Darjeeling Mandarin Orange Gets GI Tag

- 01 Dec 2025
In News:
Darjeeling Mandarin Orange, a premium citrus fruit grown in the hill regions of West Bengal, has been accorded Geographical Indication (GI) status, recognising its unique quality, flavour, and regional identity. With this, it becomes the third GI-tagged product from the Darjeeling region, after Darjeeling Tea and Dalley Khursani chilli.
About Darjeeling Mandarin Orange
- Botanical name: Citrus reticulata Blanco
- Region: Hills of Darjeeling and Kalimpong, West Bengal
- Local name: Suntala
- Economic importance: Major cash crop of the Darjeeling hills, known for distinct aroma, sweetness, and flavour
- Applicant/Owner: Darjeeling Organic Farmers Producer Organisation (DOFPO), Mirik, ensuring community ownership
Climatic & Edaphic Requirements
- Altitude: 600–1,500 metres above mean sea level
- Climate: Frost-free tropical to subtropical
- Rainfall: ~100–120 cm annually
- Temperature: 10°C–35°C
- Soil: Medium to light loamy soils
Production & Significance
- Output (2016): ~15,000 metric tonnes from Darjeeling & Kalimpong districts
- Market: Historically exported; high demand including European markets
- Challenges: Production declined over the past 15 years due to virus and pest attacks
- Expected impact of GI:
- Revival of cultivation and farmer incomes
- Protection against misuse/imitations
- Branding and premium pricing in domestic and export markets
What is a Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- A sign identifying goods as originating from a specific region where quality, reputation, or characteristics are attributable to that origin.
- Covered goods: Agricultural products, foodstuffs, wines & spirits, handicrafts, industrial products.
- Legal framework: Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999
- Validity: 10 years, renewable.
Constitution (131st Amendment) Bill, 2025

- 26 Nov 2025
In News:
The proposed Constitution (131st Amendment) Bill, 2025 has generated political debate as it seeks to bring Chandigarh under Article 240 of the Constitution, altering its existing administrative arrangement.
What is the Constitution (131st Amendment) Bill, 2025?
- Nature: A draft constitutional amendment.
- Core Proposal: To include Chandigarh within the ambit of Article 240.
- Rationale:
- Simplify the Central Government’s law-making process for Chandigarh.
- Ensure uniformity with other Union Territories (UTs) without legislatures.
What is Article 240?
- Empowers the President of India to make regulations for certain UTs.
- Such regulations have the same force as an Act of Parliament.
- Currently applies to:
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Lakshadweep
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Puducherry (when its Legislative Assembly is suspended or dissolved)
- Chandigarh is not covered at present.
Key Features of the Proposed Amendment
- Inclusion under Article 240: President can directly frame regulations for Chandigarh.
- Administrator Provision: Enables appointment of an independent Administrator, instead of the Punjab Governor holding additional charge.
- Reduced Role of Punjab: Marks a departure from the historical arrangement under the Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966.
- Administrative Shift: Strengthens direct Central control over Chandigarh’s governance.
About Chandigarh
Historical Background
- Post-Partition Context: Conceived as a new capital for Indian Punjab after Lahore went to Pakistan.
- Vision: Envisioned by Jawaharlal Nehru as a symbol of modern India, “unfettered by the traditions of the past.”
- Urban Planning: Master plan designed by Le Corbusier, making it a landmark in modernist urban design.
- Foundation Stone: Laid in 1952.
- Site Selection: Foothills of the Shivalik Range, then part of Ambala district.
After Punjab Reorganisation (1966)
- Haryana carved out of Punjab.
- Chandigarh designated as:
- A Union Territory, and
- Joint capital of Punjab and Haryana.
Existing Governance Structure of Chandigarh
- Administrative Head: Governor of Punjab acts as Administrator of Chandigarh (additional charge).
- Past Arrangement: Had an independent Chief Commissioner/Chief Secretary (1966–1984).
- Control: Directly under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Legislature: No Legislative Assembly; governance through UT ??????? (Adviser to Administrator, Home Secretary, Finance Secretary, etc.).
Nyoma Air Base Operationalised in Eastern Ladakh
- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
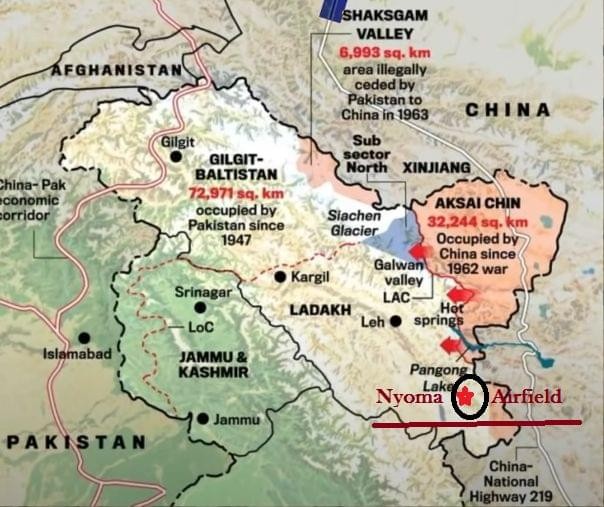
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has formally operationalised the Nyoma Air Base in Eastern Ladakh after Air Chief Marshal A.P. Singh successfully landed a C-130J aircraft on its newly completed runway. The airbase is now one of the world’s highest fully operational military airfields, marking a major milestone in India’s border infrastructure modernisation along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Location and Geography
- Situated at: Mudh-Nyoma, Leh district, Ladakh
- Altitude: ~13,700 feet
- Distance from LAC: About 23-30 km
- Located near:
- Southern bank of Pangong Tso
- Northern bank of the Indus River
- Strategic valleys of Hanle, Chumar, and Demchok
- Terrain:
- High-altitude cold desert
- Harsh temperatures reaching –30°C
- Construction possible only for limited months each year
Historical Background
- Initially built as a mud airstrip in 1962, remained unused for decades.
- Reactivated in 2009 with the landing of an AN-32 aircraft.
- After the 2020 India-China standoff, Nyoma ALG supported:
- C-130J
- AN-32
- Apache
- Chinook
helicopter and aircraft operations.
- In 2023, the BRO began converting the airstrip into a full airbase under Project Himank.
- Completed in 2024 at a cost of ?218 crore, led significantly by women officers of the BRO.
- Fully operationalised in November 2025, after installation of hangars, ATC, hardstanding, and allied facilities.
Infrastructure and Capability
Nyoma Air Base now includes:
- 2.7-km paved runway, capable of handling:
- Fighter aircraft
- Heavy-lift transport aircraft
- Helicopter operations
- Supporting infrastructure:
- Hangars
- Air Traffic Control (ATC)
- Hard surfaces for aircraft parking
- Logistics and troop accommodation
- Its flatter valley location makes operations easier and quicker compared to Leh.
Strategic Importance
- Enhanced Operational Reach
- Enables rapid deployment of troops and equipment near the LAC.
- Allows quicker launch of interdiction strikes if required.
- Strengthens high-altitude air mobility in the Indus–Pangong–Hanle corridor.
- Bolsters Border Infrastructure
- Complements existing airfields at:Leh, Kargil, Thoise, Daulet Beg Oldie, and Fukche
- Part of India’s larger infrastructure push post-2020, including new roads, bridges, tunnels, helipads, and logistics hubs.
- Strategic Deterrence Against China
- Improves surveillance and presence along a sensitive frontier.
- Counters China’s rapid infrastructure development along its side of the LAC, including new airbases, missile sites, bunkers, and underground storage facilities.
- Supports Ground Operations
- Facilitates sustained patrols in areas such as Demchok and Depsang, where the Army resumed patrolling in 2024 after a long pause.
- Helps maintain operational readiness in a “stable but sensitive” LAC environment.
- Strengthens India’s long-term defensive posture and contributes to overall border stability.
Nemaline Myopathy
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
Nemaline myopathy is a rare, inherited neuromuscular disorder that primarily affects skeletal muscles, leading to muscle weakness and impaired mobility. Recently, the condition drew public attention after D. Y. Chandrachud, the Chief Justice of India, spoke about his foster daughters’ experience with the disease, highlighting the lack of awareness, delayed diagnosis, and need for better support systems for children living with rare genetic disorders.
What is Nemaline Myopathy?
- Also known as rod myopathy, it is characterised by the presence of thread-like (rod-shaped) structures called nemaline bodies within muscle fibres.
- It is a congenital genetic disorder, caused by mutations in genes encoding muscle proteins.
- Prevalence: Approximately 1 in 50,000 births.
- The disease shows wide variability in severity, ranging from mild muscle weakness to severe, life-threatening forms.
Genetic Basis
- The disorder is hereditary, arising due to genetic mutations—permanent changes in a gene’s DNA sequence.
- These mutations disrupt the structure and function of muscle proteins, impairing muscle contraction.
- Nemaline myopathy is classified into six types, based on age of onset and severity:
- Severe congenital
- Intermediate congenital
- Typical congenital (most common)
- Childhood-onset
- Adult-onset (mildest form)
- Amish type (rare)
Clinical Features
- Muscle weakness, especially in:
- Face and neck
- Trunk and proximal muscles (near the body’s centre)
- Feeding and swallowing difficulties, particularly in infants.
- Respiratory muscle involvement in severe cases, leading to breathing difficulties and risk of respiratory failure.
- Orthopaedic complications:
- Foot deformities
- Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis)
- Joint stiffness or deformities (contractures)
- Motor development may be delayed; many individuals can walk initially, but wheelchair support may be required later in progressive cases.
Prognosis
- Severity-dependent:Severe congenital type is often life-threatening, with early childhood mortality due to respiratory failure.
- Typical congenital type presents in infancy with muscle weakness and feeding issues.
- Adult-onset type is usually mild, with symptoms appearing between 20–50 years.
Treatment and Management
- No definitive cure exists at present.
- Management is supportive and symptomatic, focusing on:
- Physiotherapy and muscle-strengthening exercises
- Respiratory support when required
- Nutritional and feeding support
- Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care can significantly improve quality of life.
Current Significance
- The recent public discussion by the CJI has underlined:
- Low awareness among doctors and caregivers
- Painful and delayed diagnostic processes
- The need for better genetic testing, counselling, and disability support systems in India
IUCN Kenton Miller Award 2025

- 14 Oct 2025
In News:
India has achieved a landmark moment in global conservation as Dr. Sonali Ghosh, Field Director of Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve (Assam), became the first Indian to receive the prestigious IUCN WCPA Kenton Miller Award 2025. The honour was announced at the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi, highlighting India’s rising leadership in biodiversity governance and protected-area innovation.
About the IUCN Kenton Miller Award
- Instituted: 1999
- Presented by:IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA)
- Named after: Dr. Kenton R. Miller, eminent conservationist & former IUCN Director-General
- Purpose:Recognisesoutstanding innovation and excellence in the sustainability and governance of protected areas
- Eligibility: Protected-area managers, researchers, community/indigenous conservation practitioners
- Award Components:
- USD 5,000 grant
- Global citation
- Sponsored participation at the IUCN Congress
Significance of Dr. Ghosh’s Contribution
Dr. Ghosh has been awarded for pioneering inclusive and sustainable protected-area management across the Kaziranga-Orang-Manas landscape. Key initiatives include:
- Community-centric conservation: Empowering local and indigenous communities as co-stewards
- Eco-tourism models: Ensuring livelihood security while safeguarding biodiversity
- Anti-poaching and habitat security: Strengthening surveillance and ecological connectivity
- Gender inclusion: Promoting women’s participation in frontline conservation forces
Her leadership reflects India’s approach to biodiversity protection through grassroots participation, science-based governance, and livelihood integration.
Broader Context: India at the IUCN Congress
At the Congress, India reiterated its commitment to global environmental cooperation. Union Minister Kirti Vardhan Singh engaged with international delegates and IUCN leadership on advancing shared conservation goals, reinforcing India's stance as a proactive global environmental actor.
About IUCN and the World Conservation Congress
- Founded: 1948
- HQ: Switzerland
- Global network of governments, NGOs, and experts from 160+ countries
- World Conservation Congress: Held every four years to set global biodiversity priorities
Previous Winner (2023)
- Maria del Carmen Garcia Rivas (Mexico) – Honoured for community-led management of marine protected areas.
Foreigners Tribunals

- 08 Sep 2025
In News:
The Union Home Ministry has recently empowered Foreigners Tribunals (FTs) with expanded judicial authority under the Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025, which came into effect in September 2025. This marks a significant shift in India’s approach to dealing with suspected illegal immigrants, particularly in states like Assam.
Background
- Earlier Framework: Foreigners Tribunals were originally set up under the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, issued under the Foreigners Act, 1946. Their main role was to determine whether a person was a foreign national.
- In Assam, such tribunals were established after the Illegal Migrants (Determination by Tribunals) Act, 1983 was struck down by the Supreme Court in 2005. Currently, around 100 FTs are functional in the state.
- Earlier, detention of declared illegal immigrants was carried out through executive orders, without direct judicial sanction.
Provisions of the 2025 Act
The Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025 repeals older legislations and replaces the 1964 Order, giving FTs enhanced powers akin to those of a civil court and a first-class judicial magistrate.
New Powers of Foreigners Tribunals:
- Summoning and enforcing attendance of individuals and examining them under oath.
- Requiring production and verification of documents.
- Issuing commissions for the examination of witnesses.
- Directing suspects (“proceedees”) to appear in person.
- Issuing arrest warrants in case of non-appearance.
- Sending suspected or declared foreigners to detention/holding centres pending deportation.
Procedural Aspects:
- Notices are served to suspected individuals to prove their citizenship within 10 days.
- Cases are to be disposed of within 60 days of reference.
- Declared foreigners are placed in detention or transit camps until deportation.
Significance
- Strengthened Legal Framework: Brings uniformity and judicial backing to the process of identifying and detaining unauthorised foreigners.
- Due Process Assurance: Ensures quasi-judicial scrutiny before declaring an individual a foreigner.
- Regional Relevance: Particularly critical in Assam and Northeast India, which face unique challenges of cross-border migration.
- Administrative Clarity: Clearly demarcates powers between executive authorities and tribunals.
India–EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)

- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
The Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) between India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) — comprising Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland — will come into force on 1 October 2025.
Key Features of TEPA
- Strategic Investment Commitment
- Legally binding commitment of USD 100 billion FDI in India over 15 years (USD 50 billion in first 10 years + USD 50 billion in next 5 years).
- Expected to generate 1 million jobs.
- Excludes foreign portfolio investment (FPI); sovereign wealth funds exempted.
- India can withdraw tariff concessions if commitments are not met.
- Market Access & Tariff Concessions
- EFTA: 92.2% tariff lines offered, covering 99.6% of India’s exports (100% non-agri products + concessions on processed agri products).
- India: 82.7% tariff lines offered, covering 95.3% of EFTA exports (including gold, which retains existing duty).
- Duty-free access: Indian basmati and non-basmati rice exports, without reciprocity.
- Exclusions: Dairy, soya, coal, and sensitive agri products; protection given to sectors linked with PLI schemes (e.g., pharma, medical devices, processed food).
- Concessions: Cheaper Swiss chocolates, wines, luxury watches (though wines < USD 5 excluded to protect Indian wineries).
- Services & Professional Mobility
- Boosts Indian services exports: IT, business, cultural, sporting, educational, and audiovisual services.
- Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs): Nursing, accountancy, and architecture professionals to gain work access in EFTA countries.
- Legal & Institutional Framework
- Covers 14 chapters: market access, trade facilitation, investment promotion, IPR, sustainable development.
- Protects India’s generic medicines; prevents evergreening of patents.
- Promotes technology collaboration but not compulsory technology transfer.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Established: 1960 (Stockholm Convention).
- Members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland (not part of the EU).
- Aim: Promote free trade and economic integration among members and global partners.
India–EFTA Trade Relations
- India is EFTA’s 5th largest trading partner (after EU, US, UK, China).
- Trade Volume (2024–25): USD 24.4 billion.
- India’s exports: USD 1.96 billion (chemicals, iron & steel, precious stones, sports goods, bulk drugs).
- Imports from EFTA: USD 22.45 billion (mainly gold, silver, coal, pharma, vegetable oil, medical equipment, dairy machinery).
- Deficit: Large trade deficit, primarily due to gold imports from Switzerland (USD 20.7 billion in 2021–22).
- India–EFTA Desk: Set up by Invest India as a single-window platform to facilitate investments under TEPA.
FASTag Annual Pass
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Union Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari announced the launch of a FASTag-based Annual Pass, offering a simplified and cost-effective tolling solution for private vehicle users on National Highways. The initiative is set to be rolled out from August 15, 2025, and aims to improve traffic flow, reduce toll disputes, and enhance ease of travel.
What is the FASTag Annual Pass?
- Cost: ?3,000
- Validity: 1 year from activation or 200 highway trips (whichever comes earlier)
- Eligibility: Only for non-commercial private vehicles (cars, jeeps, vans)
- Coverage: Valid across all National Highways in India
Key Objectives
- Hassle-free highway travel by eliminating repeated toll payments
- Reduce congestion and waiting time at toll plazas
- Simplify toll management with a one-time, prepaid model
- Address concerns regarding toll plazas located in close proximity (within 60 km)
How It Works
- Integrated with the existing FASTag system (uses RFID technology)
- Annual pass will be linked to the user's FASTag account
- Activation and renewal through:
- Rajmarg Yatra App
- NHAI website
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) website
Part of a Broader Reform in Tolling
The Annual Pass complements ongoing toll reforms:
- Introduction of ANPR-FASTag hybrid tolling system:
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) cameras
- RFID-based FASTag readers
- Enables barrier-less tolling, where vehicles are charged without stopping
- Non-compliance may result in:
- e-notices
- Penalties, including FASTag suspension or VAHAN database sanctions
Kichan and Menar Wetlands
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministry of Environment announced that Kichan (Phalodi) and Menar (Udaipur) wetlands in Rajasthan have been recognized as Ramsar Sites, bringing India’s total to 91 Ramsar-designated wetlands—the highest in Asia.
About Menar Wetland:
- A freshwater monsoon wetland complex in Udaipur district, Rajasthan.
- Formed by three primary ponds: Braham Talab, Dhand Talab, and Kheroda Talab; the latter two are connected by flooded agricultural land during the monsoon.
- Habitat for endangered and migratory birds such as:
- Critically Endangered: White-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis), Long-billed vulture (Gyps indicus)
- Other species: Himalayan griffon, Egyptian vulture, Dalmatian pelican, Ferruginous pochard, Black-tailed godwit
- Home to over 70 plant species, including mango trees (Mangifera indica) that host colonies of Indian flying foxes (Pteropus giganteus).
- Community-led conservation: Menar village residents prevent poaching and fishing, earning it the title "Bird Village".
About Kichan Wetland:
- Located in Phalodi, Jodhpur, in the northern Thar Desert of Rajasthan.
- Comprises:
- Ratri Nadi (river)
- Vijaysagar Talab (pond)
- Riparian and scrub habitats
- Notable for supporting drought-resistant flora and over 150 bird species.
- Globally known for hosting over 22,000 migratory demoiselle cranes (Anthropoides virgo) each winter.
- A hub for birdwatchers, tourists, scientists, and students.
Ramsar Convention Overview:
- An intergovernmental treaty for the conservation of wetlands, signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
- Headquartered in Gland, Switzerland.
- Wetlands listed under the convention are known as Ramsar Sites—of international importance.
- Member countries (Contracting Parties) commit to identifying and protecting these wetlands.
Sabine’s Gull Spotted at Nalsarovar
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological event, the Sabine’s Gull — a rare Arctic seabird — has been observed at Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary in Gujarat. This marks the species’ first recorded appearance in India since 2013, when it was last sighted in Kerala, underlining the dynamic migratory patterns affecting India’s wetland ecosystems.
About Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary
- Located nearly 64 km west of Ahmedabad, Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary is one of Gujarat’s most prominent wetland ecosystems. Encompassing an area of 120.82 sq km, it comprises a shallow, seasonal lake interspersed with around 360 islets, creating a rich mosaic of aquatic habitats.
- This natural lake traces its origin to the 15th century, following the construction of a check dam on the Sabarmati River. Initially designed to serve irrigation and drinking water needs of nearby villages, the lake gradually evolved into a crucial habitat for avifauna. Recognition of its ecological significance grew over time, prompting colonial authorities in the early 20th century to take protective measures.
- Eventually, in 1969, the Government of Gujarat declared Nalsarovar a bird sanctuary, and it was further accorded the status of a Ramsar wetland site in 2012, signifying its global importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Flora: The sanctuary supports a wide variety of aquatic and wetland plant life, with 48 algae species and 72 flowering plant species recorded. Common plant species include Cyperus, Scirpus, Typha ungustata, Eleocharis palustris, Ruppia, Potamogeton, Vallisneria, Naias, and Chara.
- Fauna:Nalsarovar is home to nearly 250 bird species, making it a haven for bird watchers. Regular sightings include both greater and lesser flamingos, pelicans, ducks, geese, coots, rails, cranes, and a variety of wading and aquatic birds like herons, egrets, storks, spoonbills, and sarus cranes.
- Beyond birds, the sanctuary also supports mammalian fauna. On its southern and southwestern peripheries, species such as the Indian wild ass, mongoose, jungle cat, Indian fox, jackal, wolf, and striped hyena are found.
Sabine’s Gull: Profile
- The Sabine’s Gull (Xemasabini), also known as the fork-tailed gull or xeme, is a small gull species notable for its elegant flight and distinctive wing markings. Adults can be recognized by their pale grey backs, black wingtips, white secondary feathers, and forked white tails.
- This gull breeds in high Arctic and subarctic zones across North America, Russia, Greenland, and Svalbard, and is a rare migrant in South Asia.
- According to the IUCN Red List, it is currently categorized as a species of Least Concern, although sightings in India are extremely uncommon.
IndiaAI Mission

- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
India has taken a major step toward self-reliance in Artificial Intelligence with the expansion of its national AI compute infrastructure and the selection of three new startups to build indigenous foundation models under the IndiaAI Mission.
Key Highlights
- Compute Infrastructure Boost:India’s total GPU capacity has now surpassed 34,000 units, up from the initial 10,000-target. A fresh addition of 15,916 GPUs to the existing 18,417 empanelled GPUs brings the total to 34,333 GPUs, now available through the IndiaAI Compute Portal (operational since March 2025).
- Subsidised Access:These GPUs are made available at a subsidised rate of ?67/hour, well below the global average of ?115/hour. This has been made possible through private sector empanelment instead of government-built data centres. Service providers receive up to 40% capital subsidy, enabling rapid infrastructure rollout.
- Empanelled Providers:Seven private companies were empanelled for compute provisioning:
- Cyfuture India Pvt. Ltd.
- Ishan Infotech Ltd.
- Locuz Enterprise Solutions Ltd.
- Netmagic IT Services Pvt. Ltd.
- Sify Digital Services Ltd.
- Vensysco Technologies Ltd.
- Yotta Data Services Pvt. Ltd.
Foundation Model Development
Under the IndiaAI Foundation Model initiative, three new startups have joined Sarvam AI (selected earlier in April 2025) to build India-specific Large Language Models (LLMs):
- Soket AI: Will develop a 120-billion parameter open-source model focused on Indian languages and use cases in defence, healthcare, and education.
- Gnani AI: Building a 14-billion parameter Voice AI model for real-time, multilingual speech recognition and reasoning.
- Gan AI: Developing a 70-billion parameter multilingual TTS (text-to-speech) model aiming for "superhuman" capabilities surpassing global benchmarks.
- Sarvam AI: Previously selected to create a 120-billion parameter Sovereign AI model, following the release of Sarvam-1 (2B parameters) and Sarvam-M (24B parameters).
These foundation models will be trained on Indian datasets and tailored for governance, public service delivery, and regional language support.
AI Kosh& Innovation Initiatives
- AI Kosh: A public dataset platform with 367 datasets uploaded, enabling research and model training using India-relevant data.
- IndiaAI I4C CyberGuard Hackathon: In collaboration with the Ministry of Home Affairs, AI models were developed for identifying cybercrime patterns from complex inputs like handwritten FIRs and audio calls on the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal.
- Startup Innovation & Skill Development: Funding support, AI labs in Tier-II cities, and talent development programs are part of a broader push to promote innovation and reverse brain drain.
About IndiaAI Mission
- Launched by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Cabinet Approval: March 2024 with a budget of over ?10,000 crore
- Objectives:
- Develop indigenous AI capabilities and infrastructure
- Democratize AI access for governance, startups, and citizens
- Promote ethical and safe AI use
- Position India among the global AI leaders
International Booker Prize 2025
- 23 May 2025
In News:
In a historic win, Banu Mushtaq, a prominent Kannada writer, advocate, and activist, became the first Indian author writing in Kannada to win the International Booker Prize 2025 for her short story collection Heart Lamp. The book was translated into English by Deepa Bhasthi, who also became the first Indian translator to win this prestigious award.
About the International Booker Prize
- Established: 2005 by the Booker Prize Foundation, UK.
- Awarded: Annually.
- Purpose: To honour the best work of fiction translated into English, regardless of the original language or nationality of the author.
- Prize Amount: £50,000, shared equally between the author and the translator.
- Shortlisted nominees (authors and translators) receive £2,500 each.
- Focus: Unlike the Booker Prize, which honours original English-language works, the International Booker Prize exclusively celebrates translated fiction, highlighting the importance of translators in global literature.
Key Features
- Celebrates literary excellence, cultural richness, and the art of translation.
- Initially biennial (2005–2015), it became an annual award in 2016.
- Books must be translated into English and published in the UK or Ireland.
India and the International Booker Prize
Year Author Work Language Translator
2022 Geetanjali Shree Tomb of Sand Hindi Daisy Rockwell
2025 Banu Mushtaq Heart Lamp Kannada Deepa Bhasthi
About Banu Mushtaq
- Born: April 3, 1948, in Hassan, Karnataka.
- Professions: Advocate, journalist, feminist writer, women’s rights activist, and former municipal councillor.
- Affiliation: Prominent figure in the Bandaya movement, known for protest literature in Kannada addressing social injustices.
- Journalistic Background: Reported for LankeshPatrike (1981–1990) under the mentorship of P. Lankesh.
Literary Contributions
- Started writing: In 1974; first story published in Prajamatha.
- Themes: Focuses on gender justice, religious identity, caste oppression, and female autonomy.
Heart Lamp: The 2025 Winning Work
- Genre: Short story collection comprising 12 stories written between 1990 and 2023.
- Content: Explores the lives of ordinary South Indian Muslim women, addressing themes like patriarchy, faith, family roles, and self-determination.
- Significance:
- First short story collection to win the International Booker Prize.
- First Kannada-language work to win.
- First win for Indian translator Deepa Bhasthi.
Other Notable Works by Banu Mushtaq
- Benki Male (1999): Awarded the Karnataka Sahitya Academy Award.
- HaseenaMattuItaraKathegalu (2015): Translated into English as Haseena and Other Stories.
- Black Cobra (Short Story): Adapted into the award-winning film Hasina by Girish Kasaravalli.
Dr. Ajay Kumar appointed as UPSC Chairman

- 17 May 2025
In News:
Dr. Ajay Kumar, former Defence Secretary and a 1985-batch IAS officer of Kerala cadre, took oath as the new Chairman of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) on May 2025. The oath was administered by Lt. Gen. Raj Shukla, the senior-most member of the Commission, following the end of Preeti Sudan’s tenure on April 29, 2025.
Profile of Dr. Ajay Kumar:
- Academic Qualifications:
- B.Tech in Electrical Engineering – IIT Kanpur
- M.Sc. in Applied Economics – University of Minnesota, USA
- Ph.D. in Business Administration – Carlson School of Management, USA
- Key Positions Held:
- Managing Director, IT Department, Government of Kerala
- Secretary, Defence Production
- Director General, National Informatics Centre
- Secretary, Ministry of Defence
- E-Governance Contributions:
- Initiated digital platforms like Jeevan Pramaan, MyGov, PRAGATI, and Cloud First Policy
- Introduced biometric attendance systems and digital OPD registrations in AIIMS
He brings over 35 years of administrative experience in both state and central governments and has several publications in reputed journals.
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) – At a Glance
Constitutional Backing:
- Established under Articles 315–323 of the Constitution
- Originally formed: October 1, 1926
- Became a constitutional body on January 26, 1950
Composition:
- Comprises a Chairman and other members, appointed by the President
- At least half the members must have held government office for 10+ years
- Presently, the Commission has vacancies for 2 members
Tenure:Chairman/Members hold office for 6 years or until 65 years of age, whichever is earlier
Resignation & Removal:
- Can resign by writing to the President
- Can be removed for misbehavior, only after an inquiry by the Supreme Court
Post-Tenure Restrictions:
- Chairman: Not eligible for any further government employment
- Members: Can be appointed as Chairman of UPSC or State PSC, but not to any other office of profit
Functions of UPSC:
- Central recruitment agency for:
- Civil Services Examination (CSE)
- Engineering Services (ESE)
- Combined Medical Services (CMS), and more
- Advises the government on:Recruitment rules, appointments, promotions, and disciplinary matters
Operation Keller

- 16 May 2025
In News:
On 13 May 2025, the Indian Army, in coordination with the J&K Police and CRPF, launched Operation Keller, a targeted counter-terrorism operation in the Keller forests of Shopian district, Jammu & Kashmir. The operation led to the elimination of three terrorists, including Shahid Kuttay, the chief of The Resistance Front (TRF) and the alleged mastermind behind the Pahalgam terror attack.
Key Objectives:
- Neutralise terrorists affiliated with The Resistance Front (TRF), a proxy of Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT).
- Specifically eliminate Shahid Kuttay, involved in the April 2025 Pahalgam attack that killed 26 civilians.
- Secure volatile forested zones in South Kashmir to prevent future infiltrations and retaliatory threats.
Details of the Operation:
- Launch Date: 13 May 2025
- Location:Shoekal Keller forest area, Shopian district, J&K
- Conducted By: Indian Army (Rashtriya Rifles), J&K Police, CRPF
- Method: Intelligence-based search and destroy mission
- Outcome: Elimination of three hardcore terrorists after a fierce gunfight; operation ongoing.
Pahalgam Terror Attack Link:
- Posters announcing ?20 lakh bounty per terrorist involved in the Pahalgam killings were circulated in Pulwama.
- J&K Police released sketches identifying the three LeT-linked terrorists responsible.
- Operation Keller targeted the network allegedly behind this attack.
About Shopian District:
- Location: Southern Kashmir Valley; bordered by Pulwama, Anantnag, Kulgam, and PirPanjal mountains.
- Elevation: ~2,146 metres; experiences harsh winters (up to −7°C).
- Economy: Agriculture-based, especially apple orchards.
- History:
- Upgraded to district status in 2007 (earlier part of Pulwama).
- Lies along the historic Mughal Road connecting Lahore and Srinagar.
- Name Origin: Possibly from “Shah-payan” (royal stay) or “Shin-van” (snow forest).
GhassemBasir Missile unveiled by Iran

- 08 May 2025
In News:
Iran has recently introduced a new solid-fuel medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) named GhassemBasir.
About the GhassemBasir Missile
The missile is designed to engage targets at distances exceeding 1,200 kilometers, enhancing Iran’s strategic strike capabilities.
Key Features:
- Size and Weight: The missile measures approximately 11 meters in length and weighs around 7 tons.
- Advanced Materials: Its airframe is reportedly constructed using carbon fiber composite materials, which reduce structural weight and lower its radar signature.
- Warhead: The missile carries a warhead estimated to weigh about 500 kilograms.
- Propulsion: Powered by a solid-fuel system, the missile benefits from quicker launch readiness and improved storage stability compared to liquid-fuel missiles.
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to Mach 12.
- Guidance System: Equipped with a thermal imaging sensor that enables the missile to detect and home in on targets by sensing heat signatures during the final flight phase.
- Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle (MaRV): The missile features a MaRV that separates from the booster, reducing aerodynamic drag, decreasing radar detectability, and enhancing ballistic performance.
- Mobility: It can be launched from mobile transporter-erector-launchers (TELs), including vehicles resembling civilian trucks, increasing its operational flexibility and survivability.
Alcatraz Island
- 08 May 2025
In News:
The President of the United States has recently instructed his administration to undertake a project to rebuild and expand Alcatraz, the notorious prison that has been closed for over six decades. This historic site is located on a remote island off the coast of San Francisco, California.
About Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island, often referred to as “The Rock,” is a small rocky island situated in San Francisco Bay, California, covering approximately 22 acres (9 hectares).
Historical Overview
- 1849: The island was sold to the U.S. government.
- 1854: Alcatraz became home to the first lighthouse on California’s coast.
- 1859: The first permanent army troops were stationed on the island.
- 1861: Alcatraz was converted into a military prison.
- 1907: It was officially designated as the Pacific Branch of the U.S. Military Prison.
- 1933: The U.S. Army vacated the island.
- 1934–1963: Alcatraz functioned as a federal prison, housing some of America’s most dangerous criminals.
Prison Details
The prison had a capacity to hold over 330 inmates in cells measuring approximately 10 feet by 4.5 feet (3 meters by 1.5 meters). However, the actual number of prisoners rarely exceeded 260 at any given time. Known as the most secure and inescapable prison in the United States, Alcatraz was famous for its isolation and strict security measures. Although a few inmates attempted to escape, the harsh currents of San Francisco Bay made survival unlikely.
Closure and Current Status
Due to the high costs of upkeep, the prison was officially closed in March 1963. In 1972, Alcatraz was incorporated into the newly established Golden Gate National Recreation Area and was opened to the public. Today, it remains a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world.
Rare 7th-Century Old Kannada Inscription unearthed at Madapura Lake, Karnataka

- 07 May 2025
In News:
A rare 7th-century Old Kannada inscription from the reign of Vikramaditya I of the Badami Chalukyas has been discovered at Madapura Lake in Davangere, Karnataka. The inscription sheds light on taxation, land grants, and regional governance during his rule.
About the Badami Chalukyas
- Origins: Emerged as a regional Kannada power claiming descent from Ayodhya to establish legitimacy.
- Capital:Vatapi (present-day Badami, Karnataka).
- Notable Rulers and Political History:
- Pulakesin I (543–566 CE): Founder of the dynasty; fortified Badami.
- Pulakesin II (609–642 CE): Most celebrated ruler; defeated Harshavardhana at the Narmada river; established diplomatic contacts with Persia (depicted in Ajanta caves).
- Vikramaditya I (644–681 CE): Son of Pulakesin II; reclaimed Badami from Pallavas and expanded influence over southern kingdoms like the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas.
- Administration:
- Centralised monarchy with limited autonomy granted to villages.
- Economy relied on land revenue and military conquests.
- Maintained a naval fleet—Pulakesin II had around 100 ships.
- Religion:Patronised Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism, and Jainism. Vikramaditya I and others made donations to Jain institutions; Pulakesin I performed Ashvamedha Yajna.
- Art and Architecture:
- Developed the Vesara style, a fusion of northern Nagara and southern Dravida temple architecture.
- Constructed rock-cut and structural temples in Aihole, Badami, and Pattadakal.
About Vikramaditya I
- Background: Son of Pulakesin II; ascended the throne during a period of political turmoil following his father's death and Pallava invasion.
- Military Achievements:
- Defeated Narasimhavarman I of the Pallavas, who had earlier seized Badami.
- Reunited the fractured Chalukya empire, restoring its former prestige.
- Subdued southern powers including the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas, consolidating control over the southern Deccan.
- Political Consolidation:
- Re-established central authority across Karnataka and surrounding regions.
- Appointed loyal feudatories, such as Singhavenna (mentioned in the new Davangere inscription), to manage local governance.
- Legacy:
- Known by titles such as Rajamalla (King of Kings) and Yuddhamalla (Warrior King).
- His reign marked a revival of Chalukya power and paved the way for cultural and architectural achievements under his successors Vikramaditya II and Kirtivarman II.
Khelo India Youth Games 2025

- 06 May 2025
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually inaugurated the 7th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) on May 4, 2025, marking Bihar’s first time hosting a national-level multi-sport event.
- The event will be held across five cities in Bihar: Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, and Begusarai from May 4–15, 2025.
About Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG)
Feature Details
Launch Year 2018
Nodal Ministry Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
Target Group Youth athletes under 17 and 21 years of age
Objective Promote grassroots sports, mass participation, and talent
development for global competition
Host Cities in 2025 Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, Begusarai
Total Athletes (2025) Over 6,000 participants
Special Highlights of KIYG 2025
- Medal Events: Competitions held in 27 sporting disciplines.
- New Inclusions:
- Sepaktakraw included as a medal sport for the first time.
- Esports introduced as a demonstration event, reflecting the rise of digital-age sports.
- Support for Athletes: Winners eligible for scholarships under the Khelo India Scheme to pursue professional training.
Significance
- PM Modi emphasized the role of regular tournaments like KIYG in shaping India’s sports ecosystem.
- Cited Vaibhav Suryavanshi, a 14-year-old cricketer who scored a 38-ball century in IPL 2025, as a symbol of emerging youth talent.
- Highlighted that platforms like Khelo India events (youth, para, winter, and senior levels) help identify, nurture and promote talent, building confidence among young athletes.
Previous Editions of KIYG
Edition Host City
1st (2018) New Delhi
2nd (2019) Pune
3rd (2020) Guwahati
4th (2021) Panchkula
5th (2022) Bhopal
6th (2023) Chennai
7th (2025) Bihar (multiple cities)
State of the Global Climate 2024 Report

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) released its State of the Global Climate 2024 Report at COP29 (Baku), warning that global warming is dangerously close to breaching the 1.5°C threshold set by the Paris Agreement.
About WMO
- Type: UN Specialized Agency
- Established: 1950
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Membership: 193 (187 Member States + 6 Territories)
- Mandate: Meteorology, operational hydrology, and geophysical sciences.
- Reports Released:
- State of the Global Climate Report
- Greenhouse Gas Bulletin
- Global Water Resources Report
- State of Climate Services Report
- United in Science Report
Key Findings – State of Global Climate 2024
Global Temperature Rise
- Current warming: 1.34°C–1.41°C above pre-industrial levels.
- 19 of the last 20 months crossed the 1.5°C threshold temporarily.
- 2024: Warmest year in the 175-year observational record.
- Projected crossing of the 1.5°C threshold: by September 2029.
Greenhouse Gases (2023)
- CO?: 420 ppm – 151% of pre-industrial levels (highest in 800,000 years)
- CH? (Methane): 1923 ppb – 266% of pre-industrial levels
- N?O (Nitrous Oxide): 335.8 ppb – 124% of pre-industrial levels
Ocean & Cryosphere
- Ocean Heat Content: Highest in 65 years – oceans absorb 90% of global heat
- Sea Level Rise:
- 1993–2002: 2.1 mm/year
- 2015–2024: 4.7 mm/year (rate doubled)
- Glacier Melt:
- 2022–2024: Largest 3-year negative mass balance on record
- Severe loss in Norway, Sweden, Svalbard, and Andes
- Arctic Sea Ice: Record lows for 18 consecutive years
- Antarctic Sea Ice: 2nd-lowest extent ever
- Ocean Acidification:
- Surface pH falling fastest in Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Pacific
- Effects irreversible for centuries
Extreme Weather Events & Displacement
- 2024: Record-high displacements from climate disasters
- Cyclones, floods, and droughts worsened food and humanitarian crises
- Worst-hit regions: East Asia, Southeast Europe, West Asia, Mediterranean
Reasons Behind These Trends
- GHG Emissions: Fossil fuel combustion, industrial emissions, agriculture, and deforestation.
- El Niño Effect: Warm Pacific currents intensified 2024’s global heat.
- Urban Heat Islands: Dense cities retain heat, increasing local warming.
- Ocean Absorption: Excess atmospheric CO? and heat absorbed by oceans.
Global Climate Governance
- UNFCCC (1992): Multilateral treaty for climate action.
- Paris Agreement (2015):
- Goal: Limit warming to below 2°C, aim for 1.5°C.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- $100 billion/year climate finance pledge
- Global Methane Pledge (2021): Cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030.
- Global Ocean Treaty (2023): Protect 30% of oceans by 2030.
- UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030): Forest and marine recovery.
- IPCC: UN scientific body for climate assessments (doesn’t conduct research).
India’s Climate Initiatives
Targets & Strategies
- Net Zero by 2070 (COP26)
- LT-LEDS (2022): Long-term low emissions strategy
- Updated NDC (2022):
- Reduce GDP emissions intensity by 45% by 2030 (vs. 2005)
- 50% electricity capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030
Renewable Energy & Alliances
- International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- Launched with France in 2015 (COP21)
- Aim: Mobilize $1 trillion in solar investments by 2030
Afforestation & Ecosystem Protection
- Green Credit Program (2023) – incentivizes afforestation
- Ek Ped MaaKe Naam (2024) – tree plantation campaign
- NAP, CAMPA, Forest Act 1980 – promote forest restoration
- MISHTI (2023) – Mangrove restoration (?12.55 cr in 2024–25)
Behavioral Change
- LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) – promotes sustainable consumption
Challenges to Climate Action
Sector Key Challenges
Energy High coal dependence (>50%), renewable intermittency, grid gaps, foreign tech reliance
Urbanization Rising energy/waste demand, land use conflicts
Industry Hard-to-abate emissions in cement, steel, transport
Agriculture Fossil fuel inputs, livestock methane, fertilizer N?O
Finance Climate finance disparities; India criticized COP29’s $300 bn/year goal as insufficient
Equity Developed nations emit more, but developing nations suffer more
Greenwashing Misleading climate claims by corporates/governments
Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
As of early 2025, 60% of the construction of the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is complete. The telescope is expected to begin its first scientific observations by the end of 2028.
About ELT
The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is poised to become the world’s most powerful ground-based optical and infrared telescope, with revolutionary capabilities to explore the universe.
- Location: Cerro Armazones, Atacama Desert, northern Chile
- Altitude: 3,046 meters above sea level
- Managing Body: European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Project Cost: Approximately $1.51 billion (around 1.3 billion euros)
- Completion Target: Late 2020s
- Primary Mirror: Diameter of 39 meters (128 feet) — the largest of its kind
- Constructed from 798 hexagonal segments, each 1.5 m across and 5 cm thick
Key Scientific Objectives
- Exoplanet Exploration
- Direct imaging of Earth-like exoplanets in habitable zones of nearby stars
- Analysis of atmospheric biosignatures such as oxygen, water vapor, and methane, aiding the search for extraterrestrial life
- Understanding the Early Universe
- Observation of the first stars and galaxies formed post-Big Bang
- Investigation of dark matter and dark energy, crucial for understanding cosmic expansion and the universe’s fate
- Detailed Study of Stars and Galaxies
- Identification and characterization of individual stars in distant galaxies
- Analysis of the formation, evolution, and structure of galaxies over cosmic time
- Black Holes and Cosmic Structures
- Study of supermassive black holes at galactic centers
- Understanding their role in galaxy dynamics and structure
Why Chile’s Atacama Desert?
- Dry Climate: Very low humidity and cloud cover, ensuring clearer skies
- High Altitude: Thin atmosphere reduces atmospheric interference with incoming light
- Minimal Light Pollution: Remote location offers dark skies critical for deep-space observation
- Dome Structure: Protects sensitive instruments from harsh desert conditions
About the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Nature: Leading intergovernmental science and technology organization in the field of astronomy
- Headquarters: Garching, Germany
- Members: 16 countries including Austria, Belgium, Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom
- Facilities in Chile:
- La Silla
- Paranal
- Chajnantor
- Mandate: Design, construction, and operation of advanced ground-based telescopes to promote international collaboration and facilitate path-breaking astronomical research
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
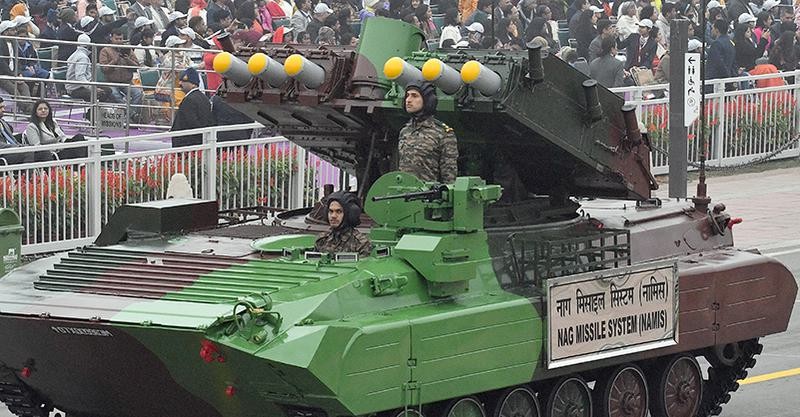
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
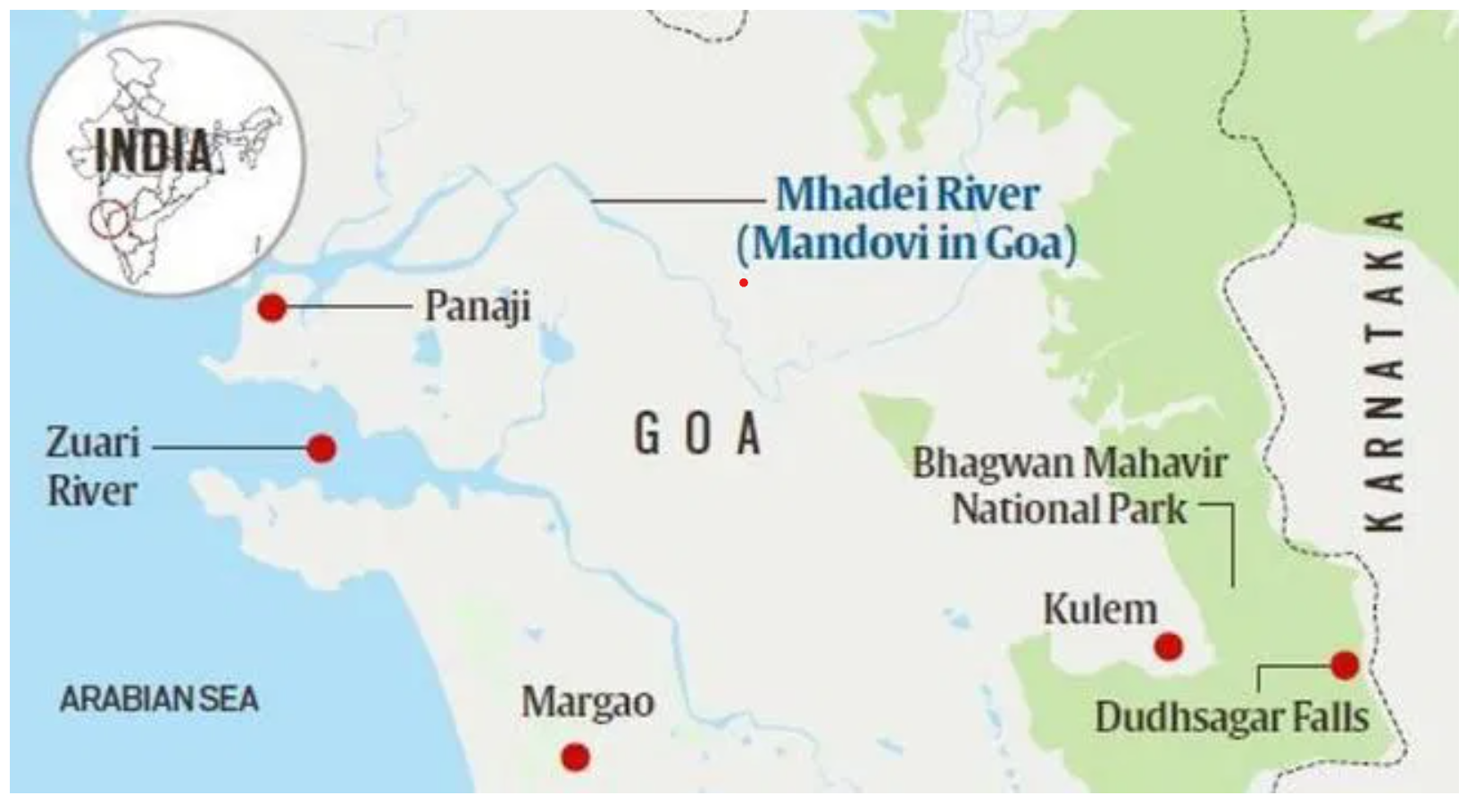
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
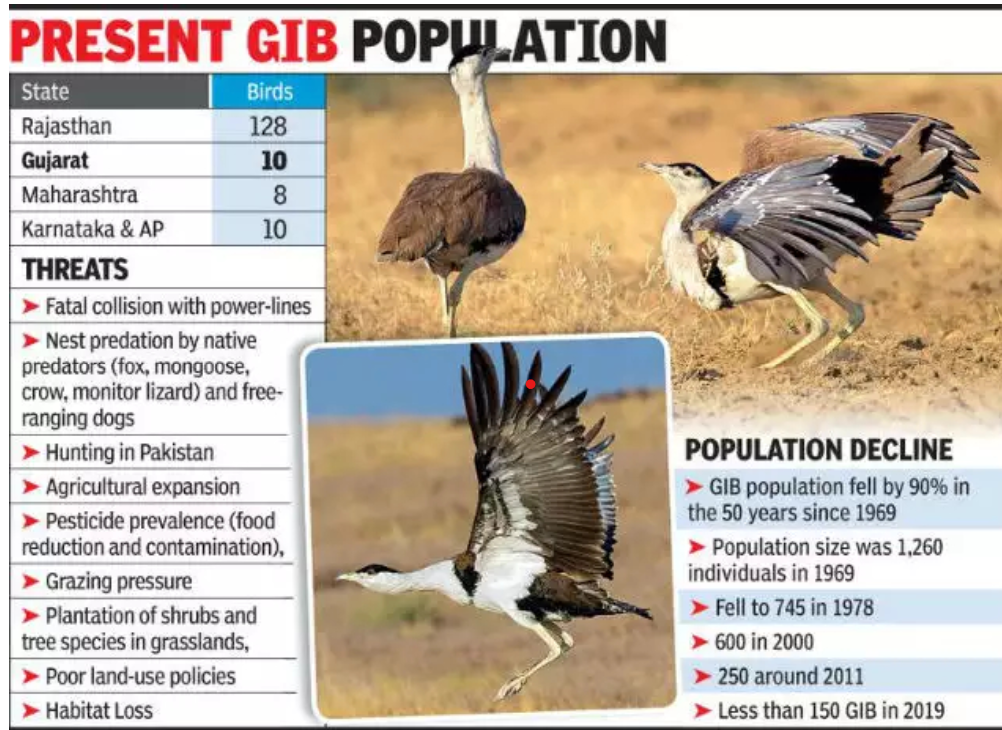
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
