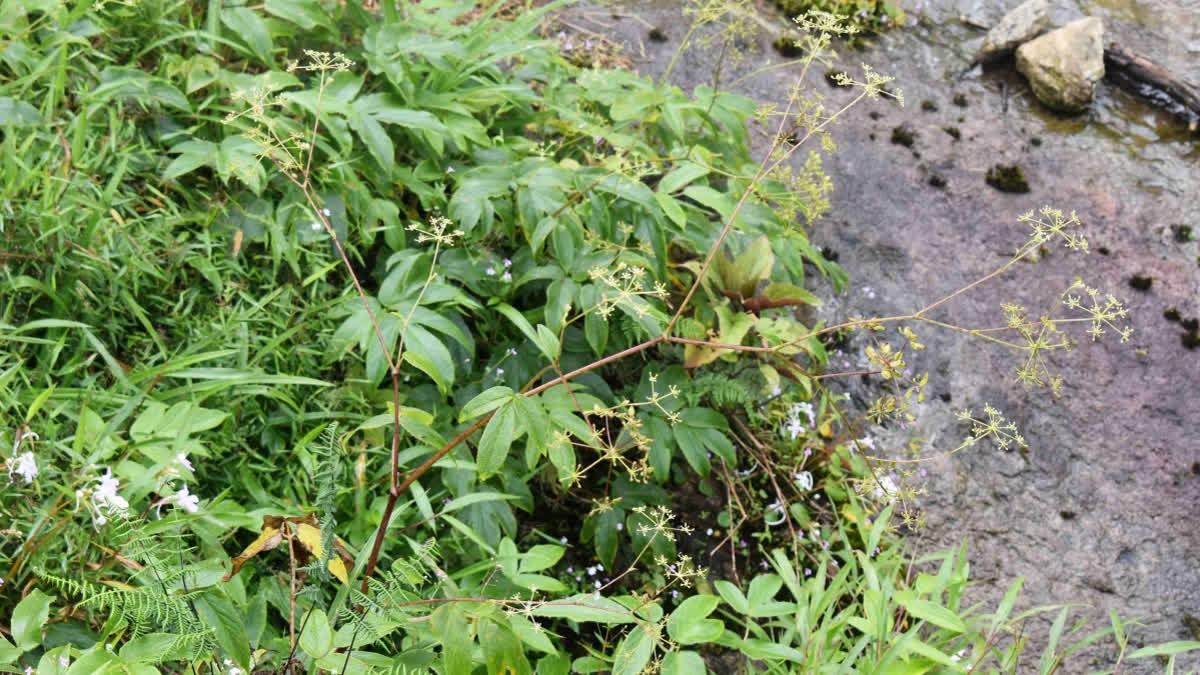
Tetrataeniummanilalianum

- 23 Oct 2025
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new plant species named Tetrataeniummanilalianum in the Eravikulam National Park, Kerala, adding to the extraordinary biodiversity of the Western Ghats, one of the eight “hottest biodiversity hotspots” in the world. The finding has been published in the Nordic Journal of Botany (Sweden), underscoring India’s growing contributions to global botanical research.
About Tetrataeniummanilalianum
- The newly identified plant belongs to the carrot family (Apiaceae/Umbelliferae), which also includes species such as carrot, coriander, cumin, fennel, and ajwain.
- It was discovered in the high-altitude grasslands bordering the shola forests of the Eravikulam National Park in Idukki district, Kerala.
- The plant bears white flowers and possesses underground rhizomes. It sprouts and blooms only during the monsoon season, adapting to the region’s moist climatic conditions.
- This discovery marks the 48th identified species within the Tetrataenium genus and is the first of its kind recorded globally.
- The species has been named in honour of Prof. K.S. Manilal, a distinguished botanist, founder president of the Indian Association for Angiosperm Taxonomy (IAAT), and former Head of the Department of Botany at the University of Calicut.=
Ecological Context – Eravikulam National Park
- Location: Situated in the Idukki district of Kerala, the park spans 97 sq. km along the summit of the Western Ghats.
- Topography: Encompasses rolling grasslands interspersed with shola forests in the upper valleys.
- Climate: Receives heavy rainfall during both the southwest (June–July) and northeast (October–November) monsoons, making it one of the wettest regions in the world.
- Flora: Rich in endemic species such as Actinodaphnebourdilloni, Microtropisramiflora, Pittosporum tetraspermium, and the once-thought-extinct orchid Brachycorythiswightii.
- Fauna: Home to the endangered NilgiriTahr, with nearly half the world’s population residing here. Other species include the Gaur, Sloth Bear, Nilgiri Langur, Tiger, Leopard, Giant Squirrel, and Wild Dog.
- The park also hosts the Anamudi Peak (2,695 m), the highest mountain in South India, and is famous for the Neelakurinji flowers that bloom once every twelve years.
Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–26 to 2030–31)

- 14 Oct 2025
In News:
- India has launched an ambitious Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–26 to 2030–31),signalling a major push toward self-sufficiency in pulses and farmer-centric agricultural transformation.
- Announced during a special programme at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), the Mission carries an outlay of ?11,440 crore and aims to meet India’s pulses requirement entirely through domestic production by December 2027.
- Pulses hold strategic importance for India as they ensure nutritional security, enrich soil through nitrogen fixation, support rural livelihoods, and reduce import bills. Despite being the world’s largest producer and consumer, India's demand-supply gap has led to significant imports—47.38 lakh tonnes in 2023-24. The Mission seeks to eliminate this dependence and strengthen farmer income security.
Key Targets (by 2030–31)
- Total production:350 lakh tonnes
- Cultivation area:310 lakh hectares (including 35 lakh ha rice fallows)
- Yield target:1,130 kg/ha
- Beneficiaries: Nearly 2 crore farmers
- Import elimination by Dec 2027
Core Components of the Mission
Seed & Technology Push
- 126 lakh quintals of certified seeds
- 88 lakh free seed kits
- Deployment of high-yielding, pest-resistant, climate-resilient varieties
- Launch of SATHI Portal (Seed Authentication, Traceability & Holistic Inventory) for seed lifecycle transparency
Assured MSP & Farmer Security
- 100% procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masoor for four years
- Procurement support via NAFED & NCCF
- Linked to PM-AASHA for guaranteed price support and reduced market risk
Cluster-Based Integrated Approach
- "One Block – One Seed Village" model
- FPO-driven clusters to streamline seed production & marketing
- Mechanization, soil health management, and balanced fertilization
- Agronomy support from ICAR, KVKs & state agriculture departments
Value Chain Strengthening
- 1,000 processing & packaging unitsincentive: up to ?25 lakh per unit
- Focus on storage, processing, branding, and market linkages
Social and Nutrition Focus
- Inclusion of pulses in PDS, ICDS, Mid-Day Meal schemes
- Strengthening food-based welfare with protein security
NITI Aayog Recommendations Integrated
- Expansion into rice fallows
- Cluster-based cultivation & seed hubs
- “One Block–One Seed Village”
- Data-driven monitoring through SATHI
- Public procurement strengthening at grassroots
- Climate-resilient, short-duration pest-resistant varieties
Strategic Significance
- Supports Vision 2047&Viksit Bharat
- Strengthens food sovereignty & rural employment
- Saves foreign exchange by cutting pulse imports
- Enhances soil fertility & climate resilience
- Boosts farmer incomes and reduces agrarian vulnerability
India–Afghanistan Relations Amid Taliban Diplomacy

- 12 Oct 2025
In News:
Afghanistan’s Foreign Minister Amir Khan Muttaqi’s six-day visit to India marks the first high-level interaction between New Delhi and the Taliban government since 2021. The visit reflects India’s cautious yet pragmatic attempt to re-engage diplomatically with Kabul amid evolving regional dynamics.
Historical Foundations of India–Afghanistan Relations
The relationship between India and Afghanistan is rooted in civilisational, cultural, and strategic linkages that predate modern statehood.
- Civilisational Bonds: The ancient Kabul–Gandhara–Taxila corridor served as a conduit for trade and Buddhist exchanges, shaping a shared heritage.
- Political Affinity: After 1947, Afghanistan stood apart by opposing Pakistan’s admission to the UN, signalling early alignment with India.
- Developmental Partnership: Since 2001, India has invested over $3 billion in Afghanistan’s reconstruction, building major projects like the Salma Dam, Afghan Parliament, and the Zaranj–Delaram Highway, solidifying India’s goodwill.
- Humanitarian Outreach: Even after the Taliban takeover in 2021, India sustained “people-centric engagement” by supplying 50,000 tonnes of wheat, medicines, vaccines, and scholarships — reflecting its long-term commitment to the Afghan people.
India’s Strategic Calculus Behind Engagement
India’s current approach combines realism and restraint, shaped by five key strategic considerations:
a. Regional Stability and Connectivity
- Afghanistan remains crucial to India’s access to Central Asian energy markets.
- Projects like Chabahar Port and the International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) rely on Afghan stability for viability.
b. Countering Pakistan and China
- Taliban-led Afghanistan has seen strained ties with Pakistan while engaging with China’s BRI framework.
- India’s outreach seeks to dilute Pakistan’s strategic depth and limit China’s westward expansion through CPEC.
c. Counterterrorism and Security Cooperation
- Groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), and Islamic State–Khorasan Province (ISKP) operate from Afghan soil.
- Diplomatic engagement allows for intelligence sharing, counterterror coordination, and crisis management.
d. Preventing Radicalisation Spillover
- Instability in Afghanistan could intensify cross-border militancy, narcotics trade, and extremist radicalisation, impacting India’s internal security.
e. Humanitarian and Soft-Power Diplomacy
- India’s assistance in education, health, and food security continues to build moral legitimacy and strengthen its image as a responsible regional power.
Policy Dilemmas and Diplomatic Constraints
Despite its engagement, India faces significant diplomatic challenges:
- Non-Recognition vs. Realpolitik: India has not formally recognised the Taliban regime but follows a de facto engagement policy to protect its strategic interests.
- Symbolic Diplomacy: Meetings in Dubai (2024) and New Delhi (2025) have carefully excluded Taliban flags and formal protocol to maintain a balance between engagement and legitimacy.
- Connectivity Challenges: The withdrawal of the Chabahar sanctions waiver constrains India’s access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- External Pressures: The US–Pakistan rapprochement, Russia–China engagement with Kabul, and Iran’s growing influence complicate India’s regional calculus.
- Human Rights Concerns: India must balance pragmatic engagement with its principled support for inclusive governance, women’s rights, and democratic values in Afghanistan.
Regional Implications of the Muttaqi Visit
|
Dimension |
Implications for India |
|
Strategic |
Strengthens dialogue on counterterrorism and connectivity; reduces Pakistan’s leverage. |
|
Economic |
Opens prospects for trade corridors via Chabahar and access to Afghanistan’s $1–3 trillion mineral reserves. |
|
Diplomatic |
Reinforces India’s position as a regional stabiliser engaging multiple stakeholders — Russia, Iran, and Central Asia. |
|
Security |
Enables real-time intelligence cooperation against extremist networks. |
|
Symbolic |
Projects India’s Strategic Autonomy Doctrine — engagement without endorsement. |
Way Forward
- Adopt a Dual-Track Policy: Continue humanitarian and developmental assistance while maintaining calibrated diplomatic engagement with the Taliban.
- Enhance Regional Coordination: Work through Moscow Format, SCO, and Heart of Asia platforms alongside Russia, Iran, and Central Asian partners.
- Revive Chabahar Connectivity: Explore limited sanctions relief through multilateral mechanisms to ensure sustained India–Afghanistan trade access.
- Institutionalise Counterterror Cooperation: Establish an India–Afghanistan Security Contact Group to share intelligence and monitor cross-border threats.
- Invest in Human Capital: Expand scholarships, online education, and women-focused programmes to strengthen long-term societal goodwill.
Conclusion
Amir Khan Muttaqi’s visit marks a diplomatic turning point — signalling India’s shift from cautious observation to strategic pragmatism in its Afghan policy. Balancing values with realism, New Delhi aims to secure its geopolitical and economic interests while upholding humanitarian principles.
India’s nuanced engagement — without formal recognition — positions it as a potential stabilising anchor in South–Central Asia, where constructive diplomacy rather than confrontation remains the key to regional peace and security.
Dhvani Missile
- 07 Oct 2025
In News:
India is on the verge of a historic breakthrough with the upcoming test of Dhvani, a cutting-edge hypersonic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). This missile positions India among an elite group of nations with hypersonic capabilities, including the United States, Russia, and China.
About Dhvani:
- Dhvani is being developed as a Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV), capable of speeds exceeding Mach 5 (over 7,400 km/h).
- Unlike conventional missiles that follow predictable trajectories, Dhvani is launched to extreme altitudes and then glides toward its target with high maneuverability, making detection and interception extremely difficult. It is designed to strike both land-based and maritime targets with precision.
- Estimated ranges are 6,000 to 10,000 kilometers, potentially doubling the reach of India’s current Agni-V intercontinental ballistic missile.
Design and Technology:
- Dimensions: Approximately 9 meters long and 2.5 meters wide with a blended wing-body configuration.
- Heat Protection: Uses ultra-high-temperature ceramic composites to withstand 2,000–3,000°C during atmospheric reentry.
- Stealth Features: Angled surfaces and smooth contours reduce radar visibility.
- Indigenous Development: Built on technologies demonstrated by the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV), including scramjet propulsion and thermal shielding.
Strategic Implications:
The Dhvani missile significantly enhances India’s strategic deterrence, creating a technological edge in South Asia. Its ability to perform unpredictable maneuvers during the terminal phase renders most current missile defense systems ineffective, thereby deterring adversaries.
Global Context:
Dhvani is comparable to China’s DF-ZF, Russia’s Avangard, and U.S. programs such as Dark Eagle and HACM, which face developmental delays. India’s achievement demonstrates self-reliance in critical defense technologies and strengthens its capability for both regional security and global power projection.
Prime Minister Inaugurates Development Projects Amid Ethnic Tensions in Manipur

- 18 Sep 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Imphal, Manipur, inaugurating and laying the foundation for multiple development projects aimed at improving infrastructure, governance, and socio-economic opportunities in the state.
The visit comes in the backdrop of ethnic tensions that erupted in May 2023 between the Meitei community in the Imphal valley and the Kuki-Zo tribes in the surrounding hills, which claimed over 250 lives and displaced more than 60,000 people.
Key Development Initiatives
- Infrastructure and Connectivity:
- Manipur Urban Roads Project: Investment of over ?3,600 crore to enhance urban road connectivity in Imphal.
- Jiribam–Imphal Railway Line: A ?22,000 crore project to connect Imphal to India’s national rail network.
- Imphal Airport Expansion: ?400 crore investment and inauguration of helicopter services to boost air connectivity.
- Civil Secretariat (?538 crore) and Police Headquarters (?101 crore) inaugurated to improve governance and law enforcement.
- Digital and IT Initiatives:Manipur Infotech Development Project aims to strengthen the state’s IT and startup ecosystem, creating employment and entrepreneurial opportunities.
- Women Empowerment:
- Four new Ima Markets (women-only markets) inaugurated, reinforcing the state’s tradition of women-led commerce.
- Construction of working women’s hostels at nine locations to support education and employment for women.
- Sports and Culture:
- Support for the National Sports University and Khelo India initiatives.
- Promotion of polo via the Marjing Polo Complex, featuring the world’s tallest polo statue.
Ethnic Conflict and Unresolved Issues
The conflict stems from the Meitei community’s demand for Scheduled Tribe (ST) status, opposed by Kuki-Zo groups. ST recognition would grant Meiteisconstitutional safeguards, including reservations in jobs, education, and political representation, and land rights in hill areas. Key unresolved issues include:
- Rehabilitation of Displaced Families: Over 280 relief camps sheltering around 57,000 people, some displaced for more than two years.
- Restrictions on Movement: Militarized buffer zones between valley and hill districts continue to limit free movement and access to services.
- Border Concerns: Porous border with Myanmar raises issues of cross-border migration, leading to the scrapping of the Free Movement Regime.
- Political Vacuum: The resignation of the Chief Minister and imposition of President’s Rule have created governance challenges.
- Dialogue Deficit: Despite reduced violence since late 2024, there is no sustained dialogue between Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities.
Demand for Separate Administration
The Kuki-Zo Council seeks administrative separation of hill areas as a Union Territory under Article 239A of the Constitution, while Meitei organizations like COCOMI oppose this, citing threats to territorial integrity.
Way Ahead
The Prime Minister emphasized the need to strengthen dialogue between the hill and valley districts to foster social harmony. Sustainable peace in Manipur requires:
- Inclusive dialogue and neutral mediation between Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities.
- Rehabilitation of displaced families with dignity and livelihood support.
- Balanced border management to address cross-border migration while respecting tribal ties.
- Strengthening local governance and administrative institutions to restore trust.
Strategic Significance
Infrastructure, IT, and women-centric initiatives are not only essential for socio-economic development but also align with the Act East Policy, facilitating regional integration and economic collaboration with Southeast Asia. Ensuring peace and development in Manipur is critical for maintaining national unity, regional stability, and long-term social cohesion.
India’s Path to Atmanirbharta in Millets

- 10 Sep 2025
In News:
The NITI Aayog report “Strategies and Pathways for Accelerating Growth in Pulses towards the Goal of Atmanirbharta” also provides broader lessons for achieving self-reliance in other food crops like millets, which face similar challenges of productivity, market stability, and sustainability.
Current Status of Millets in India
- Global Leadership: India contributes nearly 41% of world millet output (~16 million tonnes annually), making it the largest producer.
- Regional Spread: Five states—Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh—produce over 80% of India’s millets.
- Consumption Decline: Per capita consumption has dropped from 32 kg/year in the 1960s to ~4 kg/year today, largely replaced by rice and wheat due to PDS bias.
- Exports: In 2022–23, India exported 1.8 million tonnes, mainly to UAE, Nepal, and Saudi Arabia, indicating rising global demand.
- Policy Push: The Union Budget 2023–24 renamed millets as “Shree Anna”, earmarking resources for research, processing, and marketing.
Importance of Millets
- Nutritional Security: Rich in iron, calcium, fiber, and proteins, helping fight malnutrition and anemia.
- Climate Resilience: Require 70% less water than rice and withstand drought, making them suitable for rainfed regions.
- Farmer Livelihoods: Low-input crops reduce reliance on irrigation and fertilizers, benefiting smallholders.
- Food Security: Inclusion in Mid-Day Meals, ICDS, and PDS enhances nutrition for vulnerable groups.
- Global Branding: India’s “Shree Anna” campaign has positioned millets as a superfood and strengthened agri-diplomacy.
Initiatives Taken
- NFSM-Millets: Expands area under millets, provides quality seed, and boosts productivity.
- Shree Anna Mission (2023): A six-year plan for millet research, processing, branding, and market integration.
- State Schemes: Karnataka’s Ksheera Bhagya included millets in school meals.
- International Recognition: India led the UNGA resolution declaring 2023 as International Year of Millets.
- Export Promotion: APEDA supports branding, GI tagging, and product exports to West Asia, US, and EU.
Challenges
- Consumer Preference Shift: Rice and wheat dominate diets due to PDS subsidies and cooking convenience.
- Low Productivity: Millet yields (~1.2 t/ha) remain below rice/wheat due to limited R&D and weak seed systems.
- Weak Market Linkages: Fragmented value chains, inadequate FPO presence, and absence of MSP-backed assured procurement.
- Post-Harvest Constraints: Poor processing/storage technologies and limited millet-based food industry.
- Policy Bias: NFSA subsidies for rice/wheat discourage millet adoption in rainfed belts.
Strategic Framework for Atmanirbharta
- Horizontal Expansion: Cultivate millets in rice fallows and degraded lands, especially in Eastern India.
- Vertical Expansion: Develop high-yielding, bio-fortified, climate-resilient varieties with robust seed systems.
- Cluster-Based Model: District-wise crop cluster strategy for focused interventions.
- Value Chain Integration: Establish processing hubs, branding centers, and FPO-led aggregation.
- Climate-Smart Farming: Promote organic and water-efficient millet practices, aligning with SDGs and climate goals.
Afghanistan Earthquake
- 07 Sep 2025
In News:
A devastating 6.0-magnitude earthquake struck eastern Afghanistan near Jalalabad, killing over 800 people and injuring at least 2,800 across Kunar, Nangarhar, and Laghman provinces. The tremors, felt from Kabul to Islamabad, destroyed homes in remote mountainous regions and highlighted Afghanistan’s acute vulnerability to natural disasters.
Afghanistan’s Seismic Vulnerability
Afghanistan lies at the collision zone of the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates, making it one of the world’s most seismically active regions. The Hindu Kush mountain range, part of the greater Himalayan system, witnesses frequent tremors. Since 1900, at least 12 earthquakes exceeding magnitude 7 have struck northeast Afghanistan.
Most Afghans live in low-rise, mud-brick dwellings, which offer little resistance to seismic shocks. With poor infrastructure, fragile governance, and limited access to technology, the human toll of disasters is amplified.
Geographic and Geostrategic Context
Afghanistan is a landlocked, multi-ethnic nation in South-Central Asia, historically situated at the crossroads of trade and power rivalries—from the “Great Game” between Britain and Russia to Cold War confrontations.
- Capital: Kabul
- Neighbours: Pakistan, Iran, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China (via the narrow Wakhan Corridor).
- Geographic Features:
- Mountains: The Hindu Kush dominates, with passes like the Khyber and Shebar, linking Central and South Asia.
- Rivers: Amu Darya (north), Kabul River (tributary of Indus), Helmand (longest at 715 miles), and Hari Rud (Afghanistan–Iran boundary).
- Regions:
- Central Highlands – rugged, earthquake-prone terrain.
- Northern Plains – fertile, resource-rich areas with gas reserves.
- Southwestern Plateau – arid deserts such as Registan and Margow.
These geographical features make Afghanistan both strategically significant and highly disaster-prone.
VrindavaniVastra
- 03 Sep 2025
In News:
The VrindavaniVastra, a 16th-century sacred silk textile of Assam, is set to return temporarily from the British Museum, London, for exhibition in 2027. The decision marks a significant milestone in India’s efforts to reclaim its cultural heritage and present it to the public in its place of origin.
Historical Background
- The VrindavaniVastra was woven in Assam under the guidance of SrimantaSankardeva, the great Vaishnav saint-reformer, at the request of Koch King Nara Narayan.
- It depicts scenes from Lord Krishna’s childhood and divine pastimes in Vrindavan, woven intricately with silk threads.
- Historically, Nara Narayan had sheltered Sankardeva after he faced persecution by the Ahom kingdom under pressure from Brahmin priests, reflecting the socio-political tensions of the time.
Artistic and Cultural Significance
- The textile is regarded as a masterpiece of Assamese Vaishnav art, blending weaving traditions with spiritual themes.
- Originally consisting of 15 separate silk panels, the current exhibit measures around 9.5 metres in length, assembled from multiple fragments.
- It represents not only religious devotion but also the syncretic weaving traditions of Assam, incorporating motifs influenced by diverse artistic cultures.
- As a central artefact of Assamese Vaishnavism, it reinforces Sankardeva’s legacy of devotional bhakti traditions.
Journey to the West
- Fragments of the Vastra were believed to have travelled from Assam to Tibet in the 17th–18th centuries, before being collected by British explorers during the 19th–20th centuries.
- In 1904, the India Museum acquired the textile and later transferred it to the British Museum. Since then, it has been part of their South Asian collection, alongside similar pieces in other European museums.
PM SVANidhi 2.0
- 01 Sep 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme, launched on 1st June 2020 amidst the COVID-19 crisis, has emerged as a landmark initiative for supporting urban street vendors by providing collateral-free working capital loans, promoting digital inclusion, and enabling social security access.
In August 2025, the Union Cabinet approved the restructuring and extension of the scheme till 31st March 2030, with an enhanced outlay of ?7,332 crore to benefit 1.15 crore beneficiaries, including 50 lakh new entrants.
Key Features of the Restructured Scheme
- Enhanced Loan Tranches
- 1st tranche: ?15,000 (earlier ?10,000)
- 2nd tranche: ?25,000 (earlier ?20,000)
- 3rd tranche: ?50,000 (unchanged)
- UPI-linked RuPay Credit Card
- Available for vendors who have repaid the second loan.
- Ensures instant credit access for business and personal needs.
- Digital Incentives
- Cashback up to ?1,600 on digital transactions.
- Promotes financial literacy and digital adoption.
- Expanded Coverage
- From statutory towns to census towns, peri-urban areas, in a phased manner.
- Capacity Building & Convergence
- Training in entrepreneurship, financial literacy, and digital skills.
- Food safety & hygiene certification for street food vendors in partnership with FSSAI.
‘SVANidhi se Samriddhi’ Component
- Ensures saturation coverage of welfare schemes for vendors’ families.
- Monthly Lok Kalyan Melas to connect beneficiaries with schemes like PM Suraksha Bima Yojana, PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Ayushman Bharat, and PM Jan Dhan Yojana.
Achievements Till Date (as of July 2025)
- 96 lakh loans disbursed worth ?13,797 crore to 68 lakh vendors.
- 47 lakh digitally active beneficiaries with over 557 crore transactions worth ?6.09 lakh crore.
- ?241 crore cashback earned by vendors.
- 46 lakh beneficiaries profiled across 3,564 ULBs, leading to 1.38 crore scheme sanctions.
- Recognitions:
- PM’s Award for Excellence in Public Administration (2023) for Innovation.
- Silver Award (2022) for Government Process Re-engineering in Digital Transformation.
Paithani Sarees
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently highlighted the cultural and artisanal significance of Paithani sarees during the monthly ‘Mann Ki Baat’ radio programme, bringing national attention to this traditional Maharashtrian textile.
Historical Background
- Origin: Paithani sarees derive their name from Paithan, an ancient town on the banks of the Godavari River in Maharashtra.
- Antiquity: The tradition of Paithani weaving dates back over 2,000 years, with its roots in the Satavahana dynasty (2nd century BCE).
- Royal Patronage: These sarees were patronized by several royal courts, including the Satavahanas, Peshwas of Pune, Nizams of Hyderabad, and Mughal emperors.
Key Features
|
Attribute |
Description |
|
Material |
Woven using pure silk and gold/silver zari |
|
Technique |
Crafted using the tapestry weaving method, all handwoven |
|
Designs |
Intricate motifs like peacocks, parrots, lotuses, and floral vines |
|
Border & Pallu |
Known for distinctive kath (border) and padar (pallu) designs |
|
Size |
Typically six- or nine-yard sarees |
|
Cultural Significance |
Regarded as the ‘Mahavastra’ (great garment) of Maharashtra, traditionally worn by Maharashtrian brides |
Recognition and Cultural Value
- Symbol of Heritage: Paithani sarees are considered a symbol of Maharashtrian cultural identity and artisanal excellence.
- GI Tag: Granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2010, acknowledging their unique regional origin and craftsmanship.
- Artistic Value: Among the most exquisite and expensive sarees in India, valued for their aesthetic finesse and traditional techniques.
Climate-Resilient and Organic Agriculture: Parliamentary Committee Report Highlights
- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
The Committee on Estimates (2024–25) has submitted its Sixth Report to Parliament, emphasizing the pressing need for a climate-resilient and ecologically sustainable agricultural system in India. The report presents a roadmap aimed at tackling the vulnerabilities posed by climate change, soil degradation, and unsustainable farming practices.
Key Challenges in Indian Agriculture:
1. Climate Vulnerability:
- Projected Yield Decline: Crop yields may fall by 4.5% to 9% in the medium term due to climate-induced stresses.
- District-Level Risks: Out of 310 climate-vulnerable districts identified by the IPCC,
- 109 are at ‘very high risk’,
- 201 are categorized as ‘highly vulnerable’.
2. Soil Health Crisis:
- Extent of Degradation: Nearly 30% of India's land suffers from soil degradation.
- Root Causes: Excessive chemical inputs (urea and pesticides) and loss of organic matter have disrupted nutrient cycles and reduced fertility.
3. Economic Pressures: The Green Revolution model now shows diminishing returns, with rising input costs contributing to farmer indebtedness and suicides.
Policy Shift Towards Sustainable Farming:
1. Natural Farming:
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Launched in 2023–24 as an independent scheme, expanding upon the earlier Bhartiya Prakritik Krishi Paddati (BPKP).
- Focus: Chemical-free agriculture, soil regeneration, and farmer self-reliance.
2. Organic Farming Initiatives:
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): Promotes cluster-based organic farming using Participatory Guarantee Systems (PGS) for certification.
- MOVCDNER: Aims to develop organic value chains in the North Eastern Region, leveraging traditional practices and rich biodiversity.
Challenges in Transition:
- Yield reductions during the initial switch.
- Complex and often expensive certification procedures.
- Weak market linkages and poor consumer awareness.
- Training and knowledge gaps among farmers.
- Financial risks for small and marginal farmers lacking safety nets.
Recommendations of the Committee:
- Integrate climate-resilient agriculture into national schemes like PM-KISAN, MGNREGA, and RKVY.
- Provide green subsidies to farmers offering ecological services.
- Establish a national agroecological transition framework combining research, training, and market access.
- Empower Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) with digital tools and decentralized funding for field-level implementation.
Scaling Up Climate-Resilient Strategies:
National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA):
- Launched: 2011 by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Objective: Equip farming systems to adapt to climate variability.
Key Components:
- Strategic research on climate-tolerant varieties.
- Technology demonstrations in vulnerable districts.
- Capacity building for farmers and extension staff.
- Infrastructure enhancement at research institutions.
Notable Achievements in NICRA Villages:
- 2,900+ climate-resilient varieties developed (e.g., heat-tolerant wheat, drought-resistant rice).
- 28–37% rise in crop productivity.
- 10–12% increase in livestock productivity.
- 35–40% higher farm incomes compared to non-NICRA areas.
Way Forward:
- Expand NICRA initiatives to cover more vulnerable districts with dedicated funding.
- Create agroecological clusters to support localized natural/organic farming models.
- Simplify and support organic certification and branding to enhance marketability.
- Promote ministerial convergence among Agriculture, Environment, and Rural Development departments for cohesive implementation.
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- 23 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant development, the United States has announced its decision to withdraw from UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) by December 2026, citing what it perceives as the agency’s anti-Israel bias and its recognition of the State of Palestine as a full member. This marks the third withdrawal of the U.S. from UNESCO and the second under President Donald Trump’s leadership, having previously exited in 2018 and rejoined in 2023 under the Biden administration.
Reasons for U.S. Withdrawal
According to the U.S. State Department, the decision stems from:
- UNESCO’s admission of the State of Palestine as a member state, which contradicts official U.S. policy.
- Allegations that UNESCO promotes divisive social and cultural causes.
- Concerns about the proliferation of anti-Israel rhetoric within the organization.
About UNESCO
Founding and Mandate
- Founded: 16 November 1945 (Constitution in force from 1946).
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Parent Body: United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- Membership: 194 member states and 12 associate members.
- Origin: Born out of post–World War II efforts to foster peace through education, science, and culture.
Objectives
UNESCO aims to build global peace and security by:
- Promoting international cooperation in education, science, culture, and communication.
- Supporting literacy, educational access, and free universal education.
- Acting as a clearinghouse of knowledge, especially in global South nations.
Focus Areas
UNESCO operates in five major sectors:
- Education
- Natural Sciences
- Social and Human Sciences
- Culture
- Communication and Information
Key Functions and Initiatives
Flagship Initiatives
- World Heritage Convention (1972): Protects cultural and natural sites of outstanding universal value.
- Man and the Biosphere Programme (1971): Promotes sustainable development through biosphere reserves.
- Convention for Safeguarding Intangible Cultural Heritage (2003): Preserves oral traditions, performing arts, and rituals.
- Global Education Coalition (2020): Formed during COVID-19 to ensure education continuity.
- Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence (2021): Sets global standards for ethical AI development.
Important Publications
- Global Education Monitoring Report
- World Water Development Report
- World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development
Strategic Importance of UNESCO
- Acts as a platform for intercultural dialogue and peacebuilding.
- Enhances scientific cooperation for issues like climate change and disaster preparedness.
- Supports freedom of expression and combats misinformation globally.
- Promotes equity in global education and digital access.
- Plays a key role in setting ethical standards in science and technology.
U.S. and UNESCO: A Tumultuous Relationship
- The U.S. has historically had a strained relationship with UNESCO:
- 1984: First withdrawal under Ronald Reagan, citing mismanagement and politicization.
- 2002: Rejoined under George W. Bush.
- 2011: Stopped funding after UNESCO admitted Palestine as a member.
- 2018: Withdrew under Donald Trump.
- 2023: Rejoined under Joe Biden.
- 2026: Set to withdraw again.
Implications of U.S. Withdrawal
- Financial Impact: The U.S. has historically contributed around 22% of UNESCO’s budget.
- Geopolitical Signal: Reflects a broader American skepticism towards multilateral institutions.
- Operational Effect: May hamper UNESCO’s work, especially in politically sensitive or conflict regions.
- Diplomatic Fallout: Could weaken the U.S.'s soft power and global cultural influence.
Russia recognizes Taliban-led Government in Afghanistan
- 06 Jul 2025
In News:
Russia has become the first nation to officially recognize the Taliban-led Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, formalizing diplomatic relations with the regime that took control in 2021.
Context and Significance:
- This development comes amid limited international recognition of the Taliban government, which took over Kabul in 2021 after the withdrawal of U.S. and NATO forces.
- Russia’s move could reshape regional diplomacy in Central and South Asia, potentially influencing other neighboring powers like China, Iran, and the UAE, which has also shown warming ties.
- The decision also reflects Russia's strategic interests in counterterrorism cooperation, regional stability, and its broader geopolitical competition with the West.
Profile of Russia
Geographical Overview:
- Continent: Northern Eurasia, straddling both Eastern Europe and Northern Asia
- Area: Approximately 17 million square kilometers, making it the largest country in the world
- Time Zones: Spans across 11 time zones
- Capital City: Moscow
Neighbours and Boundaries:
- Land Borders: Shares land borders with 16 countries—more than any other nation:
- In Europe: Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland (via Kaliningrad), Belarus, Ukraine
- In Asia: Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, North Korea
- Maritime Borders:
- United States (via the Bering Strait)
- Japan (via the Sea of Okhotsk)
- Major Mountain Ranges:
- Ural Mountains: Traditional boundary between Europe and Asia
- Caucasus Mountains: Includes Mount Elbrus, Europe’s highest peak
- Altai, Sayan, and Kamchatka ranges in Siberia
- Key Rivers and Lakes:
- Volga River: Longest river in Europe
- Lena, Yenisei, and Ob Rivers: Flow through Siberia into the Arctic Ocean
- Lake Baikal: World’s deepest and oldest freshwater lake
- Lake Ladoga: Largest lake in Europe by area
- Climatic and Vegetation Zones:
- Encompasses tundra, taiga (boreal forest), steppes, and semi-deserts
- Permafrost regions in Siberia restrict infrastructure and habitation
Chemical Industry – Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains
- 05 Jul 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog has released a comprehensive report envisioning India’s transformation into a global chemical manufacturing hub with a projected 12% share in global value chains (GVCs) and USD 1 trillion in output by 2040.
Current Landscape of India’s Chemical Industry
- Significant Economic Contributor: India is the 6th largest chemical producer globally and 3rd in Asia, contributing over 7% to manufacturing GDP. Key linkages: Pharmaceuticals, textiles, agriculture, and construction.
- Fragmented Sector Structure: Dominated by MSMEs, the sector suffers from lack of integrated value chains and modern infrastructure. Example: Cluster-based growth is concentrated in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
- Low Global Integration: India’s 3.5% share in global chemical value chains reflects weak backward integration and poor export competitiveness. The trade deficit in 2023 was USD 31 billion.
- High Import Dependence: Heavy reliance on China and Gulf countries for feedstocks and specialty chemicals. Example: Over 60% of critical Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are sourced from China.
- Negligible R&D Investment: India invests only 0.7% of industry revenue in R&D, far below the global average of 2.3%, limiting innovation in green and specialty chemicals.
- Regulatory and Procedural Hurdles: Environmental clearance (EC) delays (up to 12–18 months) and procedural bottlenecks lead to cost and time overruns.
- Skilling Deficit:
A 30% shortage of skilled professionals in green chemistry, process safety, and nanotechnology. Example: ITIs and vocational programs lag behind industry requirements.
Emerging Opportunities
- Green Chemistry Revolution: Global shift toward sustainable chemicals presents new market opportunities.
- Geopolitical Realignment: Rising distrust of China globally enables India to emerge as an alternate supplier.
- FTA Leverage: India’s Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with UAE, EU, and ASEAN can enhance tariff-free access to major markets.
- Make in India Ecosystem: Policy support through PLI schemes, Petroleum, Chemicals and Petrochemicals Investment Regions (PCPIRs), and chemical parks.
- Job Creation Potential: The sector could generate 7 lakh skilled jobs by 2030, particularly in petrochemicals, research, and logistics.
Persistent Challenges
- Feedstock Vulnerability: Over-dependence on crude oil and naphtha imports poses price and supply risks.
- Outdated Industrial Clusters: Legacy clusters lack modern safety systems, storage infrastructure, and waste treatment facilities.
- High Logistics Costs: Freight costs are 2–3 times higher than global averages, reducing export competitiveness.
- Regulatory Complexities: Absence of single-window clearances, frequent policy shifts, and inter-state inconsistencies deter investments.
- Weak Industry-Academia Linkages: Poor collaboration leads to low patent output and limited skill development.
NITI Aayog’s Recommendations
- Develop World-Class Chemical Hubs: Upgrade existing clusters and establish empowered committees. Suggested hubs: Paradeep, Dahej, Vizag. Introduce a dedicated Chemical Infrastructure Fund.
- Opex-Based Incentives: Offer operational subsidies linked to import substitution and export potential.
- Boost Technology Access & R&D:
- Establish an industry-academia interface under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Enable technology transfer from global MNCs.
- Streamline Environmental Clearances:
- Simplify processes via DPIIT audit mechanisms.
- Ensure greater transparency and faster approvals.
- Strengthen Skill Development:
- Expand and modernize ITIs and specialized institutes.
- Introduce tailored courses in polymer science, green chemistry, and process safety.
- Negotiate Chemical-Specific FTAs:
- Incorporate product-specific clauses.
- Simplify rules of origin and documentation processes.
Hong Kong International Convention (HKC)

- 03 Jul 2025
In News:
The Hong Kong International Convention (HKC) for the safe and environmentally sound recycling of ships officially came into force on June 26, 2025.
About HKC:
- The HKC is a global treaty adopted under the aegis of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to regulate the safe and environmentally sustainable recycling of ships that have reached the end of their operational life.
Objectives:
- Protect human health, especially that of shipbreaking workers.
- Prevent environmental pollution during ship dismantling.
- Control and manage hazardous materials such as asbestos, heavy metals, and hydrocarbons.
- Ensure safe waste handling and disposal practices in recycling yards.
Key Provisions:
- Inventory of Hazardous Materials (IHM):Ships must maintain an IHM listing all hazardous substances on board.
- Ship Recycling Plan (SRP):A certified SRP must be approved before the ship is sent for dismantling.
- Recycling Completion Certificate:Recycling facilities must issue this certificate within 14 days of dismantling completion.
- Third-Party Audits and Certification:Classification societies recognized by the IMO will conduct compliance audits and issue relevant certifications.
- Authorized Recycling Yards:The convention promotes the use of regulated and approved facilities for ship recycling to ensure compliance with international safety and environmental norms.
Significance:
- Strengthens global maritime safety and sustainable shipbreaking practices.
- Encourages modernization and regulation of recycling yards, especially in developing countries like India and Bangladesh.
- Aligns ship recycling with UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those on health, environment, and decent work.
Operation Deep Manifest

- 03 Jul 2025
In News:
The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI), under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC), Ministry of Finance, launched “Operation Deep Manifest”, resulting in the seizure of Pakistani-origin goods worth ?9 crore.
Key Highlights:
- Seizure Details:39 containers carrying 1,115 metric tonnes of goods—primarily dry dates—were intercepted at Nhava Sheva Port. These goods were falsely declared as originating from the UAE.
- Route Manipulation:The consignments were illicitly routed via Dubai’s Jebel Ali Port after being shipped from Karachi, Pakistan, to obscure their true origin. Shipping documents were falsified and containers were switched during transshipment to evade detection.
- Violation of Policy:This seizure comes after India’s comprehensive ban on Pakistani-origin goods, which took effect on May 2, 2025, following the Pahalgam terror attacks. This replaced the earlier 200% customs duty imposed post-Pulwama (2019) and represents a zero-tolerance economic policy toward Pakistan.
- Financial and Security Links:Investigations uncovered financial linkages with Pakistani and UAE-based entities, pointing to an organized smuggling network with possible illicit financial flows and national security implications.
- Enforcement Action:A partner from one of the importing firms was arrested on June 26, and further criminal and financial investigations are ongoing.
Significance:
- National Security:Helps prevent economic infiltration from hostile states and curbs funding channels that could support anti-national activities.
- Trade Compliance:Acts as a deterrent against third-country transshipment—a common method to bypass sanctions or import bans.
- Tech-Driven Enforcement:Utilized document forensics, data analytics, and container surveillance to detect misdeclarations and track suspect cargo routes.
- Reinforces Policy Posture:Strengthens India's position of economic disengagement with Pakistan in response to cross-border terrorism.
International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA)

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
India, as the Vice President of the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA), actively participated in the 2nd Session of the IALA Council, held in Nice, France.
What is IALA?
The International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA) is a global intergovernmental technical body responsible for:
- Standardizing marine navigation aids (AtoN)
- Enhancing maritime safety
- Promoting environmental protection in marine navigation
Key Facts:
- Established: 1957 (as an NGO; became an IGO in 2024)
- Headquarters: Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, France
- Members: 39 countries
- Status: Transitioned to an Intergovernmental Organization in August 2024 after ratification by 30 states
India’s Role in IALA
India has been a Council Member since 1980, and was elected Vice President (2023–2027) during the 1st General Assembly in Singapore in 2023 — a significant recognition of India’s leadership in maritime affairs.
Major Indian Contributions:
- Development of Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) across 12 major ports
- Leadership in digital navigation aids and maritime innovation
- Promoting lighthouse heritage tourism
- Launching global training programs at the Kolkata Marine Navigation Training Institute
Highlights from the 2nd IALA Council Session
- Keynote: Outlined India’s achievements in integrating marine AtoN and future roadmap
- Technical Discussions:
- Standardization of AtoN and VTS systems
- Harmonized IoT protocols for visual AtoN
- Maritime Service Registry development
- Lighthouse heritage conservation
- Planning IALA’s global activity schedule for 2025–2026
India to Host Key IALA Events
- 3rd IALA General Assembly – December 2025, Mumbai
- 21st IALA Conference – 2027, Mumbai
This reflects global confidence in India’s technical capabilities and strategic importance in the maritime domain.
Significance:
- Strategic Leadership: Reinforces India’s influence in international maritime governance.
- Digital Maritime Innovation: India is contributing to cutting-edge technologies like IoT protocols and digital AtoN.
- Global Capacity Building: Hosting and training initiatives bolster the global maritime workforce.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Lighthouse tourism and heritage preservation align technology with history.
India Develops its first indigenous Mechanical Thrombectomy Device for Stroke Treatment
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s medical technology sector, the Technology Development Board (TDB) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has extended support for the development of the country’s first indigenously manufactured mechanical thrombectomy device for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
What is a Mechanical Thrombectomy Device?
The device is a minimally invasive medical tool designed to treat acute ischemic stroke, which occurs due to a blockage in a large blood vessel in the brain. Unlike conventional thrombolytic drugs that dissolve clots chemically, this device physically extracts the clot, thereby restoring blood flow swiftly and reducing the risk of severe brain damage or paralysis.
Development and Manufacturing
This pathbreaking innovation was developed by S3V Vascular Technologies Ltd, based in Mysuru, with financial backing from the TDB. The manufacturing takes place at an advanced, high-precision production facility within the Medical Devices Park in Oragadam, Tamil Nadu.
Key Features and Technological Highlights
- Indigenous Design: S3V is the first Indian company to conceptualize and produce stroke-intervention tools such as microcatheters, aspiration catheters, guidewires, and stent retrievers.
- R&D and Patents: The company has filed multiple patents, particularly for innovations in clot retriever head design and advanced catheter structures.
- Training and Capacity Building: A simulator-based training program has been initiated to train young medical professionals, with a focus on outreach in Tier-II cities.
- Global Compliance: The device aims to meet CE and USFDA standards, paving the way for international exports and aligning with global quality benchmarks.
Significance for India
- Reduces Import Dependency: The device addresses India’s reliance on expensive, imported stroke-care equipment.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare: By making stroke treatment more affordable, it enhances access to quality care for economically weaker sections.
- Supports Public Health Initiatives: It is expected to be integrated into government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, strengthening the country’s universal healthcare mission.
- Boosts MedTech Ecosystem: This innovation is a major stride in positioning India as a global player in the high-end medical devices sector.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched two major global initiatives to advance inclusive and sustainable agrifood systems:
- “Four Betters Courses” Initiative – To revolutionize agrifood systems education
- “Commit to Grow Equality” Initiative – To bridge the gender gap in agrifood sectors
1. Four Betters Courses Initiative
- Launched: October 2024 during the World Food Forum
- Objective: To integrate FAO’s expertise into global agrifood systems education through partnerships with universities and academic networks.
- Alignment: Anchored in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031
Core Philosophy – The “Four Betters” Approach:
- Better Production – Promote efficient, inclusive, and resilient food systems
- Better Nutrition – Ensure access to safe, nutritious, and affordable diets
- Better Environment – Address climate change and protect ecosystems
- Better Life – Improve rural livelihoods and reduce inequalities
- Delivery Platform: Implemented through the FAO eLearning Academy, which provides over 600 multilingual, certified courses.
2. Commit to Grow Equality (CGE) Initiative
- Launched: 2024 on the platform of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- Objective: To narrow the gender gap in agrifood systems and enhance women’s empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Key Highlights:
- Aims to benefit over 54 million women worldwide
- Mobilizes $1 billion in investments toward gender-responsive agrifood initiatives
- Provides strategic tools for tracking gender equality outcomes in public and private sectors
- Promotes gender-aligned national agricultural policies
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking and fosters collaboration across governments, NGOs, and the private sector
WMO Climate Forecast 2025–2029
- 30 May 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its latest decadal climate forecast (2025–2029), warning of a continued trend of record-breaking global temperatures. This projection raises serious concerns about climate risks, sustainable development, and international climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Key Projections:
- Annual Global Temperature Rise: Each year from 2025–2029 is projected to be 1.2°C to 1.9°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Record Heat Likelihood:
- 80% chance that at least one year will surpass 2024, currently the warmest year on record.
- 86% probability that one year will exceed the 1.5°C threshold.
- Five-Year Mean Warming: 70% chance that the 2025–2029 average will be above 1.5°C, a sharp rise from 47% (2024–2028) and 32% (2023–2027).
Note: The Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C limit refers to long-term (20-year) averages, but short-term overshoots are now increasingly probable.
Regional and Thematic Insights:
1. Arctic Amplification: Arctic winters (Nov–Mar) are projected to be 2.4°C warmer than the 1991–2020 average—3.5× faster than the global rate.
2. Sea Ice Decline: Continued sea ice reduction is expected in the Barents Sea, Bering Sea, and Sea of Okhotsk, impacting marine biodiversity and indigenous livelihoods.
3. Precipitation Variability:
- Wetter-than-average conditions likely in:
- Sahel region
- Northern Europe
- Alaska and Northern Siberia
- Drier conditions expected over:
- Amazon Basin
- Parts of South Asia
South Asia may witness generally wet years, though seasonal variability will persist.
Impact and Implications:
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased warming will fuel more intense heatwaves, extreme rainfall, droughts, and floods, stressing both urban systems and agriculture.
- Cryosphere and Ocean Changes:
- Accelerated glacier and sea ice melt will raise sea levels.
- Ocean heating contributes to acidification and marine biodiversity loss.
- Threat to Sustainable Development: Progress on SDGs, particularly food security, water availability, and health, is at risk in vulnerable regions.
Way Forward:
- Revise NDCs at COP30: Strengthen and align Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with the 1.5°C goal.
- Accelerate Clean Energy Transition: Promote renewables, energy efficiency, and net-zero strategies to reduce GHG emissions.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Climate Monitoring & Forecasting: Enhance WMO-led regional forecasts and risk assessment tools.
- Preserve Natural Carbon Sinks: Protect forests, wetlands, and oceans to mitigate atmospheric CO?.
Maasai Tribe and the Carbon Credit Conflict in Tanzania
- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
The Maasai, a prominent indigenous community in East Africa, are resisting international carbon credit projects in Tanzania. They fear these initiatives may lead to land dispossession and the erosion of their traditional pastoralist lifestyle.
Who are the Maasai?
- Ethnic Group: Semi-nomadic pastoralists found primarily in Tanzania and Kenya, especially in the Great Rift Valley and semi-arid savannas.
- Language:Maa (Eastern Sudanic branch, Nilo-Saharan family).
- Cultural Identity:
- Known for distinct attire, beadwork, and warrior traditions.
- Socially organized through patrilineal clans, divided into moieties and age-sets (from junior warriors to senior elders).
- Youth (Morans) undergo bush training for resilience and discipline.
- Livelihood:
- Rely on cattle, sheep, and goats for milk, meat, and blood.
- Practice transhumance, moving seasonally for water and pasture.
- Reside in kraals—circular enclosures with mud-dung houses and thorn fences.
Carbon Credit Projects and Rising Tensions
- Projects Involved:
- Longido and Monduli Rangelands Carbon Project (Volkswagen ClimatePartners).
- Resilient Tarangire Ecosystem Project (The Nature Conservancy).
- Area Affected: Nearly 2 million hectares of Maasai grazing land.
- Project Goal: Store soil carbon and sell offsets to polluters globally.
Maasai Concerns and Resistance
- Forced Land-Use Changes:Carbon projects impose structured rotational grazing (e.g., 14-day grazing cycles), disrupting centuries-old mobility practices.
- Lack of Consultation:Research by the Maasai International Solidarity Alliance (MISA) shows widespread violations of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC).
- Women and youth were excluded from consultations.
- Some communities unknowingly entered 30–40 year contracts.
- Payments were often tokenistic and poorly explained.
- Economic and Legal Risks:
- Villages lack clarity on revenue shares from credits.
- Contracts lock communities into rigid systems despite village land-use plans being reviewed every 10 years.
- Intermediaries—not end buyers—dominate the agreements.
Government and Global Dimensions
- Tanzania’s Push:The government expects $1 billion/year from carbon credit sales and is streamlining the sector through the National Carbon Monitoring Centre (NCMC).
- Global Scrutiny:
- Investigations reveal over 90% of rainforest offsets by some certifiers are ineffective.
- Soil carbon in semi-arid areas (like Maasai rangelands) is volatile and hard to quantify.
Grassroots Resistance and Legal Action
- Cultural and Spiritual Attachment:Land is integral to Maasai identity, beyond livestock rearing—it holds spiritual and cultural significance.
- Legal Mobilization:Young warriors, once defending livestock from predators, now advocate legally to protect ancestral land.MISA, formed after violent evictions in 2022 (Ngorongoro, Loliondo), spearheads resistance against exploitative schemes.
Asian Productivity Organization (APO)

- 25 May 2025
In News:
India has officially taken over the Chairmanship of the Asian Productivity Organization (APO) for the 2025–26 term during the 67th Governing Body Meeting.
About APO:
- Type: Regional intergovernmental organization.
- Established:1961.
- Headquarters:Tokyo, Japan.
- Membership: 21 member economies from the Asia-Pacific region, including India, Japan, Iran, Indonesia, Vietnam, Philippines, South Korea, Singapore, and others.
- India:Founding member of the APO.
Key Objectives:
- Enhance productivity in member countries through mutual cooperation.
- Foster sustainable and inclusive socioeconomic development.
- Promote innovation-led growth across industry, agriculture, services, and public sectors.
Core Functions:
- Policy Advisory:Assists governments in designing national productivity strategies.
- Capacity Building:Conducts training programs, workshops, and research initiatives to boost productivity skills.
- Centres of Excellence:Facilitates innovation and best practices sharing among members.
- Green Productivity:Promotes environmentally sustainable growth models.
- Digital & Innovation Ecosystem:Encourages digital transformation and entrepreneurship through regional collaboration.
Organizational Structure:
- Governing Body:The apex decision-making entity; sets strategic direction and reviews performance annually.
- National Productivity Organizations (NPOs):Act as nodal agencies coordinating with the APO at the national level.
- Secretariat:Based in Tokyo, headed by a Secretary-General, manages daily operations.
Significance for India:
- India’s chairmanship marks a step forward in shaping regional productivity policies and highlights India’s commitment to sustainable development and economic cooperation in the Asia-Pacific.
State of the World’s Animal Health Report 2025

- 25 May 2025
In News:
Infectious animal diseases are spreading to previously unaffected regions and species, with nearly half (47 per cent) capable of zoonotic transmission or spreading between animals, according to the inaugural State of the World’s Animal Health report released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH).
Key Details:
Published by:
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), formerly OIE (Office International des Epizooties), founded in 1924, headquartered in Paris.
- Recognized by the WTO for setting global standards on animal health and zoonotic disease control.
Objective of the Report:
- To provide a comprehensive global assessment of animal health trends, risks, and disease outbreaks.
- To promote a One Health approach, linking animal health with human health and environmental sustainability.
Major Findings:
1. Rising Zoonotic Threats:
- 47% of animal diseases reported between 2005–2023 have zoonotic potential (can spread from animals to humans).
- These include avian influenza, African swine fever (ASF), foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR).
2. Geographic Expansion of Diseases:
- Diseases are emerging in new regions and species due to climate change, global trade, and ecosystem disruptions.
- Example: ASF jumped over 1,800 km to reach Sri Lanka in 2024, marking the year's most significant disease leap.
- PPR re-emerged in Europe, traditionally limited to developing regions.
3. Avian Influenza Evolution:
- Over 630 million birds culled or lost in 20 years.
- In 2024, more outbreaks were reported in non-poultry species (55 countries) than poultry (42 countries).
- Mammal infections doubled, raising concerns of cross-species transmission.
4. Other Notable Disease Events:
- Germany faced its first FMD outbreak since 1988.
- New World Screwworm, a parasitic fly, re-emerged in Mexico and Nicaragua.
- Bluetongue virus reported in 23 countries with over 3,500 cases in 2024.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): A Global Threat
Key Data:
- By 2050, AMR may cause:
- Loss of livestock threatening food security for 2 billion people.
- $100 trillion global economic loss.
Drivers:
- Indiscriminate use of antibiotics in livestock, aquaculture, and agriculture.
- Around 20% of countries still use antimicrobials as growth promoters, including high-priority drugs like colistin and enrofloxacin.
Trends:
- Global antibiotic use in animals fell by 5% (2020–2022).
- Europe: 23% decline.
- Africa: 20% decline.
Recommendations by WOAH:
- Enhance vaccine access and distribution, especially in low-income countries.
- Strengthen Veterinary Services, surveillance, and biosecurity.
- Improve hygiene and disease prevention to reduce antibiotic dependence.
- Promote international cooperation under the One Health framework.
- Ban or regulate the use of antibiotics as growth promoters.
About WOAH:
- Intergovernmental organization with 183 member countries, including India.
- Monitors, controls, and reports on animal diseases to ensure safe trade, public health, and food security.
- Partner in Global Action Plan on AMR with WHO and FAO.
Indian Initiatives on AMR & Animal Health:
- National Action Plan on AMR (2017–2021) – Focus on awareness, surveillance, infection control, and R&D.
- FSSAI guidelines to regulate antibiotic residues in food of animal origin.
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP) – Focus on vaccination against FMD and Brucellosis.
Operation Black Forest
- 18 May 2025
In News:
One of India’s most extensive anti-Naxal offensives in recent years, Operation Black Forest, resulted in the elimination of 31 Maoists. The operation was conducted in the Kurraguttalu Hills, a strategic Maoist stronghold located on the Chhattisgarh–Telangana border.
Key Features of Operation Black Forest
- Type: High-intensity counterinsurgency operation
- Duration: 21 days
- Area of Operation:Kurraguttalu Hills (approx. 1,200 sq km), known for rugged terrain and dense forest cover
Objectives:
- Dismantle key Maoist bases and operational infrastructure
- Neutralize senior Maoist leadership
- Re-establish state control in insurgency-affected zones
- Contribute to the national target of eliminating Left Wing Extremism (LWE) by March 31, 2026
Security Forces Involved:
- Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF)
- CoBRA (Commando Battalion for Resolute Action) units
- Chhattisgarh Police, including:
- Special Task Force (STF)
- District Reserve Guard (DRG)
About Kurraguttalu (Karregutta) Hills
- Geographical Location: On the inter-state border of BhadradriKothagudem district (Telangana) and Sukma district (Chhattisgarh)
- Terrain Characteristics:
- Extends over 25–50 km
- Features include steep elevations (~5,000 feet), caves, waterfalls, and dense forest cover
- Topography ideal for guerrilla warfare and concealment
- Local Terminology: Referred to by tribal communities as “Black Hills” or “Carregutta”
Demographic & Socio-political Aspects:
- Inhabited by Koya, Gond, and Chenchu tribes
- Tribal communities have historically been vulnerable in the conflict zone, often caught between insurgents and state forces
Other Key Maoist-affected Regions
- Abujhmad (Chhattisgarh)
- Malkangiri (Odisha)
- Gadchiroli (Maharashtra)
These areas, like Karregutta, serve as critical Maoist corridors with difficult terrain and limited state presence, posing ongoing challenges to internal security operations.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- 11 May 2025
In News:
India has warned it will retaliate if the United Kingdom implements its proposed Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) from January 1, 2027, calling it a violation of the Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) principle of international climate agreements.
What is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- It is a carbon tax on imports based on their carbon intensity of production.
- Aim: Prevent carbon leakage by aligning the cost of carbon between domestic and foreign producers.
- Sectors likely to be initially targeted include steel, cement, aluminium, and energy-intensive products.
- The UK is expected to implement its version of CBAM in 2027, following a similar approach by the European Union.
India’s Concerns
- Violation of CBDR Principle
- CBAM undermines the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, which recognize that developing countries require flexibility and support for decarbonization.
- India’s per capita emissions are low, but its carbon intensity is higher due to developmental needs.
- Unfair Trade Practice
- CBAM could nullify tariff concessions negotiated under the India–UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman and Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal have labelled CBAM “unfair” and discriminatory.
- Double Taxation and Export Losses
- Indian exporters may face double taxation—domestic environmental levies and UK’s border tax.
- India proposed a ‘rebalancing mechanism’ and MSME carve-out, both of which the UK declined.
- Export-heavy sectors like textiles, leather, ceramics, engineering goods, and steel may be hit hard due to sustainability compliance burdens.
- MSME Vulnerability
- Labour-intensive MSMEs lack the capacity to meet expensive ESG norms and carbon tracking requirements.
- India's request for exemption or compensation for MSMEs was not accepted.
India’s Response Strategy
- India reserves the right to retaliate if CBAM is imposed.
- Potential responses include:
- Domestic carbon taxation to offset UK’s CBAM and use revenue for green transition.
- Invoking a rebalancing clause under the FTA’s “general exceptions” (similar to GATT), allowing trade countermeasures for environmental or public interest.
Strategic Implications for India
- Non-tariff barriers like CBAM can undermine market access gained through FTAs.
- India must stay alert to evolving trade conditions involving environment, labour, IPR, and gender standards, which often require policy adjustments.
- Calls for India to strengthen its carbon tracking, ESG frameworks, and climate-compliant production systems to remain globally competitive.
Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)

- 08 May 2025
About the OIC
The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is the world’s second-largest intergovernmental organization after the United Nations, comprising 57 member states across four continents. It was established on September 25, 1969, following the historic summit held in Rabat, Morocco, which was convened in response to the arson attack on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in occupied Jerusalem.
Objectives and Purpose
The OIC’s primary goals are to:
- Preserve and promote Islamic values.
- Safeguard the national sovereignty and independence of its member states.
- Contribute to international peace and security.
- Serve as the collective voice of the Muslim world, protecting their interests across economic, social, and political spheres.
Structure and Headquarters
- The OIC’s headquarters is located in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Its official languages are Arabic, English, and French.
Membership
Notable member countries include Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia, Maldives, Morocco, Niger, Oman, Pakistan, the Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Turkey, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, among others.
Principal Organs of the OIC
- Islamic Summit Conference (ISC):The highest authority of the OIC, meeting every three years to set the organization’s policies and strategic direction.
- Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM):Convening annually, the CFM reviews and oversees the implementation of decisions made by the Islamic Summit.
- General Secretariat:The executive branch responsible for executing the resolutions of the ISC and CFM.
Additionally, the OIC has established various ministerial-level committees—some chaired by heads of state—to coordinate cooperation among member countries in political, economic, cultural, social, spiritual, and scientific fields.
Partnerships and Global Engagement
The OIC collaborates closely with international organizations, including all specialized agencies of the United Nations, as well as governments and civil society organizations (CSOs). These partnerships help address concerns affecting its member states and the global Muslim community.
PashuAushadhi Initiative

- 12 Mar 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the PashuAushadhi initiative to establish dedicated stores across the country offering affordable, high-quality generic veterinary medicines. This move aims to reduce the out-of-pocket expenditure of farmers and enhance animal health and productivity, especially in the livestock and dairy sectors.
Key Features:
- Modelled on PMBJK: Inspired by the success of the Pradhan Mantri BharatiyaJanaushadhiKendras (PMBJK) that provide generic human medicines, the PashuAushadhiKendras will serve the same purpose for animals.
- Affordable Veterinary Drugs: These Kendras will provide non-branded (generic) veterinary medicines at significantly lower prices.
- Ethnoveterinary Medicines: Alongside allopathic drugs, they will also stock traditional remedies based on indigenous knowledge, compiled by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB). These include formulations for fever, diarrhoea, indigestion, mastitis, and more.
Implementation Framework
- The initiative is part of the revised Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP), approved by the Union Cabinet.
- Run by Co-operative Societies & PM-KisanSamriddhiKendras (PMKSKs).
- An initial budget of ?75 crore has been allocated under the LHDCP for veterinary medicine access and sales incentives.
Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP)
- With an outlay of ?3,880 crore for 2024–25 and 2025–26, the LHDCP focuses on:
- Prophylactic vaccination against major animal diseases (e.g., FMD, Brucellosis, CSF, PPR, Lumpy Skin Disease).
- Disease surveillance and veterinary infrastructure strengthening.
- Capacity building of veterinary services across India.
Need and Significance
- As per the 20th Livestock Census (2019), India has 535.78 million livestock, including over 302 million bovines.
- Livestock productivity is often hampered by preventable diseases.
- Farmers bear significant expenses on veterinary care, highlighting the need for cost-effective treatment options.
African-Asian Rural Development Organization (AARDO)

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
The 21st AARDO Conference recently concluded in New Delhi, reaffirming the commitment to community-led rural development, local knowledge sharing, and South-South cooperation.
About AARDO
- Full Form: African-Asian Rural Development Organization
- Nature: Intergovernmental, autonomous organization
- Established:March 31, 1962
- Headquarters:New Delhi, India
- Origin:
- Conceptualized at the 1955 East Asian Rural Reconstruction Conference (Tokyo)
- Formalized after the 1961 Afro-Asian Conference on Rural Reconstruction (New Delhi)
- Permanent HQ established in 1966 in India
Membership
- Full Members:32 countries from Asia and Africa (e.g., India, Bangladesh, Egypt, Zambia, Malaysia)
- Associate Members:3 entities (e.g., Korea Rural Community Corporation, Agricultural Bank of Sudan)
- Eligibility: Open to Afro-Asian countries that are full or associate members of the UN or its specialized agencies focused on rural development
Observer Status with International Organizations
AARDO has observer status with:
- FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization
- IFAD – International Fund for Agricultural Development
- UNDP – United Nations Development Programme
- UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
- UNCTAD – United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
Objectives & Aims
- South-South Cooperation: Enhance technical and economic collaboration in rural development between Asia and Africa
- Sustainable Rural Development: Promote poverty alleviation, food security, and climate-resilient agriculture
- Capacity Building & Knowledge Sharing: Encourage exchange of best practices, innovations, and research
Functions
- Policy & Dialogue Platform: Facilitates discussions among member countries on rural development strategies
- Training & Capacity Building: Organizes international, regional, and national training programs to strengthen rural institutions
- Research & Action Studies: Initiates and disseminates research on shared challenges in agriculture and rural livelihoods
- Pilot Projects: Offers technical and financial assistance for pilot projects to serve as replicable models
- International Collaboration: Partners with UN agencies, regional bodies, and NGOs for integrated rural development
- Data Sharing: Provides members with disaggregated statistics and information for informed decision-making
Mass Stranding of False Killer Whales in Tasmania

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, over 150 false killer whales were found stranded on a remote beach near Arthur River on the northwest coast of Tasmania, Australia. The incident is one of several mass strandings reported in the region in recent years.
The event echoes earlier mass strandings:
- In 2022, 230 pilot whales stranded at Macquarie Harbor.
- In 2020, 470 long-finned pilot whales were stranded at the same site—the largest mass stranding in Australian history.
Possible Causes of Whale Strandings
Although the precise cause remains uncertain, potential factors include:
- Disorientation from loud underwater noises (e.g., naval exercises, seismic surveys)
- Illness, old age, injury
- Fleeing predators
- Severe weather events
- Geomagnetic anomalies
About False Killer Whales
- False killer whales (Pseudorca crassidens) are not true killer whales but belong to the Delphinidae family, which also includes dolphins and pilot whales.
- They are large, social cetaceans, often found in warm, deep oceanic waters.
- These whales are highly vocal and social, forming strong social bonds within pods.
- Like other cetaceans, they rely on echolocation (underwater sound) for communication, hunting, and navigation.
About Killer Whales (Orcas)
- Although not involved in the stranding, killer whales (Orcinus orca) are relevant as close relatives within the same family (Delphinidae).
- Known for their distinct black and white markings, orcas are the largest members of the dolphin family.
- They are globally distributed in both open oceans and coastal waters.
- Killer whales live in stable matrilineal pods and use complex vocalizations.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List classifies false killer whales and killer whales as Data Deficient, indicating that there is insufficient information to assess their risk of extinction.
FulaniCommunity
- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The Fulani, one of Africa’s largest and most dispersed ethnic communities, trace their ancestry to the ‘Green Sahara’ period (12,000–5,000 years ago), according to recent genetic and anthropological research. This period, when the Sahara was a fertile, habitable landscape, marks the early development of African pastoralism.
The Fulani population is estimated at 40 million, spread across West and Central Africa, from Senegal and Guinea in the west to Lake Chad in the east. They are particularly concentrated in Nigeria, Mali, Guinea, Senegal, and Niger, and inhabit the Sahel-Savannah belt, straddling arid and semi-arid regions.
Nomadic Lifestyle and Social Structure
Traditionally known for their nomadic pastoralism, the Fulani have maintained a unique socio-cultural identity despite centuries of migration and contact with other African populations. Their society is internally diverse, divided into three main groups:
- Makiyaya: Nomadic herders
- FulaninSoro: Town dwellers
- Bararo: Forest dwellers, with strong ties to ancestral rituals and nature-based belief systems
Fulani communities are largely egalitarian, with a deep emphasis on kinship, family structure, and communal responsibility. Polygamy is widely practiced, and marriage ceremonies are elaborate, often involving intricate rituals and festive celebrations.
Women’s Role and Cultural Expression
Fulani women are recognized for their weaving, artisanal craftsmanship, and particularly their hairstyles, which are often elaborately styled and adorned with beads and cowrie shells—symbols of both identity and aesthetic tradition.
Linguistic and Religious Identity
The Fulani speak Fula (also called Fulfulde or Pulaar), a language belonging to the Atlantic branch of the Niger-Congo language family. Though largely Muslim, many retain spiritual connections with nature-based traditions, particularly among the Bararo groups.
Genetic Heritage and Historical Significance
A recent multinational study led by Uppsala University and Charles University analyzed biological and anthropological data from 460 Fulani individuals across 18 locations in seven African countries. It confirmed a complex genetic history, shaped by:
- Ancient North African ancestry, particularly linked to populations akin to modern-day Berbers of Morocco
- Historical interactions with West, Central, and East African communities
- A shared ancestral genetic component, likely rooted in early pastoral communities of the Green Sahara era
The research underscores that despite their high mobility and limited archaeological footprint, the Fulani have preserved a distinct genetic and cultural identity for millennia.
President’s Rule Imposed in Manipur
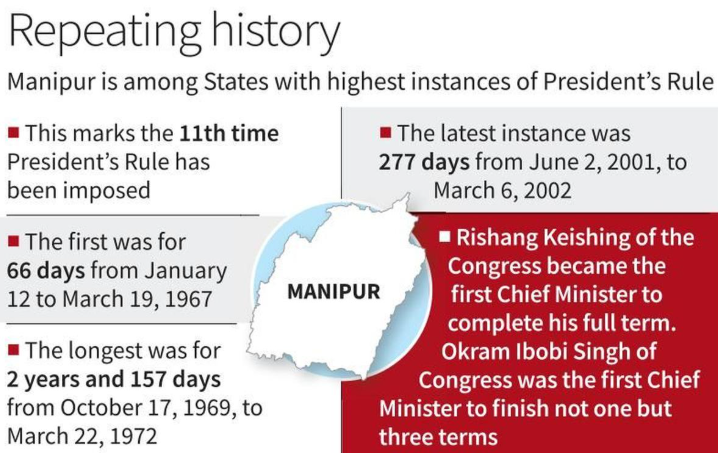
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
On 13th February 2025, President DroupadiMurmu imposed President’s Rule in Manipur under Article 356 of the Constitution, following a report submitted by the State Governor Ajay Kumar Bhalla. The move comes in the wake of a prolonged period of ethnic violence, governance vacuum, and the resignation of Chief Minister N. Biren Singh on 9th February 2025.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 356 empowers the President to assume control of a state’s administration if it is determined that the state cannot be governed as per constitutional provisions.
- The Governor’s report or other evidence of breakdown is a prerequisite.
- Under this, the elected state government is dismissed, and the Governor becomes the executive head on behalf of the President.
- The State Legislative Assembly is either dissolved or placed under suspended animation. In Manipur’s case, it is under suspended animation, with its term valid until 2027.
- The proclamation must be approved by both Houses of Parliament within two months, and if extended, it can last up to six months at a time, with a maximum duration of three years.
Crisis Background and Ethnic Conflict
Manipur has witnessed an intense ethnic conflict between the Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities since May 3, 2023. The violence has led to:
- Over 250 people killed, and
- More than 60,000 displaced.
Security concerns and political instability escalated after the Chief Minister’s resignation, with the BJP leadership unable to find a consensus candidate for replacement. The deteriorating law-and-order situation, coupled with governance paralysis, prompted the imposition of President’s Rule.
Security and Migration Concerns
Former CM N. Biren Singh raised alarm over:
- Rising illegal immigration through the 398-km porous border with Myanmar, worsened by the Free Movement Regime (FMR).
- A demographic shift threatening the State’s land, identity, and resources.
- Post-violence governance failure, as state machinery struggled to respond effectively.
He emphasized the need to intensify detection and deportation of illegal immigrants, a concern linked to the root causes of ethnic tension.
Historical Context
- This is not the first time Manipur has come under central rule. The last imposition of President’s Rule in Manipur lasted 277 days, from June 2, 2001 to March 6, 2002.
Ranikhet Disease in India

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM)
- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO (UNESCO-IOC) announced the signature of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) enabling the creation of the Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM).
What is the Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM)?
- It is a collaborative governance initiative aimed at the sustainable management of marine resources in the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf region.
- Conceived under the 10-year CLME+ Strategic Action Programme (SAP)—endorsed in 2014—it represents a transformative step toward integrated ocean governance.
Key Objectives of OCM:
- Promote sustainable fisheries
- Advance ecosystem restoration and marine spatial planning
- Establish marine protected areas (MPAs)
- Encourage pollution control and blue carbon development
- Foster cross-country and cross-institutional cooperation
It builds on lessons from earlier efforts like the Pacific Islands Regional Ocean Policy (PIROP), aiming to avoid past pitfalls such as vague targets, lack of integration, and funding shortfalls.
Significance of the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf Region:
- Coral reefs and fisheries contribute ~$610 million annually to local economies
- The North Brazil Shelf is home to over 500 fish species
- Acts as a natural barrier against storms, crucial for climate resilience
Blue Carbon and Climate Action:
The OCM promotes blue carbon projects that utilize coastal ecosystems (like mangroves and seagrasses) for carbon storage, enhancing climate resilience and providing livelihoods to local communities.
Funding Details:
- $15 million from Global Environment Facility (GEF) via the UNDP/GEF PROCARIBE+ Project (2024–2028)
- Additional $126.02 million in co-financing mobilized
- However, the funding is modest compared to initiatives like the Global Fund for Coral Reefs (targeting $3 billion by 2030), raising concerns about OCM's long-term financial sustainability.
Role of IOC-UNESCO:
Established in 1961, the IOC of UNESCO promotes international cooperation in ocean science and policy. Key functions include:
- Marine scientific research (climate, biodiversity, sustainability)
- Tsunami warning systems
- Oceanographic data collection and dissemination
- Leading the UN Ocean Decade (2021–2030) for global marine conservation
Why OCM Matters:
- Addresses the Ocean–Climate–Biodiversity nexus
- Aims to ensure equitable access to marine resources
- Prioritizes local and vulnerable communities
- Integrates traditional knowledge with scientific research for culturally inclusive conservation
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
National Gopal Ratna Award 2024
- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards(NGRA); one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA):
- Purpose:Recognize and encourage individuals, AI technicians, dairy cooperatives, and farmer organizations in the livestock and dairy sector.
- Categories:
- Best Dairy Farmer (Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds)
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT)
- Best Dairy Cooperative/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Addition (2024):Special awards for North Eastern Region (NER) to promote dairy development in the area, with winners in all three categories.
- and Prizes:
- Rs. 5 lakhs for 1st rank, Rs. 3 lakhs for 2nd rank, Rs. 2 lakhs for 3rd rank, and Rs. 2 lakhs for Special NER Award in the categories of Best Dairy Farmer and Best Dairy Cooperative/FPO/MPCs.
- For Best AIT, winners will receive a Certificate of Merit and a memento.
- Process:Winners selected from 2,574 applications via an online portal (https://awards.gov.in).
- The livestock sector is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to agriculture and providing livelihood, especially for small and marginal farmers, women, and landless laborers.
- Indigenous breeds have immense genetic potential, but their population and performance have been declining. To address this, the Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development in 2014 to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
National Milk Day
- It is celebrated annually on November 26 in India to honor the significant contributions of milk and the dairy industry to the country's development.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of Dr VergheseKurien, the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, who played a pivotal role in transforming India into the largest producer of milk globally.
- National Milk Day was first celebrated on November 26, 2014, after the Indian Dairy Association (IDA), along with various dairy institutions across the country.
Parliamentary Panel's Review on Mechanism to Curb Fake News

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology is reviewing mechanisms to curb fake news, following the Bombay High Court striking down a provision of the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
- The controversial provision allowed the government to identify and flag "fake news" on social media through its Fact Check Unit (FCU).
- The panel, led by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey, has summoned representatives from News Broadcasters and Digital Association and the Editors Guild of India to discuss the issue on November 21, 2024.
Issue with the Amended IT Rules:
- The IT Rules, 2021 were amended in April 2022 to include “government business” under the definition of fake news, expanding the scope of content flagged by the FCU.
- This amendment was challenged by media bodies and individuals like comedian Kunal Kamra, leading to the Bombay High Court striking it down in 2024.
- The court deemed the provisions unconstitutional, citing concerns about transparency and the potential misuse of power.
Types of Fake News:
- Misinformation: False information spread unintentionally.
- Disinformation: Deliberately false information meant to deceive and cause harm.
Status of Fake News in India:
- India as a major spreader of misinformation: The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2024 report identifies disinformation as a significant short-term risk, with India as one of the largest consumers and producers of false information.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and YouTube are widely used in India for news dissemination, making them a breeding ground for fake news.
- Spread of Political and Religious Misinformation: Fake news often serves political or religious agendas, leading to societal polarization and conflict.
Government Efforts to Combat Fake News:
- IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: This amendment expanded the scope of "fake news" to include “government business” and gave the FCU the authority to flag misleading content.
- Press Information Bureau (PIB) Fact Check Unit: The PIB continues to run a fact-checking initiative, but it lacks the authority to remove flagged content from social media platforms.
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) aim to improve digital literacy, especially in rural areas, to help citizens identify and avoid fake news.
Melanistic Tigers
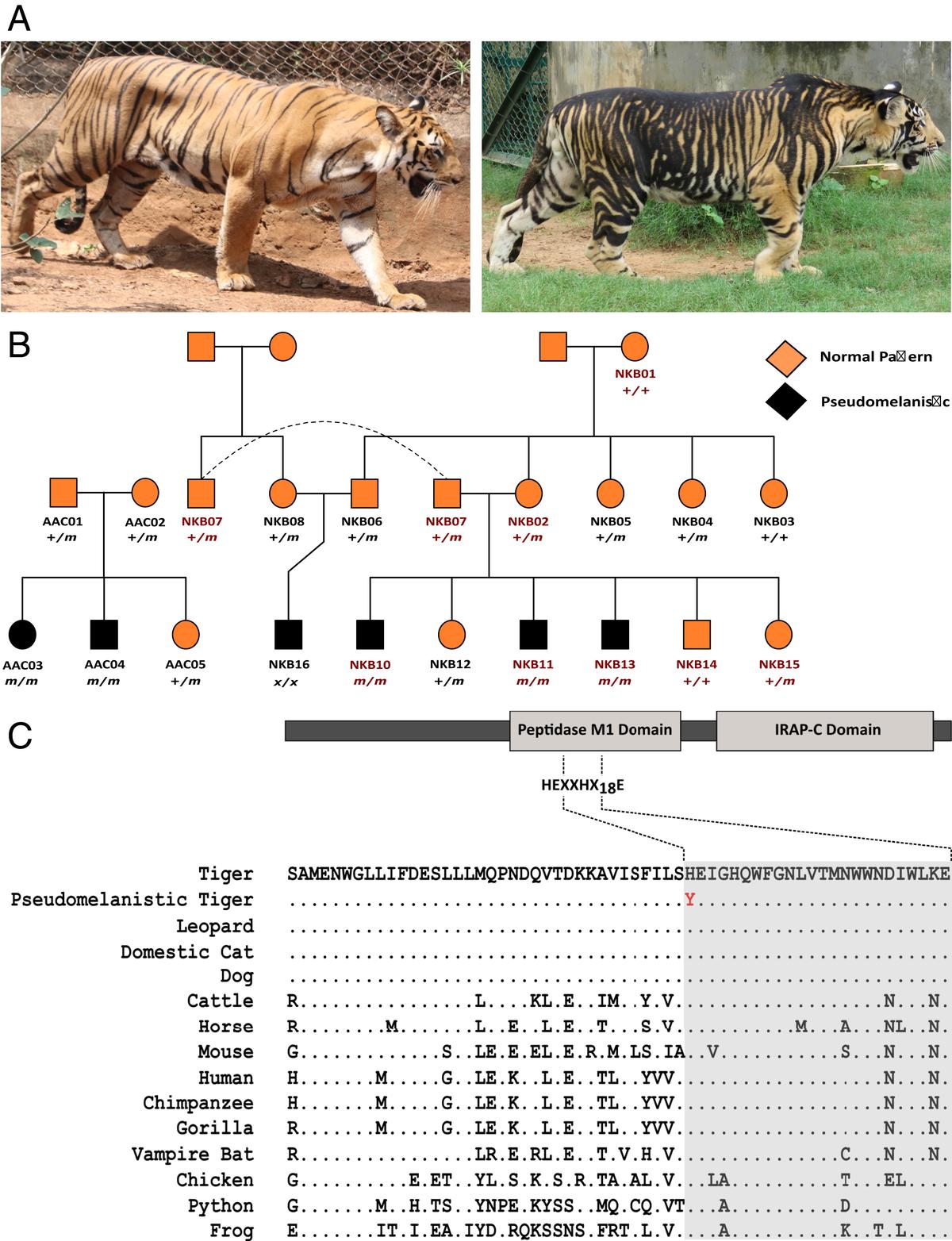
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar will attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad on October 15-16, 2023.
- This marks the first visit by an Indian External Affairs Minister to Pakistan since Sushma Swaraj in 2015.
Context of the Visit:
- The visit is primarily for the SCO meeting, reflecting India's focus on regional cooperation mechanisms.
- No bilateral meetings have been scheduled as of now, although Jaishankar's presence is based on "reciprocity" following Pakistan's participation in an earlier SCO meeting in India.
SCO Overview:
- Established on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai; evolved from the "Shanghai Five" formed in 1996.
- Original members included China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and later Uzbekistan.
- Current members: India, Pakistan, Iran, and others, with Afghanistan and Mongolia holding Observer Status.
Significance of the SCO:
- Focuses on security cooperation, primarily among Asian nations.
- Seen as an alternative to Western international frameworks, especially with heavyweights like Russia and China positioning against US influence.
- India's inclusion alongside Pakistan in 2017 reflects the geopolitical jostling between Russia and China.
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- While SCO promotes cooperation, underlying tensions remain, particularly between India and Pakistan, and India and China.
- The organization has limited tangible outcomes due to member states' rivalries and differing interests.
India's Objectives in SCO:
- Provides a platform for enhancing relations with Central Asian countries, addressing common security concerns.
- Involves participation in the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) to combat terrorism and drug trafficking.
India-Pakistan Relations:
- Jaishankar's visit is seen in light of ongoing tensions; India shares difficult relations with both China and Pakistan.
- India canceled a summit under its presidency last year, opting for a virtual format instead.
Implications for Regional Politics:
- The visit comes shortly after the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections, with potential implications for India-Pakistan ties.
- Despite attending the SCO meeting, there is little expectation of progress in the India-Pakistan peace process.
- Recent statements from the Indian government criticize Pakistan for hosting wanted individuals, reflecting ongoing diplomatic tensions.
Strategic Importance:
- Participation in SCO allows India to engage with key regional players, including Russia, China, and Central Asian leaders.
- The meeting serves as preparation for India's participation in upcoming BRICS discussions, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these groupings.
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
AVGC: The Future of Media & Entertainment Industry

- 30 Sep 2024
Introduction
- The AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics) sector is set to be the future of the media and entertainment industry.
- According to the FICCI-EY 2024 report, India now boasts the second-largest anime fan base globally and is projected to contribute 60% to the worldwide growth in anime interest in the coming years.
- In a significant step toward making India a global hub for AVGC, the Union Cabinet recently approved the establishment of a National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR) in Mumbai.
NCoE Background
- NCoE will be set up as a Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013 in India with Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry and Confederation of Indian Industry representing the industry bodies as partners with the Government of India.
- The establishment of the NCoE follows the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs 2022-23 budget announcement, which proposed the creation of an AVGC task force in the country.
- NCoE AVGC aims at creating a world class talent pool in India to cater to the Indian as well as global entertainment industry.
- Provisionally named the Indian Institute for Immersive Creators (IIIC), this center aims to revolutionize the AVGC sector and foster innovation in immersive technologies.
- It will be modeled after renowned institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
Objective of NCoE (IIIC)
Boasting a growth rate of 25% and an estimated value of ?46 billion by 2023 (FICCI-EY Report 2023), the animation industry in India is thriving and offers a promising future for passionate young talent.
Below are some of the key objectives of the NCoE (IIIC):
- Focusing of creating Indian IP
- Leveraging our cultural heritage in new age
- Create a multiplier effect in the industry
- An industry led initiative, in partnership with state and academia
- Integrated focus on education, skilling industry, development, innovation
- Hub and spoke model of development to be followed
- IIIC as the hub and several center’s as its spokes dedicated innovation and research fund to promote start-up ecosystem
Conclusion
The Union Cabinet's approval of the National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for AVGC marks a pivotal step in strengthening India’s media and entertainment industry. This initiative is set to boost the economy while creating new job opportunities in the rapidly growing AVGC sector. As a global hub for filmmaking, India's advancements in technology and infrastructure will enable the production of high-quality content, positioning the country as a leader in technological innovation and creativity.
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge was adopted at the Diplomatic Conference held under the aegis of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) at its headquarters in Geneva recently.
What is the WIPO Meeting 2024?
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024 focuses on final-stage negotiations for a proposed treaty on intellectual property, genetic resources, and associated traditional knowledge.
- The aim is to protect the rights of communities that conserve genetic resources and hold traditional knowledge of their use.
- The main goal of the treaty is to enhance the efficacy, transparency, and quality of the patent system regarding genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It aims to prevent patents for non-novel or non-inventive inventions and ensure proper disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications.
Key challenges in the negotiations:
- Key challenges include reaching a consensus on mandatory disclosure requirements, addressing biopiracy, deciding on the inclusion of DSI in the treaty, and defining traditional knowledge.
- Countries like the United States, Japan, and South Korea generally oppose mandatory disclosure requirements, adding complexity to the negotiations.
What are genetic resources and traditional knowledge associated?
- Genetic resources are genetic material of actual or potential value found in plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- These resources are essential in fields like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
- Traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources refers to the knowledge, practices, and innovations of indigenous and local communities, developed and passed down through generations.
- This knowledge is often related to the use and conservation of genetic resources.
What is Biopiracy?
- Biopiracy refers to the unauthorized use and patenting of genetic resources and traditional knowledge without proper compensation or acknowledgement to the communities that developed and conserved them.
- The treaty seeks to address biopiracy by requiring the disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications and aligning with international agreements like the Nagoya Protocol.
What is Digital sequence information (DSI)?
- Digital sequence information (DSI) refers to the digital representation of genetic material.
- The treaty currently excludes DSI from its scope, which is a point of contention as it affects the management and protection of genetic resources.
- Including DSI in the treaty is under debate to ensure comprehensive protection.
Outcomes and Significance of this Meeting:
- Expected outcomes include finalizing the treaty's text, agreeing on substantive intellectual property provisions, and administrative issues.
- Once finalized, the treaty will be open for signature and aims to provide a robust framework for protecting genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- The treaty also aims to protect the rights of indigenous and local communities by ensuring they receive fair compensation and recognition for their genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It also promotes the sustainable use and conservation of these resources, benefiting both global and local communities.
- The treaty has broader implications for international intellectual property law, biodiversity conservation, and the rights of indigenous and local communities.
- It aims to balance the interests of patent holders with the need to protect and sustainably use genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
India’s Role:
- India plays a significant role in the negotiations by advocating for strong disclosure requirements and a clear definition of traditional knowledge.
- India's participation helps ensure that the treaty provides sufficient policy space for countries to maintain their current stronger disclosure requirements under national laws.
Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Act has been notified in a gazette and has been enforced with effect from May 10, the Defence Ministry said recently.
About Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act:
- During the Monsoon Session of 2023, both houses of Parliament passed a bill aimed at enhancing the operational efficiency and coordination of Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs).
- These organisations comprise personnel from the Army, Air Force, and Navy, such as joint training institutions like the National Defence Academy, National Defence College (NDC), Defence Services Staff College (DSSC), and the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC).
Key Provisions of the ACT:
- Inter-Services Organisation Establishment: Existing Inter-Services Organisations will be considered constituted under the Act.
- The central government may establish an Inter-Services Organisation comprising personnel from at least two of the following services: the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Control of Inter-Services Organisations: The Act empowers the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command of an Inter-Services Organisation to exercise command and control over its personnel.
- They are responsible for maintaining discipline and ensuring the proper discharge of duties by service personnel.
- Supervision of an Inter-Services Organisation will be under the purview of the central government.
- Commander-in-Chief Eligibility: Officers eligible for appointment as Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command include:
- A General Officer of the regular Army (rank above Brigadier),
- A Flag Officer of the Navy (rank of Admiral of the Fleet, Admiral, Vice-Admiral, or Rear-Admiral), or
- An Air Officer of the Air Force (a rank above Group Captain).
- Commanding Officer Appointment: The Act establishes a Commanding Officer responsible for leading a unit, ship, or establishment within the Inter-Services Organisation.
- The Commanding Officer carries out duties assigned by the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command.
- They have the authority to initiate disciplinary or administrative actions for personnel within the Inter-Services Organisation.
Need for the Act:
- Theaterisation Drive: The enactment aligns with the ongoing push for theaterisation, a vital military reform aimed at optimizing resources for future combat scenarios.
- Existing Framework Challenges: Currently, armed forces personnel are governed by separate laws— the Air Force Act, 1950, the Army Act, 1950, and the Navy Act, 1957—resulting in disjointed disciplinary powers.
- Under the current setup, only officers from the same service possess disciplinary authority over personnel governed by the respective Act, leading to command, control, and discipline challenges.
- Financial Implications: The present framework entails time-consuming processes and financial expenditures for personnel transfers.
- The proposed legislation seeks to remedy these challenges by enhancing discipline enforcement, expediting case resolutions, and potentially saving public funds.
World Migration Report 2024

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the recently released World Migration Report 2024, which is published by the International Organization for Migration (IOM), India has consistently been the top recipient of remittances globally.
Key Highlights of the World Migration Report 2024:
- Resilience Amidst COVID-19: Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, international migration remains a vital driver of human development and economic progress.
- Notably, there has been a remarkable over 650 per cent surge in international remittances from 2000 to 2022, soaring from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion.
- This growth defied predictions of a substantial decrease in remittances due to COVID-19.
- Remittances to Low and Middle-income Countries: Out of the total remittances, which amounted to USD 831 billion, a significant portion of USD 647 billion was sent by migrants to low and middle-income countries.
- These remittances play a crucial role in the GDPs of these nations, surpassing foreign direct investment globally.
- Persistent Challenges: While international migration continues to foster human development, the report underscores enduring challenges.
- The global population of international migrants has reached approximately 281 million, while the number of individuals displaced by conflict, violence, disasters, and other factors has surged to a record high of 117 million.
- Urgent action is imperative to address displacement crises effectively.
- Misinformation and Politicization: Despite the fact that most migration is regular, safe, and regionally focused, public discourse has been clouded by misinformation and politicization.
- It is essential to provide a clear and accurate depiction of migration dynamics to counteract this trend.
About the International Organization for Migration (IOM):
- Established in 1951, IOM, the UN Migration Agency, is the leading inter-governmental organization in the field of migration and works closely with governmental, intergovernmental and non-governmental partners.
- IOM works to help ensure the orderly and humane management of migration, promote international cooperation on migration issues, assist in the search for practical solutions to migration problems and provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
- Membership: Currently, IOM counts 175 Member States and 8 states with Observer status.
- India joined as an IOM Member State on June 18, 2008.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, IOM's headquarters serves as a hub for its global operations.
Non-market Economy Status

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vietnam has been pushing the President Joe Biden administration to quickly change its “non-market economy” classification to “market economy”, in a bid to avoid high taxes imposed by the US on the goods imported from the Southeastern country.
Why does Vietnam Want to Get the ‘Market Economy’ Status?
- Vietnam has argued that in recent years it has implemented enough economic reforms that get its name off the non-market economies list.
- The country does meet a number of criteria for the status to be changed.
- For instance, Vietnam allows foreign investment, wages are determined by free negotiations between workers and management, and most of the means of production are not owned by the state.
- The change in status will also help Vietnam get rid of the anti-dumping duties, making its products more competitive in the US market.
- Vietnam’s Center for WTO and International Trade has said that the method of calculating anti-dumping duties is flawed as it causes “the dumping margin to be pushed up very high” and does not actually reflect the situation of Vietnamese companies.
About Non-market Economy Status:
- Non-market economy status refers to a designation applied to countries by international trade authorities, particularly the World Trade Organization (WTO), based on their economic structure and policies.
- In a non-market economy, the allocation of resources, production decisions, and pricing mechanisms are predominantly influenced by the government rather than by market forces.
- This can include state ownership of key industries, government intervention in setting prices, and restrictions on foreign investment and trade.
- For trade purposes, countries classified as non-market economies may face different treatment in anti-dumping investigations and trade disputes.
- This designation can affect how trade regulations and tariffs are applied to goods originating from these countries.
- The US designates a country as a non-market economy based on several factors which are:
- If the country’s currency is convertible
- If wage rates are determined by free bargaining between labour and management
- If joint ventures or other foreign investments are allowed whether the means of production are owned by the state; and
- If the state controls the allocation of resources and price and output decisions.
- Other factors like human rights are also considered.
- The non-market economy label allows the US to impose “anti-dumping” duties on goods imported from designated countries.
Market Economies:
- Market economies operate based on the interactions between consumers and businesses, guided primarily by the law of supply and demand, rather than by central government policies.
- Theoretical Foundation: Developed by classical economists like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and Jean-Baptiste Say, market economies emphasize the role of free markets in allocating resources efficiently.
- Modern Market Economies: Often referred to as mixed economies, modern market economies may still involve some government interventions, such as price-fixing, licensing, quotas, and industrial subsidies, but the majority of decisions are market-driven.
- Examples include countries like India, the USA, and the UK, where market forces play a significant role in shaping economic activities.
What is Anti-dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a protectionist tariff that a domestic government imposes on foreign imports that it believes are priced below fair market value.
- In order to protect their respective economy, many countries impose duties on products they believe are being dumped in their national market; this is done with the rationale that these products have the potential to undercut local businesses and the local economy.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to save domestic jobs, these tariffs can also lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
- In the long term, anti-dumping duties can reduce the international competition of domestic companies producing similar goods.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO)–an international organization that deals with the rules of trade between nations–also operates a set of international trade rules, including the international regulation of anti-dumping measures.?
Widal Blood Test

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Widal test's tendency to produce inaccurate results is clouding the understanding of India's typhoid burden, leading to increased costs, and exacerbating antimicrobial resistance risks.
What is the Widal Blood Test?
- A Widal test is a serological diagnostic test for typhoid fever.
- It helps evaluate the level of antibodies produced by the body in response to the Salmonella bacterial infection that causes typhoid fever in patients.
- Widal blood test is also known as a typhoid blood test report, as it is widely used for diagnosing typhoid fever.
- The symptoms of typhoid fever may be similar to those of other diseases, which can make the diagnosis of typhoid difficult without proper testing.
- Typhoid fever is a severe illness caused by a bacterium called Salmonella Typhi.
- This bacterium affects the gastrointestinal system and causes a range of symptoms such as high fever, diarrhoea or constipation, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss, and red spots.
- The bacteria usually enter the body through contaminated food or water.
- Typhoid requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications such as severe intestinal perforation or bleeding.
- The Widal blood test is a quick and easy serological test that can help confirm or rule out whether a fever is due to a typhoid infection.
- Typically, typhoid symptoms appear within 6 to 30 days of exposure to the bacterial infection.
- The Widal test is designed to detect antibodies against O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigens that cause the infection and typhoid fever.
- Infection through these antigens produces specific antibodies in response.
- The Widal blood test analyses the interaction between these two antigens and the antibodies produced in the patient's body through a blood sample.
- Detecting the presence of these antibodies in the Widal blood test indicates a bacterial infection.
- However, it has several limitations and has been phased out in many countries due to its potential for inaccuracy.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) advises against relying heavily on the Widal Test because various factors can influence its results.
- For example, a single positive result does not definitively confirm an active typhoid infection and a negative result does not necessarily rule it out.
- Additionally, obtaining an accurate diagnosis requires testing at least two serum samples taken 7-14 days apart, which can be time-consuming and often impractical.
- In areas with a continuous high burden of typhoid, baseline antibody levels may already be elevated, complicating the interpretation of results without knowing the appropriate cut-off values.
- Furthermore, cross-reactivity with antibodies produced against other infections or vaccinations can lead to false positives.
- Prior antibiotic therapy can also impact antibody levels, resulting in false negatives.
- Despite its accessibility and historical significance, the Widal Test's limitations emphasize the need for more accurate and reliable diagnostic methods for typhoid fever.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
Sikhs for Justice (SFJ)

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi LG V K Saxena recently recommended a (NIA) probe against jailed Delhi CM Arvind Kejriwal for allegedly receiving political funding from Sikhs for Justice (SFJ), a New York-based pro-Khalistan organisation that is banned in India.
What is Sikhs for Justice (SfJ)?
- Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) formed in 2007, is a US-based group seeking a separate homeland for Sikhs, a “Khalistan” in Punjab.
- Its founder Gurpatwant Singh Pannun, a law graduate from Panjab University and currently an attorney at law in the US, is the face of SFJ and its legal adviser.
- Panun had launched the secessionist Sikh Referendum 2020 campaign, an initiative that eventually became defunct.
- He was among the nine individuals designated as “terrorists” by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- ‘Referendum 2020’, claimed it wanted to “liberate Punjab from Indian occupation”.
- In Pannun’s words, “SFJ in its London Declaration (in August 2018) had announced to hold the first-ever non-binding referendum among the global Sikh community on the question of secession from India and re-establishing Punjab as an independent country.”
Banned in India:
- India refers to Gurpatwant Singh Pannun as a terrorist, and has banned SFJ under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967.
- The Home Ministry’s 2019 notification issuing the ban says: “In the garb of the so-called referendum for Sikhs, SFJ is actually espousing secessionism and militant ideology in Punjab, while operating from safe havens on foreign soils and actively supported by inimical forces in other countries.”
- Currently, almost a dozen cases are registered against Pannun and SFJ in India.
Critical Minerals Summit

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines today organized a summit to foster collaboration, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical mineral beneficiation and processing in New Delhi.
About Critical Minerals Summit:
- The Critical Minerals Summit was organized by the Ministry of Mines, Government of India, in collaboration with the Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation (Shakti), the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), and the Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD).
- It aims to promote collaboration and innovation in critical mineral beneficiation and processing.
- This event brings together a wide range of stakeholders, including industry leaders, startups, government officials, scientists, academics, and policy experts from both India and abroad.
Key Objectives:
- Tackling Demand: The summit seeks to address the growing demand for Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) needed for renewable energy systems and electric vehicles as part of India's strategic development goals.
- Focus on Key Minerals: The Ministry of Mines has identified eight crucial minerals for focus, including Glauconite (Potash), Lithium – Rare Earth Elements (Laterite), Chromium, Platinum Group, Graphite, Tungsten, Rare Earths (RE), and vanadium-associated with Graphite.
- Diverse Participation: The summit offers a platform for a diverse group of stakeholders to collaborate, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical minerals.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are metallic or non-metallic elements essential for modern technologies, economies, and national security, with potentially vulnerable supply chains.
- Their 'criticality' changes over time due to shifting supply and societal needs.
- Applications: Critical minerals are vital for manufacturing advanced technologies like mobile phones, computers, semiconductors, and renewable energy systems such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels, and batteries.
- They are also used in common products like stainless steel and electronics.
- Examples of Critical Minerals are antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, germanium, lithium, vanadium, and more.
- Top Producers: Countries like Chile, Indonesia, Congo, China, Australia, and South Africa lead in critical mineral production.
- Critical Minerals in India: The Indian government has identified 30 critical minerals, including antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, graphite, hafnium, indium, lithium, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, phosphorous, potash, rare earth elements, rhenium, silicon, strontium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, selenium, and cadmium.
- To meet the rising demand for critical minerals and ensure a stable supply, the Indian government is actively working on auctioning critical mineral blocks and fostering industry partnerships.
- These efforts are crucial for the country's economic development and energy transition goals.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Asia is warming faster than the global average, it is witnessing more extreme weather, climate, and water-related events than any other region across the world.
Highlights of the State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report:
- The 2023 State of the Climate in Asia Report, spearheaded by the World Meteorological Organization, sheds light on significant climate trends and events across the continent:
- In 2023, Asia witnessed 79 extreme climate events, affecting over nine million individuals, making it the most disaster-affected region.
- Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide soared to unprecedented levels in 2022.
- Oceans have absorbed approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted annually into the atmosphere since 1960, resulting in record-high ocean heat content in 2023.
- Tropical cyclone activity over the North Indian Ocean surpassed the average.
- 2023 marked Asia's second-highest mean temperature on record, with Japan and Kazakhstan experiencing record warmth.
- Glacial retreat accelerated in 2023, particularly in the East Himalayas and Central Asia's Tian Shan mountains, due to elevated temperatures and arid conditions.
About the World Meteorological Organisation:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a membership of 193 member states and territories.
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization, the roots of which were planted at the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences a year later.
- The Secretariat, headquartered in Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General.
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Each organ transplant case will receive a distinctive National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) ID assigned to both the donor and the recipient.
Highlights of the News:
- The Union Health Ministry has mandated the cessation of commercial organ transactions, particularly those involving foreign nationals, and emphasized the need for stringent oversight by local authorities.
- For deceased donor transplants, a NOTTO-ID is required for organ allocation, while in living donor transplants, the ID must be generated within 48 hours post-surgery through the NOTTO website by the hospital.
What is the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)?
- NOTTO is a national organization established under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
It serves as the central coordinating hub for:
- Organ and tissue procurement and distribution.
- Maintaining a registry of organ and tissue donation and transplantation activities across the country.
NOTTO comprises two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network:
- Acts as the primary center for nationwide coordination of organ and tissue procurement, distribution, and registry.
- Established in accordance with the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
- National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank):
- This center focuses on filling the gap between demand and supply while ensuring quality assurance in tissue availability.
- The Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 has expanded NOTTO's scope to include tissue donation and registration of tissue banks.
Activities performed by NOTTO include:
-
- Coordinating tissue procurement and distribution
- Donor tissue screening
- Tissue removal and storage
- Tissue preservation
- Laboratory screening of tissues
- Tissue tracking
- Sterilization
- Record maintenance
- Data protection and confidentiality
- Quality management in tissues
- Patient information on tissues
- Developing guidelines, protocols, and standard operating procedures
- Training and assistance in registering other tissue banks
United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to a recent report by UN Women, six months into the war, Gaza is facing a humanitarian crisis disproportionately impacting women and girls.
What is UN Women?
- Founded in 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly as part of the UN reform agenda.
- Merges resources and mandates to create a more significant impact on gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Serves as a global advocate for women and girls, addressing their needs and accelerating progress.
Key Roles:
- Supports intergovernmental bodies like the Commission on the Status of Women in developing policies, global standards, and norms for gender equality.
- Assists member states in implementing these standards and offers technical and financial support upon request.
- Builds effective partnerships with civil society organizations.
- Leads and coordinates the UN system's work on gender equality while promoting accountability through regular monitoring of progress.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Works globally to realize the SDGs for women and girls.
- Promotes women's equal participation in all aspects of life.
Country-level Support:
- Collaborates with government and non-governmental partners in countries that request assistance.
- Helps implement policies, laws, services, and resources to advance gender equality.
Grant-making Funds:
- Fund for Gender Equality: Provides grants to support innovative, high-impact programs by government agencies and civil society groups.
- UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women: Finances initiatives that address violence against women and girls.
Commission on the Status of Women (CSW):
- A global policy-making body focused on gender equality and women's advancement.
- Operates as a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
Information and Advocacy:
- Regularly provides information on women's rights issues to the General Assembly, ECOSOC, and the Security Council.
- Maintains the UN Secretary-General's database on violence against women, tracking measures taken by UN Member States and organizations.
- UN Women plays a vital role in advancing gender equality and women's empowerment worldwide by providing crucial support, resources, and advocacy through its various initiatives and collaborations.
Thiruvalluvar

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Seeking to connect with the people of Tamil Nadu where his party is trying to gain a foothold, Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced that the BJP will work towards building Thiruvalluvar cultural centers all over the world.
Who was Thiruvalluvar?
- Thiruvalluvar, the author of the revered 'Thirukkural' or 'Sacred Couplets', remains a figure of historical debate.
- His exact period and religious affiliation are uncertain, with proposed dates ranging from the 3rd or 4th century CE to the 8th or 9th century.
- Various groups regard him as a Hindu sage, a Jain sage, or a Dravidian saint with no religious identifiers except his Dravidian heritage.
- Accounts of Thiruvalluvar's origins are diverse.
- In Edward Jewitt Robinson's 1873 book, 'Tamil Wisdom: Traditions Concerning Hindu Sages and Selections from their Writings', he described Thiruvalluvar as a "Pariah" with a mother from "the low class" and a possibly Brahmin father.
- According to this narrative, Thiruvalluvar was found in a grove near a Shiva temple in Mayilapur and was taken in by the wife of a high-ranking Velalan before being entrusted to a "Pariah family."
- Despite the ambiguity surrounding Thiruvalluvar's identity, his wisdom-laden verses in 'Thirukkural' continue to influence and inspire generations across religious and cultural divides.
Why does Thiruvalluvar matter?
- Thiruvalluvar, affectionately called Valluvar by Tamils, is revered as a cultural and moral icon across caste and religious lines.
- His 'Thirukkural', a compilation of 1,330 couplets, is an integral part of Tamil culture, comparable to the Bhagavad Gita or Ramayana in North Indian Hindu households.
- It serves as a foundational text for ethical living and tracing Tamil cultural roots.
- Beyond Tamil Nadu, Thiruvalluvar's wisdom is celebrated in the context of ancient India's rich philosophical heritage, emphasizing morality and ethics.
- His enduring influence is evident as successive Indian finance ministers reference his teachings in annual Budget speeches.
- However, competing claims to Thiruvalluvar's legacy have sparked controversy, such as the 2019 debate surrounding the BJP's depiction of him in saffron robes instead of traditional white garments.
- Despite these disputes, the profound impact of Thiruvalluvar's teachings continues to resonate across various cultures and languages, fostering unity and moral guidance.
Why Are Political Parties Asserting Thiruvalluvar's Legacy?
- Political parties, both national and regional, have long vied for ownership of Thiruvalluvar's legacy. For instance, the BJP, with a limited grassroots presence in Tamil Nadu, seeks to bolster its standing through the appropriation of Tamil saints and icons.
Volcanic Vortex Rings

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since last week, Mount Etna has been sending up almost perfect rings of smoke into the air which are a rare phenomenon that scientists refer to as volcanic vortex rings.
What are Volcanic Vortex Rings?
- Vortex rings are generated when gas, predominantly water vapor, is released rapidly through a vent in the crater.
- The vent that has opened up in the crater is almost perfectly circular so the rings.
- The phenomenon was first observed at Mt. Etna and Mt. Vesuvius in Italy in 1724 and has been documented in an engraved plate from 1755.
- In more recent times, volcanic vortex rings have been observed at volcanoes such as Redoubt in Alaska, Tungurahua in Ecuador, Pacaya in Guatemala, Eyjafjallajökull and Hekla in Iceland, Stromboli in Italy, Sakurajima in Japan, Yasur in Vanuatu, Whakaari in New Zealand, and Momotombo in Nicaragua.
- According to the report, the rings can remain in the air for up to 10 minutes but tend to disintegrate quickly if conditions are windy and turbulent.
About Mount Etna:
- Mount Etna, sometimes referred to simply as Etna, is an active volcano on the east coast of Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, lying just off the toe of the Italian “boot”.
- Etna’s peak is the highest in Italy south of the Alps, and it is Europe’s largest and one of the most active volcanoes.
- Etna’s summit has five craters, which are responsible for most of the volcano’s eruptions; there are also “flank” eruptions that occur out of 300-odd vents of varying sizes along the slopes of the mountain.
- Etna is in almost constant activity and has seen, since the year 1600, at least 60 flank eruptions and many more summit eruptions.
- In recent years, summit eruptions have occurred in 2006, 2007-08, on two occasions in 2012, 2018, and 2021; flank eruptions have taken place in 2001, 2002-03, 2004-05, and 2008-09.
- Etna has been a World Heritage Site since 2013, and according to UNESCO, the volcano’s eruptive history can be traced back 500,000 years.
- At least 2,700 years of this activity have been documented.
Imposition of Anti-Dumping Duty on Sodium Cyanide

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) has now recommended the imposition of anti-dumping duty on sodium cyanide (NaCN) imported from China, the European Union, Japan, and Korea.
Key Facts About Sodium Cyanide:
- Sodium cyanide (NaCN) is a highly toxic, inorganic compound with a white, crystalline appearance.
- It is a solid at room temperature and has a high affinity for metals, making it useful in various industrial processes.
- Due to its toxic nature, proper handling and safety protocols must be followed when working with sodium cyanide.
Applications of Sodium Cyanide:
- Mining and Metallurgy: Sodium cyanide is widely used in the extraction of gold and silver from ores. It is employed in a technique called "cyanide heap leaching," where a dilute sodium cyanide solution is sprayed onto crushed ore.
- The cyanide forms a water-soluble complex with the precious metals, enabling their recovery from the ore.
- Electroplating: NaCN is utilized as an electrolyte in electroplating processes, particularly for the deposition of silver, gold, and other metals on various surfaces to improve their appearance, durability, or conductivity.
- Synthetic Fiber Production: Sodium cyanide is used in the manufacturing of synthetic fibers such as acrylic and nylon.
- It serves as a catalyst in the polymerization process, promoting the formation of long-chain polymers that make up the fibers.
- Pesticides: Due to its toxicity, sodium cyanide has been used as a fumigant to control pests and rodents.
- However, its use in this field has been largely phased out in many countries due to safety concerns and the development of safer alternatives.
- Dye and Pigment Production: NaCN can be used in the production of certain dyes and pigments, particularly those containing nitrogen.
- It acts as a precursor for the synthesis of these compounds.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a domestic government on foreign imports suspected of being sold at prices lower than those in the exporter's domestic market.
- This measure aims to prevent these products from undercutting local businesses and harming the local economy.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees a framework of international trade rules governing anti-dumping measures.
- Under this agreement, governments are permitted to address dumping practices if they pose a threat of significant harm to a domestic industry.
Calculation of Anti-Dumping Duty:
- The calculation of anti-dumping duty involves determining the difference between the normal value and the export value of the product.
- The normal value represents the market value of the product in the exporter's domestic market, while the export value denotes the price at which the product is sold when exported to India.
- The anti-dumping duty is levied to neutralize this price disparity and safeguard the domestic industry from the adverse effects of inexpensive imports.
Anti-Dumping Mechanism in India:
- India's anti-dumping mechanism is overseen by the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) under the Ministry of Finance.
- The legal framework for anti-dumping in India is established by the Customs Tariff Act of 1975 and the Customs Tariff Rules of 1995.
- The DGAD conducts investigations to assess whether a surge in below-cost imports has negatively impacted the domestic industry.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will host the fifth meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation startup forum in January next year according to the commerce and industry ministry.
About the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Startup Forum:
- The SCO Startup Forum is a platform for the stakeholders from the startup ecosystems from all SCO Member States to interact and collaborate.
- The entrepreneurial activities aim to empower the local startup communities in the SCO Member States.
- The SCO Startup Forum aims to create multilateral cooperation and engagement for startups among the SCO Member States.
- This engagement will empower the local startup ecosystems in the SCO Member States.
The following are the objectives of the engagement:
- Sharing of best practices to promote entrepreneurship and innovation to build knowledge-exchange systems
- Bringing Corporations and Investors across to work closely with startups and provide local entrepreneurs with much-needed support and market access
- Increasing scaling opportunities for startups by providing solutions in the field of social innovation and providing Governments with a plethora of innovative solutions
- Creating open procurement channels to enable matchmaking for procuring innovative solutions from startups
- Facilitating cross-border incubation and acceleration programs that will enable the startups to explore international markets and get focused mentorship.
Upcoming Events:
- India is set to host the second meeting of the Special Working Group for Startups and Innovation (SWG) in November 2024 and the SCO Startup Forum 5.0 in January 2025.
Past Initiatives:
- SCO Startup Forum 1.0: Established in 2020, laying the groundwork for multilateral cooperation among SCO Member States' startups.
- SCO Startup Forum 2.0: Held virtually in 2021, introducing the SCO Startup Hub, a centralized platform for the SCO startup ecosystem.
- SCO Startup Forum 3.0: Organized physically in 2023 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), marking a significant milestone for SCO Member States' startup collaboration.
- 1st Meeting of the SWG: Led by India, the first meeting of the SCO Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation in 2023 focused on the theme 'Growing from Roots', emphasizing foundational growth within the startup ecosystem.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
Reverse Flipping
- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Payments major Pine Labs and quick commerce firm Zepto are among the startups looking to relocate their headquarters from foreign shores to India, to capitalize on the country's burgeoning tech landscape.
What is Reverse Flipping?
- Reverse flipping is a growing trend where overseas startups relocate their domicile to India and list on Indian stock exchanges.
- The primary motivation behind this shift is the potential for a higher valuation and more certain exit opportunities in India's thriving economic landscape.
Several factors contribute to the rise of reverse flipping:
- Access to a large, expanding economy: India's significant market size and sustained economic growth offer foreign startups attractive prospects for business expansion and success.
- Abundant venture capital: India's substantial venture capital resources provide a strong financial foundation for startups, fueling innovation and growth.
- Favorable tax policies: The country's tax regulations encourage foreign startups to establish operations in India, helping them maximize profits and minimize costs.
- Enhanced intellectual property protection: India's robust IP protection framework fosters innovation and creativity, safeguarding the unique ideas and technologies of startups.
- Skilled, youthful workforce: The availability of a talented, young, and educated population provides startups with a valuable human resource pool to drive growth and success.
- Supportive government policies: The Indian government actively promotes entrepreneurship and innovation through various initiatives and policies, creating a conducive environment for startups.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 acknowledged the importance of reverse flipping and suggested measures to expedite the process, including simplifying tax vacation procedures, ESOP taxation, capital movement, and reducing tax layers.
- These efforts aim to further enhance India's appeal as a destination for foreign startups and foster economic growth.
What is Flipping?
- Flipping refers to the process by which an Indian company becomes a 100% subsidiary of a foreign entity after moving its headquarters overseas, involving a transfer of intellectual property (IP) and other assets.
- This transforms an Indian startup into a fully-owned subsidiary of a foreign entity, with founders and investors maintaining their ownership through the new overseas structure by exchanging their shares.
The process of flipping poses several concerns for India:
- The brain drain of entrepreneurial talent: As Indian startups move their operations overseas, India experiences a loss of innovative and entrepreneurial talent, which could otherwise contribute to the country's economic growth and development.
- Value creation in foreign jurisdictions: Flipping redirects potential value creation to foreign countries, depriving India of the economic benefits that could result from successful startups and innovations.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: When companies relocate and transfer their intellectual property overseas, India loses valuable IP assets, undermining the country's competitive advantage and innovation potential.
- Reduced tax revenue: Flipping also contributes to decreased tax revenue for India as companies shift their operations and profits to other jurisdictions, which may have more favorable tax policies.
Kerala declares man-animal conflict a state-specific disaster

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid repeated deaths from animal attacks and rising anger over them, Kerala recently declared man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, becoming the first state in the country to do so.
What is Man-animal Conflict?
- Man-animal conflict refers to the interaction between wild animals and humans, resulting in adverse outcomes for both people and wildlife, as well as their habitats.
- Escalating Conflict: In states across India, human-wildlife conflict has intensified, leading to a significant rise in human casualties.
- For instance, in Maharashtra, the conflict resulted in 86 in 2021 and 105 deaths in 2022, marking a sharp increase compared to previous decades.
Causes:
- Factors contributing to this conflict include the encroachment of grodeathswing human and animal populations into each other's territories, habitat fragmentation due to legal and illegal land use changes, alterations in cropping patterns attracting wildlife to agriculture, and habitat destruction from invasive alien species.
- Despite having over 700 protected areas, a substantial portion of elephant, lion, and tiger ranges lie outside these protected zones, exacerbating the conflict.
Ecologist Perspective:
- Ecologist Madhav Gadgil highlights that the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has inadvertently facilitated an environment where wild animals can invade human habitats with impunity.
- He cites the optimal foraging theory in ecology, which underscores animals' efforts to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing time, effort, and risks.
Solutions:
- Addressing the issue requires robust enforcement and pragmatic policies to mitigate conflict incidences.
- Engaging local communities, as suggested by the Future for All Report 2021 (by WWF and UNEP), fosters coexistence between humans and wildlife, acknowledging that complete elimination of conflicts is impractical.
- Additionally, awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about man-animal conflict and skill development initiatives for communities living near forests can alleviate pressures on agricultural and forest lands.
Kerala's Decision to Declare Man-Animal Conflict as a State-Specific Disaster:
- Implications of the Decision: Currently, the management of man-animal conflict falls under the jurisdiction of the forest department, operating in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act.
- By designating man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, the responsibility for addressing it shifts to the state disaster management authority, empowered by the Disaster Management Act, enabling swifter and more decisive action.
- Rationale for the Decision: Instances of loss of life due to man-animal conflict have prompted calls to tranquilize, capture, or eliminate the responsible animals.
- Presently, the chief wildlife warden, holding the sole authority in the state, makes decisions regarding wild animals causing disturbances in human settlements.
- Past decisions to tranquilize aggressive animals, like wild elephants, have faced legal challenges.
- Under the disaster management authority, actions can be taken that supersede other regulations, including those outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act.
- According to the Disaster Management Act, except for the Supreme Court or a High Court, no court has jurisdiction to entertain suits or proceedings regarding actions taken by relevant authorities in line with the Act.
- Additionally, the Act stipulates that its provisions hold precedence over any other law during the specific period of a declared disaster.
Kerala's Success in Managing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Kerala, with approximately 5,700 wild elephants in 2017, comprising 19% of the nationwide population of 30,000, witnessed a significantly lower incidence of human fatalities caused by elephants, accounting for only 81 (4%) of the 2,036 deaths recorded in India between 2018 and 2021.
- Factors Contributing to Kerala's Effective Management of Man-Animal Conflict:
- Maintenance of Unchanged Wilderness Boundaries: Kerala has largely preserved the boundaries between wilderness and civilization in recent years, contributing to the mitigation of man-animal conflicts.
- Evolution of Agricultural Practices: Changes in agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of crops like coffee, pepper, and tea, which hold less appeal for elephants, have helped reduce conflicts between humans and elephants.
- Unique Elephant Characteristics: Individual elephants are identified and named based on their distinct characteristics, such as Kabali, an elephant residing in the Athirapally jungle in Thrissur district, known for its tendency to attack or chase automobiles.
- These factors collectively contribute to Kerala's successful management of man-animal conflict, resulting in relatively fewer human fatalities caused by elephants compared to other regions in India.
ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Tamil Nadu’s Kulasekarapattinam

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the second rocket launchport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at Kulasekarapattinam on February 28.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- With the Union government’s recent policy announcing the opening of the space sector to private players, a sharp rise in the number of commercial launches is certain.
- To ensure that ISRO’s first launchport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, is not overburdened with a high number of launches, the space agency has decided to build another facility.
- While SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport will be used to launch smaller payloads.
- SHAR will also be available for India’s big ticket missions to the Moon, Venus, and much touted human-flight mission, the Gaganyaan.
- Private players could develop space-qualified sub-systems, build satellites, and even launch vehicles using the new launchport.
- It will also facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for all the on-demand commercial launches.
Why is the new ISRO launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
- Geographically, scientifically, and strategically, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport provides a natural advantage to ISRO’s future launches pertaining to the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- Allowing a direct southward and smaller launch trajectory for the light weight SSLVs carrying less fuel, the Kulasekarapattinam facility will boost ISRO’s attempts to enhance payload capacities.
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- This consumes additional fuel. However, the same would not be required for future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, which is geographically located several kilometers to the west of Colombo, thereby allowing a straight southward flight and simultaneously saving the already limited fuel available onboard SSLV.
- Notably, both the launch ports are located in Southern India, near the equator.
- For a launch site close to equator the magnitude of the velocity imparted due to Earth’s rotation is about 450 m/s, which can lead to substantial increase in the payload for a given launch vehicle.
- Geostationary satellites must necessarily be in the equatorial plane.
- So, for such satellites, the closer the launch site is to the equator the better it is.
What are SSLVs?
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- SSLV is designed with a three-stage solid propulsion and a liquid propulsion stage, which is the terminal stage.
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
- Previously, satellite projects built by college students and private players involved in the space sector have benefitted from SSLV missions.
What are the features of SHAR?
- SHAR is situated along the east coast of Andhra Pradesh and is located 80 km off Chennai.
- It currently provides launch infrastructure to all ISRO missions.
- It is equipped with a solid propellant processing setup, static testing, and launch vehicle integration facilities, telemetry services — tracking and command network to oversee the launch — and a mission control center.
- SHAR has two launch complexes that are routinely used to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Space Launch Vehicles (GSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III, now renamed as LVM3.
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
. First-of-its-kind Micro Turbojet Engine made in India

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A micro turbojet engine designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with the support of the IIT Hyderabad has been unveiled.
Key Highlights of the Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”:
- It is an indigenous micro turbojet engine made in India.
- Its primary focus is on serving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- Beyond UAVs, the engine exhibits versatile applications in air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and potential use in power generation for the future.
- Indigenous design and development: Engineered entirely in India by the Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT) team of skilled engineers & supported by IIT, Hyderabad.
- A great demonstration of the potential of Industry-Academia partnership
- Self-reliance and autonomy: By reducing reliance on imported technologies, components, and expertise, the Micro Turbojet Engine contributes to India’s goal of achieving self-sufficiency in critical sectors, bolstering national security and economic resilience
- Empowering local manufacturing: The launch of the indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine not only drives technological innovation but also stimulates the growth of the domestic aerospace and defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
What Is a Turbojet Engine and How Does It Work?
- Turbojet engines are jet engines that, like other jet engines, generate propulsion by discharging or expelling heated air.
- They feature a combustion chamber in which they burn fuel and air.
- As they burn this mixture, turbojet engines will discharge heated air.
- It can find turbojet engines in commercial airplanes, civilian airplanes, and military aircraft.
How Turbojet Engines Work?
- The process begins by drawing air through an intake.
- Turbojet engines feature an air intake, which is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Air will flow into this intake, at which point it will be redirected to the engine’s interior.
- After entering the engine, the air will become compressed.
- Turbojet engines feature a set of rotating blades. Known as compressors, these rotating blades are designed to compress the air.
- The next step in the process is combustion which involves the burning of fuel and air.
- Turbojet engines will inject fuel into the same combustion chamber where the compressed air is located.
- A spark will then ignite the mixture of fuel and compressed air, thereby generating hot, high-pressure exhaust gas.
- The exhaust gas generated by the combustion is expelled out the rear of the turbojet engine.
- This rearward expulsion allows for forward propulsion.
- As the exhaust gas is discharged out the rear of the turbojet engine, the airplane will be propelled forward.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
What Is Nazool Land Which Is At The Heart Of Haldwani Violence? (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Violence erupted in Uttarakhand’s Haldwani district recently after the administration conducted a demolition drive at the site of a mosque and madrasa, allegedly on Nazool land, killing five and injuring many more.
What is Nazool Land?
- Nazool land is owned by the government but most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazool land.
- In almost all major cities of India, Nazool land has been allotted to different entities for a variety of different purposes.
How did Nazool Land Emerge?
- During British rule, kings and kingdoms which opposed the British frequently revolted against them, leading to several battles between them and the British Army.
- Upon defeating these kings in battle, the British would often take their land away from them.
- After India gained Independence, the British vacated these lands.
- But with kings and royals often lacking proper documentation to prove prior ownership, these lands were marked as Nazool land — to be owned by the respective state governments.
How Does the Government Use Nazool Land?
- The government generally uses Nazool land for public purposes like building schools, hospitals, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
- Several cities in India have also seen large tracts of land denoted as Nazool land used for housing societies, generally on lease.
- Very often, the state does not directly administer Nazool land but rather leases it to different entities.
- While several states have brought in government orders for framing rules for Nazool land, The Nazool Lands (Transfer) Rules, 1956 is the law mostly used for Nazool land adjudication.
PM-SVANidhi Boosted the Annual Income of Street Vendors (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study that evaluated the impact of the PM SVANidhi, a small working capital loan scheme for street vendors, has found that the first tranche of `10,000 led to an additional annual income of `23,460 for each beneficiary.
News Summary:
- Commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the study was conducted by the Centre for Analytical Finance at the Indian School of Business (ISB) from January to June 2023.
- Although the report's findings will inform the Ministry's assessment of the PM SVANidhi scheme, it is not expected to be publicly released.
Key Findings of the Report:
- 94% of beneficiaries who received the initial Rs 10,000 loan reported using it for business investments, rising to 98% for those who received a second loan.
- The first loan contributed to an average additional monthly income of Rs 1,955, totalling Rs 23,460 over the one-year loan period.
- Approximately 13.9% of disbursed loans were categorized as non-performing assets (NPAs), indicating no payments for three months or more.
- Beneficiaries demonstrated a lower debt-to-income (DTI) ratio compared to typical small businesses, indicating high creditworthiness.
- Despite the PM SVANidhi program, there was limited improvement in street vendors accessing formal credit from other sources, with only 9% having loans from financial institutions.
What is PM SVANidhi?
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) stands as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched on June 1, 2020.
- Its core aim is to extend accessible credit to street vendors, enabling them to revive their businesses and achieve self-reliance.
- The scheme is specifically tailored to empower street vendors, including hawkers, rehri walas, thelewala, and those operating in urban and peri-urban areas.
- PM SVANidhi facilitates eligible street vendors to obtain working capital loans devoid of collateral requirements.
- These loans, with a maximum cap of Rs. 10,000 and a one-year tenure, are intended to support vendors in procuring essential items, securing raw materials, and meeting their operational expenses.
- Furthermore, the scheme offers a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, promoting timely repayments and fostering financial discipline.
How Does PM SVANidhi Work?
- The PM SVANidhi scheme operates through a streamlined and accessible application process designed to maximize participation and outreach among street vendors.
- Vendors can apply for the scheme via a dedicated online portal or through Common Service Centers (CSCs) established nationwide.
- Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a brief verification process conducted by relevant authorities.
- Upon successful verification, the loan amount is directly transferred to the vendor's bank account.
- Vendors can then utilize the funds to revive their businesses, purchase inventory, and cover operational expenses.
Key Features and Benefits of PM SVANidhi:
- Affordable Credit: PM SVANidhi offers accessible working capital loans of up to Rs. 10,000 to street vendors, facilitating credit access without the need for collateral.
- Interest Subsidy: The scheme provides a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, incentivizing timely repayments and easing financial burdens.
- Digital Empowerment: PM SVANidhi promotes digital transactions and payments among street vendors, fostering adaptation to evolving business practices and enhancing financial literacy.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By availing of PM SVANidhi benefits, street vendors can improve their livelihoods, expand their businesses, and generate sustainable income for themselves and their families.
- Access to Social Security Schemes: Street vendors enrolled in PM SVANidhi are eligible for various social security schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), providing financial coverage and protection during unforeseen events.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme stands as a beacon of hope for street vendors throughout India. By offering accessible credit, digital empowerment, and access to social security schemes, PM SVANidhi is propelling the advancement and prosperity of street vendors, empowering them to establish sustainable livelihoods. This groundbreaking initiative, with its manifold advantages and inspiring success stories, underscores the Government of India's dedication to fostering an inclusive and self-sufficient economy.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Prime Minister pays tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti (PIB)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi paid tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti.
Who is Savitribai Phule?
- Recognized as India's first woman teacher, Savitribai Phule was a pioneer who defied prevailing societal conventions to advance women's education, equality, and justice.
- She was a Dalit lady from the Mali community and was born on January 3, 1831, in Satara District's Naigaon (Maharashtra).
- Despite prevailing norms that limited education to affluent men, the Phules established India's first girls' school in Bhidewada, Pune, in 1848.
- Savitribai's commitment to social reform led to the establishment of Mahila Seva Mandal in 1852, advocating for women's rights.
- In 1860, she initiated a strike against shaving the hair of widowed women.
- Savitribai actively promoted inter-caste marriages, and widow remarriage, and fought against social issues like child marriage, sati, and dowry.
- In collaboration with Jyotirao, she founded the Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha, offering support to pregnant widows.
- The couple further established the Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873, aimed at dismantling caste, religion, and class hierarchies.
- Her literary contributions include "Kavya Phule" (1854), her first collection of poems, and "Bavan Kashi Subodh Ratnakar" (1892).
- Savitribai Phule's enduring legacy lies in her unwavering commitment to education and social reform, making her a pioneering figure in Indian history.
About Rani Velu Nachiyar:
- Rani Velu Nachiyar, born on January 3, 1730, in Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu, India, holds the distinction of being the first queen to actively resist British rule, predating the Sepoy Mutiny.
- Revered as Veeramangai among Tamils, she was extensively trained in martial arts, including Valari, Silambam, horse riding, archery, and various languages such as French, English, and Urdu.
- Married to King Muthuvaduganathaperiya Udaiyathevar of Sivagangai, Rani Velu Nachiyar entered the battlefield when her husband fell victim to British soldiers.
- Collaborating with Hyder Ali and Gopala Nayaker, she waged a successful war against the British, displaying exceptional military prowess.
- In 1780, she delegated authority to the Marudu brothers for the administration of the country.
- Rani Velu Nachiyar's courageous stand against colonial rule and her strategic alliances in the face of adversity mark her as an iconic figure in India's history of resistance and resilience.
UN Secretary-General Invokes Article 99 on Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire.
Context:
- The United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has decided to invoke Article 99 of the UN Charter as the death toll in Israeli bombardments on Gaza crosses 16,000.
- He also urged the UN Security Council to act on the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- The development comes as Israel increased the intensity of its operations, especially in the areas of southern Gaza with Israel's defence leadership claiming that “half of Hamas’ battalion commanders" are killed.
What is Article 99 of the UN Charter?
- The Secretary-General may bring to the attention of the Security Council any matter which in his opinion may threaten the maintenance of international peace and security.”
- It is seen as a discretionary power.
- The responsibility it confers upon the Secretary-General will require the exercise of the highest qualities of political judgment, tact and integrity” according to a 1945 report of the Preparatory Commission of the United Nations.
- According to the UN, the President of the Security Council is under the obligation to call a meeting of the Council if the Secretary-General brings to the attention of the Council any matter under Article 99.
When has Article 99 Been Activated in the Past?
- 1960: Following the Congo Crisis, Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld invoked Article 99 to address the aftermath of Belgium's withdrawal and the ensuing internal conflict.
- 1971: Amid the Bangladesh Liberation War, Secretary-General U Thant activated Article 99 to draw attention to the humanitarian crisis, urging international intervention.
- 1979: In response to the Iranian Revolution and hostage crisis, Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim triggered Article 99 to underscore the seriousness of the situation and the necessity for a peaceful resolution.
- 1989: Confronted with the ongoing Lebanese Civil War and hostage abductions, Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar invoked Article 99 to emphasize the requirement for international support and engagement.
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Delhi High Court has criticized the forest department's proposal to hold a walkathon and cyclathon in a wildlife sanctuary, calling it a "haphazard exercise."
About Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covers 32.71 sq. km on the Southern Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range, bordering Delhi and Haryana.
- It's in Southern Delhi and parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts in Haryana.
- It's a part of the Sariska-Delhi Wildlife Corridor, linking Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan to Delhi Ridge.
- The sanctuary gets its name from the contiguous Asola village near Tughlaqabad in the Delhi NCR.
- Vegetation: The vegetation is classified as Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, known for thorny appendages and special leaves.
- The climate has extreme summer heat and significant winter cold due to its inland position.
- Flora: The main exotic plant is Prosopis juliflora, and the primary native plant is Diospyros montana.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various animals like Golden Jackals, striped hyenas, Indian Crested Porcupines, Civets, Jungle Cats, Snakes, Monitor Lizards, and Mongoose.
- This sanctuary plays a crucial role in connecting wildlife across different areas.
Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) (The Hindu)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has recently requested the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) to provide access to "essential documents" related to the accusations of stock manipulation and accounting fraud against the Adani Group.
About the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP):
- The Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) is a nonprofit investigative reporting platform that collaborates with over 50 independent media outlets worldwide, producing over 100 investigations annually.
- Established in 2006, its mission is to conduct transnational investigative reporting and advocate for technology-based approaches to expose organized crime and corruption on a global scale.
- The organization strives to cultivate and empower a global network of investigative journalists, publishing their stories to shed light on crime and corruption, enabling the public to hold those in power accountable.
Vision:
- OCCRP envisions a world where lives, livelihoods, and democracy are not jeopardized by crime and corruption.
- The organization is committed to exposing malfeasance so that the public can actively hold institutions accountable.
Core Initiatives:
- Global Investigative Network: OCCRP facilitates a global network of investigative journalists, providing them with essential resources and tools.
- This includes digital and physical security measures, enabling journalists covering sensitive topics to collaborate effectively with trusted editors.
- An investigative data platform, OCCRP Aleph empowers journalists to search and cross-reference over three billion records, unveiling criminal connections and patterns.
- This platform facilitates efficient cross-border collaboration among journalists.
- Training and Skill Development: OCCRP offers training programs to reporters and partners, equipping them with advanced journalism techniques, and enhancing their investigative capabilities.
- Partnerships for Change: OCCRP collaborates with advocacy groups, arming civil society with information to advocate for justice and transformative change.
- The organization also uncovers evidence that empowers law enforcement to take meaningful action.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
New Plant Species Curcuma kakchingense Discovered in Manipur (HT)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In a remarkable botanical discovery, a team of researchers from the Department of Life Sciences at Manipur University and Kwaklei and Khonggunmelei Orchids Pvt. Ltd. has unveiled a hitherto unknown plant species named "Curcuma kakchingense."
About Curcuma Kakchingense:
- Recently identified flowering plant species in Manipur, belong to the Zingiberaceae family.
- Member of the angiospermic family Zingiberaceae, which includes well-known plants like turmeric, gingers, and cardamom.
- Plant Characteristics: Robust plant reaching a height of eight feet, characterized by large terminal inflorescence.
- Natural Habitat: Thrives along the banks of the Sekmai River in the Kakching District of Manipur.
- Resemblance to Other Species: Bears a striking resemblance to local "Yaingung" (Curcuma longa) and Curcuma phrayawan from Thailand.
- Distinguished by lemon-yellow rhizomes with a notably bitter taste.
- IUCN Red List Classification: Classified as "Data Deficient" (DD) under the IUCN Red List category.
Importance of Curcuma Plants:
- Culinary and Traditional Uses: Various Curcuma species, including turmeric (Curcuma longa), play a vital role in cuisines, traditional medicines, spices, and dyes.
- Biological Activities: Curcumin and curcuminoids found in Curcuma species are nontoxic polyphenolic compounds with diverse biological activities.
- Pharmacological Properties: Essential oil of Curcuma species possesses pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-diabetic, and anti-microbial effects.
- Versatile Applications: Widely utilized in cosmetics, perfumes, and as ornamental plants, contributing to various industries and daily life.
Manipur to Conduct Census of Amur Ffalcon (The New Indian Express)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Manipur Forest Department will conduct the first-ever Amur falcon census. This initiative in India is one of the several programs the agency is running to safeguard migrating birds.
About Amur Falcon:
- The Amur Falcon, a diminutive member of the falcon family locally known as Akhuipuina, predominantly frequents Manipur and Nagaland.
- Originating from southeastern Siberia and northern China, these birds embark on extensive migrations in vast formations to winter in Southern and East Africa, covering a one-way journey of approximately 20,000 km through India twice a year.
- In terms of conservation, the Amur Falcon is safeguarded by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, listed under Schedule IV.
- Hunting or possession of its meat is subject to legal repercussions, including imprisonment for up to three years, a fine of up to 25,000, or bonds.
- Initiating a conservation effort in 2018, the forest department employed radio tagging to study the birds' migratory routes.
- As per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Amur Falcon is categorized as "Least Concern."
- Despite this, the species faces threats such as illegal trapping and killing during migration, along with habitat loss due to agricultural practices and land reclamation.
Atomic watchdog report says Iran is increasing production of highly enriched uranium (Indian Express)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Iran has increased the rate at which it is producing near weapons-grade uranium in recent weeks, reversing a previous slowdown that started in the middle of this year, the International Atomic Energy Agency said in a report.
What is Uranium Enrichment?
- Natural uranium is comprised of two isotopes, with approximately 99% being U-238 and only about 0.7% being U-235.
- U-235 is a fissile material capable of sustaining a chain reaction within a nuclear reactor.
- The enrichment process involves increasing the proportion of U-235 through isotope separation, effectively isolating U-238 from U-235.
- For the production of nuclear weapons, enrichment is necessary up to 90% or more, referred to as weapons-grade uranium.
- Low-enriched uranium, typically containing a 3-5% concentration of U-235, is suitable for generating fuel for commercial nuclear power plants.
- In contrast, highly enriched uranium, boasting a purity of 20% or more, finds application in research reactors.
Key Facts About Uranium:
- Discovered in 1789 by the German chemist Martin Klaproth, Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element found in the periodic table, characterized by its atomic number 92.
- This element holds the distinction of having the highest atomic weight among all naturally occurring elements.
- Naturally present in low concentrations in soil, rock, and water, uranium is commercially extracted from minerals like uraninite.
- The mining of uranium ore can be undertaken through open pits or underground excavations, followed by crushing and processing at a mill to isolate the valuable uranium.
- An alternative method involves the direct dissolution of uranium from ore deposits in the ground, known as in-situ leaching, with the extracted uranium then pumped to the surface.
About the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- The International Atomic Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- Established as an autonomous entity through its international treaty, the IAEA Statute, the organization, nonetheless, reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, the IAEA collaborates with its Member States and various global partners to advance the safe and peaceful utilization of nuclear technologies.
- It employs nuclear safeguards, encompassing monitoring, inspection, information analysis, and other measures, to ensure the peaceful nature of nuclear activities and to detect and deter any potential diversion towards weapons-related purposes.
- The IAEA plays a crucial role in implementing comprehensive safeguards agreements mandated by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), acting as a frontline defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Additionally, the agency facilitates the exchange of scientific and technical information among its Member States.
- A key function of the IAEA is to bolster national, regional, and international capabilities to respond effectively to nuclear and radiological incidents, thereby minimizing their impact.
Project Nilgiri Tahr’ Launched in Tamil Nadu (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Consolidating efforts towards the conservation of Tamil Nadu’s State Animal, Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Thursday, October 12, 2023, launched the ‘Project Nilgiri Tahr’ from the Secretariat in Chennai.
About Nilgiri Tahr:
- The Nilgiri Tahr, scientifically known as Nilgiritragus hylocrius, is an endangered mountain ungulate that is native to the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Locally referred to as 'Varayaadu,' these creatures are renowned for their remarkable climbing abilities on steep cliffs, earning them the moniker "Mountain Monarch."
- Notably, the Nilgiri Tahr holds the distinction of being the state animal of Tamil Nadu.
Distribution:
- The current range of Nilgiri Tahrs is confined to approximately 5% of the Western Ghats in southern India, specifically in the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- The Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the highest density and the largest surviving population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
Habitat:
- Nilgiri Tahrs inhabit open montane grassland habitats, thriving at elevations ranging from 1200 to 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
Distinctive Features:
- Characterized by a stocky body, short coarse fur, and a bristly mane, Nilgiri Tahrs exhibit sexual dimorphism, with mature males being larger and darker in colour.
- Both males and females possess curved horns, with males having larger ones measuring up to 40 cm, while females' horns reach approximately 30 cm.
- Adult males develop a light grey area or 'saddle' on their backs, leading to the term 'saddlebacks.' The species is recognized by its short grey-brown or dark coat.
Conservation Status:
- The Nilgiri Tahr is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, signifying the critical need for conservation efforts.
- Additionally, it is accorded the highest protection under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972, listed in Schedule I.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
Himalayan Black Bear (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
An animal keeper died after being attacked by a Himalayan black bear in the animal’s enclosure of Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) here recently.
About Himalayan Black Bear:
- The Himalayan black bear (Scientific Name: Ursus thibetanus laniger) is a subspecies of the Asian black bear found in the Himalayas of India, Bhutan, Nepal, China, and Pakistan.
- In India, habitat covers the entire Himalayan range from Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh, extending to hilly areas in other northeastern states.
- Habitat: Thrives in heavily forested regions with broadleaved and coniferous forests.
- It utilizes orchards, agricultural fields, and human habitats to navigate between forest patches.
- Physical Features: Possesses soft and shiny fur, featuring a distinctive white V patch on the chest.
- Average length ranges from 1.4 to 1.7 meters, weighing between 90 to 200 kg (higher weight typically before hibernation).
- Life Span: In the wild, their life expectancy is approximately 25 to 30 years.
- Diet: Omnivorous nature, consuming acorns, nuts, fruit, honey, roots, and various insects like termites and beetle larvae.
- Behavior: Primarily diurnal by nature but often shifts to a nocturnal lifestyle to avoid human contact.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List classification: Vulnerable
- Due to encroachment of human population, forest fires and the timber industries; these have all reduced the bear's habitat.
- There is also a high mortality rate among the newborn.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
Sangai Deer (Indian Express)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Manipur Government has expressed its reservations to the Centre over a hydro-electric modernisation plan in the state’s famous Loktak Lake saying it could be detrimental to the endangered species of Sangai deer apart from disturbing the biodiversity of the lake.
About Sangai Deer:
- The sangai is an endemic and endangered subspecies of Eld's deer found only in Manipur, India.
- It is also the state animal of Manipur.
- Its common English name is Manipur brow-antlered deer or Eld's deer and the scientific name is Rucervus eldii eldii.
- It is believed to have originated from a common ancestor of the brow-antlered deer family, which is thought to have existed in the region during the Pleistocene epoch, around 12,000 years ago.
- Its original natural habitat is the floating marshy grasslands of the Keibul Lamjao National Park, located in the southern parts of the Loktak Lake, which is the largest freshwater lake in eastern India.
- Appearance: is a medium-sized deer that is unique in appearance and behavior.
- The Sangai deer is a slender and graceful deer, with long legs and a thin neck. They have a height of around 90-100 cm at the shoulder and can weigh between 70 to 120 kg.
- Food Habits: The Sangai deer is primarily found in the marshy wetlands of the Loktak Lake in Manipur, where they feed on the vegetation growing on the floating biomass called “Phumdis.”
- They are known to feed on a wide variety of plants, including grasses, sedges, and herbs.
- Vulnerable Species: The Sangai is an endangered species and is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- The population of Sangai deer has been severely threatened due to habitat loss, hunting, and poaching.
- In the 1950s, the population of the Sangai deer was estimated to be around 600-700 individuals.
- However, by the 1970s, the population had declined to less than 100 individuals due to extensive hunting and habitat loss.
- The Government of India and the State Government of Manipur took several conservation measures, including the establishment of the Keibul Lamjao National Park in 1977, to protect and conserve the Sangai deer.
- The Sangai deer is a social animal and is usually found in small herds of 2-20 individuals.
- Protecting and conserving their natural habitats is one of the most effective ways to ensure the survival of these species.
- This can be achieved through the creation and management of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, and the restoration of degraded habitats.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" launched under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 Crore supports 2 lakh micro food processing enterprises following One District One Product (ODOP) approac

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
As part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) is implementing a centrally sponsored "PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" for providing financial, technical and business support for setting up / upgradation of micro food processing enterprises in the country.
About PM Formalisation of Micro food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme:
- Launched on 29th June 2020, PMFMPE is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- It is designed to address the challenges faced by the micro-enterprises and to tap the potential of groups and cooperatives in supporting the upgradation and formalization of these enterprises.
- Aims:
- Enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector; and
- Support Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- Objectives: To build the capability of microenterprises to enable:
- Increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, FPOs, Self Help Groups, and Co-operatives.
- Integration with an organized supply chain by strengthening branding & marketing.
- Support for the transition of existing 2,00,000 enterprises into a formal framework.
- Increased access to common services like common processing facilities, laboratories, storage, packaging, marketing, and incubation services.
- Strengthening of institutions, research, and training in the food processing sector; and
- Increased access for the enterprises, to professional and technical support.
- Outlay:
- The scheme envisages an outlay of ? 10,000 crores over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- The expenditure under the scheme would be shared in a 60:40 ratio between Central and State Governments, in a 90:10 ratio with the North
- In Eastern and the Himalayan States, a 60:40 ratio with UTs with the legislature and 100% by the Center for other UTs.
- Coverage:
- Under the scheme, 2,00,000 micro food processing units will be directly assisted with credit-linked subsidies.
- Adequate supportive common infrastructure and institutional architecture will be supported to accelerate the growth of the sector.
Perucetus colossus (Indian Express)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Perucetus colossus, whose fossils were discovered in Peru, maybe the heaviest discovered animal ever, even heavier than the blue whale.
About Perucetus colossus:
- The whale species Perucetus colossus is known from a recently described fossil dating back over 38 million years.
- Despite potentially being shorter in length, scientists believe that this ancient whale species might have been heavier than the modern blue whale.
- Researchers estimate that the weight of the Perucetus colossus could have ranged from 85 to an astonishing 340 tonnes.
- The fossilized bones of this species exhibited an unusual combination of large volume and extreme density, a characteristic known as pachyosteosclerosis.
- Pachyosteosclerosis is not observed in living whales, dolphins, and porpoises, but it is present in sirenians, a marine mammal group that includes sea cows.
- Unlike deep-diving whales, Perucetus colossus likely lived in shallow coastal areas, suggesting that it might have dived with air in its lungs.
- However, diving with air in the lungs would make it challenging to stay near the seafloor.
- The heavy bones of the Perucetus colossus might have played a crucial role in enabling it to do so.
- The skeletal mass of the Perucetus colossus is estimated to have been between five and eight tons, double that of a modern blue whale.
JAMRANI DAM MULTIPURPOSE PROJECT (PTI)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
About the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project:
- According to the project, a dam will be built in the Uttarakhand district of Nainital, close to Jamrani village, across the Gola River, a tributary of the Ram Ganga.
- The neighboring state of Uttar Pradesh would receive a sizable portion of the project's irrigation benefits.
- This is the seventh project to be added to the PMKSY-AIBP list.
Facts about the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana:
It was introduced in 2015–16.
Aim: To improve physical access to water on farms, increase cultivable land under assured irrigation, increase on-farm water use efficiency, and implement sustainable water conservation practices.
Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), ongoing major and medium irrigation projects, including national projects, will be completed more quickly.
Har Khet Ko Pani: It is divided into four smaller components:
- Ground Water (GW) Development component,
- Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI),
- Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies, and
- Command Area Development & Water Management (CAD&WM).
The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, is the nodal ministry.
UNITED NATIONS WORLD TOURISM ORGANISATION (UNWTO) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Dhordo village in Gujarat's Kutch district was recently recognized as the Best Tourism Village by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), which was praised by India's Prime Minister.
Facts About:
- The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting sustainable and responsible tourism on a global scale.
- Its functions include acting as a global forum for tourism policy issues and encouraging the adoption of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism.
It was founded in 1975.
- Members: 159 countries are members of the UNWTO.
- Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish are the UNWTO's official languages.
- Structure of the organization:
The World Tourism Organization's General Assembly is the organization's main meeting.
It is made up of full members and associate members. It convenes every two years.
- The Executive Council serves as the UNWTO's governing body.
It is made up of 35 members, one for every five full members, who are elected by the General Assembly. It holds at least two meetings per year.
- Headquarters are in Madrid, (Spain).
Manis Mysteria (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In addition to the eight previously identified pangolin species, researchers have recently found a ninth variety, which is currently given the temporary name "Manis mysteria.
Facts About:
Scientists have recently made a significant discovery in the world of wildlife by identifying a previously unknown ninth species of pangolin.
- This newly found pangolin variety has been tentatively named "Manis mysteria."
Origins from Confiscated Scales: The origins of this remarkable discovery trace back to the examination of pangolin scales that were seized in China's Yunnan province during the years 2015 and 2019.
- These scales provided vital clues leading to the identification of the new species.
Ancient Divergence: Research indicates that "Manis mysteria" took a distinct evolutionary path around five million years ago, separating from its Philippine and Malayan pangolin relatives.
- This long separation in the evolutionary timeline highlights its unique characteristics.
Distinctive Features of Pangolins: Pangolins are known for their distinctive characteristics, including protective keratin scales that cover their bodies and a diet primarily consisting of ants and termites.
- They hold the distinction of being the only mammals with such specialized scales.
Defensive Behavior: One of the most intriguing aspects of pangolins is their ability to curl up into a tight, defensive ball when they feel threatened.
- This remarkable behavior helps protect them from potential predators.
- Grave Threats to Pangolins: Unfortunately, all species of pangolins face severe threats to their survival.
- Each species is currently listed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, a concerning designation that highlights their vulnerable status.
- For instance, the Indian pangolin is specifically categorized as "Endangered," underlining the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard these unique creatures.
Tasmanian Tiger (The Hindu)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Researchers have recently extracted Ribonucleic acid (RNA) from the desiccated skin and muscle of a Tasmanian tiger that had been stored at a museum in Stockholm since 1891.
Facts About:
- The Tasmanian tiger had a wolf-like appearance, distinguished by tiger-like stripes along its back.
- Regrettably, the last known Tasmanian tiger passed away in a Tasmanian zoo in 1936.
- This large carnivorous marsupial is now considered extinct.
- Among the family Thylacinidae, it stood as the sole survivor into modern times.
- Its habitat once spanned across continental Australia, reaching as far north as New Guinea and as far south as Tasmania.
- As an apex predator, it hunted kangaroos and various other prey.
What is RNA?
- RNA, short for Ribonucleic acid, is a complex compound with a high molecular weight, and it plays a crucial role in cellular protein synthesis.
- In some viruses, RNA takes on the role of carrying genetic codes, replacing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
- RNA is composed of ribose nucleotides, which are nitrogenous bases attached to a ribose sugar via phosphodiester bonds.
- The nitrogenous bases found in RNA include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
- Unlike DNA, RNA is a single-stranded molecule responsible for carrying genetic information.
- RNA's primary function is to synthesize the diverse array of proteins required by an organism for survival, while also regulating cell metabolism.
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
Phanigiri Artefacts (The Hindu)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Phanigiri artefacts, which were found in 1942 and date back to 200 BCE-400 CE, are currently showcased at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Facts About:
- The Phanigiri Buddhist site is a significant discovery in Buddhist iconography in this era.
- Phanigiri, a small village located in Telangana, is where these artefacts were unearthed.
Key Discoveries:
- The thoranas found at Phanigiri hold great importance, especially because they are some of the earliest ones discovered south of Sanchi.
- One particular thorana has a panel that depicts both Mahayana and Hinayana schools of Buddhist thought.
- Evidence from Phanigiri indicates the transformation of Buddha's status, marking a transition from a historical and spiritual figure to canonization and ritualization.
- In the monograph of this discovery, you can find an image of Buddha wearing what appears to be a Roman toga, carved in limestone.
Self Regulatory Organisation for Fintech (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has requested fintech organizations to establish a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO).
Facts About:
- A Self-Regulatory Organization is an independent entity, not affiliated with the government, responsible for formulating and enforcing industry-specific rules and standards that govern the behavior of its member entities.
- The primary objectives are safeguarding customers' interests and fostering a culture of ethics, fairness, and professionalism within the industry.
Key Functions of an SRO:
- Facilitating Communication: A recognized SRO serves as a vital bridge for communication between its members and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This ensures a seamless flow of information and feedback.
- Setting Standards: SROs play a pivotal role in establishing and upholding minimum benchmarks and standards.
This helps in cultivating professional and ethical conduct among their member entities.
- Education and Awareness: SROs contribute to enhancing industry expertise by providing training to the staff of their members and other relevant stakeholders.
They also organize awareness programs to disseminate knowledge.
- Grievance Resolution: An important function of an SRO is to create a uniform framework for addressing grievances and managing disputes across its member organizations, promoting fairness and transparency.
Schizostachyum Andamanicum (The Hindu)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Government of India's patent office recently awarded a patent to the Botanical Survey of India for a reusable straw made from bamboo (Schizostachyum andamanicum).
Facts About:
- This bamboo is pretty rare and can only be found in certain forests in the Andaman Islands.
- It likes to grow in wet tropical areas.
- This type of bamboo has tall, skinny stems that are hollow inside. It's perfect for making straws.
- It has little white flowers that grow together in groups. The seeds are small and black, and the baby plants have thin, light green leaves.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) (PIB)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY), an inventive employment incentive scheme introduced by the Central Government, has surpassed its initial objectives for generating employment. This achievement highlights its effectiveness in promoting job creation and supporting economic recovery amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Facts About:
- Launched in 2020, the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) was created to stimulate the creation of new job opportunities.
- It achieves this by providing financial support to employers who are part of the Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO).
- The primary objective of this scheme is to incentivize the employment of individuals, including those who lost their jobs due to the pandemic.
- It does so by covering both the employee and employer contributions, which amounts to 24% of wages, for establishments with up to 1000 employees.
- For larger establishments with over 1000 employees, the scheme covers only the employee's EPF contributions, which is 12% of wages, in relation to new employees.
- As of July 31, 2023, the ABRY has successfully enrolled more than 7.58 million new employees, surpassing its initial target for employment generation.
- This achievement underscores its significant contribution to revitalizing the job market and supporting economic recovery during these challenging times.
India takes first step to remove animals from Drug-testing (Indian Express)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) passed by the Government of India, aims to replace the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Facts About:
What is the reason behind shifting to Alternative testing modes?
- The drug development journey involves rigorous testing to assess the efficacy and unintended effects.
- The first step of this process has been to test the candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates
- Lack of accuracy: Human response is influenced by factors like genetics and diet, leading to a significant mismatch between animal models and human responses.
- This mismatch contributes to the high failure rate during human clinical trials, highlighting the need for more accurate testing methods.
- Animals cannot consent to their own participation in research.
- Welfare of animals: Critics argue that animal testing can cause suffering and harm to animals. Animals are held in sterile, isolated cages, forced to suffer disease and injury, and typically euthanized at the end of each study.
What are Alternative testing modes?
- Organoids: These technologies encompass three-dimensional cellular structures, known as "organoids" or "mini-organs," which closely replicate the functions of specific body organs at a miniature scale.
- Organ-on-a-chip: The "organ-on-a-chip" technology employs small chips with human cells and microchannels to simulate physiological processes.
- organ-on-a-chip are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to microchannels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- Additive manufacturing: 3D bioprinters use human cells as 'bio-ink' to build tissues. This could help make personalized drug tests and change how we create drugs.
What are Global regulatory frameworks that have adopted non-animal methods to test the effect and potential side-effects of new drug candidates?
- European Union: In 2021, the European Union adopted a resolution for an action plan promoting non-animal technologies in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- USA: The U.S. passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 in December 2022, permitting the use of these methods for drug safety and efficacy testing.
- South Korea: South Korea introduced a Bill for advancing alternatives to animal testing in December 2022.
- Canada: In June 2023, Canada amended its Environmental Protection Act to minimize vertebrate animal use in toxicity testing.
India
- In March 2023, the Indian government incorporated non-animal alternatives for drug testing and development into the drug development process by modifying the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- This step followed public input and consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, which advises governments on drug-related technical issues at both the Central and State levels.
What are the challenges with these alternate methods?
- Multidisciplinary: Developing an organ-on-a-chip system requires multidisciplinary knowledge in the fields of cell biology, materials science, fluid dynamics, electronics, engineering, and pharmacology/toxicology to accurately replicate organ behavior and assess drug effects.
- At present there is a lack of focused training and expertise in India.
- Dependence of Imports: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials, and instruments for these technologies are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- Managing Complexity: Researchers simplify recreating human tissues in the lab by minimizing components for disease simulation.
- No universal approach due to disease-specific variations; for example, a liver-on-a-chip won't fit all liver diseases.
- Variability arises from differences in lab protocols, expertise, and specific research goals. Regulators express concerns about data consistency due to these variations.
Suggestions
- Establishment of specialized institutes: Recently, a meeting organized by the Centre for Predictive Human Model Systems and Humane Society International India called for the need of specialized institutes similar to the Wyss Institute.
- WyssInsitute in Boston is a dedicated center that focuses on innovations that emulate human biology.
- The dedicated institute will facilitate effective communication and collaboration across various fields.
- Promoting innovation: Developing a comprehensive and self-sustaining ecosystem in India to address this gap in the fields of cell culture, material science, and electronics.
- Guidelines: Urgent need for guidelines establishing minimal quality criteria and standards for these systems.
- Existing guidelines on animal testing requirements need re-evaluation and updating to accommodate advancements in cell-based and gene-editing therapies.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/animal-trials-drug-development-india-amendment-2019-rules/article67019288.ece
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
