World Investment Report 2025
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Investment Report 2025, released recently by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights critical trends in global foreign direct investment (FDI).
Key Details:
Purpose of the Report:
- To track global trends in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and international production.
- To guide policymakers and investors on aligning investment flows with sustainable development objectives.
- To monitor progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Global Digital Compact through investment trends.
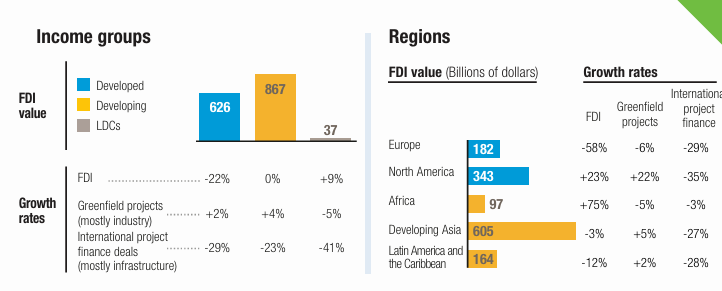
Major Global Trends Identified (2024 Data)
- Overall Decline in Global FDI: FDI declined by 11%, reaching $1.5 trillion, marking the second consecutive year of contraction.
- Digital Economy as a Growth Engine
- Value of digital-sector projects doubled, becoming the primary driver of FDI growth.
- Key growth areas: AI, data centres, cloud computing, semiconductors.
- SDG Investment Crisis: Investment in critical SDG sectors such as renewable energy, water, sanitation, and agrifood fell by 25–33%.
- Regional Divergence
- Africa: FDI surged by 75%, led by Egypt’s $35 billion megaproject.
- ASEAN: Moderate growth of 10% driven by realigned supply chains.
- China: FDI inflows fell by 29%, affected by geopolitical tensions.
- South America: Registered an 18% drop in FDI.
- Collapse in Infrastructure Finance: International Project Finance (IPF) declined by 26%, deepening the infrastructure gap in least developed countries (LDCs).
- Geopolitical Fragmentation
- Rising trade tensions, tariff barriers, and political risks are reshaping FDI flows.
- Emergence of near-shoring and regionalisation as firms relocate to reduce dependence on global supply chains.
Country-Specific Focus: India
- India received $28 billion in FDI inflows in 2024, retaining its rank among top global destinations.
- Key sectors: semiconductors, EV components, digital infrastructure.
- India ranked among top 5 global hubs for greenfield projects.
- Outbound FDI by Indian firms increased by 20%, showing strong outward investment intent.
Assessment of Positive and Negative Trends
Positive Trends:
- Digital FDI Boom: Reflects a global pivot towards a knowledge and tech-driven economy.
- Africa’s Rise: Significant confidence in Africa despite global slowdown.
- Resilient ASEAN & India: Benefitting from global supply chain realignment.
Negative Trends:
- Fall in SDG-Aligned Investments: Threatens progress towards global sustainability targets.
- Infrastructure Finance Crisis: Severely affects LDCs dependent on project finance.
- China’s FDI Decline: Raises concerns about the future of global investment flows amid US-China tensions.
- Geopolitical Fragmentation: Reduces investor appetite for long-term cross-border projects.
Strategic Recommendations
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Scale up investments in broadband, cloud infrastructure, and data hubs through public-private partnerships.
- Bridge SDG Investment Gap: Mobilize development banks, sovereign wealth funds, and climate finance to support SDG sectors.
- Policy Coherence: Align digital, industrial, and sustainability policies at national and international levels.
- De-risking Private Investment: Promote blended finance models to attract global capital to emerging markets.
- Enhance Innovation Governance: Improve IPR frameworks and cross-border data regulations to boost investor confidence in innovation sectors.
- Boost Regional Integration: Strengthen regional trade agreements and infrastructure connectivity to counter global fragmentation.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global trade dynamics are expected to remain sluggish in 2024, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has warned.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- UNCTAD’s latest projections indicate global growth of 2.6 percent in 2024, slightly slower than in 2023.
- This marks the third consecutive year in which the global economy will grow at a slower pace than before the pandemic when the average rate for 2015–2019 was 3.2 percent.
India’s growth is expected to be marginally lower than in 2023:
- Regarding India, the report stated that the economy grew at 6.7 percent in 2023 and is expected to be marginally lower at 6.5 percent in 2024.
- It noted that the expansion in 2023 was influenced by strong public investment and the services sector, which received a boost from robust local demand for consumer services along with assured external demand for business services exports.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep interest rates constant in the near term, while strong public investment expenditures will offset restrained public consumption spending.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 to promote the interests of developing countries in global trade.
- With its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD has 195 member states and collaborates with numerous nongovernmental organizations worldwide.
- The organization focuses on formulating policies related to various aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance, and technology.
- UNCTAD plays a crucial role in addressing the concerns of developing countries regarding international institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank.
- By providing a platform for these countries to discuss and tackle their unique challenges, UNCTAD contributes to global economic development and reduces inequalities.
- Some notable achievements of UNCTAD include the establishment of the Global System of Trade Preferences (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), which reduces tariffs and removes non-tariff trade barriers, the Common Fund for Commodities, providing financial assistance to countries dependent on commodity exports, and various agreements for debt relief.
- In recent years, UNCTAD has focused on addressing globalization challenges and helping the least developed countries integrate into the global economy.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (DownToEarth)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's Review of Maritime Transport 2023, international shipping witnessed a notable increase of 20 percent in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 compared to the previous decade.
Key Highlights from the Review:
- The shipping industry plays a pivotal role, accounting for over 80 percent of global trade volume, yet contributes nearly three percent of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerized trade, after a 3.7 percent decline in 2022, is projected to grow by 1.2 percent in 2023 and is expected to further expand by three percent from 2024 to 2028.
- Oil and gas trade exhibited robust growth in 2022, with tanker freight rates experiencing a significant resurgence driven by geopolitical developments.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- UNCTAD serves as the United Nations' primary institution addressing trade and development matters.
- Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly, it functions as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD's mission is to promote equitable and effective access to the benefits of a globalized economy for developing countries.
- It offers economic and trade analysis, fosters consensus-building, and provides technical assistance to assist developing nations in leveraging trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD publishes influential reports, including the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and The Least Developed Countries Report.
