Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A rare sighting of the Indian Giant Flying Squirrel (Petauristaphilippensis) has been reported in Ranikhet, a hill station in Uttarakhand, highlighting the ecological richness of the region.
About Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
Feature Description
Scientific Name Petauristaphilippensis
Size Body length: 30–45 cm; Tail length: up to 60 cm
Appearance Rufous coat, grey underparts, large eyes, and a gliding membrane from wrist
to ankle
Locomotion Glides up to 60 meters between trees using patagium (gliding membrane)
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in tropical and subtropical forests across central and southern India
- Inhabits evergreen, semi-evergreen, and deciduous forests, especially near forest edges
- Recent sighting in Uttarakhand indicates possible range expansion or overlooked presence
Ecological Role
- Diet: Fruits, nuts, leaves, and bark
- Acts as a seed disperser, supporting forest regeneration
- Considered a keystone species due to its ecological significance
Behavioural Traits
- Nocturnal and arboreal
- Emits alarm calls upon detecting predators like owls
- Active at night, gliding from tree to tree in search of food
Conservation Status
Category Status
IUCN Red List (Global) Least Concern
IUCN Status (India) Near Threatened (due to habitat loss)
Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 Schedule II
Threats
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Deforestation and degradation of forest corridors
- Increasing human encroachment in forested landscapes
World’s First 3D-Printed Train Station unveiled in Japan

- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
Japan’s West Japan Railway Company has unveiled the world’s first 3D-printed train station — Hatsushima Station in Arida city. Notably, the station was constructed in less than six hours, highlighting a major advancement in construction technology.
Understanding 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
What is 3D Printing?
3D Printing, or Additive Manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering material based on a digital design. Unlike traditional (subtractive) manufacturing, which removes material, this method adds material layer by layer, ensuring reduced waste and the ability to produce complex geometries.
How 3D Printing Works:
- Design Phase: A 3D digital model is created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software and saved in formats like .STL or .OBJ.
- Slicing: The model is sliced into horizontal layers using specialized software.
- Printing: The printer deposits material layer-by-layer according to the sliced file. Each layer solidifies to form the final shape.
- Post-Processing: The object is finished through processes such as curing, sanding, or painting.
Major 3D Printing Technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM): Uses melted thermoplastic filaments to build objects layer-by-layer.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses lasers to fuse powdered plastics or metals into solid forms.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Employs a laser to fuse metal powders — widely used in aerospace and medical sectors.
- Material Jetting: Deposits photopolymer droplets, cured with UV light — ideal for high-precision and colorful prototypes.
Limitations of 3D Printing:
- Material Restrictions: Only specific plastics, metals, and composites are compatible with given printers.
- Size Constraints: Limited build volume necessitates assembling larger items from smaller parts.
- Structural Weakness: Objects may have weak joints due to the layered structure, reducing suitability for high-stress uses.
- IP Challenges: Digital design files can be easily shared, posing risks of counterfeiting and intellectual property theft.
Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS)
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has notified the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS) in April 2025. It marks a strategic step in India’s ambition to become a global electronics manufacturing hub.
Key Highlights of ECMS
- Objective: To incentivize domestic production of passive electronic components and capital equipment, thus deepening India's electronics manufacturing value chain.
- Scheme Tenure: Valid for 6 years, with a 1-year gestation period.
- Focus Components: Includes resistors, capacitors, relays, switches, speakers, connectors, inductors, special ceramics, and other passive components.
- Active components are supported separately under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM).
- Incentive Structure:
- Turnover-linked incentive (based on incremental revenue).
- Capex-linked incentive (for investments in plant and machinery).
- Hybrid model (combining turnover and capex benefits).
Incentive rates range between 1–10%, varying by year and component type.
- Employment Mandate: All applicants—whether component manufacturers or capital equipment makers—must commit to job creation, ensuring broader socio-economic benefits.
Strategic Importance
- Horizontal Sectoral Impact: The scheme is designed to support multiple sectors including automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, power electronics, and electrical grids, promoting cross-industry multiplier effects.
- Support for Tooling & Capital Equipment Industry: Encourages design and manufacture of capital tools and machinery required for electronics production, in line with models seen under the India Semiconductor Mission.
- Global firms like Linde have begun operations, with more in pipeline.
India’s Electronics Growth Trajectory
- Export Milestone (FY 2024–25):
- Total smartphone exports: ?2 lakh crore
- iPhone exports alone: ?1.5 lakh crore
- Sectoral Growth (Last Decade):
- 5x growth in production.
- 6x growth in exports.
- Export CAGR: >20%
- Production CAGR: >17%
- Manufacturing Base Expansion: Over 400 production units (large and small) now manufacture a wide range of electronic components domestically.
- Value Chain Evolution: India has transitioned from assembling finished goods → sub-assemblies → deep component manufacturing, now entering a value-added, self-reliant phase in electronics
One State, One RRB Policy
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Government of India, through the Ministry of Finance, has implemented the "One State, One RRB" policy effective from May 1, 2025, aimed at consolidating 26 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) across 10 states and 1 Union Territory, thereby reducing the total number of RRBs to 28. This move follows the recommendation of the Dr. Vyas Committee and is intended to enhance the performance and outreach of RRBs.
Objectives of the Policy
- Improve operational efficiency and governance.
- Rationalize costs and optimize resources (human and technological).
- Eliminate intra-state competition among sponsor banks.
- Promote uniform service delivery through technological integration.
About Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Established: 1975 under the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976.
- Recommended by: Narasimham Committee (1975).
- Ownership Pattern:
- Government of India – 50%
- State Government – 15%
- Sponsor Bank – 35%
Regulatory Structure
- Regulated by: Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Supervised by: NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
Role and Objectives
- Provide institutional credit to rural India.
- Support priority sectors like agriculture, MSMEs, and rural artisans.
- Ensure financial inclusion among farmers, labourers, and small entrepreneurs.
Impact of the Reform
- Operational Scale: Enhanced credit delivery across wider geographies.
- Technological Standardization: Easier integration of IT infrastructure.
- Unified Governance: One sponsor bank per state improves accountability.
- Performance: RRBs recorded an all-time high net profit of ?7,571 crore in FY 2023–24.
- Asset Quality: GNPA (Gross Non-Performing Assets) stood at 6.1%, the lowest in a decade.
Poshan Pakhwada 2025 and Palna Scheme
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) is spearheading a dual approach to address malnutrition and childcare challenges in India through two flagship initiatives—Poshan Pakhwada 2025 and the Palna Scheme under Mission Shakti.
Poshan Pakhwada 2025
- 7th edition observed from April 8–22, 2025, under Poshan Abhiyaan.
- Focuses on four key themes:
- Nutrition in the first 1,000 days (conception to age two).
- Promotion of the Poshan Tracker digital platform.
- Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition (CMAM).
- Encouraging a healthy lifestyle to reduce childhood obesity.
- Poshan Tracker App (AI-enabled; launched in 2021):
- Registers all Anganwadi Centres (AWCs).
- Enables real-time monitoring of beneficiaries, meal distribution, and health data.
- Allows family self-registration via web.
- CMAM protocol (introduced in 2023): Empowers Anganwadi workers to detect and manage malnutrition at the grassroots.
- Special focus on tribal and remote areas, promoting awareness on breastfeeding, balanced diets, and early stimulation.
- Campaign supported by 18 partner ministries, with outreach via village camps, home visits, and awareness drives.
Palna Scheme under Mission Shakti
- Centrally sponsored scheme launched in 2022, succeeding the National Crèche Scheme.
- Operates under the Samarthya sub-scheme of Mission Shakti.
- Aims to provide quality crèche services for children aged 6 months to 6 years, especially for working mothers.
Key Features:
- Implemented by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD).
- Funding Ratio:
- 60:40 (Centre: State),
- 90:10 for NE and special category states.
- Two crèche models:
- Standalone Crèches near homes/workplaces.
- Anganwadi-cum-Crèches (AWCCs) integrated within Anganwadi Centres.
- Facilities Provided:
- Nutritional meals, growth monitoring, immunization.
- Early stimulation and pre-school education.
- Support for continued breastfeeding.
- Crèche Capacity: Each unit supports up to 25 children.
- As of March 2025:
- 11,395 AWCCs approved across 34 States/UTs; 1,761 operational, catering to ~28,783 children.
- 1,284 Standalone Crèches operational with ~23,368 children enrolled.
- 17,000 new AWCCs planned for 2024–25.
- Legal Backing: Mandated in workplaces with 50+ employees under the Maternity Benefit Act (amended).
Significance for India
Together, Poshan Pakhwada and Palna contribute to achieving SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by ensuring a lifecycle approach to nutrition and holistic early childhood care. They reflect the government's commitment to digital governance, gender empowerment, and inclusive development.
Niveshak Didi

- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant push toward inclusive financial literacy, the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, and the India Post Payments Bank (IPPB), under the Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications, have signed a Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) to launch Phase 2 of the “Niveshak Didi” initiative in April 2025.
Objective:
The Niveshak Didi initiative, launched in 2023, is a women-led, community-driven financial literacy program designed to empower rural and underserved populations by fostering responsible financial behavior, promoting digital banking, and spreading fraud awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Target Group: Rural women and semi-urban communities.
- Approach: Local women, especially postal workers, are trained as financial educators (Niveshak Didis).
- Impact of Phase 1:
- Over 55,000 beneficiaries reached, with 60% women, predominantly from deep rural areas.
- Most beneficiaries belonged to the youth and economically active age groups.
Phase 2 (2025 Onward):
- Deployment of 4,000+ financial literacy camps across rural, tribal, and semi-urban areas.
- Training of 40,000 women postal workers to serve as grassroots financial educators.
- Curriculum Focus:
- Savings and budgeting.
- Responsible investing and fraud prevention.
- Digital tools and services provided by IPPB.
- Digital Inclusion: Leveraging India Stack for paperless and presence-less banking; training delivered in 13 regional languages.
About Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- Statutory Body: Functions under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India.
- Objective: Ensures informed and protected investors across India.
- Key Role:
- Promotes financial literacy to aid budgeting, saving, and investment decisions.
- Empowers citizens to make sound financial choices.
- Focus Areas:
- Educates citizens on investor rights and responsibilities.
- Special outreach to rural and underserved areas to bridge financial knowledge gaps.
- Vision: To build a financially aware and confident India, where every citizen has the tools to secure their financial future.
About India Post Payments Bank (IPPB)
- Established: On September 1, 2018 under the Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications.
- Ownership: 100% equity owned by the Government of India.
- Mission: To be the most accessible, affordable, and trusted bank for the common man.
- Mandate:
- Bridge financial inclusion gaps for the unbanked and underbanked.
- Leverage the vast postal network of approx. 1.65 lakh post offices (1.4 lakh in rural areas) and 3 lakh postal employees.
- Technology Backbone:
- Based on India Stack: Paperless, Cashless, and Presence-less banking.
- Uses CBS-integrated smartphones and biometric devices.
- Commitment:
- Promotes a less-cash economy.
- Supports the vision of Digital India.
- Motto: Every customer is important, every transaction is significant, every deposit is valuable.
India Skills Accelerator Initiative (2025)

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) has partnered with the World Economic Forum (WEF) to launch the India Skills Accelerator—a national-level public-private collaboration platform aimed at fostering a future-ready and inclusive workforce.
Key Features:
- Purpose: To act as a systemic change enabler in India's skilling ecosystem through a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral approach.
- Core Objectives:
- Enhance awareness and shift mindsets about the need for future skills.
- Promote collaboration and knowledge sharing between government, industry, and academia.
- Reform policies and institutional structures for an agile and responsive skilling framework.
- Sectoral Priorities:
- Focus on high-growth areas: AI, robotics, cloud computing, cybersecurity, advanced manufacturing, energy, and Global Capability Centres (GCCs).
- Emphasis on formalizing the informal workforce.
- Lifelong Learning: Mobilize investments in upskilling and reskilling across various life stages to support agile career transitions.
- Data-Driven Governance: Use surveys, mapping tools, and the WEF’s Global Learning Network for peer benchmarking and progress tracking.
- Implementation Strategy:
- Identify 10–12 high-impact priorities with measurable outcomes.
- Establish thematic working groups to ensure coordinated execution.
- Align initiative with the WEF’s Future of Jobs Report 2025.
Significance
- Addresses the fact that 65% of organizations cite skill gaps as a major barrier to growth.
- Positions India to leverage its demographic dividend and become the "Skill Capital of the World".
- Supports India's goal of skilling not just for domestic needs but also for global workforce demand.
- Reinforces federal cooperation, involving institutions like NSDC, NCVET, DGT, UGC, AICTE, NCERT, and CBSE.
Quantum Supremacy Demonstrated via Simple Game
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
Researchers from the University of Oxford and Universidad de Sevilla have demonstrated quantum supremacy using a simple mathematical game based on the odd-cycle graph colouring problem. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, marks a significant milestone in quantum computing.
What is Quantum Supremacy?
Quantum supremacy refers to the ability of a quantum computer to perform a task that is practically impossible for classical computers to solve efficiently. This advancement showcases the unique capabilities of qubits, which leverage two core principles:
- Superposition: Qubits can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- Entanglement: Measurement of one qubit instantly affects another, even over a distance.
These principles enable exponential scaling of computational power. For instance, a 50-qubit quantum computer could potentially outperform the most powerful classical supercomputers.
The Odd-Cycle Game: A Novel Approach
The team implemented a game inspired by graph theory:
- Players (Alice and Bob) are tasked with colouring an odd-numbered cycle (e.g., triangle) using only two colours such that adjacent points differ in colour.
- Mathematically, this is impossible in classical terms for odd cycles due to inevitable repetition of colours.
In the experiment:
- Two strontium atoms placed 2 meters apart were entangled using lasers.
- A referee sent each atom a "question" (mapped to a point on the cycle).
- Players performed quantum operations based on the questions and returned either 0 or 1 (representing colours).
The experiment was repeated 101,000 times, covering circles from 3 to 27 points.
Results and Significance
- Classical win rate: 83.3% for 3-point cycles.
- Quantum win rate: 97.8%, clearly surpassing classical limits.
- Quantum supremacy was evident up to 19-point circles.
- The entanglement correlation was the strongest ever recorded between two separated quantum systems.
Comparison with Previous Demonstrations
- Google’s Sycamore (2019): Used 53 superconducting qubits for a complex problem called random circuit sampling.
- China’s Jiuzhang: Used Gaussian boson sampling.
- In contrast, this new approach used just two entangled qubits, making it simpler, efficient, and easier to verify.
Practical Implications
This simplified game-based model of quantum advantage could have real-world applications in problems where coordination is needed without communication—such as the "rendezvous problem". Quantum systems can dramatically reduce search steps compared to classical ones (e.g., Grover’s algorithm can reduce 1 million steps to 1,000).
ESA Biomass Satellite Mission
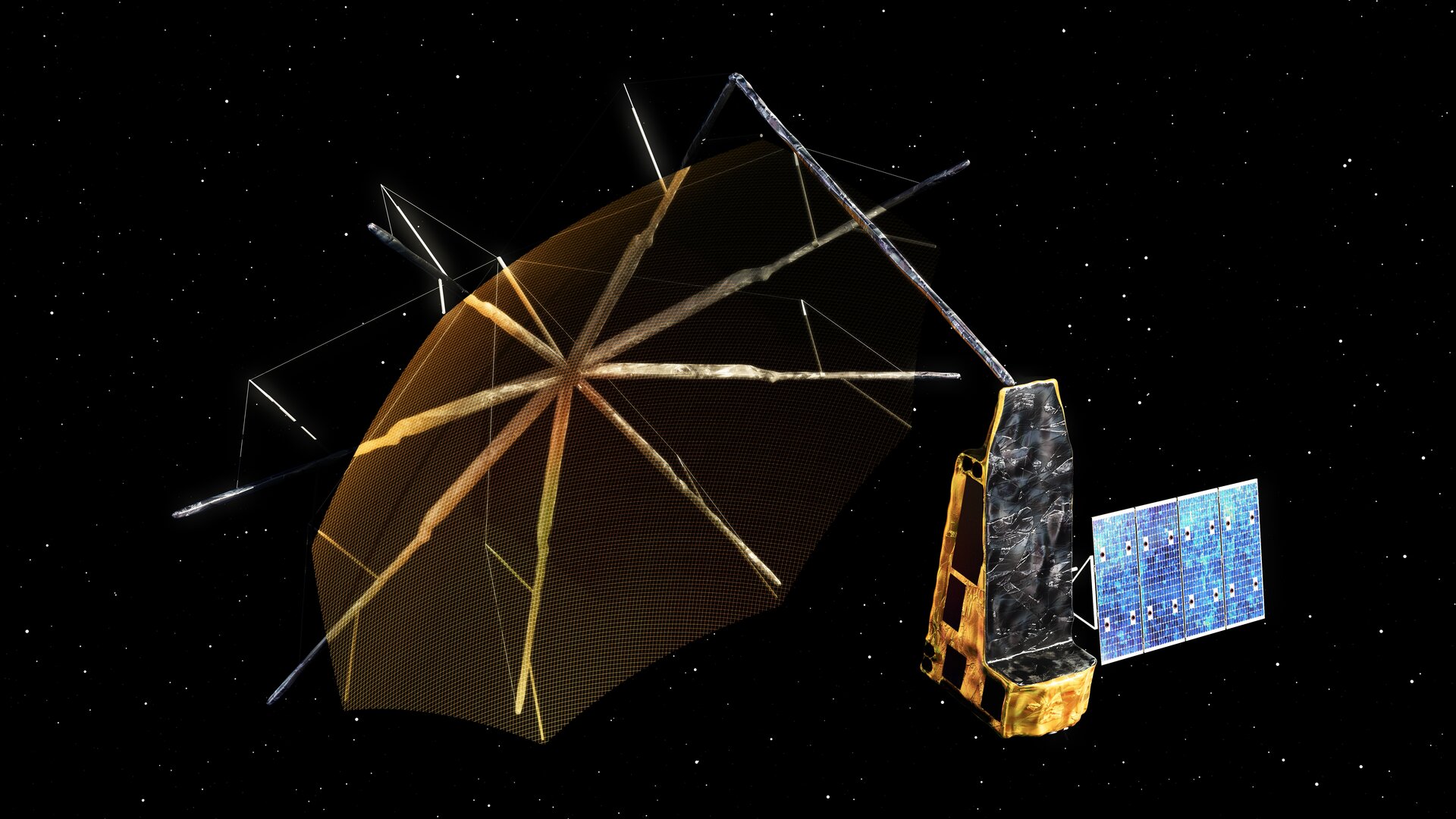

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Biomass Mission is a new Earth observation mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) aimed at enhancing our understanding of the global carbon cycle through accurate forest biomass measurements.
Launch Details:
- Rocket: Vega-C
- Launch Site: Europe’s Spaceport, French Guiana
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of ~666 km
- Scheduled Launch Date: 29 April 2025 (subject to final checks)
Key Features:
- First satellite to use P-band radar (long-wavelength synthetic aperture radar).
- Capable of penetrating dense forest canopies to scan tree trunks, branches, and stems — where most of a tree’s carbon is stored.
- Will generate 3D maps of the world’s tropical forests.
Mission Objectives:
- Measure above-ground forest biomass and forest height.
- Create five global biomass maps over its five-year mission.
- Monitor changes in forests to assess their role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
Scientific Importance:
- Forests absorb ~8 billion tonnes of CO? annually and are often referred to as "Earth’s green lungs."
- By analyzing forest carbon storage and changes, the mission will contribute significantly to:
- Monitoring climate change
- Supporting carbon accounting
- Improving air quality assessments
Phases of the Mission:
- Initial Phase: Produces detailed 3D forest maps globally.
- Second Phase: Generates global estimates of forest height and biomass.
Relevance to Climate Action:
- Helps in quantifying carbon uptake and release.
- Supports global climate models and carbon budgeting.
- Aids in policy-making for sustainable forest management.
Theobaldius konkanensis
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A new species of land snail, Theobaldius konkanensis, has been discovered by a collaborative team of Indian and UK researchers from the Konkan region of Maharashtra. This species adds to the growing biodiversity records of the northern Western Ghats, a globally recognized but under-explored biodiversity hotspot.
Key Facts at a Glance
- Scientific Name: Theobaldius konkanensis
- Discovered in: Ratnagiri and Raigad districts, Maharashtra (Dev Gireshwar Temple, Uttamrao Patil Biodiversity Garden, Kesharnath Vishnu Temple, and Phansad Sanctuary)
- Elevation: 80–240 metres above sea level
- Habitat: Tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests
- Active Months: June to September (monsoon); only shells visible in other months
- Habits: Active both day and night, often under forest canopy in shaded, moist leaf litter
Morphological Features
- Shell Characteristics:
- Slightly flattened with a raised centre and deep triangular notch near the aperture
- Operculum (protective cover) has raised whorl edges and short spines
- Corneous yellow with brown striations
- Thick, conoidally depressed, and widely umbilicated
- Body: Stout and rounded
Taxonomic Context
- Family: Cyclophoridae (Caenogastropoda)
- Genus: Theobaldius
- Now includes 20 species: 9 in India, 11 in Sri Lanka, and 1 in Sumatra (Indonesia)
- In India, 6 species are endemic to the Western Ghats
- Only T. annulatus is found in both Sri Lanka and the Western Ghats
Ecological and Conservation Significance
- Bioindicators: Land snails are sensitive to climatic changes and environmental disturbances
- Endemism: T. konkanensis is restricted to specific forest patches in the Konkan, highlighting the ecological uniqueness of the region
- Threats: Increasing anthropogenic pressures and habitat degradation threaten snail species with restricted distribution
Reproductive Biology (General Traits of Land Snails)
- Breeding mainly in monsoon
- Reproduce through both cross- and self-fertilisation
- Courtship includes dart-shooting behavior; mating may last hours
- Eggs laid in moist soil or leaf litter; hatch in 2–4 weeks
- Lifespan: 2 to 7 years
De-Extinction
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A US biotech company, Colossal Biosciences, claims to have genetically engineered three grey wolf pups to carry traits of the extinct dire wolf, calling it a de-extinction.
What is De-Extinction?
De-extinction is the process of reviving extinct species using advanced biotechnological methods such as:
- Gene editing (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9),
- Cloning (e.g., somatic cell nuclear transfer),
- Ancient DNA sequencing and genome reconstruction,
- Synthetic biology to reintroduce key traits of extinct organisms.
Colossal Biosciences and the Dire Wolf Project
In late 2024, a U.S.-based biotechnology firm, Colossal Biosciences, announced the birth of three genetically engineered wolf pups—Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi—claimed to be the world’s first successful case of "functional de-extinction."
About the Dire Wolf
- Scientific name: Aenocyon dirus
- Habitat: Grasslands and forests of North America during the Pleistocene Epoch
- Extinction: ~12,500–13,000 years ago
- Characteristics: 25% larger than modern grey wolves; strong jaws to hunt megafauna like bison and horses; light-colored dense fur; social, pack-hunting predators.
Scientific Process Involved
- DNA Extraction: Ancient DNA was recovered from dire wolf fossils (13,000 to 72,000 years old).
- Genome Reconstruction: Sequencing and comparative analysis showed ~99.5% similarity between dire wolves and modern grey wolves.
- Gene Editing: Scientists edited 20 genes in grey wolves to replicate dire wolf traits like:
- White, thick fur
- Increased body mass
- Enhanced musculature and coat pattern
- Cloning: Modified DNA was used to create embryos via somatic cell nuclear transfer.
- Surrogacy: Embryos were implanted in large domestic dogs. Of several attempts, three pups survived.
Scientific and Ethical Concerns
- Experts argue these are not true dire wolves but genetically edited grey wolves with some dire wolf-like traits.
- Critics highlight the absence of peer-reviewed publication, limited understanding of epigenetic and behavioral factors, and the artificial environment in which the pups are raised.
- Colossal terms the process "functional de-extinction", meaning re-creating genetically and ecologically similar organisms, not exact replicas.
Ecological and Conservation Relevance
- Colossal claims the technology could help endangered species like the red wolf (native to the southeastern U.S.), threatened by habitat loss and hybridization with coyotes.
- Four clones of red wolf–coyote hybrids have been produced with potential use in restoring genetic diversity.
- The company aims to democratize conservation biotechnology, pledging to share tools with global conservationists and working with Native American communities.
Contemporary Debates
- Over 60 environmental groups have protested proposed U.S. legislation to delist grey wolves from the Endangered Species Act, warning of ecological consequences.
- Scientists urge caution, stressing that true resurrection of extinct species requires more than gene editing, as behavior, evolutionary context, and environmental adaptation cannot be synthetically replicated.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched two major global initiatives to advance inclusive and sustainable agrifood systems:
- “Four Betters Courses” Initiative – To revolutionize agrifood systems education
- “Commit to Grow Equality” Initiative – To bridge the gender gap in agrifood sectors
1. Four Betters Courses Initiative
- Launched: October 2024 during the World Food Forum
- Objective: To integrate FAO’s expertise into global agrifood systems education through partnerships with universities and academic networks.
- Alignment: Anchored in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031
Core Philosophy – The “Four Betters” Approach:
- Better Production – Promote efficient, inclusive, and resilient food systems
- Better Nutrition – Ensure access to safe, nutritious, and affordable diets
- Better Environment – Address climate change and protect ecosystems
- Better Life – Improve rural livelihoods and reduce inequalities
- Delivery Platform: Implemented through the FAO eLearning Academy, which provides over 600 multilingual, certified courses.
2. Commit to Grow Equality (CGE) Initiative
- Launched: 2024 on the platform of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- Objective: To narrow the gender gap in agrifood systems and enhance women’s empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Key Highlights:
- Aims to benefit over 54 million women worldwide
- Mobilizes $1 billion in investments toward gender-responsive agrifood initiatives
- Provides strategic tools for tracking gender equality outcomes in public and private sectors
- Promotes gender-aligned national agricultural policies
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking and fosters collaboration across governments, NGOs, and the private sector
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY), a flagship initiative aimed at providing financial support to unfunded micro and small enterprises, has completed 10 years since its launch in 2015.
Overview of PMMY
- Objective: To offer collateral-free institutional credit to non-corporate, non-farm micro and small enterprises.
- Loan Limit: Up to ?20 lakh without any collateral.
- Implementing Institutions (MLIs):
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Categories of MUDRA Loans
Loan Category Loan Amount Range
Shishu Up to ?50,000
Kishor ?50,000 to ?5 lakh
Tarun ?5 lakh to ?10 lakh
Tarun Plus ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh
Key Achievements (2015–2025)
- Boost to Entrepreneurship: PMMY has sanctioned over 52 crore loans amounting to ?32.61 lakh crore, catalyzing a grassroots entrepreneurship revolution.
- MSME Sector Financing: Lending to MSMEs increased significantly:
- From ?8.51 lakh crore in FY14
- To ?27.25 lakh crore in FY24
- Projected to exceed ?30 lakh crore in FY25
- Women Empowerment: 68% of Mudra beneficiaries are women, highlighting the scheme’s impact in fostering women-led enterprises.
- Social Inclusion:
- 50% of loan accounts are held by SC, ST, and OBC entrepreneurs.
- 11% of beneficiaries belong to minority communities, showcasing PMMY’s contribution to inclusive growth.
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
World Health Day 2025
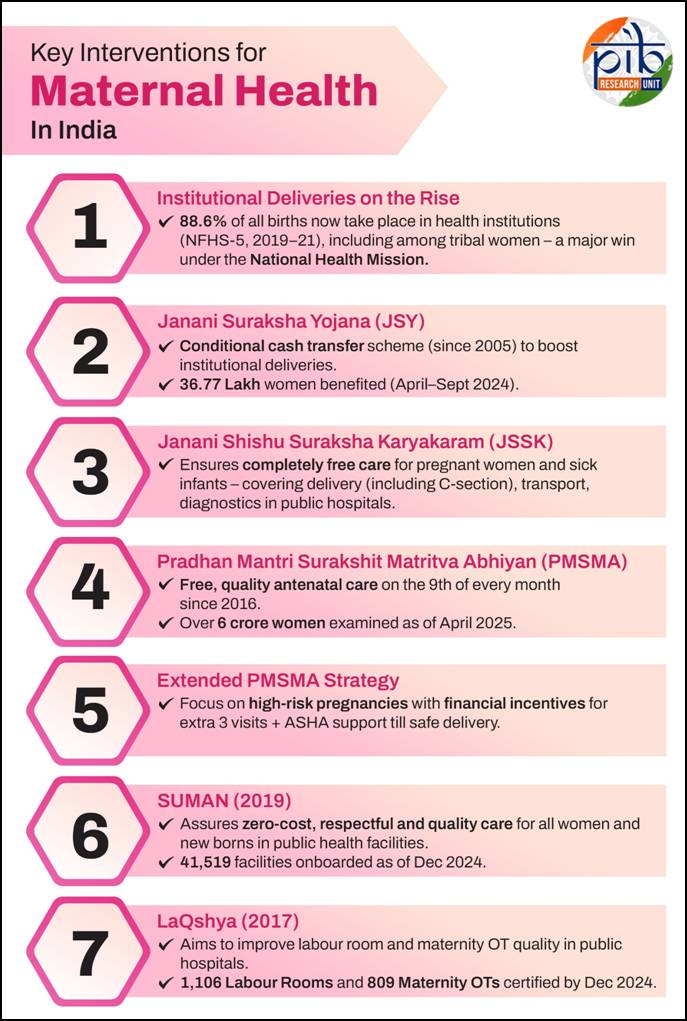
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
World Health Day, observed annually on 7 April, highlights pressing global health issues and mobilises action to improve public health outcomes.
- Established by: World Health Organization (WHO)
- First celebrated: 1950
Overview and Significance
World Health Day is commemorated to mark the founding of the WHO in 1948. It serves to raise awareness about global health issues and mobilize efforts to improve public health outcomes.
The 2025 theme, Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures, emphasizes maternal and newborn health, calling for coordinated efforts to eliminate preventable deaths and support long-term well-being of women and children.
This year’s observance launches a year-long global campaign aimed at:
- Promoting safe pregnancies and institutional deliveries
- Supporting maternal nutrition and postnatal care
- Encouraging healthcare equity for women and newborns
India’s Progress in Maternal and Child Health
India has made significant strides through initiatives under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, particularly via Ayushman Bharat and the National Health Mission (NHM).
Key Health Indicators (India vs Global, 1990–2020)
Indicator India Reduction (%) Global Reduction (%)
Maternal Mortality Ratio 83% 42%
Neonatal Mortality Rate 65% 51%
Infant Mortality Rate 69% 55%
Under-5 Mortality Rate 75% 58%
Recent National Data:
- MMR reduced from 130 (2014–16) to 97 (2018–20) per 1,00,000 live births
- IMR dropped from 39 (2014) to 28 (2020)
- NMR reduced from 26 (2014) to 20 (2020)
- U5MR declined from 45 (2014) to 32 (2020)
Major Initiatives for Maternal and Child Health
- Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR): Tracks maternal deaths and implements corrective measures.
- Mother and Child Protection (MCP) Card: Educates women on nutrition, rest, and health entitlements.
- Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Portal: Tracks maternal and child health services.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat: Focuses on anaemia reduction under POSHAN Abhiyan.
- Birth Waiting Homes: Ensures institutional deliveries in remote areas.
- VHSNDs and Outreach Camps: Deliver maternal and child services in rural and tribal areas.
Healthcare Access and Infrastructure
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (HWCs): 1.76 lakh active centers
- 107.10 crore screenings for hypertension
- 94.56 crore screenings for diabetes
- 5.06 crore wellness sessions (e.g., yoga) conducted
- 17,000+ health facilities certified under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
Digital Health Ecosystem
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- 76+ crore ABHA IDs
- 5.95 lakh verified healthcare professionals
- 52+ crore linked health records
- U-WIN Platform:
- 7.90 crore beneficiaries
- 1.32 crore vaccination sessions
- 29.22 crore vaccine doses administered
- eSanjeevani Telemedicine:
- Over 36 crore consultations
- World's largest primary telehealth platform
- 130+ specialities, 131,793 spokes, and 17,051 hubs
Disease Elimination Success
- The WHO World Malaria Report 2024 highlights India’s major strides in malaria elimination, with a 69% drop in cases and 68% reduction in deaths between 2017 and 2023.
- Contributing just 0.8% of global cases in 2023, India’s exit from WHO's High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group in 2024 marks a significant public health achievement.
- The Government of India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem in 2024, a feat recognised by the WHO.
- The Government of India’s proactive Measles-Rubella vaccination drive, strong surveillance, and public awareness efforts have greatly improved public health.
- According to WHO’s Global TB Report, India has made strong progress in tuberculosis control.
- Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), TB incidence fell by 17.7%, from 237 to 195 cases per lakh population between 2015 and 2023.
- TB-related deaths also declined from 28 to 22 per lakh.
- Notably, missing TB cases dropped by 83%, from 15 lakh in 2015 to 2.5 lakh in 2023.
- As of 6th April, 2025, the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan, launched in September 2022, has registered over 2.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitra volunteers supporting over 15 lakh TB patients. This initiative has further been expanded to include family members of TB patients.
- Kala-azar Elimination: India has successfully achieved Kala-azar elimination as of October 2024, with 100% of endemic blocks reaching the target of less than one case per 10,000 population by the end of 2023.
INS Varsha
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, its first dedicated base for nuclear-powered submarines, by 2026. Located near Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, this high-security facility is part of the classified Project Varsha, aimed at strengthening India’s maritime and nuclear deterrence capabilities in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Key Features:
- Strategic Location: Near deep waters of the Bay of Bengal, facilitating stealthy submarine movement and minimizing detection.
- Infrastructure:
- Underground pens and tunnel systems to conceal and protect nuclear submarines.
- Inner and outer harbour facilities; inner harbour completed, work ongoing on breakwaters and jetties.
- 20 sq. km area, capacity to house at least 10–12 nuclear submarines.
- Stealth Capabilities: Similar to China’s Hainan base, it offers satellite-evasion advantages, crucial for the survivability of SSBNs (nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines).
- Support Facilities: Proximity to BARC Atchutapuram for nuclear infrastructure, enabling swift integration and maintenance of strategic assets.
- Geopolitical Role: Counters Chinese dual-use naval infrastructure at Hambantota (Sri Lanka) and BNS Sheikh Hasina (Bangladesh).
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances second-strike capability, vital for nuclear deterrence under India's nuclear triad.
- Enables undetected deterrent patrols by SSBNs, ensuring survivability in case of counterforce attacks.
- Facilitates rapid access to key chokepoints, especially the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Expanding Nuclear Submarine Fleet
INS Aridhaman – Third SSBN:
- Scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- 7,000-tonne displacement, more capable than predecessors INS Arihant and INS Arighat.
- Equipped with K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) with a range of 3,500 km.
- Built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project by Shipbuilding Centre, Visakhapatnam, with BARC and DRDO support.
- Designed for long-duration deterrent patrols in deep sea.
Future Developments:
- India launched its fourth SSBN in November 2024, with ~75% indigenous content.
- Plans underway for even larger SSBNs and the construction of six nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), starting with two approved 9,800-tonne SSNs for conventional strike and escort roles.
Related Naval Expansion – Project Seabird (Karwar Base):
- Located on the western coast, expanding to accommodate 50 warships and submarines, plus 40 auxiliary vessels.
- Will include a dual-use air station, new dockyard, and multiple dry berths.
