Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
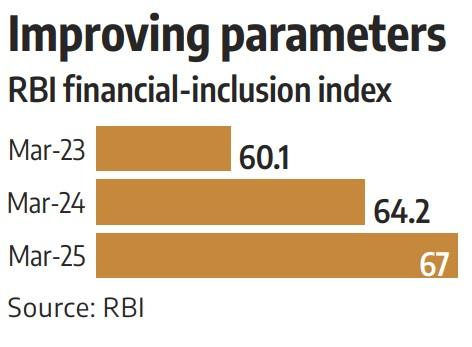
The Reserve Bank of India’s Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) saw a 4.3% rise in FY2024-25, climbing from 64.2 in March 2024 to 67 in March 2025. This growth signals India’s ongoing success in expanding access to financial services, particularly in underserved regions, and enhancing the depth and quality of financial inclusion.
Understanding Financial Inclusion
- Financial inclusion refers to ensuring that individuals and businesses have accessible, affordable, and appropriate financial services such as banking, insurance, pensions, and investments. These services should be delivered responsibly and sustainably, supporting long-term economic empowerment.
What is the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)?
- Developed by the RBI, the FI-Index offers a comprehensive measure of financial inclusion in India. It was formulated in consultation with the government and relevant financial sector regulators and captures progress across diverse financial domains—including banking, insurance, postal services, investments, and pensions.
- The Index is expressed as a single score between 0 and 100, where 0 denotes complete exclusion and 100 indicates full financial inclusion.
Components of the FI-Index
- Access (35% weight): Availability of financial services to the public.
- Usage (45% weight): Frequency and extent of usage of financial services.
- Quality (20% weight): Incorporates factors such as financial literacy, consumer protection, and equality in service delivery.
Key Insights from FY2024–25
- The FI-Index rose to 67 in March 2025, indicating broader and deeper financial engagement.
- All three sub-indices—access, usage, and quality—showed improvement.
- Notably, the rise was primarily driven by enhanced usage and service quality, reflecting the success of financial literacy campaigns and improved consumer trust in financial systems.
Importance of Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion is not just an economic tool—it is a developmental imperative. It:
- Fuels entrepreneurship and employment generation.
- Advances gender empowerment, especially among women-led households.
- Helps in poverty alleviation and the resilience of vulnerable groups against financial and climate-related shocks.
- Supports at least seven of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including reducing inequalities and promoting inclusive economic growth.
Major Government Initiatives Driving Financial Inclusion
India's focused efforts have resulted in widespread access to formal financial services:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Over 54.58 crore bank accounts opened; deposits crossed ?2.46 lakh crore by January 2025.
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Enrolments surged to 7.33 crore, with 89.95 lakh new subscribers in FY25 alone.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): Covered 22.52 crore people, disbursing over ?17,600 crore for 8.8 lakh claims.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Provided insurance to 49.12 crore individuals, settling claims worth ?2,994.75 crore.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Sanctioned loans worth ?32.36 lakh crore across 51.41 crore accounts; 68% to women and 50% to SC/ST/OBC beneficiaries.
- Stand-Up India Scheme: Loans worth ?53,609 crore sanctioned to 2.36 lakh entrepreneurs, promoting SC/ST and women entrepreneurship.
