Samriddh Gram Phygital Services Pilot Project

- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The Samriddh Gram Phygital Services Pilot Project, launched by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) through the Telecom Centres of Excellence (TCoE), is a rural digital empowerment initiative aimed at bridging the digital divide by integrating physical infrastructure with digital service delivery (“phygital model”). It leverages BharatNet — India’s flagship rural broadband programme — to ensure seamless access to essential citizen-centric services.
Pilot Locations & Implementation
The pilot is being implemented in three villages, each hosting a Samriddhi Kendra:
- Ari & Umri (Madhya Pradesh) – Partner: Digital Empowerment Foundation
- Narakoduru (Andhra Pradesh) – Partner: Corpus Enterprises Pvt. Ltd.
- Chaurawala (Uttar Pradesh) – Partner: I-Novate Infotech Pvt. Ltd.
These Kendras act as integrated digital service hubs, providing both physical support and digital-enabled services.
Objectives:
- To create a replicable and scalable rural digital service model.
- To deliver last-mile digital access through BharatNet-powered connectivity.
- To enhance education, agriculture, health, governance, and financial inclusion in rural areas.
- To enable digital entrepreneurship and strengthen participation in the digital economy.
Key Features & Services
1. Education & Skilling
- Smart classrooms, digital content
- AR/VR-based learning
- Skill development aligned with national skilling schemes
2. Agriculture
- IoT-based soil testing
- Drone-enabled services (monitoring, spraying)
- Smart irrigation solutions
3. Healthcare
- Teleconsultations
- Health ATMs for diagnostics
- Basic emergency care support
4. e-Governance
- Assisted access to government services
- Document facilitation
- Grievance redress mechanisms
5. E-Commerce & Entrepreneurship
- Integration with ONDC
- Digital marketplace access for local products
- Support for rural microenterprises
6. Financial Inclusion
- Digital banking services
- Payment systems & UPI-assisted transactions
7. Connectivity Backbone
- BharatNet FTTH connectivity
- Village Area Network (VAN)
- Public Wi-Fi hotspots
Significance
- Strengthens Digital India at the grassroots.
- Demonstrates a phygital last-mile service delivery model.
- Enhances socio-economic outcomes in rural areas by integrating technology with governance and service delivery.
- Designed as a sustainable and scalable model for nationwide expansion.
State of Social Justice 2025
- 10 Oct 2025
In News:
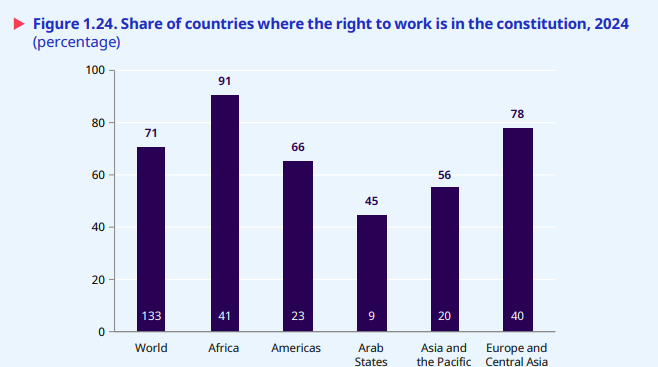
The International Labour Organization (ILO) released its landmark report, “The State of Social Justice: A Work in Progress (2025)”, ahead of the Second World Summit for Social Development. The report marks three decades since the historic 1995 Copenhagen Summit and evaluates global efforts towards achieving justice, equality, and inclusion in a rapidly transforming world.
I. Purpose and Framework
The report assesses progress over 30 years in advancing social justice—defined as fair and equitable access to opportunities, rights, and resources—through four foundational pillars:
- Fundamental Human Rights and Capabilities – promoting freedom, equality, and universal social protection.
- Equal Access to Opportunities – removing barriers to education, employment, and fair wages.
- Fair Distribution – ensuring equitable sharing of the gains from economic growth.
- Fair Transitions – managing environmental, digital, and demographic shifts inclusively.
II. Global Progress: Achievements and Trends
1. Poverty and Labour Improvements
- Extreme Poverty fell sharply from 39% (1995) to 10% (2023).
- Working Poverty declined from 27.9% (2000) to 6.9% (2024).
- Labour Productivity per worker increased by 78% globally and by 215% in upper-middle-income countries, indicating narrowing productivity gaps between nations.
- Child Labour dropped from 20.6% (1995) to 7.8% (2024), driven by education access and monitoring systems.
2. Education and Skills
- Secondary school completion rates rose by 22 percentage points since 2000, underscoring significant human capital development.
3. Social Protection Expansion
- Over half of the global population is now covered by at least one form of social protection—pensions, healthcare, or income support—up from a marginal share in 1995.
III. Persistent Challenges
Despite these gains, the report warns that social justice remains “a work in progress,” with stark inequalities continuing to undermine inclusive growth.
1. Inequality and Wealth Concentration
- The top 1% of the global population controls 20% of income and 38% of total wealth.
- 800 million people still survive on less than US$3 per day, and one in four lacks access to safely managed drinking water.
2. Gender and Birth Inequalities
- Women earn 78% of men’s wages, and gender parity in labour participation has improved by only three percentage points since 1995.
- Nearly 71% of income outcomes globally are influenced by birth circumstances, reflecting entrenched structural inequities.
3. Informality and Job Quality
- 58% of workers remain in the informal economy, with limited access to labour rights and social protection.
- Collective bargaining rights have weakened globally, as reflected in declining compliance scores across income groups.
4. Declining Trust in Institutions
Confidence in governments, corporations, and unions has steadily eroded since the 1980s due to perceptions of unfair reward systems, corruption, and widening wealth gaps—posing risks to democratic stability.
IV. India in the Global Context
India mirrors many global patterns highlighted by the ILO but also shows unique progress in certain areas:
1. Poverty and Human Development
- Multidimensional poverty reduced from 29% (2013–14) to 11% (2022–23).
- Education: Secondary school completion rate reached 79% (2024), and female literacy stands at 77%.
- Digital Empowerment: The JAM trinity (Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile) enhanced direct benefit delivery and reduced leakages.
2. Social Protection and Welfare
Schemes such as PM-KISAN, Ayushman Bharat, and e-Shram have significantly extended coverage to over 55 crore unorganised workers. The Social Security Code (2020) further streamlined pension and maternity benefits.
3. Labour Market and Gender Gaps
- Informality remains high—over 80% of India’s workforce operates outside formal contracts.
- Female labour force participation has improved to 37% (PLFS 2024–25) but remains below the global average.
V. Managing Emerging Transitions
The ILO identifies three ongoing societal transitions that must be managed fairly to sustain progress:
- Climate Transition – Ensuring green jobs and protecting workers displaced by decarbonisation.
- Technological Transition – Bridging the digital divide through skills, reskilling, and inclusive access.
- Demographic Transition – Addressing challenges of ageing populations while leveraging youth dividends in developing countries.
To navigate these, the ILO recommends:
- Applying existing labour institutions to emerging contexts.
- Adapting them to specific transition challenges.
- Amplifying them by integrating labour concerns into climate, digital, and fiscal policies.
VI. ILO’s Key Recommendations
- Embed Social Justice Across Policies – Integrate equity into finance, trade, climate, and healthcare governance.
- Rebuild Trust in Institutions – Enhance transparency, accountability, and participatory policymaking.
- Invest in People – Expand education, skills, and lifelong learning to bridge gender and digital gaps.
- Strengthen Social Protection Systems – Aim for universal and portable coverage, backed by fair minimum wages.
- Promote Fair Transitions – Ensure environmental and technological shifts generate decent work.
- Enhance Global Cooperation – Reinforce multilateralism to manage migration, inequality, and global shocks.
India’s first port-based Green Hydrogen Pilot Project

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, SarbanandaSonowal, inaugurated India’s first port-based Green Hydrogen Pilot Project at V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port, Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, marking a significant step in India’s clean energy transition and green shipping ambitions.
Key Features of the Project
- Capacity: 10 Nm³ per hour.
- Cost: ?3.87 crore.
- Uses: The green hydrogen produced will power streetlights and an EV charging station in the port colony.
- Significance: VOC Port becomes the first Indian port to generate green hydrogen, aligning with India’s vision of Viksit Bharat 2047 and clean energy leadership.
Associated Green Initiatives at VOC Port
- Green Methanol Bunkering and Refuelling Facility
- Capacity: 750 m³, at a cost of ?35.34 crore.
- Expected to make VOC Port a green bunkering hub in South India.
- Linked to the proposed Coastal Green Shipping Corridor (Kandla–Tuticorin).
- Renewable Energy and Infrastructure Projects
- 400 KW rooftop solar plant, raising total capacity to 1.04 MW (highest among Indian ports).
- Foundation for a 6 MW wind farm.
- ?24.5 crore link conveyor to improve coal handling efficiency.
- ?90 crore multi-cargo berth and 3.37 km four-lane road for port connectivity.
- Upcoming Tamil Nadu Maritime Heritage Museum to showcase maritime history.
Strategic Importance
- Port Modernisation: Chennai, Kamarajar, and VOC ports have seen rapid expansion under the SagarmalaProgramme.
- 98 projects worth ?93,715 crore initiated in Tamil Nadu’s ports in the past 11 years.
- 50 projects completed; ?16,000 crore invested in modernisation and capacity building.
- Economic Impact:
- Expected to generate thousands of jobs.
- Attract global investments in green shipping and clean fuels.
- Strengthen India’s ambition of becoming a top 10 shipbuilding nation by 2030 and top 5 by 2047.
About V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port
- Location: Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, on the Coromandel Coast.
- Status: One of India’s 13 major ports, serving as a key maritime hub for South India.
- History: Formerly Tuticorin Port, renamed in 2011 after freedom fighter V.O. Chidambaranar (KappalottiyaTamizhan).
- Role: Major centre for coal handling, container trade, and now emerging as a green energy hub.
Barbados Threadsnake (Tetracheilostoma carlae)
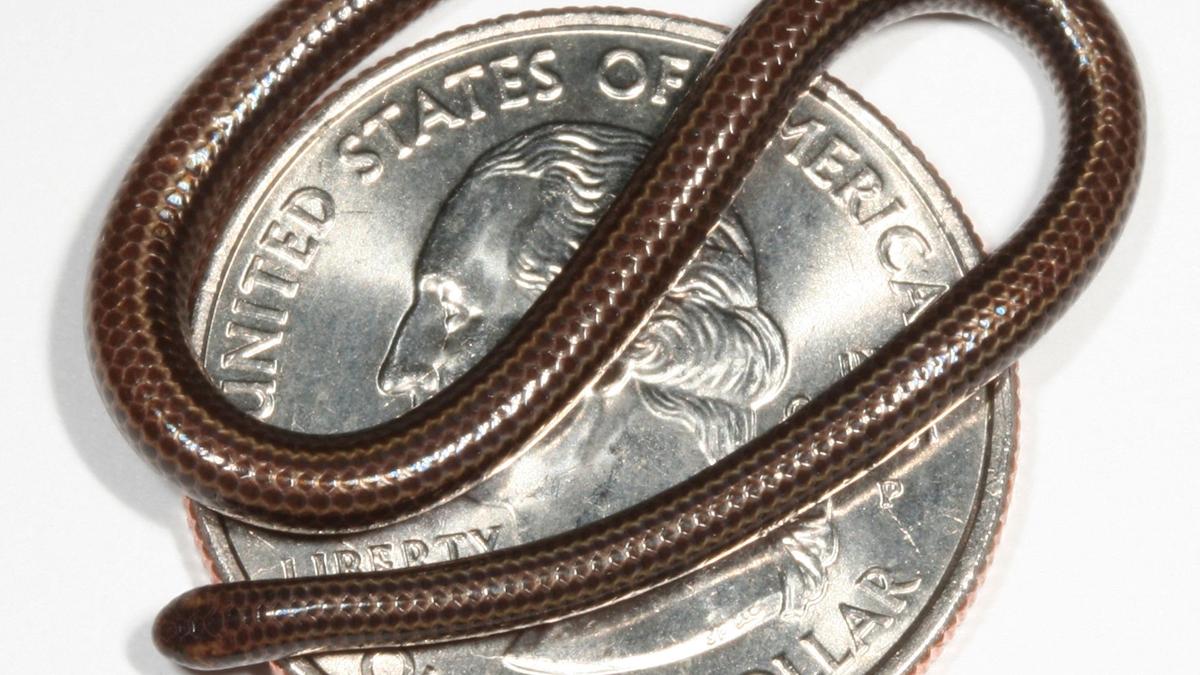

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
The Barbados threadsnake, long considered lost to science, has made a startling comeback. This diminutive reptile—no longer than a coin—was rediscovered in Barbados in March 2025, nearly two decades after its last documented sighting. Its reappearance has reignited global interest in its conservation and the fragile ecosystems it inhabits.
Key Attributes & Taxonomy
- Scientific Classification: Tetracheilostoma carlae, family Leptotyphlopida.
- Size & Weight: Adults reach approximately 9–10 cm (3–4 in) in length and weigh ~0.6 g (~0.02 oz)—making it the world’s smallest known snake
- Physical Traits: Extremely slender—about as thick as a spaghetti noodle. Distinguished by pale orange dorsal stripes and a small scale on the snout
- Vision & Behavior: A blind, fossorial snake that burrows underground, especially hiding under rocks during the day.
- Diet: Feeds on termite and ant larvae—its petite jaws prevent it from consuming larger prey.
- Reproduction: Oviparous, laying only one large egg at a time, with hatchlings already about half the size of adults.
Rediscovery: A Significant Scientific Moment
- Context: The species had not been observed since 2006, and earlier specimens were often misidentified in museum collections.
- 2025 Rediscovery: During a March ecological survey in central Barbados by the Ministry of Environment and Re:wild, the snake was found under a rock near a jack-in-the-box tree. It was confirmed after microscopic and morphological assessment at the University of the West Indies.
- Reactions: This turn of events is hailed as a conservation triumph and a poignant reminder of Barbados’s biodiversity despite its heavily altered landscape.
Conservation Context & Implications
- Habitat Loss: Over 98% of Barbados’s primary forests have been cleared, leaving threadsnake habitats limited to a few square kilometers of secondary forests, particularly in the Scotland District.
- Threats: Loss of habitat and competition from the invasive Brahminy blind snake (Ramphotyphlops braminus), which reproduces asexually and may outcompete the threadsnake.
- Conservation Action: The rediscovery falls under the broader Conserving Barbados’ Endemic Reptiles (CBER) project. Future plans focus on mapping its range, safeguarding habitats, and preserving biodiversity as part of Barbados's compliance with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
Dragon Copilot

- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
Microsoft has launched Dragon Copilot, a voice-activated AI assistant designed specifically for the healthcare sector. It aims to reduce administrative burdens on clinicians by automating documentation and providing quick access to medical information.
Key Features and Functionalities:
- Platform Integration: Part of Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, Dragon Copilot integrates with Electronic Health Records (EHR) and is accessible via desktop, browser, or mobile app.
- Technology Base: Built on Nuance’s Dragon Medical One (DMO) and DAX (Dragon Ambient eXperience) platforms, which have supported transcription of billions of patient records and over 3 million ambient patient interactions.
- Voice & AI Capabilities:
- Uses natural language dictation and ambient listening technologies.
- Enhanced with generative AI and healthcare-specific safeguards.
- Allows drafting of memos, referral letters, clinical summaries, and after-visit notes in personalized formats.
- Facilitates real-time voice-to-text transcription and AI-generated notes via user prompts or templates.
- Supports automated search for verified medical information.
Benefits:
- Reduces clinician paperwork and burnout, enhancing focus on patient care.
- Survey Data (Microsoft Findings):
- Saves ~5 minutes per patient interaction.
- 70% clinicians reported reduced fatigue.
- 62% were less likely to leave their organizations.
- 93% patients reported improved experiences.
Concerns and Risks of Healthcare AI:
- AI Hallucinations: Tools like OpenAI’s Whisper have produced fictitious content, including inappropriate or incorrect medical information.
- Regulatory Caution:
- The US FDA warns of risks from generative AI in healthcare, including false diagnoses or biased outputs.
- Emphasizes the need for transparent and accountable development practices.
- Microsoft’s Response:
- Claims to have integrated “clinical, chat, and compliance safeguards” into Dragon Copilot.
- Built in alignment with Microsoft’s Responsible AI principles, although technical specifics remain undisclosed.
Broader AI Healthcare Landscape:
- Companies like Google Cloud, Abridge, and Suki are developing similar AI-based healthcare assistants.
- Growing interest in generative AI for reducing clinician workload and improving patient outcomes is driving innovation and investment across the sector.
Giloy (Tinosporacordifolia)
- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
Giloy, also known as Guduchi and referred to as Amrita in Sanskrit—meaning the "herb of immortality"—is gaining global attention for its therapeutic potential, with scientific research on the herb witnessing a remarkable surge.
Surge in Scientific Publications
According to PubMed, a globally recognised biomedical database, there has been a 376.5% increase in research publications on Giloy between 2014 and 2024:
- 2014: 243 studies
- 2024: 913 studies
This significant rise reflects growing interest in natural and plant-based therapies, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic, which intensified focus on immunity boosters and holistic healthcare.
Therapeutic Properties and Uses
- Giloy is used in Ayush systems for:
- Fever management
- Gouty arthritis
- Autoimmune diseases
- Inflammatory disorders
- Cancer therapy (emerging evidence)
- Bioactive compounds in Giloy have shown:
- Immunomodulatoryeffects
- Anti-inflammatoryaction
- Adaptogenicandantiviralproperties
Botanical & Agricultural Features
- Scientific name: Tinosporacordifolia
- Distribution: Widely found across India
- Growth conditions:
- Grows in most soil types
- Propagated via stem cuttings (May–June)
- Large climber with corky, grooved stems
Recent Research Highlights
- Feb 2025 (Gujarat University): Giloy extracts showed promise in HPV-positive cervical cancer treatment through immunomodulation.
- Jan 2025 (Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai): Giloy-based phytopharmaceuticals were effective in managing Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis (IGM), offering a safe, steroid-free, and cost-effective alternative to surgery.
Government Initiatives
- The Ministry of Ayush has launched a technical dossier on Giloy, compiling scientific research and therapeutic insights.
- Aim: Promote evidence-based integration of Ayurveda with modern healthcare systems.
- Emphasis on global collaboration, research funding, and mainstreaming traditional medicine.
Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for Pilots
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
India has launched the Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for pilots, becoming the second country globally, after China, to implement this advanced digital licensing system.
What is EPL?
- Electronic Personnel License (EPL) is a digital version of pilot licenses, replacing the traditional physical cards.
- Pilots can securely access their EPL via the eGCA Mobile Application developed by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- It ensures real-time verification, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and security in licensing procedures.
Significance of EPL
- Aligns with:
- Digital India and Ease of Doing Business initiatives.
- ICAO’s Amendment 178 to Annex 1 on Personnel Licensing, promoting digital transformation.
- Enhances:
- Safety and efficiency in civil aviation operations.
- Environmental sustainability by reducing the use of plastic and paper.
- Global employability of Indian pilots through instant international credential verification.
Implementation & Governance
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India.
- Executing Agency: Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- EPL implementation positions India as a leader in aviation innovation and modern governance.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
- Established: 1947 under the Chicago Convention (1944).
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- Nature: A specialized intergovernmental agency affiliated with the United Nations (UN).
- Functions:
- Sets standards and regulations for aviation safety, security, efficiency, and environmental performance.
- Promotes peaceful and efficient international air transport.
- Facilitates global cooperation and market liberalization in aviation.
ILO Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers – 2022

- 21 Jan 2025
In New:
By addressing labour market shortages in host nations and contributing remittances to home countries, International Migrants (IM) continue to make contributions to world economic growth, the fourth edition of ‘Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers’, released by the International Labour Organization (ILO), stated.
Key Findings:
Global Representation:
- International Migrants (IMs) = 4.7% of global labour force - 167.7 million total:
- Employed: 155.6 million
- Unemployed (but seeking work): 12.1 million
- Increase of 30+ million migrant workers since 2013
- Growth rate dropped below 1% annually (2019–2022) due to COVID-19
Gender Composition:
- Male IMs: 61.3% (102.7 million)
- Female IMs: 38.7% (64.9 million)
- Lower female participation attributed to:
- Lower female migration rates globally
- Gender-based barriers in labour markets
- Over-representation in informal and unpaid sectors
Age Distribution:
- Prime working age (25–54 yrs): 74.9%
- Youth (15–24 yrs): 9.3%
- Older adults (55–64 yrs): 12.5%
- Seniors (65+ yrs): 3.4%
Sector-wise Employment:
Sector Share of IMs Notes
Services 68.4% Highest; women dominate (80.7%)
Industry 24.3% On par with non-migrants
Agriculture 7.4% Far lower than non-migrants (24.3%)
Care economy in high-income countries is a major pull for female migrants.
Host Country Distribution:
Region/Income Group % of IMs Notes
High-income countries 68.4% (114 million) Majorly Europe & North America
Upper-middle-income 17.4% (29.2 million)
Arab States 13.3% Declined since 2013
Europe (23.3%) and North America (22.6%) are top destinations. Arab states saw a 3% decline over the decade.
Definition: International Migrants (IMs)
As per the UN: Persons residing in a country different from their place of usual residence for at least one year, regardless of reason or legal status. Includes refugees, asylum seekers, etc.
Role & Contributions of IMs:
- Economic Drivers: Fill labour shortages (healthcare, construction, care work).
- Remittances: Boost home country economies.
- Demographic Support: Help address aging populations in developed nations.
Cultural Exchange: Promote diversity and global connectivity.
ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
DigiLocker Partners with UMANG
- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) has announced the integration of the UMANG app with DigiLocker- India’s Digital Wallet. This collaboration aims to provide citizens with seamless access to a wide range of government services bringing greater convenience and allowing users to manage multiple services through a single platform.
UMANG app
- The UMANG app is accessible to all Android users with an expansion to iOS in the pipeline.
- The UMANG mobile app is an all-in-one single, unified, secure, multi-channel, multi-lingual, multi-service mobile app.
- It provides access to high-impact services of various organizations of the Union and States.
Simplified Citizen-Government interaction
This integration makes it easier for citizens to interact with the Government in an efficient, digital-first manner. DigiLocker has always been a pioneer in simplifying access to personal and official documents, and after integration with UMANG, it has expanded the range of services you can access on the go.
About DigiLocker
DigiLocker is a flagship initiative under the Digital India program aimed at providing secure cloud-based storage of essential documents. By integrating with e-governance services such as UMANG, DigiLocker further is committed to further enhance accessibility and ease of living.
Trilobite fossils from upstate New York reveal extra set of legs
- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
A new study finds that a trilobite species with exceptionally well-preserved fossils from upstate New York has an additional set of legs underneath its head.
Key details:
- The research, led by the American Museum of Natural History and Nanjing University in China, suggests that having a fifth pair of head appendages might be more widespread among trilobites than once thought.
- Published in the journal Palaeontology, the study helps researchers better understand how trilobite heads are segmented.
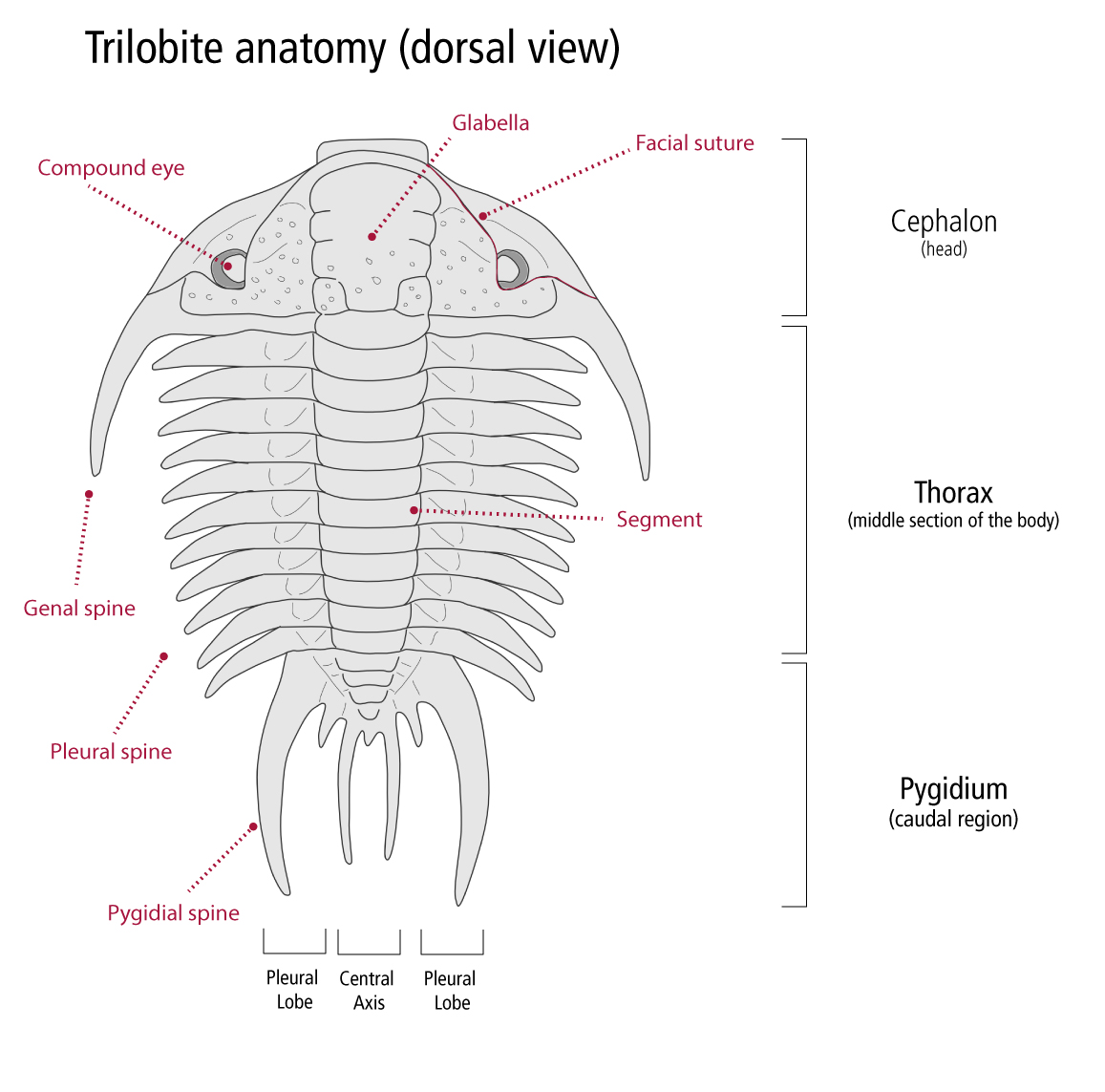
Trilobites
- Trilobites are a group of extinct arthropods whose living relatives include lobsters and spiders.
- Like other arthropods, the bodies of trilobites are made up of many segments, with the head region comprised of several fused segments.
- As with other parts of the trilobite body (the thorax and tail), these segments were associated with appendages, which ranged in function from sensing to feeding to locomotion.
- Trilobites are a group of extinct marine arthropods that first appeared around 521 million years ago, shortly after the beginning of the Cambrian period, living through the majority of the Palaeozoic Era, for nearly 300 million years. They died out at the end of the Permian, 251 million years ago, killed by the end Permian mass extinction event that removed over 90% of all species on Earth. They were very diverse for much of the Palaeozoic, and today trilobite fossils are found all over the world.
- The name 'trilobite' comes from the distinctive three-fold longitudinal division of the dorsal exoskeleton into a central axis, flanked on either side by lateral (pleural) areas.
Two ways
The segments in the trilobite head can be counted in two different ways: by looking at the grooves (called furrows) on the upper side of the trilobite fossil’s hard exoskeleton, or by counting the pairs of preserved antennae and legs on the underside of the fossil. The soft appendages of trilobites are rarely preserved, though, and when looking at the segments in the trilobite head, researchers regularly find a mismatch between these two methods.
In the new study, researchers examined newly recovered specimens of the exceptionally preserved trilobite Triarthrus eatoni from upstate New York. These fossils, known for the gold shine of the pyrite replacement preserving them, show an additional, previously undescribed leg underneath the head.
Resolving mismatch
By making comparisons with another trilobite species, the exceptionally preserved Olenoides serratusfrom the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, the researchers propose a model for how appendages were attached to the head in relation to the grooves in the exoskeleton.
This model resolves the apparent mismatch and indicates that the trilobite head included six segments: an anterior segment associated with the developmental origin of the eyes and five additional segments, associated with one pair of antennae and four pairs of walking legs, respectively.
Crystal Maze-2 Missile
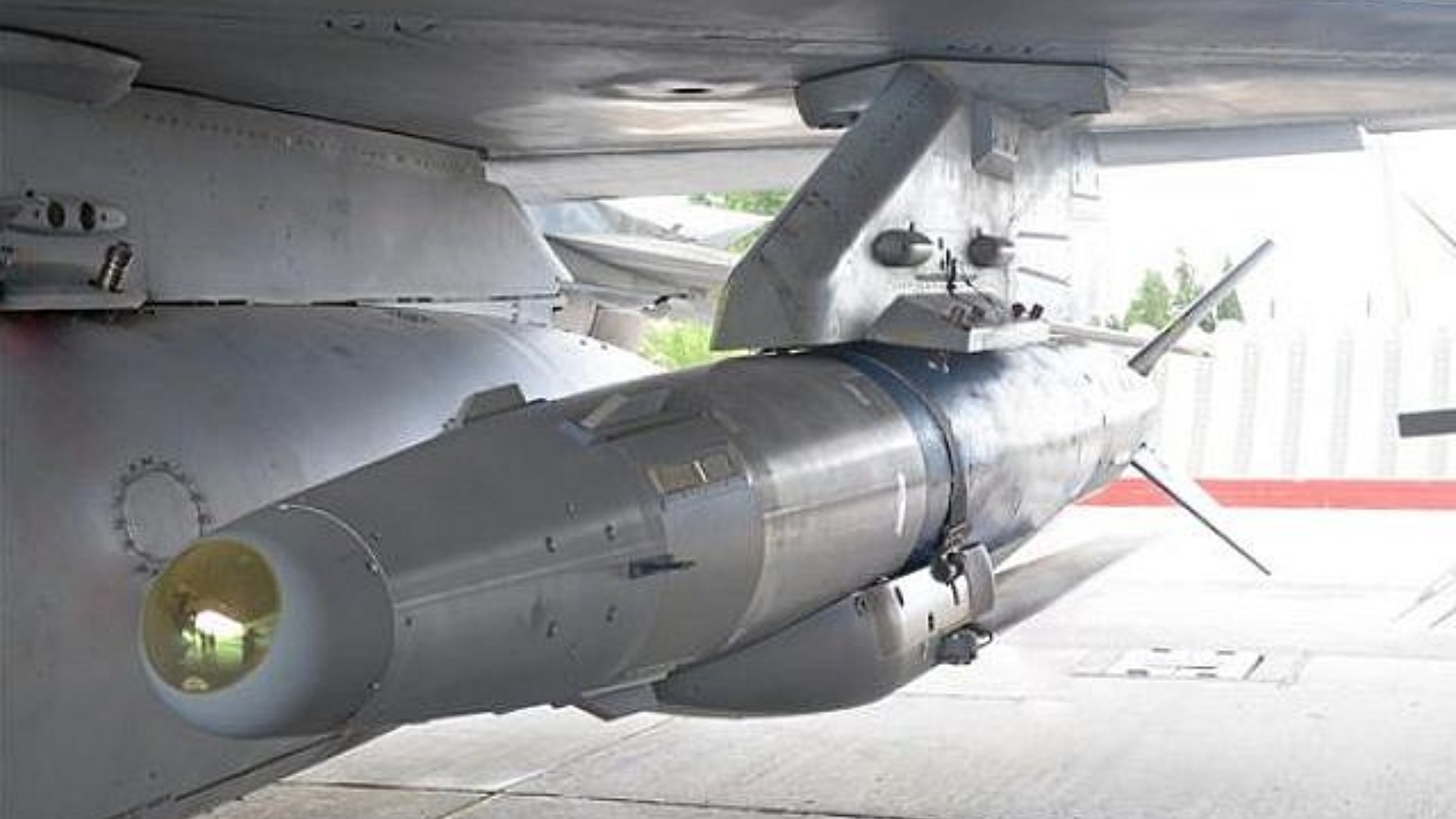

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force achieved a milestone by successfully test-firing an air-launched ballistic missile, ROCKS or Crystal Maze 2, capable of hitting targets over 250 kilometers away.
About Crystal Maze-2 Missile:
- Crystal Maze 2 missile also known as ROCKS is an advanced air-launched missile developed by Israel, designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- This missile is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
Features:
- Crystal 2 operates effectively in GPS-denied areas and can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
- With a striking distance of over 250 kilometers, it offers versatility with options for either penetration or blast fragmentation warhead, ensuring the destruction of above-ground or well-protected underground targets.
- India is currently developing the Crystal Maze 2 missile.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative.
- This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 Report (The Hindu)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The global unemployment rate is set to increase in 2024 while growing social inequalities remain a concern, according to the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 report released in Vienna recently.
Key Findings:
- Employment Trends: Joblessness and the jobs gap have both decreased below pre-pandemic levels, but global unemployment is expected to rise in 2024.
- The macroeconomic environment witnessed a significant deterioration in 2023.
- Global Economic Challenges: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and persistent inflation led to frequent and aggressive actions by central banks.
- Monetary authorities in both advanced and emerging economies implemented the fastest interest rate increases since the 1980s, with widespread global repercussions.
- Economic Slowdown in Key Economies: China, Türkiye, and Brazil experienced notable slowdowns, adversely affecting global industrial activity, investment, and trade.
- Despite the economic slowdown, global growth in 2023 surpassed expectations, and labour markets displayed unexpected resilience.
- Unemployment Dynamics: The global unemployment rate in 2023 improved modestly to 5.1% compared to 2022.
- Labour market participation rates largely recovered from pandemic lows, but concerns arise about structural imbalances persisting.
- Wage Trends: Real wages declined in most G20 countries as increases failed to keep pace with inflation.
- Workers living in extreme poverty (earning less than US$2.15 per day per person in PPP terms) increased by about one million globally in 2023.
- Positive real wage growth was observed in China, the Russian Federation, Mexico, India, and Türkiye.
Recommendations As per the Report:
- Inclusive Labor Policies: Policymakers in rapidly ageing countries should focus on supporting the participation of groups with weak labour market attachment, including youth, women, and older workers.
- Investment and Skills Strategies: Investment and skills policies should aim to enhance productivity, and potential growth, and promote a more productive utilization of technological progress.
- Sectoral Improvements: Motivating workers who leave due to low pay and challenging working conditions can be achieved by improving conditions in sectors and occupations with these challenges.
- International Workforce Matching: Facilitating the matching of internationally mobile workers to suitable jobs could alleviate some of the shortages in the labour market.
- Long-Term Engagement: Recognizing that structural challenges in labour market adjustment are unlikely to vanish in the short term, it is crucial for governments and social partners to engage in ongoing efforts to address these challenges.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) stands as the United Nations agency dedicated to the world of work.
- Mission: The core mission of the ILO is to promote social and economic justice by establishing and advancing international labour standards.
- Motto: At the heart of the ILO's mission is the pursuit of Decent Work for all, encapsulating the commitment to fostering conditions that are fair and dignified.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, the ILO operates from its global headquarters.
- Parent Organization: Functioning under the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations, the ILO is a vital component of the UN system.
- Additionally, it is a member of the United Nations Development Group (UNDP), collaborating with other UN organizations to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
- Historical Background: Established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles, following the conclusion of World War I, the ILO was conceived with the conviction that enduring and universal peace could only be realized through a foundation of social justice.
- In 1946, it transitioned into a specialized agency within the newly formed United Nations.
- Membership: The ILO boasts a diverse membership, with 187 member states, encompassing 186 out of the 193 UN member states along with the Cook Islands.
- Organizational Structure: Distinguishing itself as the only tripartite U.N. agency, the ILO brings together representatives from governments, employers, and workers of its 187-member states, fostering collaborative efforts in shaping global labour standards and policies.
Another eye in the sky, on the ground: India is now part of the world’s largest radio telescope project (Indian Express)
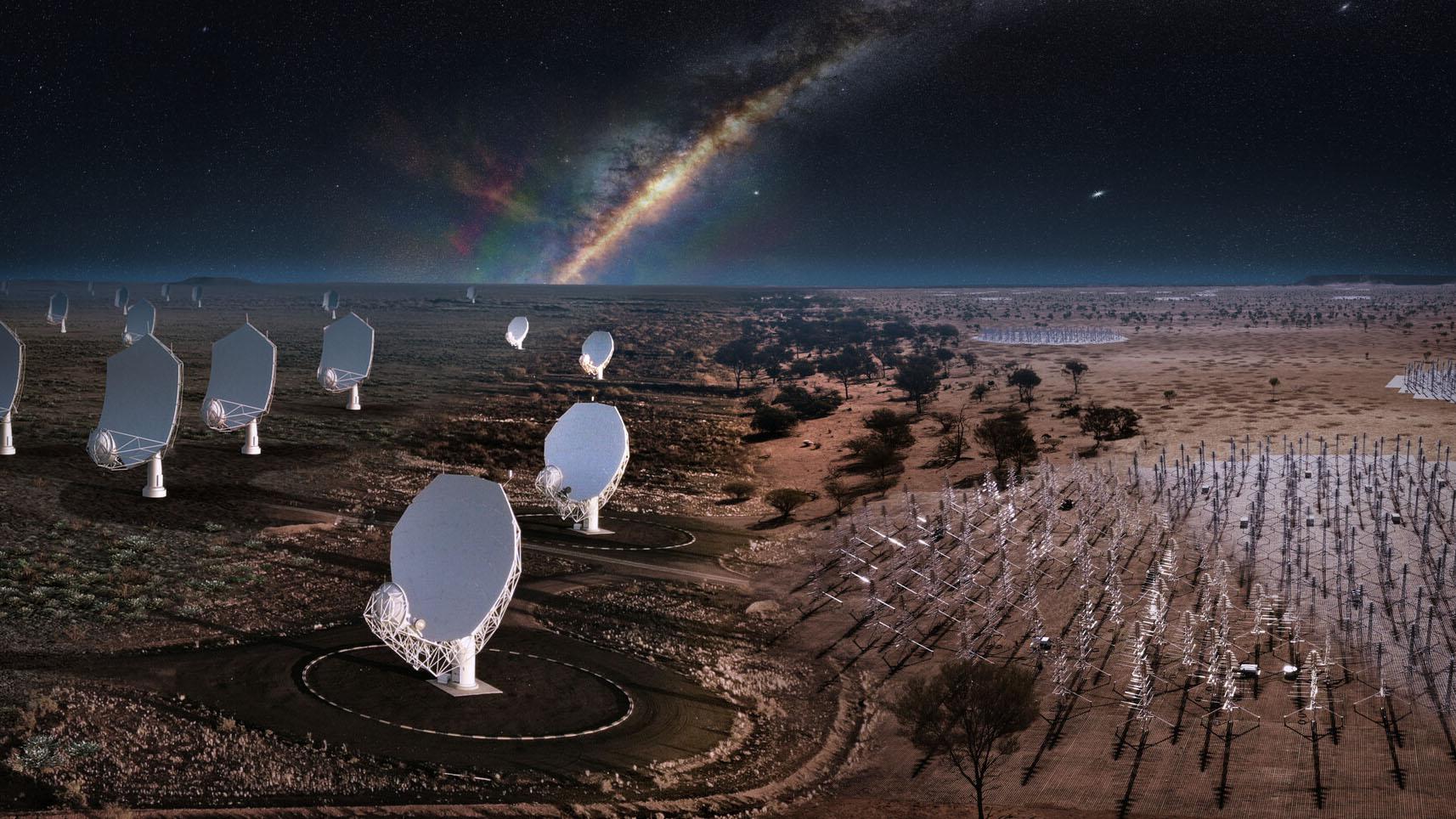

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian government’s recent approval to join the SKA project, accompanied by a financial commitment of Rs 1,250 crore, marks the initial step towards this ratification.
What is the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)?
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
- At the moment, organisations from ten countries are a part of the SKAO.
- These include Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK.
What is significant about the SKA telescope?
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- Some of the questions that scientists hope to address using this telescope include:
- Beginning of the universe
- How and when the first stars were born
- The life cycle of a galaxy
- Exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and
- Understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- As per NASA, the telescope will accomplish its scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.
- Significantly, the development of SKA will use the results of various surveys undertaken using another powerful telescope called the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is developed and operated by the country’s science agency CSIRO.
- This telescope, which has been fully operational since February 2019 mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey.
- ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
What are radio telescopes?
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Significantly, since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore them.
- According to NASA, the field of radio astronomy evolved after World War II and became one of the most important tools for making astronomical observations.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first millisecond pulsar.
Psyche Mission (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A NASA experiment on the Psyche spacecraft has beamed back a near-infrared laser that contains test data from almost 16 million kilometers away.
About the Psyche Mission:
- Psyche is a NASA mission to study a metal-rich asteroid ‘Psyche’, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission launched on October 13, 2023, from Kennedy Space Center and will arrive at Psyche in August 2029.
- The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid for about two years, studying its geology, composition, and magnetic field.
- Scientists believe that Psyche may be the exposed core of an early planet that never fully formed.
- If so, studying Psyche could provide important insights into the formation of our solar system.
- It is also the first in a series of NASA science missions to be the primary payload launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- The goals of the Psyche mission are to:
- Understand the composition and structure of a metallic asteroid.
- Determine how Psyche formed and evolved.
- Learn more about the formation of planetary cores.
- The Psyche spacecraft is a solar-powered spacecraft that uses Hall effect thrusters for propulsion.
- The spacecraft also carries a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- A magnetometer to measure Psyche's magnetic field.
- A spectrometer to measure the composition of Psyche's surface.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer to measure the abundance of elements on Psyche's surface.
India is expected to withstand global shocks as its current account deficit improves due to falling crude oil prices. (ET)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After two years of battling inflation and growth pangs, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was in for a pleasant surprise when the economic growth trumped its expectations to hit 7.2 per cent in the last month.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled its most recent monetary policy report, projecting a robust economic recovery for the country in the current fiscal year.
- Anticipating a significant upswing, the central bank foresees the gross domestic product (GDP) to expand by 7 percent in 2021-22, a notable rebound from the 7.3 percent contraction witnessed in the preceding year.
- However, the RBI issues a cautionary note about the challenges posed by inflation, which has consistently exceeded the target range of 2-6 percent over several months.
- The report attributes inflationary pressures to supply-side disruptions, escalating commodity prices, increased fuel taxes, and demand-related factors.
- The RBI anticipates inflation to remain elevated in the short term before gradually moderating in the latter half of the year.
- The RBI's stance mirrors a delicate equilibrium, emphasizing the intricate balance between fostering economic growth and managing inflation, often characterized as the Goldilocks Effect.
- This effect alludes to a scenario where the economy is neither excessively overheated nor excessively sluggish but rather poised for optimal growth with minimal inflationary pressures.
What is the Goldilocks Effect?
- The Goldilocks Effect, also known as the Goldilocks Principle, posits that individuals have a predisposition to seek an amount that is 'just right' for their specific needs or preferences.
- This concept, derived from the children's story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, reflects a preference for options that are neither too extreme nor too moderate, falling within an optimal and desirable range.
- This principle finds application across various fields and disciplines, encompassing psychology, hard sciences, economics, marketing, and engineering, each incorporating its unique interpretation of the principle.
- Goldilocks Pricing: One notable application of the Goldilocks Effect is in Goldilocks Pricing, a psychological pricing strategy grounded in concepts such as product differentiation, comparative pricing, and bracketing.
- Product differentiation involves distinguishing certain products from others, a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the Goldilocks Effect.
- This differentiation is then coupled with comparative pricing, where businesses simultaneously offer multiple versions of a product with varying quality levels attached to corresponding price points.
- The strategy hinges on providing three options: one priced too high for most, one priced too low for most, and one priced just right.
- When executed effectively, this approach enables businesses to appeal to diverse segments of the market, capturing premium buyers, standard consumers, and discount seekers.
