State of the World Population Report 2025
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
According to the United Nations Population Fund’s (UNFPA) State of the World Population Report 2025, India’s population has reached 146.39 crore as of April 2025, surpassing China (141.61 crore) to remain the world’s most populous country. Importantly, India’s Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has declined to 1.9, falling below the replacement level of 2.1.
Key Highlights:
Population Growth and Future Projections
- Current population (2025): 146.39 crore
- Projected peak: 170 crore in the next 40 years, after which population will begin to decline.
- Working-age population (15–64 years): 68%
- Youth population:
- 0–14 years: 24%
- 10–19 years: 17%
- 10–24 years: 26%
- Elderly population (65+ years): 7% (expected to rise steadily)
Fertility Trends and the Real Crisis
What is TFR?
- Total Fertility Rate measures the average number of children a woman is expected to have in her lifetime.
- Replacement level TFR: 2.1 (to maintain population size across generations)
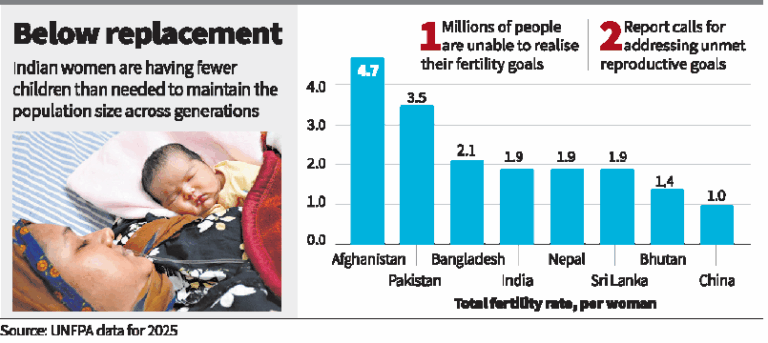
- India’s TFR in 2025: 1.9, marking a demographic shift toward stabilization.
Fertility Divergence Across States:
- High TFR states: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand
- Low TFR states: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Delhi – already below replacement level
The Real Fertility Crisis (UNFPA View):
- The true concern is unmet fertility goals, not overpopulation or underpopulation.
- Barriers to achieving desired family size:
- Financial constraints (40%)
- Job insecurity (21%) and housing issues (22%)
- Lack of childcare (18%)
- Social/family pressures (19%)
- Modern concerns like climate change and shifting gender norms
Structural & Social Challenges
- Persisting inequalities in access to reproductive health across caste, income, and regional lines
- Youth bulge in LMICs (including India) offers demographic dividend but needs skill-building and employment opportunities
- Ageing population calls for future-proof policies on healthcare, pensions, and social security
Life Expectancy & Data Reliability
- Life expectancy (2025):
- Men: 71 years
- Women: 74 years
- Data drawn from: DHS, MICS, World Population Prospects 2024, Family Planning Indicators (2024)
- India’s decennial Census delayed to 2027, limiting official data updates since 2011
UNFPA Recommendations for India:
- Expand SRH (Sexual & Reproductive Health) Services: Universal access to contraception, safe abortion, and infertility care
- Tackle Structural Barriers: Affordable housing, childcare, flexible work policies, and women’s education
- Promote Reproductive Agency: Ensure informed choices on family planning for all, including LGBTQIA+ and unmarried individuals
- Balance Youth & Elderly Policies: Invest in youth employability while preparing for ageing-related challenges
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
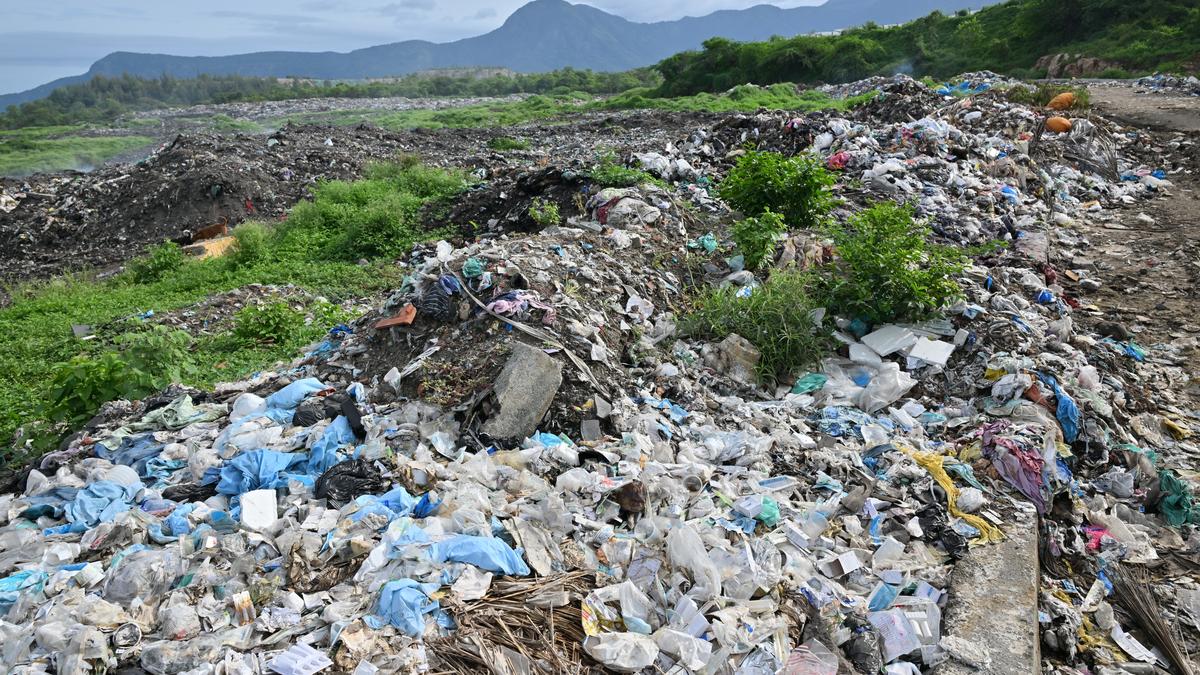
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
