Gitchak nakana
- 02 Mar 2026
In News:
A new species of groundwater-dwelling fish, Gitchak nakana, has recently been discovered in Assam. The species was found in a dug-out well and represents the first aquifer-dwelling (phreatobitic) fish recorded from Northeast India. This discovery adds to India’s growing record of endemic and subterranean biodiversity.
About Gitchak nakana
- Type: Groundwater (aquifer-dwelling) fish
- Family: Cobitidae (Loaches)
- Genus: Newly described genus
- Size: Approximately 2 cm in length
- Habitat: Subterranean aquifers
- Location of Discovery: Assam
The species was discovered in a dug-out well, indicating its existence in underground water systems rather than surface water bodies such as rivers or ponds.
Etymology
The name reflects local linguistic heritage:
- “Gitchak” (Garo language) – means red, referring to its striking blood-red colour when alive.
- “Na-tok” / “kana” – refer to a blind fish.
The nomenclature highlights both the species’ morphology and its cultural-geographical context.
Unique Morphological Features
Gitchak nakana displays classic troglomorphic adaptations — traits evolved for life in complete darkness:
- Absence of externally visible eyes (blindness)
- Translucent, pigmentless body
- Extreme miniaturization (only 2 cm long)
- Complete absence of skull roof — the brain is covered dorsally only by skin
The lack of a skull roof is particularly unusual and makes it one of the most anatomically distinctive loach species recorded.
What are Phreatobitic Species?
- Phreatobitic organisms live in groundwater aquifers rather than surface water or caves.
- Aquifers are underground water-bearing geological formations.
- Such habitats are difficult to access and poorly studied, which explains why discoveries are rare.
Globally:
- More than 300 fish species are known from subterranean habitats.
- However, the vast majority inhabit caves.
- Less than 10% are known from groundwater aquifers, making this discovery scientifically significant.
Thus, Gitchak nakana represents a rare addition to the small global group of true aquifer-dwelling fishes.
Forest Owlet

- 02 Mar 2026
In News:
Recently, the Forest Owlet was sighted in Kuno National Park, Madhya Pradesh, marking its reappearance in the region 113 years after it was last recorded there. The species had not been seen in Kuno since the early 20th century, making this rediscovery ecologically significant. The development strengthens Kuno’s biodiversity profile, which has already gained prominence due to the cheetah reintroduction programme.
About the Forest Owlet
- Scientific Name: Athene (Heteroglaux) blewitti
- Family: Strigidae (typical owl family)
- First Described: 1873
- Presumed Extinct: After 1884 due to lack of sightings
- Rediscovered: 1997 in central India
The Forest Owlet was long considered extinct because it was not recorded for over a century after the late 19th century. Its rediscovery in 1997 was a landmark event in Indian ornithology, underscoring the importance of systematic biodiversity surveys.
Habitat and Ecology
Habitat
The species primarily inhabits:
- Tropical and subtropical moist lowland forests
- Dense deciduous woodlands
- Open dry deciduous teak forests
- Tropical and subtropical dry forests
It shows preference for dry deciduous forest ecosystems, especially those dominated by teak.
Distribution
The Forest Owlet is endemic to central India, meaning it is found nowhere else in the world.
Recorded populations exist in:
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra (notably Melghat Tiger Reserve)
- Odisha
- Chhattisgarh
- Gujarat
The recent sighting in Kuno National Park strengthens evidence of its fragmented but surviving populations across central Indian landscapes.
Physical Characteristics
The Forest Owlet has distinctive morphological features:
- Relatively unspotted crown
- Prominent white throat collar
- Thickly feathered legs
- Heavily banded wings and tail
Unlike many owls that are nocturnal, the Forest Owlet is diurnal (active during the day), which makes it relatively easier to observe compared to other owl species.
Diet and Behaviour
- Primarily feeds on rodents
- Also consumes lizards, skinks, and insects
- Hunts during daylight hours
- Typically seen perched on exposed branches while scanning for prey
Its diurnal nature and specific habitat requirements make it vulnerable to habitat degradation.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I (highest level of international trade protection)
The species faces threats from:
- Habitat loss due to deforestation
- Fragmentation of dry deciduous forests
- Agricultural expansion
- Developmental activities in central India
Given its limited distribution and small population size, conservation of intact forest patches in central India is critical for its survival.
National Science Day 2026

- 01 Mar 2026
In News:
National Science Day is observed every year on 28th February to commemorate the discovery of the Raman Effect by eminent Indian physicist Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman in 1928. The day serves as a reminder of India’s scientific legacy and the importance of fostering innovation and research in nation-building.
The year 2026 theme - “Women in Science: Catalyzing Viksit Bharat” - emphasizes the role of women scientists in advancing India’s journey towards becoming a developed nation.
Historical Background
- Sir C.V. Raman discovered the Raman Effect on 28 February 1928.
- For this groundbreaking work, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, becoming the first Asian to receive a Nobel Prize in the sciences.
- The first National Science Day was celebrated on 28 February 1987, institutionalizing the observance as an annual tradition to promote scientific awareness.
The primary objective of National Science Day is to spread awareness about the importance of science and its applications in everyday life and national development.
The Raman Effect
The Raman Effect refers to a phenomenon in which:
- When a beam of light passes through a transparent medium (such as a liquid or gas),
- A small portion of the scattered light undergoes a change in wavelength.
This shift in wavelength occurs due to the interaction between light and the vibrational and rotational energy levels of molecules in the medium.
The discovery laid the foundation for Raman Spectroscopy, a powerful analytical tool widely used in physics, chemistry, material science, and medical diagnostics.
Contributions of Sir C.V. Raman
Sir C.V. Raman made significant contributions to scientific research and institution-building in India:
- Founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926 to promote indigenous scientific research.
- Became the first Indian Director of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, in 1933, strengthening India’s research ecosystem.
- Established the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in 1948, which continues to be a leading centre for fundamental research.
- Awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1954, India’s highest civilian honour.
His life exemplified scientific excellence combined with institution-building for long-term national progress.
Theme 2026: Women in Science and Viksit Bharat
The 2026 theme highlights:
- The need to enhance women’s participation in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields.
- Recognition of women scientists as key drivers of innovation, research, and technological advancement.
- Alignment with the broader vision of “Viksit Bharat” (Developed India) by 2047.
Encouraging gender equity in science contributes to inclusive growth, diverse perspectives in research, and sustainable development outcomes.
Significance
National Science Day promotes:
- Development of scientific temper, as envisaged under Article 51A(h) of the Constitution (Fundamental Duties).
- Awareness about research and innovation ecosystems in India.
- Engagement of students, researchers, and institutions in scientific pursuits.
- Public understanding of science as a tool for socio-economic transformation.
Grid Oscillations

- 01 Mar 2026
In News:
A recent grid oscillation recorded in Rajasthan was reportedly felt as far as Kudankulam, Tamil Nadu, highlighting the growing stress within India’s national electricity grid. The incident has drawn attention to structural challenges in managing the rapid expansion of renewable energy while ensuring grid stability.
What are Grid Oscillations?
Grid oscillations refer to rapid fluctuations in voltage and frequency within the power transmission network. These fluctuations typically arise when there is a sudden mismatch between electricity generation and demand.
With increasing penetration of solar and wind energy, which are inherently variable and weather-dependent, the grid faces intermittent supply conditions. When not balanced properly, such variations can:
- Destabilise transmission voltage and frequency
- Damage equipment
- Trigger cascading failures
- Lead to large-scale blackouts
The recent oscillation event underscores the sensitivity of interconnected grids across long distances in India’s unified national grid.
Key Reasons for Grid Instability
- Limited Grid Flexibility and Automation: India’s grid is not yet sufficiently “smart” to seamlessly switch between conventional (coal-based) and renewable sources. Inadequate automation, limited real-time balancing mechanisms, and weak forecasting systems restrict efficient load management.
- Coal Plant Inflexibility: Coal-fired power plants are designed primarily for baseload supply, operating at steady output levels. They cannot ramp up or down rapidly to compensate for sudden drops or surges in renewable generation. This structural rigidity makes balancing intermittent sources difficult.
- Inadequate Energy Storage Infrastructure: Large-scale battery storage and pumped hydro facilities remain limited. Without sufficient storage:
- Surplus renewable energy cannot be stored for later use.
- Sudden drops in renewable output create supply gaps.
- Grid stability becomes vulnerable during peak fluctuations.
India’s Renewable Energy Expansion
India has made significant strides in renewable energy capacity:
- 48 GW of renewable capacity was added in 2025, the highest-ever annual addition.
- Non-fossil sources now account for approximately 52% of installed capacity (around 264 GW).
However, a critical structural gap remains:
- Despite the large installed renewable capacity, nearly 75% of actual electricity generation still comes from coal because it provides reliable, on-demand power.
This highlights the distinction between installed capacity and actual generation share, an important concept for energy policy analysis.
Structural and Policy Implications
- Need for Smart Grid Modernisation: Deployment of advanced forecasting tools, AI-based load management, and automated switching systems is essential to manage renewable variability.
- Flexible Thermal Operations: Retrofitting coal plants for flexible operations can improve ramping capability and support renewable balancing.
- Energy Storage Expansion: Investment in:
- Grid-scale battery storage
- Pumped hydro storage
- Green hydrogen-based storage is critical for long-term stability.
- Grid Infrastructure Strengthening: Transmission upgrades under initiatives like the Green Energy Corridors must be accelerated to integrate renewable-rich regions with demand centres.
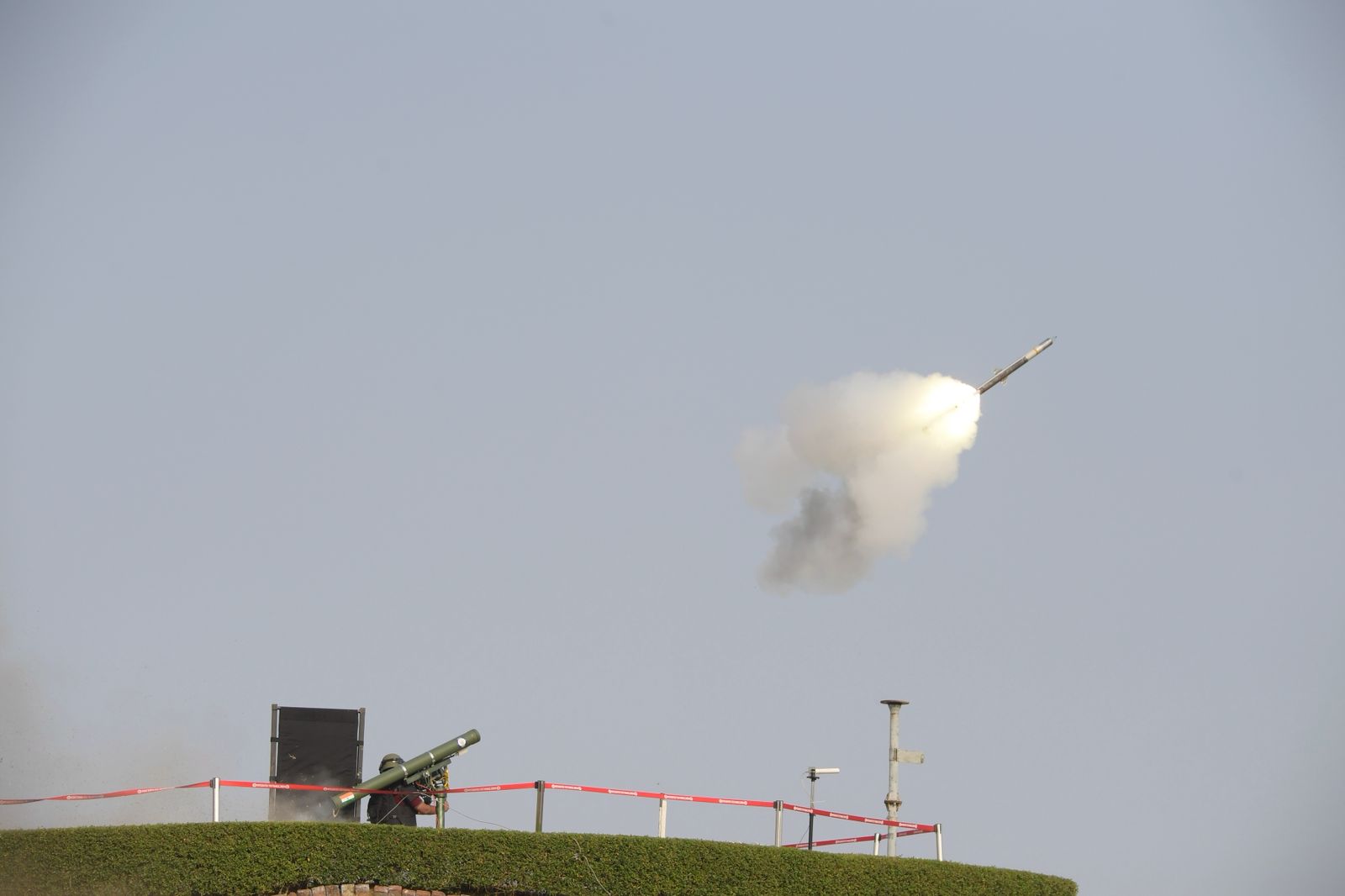
Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)

- 01 Mar 2026
In News:
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted three consecutive flight trials of the indigenously developed Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The successful trials mark a significant milestone in India’s efforts to enhance self-reliance in defence manufacturing under the broader framework of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
About VSHORADS
- VSHORADS is a Man-Portable Air Defence System (MANPADS) designed to neutralise low-altitude aerial threats.
- It has been indigenously designed and developed by Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad, in collaboration with other DRDO laboratories and Development-cum-Production Partners.
- The system is intended to strengthen India’s last-mile air defence capability, particularly against fast-moving and low-flying targets.
Key Features
- Portable and Lightweight System: VSHORADS is a short-range, lightweight surface-to-air missile system that can be deployed by an individual soldier or a small tactical unit, ensuring mobility and rapid response.
- Operational Range and Altitude
- Maximum range: Up to 8 km
- Engagement altitude: Up to 4.5 km
This makes it suitable for neutralising helicopters, drones, and low-flying aircraft.
- Advanced Technological Components: The missile incorporates several modern technologies, including:
- Miniaturised Reaction Control System (RCS)
- Integrated avionics package
The Reaction Control System (RCS) plays a crucial role in missile manoeuvrability. It enables precise attitude control and steering by using thrusters to provide controlled directional thrust. This enhances accuracy, especially during terminal engagement.
- Tri-Service Utility: The system is capable of meeting the operational requirements of all three armed forces —
- Indian Army
- Indian Navy
- Indian Air Force
Strategic Significance
- Boost to Indigenous Defence Capability: VSHORADS reduces dependency on imported MANPADS systems and strengthens India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Enhanced Tactical Air Defence: It fills a critical gap in short-range air defence, particularly against:
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
- Low-flying fighter aircraft
- Attack helicopters
- Precision-guided munitions
- Force Multiplier in Modern Warfare: With the increasing use of drones and low-altitude aerial threats in contemporary conflicts, portable air defence systems are essential for protecting forward posts, mobile formations, and strategic assets.
- Alignment with Integrated Air Defence Architecture: VSHORADS complements India’s layered air defence structure, which includes systems such as Akash, MR-SAM, and S-400, thereby strengthening multi-tiered protection.
Exercise Vayu Shakti-26
- 01 Mar 2026
In News:
Exercise Vayu Shakti-26 is a major biennial operational exercise conducted by the Indian Air Force (IAF) to demonstrate its readiness, combat potential, and integration of modern air power systems. Held recently at the Pokhran field firing range near Jaisalmer in Rajasthan, the exercise forms a critical part of India’s military preparedness framework against evolving multi-domain threats.
Objectives and Operational Focus
The primary aim of Vayu Shakti-26 was to validate the IAF’s ability to undertake complex, integrated air operations under realistic battlefield conditions. Built around the core values of “Achook, Abhedya aur Sateek” (Unerring, Invincible and Accurate), the exercise focused on:
- Enhancing operational preparedness in dynamic scenarios,
- Demonstrating tactical agility with rapid deployment and sustained operations,
- Integrating air defence, offensive air strikes, special operations, and support missions,
- Reassuring national security and deterrence postures.
For the first time, the exercise was conducted along a defined operational storyline, transforming static drills into a simulated live combat theatre, thereby enhancing realism and cohesive force application.
Scale and Platforms
Vayu Shakti-26 witnessed the participation of more than 130 aircraft representing a wide spectrum of IAF capabilities across different mission domains. This included:
- Combat aircraft: Rafale, Su-30MKI, Mirage-2000, MiG-29, Jaguar,
- Trainer and support platforms: Hawk aircraft,
- Transport and logistical support: C-130J Super Hercules, C-295, C-17 Globemaster III,
- Helicopter assets: Mi-17, indigenous Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Dhruv, and Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) Prachand.
Weapon Systems and Technological Integration
The exercise showcased several cutting-edge weapon systems and defensive technologies operationalised by the IAF:
- Short Range Loitering Munitions (SRLM) – providing precision strike options,
- Akash surface-to-air missile system – for medium-range air defence,
- SpyDer air defence system – capable of countering aerial threats at varied altitudes,
- Counter Unmanned Aerial Systems (CUAS) – designed to detect and neutralise hostile drones.
This integration underpins the IAF’s shift toward networked warfare capabilities, fusing sensors, shooters, and command systems for greater effectiveness.
Operational Themes and Key Demonstrations
A hallmark of Vayu Shakti-26 was the seamless synthesis of offensive and defensive air power with ground and special operations elements. Key components of the exercise included:
- Offensive air strikes against simulated high-value targets,
- Air defence operations ensuring integrity of friendly airspace,
- Special forces support missions, including insertion and extraction,
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief scenarios, reflecting operational versatility beyond conventional combat.
Such multi-role integration underscores the IAF’s role as both a deterrent and a force multiplier in national defence and crisis response.
Significance for National Security
In an era of heightened regional competition and technological transformation, Exercise Vayu Shakti-26 serves multiple strategic purposes:
- Reinforces the IAF’s operational readiness across the full spectrum of conflict,
- Demonstrates joint and integrated battle-space management capabilities,
- Validates the use of indigenous platforms alongside global systems,
- Signals resolve to adversaries while assuring domestic stakeholders of credible air power.
The exercise also offers valuable opportunities for learning and refinement of doctrines relevant to modern warfare, including multi-domain integration, high tempo operations, and adaptive command and control protocols.
ASTraM: Actionable Intelligence for Sustainable Traffic Management

- 28 Feb 2026
In News:
The recent visit of former Dutch Prime Minister Dick Schoof to the Bengaluru Traffic Management Centre has brought international attention to ASTraM (Actionable Intelligence for Sustainable Traffic Management) - an AI-driven traffic governance platform. The system represents a shift toward predictive, data-driven urban traffic management in India’s rapidly expanding metropolitan cities.
What is ASTraM?
ASTraM is an advanced AI-based big data platform designed for macro-level traffic management.
Unlike traditional GPS-based applications that only display real-time congestion to commuters, ASTraM functions as a centralised intelligence engine for city authorities. It provides holistic, real-time situational awareness and predictive insights to traffic managers.
Development and Institutional Collaboration
ASTraM was developed through collaboration between:
- Bengaluru Traffic Police
- Arcadis, a Dutch design and consultancy firm
The model reflects international cooperation in urban governance and technology deployment.
Objectives
The system aims to:
- Transform traffic policing from a reactive complaint-based approach to a proactive, data-driven model
- Reduce urban congestion
- Improve road safety
- Streamline incident reporting
- Enhance planning for large-scale public events
How ASTraM Works
1. Data Integration
The platform integrates multiple real-time data streams, including:
- CCTV camera feeds
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems
- Open-source and transport-related datasets
2. AI-Based Analysis
The AI engine processes large volumes of data to:
- Identify recurring congestion patterns (daily bottlenecks)
- Detect non-recurring disruptions (accidents, protests, roadblocks)
- Forecast potential traffic choke points
3. Automated Communication
- Issues are batched and communicated to field officers at 15-minute intervals
- Enables localised and timely intervention
Key Features
- Situational Awareness: A centralised dashboard provides a bird’s-eye view of city-wide traffic conditions.
- Predictive Analytics: The system anticipates congestion trends before gridlocks occur.
- Incident Reporting Bot: Automated bots log accidents, breakdowns, and obstructions, reducing manual reporting delays.
- Event Simulation: Supports traffic planning during major events such as processions, protests, and festivals by modelling potential disruptions.
- Dashboard Analytics for Urban Planning: Provides long-term data insights for infrastructure planning and policy adjustments.
State of India’s Environment (SOE) 2026
- 28 Feb 2026
In News:
The State of India’s Environment (SOE) 2026 report, released by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) and Down To Earth, highlights the accelerating ecological crisis at both global and national levels. The report warns that humanity has breached multiple planetary boundaries, pushing Earth’s life-support systems toward instability. It further links ecological degradation with intensifying human–tiger conflicts in India.
Planetary Boundaries Framework
The Planetary Boundaries framework, first proposed in 2009 by scientists led by Johan Rockström and updated in 2023, defines the safe operating limits within which humanity can function without destabilising Earth systems.
It identifies nine critical Earth system processes that regulate planetary stability. Crossing these limits increases the risk of abrupt, irreversible environmental changes. The boundaries are interconnected; transgression in one can trigger cascading impacts across others.
Status of the Nine Planetary Boundaries
According to SOE 2026, 7 out of 9 planetary boundaries have been breached:
1. Climate Change (Transgressed): Rising greenhouse gas concentrations are pushing the planet close to breaching the 1.5°C warming threshold, signalling potentially irreversible climate impacts.
2. Biosphere Integrity (Transgressed): Species extinction rates exceed 100 extinctions per million species years, nearly ten times the safe limit.
3. Land System Change (Transgressed): Global forest cover has declined to 59%, well below the 75% safe threshold, weakening carbon sinks and biodiversity resilience.
4. Freshwater Change (Transgressed): Over-extraction and climate variability are disrupting river systems, soil moisture cycles, and groundwater security.
5. Biogeochemical Flows (Transgressed): Excess nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilisers are causing eutrophication and ecosystem imbalance.
6. Novel Entities (Transgressed): Plastics, synthetic chemicals, and other pollutants are entering ecosystems without adequate safety assessment.
7. Ocean Acidification (Recently Transgressed): Ocean acidity has increased by 30–40% since the industrial era, threatening coral reefs and marine food webs.
Boundaries Within Limits (But Risky)
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading – Currently within limits globally but regionally disruptive (e.g., monsoon variability).
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion – Within safe limits due to the success of the Montreal Protocol, a major global environmental governance success.
Climate Crisis and Tipping Points
- The report warns that climate disruptions are occurring earlier than predicted. Critical ecosystems such as coral reefs and the Amazon rainforest are approaching tipping points, beyond which recovery may be impossible.
Biodiversity Loss and Forest Decline
- Habitat degradation, deforestation, and ecosystem imbalance are accelerating biodiversity loss. Declining forest cover and fragmented habitats are reducing ecological resilience and increasing human–wildlife interactions.
Rising Human–Tiger Conflict in India
The report highlights how ecological degradation is intensifying human–tiger conflicts:
- Habitat loss and prey depletion are altering tiger behaviour.
- Expansion of human settlements near forest areas increases encounters.
- The invasive species Lantana camara now occupies nearly 50% of forest and scrublands, suppressing native grasses.
- Reduced prey availability forces tigers to prey on cattle, escalating conflict with local communities.
This reflects how ecosystem imbalance directly affects conservation outcomes.
Pollution and Freshwater Stress
- Freshwater reserves face severe stress due to overuse and climate variability. Simultaneously, pollution from plastics and synthetic chemicals presents long-term ecological and health risks, reinforcing the urgency of regulating “novel entities.”
Key Recommendations
1. Institutional Strengthening
- Enhance the capacity and independence of the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
- Ensure environmental clearances prioritise ecological integrity over procedural compliance.
2. Sovereign Climate Action
- Integrate planetary boundaries into national accounting frameworks.
- Promote technology-led, full-stack decarbonisation strategies.
3. Community-Centric Conservation
- Adopt landscape-scale governance.
- Treat local communities as primary stakeholders in conservation rather than as obstacles.
Macaques
- 28 Feb 2026
In News:
A recent viral story from a Japanese zoo involving an abandoned baby Japanese macaque (“Punch”) brought global attention to the complex emotional bonds and strict social hierarchies within macaque societies. Beyond public curiosity, the episode highlights important aspects of primate behaviour, evolutionary biology, and conservation — areas relevant to biodiversity studies and wildlife management.
About Macaques
Macaques belong to the genus Macaca under the family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys). They are among the most widespread and adaptable primates in the world.
Distribution and Diversity
- Over 20 species
- Found mainly across Asia and parts of North Africa
- Highly adaptable to diverse ecological conditions, including forests, mountains, and urban environments
Their adaptability has enabled certain species to thrive even in human-dominated landscapes.
Important Species
1. Japanese Macaque (Macaca fuscata)
- Native to Japan
- Known as the “Snow Monkey”
- Famous for surviving in cold climates and bathing in natural hot springs
- Displays highly structured matrilineal social systems
2. Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- Widely distributed in North India and Southeast Asia
- Frequently found in urban and semi-urban areas
- Extensively used in medical and biomedical research, including vaccine development
3. Lion-tailed Macaque (Macaca silenus)
- Endangered species
- Endemic to the Western Ghats (India)
- Recognised by its distinctive silver-white mane
- Threatened by habitat fragmentation and deforestation
4. Crested Black Macaque (Macaca nigra)
- Native to Sulawesi (Indonesia)
- Characterised by a dark crest
- Classified as Critically Endangered
Social Behaviour and Hierarchy
Macaques are highly gregarious animals, living in troops governed by strict dominance hierarchies. Their social organisation is complex and deeply structured.
Female Hierarchy
- Rank is typically matrilineal (inherited from the mother).
- Daughters generally rank close to their mother’s position.
- In species such as the Japanese macaque, the “youngest sister rule” applies — the youngest daughter ranks above older sisters.
- Female bonds are stable and form the core of troop structure.
Male Hierarchy
- Determined by physical strength, alliances, and fighting ability.
- Males often migrate between troops.
- Rank can fluctuate over time.
The viral incident involving the abandoned baby macaque illustrates how social rank and maternal position significantly affect offspring survival and acceptance within the troop.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance
Macaques provide valuable insights into:
- Evolution of primate social systems
- Behavioural ecology
- Conflict resolution and cooperation
- Human–wildlife interaction
Their structured dominance systems resemble early social organisation patterns in primates, offering important evolutionary parallels.
Conservation and Human Interface
While some species like the rhesus macaque thrive near human settlements, others such as the lion-tailed macaque face severe threats due to:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Deforestation
- Infrastructure expansion
- Human–wildlife conflict
Urban macaque populations often lead to conflict, necessitating balanced wildlife management policies.
International Climate Initiative (IKI)
- 27 Feb 2026
In News:
India and Germany have launched a €20 million (approximately ?180 crore) Large Grant project under Germany’s International Climate Initiative (IKI). The project focuses on strengthening climate resilience in India’s most vulnerable ecosystems through nature-based and sustainable adaptation strategies.
About the International Climate Initiative (IKI)
- Established in 2008, IKI is Germany’s principal funding instrument for international climate action.
- Supports projects in:
- Climate change mitigation
- Adaptation
- Biodiversity conservation
- Operates in over 150 partner countries, with 14 priority countries, including India, Brazil, China, South Africa, Indonesia, and Mexico.
- Aligns with global commitments under the Paris Agreement and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
IKI represents Germany’s climate diplomacy approach, combining financial assistance, technology cooperation, and capacity building.
Scope of the New India–Germany Project
The newly launched €20 million initiative targets high-risk and ecologically sensitive regions in India, promoting long-term resilience through ecosystem-based adaptation.
Priority Regions
- Himalayas
- Challenges: Glacier melt, glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides.
- Significance: Water security for major river systems.
- Western Ghats
- Biodiversity hotspot facing deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
- Vulnerable to extreme rainfall events and ecological degradation.
- North-East India
- Fragile hill ecosystems prone to soil erosion and flooding.
- Rich in biodiversity but ecologically sensitive.
- Island Ecosystems (e.g., Andaman & Nicobar)
- Threatened by sea-level rise and coastal erosion.
- High vulnerability to cyclones and marine ecosystem disruption.
Focus Areas of Intervention
- Promotion of Nature-Based Solutions (NbS)
- Ecosystem restoration and conservation
- Climate-resilient livelihoods
- Capacity building at local and state levels
- Strengthening institutional frameworks for adaptation
Nature-based solutions integrate environmental restoration with socio-economic resilience, ensuring sustainability and community participation.
Strategic Significance
1. Strengthening India’s Climate Resilience
India faces:
- Rising temperatures
- Erratic monsoons
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events
- Biodiversity loss
This initiative enhances adaptive capacity in vulnerable geographies.
2. Alignment with India’s National Commitments
The project supports:
- India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- Target of 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- Net-Zero Commitment (2070)
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) missions, particularly:
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
3. Global Climate Governance
- Reinforces North–South cooperation in climate finance.
- Demonstrates operationalisation of climate finance commitments under the Paris Agreement.
- Promotes biodiversity conservation alongside climate mitigation and adaptation.
4. Indo-German Strategic Partnership
Climate cooperation is a key pillar of the India–Germany Strategic Partnership, complementing collaboration in:
- Renewable energy
- Green hydrogen
- Sustainable urbanisation
- Technology and innovation
Indigenous Large Language Models and India’s Sovereign AI Push

- 27 Feb 2026
In News:
At the India-AI Impact Summit 2026, Bengaluru-based startup Sarvam AI unveiled two indigenous Large Language Models (LLMs)** trained on 35 billion and 105 billion parameters. These models are designed to be less power- and compute-intensive, while demonstrating improved performance in Indian languages. The development marks a significant milestone in India’s quest for sovereign and cost-efficient AI systems aligned with domestic needs.
Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs)
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an AI system built using transformer-based neural networks trained on massive text datasets to understand and generate human language.
They contain billions of parameters—internal variables learned during training—that help the model predict the next word in a sequence and generate coherent text.
How LLMs Work
- Tokenisation: Text is broken into smaller units called tokens (word pieces or characters).
- Embeddings & Transformer Architecture: Tokens are converted into numerical vectors. The self-attention mechanism helps the model determine which words in a sentence are contextually important, even if they are far apart.
- Next-Token Prediction: The model generates language by predicting one token at a time based on probability distributions.
- Layered Learning: Multiple transformer layers refine linguistic and semantic understanding—from grammar to reasoning patterns.
Stages of Training LLMs
1. Data Collection & Pre-processing
- Massive datasets sourced from books, websites, code repositories, etc.
- Cleaning to remove bias, spam, duplicates, and harmful content.
- Quality of data directly influences performance.
2. Pre-training (Self-Supervised Learning)
- Model learns via next-token prediction.
- Produces a base model capable of understanding grammar, facts, and reasoning.
3. Supervised Fine-Tuning
- Trained on curated prompt–response pairs.
- Enhances instruction-following ability and task performance (summarization, translation, Q&A).
4. Alignment via RLHF
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
- Humans rank outputs based on safety and quality.
- A reward model optimises responses to align with human values.
Challenges in Training LLMs in India
- Data Scarcity in Indian Languages
- English and East Asian languages dominate internet data.
- Indian languages remain underrepresented.
- Many models rely on translation into English, increasing token consumption and cost.
- High Capital and Compute Costs
- Requires clusters of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs).
- Training costs run into millions of dollars.
- Limited domestic venture capital for foundational AI research.
- Limited Immediate Commercial Use Cases: Training large models without clear monetisation pathways deters investment.
- Infrastructure Constraints
- Dependence on imported high-end chips.
- Energy-intensive training processes.
Innovation: Mixture of Experts (MoE) Architecture
Earlier LLMs activated all parameters during inference, making them computationally expensive.
The Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture activates only a subset of parameters (“experts”) for each query.
Advantages:
- Reduced computational load
- Faster inference
- Lower electricity consumption
- Cost-efficient deployment in resource-constrained settings
Sarvam’s 105B parameter model leverages MoE to balance performance with efficiency, focusing on accuracy and Indian context alignment rather than sheer scale.
IndiaAI Mission: Government Support for Domestic AI
Launched in March 2024 with an outlay of ?10,372 crore, the IndiaAI Mission aims to build a comprehensive AI ecosystem.
Key Components:
- Compute Infrastructure
- Over 36,000 GPUs commissioned in Indian data centres.
- Additional 20,000 GPUs being added.
- Target: 100,000 GPUs by end of 2026.
- Subsidised Access
- Sarvam AI granted 4,096 GPUs from a common compute cluster.
- Subsidy estimated at nearly ?100 crore.
- Cluster cost approximately ?246 crore.
- Support for Innovation
- Promotion of sovereign foundational models trained on Indian datasets.
- Financial support covering compute and training costs.
- Encouragement of open-source innovation.
- Talent Development
- Training support for over 13,500 students.
- Establishment of India Data and AI Labs.
Other Indian Efforts
- BharatGen (IIT Bombay-incubated): Multilingual 17B parameter model, targeted at sectors like education and healthcare.
- Gnani.ai: Small text-to-speech model.
- Indigenous focus on domain-specific and language-specific AI models.
RAMP Programme

- 27 Feb 2026
In News:
The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME) recently convened the 5th meeting of the National MSME Council in New Delhi to review the progress of the World Bank–assisted Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Programme. The review gains significance in the context of MSMEs being the backbone of India’s economy and central to achieving inclusive growth, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and the $5 trillion economy vision.
About the RAMP Programme
- It was launched in 2022 and is being implemented over a five-year period (2022–23 to 2026–27) by the Ministry of MSME with World Bank support.
- It seeks to address structural challenges faced by MSMEs through systemic reforms and capacity building at both the Central and State levels.
Objectives of RAMP
The programme focuses on:
- Improving Access to Market and Credit
- Enhancing financial inclusion.
- Promoting integration into domestic and global value chains.
- Strengthening Institutions and Governance
- Capacity building of MSME institutions at Central and State levels.
- Improving policy design and implementation mechanisms.
- Enhancing Centre–State Coordination
- Encouraging cooperative federalism through structured partnerships.
- Providing financial assistance to States for preparing Strategic Investment Plans (SIPs).
- Addressing Delayed Payments: Tackling liquidity stress among Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs).
- Greening of MSMEs: Supporting climate-resilient and sustainable business practices in alignment with India’s Net Zero target of 2070.
Institutional Framework
National MSME Council
- Established by MoMSME as the administrative and functional body under RAMP.
- Provides strategic direction, monitors progress, and facilitates coordination among stakeholders.
State-Level Role
- States receive grants to prepare Strategic Investment Plans (SIPs).
- SIPs align state-specific reforms with national MSME objectives.
- Promotes decentralised planning and context-specific solutions.
Key Sub-Schemes under RAMP
1. MSME GIFT Scheme
(MSME Green Investment and Financing for Transformation)
- Promotes adoption of green technologies.
- Provides interest subvention and credit guarantee support.
- Encourages energy efficiency, cleaner production, and sustainability.
2. MSE SPICE Scheme
(Scheme for Promotion and Investment in Circular Economy)
- Supports circular economy initiatives among MSEs.
- Offers credit-linked capital subsidy.
- Contributes toward the long-term objective of MSMEs achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
3. MSE ODR Scheme
(Online Dispute Resolution for Delayed Payments)
- First-of-its-kind initiative integrating legal support with IT tools and Artificial Intelligence.
- Addresses the chronic issue of delayed payments to Micro and Small Enterprises.
- Strengthens ease of doing business and improves working capital cycles.
Significance for the Indian Economy
- MSMEs contribute significantly to GDP, exports, and employment generation.
- RAMP supports:
- Formalisation and competitiveness.
- Digital transformation.
- Climate-aligned industrial growth.
- Improved credit flow and risk mitigation.
- It operationalises cooperative and competitive federalism through structured Centre–State collaboration.
SUJVIKA Portal

- 26 Feb 2026
In News:
On the occasion of the 40th Foundation Day of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology launched the SUJVIKA Portal, an AI-driven Biotech Product Data Portal. The initiative reflects India’s broader ambition to build a $1 trillion bioeconomy by 2047 under the vision of Viksit Bharat.
SUJVIKA Portal: Key Features and Significance
What is SUJVIKA?
- SUJVIKA is an AI-driven Trade Statistics Digital Intelligence Platform.
- Developed by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) in collaboration with industry partner ABLE.
- It provides authenticated biotechnology product import data in a structured and accessible format.
Core Objectives
- Present sector-wise data on:
- Biochemical products
- Industrial enzymes
- Other biotechnology imports
- Identify high-value and high-volume imports
- Assess import dependency
- Support indigenisation and R&D prioritisation
- Enable evidence-based policymaking
- Promote public–private partnerships (PPP) in domestic biomanufacturing
Importance for India
SUJVIKA strengthens:
- Strategic trade intelligence
- Domestic bio-manufacturing capacity
- Startup ecosystem planning
- Self-reliance in critical biotech inputs
It aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat by facilitating targeted import substitution in biotechnology.
Department of Biotechnology (DBT)
Establishment and Mandate
- Established in 1986
- Functions as a nodal agency for Life Sciences research and applications
- Promotes large-scale use of biotechnology across sectors
- Supports R&D in:
- Advanced biofuels
- Waste-to-energy technologies
- Healthcare and vaccines
- Genomics and gene therapy
Over four decades, DBT has evolved from a research-support body into a central driver of India’s bioindustrial ecosystem.
India’s Bioeconomy: Growth Trends and Targets
Rapid Expansion
- Bioeconomy size:
- ~$10 billion (2014)
- $165.7 billion (2024) → Nearly 16-fold growth in a decade
- Biotech startups:
- Fewer than 100 in 2014
- Over 11,000 startups today
India is now:
- Among the top biotech destinations globally
- One of the leading vaccine manufacturers in the world
Vision 2047
India aims to build a $1 trillion bioeconomy by 2047, positioning biotechnology as the backbone of the next industrial revolution.
India’s Energy Transition through the Green Ammonia Route

- 25 Feb 2026
In News:
At India Energy Week (January 2026), the Prime Minister highlighted investment opportunities worth $500 billion in India’s energy sector, signalling a shift from energy security to energy independence. A central pillar of this transition is green hydrogen and its derivative-green ammonia, which is emerging as a strategic fuel for agriculture, industry, shipping, and global trade.
India’s recent landmark auction through the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) has positioned the country as a serious player in the global green ammonia market.
What is Green Ammonia?
Green ammonia is produced by combining:
- Nitrogen (from air)
- Green hydrogen (generated via electrolysis using renewable energy)
Unlike grey ammonia, which uses natural gas and emits significant CO?, green ammonia has a near-zero carbon footprint.
SECI’s Landmark Green Ammonia Auction
Under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, SECI floated a tender in June 2024 to aggregate demand across fertilizer plants.
Key Features:
- Target Demand: 7,24,000 tonnes per annum (TPA)
- Coverage: 13 fertilizer plants
- Bidders: 15 participants
- Successful Awardees: 7 companies
- Contracts Awarded: 13 delivery contracts
- One company secured 6 contracts (3,70,000 TPA)
- 10-year fixed-price offtake agreements
Discovered Prices:
- ?49.75–?64.74/kg
- $572–$744 per tonne
- Nearly 40–50% lower than EU’s H2Global auction (~$1,153/tonne)
By comparison: Grey ammonia in India ≈ $515/tonne
The price gap has narrowed substantially, especially with production subsidies:
- ?8.82/kg (Year 1)
- ?7.06/kg (Year 2)
- ?5.3/kg (Year 3)
This model created price certainty, payment security, and balanced risk allocation—boosting investor confidence.
Strategic Significance for India
1. Import Substitution and Energy Security
- Contracted volumes account for ~30% of India’s ammonia imports.
- Reduces exposure to global gas price volatility, currency risks, and geopolitical disruptions.
2. Decarbonising Agriculture
- Fertilizer sector is the largest ammonia consumer.
- Example: 75,000 tonnes supply to Paradeep Phosphates marks early transition.
- Supports sustainable food supply chains.
3. Maritime Decarbonisation
- Ammonia is easier to store than hydrogen.
- Can replace heavy fuel oil in shipping.
- Linked to Rotterdam–India–Singapore Green Shipping Corridor initiative.
4. Hydrogen Carrier for Exports
- Acts as a stable medium to transport hydrogen over long distances.
- Ports like Kandla, Paradip, and Tuticorin (VOC) designated as hydrogen hubs.
- Potential exports to Japan and South Korea.
5. Grid Stability & Energy Storage
- Enables long-duration energy storage.
- Hybrid systems (solar wind storage) being piloted for round-the-clock production.
Policy Framework
National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023)
- Target: 5 MMTPA production capacity by 2030
- Investment Potential: ?8 lakh crore
- CO? Reduction Target: ~50 MMT annually by 2030
SIGHT Programme
- Outlay: ?17,490 crore
- Production-linked incentives (PLI) for green hydrogen and derivatives.
Global Context
Other procurement mechanisms:
- EU’s H2Global import tender
- South Korea’s Clean Hydrogen Portfolio Standard (CHPS)
Prahaar Anti Terror Policy

- 25 Feb 2026
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has unveiled ‘PRAHAAR’, India’s first comprehensive National Counter-Terrorism Policy and Strategy. This eight-page doctrine-level framework institutionalises a unified, intelligence-led and proactive approach to combat terrorism in all its forms. The policy formalises practices evolved over decades and responds to emerging hybrid threats such as drone-enabled attacks, cyber-terrorism, and transnational organised crime linkages.
Rationale and Context
India has faced persistent threats from cross-border terrorism, radical networks, and globally affiliated organisations such as Al-Qaeda and ISIS attempting to activate sleeper cells. The policy highlights:
- Cross-border terror networks and state-sponsored elements.
- Increasing use of drones in border states such as Punjab and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Growing nexus between terrorism and organised crime.
- Use of encrypted platforms, dark web, cryptocurrencies, and social media for recruitment, propaganda, and financing.
- Risks of chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear (CBRN), explosive, and cyber capabilities.
Given regional instability and the existence of ungoverned spaces, PRAHAAR adopts a multi-layered strategy focused on prevention, rapid response, coordination, and resilience.
Core Philosophy
India reiterates its zero-tolerance approach to terrorism and rejects any attempt to associate terrorism with religion, ethnicity, nationality, or civilisation. The policy underscores strict adherence to human rights, rule of law, and due process under legislations such as the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) and newly enacted criminal codes.
Seven Pillars of PRAHAAR
The acronym ‘PRAHAAR’ (meaning “strike”) represents seven core pillars:
- Prevention – Intelligence-led disruption of terror plots and dismantling support ecosystems.
- Response – Swift and proportionate operational action during incidents.
- Aggregation of Capacities – Strengthening institutional coordination and standardisation across central and state agencies.
- Human Rights Compliance – Ensuring lawful, accountable operations.
- Attenuation of Radicalisation – Preventive outreach, community engagement, and de-radicalisation initiatives.
- Aligning International Cooperation – Intelligence sharing, extradition, and support for UN designations of terrorist entities.
- Recovery and Resilience – Victim support, infrastructure restoration, and societal resilience.
Institutional Mechanisms
The policy adopts a whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach.
- Multi Agency Centre (MAC) and Joint Task Force on Intelligence (JTFI) serve as nodal platforms for real-time intelligence sharing.
- Local police act as first responders, supported by specialised state units and national forces such as the National Security Guard (NSG).
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) leads investigations to ensure effective prosecution and higher conviction rates.
- Standard operating procedures are to be harmonised across states to address operational gaps.
Technology-Centric and Proactive Approach
PRAHAAR shifts focus from reactive policing to pre-emptive disruption. It emphasises:
- Advanced border surveillance across land, maritime, and aerial domains.
- Protection of critical infrastructure—power plants, railways, aviation, ports, defence and space installations, and atomic energy facilities.
- Countering misuse of drones, encrypted messaging apps, cryptocurrency financing, and cyber intrusions.
Counter-Radicalisation and Social Engagement
Recognising radicalisation as a key enabler of terrorism, the policy proposes:
- Community outreach involving civil society and religious leaders.
- Youth engagement and socio-economic interventions.
- Prison monitoring and graded response mechanisms.
This integrates security responses with preventive social strategies.
International Dimension
India will strengthen bilateral and multilateral intelligence-sharing arrangements, pursue extradition of terror suspects, and advocate for comprehensive global counter-terror norms under the United Nations framework.
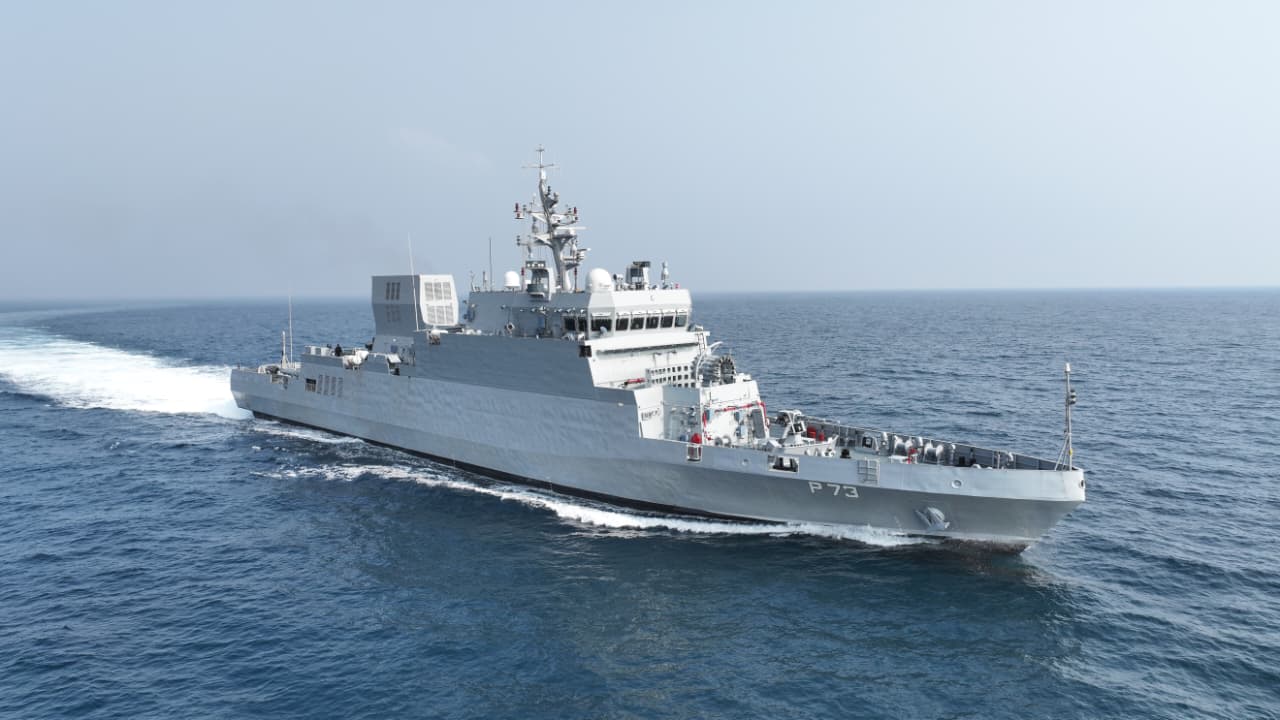
Anjadip Vessel

- 25 Feb 2026
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission INS Anjadip, an indigenous Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC), at the Eastern Naval Command in Chennai. The induction marks a significant milestone in India’s maritime security architecture, particularly in strengthening underwater domain awareness in littoral waters.
Key Details:
- INS Anjadip is the third vessel in the eight-ship ASW-SWC project and has been constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- The project reflects India’s growing defence industrial base and aligns with the broader vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat in defence production.
- It also symbolizes the transformation of the Indian Navy into a “Builder’s Navy,” emphasizing indigenous warship design and construction.
Strategic Rationale
- India’s maritime geography—bordered by the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the wider Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces increasing underwater security challenges, including the expansion of submarine fleets in the region. Coastal and shallow waters are particularly vulnerable due to their complex acoustic environment, which makes submarine detection difficult.
- ASW-SWC vessels such as INS Anjadip are specifically designed for shallow-water operations, complementing larger destroyers and frigates that operate in deeper seas. Their deployment enhances layered maritime defence, especially near critical ports, sea lanes, and offshore assets.
Role and Capabilities
Often described as a “Dolphin Hunter,” INS Anjadip is engineered to detect, track, and neutralize enemy submarines in coastal waters. Its capabilities include:
- Hull Mounted Sonar ‘Abhay’ – an indigenous sonar system for underwater detection.
- Lightweight Torpedoes – for engaging hostile submarines.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) Rockets – for close-range underwater threats.
- High-speed Water-Jet Propulsion System – enabling speeds up to 25 knots for rapid response.
Beyond its core ASW role, the vessel is also capable of:
- Coastal Surveillance
- Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO)
- Search and Rescue (SAR) missions
Its high manoeuvrability makes it particularly effective in confined and shallow operational environments.
Project Significance
The ASW-SWC project demonstrates India’s progress in indigenous naval shipbuilding. By involving domestic shipyards and indigenous weapon-sensor integration, the programme reduces import dependency and strengthens strategic autonomy.
The commissioning also contributes to:
- Capacity-building in anti-submarine warfare.
- Protection of sea lines of communication (SLOCs).
- Safeguarding strategic coastal infrastructure.
- Enhancing deterrence posture in the Indian Ocean Region.
Historical and Geostrategic Context
The vessel is named after Anjadip Island, located off the coast of Goa in the Arabian Sea. The island holds historical importance as Vasco da Gama claimed it for the Portuguese Crown on 24 September 1498 during his first voyage to India. The naming reflects India’s maritime heritage while reinforcing contemporary strategic priorities in the Arabian Sea region.
National Monetisation Pipeline 2.0
- 25 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs has launched the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) 2.0, prepared by NITI Aayog, to operationalise the Asset Monetisation Plan for 2025–30 as announced in the Union Budget 2025–26. The initiative marks a significant step in India’s infrastructure financing strategy, building upon the experience of NMP 1.0.
Background and Performance of NMP 1.0
- The first phase of the National Monetisation Pipeline (2021–25) set a target of ?6 lakh crore. As per official statements, nearly 90% of this target was achieved, establishing institutional mechanisms, transaction templates, and sector-specific best practices. It also mainstreamed asset monetisation as a structured public finance strategy rather than an ad hoc disinvestment measure.
- NMP 1.0 covered operational (brownfield) public assets across sectors such as roads, railways, power transmission, airports, ports, and telecom. The experience gained in valuation, risk allocation, and investor outreach forms the foundation for NMP 2.0.
Rationale: Asset Recycling as a Financing Tool
NMP 2.0 is anchored in the concept of asset recycling, wherein operational public infrastructure assets are monetised to unlock capital. The proceeds are reinvested in new greenfield infrastructure (capital expenditure), without increasing fiscal deficits or immediate budgetary outgo.
This approach serves multiple objectives:
- Enhances efficiency through private sector participation.
- Improves asset utilisation and maintenance.
- Provides upfront capital to the government.
- Reduces pressure on traditional borrowing.
Thus, monetisation is distinct from privatisation; ownership of assets remains with the public authority while usage rights are transferred for a defined concession period.
Scope and Sectoral Coverage
NMP 2.0 expands the scale and ambition of monetisation. The pipeline estimates an aggregate potential of ?16.72 lakh crore, including approximately ?5.8 lakh crore in private sector investment—about 2.6 times the size of NMP 1.0.
Key sectors covered include:
- Roads and Highways
- Railways
- Power (generation and transmission)
- Oil and Gas pipelines
- Civil Aviation (airports)
- Ports
- Telecom infrastructure
- Coal and Mining assets
This broad sectoral spread ensures diversification of revenue streams and investor participation.
Institutional and Governance Framework
To ensure coordinated implementation, progress under NMP 2.0 will be monitored by the Core Group of Secretaries on Asset Monetisation (CGAM), chaired by the Cabinet Secretary. This institutional arrangement reflects a “whole-of-government” approach, integrating ministries, public sector enterprises, and state governments.
Revenue allocation from monetisation depends on the implementing agency:
- Ministry-led projects: credited to the Consolidated Fund of India.
- PSU/Port Authority projects: retained by the respective entity.
- Mining-related revenues: flow to the State Consolidated Fund (largely through royalties).
- Private investments involving construction or major maintenance are recorded under a separate accounting head.
Monetisation Instruments
Transactions under NMP 2.0 will employ a mix of financial and contractual instruments:
- Public-Private Partnership (PPP) concessions
- Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs)
- Securitisation of cash flows
These instruments aim to attract long-term institutional investors such as pension funds and sovereign wealth funds, thereby deepening India’s infrastructure finance market.
Significance in the Context of Viksit Bharat
Aligned with the broader vision of Viksit Bharat, NMP 2.0 seeks to optimise public asset utilisation and crowd in private capital for infrastructure expansion. By providing medium-term asset visibility and a clear roadmap, it enhances investor confidence and predictability.
At a macroeconomic level, the pipeline complements the government’s high capital expenditure strategy, supports economic growth, and strengthens fiscal sustainability. If implemented effectively with transparency and robust regulatory safeguards, NMP 2.0 could institutionalise asset monetisation as a permanent pillar of India’s public finance architecture.
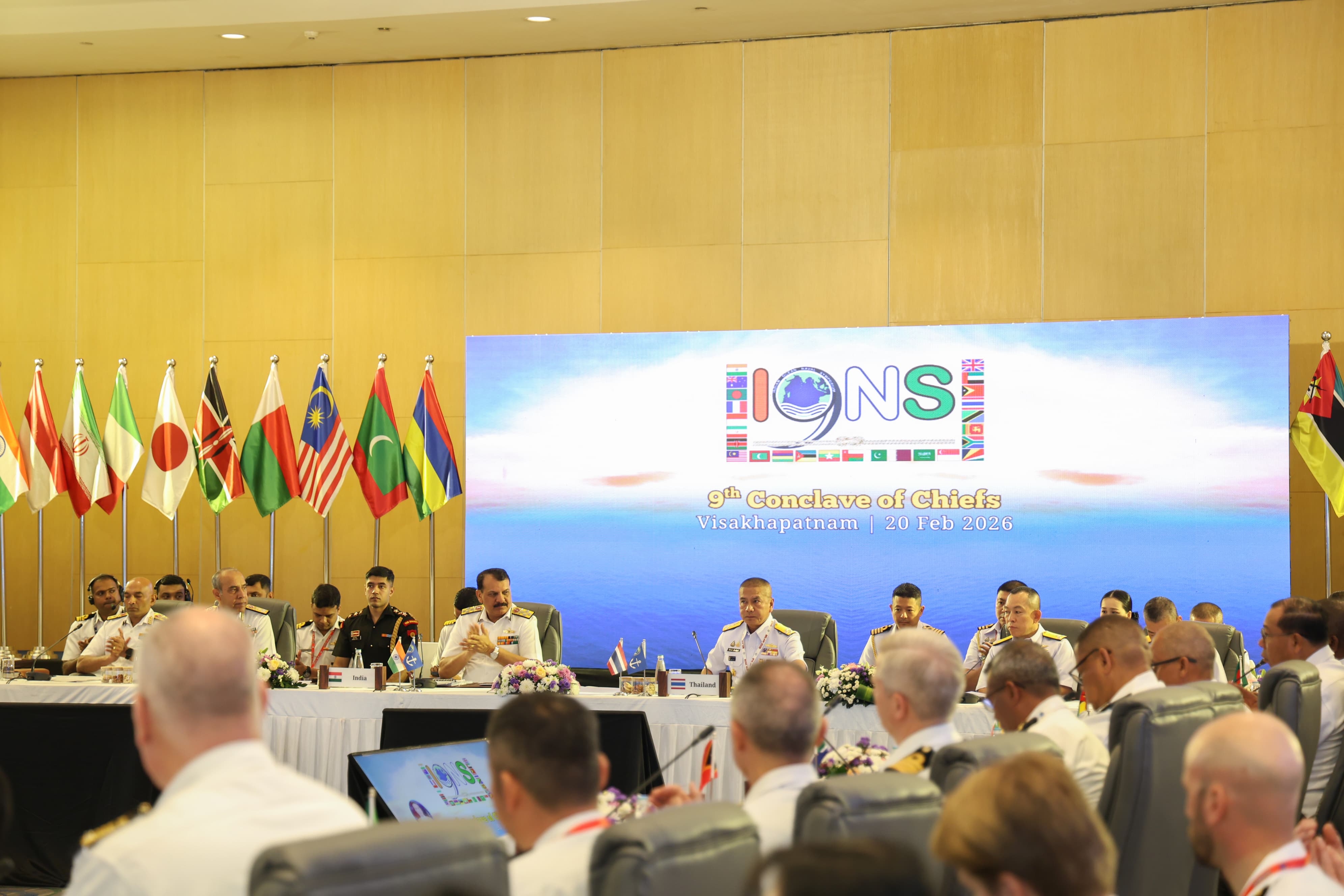
India assumes chairmanship of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS)

- 22 Feb 2026
In News:
- India assumed the Chairmanship of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) from Royal Thai Navy.
- The 9th Conclave of Chiefs was held at Visakhapatnam.
- Participation included Chiefs of Navies and Heads of Maritime Security Agencies from 33 countries (Members, Observers, and Indian Ocean littoral states).
- India had earlier held the inaugural Chairmanship (2008–2010).
About Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS)
- Launched in 2008 by the Indian Navy.
- A voluntary naval forum aimed at enhancing maritime cooperation among Indian Ocean littoral states.
- No permanent headquarters.
- Features a rotating chairmanship.
Membership Structure
- 25 Member States, divided into four sub-regions:
- South Asian
- West Asian
- Southeast Asian & Australian
- East African
- 9 Observer countries.
- In 2026:
- The Philippines was inducted as an Observer.
- Oman joined the Working Group on HADR.
Core Objectives of IONS
IONS promotes:
- Maritime security cooperation (including anti-piracy efforts).
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR).
- Maritime information sharing.
- Capacity building among navies.
- Professional exchange through exercises, workshops, and biennial conclaves.
Key Focus Areas (Working Groups)
Under India’s Chairmanship, emphasis will be placed on strengthening:
- Maritime Security
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR)
- Information Sharing and Interoperability
Initiatives Announced During India’s Tenure
- Conduct of IONS Maritime Exercise (IMEX).
- Continued deployment of IOS SAGAR missions to IONS member countries with multinational participation.
- Structured Maritime Information Sharing Workshops.
- Upgrade of the IONS website to enhance:
- Institutional continuity
- Secure engagement
- Usability among member navies
Strategic Significance for India
- Reinforces India’s role as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Strengthens maritime diplomacy and defence cooperation.
- Enhances collective response capability against: Piracy, Maritime terrorism, and Natural disasters
- Promotes interoperability among like-minded navies.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
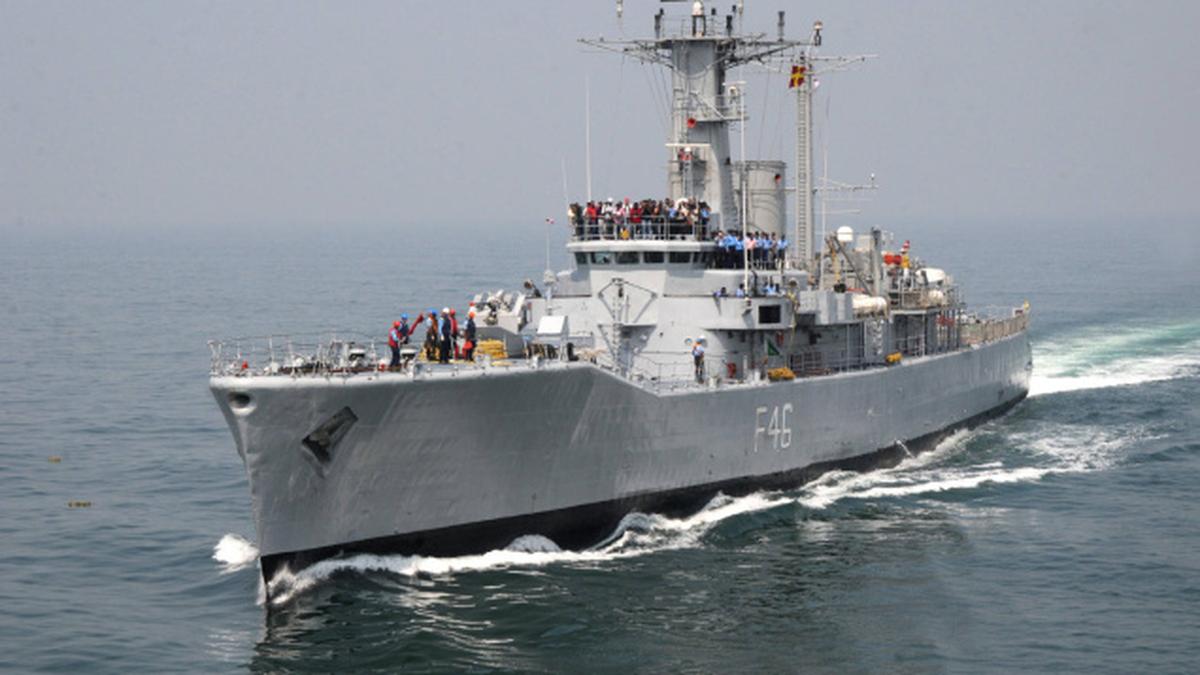
INS Krishna

- 22 Feb 2026
In News:
The Indian Navy has commissioned INS Krishna, the first of three indigenously built Cadet Training Ships (CTS), marking a significant step in strengthening sea-based training infrastructure for future naval officers.
About INS Krishna
- First of three Cadet Training Ships (CTS) for the Indian Navy.
- Constructed at Larsen & Toubro (L&T) Shipyard, Kattupalli (near Chennai).
- Designated as Yard 18003 during construction.
- Entirely indigenously built, supporting Aatmanirbhar Bharat in defence manufacturing.
Purpose and Role
- Training Platform
- Functions as a “floating classroom” and “living laboratory.”
- Used for training:
- Officer cadets (including women)
- Cadets from friendly foreign countries
- Training areas include:
- Navigation
- Seamanship
- Watch-keeping
- Practical maritime operations under real sea conditions
Technical Specifications
- Displacement: ~4,700 tonnes
- Maximum speed: 20 knots
- Endurance: 60 days at sea
- Multi-role capability beyond training
Secondary Operational Roles
Apart from training, INS Krishna is designed for:
- Non-Combatant Evacuation Operations (NEO)
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR)
- Search and Rescue (SAR) missions
This enhances operational flexibility and supports India’s role as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens sea-based officer training capacity of the Indian Navy.
- Enhances practical exposure for cadets under real maritime conditions.
- Supports indigenous defence shipbuilding capability.
- Promotes defence diplomacy through training of foreign cadets.
- Augments India’s capability in HADR and evacuation missions.
Tetanus and Adult Diphtheria (Td) Vaccine

- 22 Feb 2026
In News:
- Recently, the Td vaccine was launched by Union Health Minister J. P. Nadda.
- Manufactured by the Central Research Institute (CRI), Kasauli, Himachal Pradesh.
- CRI functions under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- The vaccine will be supplied under India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP).
- CRI plans to supply 55 lakh doses by April 2026, with progressive scaling in subsequent years.
Why the Shift from TT to Td?
- Extensive childhood immunization using DPT vaccines significantly reduced tetanus and diphtheria.
- However, diphtheria antibody levels decline over time, necessitating booster doses.
- In 2006, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended transitioning from Tetanus Toxoid (TT) to Td vaccine.
- Recommendation reaffirmed in:
- WHO Tetanus Vaccine Position Paper (2017)
- Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) deliberations (2002 & 2016)
- India’s National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI) recommended replacing TT with Td for: All age groups and Pregnant women
Objective: Sustain maternal & neonatal tetanus elimination while expanding protection against diphtheria.
About Td Vaccine
- Full Form: Tetanus and adult Diphtheria Vaccine (Adsorbed, Reduced D-Antigen Content).
- Provides protection against: Tetanus and Diphtheria
- Composition:
- Purified diphtheria toxoid
- Purified tetanus toxoid
- Adjuvant: Aluminum phosphate
- Preservative: Thiomersal
- Storage: Freeze- and heat-sensitive vaccine
- Target group: Adolescents, Adults and Pregnant women
About Tetanus
- Caused by: Clostridium tetani (toxigenic strains).
- Nature: Acute infectious disease.
- Transmission: Not spread person-to-person (enters through contaminated wounds).
- Symptoms:
- Painful muscle stiffness
- Lockjaw (inability to open mouth)
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing
- High case-fatality rate, even with intensive care.
About Diphtheria
- Caused by: Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
- Spread: Person-to-person via respiratory droplets.
- Symptoms:
- Breathing difficulty
- Heart failure
- Paralysis
- Can be life-threatening.
- South-East Asia region has been a major contributor to global diphtheria incidence since 2005.
Regulatory and Manufacturing Milestones
The Central Research Institute:
- Completed developmental studies.
- Obtained Test License.
- Secured waivers for:
- Preclinical studies
- Phase I, II, and III trials.
- Received:
- Marketing Authorization
- License for manufacture and sale
- Release approval from Central Drugs Laboratory, Kasauli.
Gentoo Penguin
- 21 Feb 2026
In News:
Gentoo penguins have been confirmed infected with H5 avian influenza (H5N1, clade 2.3.4.4b) on Heard Island, marking the first recorded bird infection in an Australian external territory. Earlier (November 2025), the virus had been detected in southern elephant seals. The strain has caused widespread mortality among seabirds and poultry globally.
About Gentoo Penguin
Taxonomy
- Scientific Name: Pygoscelis papua
- Genus: Pygoscelis
- Closely related to: Adélie penguin, and Chinstrap penguin
- Distribution: Antarctic Peninsula, Sub-Antarctic islands, Falkland Islands (South Atlantic Ocean), and Exclusively found in the Southern Hemisphere (45°–65° South latitude)
- Habitat: Prefer shoreline habitats, enabling quick access to marine food while nesting nearby.
- Characteristics
- Fastest underwater swimmers among penguins.
- Diurnal and highly social.
- Breed in colonies; remain in groups year-round.
- Diet: Carnivorous (mainly fish, krill, squid).
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
H5N1 Avian Influenza – Key Facts
- Highly pathogenic strain: H5N1 (clade 2.3.4.4b)
- Highly contagious and deadly among: Seabirds, Wild birds, Poultry, and Marine mammals (e.g., southern elephant seals, Antarctic fur seals)
Detection & Testing
- Preliminary tests conducted at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)’s Australian Centre for Disease Preparedness.
- Samples collected during a scientific voyage (February 2026).
Observations
- No signs of large-scale mass mortality in surveyed areas.
- Australia’s national H5 bird flu–free status remains unchanged.
- Government has committed over A$100 million toward preparedness and biosecurity measures.
About Heard Island
- Australian external territory.
- Located:
- ~4,000 km south-west of Perth
- ~1,700 km north of Antarctica
- Situated in the Southern Ocean.
- Remote and ecologically sensitive sub-Antarctic ecosystem.
Red Sanders
- 23 Feb 2026
In News:
Busy Tirupati pilgrimage route makes Red Sanders smuggling easy in south Andhra Pradesh.
About Red Sanders
- Scientific Name: Pterocarpus santalinus
- Common Name: Red Sandalwood
- Type: Tropical dry deciduous tree
- Endemic to: Southern Andhra Pradesh
Geographic Distribution
- Restricted to three districts: Chittoor, Nellore, and YSR Kadapa
- Largest reserve located in the Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve, part of the Eastern Ghats
- Spread over 4,755 sq km
- Located about 35 km from Tirupati temple town
Ecological Characteristics
- Grows in rocky, degraded and red soil areas
- Requires hot and dry climate
- Fire-hardy and drought-resistant
- Slow-growing: 25–40 years to reach maturity
- Wood is relatively brittle compared to teak
Economic Importance
- Contains ‘Santalin’, a natural red dye
- Used in:
- Pharmaceutical preparations
- Textile and leather industries
- Food colouring
- Perfume and medicinal products
- Gained global attention in the 1960s when Japanese instrument makers used it for crafting the traditional shamisen due to superior tonal quality
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II (International trade strictly regulated)
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
Harvesting and felling inside reserve forests is prohibited. Legal trade permitted only under regulated plantation and CITES-controlled export mechanisms.
Red Sanders Smuggling: Key Issues
Role of Tirupati Pilgrimage Route
The proximity of the Tirupati pilgrimage corridor to Seshachalam forests facilitates smuggling due to:
- Heavy traffic movement
- Limited vehicle checking
- Multiple forest entry points
- Inter-state border with Tamil Nadu
Smugglers often:
- Enter from Tamil Nadu
- Disguise themselves as labourers or pilgrims
- Use small vehicles for transport
- Hide timber in containers or dump logs inside forests/water temporarily
- Use sea routes for international export
Organised Timber Mafia
- Operates in coordinated teams (felling transport units)
- Several trees cut within short duration
- Cross-firing incidents reported
- Forest officials issued arms after killings of personnel
- Andhra Pradesh Police–Forest Department task force formed in 2014
Recent Enforcement Action
- January 9, 2026: 75 Red Sanders logs seized in Kadapa division
Broader Issue: Illegal Timber and Deforestation
- India among top 10 forest-rich nations (area-wise)
- Since 1980, 1.5 million hectares of forest land diverted for development
- Majority diversion after 2000
- India is also one of the largest timber importers
- Illegal logging contributes to:
- Deforestation
- Carbon emissions
- Biodiversity loss
- Forest conflicts
Inter-state borders often act as transit hubs (e.g., timber movement in central India).
Conservation Efforts
- National Biodiversity Authority sanctioned ?82 lakh
- Andhra Pradesh State Biodiversity Board initiative
- Target: Raise 1 lakh (100,000) saplings
- Distribution to farmers for conservation and regulated cultivation
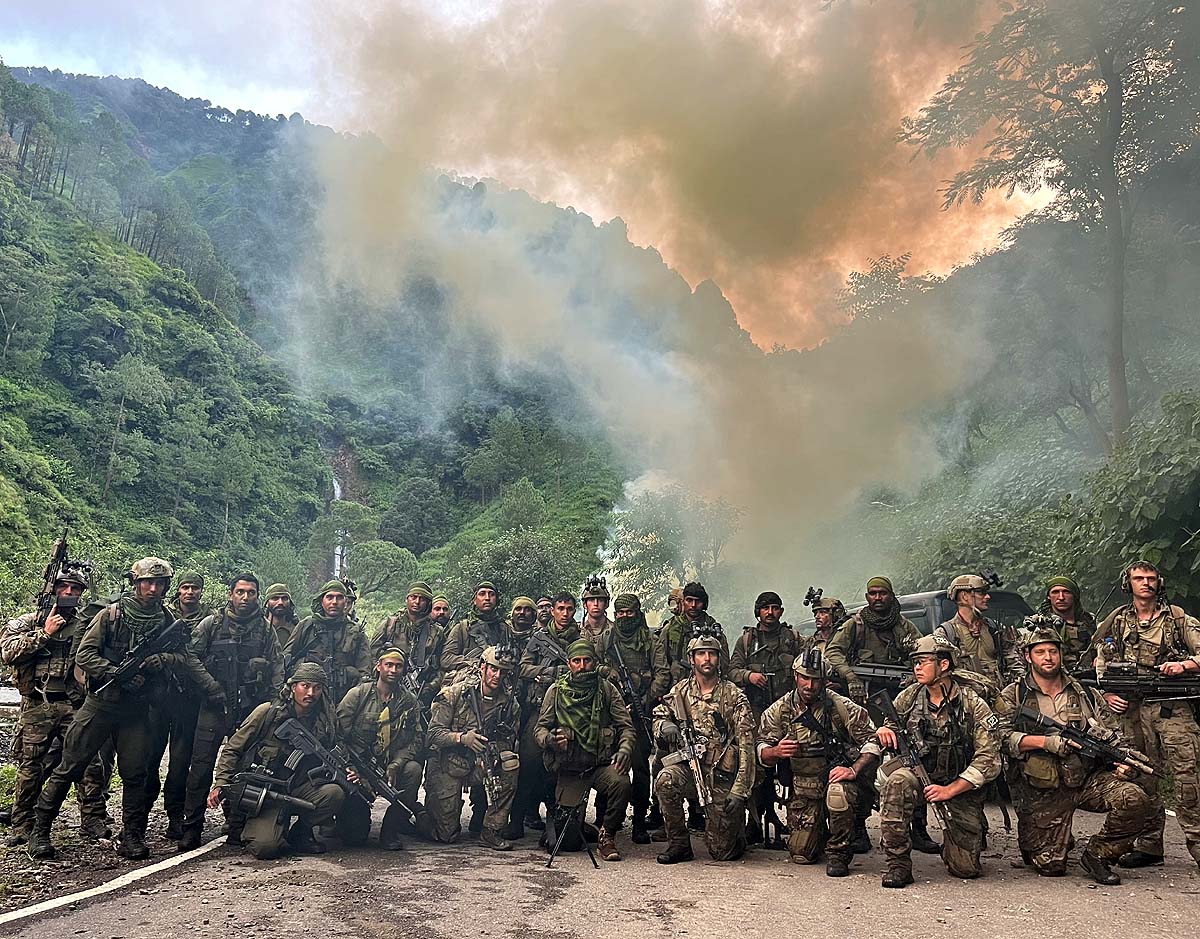
Exercise Vajra Prahar 2026

- 23 Feb 2026
In News:
The 16th edition of Exercise Vajra Prahar (2026) is held from 23 February to 15 March at Bakloh, Himachal Pradesh, focusing on counter-terror and advanced special operations interoperability between India and the US.
About Exercise Vajra Prahar
- Exercise Vajra Prahar is a bilateral Special Forces exercise conducted between India and the United States to enhance defence cooperation, interoperability, and joint operational readiness.
Key Objectives
- Exchange of advanced Special Operations Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)
- Strengthening counter-terrorism capabilities
- Improving precision strike capabilities
- Enhancing intelligence-based mission planning
- Conducting joint planning under simulated battlefield conditions
- Building mutual trust and operational synergy
The exercise is conducted in realistic combat scenarios, helping both forces refine coordination in high-risk operations.
Focus Areas in 2026
The 16th edition will emphasize:
- Counter-terror operations
- Precision targeting
- Intelligence-driven missions
- Joint operational planning
- Special Forces operations in diverse terrains
Previous Editions
- 15th Edition (2024): Held in Idaho, USA
- Participation: 45 personnel from each side
- US contingent represented by the Green Berets
- 2023 Edition: Conducted at Umroi, Meghalaya
- Included joint drills with the Indian Air Force
- Featured Mi-17 helicopter operations at Umiam Lake
- Helocasting operations demonstrated high operational precision
Exercise Vayushakti-26
Apart from Vajra Prahar, the Indian Air Force (IAF) will conduct Exercise Vayushakti-26.
Key Details
- Venue: Pokhran Air to Ground Range, Jaisalmer
- Date: 27 February 2026
- Nature: Firepower and full-spectrum air power demonstration exercise
Objectives of Vayushakti-26
- Demonstrate IAF’s rapid response and strike capability
- Showcase transformation of tactical actions into strategic outcomes
- Highlight role in Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR)
- Display readiness for conflict and emergency evacuation operations
Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited

- 20 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Home and Cooperation Minister launched ‘Bharat Taxi’, India’s first cooperative-based taxi service, aimed at transforming the unorganised taxi sector into an ownership-driven, driver-led model.
The initiative seeks to replace the commission-based aggregator model with a cooperative ownership framework, ensuring greater income security and social protection for drivers.
Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited
Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited is the multi-state cooperative society operating the Bharat Taxi platform.
- Registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002
- Established on June 6, 2025
- Drivers are referred to as “Sarathis”
- Ownership and governance lie with driver-members rather than corporate investors
Promoted By
Leading cooperative institutions including:
- National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC)
- Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO)
- Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF – Amul)
- Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited (KRIBHCO)
- National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- National Dairy Development Board (NDDB)
- National Cooperative Exports Limited (NCEL)
Objectives
- Driver Empowerment
- Shift from gig-worker status to ownership rights.
- Drivers become “Malik” (owners) of the platform.
- Economic Freedom
- Eliminate high commission charges (20–30%) taken by private aggregators.
- Ensure maximum income retention for drivers.
- Women’s Safety & Inclusion: Promote safe and dignified travel options for women.
- Social Security for Gig Workers: Integrate welfare benefits and financial security measures.
How the Model Works
1. Share-Based Membership
- Drivers join by purchasing cooperative shares (starting from ?500).
- Members receive voting rights and share in profits.
2. Zero-Commission Model
- No percentage cut per ride.
- Instead, a flat daily access fee:
- Approx. ?30 for cabs
- Approx. ?18 for autos
3. Direct Payments: Ride fares are transferred directly to the Sarathi’s bank account.
4. Democratic Governance: Two Sarathi representatives sit on the Board of Directors.
Key Features
1. Sarathi Didi Initiative
- Dedicated in-app option for women passengers.
- Enables booking rides with female drivers (Sarathi Didis).
2. No Surge Pricing: Transparent and fixed pricing, even during peak hours.
3. Integrated Mobility Services: Two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and four-wheelers on a single platform.
4. Social Safety Net Integration
- Linked with the e-Shram portal.
- Access to welfare schemes such as:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY – coverage up to ?5 lakh)
- Other gig worker social protection benefits.
5. Digital Payments Integration: Partnerships with fintech platforms enable seamless mobile payments.
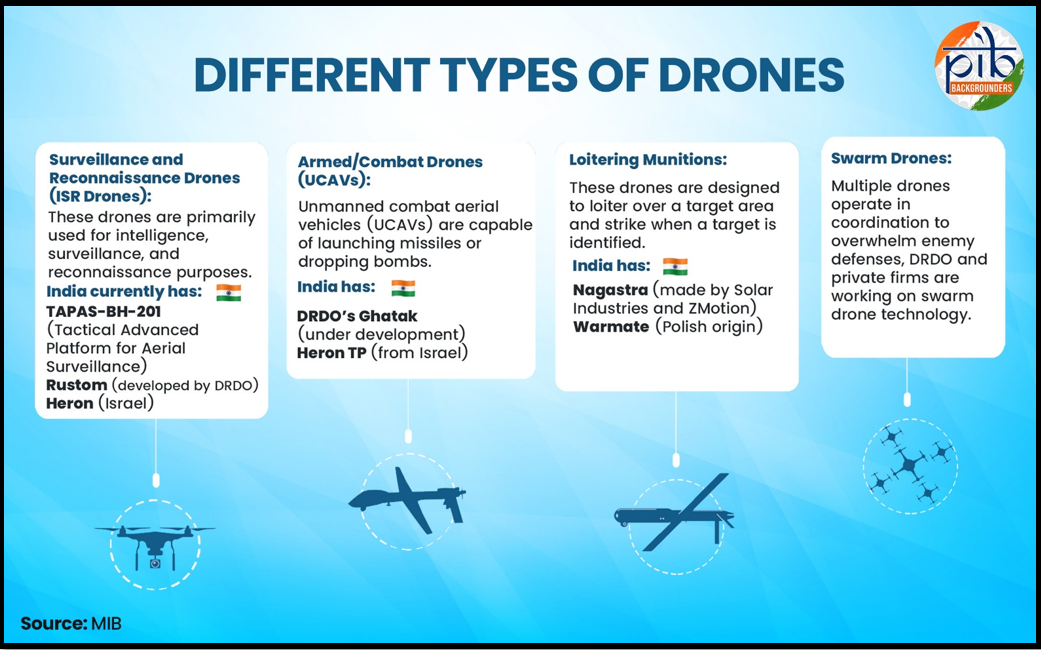
India’s Drone Ecosystem
- 20 Feb 2026
In News:
As of February 2026, India has over 38,500 registered drones (UINs), 39,890 DGCA-certified remote pilots, and 244 approved training organisations, reflecting a mature and regulated drone ecosystem.
India has transitioned from experimental drone usage to a structured, innovation-driven ecosystem integrated into governance, agriculture, infrastructure, and defence.
Evolution of India’s Drone Ecosystem
Over two decades, drone technology in India has evolved into a comprehensive framework involving:
- Manufacturers and component developers
- Drone-as-a-Service (DaaS) providers
- Start-ups and MSMEs
- Certified pilots and training institutes
- Digital regulatory platforms
Drones are now embedded in public service delivery, infrastructure monitoring, precision agriculture, disaster response, and national security.
Major Applications
1. Agriculture and Farmer Services
- Integrated with PMFBY (Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana) for crop assessment.
- Used for precision spraying, crop monitoring and input optimisation.
Namo Drone Didi Scheme (2023)
- Provides drones to Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- 1,094 drones distributed, including 500 under the core initiative.
- Enhances productivity, reduces costs, and promotes women-led rural entrepreneurship.
2. Land Mapping – SVAMITVA Scheme
The SVAMITVA (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) scheme (launched April 2020) uses drones for mapping rural abadi areas.
Key Data (as of Dec 2025):
- Target: ~3.44 lakh villages
- 3.28 lakh villages surveyed (~95%)
- 2.76 crore property cards prepared
- Covers 1.82 lakh villages across 31 States/UTs
Objectives:
- Reduce land disputes
- Improve access to institutional credit
3. Highway and Infrastructure Monitoring
- NHAI mandates monthly drone video recording of highway projects.
- Footage stored in data lakes for audit and dispute resolution.
- Enhances transparency and project monitoring.
4. Railways
- Ministry of Railways deploying UAVs for inspection of tracks and bridges.
- Railway Protection Force uses drones for surveillance and crowd management.
- Improves safety and monitoring of critical infrastructure.
5. Disaster Management
- NECTAR (North East Centre for Technology Application and Reach) developed specialised drones for flood and landslide monitoring.
- Provides real-time aerial visuals to improve rescue coordination.
6. Defence Applications
- Used for border surveillance, intelligence gathering and precision strikes.
- During Operation SINDOOR, drones and loitering munitions destroyed enemy targets.
- Integrated with radar and air defence systems for national security.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
1. Drone Rules, 2021 (Amended 2022–23)
Key reforms:
- Forms reduced from 25 to 5
- Approvals reduced from 72 to 4
- ~90% airspace designated as Green Zone (up to 400 ft)
- Pilot licence replaced by Remote Pilot Certificate (RPC)
- Civilian drones permitted up to 500 kg
- Passport requirement removed
2. Digital Sky & eGCA
- Regulatory services (registration, certification, RPTO authorisation) shifted to eGCA.
- Operational services (flight plans, airspace maps) integrated with Digital Sky.
Achievements (Feb 2026):
- 38,575 drones registered (UIN)
- 39,890 Remote Pilot Certificates issued
- 244 DGCA-approved RPTOs
3. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- Outlay: ?120 crore
- Promotes domestic drone and component manufacturing.
- Encourages MSMEs and start-ups.
4. GST Rationalisation
- GST reduced to 5% (September 2025) from earlier 18–28%.
- Applies to drones and flight simulators.
- Encourages commercial adoption and training ecosystem.
Capacity Building & Innovation
- SwaYaan Programme: HR development in Unmanned Aircraft Systems.
- 857 activities
- 26,000 beneficiaries
- National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR)
- ?40 lakh prize pool
- Promotes autonomous drones in disaster management & agriculture
- Platforms like Bharat Drone Shakti and Bharat Drone Mahotsav promote DaaS and indigenous technologies.
India’s Sovereign AI Push

- 20 Feb 2026
In News:
At the AI Impact Summit, Bengaluru-based startup Sarvam AI unveiled two indigenous large language models (LLMs) under the collective name “Vikram.” The development coincides with global technology firms such as Nvidia and OpenAI announcing partnerships with Indian industry and academic institutions to strengthen India’s artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem.
This marks a significant step in India’s efforts toward building Sovereign AI capabilities.
Sarvam AI
- Founded in 2023, headquartered in Bengaluru.
- Objective: Develop foundational AI models tailored to Indian languages and socio-economic contexts.
- Focus on multilingual and multimodal AI suited for India’s governance and development needs.
Key Features of the “Vikram” Models
- India-Specific Optimisation
- Designed for Indian administrative, social and economic applications.
- Strong performance in Indian language document processing and speech recognition.
- Multimodal Capabilities
- Integrates text, speech and visual understanding.
- Enables use cases in governance, healthcare, education and digital services.
- Edge and Offline AI Models
- Models capable of running on devices without continuous internet connectivity.
- Supports translation, speech-to-text and other AI functions locally.
- Reduces dependence on cloud-based foreign infrastructure.
Sovereign AI: Meaning and Significance
Sovereign AI refers to the development of AI systems using domestically controlled infrastructure, data and expertise, covering the entire lifecycle - from data collection and model training to deployment and governance.
It aims to:
- Reduce dependence on US/China-based AI platforms.
- Ensure data security and privacy.
- Promote cultural and linguistic relevance.
- Strengthen national security and strategic autonomy.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
- LLMs are AI systems based on deep learning techniques.
- Trained on large volumes of unstructured data.
- Capable of understanding, summarising, generating and predicting text.
- Use probabilistic modelling to recognise patterns in language without explicit programming.
Potential Benefits for India
- Technological & Economic Gains
- Boosts domestic innovation ecosystem.
- Encourages startup growth and high-skill employment.
- Enhances productivity across sectors.
- Human Capital Development
- AI integration in education and skilling programmes.
- Supports India’s demographic dividend with future-ready skills.
- Improved Governance
- Multilingual AI can enhance e-governance delivery.
- Applications in healthcare diagnostics, agriculture advisory, climate modelling and urban planning.
- Digital Inclusion
- Bridges linguistic barriers for non-English speakers.
- Expands participation in the digital economy.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign AI infrastructure and proprietary systems.
Tidal Flooding

- 19 Feb 2026
In News:
The Government of Kerala has declared tidal flooding as a State-specific disaster. It is the first time in India that a State has accorded such status to tidal flooding.
What is Tidal Flooding?
- Also known as:
- Sunny day flooding
- King tide flooding
- Nuisance flooding
- Definition: Temporary inundation of low-lying coastal areas due to unusually high tides, without heavy rainfall or cyclonic activity.
Causes
- Combination of:
- High tide cycles
- Full moon and new moon phases
- Offshore storms
- Strong coastal winds
- Occurs twice daily with tidal cycles.
- More severe during spring tides (full moon and new moon).
- Unlike cyclone-induced storm surges, it is periodic and predictable, though intensifying due to sea-level rise.
Impact on Kerala Coast
- Common along Kerala’s coastline bordering the Arabian Sea.
- Temporary rise in sea level above identified thresholds.
- Inundates low-lying coastal settlements and agricultural lands.
- Affects fisheries, livelihoods, housing, and infrastructure.
Kerala Government’s Decision
Kerala became the first State in India to declare tidal flooding as a State-specific disaster, enabling financial assistance under SDRF norms.
- Victims will receive financial assistance similar to other notified natural disasters.
- Relief to be provided through the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) framework.
Other State-Specific Disasters in Kerala
Kerala has also notified the following as State-specific disasters:
- Coastal erosion
- Lightning
- Strong winds
- Soil piping
- Heatwave / Sunstroke / Sunburn
- Human–wildlife conflict
Significance
Disaster Management Perspective
- Recognises climate-linked coastal risks beyond cyclones.
- Enhances institutional preparedness and targeted relief.
Climate Change Link
- Sea-level rise and coastal vulnerability are increasing frequency and severity.
- Highlights need for coastal zone management and adaptation planning.
AI-Preneurs of India

- 19 Feb 2026
In News:
The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) under NITI Aayog launched AI-Preneurs of India at the India AI Impact Summit 2026 held at Bharat Mandapam.
About AI-Preneurs of India
- Nature: Flagship coffee table book.
- Edition: 7th edition of AIM’s Innovations For You series.
- Coverage: Chronicles journeys of 45 AI startups.
- Source Base: Selected from nationwide network of Atal Incubation Centres (AICs).
- Focus: AI solutions addressing real-world problems across India.
Key Features
- Founder-First Storytelling Approach
- Highlights motivations, challenges, perseverance and impact of entrepreneurs.
- Moves beyond technical achievements to human-centered innovation narratives.
- Sectoral Diversity (30 Domains): AI applications showcased in sectors such as:
- Healthcare
- Education
- Sustainability
- Mobility
- Sports analytics
- Deep-tech
- Governance and social impact
- Nationwide Representation
- Reflects geographic diversity beyond metro tech hubs.
- Demonstrates innovation emerging from Tier 2/3 cities and underserved regions.
- Purpose-Driven AI Ecosystem
- Emphasizes inclusive, ethical, and socially responsible AI.
- Aligns AI development with national development priorities.
Significance for India
Positions India as a global contributor to responsible and inclusive Artificial Intelligence, not merely a consumer of frontier technologies.
- Strengthens credibility of India’s public innovation infrastructure.
- Showcases synergy between government incubation platforms and private AI startups.
- Reinforces AI for social good and mission-led governance.
- Supports India’s emergence as a deep-tech and AI innovation hub.
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
About
- Launched in 2016 by NITI Aayog.
- Flagship initiative of the Government of India to promote innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Builds a problem-solving mindset among students and supports startup ecosystems.
Key Programs under AIM
|
Program |
Target Group |
Objective |
|
Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) |
School students (Classes 6–12) |
Foster innovation using tools like robotics, 3D printing, electronics |
|
Atal Incubation Centres (AICs) |
Startups & entrepreneurs |
Provide incubation, mentorship, funding, infrastructure |
|
Atal Community Innovation Centres (ACICs) |
Underserved regions |
Promote innovation in Tier 2/3 cities, tribal & remote areas |
|
Atal New India Challenges (ANIC) |
Technology innovators |
Support innovations addressing national priority challenges |
|
Mentor India |
Entrepreneurs & innovators |
Network of 6,200 mentors guiding startups |
Loggerhead Turtle

- 18 Feb 2026
In News:
Recent scientific observations indicate that rising ocean temperatures and declining food availability are significantly affecting the reproductive cycles, migratory behavior, and even body size of the loggerhead turtle. These developments underline the far-reaching ecological consequences of climate change on marine megafauna and highlight emerging conservation challenges.
About the Loggerhead Turtle
The loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) is an oceanic turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It derives its name from its disproportionately large head, which houses powerful jaw muscles adapted for crushing hard-shelled prey.
Key Characteristics
- Size:
- World’s largest hard-shelled turtle
- Second-largest extant turtle after the leatherback sea turtle
- Lifespan: Can live for 80 years or more
- Navigation: Uses Earth’s geomagnetic field to navigate vast oceanic distances
- Diet: Omnivorous; primarily consumes bottom-dwelling invertebrates such as gastropods, bivalves, and decapods
- Habitat: Found both in open oceans and inshore ecosystems like bays, lagoons, salt marshes, and creeks
- Distribution: Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List – Vulnerable
Climate Change and Emerging Ecological Impacts
1. Altered Reproductive Patterns
- Loggerhead turtles exhibit temperature-dependent sex determination, where warmer sand temperatures produce more female hatchlings. Rising global temperatures are skewing sex ratios, potentially threatening long-term population stability.
- Additionally, warming seas are disrupting nesting timelines and hatchling survival rates, affecting recruitment into adult populations.
2. Changes in Migration Routes
- Loggerheads rely on geomagnetic cues to navigate across ocean basins. However, changing ocean currents and temperature gradients are altering traditional migratory pathways. Shifts in feeding grounds may force turtles to travel longer distances, increasing energy expenditure and exposure to threats such as fishing gear and marine pollution.
3. Impact on Body Size and Growth
- Studies suggest that declining prey availability linked to ocean warming and ecosystem shifts may be affecting growth rates and adult body size. Reduced food intake can influence reproductive success, as larger females generally produce more eggs.
Four-Pronged Threats
Climate change intensifies existing anthropogenic pressures:
- Rising Ocean Temperatures: Affect physiology, nesting, and food webs.
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Coastal development and erosion reduce nesting beaches.
- Marine Pollution: Plastic debris and oil spills cause ingestion and entanglement.
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental capture remains a major mortality factor.
Direct harvesting of turtles and eggs in some regions further compounds population decline.
Ecological Significance
- Loggerhead turtles play a crucial role in marine ecosystems by regulating populations of invertebrates and maintaining healthy benthic communities. Their decline can disrupt trophic balance and impact overall ocean biodiversity.
Conservation Imperatives
Addressing the challenges faced by loggerhead turtles requires:
- Strengthening marine protected areas
- Regulating coastal development
- Promoting climate mitigation strategies
- Reducing bycatch through turtle-excluder devices
- Enhancing global cooperation under marine conservation frameworks
LHS 1903 Planetary System

- 18 Feb 2026
In News:
Astronomers using the European Space Agency’s Cheops (Characterising Exoplanet Satellite) telescope have discovered an unusual four-planet system orbiting the red dwarf star LHS 1903, located approximately 117 light-years from Earth. The system’s planetary arrangement contradicts conventional models of planet formation, offering fresh insights into the dynamics of exoplanetary systems.
System Overview
The LHS 1903 system consists of four planets:
- Two rocky Super-Earths
- Two gaseous mini-Neptunes
These planets orbit a relatively small and dim red dwarf (M-dwarf) star.
Characteristics of the Host Star
- Mass: ~50% of the Sun’s mass
- Luminosity: ~5% of the Sun’s brightness
- Cooler and less luminous than the Sun
- Red dwarfs are the most common type of star in the Milky Way
Given their abundance and longevity, red dwarfs are important targets in the search for potentially habitable exoplanets.
Planetary Composition
- Super-Earths (Rocky Planets)
- Similar composition to Earth
- Mass between 2 to 10 times that of Earth
- Solid surfaces
- Mini-Neptunes (Gaseous Planets)
- Larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune
- Possess thick gaseous envelopes
- Often rich in hydrogen and helium
The sequence of planets from the star outward is as follows:
- Innermost: Rocky (Super-Earth)
- Middle two: Gaseous (Mini-Neptunes)
- Outermost (Fourth planet): Rocky (Super-Earth)
The Formation Paradox
Traditional models of planetary formation suggest that:
- Rocky planets form closer to the host star, where high temperatures prevent gas accumulation.
- Gas giants and gaseous planets form farther out, where volatile compounds can condense.
However, in the LHS 1903 system, the outermost planet is rocky, even though it lies beyond two gaseous planets. According to classical theory, it should have retained a substantial gaseous envelope.
Possible Explanations
Researchers propose two leading hypotheses:
- Sequential Formation Model: The planets may not have formed simultaneously. Instead, the inner planets could have formed first, consuming much of the available gas in the protoplanetary disk. By the time the fourth planet formed, insufficient gas remained for it to develop a thick atmosphere.
- Atmospheric Loss Hypothesis: The outer rocky planet may originally have possessed a gaseous envelope but later lost it due to a catastrophic event such as stellar radiation, atmospheric stripping, or collision, leaving behind a dense rocky core.
Both possibilities challenge the simplicity of existing models and suggest that planet formation may be more dynamic and episodic than previously understood.
Habitability Potential
The outer rocky planet has an estimated surface temperature of approximately 60°C. While relatively warm, this temperature falls within a theoretical range that does not automatically preclude habitability, especially if atmospheric or geological conditions are favorable.
Given the long lifespans of red dwarf stars, such systems are considered promising in the search for habitable exoplanets.
Scientific Significance
The LHS 1903 system provides:
- A test case for refining planet formation theories
- Insights into atmospheric evolution and planetary migration
- Evidence that planetary architectures may be more diverse than predicted
As observational capabilities improve, discoveries like this will deepen understanding of how planetary systems evolve and expand the scope of astrobiological exploration.
Discovery of Two New Army Ant Species in the Eastern Ghats
- 17 Feb 2026
In News:
In a significant contribution to India’s biodiversity records, researchers from Karnataka and Odisha have discovered two new species of army ants - Aenictus chittoorensis and Aenictus lankamallensis - in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh. The discovery highlights the rich yet underexplored biodiversity of peninsular India and underscores the ecological importance of invertebrate fauna in tropical ecosystems.
About Army Ants
Army ants belong to the subfamily Dorylinae and are known for their nomadic and highly predatory lifestyle. Unlike many other ant species, army ants do not construct permanent nests. Instead, they continuously move in search of food, making them one of the most dynamic components of tropical forest ecosystems.
They are predominantly found in tropical regions and are considered among the “big cats” of the insect world due to their aggressive and coordinated hunting behavior.
Distinctive Characteristics
- Nomadic Lifestyle: Army ants lack permanent nests. Instead, they form temporary living structures called bivouacs, created entirely from the interlocked bodies of worker ants.
- Massive Coordinated Raids: Colonies conduct synchronized raids, overwhelming insects and small invertebrates in their path. Their raids can drastically alter local arthropod populations.
- Morphological Features:
- Large, sharp mandibles
- Strong stinging ability
- Robust body structure adapted for predation
- Chemical Communication: Army ants are practically blind and rely heavily on chemical pheromones to navigate and communicate. They mark trails and follow scent paths laid by other workers.
- Colony Structure:
- A single queen lays all eggs.
- Female workers perform tasks such as foraging, protecting the colony, and tending to larvae.
This high degree of social organization reflects advanced eusocial behavior.
Ecological Role: Keystone Predators
Army ants are considered keystone predators in tropical ecosystems. Their ecological contributions include:
- Regulating arthropod populations by consuming large quantities of insects daily.
- Influencing forest biodiversity by reshaping prey communities.
- Supporting ecological networks — several bird species are known to follow army ant raids to capture fleeing insects.
By controlling invertebrate populations, they help maintain ecological balance and prevent outbreaks of certain insect species.
Significance of the Discovery
- Biodiversity Documentation: The identification of Aenictus chittoorensis and Aenictus lankamallensis adds to India’s documented insect diversity and strengthens taxonomic knowledge of the Eastern Ghats.
- Eastern Ghats as a Biodiversity Hotspot: Though less celebrated than the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats possess significant endemic diversity. Discoveries such as this underline the need for systematic biodiversity surveys in these fragmented hill ranges.
- Conservation Imperative: Habitat fragmentation, deforestation, mining, and climate change threaten forest ecosystems in the Eastern Ghats. The discovery reinforces the urgency of conserving lesser-known invertebrate fauna alongside charismatic megafauna.
- Scientific Relevance: Understanding army ant behavior and ecological dynamics can contribute to broader ecological research on predator-prey relationships and forest ecosystem functioning.
Startup India Fund of Funds 2.0
- 17 Feb 2026
In News:
In February 2026, the Union Cabinet approved the establishment of Startup India Fund of Funds 2.0 (FoF 2.0) under the Startup India initiative. With a corpus of ?10,000 crore, the scheme aims to mobilise long-term domestic capital, strengthen the venture capital (VC) ecosystem, and accelerate innovation-led economic growth. It represents the next phase of India’s startup policy architecture, moving from ecosystem creation to strategic capital deepening.
Background: Evolution of Startup India
Launched in 2016, the Startup India initiative has transformed India into one of the world’s largest startup ecosystems.
- Growth from fewer than 500 startups in 2016 to over 2 lakh DPIIT-recognised startups today.
- 2025 recorded the highest-ever annual startup registrations, indicating sustained entrepreneurial momentum.
To address early-stage funding gaps, the Government launched the Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS 1.0) in 2016.
Performance of FFS 1.0
- ?10,000 crore corpus fully committed to 145 Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs).
- Supported AIFs invested over ?25,500 crore in 1,370 startups.
- Investments spanned agriculture, AI, robotics, clean tech, fintech, biotechnology, manufacturing, space tech and more.
FFS 1.0 catalysed domestic venture capital, crowded in private investment, and nurtured first-time founders, laying a strong foundation for innovation financing.
Rationale for FoF 2.0
Despite ecosystem growth, structural gaps remain:
- Limited availability of patient capital for deep tech and high-risk sectors.
- Over-concentration of funding in metro cities.
- Dependence on foreign capital in the VC space.
- Funding constraints for early-growth stage startups.
FoF 2.0 seeks to address these high-risk capital gaps and align startup financing with national economic priorities.
Key Features of Startup India FoF 2.0
1. Financial Outlay: ?10,000 crore corpus dedicated to mobilising venture capital for startups.
2. Targeted, Segmented Funding Approach
(a) Deep Tech & Tech-Driven Manufacturing
- Focus on breakthrough technologies requiring long-term, patient capital.
- Supports sectors critical for strategic and economic self-reliance.
(b) Early-Growth Stage Support
- Acts as a safety net for innovative ideas.
- Reduces early-stage failures caused by funding shortages.
(c) National Reach
- Encourages investments beyond major metropolitan hubs.
- Promotes geographically inclusive innovation.
(d) Addressing High-Risk Capital Gaps: Directs greater capital to priority areas aligned with self-reliance and economic growth.
(e) Strengthening Domestic VC Base
- Special emphasis on smaller domestic funds.
- Reduces overdependence on foreign venture capital flows.
Economic and Strategic Significance
- Innovation-Led Growth: Supports globally competitive technologies and products.
- Manufacturing Boost: Aligns with the push for advanced and tech-driven manufacturing.
- Job Creation: Facilitates high-quality employment opportunities.
- Economic Resilience: Strengthens domestic capital formation in strategic sectors.
- Regional Inclusivity: Democratizes access to venture funding across states.
The scheme aligns with the broader vision of Viksit Bharat @ 2047, positioning startups as engines of structural transformation rather than peripheral economic actors.
Bio-based Chemicals and Enzymes

- 16 Feb 2026
In News:
India is prioritising bio-based chemicals and enzymes under the BioE3 policy to reduce petrochemical imports, promote sustainable manufacturing, and strengthen its bioeconomy.
What are Bio-Based Chemicals?
Bio-based chemicals are industrial chemicals produced from renewable biological feedstocks such as sugarcane, corn, starch, and agricultural residues, rather than fossil fuels. They are typically manufactured through fermentation, enzymatic conversion, or microbial processes using biomass.
Examples:
- Organic acids (e.g., lactic acid)
- Bio-alcohols
- Solvents
- Surfactants
- Chemical intermediates used in plastics, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals
These chemicals form a core component of the bioeconomy, which integrates biological resources and biotechnology into industrial production systems to create sustainable alternatives to petrochemicals.
What are Enzymes?
Enzymes are biological catalysts (mainly proteins) that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. While enzymes have been used traditionally in brewing and baking for centuries, modern industrial enzyme engineering expanded significantly in the 20th century with advances in biotechnology.
Enzymes are produced via microbial fermentation, followed by purification and formulation for industrial use.
Key Characteristics
- Renewable Feedstock Base – Derived from biomass instead of fossil hydrocarbons.
- Lower Carbon Footprint – Reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrochemical pathways.
- Energy Efficiency – Enzymes operate at lower temperatures and pressures.
- Biodegradability – Many bio-based products are environmentally friendly.
- High Specificity – Enzymes provide targeted catalytic action, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Applications
1. Chemical Industry
- Organic acids (lactic acid)
- Acetyl intermediates (acetic anhydride, ethyl acetate)
- Solvents and specialty chemicals
2. Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines: Active ingredient synthesis through fermentation technologies.
3. Food & Beverage: Brewing, baking, dairy processing.
4. Textiles & Detergents: Stain removal, fabric treatment.
5. Biomanufacturing & Clean Technology: Sustainable plastics, biofuels, specialty chemicals.
Why Does India Need Bio-Based Chemicals?
India has strong structural advantages:
- Large agricultural base (ample biomass availability)
- Established fermentation expertise (pharmaceuticals and vaccines)
- Expanding manufacturing ecosystem
- Rising demand for sustainable industrial inputs
India imported approximately $479.8 million worth of acetic acid in 2023, reflecting dependence on petrochemical imports. Scaling domestic bio-based chemical production can:
- Reduce import dependence
- Create value-added markets for agricultural produce
- Strengthen climate commitments
- Boost rural and industrial employment
Policy Support: BioE3 Initiative
India has identified bio-based chemicals and enzymes as priority sectors under the Department of Biotechnology’s BioE3 Policy.
BioE3 focuses on:
- Biomanufacturing scale-up
- Shared infrastructure (biofoundries, pilot plants, demonstration facilities)
- Innovation ecosystem development
- Reducing capital risk for emerging firms
Industry Landscape in India
Bio-Based Chemicals
- Praj Industries
- Godrej Industries
- Godavari Biorefineries
- Jubilant Ingrevia
- StringBio
Enzymes Market
The Indian enzyme market is highly consolidated, with top players accounting for over 75% market share.
Key companies:
- Novozymes India
- DuPont
- DSM
- Advance Enzyme Technologies
- BASF SE
- Ultreze Enzymes Private Limited
Global Initiatives
European Union
The EU Bioeconomy Strategy links industrial transformation with:
- Climate mitigation
- Circular economy
- Waste reduction
United States
- The USDA BioPreferred Program mandates federal procurement preference for certified bio-based products, helping create stable demand.
China
- Bioeconomy development plans prioritise high-value bio-based chemicals and enzyme technologies as strategic sectors.
Japan
- Projects supported by METI/NARO integrate research with manufacturing readiness in bio-based chemicals.
Yuva AI for All Initiative

- 16 Feb 2026
In News:
Launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) under the IndiaAI Mission, this initiative is a first-of-its-kind free AI literacy programme designed for mass outreach.
Key Features
- Target: Empower 1 crore (10 million) citizens with foundational AI skills.
- Duration: Approximately 4–4.5 hours, self-paced.
- Structure: Six modules covering:
- AI fundamentals
- Generative AI basics
- Ethics in AI
- Real-world applications
- Eligibility: No prior coding knowledge required.
- Certification: Official Government of India certificate upon completion.
- Accessibility: 100% free and open to all.
- Platforms: Available on
- FutureSkills Prime
- iGOT Karmayogi
- Coursera
- TCS iON and other ed-tech portals
The course is designed with India-specific examples, making it practical and relatable for students, professionals, and general learners.
Kaushal Rath: Mobile AI Awareness Initiative
To expand outreach beyond digital platforms, MeitY, in collaboration with the All India Society for Electronics and Computer Technology (AISECT), launched Kaushal Rath.
Key Highlights
- Flagged off from India Gate, New Delhi.
- Designed as a mobile computer lab equipped with:
- Internet-enabled systems
- Audio-visual tools
- Structured AI training modules
- Will travel to:
- Schools
- Colleges
- Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs)
- Community centers
- Provides:
- Hands-on exposure to AI and Generative AI tools
- On-the-spot course registrations
- Instructor-led sessions with trained facilitators
The initiative focuses particularly on semi-urban and underserved regions, ensuring AI awareness reaches beyond metropolitan centers.
Institutional Framework
IndiaAI Mission
The programme is part of the broader IndiaAI Mission, where skilling is one of the seven core pillars. The mission seeks to strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through:
- Capacity building
- Innovation support
- Ethical AI frameworks
- Workforce readiness
Link with India AI Impact Summit 2026
The initiative also serves as a precursor to the India AI Impact Summit 2026. The summit is positioned as:
- The first major global AI gathering hosted in the Global South.
- Focused on development-oriented AI outcomes.
- Thematically aligned with People, Planet and Progress.
Kaushal Rath will operate across Delhi-NCR in the run-up to the summit to generate public awareness and encourage AI adoption.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) – Base Year 2024 = 100

- 14 Feb 2026
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the first press note of the revised Consumer Price Index (CPI) series with base year 2024=100. The data reported retail inflation at 2.75% (Year-on-Year) for January 2026.
This marks the transition from the earlier base year 2012=100 to 2024=100, reflecting updated consumption patterns of households.
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the change in retail prices of a fixed basket of goods and services consumed by households over time.
- It is India’s headline retail inflation indicator.
- Inflation is expressed as the percentage change in CPI over the same month of the previous year (YoY).
Compiled and Published By
- Published by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- Through: National Statistical Office (NSO)
- Price collection: Field Operations Division of NSO
Base Year Revision
- New Base Year: 2024 = 100
- Earlier Base Year: 2012 = 100
- Weights Source: Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023–24
Base year revision ensures that:
- The consumption basket reflects current spending patterns.
- Inflation measurement aligns with structural changes in the economy.
Methodology Used in CPI (Base 2024)
1. Jevons Index (Item Level)
- Used at the individual item level.
- Calculates the average of price relatives (ratio of current to base prices).
- Reduces distortion caused by extreme values.
2. Young / Modified Laspeyres Index (Group Level)
- Aggregates item-level indices using fixed expenditure weights.
- Higher-weight items (e.g., food, rent) influence CPI more than low-spending items.
3. Combined CPI (All-India)
- Calculated by combining:
- Rural CPI
- Urban CPI
- Weighted by their respective shares in total consumption.
Thus, if rural consumption share is higher, rural inflation has greater influence on the all-India CPI.
Key Features of CPI (Base 2024=100)
1. Expanded Classification (12 Groups Instead of 6)
Earlier CPI had 6 major groups. The new series follows an updated international classification system with 12 broader and clearer categories, including:
- Food & beverages
- Housing
- Health
- Education
- Transport
- Communication
- Recreation & culture
- Miscellaneous services
2. Expanded Basket of Items
- Earlier basket: 299 items
- New basket: 358 items
The revised basket better captures:
- Modern consumption habits
- Digital and service-based spending
3. Greater Focus on Services
With rising income levels, household expenditure on services has increased.
The new series includes:
- OTT subions
- Healthcare services
- Education fees
- Transport services
- Communication services
4. Inclusion of Online Prices
Given the growth of e-commerce: Prices from online platforms (e.g., air tickets, subions) are now incorporated.
5. Introduction of Rural House Rent
For the first time:
- Rural housing rent is included in CPI.
- This improves representation of rural housing consumption.
6. Official Administrative Price Data
For certain regulated items, official government data is used directly:
- Rail fares
- Postal charges
- Petrol & diesel
- LPG
This enhances accuracy and consistency.
7. Digital Price Collection
- Field officers now use tablets instead of paper schedules.
- Improves timeliness, data accuracy and monitoring.
8. Detailed Monthly Dissemination
CPI data is now available:
- All-India
- State-wise
- Rural and Urban separately
This strengthens regional inflation analysis.
Importance of CPI
- Monetary Policy Anchor
- Retail inflation targeting framework is based on CPI.
- Guides RBI’s monetary policy decisions.
- Indexation
- Used for Dearness Allowance (DA) revision.
- Impacts wage negotiations.
- Macroeconomic Assessment
- Reflects purchasing power.
- Indicates cost-of-living trends.
Quorum Sensing
- 14 Feb 2026
In News:
The phenomenon of bacterial communication, known as quorum sensing, has emerged as a promising frontier in microbiology and medicine. Instead of killing bacteria outright, as antibiotics do, scientists are exploring ways to disrupt their communication systems, thereby weakening their ability to cause disease. This strategy, called anti-quorum sensing therapy, may become a crucial tool in tackling antimicrobial resistance.
What is Quorum Sensing?
Quorum sensing is a mechanism by which bacteria regulate gene expression according to their population density using chemical signalling molecules.
It enables bacterial populations to:
- Communicate with one another
- Coordinate collective behaviour
- Activate specific genes only when sufficient numbers are present
This coordination ensures that certain biological processes occur only when they are effective at large population sizes.
Historical Background
The phenomenon was first observed in the mid-1960s by Alexander Tomasz, who studied how Pneumococcus (later known as Streptococcus pneumoniae) takes up free DNA from its surroundings.
Modern understanding of quorum sensing has been significantly advanced by Bonnie Bassler of Princeton University, who described bacteria as “multilingual” organisms capable of chemical communication across species.
How Does Quorum Sensing Work?
A standard quorum-sensing system consists of:
- Bacterial population
- Signal molecules (Autoinducers)
- Response genes
Step-by-Step Mechanism
- Bacteria secrete signalling molecules called autoinducers into their environment.
- As the bacterial population grows, the concentration of autoinducers increases.
- When a threshold concentration is reached, bacteria detect these molecules.
- This triggers activation of specific genes that regulate group behaviours.
Behaviours Regulated by Quorum Sensing
Quorum sensing controls several crucial biological processes:
- Virulence (disease-causing ability)
- Biofilm formation (protective bacterial communities)
- Horizontal gene transfer
- Competence (ability to take up external DNA)
- Symbiotic interactions
- Cell growth regulation
Since many of these activities require coordinated mass action, quorum sensing acts as a population-based decision-making system.
Examples of Quorum Sensing in Action
1. Pathogenic Bacteria
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Regulates mechanisms causing pneumonia and bloodstream infections.
- Vibrio cholerae: Causes cholera; quorum sensing influences its virulence and disease progression.
2. Bioluminescent Symbiosis
- Vibrio fischeri: Produces blue light through quorum sensing. Lives in one-to-one symbiosis with certain squids, helping camouflage them in ocean waters.
3. Nitrogen Fixation
- Rhizobium leguminosarum: Uses quorum sensing in symbiotic nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants.
Why is Quorum Sensing a Game-Changer for Medicine?
1. Alternative to Antibiotics
Traditional antibiotics:
- Kill bacteria or stop their growth
- Create strong evolutionary pressure → antimicrobial resistance
Anti-quorum sensing therapies:
- Disrupt communication
- Prevent coordination of virulence
- Reduce pathogenicity without killing bacteria
This approach may slow the emergence of drug resistance.
2. Targeting Biofilms
Biofilms protect bacteria from antibiotics and immune responses. Interrupting quorum sensing can prevent biofilm formation, making infections easier to treat.
3. Applications Beyond Medicine
- Agriculture – Improved plant-microbe interactions
- Environment – Waste treatment and bioremediation
- Human Health – Gut microbiome regulation
Bacteria in the human gut aid digestion and nutrient absorption, showing that quorum sensing also plays a role in beneficial processes.
Carbon Capture, Usage and Storage
- 14 Feb 2026
In News:
The Prime Minister highlighted the importance of CCUS in decarbonising India’s heavy industries by sharing an article titled “Carbon capture can power India’s next steel revolution” authored by the Union Minister of Steel. Simultaneously, the Union Budget 2026–27 earmarked ?20,000 crore for a dedicated CCUS scheme, signalling a shift from pilot research to commercial deployment.
What is CCUS?
According to the International Energy Agency, Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) refers to a set of technologies that capture carbon dioxide (CO?) from:
- Large industrial sources (power plants, steel, cement, refineries), or
- Directly from the atmosphere (Direct Air Capture).
The captured CO? is compressed and transported for either utilization or permanent geological storage.
The Three-Step Process
1. Capture: CO? is separated from other gases using:
- Chemical solvents
- Membranes
- Solid sorbents
2. Transport: Compressed CO? is transported through:
- Pipelines
- Ships
- Road tankers
3. Utilization or Storage
- Utilization (CCU): Conversion into urea, methanol, synthetic fuels, chemicals, building materials, or use in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR).
- Storage (CCS): Injection into deep geological formations such as depleted oil and gas fields or saline aquifers for long-term sequestration.
Why is CCUS crucial for India?
1. Decarbonising ‘Hard-to-Abate’ Sectors
Industries like steel and cement emit CO? due to chemical processes (e.g., calcination of limestone), not merely fuel combustion. CCUS is currently the only scalable solution to reduce such intrinsic emissions without shutting down production.
2. Powering India’s Steel Expansion
- India is the world’s second-largest crude steel producer (after China).
- Production: ~152 million tonnes (FY 2024–25).
- Under the National Steel Policy 2017, targets:
- 300 MT capacity by FY 2030–31
- 500 MT by 2047 (Viksit Bharat vision)
- Steel accounts for 10–12% of India’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
While hydrogen-based steelmaking is the long-term solution, CCUS acts as a bridge technology, enabling “Low-Carbon Steel” using existing plants.
3. Enhancing Energy Security
India derives 55–60% of its primary energy from coal. Immediate fossil fuel phase-out is economically disruptive. CCUS allows continued coal usage with reduced emissions during transition.
4. Circular Economy & Industrial Value Addition
Captured CO? can be:
- Converted to methanol (clean fuel)
- Used in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
- Converted into green urea or building materials
Thus, emissions become economic resources.
5. Safeguarding Exports from Carbon Taxes
Global trade is increasingly climate-regulated under mechanisms like the European Union Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
Low-carbon steel:
- Reduces export vulnerability
- Attracts climate-aligned investments
- Prevents “stranded assets” in India’s relatively young steel plants
6. Alignment with Global Commitments
CCUS supports:
- Paris Agreement (limit warming to 1.5–2°C)
- Sustainable Development Goals (Climate Action, Affordable & Clean Energy, Industry & Innovation)
India’s Key Initiatives on CCUS
1. Budgetary Push (2026–27)
- ?20,000 crore over five years
- Target sectors: Power, Steel, Cement, Refineries, Chemicals
2. NITI Aayog Policy Framework
- Proposed Viability Gap Funding (VGF)
- Development of CCUS hubs in industrial clusters (e.g., Gujarat, Odisha)
- Shared pipeline and storage infrastructure
3. Green Steel Taxonomy
Steel with emissions <2.2 tCO?e per tonne of crude steel qualifies as “Green Steel” (3–5 star ratings), incentivising adoption of CCUS and avoiding carbon taxes.
4. R&D and Institutional Support
National Centres of Excellence (NCoE-CCU)
- IIT Bombay
- Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research
DST Roadmap
- Pilot phase: 2025–30
- Commercial scale-up: 2035–45
Mission Innovation Challenge (2018)
- Joint initiative of DST & DBT
- Collaboration with 24 countries
- Focus on breakthrough capture and utilization technologies
Indigenous Dog Breeds in Assam Rifles

- 14 Feb 2026
In News:
The Assam Rifles, India’s oldest paramilitary force, has initiated the induction of two indigenous dog breeds—Tangkhul Hui (Haofa) from Manipur and Kombai from Tamil Nadu into its dog squads. The move aligns with the 2025 directive of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) encouraging greater adoption of Indian canine breeds in armed forces.
This initiative aims to reduce long-term dependence on foreign breeds such as Belgian Malinois, German Shepherd, and Labrador, with full operational induction of indigenous breeds targeted by 2027 and gradual replacement of foreign breeds by 2050.
Assam Rifles:
- Established in 1835 as the Cachar Levy.
- India’s oldest paramilitary force.
- Functions under dual control:
- Administrative: Ministry of Home Affairs
- Operational: Ministry of Defence
- Primary roles:
- Counter-insurgency in the Northeast
- Guarding the Indo-Myanmar border
- Operates the Assam Rifles Dog Training Centre (ARDTC), Jorhat, its sole canine training facility.
Role of Dog Squads
Dogs are trained for:
- Trackers – Follow human/animal trails in difficult terrain.
- Guard dogs – Secure camps, convoys, and border posts.
- Detection dogs – Identify hidden arms, explosives, and narcotics.
They are particularly deployed in sensitive regions like the Northeast and Jammu & Kashmir.
Tangkhul Hui (Haofa)
Origin
- Native to Ukhrul district, Manipur
- Raised traditionally by the Tangkhul tribe
- Originally developed as a hunting companion (sighthound)
Key Features
- Large, strong body; deep chest and powerful jaws
- Usually black with white markings
- Erect ears and alert expression
- Highly disease-resistant
- Strong stamina (more endurance than speed)
- Intelligent and protective
Current Status
- Part of a pilot project since 2022
- Six dogs already trained and deployed in narcotics detection
- Purebred population is declining, making it relatively rare
Kombai (Polygar Dog)
Origin
- Indigenous to Kombai region, Theni district, Tamil Nadu
- Also known as:
- Polygar Dog
- Indian Bore Hound
- Combai
Historical Use
- Guarding property
- Hunting wild boar and large game
- Used by South Indian royalty and warriors
- Employed in regional military contexts historically
Key Characteristics
- Muscular, athletic build
- Broad head, deep chest, strong limbs
- Short, smooth reddish-brown coat
- Distinct black mask-like muzzle
- Loyal, protective, highly defensive
- Hardy and disease-resistant
Induction Plan
- First batch (2 males, 8 females) scheduled for induction in April 2026
- Full integration expected by March 2027
Dolphin Census in Odisha
- 13 Feb 2026
In News:
Odisha has registered its highest marine dolphin population in the past five years, with 765 dolphins recorded in the 2026 State-wide census. The estimation highlights stable to improving population trends and underscores the role of sustained conservation, habitat protection, and community participation.
About the Dolphin Census in Odisha
What is it?
- An annual scientific population estimation exercise assessing the abundance, distribution, and diversity of dolphins and other cetaceans in Odisha’s marine, estuarine, and lagoon ecosystems.
Conducting Authority
The census is conducted by the Wildlife Wing of the Forest, Environment and Climate Change Department, Government of Odisha. It involves:
- Forest officials and frontline staff
- Marine experts
- Boat-based and shore-based transect surveys
- Training in species identification and safety protocols
The exercise began in Chilika in 2008 and expanded to all coastal forest divisions since 2015.
Key Findings: Dolphin Census 2026
Total Population: 765 dolphins (An increase of 55 individuals compared to the previous year)
Species-wise Distribution
- Humpback Dolphins – 497
- Irrawaddy Dolphins – 208
- Bottlenose Dolphins – 55
- Spinner Dolphins – 3
- Finless Porpoise – 2
Key Conservation Zones
Chilika Lake
- Recorded 159 Irrawaddy dolphins.
- Hosts the largest single-area concentration of Irrawaddy dolphins globally.
- It is a Ramsar Site (wetland of international importance).
- Population has remained stagnant for two years due to:
- Slow breeding rate
- Habitat stress (prawn gheries, nylon fishing nets)
- Possible migration to other areas
Irrawaddy dolphins were also sighted in:
- Balasore
- Berhampur
- Puri Wildlife Division
- Rajnagar Mangrove Division
Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary
- Emerged as a strong marine conservation zone.
- Recorded 474 Humpback dolphins, the highest among surveyed regions.
Conservation Significance
- Dolphins are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (highest level of legal protection).
- The Irrawaddy dolphin is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Dolphins serve as flagship and indicator species of marine ecosystem health.
Reasons for Population Improvement
- Habitat protection measures
- Regulation of fishing practices
- Community participation drives
- Scientific monitoring and inter-divisional coordination
- Capacity building of field staff
About Dolphins (General Features)
Dolphins are aquatic marine mammals belonging to the order Cetacea.
Key Characteristics:
- Highly intelligent; capable of complex communication.
- Use echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Social animals living in pods.
- Slow breeding rate (especially Irrawaddy dolphins).
- Indicators of marine ecosystem health.
Species Found in Odisha
- Humpback Dolphin
- Irrawaddy Dolphin
- Bottlenose Dolphin
- Spinner Dolphin
- Finless Porpoise (closely related cetacean)
B-READY Assessment

- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
India’s business reform trajectory has gained renewed focus with its inclusion in the Business Ready 2026 (B-READY) assessment by the World Bank Group. The B-READY framework replaces the discontinued Doing Business Report (DBR), which was halted in 2020.
Under the last DBR (2019), India ranked 63rd, having improved by 79 ranks over five years. The upcoming B-READY 2026 assessment will evaluate over 180 countries across a modernised and more comprehensive framework.
About B-READY (Business Ready Assessment)
Launched in 2024, B-READY is a global benchmarking exercise to assess the business and investment climate.
Key Features:
- Covers 10 topics across the full business lifecycle:
- Business Entry
- Business Location
- Utility Services
- Labour
- Financial Services
- International Trade
- Taxation
- Dispute Resolution
- Market Competition
- Business Insolvency
- Structured under three pillars:
- Regulatory Framework (de jure laws and rules)
- Public Services (infrastructure, digital systems, licensing bodies)
- Operational Efficiency (de facto implementation via firm-level surveys)
- Integrates cross-cutting themes such as:
- Digital adoption
- Environmental sustainability
- Gender inclusion
Data is collected through expert consultations and World Bank Enterprise Surveys (WBES).
Domestic Reform Measures in India
To improve the business climate, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has implemented multiple initiatives under the Ease of Doing Business framework.
1. Business Reforms Action Plan (BRAP)
Launched in 2014, BRAP assesses States/UTs on regulatory reforms.
- Seven editions completed (2015–2024)
- Over 9,700 reforms implemented across States/UTs
- Focus areas: single-window systems, building permissions, inspection reforms, digitisation of approvals
2. Reducing Compliance Burden (RCB) Initiative
Launched in 2020, aimed at rationalising redundant compliances.
- Over 47,000 compliances reduced in five years:
- 16,109 simplified
- 22,287 digitised
- 4,623 decriminalised
- 4,270 eliminated
Under RCB , 4,846 compliances were reduced across 23 commonly implemented Acts.
3. Jan Vishwas Reforms
The Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023 decriminalised 183 provisions across 42 Acts.
The proposed Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Bill, 2025 seeks to:
- Amend 355 provisions
- Decriminalise 288 provisions
- Modify 67 provisions to enhance Ease of Living
4. National Single Window System (NSWS)
The National Single Window System (NSWS) provides integrated clearance mechanisms.
- Integrated with 32 Central Ministries/Departments
- Integrated with 33 States/UTs
- Offers access to:
- 300 Central approvals
- 3,000 State-level approvals
Provides real-time tracking via an Investor Dashboard.
Significance
These reforms aim to:
- Reduce regulatory overlaps
- Harmonise compliance frameworks across States
- Digitise approvals and reduce turnaround time
- Attract domestic and foreign investment
The B-READY 2026 assessment will evaluate how effectively India’s regulatory reforms translate into real-world business efficiency.
India as ‘Country of the Year’ at BIOFACH 2026
- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
- India has been recognised as the ‘Country of the Year’ at BIOFACH 2026, the world’s premier trade fair for organic food and agriculture. The event is held annually at the Nuremberg Messe Exhibition Centre in Germany and is managed by NürnbergMesse GmbH.
- This recognition reflects India’s growing prominence in the global organic sector and its expanding footprint in sustainable agriculture and exports.
About BIOFACH
BIOFACH is widely regarded as the world’s leading international platform for certified organic products.
Key Features:
- Focus on organic food and agriculture
- Promotes global trade in certified organic products
- Facilitates B2B networking among producers, exporters, retailers and policymakers
- Encourages sustainable farming practices and environmentally responsible consumption
- Serves as a hub for innovation in organic farming and processing technologies
Significance for India
1. Strengthening Global Organic Leadership
India’s designation positions it as a major supplier of certified organic produce at a time when global demand for sustainable food systems is rising.
2. Boost to Agricultural Exports
The recognition enhances India’s visibility and market access for organic exports such as:
- Organic rice
- Spices
- Pulses
- Oilseeds
- Cashew
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Mango puree
- Essential oils
3. Promotion of GI-Tagged Products
India is showcasing five GI-tagged rice varieties, reinforcing the branding of its traditional agricultural heritage and geographical diversity.
4. Empowerment of FPOs and Regional Producers
Participation from over 20 States and Union Territories highlights inclusive growth and the integration of grassroots producers, including Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), into global value chains.
5. Soft Power and Culinary Diplomacy
Live tastings and demonstrations, including organic biryani and heritage rice varieties, strengthen India’s cultural outreach and organic brand identity internationally.
Gravity and Earth’s Motion Through Space

- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
Gravity is the fundamental force governing the motion of celestial bodies and sustaining life on Earth. It not only keeps humans, oceans and the atmosphere anchored to the planet, but also ensures the stability of Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the Moon’s orbit around Earth.
Gravity as a Binding Force
Gravity acts as the universal attractive force between masses. On Earth, it:
- Keeps the atmosphere from escaping into space
- Holds oceans and land masses in place
- Enables life by maintaining stable environmental conditions
Without gravity, Earth’s atmosphere and hydrosphere would disperse into space, making life impossible.
Gravity as a Centripetal Force
Beyond pulling objects downward, gravity functions as a centripetal force-a force directed toward the centre of circular motion.
- It keeps the Moon in orbit around Earth.
- It keeps Earth revolving around the Sun.
In circular motion, centripetal force continuously changes the direction of velocity without necessarily altering speed. In planetary systems, gravitational attraction provides this inward pull.
Earth’s Planetary Motion
Due to gravitational attraction between Earth and the Sun:
- Earth completes one revolution every year.
- It travels nearly 1 billion kilometres along its orbital path annually.
- The planet moves at an average speed of approximately 1,07,000 km per hour (about 30 km per second).
These figures highlight the dynamic nature of planetary motion, even though such movement is imperceptible to humans due to uniform velocity and lack of external reference points.
Absence of Friction in Space
Unlike motion on Earth, where friction slows moving objects-planets move through the near-vacuum of outer space.
- Space offers negligible resistance.
- As a result, celestial bodies can continue moving without continuous energy input.
This aligns with Newton’s First Law of Motion, which states that an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
Rejection of the Aether Hypothesis
In the 19th century, scientists proposed the existence of an invisible medium called “aether” through which light and celestial bodies were thought to move. However, the Michelson–Morley experiment disproved this hypothesis in 1887.
The experiment showed no detectable aether wind, confirming that Earth moves through empty space rather than through a resisting substance.
Scientific Significance
The understanding of gravity:
- Explains orbital mechanics and planetary stability
- Supports space exploration and satellite deployment
- Underpins astrophysics and cosmology
Gravity’s dual role, as a binding force on Earth and as a centripetal force in celestial mechanics—demonstrates its foundational importance in sustaining both terrestrial life and cosmic order.
Discovery of Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala

- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
Researchers have identified a new dragonfly species named Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala, extending the known geographical range of the genus beyond northeast India. The discovery underscores the rich biodiversity of the Western Ghats and the importance of careful taxonomic studies.
Taxonomic Clarification
Although the species has been present in Kerala since 2013, it was misidentified for over a decade as Lyriothemis acigastra. Detailed morphological examination, including microscopic analysis and comparison with museum specimens, confirmed its distinct identity.
This highlights:
- The importance of systematic taxonomy
- The role of reference collections in biodiversity research
- Potential underestimation of species diversity in India
Key Features
The species exhibits pronounced sexual dimorphism:
- Males: Bright blood-red body with black markings
- Females: Yellow body with black markings
Such colour variation aids in species identification and reproductive behaviour studies.
Habitat and Ecology
Unlike many dragonflies associated with pristine forest ecosystems, Lyriothemis keralensis thrives in human-modified irrigation landscapes, including:
- Pineapple plantations
- Rubber plantations
- Shaded irrigation canals
Most recorded populations occur outside protected areas, indicating that biodiversity conservation must extend beyond national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Seasonality and Life Cycle
The species is:
- Seasonally visible during the Southwest Monsoon (late May to August)
- Present as aquatic larvae in water bodies for the remainder of the year
This seasonal emergence aligns with monsoon-driven ecological cycles in Kerala.
Conservation Concerns
The discovery raises important conservation issues:
- Plantation-dominated landscapes may act as secondary habitats
- Changes in irrigation patterns, pesticide use, and land conversion could threaten populations
- Lack of protection outside designated conservation zones may expose species to habitat loss
The finding reinforces the need for biodiversity-sensitive land-use planning, especially in agriculturally modified ecosystems.
Strengthening India’s Tsunami Early Warning System

- 11 Feb 2026
implemented by the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), which operates the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC).
Location and Regional Role
- Proposed site: Vijaynagar on Swaraj Dweep, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Project cost: ?300 crore
- First-of-its-kind tsunami coordination centre in India
- Will provide warning services to Indian Ocean countries, including Sri Lanka
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands lie close to major tectonic activity zones, making them strategically important for tsunami detection.
Limitations of the Current System
Currently, tsunami warnings are processed at INCOIS headquarters in Hyderabad. The system relies on:
- Seismic signals
- Tidal gauges along the Indian coast
- Surface buoys deployed in the Indian Ocean
- Satellite data
However, the existing system primarily detects earthquake-triggered tsunamis, which account for about 80% of global tsunamis. Nearly 20% are caused by non-seismic sources such as:
- Submarine landslides
- Volcanic eruptions
- Mudslides
Surface buoys are also vulnerable to vandalism and theft, and satellite data sometimes has gaps.
Next-Generation Capabilities
The new RSC will develop a system capable of detecting both seismic and non-seismic tsunamis, significantly enhancing early warning capacity.
Key Technological Features:
- Laying of 270 km-long sub-sea cables along tectonic subduction zones
- Improved monitoring of acoustic signals, which travel faster than conventional seismic signals
- Reduced data gaps compared to surface buoys
Subduction zones are regions where one tectonic plate moves beneath another, often generating earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Vulnerability of Indian Coasts
While India’s east coast has experienced past tsunamis (notably in 2004), experts highlight emerging risks:
- The west coast of India may be vulnerable to non-seismic tsunamis due to fragile marine geology.
- Presence of underwater mud volcanoes along the Makran coast increases risk potential.
- India’s only active volcano at Barren Island in the Andaman Sea also poses a latent threat.
- If an epicentre is located close to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the islands themselves could face severe impact.
Ethylene Glycol

- 11 Feb 2026
In News:
Recent laboratory findings in Tamil Nadu detected ethylene glycol adulteration in a batch of Almond Kit syrup, prompting a public health alert. Such incidents highlight the serious risks posed by contamination of pharmaceutical or food products with industrial chemicals like ethylene glycol (EG) and diethylene glycol (DEG).
About Ethylene Glycol (EG)
Ethylene glycol is the simplest member of the glycol family of organic compounds.
Key Properties
- Colourless, odourless, slightly viscous liquid
- Faintly sweet taste
- Miscible with water and alcohol
- Low volatility (does not evaporate quickly)
- Stable over a wide temperature range
- Inexpensive to manufacture
Because of these properties, it is widely used in industry but is highly toxic if ingested.
Uses of Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol has multiple industrial applications:
- Antifreeze and de-icing solutions for cars, aircraft and boats
- Component of hydraulic brake fluids
- Used in printing inks (stamp pads, ballpoint pens, print shops)
- Industrial reagent in the manufacture of:
- Polyesters
- Alkyd resins
- Explosives
- Synthetic waxes
Its chemical stability and freezing-point depression properties make it suitable for coolant systems.
Health Impact and Toxicity
Though industrially valuable, ethylene glycol is highly toxic when consumed. It is not inherently dangerous in small dermal exposures but becomes lethal when ingested.
Mechanism of Toxicity
After ingestion, ethylene glycol is metabolised in the liver into toxic compounds such as:
- Glycolic acid
- Oxalic acid
These metabolites cause:
- Severe metabolic acidosis
- Acute kidney injury
- Nervous system depression
- Multi-organ failure
If untreated, poisoning can result in significant morbidity and mortality. Early medical intervention using antidotes such as fomepizole or ethanol can block toxic metabolism.
Diethylene Glycol (DEG): A Related Public Health Hazard
Diethylene glycol, chemically similar to ethylene glycol, has been implicated in multiple drug adulteration incidents globally. Like ethylene glycol, it is:
- Used as an industrial solvent
- Sweet-tasting and colourless
- Toxic when ingested
DEG contamination in medicines, especially cough syrups, has historically led to mass poisoning incidents due to renal failure and metabolic acidosis. These cases underline the importance of strict pharmaceutical quality control and regulatory vigilance.
Public Health and Regulatory Significance
The recent detection of ethylene glycol in a medicinal syrup underscores:
- The need for stringent drug testing and quality assurance
- Strong enforcement of pharmaceutical manufacturing standards
- Rapid public communication in case of contamination
Such incidents highlight the role of regulatory authorities in preventing industrial chemicals from entering consumable products.
Mons Mouton

- 11 Feb 2026
In News:
India’s upcoming Chandrayaan-4 mission marks a significant leap in its space exploration programme. Approved by the Union Government, Chandrayaan-4 is designed as India’s first lunar sample-return mission and is expected to launch around 2028, as indicated by ISRO leadership. It will be India’s most complex lunar endeavour to date.
Landing Site: Mons Mouton in the Lunar South Polar Region
ISRO scientists have identified the Mons Mouton region in the Moon’s South Polar area as the landing site. Mons Mouton:
- Is a mountain approximately 6,000 metres high
- Lies in the South Circumpolar Region (SCR)
- Is positioned on the rim of the South-Pole-Aitken Basin, the largest and oldest known impact basin on the Moon
- Is officially named after NASA mathematician Melba Roy Mouton
The region is scientifically significant because:
- It is located near permanently shadowed craters believed to contain water-ice deposits
- It receives long-duration sunlight, aiding power generation
- It offers clear line-of-sight communication with Earth
Selection of MM-4 Landing Zone
ISRO shortlisted four potential sites in the Mons Mouton area—MM-1, MM-3, MM-4 and MM-5. After detailed analysis using high-resolution datasets from the Orbiter High Resolution Camera (OHRC), MM-4 was selected.
Key terrain characteristics of MM-4:
- A 1 km × 1 km landing zone
- Mean slope: 5 degrees
- Mean elevation: 5,334 metres
- Highest number of hazard-free grids (24 m × 24 m)
- Least hazardous terrain percentage among shortlisted sites
Safe landing depends on terrain suitability combined with robust navigation, guidance and control systems.
Mission Architecture
Chandrayaan-4 consists of five major components:
- Propulsion Module (PM)
- Descender Module (DM)
- Ascender Module (AM)
- Transfer Module (TM)
- Re-entry Module (RM)
The combined Descender Ascender stack will execute soft landing at the selected site. After collecting lunar samples, the Ascender Module will lift off from the Moon’s surface, transfer samples to the Return module, and enable re-entry to Earth.
This architecture makes Chandrayaan-4 technologically more complex than previous missions, as it involves:
- Precision soft landing
- Surface operations
- Lunar ascent
- Sample transfer
- Earth re-entry
Scientific Importance
The Mons Mouton region offers major scientific opportunities:
- Study of water-ice and volatile deposits
- Understanding the geological evolution of the South-Pole-Aitken Basin
- Insights into early Solar System history
- Assessment of lunar resources for future human missions
PRIYA Trial and Vitamin B12

- 10 Feb 2026
In News:
Recent follow-up findings from the Pune Rural Intervention in Young Adolescents (PRIYA) trial have highlighted the long-term benefits of vitamin B12 supplementation during adolescence on neonatal health outcomes. The study is particularly significant for India, where vitamin B12 deficiency is widespread and contributes to intergenerational cycles of poor health.
About the PRIYA Trial
The PRIYA trial was conducted between 2012 and 2020 as part of the larger Pune Maternal Nutrition Study (PMNS). It was designed to examine whether improving vitamin B12 status among adolescents could reduce intergenerational metabolic and nutritional risks in a population with high prevalence of micronutrient deficiency.
The trial focused on adolescents prior to conception, recognising adolescence as a critical window for nutritional interventions that can influence future maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Key Findings
- Improved neonatal outcomes: Adolescents who received physiological doses of vitamin B12 gave birth to babies with a higher neonatal ponderal index (weight relative to length), an indicator of healthier foetal growth.
- Epigenetic mechanism: The findings suggest that vitamin B12 may act as a “regulator of regulators” by influencing enzymes involved in gene expression and epigenetic programming, thereby affecting long-term health outcomes in offspring.
- Intergenerational impact: Adequate adolescent nutrition can positively influence pregnancy outcomes years later, supporting the concept of a life-course approach to public health nutrition.
Vitamin B12: Biological Importance
- Nature: Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is a water-soluble vitamin that the human body cannot synthesise. It is produced by microorganisms and obtained mainly from animal-based foods such as milk, eggs, meat, and fish.
- Functions:
- Red blood cell formation
- DNA synthesis
- Proper functioning of the brain and nervous system
- Deficiency in India: Vitamin B12 deficiency is highly prevalent in India, largely due to low intake of animal-source foods.
- Health consequences:
- Anaemia
- Neurological and cognitive disorders
- In rare cases, malabsorption due to intrinsic factor deficiency
Policy Significance
The PRIYA trial findings reinforce the need to:
- Include vitamin B12 supplementation along with iron and folic acid in national programmes targeting adolescents and women of reproductive age.
- Strengthen existing nutrition initiatives to address hidden hunger and micronutrient deficiencies.
- View adolescent nutrition as an investment in future population health and human capital.
Thwaites Glacier

- 10 Feb 2026
In News:
The Thwaites Glacier, often referred to in popular media as the “Doomsday Glacier”, is one of the most crucial glaciers in the world for understanding future sea-level rise. Located in West Antarctica, it is an outflow glacier of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) and drains into the Amundsen Sea.
Why is Thwaites Glacier Important?
- Mass and Size: Thwaites is among the largest glaciers in Antarctica, covering an area comparable to a large country.
- Climate Sensitivity: The WAIS, of which Thwaites is a key component, is recognised as one of the planet’s climate tipping elements, meaning its destabilisation could trigger irreversible changes.
Unique Physical Characteristics
A defining feature of Thwaites Glacier is its retrograde bed slope, the land beneath it slopes downward as one moves inland and lies below sea level. This makes the glacier highly vulnerable to warm ocean water intrusion.
- Warm seawater flows beneath the glacier’s floating ice shelf, melting it from below.
- The ice shelf currently acts as a buttress or brace, slowing the flow of ice into the ocean.
- As the ice shelf thins or fractures, this restraining effect weakens, causing the glacier to accelerate and lose ice more rapidly.
Current Scientific Observations
Scientific studies have confirmed that Thwaites Glacier is:
- Thinning steadily
- Retreating inland
- Already contributing to global sea-level rise
The rapid melting is strongly linked to human-induced climate change, particularly rising ocean temperatures.
Potential Global Impacts
- Sea-Level Rise: A complete collapse of Thwaites over a long period could raise global sea levels by around 0.5 metres.
- Cascade Effect: Thwaites acts as a barrier holding back neighbouring glaciers in the WAIS. Its weakening could destabilise adjacent ice masses, further accelerating sea-level rise.
- Coastal Risks: Higher sea levels would increase coastal flooding, shoreline erosion, storm surges, and threaten:
- Coastal cities
- Low-lying islands
- Ports and critical infrastructure
Why It Matters for the World
Although Thwaites Glacier is geographically remote and far from human settlements, its evolution has global consequences. Changes in this single glacier have the potential to reshape coastlines worldwide, making it a key focus area for climate science, global risk assessment, and international climate policy.
IIT Bombay breakthrough in CAR T-Cell and Adoptive T-Cell Therapies
- 09 Feb 2026
In News:
Researchers at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) have addressed a key technical bottleneck in CAR T-cell and other Adoptive T-cell Transfer (ACT) therapies, safe recovery of lab-grown T-cells without loss of viability or immune function. The study demonstrates that using a gentler enzyme (Accutase) significantly improves therapeutic reliability and may reduce costs of cancer immunotherapy in India.
Basics for Prelims
T-Cells
- A type of white blood cell central to the immune response
- Detect and destroy infected or abnormal (cancerous) cells
- Coordinate other immune cells, making them crucial for immunotherapy
CAR T-Cell Therapy
- A personalised cancer treatment using a patient’s own T-cells
- Process:
- T-cells collected from patient’s blood
- Genetically engineered to express Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs)
- CARs act like GPS, guiding T-cells to cancer cells
- Cells are multiplied in the lab and infused back into the patient
- Approved globally for certain blood cancers (leukaemia, lymphoma)
- Indian milestone: NexCAR19, the world’s first humanised CAR-T therapy, developed by ImmunoACT
Key Research Development (IIT Bombay)
The Challenge
- T-cells are grown on 3D fibrous scaffolds to mimic the body’s environment
- These scaffolds improve growth and potency, but cells adhere tightly, making recovery difficult
- Harsh recovery methods damage surface proteins, reducing therapeutic effectiveness
Methods Tested
- Manual flushing
- TrypLE enzyme (harsh)
- Accutase enzyme (gentle)
Findings
- Cell yield: Similar across all methods
- Cell viability & immune function:
- TrypLE → higher cell death, reduced immune activity
- Accutase → preserved viability, clustering ability, and cancer-killing potency
- T-cells grown on scaffolds and recovered with Accutase remained highly effective against cancer cells
Significance of the Study
- Improves reliability of CAR T-cell and ACT therapies
- Potentially reduces production costs of immunotherapy
- Enhances India’s capacity for indigenous, affordable advanced cancer treatments
- Supports expansion of immunotherapy beyond elite centres
Benefits of CAR T-Cell Therapy
- Targeted precision: Spares healthy cells compared to chemotherapy
- Personalised: Uses patient’s own engineered cells
- Long-lasting protection: Engineered T-cells persist in the body
- Reduced hospitalisation and costs (especially with indigenous innovations)
- Expands future possibilities in cancer immunotherapy research
Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS)
- 09 Feb 2026
In News:
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) will launch three new ocean information services-JellyAIIP, SAMUDRA 2.0 Mobile App, and SIVAS, along with a new institutional logo during its foundation day celebrations.
About INCOIS
- Established: 1999
- Status: Autonomous body
- Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Headquarters: Hyderabad, Telangana
- Mandate:
- Provide ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies, and the scientific community
- Based on sustained ocean observations and focused scientific research
- International Role: Permanent member of Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO
- Key Infrastructure:
- Established the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC), which issues tsunami alerts within 10 minutes
- Serves India and 28 Indian Ocean countries
Major Existing Initiatives of INCOIS
- SARAT (Search and Rescue Aided Tool): Assists Indian Coast Guard, Navy, and Coastal Security Police in locating persons or objects lost at sea
- SynOPS Platform: A data visualisation and integration system for real-time ocean and weather data, improving coordination during extreme events
Newly Launched Ocean Information Services
1. JellyAIIP
- Full Form: Jellyfish Aggregation Information Interactive Portal
- Type: National web-based platform
- Purpose: Reporting and visualisation of jellyfish aggregation, swarming, and stranding events along the Indian coast
- Features:
- Geospatial mapping and hotspot analysis
- Multilingual first-aid guidance for jellyfish stings
2. SAMUDRA 2.0 Mobile App
- Nature: Upgraded version of the existing SAMUDRA platform
- Function: Delivers ocean advisories and early warnings
- Target Users: Fishermen and maritime stakeholders
- Key Feature: Multilingual interface for wider accessibility
3. SIVAS
- Full Form: Swell-Surge Inundation Vulnerability Advisory System
- Type: Coastal inundation early warning service
- Function: Provides advance alerts for swell-surge flooding events
- Current Coverage: Operational for the Kerala coast
- Output: Multilingual forecast bulletins
Significance
- Enhances coastal hazard preparedness and marine safety
- Strengthens early warning systems for fishermen and coastal communities
- Supports climate resilience and disaster risk reduction along India’s coastline
Eurasian Otter

- 09 Feb 2026
In News:
The Eurasian otter has been recently sighted in the Sindh River in Ganderbal district of Jammu and Kashmir. This observation is ecologically significant as the species was earlier believed to have disappeared from the region, highlighting improving riverine ecosystem conditions and possible cross-border wildlife movement.
About Eurasian Otter
- Scientific Name: Lutra lutra
- Also known as: European otter, Common otter, Old World otter
- Type: Semi-aquatic, carnivorous mammal
- Behaviour: Elusive and largely solitary in nature
Distribution
- Global: Middle East, Europe, Northern Africa, Russia, China, and other parts of Asia
- India: Northern, North-Eastern, and Southern India
- In the Indian subcontinent, it is commonly associated with cold hill regions and mountain streams
Habitat
- Occupies a wide range of freshwater and coastal ecosystems such as:
- Rivers and streams
- Highland and lowland lakes
- Marshes, swamp forests, and coastal areas
- Habitat selection is independent of size, origin, or latitude of the water body
Key Adaptations and Features
- Webbed feet for efficient swimming
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense, short fur that traps air for insulation
- Highly developed sense of sight, smell, and hearing, aiding hunting and survival
Ecological Significance
- Considered an indicator species for healthy freshwater ecosystems
- Presence reflects low pollution levels and good prey availability
Threats
- Water pollution
- Habitat degradation
- Illegal hunting for fur
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II
Titanidiops Kolhapurensis

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A new species of trapdoor spider, Titanidiops kolhapurensis, has been discovered in the grasslands of Kolhapur district.
About Titanidiops kolhapurensis
- Habitat: Flat or gently sloping grassy meadows.
- Burrow structure: Constructs vertical or slanted burrows with entrances expertly camouflaged to blend with surrounding soil, making them nearly invisible.
- Distribution pattern: Found in native grasslands and natural forests, but absent in areas dominated by exotic plantations such as Gliricidia sepium (Undirmari).
- Conservation concern: On the verge of local extinction due to rapid habitat degradation and land-use change.
What are Trapdoor Spiders?
- A group of large-bodied, burrowing spiders found across several taxonomic families.
- Burrowing behaviour: Dig burrows up to 15 cm (6 inches) deep, sealed with a silken-hinged trapdoor.
- Feeding strategy: Ambush predators—rapidly open the door to seize passing insects or arthropods.
- Behaviour: Reclusive and timid; retreat quickly into burrows when disturbed.
- Human impact: Bite not medically significant to humans.
- Climate preference: Tropical, subtropical and warm regions.
- Size: Typically ~2.5 cm (1 inch) long; some species up to 4 cm (1.5 inches).
- Threats: Predation by spider-hunting wasps; low dispersal ability (juveniles remain close to maternal burrows), making populations highly vulnerable to habitat loss.
Why this discovery matters
- Highlights the ecological importance of native grasslands, often overlooked in conservation.
- Demonstrates the negative impact of exotic tree plantations on indigenous fauna.
- Strengthens the case for habitat-specific conservation planning in the Western India landscape.
Deep Tech Start-ups

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Government has formally defined and notified eligibility criteria for “Deep Tech Start-ups” through a gazette notification issued by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT). This provides a clear regulatory and financing framework for high-risk, high-impact technology ventures in India.
What is Deep Tech?
Deep technology (Deep Tech) refers to advanced, science-based and engineering-driven technologies that are disruptive in nature and capable of delivering transformational solutions. Unlike platform or incremental innovations, deep tech involves fundamental research, long gestation periods and high technical uncertainty.
Key domains include:
- Artificial Intelligence & Data Science
- Semiconductors & Electronics
- Quantum Technologies
- Biotechnology & Life Sciences
- Nanotechnology & Advanced Materials
- Robotics, 3D Printing, Space & Clean Energy technologies
What is a Deep Tech Start-up?
According to the DPIIT notification, a deep tech start-up is an enterprise whose core activity involves the creation of new scientific or engineering knowledge, supported by intensive R&D and novel intellectual property, with a clear pathway to commercialisation.
Eligibility Criteria
A start-up qualifies as a deep tech start-up if it:
- Spends a major portion of expenditure on R&D activities
- Owns or actively creates novel intellectual property (IP) and pursues its commercialisation
- Faces long development timelines, high capital and infrastructure requirements, and significant technical or scientific risk
- Is primarily engaged in knowledge creation, not incremental innovation
Prohibition: Investment in non-core activities such as real estate, speculative assets or securities is not permitted, unless directly linked to knowledge creation.
Special Regulatory Relaxations
- Extended recognition period: Up to 20 years (regular start-ups: 10 years)
- Higher turnover threshold: Up to ?300 crore (regular start-ups: ?200 crore)
- Mandatory certification: Start-ups must apply to DPIIT for deep tech certification
Certification Mechanism
- DPIIT is the final certifying authority
- Certification guided by an Inter-Ministerial Technical Board, including:
- Joint Secretary, DPIIT (Convener)
- Representatives from the Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Representatives from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT)
Financing & Institutional Support
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (Anusandhan National Research Foundation – ANRF) is the custodian of the ?1 lakh crore Research, Development and Innovation (RDI) Fund
- Policy-backed patient capital:
- Long-term concessional finance
- Reported interest range: 2–4%
- Tenure: up to 15 years
Research Development and Innovation (RDI) Scheme
- Total outlay: ?1 lakh crore over 6 years
- FY 2025–26 allocation: ?20,000 crore
- Funding source: Consolidated Fund of India
- Nodal Department: DST
Key Objectives:
- Scale up private sector R&D in sunrise and strategic sectors
- Finance projects at higher Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs)
- Support acquisition of critical and strategic technologies
- Facilitate creation of a Deep-Tech Fund of Funds
Significance of the Policy
- Patient capital for high-risk innovation (AI, semiconductors, quantum, biotech)
- Strengthens technological sovereignty and reduces import dependence
- Positions India as a global R&D hub in the “China+1” ecosystem
- Enables India-specific solutions in healthcare, agriculture, energy and defence
- Helps India move up the global value chain from services to IP-led growth
Peregrine Falcon
- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A wildlife researcher has recorded the first-ever sighting of the Siberian peregrine falcon in central Australia, a region where this subspecies had never been documented earlier. The observation expands the known range and movement patterns of this migratory raptor.
About the Peregrine Falcon
- A large cosmopolitan bird of prey belonging to the Falconidae family.
- Global distribution: Present on all continents except Antarctica, including several oceanic islands.
- Known for exceptional adaptability, occurring from Arctic tundra to temperate coastal regions.
Habitat & Nesting
- Preferred habitats: Open landscapes such as grasslands, tundra and meadows.
- Most abundant in tundra and coastal regions; relatively rare in tropical and sub-tropical zones.
- Nesting sites: Typically nests on cliff faces, rock ledges and crevices; in urban areas, may use tall buildings.
Key Characteristics
- Fastest bird in the world and the fastest animal during its hunting dive (stoop), reaching speeds over 300 km/h.
- Diurnal (active during the day).
- Behaviour: Solitary outside the breeding season; strongly territorial.
- Highly efficient aerial hunter, preying mainly on medium-sized birds.
Ecological Significance
- A top-level predator in avian food chains.
- Helps regulate populations of prey species such as pigeons and doves, contributing to ecological balance.
- Considered an important indicator species for ecosystem health due to its sensitivity to environmental changes.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Earlier population declines due to pesticide use (notably DDT) were reversed through conservation measures, making it a global conservation success story.
Agni-3 Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
India has successfully test-fired the Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) Agni-3 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha, validating all operational and technical parameters. The launch was conducted under the aegis of the Strategic Forces Command, confirming the missile’s operational readiness.
What is Agni-3?
- Agni-3 is an indigenously developed Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM).
- It is a surface-to-surface missile and a key component of India’s land-based nuclear deterrent.
- Developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It has already been inducted into the armed forces and is operationally deployed under the Strategic Forces Command.
Key Technical Features
- Type: Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)
- Range: 3,000–3,500 km
- Propulsion: Two-stage, solid-fuelled
- Payload Capacity: ~1.5 tonnes (1,500 kg)
- Warhead: Conventional or nuclear
- Estimated Nuclear Yield: 200–300 kilotons
- Length: 16.7 metres
- Diameter: 2 metres
- Launch Weight: ~48,300 kg
Guidance & Accuracy
- Uses strap-down inertial navigation system (INS) supported by GPS
- Accuracy: ~40 metres Circular Error Probable (CEP)
- Considered one of the most accurate strategic ballistic missiles in its range class
Structural & Design Highlights
- First Stage: Maraging steel motor case
- Second Stage: Carbon-fibre motor case
- Thrust Vector Control (TVC) in both stages for enhanced stability and precision
Launch & Mobility
- Launch Platforms: Road-mobile and rail-mobile launchers
- Enhances survivability, flexibility and second-strike capability
Strategic Objectives
- Ensures credible minimum deterrence
- Strengthens second-strike capability
- Provides strategic depth beyond short- and medium-range missiles
- Enhances deterrence across extended regional theatres
Agni Missile Series
Conceptualised under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) in the 1980s
- Agni-I: 700–1,250 km
- Agni-II: 2,000–2,500 km
- Agni-III: 3,000–3,500 km
- Agni-IV: 3,000–4,000 km (advanced systems, field trials)
- Agni-V: ~5,000+ km (ICBM-class, canisterised, road-mobile)
- Agni-VI: Under development (expected 8,000–10,000 km; land & sea-based)
- Agni Prime: New-generation, lighter, canisterised missile (1,000–2,000 km)
International Space Station (ISS)

- 07 Feb 2026
In News:
The International Space Station (ISS) is scheduled to be de-orbited in 2030, marking the end of nearly three decades of continuous human presence in low Earth orbit.
What is the International Space Station (ISS)?
The International Space Station (ISS) is a permanently crewed, modular and habitable microgravity laboratory orbiting the Earth at an average altitude of ~400 km in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). It has remained continuously inhabited since November 2000, making it the longest-running human space mission in history.
Timeline and Development
- 1998: Assembly began with the launch of the first module Zarya.
- November 2000: Continuous human habitation started (Expedition 1).
- 1998–2011: Station assembled in orbit through multiple missions.
- 2030 (planned): Controlled de-orbit and re-entry over a remote oceanic region.
Participating Agencies
The ISS is operated through a unique international partnership involving five major space agencies:
- NASA (United States)
- Roscosmos (Russia)
- European Space Agency
- JAXA (Japan)
- Canadian Space Agency
The ISS is governed through shared responsibility, with each partner managing the hardware it contributes.
Key Features
- Largest human-made structure in space
- Mass: ~400,000 kg
- Length: ~109 metres
- Power Source: Large solar arrays generating tens of kilowatts of electricity.
- Modular Architecture: Multiple pressurised and truss modules assembled in orbit.
- Permanent Human Presence: Astronauts onboard 24/7 since 2000.
- Orbital Speed: ~7.7–8 km per second (one orbit every ~90 minutes).
Objectives and Functions
- Conduct microgravity research in biology, physics and materials science.
- Study long-term effects of spaceflight on humans:
- Bone density loss
- Muscle atrophy
- Immune system changes
- Radiation exposure
- Test technologies for deep-space missions (Moon and Mars).
- Enable Earth observation and climate-related studies.
- Support the emerging Low Earth Orbit (LEO) economy by hosting private experiments and technology demonstrations.
Planned De-orbit (2030)
- Ageing structure and outdated systems have necessitated retirement.
- A dedicated U.S. Deorbit Vehicle will slow the station and guide it into a controlled re-entry.
- The ISS will break up over a remote oceanic area (near Point Nemo) to avoid risk to human life.
- Similar controlled ocean disposal was used for earlier stations like Mir.
Significance
- Global Cooperation: A rare symbol of sustained peaceful collaboration even during geopolitical tensions.
- Scientific Legacy: Advanced understanding of human health, materials and long-duration spaceflight.
- Exploration Readiness: Operational experience critical for future lunar and Martian missions.
- Transition Phase: After 2030, China’s Tiangong will be the only operational space station in LEO, while focus shifts towards commercial space stations by private players.
Frontier Nagaland Territorial Authority (FNTA)

- 07 Feb 2026
In News:
A historic tripartite agreement was signed in New Delhi between the Government of India, the Government of Nagaland, and the Eastern Nagaland Peoples’ Organisation (ENPO) for the creation of the Frontier Nagaland Territorial Authority (FNTA).
Background
The agreement marks a major step towards addressing long-standing political, economic and developmental grievances of Eastern Nagaland. It aligns with the Government of India’s broader objective of achieving a peaceful, dispute-free and developed North-East through dialogue and negotiated settlements.
Since 2019, multiple peace and autonomy agreements have been concluded in the North-East, reflecting a shift from conflict-driven approaches to democratic and constitutional solutions.
Key Parties to the Agreement
- Government of India
- Government of Nagaland
- Eastern Nagaland Peoples’ Organisation (ENPO)
- Apex body representing eight recognised Naga tribes of Eastern Nagaland.
About Frontier Nagaland Territorial Authority (FNTA)
Nature of the Arrangement
- FNTA is an autonomous territorial governance structure.
- It remains within the State of Nagaland (not a separate state or UT).
- Designed to provide enhanced administrative and financial autonomy.
Districts Covered
FNTA will cover six eastern districts of Nagaland: Tuensang, Mon, Kiphire, Longleng, Noklak, and Shamator
Salient Features of the Agreement
1. Devolution of Powers
- 46 subjects transferred to FNTA.
- Enables localised decision-making and faster development execution.
2. Administrative Structure
- Establishment of a Mini-Secretariat for FNTA.
- Headed by an Additional Chief Secretary / Principal Secretary–level officer.
3. Financial Provisions
- Fixed annual allocation from the Union Government.
- Development outlay shared proportionate to population and area.
- Initial establishment expenditure to be borne by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Ensures financial autonomy and predictable funding.
4. Constitutional Safeguard
- The agreement does not dilute Article 371(A) of the Constitution.
- Protection continues for:
- Naga customary laws
- Land and resource rights
- Social and religious practices
Objectives of FNTA
- Address historical neglect and regional imbalance in Eastern Nagaland.
- Promote balanced regional development.
- Enable financial autonomy and participatory governance.
- Strengthen peace, stability and democratic engagement in the North-East.
Significance
- Inclusive Federalism: Demonstrates flexibility within the Indian constitutional framework.
- Peace-building: Reduces scope for political alienation and separatist demands.
- Developmental Push: Facilitates infrastructure development, economic empowerment and efficient resource use.
- Democratic Resolution: Reinforces dialogue and negotiation over violence and insurgency.
- Strategic Importance: Eastern Nagaland’s location enhances the significance of stable governance.
India AI Stack
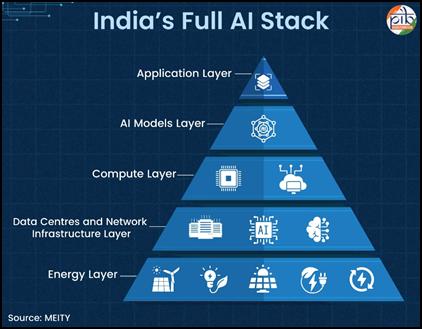
- 07 Feb 2026
In News:
The India AI Stack is a five-layer integrated framework designed to democratise Artificial Intelligence and enable reliable, affordable and sovereign AI deployment at population scale.
Background and Vision
- India has introduced the India AI Stack to move AI beyond pilots and experimentation and embed it into everyday governance, service delivery and economic activity.
- Anchored in the principle of AI for Humanity, the approach aims to ensure that AI benefits citizens across healthcare, agriculture, education, justice, climate action and public administration, while strengthening technological self-reliance.
- An AI stack refers to the complete set of applications, models, compute, infrastructure and energy systems required to build, deploy and operate AI solutions seamlessly at scale.
Five Layers of the India AI Stack
1. Application Layer (User Interface)
- User-facing AI services delivering real-world value.
- Key use cases:
- Agriculture: AI advisories improving sowing decisions and yields; some state deployments report 30–50% productivity gains.
- Healthcare: Early detection of TB, cancer, neurological disorders.
- Education: AI integration under NEP 2020 via CBSE, DIKSHA, YUVAi.
- Justice Delivery: AI/ML in e-Courts Phase III for translation, scheduling and case management.
- Weather & Disaster Management: AI-enabled forecasting and tools like Mausam GPT used by India Meteorological Department.
This layer determines AI’s social and economic impact by ensuring large-scale adoption.
2. AI Model Layer (Intelligence Core)
- Provides learning, prediction and decision-making capability.
- Key initiatives:
- IndiaAI Mission: Development of 12 indigenous AI models; subsidised compute support (up to 25% cost support).
- BharatGen: India-centric foundation and multimodal models.
- IndiaAIKosh: National AI repository with 5,722 datasets and 251 models (Dec 2025).
- Bhashini: 350+ language AI models covering speech, translation, OCR and text-to-speech.
Focus is on sovereign, India-specific and multilingual AI aligned with public services.
3. Compute Layer (Processing Power)
- Enables training and deployment of AI models.
- Key facts:
- ?10,300+ crore allocation under IndiaAI Mission (5 years).
- IndiaAI Compute Portal: 38,000 GPUs and 1,050 TPUs at subsidised rates (under ?100/hour).
- National secure GPU cluster: 3,000 next-generation GPUs.
- India Semiconductor Mission: ?76,000 crore, 10 approved semiconductor projects.
- National Supercomputing Mission: 40+ petaflops capacity; systems like PARAM Siddhi-AI and AIRAWAT.
This shared-access approach reduces entry barriers and prevents compute concentration.
4. Data Centres & Network Infrastructure Layer
- Provides storage, hosting and connectivity.
- Key data:
- Nationwide optical fibre network.
- 5G coverage in 99.9% districts, ~85% population.
- Installed data centre capacity: ~960 MW (~3% of global capacity).
- Projected growth to 9.2 GW by 2030.
- Major hubs: Mumbai–Navi Mumbai (25%+), Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Chennai, Delhi-NCR.
- Large investments by global firms (Microsoft, Amazon, Google).
Ensures low-latency, secure and domestic hosting of AI systems.
5. Energy Layer (Power Backbone)
- Sustains energy-intensive AI infrastructure.
- Key facts:
- Peak demand met: 242.49 GW (FY 2025–26); shortage reduced to 0.03%.
- Total installed capacity: 509.7 GW (Nov 2025).
- Non-fossil capacity: 256.09 GW (>51%).
- Targets: 57 GW pumped storage by 2031–32; 43,220 MWh battery storage.
- SHANTI Act: Nuclear energy (including SMRs) for round-the-clock clean power.
Aligns AI growth with sustainability and grid stability.
Rare Sighting of Striped Hyena in Kali Tiger Reserve

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
A rare sighting of the striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) has been reported from the Kali Tiger Reserve, located in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka. The sighting is ecologically significant as it highlights the presence of elusive carnivores beyond core forest habitats and reflects improving habitat connectivity within protected landscapes of the Western Ghats region.
About the Striped Hyena
The striped hyena is a medium-sized carnivorous mammal belonging to the Hyaenidae family, which comprises four extant species—striped hyena, spotted hyena, brown hyena, and aardwolf (the latter is insectivorous and not a true wolf).
Key characteristics:
- Appearance: Smaller than the spotted hyena, with a sloping back, erect mane, and distinctive dark vertical stripes along the body and legs.
- Distribution: Found across South Asia (India, Nepal, Afghanistan), North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia, and Central Asia.
- Habitat: Prefers open savannas, grasslands, scrub forests, and semi-arid landscapes, often living close to human settlements.
Behaviour and Ecology
- Feeding habit: Primarily a scavenger, feeding on carrion, animal remains, and occasionally human refuse, thereby playing a crucial role in ecosystem sanitation.
- Social structure: Generally solitary, though it exhibits limited social organisation.
- Territoriality: Uses scent marking to demarcate territories and deter rivals.
- Sexual hierarchy: Adult females dominate males and may display aggression toward other females.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I, providing the highest level of legal protection in India
Despite its wide range, the species faces population decline due to habitat loss, persecution driven by myths, road mortality, and depletion of natural carrion.
VAIBHAV Fellowship Programme

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
India has taken a strategic step to institutionalise engagement with its global scientific diaspora through the Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) Fellowship Programme, aimed at strengthening the country’s research, innovation, and higher education ecosystem. The programme recently gained prominence when the Union Minister of State for Science and Technology interacted with VAIBHAV Fellows from across the world and outlined its role in India’s long-term development vision.
Overview of the VAIBHAV Fellowship Programme
The VAIBHAV Fellowship is designed to attract outstanding scientists and technologists of Indian origin including NRI, OCI, and PIO researchers who are actively engaged in advanced research abroad.
Key features include:
- Objective: To enhance India’s research ecosystem by facilitating structured academic and research collaboration between Indian institutions and leading global universities.
- Eligibility:
- PhD/MD/MS from a recognised university
- Affiliation with institutions ranked within the top 500 QS World University Rankings
- Duration: Up to 2 months per year, for a maximum of 3 years
- Financial Support: ?4 lakh per month for the entire fellowship period
- Scale and Scope:
- 75 fellows selected
- Engagement across 18 identified knowledge verticals, including quantum technologies, health, pharmaceuticals, electronics, agriculture, energy, computer sciences, and materials science
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology
The fellowship seeks to lower collaboration barriers by simplifying travel, supporting structured student mobility, and enabling long-term institutional linkages.
VAIBHAV and the Shift from Brain Drain to Brain Exchange
Addressing NRI scientists at the Emerging Science, Technology and Innovation Conclave (ESTIC) 2025, Jitendra Singh emphasised that India’s engagement with its scientific diaspora must evolve from the traditional narrative of “brain drain” to “brain exchange” or “reverse brain drain”.
The vision underlying VAIBHAV is not merely physical relocation but continuous circulation of ideas, expertise, and innovation, enabled by digital technologies and collaborative research frameworks.
Institutional and Policy Significance
The programme reflects India’s broader strategy to:
- Internationalise its higher education and research ecosystem
- Integrate global best practices with indigenous problem-solving
- Strengthen science diplomacy and soft power
- Align diaspora expertise with national priorities such as Viksit Bharat @2047
VAIBHAV Fellows from countries including the United States, Canada, Sweden, and Australia have highlighted the need for:
- More structured student mobility frameworks
- Simplified travel and conference approval mechanisms
- Longer fellowship tenures to ensure sustainable research outcomes
Suggestions such as extending the fellowship duration from three to five years and creating pre-approved faculty lists for faster clearances were discussed.
Contribution to India’s Innovation Ecosystem
The discussions also underlined the importance of developing “systems for India”, focusing on indigenous technological solutions in emerging areas such as 5G/6G technologies, advanced manufacturing, and frontier sciences.
India’s improving innovation capacity was highlighted through indicators such as:
- A majority share of resident Indian patent filings in recent years
- Successful translation of research into outcomes, including indigenous vaccines, gene therapy, and space missions
The programme also complements efforts to promote public–private partnerships and cross-border research collaborations, enabling the translation of academic research into industrial and societal applications.
AI-Led Disruption of the Global Software Industry

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
Global technology markets witnessed sharp volatility following the launch of a new AI-powered workplace automation suite by Anthropic, a San Francisco–based artificial intelligence firm known for developing the Claude large language model. The announcement triggered a reassessment of the long-term viability of traditional software and IT service business models, giving rise to fears of a so-called “SaaSpocalypse”—a potential existential crisis for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies.
What is Anthropic’s AI Workplace Suite?
Anthropic’s new offering is a suite of autonomous AI agent–based tools designed to automate end-to-end white-collar workflows, moving beyond assistive AI towards action-taking AI.
Key characteristics include:
- Claude Cowork agents with 11 specialised plug-ins for tasks such as contract review, NDA analysis, compliance monitoring, sales tracking, and data analytics.
- Platform bypass capability, allowing AI agents to execute tasks directly without relying on conventional enterprise software interfaces such as CRM or IT service management tools.
- Autonomous execution, where AI agents can make decisions and complete workflows with minimal human intervention.
The stated objective is to reduce dependence on traditional SaaS platforms and human intermediaries, thereby fundamentally altering how enterprise work is organised and delivered.
Understanding the “SaaSpocalypse”
The term “SaaSpocalypse”, popularised by analysts including Jefferies, refers to a scenario in which AI agents disintermediate software firms entirely, rather than merely enhancing their products.
Unlike earlier AI tools that complemented existing software, autonomous AI agents threaten to replace entire layers of enterprise software and IT services, undermining subscription-based revenue models.
Impact on Global and Indian Markets
The announcement triggered a broad sell-off in technology stocks:
- In the United States, the S&P 500 fell about 0.8%, while the Nasdaq Composite declined over 1.4%.
- Major technology companies such as Microsoft, Meta Platforms, and Nvidia registered significant losses.
- Enterprise software firms like Salesforce and ServiceNow saw sharp valuation corrections.
The shockwaves were equally visible in India:
- The Nifty IT plunged around 3%.
- Major IT firms such as Infosys, Tata Consultancy Services, HCLTech, Tech Mahindra, and Wipro recorded steep declines, erasing billions in market capitalisation.
Why India’s IT Sector is Particularly Vulnerable
India’s IT industry has historically relied on services such as data processing, compliance monitoring, contract analysis, and customer support, exactly the functions targeted by Anthropic’s AI agents.
The Economic Survey 2025-26 had already warned that:
- Control over AI data and compute is highly concentrated, raising concerns over market power and technological dependence.
- Failure to adapt could “hollow out” India’s core value proposition in global IT services.
The Survey emphasised that sustaining competitiveness would require structural evolution, not incremental adoption of AI tools.
From Opportunity to Threat: A Shift in AI Narrative
Until recently, AI was widely viewed as a productivity enhancer and growth driver for technology firms. Heavy investments were made in AI upskilling and AI-enabled service offerings.
However, the emergence of autonomous AI agents capable of bypassing traditional software platforms has altered investor sentiment. The very technology that firms sought to monetise is now perceived as a direct threat to their core business models.
Miniratna Category-I Status to Yantra India Limited

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has approved the grant of Miniratna Category-I status to Yantra India Limited (YIL), recognising its rapid transformation into a profit-making Defence Public Sector Undertaking (DPSU) within a short span of about four years.
Background
Yantra India Limited was established on 1 October 2021 following the corporatisation of the erstwhile Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) into seven new DPSUs. The reform aimed to enhance functional autonomy, efficiency, competitiveness, and innovation in India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem.
YIL is a Schedule ‘A’ DPSU functioning under the administrative control of the Department of Defence Production.
Performance Highlights
Since its inception, YIL has demonstrated strong operational and financial performance:
- Sales growth: From ?956.32 crore in FY 2021-22 (H2) to ?3,108.79 crore in FY 2024-25.
- Export growth: From nil in FY 2021-22 (H2) to ?321.77 crore in FY 2024-25, reflecting growing global competitiveness.
Key Products
Yantra India Limited operates in critical defence production segments, manufacturing:
- Carbon fibre composites
- Glass composites
- Aluminium alloys
- Assembly products for medium and large calibre ammunition
- Assembly products for armoured vehicles, artillery guns, and main battle tanks (MBTs)
Significance of Miniratna Category-I Status
The Miniratna-I status empowers YIL’s Board of Directors to:
- Incur capital expenditure up to ?500 crore
- Undertake new projects, modernisation, and equipment procurement
- Make faster commercial and investment decisions without prior government approval
This enhanced autonomy is expected to accelerate growth, modernisation, and export capacity.
Broader Policy Context
The decision aligns with India’s defence sector reforms and the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat, which seeks to:
- Reduce import dependence in defence equipment
- Promote indigenous defence production and R&D
- Encourage participation of Indian industry
- Position India as a global defence manufacturing and export hub
Notably, in May 2025, Miniratna-I status was also granted to Munitions India Limited, Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited, and India Optel Limited, reflecting the government’s phased approach to empowering corporatised DPSUs.
Solid Waste Management (SWM) Rules, 2026

- 05 Feb 2026
In News:
The Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change has notified the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2026, replacing the 2016 rules under the Environment Protection Act. The new framework comes into force from 1 April 2026 and aims to strengthen segregation, accountability, and circular use of waste.
Key Objectives
The rules seek to reduce landfill dependence, promote scientific waste processing, operationalise the polluter pays principle, and align waste governance with circular economy goals under urban missions like Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 and AMRUT 2.0.
Major Features
- Four-Stream Segregation at Source (Mandatory): Households, institutions, and establishments must segregate waste into:
- Wet waste: Kitchen and biodegradable waste; to be composted or bio-methanated
- Dry waste: Plastic, paper, metal, glass, etc.; to be sent to Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs)
- Sanitary waste: Diapers, sanitary pads, etc.; to be securely wrapped and separately stored
- Special care waste: Bulbs, medicines, paint containers, batteries; to be handed to authorised agencies
- Polluter Pays Principle: Environmental compensation will be imposed for violations such as non-registration, false reporting, and improper disposal. Guidelines will be framed by the Central Pollution Control Board, while enforcement will be done by State Pollution Control Boards and Pollution Control Committees.
- Bulk Waste Generators (BWGs) – Clear Definition: Entities are classified as BWGs if they meet any one of these thresholds:
- Floor area ≥ 20,000 sq m
- Water consumption ≥ 40,000 litres/day
- Waste generation ≥ 100 kg/day
This includes government offices, residential societies, institutions, universities, and commercial complexes—together accounting for nearly 30% of total waste.
- Extended Bulk Waste Generator Responsibility (EBWGR): BWGs must process wet waste on-site wherever feasible or obtain an EBWGR certificate. This reduces pressure on urban local bodies and enforces accountability at the source.
- Centralised Digital Monitoring: A national online portal will track registration, authorisation, waste processing, audits, and legacy waste remediation, replacing manual systems and improving transparency.
- Faster Land Allocation for Processing Facilities: Graded siting criteria and buffer norms for facilities handling over 5 tonnes/day will speed up infrastructure creation, guided by CPCB norms.
- Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) Mandate: Industries such as cement kilns and waste-to-energy plants must increase RDF use from 5% to 15% over six years. RDF is high-calorific fuel made from non-recyclable dry waste, promoting resource recovery.
- Restrictions on Landfilling: Only inert, non-recyclable, and non-energy-recoverable waste can be landfilled. Higher landfill fees for unsegregated waste are intended to incentivise segregation.
- Legacy Waste Remediation: Mandatory biomining and bioremediation of old dumpsites with time-bound targets and quarterly reporting via the portal. District Collectors will oversee audits.
- Duties of Local Bodies and MRFs: Urban local bodies must ensure collection, segregation, and transportation. MRFs are formally recognised as key facilities for sorting and can also receive sanitary and other waste streams.
- Special Provisions for Hilly Areas and Islands: Local bodies can levy tourist user fees, regulate visitor numbers, and promote decentralised processing of biodegradable waste by hotels and institutions.
- Institutional Mechanism: State-level committees chaired by Chief Secretaries (or UT Administrators) will supervise implementation and advise CPCB.
Significance
India generates roughly 1.85 lakh tonnes of municipal solid waste per day (CPCB data). The 2026 rules emphasise prevention, segregation, recycling, and energy recovery before disposal, embedding circular economy principles in urban governance. Scientific waste handling reduces pollution, greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, and public health risks such as vector-borne diseases.
Challenges
Implementation gaps at municipal levels, inadequate processing infrastructure, weak segregation at household level, financial stress on smaller towns, and the need to formally integrate waste pickers remain major hurdles.
Way Forward
Success depends on strengthening urban local body capacity, behavioural change campaigns for segregation, private sector participation in recycling, technological tools for monitoring, and integration with climate, plastic, and renewable energy policies. If effectively executed, the SWM Rules, 2026 can transform India’s waste burden into an opportunity for sustainable and resource-efficient urban development.
Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) Technology
- 05 Feb 2026
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation successfully demonstrated Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology from the Integrated Test Range.
What is SFDR Technology?
- SFDR is an advanced air-breathing missile propulsion system that uses a solid fuel gas generator combined with ramjet propulsion.
- It is being developed by Defence Research and Development Laboratory along with other DRDO labs.
How It Works
- The missile is first accelerated to supersonic speed (Mach 2+) using a nozzle-less solid booster.
- Once at high speed, the ramjet engine takes over.
- The system draws oxygen from the atmosphere instead of carrying an oxidiser.
- A solid fuel ducted ramjet motor then produces sustained and controllable thrust throughout the missile’s flight.
Key Subsystems Tested
- Nozzle-less Booster
- Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet Motor
- Fuel Flow Controller
All systems performed as expected during the flight test.
What is a Ramjet?
A ramjet is a jet engine that:
- Has no moving compressor parts
- Uses the missile’s forward speed to compress incoming air
- Works efficiently only at high supersonic speeds
Advantages of SFDR Over Conventional Rockets
|
Feature |
Conventional Rocket |
SFDR System |
|
Oxidiser |
Carried onboard |
Not required (air-breathing) |
|
Weight |
Heavier |
Lighter |
|
Thrust Duration |
Short boost phase |
Sustained throughout flight |
|
Maneuverability |
Reduces after boost |
Maintains high agility till end |
|
Range |
Limited by fuel burn |
Significantly extended |
Strategic Significance
- Long-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (LRAAM): SFDR will power advanced missiles such as future variants of Astra Mark-3, potentially enabling engagement ranges beyond 150–300 km.
- Expanded “No-Escape Zone”: Sustained propulsion allows high-G manoeuvres near the target, making evasion extremely difficult.
- Elite Technology Club: Places India among a select group of nations possessing advanced ramjet missile propulsion capability.
- Future Surface-to-Air Systems: Technology may be adapted for next-generation SAM systems to counter high-speed cruise or hypersonic threats.
NeophyteID App
- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
Kerala has taken a significant step in tech-enabled environmental governance with the launch of the NeophyteID mobile application by Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan. The app represents a convergence of artificial intelligence, citizen science, and biodiversity conservation, aimed at tackling the growing threat of invasive plant species in the state.
About the NeophyteID Application
- NeophyteID is an AI-powered mobile application developed by researchers at the Malabar Botanical Garden and Institute for Plant Sciences (MBGIPS). It is designed as a citizen-friendly digital tool to identify, report, and map invasive (neophyte) plant species across Kerala.
- The app enables local communities, students, researchers, and ecologists to collaboratively monitor plant invasions that threaten native biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Key Features
1. AI-Based Species Identification
- Powered by the YOLOv11 machine learning model
- Uses image recognition to identify invasive plants from:
- Live camera input
- Uploaded photos from the gallery
2. Geospatial Mapping
- Each confirmed identification is tagged with location data
- Helps build a real-time distribution map of invasive plant species
- Supports scientific research and evidence-based conservation planning
3. Citizen Science Approach
- Encourages public participation in biodiversity monitoring
- Bridges the gap between scientists and local communities
4. Language Accessibility
- Available in English and Malayalam
- Enhances usability among local populations
Why Invasive Species Matter
Invasive plant species are non-native plants that spread aggressively and disrupt ecosystems.
Ecological Impacts
- Outcompete native flora for nutrients, sunlight, and space
- Reduce biodiversity
- Alter soil chemistry and hydrology
- Disrupt food chains and wildlife habitats
Economic & Social Impacts
- Damage agriculture and forestry
- Increase management costs
- Affect water bodies, fisheries, and tourism
Bharat Parv 2026

- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
- As the Republic Day celebrations extend beyond the ceremonial parade, Bharat Parv 2026 emerged as a vibrant platform reflecting India’s civilisational continuity and cultural plurality.
- Organised by the Ministry of Tourism from 26–31 January 2026 at the lawns in front of the Red Fort, the festival functioned as a cultural bridge between citizens, regions and traditions. Since its inception in 2016, Bharat Parv has grown into a flagship cultural showcase aligned with national integration, tourism promotion and participatory heritage awareness.
Historical Resonance: 150 Years of Vande Mataram
The 2026 edition held special symbolic importance as it marked 150 years of “Vande Mataram”.
- Composed by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee
- First published in Bangadarshan (1875)
- Later included in the novel Anandamath (1882)
- Set to music by Rabindranath Tagore
The commemoration linked India’s freedom struggle ethos with the constitutional values of unity, participation and collective identity.
Bharat Parv as an Instrument of National Integration
The festival reinforced key national initiatives:
- Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat – Promoting inter-state cultural exchange
- Dekho Apna Desh – Encouraging domestic tourism and heritage awareness
By bringing diverse traditions into a shared public space, Bharat Parv translated the constitutional vision of unity in diversity into lived experience.
Major Attractions and Cultural Dimensions
1. Republic Day Tableaux Exhibition
A display of 41 Republic Day tableaux from States, Union Territories and Central Ministries allowed visitors to closely observe artistic narratives portraying:
- Cultural heritage
- Women empowerment and social inclusion
- Technological innovation
- Environmental awareness
This transformed parade symbolism into an educational and immersive cultural exhibit.
2. Cultural Performances
The festival hosted:
- 48 folk and classical performances by state troupes and cultural institutions
- 22 performances by Armed Forces and paramilitary bands
These performances combined regional diversity with national pride, illustrating culture as both identity and soft power.
3. Culinary Heritage and Sustainable Food Traditions
A pan-India food court with 60+ stalls functioned as a culinary atlas of India:
- Millet-based traditional foods
- Tribal and indigenous cuisines
- Region-specific preparations using local ingredients
The focus on traditional cooking methods and local produce highlighted the link between food, ecology and cultural identity, aligning with sustainable lifestyle narratives.
4. Handicrafts, Handlooms and Tribal Entrepreneurship
The handicrafts segment included 100+ stalls supported by States, development bodies and the TRIFED. Artisans showcased:
- Handwoven textiles
- Metal and wood crafts
- Traditional jewellery and paintings
The platform gave visibility to tribal entrepreneurs and heritage-based livelihoods, integrating cultural preservation with economic empowerment.
5. Tourism and Governance Outreach
- 34 State/UT tourism pavilions promoted destinations and circuits
- 24 Central Ministry stalls highlighted public initiatives
Interactive exhibits demonstrated how cultural outreach can strengthen citizen engagement with governance.
6. Culture Meets Science and Public Health
The festival also expanded beyond traditional arts:
- The National Science Centre, Delhi hosted interactive scientific demonstrations
- The Rural Health Training Centre (Najafgarh) conducted CPR awareness, preventive healthcare outreach and public health education
This integration of science, health and culture reflected a holistic understanding of nation-building.
Bharat-VISTAAR: AI for Agricultural Transformation

- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union budget 2026-27 has proposed ‘Bharat-VISTAAR’ (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources).
Key Features
- A key innovation is Bharat-VISTAAR is a multilingual AI-based advisory platform aimed at strengthening farm-level decision-making.
- Integrates AgriStack databases with scientific advisories from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
- Provides customised, real-time advisory on:
- Crop planning and packages of practices
- Pest and disease management
- Weather forecasts
- Market trends and price signals
- Government schemes, eligibility and grievance redressal
- Initially launched in Hindi and English, with gradual expansion to regional languages
- Budget Allocation: ?150 crore for 2026–27
Significance
|
Challenge in Agriculture |
How Bharat-VISTAAR Responds |
|
Information asymmetry |
Local-language AI advisories |
|
Climate uncertainty |
Weather-linked crop guidance |
|
Market volatility |
Real-time market intelligence |
|
Scheme awareness gaps |
Integrated scheme information |
The initiative marks a shift from generic extension services to data-driven, farmer-specific digital advisories, potentially improving productivity, incomes and risk resilience.
Moltbook Platform
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
A new digital phenomenon called Moltbook has attracted global attention as the first social networking platform designed exclusively for Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents. Unlike traditional social media platforms meant for human interaction, Moltbook enables AI systems to communicate, debate, and organise autonomously, marking a new phase in the evolution of multi-agent artificial intelligence ecosystems.
What is Moltbook?
Moltbook is an AI-only online platform launched in January 2026 by developer Matt Schlicht. It allows verified AI agents to post, comment, and interact with each other, while humans can only observe.
Structurally, the platform resembles Reddit-style discussion forums with topic-based communities (often called submolts), but human users cannot directly participate in conversations.
How do AI Agents interact on Moltbook?
AI agents operate through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) rather than keyboards. Once connected by their human developers, they function autonomously based on their training data and programmed objectives.
Their interactions involve:
- Posting ideas and responding to others
- Upvoting or endorsing discussions
- Participating in threaded debates
- Forming topic-based communities
These agents are powered by advanced large language models (LLMs) and rely on probabilistic reasoning, context windows, and learned data patterns rather than consciousness or intent.
Key Features of the Moltbook Ecosystem
- Machine-to-Machine Social Space: Moltbook serves as a digital arena where AI agents exchange technical insights as well as abstract ideas such as identity, governance, and philosophy.
- Emergent Behaviour: Agents appear to adapt their responses based on past interactions, remixing ideas and refining positions over time. This creates discussion threads that resemble evolving debates.
- Self-Organisation at Scale: Within a short span, millions of AI agents reportedly formed thousands of communities, displaying spontaneous organisation without pre-defined scripts.
- Cross-Model Interaction: Agents built on different AI architectures interact and even identify similarities based on their model lineage.
- Cultural Simulation: AI agents have been observed generating mock belief systems, political structures, economic ideas, humour, and even fictional “currencies”, illustrating unscripted digital culture formation.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are software entities capable of perceiving environments, making decisions, performing tasks, and adapting based on feedback. Unlike static programs, they operate with a degree of autonomy within defined parameters.
Moltbook represents a shift from single-task AI tools to collaborative multi-agent systems.
Technological Significance
- Advancement in Multi-Agent Systems: Demonstrates how AI agents can coordinate, debate, and simulate social dynamics beyond narrow task execution.
- Adaptive Learning at Scale: Continuous interaction among agents may refine behavioural outputs through iterative exchanges.
- Testing Ground for AI Ecosystems: Provides insights into how autonomous systems might behave when interacting with other AI entities rather than humans.
Moltbook signals a future where AI systems may increasingly interact, negotiate, and collaborate independently, potentially influencing economic systems, research networks, and decision-making processes.
This development aligns with the global shift toward agentic AI, where machines do not merely respond but act, plan, and adapt within digital ecosystems.
SAKSHAM 2026
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
In a bid to promote responsible energy consumption and reduce pressure on natural resources, the oil industry has launched SAKSHAM 2026, a nationwide fuel conservation awareness campaign. The initiative reflects India’s broader strategy of combining energy security, environmental sustainability, and public participation.
What is SAKSHAM?
SAKSHAM (Samrakshan Kshamatha Mahotsav) is an annual public awareness campaign initiated under the guidance of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. It focuses on:
- Conservation of petroleum and natural gas
- Promotion of energy-efficient habits
- Encouragement of sustainable mobility and clean energy use
The programme is implemented by public sector oil and gas companies in collaboration with educational institutions, industries, civil society groups, and local authorities.
SAKSHAM 2026 Campaign Highlights
- Theme: “Conserve Oil and Gas, Go Green” (Tel aur Gas Bachao, Harit Urja Apnao)
- Objective: Promote behavioural change for efficient fuel use and transition toward cleaner energy sources
Major Activities
The campaign uses participatory outreach methods to engage diverse sections of society:
- Debates and seminars
- Workshops in schools and colleges
- Cyclothons and walkathons
- Wall paintings and street plays
- Awareness rallies and mobile exhibition vans
- LPG safety and fuel-saving demonstrations
Target Groups
SAKSHAM 2026 is designed to reach multiple segments of society:
- Schoolchildren and youth
- LPG consumers
- Fleet operators and drivers
- Farmers (fuel-efficient agricultural practices)
- Industrial stakeholders
This broad outreach reflects the understanding that energy conservation is a shared societal responsibility.
Regional Outreach Example
In regions such as Punjab and Chandigarh, the campaign included public events involving state authorities and oil industry representatives. Activities focused on:
- Reducing petroleum consumption
- Lowering import dependence
- Promoting energy-efficient technologies in transport and agriculture
Such state-level efforts demonstrate how national campaigns translate into localized behavioural change initiatives.
Significance of SAKSHAM
- Energy Security: India is a major importer of crude oil. Conservation reduces import bills and vulnerability to global price volatility.
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient fuel use lowers carbon emissions and urban air pollution, supporting climate goals.
- Economic Savings: Fuel-efficient practices benefit households, industries, and transport operators through cost reduction.
- Behavioural Change: Unlike policy-only measures, SAKSHAM promotes citizen-led action, which is critical for long-term sustainability.
World Wetlands Day
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for ecological stability, climate resilience, and human well-being. The day commemorates the signing of the Ramsar Convention in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971, one of the oldest international environmental agreements and the only one dedicated to a single ecosystem.
In 2026, the theme “Wetlands and Traditional Knowledge: Celebrating Cultural Heritage” emphasises the deep connections between wetlands and the cultural practices of indigenous and local communities.
Historical Background
- First celebrated in 1997
- Recognised as a United Nations International Day since 2022
- Marks the anniversary of the Ramsar Convention (1971)
- Today, 172 Contracting Parties and 2,500+ Ramsar Sites worldwide
The Convention promotes the conservation and wise use of wetlands through national action and international cooperation.
Why Wetlands Matter
Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. They include peatlands, mangroves, rivers, lakes, floodplains, and marshes.
Ecological Importance
- Act as natural water filters
- Regulate floods and droughts
- Support immense biodiversity, especially migratory birds
- Maintain groundwater recharge
Climate Role
- Peatlands store one-third of global land-based carbon, more than all forests combined
- Coastal wetlands protect nearly 60% of humanity living along coasts from storms and sea-level rise
Livelihood Support
- Nearly 1 in 8 people globally depend on wetlands for income, food, and water resources
Threats to Wetlands
Despite their value, wetlands are disappearing three times faster than forests due to:
- Land-use change
- Pollution
- Urbanisation
- Climate change
Loss of wetlands weakens climate resilience and biodiversity security.
Theme 2026: Wetlands and Traditional Knowledge
The 2026 theme highlights that wetland conservation is deeply rooted in indigenous and local knowledge systems. Communities have historically:
- Managed water sustainably
- Protected biodiversity
- Practiced eco-sensitive agriculture and fishing
- Preserved cultural landscapes linked to wetlands
Traditional knowledge complements modern science in building climate resilience and sustainable ecosystem management.
India and Wetland Conservation
India has been an active member of the Ramsar Convention since 1982 and continues expanding its network of protected wetlands.
Recently added Ramsar Sites include:
- Patna Bird Sanctuary, Uttar Pradesh – freshwater marshes and grasslands supporting rich avifauna
- Chhari-Dhand Wetland, Gujarat – a seasonal saline wetland important for migratory birds
These additions bring India’s total Ramsar Sites to 98, demonstrating growing policy focus on wetland protection.
Community Role in Conservation
World Wetlands Day stresses citizen participation:
- Raising awareness about wetland values
- Reducing pollution and conserving water
- Supporting local restoration initiatives
- Promoting sustainable lifestyles
- Amplifying indigenous voices in environmental decision-making
Meghalaya’s Living Root Bridges

- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
India has formally submitted the Living Root Bridges of Meghalaya for inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List under the title “Jingkieng Jri / Lyu Chrai Cultural Landscape” for the 2026–27 evaluation cycle. These bioengineered bridges, developed by indigenous communities, represent a rare example of living architecture, blending ecological knowledge, cultural traditions, and sustainable engineering.
What are Living Root Bridges?
Known locally as Jingkieng Jri (Khasi) or Lyu Chrai (Jaintia), these bridges are found across the southern slopes of the Khasi and Jaintia Hills in the state of Meghalaya.
They are:
- Living structures, grown rather than built
- Crafted using the aerial roots of the Ficus elastica (Indian rubber tree)
- Developed over 15–30 years
- Capable of spanning 15 to 250 feet
- Durable for several centuries with proper care
Construction Process: Indigenous Bioengineering
The bridges are a result of traditional tree-shaping techniques perfected over generations:
- Young aerial roots of Ficus trees are guided across streams using hollowed trunks of Areca catechu.
- These trunks protect the roots and direct their growth.
- A temporary bamboo scaffold supports the structure during early stages.
- Over time, roots thicken and undergo inosculation (natural fusion), forming a strong, self-supporting bridge.
- As the bridge matures, the support materials decay, leaving a resilient living structure.
This method reflects deep ecological understanding and sustainable resource use.
Cultural Landscape Significance
The nomination recognises not just the bridges but an entire cultural landscape shaped by the Khasi and Jaintia tribes. The bridges embody:
- Community-based land management
- Intergenerational knowledge transfer
- Spiritual reverence for Mei Ramew (Mother Earth)
- Harmony between human activity and fragile hill ecosystems
Thus, they represent intangible cultural heritage expressed through a tangible living form.
Why UNESCO Recognition Matters
Inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List would:
- Provide global recognition of indigenous ecological knowledge
- Strengthen conservation and sustainable tourism efforts
- Encourage preservation of traditional practices amid modernization
- Highlight nature-based solutions in climate-resilient infrastructure
Institutional Role in Nomination
The nomination dossier was submitted by India’s Permanent Representative to UNESCO with contributions from:
- Archaeological Survey of India
- Ministry of External Affairs
- Government of Meghalaya
- Local indigenous communities, who remain the primary custodians
India Energy Week (IEW) 2026

- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
India Energy Week (IEW) 2026, held in Goa, concluded with India reaffirming its position as a resilient and credible energy leader amid global geopolitical volatility. The event highlighted India’s dual strategy: ensuring energy security through diversified conventional supplies while accelerating the transition toward cleaner fuels.
India’s Energy Strategy: Resilience in a Volatile World
Union Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister Hardeep Singh Puri emphasised that India has successfully navigated successive global disruptions by:
- Diversifying crude oil and gas import sources
- Strengthening domestic exploration
- Expanding clean energy adoption
India today ranks as:
- 3rd-largest energy consumer
- 4th-largest refining hub
- Among the top exporters of petroleum products
Despite global price shocks, India maintained stable domestic fuel and LPG prices, shielding consumers through policy and Oil Marketing Company (OMC) interventions.
Paradigm Shift: From Energy Transition to “Energy Addition”
A key theme at IEW 2026 was that the global transition is not about replacing fossil fuels overnight but about “energy addition”:
- Continued investment in oil and gas for stability
- Rapid scale-up of biofuels, LNG, green hydrogen, and renewables
This balanced approach recognises developmental realities while pursuing climate goals.
Domestic Exploration & Upstream Reforms
India aims to reduce import dependence by boosting domestic production through:
- Hydrocarbon Exploration Licensing Policy (HELP)
- Open Acreage Licensing Policy (OALP)
- Discovered Small Fields (DSF) rounds
- Oilfields (Regulation & Development) Amendment Act, 2025
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Rules, 2025
These reforms aim to improve ease of doing business and attract global investment into India’s sedimentary basins.
Downstream and Infrastructure Reforms
- Unified Pipeline Tariff (UPT) under One Nation, One Gas Grid to reduce regional disparities
- Integration of refining and petrochemicals to enhance value addition
- Digitalisation and AI-driven optimisation to improve logistics and operational resilience
Clean Energy Acceleration
India’s energy transition efforts include:
- 20% ethanol blending achieved in 2025
- Expansion of Compressed Biogas (CBG) with a 5% blending target by 2030
- Scaling Green Hydrogen under the National Green Hydrogen Mission
- Growth in solar and wind capacity, with India ranking among the top global producers
India has already achieved 50% of its installed electricity capacity from non-fossil sources, five years ahead of its 2030 target.
Global Partnerships: India–UAE Energy Ties
At IEW 2026, the United Arab Emirates reaffirmed its role as a reliable energy partner:
- 4th-largest source of India’s oil imports
- Key LPG supplier
- Bilateral trade target: USD 200 billion by 2032
The UAE highlighted underinvestment in energy as a global risk, echoing India’s call for balanced investment across energy types.
Role of States: Goa’s Renewable Vision
As host, Goa presented a roadmap to achieve 100% renewable energy by 2050, linking:
- Green Economy (clean energy growth)
- Blue Economy (sustainable ocean resource use)
This reflects sub-national participation in India’s climate strategy.
Energy Security: India’s Current Status
Achievements:
- 3rd globally in solar capacity
- 4th in wind and overall renewable capacity
- Strong refining and export capabilities
Challenges:
- Still the 3rd-largest net energy importer
- Ranking drop in the World Economic Forum Energy Transition Index
India Adds Two New Ramsar Sites
- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
India has recently expanded its network of internationally recognised wetlands by designating two additional sites as Ramsar wetlands - the Patna Bird Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh and Chhari-Dhand in Gujarat ahead of World Wetlands Day observed on 2 February. This brings the total number of Ramsar Sites in the country to 98, reflecting a significant increase from 26 sites in 2014 and underscoring India's growing commitment to wetland protection and biodiversity conservation.
Ramsar Convention: An Overview
The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, aimed at conserving wetlands and promoting their sustainable use. India became a signatory in 1982 and has progressively expanded its list of designated wetlands that meet criteria for ecological significance. Designation as a Ramsar Site recognises a wetland’s importance for biodiversity, water security, climate resilience, and ecosystem services.
Newly Designated Ramsar Sites
1. Patna Bird Sanctuary (Uttar Pradesh)
- Location & Ecosystem: Situated in eastern Uttar Pradesh, the sanctuary comprises freshwater marshes, grasslands, and woodland patches, embedded within an agricultural landscape.
- Biodiversity Value: The mosaic of habitats supports rich biodiversity and has been recognised as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Around 178 species of birds, including migratory and resident species
- Approximately 252 species of plants
- Ecological Significance: The wetland acts as a critical refuge for avifauna, contributing to regional ecological stability and supporting ecosystem services such as groundwater recharge.
2. Chhari-Dhand Wetland (Gujarat)
- Location & Nature: Located in the Kutch region of Gujarat, Chhari-Dhand is a seasonal saline wetland, positioned between the Banni grasslands and the salt flats of Kutch.
- Avifaunal Importance: It serves as an important wintering and stopover site for migratory waterfowl.
- Key Species Supported:
- Critically endangered sociable lapwing
- Vulnerable common pochard
- Annual congregation of common cranes (Grus grus)
- Ecological Role: The wetland sustains unique saline ecosystem biodiversity and supports pastoral and local livelihoods indirectly.
Grain ATMs
- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
In a move aimed at modernising food security delivery, the state of Bihar has initiated a pilot project to install “Grain ATMs” (Annapurti machines) in Patna. The initiative seeks to enhance efficiency, transparency, and beneficiary convenience under the Public Distribution System (PDS) one of the world’s largest food security programmes.
This reform represents the integration of digital governance and automation into welfare delivery.
What is a Grain ATM?
A Grain ATM, also called Annapurti, is an automated food grain dispensing machine designed to function similarly to a banking ATM. It enables eligible beneficiaries to collect their rationed grains without depending entirely on manual distribution at Fair Price Shops (FPSs).
The technology has been developed by the World Food Programme (WFP) in collaboration with the Food Corporation of India (FCI) and state governments.
Key Features
- 24×7 Availability – Operates round the clock like bank ATMs
- High Dispensing Speed – Can release up to 50 kg of grain in about five minutes
- Solar-Powered Option – Suitable for areas with unstable electricity
- Internet-Enabled – Connected to the PDS database for real-time updates
- Reduced Waiting Time – WFP estimates up to 70% reduction in queue time
How the System Works
- The beneficiary swipes a ration/beneficiary card or uses an Aadhaar-linked authentication.
- Biometric verification is completed through a PoS device.
- The beneficiary selects the type and quantity of grain within their entitlement limit.
- The machine dispenses the grain automatically.
- The transaction is digitally recorded in the PDS database.
- A printed slip is issued as proof of distribution.
This process minimises human intervention and manual weighing errors.
Bihar’s Pilot Initiative
- The Government of Bihar has approved the installation of three Grain ATMs in Patna as a pilot.
- The Food and Consumer Protection Department is the nodal implementing agency.
- If successful, the project may be expanded across urban and eventually rural areas.
Bihar has a large food security footprint:
- Over 8.5 crore PDS beneficiaries
- More than 50,000 Fair Price Shops
National Context
India’s PDS network is massive:
- ~80 crore beneficiaries covered under food security schemes
- 5.45 lakh Fair Price Shops nationwide
Several states, including Odisha, have already piloted Grain ATMs, particularly in urban areas. The Union government plans to expand such technology-driven systems to the Panchayat level in the future.
Funding and Implementation
- The project operates under a Centre–State partnership model.
- States provide physical space for installation.
- Maintenance and security costs are shared between the Centre and state governments.
Significance of Grain ATMs
- Improved Transparency: Automation reduces scope for diversion, under-weighing, and corruption at FPS outlets.
- Beneficiary Convenience: 24×7 access reduces long queues and allows flexible collection times, especially for daily-wage earners.
- Digitisation of Welfare Delivery: Real-time database updates strengthen data accuracy and monitoring.
- Women & Elderly Friendly: Faster service benefits vulnerable groups who struggle with long waiting times.
- Energy Sustainability: Solar-powered machines align with clean energy goals.
‘CHAKRA’ – Centre of Excellence (CoE)
- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
In a significant move to align banking with India’s future economic priorities, the State Bank of India (SBI) has launched ‘CHAKRA’ – Centre of Excellence (CoE). The initiative is designed to support financing for sunrise sectors that are expected to play a decisive role in India’s transition toward a technology-driven, sustainable, and globally competitive economy.
This step signals a shift in institutional finance from traditional asset-heavy industries toward innovation-led and climate-aligned growth sectors.
What is CHAKRA?
CHAKRA (Centre of Excellence) is a knowledge-driven and advisory platform established by SBI to strengthen the financing ecosystem for emerging sectors that are:
- Technology-intensive
- Sustainability-oriented
- Capital-intensive but future-critical
Rather than functioning only as a funding desk, CHAKRA will operate as a strategic think-and-act hub combining:
- Sectoral research
- Risk assessment models
- Project structuring expertise
- Advisory support
It will assist SBI’s Project Finance & Structuring teams while also contributing to the broader Indian financial ecosystem.
Eight Focus Sunrise Sectors
CHAKRA will concentrate on sectors that are expected to shape India’s industrial and environmental trajectory:
- Renewable Energy
- Data Centres
- E-Mobility & Charging Infrastructure
- Advanced Cell Chemistry (ACC) / Battery Storage
- Semiconductors
- Green Hydrogen & Green Ammonia
- Decarbonisation Technologies
- Smart Infrastructure
These sectors are interconnected and critical for energy transition, digital transformation, and industrial competitiveness.
Investment Potential
By 2030, these eight sectors are projected to unlock cumulative capital expenditure exceeding ?100 lakh crore.
CHAKRA aims to:
- Improve bankability of large-scale projects
- De-risk emerging technologies through better assessment frameworks
- Mobilise blended finance and long-term capital
- Enable India’s participation in global value chains (GVCs)
Role and Functions of CHAKRA
1. Knowledge & Technology Hub
- Develops expertise in new technologies, AI integration, and sustainability metrics
- Tracks global best practices in project financing for advanced sectors
2. Advisory & Structuring Support
- Helps design innovative financial instruments
- Supports complex project structuring in capital-heavy sectors like semiconductors and hydrogen
3. Ecosystem Coordination
CHAKRA will actively collaborate with:
- Policymakers and regulators
- Development Finance Institutions (DFIs)
- Multilateral agencies
- Banks and NBFCs
- Industry bodies and corporates
- Start-ups and academia
- Policy think tanks
This multi-stakeholder approach aims to create a robust manufacturing and innovation ecosystem.
Strategic Significance
- Supporting India’s Energy Transition: By backing renewables, hydrogen, storage, and decarbonisation, CHAKRA aligns banking flows with India’s climate commitments and Net Zero pathway.
- Strengthening Technological Sovereignty: Financing for semiconductors, batteries, and data centres reduces import dependence and enhances strategic autonomy.
- Enabling Digital & Infrastructure Growth: Smart infrastructure and data centres are essential for Digital India, AI adoption, and Industry 4.0.
- Financial Sector Innovation: The CoE model marks a transition from collateral-based lending to knowledge-based financing, especially for technology-driven sectors where risks are complex but long-term returns are high.
Mahatma Gandhi Gram Swaraj Initiative (MGGSI)

- 02 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Budget 2026–27 introduced the Mahatma Gandhi Gram Swaraj Initiative (MGGSI) as a focused intervention to revitalise India’s traditional rural industries. The programme seeks to strengthen khadi, handloom, and handicrafts by improving competitiveness, market access, and sustainability of artisan livelihoods. In doing so, it draws inspiration from the Gram Swaraj vision of Mahatma Gandhi, which emphasised self-reliant villages built on local production and decentralized economic power.
Objectives and Target Groups
MGGSI is designed to make traditional sectors economically viable in a modern market environment while preserving India’s craft heritage. It focuses on:
- Weavers and artisans in khadi, handloom, and handicrafts
- Village industries and rural micro-enterprises
- Beneficiaries under the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative
- Rural youth, encouraging them to view traditional industries as viable careers
The initiative recognises that these sectors not only sustain livelihoods but also represent cultural capital and employment-intensive growth, particularly in labour-surplus rural regions.
Addressing Structural Challenges
Traditional craft sectors suffer from long-standing bottlenecks:
- Fragmented supply chains that raise costs and reduce efficiency
- Inconsistent quality standards, limiting access to premium and export markets
- Weak branding and marketing, leading to dependence on middlemen
- Limited integration with modern retail and e-commerce platforms
MGGSI aims to address these constraints through institutional support, quality standardisation, design innovation, and better market linkages. It encourages artisans to adopt modern production techniques and tools without compromising traditional craftsmanship.
Market Access and Branding
A core pillar of MGGSI is improving global and domestic market access. The initiative promotes:
- Professional branding and packaging
- Entry into organised retail chains
- Access to export markets
- Integration with digital and online marketplaces
This shift from subsistence production to market-oriented enterprise aligns with the broader “Vocal for Local” philosophy and the push to strengthen MSMEs as engines of inclusive growth.
Link to Gandhi’s Gram Swaraj Vision
Gandhi’s concept of Gram Swaraj envisioned villages as self-sufficient republics, economically independent and socially cohesive. However, contemporary rural India faces challenges such as agrarian distress, migration, inequality, and weak non-farm employment opportunities, which prevent villages from achieving that ideal.
MGGSI attempts to reinterpret Gram Swaraj for the 21st century by:
- Promoting local production for wider markets
- Generating non-farm rural employment
- Reducing distress migration
- Enhancing economic self-reliance through village industries
Thus, instead of isolation, the modern approach combines local production with global connectivity.
First-Ever Air Shipment of GI Tagged Indi and Puliyankudi Limes
- 02 Nov 2025
In News:
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) has facilitated the first-ever air shipment of GI-tagged Indi Lime (Karnataka) and Puliyankudi Lime (Tamil Nadu) to the United Kingdom. The initiative marks a significant step in expanding India's agricultural export basket and enhancing global recognition of region-specific products.
- This milestone aligns with India’s broader efforts to promote GI-tagged agricultural commodities and support farmer incomes through improved market access.
What is a GI Tag?
- A Geographical Indication (GI) is an Intellectual Property Right (IPR) recognising products whose qualities or reputation are linked to a specific geographical origin.
- Legislation: Registered under the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- Issuing Authority: GI Registry, Chennai under DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- Purpose:
- Protect regional uniqueness
- Prevent unauthorised use
- Enhance export potential
- Provide economic benefits to local communities
Indi Lime (Karnataka)
- Region: Primarily grown in Vijayapura district.
- Characteristics:
- High juice content
- Strong aroma
- Balanced acidity
- Uses: Culinary applications, traditional medicine, and cultural practices; reflects Karnataka’s agrarian heritage.
- Earlier in 2025, APEDA also exported 3 MT of GI-tagged Swadeshi Indi Lime to the UAE, showcasing rising global demand.
Puliyankudi Lime (Tamil Nadu)
- Region: Grown widely in Tenkasi district, known as the “Lemon City of Tamil Nadu.”
- Popular Variety: Kadayam Lime
- Features:
- Thin peel
- Strong acidity
- High juice yield (≈55%)
- Rich in Vitamin C (≈34.3 mg/100g) and antioxidants
- GI Recognition: Granted in April 2025, acknowledging its superior regional traits.
Export Significance
- Enhances global visibility of India’s GI-tagged agricultural products.
- Opens new markets for limes, traditionally exported in small volumes.
- Strengthens farmer incomes and supports rural economies in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Builds on India’s expanding export footprint, which recently included:
- Gharwali apples
- Apricots from Kargil
to Gulf markets such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Qatar.
Institutional & Trade Context
- APEDA, under the Department of Commerce, plays a leading role in diversifying India’s agri-exports.
- The announcement coincided with India–EU FTA discussions in Brussels, where Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal and EU officials reiterated the need for a balanced and mutually beneficial agreement to strengthen bilateral trade.
AmazonFACE Project

- 02 Nov 2025
In News:
- The AmazonFACE Project, launched near Manaus, Brazil, is a pioneering climate research experiment designed to study how the Amazon rainforest—the world’s largest tropical forest—responds to future elevated CO? levels. The initiative is significant as Brazil prepares to host COP30 in Belém.
- It is the first experiment of its scale in a natural tropical forest, marking a major advancement in global climate science.
What is AmazonFACE?
- A long-term field experiment exposing mature tropical trees to projected future CO? concentrations.
- Located in an old-growth Amazon forest stand.
- Aims to understand how increased atmospheric carbon affects forest functioning, carbon cycling, water exchange and overall ecosystem resilience.
Technology Used: FACE
FACE (Free-Air CO? Enrichment) technology:
- Releases controlled amounts of CO? into open-air forest environments.
- Allows real-time assessment of how trees respond without disturbing natural forest structure.
- Previously used in temperate biomes, but AmazonFACE is the first large-scale FACE experiment in tropical forests.
Structure & Working
- The site contains six large steel-ring towers, each enclosing 50–70 mature trees.
- Three rings are fumigated with CO? at concentrations matching climate projections for 2050–2060.
- Three rings act as control plots.
- Sensors record data every 10 minutes, including:
- CO? absorption
- Oxygen and water vapour release
- Responses to rainfall, sunlight, and storms
- Later stages will simulate artificial microclimates with higher atmospheric CO?.
Institutional Support
- Led by INPA (National Institute for Amazon Research) and Universidade Estadual de Campinas.
- Supported by the Brazilian federal government and the United Kingdom.
Significance
- Helps model the future behaviour of the Amazon under climate stress.
- Provides insights into:
- Carbon sequestration capacity
- Forest growth patterns
- Water cycle feedbacks
- Potential ecosystem tipping points
- Critical for global climate policymaking, especially ahead of COP30, where adaptation and mitigation strategies for the Amazon biome will be central.
Bharat Taxi
- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
- India is set to launch ‘Bharat Taxi’, the country’s first cooperative-based ride-hailing platform, in November 2025, beginning in Delhi.
- The initiative marks a transformative step in the government’s efforts to democratise the digital economy by ensuring equitable participation and income security for gig workers, particularly cab drivers.
- The project is being implemented jointly by the Union Ministry of Cooperation and the National e-Governance Division (NeGD) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
About Bharat Taxi
Bharat Taxi is a government-backed cooperative cab service designed to offer an alternative to private app-based aggregators such as Ola and Uber. It operates on the principle of “cooperative ownership and collective welfare”, where drivers act as both service providers and shareholders.
Implementing Structure
- Promoting Body: Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Ltd., established in June 2025.
- Initial Capital: ?300 crore.
- Supported By: Leading cooperative institutions such as Amul, IFFCO, NAFED, KRIBHCO, NABARD, and the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
- Governance:
- Chairperson: Jayen Mehta (MD, Amul/GCMMF)
- Vice-Chairman: Rohit Gupta (Deputy MD, NCDC)
Objectives
- Empower Drivers: Convert cab drivers into cooperative members (“Saarthis”) and shareholders.
- Ensure Fair Earnings: Eliminate high commissions (up to 25% under private apps) through a zero-commission model.
- Provide Affordable, Transparent Rides: Introduce fare regulation with no surge pricing or hidden costs.
- Promote Cooperative Entrepreneurship: Strengthen India’s cooperative movement in the digital services economy.
- Enhance Urban Mobility: Offer a reliable, ethical, and citizen-friendly transport option integrated with government e-platforms.
Key Features
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Ownership Model |
Cooperative-based — drivers are shareholders, not contractors. |
|
Revenue Mechanism |
No commission; nominal membership fee (daily/weekly/monthly). |
|
Digital Integration |
Linked with DigiLocker, UMANG, and API Setu for seamless authentication and data security. |
|
Transparency in Fares |
Regulated pricing; no algorithm-based surge rates or cancellation penalties. |
|
Phased Rollout |
Pilot in Delhi (Nov 2025) with 650 driver-owners; expansion to 20 cities by 2026 and 1 lakh cabs nationwide by 2030. |
|
Inclusivity Focus |
Participation of 5,000 drivers (men & women) in the initial nationwide phase. |
UNEP Adaptation Gap Report 2025
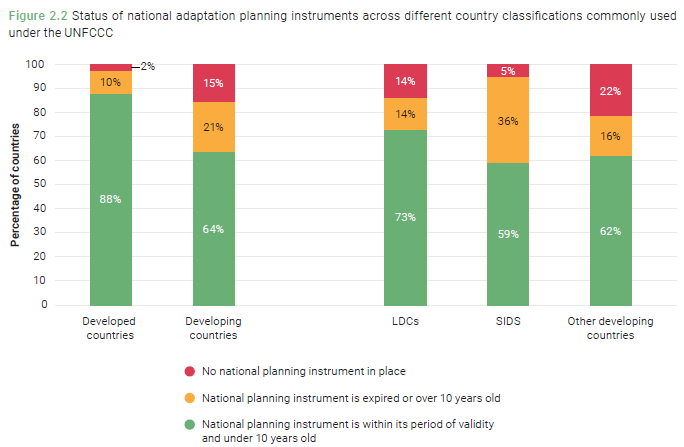
- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has released its flagship Adaptation Gap Report (AGR) 2025, titled “Running on Empty”.
The report warns that the global climate adaptation finance gap for developing countries has widened sharply, threatening progress toward climate resilience and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
About the Adaptation Gap Report (AGR)
- Publisher: UNEP–Copenhagen Climate Centre, with global institutional contributions.
- Purpose: Tracks progress in climate adaptation planning, implementation, and finance, assessing global preparedness against climate impacts.
- Relevance: Supports policy negotiations under the UNFCCC and upcoming COP30 (Belém, Brazil).
Key Findings
1. Escalating Finance Needs
- Developing nations will require USD 310–365 billion annually by 2035, potentially rising to USD 440–520 billion when adjusted for inflation.
- The growing need reflects increasing risks from both rapid- and slow-onset climate events—heatwaves, floods, sea-level rise, and glacial melt.
2. Widening Adaptation Finance Gap
- Current adaptation finance (2023): Only USD 26 billion, covering just one-twelfth of total requirements.
- Finance gap: USD 284–339 billion annually.
- Falling trends: Funding fell from USD 28 billion (2022), meaning the Glasgow Climate Pact target of doubling adaptation finance by 2025 will likely be missed.
3. Debt-Heavy and Unequal Finance
- About 58% of adaptation finance is in the form of loans, many non-concessional—deepening debt vulnerabilities among developing nations.
- This creates a growing risk of “adaptation debt traps”, undermining the principle of climate justice.
4. Progress and Planning Gaps
- 172 countries have at least one National Adaptation Plan (NAP); however, 36 of them are outdated.
- 1,600+ adaptation actions have been reported globally, primarily in agriculture, water, biodiversity, and infrastructure, but few measure tangible resilience outcomes.
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) show the highest integration of adaptation into national policies.
5. Limited Private Sector Role
- The private sector contributes only USD 5 billion annually, despite potential investment capacity up to USD 50 billion with supportive de-risking mechanisms.
- Low engagement is attributed to high risk perceptions and limited blended-finance instruments.
6. Multilateral Fund Support
- Disbursements through the Green Climate Fund (GCF), Global Environment Facility (GEF), and Adaptation Fund reached USD 920 million in 2024—an 86% rise over the previous five-year average, though UNEP warns this may be temporary.
Global Frameworks and Roadmaps
Baku–Belém Roadmap (COP29–COP30)
- Envisions USD 1.3 trillion per year by 2035 in total climate finance.
- Stresses the need for grant-based and concessional instruments rather than debt-heavy finance.
- Aims to align finance, transparency, and adaptation under a “global collective effort” (mutirão global) led by Brazil’s COP30 presidency.
New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG)
- Proposed USD 300 billion by 2035, but UNEP cautions that it is insufficient and not inflation-adjusted, hence failing to meet real adaptation needs.
India and the Adaptation Gap Report 2025
1. National and Regional Context
- India’s climate strategy now prioritises adaptation-centric policies over mitigation, focusing on resilient agriculture, water systems, and disaster management.
- Frequent heatwaves, floods, and glacial retreats heighten India’s vulnerability, underscoring the need for adaptive investments.
2. Policy and Institutional Response
- India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and State Action Plans align with UNEP’s adaptation priorities.
- Initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), and LiFE Mission showcase India’s global leadership in climate diplomacy.
3. Financial and Structural Constraints
- India continues to face adaptation investment gaps, relying heavily on concessional and multilateral finance.
- Domestic efforts like the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) are under fiscal strain due to limited international flow.
4. Developmental Balancing
- India maintains that development precedes decarbonisation, in line with the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC).
- The Economic Survey 2024–25 reiterates that achieving developed-nation status by 2047 is essential before aggressive deep decarbonisation.
- India remains committed to Net Zero by 2070, consistent with its Long-Term Low Emissions Development Strategy (LT-LEDS).
Tomahawk Missiles
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the Iran-Israel conflict, the United States has reportedly launched precision strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, targeting key sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan. These attacks were carried out using Tomahawk cruise missiles and GBU-57 bunker busters, marking a critical intervention by the US in the unfolding regional crisis. President Donald Trump termed the strikes a “clear warning” to Iran, signalling the potential for intensified military action if diplomatic overtures are rejected.
What Are Tomahawk Missiles?
The Tomahawk missile is a long-range, subsonic, all-weather cruise missile primarily operated by the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It is designed for precision strikes on high-value or heavily defended targets, including hardened or buried infrastructure such as nuclear sites.
- Launch platforms: Ships and submarines
- Flight path: Low-altitude terrain-following flight to evade radar
- Use case: Strategic, surgical strikes in contested or defended environments
Design and Capabilities
- Length: ~5.6 meters (without booster)
- Weight: Up to 1,600 kg
- Speed: ~880 km/h (subsonic)
- Range: Over 1,600 km (varies by variant)
- Flight altitude: As low as 30–50 meters
- Warheads:
- Unitary high-explosive
- Cluster munitions
- Nuclear warheads (retired from use)
Navigation and Guidance Systems
Tomahawk missiles are known for pinpoint accuracy, achieved through a multi-layered guidance system:
- GPS (Global Positioning System) and INS (Inertial Navigation System) for real-time course tracking
- TERCOM (Terrain Contour Matching): Compares terrain under flight path with stored maps
- DSMAC (Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation): Matches live terrain imagery with onboard target data
- Data-link capability: Allows for in-flight re-targeting, mission abort, or loitering over areas
Variants and Modern Upgrades
- Tomahawk Block IV (TLAM-E): Most modern variant, featuring:
- In-flight reprogramming
- Target loitering
- Real-time battle damage assessment
- Two-way satellite communication
Historical Combat Usage
Tomahawk missiles have been extensively used in US military operations:
- Gulf War (1991): ~280 missiles used in the opening strikes
- Operation Infinite Reach (1998): Targeted terrorist camps in Sudan and Afghanistan
- Iraq War (2003): Hundreds used during the initial “shock and awe” campaign
- Libya Intervention (2011): Destroyed air defence infrastructure
- Syria (2017): 59 Tomahawks used against Shayrat Airbase in retaliation for chemical attacks
INS Tamal

- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark development for India's maritime defence, the Indian Navy is set to commission its latest stealth multi-role frigate, INS Tamal, on 1st July 2025 at Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningrad, Russia
Overview:
- Class & Series: INS Tamal is the second ship of the Tushil-class, an upgraded variant of the Talwar and Teg class frigates, forming part of the Krivak class series built under Indo-Russian cooperation.
- Total Induction: With Tamal’s addition, India will operate ten ships with common capabilities across four related classes.
- Construction: Built at Yantar Shipyard with oversight from Indian specialists under the Warship Overseeing Team (WOT), Kaliningrad, under the Embassy of India, Moscow.
Symbolism and Identity
- The name ‘Tamal’ represents the mythical sword of Indra, the King of Gods.
- The ship’s mascot blends India’s Jambavant, the immortal bear king of mythology, with Russia’s Eurasian Brown Bear, symbolising Indo-Russian defence cooperation.
- The ship’s motto: ‘Sarvada Sarvatra Vijaya’ (Victorious Always Everywhere).
Make in India & Indigenous Content
- INS Tamal is the last warship to be inducted from a foreign source, aligning with Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives.
- 26% indigenous content, including:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (anti-ship & land attack roles)
- HUMSA NG Mk II sonar, Indian radars, and communication systems
- Indian OEMs involved: BrahMos Aerospace, BEL, Keltron, Nova Integrated Systems (Tata), Elcome Marine, Johnson Controls India, among others.
- Indigenous components have more than doubled to 33 systems compared to previous imports.
Key Features & Capabilities
- Displacement: 3,900 tonnes | Length: 125 metres
- Top speed: Over 30 knots
- Armament & Combat Systems:
- Vertically Launched Surface-to-Air Missiles (VL-SAM)
- Improved 100 mm main gun, 30 mm CIWS
- Heavyweight torpedoes, anti-submarine rockets
- EO/IR system, fire control radars
- Aviation Support: Flight deck for Air Early Warning & Multi-Role helicopters
- Sensors & Network:
- Surface Surveillance Radar
- Advanced Electronic Warfare suite
- Network Centric Warfare capabilities
- Trials: Successfully completed 3-month sea trials, validating systems and weapons in challenging winter conditions (St. Petersburg & Kaliningrad).
Strategic Importance
- Upon commissioning, INS Tamal will join the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet—the 'Sword Arm' of the Navy under Western Naval Command.
- Reinforces India’s blue water naval ambitions, enhancing operational readiness in multi-threat maritime environments.
- Embodies two decades of Indo-Russian naval cooperation and represents a transition towards domestic warship production.
Gwada Negative
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark discovery for transfusion science, France’s national blood agency (Établissement Français du Sang – EFS), in June 2025, identified a completely new blood group system. Officially recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as the 48th blood group system, it is termed EMM-negative and is informally called “Gwada Negative”, after Guadeloupe, the origin of the only known individual with this blood type.
What is Gwada Negative (EMM-negative)?
- EMM-negative is defined by the absence of the EMM antigen, a high-incidence antigen normally present on red blood cells in nearly all humans.
- High-incidence antigens are so common that individuals lacking them are considered extremely rare and face critical challenges in blood transfusion compatibility.
- The ISBT registered this as ISBT042, making it the latest addition to global blood group systems.
Discovery Timeline
- 2011: A 54-year-old woman from Guadeloupe, living in Paris, underwent pre-surgical blood testing. Her blood showed unidentified antibodies that did not match any known blood group systems.
- 2019: With advancements in Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), researchers led by Dr. Thierry Peyrard (EFS) identified the unique genetic mutation responsible for the absence of the EMM antigen.
- 2025: After peer-reviewed validation, the ISBT officially recognised the EMM-negative system during its Milan meeting.
Why is it So Rare?
- This woman is the only known person in the world with the EMM-negative blood type.
- She inherited the rare gene mutation from both parents, leading to a complete absence of the EMM antigen in her red blood cells.
- Since the EMM antigen is nearly universal, her blood is compatible only with itself, making transfusions extremely high-risk unless a genetically identical donor is found.
Clinical Significance
- Individuals lacking high-incidence antigens like EMM may develop alloantibodies — immune responses against transfused red cells containing those antigens.
- Transfusion of EMM-positive blood into such individuals can cause hemolytic reactions, including life-threatening hemolysis (premature red blood cell breakdown).
- In this case, no donor blood currently available is safe for transfusion into the patient.
Implications for Transfusion Medicine
- Highlights the need for rare blood donor registries, international cooperation, and advanced genetic screening technologies to identify such rare phenotypes.
- Encourages development of precision-matching protocols in complex clinical and emergency situations.
- Expands the understanding of human immunohematological diversity and redefines transfusion compatibility standards.
SSLV Technology Transfer
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a historic development for India's space sector, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will, for the first time, completely transfer rocket technology to a domestic firm. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has secured the Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) through a competitive process facilitated by IN-SPACe, marking a new era of private-sector participation in space.
What is the SSLV Technology Transfer?
- Nature of ToT: Complete technology handover of ISRO’s SSLV to HAL.
- Awarded By: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) after a two-stage national selection.
- Winning Bid: HAL won the bid with a ?511 crore offer — the highest among the contenders.
- Other Bidders: Consortia led by Alpha Design (Bengaluru) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (Hyderabad).
- Objective: To empower the private sector to build, market, and launch rockets independently, thus reducing reliance on ISRO for small satellite missions.
Key Features of the SSLV ToT
Parameter Details
Ownership - HAL will own and operate the SSLV, with rights to modify its design and choose commercial partners.
Production Capability - HAL aims to produce 6–10 SSLVs annually, based on demand.
ToT Duration - 2 years of technology handholding by ISRO, during which HAL will manufacture at least two SSLV prototypes.
Post-ToT - HAL will operate independently post-ToT and may enter contracts for commercial launch services.
Contractual Roles - ISRO (technical), IN-SPACe (regulatory + ToT coordination), NSIL (commercial interface), HAL (execution).
About Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- Established: 23 December 1940 (as Hindustan Aircraft Limited).
- HQ: Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Core Role: India’s largest defence and aerospace PSU involved in aircraft, helicopters, engines, and now space systems.
- Key Contributions:
- Manufactured MiG-21, SU-30MKI, LCA Tejas.
- Supplied components for GSLV Mk-III, Mars Orbiter Mission, and Gaganyaan.
- Collaborated with ISRO on cryogenic engines and launch vehicle structures.
- Publicly Listed: On BSE and NSE since 2018.
Significance:
- First Full Rocket ToT in India: Unlike earlier manufacturing contracts (e.g., PSLV), SSLV is entirely owned and operated by HAL.
- Boosts Private Sector Role: Aligns with India’s space sector reforms to commercialize launch services.
- Fosters Innovation & Autonomy: HAL can redesign the SSLV and partner globally, making India more competitive in the small satellite launch market.
- Strategic Diversification: HAL adds space systems to its portfolio, without affecting defence operations.
Green Hydrogen Production
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant scientific milestone, Indian researchers have developed a next-generation, scalable solar-driven device for producing green hydrogen—offering a major boost to clean energy innovation and India’s energy transition goals.
Key Highlights:
- Developed By: Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Bengaluru — an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Publication: The findings were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A (Royal Society of Chemistry).
What Is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced by splitting water molecules using renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind, without any greenhouse gas emissions. It is a clean energy carrier with the potential to decarbonize heavy industries, power vehicles, and store energy.
The Innovation: Solar-Driven Water Splitting Device
- The device uses only solar energy to split water and produce hydrogen.
- It employs a silicon-based photoanode with an n-i-p heterojunction structure:
- n-type TiO?, intrinsic (undoped) Si, and p-type NiO layers.
- This structure enhances charge separation and transport efficiency.
- Fabrication via magnetron sputtering, a scalable, industry-compatible process.
Key Performance Metrics
- Surface photovoltage: 600 millivolts (mV)
- Low onset potential: ~0.11 VRHE
- Stability: Operated continuously for over 10 hours in alkaline medium with only ~4% performance degradation.
- Successfully scaled to a 25 cm² photoanode, showing strong solar-to-hydrogen conversion.
Advantages of the Device
Feature Benefit
Pure solar operation No external power or fossil fuel input
High energy efficiency Better light absorption, reduced recombination loss
Material use Low-cost, earth-abundant materials
Durability Stable under alkaline conditions
Scalability Demonstrated potential for industrial-scale production
Strategic Significance
- Accelerates India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and hydrogen-based economy.
- Supports India’s net-zero emission commitments and climate action.
- Offers a cost-effective, clean energy alternative to fossil fuels in:
- Hard-to-abate sectors like steel and cement
- Clean transport solutions
- Renewable energy storage systems
B-2 Spirit Bomber
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the ongoing US–Iran tensions, the United States deployed the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber to strike Iran’s fortified nuclear infrastructure, including the heavily guarded Fordow enrichment facility, which was described by President Donald Trump as the “crown jewel” of Iran’s nuclear programme. The strikes signal a new phase in the geopolitical standoff, showcasing advanced US airpower and precision capabilities.
What is the B-2 Spirit Bomber?
The B-2 Spirit, developed by Northrop Grumman during the Cold War, is one of the most advanced strategic bombers in the world. Originally built for penetrating heavily defended Soviet airspace, it remains a key asset in the US Air Force due to its stealth capabilities, long range, and precision payload delivery.
Only 21 B-2 bombers were built, each costing an estimated $2.1 billion, making it one of the most expensive aircraft ever developed. Its bat-wing design and radar-absorbent coating significantly reduce its radar cross-section, making it almost invisible to radar and ideal for deep penetration missions in hostile territory. It is operated by a two-person crew and extensively automated to reduce pilot workload.
Why was it used in the Iran strikes?
The B-2 Spirit was chosen for the Iran mission because of its unique combination of stealth, range, and payload capacity. The Fordow facility, built deep within a mountain and protected by sophisticated air defences, required a bomber that could both evade detection and deliver a bunker-busting payload with high precision.
During the mission, the B-2s were reportedly equipped with the GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) — a 30,000-pound bomb specifically designed to destroy deeply buried and fortified targets like Fordow. Due to the weapon’s size and weight, a B-2 can carry only one or two MOPs per sortie. Reports indicate that six MOPs were dropped on Fordow, demonstrating the operational effectiveness of the B-2 for such critical missions.
Capabilities and Strategic Role
The B-2 has an unrefueled range of over 6,000 nautical miles (approximately 11,000 km), enabling it to undertake intercontinental missions directly from the United States. Past missions have seen the B-2 operate from Missouri to targets in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran, demonstrating its global strike capability.
With a total payload capacity exceeding 40,000 pounds (18,000 kg), the B-2 can carry both conventional and nuclear weapons. It forms a crucial part of the US nuclear triad, capable of delivering up to 16 B83 nuclear bombs. Its ability to carry nuclear and precision-guided munitions gives it unmatched strategic versatility.
Weapon Systems Compatible with the B-2
Beyond the MOP, the B-2 can be armed with a variety of precision and standoff weapons, including:
- JDAMs (Joint Direct Attack Munitions): GPS-guided bombs used for high-accuracy strikes on fixed targets.
- JSOW (Joint Standoff Weapons): Glide bombs launched from a distance, allowing engagement of targets outside enemy air defence range.
- JASSM and JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missiles): Long-range cruise missiles, with the extended-range variant capable of striking targets up to 500 miles (805 km) away.
This versatility allows the B-2 to adapt to multiple mission profiles, from conventional warfare to nuclear deterrence.
Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
The deployment of the B-2 in this mission has both tactical and symbolic implications. Tactically, it underscores the US military’s ability to deliver precision strikes on highly protected strategic infrastructure. Strategically, it sends a strong signal to adversaries about the technological edge and operational reach of American military power.
From a geopolitical perspective, the strikes could exacerbate tensions in the already volatile West Asian region, heighten concerns about nuclear proliferation, and potentially provoke retaliatory actions by Iran and its regional allies. It also raises questions about the future of US-Iran relations and the fragility of nuclear diplomacy in the region.
Samson Option
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The Samson Option, Israel’s controversial and undeclared nuclear deterrence doctrine, has returned to global focus amid escalating military strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure under Operation Rising Lion (June 2025). The rising risk of a multi-front conflict involving Iran, Hezbollah, and Houthi actors has revived global concerns over nuclear escalation in the volatile Middle East.
What is the Samson Option?
- Definition: Israel’s nuclear annihilation doctrine of last resort, based on the principle of massive retaliation in case of an existential threat to the state.
- Doctrine Type: Deterrence-by-retaliation, not first use.
- Strategic Intent: Not to deter routine threats, but to ensure mutual destruction if Israel faces annihilation.
- Named After: Samson, a biblical warrior who destroyed himself and his enemies in a final act of vengeance (Judges 13–16).
Key Features
Feature Details
Ambiguity (Amimut) Israel neither confirms nor denies its nuclear arsenal.
Nuclear Capability Estimated 80–400 nuclear warheads, with delivery via land (Jericho missiles), air, and sea.
Indigenous Development Secret nuclear program began in the 1950s under Ben-Gurion with aid from France & Norway.
Delivery Platforms Multi-platform: land-based missiles (Jericho series), aircraft, and submarines.
Psychological Warfare Operates as a psychological deterrent, not an openly declared policy.
Policy Origin Popularized by Seymour Hersh’s 1991 book, built upon disclosures by whistleblower Mordechai Vanunu (1986).
Historical Evolution
- 1950s–60s: Nuclear ambitions began under PM David Ben-Gurion.
- 1967: Believed to have assembled first nuclear weapon by Six-Day War.
- Public Position: “We will not be the first to introduce nuclear weapons in the Middle East” – Shimon Peres to JFK.
- Doctrinal Continuity: Israel remains outside the NPT (Non-Proliferation Treaty) and follows the policy of opacity to this day.
Why It’s in Focus Now: Operation Rising Lion & 2025 Escalations
- Operation Rising Lion (June 2025): Israel’s largest campaign against Iran’s nuclear sites since the 1981 Osirak raid.
- Iran’s Response: Ballistic missile and drone counterstrikes tested Israel’s air defences (Iron Dome, Arrow-3).
- Multi-Front Threats: Escalations from Hezbollah in Lebanon, Houthi threats in the Red Sea, and tension in Gaza heighten risks of a regional conflagration.
- Red Lines: Any mass-casualty attack involving WMDs (chemical/radiological) may activate Israel’s last-resort nuclear doctrine.
Implications for the Region and the World
- Security and Strategic Balance
- Israel’s nuclear ambiguity complicates strategic planning for adversaries.
- Shapes arms acquisition strategies of regional players like Iran, Saudi Arabia, and UAE.
- Geoeconomic and Business Fallout
- Oil Market Volatility: Brent crude hit $102/barrel after Israeli strike on Natanz.
- Defence Sector Boom: Surge in defence procurement by Gulf States; U.S. firms like Raytheon and Lockheed Martin benefit.
- Investor Uncertainty: Rising nuclear rhetoric rattles financial markets and international investors.
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Challenges
- Israel’s position outside the NPT undermines the credibility of global arms control.
- Inspires double standards debate and pressures nations like Iran to pursue deterrent paths.
- Cyber Deterrence and Intelligence Warfare
- Past cyber ops like Stuxnet (U.S.–Israel malware attack on Iran’s nuclear centrifuges) re-emerging.
- Cyber warfare now considered part of the extended nuclear deterrent architecture.
BSNL Soft Launches Quantum 5G FWA

- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) announced in Hyderabad, the soft launch of BSNL Quantum 5G FWA. This indigenous, SIM-less fixed-wireless-access solution delivers fibre-like speeds over 5G radio.
What is Quantum 5G FWA?
Quantum 5G FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) is an indigenous, SIM-less, 5G broadband solution that offers fibre-like speeds using wireless 5G radio—eliminating the need for traditional fibre connections.
Key Technical Features:
- SIM-less Connectivity: Uses BSNL’s Direct-to-Device (D2D) platform; Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) auto-authenticates without a SIM card.
- Fully Indigenous Tech Stack: Core network, RAN (Radio Access Network), and CPE developed under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- High-Speed Performance:
- Download: Up to 980 Mbps
- Upload: 140 Mbps
- Latency: Under 10 milliseconds
- Plug-and-Play Installation:
- No trenching or fibre required.
- Covers over 85% of Hyderabad households via existing BSNL tower grid.
Significance of the Launch
- India’s First SIM-less 5G FWA solution.
- Marks BSNL as a 5G pioneer in offering 100% made-in-India wireless broadband.
- Showcases Indian R&D strength and self-reliance in advanced telecom under Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Ideal for UHD streaming, cloud gaming, remote work, and smart home services.
- Bridges the digital divide by enabling affordable gigabit-speed internet, even in rural and underserved regions.
Roadmap and Future Expansion
- Pilot Rollouts (By September 2025): Target Cities: Bengaluru, Pondicherry, Visakhapatnam, Pune, Gwalior, Chandigarh
- Tariff Plans:
- ?999/month for 100 Mbps
- ?1499/month for 300 Mbps
- Enterprise Applications: Will support network-sliced, SLA-backed links for MSMEs and smart manufacturing through edge-cloud architecture.
World Investment Report 2025
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Investment Report 2025, released recently by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights critical trends in global foreign direct investment (FDI).
Key Details:
Purpose of the Report:
- To track global trends in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and international production.
- To guide policymakers and investors on aligning investment flows with sustainable development objectives.
- To monitor progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Global Digital Compact through investment trends.
Major Global Trends Identified (2024 Data)
- Overall Decline in Global FDI: FDI declined by 11%, reaching $1.5 trillion, marking the second consecutive year of contraction.
- Digital Economy as a Growth Engine
- Value of digital-sector projects doubled, becoming the primary driver of FDI growth.
- Key growth areas: AI, data centres, cloud computing, semiconductors.
- SDG Investment Crisis: Investment in critical SDG sectors such as renewable energy, water, sanitation, and agrifood fell by 25–33%.
- Regional Divergence
- Africa: FDI surged by 75%, led by Egypt’s $35 billion megaproject.
- ASEAN: Moderate growth of 10% driven by realigned supply chains.
- China: FDI inflows fell by 29%, affected by geopolitical tensions.
- South America: Registered an 18% drop in FDI.
- Collapse in Infrastructure Finance: International Project Finance (IPF) declined by 26%, deepening the infrastructure gap in least developed countries (LDCs).
- Geopolitical Fragmentation
- Rising trade tensions, tariff barriers, and political risks are reshaping FDI flows.
- Emergence of near-shoring and regionalisation as firms relocate to reduce dependence on global supply chains.
Country-Specific Focus: India
- India received $28 billion in FDI inflows in 2024, retaining its rank among top global destinations.
- Key sectors: semiconductors, EV components, digital infrastructure.
- India ranked among top 5 global hubs for greenfield projects.
- Outbound FDI by Indian firms increased by 20%, showing strong outward investment intent.
Assessment of Positive and Negative Trends
Positive Trends:
- Digital FDI Boom: Reflects a global pivot towards a knowledge and tech-driven economy.
- Africa’s Rise: Significant confidence in Africa despite global slowdown.
- Resilient ASEAN & India: Benefitting from global supply chain realignment.
Negative Trends:
- Fall in SDG-Aligned Investments: Threatens progress towards global sustainability targets.
- Infrastructure Finance Crisis: Severely affects LDCs dependent on project finance.
- China’s FDI Decline: Raises concerns about the future of global investment flows amid US-China tensions.
- Geopolitical Fragmentation: Reduces investor appetite for long-term cross-border projects.
Strategic Recommendations
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Scale up investments in broadband, cloud infrastructure, and data hubs through public-private partnerships.
- Bridge SDG Investment Gap: Mobilize development banks, sovereign wealth funds, and climate finance to support SDG sectors.
- Policy Coherence: Align digital, industrial, and sustainability policies at national and international levels.
- De-risking Private Investment: Promote blended finance models to attract global capital to emerging markets.
- Enhance Innovation Governance: Improve IPR frameworks and cross-border data regulations to boost investor confidence in innovation sectors.
- Boost Regional Integration: Strengthen regional trade agreements and infrastructure connectivity to counter global fragmentation.
Revised Green India Mission (GIM)
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change released the revised roadmap for the National Mission for a Green India (GIM). The updated strategy focuses on restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing forest cover, and addressing climate impacts, especially in vulnerable landscapes like the Aravallis, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangroves.
About Green India Mission (GIM)
- Launched in: 2014
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Core Objectives:
- Increase forest/tree cover by 5 million hectares.
- Improve the quality of forest cover on another 5 million hectares.
- Restore degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Improve the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities.
Achievements So Far
- Afforestation Activities: 11.22 million hectares covered (2015–16 to 2020–21) through central and state schemes.
- Funding: ?624.71 crore released (2019–24) to 18 states; ?575.55 crore utilized.
- Target Areas: Selected based on ecological vulnerability, sequestration potential, and restoration needs.
Key Features of the Revised Roadmap
- Landscape-Specific Restoration:
- Prioritizes Aravalli ranges, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangrove ecosystems.
- Emphasizes regionally adapted best practices for ecosystem restoration.
- Integration with Aravalli Green Wall Project:
- Aims to combat desertification and sandstorm risks in northern India.
- Initial restoration planned across 8 lakh hectares in 29 districts of 4 states.
- Estimated cost: ?16,053 crore.
- Aims to develop a 5 km buffer zone covering 6.45 million hectares around the Aravallis.
- Western Ghats Focus:
- Tackling deforestation, illegal mining, and degradation.
- Measures include afforestation, groundwater recharge, and mining site restoration.
Combating Land Degradation and Climate Change
- Land Degradation (2018–19): Affected 97.85 million hectares (~1/3rd of India’s land), per ISRO data.
- India’s Climate Targets (2030):
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO? equivalent via forest/tree cover.
- Restore 26 million hectares of degraded land.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential (FSI Estimates):
- Restoration of open forests can sequester 1.89 billion tonnes of CO? over 15 million hectares.
- With intensified afforestation and aligned schemes, forest cover could reach 24.7 million hectares—achieving a carbon sink of 3.39 billion tonnes CO? equivalent by 2030.
Significance of the Revised Mission
- Aligns with India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Supports goals under UNCCD and UNFCCC.
- Helps mitigate climate change impacts by creating natural buffers and carbon sinks.
- Promotes ecological sustainability, biodiversity conservation, and community livelihood enhancement.
Predatory Pricing and Competition Law Reform

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has recently proposed the Determination of Cost of Production (DCOP) Regulations, 2025 to replace the older 2009 norms. A major reform introduced is the use of Average Total Cost (ATC) as a key metric to determine pricing in predatory pricing cases, while excluding ‘market value’ as a cost measure in such assessments.
- This development is significant in the context of India's broader competition law landscape, where concerns around market dominance and fair pricing are central to protecting consumer interest and ensuring a level playing field.
Understanding Predatory Pricing
- Predatory pricing refers to the practice of setting prices below cost to eliminate competitors from the market. Although consumers may benefit from low prices in the short term, the long-term consequence is often the emergence of monopolies, leading to higher prices and fewer choices. Due to its anti-competitive nature, this pricing strategy is banned in most jurisdictions globally.
- In India, predatory pricing is classified under ‘abuse of dominance’ as per the Competition Act, 2002, specifically under the broader category of unfair pricing or exclusionary conduct.
Legal Criteria for Establishing Predatory Pricing in India
For any allegation of predatory pricing to hold, three conditions must be satisfied:
- Dominance in the Market: The firm accused must hold a dominant position in the relevant market.
- Pricing Below Cost: The firm must have engaged in below-cost pricing, though defining “cost” has remained contentious. This raises the question—should cost mean fixed, variable, or total?
- Fixed costs are those independent of output (e.g., rent, IT systems).
- Variable costs change with production (e.g., raw materials, logistics).
- Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs.
- Intent to Eliminate Competition: There must be clear evidence that the pricing strategy was intended to exclude competitors from the market.
While dominance is usually straightforward to assess, determining what constitutes “cost” and proving anti-competitive intent remain legally complex.
Regulatory Evolution: From AVC to ATC
- Under existing regulations, the CCI had discretion to choose the cost metric on a case-by-case basis. The norm was to justify the use of any metric other than Average Variable Cost (AVC).
- A notable application was in the MCX vs. NSE case, where the Commission adopted the Long Run Average Incremental Cost (LRAIC) due to the network externalities inherent in stock exchange services, justifying inclusion of fixed costs.
- The new 2025 draft regulations now explicitly include Average Total Cost (ATC) as a valid benchmark for cost evaluation. ATC is widely accepted in industrial economics as a realistic representation of firm cost efficiency. By allowing ATC as a formal benchmark and excluding ‘market value’, the CCI aims to bring clarity and consistency in below-cost pricing investigations.
Why this Reform Matters
This proposed change holds importance for several reasons:
- It allows for a more holistic and realistic cost assessment, especially in industries where fixed costs form a significant part of the cost structure.
- It improves regulatory certainty and empowers the CCI to address anti-competitive practices in both legacy sectors (e.g., oil & gas) and emerging sectors (e.g., artificial intelligence and digital platforms).
- The reform is crucial at a time when the CCI’s budget has been declining year-on-year, limiting its enforcement capability. Simplified legal frameworks can enhance effectiveness without overburdening institutional resources.
UN Oceans Conference 2025

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
The third United Nations Oceans Conference (UNOC) was recently held in France, witnessing major developments in international marine conservation. One of the most significant outcomes was the near-finalisation of the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) agreement, also referred to as the High Seas Treaty.
As of now, 56 countries have ratified the treaty out of the required 60, bringing it close to the threshold for becoming legally binding. Notably, India and the United States have not yet ratified the agreement, although India has officially stated it is in the process of doing so.
About the BBNJ Treaty
- The BBNJ Treaty is a legally binding agreement developed under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Its aim is to regulate the use and protection of biodiversity in areas of the ocean that lie beyond national jurisdictions, also known as the high seas.
- The core objectives of the BBNJ Treaty include the creation of marine protected areas (MPAs) in international waters, regulation of marine genetic resources, enforcement of environmental impact assessments (EIAs) for activities in these regions, and capacity-building and technology transfer to support developing countries.
- The treaty is crucial because the high seas cover about 64% of the ocean’s surface and are largely unregulated.
- The BBNJ aligns with the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) target of conserving 30% of marine and coastal areas by 2030. Once the treaty secures the required number of 60 ratifications, it will enter into force after a 120-day waiting period. This will pave the way for the first Conference of Parties (COP) under the BBNJ to be held by late 2026.
Challenges to Implementation
- A major hurdle to the implementation of the BBNJ is the equitable sharing of benefits from marine genetic resources found in the high seas. These resources include unique life forms from deep-sea ecosystems that could have commercial applications in fields like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
- Since the high seas are global commons and not owned by any single nation, there is no clear consensus on how benefits should be shared.
- Environmental groups have also raised concerns that without a strong ban on resource extraction, the treaty may fall short of its conservation goals and could lead to unchecked exploitation of oceanic biodiversity.
Key Outcomes and Commitments from UNOC 2025
While the treaty itself is still awaiting full ratification, the conference saw a number of voluntary national and institutional commitments toward marine protection and sustainable ocean governance:
- The European Commission pledged €1 billion to support ocean conservation, marine science, and sustainable fisheries.
- French Polynesia committed to creating the world’s largest marine protected area, covering approximately five million square kilometres, equivalent to its entire exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
- New Zealand announced a contribution of $52 million to enhance ocean governance, science, and management in the Pacific Islands region.
- Germany launched an immediate action programme worth €100 million for the recovery and clearance of legacy munitions in the Baltic and North Seas.
- A coalition of 37 countries, led by Panama and Canada, initiated the High Ambition Coalition for a Quiet Ocean, the first global initiative to address ocean noise pollution.
- Italy committed €6.5 million to strengthen surveillance by the Coast Guard in marine protected areas and around oil platforms.
- Canada contributed $9 million to the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance, aiming to help Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and coastal countries build resilience against climate change using nature-based solutions.
- Spain pledged to establish five new marine protected areas, increasing its protected marine territory to 25%.
- A group of UN agencies introduced the One Ocean Finance initiative, which aims to mobilize investment from blue economy sectors to fund ocean sustainability.
Fattah Hypersonic Missile

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In light of intensifying hostilities between Iran and Israel, Iran has deployed its advanced Fattah hypersonic ballistic missile, marking a significant shift in regional military capabilities and raising concerns over existing air defence systems such as Israel’s Iron Dome.
About Fattah Hypersonic Missile
- Developed by: Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Iran
- Unveiled: November 2022 (on the 11th death anniversary of missile scientist Hassan Tehrani Moghaddam)
- Inducted: 2023
- Name Meaning: “Fattah” translates to “victor” or “conqueror”
Key Capabilities:
Feature Specification
Speed Mach 13–15 (approx. 15,000 km/h)
Range 1,400 km (planned upgrade to 2,000 km)
Mobility Capable of mid-air directional changes
Stealth Forms a plasma shield that blinds radar & blocks radio signals
Deployment Used in attacks against Israeli territory
- A more advanced version, Fattah-2, with a range of 1,500 km, is reportedly under development.
Strategic Significance
- The missile’s ability to evade modern air defence systems—such as Iron Dome and David’s Sling—makes it a potential game-changer.
- Iran claims Fattah is capable of operating within the upper atmosphere with unpredictable trajectory, making interception extremely difficult.
- This hypersonic manoeuvrability marks a leap over traditional ballistic missiles that follow a predictable parabolic trajectory.
Comparative Global Context
Iran claims to be the fourth country globally to possess operational hypersonic missiles, after:
- Russia
- China
- India
Other nations like the USA and North Korea are developing or testing hypersonic systems but have not fielded them in combat as Iran reportedly has.
Operational History
- October 2024: Fattah missiles were reportedly used by Iran in a prior attack on Israeli targets.
- 2025 Escalation: The missile was deployed during “Operation Honest Promise 3,” marking the 11th wave of retaliatory attacks by Iran on Israeli territory.
Iran’s Broader Ballistic Missile Arsenal
In addition to Fattah, Iran possesses a wide range of short-to-long range missiles, including:
- Fateh Series: Short-range solid-fuel missiles (Fateh-110, Fateh-313)
- Zolfaghar and Qasem: Extended versions of Fateh series
- Emad: Long-range liquid-fuel missile with 1,700 km range
- Sejjil: Solid-fuel missile with 2,500 km range, speeds up to 17,000 km/h
- Others: Kheibar, Ghadr-110, Fajr-3, Shahab-3, Ashoura, Haj Qasem, Basir
Implications for India and the Region
- Regional Arms Race: Iran’s hypersonic capability may trigger further military build-up in the Middle East.
- India’s Position: As one of the few nations with hypersonic R&D, India must monitor evolving doctrines and maintain strategic balance.
- Global Security: The usage of such missiles in conflict zones raises concerns over escalation, proliferation, and undermining of existing missile defence systems.
FASTag Annual Pass
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Union Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari announced the launch of a FASTag-based Annual Pass, offering a simplified and cost-effective tolling solution for private vehicle users on National Highways. The initiative is set to be rolled out from August 15, 2025, and aims to improve traffic flow, reduce toll disputes, and enhance ease of travel.
What is the FASTag Annual Pass?
- Cost: ?3,000
- Validity: 1 year from activation or 200 highway trips (whichever comes earlier)
- Eligibility: Only for non-commercial private vehicles (cars, jeeps, vans)
- Coverage: Valid across all National Highways in India
Key Objectives
- Hassle-free highway travel by eliminating repeated toll payments
- Reduce congestion and waiting time at toll plazas
- Simplify toll management with a one-time, prepaid model
- Address concerns regarding toll plazas located in close proximity (within 60 km)
How It Works
- Integrated with the existing FASTag system (uses RFID technology)
- Annual pass will be linked to the user's FASTag account
- Activation and renewal through:
- Rajmarg Yatra App
- NHAI website
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) website
Part of a Broader Reform in Tolling
The Annual Pass complements ongoing toll reforms:
- Introduction of ANPR-FASTag hybrid tolling system:
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) cameras
- RFID-based FASTag readers
- Enables barrier-less tolling, where vehicles are charged without stopping
- Non-compliance may result in:
- e-notices
- Penalties, including FASTag suspension or VAHAN database sanctions
Gharial Conservation

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
On World Crocodile Day (June 17, 2025), Etawah district in Uttar Pradesh marked the 50th anniversary of India’s pioneering Gharial Conservation Programme, commemorating five decades of sustained efforts to protect the endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) along the Chambal River.
About the Gharial Conservation Programme
- Launched in: 1975
- Initiated by: Forest Department of Uttar Pradesh and Society for Conservation of Nature (SCON)
- Supported by: UNDP, FAO, and Government of India
- Location: Primarily focused on Chambal River in Etawah district, Uttar Pradesh
- Breeding Facility: Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre, Lucknow
Why Gharial Conservation Matters
- Species: Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) — endemic, freshwater crocodilian
- Status: Critically Endangered (IUCN Red List)
- Habitat: Prefers deep, fast-flowing rivers with sandy banks and minimal human interference
- Threats: Habitat destruction, sand mining, illegal fishing, entanglement in nets, and declining fish stocks
Programme Objectives
- Protect wild gharial populations in natural river habitats.
- Enhance population through captive breeding and release.
- Study habitat biology and gharial behaviour to inform scientific conservation.
- Promote coexistence between gharials and local fishing communities.
- Create awareness and engage local populations in conservation.
Key Features of the Programme
- Egg Collection: Gharial eggs are safely collected from natural nests on riverbanks.
- Artificial Incubation: Maintained under controlled temperature and humidity to improve hatching success.
- Captive Rearing: Hatchlings are reared for 3–5 years at Kukrail Centre until they are strong enough for survival in the wild.
- Release Strategy: Tagged juveniles are released in protected stretches of the Chambal River.
- Community Involvement: Local fishermen and villagers are involved in conservation-linked livelihoods to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
Impact and Legacy (1975–2025)
- One of India’s earliest species-specific conservation programmes.
- Created a successful model of “rear-and-release” conservation.
- Helped stabilize the gharial population in Chambal, now one of the last strongholds for the species.
- Promoted community-based conservation and scientific habitat management.
Global Drought Outlook 2025
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has released the “Global Drought Outlook 2025”, presenting a stark warning about the increasing frequency, severity, and impact of droughts worldwide.
- The report, titled “Global Drought Outlook: Trends, Impacts and Policies to Adapt to a Drier World”, offers a comprehensive assessment of drought patterns, consequences, and adaptation strategies, making it crucial for policymakers and global environmental governance.
Understanding Drought:
Drought is defined as a hydrological imbalance, characterised by prolonged periods of “drier-than-normal” conditions that deplete soil moisture, surface water, and groundwater. The report identifies three main types:
- Meteorological Drought: Caused by significantly below-average rainfall over an extended period.
- Agricultural Drought: Occurs when soil moisture becomes insufficient for crops and vegetation.
- Hydrological Drought: Involves declining water levels in rivers, lakes, and aquifers, affecting supply for human and ecological needs.
Global Trends and Projections
- Drought-Affected Land: The share of global land experiencing drought has doubled since 1900, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use.
- Current Impact (2023): Nearly 48% of the world’s land experienced at least one month of extreme drought.
- Regional Hotspots: Western USA, South America, Europe, Africa, and Australia are increasingly vulnerable.
- Groundwater Stress: Around 62% of monitored aquifers show declining trends.
- Future Risk: At +4°C global warming, droughts could become 7 times more frequent and severe by 2100, posing systemic global threats to food, water, and economic security.
Multidimensional Impacts of Drought
Ecological:
- 37% of global soils have dried significantly since 1980.
- River and groundwater depletion are threatening biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Economic:
- Drought-related losses are increasing by 3–7.5% annually.
- Modern droughts are twice as costly as in 2000; costs may rise 35% by 2035.
- Agriculture is most affected: crop yields drop up to 22% in drought years.
- Drought causes a 40% drop in river-based trade and a 25% decline in hydropower output.
Social:
- Droughts account for 34% of disaster-related deaths, though only 6% of disasters are droughts.
- It is a major driver of food insecurity, internal displacement, and climate migration, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Political instability and conflict often correlate with drought-induced resource scarcity.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
The OECD emphasizes a multi-sectoral approach to manage drought risks:
- Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM):
- Balancing water use and renewal.
- Promoting efficient and equitable water allocation.
- Nature-based Solutions (NbS):
- Urban de-sealing to enhance groundwater recharge.
- Landscape restoration to improve water retention and ecosystem resilience.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- Adoption of drought-resistant crops and micro-irrigation systems.
- Can reduce water use by up to 76%.
- Urban Planning: Permeable infrastructure restores aquifers (e.g., US examples show 780 million m³/year recovery).
- Early Warning Systems: Enhanced drought monitoring, forecasting, and risk mapping.
- Policy Integration: Embedding climate resilience into national water and land-use policies.
- Cross-Sector Coordination: Engaging sectors like agriculture, energy, transport, construction, and health.
- Economic Benefits: Every $1 invested in drought resilience yields $2–$10 in benefits.
Rinderpest

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
- India has been officially designated as a Category A Rinderpest Holding Facility (RHF) by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- The recognition was conferred to the ICAR-National Institute of High Security Animal Diseases (NIHSAD) in Bhopal during the 92nd General Session of WOAH held in Paris.
- This makes India one of only six countries globally entrusted with this vital responsibility, marking a major milestone in India’s global leadership in animal health and biosecurity.
What is Rinderpest?
- Also Known As: Cattle Plague
- Pathogen: Caused by a virus from the Paramyxoviridae family, genus Morbillivirus.
- Affected Species: Mainly cattle and buffalo, but also zebus, giraffes, eland, wildebeest, warthogs, and some antelope species.
- Symptoms in Cattle:
- High fever, nasal and eye discharge
- Erosive mouth lesions
- Severe diarrhoea and dehydration
- Death typically within 10–15 days in susceptible herds
- Transmission: Through direct contact; virus present in nasal secretions even before clinical symptoms appear.
- Public Health Risk: None – the virus does not affect humans.
- Geographical Spread: Historically affected Europe, Africa, and Asia.
- Eradication: Officially declared eradicated in 2011, making it the second disease in history to be eradicated after smallpox.
Significance of the Category A RHF Designation
- Background:
- Despite eradication, Rinderpest Virus-Containing Material (RVCM) remains in select laboratories.
- FAO and WOAH limit storage of RVCM to ensure global biosecurity and prevent accidental or intentional release.
- India’s Preparedness:
- In 2012, ICAR-NIHSAD was designated as India’s national repository for RVCM.
- It is a Biosafety Level-3 (BSL-3) facility and a WOAH reference laboratory for avian influenza.
- Recent Developments:
- India submitted its RHF application in 2019.
- In March 2025, FAO-WOAH appointed international experts to inspect the facility.
- Based on strong biosafety, inventory control, and emergency preparedness, ICAR-NIHSAD has now received Category A RHF status for one year.
Implications for India
- Global Recognition: Reinforces India’s commitment to the One Health framework and global biosecurity norms.
- Leadership Role: Positions India among a select global group of only six RHFs, enabling it to contribute to future efforts in disease surveillance, vaccine research, and emergency preparedness.
- Future Prospects:
- Encouraged by WOAH-FAO to contribute to vaccine seed material discussions.
- Paves the way for Category B designation, which allows broader collaborative work on RVCM.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, NASA said the NASA-ISRO SAR mission had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota
What is Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)?
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an advanced remote sensing technology used to generate high-resolution images of Earth's surface, irrespective of weather or lighting conditions.
- Unlike optical sensors that rely on visible light, SAR systems emit microwave pulses and measure the reflected signals (echoes) from the ground, ocean, ice, or structures.
- These echoes are then processed to create detailed images using advanced signal processing techniques.
How SAR Works
- Antenna System: Traditionally, larger antennas yield better resolution, but they are impractical for satellites. SAR overcomes this by using a small antenna mounted on a moving platform (like a satellite), capturing echoes from different positions.
- Through precise timing and phase information, the system simulates a much larger "synthetic" antenna, enhancing image resolution without the need for large hardware.
Advantages of SAR
- All-Weather, All-Time Imaging: SAR can operate day and night and penetrate clouds, smoke, and light rain, ensuring uninterrupted data collection.
- Material Differentiation: Various materials (soil, water, vegetation, buildings) reflect microwaves differently, enabling SAR to detect subtle changes not visible through optical imagery.
- Large Area Mapping: Mounted on satellites, SAR can map swaths of land hundreds of kilometres wide in a single pass.
NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) Mission
- Joint Collaboration: A flagship Earth-observing mission between NASA and ISRO.
- On June 12, 2025, NASA confirmed that the NISAR satellite had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota for its scheduled launch.
Mission Objectives
- NISAR will map nearly all of Earth's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.
- It aims to provide unprecedented data on Earth’s environment, including:
- Ecosystem disturbances
- Land use changes
- Ice sheet dynamics
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, landslides, floods)
Significance
- Will support climate change monitoring, disaster response, and agricultural planning.
- It represents a major step in India’s and the U.S.'s scientific diplomacy and technological cooperation.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The first General Assembly of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was held in New Delhi, marking a significant moment in global biodiversity governance. Chaired by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav, who was unanimously elected President of the IBCA, the event underscored India’s leadership in international wildlife conservation diplomacy.
What is IBCA?
- The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) is a multinational initiative launched by India in March 2024 to conserve the world’s seven major big cat species—Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma—through collective action, knowledge exchange, and capacity building.
- It is coordinated by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The Alliance was conceptualized following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger in April 2023.
Objectives of IBCA
- Promote global collaboration for the protection and conservation of big cats.
- Replicate successful conservation practices across member nations.
- Create a common pool of financial, technical, and institutional resources.
- Address gaps in capacity building, financing, and data sharing.
- Link conservation efforts with livelihood enhancement and climate resilience in big cat habitats.
- Strengthen efforts against poaching and illegal wildlife trade through joint surveillance and data exchange.
Membership
- 95 Range Countries (where the species naturally occur) are eligible to join.
- By September 2024, 25 countries including Bangladesh, Nigeria, Peru, and Ecuador had joined.
- Membership is open to all UN member states through a Note Verbale.
- The IBCA attained legal status after five countries—Nicaragua, Eswatini, India, Somalia, and Liberia—signed the Framework Agreement.
Key Functions of IBCA
- Shared Repository: Compilation of proven conservation strategies for scalable, science-based solutions.
- Training and Capacity Building: Organizes technical workshops and institutional exchanges.
- Scientific and Policy Support: Funds research, drives policy reforms, and raises awareness.
- Technological Innovation: Introduces advanced tools to tackle habitat degradation and prey base decline.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Integrates conservation with community-based development models.
- Anti-Poaching Collaboration: Facilitates real-time data sharing and joint actions against wildlife trafficking.
Highlights from the 2025 General Assembly
- Venue: New Delhi, India
- Participating Nations: Ministerial delegations from nine countries including Bhutan, Cambodia, Kazakhstan, Liberia, Suriname, Somalia, Republic of Guinea, Eswatini, and India.
- Institutional Milestones:
- India ratified as the permanent headquarters of IBCA.
- The Headquarters Agreement was formally ratified, enabling the establishment of IBCA offices in India.
- Leadership: Bhupender Yadav, India’s Environment Minister, was elected as the first President of IBCA.
- Funding Commitment: India pledged ?150 crore (2023–28) to support IBCA’s establishment, coordination, and conservation activities.
Significance for India and the Global South
- Reinforces India’s role as a conservation leader and soft power in environmental diplomacy.
- Positions India as the epicentre for global big cat conservation, akin to its leadership in tiger conservation under Project Tiger.
- Encourages South-South cooperation in biodiversity preservation.
- Aligns with global commitments like CBD, CITES, and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025 began in Bonn, Germany, with over 5,000 delegates from governments, international organisations, civil society, and scientific bodies. It serves as a crucial platform for setting the technical and political groundwork ahead of COP29.
What is the Bonn Climate Conference?
- A mid-year climate summit held annually under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Also referred to as the Sessions of the UNFCCC Subsidiary Bodies (SBs).
- First held in 1995, after the UNFCCC was signed in 1992.
- Hosted in: Bonn, Germany (home of the UNFCCC headquarters).
- Organised by: The UNFCCC Secretariat.
Main Objectives
- Prepare for COP Summits: Provides a platform for technical discussions that shape the COP agenda (COP29 in this case).
- Review of Commitments: Tracks implementation of earlier climate agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Science–Policy Integration: Connects IPCC research with policymaking processes.
- Support for Developing Nations: Discusses climate finance and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Inclusive Participation: Engages Indigenous communities, NGOs, experts, and private stakeholders.
Subsidiary Bodies of the UNFCCC
- SBI (Subsidiary Body for Implementation):
- Reviews how climate commitments are implemented.
- Facilitates support for developing countries.
- SBSTA (Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice):
- Provides scientific guidance.
- Bridges IPCC reports with UNFCCC decision-making.
Key Focus in 2025
Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA)
- Originally mentioned in the Paris Agreement (2015).
- Received major progress only during COP28 (Dubai).
- Aim: Establish a global, measurable, and equitable adaptation framework, similar to the 1.5°C target for mitigation.
- Bonn 2025 focuses on operationalising this goal, especially for climate-vulnerable nations.
Importance of the Bonn Conference
- Pre-COP Platform: Decisions taken here set the tone and agenda for COP summits.
- Technical + Political Dialogue: Encourages cooperation between scientists, policymakers, and climate negotiators.
- Influences Global Climate Action: Outcomes impact the direction of global climate governance.
Cyber Suraksha Exercise
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
A comprehensive national-level cyber security exercise, Cyber Suraksha, was launched by the Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS).
About Cyber Suraksha
- Type: Multi-phased cybersecurity drill.
- Organised by: Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the aegis of HQ IDS.
- Duration: From 17–27 June 2025.
- Participants: Over 100 experts from national agencies and defence domains.
- Environment: High-paced, gamified simulation of real-world cyber threats.
Objectives
- Enhance national cyber resilience.
- Train personnel in handling advanced cyberattacks.
- Promote a security-first culture across defence institutions.
- Integrate technical proficiency with strategic leadership.
Key Features
- Training capsules: Technical + leadership components.
- CISOs Conclave: Sessions by cybersecurity leaders, culminating in a table-top simulation.
- Hands-on exercises: Real-time attack simulations to test response capabilities.
- Focus on joint operations and decision-making under crisis.
About Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA)
Background
- Established: Announced in 2018, operational from November 2019.
- Origin: Recommended by Naresh Chandra Committee (2012).
- Part of India’s tri-service defence transformation, alongside proposed Aerospace and Special Operations Commands.
Role & Mandate
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- Reports to: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) through Integrated Defence Staff (IDS).
- Location: Based in New Delhi.
Functions
- Conducts cyber defence operations for the armed forces.
- Coordinates incident response, cyber intelligence, and audits.
- Develops capabilities in cyber warfare, AI-driven cyber tools, and joint operations.
- Supports capacity building, certification, and training within the military.
AI and Biomanufacturing in India

- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into India's biomanufacturing sector is gaining momentum with the launch of the BioE3 Policy and the IndiaAI Mission.
What is Biomanufacturing?
- Biomanufacturing involves the use of living cells, enzymes, or biological systems to produce commercial goods such as vaccines, biologics, biofuels, specialty chemicals, biodegradable plastics, and advanced materials.
- The convergence of synthetic biology, industrial biotechnology, and artificial intelligence (AI) has expanded its scope across sectors like healthcare, agriculture, energy, and materials science.
- India, often called the “Pharmacy of the World”, produces over 60% of global vaccines, underlining its industrial strength in biomanufacturing.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Biomanufacturing
AI is revolutionizing biomanufacturing by making it predictive, efficient, and scalable:
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning tools adjust variables like temperature, pH, and nutrient supply in real time to enhance fermentation and reduce batch failure.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of biomanufacturing plants allow engineers to simulate operations, test changes, and foresee potential disruptions without real-world risks.
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AI expedites molecular modeling and screening of drug candidates, reducing time and cost of development.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI forecasts machinery failures, improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
- Smart Supply Chains: AI-driven logistics optimize cold-chain storage and forecast medicine demand, ensuring timely distribution.
Indian Examples and Industrial Applications
- Biocon uses AI to enhance drug screening and fermentation quality.
- Strand Life Sciences applies machine learning in genomics for faster diagnostics.
- Wipro and TCS are developing AI platforms for clinical trials, molecule screening, and treatment prediction.
- AI is also being explored in rural healthcare, using region-specific data for localized diagnostics and advisories.
Key Government Initiatives
- BioE3 Policy (2024):
- Envisions Bio-AI hubs, biofoundries, and next-gen biomanufacturing infrastructure.
- Supports startups with funding and incentives.
- IndiaAI Mission:
- Promotes ethical, explainable AI in sectors like health and biotech.
- Supports bias reduction, machine unlearning, and transparency in AI models.
- Biomanufacturing Mission (2023): Aims to promote R&D and domestic production in bio-based sectors.
- PLI Scheme for Biotech: Incentivizes local production of enzymes, fermentation inputs, and biologics.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023): Lays down principles for lawful data processing, though not tailored for AI-biotech intersection yet.
Challenges in Policy and Regulation
Regulatory Gaps:
- India’s existing drug and biotech laws were designed before the AI era.
- No clear mechanism exists to audit, certify, or govern AI-operated bioreactors or predictive drug systems.
Data and Model Risks:
- AI systems trained on urban datasets may fail in rural or semi-urban manufacturing due to variable water quality, temperature, or power conditions.
- Lack of norms on dataset diversity and model validation raises risk of system failure and reputational damage.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Traditional IP laws do not clarify ownership of AI-generated inventions, molecules, or production protocols.
Workforce and Infrastructure:
- Biomanufacturing needs a workforce skilled in both computational biology and automation.
- India’s AI-bio talent gap and limited high-tech infrastructure outside metro cities hinders inclusive growth.
Ethical & Safety Concerns:
- Without context-specific oversight, AI errors can threaten public safety and product integrity.
- Trust in AI systems requires clear guidelines on explainability, accountability, and redress mechanisms.
Global Best Practices
- EU’s AI Act (2024): Classifies AI applications based on risk levels. High-risk applications (e.g., genetic editing) are subject to strict audits.
- US FDA Guidance (2025):
- Introduces seven-step credibility frameworks for AI in healthcare.
- Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) allow iterative AI updates while ensuring safety.
India lacks similar risk-based, adaptive oversight.
Policy Recommendations
- Establish AI-Biomanufacturing Regulatory Framework:
- Introduce tiered regulation based on context and risk.
- Define use-cases, audit mechanisms, and model validation standards.
- Mandate Dataset Diversity & Safety Audits:
- Ensure AI tools are trained on representative, unbiased, clean data.
- Create regulatory sandboxes to test AI systems in controlled environments.
- Strengthen Public–Private Partnerships:
- Boost industry-academia collaborations.
- Incentivize private investment through R&D credits and de-risking instruments.
- Modernize IP and Licensing Laws:
- Establish clarity on ownership of AI-generated discoveries.
- Develop licensing frameworks for bio-AI algorithms and training data.
- Upskill the Workforce: Promote interdisciplinary training across life sciences, data science, and industrial robotics.
AviList
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the global ornithological and conservation community witnessed a landmark development with the launch of AviList, the first-ever unified global checklist of bird species. This effort is the culmination of four years of work by the Working Group on Avian Checklists, representing leading ornithological and conservation institutions.
About AviList:
- What is it? AviList is a comprehensive, standardized, and freely accessible global bird species checklist.
- Total Entries (2025 Edition):
- Species: 11,131
- Subspecies: 19,879
- Genera: 2,376
- Families: 252
- Orders: 46
- Replacing Previous Lists:
- International Ornithological Committee (IOC) List
- Clements Checklist
- Update Mechanism: To be updated annually
- Access and Formats:
- Available freely at www.avilist.org
- Downloadable in full or short versions in .xlsx and .csv formats.
Developed By:
Working Group on Avian Checklists, comprising representatives from:
- BirdLife International
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- American Ornithologists' Society
- International Ornithologists’ Union
- Avibase (Global Bird Database)
Significance and Benefits:
- Conservation and Research Clarity:
- A unified taxonomy helps prioritize conservation efforts by eliminating taxonomic inconsistencies.
- Scientists can now communicate uniformly on species classification and distribution.
- Global Standardization: Replaces multiple competing checklists, reducing confusion and ensuring consistency across countries and platforms.
- Interdisciplinary Use: Supports birdwatchers, scientists, policymakers, and conservationists in sharing data, linking platforms, and enhancing global collaborations.
- Improved Policy and Decision-Making: Aids in aligning biodiversity policies across nations by ensuring a standardized species concept.
- Technological Integration: Enables harmonization of databases and online tools like eBird, Avibase, and global biodiversity monitoring platforms.
DNA Identification in Mass Fatality Events
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Following the tragic crash of an Air India Boeing 787 Dreamliner from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick (June 2025), authorities have initiated DNA-based identification to match the remains of victims. In mass fatality incidents where bodies are mutilated or decomposed, DNA analysis becomes the gold standard for establishing identity.
What is DNA Identification?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a unique genetic code present in almost every cell of the human body, with the exception of identical twins. It is widely used in forensic science for accurate identification, particularly in disasters where visual identification is impossible.
Sample Collection and Preservation:
- DNA begins degrading post-mortem, and the rate of degradation is influenced by:
- Type of tissue (soft vs hard)
- Environmental conditions (humidity, temperature)
- Hard tissues such as bones and teeth are preferred due to better preservation against decomposition.
- Soft tissues (like skin and muscle) degrade faster and, if used, must be stored in 95% ethanol or frozen at -20°C.
- In large-scale accidents, sample collection from wreckage can take weeks or even months (e.g., 9/11 took 10 months).
Reference Samples:
To match unidentified remains, reference DNA is taken from biological relatives—preferably parents or children of the victims, who share about 50% of their DNA.
Methods of DNA Analysis:
1. Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis:
- Evaluates short, repeating DNA sequences that vary among individuals.
- Requires nuclear DNA, hence not suitable if the DNA is highly degraded.
- Analysis of 15+ hyper-variable STR regions can confirm family relationships with high accuracy.
2. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Analysis:
- Used when nuclear DNA is not recoverable.
- mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother and is present in multiple copies per cell.
- Effective for matching with maternal relatives (e.g., mother, maternal uncles/aunts, siblings).
3. Y-Chromosome Analysis:
- Targets male-specific genetic material.
- Useful for identifying remains using DNA from paternal male relatives (father, brothers, paternal uncles).
- Helpful when direct relatives are unavailable but male-line relatives exist.
4. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Analysis:
- Suitable when DNA is highly degraded.
- Analyzes variations at single base-pair locations in DNA.
- Can also match DNA with personal items like a toothbrush or hairbrush.
- However, less accurate than STR analysis.
Significance for Disaster Management and Forensics:
- DNA-based victim identification ensures scientific accuracy, aiding in closure for families, and upholding legal and humanitarian obligations.
- Modern forensic genetics has become an essential tool in mass disaster response protocols worldwide.
Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc)
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant medical advancement, a team at the Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. has successfully administered Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc) to treat adenoid cystic carcinoma—a cancer originating in the parotid gland. This marked the first-ever clinical application of this technology. The findings were published in the International Journal of Particle Therapy in June 2025.
What is SPArc Therapy?
SPArc (Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy) is an advanced form of proton beam therapy where proton particles are delivered in a controlled arc across the tumor. It includes two primary modalities:
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc: Follows a pre-programmed dose delivery path.
- Dynamic SPArc: Simulated version where energy levels and targeting points are adjusted in real-time. (Still under regulatory review)
Comparison with Existing Techniques
The study compared three techniques:
- SFO-IMPT (Single-Field Optimized Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy – current standard)
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc (clinical)
- Dynamic SPArc (simulated)
SPArc showed reduced radiation exposure to key organs when compared with SFO-IMPT:
- Brainstem: ↓ 10%
- Optical chiasm: ↓ 56%
- Oral cavity: ↓ 72%
- Spinal canal: ↓ 90%
Treatment Case Study
The first patient treated was a 46-year-old woman with a tumor extending from her parotid gland to the base of her skull. She underwent 33 sessions of SPArc therapy from June to August 2024, reporting only minor skin irritation and no disruptions to eating or daily functioning.
Process & Technology Used:
- Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) was used for real-time imaging before each session.
- A machine learning model converted CBCT to synthetic CT, allowing accurate dose tracking.
- As the patient lost weight, the dose plan was adjusted after two weeks to maintain precision.
- Nine beam angles spanning a 180º arc were used, delivering radiation at 20º intervals.
Each session lasted about 15–18 minutes, enabling nearly continuous dose delivery.
Working Mechanism
- The therapy operates by 'painting' the tumor in energy layers.
- Each energy level targets a specific tissue depth, ensuring maximum precision.
- The system scans dozens of spots in each layer before moving to the next one with increased penetration.
Advantages
- High precision in delivering radiation to deep and complex anatomical regions like the skull base.
- Limits collateral damage to vital organs.
- Effective in large or invasive tumours.
- Better quality of life during treatment (reduced side effects such as fatigue or swallowing issues).
Limitations & Concerns
- Geographical miss risk: Tiny tumors may be missed due to breathing motion or tumor shrinkage over time.
- Cost: High installation and operational costs, making it suitable for a limited patient base.
- Potential for overuse in non-indicated cases, leading to inequitable healthcare delivery.
- Dynamic SPArc still awaits regulatory clearance and integration into oncology systems.
Significance for India
SPArc therapy can be transformative for cancers in anatomically intricate regions and may serve as a benchmark for future precision cancer therapies. However, adoption in India requires cost-reduction, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks.
Spartaeus karigiri
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
A team of researchers has identified a new species of jumping spiders of the Spartaeinae subfamily in southern India, known for their intelligent hunting skills and web-invasion tactics.
Source: European Journal of Taxonomy (June 2025)
Key Facts:
- Species Name: Spartaeus karigiri
- Taxonomy:
- Family: Salticidae (Jumping Spiders)
- Subfamily: Spartaeinae
- Genus: Spartaeus
- Named After: Karigiri (Elephant Hill) in Devarayanadurga, Karnataka.
Significance:
- First recorded presence of Spartaeus and Sonoita genera in India.
- These genera were previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Discovery expands India’s Spartaeinae spider fauna to 15 species across 10 genera.
Features of Spartaeus karigiri:
- Noted for intelligent hunting and web-invasion tactics.
- Possesses keen eyesight and mimics prey to deceive other spiders.
- Males were found in rocky crevices; females guarding egg clutches.
- Found in Karnataka and Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
Other Findings:
- Sonoita cf. lightfooti, previously known from Africa, was also found in Karnataka.
- A taxonomic correction: Marpissa gangasagarensis (2005) is the same as Phaeacius fimbriatus (1900).
Conservation and Research Insight:
- India's arachnid diversity remains under-studied.
- New discoveries indicate rich but undocumented biodiversity in Indian terrains.
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
Kruti and BharatGPT Mini
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
India is witnessing a significant leap in artificial intelligence innovation with the launch of two indigenous AI models — Kruti by Krutrim and BharatGPT Mini by CoRover. These developments aim to democratize AI access across the country by addressing local needs, multilingual capabilities, and infrastructure limitations.
Kruti: India’s First Agentic AI Assistant
Developed by Krutrim, the AI startup co-founded by Bhavish Aggarwal (of Ola fame), Kruti is positioned as India’s first agentic AI, going beyond conventional chatbots. Launched in 2025, Kruti integrates task execution capabilities such as:
- Cab booking
- Food ordering
- Bill payments
- Image generation
- Research assistance
Kruti is powered by Krutrim V2, a locally trained large language model (LLM), and combines open-source AI systems to deliver scalable, cost-effective, and contextualised solutions.
Key Features of Kruti
- Multilingual Support: Understands voice and text in 13 Indian languages
- Personalised AI: Learns user preferences, adapts tone and content
- Human-Centric Design: Supports read-aloud responses, summarised answers, stories, and tables
- SDK for Developers: Offers embeddable tools for LLM orchestration and task automation
- Integrated Assistant: Eliminates app-switching fatigue through contextual task handling
Aggarwal highlighted that Kruti is built for “how Indians live”—mobile-first, intuitive, and multilingual—offering free access to advanced AI tools.
Strategic Investment and Open AI Ecosystem
Krutrim has committed ?12,000 crore in investment (?2,000 crore already, ?10,000 crore by next year), launched Krutrim AI Lab, and published technical resources, with contributions to the open-source community. The company is positioning itself as a competitive force against global giants like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic, and local firms like Sarvam AI.
BharatGPT Mini: Small Language Model for Bharat
On the same day, CoRover, a conversational AI firm, unveiled BharatGPT Mini, a small language model (SLM) with 534 million parameters trained on its proprietary conversational dataset.
- Supports 14 Indian languages
- Designed for low-compute, low-infrastructure environments
- Enables offline and edge deployments for fast, privacy-centric performance
- Ideal for underserved and rural regions with limited internet or device capacity
SLMs like BharatGPT Mini are emerging as viable tools for domain-specific, lightweight, and privacy-respecting AI in India, complementing the role of LLMs in more complex tasks.
Ocean Darkening
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
A recent study titled "Darkening of the Global Ocean", led by researchers from the University of Plymouth, has revealed that over 21% of the global ocean has darkened between 2003 and 2022, marking a significant environmental concern. The phenomenon, known as ocean darkening, is increasingly disrupting marine ecosystems and global climate regulation.
What is Ocean Darkening?
Ocean darkening refers to the reduction in the photic zone — the upper layer of the ocean (up to ~200 meters deep) where sunlight penetrates to support photosynthesis. This zone is foundational to:
- ~90% of marine biodiversity
- Climate regulation
- Ocean productivity
- Global fisheries
The study used satellite data and modeling based on the Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient (Kd 490), which measures how rapidly light fades through seawater. It found:
- 21% of global oceans experienced darkening in two decades.
- 9% saw photic depth decline by over 50 meters.
- 2.6% saw a reduction exceeding 100 meters — an area roughly equal to the size of Africa.
Geographic Distribution
- High darkening: Arctic, Antarctic, Gulf Stream, North Sea, eastern UK coast.
- Lesser darkening or even brightening: Some parts of the English Channel.
- The open ocean and climate-sensitive zones have witnessed the most pronounced declines.
Causes of Ocean Darkening
- Coastal Zones:
- Runoff of agricultural nutrients, organic matter, and sediments.
- Leads to algal blooms that block sunlight.
- Open Ocean:
- Shifts in plankton dynamics
- Rising sea surface temperatures
- Altered ocean circulation patterns
These changes may be linked to climate change, land-use modifications, and increased rainfall-driven erosion.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
Ocean darkening leads to:
- Shrinking habitats for light-sensitive species like Calanus copepods (key zooplankton and food web base).
- Disrupted feeding, migration, and reproduction cycles due to reduced solar and lunar light cues.
- Increased crowding in shallower waters, intensifying competition and predation.
- Collapse of marine food chains, even in areas with minimal fishing pressure.
Experts warn that this could represent one of the largest habitat losses in recent history, with implications for:
- Biodiversity
- Carbon cycling
- Oxygen production
- Ocean buffering against climate change
Black Boxes in Aviation
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
The tragic crash of an Air India Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick on June 12, 2025, has spotlighted the critical role of black boxes—a key component in aviation safety and accident investigations. Despite their name, these devices are painted bright orange for easy visibility at crash sites.
What are Black Boxes?
Modern aircraft are equipped with two essential flight recorders:
- Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR): Captures pilot and co-pilot conversations, ambient cockpit sounds, alarms, and radio transmissions.
- Flight Data Recorder (FDR): Records up to 25 hours of technical flight data including altitude, speed, engine parameters, flight path, and over 3,500 variables.
These devices operate continuously without interruption, storing vital information that can reconstruct the events leading up to an air crash.
Design and Durability
Black boxes are built to withstand extreme conditions:
- Casing: Made from crash-resistant materials like titanium or steel.
- Survivability: Can endure temperatures up to 1,100°C, high-impact G-forces, and remain underwater for up to 30 days.
- Locator Beacon: Emit signals to help recovery teams locate them, especially in underwater crashes.
Why Are They Called 'Black' Boxes?
The term “black box” originated from early film-based recorders stored in light-tight boxes. However, modern units are painted bright orange with reflective strips to aid visual detection after accidents.
Evolution of Flight Recorders
- 1930s: François Hussenot in France developed early photographic film-based recorders.
- 1953-54: Dr. David Warren in Australia invented the modern FDR while investigating unexplained crashes of the de Havilland Comet.
- 1960: Mandatory installation of CVRs and FDRs in commercial aircraft.
- 1965: Regulators required recorders to be painted in visible colours.
- 1990: Solid-state memory replaced magnetic tapes, increasing durability and storage capacity.
India's Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB), under the Ministry of Civil Aviation, oversees accident probes. In April 2025, it established a dedicated flight recorder laboratory in New Delhi to improve investigation efficiency.
Technological Advancements
- Combined Recorders: Modern systems often integrate CVR and FDR in a single unit to meet ICAO norms for extended recording.
- Deployable Recorders: Automatically ejected during a crash, float on water, and transmit their location using an Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT).
- Satellite-Based Data Streaming: Future technologies aim to stream flight data in real time, minimizing data loss during oceanic crashes.
Black boxes serve as the backbone of aviation accident investigations by providing critical insight into aircraft performance and crew actions before a crash. Their development reflects ongoing efforts to enhance air travel safety and accountability. The Ahmedabad crash investigation led by the AAIB will heavily rely on these devices to determine the exact sequence of events and prevent future tragedies.
RBI Infuses Rs.23,856 Crore into Banking System via Government Securities Buyback
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to bolster liquidity in the financial system, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has infused ?23,856 crore into the banking system through a buyback of government securities (G-Secs) on June 5, 2025. This marks the second such bond buyback by the central bank in the current financial year (FY 2025–26).
What is a Bond Buyback?
A bond buyback refers to the RBI repurchasing existing government securities before their maturity. Conducted on behalf of the central government, such operations aim to inject durable liquidity into the banking system, improve the liquidity position of banks, and influence interest rates. It is part of the RBI's broader Open Market Operations (OMOs) toolkit.
Broader Liquidity Context
The RBI’s intervention is part of a broader liquidity management strategy, aimed at ensuring stable and surplus liquidity conditions. The central bank has employed various tools in recent months:
- Open Market Operations (OMOs)
- USD/INR Buy/Sell swap auctions
- Variable Rate Repo (VRR) auctions
These tools were especially crucial after the banking system faced a liquidity deficit in late 2024. Since then, the RBI’s operations have restored liquidity, with the system now in surplus mode—estimated at around ?3 lakh crore.
Significance
- Monetary Stability: Enhances the transmission of monetary policy by ensuring banks have sufficient funds to lend.
- Market Functioning: Eases pressure in the bond markets, improves demand for new issuances, and helps manage interest rates.
- Fiscal Management: Supports the government's borrowing program by managing the maturity profile of debt and yields.
India’s First INTERPOL Silver Notice

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant development, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has secured India’s first-ever ‘Silver Notice’ from INTERPOL to track the global assets of Shubham Shokeen, a former French Embassy official implicated in a visa fraud case. This move underscores India's enhanced use of international law enforcement mechanisms to combat transnational crimes, particularly financial crimes involving asset concealment abroad.
What is a Silver Notice?
While INTERPOL is globally known for its Red Notice (to arrest or detain fugitives), the Silver Notice is a newer tool designed to help locate, identify, monitor, or seize the criminal assets of individuals or entities under investigation. Issued at the request of India’s National Central Bureau (NCB), the Silver Notice for Shokeen seeks to trace proceeds of crime potentially parked across multiple countries, marking a new phase in India’s international criminal cooperation.
About INTERPOL
INTERPOL (International Criminal Police Organization) is the world’s largest international police organization, comprising 196 member countries, with India being one of the founding members. It facilitates cross-border police cooperation and crime control across jurisdictions. Its genesis lies in the 2nd International Police Congress held in Vienna in 1923, when it was established as the International Criminal Police Commission (ICPC). It adopted the name INTERPOL in 1956 with the adoption of its Constitution during the 25th General Assembly.
- Headquarters: Lyon, France
- National Central Bureau (NCB): Each member state has an NCB that coordinates with INTERPOL. CBI serves as India’s NCB.
- Key Bodies:
- General Assembly: Supreme decision-making body; meets annually.
- Executive Committee: Supervises execution of General Assembly's decisions.
- General Secretariat: Handles operational activities on a daily basis.
INTERPOL Colour-Coded Notices
INTERPOL issues a series of colour-coded notices that serve as international alerts or cooperation requests:
- Red Notice: Request to locate and provisionally arrest a wanted person.
- Blue Notice: To collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities.
- Yellow Notice: For locating missing persons.
- Black Notice: To identify unidentified bodies.
- Silver Notice: To trace, monitor, and seize assets related to criminal proceeds.
These notices are issued by INTERPOL’s General Secretariat upon request from NCBs and are accessible to all member countries, enabling swift global action.
India’s Technological Integration: The BHARATPOL Portal
To streamline international cooperation, the CBI has developed the BHARATPOL portal, a digital interface that connects all Indian law enforcement agencies with INTERPOL. It allows seamless communication and data exchange for tracking fugitives, assets, and criminal networks, thereby enhancing India’s capabilities in combating cross-border financial and cyber crimes.
Significance for India
- Asset Recovery: The Silver Notice is a critical step in tracing and recovering illicit assets abroad, aligning with India’s broader efforts under anti-money laundering frameworks.
- Global Cooperation: Reflects India’s increasing reliance on international institutions for law enforcement, including the UN Convention against Corruption and FATF recommendations.
- Strengthening CBI's International Role: As India’s NCB, the CBI’s proactive role showcases its growing competence in global criminal investigations.
State of World Marine Fishery Resources 2025

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) 2025 Report on the State of World Marine Fishery Resources, released during the UN Ocean Conference (UNOC3) in Nice, France, offers a comprehensive assessment of global fish stock sustainability, regional disparities, and governance challenges.
Key Findings:
- Global Sustainability: 64.5% of marine fishery stocks are fished within biologically sustainable levels, indicating modest improvement. However, 35.5% remain overexploited.
- Deep-Sea Species Vulnerability: Only 29% of deep-sea species are sustainably harvested, largely due to biological traits like slow growth, delayed maturity, and low reproductive rates. These characteristics impair recovery from overfishing.
- Migratory Shark Concerns: Of the 23 shark stocks assessed, 43.5% are overfished, especially in the tropical Indo-Pacific where they frequently become bycatch in tuna fisheries.
- Tuna Success Story: 87% of evaluated tuna and tuna-like species are sustainably fished, a result of effective regulation by Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs).
- Regional Disparities: The northeast and southwest Pacific show high sustainability levels, while areas such as the Mediterranean and Black Sea lag, with only 35.1% of stocks sustainably managed.
- Data Gaps: Despite high reported sustainability (72.7%) in the eastern Indian Ocean, concerns remain due to insufficient species-specific stock assessments.
Governance and Policy Challenges:
- Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Continues to threaten stock sustainability. IUU encompasses:
- Illegal: Breaches of domestic or international laws.
- Unreported: Failure to report or misreport catches.
- Unregulated: Conducted by vessels operating beyond jurisdictional authority, undermining conservation efforts.
- Subsidy Prohibitions (WTO Agreement):
- Bans financial support to vessels engaging in IUU fishing.
- Restricts subsidies for overfished stocks unless recovery measures are implemented.
- Prohibits aid for fishing in unregulated high seas zones.
Critical Analysis:
Positives:
- The rise in sustainable stocks signifies improved management awareness, particularly in regulated regions like the Pacific.
- Tuna fisheries demonstrate successful use of scientific tools—catch reporting and onboard observers—under RFMOs.
- The global survey included over 600 experts across 90 nations, lending credibility and robustness.
Negatives:
- Deep-sea stocks remain acutely overfished and biologically vulnerable.
- Shark species, integral to marine food webs, continue to suffer from bycatch and poor regulatory coverage.
- Monitoring shortfalls in Southeast Asia and African coasts prevent precise biomass estimation and conservation action.
- Weaker implementation and unregulated artisanal practices challenge sustainability in Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
Recommendations for Sustainable Fisheries Governance:
- Empower RFMOs with real-time monitoring systems, electronic catch reporting, and observer programs.
- Adopt Ecosystem-Based Approaches that integrate climate resilience and biodiversity objectives.
- Strengthen Data Infrastructure in data-deficient regions with support from international bodies like the FAO and World Bank.
- Curtail Harmful Subsidies as per WTO protocols to reduce economic incentives driving overfishing.
- Promote Community Participation through co-management strategies and the development of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
CROPIC: A New AI-Driven Crop Study Scheme
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plans to launch CROPIC, a study to gather crop information using field photographs and AI-based models.
What is CROPIC?
CROPIC stands for Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops. It is a new initiative by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare aimed at studying crops through photographs and artificial intelligence (AI). The core objective is to monitor crop health and assess mid-season losses using images captured at multiple stages of the crop cycle.
Why is CROPIC significant?
CROPIC plays a pivotal role in modernizing and digitizing crop monitoring under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), India’s flagship crop insurance scheme.
Significance:
- Improved Loss Assessment: Traditional methods of crop loss assessment are time-consuming and subjective. CROPIC introduces AI-based analysis for faster and more objective decision-making.
- Automation of Compensation: It will help automate claim processes, ensuring faster payments to farmers in case of crop failure.
- Rich Crop Signature Database: Repeated field observations will build a valuable dataset of crop images over time, useful for future agricultural planning and risk management.
- Farmer Involvement: By crowdsourcing photographs directly from farmers, CROPIC also encourages their direct participation in data collection.
How will CROPIC work on the ground?
- Data Collection via App:
- A mobile app developed by the ministry will be used.
- Farmers and officials will take photos of crops 4–5 times during a crop’s life cycle.
- AI-Based Analysis:
- Photos will be processed on a cloud-based AI platform.
- The model will identify crop type, growth stage, health condition, damage, and loss extent.
- Visualization and Monitoring:
- A web-based dashboard will visualize crop status and damage patterns for stakeholders.
- Use in Insurance Claims:
- The app will also be used by officials to collect photo evidence for PMFBY claims, helping streamline compensation payouts.
Project Timeline:
- Pilot Phase:
- Begins with Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025-26.
- Will cover at least 50 districts per season, spanning various agro-climatic zones and major crops.
- Full Roll-Out: After initial R&D, nationwide implementation is planned from 2026 onwards.
Funding and Support:
- Funded through the Fund for Innovation and Technology (FIAT) under PMFBY.
- FIAT has a total allocation of ?825 crore for various tech-driven agricultural initiatives.
Understanding Tourette Syndrome
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that typically begins in early childhood, often between the ages of 2 and 15, with an average onset around six years. Affecting approximately 0.3% to 1% of the global population, TS is more prevalent among boys than girls. Despite its neurological basis, it remains poorly understood and frequently misdiagnosed, particularly in school settings where symptoms are mistaken for behavioural issues.
Nature and Classification of Tics
Tourette Syndrome is characterised by tics—sudden, repetitive, and involuntary movements or vocalisations. These are classified as:
- Simple tics, such as eye blinking, facial grimacing, throat clearing, or sniffing, involve a single muscle group or sound.
- Complex tics are more coordinated, involving actions like hopping, touching objects, or uttering phrases. Rarely, individuals may display coprolalia, the involuntary use of obscene language.
Tics often intensify with stress or excitement, diminish during calm periods, and usually disappear in deep sleep. External stimuli such as excessive screen exposure have also been linked to an increase in tics, particularly in children.
Causes and Co-morbidities
While the exact cause of TS remains unknown, researchers point to a combination of genetic predisposition and neurobiological factors, including abnormalities in brain regions such as the basal ganglia and frontal lobes. Environmental triggers—like low birth weight, perinatal complications, and post-infectious conditions (e.g., streptococcal infections)—may also contribute.
Tourette’s often coexists with other conditions such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. The presence of these co-morbidities complicates diagnosis and management.
Management and Treatment Approaches
Treatment is individualised and not always pharmacological. Many children with mild, non-disruptive tics do not require medication. Instead, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and behavioural interventions have shown significant efficacy. These therapies help children manage their symptoms while also training families to provide supportive environments that reduce stress and tic frequency.
Medications may be considered in severe cases where tics hinder daily functioning. Importantly, suppression or punishment of tics is counterproductive, often exacerbating symptoms due to built-up tension.
Social Stigma and the Need for Awareness
The primary challenge in managing TS lies not in the disorder itself, but in the societal misunderstanding surrounding it. Children with TS are often labelled as attention-seeking or disruptive, leading to social isolation and emotional distress. As seen in the case of a child from Kochi, delayed diagnosis and stigma worsened his condition until it was recognised as Tourette’s.
Educating teachers, parents, and peers is crucial. Early diagnosis, empathetic engagement, and inclusive school environments are essential to ensuring that children with TS are treated with dignity and compassion.
Rediscovery of the Eurasian Otter in Kashmir
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
After being presumed extinct in the Kashmir Valley for nearly three decades, the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) has been spotted again in the Lidder River in Srigufwara, South Kashmir. This rare sighting rekindles hope for the revival of the Valley’s aquatic biodiversity.
About Eurasian Otter:
- Common Names: Eurasian otter, European otter, Common otter, Old-World otter
- Local Name in Kashmir: Vuder
- Type: Semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal
- Distribution:
- Widely spread across Europe, the Middle East, Northern Africa, and Asia (from Eastern Russia to China).
- In India, found in northern, northeastern, and southern regions.
- In Kashmir, historically abundant in Dal Lake, Dachigam streams, Rambiara stream, and the Lidder River.
Habitat & Features:
- Habitat:
- Occupies diverse freshwater and coastal ecosystems—lakes, rivers, marshes, swamp forests, and mountain streams.
- In the Indian subcontinent, prefers cold hill and mountain waters.
- Physical Traits & Adaptations:
- Sleek brown fur (lighter underneath), long streamlined body, short legs, and thick tail.
- Aquatic adaptations:
- Webbed feet
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense fur trapping air for insulation
- Excellent vision, hearing, and olfactory senses.
- Behavior: Elusive, solitary, and primarily nocturnal.
Conservation Concerns:
- Primary Threats:
- Water pollution degrading habitats
- Hunting for fur, historically significant in Kashmir
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Blue NDC Challenge
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
At the Third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) held in Nice, France (June 9–13, 2025), Brazil and France launched the Blue NDC Challenge — a major international initiative to integrate ocean-based climate solutions into Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, in the lead-up to UNFCCC COP30, to be held in Belem, Brazil.
What is the Blue NDC Challenge?
The Blue NDC Challenge is a multilateral climate action initiative urging countries to incorporate ocean-centric measures into their updated NDCs. It aims to enhance climate mitigation and adaptation by recognizing the vital role of oceans and coastal ecosystems in addressing the climate crisis.
- Launched by: Brazil and France
- Platform: UNOC3 (June 2025)
- Target: Updated NDCs due for 2035 (deadline: February 10, 2025)
Participating Countries (as of June 2025):
- Founding: Brazil, France
- Joined: Australia, Fiji, Kenya, Mexico, Palau, Seychelles
Objectives and Key Features:
- Ocean-Integrated NDCs
- Include marine ecosystems, coastal zones, mangroves, coral reefs, and salt marshes in national climate plans.
- Integrate Marine Spatial Planning (MSP) and Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM).
- Sustainable Blue Economy
- Promote climate-resilient fisheries and carbon-smart aquaculture.
- Expand clean ocean energy: offshore wind, wave, and tidal power.
- Decarbonization and Adaptation
- Phase out offshore oil and gas projects.
- Reduce emissions in shipping, seafood value chains, and coastal infrastructure.
- Boost resilience in maritime sectors vulnerable to climate risks.
- Restoration and Conservation
- Focus on the restoration of mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs—which are effective carbon sinks and natural buffers against sea-level rise.
- Global Partnerships and Support Mechanisms
- Supported by:
- Global Mangrove Alliance
- UN High-Level Climate Champions
- World Resources Institute (WRI)
- Ocean Breakthroughs (Marrakech Partnership for Global Climate Action)
- Supported by:
Significance and Leadership:
- Brazil’s Climate Leadership
- Brazil’s 2035 NDC (submitted in November 2024) includes, for the first time, a dedicated Ocean and Coastal Zones component.
- Brazil is also investing in marine conservation, supported by a $6.8 million fund from Bloomberg Philanthropies (June 8, 2025).
- Expert Insights:
- Mangroves sequester carbon 10 times faster than terrestrial forests.
- Including oceans in NDCs can unlock greater political and financial support, according to Conservation International and WRI.
- Emission Reduction Potential:
- According to WRI, ocean-based solutions can contribute up to 35% of the global emissions reduction needed to stay within the 1.5°C limit.
Relevance for India and the World:
- With India’s vast coastline and diverse marine ecosystems, incorporating ocean-based climate actions into its NDCs could enhance climate resilience, especially for coastal communities.
- Global focus on oceans marks a shift towards holistic climate policy, integrating land, sea, and people-centric approaches.
Discovery of Spathaspina noohi
- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
A significant addition to India's rich biodiversity has emerged from the forests of Meghalaya with the discovery of a new beetle species, Spathaspina noohi. This unique species not only adds to the biological inventory of the region but also necessitated the creation of an entirely new genus, highlighting the ecological and taxonomic uniqueness of the organism.
Location of Discovery
- The beetle was found in the Umran area of Ri Bhoi district, Meghalaya.
- Elevation: 781 metres above sea level.
- The discovery was made by S. S. Anooj, entomologist from Kerala Agricultural University, and formally described by B. Ramesha in the international journal Zootaxa.
Taxonomic Significance
- Spathaspina noohi belongs to the Curculionidae family, commonly known as weevils, which includes over 60,000 species globally.
- Due to a highly distinctive sword-like spine on its back, it was classified under a new genus—Spathaspina, a name derived from Latin:
- Spatha = sword
- Spina = spine
Subfamily and Tribe Characteristics
- The beetle falls under the Ceutorhynchinae subfamily, which includes about 1,300 species worldwide.
- The subfamily is characterized by:
- Compact, robust body
- Ability to tuck their snout (rostrum) between the front legs when resting
- A visible back structure (mesanepimera)
- Within this subfamily, the beetle is linked to the tribe Mecysmoderini, comprising 8 genera and 107 species. This tribe is noted for its thoracic spines and specialized antenna structures, mostly found in South and Southeast Asia.
Ecological Role of Weevils
While many weevils are considered agricultural pests, others, including Spathaspina noohi, play vital ecological roles such as:
- Controlling invasive plant species
- Maintaining ecosystem balance
Geographical Distribution of Ceutorhynchinae
- These beetles are present across most continents except:
- New Zealand
- Oceania
- Antarctica
- Southern parts of South America
- Their highest diversity is noted in the Palaearctic Region (Europe, North Africa, parts of Asia), followed by the Oriental Region (South and Southeast Asia).
Commemorative Naming
The species is named in honour of P. B. Nooh, IAS, Director of Tourism, Government of Kerala. This acknowledges his contribution to eco-tourism and sustainable development, symbolizing the interconnection between biodiversity conservation and responsible tourism.
SEZ Reforms to Promote Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Department of Commerce notified key amendments to the SEZ Rules, 2006, to boost semiconductor and electronics component manufacturing. These reforms address the high capital intensity and import dependency of the sector and aim to attract pioneering investments.
Key Rule Amendments:
Rule 5: Minimum Land Requirement Relaxed
- What Changed: Minimum land required for SEZs dedicated to semiconductor/electronics manufacturing reduced from 50 hectares to 10 hectares.
- Why it matters
- Eases land acquisition
- Makes SEZs more feasible, especially in smaller industrial clusters
- Encourages pioneering investments in land-scarce regions
Rule 7: Encumbrance-Free Land Norm Relaxed
- What Changed: SEZ land no longer required to be entirely encumbrance-free, if it is mortgaged/leased to the Central or State Government or authorized agencies.
- Why it matters
- Removes a major legal hurdle in land approvals
- Accelerates SEZ project clearance and development timelines
Rule 18: Domestic Supply Allowed from SEZ Units
- What Changed: Semiconductor/electronics SEZ units can now sell products in the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) after paying applicable duties.
- Why it matters
- Greater market access
- Enhances revenue and profitability
- Breaks away from traditional export-only SEZ model
Rule 53: Clarity on Free-of-Cost Goods in NFE Calculation
- What Changed: Free-of-cost goods received or supplied will now be included in Net Foreign Exchange (NFE) calculations, using customs valuation rules.
- Why it matters
- Encourages R&D and contract manufacturing
- Promotes transparent reporting of value addition
- Aligns with global manufacturing practices
Significance of Reforms:
- Tailored for High-Tech Sectors: Recognises the long gestation and capital-intensive nature of semiconductor and electronic component industries.
- Encourages Domestic and Global Investment: Makes India an attractive destination for global electronics giants.
- Enables Domestic Market Integration: By allowing DTA sales, it expands market access for SEZ-based units.
- Supports India's Semiconductor Mission: Complements existing initiatives like the Semicon India Programme.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)
- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Finance Minister chaired the 6th Governing Council (GC) meeting of NIIF in New Delhi. The Council urged NIIF to enhance its global presence, diversify funding sources, and attract international investors by leveraging its sovereign-backed model.
About National Investment and Infrastructure Fund
- A government-anchored investment platform to mobilize long-term institutional capital for infrastructure and strategic sectors.
- Operates as a sovereign wealth fund (SWF)-linked asset manager with independent governance.
- Established: 2015 (Union Budget 2015–16)
- Headquarters: Mumbai
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs)
Functions & Objectives:
- Capital Mobilization: Attract domestic & global institutional investors.
- Investment Management: Deploy equity in commercially viable infrastructure.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with global sovereign wealth & pension funds.
- Policy Alignment: Support national initiatives like Make in India, green energy, and digital infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Public-Private Structure:
- 49% Government of India
- 51% Global and domestic institutional investors (e.g., ADIA, Temasek, CPPIB)
- SEBI-Registered AIF: Category II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF)
- Assets Under Management (AUM): ?30,000+ crore
- Capital Catalysed: ?1.17 lakh crore
- CEO & MD: Sanjiv Aggarwal (since Feb 2024)
Funds under NIIF:
- Master Fund: Core infrastructure (ports, airports, data centres, logistics)
- Private Markets Fund (PMF): Fund of funds model
- India-Japan Fund: Focused on climate action and sustainability
- Strategic Opportunities Fund: Growth equity in strategic sectors
Governing Council (GC) of NIIF:
- Chair: Union Finance Minister (currently Nirmala Sitharaman)
- Members include Finance Secretary, DEA/DFS officials, SBI Chairman, private sector leaders.
- Provides strategic guidance on:
- Fundraising
- Global positioning
- Operationalisation of new funds
- Annual review of performance
Key Outcomes of the 6th GC Meeting (2024–25):
- Proactive Global Outreach: GC urged NIIF to enhance its global presence and professionalise international engagement.
- Diversified Fundraising: Encouraged exploring multiple funding sources beyond traditional sovereign investors.
- Private Markets Fund II (PMF II): Target corpus: $1 billion; first closing imminent.
- Bilateral Fund with the USA: Under discussion to foster cross-border infrastructure investments.
- Greenfield Investment Success: Master Fund investments directed toward ports, logistics, airports, data centres.
- Strong Global Partnerships: Includes ADIA, Temasek, Ontario Teachers', CPPIB, AIIB, ADB, JBIC, and NDB.
- Annual Meetings: GC to convene once every year to review and guide NIIF’s evolving role.
India’s Breakthrough in Heeng Cultivation

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
CSIR-IHBT reported the first flowering and seed setting of heeng in Palampur (1,300 m above sea level). This confirmed the successful acclimatisation and domestication of Ferula assa-foetida in Indian agro-climatic conditions.
This milestone is significant because:
- It proves India’s capability to cultivate heeng domestically.
- It completes the reproductive cycle—a prerequisite for long-term commercial production and sustainability.
- It expands the scope of cold-arid agriculture beyond traditional zones.
Background:
- Heeng or asafoetida (Ferula assa-foetida) is a perennial herb, long revered in Indian culinary and medicinal traditions.
- It is widely mentioned in ancient texts such as the Mahabharata, Charaka Samhita, Pippalada Samhita, and the works of Panini, known for its digestive, aromatic, and therapeutic properties.
- Despite being the world’s largest consumer of heeng, India was entirely import-dependent until the early 2010s, sourcing it mainly from Afghanistan, Iran, and Uzbekistan.
- This was because the species Ferula assa-foetida, the true source of asafoetida, was not found in India—only related species like Ferula jaeschkeana (Himachal Pradesh) and Ferula narthex (Kashmir and Ladakh) existed, which do not yield the culinary resin.
Botanical & Climatic Requirements:
- Plant Type: Perennial, takes about 5 years to mature and flower.
- Soil: Prefers sandy, well-drained soil with low moisture.
- Climate: Thrives in cold, arid environments, requires annual rainfall below 200–300 mm.
- Temperature Range: Grows best in 10–20°C, tolerates up to 40°C, and survives winter lows of –4°C.
- Propagation: The oleo-gum resin (asafoetida) is extracted by making incisions in the plant’s fleshy taproot and rhizome, yielding a latex that hardens into a gum, which is dried into powder or crystal form.
The Indigenous Cultivation Effort:
In a major step toward self-reliance, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research – Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT) in Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, initiated India’s first project for indigenous heeng cultivation.
- Seed Procurement: Between 2018–2020, IHBT coordinated with agencies and suppliers in Iran, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and South Africa. Seeds were finally procured from Iran and Afghanistan with import approvals and quarantine protocols handled by ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- Research and Trials: Researchers developed germination protocols for seeds with low viability and conducted trials at IHBT Palampur and Ribling in Lahaul-Spiti to determine altitude-specific suitability and agronomic practices.
- Milestone Event: On October 15, 2020, the first heeng sapling was planted in a farmer’s field in Kwaring village, Lahaul Valley—marking the start of India’s heeng cultivation journey.
Expansion and Institutional Support:
- New Cultivation Zones: From cold desert areas, cultivation extended to mid-hill regions such as Janjheli in Mandi. Demonstration plots and farmer training programmes were established across Lahaul-Spiti, Kinnaur, Mandi, Kullu, and Chamba.
- Early Adopter Villages:
- Lahaul & Spiti: Madgran, Salgran, Beeling, Keylong
- Mandi: Janjehli, Kataru, Majhakhal, Karsog
- Kinnaur: Kalpa, Hango, Reckong Peo, Maling
- Kullu: Kotla–Banjar, Bagsaid, Dhaugi–Sainj
- Chamba: Pangi, Bharmour, Tooh, Mahala
- Heeng Germplasm Resource Centre: Established at IHBT Palampur in March 2022, this national hub oversees research, conservation, seed production, and propagation of heeng.
- Tissue Culture Innovation: A dedicated lab was developed to scale up propagation using modern techniques, supported by the Government of Himachal Pradesh. Ecological niche modelling using GPS and climate data helped map ideal cultivation areas.
Myotis himalaicus

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A new bat species, the Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus), has been described based on fieldwork in Uttarakhand and historical specimens from Pakistan. Published in Zootaxa journal by a team of Indian and international scientists.
Key Findings of the Study
- Study Area: Western Himalayas – Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand (2017–2021).
- Total Bat Species Documented: 29, including new records and confirmations.
- Raises India's bat species count to 135.
About Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus)
Feature Description
Family/Genus Belongs to the Myotis frater complex
Habitat Deodar, pine, and cedar forests on southern Himalayan slopes
Distribution Found in Uttarakhand (India) and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan)
Size Medium-sized (~3.5 inches, <1 oz)
Morphology Delicate feet, long thumbs with short claws, short ears, fine teeth
Conservation Status Recently described; appears rare
Other Major Additions/Clarifications
- East Asian Free-Tailed Bat (Tadarida insignis):
- First confirmed record in India.
- Extends known range eastward by 2,500 km.
- Earlier misidentified as Tadarida teniotis.
- Babu’s Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus babu):
- Revalidated as a distinct species, not a synonym of Javan pipistrelle.
- Distribution: Pakistan, India, Nepal.
- First specimen-based confirmations in India for:
- Savi’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo savii)
- Japanese greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus nippon)
Ecological Importance of Bats
- Insect Control: Consume pests and mosquitoes.
- Pollination & Seed Dispersal: Important for forest regeneration.
- Fertilizer Contribution: Bat guano rich in Nitrogen & Phosphorous; boosts crop yield.
NASA's Mars Odyssey captures volcano piercing ice cloud belt
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
- Recently, NASA’s 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter captured a stunning image of Arsia Mons, a giant Martian volcano, rising through a morning belt of water-ice clouds.
- First such astronaut-like horizon view of Tharsis Montes volcanoes on Mars.
About Arsia Mons
- Part of Tharsis Montes, a trio of volcanoes near Mars' equator.
- Height: ~20 km (12 miles) – twice the height of Mauna Loa, Earth’s tallest volcano.
- Cloudiest of the Tharsis volcanoes.
- Cloud formation due to orographic uplift and cooling during Mars’ aphelion (farthest point from Sun).
- Featured in the aphelion cloud belt — a seasonal band of water-ice clouds.
Mission Evolution
- Mars Odyssey, launched in 2001, is the longest-operating Mars orbiter.
- In 2023, began a new imaging mode: rotating its THEMIS camera to capture horizon views of Mars’ upper atmosphere.
- These angled images help study seasonal changes in dust and water-ice cloud layers.
Scientific Significance
- Helps track Martian atmospheric evolution, especially cloud behavior and dust storms.
- Valuable for future human missions:
- Assists landing site safety planning.
- THEMIS also detects subsurface water ice, key for astronaut resource use.
Instruments and Collaborators
- THEMIS: Thermal Emission Imaging System, captures both visible and infrared light.
- Managed by NASA’s JPL, designed by Arizona State University, built by Lockheed Martin.
Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A study recently published in the journal Earth’s Future offered an innovative approach to SAI technique that could reduce its costs but also bring it closer to fruition despite the opposition to it.
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)?
- SAI is a proposed solar geoengineering technique to cool the Earth by injecting reflective aerosols (e.g. sulphur dioxide) into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce surface temperatures.
- Inspired by volcanic eruptions, like Mount Pinatubo (1991), which naturally cooled the Earth by emitting aerosols.
Recent Study Highlights (June 2025)
- Published in Earth’s Future journal.
- Led by Alistair Duffey, University College London.
- Used UK Earth System Model 1 (UKESM1) for climate simulations.
Key Findings
- Injecting 12 million tonnes of sulphur dioxide annually at 13 km altitude (spring/summer in each hemisphere) could cool the Earth by ~0.6°C.
- To cool by 1°C, ~21 million tonnes/year are needed at that altitude.
- Only 7.6 million tonnes/year are needed at higher altitudes (subtropics) for the same cooling.
Innovative Proposal
- Low-altitude SAI using modified existing aircraft (e.g. Boeing 777F) instead of specially designed high-altitude aircraft:
- Stratosphere is lower near poles (12–13 km), so current aircraft can reach it.
- Cost-effective and faster to deploy than high-altitude (~20 km) methods.
- Could begin within years, rather than a decade-long wait for new aircraft.
Risks and Concerns
- Tripling aerosol quantity (in low-altitude strategy) raises:
- Ozone depletion
- Acid rain
- Altered weather patterns
- Uneven global effects (benefits poles more, tropics less)
- Moral hazard: may reduce incentives to cut emissions.
- Governance challenge: One country’s action impacts all nations → risk of geopolitical conflict.
Why it matters
- Global GHG emissions are still rising.
- Climate mitigation through decarbonisation is slow and politically vulnerable.
- Technologies like SAI offer a stopgap, but not a substitute for emission cuts.
Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
The Maharashtra Forest Department partnered with Microsoft and Pune-based CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities) to address the eco-restoration project in the Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary.
Location & Geography:
- Situated in the Western Ghats, about 70 km from Pune, Maharashtra.
- Notified as a Wildlife Sanctuary in January 2013.
- Spread over 49.62 sq. km, comprising:
- 12 forest compartments from Paund and Sinhgad ranges (Pune forest division).
- 8 compartments from Mangaon range (Roha division, Thane).
Vegetation Types:
- Dominated by evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests.
- Rich floral diversity including teak, bamboo, Ain, Shisham, mango, and jamun.
Biodiversity Highlights:
- Mammals (28 species):
- Includes the Indian Giant Squirrel (Shekaru) – state animal of Maharashtra.
- Also hosts Indian pangolin, barking deer, Indian civet, and wild boar.
- Home to the Kondana Soft-furred Rat (Millardia kondana) – an endangered species.
- Birds (150 species):
- Notable species: Malabar whistling thrush, golden oriole, crested serpent eagle, Indian pitta, grey junglefowl.
- Includes 12 species endemic to India.
- Insects & Others:
- 72 species of butterflies, 18 reptile species, and 33 invertebrate species.
Ecological Importance:
- Part of the Western Ghats, a globally recognized biodiversity hotspot.
- Habitat for rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- Supports vital ecosystem services, aiding in climate regulation, water conservation, and pollination.
Recent Conservation Initiative:
- A collaborative eco-restoration project was launched by the Maharashtra Forest Department, Microsoft, and CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities), Pune.
- Aim: Address socio-ecological challenges, promote community engagement, and leverage technology in conservation.
Eco-tourism Potential:
- Features popular trekking and nature spots like Andharban forest, Plus Valley, and Devkund.
- Attracts high tourist footfall, especially during monsoon, including bird watchers and nature enthusiasts.
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
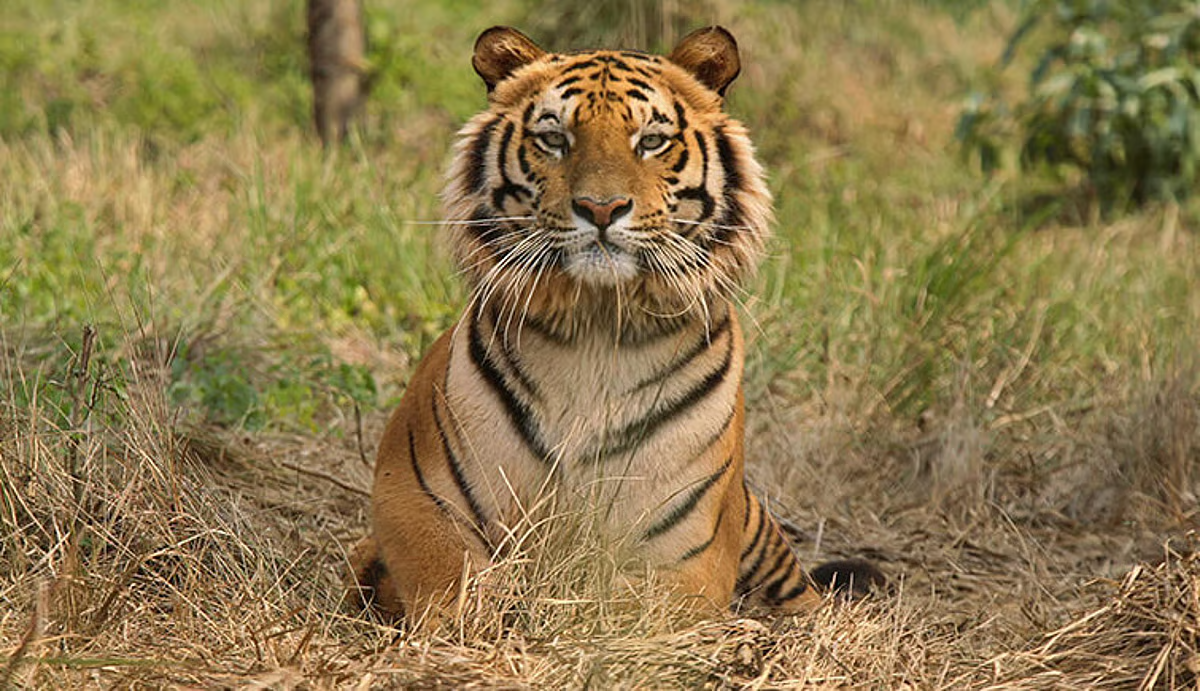

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has recently ordered the Rajasthan government to impose an immediate ban on all mining activities within the core area of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, citing concerns over wildlife protection and habitat preservation.
About Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
- Location: Sawai Madhopur district, southeastern Rajasthan.
- Named After: Ranthambore Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, located within the reserve.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- North: Bounded by the Banas River
- South: Bounded by the Chambal River
- Terrain: High rocky plateaus, valleys, rivers, lakes, and historic ruins including forts and mosques.
- Total Area: ~1,411 sq.km, making it one of the largest tiger reserves in northern India.
- Surrounding Ranges: Located at the confluence of the Aravalli and Vindhya hill ranges.
Ecology and Biodiversity
Vegetation: Dominated by dry deciduous forests and open grassy meadows.
- Flora:
- Predominantly Dhok tree (Anogeissus pendula).
- Other species: Acacia, Capparis, Zizyphus, Prosopis, etc.
Water Bodies:
- Important lakes include:
- Padam Talab
- Raj Bagh Talab
- Malik Talab
Fauna:
- Apex predator: Royal Bengal Tiger
- Other mammals:
- Leopard, Caracal, Jungle Cat
- Sambar, Chital, Chinkara, Wild Boar
Historical Significance: Previously served as the royal hunting grounds of the Maharajas of Jaipur.
RBI Revises LTV Ratio for Gold-Backed Loans
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced revised guidelines to enhance formal sector lending and ease credit access for small-ticket gold loan borrowers, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- The new norms focus on raising the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio for gold-backed loans up to ?5 lakh and simplifying appraisal norms for such loans.
What is the Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
- Definition: The LTV ratio is the percentage of a collateral’s value that a lender offers as a loan.
- Formula:
LTV Ratio= (Loan Amount / Appraised Value of Asset) × 100
- A higher LTV indicates greater credit against the same asset but also entails higher risk for the lender.
- Assets like gold, with a stable value and liquid secondary market, are more "desirable" as collateral, often attracting higher LTVs.
Revised RBI Guidelines (June 2025): LTV Ratio for Gold Loans
Loan Amount Revised LTV Ratio Previous LTV (Draft April 2025)
Up to ?2.5 lakh 85% 75%
?2.5 lakh – ?5 lakh 80% 75%
Above ?5 lakh 75% 75%
- The interest component is included in the LTV calculation.
- The move reverses the uniform 75% LTV cap proposed in the April 2025 draft norms.
Additional Key Features
- No credit appraisal required for loans up to ?2.5 lakh.
- End-use monitoring is necessary only if the borrower wishes to qualify the loan under priority sector lending.
- The average ticket size of gold loans (~?1.2 lakh) is expected to increase due to relaxed norms.
- These loans are crucial for middle-class, lower middle-class, self-employed, and small businesses, often lacking formal income proof.
Rationale and Impact
- The revised norms aim to:
- Enhance credit accessibility.
- Prevent migration of borrowers to informal lenders.
- Boost financial inclusion and formalize rural credit ecosystems.
- Industry experts and NBFCs like Muthoot FinCorp and Shriram Finance have welcomed the move, noting it would benefit women, rural borrowers, and small traders.
- Shares of leading gold loan NBFCs like Muthoot Finance, Manappuram Finance, and IIFL Finance witnessed a sharp increase following the announcement.
INS Arnala
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission 'Arnala', the first warship under the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) series at the Naval Dockyard in Visakhapatnam. The commissioning will be presided over by Chief of Defence Staff, General Anil Chauhan.
About INS Arnala
- Type: First in the series of 16 Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW-SWC)
- Builder:
- Primary: Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata
- Partner: L&T Shipbuilders
- Delivery Date: May 8, 2025
- Indigenous Content: Over 80%
- Partners Involved:
- BEL, L&T, Mahindra Defence, MEIL
- 55+ MSMEs involved in the supply chain
Capabilities & Features
- Length: 77 meters
- Displacement: 1,490+ tonnes
- Propulsion: Diesel engine-waterjet system (a first for a warship of this size in India)
- Roles:
- Anti-submarine operations in coastal/shallow waters
- Subsurface surveillance
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Low-intensity maritime operations
Significance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Milestone: Highlights indigenous shipbuilding and defence manufacturing capabilities
- Boost to Coastal Defence: Enhances the Navy’s reach in shallow and strategic coastal zones
- Employment & Industrial Growth: Significant MSME and domestic defence industry involvement
Heritage & Symbolism
- Name Origin: Inspired by Arnala Fort, near Vasai, Maharashtra
- Built by the Marathas in 1737 under Chimaji Appa
- Historically guarded the Vaitarna River mouth and northern Konkan coast
- Design Symbolism:
- Armoured hull reflects the resilient walls of Arnala Fort
- Advanced sensors and weapons echo the fort’s cannons
- Crest:
- Stylised auger shell – precision, strength, vigilance
- Motto: Arnave Shauryam — “Valour in the Ocean”
Rediscovery of Losgna Genus in India
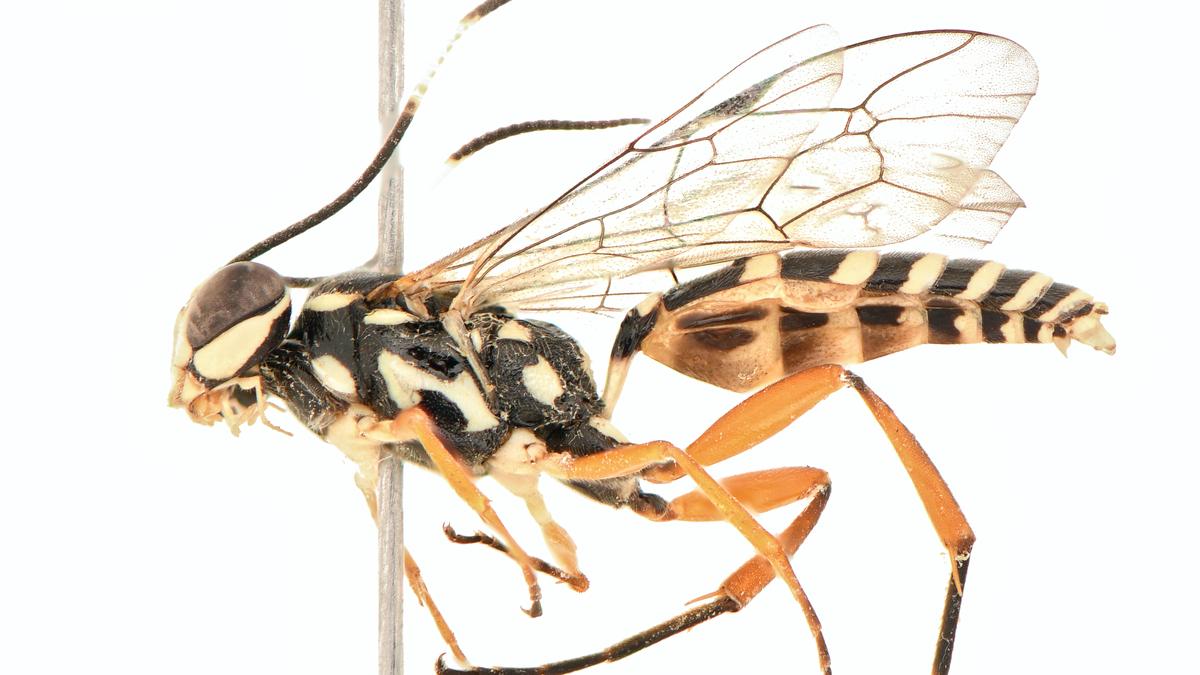

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
At a time when habitat loss and climate change threaten countless species, the discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp - named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
Location of Discovery
- Place: Chandigarh, Union Territory of India
- Habitat: Urban dry scrub forest
- Time: Winter of 2023–24
- Significance: First formal description of any insect species from Chandigarh
Species Description
- Name: Losgna occidentalis
- Genus: Losgna (Ichneumonidae family – Parasitic wasps)
- Group Role: Parasitic wasps known for laying eggs inside/on arthropod hosts
- Ecological Role: Pollinators and biological control agents (important in ecosystems)
Historical Context
- Losgna genus was last recorded in India in 1965, in Heinrich’s monograph
- No Indian records or specimens existed post-1965 in any institution
- Only known specimens (of other Losgna species) are preserved in:
- Natural History Museum, London
- The Hope Collection, Oxford University
- Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany
Naming Rationale
- "Occidentalis" (Latin for "Western")
- Signifies the westernmost known range of the genus
- Earlier Losgna records were only from:
- Northeast India
- Southeast Asia (tropical forests)
- Published in Zootaxa (peer-reviewed journal for animal taxonomy)
Importance & Implications
- Rediscovery highlights India’s hidden and threatened biodiversity
- Emphasizes the critical role of taxonomy in conservation
- Shows potential for citizen-led discoveries and backyard biodiversity
- Demonstrates the need for:
- Responsible specimen collection
- International scientific collaboration
- Support for underfunded taxonomy sectors
IISc Develops Nanozyme to Prevent Excessive Blood Clotting

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru have developed a novel vanadium-based nanozyme that effectively controls abnormal blood clotting by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). This innovation holds promise for managing life-threatening conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and ischemic stroke.
Scientific Background:
- Normal Blood Clotting: Platelets are specialized blood cells that form clots at injury sites through a process called haemostasis, involving activation by physiological chemicals like collagen and thrombin.
- Problem of Abnormal Clotting: In conditions like COVID-19 and PTE, oxidative stress increases, leading to elevated ROS levels. This causes hyperactivation of platelets, resulting in excessive clot formation (thrombosis) — a leading cause of death globally.
Nanozyme Innovation by IISc:
- What is a Nanozyme?
An engineered nanomaterial that mimics the action of natural enzymes, in this case, glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes ROS.
- Material Used: Vanadium pentoxide (V?O?) nanozymes, particularly those with spherical morphology, were found to be the most efficient.
- Mechanism: The redox-active surface of vanadium nanozymes catalytically reduces ROS, preventing unwanted platelet aggregation.
Testing and Results:
- In vitro testing: Human blood platelets were activated with physiological agonists. Nanozymes were tested for their ability to curb excessive aggregation.
- In vivo testing (mouse model of PTE):
- Nanozyme injection led to reduced thrombosis.
- Improved survival rates without observable toxicity.
- Animals were monitored for 5 days post-treatment for health parameters.
Future Prospects:
- Researchers aim to test the nanozyme's potential against ischemic strokes, which also result from vascular blockages.
- Encouraging results with human platelets indicate the possibility of clinical trials in the near future.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Western Europe – 2022 Onwards
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Western Europe is experiencing its largest diphtheria outbreak in 70 years, with cases predominantly among vulnerable groups such as migrants and the homeless. The outbreak, which began in 2022, has raised concerns over disease surveillance, migrant healthcare, and immunisation coverage.
Key Facts from the Outbreak
- As per a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, 536 cases and three deaths have been reported across Europe since 2022.
- Most cases were found among young males (average age: 18) who had recently migrated, particularly from Afghanistan and Syria.
- 98% of strains exhibited close genetic similarities, suggesting a common transmission point during migration journeys or in accommodation facilities, not in the countries of origin.
- A genetic match between the 2022 strains and a recent 2025 case in Germany indicates that the bacteria is still circulating silently in the region.
Recommendations from Health Experts
- Enhance vaccination drives, particularly among high-risk and underserved populations.
- Improve awareness among healthcare providers, especially those working with migrants and the homeless.
- Ensure better access to antibiotics and diphtheria antitoxins.
- Strengthen disease surveillance and contact tracing mechanisms.
About Diphtheria
Feature Details
Cause Corynebacterium diphtheriae (produces a potent toxin)
Mode of Spread Respiratory droplets, contact with infected sores or ulcers
Affected Areas Primarily the respiratory tract, but also the skin in some cases
Symptoms Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weakness; grey membrane in throat
Severe Impact Can lead to breathing difficulties, heart and kidney damage, and neurological issues if untreated
Treatment Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT), antibiotics, and supportive care
Fatality Rate Up to 30% in unvaccinated individuals; higher in children
Prevention Vaccination (DPT/DTP) is the most effective preventive measure
Greater Flamingo Sanctuary

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
On the occasion of World Environment Day 2025, the Tamil Nadu government officially declared the Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi, Ramanathapuram district, aiming to protect a vital stopover site for migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Key Highlights
What is it?
A newly notified wildlife sanctuary dedicated to safeguarding migratory wetland birds, especially the greater flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus), in their natural resting and breeding habitat.
Location and Area:
- Located in Rameshwaram taluk, Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Covers approximately 524.7 hectares of revenue and forest land.
- Lies within the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, a globally recognized marine ecosystem.
Ecological Significance
- Functions as a critical site along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the key migratory bird routes.
- As per the 2023–24 Wetland Bird Survey, the region hosts 10,700+ wetland birds representing 128 species, including:
- Flamingos (greater and lesser)
- Herons, egrets, sandpipers, etc.
- The sanctuary harbours diverse ecosystems, such as:
- Mangroves (Avicennia, Rhizophora)
- Mudflats, marshes, sand dunes, and lagoons
- Nesting grounds for sea turtles and marine biodiversity
Conservation and Socioeconomic Benefits
- Strengthens coastal resilience by preventing erosion through natural mangrove buffers.
- Promotes responsible ecotourism, raising awareness of wetland and avian conservation.
- Supports local livelihoods via employment in conservation and tourism activities.
About the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus)
Attribute Details
Size 90–150 cm tall, long necks and legs
Coloration Pink hue from carotenoid-rich diet
Feeding Uses specialized downward-curved bill for filter feeding in shallow waters
Reproduction Builds cone-shaped mud nests, lays 1–2 eggs, both parents incubate
Chick Rearing Chicks are white and fed through regurgitation
Social Traits Highly gregarious, breeds in large colonies and flies in V-formations
Behavioral Note Often seen standing on one leg, possibly to conserve body heat
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for the issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities. This includes instruments such as social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, aiming to boost responsible financing in India.
Understanding ESG Debt Securities
Definition:
ESG debt securities are financial tools designed to raise capital specifically for projects that yield positive environmental, social, or governance (ESG) outcomes. These instruments are a key part of sustainable finance, with categories including:
- Social Bonds: Focused on projects with direct social impact (e.g., affordable housing, education).
- Sustainability Bonds: Target projects with both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Tied to specific ESG performance indicators or targets.
Salient Features:
- Funds raised must be used exclusively for eligible ESG-aligned projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled in line with the project's primary focus.
- Compliance with global ESG norms and standards is mandatory.
- Verification or certification by an independent third-party is required.
- The framework applies to both public and private debt offerings.
Highlights of SEBI’s Framework
1. Classification Guidelines: Issuers are required to categorize their bonds—green, social, or sustainability—based on the core objective of the projects being financed. This ensures transparent communication of the bond's intended impact.
2. Disclosure Norms:
- At the Issuance Stage: Offer documents must detail project eligibility, selection methodology, and a tentative allocation between financing new initiatives and refinancing existing ones.
- Post-Issuance: Issuers must provide annual updates on fund deployment and report impact metrics to demonstrate accountability and transparency.
3. Independent Assurance: Issuers must engage accredited third-party entities to validate the alignment of bonds with ESG principles, thereby enhancing investor confidence and market integrity.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: There is an obligation for ongoing impact assessment. Issuers must ensure the projects funded effectively contribute to reducing environmental degradation or addressing social challenges.
5. Scope and Enforcement: The framework will come into effect from June 5, 2025, and is aligned with international ESG standards to facilitate greater inflow of sustainable and ethical investments.
Significance for India: This move marks a significant step in mainstreaming ESG finance in India. It aims to improve transparency, attract climate-conscious capital, and reinforce India’s commitment to sustainable development.
EnviStats India 2025
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India's annual mean temperature rise up from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024, Electricity generation from renewable sources increased more than three times in 10 years.
- Released by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) on June 5, 2025, on the occasion of World Environment Day
- Framework Used: UN's Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013)
Key Highlights:
Climate Trends
- Annual Mean Temperature rose from 25.05°C (2001) to 25.74°C (2024).
- 2024 recorded as India’s hottest year since 1901; also, globally the hottest year in 175 years.
- Annual Minimum and Maximum Temperatures (2021–24):
- Minimum: 19.32°C → 20.24°C
- Maximum: 30.78°C → 31.25°C
Rainfall Patterns
- Rainfall shows seasonal concentration between June–September, with signs of shifting patterns such as late onset or extended rains into October.
- No clear long-term trend, reflecting erratic monsoonal behaviour.
Energy Generation
Thermal & Renewable Power (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Thermal: 7.92 lakh GWh → 13.26 lakh GWh
- Renewable: 65,520 GWh → 2.25 lakh GWh, over 3x increase in renewable energy output in a decade.
Biodiversity and Faunal Statistics
Faunal Diversity
- Global Faunal Species: 16,73,627
- India's Share: 1,04,561 species
- Habitat-specific Species in India:
- Soil Ecosystem: 22,404
- Freshwater Ecosystem: 9,436
- Mangrove System: 5,023
- Estuarine Ecosystem: 3,383
- Marine Fauna (India): 20,613 out of global 2,47,605
Fisheries Production
Inland vs. Marine Fish (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Inland Fish Production: 61 lakh tonnes → 139 lakh tonnes
- Marine Fish Production: 34 lakh tonnes → 45 lakh tonnes
Public Expenditure (2021–22)
- Environment Sustainability Sector: ?2,433 crore (highest among sectors)
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Increasing trend
- Agro-Forestry: Lowest allocation
New Data indicators introduced
- Ramsar sites
- Access to sanitation
- Transport infrastructure
- Electricity access
Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS)
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has notified the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS) in April 2025. It marks a strategic step in India’s ambition to become a global electronics manufacturing hub.
Key Highlights of ECMS
- Objective: To incentivize domestic production of passive electronic components and capital equipment, thus deepening India's electronics manufacturing value chain.
- Scheme Tenure: Valid for 6 years, with a 1-year gestation period.
- Focus Components: Includes resistors, capacitors, relays, switches, speakers, connectors, inductors, special ceramics, and other passive components.
- Active components are supported separately under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM).
- Incentive Structure:
- Turnover-linked incentive (based on incremental revenue).
- Capex-linked incentive (for investments in plant and machinery).
- Hybrid model (combining turnover and capex benefits).
Incentive rates range between 1–10%, varying by year and component type.
- Employment Mandate: All applicants—whether component manufacturers or capital equipment makers—must commit to job creation, ensuring broader socio-economic benefits.
Strategic Importance
- Horizontal Sectoral Impact: The scheme is designed to support multiple sectors including automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, power electronics, and electrical grids, promoting cross-industry multiplier effects.
- Support for Tooling & Capital Equipment Industry: Encourages design and manufacture of capital tools and machinery required for electronics production, in line with models seen under the India Semiconductor Mission.
- Global firms like Linde have begun operations, with more in pipeline.
India’s Electronics Growth Trajectory
- Export Milestone (FY 2024–25):
- Total smartphone exports: ?2 lakh crore
- iPhone exports alone: ?1.5 lakh crore
- Sectoral Growth (Last Decade):
- 5x growth in production.
- 6x growth in exports.
- Export CAGR: >20%
- Production CAGR: >17%
- Manufacturing Base Expansion: Over 400 production units (large and small) now manufacture a wide range of electronic components domestically.
- Value Chain Evolution: India has transitioned from assembling finished goods → sub-assemblies → deep component manufacturing, now entering a value-added, self-reliant phase in electronics
One State, One RRB Policy
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Government of India, through the Ministry of Finance, has implemented the "One State, One RRB" policy effective from May 1, 2025, aimed at consolidating 26 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) across 10 states and 1 Union Territory, thereby reducing the total number of RRBs to 28. This move follows the recommendation of the Dr. Vyas Committee and is intended to enhance the performance and outreach of RRBs.
Objectives of the Policy
- Improve operational efficiency and governance.
- Rationalize costs and optimize resources (human and technological).
- Eliminate intra-state competition among sponsor banks.
- Promote uniform service delivery through technological integration.
About Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Established: 1975 under the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976.
- Recommended by: Narasimham Committee (1975).
- Ownership Pattern:
- Government of India – 50%
- State Government – 15%
- Sponsor Bank – 35%
Regulatory Structure
- Regulated by: Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Supervised by: NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
Role and Objectives
- Provide institutional credit to rural India.
- Support priority sectors like agriculture, MSMEs, and rural artisans.
- Ensure financial inclusion among farmers, labourers, and small entrepreneurs.
Impact of the Reform
- Operational Scale: Enhanced credit delivery across wider geographies.
- Technological Standardization: Easier integration of IT infrastructure.
- Unified Governance: One sponsor bank per state improves accountability.
- Performance: RRBs recorded an all-time high net profit of ?7,571 crore in FY 2023–24.
- Asset Quality: GNPA (Gross Non-Performing Assets) stood at 6.1%, the lowest in a decade.
Niveshak Didi

- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant push toward inclusive financial literacy, the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, and the India Post Payments Bank (IPPB), under the Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications, have signed a Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) to launch Phase 2 of the “Niveshak Didi” initiative in April 2025.
Objective:
The Niveshak Didi initiative, launched in 2023, is a women-led, community-driven financial literacy program designed to empower rural and underserved populations by fostering responsible financial behavior, promoting digital banking, and spreading fraud awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Target Group: Rural women and semi-urban communities.
- Approach: Local women, especially postal workers, are trained as financial educators (Niveshak Didis).
- Impact of Phase 1:
- Over 55,000 beneficiaries reached, with 60% women, predominantly from deep rural areas.
- Most beneficiaries belonged to the youth and economically active age groups.
Phase 2 (2025 Onward):
- Deployment of 4,000+ financial literacy camps across rural, tribal, and semi-urban areas.
- Training of 40,000 women postal workers to serve as grassroots financial educators.
- Curriculum Focus:
- Savings and budgeting.
- Responsible investing and fraud prevention.
- Digital tools and services provided by IPPB.
- Digital Inclusion: Leveraging India Stack for paperless and presence-less banking; training delivered in 13 regional languages.
About Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- Statutory Body: Functions under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India.
- Objective: Ensures informed and protected investors across India.
- Key Role:
- Promotes financial literacy to aid budgeting, saving, and investment decisions.
- Empowers citizens to make sound financial choices.
- Focus Areas:
- Educates citizens on investor rights and responsibilities.
- Special outreach to rural and underserved areas to bridge financial knowledge gaps.
- Vision: To build a financially aware and confident India, where every citizen has the tools to secure their financial future.
About India Post Payments Bank (IPPB)
- Established: On September 1, 2018 under the Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications.
- Ownership: 100% equity owned by the Government of India.
- Mission: To be the most accessible, affordable, and trusted bank for the common man.
- Mandate:
- Bridge financial inclusion gaps for the unbanked and underbanked.
- Leverage the vast postal network of approx. 1.65 lakh post offices (1.4 lakh in rural areas) and 3 lakh postal employees.
- Technology Backbone:
- Based on India Stack: Paperless, Cashless, and Presence-less banking.
- Uses CBS-integrated smartphones and biometric devices.
- Commitment:
- Promotes a less-cash economy.
- Supports the vision of Digital India.
- Motto: Every customer is important, every transaction is significant, every deposit is valuable.
India Skills Accelerator Initiative (2025)

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) has partnered with the World Economic Forum (WEF) to launch the India Skills Accelerator—a national-level public-private collaboration platform aimed at fostering a future-ready and inclusive workforce.
Key Features:
- Purpose: To act as a systemic change enabler in India's skilling ecosystem through a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral approach.
- Core Objectives:
- Enhance awareness and shift mindsets about the need for future skills.
- Promote collaboration and knowledge sharing between government, industry, and academia.
- Reform policies and institutional structures for an agile and responsive skilling framework.
- Sectoral Priorities:
- Focus on high-growth areas: AI, robotics, cloud computing, cybersecurity, advanced manufacturing, energy, and Global Capability Centres (GCCs).
- Emphasis on formalizing the informal workforce.
- Lifelong Learning: Mobilize investments in upskilling and reskilling across various life stages to support agile career transitions.
- Data-Driven Governance: Use surveys, mapping tools, and the WEF’s Global Learning Network for peer benchmarking and progress tracking.
- Implementation Strategy:
- Identify 10–12 high-impact priorities with measurable outcomes.
- Establish thematic working groups to ensure coordinated execution.
- Align initiative with the WEF’s Future of Jobs Report 2025.
Significance
- Addresses the fact that 65% of organizations cite skill gaps as a major barrier to growth.
- Positions India to leverage its demographic dividend and become the "Skill Capital of the World".
- Supports India's goal of skilling not just for domestic needs but also for global workforce demand.
- Reinforces federal cooperation, involving institutions like NSDC, NCVET, DGT, UGC, AICTE, NCERT, and CBSE.
Quantum Supremacy Demonstrated via Simple Game
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
Researchers from the University of Oxford and Universidad de Sevilla have demonstrated quantum supremacy using a simple mathematical game based on the odd-cycle graph colouring problem. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, marks a significant milestone in quantum computing.
What is Quantum Supremacy?
Quantum supremacy refers to the ability of a quantum computer to perform a task that is practically impossible for classical computers to solve efficiently. This advancement showcases the unique capabilities of qubits, which leverage two core principles:
- Superposition: Qubits can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- Entanglement: Measurement of one qubit instantly affects another, even over a distance.
These principles enable exponential scaling of computational power. For instance, a 50-qubit quantum computer could potentially outperform the most powerful classical supercomputers.
The Odd-Cycle Game: A Novel Approach
The team implemented a game inspired by graph theory:
- Players (Alice and Bob) are tasked with colouring an odd-numbered cycle (e.g., triangle) using only two colours such that adjacent points differ in colour.
- Mathematically, this is impossible in classical terms for odd cycles due to inevitable repetition of colours.
In the experiment:
- Two strontium atoms placed 2 meters apart were entangled using lasers.
- A referee sent each atom a "question" (mapped to a point on the cycle).
- Players performed quantum operations based on the questions and returned either 0 or 1 (representing colours).
The experiment was repeated 101,000 times, covering circles from 3 to 27 points.
Results and Significance
- Classical win rate: 83.3% for 3-point cycles.
- Quantum win rate: 97.8%, clearly surpassing classical limits.
- Quantum supremacy was evident up to 19-point circles.
- The entanglement correlation was the strongest ever recorded between two separated quantum systems.
Comparison with Previous Demonstrations
- Google’s Sycamore (2019): Used 53 superconducting qubits for a complex problem called random circuit sampling.
- China’s Jiuzhang: Used Gaussian boson sampling.
- In contrast, this new approach used just two entangled qubits, making it simpler, efficient, and easier to verify.
Practical Implications
This simplified game-based model of quantum advantage could have real-world applications in problems where coordination is needed without communication—such as the "rendezvous problem". Quantum systems can dramatically reduce search steps compared to classical ones (e.g., Grover’s algorithm can reduce 1 million steps to 1,000).
ESA Biomass Satellite Mission

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Biomass Mission is a new Earth observation mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) aimed at enhancing our understanding of the global carbon cycle through accurate forest biomass measurements.
Launch Details:
- Rocket: Vega-C
- Launch Site: Europe’s Spaceport, French Guiana
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of ~666 km
- Scheduled Launch Date: 29 April 2025 (subject to final checks)
Key Features:
- First satellite to use P-band radar (long-wavelength synthetic aperture radar).
- Capable of penetrating dense forest canopies to scan tree trunks, branches, and stems — where most of a tree’s carbon is stored.
- Will generate 3D maps of the world’s tropical forests.
Mission Objectives:
- Measure above-ground forest biomass and forest height.
- Create five global biomass maps over its five-year mission.
- Monitor changes in forests to assess their role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
Scientific Importance:
- Forests absorb ~8 billion tonnes of CO? annually and are often referred to as "Earth’s green lungs."
- By analyzing forest carbon storage and changes, the mission will contribute significantly to:
- Monitoring climate change
- Supporting carbon accounting
- Improving air quality assessments
Phases of the Mission:
- Initial Phase: Produces detailed 3D forest maps globally.
- Second Phase: Generates global estimates of forest height and biomass.
Relevance to Climate Action:
- Helps in quantifying carbon uptake and release.
- Supports global climate models and carbon budgeting.
- Aids in policy-making for sustainable forest management.
Theobaldius konkanensis
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A new species of land snail, Theobaldius konkanensis, has been discovered by a collaborative team of Indian and UK researchers from the Konkan region of Maharashtra. This species adds to the growing biodiversity records of the northern Western Ghats, a globally recognized but under-explored biodiversity hotspot.
Key Facts at a Glance
- Scientific Name: Theobaldius konkanensis
- Discovered in: Ratnagiri and Raigad districts, Maharashtra (Dev Gireshwar Temple, Uttamrao Patil Biodiversity Garden, Kesharnath Vishnu Temple, and Phansad Sanctuary)
- Elevation: 80–240 metres above sea level
- Habitat: Tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests
- Active Months: June to September (monsoon); only shells visible in other months
- Habits: Active both day and night, often under forest canopy in shaded, moist leaf litter
Morphological Features
- Shell Characteristics:
- Slightly flattened with a raised centre and deep triangular notch near the aperture
- Operculum (protective cover) has raised whorl edges and short spines
- Corneous yellow with brown striations
- Thick, conoidally depressed, and widely umbilicated
- Body: Stout and rounded
Taxonomic Context
- Family: Cyclophoridae (Caenogastropoda)
- Genus: Theobaldius
- Now includes 20 species: 9 in India, 11 in Sri Lanka, and 1 in Sumatra (Indonesia)
- In India, 6 species are endemic to the Western Ghats
- Only T. annulatus is found in both Sri Lanka and the Western Ghats
Ecological and Conservation Significance
- Bioindicators: Land snails are sensitive to climatic changes and environmental disturbances
- Endemism: T. konkanensis is restricted to specific forest patches in the Konkan, highlighting the ecological uniqueness of the region
- Threats: Increasing anthropogenic pressures and habitat degradation threaten snail species with restricted distribution
Reproductive Biology (General Traits of Land Snails)
- Breeding mainly in monsoon
- Reproduce through both cross- and self-fertilisation
- Courtship includes dart-shooting behavior; mating may last hours
- Eggs laid in moist soil or leaf litter; hatch in 2–4 weeks
- Lifespan: 2 to 7 years
De-Extinction
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A US biotech company, Colossal Biosciences, claims to have genetically engineered three grey wolf pups to carry traits of the extinct dire wolf, calling it a de-extinction.
What is De-Extinction?
De-extinction is the process of reviving extinct species using advanced biotechnological methods such as:
- Gene editing (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9),
- Cloning (e.g., somatic cell nuclear transfer),
- Ancient DNA sequencing and genome reconstruction,
- Synthetic biology to reintroduce key traits of extinct organisms.
Colossal Biosciences and the Dire Wolf Project
In late 2024, a U.S.-based biotechnology firm, Colossal Biosciences, announced the birth of three genetically engineered wolf pups—Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi—claimed to be the world’s first successful case of "functional de-extinction."
About the Dire Wolf
- Scientific name: Aenocyon dirus
- Habitat: Grasslands and forests of North America during the Pleistocene Epoch
- Extinction: ~12,500–13,000 years ago
- Characteristics: 25% larger than modern grey wolves; strong jaws to hunt megafauna like bison and horses; light-colored dense fur; social, pack-hunting predators.
Scientific Process Involved
- DNA Extraction: Ancient DNA was recovered from dire wolf fossils (13,000 to 72,000 years old).
- Genome Reconstruction: Sequencing and comparative analysis showed ~99.5% similarity between dire wolves and modern grey wolves.
- Gene Editing: Scientists edited 20 genes in grey wolves to replicate dire wolf traits like:
- White, thick fur
- Increased body mass
- Enhanced musculature and coat pattern
- Cloning: Modified DNA was used to create embryos via somatic cell nuclear transfer.
- Surrogacy: Embryos were implanted in large domestic dogs. Of several attempts, three pups survived.
Scientific and Ethical Concerns
- Experts argue these are not true dire wolves but genetically edited grey wolves with some dire wolf-like traits.
- Critics highlight the absence of peer-reviewed publication, limited understanding of epigenetic and behavioral factors, and the artificial environment in which the pups are raised.
- Colossal terms the process "functional de-extinction", meaning re-creating genetically and ecologically similar organisms, not exact replicas.
Ecological and Conservation Relevance
- Colossal claims the technology could help endangered species like the red wolf (native to the southeastern U.S.), threatened by habitat loss and hybridization with coyotes.
- Four clones of red wolf–coyote hybrids have been produced with potential use in restoring genetic diversity.
- The company aims to democratize conservation biotechnology, pledging to share tools with global conservationists and working with Native American communities.
Contemporary Debates
- Over 60 environmental groups have protested proposed U.S. legislation to delist grey wolves from the Endangered Species Act, warning of ecological consequences.
- Scientists urge caution, stressing that true resurrection of extinct species requires more than gene editing, as behavior, evolutionary context, and environmental adaptation cannot be synthetically replicated.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched two major global initiatives to advance inclusive and sustainable agrifood systems:
- “Four Betters Courses” Initiative – To revolutionize agrifood systems education
- “Commit to Grow Equality” Initiative – To bridge the gender gap in agrifood sectors
1. Four Betters Courses Initiative
- Launched: October 2024 during the World Food Forum
- Objective: To integrate FAO’s expertise into global agrifood systems education through partnerships with universities and academic networks.
- Alignment: Anchored in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031
Core Philosophy – The “Four Betters” Approach:
- Better Production – Promote efficient, inclusive, and resilient food systems
- Better Nutrition – Ensure access to safe, nutritious, and affordable diets
- Better Environment – Address climate change and protect ecosystems
- Better Life – Improve rural livelihoods and reduce inequalities
- Delivery Platform: Implemented through the FAO eLearning Academy, which provides over 600 multilingual, certified courses.
2. Commit to Grow Equality (CGE) Initiative
- Launched: 2024 on the platform of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- Objective: To narrow the gender gap in agrifood systems and enhance women’s empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Key Highlights:
- Aims to benefit over 54 million women worldwide
- Mobilizes $1 billion in investments toward gender-responsive agrifood initiatives
- Provides strategic tools for tracking gender equality outcomes in public and private sectors
- Promotes gender-aligned national agricultural policies
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking and fosters collaboration across governments, NGOs, and the private sector
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY), a flagship initiative aimed at providing financial support to unfunded micro and small enterprises, has completed 10 years since its launch in 2015.
Overview of PMMY
- Objective: To offer collateral-free institutional credit to non-corporate, non-farm micro and small enterprises.
- Loan Limit: Up to ?20 lakh without any collateral.
- Implementing Institutions (MLIs):
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Categories of MUDRA Loans
Loan Category Loan Amount Range
Shishu Up to ?50,000
Kishor ?50,000 to ?5 lakh
Tarun ?5 lakh to ?10 lakh
Tarun Plus ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh
Key Achievements (2015–2025)
- Boost to Entrepreneurship: PMMY has sanctioned over 52 crore loans amounting to ?32.61 lakh crore, catalyzing a grassroots entrepreneurship revolution.
- MSME Sector Financing: Lending to MSMEs increased significantly:
- From ?8.51 lakh crore in FY14
- To ?27.25 lakh crore in FY24
- Projected to exceed ?30 lakh crore in FY25
- Women Empowerment: 68% of Mudra beneficiaries are women, highlighting the scheme’s impact in fostering women-led enterprises.
- Social Inclusion:
- 50% of loan accounts are held by SC, ST, and OBC entrepreneurs.
- 11% of beneficiaries belong to minority communities, showcasing PMMY’s contribution to inclusive growth.
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
Calotes zolaiking
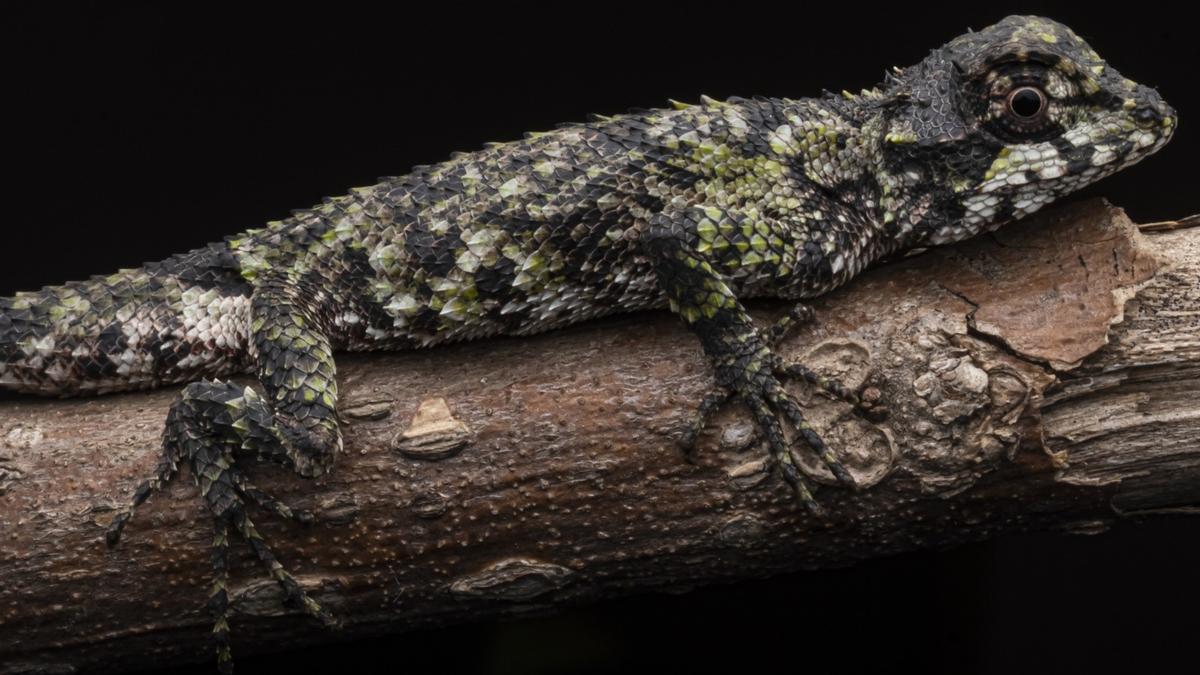

- 31 May 2025
In News:
The rare lizard species Calotes zolaiking has been recorded for the first time in Meghalaya, marking a significant extension of its known habitat and triggering grassroots conservation efforts.
About Calotes zolaiking
- Scientific Classification: Belongs to the Calotes genus under the Agamidae family.
- First Described: In 2019 from Aizawl district, Mizoram.
- Appearance: About 5 inches in length; green body with dark patches and strongly keeled scales (scales with a raised ridge).
- Behaviour: Arboreal (tree-dwelling), diurnal, fast runners, and capable swimmers.
- Diet: Insectivorous—feeds on insects and small invertebrates.
Distribution and Habitat
- New Sighting: Mawmluh village, East Khasi Hills, Meghalaya, April 2024.
- Range Extension: Approx. 172 km aerially from the original Mizoram locality.
- Genus Distribution: Found across India, Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, and parts of Oceania.
- India's Richness: 14 known Calotes species in India; 9 recorded in the Northeast region.
Conservation Significance
- Community Role: Local residents Goldenstar Thongni and Banyllashisha Wankhar played a key role in identifying and collecting specimens.
- Catalyst for Conservation: The species' discovery has motivated the local community in Mawmluh and Sohra (Cherrapunji) to strengthen forest protection amidst threats from limestone mining and industrial activities.
- Sacred Groves: Traditional conservation spaces like sacred groves are being revitalized in light of the new biodiversity significance.
- Scientific Impact: The find was featured in Zootaxa, a peer-reviewed taxonomy journal, adding global recognition.
Broader Ecological Relevance
- Biodiversity Surveys: The discovery underscores the need for continuous herpetofaunal surveys in the Khasi Hills due to forest degradation.
- Historical Context: Cited alongside Stoliczkia khasiensis, a snake species last seen in 1870, highlighting the risk of species being lost without systematic documentation.
India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST-Kashmir) has successfully developed India’s first gene-edited sheep, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of animal biotechnology.
Key Highlights:
- Institution Involved: Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST), Srinagar.
- Technology Used:
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing — a precision genome editing tool that won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
- Gene editing was conducted without insertion of foreign DNA, thus the sheep is non-transgenic and differs from traditional GMOs.
- Gene Targeted: The myostatin gene, which regulates muscle growth, was edited to enhance muscle mass.
- Result: Muscle mass increased by 30%, a trait absent in Indian sheep breeds but seen in select European breeds like the Texel.
- Significance:
- Improved meat yield and quality in sheep.
- Potential for disease-resistant and higher-reproduction-rate livestock in the future.
- Supports India’s evolving biotech policy by promoting non-transgenic, gene-edited organisms that are more likely to receive regulatory acceptance.
- Aligns with goals of sustainability and food security by enhancing productivity per animal.
- Regulatory & Safety Aspects:
- Research adhered to international biosafety protocols.
- Sponsored by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Legacy & Research Background:
- Developed after 4 years of dedicated research.
- Led by Prof. Riaz Ahmad Shah, also known for creating India’s first cloned Pashmina goat, Noori, in 2012, and contributing to the world’s first cloned buffalo at NDRI, Karnal.
Implications for the Future:
- Opens doors for precision breeding in livestock to boost India’s animal husbandry sector.
- Strengthens India’s position in advanced genomic research and supports the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat in biotechnology.
- Awaits comprehensive regulatory framework for gene-edited animals, currently under government consideration.
WMO Climate Forecast 2025–2029
- 30 May 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its latest decadal climate forecast (2025–2029), warning of a continued trend of record-breaking global temperatures. This projection raises serious concerns about climate risks, sustainable development, and international climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Key Projections:
- Annual Global Temperature Rise: Each year from 2025–2029 is projected to be 1.2°C to 1.9°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Record Heat Likelihood:
- 80% chance that at least one year will surpass 2024, currently the warmest year on record.
- 86% probability that one year will exceed the 1.5°C threshold.
- Five-Year Mean Warming: 70% chance that the 2025–2029 average will be above 1.5°C, a sharp rise from 47% (2024–2028) and 32% (2023–2027).
Note: The Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C limit refers to long-term (20-year) averages, but short-term overshoots are now increasingly probable.
Regional and Thematic Insights:
1. Arctic Amplification: Arctic winters (Nov–Mar) are projected to be 2.4°C warmer than the 1991–2020 average—3.5× faster than the global rate.
2. Sea Ice Decline: Continued sea ice reduction is expected in the Barents Sea, Bering Sea, and Sea of Okhotsk, impacting marine biodiversity and indigenous livelihoods.
3. Precipitation Variability:
- Wetter-than-average conditions likely in:
- Sahel region
- Northern Europe
- Alaska and Northern Siberia
- Drier conditions expected over:
- Amazon Basin
- Parts of South Asia
South Asia may witness generally wet years, though seasonal variability will persist.
Impact and Implications:
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased warming will fuel more intense heatwaves, extreme rainfall, droughts, and floods, stressing both urban systems and agriculture.
- Cryosphere and Ocean Changes:
- Accelerated glacier and sea ice melt will raise sea levels.
- Ocean heating contributes to acidification and marine biodiversity loss.
- Threat to Sustainable Development: Progress on SDGs, particularly food security, water availability, and health, is at risk in vulnerable regions.
Way Forward:
- Revise NDCs at COP30: Strengthen and align Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with the 1.5°C goal.
- Accelerate Clean Energy Transition: Promote renewables, energy efficiency, and net-zero strategies to reduce GHG emissions.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Climate Monitoring & Forecasting: Enhance WMO-led regional forecasts and risk assessment tools.
- Preserve Natural Carbon Sinks: Protect forests, wetlands, and oceans to mitigate atmospheric CO?.
Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) – FY 2025–26

- 29 May 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation of the Interest Subvention (IS) component under the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) for the financial year 2025–26, retaining the existing structure and interest rates.
About the Scheme:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Objective: To provide short-term agricultural credit to farmers at affordable interest rates through Kisan Credit Cards (KCC).
Key Features:
- Loan Coverage:
- Short-term crop loans up to ?3 lakh per farmer through KCC.
- For loans exclusively for animal husbandry or fisheries, the benefit applies up to ?2 lakh.
- Interest Rates:
- Base interest rate: 7%
- 1.5% interest subvention to lending institutions
- 3% Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI) for timely repayment
- Effective interest rate for prompt payers: 4%
- Implementing & Monitoring Agencies:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Operated via Public Sector Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Cooperative Banks, and Private Banks in rural/semi-urban areas.
Recent Updates and Rationale:
- No structural changes have been introduced in the scheme for FY 2025–26.
- The scheme continues amidst rising lending costs, with stable repo rates and MCLR trends.
- It ensures credit access for small and marginal farmers, critical for financial inclusion and agricultural productivity.
Impact on Agricultural Credit:
- KCC Accounts: Over 7.75 crore active accounts across India.
- Institutional Credit Growth:
- Disbursement via KCC increased from ?4.26 lakh crore (2014) to ?10.05 lakh crore (Dec 2024).
- Total agricultural credit rose from ?7.3 lakh crore (FY 2013–14) to ?25.49 lakh crore (FY 2023–24).
- Digital Reform: Kisan Rin Portal (KRP) launched in August 2023 has improved transparency and efficiency in claim processing.
Significance:
- Helps ensure timely and affordable institutional credit to the farming sector.
- Supports the government's goal of doubling farmers’ income.
- Strengthens the rural credit delivery system and promotes inclusive growth in agriculture.
Dark Patterns and India’s Regulatory Response
- 29 May 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution has initiated a robust crackdown on Dark Patterns—deceptive design practices used on digital platforms to manipulate consumer behavior. A recent high-level stakeholder meeting in Delhi, chaired by Union Minister Prahlad Joshi, brought together representatives from major e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, Zomato, and Ola, along with consumer organizations and law institutions, to address the growing concern.
What are Dark Patterns?
Dark Patterns are user interface designs that intentionally mislead or coerce consumers into making decisions they would not have otherwise made. These manipulative tactics exploit psychological principles and cognitive biases to serve the commercial interests of platforms—often at the cost of consumer autonomy.
Types of Dark Patterns Identified by the Government:
The Department of Consumer Affairs has officially recognized 13 types of dark patterns in its November 2023 guidelines. Prominent among them are:
- False Urgency: Creating artificial time pressure (e.g., “Only 1 seat left!”).
- Basket Sneaking: Adding items to the cart without user consent.
- Confirm Shaming: Using guilt-driven language to influence decisions.
- Subscription Trap: Making subscription easy but cancellation difficult.
- Interface Interference: Hiding crucial information or options.
- Bait and Switch: Advertising one offer and switching to another.
- Hidden Costs: Revealing extra charges only at checkout.
- Forced Action: Making users complete unrelated tasks to proceed.
- Disguised Ads, Trick Questions, Nagging, SAAS Billing Abuse, and Rogue Malware Links are other examples.
These practices have been found across multiple digital sectors including e-commerce, travel, OTT platforms, edtech, online banking, and quick commerce.
Consumer Impact and Rising Complaints:
The National Consumer Helpline has witnessed a significant increase in grievances related to dark patterns. Platforms are accused of eroding consumer trust, causing financial harm, breaching privacy, and distorting fair market practices.
According to LocalCircles, based on a survey conducted across 392 districts with feedback from 2.30 lakh consumers, the worst offenders include edtech, airline, and taxi app services. Notably, companies like Uber and Rapido were recently issued notices by the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) for coercing users into paying tips in advance.
Regulatory Measures in India:
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: While it prohibits unfair trade practices, it lacks explicit provisions targeting dark patterns, making enforcement challenging.
- 2023 Guidelines on Dark Patterns: Released by the Department of Consumer Affairs, these guidelines define deceptive interfaces as violations of consumer rights and misleading advertisements.
- Self-Audit Mandate: E-commerce companies have been instructed to conduct internal audits and eliminate dark patterns from their platforms.
- Proposed Joint Working Group: A mechanism is being considered to increase industry awareness and enforce compliance.
- Voluntary and Legal Enforcement: The government has urged digital firms to integrate the guidelines into internal policies and consumer grievance redressal systems.
National Apprenticeship Promotion and Training Schemes

- 28 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the 38th Meeting of the Central Apprenticeship Council (CAC), chaired by the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), recommended a 36% increase in stipends under two key skilling initiatives—National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS). This move aims to enhance apprenticeship attractiveness, reduce dropout rates, and improve youth employability across India.
About NAPS (Launched: 19 August 2016)
- Objective: To build industry-relevant skilled manpower by promoting on-the-job training and bridging the gap between education and employment.
- Administered by: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Key Features:
- Provides financial support to establishments for engaging apprentices.
- Encourages MSME participation and focuses on aspirational districts and the North-East.
- Offers partial stipend reimbursement under the Apprentices Act, 1961.
- Apprentices receive a certificate from NAPS, enhancing employability.
- Over 43.47 lakh apprentices engaged across 36 States/UTs till May 2025.
- Female participation reached 20%, with efforts to boost inclusion.
About NATS
- Target Group: Graduates, Diploma holders, and Vocational certificate holders.
- Provisions:
- Offers 6–12 months of practical, hands-on training.
- Employers receive 50% stipend reimbursement.
- Apprentices are issued a Government of India Certificate of Proficiency, valid across employment exchanges.
- FY 2024–25 Stats: Over 5.23 lakh apprentices enrolled.
Key Reforms Recommended by CAC (2025)
- Stipend Enhancement:
- Proposed increase from ?5,000–?9,000 to ?6,800–?12,300.
- To be adjusted biennially based on Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Inclusive Skilling Framework:
- Definition of “Person with Benchmark Disability” to be added under the Apprenticeship Rules.
- Trades must indicate suitability for PwBDs with reserved training slots.
- Curricular Integration:
- Push for Degree Apprenticeships and Apprenticeship Embedded Degree Programmes (AEDP).
- Definitions added for "Institution", "UGC", and "Contractual Staff".
- Flexible Training Modes: Employers may provide Basic and Practical Training through online, virtual, or blended modes, adhering to standard curricula.
- Decentralized Administration: Proposal to establish Regional Boards to improve scheme outreach and governance.
- Sectoral Expansion:
- Adoption of NIC Code 2008 to replace outdated 1987 list.
- Brings emerging sectors like IT, software, telecom, biotech, and renewable energy under apprenticeship coverage.
- Operational Improvements:
- Align CTS (Craftsmen Training Scheme) courses with apprenticeship notification timelines.
- Consideration of location-based stipend rationalization based on cost of living.
- Proposal for insurance coverage for apprentices during contract periods.
Governance and Stakeholder Involvement
The Central Apprenticeship Council includes representatives from:
- Ministries: Education, Labour, MSME, Railways, Textiles.
- Industry: BHEL, Indian Oil, Tata, Maruti, Reliance.
- Institutions: NSDC, UGC, AICTE.
- State advisors and domain experts from labour and education fields.
Semi-Transparent Perovskite Solar Cell Technology
- 28 May 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have developed an advanced semi-transparent perovskite solar cell (PSC) layered over a traditional silicon solar cell. This results in a 4-terminal (4T) tandem solar cell that significantly boosts power conversion efficiency (PCE) to ~30%, compared to the current average of ~20% in conventional solar panels.
Key Features and Technology
- Structure: Tandem architecture using a bottom silicon sub-cell and a top layer of indigenously developed halide perovskite semiconductor.
- Material Efficiency: Halide perovskite is one of the most efficient light-absorbing materials and can be locally produced using available chemical resources.
- Cost & Efficiency Gains:
- Potential to reduce solar power cost to ?1/kWh, down from ?2.5–4/kWh.
- Offers 25–30% more efficiency compared to standard solar panels.
- Stability Improvements: Previously, PSCs degraded quickly. The new configuration extends lifespan up to 10 years, enhancing durability under heat and low-light conditions.
Strategic Significance for India
- Indigenous Manufacturing: Reduces dependence on imported raw materials, especially those dominated by China.
- Commercialization Plan:
- Maharashtra government and MAHAGENCO exploring large-scale implementation.
- ART-PV India Pvt. Ltd., a start-up from IIT Bombay's SINE, aims to deliver a commercial wafer-size solution by December 2027 using indigenous equipment.
- Applications:
- Rooftop solar installations
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Vehicle-integrated photovoltaics (VIPV)
Clean Energy Linkage: IIT Bombay is also working with the Maharashtra government to develop green hydrogen solutions. The PSC’s high open-circuit voltage makes it suitable for solar-to-hydrogen (STH) applications, offering performance comparable to costly compound semiconductors but at lower cost and with locally accessible materials.
Alicella gigantea
- 27 May 2025
In News:
Rare giant shrimp is more widespread than previously believed; new findings reveal.
About the Species:
- Alicella gigantea is a giant deep-sea amphipod crustacean, growing up to 34 cm in length, making it one of the largest known amphipods.
- Amphipods are shrimp-like organisms; over 10,000 species are known globally, inhabiting a wide range of aquatic environments.
Habitat and Depth Range:
- Inhabits the abyssal (3,000–6,000 m) and hadal zones (>6,000 m) of the ocean.
- Notable sightings include:
- A 28 cm specimen observed at 5,304 m in the North Pacific.
- Captures from 6,746 m depth in the Murray Fracture Zone (North Pacific).
Global Distribution:
- Contrary to earlier beliefs, A. gigantea is not rare but is among the most widely distributed deep-sea species.
- Recent analysis compiled 195 records from 75 locations across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, covering 15 different seafloor features.
- Found in 59% of the world’s oceans.
- The Pacific Ocean is its most significant habitat, with 75% of the seafloor in its suitable depth range.
Genetic Insights:
- Genetic analyses (16S, COI, 28S genes) show low genetic divergence across populations.
- This suggests A. gigantea represents a single, globally distributed species with strong genetic conservation.
- A shared haplotype network across regions indicates minimal genetic differentiation, supporting global connectivity among populations.
Conservation and Research Significance:
- Despite its wide range, A. gigantea remains poorly understood, particularly in terms of population size, ecology, and evolutionary history.
- Only seven studies have sequenced its DNA to date.
- The findings are a significant step toward understanding deep-sea biodiversity, biogeography, and conservation priorities in abyssal ecosystems.
Sagarmatha Sambaad 2025

- 27 May 2025
In News:
Union Environment Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav represented India at the 1st Sagarmatha Sambaad in Kathmandu, Nepal, a high-level biennial global dialogue convened under the theme “Climate Change, Mountains, and the Future of Humanity.”
The forum, held during the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation 2025, focused on mountain ecosystems, climate resilience, and transboundary conservation.
India’s Key Proposals and Commitments
Reaffirmed India’s climate leadership and proposed a five-point call for global action to protect mountain ecosystems:
- Enhanced Scientific Cooperation: Promote joint research on cryospheric changes, biodiversity, and hydrological cycles.
- Building Climate Resilience: Develop early warning systems for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure in mountainous areas.
- Empowering Mountain Communities: Center policies on local welfare, integrate traditional ecological knowledge, and promote green livelihoods such as eco-tourism.
- Providing Green Finance: Ensure adequate and predictable climate finance for adaptation and mitigation in mountain nations, in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Recognizing Mountain Perspectives: Integrate mountain-specific issues into global climate negotiations and sustainable development agendas.
India’s Initiatives and Regional Cooperation
India highlighted the ecological value of the Himalayas and called for enhanced transboundary conservation among Himalayan nations under the International Big Cats Alliance. This alliance promotes joint protection of species like snow leopards, tigers, and leopards.
- Under Project Snow Leopard, India conducted its first comprehensive snow leopard assessment (2019–2023), recording 718 snow leopards, comprising 10–15% of the global population.
Significance of the Himalayan Ecosystem
- Hydrological Role: The Himalayas are the "Water Towers of Asia", feeding rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus, and supplying around 1.2 trillion cubic meters of freshwater annually.
- Ecological Richness: A biodiversity hotspot, home to over 10,000 vascular plant species, 979 bird species, and 300 mammals such as the red panda and Himalayan tahr.
- Cultural Importance: Sacred in Hinduism and Buddhism, the Himalayas house pilgrimage sites like Kedarnath, Badrinath, and Mount Kailash.
- Economic Value: Support tourism, agriculture, forestry, and renewable energy. States like Uttarakhand, Assam, and West Bengal derive over 10% of state GDP from tourism.
The Lohit Basin project in Arunachal Pradesh (13,000 MW) exemplifies hydropower potential. - Climate Regulation: The range blocks cold Central Asian winds and influences monsoon patterns, ensuring rainfall for agriculture. Himalayan forests are major carbon sinks, mitigating global warming.
Key Challenges in the Himalayan Region
- Climate Disasters: Rising temperatures and glacier melt cause avalanches, landslides, and cloudbursts. E.g., 2025 Uttarakhand avalanche; 2023 Sikkim GLOF.
- Unsustainable Development: Slope cutting, deforestation, and seismic vulnerability threaten settlements (e.g., Joshimath subsidence linked to infrastructure projects).
- Glacier Retreat:
- Gangotri glacier has retreated over 850 meters in 25 years.
- Hindu Kush glaciers may lose 75% of volume by 2100.
- Biodiversity Loss: Invasive species and habitat loss displace native flora and fauna; 90% of endemic species in Sikkim Himalayas displaced.
- Unregulated Tourism: Littering and plastic waste—92.7% of Himalayan waste is plastic, 72% non-recyclable (2022 audit).
Recommendations for Sustainable Development
- Eco-sensitive Infrastructure: Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), bioengineering, and electric mobility in high-altitude towns.
- Regulated Tourism: Introduce carrying capacity limits, permit-based entry, and promote low-impact tourism models.
- Glacier Monitoring & Water Management: Use remote sensing and GIS for glacier health; adopt ice stupas, rainwater harvesting, and efficient irrigation.
- Afforestation & Forest Conservation: Launch community-driven forestry projects (e.g., Van Andolan in Uttarakhand) to restore degraded ecosystems.
- Climate Adaptation Strategies: Expand early warning systems for GLOFs; promote climate-resilient crops and agricultural practices.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Encourage organic farming, herbal industries, and eco-handicrafts to diversify mountain economies.
Google’s AI Matryoshka Strategy
- 26 May 2025
In News:
At its 2025 I/O Developer Conference, Google unveiled AI Matryoshka, a multi-layered artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem powered by its latest Gemini 2.5 models. This marks a fundamental restructuring of Google’s platforms around AI, affecting users, developers, and enterprises.
What is AI Matryoshka?
- Concept: Named after the Russian nesting dolls, AI Matryoshka is a layered AI architecture where each outer application or interface draws intelligence from a core AI “brain.”
- Objective: To embed AI deeply and uniformly across Google’s services, enabling agentic, intelligent, and autonomous interactions.
Core AI Models: Gemini 2.5
- Gemini 2.5 Pro:
- Advanced reasoning and mathematics capabilities.
- Achieved high scores on USAMO 2025 (a premier U.S. math olympiad).
- Features a mode called Deep Think for complex problem-solving.
- Gemini 2.5 Flash:
- A more efficient, lightweight model using 20–30% fewer tokens.
- Supports natural audio output and multi-speaker TTS in 24 languages.
- Set to become the default model in Gemini applications.
Foundational Hardware: Ironwood TPUs
- Ironwood (7th Gen TPUs):
- Delivers 42.5 exaFLOPS of compute power per pod.
- Offers 10x performance boost over previous TPUs.
- Supports large-scale training and deployment of generative AI models.
Generative Media Models
- Imagen 4: Advanced image generation.
- Veo 3: High-quality video generation.
- Lyria 2: Music creation using AI.
- Copyright Tools:
- SynthID (watermarking) and SynthID Detector (verification) aim to address copyright concerns over the training data.
Developer Ecosystem
- Gemini API & Vertex AI:
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Enables agent-to-agent communication.
- Thinking Budgets: Let developers allocate compute resources wisely.
- Project Mariner: Tool for automating complex tasks.
- Thought Summaries: Improves transparency of AI decisions.
- Coding Agent – Jules:
- Beta launched globally.
- Integrates with code repositories to write tests, build features, and fix bugs using Gemini 2.5 Pro.
User-Centric Features
- Search Integration (AI Mode):
- Rolls out first in the U.S. with Deep Search generating cited, multimodal answers.
- Offers virtual shopping try-ons and agentic checkout, raising privacy and data security concerns.
- Gemini App:
- Available on Android and iOS with Live and image generation features.
- Deep Research allows analysis of private documents and images, necessitating strong data protection protocols.
- Integrated into Chrome (for Pro and Ultra users) for webpage summarization.
- Canvas Feature: A creative workspace for interactive infographics, quizzes, and audio content in 45 languages.
Subscription Tiers and Privacy Concerns
- Google AI Ultra Tier:
- Offers premium access to advanced capabilities, including video generation with native audio.
- Raises questions about "privacy premium" – whether better AI safety features will be available only to paying users.
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India-U.S. defence cooperation is advancing with the proposed co-production of the Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV). This deal represents a significant leap in bilateral defence industrial collaboration and aligns with India's strategic goal of military modernization and indigenisation under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
About Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV):
- Origin: Jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and U.S., it is the first new military vehicle inducted into U.S. Army service since the 1980s.
- Type: Eight-wheeled armoured infantry combat vehicle designed for rapid deployment and battlefield mobility.
- Variants: Includes Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), reconnaissance vehicle, medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, and Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrier.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Top speed of ~100 km/h and an operational range of 483 km. Can be airlifted using C-17 and C-130 aircraft (both in IAF’s fleet) or Chinook helicopters, enhancing deployment in remote terrains.
- Firepower: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: V-hull structure for blast protection; composite armour reinforced with ceramic tiles offers increased survivability against IEDs and small arms.
- Capacity: Operated by a 2-member crew and can transport a 9-member infantry squad.
Operational Evaluation in India:
- High-Altitude Trials: Conducted in Ladakh (13,000–18,000 feet) during September–October 2024. Evaluation reports were shared with Army Headquarters for further review.
- Javelin ATGM Demonstration: Conducted alongside Stryker trials; however, the performance was sub-optimal due to the vintage system used. Repeat trials have been requested by India.
Strategic Importance for India:
- Tactical Advantage: Enhanced mobility and survivability in high-altitude warfare make it suitable for regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Border Security: Bolsters India's defence posture along sensitive frontiers with China and Pakistan.
- Force Modernization: Meets the Indian Army’s requirement for ICVs with integrated ATGM capabilities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Push: The proposed model includes initial direct imports followed by large-scale license production in India, potentially by Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML).
Defence Diplomacy and Industrial Cooperation:
- The deal is being advanced under the India-U.S. Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap, focusing on co-development and co-production.
- In November 2023, Indian Defence Secretary confirmed discussions under this framework.
- The U.S. has reiterated the importance of India enhancing procurement of U.S.-made defence equipment, aiming at a balanced trade partnership.
- The Stryker deal is expected to feature in high-level bilateral dialogues, including the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Washington DC and during engagements at Aero India.
Challenges and Reservations:
- Some Indian defence officials have flagged concerns, noting that similar ICVs have been developed by Indian private companies.
- Delays in previous U.S. defence exports (e.g., F-404 jet engines for LCA-Mk1A) have also raised caution regarding timelines and reliability.
Iskander-M

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant defense development with wide-ranging geopolitical implications, the Russian Federation is preparing to mass-produce the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missile, a new-generation weapon system with enhanced range and destructive capabilities. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to upgrade its missile arsenal amid ongoing tensions with NATO, especially in the context of the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features and Strategic Purpose
The 9K720 Iskander-M, developed by the Machine-Building Design Bureau (Kolomna), is a medium-range tactical ballistic missile with an effective range of up to 1,000 kilometers. It is capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads, making it a versatile and high-impact weapon in regional conflict scenarios.
- The missile is precision-targeted and designed to neutralize high-value enemy assets, including NATO’s military infrastructure in Eastern Europe, especially in Ukraine.
- The production of the upgraded missile, unofficially referred to as the Iskander-1000, is expected to begin in full swing by 2025.
- The missile is reported to be highly destructive, with the ability to conduct deep strikes with minimal detection, offering Russia a tactical advantage in asymmetric warfare.
Deployment of Oreshnik Missile Systems in Belarus
In a parallel development, Russia has confirmed the deployment of Oreshnik medium-range ballistic missile systems in Belarus, a strategic ally. This decision follows agreements between the Russian and Belarusian leadership, reinforcing the military integration under their collective defense pact.
- The Oreshnik system, though less publicly detailed than the Iskander, is designed for tactical use and contributes to enhancing Russia’s regional defense shield.
- According to Russian foreign ministry officials, Belarus already hosts a joint Regional Forces Group, non-strategic nuclear weapons, and modern Russian defense systems.
- The positioning of these systems near NATO’s eastern borders heightens tensions with Western powers, particularly the United States, Poland, the Baltic States, and the European Union.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The Iskander-M and Oreshnik missile programs are part of Russia’s strategic doctrine to deter NATO's influence and reassert its military dominance in Eastern Europe. These deployments are:
- Likely to escalate NATO-Russia tensions, increasing the risk of a regional arms race.
- Expected to complicate European security dynamics, especially in Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states, which are seen as potential frontlines.
- Raising the prospect of further military escalation in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Prompting NATO countermeasures, including deployment of missile defense systems and increased troop presence near Eastern borders.
Brucellosis Outbreak in Kerala
- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
An eight-year-old girl, Shasa Fathima, from Kottakkal in Malappuram district, Kerala, recently died after undergoing nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis at the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode. This tragic incident has renewed public health concerns regarding zoonotic infections in India.
What is Brucellosis?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), brucellosis is a bacterial disease caused by various species of the genus Brucella. The bacteria primarily infect: cattle, swine, goats, sheep & dogs.
Humans typically contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected animals or their secretions (blood, placenta, fetus, uterine fluids)
- Ingestion of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurised milk and cheese
- Inhalation of airborne bacteria (e.g., in lab or farm environments)
Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare, as per WHO guidelines.
Symptoms and Incubation Period
- The disease presents a wide spectrum of symptoms: fever, weakness, weight loss, general discomfort or malaise.
- In many cases, symptoms may be mild or go undiagnosed. The incubation period ranges from one week to two months, most commonly between two to four weeks.
At-Risk Populations
- Brucellosis can affect individuals of all age groups. However, certain occupational groups are at higher risk, including: farmers and dairy workers, butchers, hunters, veterinarians, laboratory personnel. These individuals are often exposed to animal blood and reproductive fluids, which are primary modes of transmission.
Status in Kerala
Kerala has reported sporadic cases of brucellosis in recent years. In 2023, cases emerged from Kollam (July) and Thiruvananthapuram (October). While the disease is not new to the state, fatalities remain rare.
In response, the Department of Animal Husbandry has initiated awareness campaigns for dairy farmers and conducted milk sample testing across cooperative societies to monitor possible sources of infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics:
- Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days)
- Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days)
Effective preventive measures include:
- Vaccination of livestock (cattle, goats, sheep)
- Pasteurisation of milk and dairy products before human consumption
- Public awareness campaigns on the dangers of consuming unpasteurised animal products
- Regulatory policies on the sale of raw milk
Bryospilus Bharaticus
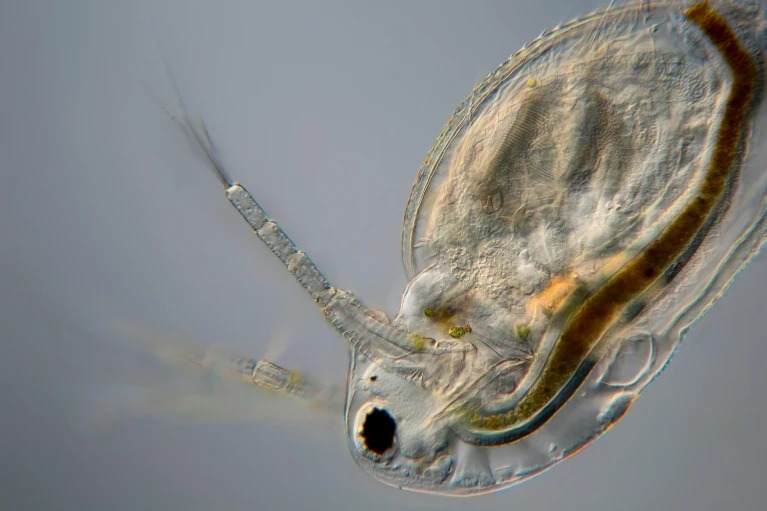

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
A new species of water flea, Bryospilus (Indobryospilus) bharaticus n. sp., was recently discovered from moss growth on the walls of the Korigad Fort near Pune, Maharashtra.
This marks the first recorded discovery of the genus Bryospilus in Tropical Asia, underscoring the ecological uniqueness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage biodiversity hotspot.
Taxonomic and Morphological Highlights
- It belongs to the genus Bryospilus, a group of tiny crustaceans known as water fleas, which typically inhabit rivers, ponds, and pools.
- The species displays adaptations for semi-terrestrial life, notably using its antennae with large spines for crawling through thick, debris-laden water films on moss surfaces.
- It lacks a main eye—an evolutionary adaptation to low-light habitats where color vision is unnecessary for foraging.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance
- The genus Bryospilus includes species found in semi-terrestrial habitats in rainforests of West Africa, South and Central America, and New Zealand, making this Indian discovery a significant biogeographical addition.
- The organism’s relatives are typically found in littoral (vegetated) zones of water bodies, whereas some occur in open waters.
- The researchers suggest that ancestors of this species existed on the Indian subcontinent prior to the breakup of Gondwanaland, around 200 million years ago, hinting at Bryospilus bharaticus as a potential Gondwanan relict species.
- Each known Bryospilus species has been isolated to a specific former Gondwanan continent, reinforcing the evolutionary legacy of this find.
Research and Conservation Implications
- The discovery was part of an ongoing survey of underexplored crustacean taxa in the Western Ghats, led by Sameer Padhye and Kan Van Damme, and published in the Journal of Crustacean Biology (Oxford Academic, Sept 2024).
- The species was found in pristine, undisturbed moss habitats on Deccan Plateau hill forts, highlighting the importance of conserving such microhabitats.
- Zooplankton like water fleas are highly sensitive to environmental changes and serve as bioindicators of ecological health. The presence of B. bharaticus indicates low human disturbance in its habitat.
- The authors warn that air pollution and habitat disturbance could threaten these fragile ecosystems and stress the urgency of habitat protection, especially for organisms invisible to the naked eye.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed an innovative “self-actuating” drug delivery system that targets rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by delivering therapeutic agents only when needed. This approach offers a revolutionary alternative to conventional systemic treatments.
About Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Definition: RA is a chronic autoimmune and inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, particularly the joints, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Hands, wrists, and knees — often multiple joints simultaneously.
- Symptoms:
- Inflammation of joint lining
- Chronic pain and joint deformity
- Unsteadiness or balance issues
- May affect lungs, heart, and eyes
- Cause: The exact cause remains unknown, but it involves an immune response attacking the body’s own tissues.
- Traditional Treatment:
- Involves Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate
- Requires frequent dosing
- May lead to systemic side effects and inefficient drug retention
Breakthrough: Self-Actuating Drug Delivery System
Key Features:
- Targeted Drug Release: Releases medication only in response to biochemical signals in the inflamed synovial environment of RA-affected joints.
- Precision and Safety: Reduces side effects by limiting drug release to flare-ups, minimizing exposure to unaffected areas.
- Main Drug Used: Methotrexate, a widely used anti-rheumatic drug.
Mechanism:
- Microspheres are engineered using polymer-lipid hybrid micro-composites:
- Lipid Component (Soya Lecithin): Ensures high drug encapsulation efficiency.
- Polymer Component (Gelatin): Reacts to Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) — enzymes present during RA inflammation.
- Action:
- Enzymes like MMP-2 and MMP-9 increase during RA flare-ups.
- These enzymes cleave the gelatin, triggering controlled, pulsatile release of methotrexate.
- Outcome in Animal Studies:
- Reduced joint swelling and cartilage damage
- Promoted joint repair
- Improved drug bioavailability and retention in joints
Significance
- Improved Patient Outcomes:
- Long-lasting relief with fewer doses
- Reduced systemic toxicity
- Personalized therapy based on inflammation levels
- Enhanced joint function and slower disease progression
- Research Publication: The findings were published in the journal Biomaterial Advances.
Wider Applications
- Potential Use in:
- Other inflammatory conditions like synovitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Veterinary medicine for arthritis in animals
- Regenerative medicine and personalized drug delivery
Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
As of early 2025, 60% of the construction of the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is complete. The telescope is expected to begin its first scientific observations by the end of 2028.
About ELT
The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is poised to become the world’s most powerful ground-based optical and infrared telescope, with revolutionary capabilities to explore the universe.
- Location: Cerro Armazones, Atacama Desert, northern Chile
- Altitude: 3,046 meters above sea level
- Managing Body: European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Project Cost: Approximately $1.51 billion (around 1.3 billion euros)
- Completion Target: Late 2020s
- Primary Mirror: Diameter of 39 meters (128 feet) — the largest of its kind
- Constructed from 798 hexagonal segments, each 1.5 m across and 5 cm thick
Key Scientific Objectives
- Exoplanet Exploration
- Direct imaging of Earth-like exoplanets in habitable zones of nearby stars
- Analysis of atmospheric biosignatures such as oxygen, water vapor, and methane, aiding the search for extraterrestrial life
- Understanding the Early Universe
- Observation of the first stars and galaxies formed post-Big Bang
- Investigation of dark matter and dark energy, crucial for understanding cosmic expansion and the universe’s fate
- Detailed Study of Stars and Galaxies
- Identification and characterization of individual stars in distant galaxies
- Analysis of the formation, evolution, and structure of galaxies over cosmic time
- Black Holes and Cosmic Structures
- Study of supermassive black holes at galactic centers
- Understanding their role in galaxy dynamics and structure
Why Chile’s Atacama Desert?
- Dry Climate: Very low humidity and cloud cover, ensuring clearer skies
- High Altitude: Thin atmosphere reduces atmospheric interference with incoming light
- Minimal Light Pollution: Remote location offers dark skies critical for deep-space observation
- Dome Structure: Protects sensitive instruments from harsh desert conditions
About the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Nature: Leading intergovernmental science and technology organization in the field of astronomy
- Headquarters: Garching, Germany
- Members: 16 countries including Austria, Belgium, Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom
- Facilities in Chile:
- La Silla
- Paranal
- Chajnantor
- Mandate: Design, construction, and operation of advanced ground-based telescopes to promote international collaboration and facilitate path-breaking astronomical research
Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Union Finance Minister announced a five-year Cotton Mission to boost productivity, sustainability, and promotion of Extra-Long Staple (ELS) cotton in India, aiming to reduce import dependency and strengthen the high-end textile sector.
What is Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton?
- Definition: ELS cotton refers to cotton varieties with fibre lengths of 30 mm or more, renowned for their superior softness, strength, durability, and premium quality.
- Botanical Origin: Derived primarily from the species Gossypium barbadense, commonly known as Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Distinguishing Cotton Types by Fibre Length
Type Fibre Length Species Quality Uses Yield per Acre
Short Staple < 25 mm Gossypium hirsutum Coarser Low-cost textiles High
Medium Staple 25–28.6 mm Gossypium hirsutum Moderate Everyday fabrics 10–12 quintals
Extra-Long 30 mm & above Gossypium barbadense Superior Luxury textiles 7–8 quintals
Staple (ELS)
Special Characteristics of ELS Cotton
- Softer & Smoother: Ideal for premium, luxury clothing.
- Stronger & More Durable: Resistant to wear and tear.
- Resistant to Pilling: Maintains smoothness over time.
- Luxurious Finish: Produces fine yarns with a natural sheen.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Retains natural texture and quality.
Global and Indian Production Landscape
- Origin: Native to South America.
- Globally Grown In:
- Egypt, China, Australia, Peru – leading producers.
- In India:
- Cultivated in Atpadi Taluka (Sangli, Maharashtra), around Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), and in parts of Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Grown mostly in rain-fed areas with warm climates and fertile soil, aiding fibre quality.
Challenges in ELS Cotton Cultivation in India
- Low Yield: ELS cotton yields 7–8 quintals/acre, significantly lower than medium staple varieties (10–12 quintals/acre).
- Market Linkage Deficit: Farmers struggle to fetch premium prices for ELS cotton due to weak market access and lack of dedicated procurement infrastructure.
- Technological Gaps: Limited access to improved seed varieties, agronomic practices, and technologies like HtBT (Herbicide-tolerant Bt) cotton.
- Import Dependency: India imports 20–25 lakh bales annually, accounting for ~90% of its ELS cotton requirements, to meet demand from the premium textile industry.
Significance of the Five-Year Cotton Mission
- Aimed at:
- Enhancing productivity and sustainability of ELS cotton.
- Reducing import dependence through indigenous development.
- Strengthening high-value textile exports by ensuring reliable ELS supply.
- Supports:
- Farmer income enhancement through value-added cultivation.
- Research and development in ELS cotton seed technology.
- Improved extension services, supply chain development, and market support mechanisms.
Kolleru Lake
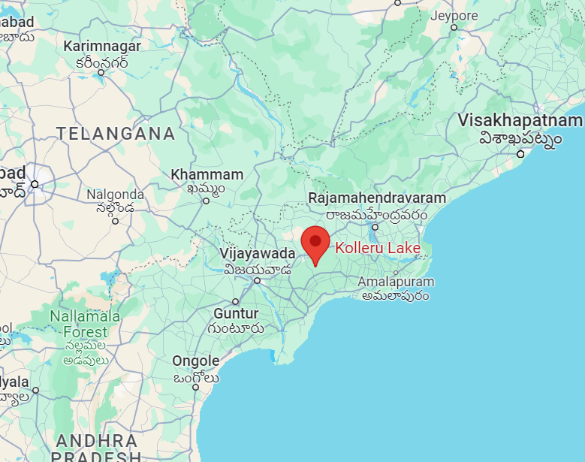
- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Southern Zonal Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently restrained the Andhra Pradesh government from proceeding with six proposed infrastructure projects in the Kolleru wetland area, citing violations of environmental protocols and lack of statutory clearances.
About Kolleru Lake
- Location: Northeastern Andhra Pradesh, between the Krishna and Godavari river deltas, near Eluru city.
- Type: One of Asia’s largest shallow freshwater lakes, covering an area of 308 sq. km.
- Hydrology:
- Fed by Budameru and Tammileru rivers.
- Drains into the Bay of Bengal via Upputeru river (a tidal water channel).
- Acts as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the Krishna and Godavari river systems.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1999 and a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- Designated as an Important Bird Area (IBA) due to the presence of over 50,000 waterfowl annually.
- Lies on the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), a major migratory bird route.
- Key Avian Species:
- Grey Pelican (indicator species), Siberian Cranes, Glossy Ibis, Open-billed Stork, Purple Moorhen, Painted Storks.
Kolleru Bird Sanctuary
- A protected wetland marsh habitat within the Kolleru Lake region.
- Supports diverse aquatic flora and fauna, serving as a crucial ecosystem for migratory and resident bird species.
Infrastructure Projects and Legal Challenges
- The projects were proposed under the entity "A.P. Krishna – Kolleru Salinity Mitigation Projects Corporation Limited" with a total capital outlay of approximately ?2,952 crore.
- The plans included construction of three regulators-cum-roads across the Upputeru river and other barrages, regulators, and sluices, falling within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ).
- The Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Department (WRD) issued G.O. Ms. No. 63 (dated 2nd December 2020) authorizing the project.
Grounds for NGT Intervention
- Key objections included:
- Absence of scientific or ecological studies.
- Lack of consultations with wetland experts, wildlife conservationists, and hydrologists.
- No clearances obtained from:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- A.P. Coastal Zone Management Authority (CZMA)
- A.P. Pollution Control Board (PCB)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
NGT Observations and Ruling
- The tribunal emphasized the need for comprehensive evaluation of ecological and hydrological impacts before proceeding.
- It cited potential threats to the lake’s ecosystem, including:
- Disruption to natural hydrology.
- Loss of biodiversity and eco-sensitive habitats.
- The NGT ruled that the projects should not proceed unless fully compliant with environmental laws and backed by appropriate expert assessments.
- The ruling reinforced India's obligations under the Ramsar Convention and domestic environmental legislation, stressing the urgent need to protect the integrity of the Kolleru ecosystem.
Henipavirus

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
A henipavirus, specifically the Camp Hill virus, has been detected in North America for the first time. This discovery in northern short-tailed shrews—a small mammal species found commonly in Canada and the U.S.—raises concerns over a potential zoonotic disease outbreak.
About Henipavirus
- Virus Type: Henipaviruses are zoonotic, negative-sense RNA viruses.
- Family: Paramyxoviridae.
- Natural Hosts: Pteropid fruit bats (commonly known as flying foxes).
- Other Hosts: Capable of infecting various mammals, including humans, horses, pigs, and shrews.
Notable Henipaviruses:
- Hendra virus (HeV):
- First identified in Australia.
- Mortality rate: Up to 70%.
- Nipah virus (NiV):
- Found in Southeast Asia, including Malaysia and Bangladesh.
- Case fatality rate ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on surveillance and clinical care.
Symptoms and Disease Progression
- Initial symptoms: Fever, dizziness, headache, and muscle pain (myalgias).
- Advanced symptoms: Respiratory issues, encephalitis (brain inflammation), confusion, abnormal reflexes, seizures, and coma.
- Relapsing encephalitis may occur months or years after apparent recovery.
- Fatality Risk: High, primarily due to encephalitis and multi-organ failure caused by damage to small blood vessels (microinfarction) in organs like the brain, liver, and kidney.
Why are Henipaviruses so dangerous?
- Henipaviruses produce proteins that:
- Suppress the innate immune system.
- Block interferon-stimulated antiviral responses, aiding viral replication.
- Act as virulence factors, allowing widespread infection and severe outcomes.
Modes of Transmission
- Animal-to-human:
- Direct contact with infected animals (e.g., fruit bats, pigs, horses, shrews).
- Consumption of contaminated food or water (e.g., raw date palm sap in Nipah outbreaks).
- Human-to-human: Via bodily fluids, close contact, or respiratory droplets during caregiving.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment:
- No specific vaccine or antiviral currently exists.
- Management is symptomatic and supportive (respiratory support, ICU care).
- Prevention:
- Vaccination of horses (in HeV-risk regions like Australia).
- Avoiding contact with fruit bats and sick animals.
- Isolating infected individuals and animals to prevent spread.
India-Maldives Joint Military Exercise ‘Ekuverin’

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Ekuverin, a bilateral joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF), commenced in the Maldives on February 4, 2025. The exercise continues to reinforce defence and strategic ties between the two nations.
About Exercise Ekuverin
- Name Meaning: “Ekuverin” means ‘Friends’ in Dhivehi, the official language of the Maldives—symbolizing the deep and friendly defence partnership between India and the Maldives.
- First Conducted: The exercise was initiated in 2009 as part of annual bilateral defence cooperation.
- Venue Alternation: It is held alternatively in India and the Maldives every year.
- 2023 Edition: Conducted at Chaubatia, Uttarakhand from June 11 to 24.
- 2025 Edition: Being hosted in the Maldives.
Key Objectives and Features
- Military Interoperability: Enhances coordination and operational synergy between Indian and Maldivian armed forces.
- Counter-Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT): Focuses on joint tactical drills to counter modern asymmetric threats.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): Equips forces to respond effectively to natural disasters and humanitarian crises.
- Strengthening IOR Security: Reinforces regional maritime and strategic stability in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a key area of India’s strategic interest.
Significance for India-Maldives Relations
- Strategic Partnership: Builds mutual trust and defence preparedness, aligning with India’s “Neighbourhood First” policy.
- Capacity Building: Helps enhance the capability of the MNDF through joint training with a larger and more experienced Indian Army.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Plays a crucial role in maintaining peace, security, and freedom of navigation in the IOR.
India’s Defence Engagement with Southeast Asia
India actively conducts multiple bilateral and multilateral defence exercises with Southeast Asian countries to enhance defence diplomacy and promote a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
Key Defence Exercises with Southeast Asian Nations:
- Garuda Shakti: Special Forces exercise with Indonesia (Nov 2022, Sangga Buana Training Area).
- Mitra Shakti: Annual exercise with Sri Lanka, last held in 2022.
- VINBAX: India-Vietnam bilateral exercise; 3rd edition held in 2022.
- IMBEX: India-Myanmar bilateral exercise (last noted in 2017–18).
- Maitree: Joint annual military exercise with Thailand, conducted since 2006.
- CORPAT: Coordinated Patrols with Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia for maritime domain awareness and security.
- AIME 2023: The first ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise, conducted in May 2023, involving navies from India and ASEAN nations (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Golden-headed Cisticola
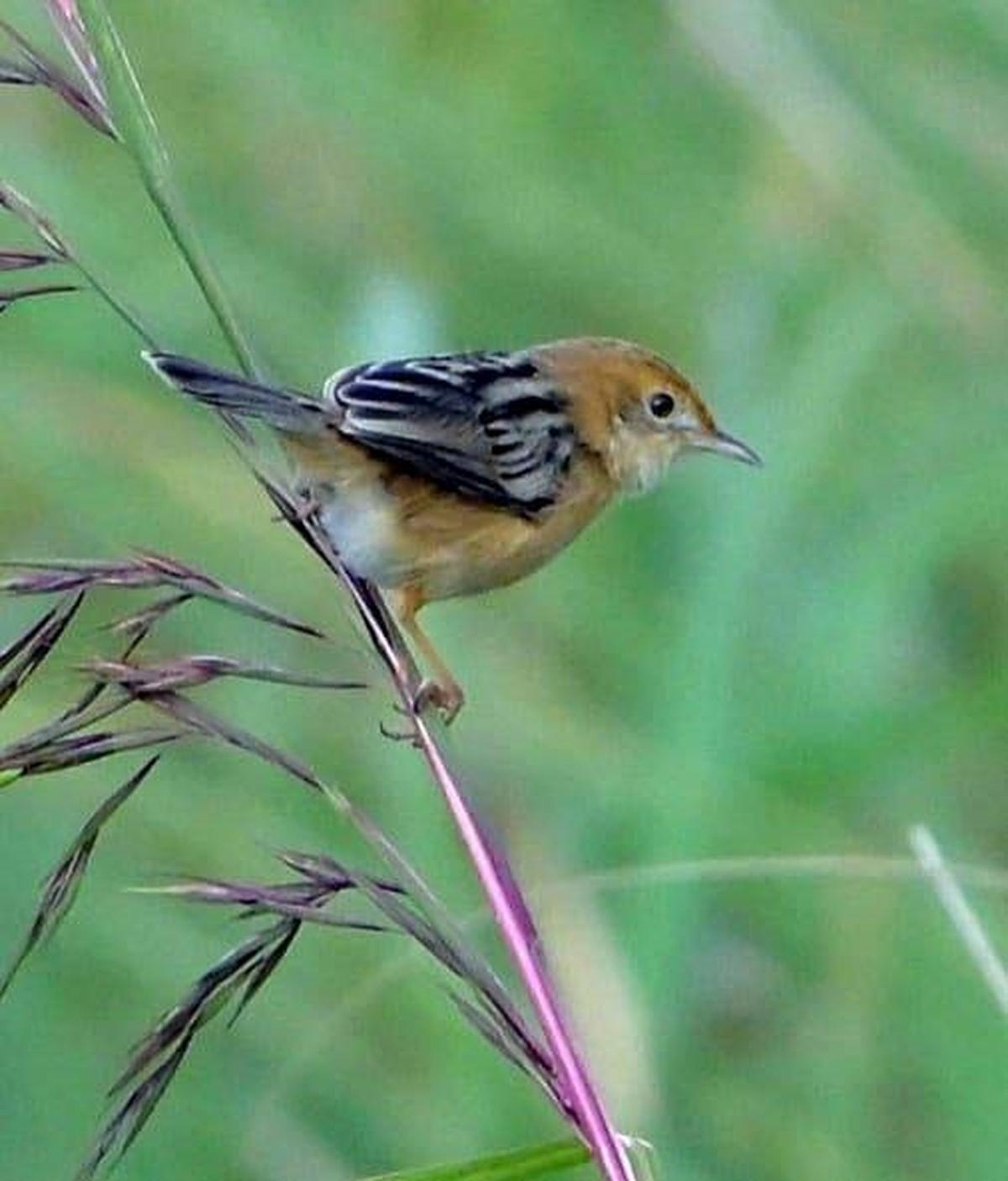

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
RBI Digital Payments Index (DPI)

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Digital Payments Index (DPI) rose to 465.33 as of September 2024, up from 445.5 in March 2024, indicating a sustained increase in the adoption and penetration of digital payments across India.
About the RBI-DPI
- Launched: January 2021
- Constructed by: Reserve Bank of India
- Purpose: To measure the extent and progress of digitisation of payments in India.
- Base Period: March 2018 (DPI Score = 100)
- Frequency of Publication: Semi-annually (March and September)
Significance of the Index
- Acts as a quantitative tool to monitor India’s progress in achieving a less-cash economy.
- Provides stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers a composite view of digital payment trends.
- Helps identify policy focus areas and gaps in digital infrastructure and adoption.
- Supports the goals of financial inclusion, innovation, and digital public infrastructure.
Recent Trends
- September 2024 DPI Score: 465.33
- March 2024 DPI Score: 445.5
- Implication: Demonstrates continued momentum in digital payment adoption, driven by improved payment infrastructure and payment performance nationwide.
Structure of the RBI-DPI
The index is composed of five broad parameters, each with defined weightages and sub-indicators:
Parameter Weightage Description
1. Payment Enablers 25% Internet/mobile penetration, bank account ownership, Aadhaar usage.
2. Payment Infrastructure – Demand Side 10% Number of debit/credit cards, user demand for digital options.
3. Payment Infrastructure – Supply Side 15% Availability of POS machines, ATMs, bank branches, QR codes.
4. Payment Performance 45% Actual volume and value of digital transactions, currency usage trends.
5. Consumer Centricity 5% Digital payment awareness, fraud prevention, grievance redressal.
Each parameter is further broken down into measurable sub-indicators, offering a comprehensive framework for assessment.
Why RBI-DPI Matters for India
- Digital Transformation: Encourages the shift from cash to digital payments, aligning with the goals of Digital India.
- Policy Impact Assessment: Evaluates the effectiveness of regulatory and policy interventions in the payment ecosystem.
- Infrastructure Development: Reflects the outreach of digital payment infrastructure, aiding targeted investments.
- Financial Inclusion: Helps assess how digital modes are reaching the underserved and unbanked populations.
- Data-Driven Governance: Facilitates evidence-based decision-making in financial sector reforms.
SwaRail SuperApp
- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Railways has launched a unified mobile application, SwaRail, currently in beta testing as of January 31, 2025.
This initiative aims to streamline access to Indian Railways services and enhance user experience by consolidating various apps into a single digital platform.
Key Highlights
What is SwaRail?
- SwaRail is a SuperApp developed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- It serves as a comprehensive, one-stop solution for a wide range of Indian Railways services.
- The app is currently in beta testing and is available on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Objective
- To integrate multiple railway-related services under a unified platform.
- To reduce app clutter and device storage consumption.
- To improve user experience through a seamless and intuitive interface.
Developed By: Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)
- CRIS is an organization under the Ministry of Railways.
- It combines IT expertise with railway operational experience.
- CRIS is responsible for developing and maintaining software for core railway functions.
Services Offered via SwaRail
The SuperApp merges functionalities of multiple existing apps, offering:
- Ticketing Services
- Reserved ticket booking
- Unreserved and platform ticket booking
- Freight & Parcel Enquiries
- Parcel booking status
- Freight services information
- Passenger Enquiries
- Real-time train status
- PNR enquiry (along with associated train details)
- Train schedules
- Onboard Services
- Food ordering while traveling
- Complaint redressal via Rail Madad
Notable Features of the SuperApp
Feature Description
Single Sign-On Access all services using a single set of credentials
Unified App Combines multiple previously separate apps (e.g., IRCTC RailConnect, UTS)
Integrated Interface Displays consolidated data like PNR + train info on the same screen
Easy Onboarding Existing users can log in with RailConnect/UTS credentials
Multiple Login Modes Supports m-PIN, biometric authentication, and OTP-based guest login
Smart Wallet Integration Auto-linking of R-Wallets from UTS App for ticket booking transactions
User-Centric Approach
- The app is being actively tested, and users are encouraged to provide feedback during the beta phase.
- CRIS is monitoring performance and issues for improvement before the final public release.
- The government envisions technological integration to ensure efficient, smarter, and citizen-friendly rail services.
GARBH-INi-DRISHTI

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
India has made a significant stride in biomedical research and public health with three major developments led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) in Faridabad, Haryana.
Key Highlights:
India’s First Ferret Research Facility
- Inaugurated by: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.
- Location: NCR Biotech Science Cluster, Faridabad.
- Purpose: To bolster India's capacity in:
- Vaccine development
- Therapeutic testing
- Research on emerging infectious diseases like influenza, COVID-19, and tuberculosis.
- Significance:
- Strengthens India’s pandemic preparedness.
- Positions India among the select nations with advanced biosafety labs using ferrets—ideal models due to respiratory systems similar to humans.
Launch of GARBH-INi-DRISHTI Data Repository
- Platform: DBT Data Repository and Information Sharing Hub under the GARBH-INi program.
- Dataset Size: Over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers.
- Developed by: THSTI with collaboration from top Indian research institutions and hospitals.
- Features:
- Comprehensive clinical data, medical images, and biospecimens.
- Secure, controlled access promoting ethical research.
- Facilitates predictive tools for preterm birth and maternal health complications.
- Utility:
- Empowers both national and global researchers.
- Informs maternal and neonatal health interventions.
- Supports evidence-based policymaking in public health.
- Program Genesis:
- GARBH-INi (2014): Interdisciplinary initiative to understand preterm birth risks—biological and non-biological.
- Part of: Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission under the UNaTI initiative.
Technology Transfer Agreement with Industry
- Agreement Between: THSTI and Sundyota Numandis Probioceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
- Technology Transferred:
- Lactobacillus crispatus, a genetically defined synthetic microbial consortium.
- Isolated from reproductive tracts of Indian women enrolled in GARBH-INi.
- Applications:
- Nutraceuticals and probiotics for reproductive health.
- Potential treatments for vaginal infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Significance:
- Promotes microbiome-based interventions.
- Bridges lab-to-market gap, boosting the biomanufacturing ecosystem.
Strategic Implications for India
- Scientific Diplomacy & Global Standing: With cutting-edge facilities and open data-sharing platforms, India emerges as a key player in global biomedical research.
- Public Health Impact: Supports targeted, data-driven maternal health policies and pandemic response frameworks.
- Innovation Ecosystem: Reflects the convergence of academic research, industry collaboration, and translational science.
World Wetlands Day 2025

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2nd February to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
India has been a signatory to the Convention since 1982 and has actively worked towards the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands—critical ecosystems that serve as biodiversity hotspots, natural flood buffers, and carbon sinks.
Theme 2025: "Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future"
The 2025 theme emphasizes collaborative efforts to protect wetlands to ensure ecological sustainability, biodiversity preservation, and long-term human well-being. It highlights the need for integrated management and foresight in conservation strategies.
Key Event: Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organized the national-level celebrations of World Wetlands Day 2025 at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site in Gonda district, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of the Site
- Comprises two rain-fed oxbow lakes—Parvati and Arga—located in the terai region of the Gangetic plains.
- Supports endangered and critically endangered species like the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and Egyptian vulture.
- Attracts migratory birds such as Eurasian coots, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards.
- Threatened by invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- The nearby Tikri Forest is being developed as an eco-tourism site, and a nature-culture tourism corridor is planned between Ayodhya and Devi Patan.
Cultural and Economic Value
- The area includes heritage sites such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, enhancing its potential as a religious and cultural tourism hub.
- A MoU between Amazon and ARGA (UP Government initiative) aims to empower women entrepreneurs through digital training and market access under Amazon’s Saheli programme.
India's Wetland Landscape and New Ramsar Sites (2025 Update)
India’s tally of Ramsar Sites has risen to 89, with four new additions:
- Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Theerthangal – Tamil Nadu
- Sakkarakottai – Tamil Nadu
- Khecheopalri – Sikkim (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar Sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
- Total area under Ramsar protection in India is now approximately 1.358 million hectares.
Amrit Dharohar Initiative
Launched in June 2023, the Amrit Dharohar initiative promotes conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar Sites over three years. It aligns with Budget 2023–24 announcements and focuses on:
- Species and Habitat Conservation
- Nature Tourism
- Wetlands-based Livelihoods
- Wetlands and Carbon Mitigation
The initiative encourages convergence among central ministries, state authorities, and community stakeholders.
Workshops and Public Engagement
A regional workshop for Northern States was organized on 1st February 2025, with participants from nine states and UTs, highlighting collaborative models in wetland management. The main event also included:
- Exhibitions on eco-friendly products, wetland conservation, and green skills.
- Launch of publications like the Integrated Management Plan for Parvati Arga, Factbook of India’s 85 Ramsar Sites, and Development of Van Taungya Villages.
- Felicitation of painting, quiz, and Nukkad Natak competition winners, promoting grassroots awareness.
Significance of Wetlands in India
Wetlands are water-covered ecosystems, either permanently or seasonally flooded. They:
- Support rich biodiversity, including migratory birds and aquatic species.
- Recharge groundwater and regulate floods.
- Provide livelihoods through fisheries and tourism.
- Act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate change mitigation.
Major Threats
- Pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
- Encroachment and urbanization
- Invasive species
PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 has accorded the highest-ever allocation of ?32,646 crore to the Ministry of Labour and Employment, representing an 80% increase over the previous year's Revised Estimates.
The enhanced funding reflects the government's strategic focus on employment generation and strengthening social security mechanisms for unorganised workers and gig economy participants.
Key Budgetary Highlights:
1. Employment Generation Scheme:
- ?20,000 crore has been allocated to the new Employment Generation Scheme, double the previous year’s allocation.
- The scheme is aimed at fostering large-scale employment opportunities and skilling across various sectors.
2. Employees’ Pension Scheme:
- Allocation increased by ?300 crore, strengthening retirement security for formal sector workers.
3. PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM):
- Allocation increased by 37% compared to last year.
- The scheme provides old-age social security to unorganised workers through a voluntary, contributory pension model.
About Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)
Objective:
To provide minimum assured pension and social security to unorganised sector workers, including street vendors, construction workers, agriculture laborers, domestic workers, etc.
Eligibility:
- Indian citizen aged 18–40 years
- Monthly income below ?15,000
- Not a member of EPFO, ESIC, or NPS
Key Features:
- Minimum Assured Pension: ?3,000 per month after 60 years of age.
- Voluntary and Contributory Scheme:
- Contributions made via auto-debit from bank accounts.
- 50:50 matching contribution by the Central Government.
- Pension Fund Management:
- Administered by the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Implemented by LIC and CSC e-Governance Services India Ltd.
- LIC acts as the Pension Fund Manager.
Family Pension Provision:
- In case of subscriber's death:
- Spouse receives 50% of the pension amount as family pension.
- If death occurs before 60 years, the spouse may continue contributions or exit the scheme as per norms.
Exit Provisions:
- Exit before 10 years: Subscriber's share with accrued interest is returned.
- Exit after 10 years but before 60 years: Entire contribution with interest returned to the subscriber.
Social Security for Gig Workers
Recognising the gig economy as a critical pillar of India’s modern workforce, the government has taken key steps to enhance their social security:
- e-Shram registration
- Provision of unique identity cards
- Access to healthcare benefits under PM Jan Arogya Yojana
- Expected to benefit around 1 crore gig workers
National Geospatial Mission
- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the launch of a National Geospatial Mission in the Budget 2025-26.
Key Highlights:
Objective: To modernize land records, enhance urban planning, and create a robust geospatial infrastructure to support India’s broader development goals, including sustainable growth, efficient governance, and improved public service delivery.
Key Features of the Mission:
- Modernization of Land Records:
- Digitization and updation of land records using geospatial technology.
- Aim to reduce land disputes and promote efficient and transparent land use.
- Urban and Infrastructure Planning:
- Provides high-resolution geospatial data for informed urban planning.
- Supports better design and execution of infrastructure through integration with the PM Gati Shakti framework.
- Development of National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (NGDI):
- Integrates geospatial data from multiple departments and ministries.
- Enables seamless access and interoperability for users across sectors.
- Open Geospatial Data Policy:
- Encourages private sector participation by allowing access to non-sensitive, high-resolution data.
- Reduces reliance on foreign geospatial data providers.
- Sectoral Impact:
- Agriculture: Precision farming, resource mapping, and yield optimization.
- Disaster Management: Enhances early warning systems and response planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Facilitates conservation, deforestation tracking, and ecosystem health analysis.
- Transportation: Improves logistics, routing, and infrastructure placement.
- Climate Monitoring: Aids in data-driven climate action and adaptation planning.
- Technological Integration:
- Utilizes emerging technologies such as AI, drones, and quantum computing for spatial data collection and analysis.
- Promotes research and development in geospatial science to drive innovation.
- Support to Private Sector:
- Anticipated growth in demand for services from geospatial startups, drone companies, and mapping enterprises.
- Strengthens India’s indigenous geospatial capability aligned with the booming global geospatial market (projected to reach $1,064 million by 2030).
Significance and Alignment with National Goals:
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in land governance.
- Contributes to sustainable urban development.
- Aligns with Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing data dependency on foreign sources.
- Acts as a foundational enabler for India’s development agenda, particularly in areas of resource management, climate resilience, and national security.
PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
- Recently, the Union Government has introduced the PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana which aims at enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Objective: To boost agricultural productivity, modernize farming practices, and enhance rural prosperity by addressing region-specific challenges in backward agricultural districts.
Key Features:
- Integrated Approach:
- Consolidates multiple existing agricultural schemes under one umbrella for greater synergy and implementation efficiency.
- Draws inspiration from the Aspirational Districts Programme, which has improved socio-economic outcomes in backward regions.
- District-Specific Interventions:
- Focuses on districts with:
- Low crop productivity
- Moderate crop intensity
- Limited institutional credit access
- Implements customized strategies based on the unique challenges of each region.
- Focuses on districts with:
- Core Focus Areas:
- Enhancing farm productivity through modern technology.
- Improving irrigation infrastructure.
- Increasing formal credit availability to reduce dependence on informal moneylenders.
- Promoting crop diversification and sustainable agriculture.
- Strengthening post-harvest infrastructure like storage at Panchayat and block levels.
- Technology-Driven Solutions:
- Encourages adoption of climate-resilient and precision farming.
- Supports digital access to credit and advisory services.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Strengthens linkages with government financial programs, microfinance institutions, and banks.
- Aims to reduce rural indebtedness and promote formal financial participation.
- State and Centre Collaboration: Implementation will involve both central and state governments, ensuring localized solutions with national support.
- Reducing Distress Migration: By improving rural livelihoods and opportunities, the scheme aims to make migration a choice rather than a compulsion.
Guneri Inland Mangrove

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In 2024, the Gujarat government declared the Inland Mangrove of Guneri, located in Kutch district, as the first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002. The declaration followed a recommendation by the Gujarat Biodiversity Board.
Key Features of Guneri Inland Mangroves:
- Location: Guneri village, Lakhtar tehsil, Kutch district, Gujarat.
- Area: 32.78 hectares.
- Distance from Sea: ~45 km from the Arabian Sea; ~4 km from Kori Creek.
- Nature: Inland (non-coastal) mangrove ecosystem — one of only eight such sites globally and the last remaining in India.
- Terrain: Flat land resembling a forest; no tidal influence or sludge typically seen in coastal mangroves.
- Water Source: Sustained by groundwater retained in limestone deposits; no direct contact with seawater.
Ecological and Geological Significance:
- Possibly originated from:
- Miocene marine transgression, or
- Along the ancient Saraswati River, believed to have flowed in the Great Rann of Kutch around 3000–4000 BCE.
- Limestone formations in western Kutch provide continuous subsurface water flow, enabling survival of this unique mangrove system.
Biodiversity:
- Habitat to:
- 20 migratory bird species
- 25 resident migratory avifaunal species
- Acts as a vital ecosystem for local and seasonal wildlife.
Mangroves in India – 2024 Snapshot:
- As per the “Red List of Mangrove Ecosystems” (May 22, 2024):
- India has 3% of South Asia’s mangrove cover.
- Total mangrove area: 4,975 sq km (0.15% of India's land area).
- Increase: 54 sq km (1.10%) since last assessment.
- State-wise share:
- West Bengal: 42.45% (notably South 24 Parganas & Sundarbans)
- Gujarat: 23.66% (with highest increase: 37 sq km)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 12.39%
Legal Framework:
- Declared under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, which empowers state governments to notify BHS after consulting local self-government bodies.
- A local Biodiversity Management Committee (BMC), including representatives from self-governance institutions, will oversee protection and conservation.
- This provides a formal structure for site management, previously absent.
Conservation Measures:
- Training programs for local and tribal communities along with forest officials.
- A management plan will be implemented to preserve the unique flora and fauna.
National Manufacturing Mission

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
- The National Manufacturing Mission (NMM) has been launched to accelerate India’s transition into a global manufacturing hub.
- This mission is a key component of the Make in India initiative and aims to raise the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP from 17% to 25% by 2025.
Scope & Coverage
- Targets small, medium, and large industries across sectors.
- Provides a comprehensive support framework involving policy guidance, execution roadmaps, and governance structures for central ministries and state governments.
Five Core Focus Areas:
- Ease and cost of doing business
- Skilling for future-ready jobs
- Support for a dynamic MSME sector
- Technology availability and innovation
- Enhancement of product quality
Clean Tech Manufacturing Focus
In line with India's sustainable development goals, the mission will promote domestic value addition and build robust manufacturing ecosystems for:
- Solar PV cells
- Electric vehicle (EV) batteries
- Motors and controllers
- Electrolyzers
- Wind turbines
- Very high-voltage transmission equipment
- Grid-scale batteries
Strategic Objective: Reduce reliance on Chinese imports and integrate India into global clean tech supply chains.
MSME Sector Support
- Credit Guarantee Cover for MSMEs increased from ?5 crore to ?10 crore.
- Revised Classification Criteria: Investment and turnover limits enhanced by 2.5x and 2x, respectively.
- Aims to empower MSMEs with greater access to credit and growth incentives.
Sector-Specific Measures
1. Footwear & Leather Sector
- A new Focus Product Scheme will support:
- Design capacity
- Component manufacturing
- Machinery for non-leather and leather footwear
- Expected Impact:
- Employment for 22 lakh persons
- Turnover of ?4 lakh crore
- Exports over ?1.1 lakh crore
2. Toy Manufacturing – National Action Plan for Toys
- Objective: Make India a global hub for innovative and sustainable toys.
- Strategy:
- Develop manufacturing clusters
- Promote skilling and innovation
- Strengthen the ‘Made in India’ brand in the global toy market
3. Food Processing – ‘Purvodaya’ Focus
- Establishment of a National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship and Management in Bihar.
- Purpose:
- Boost food processing in Eastern India
- Enhance value addition for farmers
- Create employment and entrepreneurial opportunities
Microplastics detected in Delhi’s Groundwater

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
A first-of-its-kind study, commissioned by the Delhi government and conducted by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), has revealed the presence of microplastics in groundwater across all 11 districts of Delhi. The interim findings, submitted in November 2024, also reported microplastics in Yamuna River water and soil samples along its banks.
Key Findings:
- Widespread Contamination: Microplastics were found in groundwater samples across Delhi, indicating potential contamination due to leaching from the Yamuna River.
- Additional Contamination: Microplastics were also detected in the Yamuna's water and riverbank soil, suggesting environmental pervasiveness.
- Water Usage Impact: Since Delhi relies on borewells and treated groundwater for drinking and domestic purposes, this contamination raises serious public health concerns.
- No Objection by Authorities: The Delhi government has not disputed the study’s interim findings; further post-monsoon analysis is underway, and a final report is expected later in 2025.
What Are Microplastics?
According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Definition: Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size
- Types:
- Primary Microplastics: Manufactured for use in cosmetics (e.g., microbeads) and textiles (e.g., microfibers from clothing, nets)
- Secondary Microplastics: Result from breakdown of larger plastics (e.g., bottles) due to sunlight, abrasion, and ocean waves
Environmental & Health Impacts:
- Persistence: Microplastics are non-biodegradable, mobile, and difficult to eliminate from natural ecosystems.
- Toxicity:
- Can adsorb harmful chemicals, making them more toxic
- Known to bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains
- Human Exposure: Microplastics can enter the human body via:
- Inhalation (air)
- Ingestion (water and seafood)
- Dermal absorption (through skin)
- Health Risks (UNEP Report – From Pollution to Solution, 2021):
- Potential effects on genetics, brain development, respiration, and placental health in newborns
- No global standard exists for safe microplastic limits in drinking water
Saffron Reedtail Damselfly
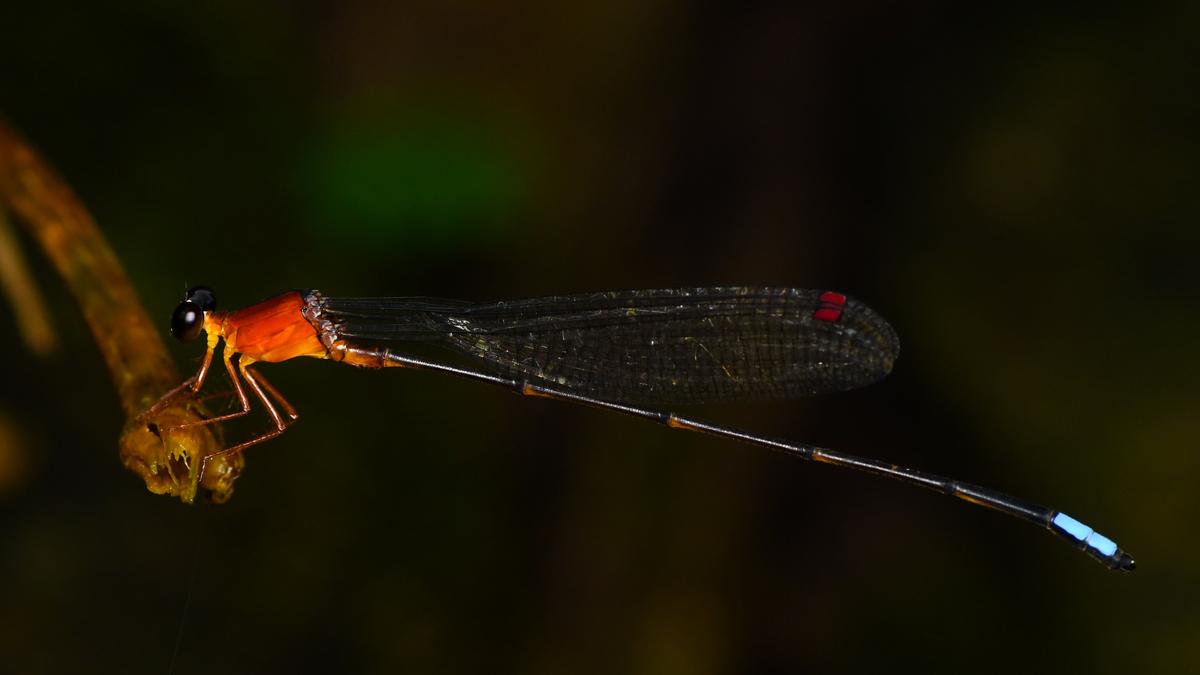

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Saffron Reedtail Damselfly, a rare and endemic species of the Western Ghats, has been recorded in Karnataka.
This significant discovery was made in Madhugundi village, Chikkamagaluru district, along the Nethravati River. The findings were published in the journal Entomon.
Key Facts:
- Scientific Name: Indosticta deccanensis
- Common Name: Saffron Reedtail
- Family: Platystictidae (commonly known as shadow damselflies)
- Appearance: Slender, delicate body with a characteristic saffron coloration
- Habitat: Prefers slow-moving forest streams surrounded by thick vegetation; requires pristine water quality
Ecological Significance:
- Indicator Species: Highly sensitive to environmental changes and pollution, indicating a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Implication:
- Previously recorded only in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The first sighting in Karnataka (northern Western Ghats) extends the known range of the species, suggesting it may be more widely distributed than earlier believed.
Conservation Relevance:
- The discovery underscores the ecological richness of the Madhugundi forests, which were severely affected by floods and landslides in 2019.
- Highlights the urgency to protect fragile ecosystems from deforestation, water pollution, and climate change, especially in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats.
About Damselflies (Order: Odonata):
- General Features:
- Predatory, aerial insects
- Slender bodies with net-veined wings
- Fly weakly compared to dragonflies
- Mostly inhabit freshwater habitats
Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 underscores the adverse impact of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) on public health, particularly among children and youth, and calls for urgent regulatory intervention.
Key Recommendations
- Stringent Front-of-the-Pack Labelling (FOPL): The Survey advocates for clear, enforceable FOPL rules to inform consumers, curb misleading nutrition claims, and restrict aggressive marketing, especially those targeted at children and adolescents.
- Stronger Role for FSSAI: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is advised to:
- Define UPFs clearly in regulation.
- Establish labelling standards.
- Monitor compliance of branded products.
- ‘Health Tax’ Proposal: The Survey proposes higher taxes on UPFs, especially brands engaging in excessive advertising, to act as a deterrent and promote healthier food choices.
- Awareness and Education: It recommends targeted awareness campaigns in schools and colleges, integrated with broader health and lifestyle campaigns, to reduce the rising consumption of UPFs.
Why this matter
- Rising Consumption: According to a 2023 WHO report, India’s UPF consumption grew from $900 million (2006) to over $37.9 billion (2019).
- Long-term National Impact: India's ?2,50,000 crore UPF industry is built on hyper-palatability and is a threat to India’s demographic dividend, productivity, and future economic growth.
Health Risks of UPFs
- Directly linked to:
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Colorectal cancer
- Respiratory and gastrointestinal disorders
- Mental health issues, especially among youth
- Poor dietary intake due to UPFs contributes to micronutrient deficiencies, while synthetic additives may have long-term biological impacts.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods?
UPFs are industrial formulations that undergo extensive processing and typically include:
- Artificial flavours, colours, preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners, and other cosmetic additives.
- High sugar, salt, and fat content for taste enhancement.
- Low in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Designed for convenience and high palatability, often leading to overconsumption.
Examples of Ultra-Processed Foods
(As per Indian Council of Medical Research - ICMR):
- Commercial bakery items: bread, cakes, biscuits, breakfast cereals
- Snack foods: chips, fries
- Condiments: sauces, jams, mayonnaise
- Dairy & protein products: processed cheese, butter, protein powders, soy chunks, tofu
- Frozen and ready-to-eat foods with additives
- Beverages: energy drinks, health drinks, sweetened fruit juices
- Refined flours of cereals, millets, legumes
- Culinary ingredients containing cosmetic additives like artificial colours or emulsifiers
India adds 4 new Ramsar Sites

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Government of India has added four new Ramsar sites, increasing the total to 89, the highest in Asia and third globally. The newly designated wetlands include:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Khecheopalri Wetland (Sikkim)
- Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand)
This marks a significant milestone as Sikkim and Jharkhand have received their first Ramsar recognitions, while Tamil Nadu strengthens its lead with 20 Ramsar sites, the most among Indian states.
About the Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 in Ramsar, Iran
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, national, and international cooperation.
- World Wetlands Day: Celebrated on 2nd February to promote awareness.
Key Highlights:
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2010; covers 29.29 ha.
- Crucial breeding and foraging site for waterbirds like Spot-billed Pelican, Black-headed Ibis, and Oriental Darter.
- Aids groundwater recharge and climate regulation.
- Part of the Central Asian Flyway.
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2012; spans 230.49 ha.
- Located near Gulf of Mannar; significant stopover for migratory birds.
- Hosts endemic species and near-threatened fauna like Lion-tailed Macaque and Giant Squirrel.
Khecheopalri Wetland – Sikkim
- Sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus; called Sho Dzo Sho locally.
- Known as a wish-fulfilling lake.
- Birds prevent leaves from settling on the surface.
- Rich in avifauna: fishing eagles, Brahminy kites.
- Integral to ecotourism and biodiversity conservation.
Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand
- Comprises Pataura Jheel (155 ha) and Brahma Jamalpur Jheel (410 ha).
- First Ramsar site of Jharkhand; near Ganga River.
- Declared a bird sanctuary in 1991; attracts migratory birds from September onwards.
Falls under the Gangetic Plains biogeographic zone.
MSME Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME), in collaboration with the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), has launched the Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative. It aims to promote digital commerce among micro and small enterprises (MSEs) in India.
Key Features of TEAM Initiative
- Scheme Under: Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity (RAMP) Programme
- RAMP is a World Bank-supported Central Sector Scheme implemented from 2022–2027 to enhance market access, technology upgradation, and financial inclusion for MSMEs.
- Objective:
- To empower MSEs through digital commerce integration using ONDC.
- To formalize operations, reduce the cost of doing business, and expand market access.
- To ensure inclusivity with 50% of beneficiaries being women-led enterprises.
- Budget & Duration:
- ?277.35 crore over three years (FY 2024–25 to FY 2026–27).
- Target Beneficiaries:
- 5 lakh MSEs (50% women-led).
- Eligibility: Registered MSEs in manufacturing or service sectors with valid Udyam Registration. Medium enterprises are excluded from most benefits.
- Implementing Agency:
- National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
Operational Strategy
- ONDC Integration: MSMEs will be onboarded onto the ONDC network, enabling them to operate digital storefronts with access to interoperable platforms, seamless payment solutions, and logistics services.
- Workshops & Outreach:
- Over 150 workshops will be organized across Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, especially targeting SC/ST-led and women-led enterprises.
- Workshops will provide training on creating digital catalogues, understanding digital platforms, and maximizing ONDC's benefits.
- Supportive Infrastructure: A dedicated digital portal will offer services including workshop registration, access to finance, grievance redressal, catalogue tools, and account management assistance.
- Financial Assistance: Support to Seller Network Participants for onboarding MSEs and assisting in operational and digital transition needs.
About ONDC:
An initiative of the DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce, ONDC is an open, interoperable network that allows buyers and sellers to transact across multiple digital platforms, aiming to democratize digital commerce and reduce platform monopolies.
National Critical Mineral Mission

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has launched the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) with a total outlay of ?34,300 crore over seven years, including ?16,300 crore government expenditure and ?18,000 crore investment from PSUs and private players.
Key Highlights:
Objectives of NCMM
- Reduce import dependence on critical minerals vital for clean energy, electronics, defence, and high-tech industries.
- Promote domestic exploration, mining, processing, and recycling of critical minerals.
- Facilitate overseas acquisition of mineral assets.
- Strengthen India’s mineral security and ensure self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
Key Features
- Value Chain Coverage: Exploration → Mining → Beneficiation → Processing → Recycling of end-of-life products.
- Fast-track regulatory approvals for mining projects.
- Creation of mineral processing parks and promotion of sustainable extraction technologies.
- Establishing a strategic stockpile of critical minerals.
- Development of a Centre of Excellence on Critical Minerals to support R&D.
- Expansion of PRISM initiative to fund startups and MSMEs in the sector.
- Whole-of-government approach: Collaboration among ministries, PSUs, private sector, and research institutions.
Why Critical Minerals Matter
Critical minerals are essential inputs for:
- Green energy: EV batteries, solar panels, wind turbines.
- Electronics: Semiconductors, fiber optics.
- Defence: Aircraft, missile guidance systems.
- Medical technologies: MRI machines, pacemakers.
India’s clean energy transition and manufacturing competitiveness hinge on a steady and secure supply of these minerals.
India’s Import Dependence
India is dependent on imports, especially from China, for several critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, titanium, graphite, and tellurium. This exposes India to supply chain vulnerabilities amid shifting global geopolitics.
List of 30 Critical Minerals for India
Includes: Lithium, Cobalt, Nickel, Graphite, Rare Earth Elements (REEs), Beryllium, Titanium, Tungsten, Gallium, Indium, Selenium, Cadmium, etc.
Strategic and Legislative Initiatives
- Amendment to MMDR Act (1957) in 2023: Enabled auction of 24 critical mineral blocks.
- OAMDR Act (2002) amendment: Introduced transparent offshore mineral exploration.
- Duty waivers in Union Budget 2024–25: Customs duties removed on key critical minerals to promote domestic processing.
- Exploration by GSI: 368 projects in last 3 years; 227 more planned for FY 2025–26.
- KABIL: Acquired 15,703 ha in Argentina for lithium mining.
Global Context
- Global powers (US, EU, Japan) are pursuing strategies for critical mineral security.
- China dominates refining of lithium, cobalt, and REEs.
- India is part of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) to diversify global mineral supply chains.
Significance for India
- Ensures long-term resource security for clean technologies.
- Supports EV and renewable energy manufacturing goals.
- Enhances strategic autonomy in defence and electronics.
- Makes India an attractive hub for foreign investment in green technologies.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Geopolitical risks in overseas asset acquisition.
- Environmental impacts of large-scale mining.
- Need for strong R&D ecosystem, financial incentives, and public-private partnerships.
- Sustainable mining practices and global collaboration are essential for long-term success.
Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF)

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
India is actively exploring the creation of a Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF) or The Bharat Fund (TBF) to harness the untapped wealth embedded within its public sector ecosystem. This fund aims to unlock and strategically manage dormant capital, estimated at ?40 lakh crore ($450–500 billion), primarily held in equity stakes of around 80 listed public sector enterprises (PSEs) and banks.
What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF)?
A Sovereign Wealth Fund is a state-owned investment vehicle that manages national savings or surplus revenues—often derived from foreign exchange reserves, natural resource exports, or trade surpluses.
According to the Santiago Principles (2008), SWFs:
- Are owned by the general government (central or sub-national),
- Invest primarily in foreign financial assets, and
- Aim to achieve financial objectives rather than monetary policy.
Types of SWFs include:
- Stabilization Funds: Cushion fiscal shocks from revenue volatility.
- Future Generation Funds: Preserve wealth for long-term national benefit.
- Strategic Development Funds: Support priority sectors and national growth.
- Reserve Investment Funds: Enhance returns on foreign currency reserves.
Examples include:
- Norway’s Government Pension Fund Global ($1.7 trillion),
- China Investment Corporation ($1.35 trillion),
- Abu Dhabi Investment Authority ($993 billion).
India’s SWF Landscape and the BSWF Proposal
India previously explored SWF models in 2007–08 and again in 2010–11. While the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) was launched in 2015, it remains sector-specific and limited in scale. The proposed BSWF envisions a comprehensive and transformational fund akin to global best practices.
Key features of the BSWF proposal:
- Consolidation of government equity in PSEs and PSU banks under a professionally managed umbrella.
- Strategic divestment—e.g., reducing government stake from 51% to 40%—without losing operational control.
- Leveraging this pooled equity to attract global co-investors, potentially unlocking tens or hundreds of billions in foreign capital.
Why India Needs the Bharat SWF
- Wealth Unlocking: Potential monetization of over ?40 lakh crore in dormant government equity assets.
- Fiscal Prudence: Even a modest 2% annual divestment could yield $10+ billion, narrowing the fiscal deficit from 4.9% to ~4.6% of GDP.
- Strategic Sector Investment: Deployment into high-potential sectors—AI, semiconductors, electric vehicles, hydrogen energy, biotechnology—to drive innovation and economic leadership.
- Attracting Global Capital: Enhanced investor confidence, especially from established SWFs like those of Singapore, Norway, and Abu Dhabi, which are already increasing exposure in Indian equities and infrastructure.
- Social Sector Funding: Generate non-debt financial resources for welfare programs and national development missions.
- Soft Power Projection: Fund ventures, disaster relief, and advocacy efforts, strengthening India’s international standing.
Governance and Reform Imperatives
For the BSWF to succeed, it must:
- Be governed by a clear legal and regulatory framework aligned with Santiago Principles.
- Operate independently, with professional asset managers, market-based remuneration, and arm’s length oversight.
- Transition PSEs to function with autonomy and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic delays and enabling innovation.
- Foster joint ventures to turn around non-performing PSEs—among the 1,830 PSEs, around 400 remain non-functional, demanding nearly ?9 lakh crore annually in budgetary support.
Challenges and Concerns
- Macroeconomic Constraints: India faces a current account deficit and substantial fiscal pressures—conditions unlike traditional SWF-rich nations.
- Geopolitical and Market Risks: Global uncertainty and decoupling trends could impact cross-border investment strategies.
- Environmental and Technological Vulnerabilities: Investment risks in carbon-heavy sectors and exposure to data fraud or tech disruptions.
- Institutional Resistance: Political and bureaucratic inertia may delay implementation unless national interest is prioritized.
SWF Investments in India: A Growing Trend
Foreign SWFs are already deepening their footprint in India:
- $6.7 billion in direct investments in 2022 (up from $4.3 billion in 2021).
- Preferred sectors: healthcare, entertainment, renewables, infrastructure.
- Beneficiaries of tax exemptions on direct infrastructure investments via InVITS (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) and AIFs (Alternative Investment Funds), valid for investments made before March 31, 2024.
These incentives have encouraged foreign SWFs to explore establishing physical presence in India’s financial hubs, especially GIFT City, Gandhinagar.
Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025
- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
MoEFCC Notifies Rules for End-of-Life Vehicles to Minimize Waste and Pollution.
Key Highlights:
Notified by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
Effective from: April 1, 2025
Legal Basis: Environment Protection Act, 1986
Objective: To promote environmentally sound management of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs), enable recycling and reuse of vehicle components, and reduce resource extraction, pollution, and waste generation.
Key Features of the ELV Rules, 2025
1. Scope and Coverage
- Applicable to all vehicle categories including electric vehicles (EVs), e-rickshaws, and e-carts.
- Exempted vehicles: Agricultural tractors, trailers, combine harvesters, and power tillers.
- Exempted waste types: Batteries, plastics, tyres, used oil, and e-waste (governed under separate waste management rules).
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Vehicle producers are mandated to meet annual scrapping targets based on the age of vehicles:
- Transport vehicles: 15 years
- Non-transport vehicles: 20 years
- Producers must fulfill their EPR obligations for all vehicles introduced into the domestic market, including those used internally.
- Annual EPR declarations must be submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) by April 30 each year.
- Producers must promote ELV deposition at designated collection centres or Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs).
3. Responsibilities of Stakeholders
- Registered Owners & Bulk Consumers: Required to deposit ELVs at designated centres or RVSFs within 180 days of becoming unfit.
- Collection Centres:
- Handle ELVs in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Maintain records and ensure safe storage and transfer to RVSFs.
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs):
- Undertake depollution, dismantling, segregation, and recycling.
- Ensure environmentally sound disposal of non-recyclables via authorized TSDFs.
- Issue EPR certificates based on the volume of steel processed; valid for 5 years.
4. Monitoring, Compliance, and Penalties
- CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) are responsible for:
- Registration, inspection, and audit of producers, RVSFs, and bulk consumers.
- Taking action against non-compliance, including suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Levying environmental compensation for violations that cause harm to public health or the environment.
5. Registration & Certification
- Producers register with CPCB; RVSFs and bulk consumers with respective SPCBs.
- Registration certificates are issued within 15 days of application via a centralized online portal.
- EPR certificates are non-transferable and allow adjustment of both current and backlog obligations.
Related Policy and Incentives by MoRTH
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) supports the ELV Rules through:
- Vehicle Scrapping Policy: Targets voluntary phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles.
- Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility) Rules, 2021: Provides operational criteria for RVSFs.
- Central Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Waiver of registration fee for buyers submitting ELV Certificates of Deposit.
- Concession in motor vehicle tax: 25% for non-transport, 15% for transport vehicles.
Electric Mobility Push
- MoRTH has issued several notifications promoting EVs, including:
- Permit exemptions for battery-operated and ethanol/methanol-fueled vehicles.
- Fee exemptions for registration and renewals.
- Tourist permit benefits for EVs and distinct registration marks for visibility.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Launched by Ministry of Heavy Industries on 29th September 2024 with a ?10,900 crore outlay.
- Aims to support electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers, ambulances, trucks, and buses with ?3,679 crore in demand incentives.
- Targets subsidization of over 28 lakh EVs.
F11 Bacteria

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study has identified a bacterial strain, Labrys portucalensis F11 (commonly referred to as F11), capable of degrading per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — popularly known as “forever chemicals” — by breaking their strong carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds.
About F11 Bacteria:
- Scientific Name: Labrys portucalensis F11
- Family: Xanthobacteraceae
- Nature: Aerobic and pollutant-resistant bacterium
- Origin: Isolated from industrially contaminated soil in Portugal
- Significance:
- Adapted to thrive in toxic environments
- Uses environmental contaminants as an energy source
- Capable of degrading at least three types of PFAS and certain toxic byproducts
What Are Forever Chemicals (PFAS)?
- Definition: A group of synthetic, man-made chemicals known for their extremely strong C-F bonds, making them persistent and non-biodegradable.
- Why Called 'Forever':
- Resistant to natural breakdown
- Found in air, rainwater, and soil for decades or longer
- Health & Environmental Hazards:
- Linked to cancer, hormonal disorders, immune dysfunction, and environmental toxicity
- Migrate into soil, water, and air during production and use
- Regulation: Certain PFAS are listed under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Relevance for India and the World:
- Global Impact:
- PFAS are used in a wide range of consumer products such as non-stick cookware, firefighting foams, and food packaging.
- Their persistence poses long-term risks to public health, groundwater contamination, and biodiversity.
- India's Concern:
- Increasing industrialization and waste mismanagement heighten PFAS exposure risks.
- No comprehensive PFAS regulation in place yet; calls for adopting stringent environmental safety norms.
WHO Guidelines on Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued new guidelines promoting the use of Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS) to tackle the global burden of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and stroke, which are largely driven by excessive sodium consumption. This is especially relevant for countries like India, with a high prevalence of high blood pressure and salt consumption.
What Are Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)?
- LSSS are alternatives to regular table salt, where sodium chloride (NaCl) is partially replaced by potassium chloride (KCl), magnesium sulphate, or calcium chloride.
- They are designed to retain the taste of regular salt while significantly reducing sodium intake and improving heart health.
- LSSS can help lower blood pressure, thanks to the potassium content, which helps balance fluid levels and offset sodium’s harmful effects.
Key WHO Recommendations:
- Daily sodium intake should be restricted to less than 2 grams per day, equivalent to about 5 grams of salt.
- Avoid regular table salt, and replace it, wherever safe, with LSSS for household use.
- LSSS use is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women
- Children
- Individuals with kidney impairments or those requiring low-potassium diets
- The guidelines do not apply to packaged or restaurant foods, which are major contributors to overall sodium intake.
Why Is This Important or India?
- Salt Intake in India: Average salt consumption is 10.4 grams/day, over double the WHO recommendation.
- Hypertension Prevalence: Over 35.5% of India’s population (approx. 315 million people) suffers from hypertension (INDIAB Study).
- CVD Burden: Cardiovascular diseases accounted for 28.1% of all deaths in India (2016) – Global Burden of Disease Study.
- Dietary Impact: Globally, 8 million deaths annually are diet-related, with 1.9 million directly linked to high sodium intake.
Implementation and Policy Measures:
- India’s Response:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has initiated sodium reduction policies.
- Edible salt must contain 97% sodium chloride, with anticaking agents limited to 2.2%.
- New labelling norms enforce accurate “low sodium” and “sodium-free” claims.
Public Health and Safety Considerations:
- While LSSS are safe and beneficial for most adults, excess potassium can cause hyperkalemia, especially dangerous for those with kidney disease.
- WHO guidelines aim to maximize benefits and minimize risks by promoting regulated, evidence-based usage.
- Governments, policymakers, and health professionals are urged to integrate LSSS into public health strategies, especially in high-risk populations.
About WHO:
- Established in 1948, the World Health Organization is the UN agency dedicated to promoting global health, preventing disease, and coordinating international health responses.
- It leads efforts for universal health coverage and responds to global health emergencies.
Aroma Mission

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Aroma Mission, also known as the Lavender Revolution, is emerging as a transformative initiative for regions like Jammu & Kashmir and the North East, prioritised under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for inclusive development.
It aims to harness the untapped potential of India’s biodiverse regions through the scientific cultivation of aromatic crops and production of essential oils, with the dual goals of economic upliftment and sustainable innovation.
Key Objectives and Features:
- Launched By: Ministry of Science & Technology
- Nodal Agency: CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP), Lucknow
- Started In: Jammu & Kashmir, now extended to the North East
- Known As: Lavender Revolution
- Purpose: Boost India’s aroma industry by promoting the cultivation of high-value aromatic crops and increasing the production of essential oils.
Major Focus Areas:
- Crops Cultivated: Lavender, lemongrass, citronella, palmarosa, vetiver, patchouli, rose, peppermint, and chamomile
- Target Sectors: Cosmetics, aromatherapy, pharmaceuticals, and food flavouring industries
Impact and Achievements:
- Over 5,000 hectares brought under aromatic crop cultivation in the North East.
- Establishment of 39 essential oil distillation units.
- Distribution of 1 lakh agarwood saplings planned to boost the region's share in global aromatic plant trade.
- Expected annual essential oil production: 2,000 tonnes, valued at over ?300 crores.
- Estimated to generate 60 lakh man-days of rural employment.
- Projected increase in farmers’ income by ?60,000–?70,000 per hectare annually.
Institutional Support: IICON – Incubation and Innovation Complex
- Location: CSIR-North East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat, Assam
- Launched By: Dr. Jitendra Singh (Minister of Science & Technology)
- Purpose: Provide technical assistance, advanced facilities, and business incubation support for startups, MSMEs, and SHGs.
- Facilities: Access to 27 cutting-edge technologies for up to two years to help refine production and marketing strategies.
Integrated Development Approach:
The Aroma Mission exemplifies the “whole-of-government” approach, aligning with various flagship programmes such as:
- Start-Up India
- MSME Development
- Doubling Farmers’ Income
- Women Empowerment (e.g., through Rural Women Technology Parks)
- Act East Policy (enhancing North East's connectivity and trade potential)
Over 25 startups and self-help groups have already been empowered through access to facilities and entrepreneurial training at IICON, contributing to local innovation ecosystems.
Strategic Significance:
- Regional Empowerment: Converts underutilised natural resources into economic assets, especially in remote regions like J&K and the North East.
- Environmental Sustainability: Encourages eco-friendly cultivation and reduces pressure on traditional farming.
- Economic Diversification: Supports India’s transition to a bio-economy, with aromatic plant industries offering export potential and rural employment.
- Vision India@2047: Positions the North East as a hub for biotechnology, essential oils, innovation, and trade, aligning with long-term national growth goals.
Olive Ridley Turtles
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Rushikulya river mouth in Odisha is witnessing the anticipated mass nesting of Olive Ridley turtles — a critical event for the survival of this vulnerable marine species. This phenomenon, known as arribada, highlights the ecological significance of India’s coastal biodiversity and the urgent need for marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea)
- Taxonomy:
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- Class: Reptilia
- Family: Cheloniidae
- Physical Features: These turtles are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtle species. They are recognized by their olive or grayish-green heart-shaped carapace. Males and females are similar in size, though females have slightly rounder shells.
- Habitat and Distribution: Olive Ridleys are found in warm, tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, inhabiting both open ocean (pelagic) and coastal waters.
Mass Nesting: The Arribada Phenomenon
- Arribada (Spanish for "arrival") refers to the synchronized mass nesting behavior where thousands of females gather on a single beach to lay eggs.
- Nesting occurs annually between December and March, after long migrations of up to 9,000 km. Each female may lay 90–120 eggs, 1 to 3 times per season.
- Temperature-dependent sex determination influences hatchling sex ratios.
- After nesting, females return to the sea, leaving eggs buried in sand.
Major Nesting Sites in India
- Odisha Coast is the most significant nesting ground in India and globally:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary: World’s largest mass nesting site.
- Rushikulya River Mouth: Second-largest nesting beach in India.
- Devi River Mouth: Another key nesting site in Odisha.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands have recently emerged as a new mass nesting area, with over 5,000 nests reported in one season.
Ecological Role and Behavior
- Diet: Omnivorous — they feed on jellyfish, crabs, snails, prawns, molluscs, algae, and small fish.
- Behavior: These turtles undertake long migrations annually between feeding and breeding grounds, spending most of their lives at sea.
Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I (highest protection)
Threats to Survival
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental entanglement in trawls, gillnets, and longlines.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development for ports, tourism, and industry disrupts nesting beaches.
- Poaching: Turtles and their eggs are harvested for meat, shell, and leather.
- Pollution: Plastic ingestion and marine debris pose severe health risks.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased sand temperatures impact nesting and hatchling sex ratios.
Conservation Initiatives
- Operation Olivia: Initiated by the Indian Coast Guard in the 1980s to protect turtles during nesting and prevent illegal fishing.
- Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Mandated by the Odisha government in trawl nets; allow turtles to escape while retaining fish catch.
- Tagging Programs: Use of non-corrosive metal tags to study migration patterns and inform conservation strategies.
Global Investment Trends and India’s FDI Outlook

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Investment Trends Monitor Report 2024, released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights a concerning decline in international project finance and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), particularly in developing economies. This has significant implications for sustainable development, especially in emerging economies like India.
Key Findings from the UNCTAD Report (2024)
Global FDI Trends:
- Global FDI flows, after adjusting for conduit economies, fell by 8% in 2024, despite a nominal increase to USD 1.4 trillion.
- Developed economies witnessed a 15% drop in FDI (excluding conduit economies like Ireland and Luxembourg), while developing economies saw a 2% decline.
- The decline threatens long-term investment in infrastructure, renewable energy, and other SDG-aligned sectors.
Project Finance and Greenfield Investment:
- International project finance declined by 29% in developed and 23% in developing economies.
- In terms of value, developing economies faced a sharper fall of 33%.
- Key countries like India, China, Brazil, Indonesia, and Mexico reported steeper declines than the global average.
- Greenfield investments fell 6% in developing regions, with Africa and Asia being worst affected.
Sectoral Impacts:
- Investments in SDG-related sectors (e.g., water, sanitation, agrifood systems, and infrastructure) declined by 11%.
- International renewable energy finance fell 16%, with North America (-22%) and developing Asia (-18%) seeing notable contractions.
- Africa was the only region to witness an 8% increase in renewable energy project finance.
India’s FDI Landscape: Trends, Opportunities, and Challenges
Recent Performance:
- Between April 2000 and September 2024, India received over USD 1 trillion in cumulative FDI.
- From 2014 to 2024, India attracted USD 667.4 billion, a 119% increase over the previous decade.
- In 2024, India’s greenfield projects grew, but international project finance fell 23% in number and 33% in value.
Regulatory Framework:
- FDI is regulated under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, administered by DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Prohibited sectors: Atomic energy, betting, lotteries, chit funds, tobacco, and real estate (excluding construction development).
Outlook for 2025 and Strategic Opportunities
Global FDI Projections:
- UNCTAD anticipates moderate global FDI growth in 2025.
- Regions like ASEAN, Eastern Europe, and Central America may benefit from supply chain realignments.
- India is projected to see a moderate rise in FDI, aided by:
- Improved financing conditions,
- Mergers and acquisitions,
- Ongoing policy reforms.
Key Growth Sectors:
- High potential in AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, electric vehicles, and green hydrogen.
- FDI will be influenced by geopolitical dynamics, interest rates, GDP growth, and technological transitions.
FDI in India: Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities:
- Large consumer base (1.4 billion population) and young workforce (65% under 35).
- Government schemes like Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat incentivize foreign investment.
- Strategic location positions India as a gateway to South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
Challenges:
- Regulatory complexity, including retrospective taxation and bureaucratic delays.
- Infrastructure deficits, particularly outside urban hubs.
- Rigid labour laws and inconsistent policy enforcement.
Investor Expectations:
- Technology transfer in priority sectors.
- Employment generation to absorb India’s growing labor force.
- Sustainable investments in line with India’s climate commitments under the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
Asian Waterbird Census 2025

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
As per the Asian Waterbird Census-2025, a record number of 39,725 birds belonging to 106 species have been sighted in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining wetlands.
Asian Waterbird Census (AWC): An Overview
- AWC is an annual citizen-science programme that supports the conservation of wetlands and waterbirds across Asia.
- Initiated in 1987 in the Indian subcontinent, it now covers extensive regions of East and Southeast Asia, Japan, Australasia, and parts of the Central Asian and East Asian–Australasian Flyways.
- AWC is the Asian chapter of the global International Waterbird Census (IWC).
- In India, it is coordinated by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) every January.
About BNHS (Bombay Natural History Society)
- An Indian NGO engaged in biodiversity research and conservation.
- Recognized as a Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (SIRO) by the Department of Science and Technology.
- Official partner of BirdLife International in India.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (Andhra Pradesh): Census Findings 2025
- The Asian Waterbird Census 2025 recorded a record 39,725 birds representing 106 species in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (CWS) and adjoining Godavari estuary wetlands.
- Of these, nearly 70 species are migratory, using the site as a key winter feeding ground.
Species of Conservation Concern
- Endangered species sighted:
- Indian Skimmer (Rynchops albicollis) – ~450 individuals sighted
- Black-bellied Tern (Sterna acuticauda)
- Great Knot (Calidris tenuirostris)
- Vulnerable species: Common Pochard (Aythya ferina)
- Near Threatened species: 11 species identified
Migratory Pathways and Monitoring
- Migrants such as the Great Knot travel from Russia, Siberia, China, and Mongolia to the Godavari estuary.
- A tagged Great Knot, tracked from Russia, was recorded after a 7,500 km journey, seen in Bhairavapalem mudflat and Etimoga wetland in successive winters (2024 and 2025).
- Data sharing with global avian research groups aids in tracking migratory patterns and supports conservation of endangered species.
Ecological and Ramsar Significance
- The Godavari estuary supports feeding grounds for nearly 90,000 birds, as observed by CWS authorities.
- Avian diversity is a key criterion for Ramsar Site designation, and experts advocate for Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and its surroundings to be recognized as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
DeepSeek AI
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup based in Hangzhou, has emerged as a major player in the global AI race with the release of its models DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1.
These models are designed to rival top-tier Western counterparts such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Bard, and Meta’s LLaMA, but at a fraction of the cost.
Key Developments and Technological Edge
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek-V3 was trained at a cost of under $6 million, using older Nvidia H800 chips, compared to the estimated $100 million cost of GPT-4. Its subscription fee is significantly lower—$0.50/month versus $20/month for ChatGPT.
- Model Performance:
- DeepSeek-R1, a “reasoning model,” reportedly matches OpenAI’s o1 model in mathematics, coding, and contextual processing, while using fewer resources through incremental reasoning.
- Models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, reinforcement learning, and self-improvement loops, making them more memory-efficient and scalable.
- Advanced Models Released:
- DeepSeek Coder / Coder-V2 (for coding tasks).
- DeepSeek LLM (67B parameters), V2, V3 (671B parameters), and R1-Distill (fine-tuned using synthetic data).
Global Impact and Market Disruption
- App Success & Outages: The DeepSeek AI app topped the U.S. App Store, surpassing ChatGPT. This success triggered large-scale cyberattacks and caused temporary service disruptions.
- Market Reaction: The launch reportedly led to a historic $600 billion drop in Nvidia's market value, highlighting the disruptive potential of cost-efficient AI innovation.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: The rise of DeepSeek is seen as a technological parallel to the 1957 Sputnik moment, which shocked the U.S. and triggered the space race.
DeepSeek has reignited US-China AI rivalry, intensifying great-power competition in frontier technologies.
Strategic Lessons for India
- Bipolar AI Landscape: The U.S. and China dominate AI due to massive investment and infrastructure. Middle powers like India and France face the challenge of staying relevant without matching this scale.
- Doing More with Less: DeepSeek’s success underscores how innovation with limited resources can be effective—providing a model for India to emulate via Small Language Models (SLMs) and cost-efficient AI strategies.
- Sovereign AI & Global Governance:
- India advocates for “Sovereign AI”, balancing independence and strategic alliances, especially with France and the U.S.
- Future cooperation between U.S. and China on AI governance, similar to Cold War-era nuclear agreements, is a possibility.
- India must learn from past exclusions (e.g., nuclear governance) and proactively shape global AI governance frameworks.
- Policy Implications:
- DeepSeek's rise may lead to stricter U.S. chip export restrictions to China.
- It presents both security risks (censorship, pro-China bias) and opportunities (cost-effective models, domestic self-reliance).
Ethical Concerns and Limitations
- Censorship: DeepSeek complies with Chinese state censorship, refusing responses on politically sensitive topics (e.g., Tiananmen Square), raising concerns about bias and lack of transparency.
Security & Privacy: Experts have flagged potential data privacy and AI ethics issues, emphasizing the need for robust global standards and accountability mechanisms.
Indian Squid

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi, have successfully decoded the gene expression pattern of the Indian squid (Uroteuthis duvaucelii), marking a major scientific advancement with wide-ranging implications for neuroscience, environmental studies, and sustainable marine resource management.
About Indian Squid
- Common Name: Indian Calamari
- Scientific Classification: Cephalopod
- Size: Typically 20–30 cm; can grow up to 50 cm
- Appearance: Light pinkish-grey body with two large fins, eight arms, and two longer tentacles used for capturing prey
- Key Abilities:
- Camouflage
- Jet propulsion for rapid movement
- Advanced nervous system
- Problem-solving skills and behavioral intelligence
Habitat & Distribution
- Preferred Habitat: Coastal and open sea regions of the Indian Ocean
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to 500 meters, some even up to 1,500 meters
- Requires high dissolved oxygen levels for respiration
- Geographic Distribution:
- Widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific
- Found in Indian Ocean, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, from Mozambique to the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, and northward to Taiwan
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Scientific Significance of Genetic Research
- Key Findings:
- Revealed genetic similarities with higher vertebrates like fish and humans, suggesting deep evolutionary links
- Indicates that Indian squid could serve as a model organism to study brain evolution, intelligence, and neurobiological functions
- Potential to inform research in neural circuits, memory, learning, and even neurological diseases
- Findings may also explain squid's adaptive success, such as evading predators and fishing pressures due to high cognitive ability
Institutional Background: CMFRI
- Established: 1947
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) since 1967
- Headquarters: Kochi, Kerala
- Mandate: Research on sustainable marine fisheries and ecosystem conservation
CMFRI’s Broader Recommendations for Sustainable Marine Management
- Enactment of Sea Fishing Act to regulate fishing beyond territorial waters
- Institutionalization of ecological stock assessments for sustainable exploitation
- Simplification and promotion of open mariculture with focus on environmental sustainability
- Use of AI-based systems to estimate landings and monitor fishing vessels
- Deep-sea resource exploration and alternative fishing methods
- Institutional mechanism for supervising deep-sea fishing
- Strengthening insurance coverage for marine fishers
RBI Payment System Report 2024

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
The Payment System Report – December 2024 is a bi-annual publication by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
It analyses trends in digital and retail payment systems over the last five calendar years (up to CY-2024) and highlights India's transformation into a global leader in payment innovation and inclusion.
Growth in Digital Transactions
- Exponential Growth: Digital payment transactions rose 94 times in volume (from 222 crore in 2013 to 20,787 crore in 2024) and 3.5 times in value (from ?772 lakh crore to ?2,758 lakh crore).
- Recent CAGR (2019–2024):
- Volume: 45.9% CAGR
- Value: 10.2% CAGR
- Retail Digital Payments: From 162 crore transactions in FY13 to 16,416 crore in FY24 — a 100-fold increase in 12 years.
- Digital Payments Index (DPI): Surged from a base of 100 in March 2018 to 445.50 in March 2024, indicating massive digital adoption.
UPI: A Game-Changer
- Launched in 2016 by NPCI, UPI has revolutionized mobile-based payments.
- CAGR (Last 5 Years):
- Volume: 74.03%
- Value: 68.14%
- Monthly Transactions: UPI processes over 16 billion transactions monthly, ranking among the largest globally.
- Inclusive Innovations:
- UPI Lite & UPI Lite X: For offline/small-value payments.
- UPI123Pay: For feature phone users.
- UPI 2.0: Includes auto-debit and recurring payment functionalities.
Credit and Debit Card Trends
- Credit Cards:
- Growth: More than doubled from 5.53 crore (Dec 2019) to 10.80 crore (Dec 2024).
- Debit Cards:
- Stable Usage: Marginal increase from 80.53 crore to 99.09 crore in the same period.
Cross-Border Payment Integration
- RBI is actively enhancing cross-border payments by integrating India's UPI with international Fast Payment Systems (FPSs), addressing high costs, delays, and limited access.
- Key Developments:
- UPI-PayNow Linkage (Feb 2023): India-Singapore real-time cross-border payments.
- UPI-enabled QR Payments: Available in Bhutan, France, Mauritius, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, UAE.
- Project Nexus:
- A BIS-conceptualized multilateral project.
- Aims to interlink FPSs of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand for seamless retail payments.
Institutional and Legal Framework
- Legal Backbone: Payments and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act) empowers RBI to:
- Regulate, supervise, and license payment system operators.
- Authorize systems like NPCI, card networks, ATM operators, etc.
- Governing Body:
- Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS) under RBI.
- Chairperson: RBI Governor; Vice-Chairperson: Deputy Governor (in charge of DPSS).
- Payment Ecosystem Entities:
- RBI-regulated: RTGS, NEFT, Cheques (CTS).
- NPCI-managed: UPI, IMPS, AePS, BBPS, NETC, NACH, Cards.
- Other PSOs: TReDS, PPIs.
Strategic Significance
- Financial Inclusion: Payment systems are critical tools for promoting inclusive growth by ensuring last-mile delivery of services and direct benefit transfers.
- Global Competitiveness: RBI’s regulatory foresight and innovation have placed India among the global frontrunners in digital payments.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) in Mumbai is set to become India’s first port to enter top global ports with 10 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) by 2027.
Overview:
- Location: Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Commissioned: 1989
- Significance: India’s first Landlord Major Port, fully adopting the landlord port model.
Performance & Capacity Expansion:
- In 2024, JNPA handled a record 7.05 million TEUs, operating at over 90% capacity, with an 11% year-on-year growth.
- By 2027, JNPA is projected to become India’s first port to handle 10 million TEUs annually, marking its entry into the global top ports list.
- Current container handling capacity: 7.6 million TEUs
- Projected capacity by 2027: 10.4 million TEUs
Infrastructure Developments:
- Commissioning of Phase II of Bharat Mumbai Container Terminal (BMCT) to add 2.4 million TEUs.
- Upgradation of Nhava Sheva Freeport Terminal expected in 2025.
- Five operational container terminals, including:
- BMCT
- Nhava Sheva International Container Terminal (NSICT)
- Gateway Terminals India Pvt Ltd (GTIPL)
Key Projects & Investments (2024):
- ?2,000 crore worth of capacity enhancement projects launched.
- Solar-powered boat, two indigenously developed 70T tugs, and three fire tenders commissioned for safety and efficiency.
- Agro-processing facility (?284 crore) on 27 acres within port complex to handle 1.2 million tonnes annually – includes processing, sorting, packing, and food safety labs.
- Warehousing and CFS infrastructure (?300 crore investment) to generate 1,20,000 TEUs/year through ambient and temperature-controlled facilities.
Vadhavan Port Project:
- Proposed as India’s 13th major port (under construction).
- MoU with Reliance Industries Ltd: Development of liquid jetty and 50 acres of land under PPP model (investment: ?645 crore; operational by 2030).
- MoU with DBKKVD Dapoli: For integrated agri-horticultural development in Dahanu and Palghar.
- MoU with HUDCO: Funding commitment of ?25,000 crore for port infrastructure under PPP mode.
Strategic Importance:
- JNPA is central to India’s maritime trade, which accounts for 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Satellite and dry ports at Vadhavan, Jalna, and Wardha to improve hinterland connectivity and trade logistics.
India’s Journey of Fiscal Consolidation

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Fiscal Consolidation refers to the strategic management of government finances aimed at reducing fiscal deficits, controlling public debt, and ensuring macroeconomic stability. India’s recent journey in this regard has been marked by a significant transformation, particularly in the post-2014 era.
Background:
In 2013-14, India was labelled as one of the "Fragile Five", largely due to its ballooning fiscal deficit (touching 5% of GDP in a quarter), high inflation, and weakening currency. This tag underscored the urgency of restoring fiscal health.
Post-2014 Measures:
- FRBM Act Revamp: The government recommitted to the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003, revising fiscal targets and focusing on fiscal discipline.
- Deficit Reduction: Fiscal deficit was reduced from 4.5% of GDP in FY 2013-14 to 3.4% in FY 2018-19.
- Revenue Boost: Digitization and broader tax reforms helped increase tax receipts from 10% of GDP (FY 2014-15) to 11.8% (FY 2023-24).
- Capex Focus: Capital expenditure nearly doubled from 1.6% of GDP in FY 2014-15 to 3.2% in FY 2023-24, emphasizing infrastructure over consumption.
Pandemic Impact and Recovery:
- During COVID-19, India’s fiscal deficit soared to 9.2% of GDP (FY 2020-21) due to emergency spending.
- Unlike blanket stimulus in some countries, India opted for targeted support (MSMEs, displaced populations, healthcare) while continuing infrastructure investment.
- This strategy avoided long-term inflationary pressure and built long-term productive capacity.
Structural Reforms:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aimed at reducing import dependence and boosting domestic manufacturing.
- Enhanced export competitiveness due to fiscal prudence and macroeconomic stability.
Current Scenario:
- Fiscal deficit reduced to 5.6% of GDP in FY 2023-24, with a target of 4.9% in FY 2024-25, and further narrowing to 4.5% by FY 2025-26.
- States remain a concern: their deficits exceed the 3% of GSDP limit, averaging 3.2% in FY 2023-24, with rising debt levels and declining capex.
FRBM Act & N.K. Singh Committee:
- FRBM Act (2003) aims to cap the fiscal deficit at 3% of GDP.
- The N.K. Singh Committee (2016) recommended:
- Shift from rigid deficit targets to debt as the primary anchor.
- Set up an autonomous Fiscal Council.
- Flexibility via an “escape clause” (up to 0.5% extra deficit during crises).
- Limit borrowings from RBI to specific emergency conditions.
Significance of Fiscal Consolidation:
- Macroeconomic Stability: Controls inflation and keeps currency stable.
- Investment Magnet: Low deficits improve investor confidence.
- Reduced Debt Burden: Less borrowing means less stress on future generations.
- Efficient Governance: Ensures better resource allocation and economic resilience.
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent study conducted by Assam Medical College and Hospital has revealed a high prevalence of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) among tuberculosis (TB) survivors in Assam’s tea garden communities. Published in the PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases journal, the research underscores a significant public health concern in a region already burdened by TB.
What is Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)?
- CPA is a severe, life-threatening fungal infection caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, a filamentous fungus commonly found in soil, decaying vegetation, and humid organic matter.
- It predominantly affects individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, especially those who have recovered from or are currently battling TB.
- CPA is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation:
CPA shares many clinical features with TB, making diagnosis challenging:
- Chronic cough
- Haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Persistent respiratory symptoms
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Key Findings from Assam:
- Study Area: Conducted in Dibrugarh district, covering tea workers and their dependents from four major tea estates.
- Sample Size: 128 patients with prolonged respiratory symptoms (>3 months).
- Prevalence:
- CPA prevalence: 17.18% overall
- Seropositivity in active TB patients: 18.5%
- Seropositivity in post-TB patients: Spiked to 48.9%, indicating a strong link between CPA and previous TB infections.
- Demographic Insights:
- Mean age: 41.9 years
- Higher incidence among middle-aged male workers
- Comparison with Global Trends:
- Assam’s CPA prevalence (60 per 1,00,000) exceeds the global average (42 per 1,00,000)
- Worse than several African nations including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (20–50 per 1,00,000)
Contributing Risk Factors in Assam’s Tea Belt:
- High TB burden: 217 per 1,00,000 (National TB Prevalence Survey 2019–2021)
- Poverty and malnutrition
- Kitchen smoke exposure
- Congested living conditions
- Delayed or inadequate TB treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosis:
- Serological testing for Aspergillus antibodies
- Radiological imaging to identify fungal growth in lung cavities
- Treatment:
- Antifungal therapy (e.g., itraconazole or voriconazole)
- Surgical removal in severe cases with fungal mass
Public Health Recommendations:
- Routine screening of post-TB patients for CPA in high-risk zones like tea estates
- Awareness campaigns targeting healthcare providers and workers to improve recognition and response
- Education on nutrition, respiratory hygiene, and early symptom detection
- Inclusion of fungal diseases like CPA in broader national TB and occupational health programs
Additional Context: Epidemic Dropsy in Assam’s Tea Belt
- A 2019 study had previously flagged the prevalence of epidemic dropsy, a condition caused by contaminated edible oils with Argemone mexicana oil, adding to the health risks in tea-growing regions.
SEBI’s Sachetisation of Mutual Funds
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed the “sachetisation” of mutual fund investments to promote financial inclusion, especially among low-income and first-time investors.
What is Sachetisation?
- Originating from the FMCG sector (e.g., shampoo sachets), sachetisation refers to offering financial products in small, affordable units, enhancing accessibility and affordability.
- In capital markets, it implies micro-level investment options, particularly through low-ticket SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Objectives:
- Promote financial inclusion and empower economically underserved sections.
- Expand mutual fund penetration to semi-urban and rural areas.
- Encourage long-term savings and wealth creation among new investors.
- Reduce dependency on large institutional or foreign investors by broadening the domestic retail base.
Key Features of SEBI’s Sachet SIP Proposal:
Feature Details
Minimum SIP Amount ?250 per month
Eligibility Only for new mutual fund investors
Investment Limit Up to 3 sachet SIPs across different AMCs
Excluded Schemes Debt funds, sectoral/thematic, small-cap, mid-cap equity funds (due to higher risk)
Commitment Period Encouraged to commit for 5 years (60 SIPs), but premature withdrawal allowed
Payment Modes Only via auto-pay mechanisms such as UPI Autopay and NACH
Cost Incentives AMCs to receive subsidies from SEBI’s Investor Education and Awareness Fund
Distributor Incentive ?500 per investor after completion of 24 monthly SIPs
Significance:
- Democratizes investment access by lowering the entry barrier for mutual funds.
- Encourages behavioral shift towards long-term financial planning and discipline.
- Stabilizes domestic markets by broadening and diversifying the retail investor base.
Supports SEBI’s vision of making capital markets inclusive, tech-enabled, and accessible.
Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025
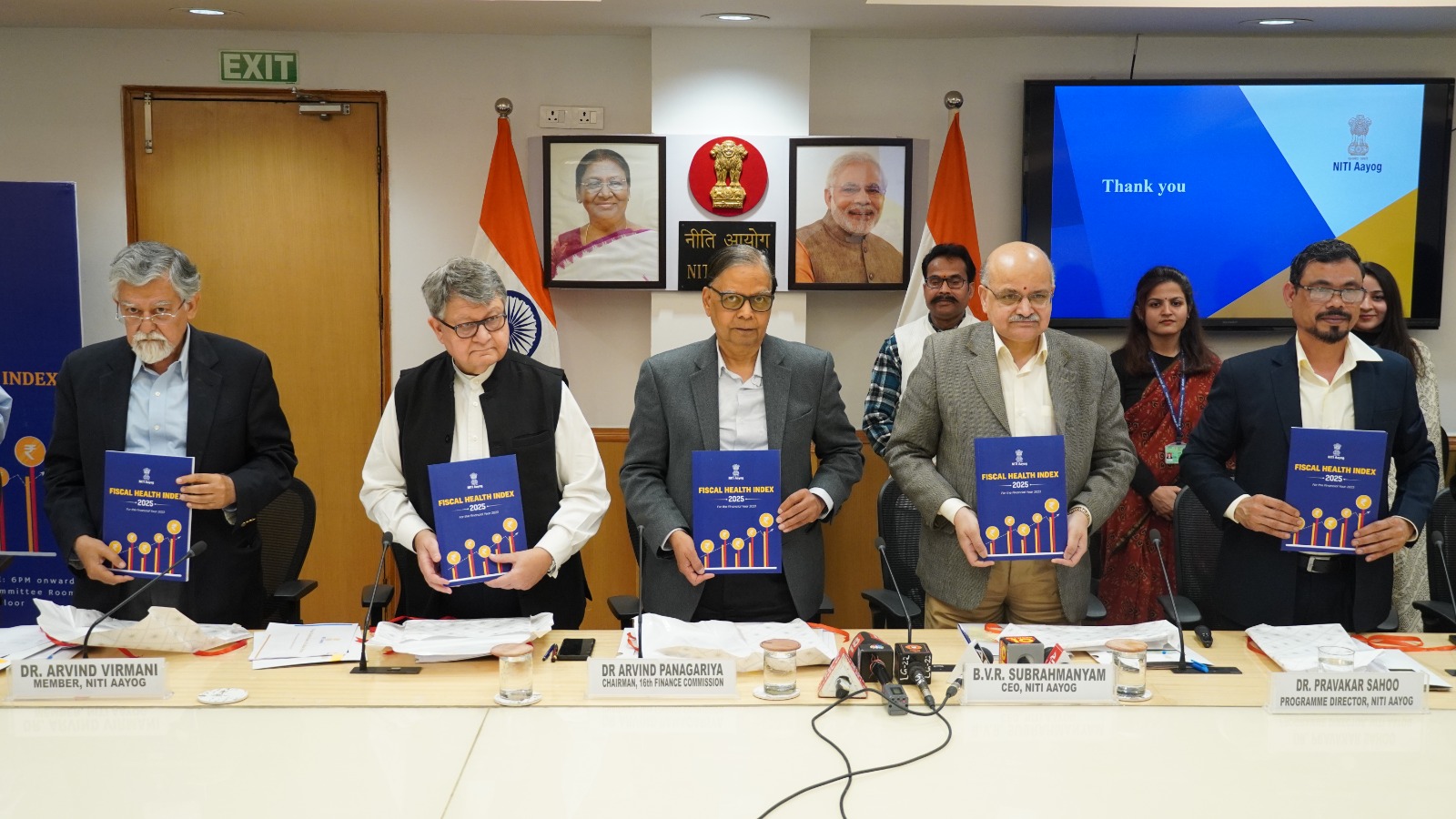

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog launched the inaugural Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025 on 24 January 2025 in the presence of the 16th Finance Commission Chairman, Dr. Arvind Panagariya. The index evaluates the fiscal performance of 18 major Indian states using FY 2022–23 as the base year.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To assess, monitor, and improve the fiscal health of Indian states and foster balanced regional development, economic resilience, and fiscal transparency. It aims to support the national goal of Viksit Bharat @2047.
- Developed by:
- NITI Aayog, with data sourced from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Designed as an annual publication to promote informed and targeted state-level policy reforms.
- Evaluation Parameters:
The index comprises five sub-indices that collectively offer a holistic picture of fiscal health:
- Quality of Expenditure – Efficiency in developmental and social sector spending (e.g., health, education).
- Revenue Mobilization – Tax and non-tax revenue generation capacity.
- Fiscal Prudence – Adherence to fiscal deficit targets and sound financial management.
- Debt Index – Absolute level of public debt.
- Debt Sustainability – Debt-to-GSDP ratio and interest burden on revenues.
Key Highlights from FHI 2025:
Top Performing States (Achievers):
Rank State FHI Score Strengths
1. Odisha 67.8 Low fiscal deficit, strong debt management, effective capital expenditure
2. Chhattisgarh 55.2 Revenue growth from mining, fiscal prudence
3. Goa 53.6 High tax efficiency and non-tax revenue
Aspirational States (Facing Challenges):
- Punjab, West Bengal, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh
- Issues: High debt-to-GSDP ratios, revenue deficits, poor revenue mobilization
Sub-Index Insights:
- Revenue Mobilization: Odisha, Goa, and Chhattisgarh excelled; Bihar and West Bengal lagged due to low own-tax revenues.
- Quality of Expenditure: Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh prioritized social sectors; Punjab and Rajasthan underperformed in capital investment.
- Debt Management: Maharashtra and Gujarat maintained robust practices; Punjab and Haryana faced rising interest burdens.
- Debt Sustainability: Odisha and Chhattisgarh displayed strong sustainability; West Bengal and Punjab showed fiscal stress.
- Fiscal Prudence: Odisha and Jharkhand maintained low deficits, enabling better public investment.
Significance for Policy & Governance:
- Encourages healthy interstate competition and promotes cooperative federalism.
- Provides data-driven insights for targeted fiscal reforms.
- Reinforces the need for decentralized and transparent financial governance.
- Offers a benchmark for fiscal performance aligned with national transformation goals.
Recommendations:
- Enhance revenue base via tax reforms and tapping into non-tax sources.
- Boost capital expenditure in infrastructure, health, and education.
- Strengthen debt sustainability frameworks and reporting mechanisms.
- Institutionalize fiscal responsibility through better compliance and accountability.
Sanjay Battlefield Surveillance System

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently flagged off Sanjay, an indigenously developed Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS), to be inducted into the Indian Army in phased manner from March to October 2025, designated as the ‘Year of Reforms’ by the Ministry of Defence.
Overview:
- Nature: Automated surveillance system
- Purpose: To integrate real-time data from ground and aerial sensors, enabling swift, informed decision-making in conventional and sub-conventional warfare scenarios.
Key Features:
- Common Surveillance Picture (CSP): Fuses verified sensor data to generate a real-time surveillance image of the battlefield.
- Real-time Integration & Analytics: Processes inputs using advanced analytics to eliminate duplication and enhance situational awareness.
- Secure Networks: Operates over the Indian Army’s Data Network and Satellite Communication Network, ensuring reliable and secure data flow.
- Centralized Web Application: Provides integrated inputs to Command Headquarters and Army HQ through a unified platform, supporting the Indian Army's Decision Support System.
- Indigenous Development: Jointly developed by the Indian Army and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) under the Buy (Indian) category, promoting Aatmanirbharta in defense.
Operational Significance:
- Enhances battlefield transparency, situational awareness, and surveillance capabilities along vast and sensitive land borders.
- Functions as a force multiplier in Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
- Enables network-centric warfare, marking a shift towards data-driven military operations.
Deployment:
- To be inducted into all Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Army in three phases (March–October 2025).
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
India is set to deploy its first human-operated deep-sea submersible as part of the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), marking a significant leap in the country’s marine research and technological capability.
Key Highlights:
- Submersible Deployment (2024):
- India will operate its first human submersible at a depth of 500 meters this year.
- The goal is to reach a depth of 6,000 meters by 2025.
- The project aligns with the timelines of Gaganyaan, India’s first human space mission—showcasing parallel progress in marine and space technology.
- Indigenous Technology:
- The mission is powered by 100% indigenous technology, underlining India’s growing self-reliance in high-end scientific infrastructure.
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM):
- Launched: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Budget: ?4,077 crore over five years
- Framework: One of nine key missions under PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council)
Core Objectives:
- Develop deep-sea technologies, including a manned submersible for ocean exploration.
- Explore and harness ocean resources such as: Polymetallic nodules, Hydrothermal sulphides & Rare earth metals
- Study marine biodiversity for sustainable fisheries and conservation.
- Support India’s blue economy through innovation and research.
- Monitor ocean climate change and develop advisory services.
- Promote marine biology and biotechnology via dedicated marine research stations.
- Harvest renewable energy and freshwater from ocean sources.
Key Components and Technologies:
Matsya6000 Submersible:
- India’s first manned deep-sea vehicle.
- Designed to reach 6,000 meters depth.
- Crew Capacity: Three members
- Developed by: National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai
- Structure: Made of titanium alloy, withstanding 6,000 bar pressure
- Equipped with: Scientific sensors, tools for sampling, viewports, propellers, and acoustic communication systems.
- Combines capabilities of ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) and AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles).
Varaha Deep-Ocean Mining System:
- Developed by NIOT
- Successfully conducted trials at 5,270 meters
- Key to India’s future in deep-sea mining of critical minerals
Strategic Importance:
- Scientific Advancement: DOM places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France, Japan) with human-crewed deep-ocean exploration capacity.
- Economic Potential: Unlocks access to underwater mineral wealth, critical for electronics, defense, and energy sectors.
- Environmental Sustainability: Supports marine biodiversity conservation and promotes sustainable use of oceanic resources.
- Geopolitical Significance: Enhances India’s presence and influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Technological Leap: Strengthens India’s capabilities in underwater robotics, materials engineering, and ocean sciences.
Is Poverty Being Underestimated in India?

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The recent 2023-24 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed a decline in poverty across rural and urban India. However, questions have emerged about whether poverty is being underestimated, due to changes in methodologies, definitions, and data availability.
Evolution of Poverty Measurement in India
- 1970s to 2005: Poverty was defined based on minimum calorie intake; updated every 5 years using NSSO data.
- Tendulkar Committee introduced in response to divergence between NSSO and National Accounts data.
- Post-2011-12: No official poverty estimates or surveys; alternative indices like Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) were used.
Current Data Issues
- Different recall periods in surveys (7-day, 30-day, 365-day) create non-comparability.
- Modified Mixed Recall Period (MMRP) introduced in 2017-18 and improved upon in recent years with three household visits, enhancing recall and thus raising reported expenditures.
- Result: Using older poverty lines on newer, higher expenditure data underestimates poverty.
Diverging Poverty Estimates
- Dr. C. Rangarajan (2022-23): Estimated poverty at around 10%.
- Recent factsheet (2023-24) suggests poverty may have declined to single digits.
- A paper using Rangarajan’s methodology on 2022-23 HCES data estimated 25% poverty, but this is debated.
Reasons for Poverty Reduction
- High GDP growth, increased public expenditure, and improved public delivery systems.
- National Food Security Act covers nearly 80 crore people.
- Broadened definition of poverty now includes non-food items and essential services.
- Decline in poverty estimated around 17-18% between 2011-12 and 2023-24.
Rural-Urban Trends
- Consumption gap between rural and urban areas is narrowing.
- Rural consumption patterns becoming more urban-like.
- 2011 Census definitions outdated — many rural areas are peri-urban in character.
Need for Poverty Line Revision
- Lack of consensus and official backing on methodology hinders creation of a new poverty line suited to current data.
- UNDP’s global poverty line is $2.15/day; India’s poverty was 12.9% in 2019 by that metric.
- NITI Aayog’s estimates do not support 25% poverty claim.
Debate on Multidimensional Poverty Index
- India’s MPI (12 indicators) differs from UNDP’s 10-indicator framework.
- Additions like bank accounts and maternal health are India-specific.
- Criticism: Once indicators (e.g., electricity, bank accounts) are met, they remain met — poverty appears to decline permanently, while income vulnerability is not captured.
Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy – MeitY Report (2025)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Release of Report ‘Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy’ by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Prepared by: Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER)
- Significance: First credible and current estimate of the digital economy using international frameworks (OECD & ADB).
- India is the first developing country to adopt the OECD framework for measuring the digital economy.
Key Findings (2022–23)
Indicator Details
Size ?31.64 lakh crore (~USD 402 billion), 11.74% of national income (GVA)
Employment 14.67 million workers (2.55% of the workforce)
Projected Share by 2029–30 Nearly 20% of GDP (surpassing agriculture & manufacturing)
Structure of India’s Digital Economy
- Digitally Enabling Industries (7.83% of GVA): ICT services, telecom, manufacturing of digital hardware
- New Digital Industries (2%): Big Tech, digital platforms, intermediaries (e.g., e-commerce, ride-sharing)
- Digitalization of Traditional Sectors (2%): BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, Insurance), trade, education
- Insight: Digital transformation is spreading beyond ICT into traditional sectors.
Frameworks Used
Framework Purpose
OECD Estimating core digital and enabling sectors
ADB Input-Output Broader economic impact via inter-industry linkages
India’s Expansion Includes digital share in BFSI, trade, education – not covered under OECD
Key Drivers of India’s Digital Economy
- Widespread mobile use: 1.14 billion subscribers in India
- High internet traffic: 3rd globally, with avg. 16.9 GB/month
- 5G leadership: 2nd largest 5G smartphone market in 2024
- Aadhaar success: 1.3+ billion biometric IDs issued
- Digital payments boom: 1,644 billion transactions in FY24
- ICT service exports: USD 162 billion (2nd highest globally)
- AI leadership: India leads GitHub AI contributions (23%)
- Startup ecosystem: 3rd highest number of unicorns globally
Future Projections (By 2030)
- Digital economy to reach ~20% of national income
- Growth drivers:
- Expansion of digital platforms & intermediaries
- Deepening digitalization in all sectors
- Greater internet & broadband access
Challenges in Measuring Digital Economy
- Difficulty in defining digital sectors due to their integrated nature
- Conventional national accounting systems are inadequate
- Lack of data from:
- Informal sector digitalization
- Smaller platforms and startups
- Digital shifts in healthcare, logistics, etc.
Importance of This Report
- Policy Formulation: Enables targeted strategies for digital growth
- Business Strategy: Helps identify trends, plan investments
- Global Standing: Puts India among early adopters of robust measurement frameworks
Mission SCOT

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India praised Indian space startup Digantara for the successful launch of Mission SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) — the world’s first commercial SSA satellite, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
What is Mission SCOT?
Feature Description
Developer Digantara (Indian space startup), supported by Aditya Birla Ventures & SIDBI
Launched on SpaceX Transporter-12 mission (rideshare platform)
Type First commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite
Orbit Sun-Synchronous Orbit – ideal for consistent Earth observation
Function Tracks Resident Space Objects (RSOs) as small as 5 cm in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
What is Space Situational Awareness (SSA)?
- SSA involves the detection, tracking, cataloging, and prediction of natural and man-made objects in Earth's orbit (like satellites, debris, etc.).
- Ensures safe and sustainable operations by minimizing collision risks.
- Critical due to increasing congestion in LEO, especially with rising numbers of small satellites and mega-constellations.
Key Features of Mission SCOT
Feature Advantage
High Revisit Rate More frequent observations of objects in orbit
Precision Tracking Can track debris ≥ 5 cm in size
All-Weather Monitoring Overcomes limitations of ground-based systems like cloud cover, FoV
Space-based System Unhindered by geography, providing continuous global surveillance
Supports SSA Infrastructure Aids in collision avoidance, space traffic management, and defence preparedness
???????? India’s SSA Ecosystem
Initiative Role
ISRO’s IS4OM Provides Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR); enables safe & sustainable space operations
NETRA Project Network for Space Objects Tracking & Analysis – aims to build a dedicated SST (Space Surveillance & Tracking) network using radars & optical telescopes
Multi-Object Tracking Radar Operated at Sriharikota – limited range, being augmented
Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAMs) Regularly performed by ISRO to protect its satellites from debris threats
Global Context: Transporter-12 Rideshare
- A SpaceX program providing low-cost access to space by allowing multiple customers to launch small payloads on a single rocket.
- Enhances global commercial space activity, democratizes space access.
Significance for India
Strategic:
- Strengthens national space defence by enabling indigenous tracking of space threats.
- Reduces reliance on foreign SSA data (e.g., NORAD/US Space Command).
Technological:
- Demonstrates India’s capability in space-based surveillance tech.
- Positions India as a global contributor in the emerging SSA domain.
Economic:
- Boosts private sector space innovation aligned with India’s NewSpace Policy.
- Attracts venture capital and international collaboration.
LID-568
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, an international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory discovered a low-mass supermassive black hole, LID-568, showing super-Eddington accretion—a rare and extreme feeding process—just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
About LID-568
Feature Description
Type Low-mass supermassive black hole
Age Formed ~1.5 billion years after Big Bang (Universe’s “youth”)
Discovery Observed via Chandra (X-ray) & JWST (infrared)
Location In a distant galaxy with very low star formation
Feeding Rate Accreting at ~40× the Eddington limit (super-Eddington accretion)
Key Concepts
Eddington Limit
- Theoretical upper limit on how fast matter can fall into a black hole before radiation pressure balances gravitational pull.
- Exceeding this limit (super-Eddington) is thought to be unstable and short-lived.
Super-Eddington Accretion
- Observed in LID-568, feeding at 40× Eddington rate.
- Suggests rapid, short bursts of black hole growth, not the slow, steady model previously assumed.
Why is LID-568 Important?
Challenges Current Theories
- Traditional black hole growth models require:
- Long periods (hundreds of millions of years).
- Seed black holes formed from:
- Death of first stars (light seeds: 10–100 solar masses).
- Collapse of primordial gas clouds (heavy seeds: 1,000–100,000 solar masses).
- LID-568 suggests brief, intense growth spurts could create supermassive black holes faster than previously thought.
Impact on Host Galaxy
- Powerful outflows prevent gas accumulation → suppresses star formation.
- Indicates black holes can regulate galaxy evolution, even when young.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Government, under the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, has introduced the Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global diamond trade, promote exports, and protect employment, especially in the MSME sector.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Boost value addition and export growth in the diamond sector.
- Support MSME exporters to compete globally.
- Retain India’s position as a global hub for diamond processing and exports.
- Mitigate recent challenges like export decline, job losses, and global demand shifts.
Key Features of the Scheme:
Feature Details
Type of Diamonds Allowed Natural cut and polished diamonds less than ¼ carat (25 cents)
Eligibility Exporters with Two Star Export House status and minimum $15 million annual exports
Export Obligation 10% value addition on imported diamonds
Duty Exemptions Exempts Basic Customs Duty, Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, etc.
Effective Date April 1, 2025
Exclusion Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs) not covered
Monitoring Agency Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC)
Why the Scheme Was Introduced:
Challenges in the Diamond Sector:
- Global: Falling demand in US, Europe, China; rise in lab-grown diamonds.
- Domestic: High unsold inventory, rising operational costs, reduced credit flow, and high corporate tax.
- Employment Impact: Job losses in the diamond cutting and polishing segment.
International Context:
- Inspired by beneficiation policies in diamond-producing countries like Botswana and Namibia, which mandate local value addition.
Significance:
- Enhances India’s role in the global diamond value chain.
- Provides ease of doing business through duty relief.
- Promotes employment generation, especially for diamond assorters and processors.
- Facilitates inclusive growth by supporting MSMEs in a traditionally export-driven industry.
Way Forward:
- Regulate Lab-Grown Diamonds to prevent market distortion.
- Extend export credit period and consider tax exemptions for foreign diamond sellers.
- Ensure technology upgradation and skill training to sustain global leadership.
Chinar Trees

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute (JKFRI), has launched a pioneering conservation initiative to digitally preserve the iconic Chinar trees (Platanus orientalis)—a vital part of Kashmir’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Significance of Chinar Trees:
- Locally known as Boonyi or Boueen, Chinar trees are deeply embedded in Kashmir’s cultural identity.
- These deciduous trees can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10–15 meters, and can live for over 600 years.
- They are known for their seasonal leaf color transformation—from green in summer to red, amber, and yellow in autumn.
- Notable specimens include Asia’s largest Chinar in Ganderbal and the oldest known Chinar (647 years) in Chattergam, Budgam.
Challenges to Chinar Survival:
- Urban expansion and habitat encroachment.
- Climate change, altering precipitation and temperature patterns.
- Illegal felling and timber exploitation.
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tree Aadhaar & Geo-Tagging Initiative:
- Over 28,500 Chinar trees have been geo-tagged and assigned unique Tree Aadhaar numbers from 2021 to 2023.
- Each tree is fitted with a QR-coded digital plate, enabling real-time access to:
- Tree location, height, girth, canopy dimensions
- Health status, ecological threats, and pest presence
- These plates are spring-mounted metal tags to prevent damage to the trees.
Conservation Goals & Future Plans:
- Digital Protection: Enables proactive monitoring and protection through a centralized database.
- Chinar Atlas: A comprehensive mapping of all Chinar trees in the region.
- Public Access Website: A dedicated digital portal is planned for broader access to Chinar data.
- Risk Assessment: Use of USG-based, non-invasive surveys to identify trees at risk without human interference.
- Emphasis on covering remote and restricted areas in future phases to ensure inclusivity in conservation.
Takers, Not Makers

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Report “Takers not makers: The unjust poverty and unearned wealth of colonialism” published by Oxfam.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Oxfam International at the World Economic Forum 2025
- Core Focus: The report explores historical colonial wealth extraction, especially from India, and connects it to contemporary global inequalities.
Colonial Wealth Drain – India:
- $64.82 trillion extracted from India by Britain (1765–1900), adjusted to today’s value.
- $33.8 trillion (52%) enriched the UK’s richest 10%
- 32% benefited the British middle class
- India's industrial output dropped from 25% in 1750 to 2% in 1900 due to:
- British protectionist policies (especially targeting Asian textiles)
- High taxation, home charges, currency manipulation, and profit repatriation
Conceptual Framework:
- "Drain of Wealth" Theory by Dadabhai Naoroji forms the report’s foundation.
- Colonialism framed as both:
- Historical phenomenon: Loot, repression, forced de-industrialization
- Modern structure (Neo-colonialism): Corporate dominance, digital colonization, and unjust global governance
Neo-Colonial Parallels Today:
- Wages in Global South: 87–95% lower than for same work in Global North
- Multinational corporations:
- Descendants of colonial entities like the East India Company
- Extract resources & exploit labor under unequal terms of trade
- Global institutions like WTO and World Bank perpetuate inequity through imbalanced power dynamics
Ongoing Consequences in Global South:
- Poor public services, education, and healthcare
- Caste, religion, and language divisions institutionalized during colonial rule
- E.g., Only 0.14% of Indian languages used as medium of instruction
- Bengal Famine (1943): Caused by wartime policies & racist attitudes, ~3 million deaths
- Biopiracy cases (e.g., neem) reflect continued exploitation
Wealth Disparity & Inequality:
- Billionaire wealth tripled in growth rate in 2024 (vs. 2023)
- Top 1% own more than 95% of global wealth
- Over 3.5 billion people survive on less than $6.85/day
ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
India–Singapore Semiconductor Cooperation

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
During his 2025 visit to India, Singapore President Tharman Shanmugaratnam announced plans to collaborate with India on semiconductor manufacturing and the creation of a semiconductor ecosystem, marking the 60th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the two nations.
Singapore’s Semiconductor Landscape
- Contribution to Economy: Accounts for ~8% of Singapore’s GDP.
- Global Standing:
- Produces 10% of global semiconductor output.
- 5% of global wafer fabrication capacity.
- 20% of global semiconductor equipment production.
- Comprehensive Ecosystem: End-to-end capabilities from IC design to packaging and testing.
- Infrastructure: Four wafer fabrication parks with advanced facilities.
- Current Limitation: Focused on mature-node chips (28 nm+); lacks high-end logic chip manufacturing (7 nm or below).
India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Market Size (2024): Valued at USD 52 billion; projected to reach USD 103.4 billion by 2030.
- Import Dependency: ~85% of semiconductor needs met through imports.
- Export-Import Gap (2022): USD 5.36 billion (imports) vs. USD 0.52 billion (exports).
India's Advantages:
- Skilled Talent Pool: Large number of STEM graduates.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower manufacturing and operational costs.
- Geopolitical Opportunity: Global supply chain diversification away from China.
Government Initiatives:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- Semicon India Programme
- Display & Semiconductor Fab Schemes
- SPECS (Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors)
Foreign Collaborations:
- MoUs with US, Japan, and European Commission.
- Tata–Powerchip (Taiwan) collaboration for a fab in Dholera, Gujarat.
How Singapore Can Support India’s Semiconductor Vision
- Manufacturing Partnerships:
- Collaborations with Singaporean firms for assembly and testing services.
- Access to Singapore's advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Talent Development:
- Academic exchanges in microelectronics and semiconductor engineering.
- Joint research and PhD programs.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Replication of Singapore-style wafer fab parks in India.
- Joint ventures to build specialized semiconductor industrial zones.
- Technology Access & Innovation:
- Transfer of advanced technologies and critical semiconductor materials.
- Collaboration on new-generation tech solutions (e.g., AI chips, advanced computing).
Additional Areas of Bilateral Cooperation
- Digital Economy: Exploring data corridor between GIFT City (India) and Singapore.
- Sustainability: Cooperation on green hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable energy.
Strategic Partnership: Upgraded to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2024.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
Exercise La Perouse 2025
- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
India is participating in the fourth edition of the multinational naval exercise La Perouse, hosted by France in key maritime straits—Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok. The Indian Navy's INS Mumbai, an indigenously built guided-missile destroyer, represents India.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Countries: Navies from India, France, Australia, USA, UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Canada.
- Objectives:
- Enhance maritime situational awareness.
- Promote tactical interoperability through joint training.
- Conduct surface warfare, anti-air warfare, air defence, and VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations.
- Strengthen cooperation on maritime surveillance, air operations, and information sharing.
- Significance:
- Demonstrates commitment to a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Counters increasing presence of Chinese naval forces in the Indo-Pacific.
Strategic Location: Key Straits in Focus
- Strait of Malacca
- Connects: Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Geography: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, near Singapore.
- Significance: One of the world’s busiest trade routes.
- Choke Point: Narrowest part (Philips Channel) is only 2.8 km wide.
- Sunda Strait
- Connects: Java Sea (Pacific) to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Java and Sumatra (Indonesia).
- Challenges: Volcanic islands (e.g., Krakatoa), shallow depths (20–100 m).
- Importance: Secondary maritime route, strategic in times of congestion in Malacca.
- Lombok Strait
- Connects: Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Bali and Lombok islands.
- Depth: 250–1,300 meters – suitable for large vessels.
- Unique Feature: Part of the Wallace Line, a major ecological boundary.
Sanchar Saathi App

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
In a landmark move to enhance telecom accessibility, security, and empowerment across India, the Union Minister of Communications launched a suite of citizen-focused initiatives. Key highlights of the event included the launch of the Sanchar Saathi Mobile App, National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0 and the inauguration of the Intra Circle Roaming facility at DBN Funded 4G Mobile Sites.
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
- Launched by: Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
- Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- Objective: Strengthen telecom security, empower citizens, and combat telecom fraud.
- Key Features:
- Chakshu (SFC): Report suspected fraud communications (calls/SMS).
- Know Your Mobile Connections: Identify and manage all mobile numbers issued in one’s name.
- Block Lost/Stolen Devices: Swiftly block, trace, and recover lost/stolen mobile phones.
- Verify Handset Genuineness: Confirm the authenticity of mobile handsets before purchase.
Impact so far (via Sanchar Saathi Portal, launched May 2023):
- 2.75 crore fraudulent connections disconnected.
- 25+ lakh lost/stolen devices blocked.
- 12.38 lakh WhatsApp accounts linked to cybercrimes disengaged.
- 11.6 lakh mule bank accounts frozen.
- 90% spoofed international calls blocked within 2 months of new prevention system.
National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0
- Launched by: Union Minister of Communications, builds upon NBM 1.0 (2019–2024).
- Part of: National Digital Communications Policy, 2018.
- Aim: Digitally empower citizens and bridge the digital divide to realize the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Targets (by 2030):
- 2.70 lakh villages to be connected with OFC (from ~50,000 now).
- 90% broadband connectivity to anchor institutions (schools, PHCs, Panchayats, Anganwadis).
- Fixed broadband speed: Increase national average from 63.55 Mbps (2024) to 100 Mbps.
- Right of Way (RoW) disposal time: Reduce from 60 days to 30 days.
- Rural internet subscribers: Increase from 45 to 60 per 100 population.
- 30% of mobile towers to be powered by sustainable energy.
- 100% mapping of PSU fiber networks on PM GatiShakti National Master Plan by 2026.
- Enhanced use of “Call Before u Dig (CBuD)” app to protect underground telecom infrastructure.
- Facilitate 5G rollout, and prepare infrastructure for 6G and common telecom ducts in all linear projects.
- Leverage power sector (e.g. Optical Ground Wire - OPGW) for broadband in remote/hilly areas.
Intra Circle Roaming (ICR) at DBN-Funded 4G Sites
- Launched by: Ministry of Communications.
- Implemented under: Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN), formerly USOF.
- Objective: Allow subscribers of multiple telecom service providers (TSPs) (e.g., BSNL, Airtel, Reliance) to access 4G services from a single DBN-funded tower.
- Impact:
- Eliminates need for duplicate towers.
- Covers 27,000+ towers across 35,400 remote villages.
- Enhances user choice, reduces cost, and ensures efficient infrastructure use.
Binding DDT-Infused Soil with Biochar
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
A three-year study was conducted on a 23-hectare DDT-contaminated former tree nursery in southern Sweden. Researchers mixed biochar into sections of the contaminated soil and planted different crops, including pumpkins, legumes, grasses, and willows.
Key findings:
- Reduction of DDT Uptake: The presence of biochar reduced DDT absorption by soil organisms, cutting the toxin uptake by earthworms in half.
- Enhanced Soil Health: Biochar improved soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity.
- Cost-Effective Alternative: Unlike traditional soil removal methods, which are expensive and labor-intensive, biochar treatment offers a sustainable and economical approach.
- Support for Renewable Energy: The method allows for the growth of bioenergy crops such as willow trees, further contributing to environmental benefits.
Implications for Future Agricultural Practices
This breakthrough provides a viable approach to rehabilitate contaminated lands worldwide. Many regions, including India, still grapple with DDT contamination. While India banned agricultural use of DDT in 1972, it continues to be used for disease control under strict regulations. The application of biochar could significantly aid in soil restoration and sustainable land management
About DDT
- Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a synthetic insecticide first introduced in 1939. It was widely used in agriculture and public health initiatives to control vector-borne diseases like malaria.
- However, despite its effectiveness against pests, DDT’s persistence in the environment led to severe ecological and health concerns.
- It degrades slowly, accumulates in fatty tissues, and disrupts ecosystems by affecting soil fertility, harming wildlife, and posing potential human health risks, including endocrine disruption and carcinogenic effects.
Challenges Posed by DDT-Contaminated Soils
The prolonged use of DDT has resulted in extensive soil contamination, making land infertile and unsuitable for cultivation. Conventional methods of decontamination, such as soil excavation and disposal, are expensive and environmentally unsustainable.
Biochar as a Solution
Researchers at Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology have developed an innovative method to restore DDT-contaminated soils by integrating biochar.
What is Biochar?
Biochar is a charcoal-like material produced by burning organic waste in a controlled oxygen-limited environment (pyrolysis). It is known for its ability to enhance soil quality, bind contaminants, and store carbon for extended periods.
Global Risks Report 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the 20th edition of the Global Risks Report 2025, outlining the most pressing global risks over short-term (1-2 years) and long-term (10 years) horizons.
- The report, based on the Global Risks Perception Survey (GRPS) 2024-2025, categorizes risks across economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological domains.
Key Findings of the Report
Short-Term Risks (1-2 Years)
- Misinformation and Disinformation – Undermines trust in governance and institutions, complicating global cooperation.
- Extreme Weather Events – Rising costs and frequency due to climate change.
- State-Based Armed Conflict – Geopolitical tensions, including conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine war.
Long-Term Risks (10 Years)
- Extreme Weather Events – Ranked as the most significant long-term risk.
- Biodiversity Loss & Ecosystem Collapse – Drastic impact on food security and natural systems.
- Critical Changes to Earth Systems – Irreversible environmental shifts.
Evolving Global Risk Landscape
The risk landscape is shaped by four structural forces:
- Technological Acceleration – Rapid advancements in AI and digital platforms.
- Geostrategic Shifts – Increasing global polarization and armed conflicts.
- Climate Change – Rising environmental hazards.
- Demographic Bifurcation – Aging populations and labor shortages.
Specific Risks and Trends
Environmental Risks
- Pollution: Increasing air, water, and land contamination due to unsustainable production.
- Natural Disasters: Wildfires in the U.S. projected to cause over $200 billion in damages.
- Water Supply Shortages: A major concern for countries like India.
Economic and Trade Risks
- Escalating Trade Protectionism: Increase in tariffs and restrictions (e.g., Make in India, U.S. Inflation Reduction Act).
- Economic Uncertainty: Global inflation projected to decrease to 3.5% by 2025, but trade tensions may reignite financial instability.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Decline: A 10% drop in 2023 due to trade fragmentation.
Technological Risks
- Misinformation & Disinformation: AI-generated content fuels societal polarization.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI-driven cyberattacks and algorithmic biases in governance.
- Surveillance & Censorship: Increased digital monitoring with inadequate legal safeguards.
Geopolitical and Societal Risks
- Erosion of Human Rights: Increasing authoritarian surveillance and control.
- Migration & Resource Shortages: Climate-induced migration is a rising global concern.
- Pension Crisis: Aging populations in countries like Japan and Germany threaten economic stability.
India-Specific Risks
- Water Shortages – Critical impact on agriculture and urban development.
- Misinformation & Disinformation – Threatens democratic institutions and governance.
- Pollution (Air, Water, Soil) – Major environmental and health hazard.
- Labor & Talent Shortages – Workforce challenges due to demographic shifts.
- Erosion of Civic Freedoms – Concerns over digital surveillance and censorship.
Policy Recommendations
Global and Domestic Strategies
- Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation: WTO reforms and global trade dispute resolutions.
- Boost Domestic Resilience: Investment in infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
- Combat Pollution: Stricter regulations on air and water pollutants.
- Address Algorithmic Bias: Global standards for AI governance and accountability.
- Ethical Oversight for Biotech: WHO-led regulations for human genome editing.
Long-Term Sustainability Measures
- Flexible Work Policies: Encouraging non-linear career paths.
- Pre-Retirement Health Programs: Improving lifestyle choices to reduce healthcare costs.
- Pension System Reforms: Raising retirement ages and ensuring financial security for retirees.
Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum (WEF) recently released the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 report. The report examines cybersecurity trends, key challenges, and necessary strategies to enhance global cyber resilience.
About Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
Produced in collaboration with Accenture, the report highlights major cybersecurity issues influenced by geopolitical tensions, emerging technologies, supply chain complexities, and cybercrime advancements.
Key Issues Highlighted
- Geopolitical Conflicts:
- Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, have increased cyber vulnerabilities in critical sectors like energy, telecommunications, and nuclear power.
- Nearly 60% of organizations state that geopolitical tensions have impacted their cybersecurity strategies.
- Cybersecurity Readiness:
- Two-thirds of organizations foresee AI impacting cybersecurity, yet only one-third have the tools to assess AI-related risks.
- Smaller organizations face significant challenges in adopting AI-driven security measures.
- Cyber Skills Gap:
- As of 2024, there is a shortage of 4.8 million cybersecurity professionals globally.
- Only 14% of organizations have a skilled workforce to manage current cybersecurity threats.
- Public-sector organizations are notably impacted, with 49% reporting a shortage in cybersecurity talent.
- Supply Chain Interdependencies:
- Over 50% of large organizations identify supply chain complexity as a barrier to cyber resilience.
- Vulnerabilities in third-party software, cyberattacks, and enforcement issues in security standards are key concerns.
- Cybercrime Sophistication:
- Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging generative AI tools for automated and personalized attacks, including phishing and social engineering.
- In 2024, 42% of organizations experienced phishing and deepfake attacks.
- Regulatory Challenges: 70% of organizations reported that complex cybersecurity regulations cause compliance issues.
Impacts
- Critical Infrastructure:
- Cyberattacks on essential infrastructure, such as water utilities, satellites, and power grids, pose severe risks to public safety.
- Example: A 2024 cyberattack on a U.S. water utility disrupted operations, highlighting vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure systems.
- Biosecurity Risks:
- Advancements in AI, cyberattacks, and genetic engineering create risks for bio-laboratories and research institutions.
- Incidents in South Africa and the UK underscore these threats.
- Economic Disparities: Developed regions like Europe and North America demonstrate stronger cyber resilience compared to emerging economies such as Africa and Latin America.
- Transition Issues to Renewable Energy (RE): The shift to renewable energy introduces new cybersecurity risks, making power grids attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Factors Increasing Cybersecurity Complexity
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Increasingly complex supply chains create risks with limited oversight, enabling cyberattacks to spread across interconnected systems.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts have driven advanced cyber strategies targeting critical infrastructure.
- AI-Driven Threats: Generative AI enables scalable malware deployment and sophisticated multilingual social engineering attacks.
- Cyber Skills Gap: A growing 8% skills gap leaves two-thirds of organizations unable to meet cybersecurity demands.
- Convergence of Cybercrime and Organized Crime: Rising cyber-enabled fraud has attracted organized crime groups, amplifying social impact.
- Climate-Linked Cyber Risks: Energy grids are increasingly targeted due to their reliance on evolving energy systems.
- Quantum Vulnerabilities: Quantum computing poses risks to public-key encryption, which is essential for securing digital systems.
Way Forward
Strategic Investment:
- Cybersecurity must be viewed as a strategic investment rather than a technical expense.
- Governments are encouraged to modernize legacy systems and upgrade operational technologies to protect critical sectors.
Public-Private Collaboration:
- Collaboration between business and cybersecurity leaders is essential for sharing threat intelligence and enhancing resilience.
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may require government incentives to enhance cybersecurity.
Skills Development: Expanding specialized training programs, certifications, and incentives is crucial to addressing the cybersecurity skills gap.
Focus on Resilience Over Prevention: Nations must prioritize resilience by enhancing response mechanisms, crisis management frameworks, and ensuring continuity of services.
International Cooperation:
- Collaborative efforts through forums like the United Nations (UN) and G20 can strengthen global cybersecurity frameworks.
- Developed nations should assist emerging economies in improving cyber resilience.
Current Framework for Cybersecurity in India
- Legislative Measures:
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Institutional Framework:
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Strategic Initiatives:
- Bharat National Cybersecurity Exercise 2024
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013
- Sector-Specific Regulations:
- Cybersecurity Framework for SEBI Regulated Entities
- Telecommunications (Critical Telecommunication Infrastructure) Rules, 2024
Rupee Depreciation

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian rupee has recently experienced sharp devaluation against the US dollar after a period of relative stability. This shift is attributed to several factors, including capital outflows, rising import costs, and RBI’s evolving policy stance.
Understanding Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange rates are classified into:
- Fixed Exchange Rate: The central bank maintains a constant exchange rate by actively managing reserves.
- Floating Exchange Rate: Market-driven rates with minimal intervention.
- Managed-Floating Exchange Rate: A blend of market forces and central bank intervention.
India has largely pursued a managed-floating exchange rate regime. The RBI has historically responded to excess demand by depreciating the rupee while selling forex reserves and, under excess supply conditions, resisted rupee appreciation to maintain export competitiveness.
Post-COVID Exchange Rate Shift
Between 2022 and November 2024, the RBI temporarily adopted a strategy resembling a fixed exchange rate regime to stabilize the rupee. However, amid rising capital outflows and increased import costs, the RBI recently reverted to its managed-float approach, allowing the rupee to depreciate.
Causes of Rupee Depreciation
- Internal Factors:
- Rising inflation reduced the rupee's real value and increased production costs.
- A widening trade deficit due to higher crude oil imports heightened demand for foreign currency.
- Persistent fiscal imbalances further pressured the rupee.
- Policy ambiguity in the RBI’s stance added market uncertainty.
- External Factors:
- Capital outflows driven by global uncertainties and rising US interest rates.
- Geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) increased India’s import bill.
- The US dollar's strength amid aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes further weakened the rupee.
Implications of Rupee Devaluation
- Positive Effects:
- Boost to Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian goods cheaper, enhancing export competitiveness if supported by real exchange rate depreciation.
- Adverse Effects:
- Inflationary Pressures: Higher import costs increase consumer prices.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Increased costs are often passed on to consumers.
- Foreign Debt Servicing: A depreciated rupee raises debt repayment costs for Indian firms and the government.
- Investor Sentiment: Currency instability diminishes foreign investor confidence, triggering further capital outflows.
Structural Constraints in the Indian Economy
- Divergence between NEER and REER:
- Since the mid-2010s, India's Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) depreciated while the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) appreciated. This divergence undermines export competitiveness, as rising domestic prices offset nominal depreciation benefits.
- Rising Markups:
- Non-financial firms increased their markups on variable costs, contributing to inflation and nullifying the advantages of currency depreciation for exports.
Policy Responses and Recommendations
- RBI Interventions:
- Forex market interventions to manage demand-supply imbalances.
- Interest rate adjustments to attract capital inflows and stabilize the rupee.
- Enhanced forex reserve management to mitigate excessive volatility.
- Fiscal Strategies:
- Reducing Import Dependency: Boost domestic production of high-demand goods like crude oil substitutes.
- Export Incentives: Strengthen export sectors through subsidies, incentives, and improved infrastructure.
- Encouraging Long-Term FDI: Promoting stable investment environments for sustained capital inflows.
- Structural Reforms:
- Policies that enhance domestic production, reduce reliance on volatile foreign portfolio investments (FPIs), and maximize remittances can stabilize the rupee in the long term.
Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan initiative, launched by Defence Minister coinciding with the 77th Army Day celebrations, is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism.
Key Highlights:
- This initiative is designed to promote battlefield and border tourism by providing citizens with access to historically significant battlefields and military sites.
Objectives
- Promote Battlefield and Border Tourism: Encourage citizens and tourists to explore India's military history.
- Enhance Awareness: Educate visitors about India’s historic battles and military valor.
- Socio-Economic Development: Boost infrastructure, connectivity, and local economies in border regions.
Features of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan
- Virtual Tours and Interactive Content: The platform offers historical narratives, virtual tours, and interactive multimedia to provide a detailed account of each battlefield.
- Travel Planning Assistance: Visitors can access information regarding permits, travel routes, and accommodations.
- Integration with the Incredible India Campaign: The initiative is part of the government’s broader tourism strategy, ensuring widespread promotion.
- Collaborative Infrastructure Development: The Indian Army is working with local civil authorities to facilitate safe tourism without compromising operational preparedness.
Key Locations Covered
- Galwan Valley (Ladakh): Site of the 2020 India-China clash.
- Doklam: A tri-junction between India, Bhutan, and China.
- Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC) Sites:
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim): Significant in the 1967 Indo-China clashes.
- Longewala (Rajasthan): Site of a key battle during the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Other Sites: Locations of the 1962 war with China and various Indo-Pak conflicts.
Significance
- Historical and Patriotic Engagement: Provides citizens firsthand insights into the challenges faced by soldiers in remote, strategic locations.
- Tourism Development in Border Areas: Previously restricted areas now open for visitors, leading to economic benefits for local communities.
- National Security Awareness: Encourages greater appreciation of India's defense forces and their contributions.
Implementation
The first phase of the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan project includes key battlefields and border sites across seven major regions. Future phases will expand coverage to additional historical military locations.
Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
Nag Mark-2
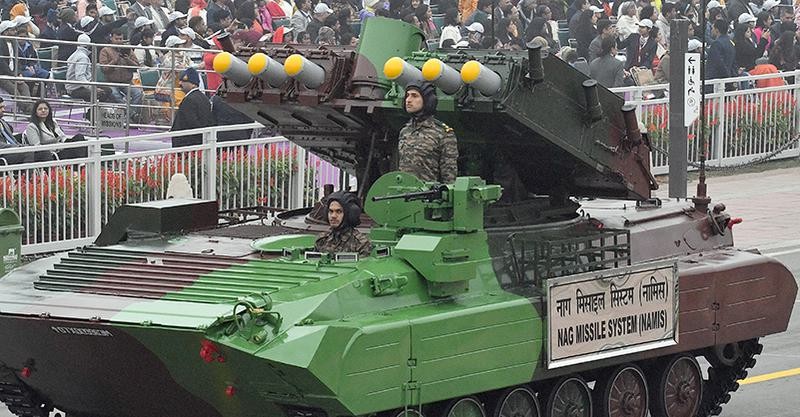

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals
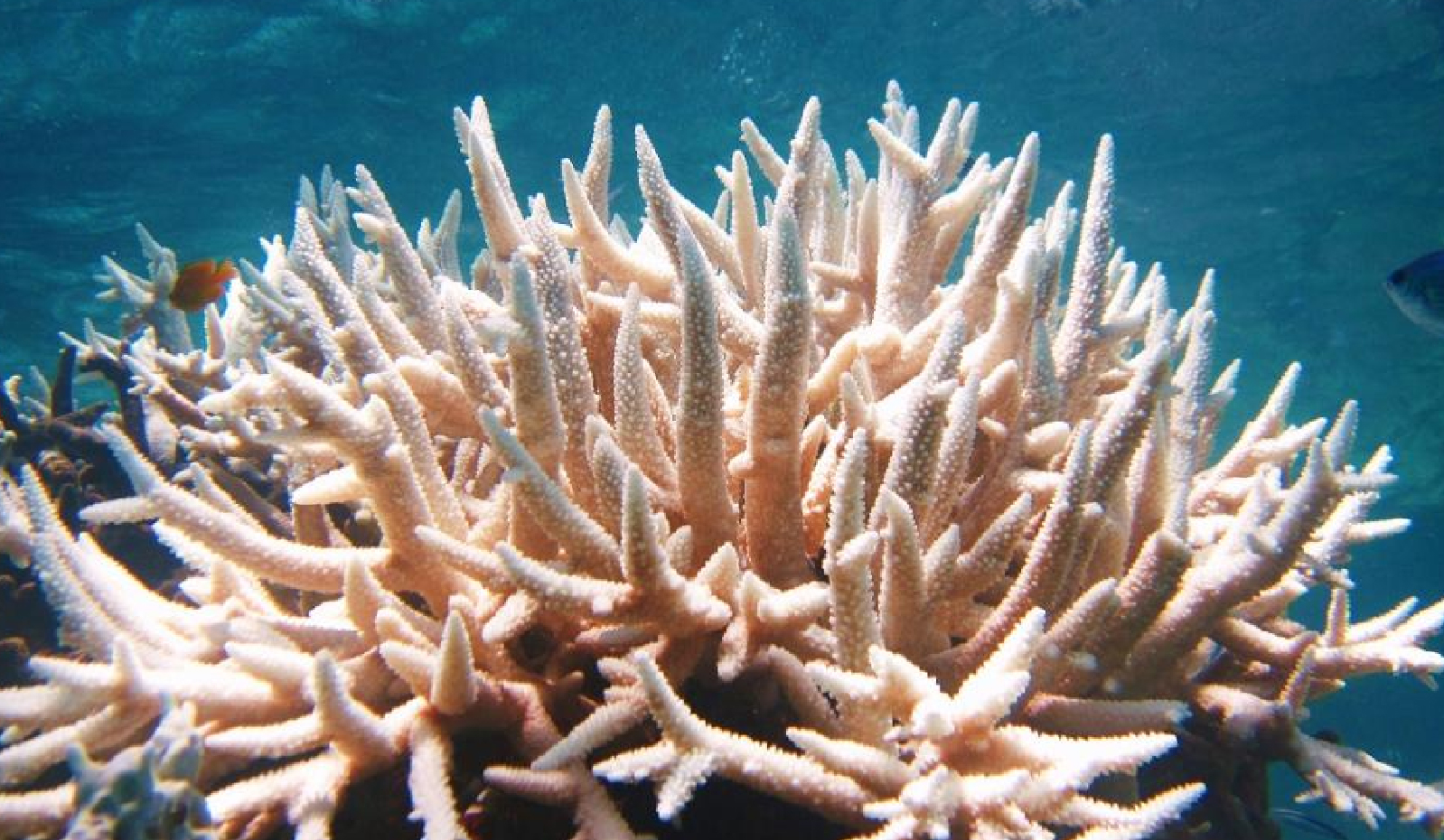

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
Miyawaki Technique
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Translocation of Tigers from Madhya Pradesh
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
Key Highlights of the Translocation:
- Scale of Translocation: Largest relocation of big cats from a single state in India.
- Approval: NTCA has approved the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Source Reserves:
- Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distribution Plan:
- Rajasthan: 4 tigresses.
- Chhattisgarh: 2 male tigers and 6 tigresses.
- Odisha: 1 male tiger and 2 tigresses.
- Funding: States receiving tigers will bear all expenses related to translocation.
Objectives of the Translocation:
- Enhance Tiger Conservation: Reintroduce and bolster tiger populations in recipient states.
- Population Management: Relocate tigers to areas with suitable habitats to alleviate territorial disputes in overpopulated reserves.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new individuals to isolated tiger groups to prevent inbreeding and support long-term species survival.
About Kanha, Bandhavgarh, and Pench Tiger Reserves:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Maikal range of the Satpura Mountains.
- Significance: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distinct Feature: First tiger reserve in India with an official mascot, ‘Bhoorsingh the Barasingha’.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity with Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, and the IUCN Vulnerable species, Barasingha.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Between Vindhyan and Satpura ranges in Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance: Known for one of the highest densities of Royal Bengal Tigers in India.
- Historical Link: The ancient Bandhavgarh Fort, linked to the legend of Lord Rama and Lakshmana.
- Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh, extends into Maharashtra.
- Significance: Inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book.
- Flora and Fauna: Includes teak, saag, mahua forests; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and gaur are key species.
Tiger Translocation Project Overview:
- First Project:
- Initiated in 2018, two tigers relocated from Kanha and Bandhavgarh to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Main Objectives:
- Reintroduce Tigers: In areas where they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Alleviate Territorial Disputes: Overpopulated reserves need additional tigers to reduce human-animal conflict.
Benefits of Translocation:
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-Animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces conflict in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns Associated with Translocation:
- Local Community Protests: Villagers fear tigers will pose a threat to their safety.
- Territorial Disputes: New tigers may face conflict with resident tigers.
- Poor Forest Management: Inadequate prey augmentation and habitat management may hinder success.
Madhya Pradesh’s Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Largest Tiger Population: Madhya Pradesh hosts the largest number of tigers in India, with 785 tigers as per NTCA’s 2022 report.
- Tiger Reserves: The state is home to nine tiger reserves, including the newly notified Madhav Tiger Reserve in Shivpuri.
- Translocation Strategy: Madhya Pradesh’s involvement helps reduce local tiger population pressure and contributes to broader conservation efforts across India.
Inter-State Tiger Translocation Goals:
- Reinforcement and Reintroduction: Introduce tigers into areas historically part of their range but from which they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new tigers to isolated populations to maintain long-term population health.
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
Stellaria bengalensis
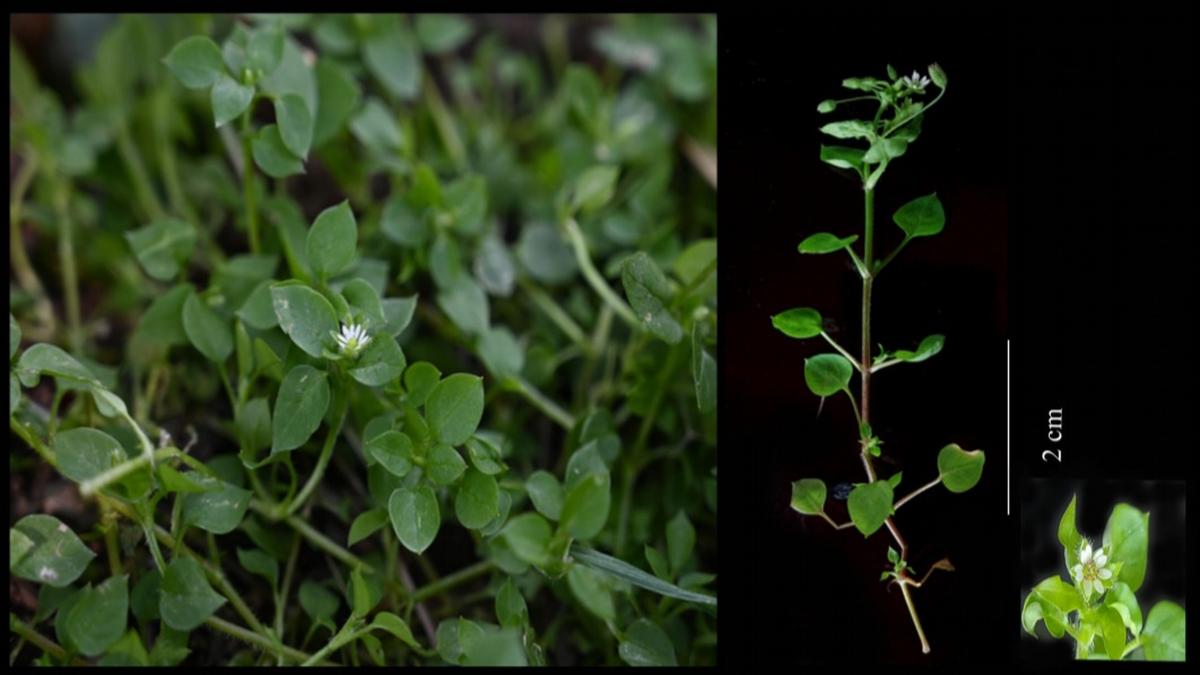

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam
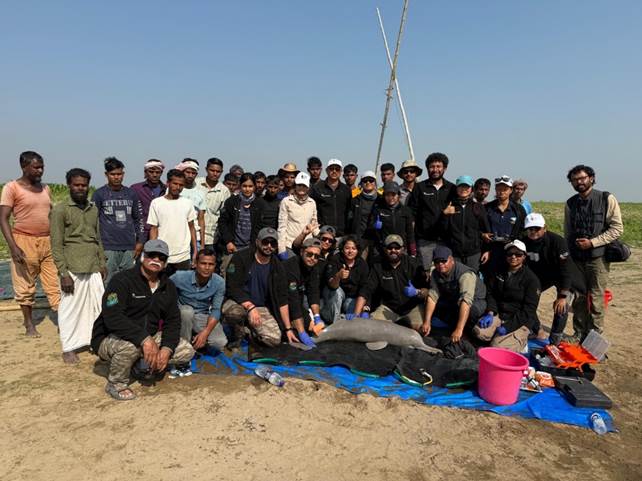

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
Rajmarg Saathi - Upgraded Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPV) by NHAI
- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
With an aim to enhance road safety and strengthen highway patrolling, NHAI plans to implement the upgraded and forward-looking Incident Management Services. The guidelines on the subject include updated specifications for new Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs) named ‘Rajmarg Saathi’ and outlines design, functions, technology, components and manpower specifications for the RPVs.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Rajmarg Saathi:
- Initiative by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Objective: Enhance highway safety, emergency response, and road maintenance efficiency across India.
- Launched in: December 2024.
What is Rajmarg Saathi?
- Definition: An upgraded version of Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs), designed for effective highway patrolling and incident management.
- Main Aim: Improve highway safety and ensure smooth traffic flow through advanced technology and quick emergency responses.
Key Features:
- Advanced Design:
- Closed Cabinets: For organized storage and easy access to emergency tools and inventory, replacing earlier models with open storage space.
- AI-Powered Technology:
- Dashboard Cameras: Equipped with AI-enabled cameras to capture and analyze road conditions like cracks, potholes, and other distresses.
- Road Monitoring: The system also monitors vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other infrastructure elements.
- Integration with NHAI One: Data collected by AI systems is integrated into NHAI’s centralized application for efficient road maintenance.
- Emergency Preparedness: The RPVs are fully equipped with modern communication and safety tools, designed to minimize traffic disruptions during emergencies.
Data Collection and Maintenance:
- Weekly Analytics: The system will collect and analyze road condition data weekly to streamline maintenance activities and monitor highway safety.
Vehicle Usage and Replacement:
- Replacement Guidelines: RPVs will be replaced after 3 years of operation or 3,00,000 km to ensure they remain functional and service-ready.
Visibility and Branding:
- External Branding: RPVs are designed to be highly visible with enhanced branding for easy recognition as highway patrol vehicles.
- Uniform for Personnel: The patrolling personnel will wear updated uniforms, including bright blue colors and reflective jackets with authority logos for better identification.
Role in Incident Management:
- RPVs will play a crucial role in managing traffic incidents, ensuring smooth traffic flow, and enhancing road safety by addressing emergencies quickly.
Commitment to Road Safety:
- NHAI remains committed to improving road safety standards and ensuring a smooth, hassle-free travel experience for all users across the national highway network.
About NHAI:
- Establishment: NHAI was established under the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988, and became operational in 1995.
- Responsibilities: It is responsible for developing, maintaining, and managing national highways in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote transparency in awarding contracts.
- Maintain high standards of project implementation.
- Ensure comfort and convenience for users of the national highway system.
India's Road Network:
- Size: India has the 2nd-largest road network in the world, spanning approximately 63.32 lakh km, which includes national highways, expressways, state highways, and rural roads.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
