Tomahawk Missiles
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the Iran-Israel conflict, the United States has reportedly launched precision strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, targeting key sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan. These attacks were carried out using Tomahawk cruise missiles and GBU-57 bunker busters, marking a critical intervention by the US in the unfolding regional crisis. President Donald Trump termed the strikes a “clear warning” to Iran, signalling the potential for intensified military action if diplomatic overtures are rejected.
What Are Tomahawk Missiles?
The Tomahawk missile is a long-range, subsonic, all-weather cruise missile primarily operated by the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It is designed for precision strikes on high-value or heavily defended targets, including hardened or buried infrastructure such as nuclear sites.
- Launch platforms: Ships and submarines
- Flight path: Low-altitude terrain-following flight to evade radar
- Use case: Strategic, surgical strikes in contested or defended environments
Design and Capabilities
- Length: ~5.6 meters (without booster)
- Weight: Up to 1,600 kg
- Speed: ~880 km/h (subsonic)
- Range: Over 1,600 km (varies by variant)
- Flight altitude: As low as 30–50 meters
- Warheads:
- Unitary high-explosive
- Cluster munitions
- Nuclear warheads (retired from use)
Navigation and Guidance Systems
Tomahawk missiles are known for pinpoint accuracy, achieved through a multi-layered guidance system:
- GPS (Global Positioning System) and INS (Inertial Navigation System) for real-time course tracking
- TERCOM (Terrain Contour Matching): Compares terrain under flight path with stored maps
- DSMAC (Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation): Matches live terrain imagery with onboard target data
- Data-link capability: Allows for in-flight re-targeting, mission abort, or loitering over areas
Variants and Modern Upgrades
- Tomahawk Block IV (TLAM-E): Most modern variant, featuring:
- In-flight reprogramming
- Target loitering
- Real-time battle damage assessment
- Two-way satellite communication
Historical Combat Usage
Tomahawk missiles have been extensively used in US military operations:
- Gulf War (1991): ~280 missiles used in the opening strikes
- Operation Infinite Reach (1998): Targeted terrorist camps in Sudan and Afghanistan
- Iraq War (2003): Hundreds used during the initial “shock and awe” campaign
- Libya Intervention (2011): Destroyed air defence infrastructure
- Syria (2017): 59 Tomahawks used against Shayrat Airbase in retaliation for chemical attacks
Operation Midnight Hammer
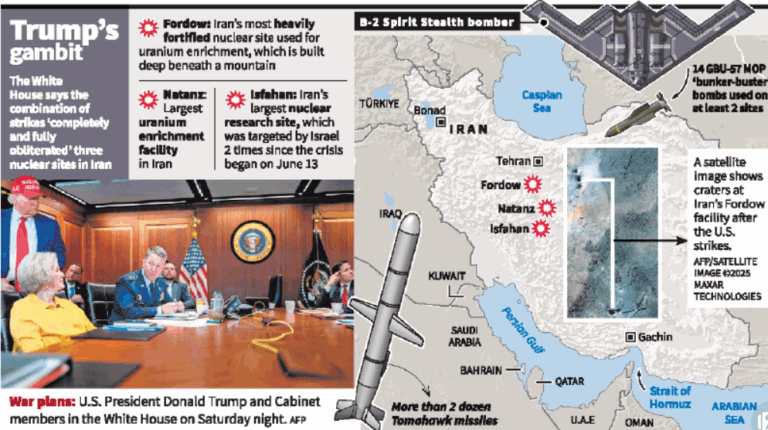
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The United States launched a classified military operation named Operation Midnight Hammer, targeting Iran’s major nuclear sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan, claiming significant damage to its nuclear infrastructure.
About Operation Midnight Hammer:
- A covert US airstrike intended to degrade Iran’s nuclear weapons program.
- Launched by: US Department of Defense.
- Objective: Destruction of fortified nuclear facilities and demonstration of US strategic air power.
Key Assets Deployed:
- B-2 Spirit Stealth Bombers equipped with GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrators (MOPs) – “bunker-buster” bombs designed to penetrate over 200 feet of reinforced concrete.
- Tomahawk Land Attack Cruise Missiles launched from US submarines.
- Support aircraft and decoys for air defence suppression.
B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber:
- Type: Long-range strategic stealth bomber of the US Air Force.
- Developed by: Northrop Grumman (1980s).
- Cost: Approx. $2.1 billion per unit – one of the most expensive aircraft in the world.
- Range: Over 6,000 nautical miles without refuelling.
- Crew: Operated by two pilots.
Weapons and Capabilities:
- Payload Capacity: Over 40,000 pounds.
- Armament Options:
- 2 × GBU-57A/B MOPs
- 16 × B83 nuclear bombs (part of US nuclear triad)
- Precision-guided weapons: JDAM, JSOW, JASSM-ER.
- Stealth Features: Radar cross-section as small as a bird – allows evasion of sophisticated air defences.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances the US’s global precision strike capabilities.
- Reinforces the deterrence role of the B-2 in both conventional and nuclear domains.
- Capable of targeting heavily fortified underground facilities.
- Proven operational effectiveness in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran.
