United Nations Alliance of Civilizations (UNAOC)

- 18 Dec 2025
In News:
India recently reaffirmed its civilisational philosophy of VasudhaivaKutumbakam (“the world is one family”) and commitment to religious harmony at the 11th UNAOC Global Forum held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
The Indian delegation highlighted India’s long-standing belief in pluralism, intercultural dialogue, and Sarva Dharma Samabhav (equal respect for all religions).
About the UNAOC
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Launched |
2005 |
|
Initiative of |
Kofi Annan (former UN Secretary-General) |
|
Co-sponsored by |
Governments of Spain and Türkiye |
|
Nature |
UN “soft-power” political initiative |
|
Secretariat |
New York, USA |
|
Funding |
Voluntary Trust Fund administered by the UN Secretariat |
|
Participants |
Governments, regional bodies, civil society, private sector, youth groups |
Core Objectives of UNAOC
UNAOC aims to:
- Promote intercultural and interreligious dialogue
- Reduce polarisation, extremism, xenophobia and hate speech
- Encourage mutual respect, inclusion and peaceful coexistence
- Serve as a platform for conflict prevention and resolution through dialogue
Global Forum of UNAOC
The Global Forum is the flagship event of UNAOC:
- Brings together political leaders, religious figures, youth, media and civil society
- Focuses on bridging cultural divides
- Acts as a high-level platform for policy dialogue and partnership-building
The 11th Forum marked two decades of UNAOC’s work in strengthening intercultural cooperation.
Funding Mechanism
- Operates through a Voluntary Trust Fund
- Contributions from:
- UN Member States
- International organizations
- Foundations
- Private sector
- Fund supports projects, outreach, and administrative functions
Famine in Gaza
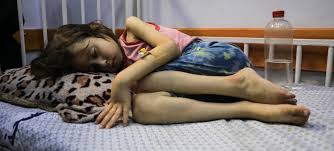
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The United Nations has confirmed a famine in Gaza City and surrounding areas, describing it as a “failure of humanity” and a man-made disaster. The declaration follows a report by the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC), which raised food insecurity in parts of Gaza to Phase 5, the highest level, indicating catastrophic conditions of starvation, destitution, and death.
Scale of the Crisis
- Population affected: Nearly 641,000 people are facing IPC Phase 5 conditions, while 1.14 million (58% of Gaza’s population) are projected to experience emergency-level food insecurity (IPC Phase 4) between mid-August and end of September.
- Children at risk: By June 2026, 132,000 children under five may face life-threatening malnutrition.
- Mortality: Gaza’s Hamas-run health ministry reports 271 deaths due to malnutrition, including 112 children.
- Historical Context: Since 2004, IPC has officially classified only four famines, with the last one in Sudan, 2024.
Causes
The famine is described as “starvation by design” by UN officials:
- Aid Restrictions: Israel has been accused of systematically obstructing humanitarian aid. The UN estimates 600 aid trucks per day are needed, but only 300 trucks are entering daily.
- Conflict Impact: Israel launched a military campaign in response to the Hamas attack on southern Israel in October 2023, leading to mass casualties and displacement. Over 62,000 deaths have been reported in Gaza, with more than 90% of homes damaged or destroyed.
- Infrastructure Collapse: Healthcare, water, sanitation, and hygiene systems have collapsed, exacerbating malnutrition and disease.
International Response
- UN Officials:
- Secretary-General Antonio Guterres called the famine a “moral indictment” and a man-made disaster.
- UNRWA Chief Philippe Lazzarini termed it “starvation by design”.
- UN Human Rights Chief Volker Turk attributed the famine to Israel’s unlawful restriction of aid.
- Global Condemnation:
- UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy described it as a “moral outrage”.
- Humanitarian groups and UN bodies have called for an immediate, at-scale response to prevent widespread starvation.
- Israeli Position: Israel denies a policy of starvation, claiming it has allowed 2 million tons of aid since the conflict began and continues to organize humanitarian corridors and airdrops, though the UN calls these efforts insufficient and sometimes unsafe.
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- 23 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant development, the United States has announced its decision to withdraw from UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) by December 2026, citing what it perceives as the agency’s anti-Israel bias and its recognition of the State of Palestine as a full member. This marks the third withdrawal of the U.S. from UNESCO and the second under President Donald Trump’s leadership, having previously exited in 2018 and rejoined in 2023 under the Biden administration.
Reasons for U.S. Withdrawal
According to the U.S. State Department, the decision stems from:
- UNESCO’s admission of the State of Palestine as a member state, which contradicts official U.S. policy.
- Allegations that UNESCO promotes divisive social and cultural causes.
- Concerns about the proliferation of anti-Israel rhetoric within the organization.
About UNESCO
Founding and Mandate
- Founded: 16 November 1945 (Constitution in force from 1946).
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Parent Body: United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- Membership: 194 member states and 12 associate members.
- Origin: Born out of post–World War II efforts to foster peace through education, science, and culture.
Objectives
UNESCO aims to build global peace and security by:
- Promoting international cooperation in education, science, culture, and communication.
- Supporting literacy, educational access, and free universal education.
- Acting as a clearinghouse of knowledge, especially in global South nations.
Focus Areas
UNESCO operates in five major sectors:
- Education
- Natural Sciences
- Social and Human Sciences
- Culture
- Communication and Information
Key Functions and Initiatives
Flagship Initiatives
- World Heritage Convention (1972): Protects cultural and natural sites of outstanding universal value.
- Man and the Biosphere Programme (1971): Promotes sustainable development through biosphere reserves.
- Convention for Safeguarding Intangible Cultural Heritage (2003): Preserves oral traditions, performing arts, and rituals.
- Global Education Coalition (2020): Formed during COVID-19 to ensure education continuity.
- Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence (2021): Sets global standards for ethical AI development.
Important Publications
- Global Education Monitoring Report
- World Water Development Report
- World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development
Strategic Importance of UNESCO
- Acts as a platform for intercultural dialogue and peacebuilding.
- Enhances scientific cooperation for issues like climate change and disaster preparedness.
- Supports freedom of expression and combats misinformation globally.
- Promotes equity in global education and digital access.
- Plays a key role in setting ethical standards in science and technology.
U.S. and UNESCO: A Tumultuous Relationship
- The U.S. has historically had a strained relationship with UNESCO:
- 1984: First withdrawal under Ronald Reagan, citing mismanagement and politicization.
- 2002: Rejoined under George W. Bush.
- 2011: Stopped funding after UNESCO admitted Palestine as a member.
- 2018: Withdrew under Donald Trump.
- 2023: Rejoined under Joe Biden.
- 2026: Set to withdraw again.
Implications of U.S. Withdrawal
- Financial Impact: The U.S. has historically contributed around 22% of UNESCO’s budget.
- Geopolitical Signal: Reflects a broader American skepticism towards multilateral institutions.
- Operational Effect: May hamper UNESCO’s work, especially in politically sensitive or conflict regions.
- Diplomatic Fallout: Could weaken the U.S.'s soft power and global cultural influence.
India and the United Nations Peacekeeping
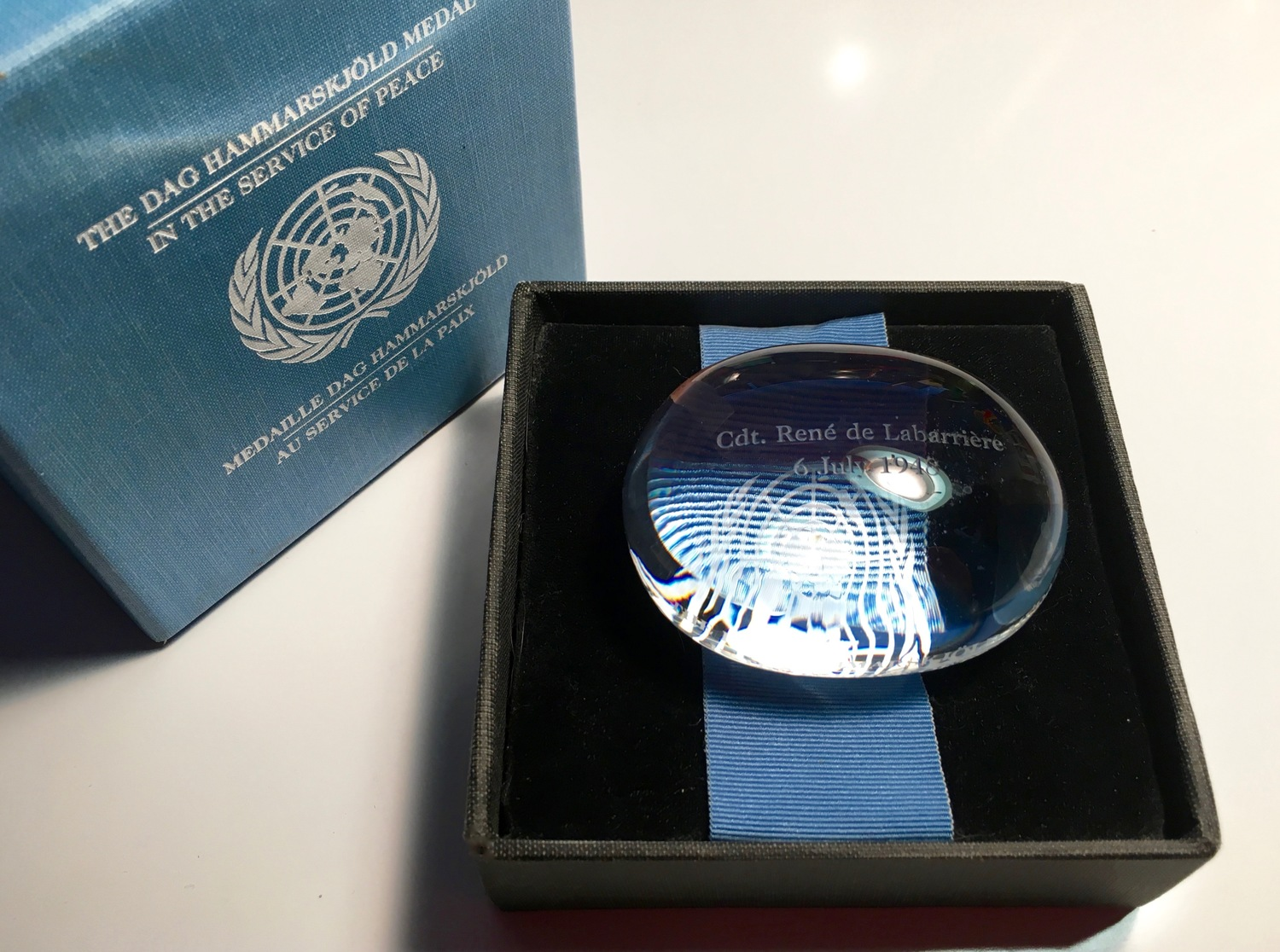

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Two Indian peacekeepers—Brigadier General Amitabh Jha (UNDOF) and Havildar Sanjay Singh (MONUSCO)—are being posthumously awarded the Dag Hammarskjöld Medal by the United Nations. Their sacrifice will be honoured at the U.N. Headquarters during the International Day of U.N. Peacekeepers on May 29, 2025.
Overview:
- Instituted: 1997
- Purpose: Posthumous honour to U.N. peacekeepers who die in service under U.N. authority.
- Awarded on: Peacekeepers' Day (May 29) annually.
- Named after: Dag Hammarskjöld, the 2nd U.N. Secretary-General, who died in a 1961 plane crash during a peace mission in Congo.
- First award (1998): Dag Hammarskjöld and Commandant René de Labarrière (first peacekeeper to die in a U.N. mission, 1948).
Other UN Peacekeeping Awards
- Captain Mbaye Diagne Medal for Exceptional Courage: Recognizes U.N. personnel displaying exceptional bravery.
- UN Military Gender Advocate of the Year Award: Recognizes peacekeepers promoting gender equality under UNSC Resolution 1325.
- 2023 recipient: Major Radhika Sen (India, MONUSCO).
- 2024 recipients: Sqn. Ldr. Sharon Syme (Ghana) and Superintendent Zainab Gbla (Sierra Leone), both serving in UNISFA.
India’s Contribution to UN Peacekeeping
- Total personnel deployed (2025): Over 5,300 Indian troops in missions in: Abyei, Central African Republic, DR Congo, Lebanon, Somalia, South Sudan, and Western Sahara.
- Historical role:
- Since 1950s, India has contributed over 290,000 personnel to 50+ peacekeeping missions.
- India is among the top four contributors of uniformed personnel.
- Engagement includes training, capacity building, and technology support for U.N. missions.
UN Peacekeeping: Global Overview
- Established: 1948 (First mission: United Nations Truce Supervision Organization in the Middle East).
- Cumulative personnel served: Over 2 million in 71 operations.
- Current strength (2025): Around 68,000 personnel from 119 countries in 11 missions across Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Peacekeepers who have died since 1948: Over 4,400.
Theme 2025: ‘The Future of Peacekeeping’
- Linked to: Pact for the Future adopted in 2024 by global leaders.
- Aim: To reform peacekeeping for modern challenges.
- UN Secretary-General António Guterres emphasized the need for a peacekeeping force ready to face "increasingly complex" global situations.
20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20)

- 13 May 2025
In News:
India actively participated in the 20th session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20) held from May 5 to 9, 2025, at the United Nations Headquarters, New York. UNFF, established in 2000 by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), is the sole intergovernmental platform dedicated to global forest policy dialogue and coordination, aiming to promote sustainable forest management (SFM) and strengthen political commitment worldwide.
Key Objectives and Functions of UNFF
- Promotes conservation, management, and sustainable development of all forest types.
- Supports the implementation of Agenda 21, Rio Forest Principles, and the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030.
- Oversees six voluntary Global Forest Goals (GFGs) and 26 targets, including reversing deforestation and enhancing forest governance.
- Facilitates cooperation through technical exchanges, policy development, financing mechanisms like the Global Forest Financing Facilitation Network, and advocacy linking forests with climate, biodiversity, and sustainable development.
India’s Highlights at UNFF20
India reaffirmed its commitment to the Voluntary National Contributions (VNCs) under the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030, reporting progress in increasing its forest and tree cover, which now constitutes 25.17% of the country’s geographical area, as per the latest India State of Forest Report. Major achievements include:
- Restoration efforts under the Aravalli Green Wall project.
- A 7.86% increase in mangrove cover over the past decade.
- Afforestation of over 1.55 lakh hectares through the Green India Mission.
- Plantation of 1.4 billion seedlings under the “Ek Ped MaaKe Naam” (Plant4Mother) campaign.
Global Contributions and Initiatives
India extended an invitation to all UN member states to join the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)—a global platform launched by India to conserve seven big cat species through collaborative research, knowledge exchange, and capacity-building.
India also emphasized the importance of incorporating the outcomes of the Country-Led Initiative (CLI) on forest fire management and forest certification—hosted by India in Dehradun in October 2023—into formal global mechanisms. It acknowledged contributions from other countries such as the Republic of Congo, Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, and Austria in this initiative.
Policy and Technical Engagements
India hosted a side event titled “Restoring Degraded Forest Landscapes: India’s Approach to Sustainable Forest Management and Climate Resilience”, showcasing integrated forest restoration strategies combining policy innovation, resource convergence, community participation, and technology.
In a high-level panel on “Valuing Forest Ecosystems in National Policy and Strategy,” India shared pilot study findings from Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, and tiger reserves that quantified ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation. India stressed the need to incorporate ecosystem valuation into national planning to enhance forest governance and ecological sustainability.
Significance of UNFF20
The session focused on advancing three Global Forest Goals:
- Reversing forest cover loss.
- Increasing protected and sustainably managed forests.
- Promoting forest governance and legal frameworks.
UNFF20 aimed to strengthen global dialogue following the 2024 midterm review of the international arrangement on forests and set the agenda for future policy deliberations in 2026. It underscored the critical role forests play in climate resilience, biodiversity, livelihoods, and sustainable development.
United Nations Day 2024

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on October 24 to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter's entry into force, aiming to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Celebrates the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- Goal: Raise awareness about the UN’s objectives and accomplishments.
UN Charter Overview
- Signing & Implementation:
- Signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco.
- Came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945.
- Predecessor: The League of Nations, created in 1919 after WWI, aimed at promoting international cooperation and peace.
- Content:
- Foundational document of the UN, binding all member states.
- Establishes principles of international relations, including equality of nations and the prohibition of force between countries.
- Amended three times: 1963, 1965, and 1973.
UN's Core Objectives
- Peace and Security: Maintaining global peace and preventing conflicts.
- Humanitarian Aid: Providing assistance to those in need.
- Human Rights: Protecting and promoting human rights globally.
- International Law: Upholding the rule of law on the global stage.
Main Organs of the UN
- General Assembly (UNGA):
- Comprises all 193 Member States, each with one vote.
- Main policy-making body, addressing international issues covered by the UN Charter.
- Security Council (UNSC):
- Consists of 15 members (5 permanent, 10 elected for two-year terms).
- Permanent members: China, France, Russia, UK, USA.
- India has been elected to the UNSC eight times.
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC):
- Composed of 54 members elected by the General Assembly.
- Coordinates policy and addresses economic, social, and environmental issues.
- Trusteeship Council:
- Established to oversee trust territories transitioning to independence.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The only international court resolving disputes between UN member states.
- Handles contentious cases and provides advisory opinions.
- Secretariat:
- Led by the Secretary-General, appointed by the General Assembly based on Security Council recommendations.
- Acts as the chief administrative body of the UN.
Note: Most UN organs, including the UNGA, UNSC, ECOSOC, Trusteeship Council, and Secretariat, are based in New York, while the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
Small Island Developing States

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Fourth International Conference on Small Island Developing States (SIDS-4) will be convened from May 27-30, 2024.
About Small Island Developing States (SIDS):
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a distinct group of 39 States and 18 Associate Members of United Nations regional commissions that face unique social, economic and environmental vulnerabilities.
- The three geographical regions in which SIDS are located are:
- The Caribbean
- The Pacific
- The Atlantic, Indian Ocean and South China Sea (AIS)
- SIDS were recognized as a special case both for their environment and development at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- The aggregate population of all the SIDS is 65 million, slightly less than 1% of the world’s population, yet this group faces unique social, economic, and environmental challenges.
- SIDS face a host of challenges including for many, their remote geography.
- As a result, many SIDS face high import and export costs for goods as well as irregular international traffic volumes.
- For SIDS, the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)—the ocean under their control—is, on average, 28 times the country’s land mass.
- Thus, for many SIDS the majority of the natural resources they have access to comes from the ocean.
- Factors like small population size, remoteness from international markets, high transportation costs, vulnerability to exogenous economic shocks and fragile land and marine ecosystems make SIDS particularly vulnerable to biodiversity loss and climate change because they lack economic alternatives.
- Climate change has a very tangible impact on SIDS.
- Slow onset events such as sea level rise pose an existential threat to small island communities, requiring drastic measures such as relocation of populations, and the related challenges this poses.
- These challenges are compounded by limited institutional capacity, scarce financial resources and a high degree of vulnerability to systemic shocks.
- Industries like tourism and fisheries can constitute over half of the GDP of small island economies.
- However, the importance of these natural resources extends beyond the economy; biodiversity holds aesthetic and spiritual value for many island communities.
- For centuries, these communities have drawn benefits from biodiversity in the form of food supply, clean water, reduced beach erosion, soil and sand formation, and protection from storm surges.
- At the regional level, SIDS are also supported by inter-governmental organisations, primarily the?Caribbean Community (CARICOM),?the?Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)?and the Indian Ocean Commission (IOC).
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global trade dynamics are expected to remain sluggish in 2024, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has warned.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- UNCTAD’s latest projections indicate global growth of 2.6 percent in 2024, slightly slower than in 2023.
- This marks the third consecutive year in which the global economy will grow at a slower pace than before the pandemic when the average rate for 2015–2019 was 3.2 percent.
India’s growth is expected to be marginally lower than in 2023:
- Regarding India, the report stated that the economy grew at 6.7 percent in 2023 and is expected to be marginally lower at 6.5 percent in 2024.
- It noted that the expansion in 2023 was influenced by strong public investment and the services sector, which received a boost from robust local demand for consumer services along with assured external demand for business services exports.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep interest rates constant in the near term, while strong public investment expenditures will offset restrained public consumption spending.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 to promote the interests of developing countries in global trade.
- With its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD has 195 member states and collaborates with numerous nongovernmental organizations worldwide.
- The organization focuses on formulating policies related to various aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance, and technology.
- UNCTAD plays a crucial role in addressing the concerns of developing countries regarding international institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank.
- By providing a platform for these countries to discuss and tackle their unique challenges, UNCTAD contributes to global economic development and reduces inequalities.
- Some notable achievements of UNCTAD include the establishment of the Global System of Trade Preferences (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), which reduces tariffs and removes non-tariff trade barriers, the Common Fund for Commodities, providing financial assistance to countries dependent on commodity exports, and various agreements for debt relief.
- In recent years, UNCTAD has focused on addressing globalization challenges and helping the least developed countries integrate into the global economy.
UNITED NATIONS FORUM ON FORESTS (PIB)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) will organise a Country-Led Initiative (CLI) event hosted by the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change from October 26–28, 2023, at the Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
Facts About:
- It encourages the sustainable development, preservation, and management of all kinds of forests.
- The UNEconomic and Social Council of the United Nations (ECOSOC) was founded it in 2000.
- Every year, the Forum gathers at the UN Headquarters in New York to discuss high-level policy issues in even years and technical issues in odd years, bringing together representatives of all member states and agencies with an interest in forests.
- All United Nations members as well as specialized agencies make up the forum, which has universal membership.
- India is one of UNFF's founding members.
UNITED NATIONS WORLD TOURISM ORGANISATION (UNWTO) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Dhordo village in Gujarat's Kutch district was recently recognized as the Best Tourism Village by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), which was praised by India's Prime Minister.
Facts About:
- The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting sustainable and responsible tourism on a global scale.
- Its functions include acting as a global forum for tourism policy issues and encouraging the adoption of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism.
It was founded in 1975.
- Members: 159 countries are members of the UNWTO.
- Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish are the UNWTO's official languages.
- Structure of the organization:
The World Tourism Organization's General Assembly is the organization's main meeting.
It is made up of full members and associate members. It convenes every two years.
- The Executive Council serves as the UNWTO's governing body.
It is made up of 35 members, one for every five full members, who are elected by the General Assembly. It holds at least two meetings per year.
- Headquarters are in Madrid, (Spain).
