Italy recognises Femicide as a Crime
- 08 Mar 2026
In News:
The Italian Parliament recently enacted a landmark law that recognises femicide as a distinct criminal offence and prescribes life imprisonment for the gender-motivated killing of women. The legislation, passed with bipartisan support, marks a significant step in addressing gender-based violence and aligns Italy with a small but growing group of countries that legally recognise femicide as a specific crime.
What is Femicide?
Femicide refers to the intentional killing of women or girls because of their gender. It is widely recognised by international organisations as the most extreme form of violence against women and girls (VAWG).
According to the United Nations, femicide often occurs in contexts such as:
- Intimate partner violence (current or former partners)
- Family-related killings, including so-called honour killings
- Gender-motivated murders by other perpetrators
Globally, many cases of femicide occur within domestic settings, reflecting deeper structural inequalities and patriarchal norms that perpetuate violence against women.
Italy’s Law Against Femicide
Italy’s legislation introduces femicide as a separate category within the criminal code, making gender-motivated killing punishable with life imprisonment.
Key Features of the Law
- Recognises gender as a motive for homicide.
- Introduces life imprisonment as the maximum penalty.
- Strengthens legal responses to crimes linked with gender-based violence.
- Passed amid growing concern over violence against women in the country.
The law was passed on 25 November, coinciding with the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, highlighting the symbolic and policy significance of the measure.
Why Recognising Femicide as a Separate Crime Matters
Treating femicide as a distinct offence has several legal and policy implications:
- Acknowledging Gender Motivation: It explicitly recognises that certain killings stem from systemic discrimination and patriarchal violence.
- Improved Data Collection: Legal recognition enables governments to track gender-based killings more accurately, aiding evidence-based policymaking.
- Targeted Criminal Justice Response: Special legal provisions allow harsher penalties and focused investigations.
- Public Awareness and Social Change: Naming the crime brings visibility to the structural nature of violence against women and helps mobilise social and institutional responses.
Global Legal Trends
- Italy joins a limited number of countries that have adopted specific legal provisions for femicide, including: Mexico, Chile, Cyprus, Morocco, North Macedonia, Türkiye and Gabon
- Several Latin American countries have also criminalised femicide as part of broader gender-violence laws, reflecting the region’s efforts to combat high rates of gender-based killings.
India’s Legal Framework on Gender-Based Killings
India does not legally recognise femicide as a separate criminal category. Instead, gender-based violence and killings are addressed through general criminal provisions and specific protective laws for women.
Important legislations include:
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- National Commission for Women Act, 1990
Murders of women motivated by dowry demands, honour, or domestic violence are typically prosecuted under general homicide provisions of the Indian Penal Code along with these special laws.
International Observance
- The International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women is observed annually on 25 November, following its designation by the United Nations General Assembly in 1999. The day seeks to raise awareness and mobilise action against violence directed at women and girls worldwide.
Meningococcal Infections
- 01 Mar 2026
In News:
In late February 2026, the Government of Meghalaya issued a public health advisory after suspected cases of meningococcal infection were reported among trainees at an Army training centre in Shillong, prompting heightened surveillance and containment measures.
Context and Incident Overview
The advisory by the State’s Health and Family Welfare Department was prompted by the deaths of two Agniveer trainees due to suspected meningococcal infection at the Assam Regimental Centre (ARC) in Shillong. All close contacts of the affected individuals were identified, isolated, and placed under medical observation.
Health authorities, including the State Surveillance Unit (SSU) and the District Surveillance Unit (DSU), East Khasi Hills, have initiated active epidemiological investigation, including case investigation, contact tracing, laboratory sample review, and enhanced surveillance in the affected institution and surrounding areas.
Officials have stated that no new suspected cases have been detected outside the initial cluster and that the situation is under close monitoring, with no current indication of wider spread.
About Meningococcal Infection
Meningococcal disease is caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis, which can cause:
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
- Meningococcemia: Bloodstream infection that can progress rapidly and be fatal.
It is transmitted through respiratory and throat secretions via close or prolonged contact. It is less contagious than common cold or influenza pathogens but can spread quickly in crowded settings like hostels, barracks, or training facilities.
Although meningococcal disease occurs sporadically, the region has history of outbreaks; for instance, significant outbreaks were reported in North East India, including Meghalaya, in the past.
Clinical Features and Treatment
Initial symptoms often resemble mild illnesses but may quickly escalate, including:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Neck stiffness
- Nausea, vomiting
- Non-blanching purpuric rash
- Confusion or altered consciousness
Early recognition and swift treatment are critical, as untreated cases can result in rapid deterioration and high mortality. Standard management includes prompt antibiotic therapy and supportive care such as fluid management and respiratory support.
Public Health Measures and Advisory
In its advisory, the Meghalaya government urged citizens to:
- Avoid crowded places and follow respiratory hygiene by covering mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing.
- Maintain hand hygiene using soap and water or sanitiser.
- Wear masks, especially if experiencing symptoms or in densely populated settings.
- Monitor for symptoms such as fever, severe headache, or rash, and seek immediate medical care if signs appear.
These steps align with standard outbreak response protocols, including identification and monitoring of close contacts.
Public Health Importance and Surveillance
Meningococcal disease is a notifiable condition under India’s Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP), which aims to detect early warning signals of outbreaks and initiate appropriate follow-up actions.
Strengthened surveillance, especially in institutional settings and among populations engaged in close living quarters, helps prevent potential outbreaks and supports early containment.
Divyangjan-Focused Initiatives in Budget 2026–27

- 02 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Budget 2026–27 reinforces the commitment to inclusive development by introducing two targeted initiatives for persons with disabilities (Divyangjan): the Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana and the Divyang Sahara Yojana. These schemes aim to enhance dignified livelihood opportunities and ensure access to advanced assistive technologies, aligning with the broader vision of equitable participation in economic and social life.
Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana: Industry-Linked Skilling
The Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana focuses on providing customised, industry-relevant skill training tailored to different disability categories. With an allocation of ?200 crore, the scheme targets sectors that offer task-oriented and process-driven roles, making them more adaptable for diverse abilities.
Key Features:
- Training in Information Technology (IT)
- Skills development in Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming and Comics (AVGC)
- Employment pathways in Hospitality, Food & Beverages
- Emphasis on customised pedagogy, assistive learning tools, and workplace readiness
The scheme shifts the approach from welfare to capability-building, enabling Divyangjan to access mainstream employment and entrepreneurial avenues.
Divyang Sahara Yojana: Expanding Assistive Technology Access
With an allocation of ?100 crore, the Divyang Sahara Yojana aims to strengthen the ecosystem for assistive devices and rehabilitation services.
Major Components:
- Support to Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO) to:
- Scale up production of high-quality assistive devices
- Invest in R&D and AI-enabled innovations
- Improve design, durability, and affordability
- Strengthening of PM Divyasha Kendra: These centres provide integrated services including:
- Assessment and evaluation
- Counselling
- Distribution of assistive aids
- Post-distribution care and follow-up
- Establishment of Assistive Technology Marts: These will function as modern retail-style centres where Divyangjan and senior citizens can:
- See and compare assistive products
- Try devices before purchase
- Access professional guidance
This retail-style approach improves choice, awareness, and accessibility, reducing dependence on ad hoc distribution models.
Significance for Inclusive Development
These initiatives reflect a rights-based and empowerment-oriented approach:
- Promote economic independence through skill integration
- Leverage technology and AI for better assistive solutions
- Support accessible infrastructure and service delivery models
- Align with the goals of social justice, human dignity, and equal opportunity
By combining skilling, employment linkage, and assistive support, the government seeks to ensure that Divyangjan move from beneficiaries of aid to active participants in India’s growth story.
India’s Commitment to Disability Rights and Inclusive Growth

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
India reaffirmed its commitment to disability inclusion around the International Day of Persons with Disabilities (3 December), with renewed focus on accessibility, digital empowerment, education, livelihoods, and rights-based governance for persons with disabilities (PwDs).
Disability Scenario in India
According to the Census 2011, India has 2.68 crore persons with disabilities, constituting 2.21% of the total population. The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016 defines a person with disability as someone with long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairment which, in interaction with barriers, hinders full and effective participation in society.
Disability and poverty are closely linked, making inclusive growth essential for ensuring dignity, independence, and equal opportunity.
Constitutional and International Commitments
The Indian Constitution supports disability rights through:
- Article 21, which ensures the right to live with dignity
- Article 41 (DPSP), which directs the State to provide assistance in cases of disability
- The State List (Seventh Schedule) includes relief of the disabled
India is also a signatory to the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), committing to a rights-based approach to inclusion.
Legal and Policy Framework
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 is the cornerstone law. It recognises 21 categories of disabilities, mandates reservations in education and employment, and enforces accessibility, non-discrimination, and inclusive education.
- The National Trust Act, 1999 supports persons with autism, cerebral palsy, intellectual and multiple disabilities.
- The Rehabilitation Council of India (RCI) Act, 1992 regulates training of rehabilitation professionals and maintains a national register.
- The Scheme for Implementation of RPwD Act (SIPDA) supports ministries and states in making infrastructure and services accessible.
Major Government Initiatives
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan (Accessible India Campaign), launched in 2015, aims to improve accessibility in public buildings, transport systems, and information and communication technology. The revamped Sugamya Bharat App now serves as a digital accessibility hub with mapping tools, scheme directories, and grievance reporting.
- The Unique Disability ID (UDID) Project creates a national database and provides a universal disability identity card, improving transparency and access to benefits.
- The ADIP Scheme provides assistive devices, including advanced aids like cochlear implants, to support independent living.
- The Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS) funds NGOs working in rehabilitation and education.
- The National Divyangjan Finance and Development Corporation (NDFDC) provides concessional loans for self-employment under schemes such as Divyangjan Swavalamban Yojana.
- ALIMCO, a government-owned enterprise, manufactures and distributes assistive devices nationwide.
Digital and Educational Inclusion
- The PM-DAKSH DEPwD portal links PwDs to skill training and employment opportunities.
- The Indian Sign Language Research and Training Centre (ISLRTC) promotes Indian Sign Language (ISL). The launch of PM e-Vidya Channel 31 provides dedicated ISL training. ISLRTC has also created the world’s largest ISL digital repository and expanded the ISL dictionary to over 10,000 terms.
- The PRASHAST App enables early screening of disabilities in schoolchildren.
Inclusion Through Culture and Enterprise
- The Divya Kala Mela provides market linkages to Divyang artisans and entrepreneurs under the “Vocal for Local” initiative.
- The Purple Fest celebrates inclusion, assistive technologies, and accessibility innovations.
Key Challenges
- Despite progress, barriers remain in accessibility, employment, healthcare costs, awareness, and last-mile delivery. Digital divides and social stigma continue to hinder full participation.
India’s disability framework is shifting toward rights-based, technology-enabled, and inclusion-driven governance. Strengthening awareness, enforcing accessibility standards, expanding financial support, and improving implementation will be crucial for achieving the goal of “inclusive growth with dignity”.
International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women

- 27 Nov 2025
In News:
- November 25, observed as the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, marks the beginning of the 16 Days of Activism against Gender-Based Violence (Nov 25–Dec 10), as recognised by the United Nations General Assembly.
- The 2025 global theme — “UNiTE to End Digital Violence against All Women and Girls” — highlights rising threats such as cyberstalking, online harassment, doxxing, deepfakes, and coordinated misogynistic attacks.
- India has adopted a multi-pronged approach combining legal reforms, institutional mechanisms, digital tools, and welfare schemes to address both offline and online violence against women.
Institutional Framework
National Commission for Women (NCW)
- Established in January 1992 as a statutory body.
- Mandate: Review legal safeguards, recommend law reforms, and address complaints of women’s rights violations.
- Enables online complaint registration and runs 24×7 domestic violence support helplines, integrated with police, hospitals, legal services, and counsellors through Digital India platforms.
Key Legal Provisions
Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
- In force from 1 July 2024, replacing the IPC.
- Introduces stricter punishments for sexual offences, including life imprisonment for rape of minors.
- Expands definitions of sexual crimes, mandates audio-video recording of victim statements, and prioritises fast-track trials for crimes against women and children.
Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005 (PWDVA)
- Covers physical, sexual, verbal/emotional, and economic abuse, including dowry-related harassment.
- Applies to women in domestic relationships (by marriage, adoption, or family ties).
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013 (POSH Act)
- Applicable to all women, irrespective of age or employment type.
- Mandates Internal Committees (ICs) and Local Committees (LCs).
- Complaints to be resolved within 90 days.
Mission Shakti: Umbrella Scheme
Implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Mission Shakti integrates:
- Sambal – safety and security
- Samarthya – empowerment and rehabilitation
Major Components
- One Stop Centres (OSCs): District-level centres providing medical, legal, police, counselling, and temporary shelter services under one roof (operational since 2015).
- Swadhar Greh: Shelter, food, legal aid, counselling, and rehabilitation for women in difficult circumstances.
- Stree Manoraksha: Mental health and psycho-social training for OSC staff, implemented with National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS).
Helplines and Emergency Support
- Women Helpline (181): 24×7 national support for women in distress.
- Emergency Response Support System (112): Pan-India emergency number for police, fire, and ambulance services (Nirbhaya Fund).
- NCW-supported digital and WhatsApp-based emergency reporting mechanisms.
Technology-Enabled Safety Measures
Digital Shakti Campaign
- Implemented by NCW to digitally empower women and girls, promoting safe online behaviour and awareness against cybercrimes.
SHe-Box Portal
- Centralised online platform for workplace sexual harassment complaints under the POSH Act.
- Automatically routes complaints to the relevant IC/LC and enables real-time tracking.
Other Key Digital Initiatives
- Investigation Tracking System for Sexual Offences (ITSSO): Monitors police investigations to ensure timely completion.
- National Database on Sexual Offenders (NDSO): Registry of convicted sexual offenders.
- Crime Multi-Agency Centre (Cri-MAC): Enables real-time sharing of information on heinous crimes across States/UTs.
Judicial & Policing Mechanisms
- Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs): Established under the Nirbhaya Fund for speedy trials of rape and POCSO cases.
- Women Help Desks (WHDs): Set up in police stations to ensure gender-sensitive reporting, counselling, and legal aid.
Maram Naga Tribe
- 19 Nov 2025
In News:
The Central Government has recently sanctioned ?9 crore under the Jan Man Scheme (JanMan) for the development, welfare, and cultural preservation of the Maram Naga tribe of Manipur. This initiative aims to uplift vulnerable and marginalized tribal groups through targeted infrastructure creation, social welfare schemes, and cultural conservation.
Who are the MaramNagas?
- The Maram Naga tribe is part of the Naga ethnic group inhabiting:
- Northeastern India, primarily Manipur
- Western Myanmar
- Major concentration is in:
- Senapati district (primary habitat)
- Kangpokpi district
- Estimated population in Manipur: around 50,000
- They belong ethnically to the Mongoloid race within the Tibeto-Burman family.
Language
- The Maram language belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family.
- Dialects vary by geographical region.
- Written using Roman script.
Occupation and Livelihood
- Agriculture is the dominant occupation.
- Practice both:
- Shifting cultivation (jhum)
- Wet cultivation
- Hunting serves as an important secondary occupation.
Belief System and Festivals
- They worship supernatural benevolent and malevolent forces, reflecting animistic traditions.
- Major festivals include:
- Punghi – celebrated in July
- Kanghi – celebrated in December
- A unique women-centric festival, Mangkang, is observed annually in April.
- Traditional Morungs (youth dormitories) form the core of their socio-cultural life.
Government Initiatives under Jan Man Scheme
The ?9 crore sanctioned fund will support:
1. Welfare and Housing
- Implementation of:
- PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana)
- Ayushman Bharat
- Construction of Anganwadi Centres.
2. Community Infrastructure
- Building of:
- Community halls
- Water storage structures
- Basic civic amenities
3. Cultural Preservation
- Protection and restoration of:
- Traditional Morungs
- Indigenous art forms
- Ancestral practices
4. Empowerment and Self-reliance
- Boosting local livelihoods and skill development in line with:
- “Development for everyone – together we trust progress.”
- Enhancing tribal access to government schemes.
Ramnami Tribe
- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ramnami tribe of Chhattisgarh recently came into national focus when two members of the community emotionally expressed gratitude after the Prime Minister allowed them to adorn him with their traditional peacock-feather crown, breaking official protocol. This gesture highlighted the tribe’s unique cultural identity and historical struggle for social equality.
Who Are the Ramnamis?
- A distinctive devotional sect from central and northern Chhattisgarh.
- Known for tattooing the word “Ram” across their faces and bodies, symbolising the omnipresence of God.
- Their belief centres on nirgun Ram—the formless, unmanifest divine.
Origin and Historical Background
- Emerged in the late 19th century as a peaceful socio-religious resistance against caste discrimination.
- Traditionally, many Ramnamis were denied access to temples.
- Founder is believed to be Parsuram Bhardwaj, the son of a low-caste sharecropper.
- Tattoos became a form of protest, asserting that God is accessible to all, irrespective of caste hierarchy.
Legal Recognition
- In 1910, upper-caste groups filed a case against the community for tattooing "Ram" on their bodies and garments.
- The Ramnami Samaj won the case, affirming their right to inscribe the divine name on their skin, attire, and homes.
Cultural Features
- Clothing: Plain white garments adorned with repeated inscriptions of “Ram”.
- Headgear: A crown made of peacock feathers, carrying symbolic and mythological significance.
- Music & Rituals:
- Use of ghungroos during devotional dances and bhajans.
- Emphasis on simplicity, devotion, and gender equality.
- Devotional Practice: Worship of Ram in any form—saffron robes, shaved head, or tattooed body—reflecting spiritual inclusivity.
Demographic Snapshot
- Historically estimated at ~6 lakh members.
- Numbers have declined significantly; current estimates range between 20,000 to 1,00,000 individuals.
Maldives Achieves Triple Elimination of Mother-to-Child Transmission (MTCT)
- 18 Oct 2025
In News:
In a landmark development in global public health, the Maldives has become the first country in the world to be validated by the World Health Organization (WHO) for eliminating mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis-B. This achievement represents a major milestone in protecting newborns from lifelong infections and advancing maternal-child health security.
Significance of the Achievement
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis-B remains a pressing concern worldwide, particularly in developing regions. In the WHO South-East Asia Region alone, thousands of infants are still born with congenital infections annually. Against this backdrop, Maldives’ accomplishment sets a benchmark for public health governance and disease elimination.
Key Drivers Behind Maldives’ Success
The achievement results from a comprehensive, integrated and equity-based healthcare strategy, backed by political commitment and strong health investments.
1. Universal Maternal Care and Screening
- Over 95% of pregnant women in Maldives receive antenatal care.
- Nearly all are screened for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis-B.
- Universal access extends to migrants and remote island populations.
2. Robust ImmunisationProgramme
- Above 95% hepatitis-B birth-dose coverage within 24 hours of birth.
- Full childhood immunisation coverage consistently maintained.
3. Demonstrated Zero Transmission
- No infant HIV or syphilis cases reported since 2022.
- National survey (2023) confirmed zero hepatitis-B among school-entry children.
4. Strong Public Health Infrastructure
- Universal health coverage system offering free antenatal and diagnostic services.
- Government spends over 10% of GDP on health, among the highest in the region.
- Effective partnerships across public, private, and civil society sectors, supported by WHO technical assistance.
Strategic Measures Adopted
- Integrated maternal-child health services
- Early testing and treatment protocols
- Strong laboratory systems and surveillance
- Community outreach and migrant health inclusion
- High-quality vaccination logistics
Future Roadmap
To sustain the elimination status and deepen maternal-newborn care outcomes, Maldives plans to:
- Expand digital public-health systems
- Strengthen laboratory and monitoring quality
- Enhance services for key and migrant populations
- Increase private-sector collaboration
WHO will continue supporting Maldives to maintain momentum toward broader maternal, child, and adolescent health goals.
Maldives at a Glance
- Location: North-central Indian Ocean; southwest of India and Sri Lanka
- Capital:Malé
- Population: ~5.6 lakh (2025)
- Geography: ~1,200 coral islands across 26 atolls; ~200 inhabited
- Feature: Lowest-lying nation globally (maximum elevation ~1.8m)
- Climate: Tropical; Southwest monsoon (May–Aug), Northeast monsoon (Dec–Mar)
Adi Yuva Fellowship & Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme

- 29 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in partnership with the United Nations in India, has launched the Adi Yuva Fellowship and the Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme under the umbrella of the Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan — a flagship initiative envisioned as the world’s largest tribal grassroots leadership movement.
- These initiatives aim to empower tribal youth, strengthen grassroots governance, and promote inclusive development in alignment with the goals of Viksit Bharat 2047 and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan
- Coverage: Targets 11 crore citizens across 1 lakh tribal-dominated villages in 550 districts of 30 States and UTs.
- Objective: To transform governance into a people’s movement rooted in responsive, accountable, and citizen-centric administration.
- The ongoing Adi SewaParv (17 September – 2 October 2025) focuses on preparing Tribal Village Vision 2030 Action Plans through community–government collaboration.
1. Adi Yuva Fellowship
Overview
The Adi Yuva Fellowship, supported by UN India, is a first-of-its-kind national programme designed to nurture tribal youth leadership through structured learning, mentorship, and professional development.
Key Features
- Duration: 12-month paid fellowship with a tailored learning plan combining knowledge-building, on-the-job training, and reflective practice.
- Support Package: Monthly allowances, comprehensive health and life insurance, and access to UN and commercial learning platforms.
- Skill Linkages: Fellows will be connected to national employability schemes such as:
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 4.0
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
- PM Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana
- Mentorship and Exposure: Fellows will receive structured mentorship, engage in peer learning, and gain exposure to national and international platforms.
- Deployment: The first batch of 16 Fellows will be selected through a competitive process and placed with UN agencies at national, state, and district levels.
Objective
To build a cadre of empowered tribal youth who can contribute to governance, entrepreneurship, innovation, and community-led development, ensuring that tribal voices shape India’s growth story.
2. Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme
Overview
Supported by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), the Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme is aimed at strengthening last-mile service delivery and promoting community participation in tribal regions.
Key Features
- Deployment:
- 82 Adi Karmayogi Volunteers (UN Community Volunteers) deployed across 82 blocks in 13 districts of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- They will engage in anintensive two-month grassroots programme.
- Role and Activities:
- Support preparation of Village Vision 2030 Action Plans.
- Conduct awareness campaigns, outreach drives, and capacity-building sessions.
- Facilitate improved access to government schemes and services.
- Outcome: Strengthen inclusive governance, local participation, and service delivery at the village level.
Significance of the Initiatives
1. Empowering Tribal Youth
- Provides structured opportunities for skill enhancement, leadership, and employability.
- Bridges the gap between education, governance, and community development.
2. Strengthening Governance
- Promotes citizen-centric and participatory governance in tribal regions.
- Empowers communities to actively contribute to their own development vision.
3. Advancing India–UN Partnership
- Demonstrates India’s collaborative approach towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Highlights the One UN approach for inclusive and sustainable growth.
World Food India (WFI) 2025

- 29 Sep 2025
In News:
The fourth edition of World Food India (WFI) 2025was held at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, organised by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
Overview
World Food India is the flagship global event of MoFPI that brings together key stakeholders from across the food ecosystem — governments, industry leaders, investors, and innovators — to strengthen India’s positioning as the “Food Basket of the World.”
Since its inception in 2017, the event has evolved into a transformative platform for food innovation, investment, and sustainability. The 2025 edition, spread across 1,00,000 sq. metres, is the largest congregation in the history of India’s food processing sector, with participation from:
- 21 countries, 21 States/UTs, 10 Central Ministries, and 5 allied organisations
- Over 1,700 exhibitors, 500 international buyers, and representatives from 100+ nations
Key Highlights of World Food India 2025
Partner and Focus Countries
- Partner Countries: New Zealand and Saudi Arabia
- Focus Countries: Japan, Russia, UAE, and Vietnam
Parallel and Thematic Events
- 3rd Global Food Regulators Summit (FSSAI): To harmonise international food safety standards.
- 24th India International Seafood Show (SEAI): To promote India’s seafood export potential.
- Reverse Buyer–Seller Meet (APEDA): Featuring over 1,000 buyers to boost agri-food exports.
- Knowledge Sessions: 45+ conferences, thematic discussions, and CXO roundtables with 100+ global agri-food leaders.
- Special Pavilions: Dedicated spaces for States, Ministries, Pet Food, Technology, Startups, and International exhibitors.
Core Pillars of WFI 2025
The 2025 edition revolves around five strategic pillars reflecting the government’s holistic vision for the food processing sector:
- Sustainability and Net Zero Food Processing – promoting climate-resilient and energy-efficient processing systems.
- India as a Global Food Processing Hub – showcasing India’s vast agri-resource base and processing potential.
- Frontiers in Food Processing, Products, and Packaging Technologies – highlighting innovation and technology adoption.
- Food for Nutrition, Health, and Wellness – aligning with the goals of nutritional security and public health.
- Livestock and Marine Products Driving the Rural Economy – boosting rural livelihoods and export competitiveness.
Significance of World Food India 2025
Economic Impact
- Attracts global and domestic investment in R&D, startups, logistics, and cold chain infrastructure.
- Enhances farm-to-fork linkages and promotes value addition across the supply chain.
Strategic Importance
- Reinforces India’s commitment to sustainable food systems in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Fosters international collaboration in technology, innovation, and regulatory frameworks.
Global Positioning
- Projects India as a leader in food innovation, safety, and sustainability.
- Strengthens India’s image as a trusted global supplier of high-quality, nutritious, and sustainable food products.
SwasthNari, SashaktParivarAbhiyaan

- 22 Sep 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘SwasthNari, SashaktParivar (SNSP) Abhiyaan’ and the 8thRashtriyaPoshanMaah from Dhar, Madhya Pradesh, marking one of India’s largest-ever health outreach campaigns for women and children. The initiative reflects the government’s commitment to promoting women-led development and holistic family well-being through accessible and equitable healthcare.
About the SwasthNari, SashaktParivarAbhiyaan
- The SNSP Abhiyaan is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) and the Ministry of Women & Child Development (MoWCD).
- It aims to provide preventive, promotive, and curative health services to women and children, particularly in underserved regions.
- The campaign will organize over 10 lakh health camps between 17th September and 2nd October 2025 at Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, Community Health Centres (CHCs), District Hospitals, and other public health facilities across the country.
- This mass mobilisation aligns with the broader vision of Viksit Bharat (Developed India), where “Nari Shakti” (women power) forms the foundation of national progress.
Key Objectives
- Enhance Women’s Health through Screening and Care:Regular health check-ups for women, focusing on non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as hypertension, diabetes, cancer, anaemia, tuberculosis, and sickle cell disease.
- Promote Maternal and Child Well-being:Strengthening antenatal care, immunisation, nutrition counselling, menstrual hygiene awareness, and adolescent health initiatives.
- Foster Behavioural Change and Health Education:Conducting awareness drives on healthy lifestyle practices, mental health, obesity prevention, and voluntary blood donation.
- Encourage Community Participation:Mobilisation through ASHAs, ANMs, Anganwadi workers, Self-Help Groups (SHGs), Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs), MY Bharat volunteers, and youth networks.
- Integrate Digital and Media Outreach:Real-time monitoring through the SASHAKT Portal, along with mass awareness via Doordarshan, All India Radio (AIR), and social media platforms.
Implementation Framework
- Nationwide Health Camps:Health facilities at all levels — from Ayushman Arogya Mandirs to tertiary hospitals — will provide free diagnostic tests, medicines, and specialist consultations.
- Specialist Services:Departments such as Gynaecology, Paediatrics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Dental, Dermatology, and Psychiatry will extend services through AIIMS, ESIC hospitals, Railway and Defence hospitals, and Institutes of National Importance (INIs).
- Public–Private Collaboration:Private hospitals and medical institutions have been encouraged to contribute to the outreach, ensuring broader reach and continuity of care.
- Community Health Monitoring:Volunteer initiatives like Nikshay Mitra will support tuberculosis prevention, while local youth networks promote healthy practices at the grassroots level.
Focus on Sickle Cell Anaemia
- During the launch, the Prime Minister handed over the 1 croreth Sickle Cell Card, underscoring the government’s National Sickle Cell Anaemia Mission. Over 5 crore individuals have been screened so far, especially in tribal-dominated regions, where the disease burden is highest. The mission aims at eliminating Sickle Cell Anaemia by 2047, ensuring improved tribal health outcomes.
Institutional and Grassroots Coordination
- Chief Ministers, Governors, Union Ministers, and local representatives across states participated in the launch events simultaneously. Ground-level implementation is being led by health workers, SHGs, PRIs, and community volunteers, ensuring last-mile outreach and inclusive participation.
Significance
- Largest Health Outreach in India: Over 10 lakh health camps make it the widest public health drive for women and children.
- Women-Centric Development: Strengthens India’s shift toward women-led welfare models under the vision of Viksit Bharat.
- Integrated Governance Model: Combines health, nutrition, and social empowerment across multiple ministries.
- Public Health Transformation: Promotes preventive healthcare, early detection, and equitable access to medical services.
- Focus on Tribal and Rural Health: Addresses critical health challenges in vulnerable and remote regions.
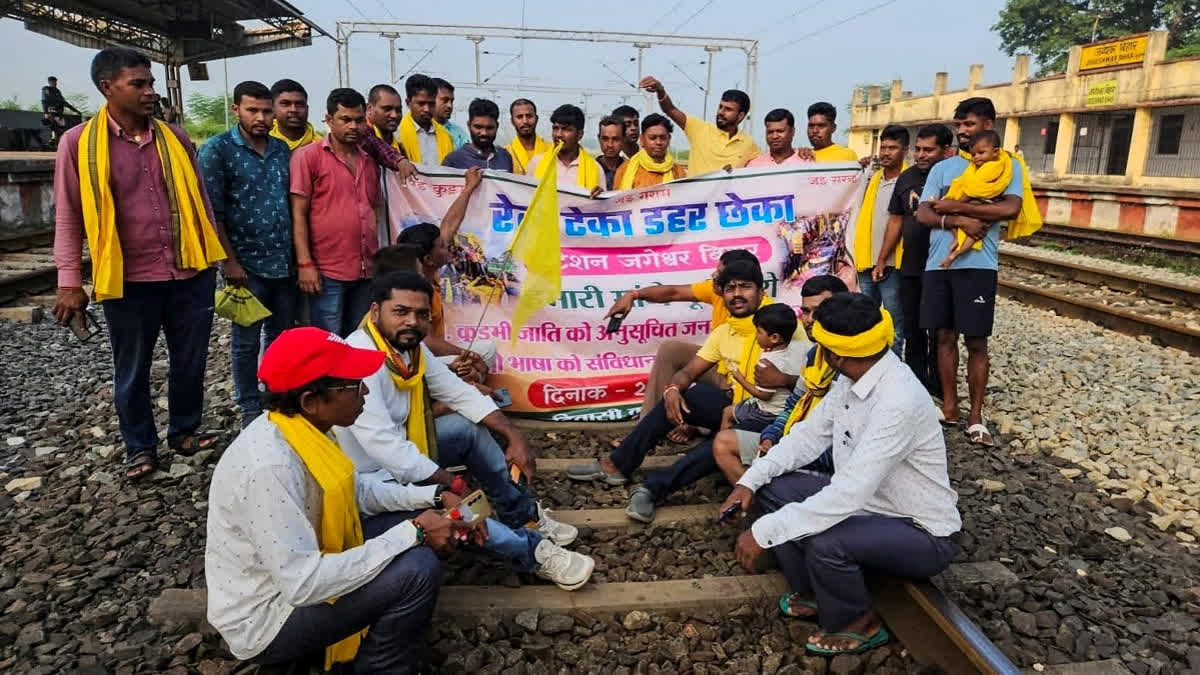
Kurmi Community

- 22 Sep 2025
In News:
Defying prohibitory orders, members of the Kurmi community in Jharkhand launched a rail blockade across several stations to demand Scheduled Tribe (ST) status and the inclusion of the Kurmali language in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution. The agitation, organized under the banner of the Adivasi KurmiSamaj (AKS), disrupted train services across the South Eastern and East Central Railway divisions.
About the Kurmi Community
- Origins and Identity:The Kurmis (also known as Kunbi in some regions) are traditionally an agricultural community, predominantly Hindu, found across eastern Uttar Pradesh, southern Awadh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and parts of Odisha.The name “Kurmi” is derived from the Sanskrit word “Krishi” (agriculture), symbolizing their deep connection with farming.
- Historical Background:Historically, Kurmis are believed to be descendants of Kshatriya warriors who took to agriculture. Renowned for their hard work, soil management, and egalitarian culture, the community was lauded by both Mughal and British administrators for its agrarian contributions.
- Social Status:Currently, Kurmis are classified as Other Backward Class (OBC) in most Indian states. However, the community contends that their socio-cultural roots align more closely with tribal heritage, warranting ST recognition.
- Sub-Groups and Culture:The community is divided into several gotras (clans), including Chandel, Chauhan, Solanki, Tomar, Baghel, and Sengar. They are known for maintaining strong community networks and gender-inclusive social practices.
About the Kurmali Language
- Linguistic Affiliation:Kurmali belongs to the Indo-Aryan language family and is primarily spoken in Jharkhand, Bihar, and Odisha.
- Cultural Significance:It serves as a marker of Kurmi identity and is used in folk traditions, oral histories, and local communication.
- Demand for Recognition:Inclusion in the Eighth Schedule would ensure state-supported promotion, education, and preservation of the language, similar to other recognized regional languages.
Government Response and Implications
The Jharkhand administration has maintained a cautious approach, emphasizing the need for maintaining law and order while acknowledging the sensitivity of the community’s demands.The demand for ST status involves constitutional and demographic considerations, requiring evaluation by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and approval by Parliament under Article 342 of the Constitution.
Ramon Magsaysay Award 2025
- 06 Sep 2025
In News:
The Ramon Magsaysay Award 2025, Asia’s most prestigious honour, has been conferred on ‘Educate Girls’, an Indian non-profit organisation working to promote girls’ education in rural and remote areas. This marks the first time an Indian NGO has received this award, making it a historic milestone for the country.
About Educate Girls
- Founded by Safeena Husain, Educate Girls (also known as the Foundation to Educate Girls Globally) has been instrumental in addressing gender inequality in education.
- The organisationmobilises communities to enrol out-of-school girls, improve learning outcomes, and empower them to continue education.
- Its grassroots volunteers, known as Team Balika and preraks, work in partnership with governments, donors, and local communities.
About Ramon Magsaysay Award
- Instituted in 1958 to celebrate “greatness of spirit and transformative leadership in Asia”.
- Named after Philippine President Ramon Magsaysay, remembered for his integrity and people-centric leadership.
- From 1958–2008, the award was given in six categories: Government Service, Public Service, Community Leadership, Journalism & Creative Communication Arts, Peace & International Understanding, and Emergent Leadership.
- Since 2009, except for Emergent Leadership, it is presented without fixed categories.
- Winners receive a certificate and a medallion bearing the image of Ramon Magsaysay.
- The award ceremony takes place annually in Manila, Philippines on 31st August, Magsaysay’s birth anniversary.
- Till date, over 300 individuals and organisations across Asia have been recognised.
Other 2025 Awardees
- Shaahina Ali (Maldives): Environmental activist.
- Fr. Flaviano Antonio L. Villanueva (Philippines): Human rights advocate known for opposing extrajudicial killings during the Duterte administration.
Project Aarohan

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), in collaboration with Vertis Infrastructure Trust, has launched Project Aarohan, a nationwide scholarship and mentorship program aimed at supporting the educational aspirations of the children of toll plaza employees, particularly those from economically weaker sections (EWS) and disadvantaged communities.
Key Objectives
- Remove financial barriers to education.
- Ensure equal access to quality education for children of toll plaza staff.
- Bridge socio-economic divides while nurturing talent among first-generation learners, girls, and students from EWS, SC, ST, OBC, and minority groups.
- Prepare students for higher education, employment, and entrepreneurship through holistic guidance.
Features of Project Aarohan
- Coverage: 500 students from Class 11 to the final year of graduation.
- Scholarships: Each selected student will receive ?12,000 annually (FY 2025–26).
- Higher Studies Support: 50 bright students aspiring for postgraduate and higher studies will get ?50,000 each.
- Beyond Finance: Mentorship, skill-building workshops, career guidance, and structured progress tracking to foster holistic growth.
- Fund Allocation: ?1 crore for the first phase (July 2025–March 2026).
- Application Process: Through an online portal, requiring academic records, income proof, caste certificate, ID proof, etc., with a transparent selection and renewal mechanism.
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2025

- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
According to the UN’s “State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2025”, global undernourishment decreased to 8.2% (673 million individuals) in 2024, down from 8.5% in 2023.
India has been instrumental in this turnaround—its prevalence of undernourishment fell from 14.3% (2020–22) to 12% (2022–24), equating to 30 million fewer hungry people. These outcomes underscore India’s unique role in advancing SDG 2: Zero Hunger globally.
Defining Hunger: Layers and Causes
- Undernourishment: Insufficient calorie intake.
- Malnutrition: Poor diet quality lacking protein and essential micronutrients.
- Hidden Hunger: Micronutrient deficiencies (iron, iodine, vitamin A, zinc).
Root Causes:
- Economic barriers: Poverty limits access to nutritious food (NITI Aayog Index: ~11.3% multidimensionally poor).
- Agricultural inefficiencies: Fragmented holdings, climate variability, poor irrigation, and 13% post-harvest losses.
- High food costs: A nutritious diet remains unaffordable for over 60% of Indians.
- Weak infrastructure: Poor cold storage and logistics aggravate food wastage.
- Health and sanitation challenges: NFHS-5 (2019–21): 35.5% of children under five are stunted; 19.3% are wasted.
- Macro-disruptions: Global conflicts, pandemics, and climate shocks affect food systems, impacting India too.
India’s Strategic Interventions: From Policies to Systems
- Public Distribution System (PDS) Reforms
- Extensive digital overhaul: Aadhaar-based targeting, biometric authentication, real-time inventory tracking, and ONORC (One Nation One Ration Card) ensuring portability and inclusion for migrants and the vulnerable.
- Served over 800 million beneficiaries during COVID-19—a monumental welfare scaling.
- Emphasis on Nutrition Over Mere Calories
- Continued unaffordability of healthy diets (60%+ can’t afford) due to price inflation and weak linkages.
- Nutrition-centric interventions:
- PM POSHAN (2021): Expanded mid-day meals into nutrition-sensitive programs.
- ICDS & POSHAN Abhiyaan: Enhanced focus on dietary diversity and maternal-child health.
- AnaemiaMukt Bharat: Tackles widespread anaemia among women and children.
- Agrifood System Transformation
- Promote nutrient-dense food affordability (pulses, fruits, vegetables, animal-source proteins).
- Address 13% food loss via upgraded cold-chain infrastructure and logistics.
- Support women-led enterprises and FPOs, especially in climate-resilient, biofortified crop cultivation.
- Digital Innovations in Agriculture: Tools such as AgriStack, e-NAM, and geospatial platforms enhance market access, planning, and transparency.
Strategies for Sustainable Impact
|
Strategy |
Actions |
|
Nutrition-centric policy shift |
Fortify staples, subsidise nutrient-rich foods (pulses, eggs, milk) |
|
Infrastructure strengthening |
Upgrade cold storage, logistics, and digital post-harvest systems |
|
Inclusive economy |
Scale women-led food enterprises, FPOs, and biofortified crop cultivation |
|
Digital expansion |
Broaden use of AgriStack, e-NAM, geospatial tools for planning & targeting |
|
Urban nutrition resilience |
Launch community kitchens, food banks, awareness drives |
|
Global sharing & leadership |
Replicate ONORC, PDS digitalisation, nutrition models in the Global South |
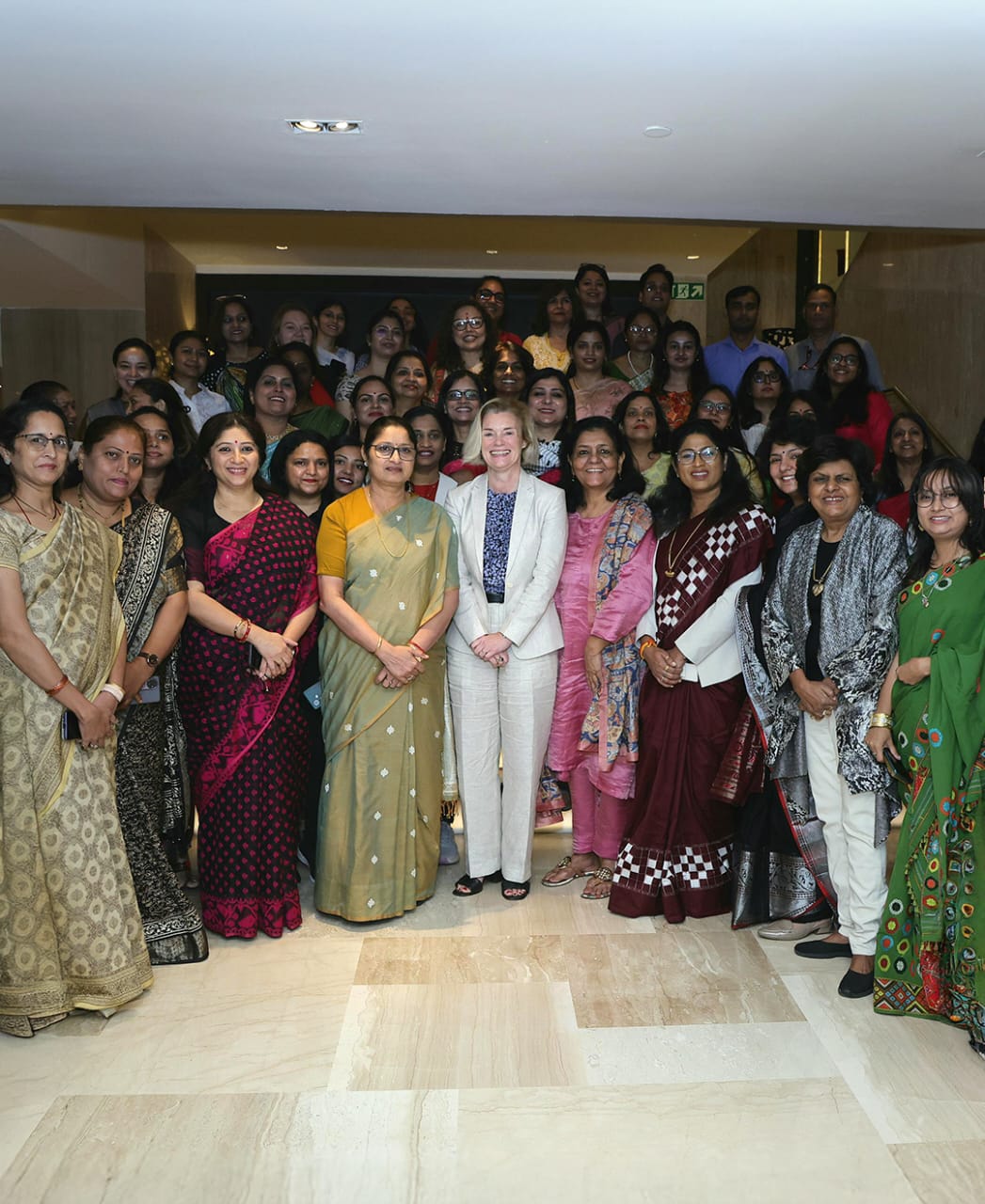
SheLeadsProgramme

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Minister for Women and Child Development, inaugurated the second edition of UN Women’s flagship capacity-building programme — SheLeads II: Workshop for Women Leaders in New Delhi (August 2025). The initiative seeks to strengthen women’s political leadership, a crucial step towards women-led development and the vision of a Viksit Bharat.
Key Highlights:
- The workshop comes in the backdrop of the Women’s Reservation Act, 2023, mandating 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Despite this landmark reform, only 14% of seats in the 18th Lok Sabha are currently occupied by women, highlighting the urgent need for leadership training and political empowerment.
About SheLeadsProgramme
- Flagship Initiative: Launched by the UN Women India Country Office.
- Aim: Advance gender equality in public and political leadership, equipping women with skills, confidence, and networks to contest elections and participate effectively in governance.
- Scope: Supports women leaders in shaping policies, governance structures, and electoral narratives that reflect the aspirations of all citizens.
- Participation: In 2025, over 260 applications from 22 states were received; 36 participants were selected for the two-day workshop.
- Engagement: Interactive sessions with MPs, policy experts, and media strategists on electoral campaigning, governance, narrative building, and media engagement.
About UN Women
- Established in 2010 by the UN General Assembly, consolidating resources and mandates under one entity.
- Mandate:
- Support intergovernmental bodies (e.g., Commission on the Status of Women) in framing global standards.
- Assist member states in implementing gender equality commitments through technical and financial support.
- Partner with civil society to advance women’s rights and empowerment.
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) 2025 Report

- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
Hunger affected up to 720 million people worldwide in 2024 — around 8.2 per cent of the global population, while 2.3 billion people in the world were estimated to have been moderately or severely food insecure, according to the ‘State of Food and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Jointly published by FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP, and WHO.
- Purpose:
- Annual global assessment to monitor progress on Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2:
- Target 2.1: End hunger and ensure access to safe, nutritious food.
- Target 2.2: End all forms of malnutrition.
Key Global Findings (2024 Data)
- Chronic Hunger:
- 720 million people (approx. 8.2% of global population) suffered from chronic hunger in 2024.
- Although lower than 8.5% (2023) and 8.7% (2022), it remains above pre-pandemic (2015) levels.
- 96 million more people are hungry now than in 2015.
- Food Insecurity:
- 2.3 billion people were moderately or severely food insecure in 2024.
- This is 335 million more than in 2019 (pre-COVID) and 683 million more than in 2015.
- Regional Distribution:
- Asia: 323 million undernourished (highest in absolute numbers).
- Africa: 307 million (highest prevalence, over 20% of population).
- Latin America & Caribbean: 34 million.
- Trends & Progress:
- Modest improvements in Southeast Asia, Southern Asia, and South America.
- Worsening hunger in parts of Africa and Western Asia due to conflict and climate stress.
Projections for 2030
- By 2030, 512 million people (6% of global population) may remain chronically undernourished.
- A decline of only 65 million since 2015, far short of the Zero Hunger target.
- 60% of these undernourished people are projected to be in Africa, with 17.6% prevalence.
India-Specific Insights
- Nutritional Affordability:
- 6% of Indians cannot afford a healthy diet despite food surplus.
- Urban areas show improvement due to post-pandemic income recovery.
- Rural areas face continued hardship due to PDS inefficiencies and price volatility.
- Child Malnutrition:
- High rates of stunting and wasting persist.
- Micronutrient deficiencies (hidden hunger) are common due to cereal-heavy diets lacking diversity.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Strengthen inclusion of millets, pulses, and fortified foods in public nutrition schemes.
- Address regional and demographic disparities through targeted interventions.
Major Drivers of Food Insecurity
- Post-COVID Aftermath: Reversed a decade of gains in global food security.
- Climate Events: Floods, droughts, and heatwaves have disrupted food systems.
- Conflicts & Wars: Ongoing wars (e.g. Ukraine) have triggered food price inflation and supply disruptions.
- Inflation:
- Since 2020, food price inflation has outpaced general inflation globally.
- Disproportionately affects low-income and vulnerable populations.
SOFI 2025: Recommendations
- Protect vulnerable populations via targeted fiscal support.
- Align macroeconomic policies to stabilize food markets.
- Invest in resilient agrifood systems and nutrition-sensitive agriculture.
- Strengthen food and nutrition data systems for informed policymaking.
- Promote dietary diversity and nutrition education.
SDG Context & Governance
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) is among the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals adopted in 2015.
- These are non-binding, but serve as guiding principles for national policy and international cooperation.
- The SOFI report tracks progress annually against Targets 2.1 & 2.2.
- With only 5 years left to 2030, the current pace is inadequate for achieving global food and nutrition targets.
Hatti Tribe
- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
Recently, two brothers from the Hatti tribe in the Trans-Giri region of Sirmaur district, Himachal Pradesh, married the same woman under the traditional custom of polyandry. The wedding, held in Shillai village, was conducted openly and witnessed by hundreds, reviving attention to this rare tribal practice.
About the Hatti Tribe
- The Hatti community derives its name from the traditional occupation of selling agricultural produce, meat, and wool in local markets called haats.
- They reside primarily in the Himachal–Uttarakhand border region, especially in the basins of the Giri and Tons rivers, both tributaries of the Yamuna.
- The Hattis are divided into two major groups:
- One in Trans-Giri, Sirmaur district (Himachal Pradesh)
- Another in Jaunsar-Bawar (Uttarakhand)
- They maintain similar cultural practices, and intermarriage between these clans is common.
- The community follows a traditional council system called ‘Khumbli’ for resolving social issues.
- As of 2023, the Hatti tribe in Himachal Pradesh was granted Scheduled Tribe (ST) status, while Jaunsar-Bawar in Uttarakhand received tribal status in 1967.
- Their economy is largely agrarian, with a focus on cash crops due to favorable climatic conditions.
The Tradition of Polyandry ("Jajda")
- Polyandry in the Hatti community is locally called “Jajda” and was historically practiced to prevent division of ancestral land.
- The ritual includes a marriage procession of the bride to the groom’s village and a ceremony called “Seenj”.
- Local priests chant mantras in the native language and conclude the ceremony with blessings and offerings like jaggery.
- This practice has declined in recent decades due to increasing literacy among women, social modernization, and economic shifts.
Legal and Social Acceptance
- Polyandrous marriages are informally recognized under Himachal Pradesh revenue laws, where the practice is referred to as “Jodidara”.
- Though rare, such marriages continue to be socially accepted in some remote villages of Trans-Giri, Kinnaur, and Jaunsar-Bawar.
Demographics
- As per the 2011 Census, the Hatti population was around 2.5 lakh, and estimates now suggest about 3 lakh people across 450 villages in the Trans-Giri region alone.
Cultural and Practical Rationale
According to Hatti elders and community leaders:
- Land Preservation: Prevents fragmentation of ancestral property.
- Joint Family Bonding: Promotes unity and mutual understanding among brothers.
- Labor Sharing: Ensures adequate manpower to manage scattered agricultural lands in hilly terrain.
- Security: A larger family offers greater social and economic protection in tribal settings.
Jarawa Tribe

- 16 Jul 2025
In News:
The 16th Census of India, scheduled for 2026–27, will include a special effort to enumerate the six main indigenous tribes of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, including the Jarawa, one of the world’s oldest surviving tribal groups.
About the Jarawa Tribe:
- Status: Recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- Location: Reside in Middle and South Andaman Islands, primarily in dense tropical forests and coastal zones.
- Lifestyle:
- Nomadic hunter-gatherers living in small groups of 40–50.
- Depend on forest produce, marine fishing, and traditional medicine.
- Exhibit robust health, with low incidence of lifestyle diseases.
- Cultural Characteristics:
- Minimal attire suited to the climate.
- Known for strong territorial identity and historical resistance to outsiders.
- Maintain a natural diet and traditional healing practices.
Population Trends:
- 1998 Estimate: ~260 individuals (based on limited contact).
- 2011 Census: 380 individuals (out of 28,530 STs in A&N Islands).
- 2025 Official Estimate: 647 individuals.
- Increase attributed to improved healthcare, trust-building, and non-intrusive welfare policies.
Government Interventions & Welfare Initiatives:
- Healthcare: Preventive medical support (measles, hepatitis, malaria) provided without interfering in traditional practices.
- Welfare Access: Increased interaction since 1998 has enabled better outreach, aiding accurate population tracking.
- PM-JANMAN Scheme: Under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan, 191 PVTG individuals have been identified in the islands for targeted welfare.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations:
- Andaman Trunk Road (ATR): Provides physical access but raises concerns of cultural intrusion.
- Expert Opinion: Minimum intervention is essential for preserving the Jarawa way of life. Trust and respect for autonomy remain key.
16th Census of India: Timeline & Relevance:
- Reference Dates:
- October 1, 2026: Snow-bound areas (e.g., Ladakh, A&N Islands).
- March 1, 2027: Rest of India.
- Special Feature: Will include caste enumeration, the first since 1931.
- Jarawa Inclusion: Officials expect smooth access to PVTGs like the Jarawas due to longstanding trust and contact.
Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark initiative for tribal inclusion, the Government of India has launched the Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)—India’s largest-ever tribal outreach and empowerment campaign. The programme aims to ensure saturation of welfare schemes and promote tribal pride and participation, covering over 1 lakh tribal villages and PVTG habitations across 31 States and Union Territories.
What is DAJA?
- Full Name: Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan — named in honour of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, a revered tribal freedom fighter.
- Launched by: Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India.
- Nature: A people-centric campaign focused on participatory governance and last-mile delivery of services among Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
Objectives of DAJA
- Saturate government welfare schemes across all tribal settlements.
- Empower over 5.5 crore tribal citizens through Janbhagidari (people’s participation).
- Preserve and promote tribal identity and cultural heritage, invoking the legacy of Birsa Munda.
- Strengthen last-mile governance through technological and administrative convergence.
Key Features:
Feature Description
Geographic Coverage - 1 lakh+ tribal villages, including remote PVTG habitations, across 31 States/UTs.
Scheme Integration - Converges services such as Aadhaar, Ayushman Bharat, PM Kisan, PM
Ujjwala, Jan Dhan, pension schemes, and Forest Rights Act (FRA) claims.
Five Foundational Pillars -
- Janbhagidari (people’s participation)
- Saturation of welfare benefits
- Cultural inclusion
- Convergence of schemes
- Last-mile delivery
Technology-Driven Monitoring - Use of real-time dashboards and data analytics for
transparent tracking and reporting.
Cultural Revival - Celebrates tribal cuisines, folk arts, handicrafts, and oral traditions
during outreach camps to reaffirm cultural identity.
Significance:
- Governance: Represents a shift toward targeted and integrated tribal welfare, reducing administrative fragmentation.
- Inclusion: PrioritisesPVTGs, often the most marginalised and underserved groups.
- Empowerment: Embeds a participatory model, aligning with the spirit of democratic decentralisation.
- Cultural Reaffirmation: Bridges the gap between development and cultural identity, crucial for tribal dignity and preservation.
Global Gender Gap Report 2025
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The 19th edition of Global Gender Gap Report 2025 was released by World Economic Forum (WEF).
Key Highlights:
Countries Covered: 148
Global Parity Status:
- Overall Gender Gap Closed: 68.8%
- Estimated Time to Full Parity: 123 years (at current pace)
Assessment Criteria (Four Dimensions):
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
The index uses a parity score (0–100%) to quantify gender equality, where 100% indicates full parity.
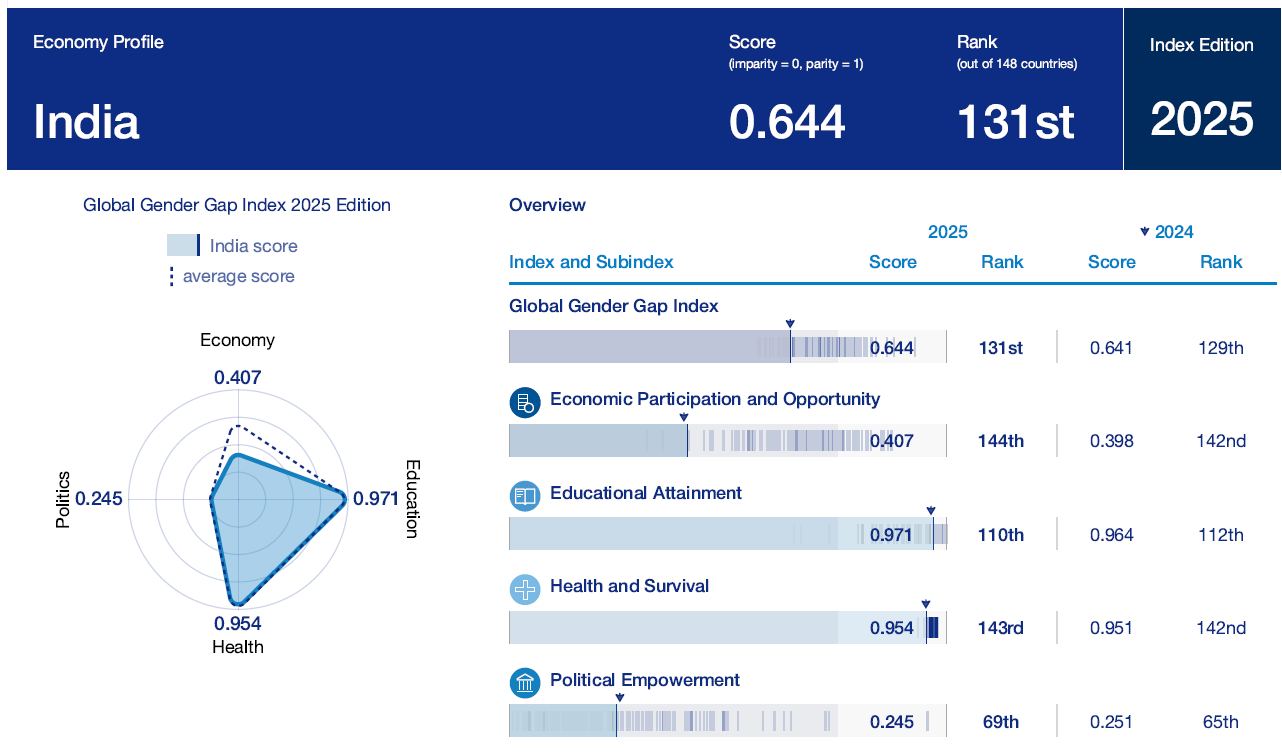
India’s Performance (Rank: 131/148)
- Parity Score: 64.1%
- South Asia Rank: Among the lowest; only Maldives (138) and Pakistan (148) rank below
- India’s 2024 Rank: 129 (slipped 2 positions in 2025)
Domain-wise Performance:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Improved: Score increased by 0.9 percentage points to 40.7%
- Earned Income Parity: Rose from 28.6% to 29.9%
- Labour Force Participation: Stagnant at 45.9%
- Insight: Despite income parity gains, the gap in actual earnings and participation remains wide.
- Educational Attainment
- Near Parity Achieved: 97.1%
- Driven by rising female literacy and higher tertiary enrolment
- Challenge: Translating education into workforce participation remains limited.
- Health and Survival
- Marginal Gains: Improved parity in sex ratio at birth and healthy life expectancy
- However, overall life expectancy declined for both genders, muting the parity effect.
- Political Empowerment
- Significant Decline:
- Women MPs fell from 14.7% to 13.8%
- Women ministers dropped from 6.5% to 5.6%
- Trend: Continued decline from the 2019 peak of 30% female political representation
- Significant Decline:
South Asia and Global Comparison
- Bangladesh: Best performer in South Asia, ranked 24th globally (up by 75 positions)
- Other Neighbours:
- Bhutan (119),
- Nepal (125),
- Sri Lanka (130),
- Maldives (138),
- Pakistan (148 – last)
- Global Top 5 Countries:
- Iceland (Top for 16th year in a row)
- Finland
- Norway
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
Key Global Insights
- Women in Workforce: 41.2% of global workforce
- Leadership Representation: Only 28.8% of leadership roles are held by women
- Despite post-pandemic recovery in gender parity, leadership gaps and decision-making roles remain major bottlenecks.
Implications for India
- The report underscores that gender parity is not just a social imperative, but also crucial for inclusive and resilient economic growth.
- India’s sluggish progress in political empowerment and gender wage gap highlight the need for institutional reforms, affirmative actions, and gender-sensitive policies in governance, employment, and leadership.
Beijing+30 India Report

- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
India’s official submission on the Beijing+30 Report marks three decades since the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995), a landmark framework advancing gender equality across 12 key areas such as education, health, economy, and political participation.
While the report acknowledges past progress—including enactment of laws like the Domestic Violence Act (2005) and the POSH Act (2013)—it lacks an integrated climate-gender perspective, an urgent gap given rising climate vulnerabilities affecting women disproportionately.
Climate Change and Gender Inequality: A Dual Challenge
- Rural women, particularly in agrarian and forest-dependent regions, face acute consequences of climate change—loss of livelihood, food insecurity, and health risks.
- India’s rural women often bear the brunt of extreme weather events, droughts, and resource scarcity.
- According to reports:
- 33% loss of income occurs due to climate-induced productivity disruption, especially from non-farm sources.
- Women perform over 8 hours of daily work, of which 71% is unpaid.
- By 2050, unpaid care work is projected to rise to 8.3 hours/day without mitigation.
Key Data and Impacts
Indicator Insight
Pregnant women (India) 50%+ are anaemic; worsened by food insecurity
Temperature–Violence Link +1°C rise → 8% rise in physical violence, 7.3% rise in sexual violence
Climate policies (FAO) Only 6% mention women; 1% mention poor people
Agriculture Potential Closing gender gap in agri-inputs could raise yields by 20–30%
Women as Agents of Climate Resilience
- Women contribute to 50% of global food production and lead community efforts in seed preservation, sustainable farming, and disaster response.
- Indigenous and rural women prioritize livelihood security (Mahua), safety (Mao), and managing migration—termed the three M's.
- Informal women’s collectives are key in disaster resilience, ecosystem protection, and productivity gains.
Recommendations for Climate-Gender Integration
- Policy Interventions:
- Introduce gender-responsive climate budgeting to prevent greenwashing and ensure equitable allocation.
- Incorporate gender in NAPCC, SAPCC, and ensure percolation to local governance and disaster planning.
- Address emerging risks—trafficking, migration, health, and geriatric safety in disaster zones.
- Data and Monitoring:
- Establish indicators and research on gendered climate impacts.
- Conduct inclusive climate consultations to enable community-driven planning.
- Private Sector & Green Finance:
- Encourage women-led green enterprises, climate-resilient technologies, and inclusive innovations.
- Allocate climate adaptation funds to skill-building, non-farm livelihoods, and local resilience-building.
- Partnership Model:
- Promote collaboration between government, civil society, research institutions, private sector, and international organisations.
- Foster knowledge exchange, capacity building, and public recognition of women climate leaders.
Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023

- 11 Apr 2025
In News:
A recent United Nations report titled ‘Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023’, released by the Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (MMEIG), highlights global progress and setbacks in maternal health. While acknowledging India's significant gains, the report places India second in global maternal deaths, behind Nigeria.
India’s Maternal Mortality Statistics (2023)
- Maternal deaths in India: 19,000(7.2% of global total)
- Rank: Second globally, tied with the Democratic Republic of Congo
- MMR: Reduced from 362 per 1 lakh live births (2000) to 80 in 2023 — a 78% decline
- Global average decline: 40% (2000–2023), but India achieved 86% decline
- Comparison with Nigeria:
- Nigeria: 75,000 deaths, contributing 28.7% of global maternal deaths
- India's Health Ministry deemed the comparison unfair given population differences (India: 145 crore, Nigeria: 23.26 crore)
Definition and Importance of MMR
According to WHO, Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) refers to:
“The death of a woman during pregnancy or within 42 days of termination, from pregnancy-related causes excluding accidental ones.”
MMR is a critical indicator for assessing healthcare quality and maternal well-being.
UN Global Findings
- Estimated maternal deaths globally (2023): 260,000
- Daily deaths: Over 700 women; about one death every two minutes
- Leading causes: Post-partum haemorrhage, hypertensive disorders, infections
- SDG 3.1 Target: Reduce MMR to <70 per 1 lakh live births by 2030
India-Specific Causes of Maternal Deaths
- Medical reasons:
- Post-partum haemorrhage
- Hypertensive disorders (e.g. pre-eclampsia)
- Infections related to pregnancy
- Co-morbidities: Anaemia, diabetes, hypertension
- Systemic challenges:
- Inadequate emergency obstetric care at Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and Community Health Centres (CHCs)
- Lack of infrastructure, trained personnel, and referral systems
- Socio-economic backwardness and poor access to healthcare in northern India
Concerns Highlighted in the Report
- Slowing progress post-2016 despite early improvements
- Humanitarian funding cuts impacting:
- Health worker retention
- Facility operations
- Availability of essential drugs (for haemorrhage, malaria, pre-eclampsia)
- Disruption in maternal care supply chains, especially in low-resource regions
India’s Stand
The Union Health Ministry has contested comparisons with smaller nations like Nigeria, asserting that India's maternal health progress is notable given its large population. The Ministry emphasized the 86% decline in MMR since 1990, as opposed to a global decline of 48% in the same period.
'Bal VivahMukt Bharat' Campaign

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Minister for Women and Child Development launched the “Bal VivahMukt Bharat” campaign aimed at eradicating child marriage in India.
- Goal: Reduce child marriage rates to below 5% by 2029.
- Focus: Engage multiple stakeholders, raise awareness, and leverage technology for eradication.
Target Areas:
- Target States: West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Tripura, Assam, Andhra Pradesh.
- High-Burden Districts: Nearly 300 districts with higher rates of child marriage.
Child Marriage Free Bharat Portal:
- A digital platform to raise awareness, report cases, and track progress on child marriage prevention.
- Real-time tracking by Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPOs).
Monitoring and Accountability:
- Central nodal officers and CMPOs will oversee the campaign’s implementation at state and district levels.
- The portal facilitates citizens’ participation by allowing complaints and providing information on legal remedies.
Progress and Impact:
- Child marriage rates have reduced from 47.4% (2005-06) to 23.3% (2019-21).
- The goal is to reduce these rates further to below 5% by 2029.
Awareness and Community Engagement:
- Public campaigns and community mobilization to challenge societal norms and change attitudes towards child marriage.
- The campaign will continue through various channels, including the BetiBachaoBetiPadhao initiative.
Legal Framework:
- Strengthening the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, which sets the legal marriage age at 18 for women and 21 for men.
- Penalties for those involved in child marriage include imprisonment and fines.
Key Challenges for Child Marriage:
- Poverty: Families may view early marriage as a financial relief.
- Cultural Norms: Deep-rooted societal beliefs about preserving family honor.
- Gender Inequality: Patriarchal systems view girls as burdens.
- Lack of Education: Limited access to schooling forces early marriages.
- Fear of Sexual Assault: Misguided belief that early marriage protects girls.
- Weak Law Enforcement: Corruption and inadequate resources hinder the law’s implementation.
- Pandemic Impact: Economic hardships during COVID-19 led to an increase in child marriages.
Related Initiatives:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006: Strengthens child marriage laws and establishes CMPOs.
- Success Stories: Individuals like BuchaRamanamma, Durga, and Roshni Perween have inspired others by stopping their own child marriages and advocating for change.
Campaign and National Vision:
- The campaign aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision for a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
- It aims to empower women and girls, providing them with opportunities for education, health, and safety.
- Collective effort from the government, social organizations, and citizens is crucial to eliminating child marriage.
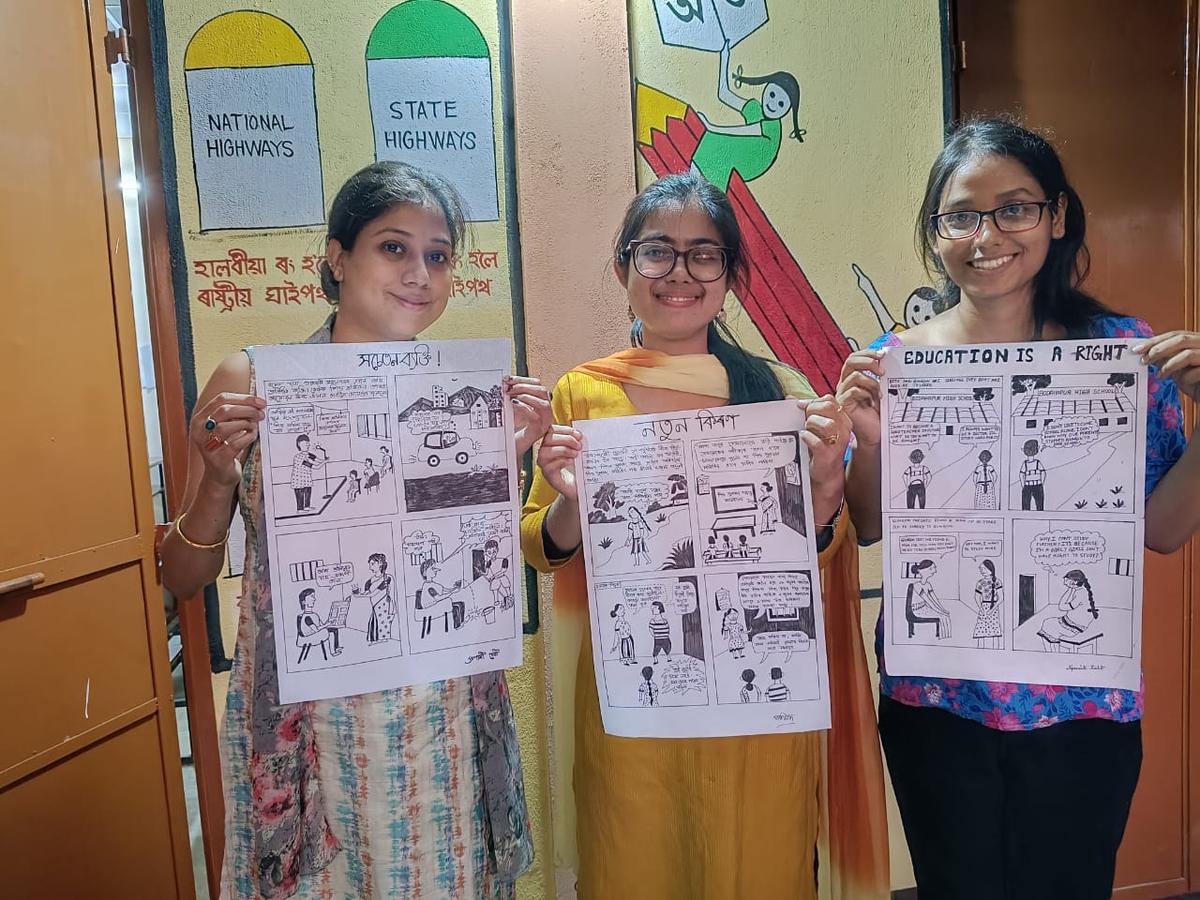
Comics Commandos in Assam

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- "Comics Commandos" is an innovative initiative launched in Goalpara district, Assam, aimed at combating child labour and child marriage through the creative medium of comics.
- The initiative trains 30 local youths to create comic strips that use humour and minimal text for effective communication and public engagement.
Purpose and Objectives:
- Primary Goal: To raise awareness about child labour and child marriage, two major social issues prevalent in the region, by using visual storytelling.
- The initiative aims to resonate with the local community, focusing on everyday struggles like economic hardship, child abuse, and the social norms that perpetuate these issues.
- Rising Dropout Rates: Assam has witnessed an increase in school dropout rates, from 3.3% in 2020-21 to 6.02% in 2021-22, exacerbated by economic pressures like poverty, which force children to work or marry early.
Execution and Approach:
- Training: Thirty local youths are trained to design caricatures and doodles for the comics, ensuring the messages are both simple and engaging for a broader audience.
- Visual Storytelling: The use of visuals over text helps overcome literacy barriers and makes the message more impactful and accessible.
- Community Involvement: The program collaborates with teachers and school committees to facilitate wider participation and support in creating social awareness.
Government Support:
- Chief Minister HimantaBiswaSarma initiated a state-wide campaign in 2023 against child marriage, with the ambitious goal of eradicating it by 2026. This initiative aligns with the state's broader efforts to address social issues.
Impact of the Initiative:
- Comics Commandos is being seen as an effective tool for community empowerment and awareness generation in a region that faces persistent social challenges.
- By involving local youths in the campaign, the initiative ensures community participation and ensures that the message is communicated in a culturally relevant manner.
- The program also empowers young people to use their creativity for social change, thus helping build leadership and social responsibility among the youth.
PM rolls out Ayushman Bharat for Citizens aged 70 and above

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has expanded the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) to provide health coverage to citizens aged 70 years and above, regardless of their income or economic status. This move is aimed at addressing the healthcare challenges faced by India's elderly population, which has been growing rapidly.
Key Highlights of the Ayushman Bharat Expansion:
- Health Coverage for Elderly:
- Ayushman Vaya Vandana Card: This new health card offers Rs 5 lakh annually for individuals aged 70 and above. The coverage is shared within the family, so if there are multiple elderly beneficiaries in one household, the total cover will be split.
- Scope: This initiative is designed to provide a safety net for elderly people, many of whom had previously been unable to access treatment due to high costs.
- Significance of the Scheme:
- India’s elderly population is rapidly growing, with the number of people over 60 expected to reach 319 million by 2050, up from 103 million in 2011.
- The expansion of PM-JAY to include those aged 70+ is a critical step in making universal health coverage more inclusive as India’s population ages.
- Eligibility and Registration:
- Individuals aged 70 years and above must register on the PM-JAY portal or through the Ayushman app. Those who already have an Ayushman Bharat card must complete an eKYC process to receive the new card and coverage.
- Exclusions: The scheme is not available in Delhi and West Bengal, as these states have not adopted the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- Financial Details:
- The initial outlay for this expansion will be Rs 3,437 crore, covering the remainder of the current financial year and the next year.
- Cover for Overlapping Health Schemes: Elderly individuals who are already covered under other government schemes (e.g., CGHS, Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme) will have the option to either continue with their current coverage or choose Ayushman Bharat. Those with ESIC or private insurance can access both Ayushman Bharat and their existing cover.
- Coverage Scope:
- The expansion is expected to benefit approximately 6 crore individuals across 4.5 crore families.
- Existing Coverage: Around 1.78 crore elderly people are already covered under the scheme. Additional coverage will be provided to those not currently included in the scheme.
- Interoperability with Other Schemes:
- Those under the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or other similar schemes will need to choose between their current insurance and the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- However, individuals enrolled in Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) can have both their existing cover and the Ayushman Bharat coverage.
- Rollout and Reach:
- The scheme will be implemented across 33 states and Union Territories, except Delhi, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Over 29,600 hospitals, including more than 12,600 private facilities, are empanelled to provide treatment under PM-JAY.
Other Key Announcements:
- U-WIN Portal: A pan-India digital platform for routine vaccinations, aimed at enhancing the efficiency of vaccination programs.
- Critical Care Facilities: The Prime Minister also launched critical care infrastructure, including new facilities in AIIMS Bhubaneswar, Kalyani, and super-specialty units in Himachal Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
'Act4Dyslexia' Campaign

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- On October 27, 2024, prominent landmarks such as Rashtrapati Bhawan, Parliament House, India Gate, and the North and South Blocks in Delhi were illuminated in red to raise awareness for Dyslexia and other learning disabilities.
- Similar illuminations took place in major cities like Patna, Ranchi, Jaipur, Kohima, Shimla, and Mumbai, highlighting the importance of dyslexia awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Collaboration for Awareness:
- The campaign is organized in collaboration with UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace and Sustainable Development (MGIEP) and the ChangeInkk Foundation.
- Its goal is to remove stigma and foster understanding of dyslexia and other learning disabilities, which affect 20% of India’s population—around 35 million students.
- Flagging off the ‘Walk4Dyslexia’:
- The ‘Walk4Dyslexia’ event, aimed at promoting collective action for dyslexia awareness, was flagged off by Shri Rajesh Aggarwal, Secretary of the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), along with Mr. Shombi Sharp, UN Resident Coordinator in India.
- The walk was organized by ChangeInkk Foundation, UNESCO MGIEP, Orkids Foundation, and Soch Foundation.
- Growth of the Campaign:
- The Act4Dyslexia campaign saw a significant expansion in 2024, with over 1,600 walks held across the country, from state capitals to villages, engaging over 4 lakh participants.
- The campaign mobilized 2 billion steps in support of dyslexia awareness, with 150+ organizations joining forces.
- Focus on Equal Rights and Opportunities:
- Dyslexia and other specific learning disabilities (SLDs) were officially recognized under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. This law mandates equal educational and employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 further emphasizes inclusive education, calling for early identification, teacher capacity building, and necessary support and accommodations.
- Understanding Dyslexia:
- Dyslexia is often misunderstood as a sign of being a "slow learner", but people with dyslexia often excel in areas like logical reasoning, problem-solving, and innovation.
- Notably, 40% of self-made millionaires have dyslexia, and historical figures like Albert Einstein were also dyslexic.
- Global Impact:
- The campaign aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aiming to unlock the untapped potential of individuals with learning disabilities, thereby contributing to societal development at a global level.
Chenchu Tribe

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
The Chenchus of Penukumadugu have lived in the dense Nallamala forests for centuries, their existence intertwined with the wilderness around them. However, their inability to keep up with the relentless pace of modernisation has led to dwindling work opportunities under the MGNREGA.
Chenchu Tribe Overview
- Location: Primarily in the dense Nallamala forests, Andhra Pradesh (AP).
- Tradition: Historically hunter-gatherers, now relying on subsistence farming.
- Vulnerable Status: Classified as one of the 12 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Andhra Pradesh due to low literacy, stagnant population growth, and limited access to development.
- Livelihood: Dependent on forest resources (Non-Timber Forest Produce - NTFP) and agricultural labor.
Impact of MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
- MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project: Launched in 2009 to address specific needs of the Chenchus, such as physical strength, food insecurities, and cultural practices.
- Before Discontinuation: Provided 180 days of work per person annually, which helped Chenchus access regular income, improving food security and living conditions.
- Post-Discontinuation (2022):
- The project was integrated into a nationwide MGNREGS framework, reducing workdays to the standard 100 days per household.
- Consequences: Many Chenchus stopped engaging with MGNREGS due to bureaucratic hurdles (Aadhaar and bank linkage), reduced job days, and irregular wage payments.
- Only 1,500 out of 4,000 enrolled households currently participate in MGNREGS work.
Key Issues Post-MGNREGS Reform
- Aadhaar & Bank Account Challenges:
- Lack of literacy and digital skills makes the Aadhaar-based system intimidating.
- Many Chenchus are excluded from PDS and health benefits due to missing or unlinked Aadhaar cards.
- Absence of mobile phones and access to banks makes wage disbursement difficult.
- Irregular Payments & Trust Issues:
- The shift to bank payments has created trust issues, as many Chenchus are illiterate and cannot verify wage deposits.
- Distance from banks (up to 30 km) adds to the difficulty in accessing payments.
Forest Rights and Wildlife Conservation
- Forest Dependency: The Chenchus continue to depend on the forest for food and livelihood, but increasing restrictions due to wildlife conservation (e.g., Nagarjuna-Srisailam Tiger Reserve) have further curtailed their access to forest produce.
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Many Chenchus have land pattas under the FRA but lack resources or support to utilize their land effectively due to the discontinuation of MGNREGS.
Government and Policy Response
- PVTG Initiatives: Various government initiatives like PM PVTG Mission, Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, and Janjatiya Gaurav Divas aim to uplift PVTGs, but their impact remains limited without proper implementation of specialized support programs like the MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)

- 09 Oct 2024
Recent Initiatives:
- The Indian government has launched a nationwide survey of kutcha houses.
- Introduction of the Awas Sakhi mobile app to streamline housing assistance.
Purpose of the Kutcha House Survey
- Identify Housing Needs: The survey aims to collect data on families living in kutcha (temporary) houses, enabling targeted support for those in need.
- Support for Awas Sakhi App: The survey will enhance the functionality of the Awas Sakhi app, facilitating the application process and providing beneficiaries with vital housing information.
Overview of PMAY-G
- Launch: Initiated in 2016, PMAY-G aims to provide secure housing for the poorest communities.
- Beneficiary Selection Process: A comprehensive three-stage validation, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensures that aid reaches those most deserving.
Benefits for PMAY-G Beneficiaries
- Financial Assistance:
- ?1.20 lakh for families in plain areas.
- ?1.30 lakh for families in hilly regions, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Support for Sanitation:
- An additional ?12,000 for toilet construction, aligned with the Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin or MGNREGS.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Provision of 90/95 days of unskilled wage employment through MGNREGA for house construction.
- Access to Basic Amenities:
- Connections for water, LPG, and electricity facilitated through relevant schemes.
- Cost Sharing Structure:
- Expenses are shared in a 60:40 ratio for plain areas and a 90:10 ratio for northeastern states and selected Himalayan states. The Centre covers 100% of costs for other Union Territories.
Progress Under PMAY-G
- Targets: The government aims to construct 2.95 crore houses.
- Current Status: As of August 2024, 2.94 crore houses have been sanctioned, with 2.64 crore completed, enhancing living conditions for millions in rural areas.
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, the Union Cabinet approved funding for two crore additional houses at existing assistance rates.
- Eligibility Criteria Changes:
- Individuals owning bikes or scooters are now eligible.
- The income limit for eligibility has been raised from ?10,000 to ?15,000 per month.
Future Goals
- This initiative, spanning FY 2024-2029, aims to address ongoing housing demands, benefiting approximately 10 crore individuals by providing safe, hygienic, and socially inclusive housing.
PM Internship Scheme

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme, announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman during her Budget speech on July 23, was launched on October 3. The PM Internship Scheme aims to provide internship opportunities to one crore youth in the top 500 companies over the next five years.
Companies will upload their internship positions, and candidates can submit applications starting October 12.
What is the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme?
The PM Internship Scheme will enhance youth employability in India by offering them hands-on exposure to real-world business environments. The scheme represents a transformative opportunity to bridge the skills gap and drive sustainable growth in India.
A monthly stipend of ?4,500 will be provided to the interns from the central government via DBT (Direct Benefit transfer), with an additional ?500 offset provided by the company’s CSR fund.
Who is eligible for the PM internship scheme?
- Candidates aged between 21 and 24 years who are not engaged in full-time employment are eligible for the one-year internship programme.
- Internships are available to those who have passed class 10 or higher.
- Individuals from families with government jobs are excluded
- The scheme is not open to post-graduates
- A candidate who graduated from premier institutes such as IIT, IIM, or IISER, and those who have CA, or CMA qualification would not be eligible to apply for this internship.
- Anyone from a household that includes a person who earned an income of ?8 lakh or more in 2023-24, will not be eligible.
How to apply for the PM internship scheme?
- Interns can register in the portal and apply for internships. The portal, pminternship.mca.gov.in, is likely to be opened up for youngsters to enroll for consideration by companies on October 12. This window will be open till October 25 for the first batch of internships. Candidates must share and self-certify some data about their educational qualifications and residential pin codes.
- Candidates’ data will be matched with companies’ needs and locations using Artificial Intelligence tools, and a shortlist of candidates will then be generated for companies to consider.
- The portal is designed to streamline the application process and make candidate selection more transparent. Applicants can check the status of their applications in the portal once they have applied to the available posts.
What is the benefit of the scheme?
The scheme is to provide on-job training to youth and an exposure to real-life work environment. The scheme will also benefit the industry by creating a pipeline of skilled, work-ready youth who can be employed post-internship both in large as well as micro, small and medium enterprise.
Poshan Tracker Initiative
- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development recently earned the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for its Poshan Tracker initiative, which has made significant strides in enhancing child health and nutrition.
About the Poshan Tracker Initiative
The Poshan Tracker initiative focuses on identifying and addressing growth-related issues in children aged 0-6 years. By using real-time monitoring and WHO growth charts, the program ensures that children receive optimal nutrition.
Key components of the initiative include:
- Role of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs): These workers are essential in assessing children's health and implementing necessary interventions when deviations from expected growth are observed.
- Technology Integration: The program employs advanced ICT tools and Growth Measuring Devices (GMD) at Anganwadi Centers (AWCs) to enable precise data collection and regular monitoring.
- Impact: Real-time growth monitoring through the Poshan Tracker has substantially improved child health outcomes in India, benefiting millions of children under the Mission Poshan 2.0 initiative.
Key Features of the Poshan Tracker App
- Comprehensive Overview: The app offers a complete view of Anganwadi Centre activities, including service deliveries and beneficiary management for pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children under six.
- Digitization and Automation: It replaces physical registers used by workers with digital records, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of their work.
- Smartphone Provision: Anganwadi workers have been provided with smartphones through the Government e-Market (GeM) to streamline service delivery.
- Technical Support: Each state has a designated nodal person to provide technical assistance and resolve issues related to the Poshan Tracker application.
- Service Accessibility: Migrant workers who registered in their original state can access services at the nearest Anganwadi in their current location.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of State for Women and Child Development, launched the Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024 in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh on 1st September,2024.
Key Highlights:
- As part of the 7th Rashtriya POSHAN Maah, awareness programs are being organized at various levels.
- Under the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services) Project, complementary feeding activities were conducted at Anganwadi Centres (AWC) Paduck Bagicha, South Andaman.
- Also, at AWC, Champin Nancowrie, Nicobar district (Andaman & Nicobar) under the ICDS Tribal initiative, local food items and nutrition sources were displayed.
- These efforts aim to further the Prime Minister's vision of a ‘Suposhit Bharat’ by conducting diverse large-scale activities, harnessing the potential of Gram Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The programme is annually celebrated in the month of September, with a different theme each year, primarily focusing on addressing malnutrition by ensuring convergence of various nutrition-related schemes and programmes.
- The objective of the Poshan Maah is to ensure community mobilisation and bolster people’s participation for addressing malnutrition amongst young children, and women and to ensure health and nutrition for everyone.
Poshan Abhiyaan:
- POSHAN Abhiyan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment) focuses on advancing nutritional outcomes for children under six years, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- To cultivate widespread awareness about nutrition at each stage of life, it is celebrated annually as Poshan Maah (1st—30th September) and Poshan Pakhwada (fortnight of March).
- POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Month) aims to strengthen efforts to end hunger and malnutrition.
- It focuses to improving the nutritional outcomes among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers by focusing on prenatal care, diet, and optimal breastfeeding.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development plans month-long activities under Poshan Maah, focusing on issues such as the hygiene and sanitation, anaemia prevention, maternal and infant health, among others.
- There are outreach programmes, identification drives, camps, and fairs with a special focus on pregnant and lactating women, children below six years, and adolescent girls in order to realise the vision of ‘Swasth Bharat’.
Swachh Bharat Mission averted 60,000-70,000 infant deaths annually: Study
- 09 Sep 2024
- Launched on October 2, 2014, the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) has been pivotal in advancing sanitation infrastructure in India.
- By 2020, the mission had facilitated the construction of over 11 crore household toilets under its Grameen component and over 63 lakh individual and 6.36 lakh community public toilets under its Urban component. This extensive sanitation drive aimed at eradicating open defecation and improving public health.
Impact on Infant Mortality
A recent study published in Nature has highlighted the significant health benefits resulting from SBM. According to the report, titled ‘Toilet Construction under the Swachh Bharat Mission and Infant Mortality in India,’ the initiative may have averted approximately 60,000 to 70,000 infant deaths annually between 2014 and 2020. The study, analyzed data from 35 states and 640 districts from 2011 to 2020, focusing on the infant mortality rate (IMR) and under-five mortality rate (U5MR).
Key Findings
- Decrease in Infant Mortality:
- The study established an inverse relationship between toilet access and infant mortality. It noted that districts with increased toilet coverage saw a marked decline in infant deaths.
- In 2003, the average toilet coverage in districts was below 40%, rising to over 60% by 2020. Correspondingly, infant mortality rates fell from an average of 48.9 per 1,000 live births in 2003 to 23.5 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
- Significant Decline:
- The research observed a substantial decline in infant mortality rates from 40 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 per 1,000 live births by 2019.
- The mortality rate for children under five also dropped from about 44 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 by 2019.
- Regional Variations:
- Despite the overall improvement, certain regions like parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh continued to report higher infant mortality rates, ranging between 45-60 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
Conclusion
The SBM has demonstrably improved sanitation in India, with a notable reduction in infant mortality rates attributed to the increased availability of household toilets. While the mission has achieved significant progress, ongoing efforts and investments in broader public health infrastructure are essential to address persistent regional disparities and sustain health gains.
