Financial Stability Report – June 2025
- 04 Jul 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently released the Financial Stability Report for June 2025.
What is the Financial Stability Report (FSR)?
- The Financial Stability Report (FSR) is a biannual publication by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- It presents the collective assessment of the Sub-Committee of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC-SC) regarding:
- Resilience of the Indian financial system
- Emerging systemic risks
- Outlook for macro-financial stability
Key Highlights – FSR June 2025
Macroeconomic & Global Outlook
- India remains a key driver of global growth, supported by strong macroeconomic fundamentals and prudent policies.
- Risks to growth include:
- Prolonged geopolitical tensions
- Trade and supply chain disruptions
- Weather-related uncertainties impacting agricultural output
Banking Sector Performance
- Gross Non-Performing Asset (GNPA) ratio:
- Stands at 2.3% as of March 2025, a multi-decadal low
- May rise modestly to 2.5% in baseline and 2.6% under adverse conditions by March 2027 (based on stress tests on 46 banks covering 98% of SCB assets)
- Capital Adequacy Ratios (CAR):
- Remain well above regulatory thresholds across the sector
- Even under severe stress scenarios, banks maintain adequate buffers — indicating robust financial health
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- NBFCs are in good financial health with:
- Strong capital buffers
- Robust earnings
- Improving asset quality
- Continued financial resilience contributes to the overall stability of the financial system
Domestic Demand and Inflation Outlook
- Growth remains domestically driven
- Food inflation outlook favorable:
- Price moderation observed
- Crop output at record levels, supporting price stability
Significance for Financial Policy
- The report signals that India’s financial institutions are resilient and well-equipped to absorb economic shocks
- RBI's stress-testing framework confirms systemic soundness
- Reinforces India's investor confidence, especially in volatile global conditions
Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4)

- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
India marked a historic moment in space exploration as Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla became the first Indian to reach the International Space Station (ISS), 41 years after Rakesh Sharma’s 1984 mission.
Organizations Involved:
- Axiom Space – Mission organizer
- NASA – ISS host and operations support
- SpaceX – Provided Falcon 9 launch vehicle and Dragon capsule
Launch Details:
- Launch Date: June 25, 2025
- Launch Site: Launch Complex 39A, Kennedy Space Center, Florida
- Mission Duration: ~14 days aboard the ISS
Mission Objectives:
1. Scientific Research in Microgravity:
- Over 60 research experiments conducted across:
- Life sciences
- Material sciences
- Human physiology
- Earth observation
2. International Space Cooperation:
- Promotes global collaboration in low-Earth orbit science.
- Supports capacity-building for emerging space nations, including India, Poland, and Hungary.
3. National Space Program Development:
- Enables participating nations to strengthen human spaceflight capabilities.
- Acts as a stepping stone for India’s Gaganyaan and future space station plans.
Significance for India:
- Revival of Human Spaceflight:
- Marks India’s return to human space missions after four decades.
- Reinforces India's presence in international human space exploration.
- Boost to Gaganyaan Mission:
- Offers valuable operational experience and technical collaboration.
- Supports India’s vision to launch Gaganyaan, its first indigenous human spaceflight mission.
- Long-Term Space Ambitions:
- Aids India’s goal to establish its own space station by 2035.
- Positions India as a partner in space science diplomacy and global research.
- Scientific Prestige:India contributes to key microgravity experiments, enhancing its global research footprint in space.
Banakacherla Reservoir Project Dispute
- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
A fresh inter-state water dispute has surfaced between Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, with Telangana accusing Andhra Pradesh of violating provisions of the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 through its proposed Banakacherla Reservoir Project.
About the Banakacherla Reservoir Project
- Location: Banakacherla, Nandyal district, Andhra Pradesh
- Implementing State: Andhra Pradesh
- Objecting State: Telangana
- Purpose: To divert surplus Godavari river water to the drought-prone Rayalaseema region via the Krishna river system.
Key Features of the Project:
River Diversion and Infrastructure Upgrades:
- Polavaram Right Main Canal capacity to be increased from 17,500 to 38,000 cusecs.
- Thatipudi Lift Canal capacity to be enhanced from 1,400 to 10,000 cusecs.
- New reservoir at Bollapalli, with a tunnel through the Nallamala forest to transfer water to Banakacherla.
Lift Irrigation Points:
Five major lift stations planned:
- Harischandrapuram
- Lingapuram
- Vyyandana
- Gangireddypalem
- Nakirekallu
Inter-Basin Linkage:
- Connects Godavari → Krishna → Penna rivers.
- Aims to ensure water availability in Rayalaseema and address regional droughts.
Telangana’s Objections
1. Violation of the AP Reorganisation Act, 2014:Telangana alleges the project bypasses the statutory requirement of prior approval for new inter-basin water projects between the successor states.
2. Absence of Statutory Clearances:
- The project has not been cleared by:
- Krishna River Management Board (KRMB)
- Godavari River Management Board (GRMB)
- Central Water Commission (CWC)
3. Godavari Tribunal Allocation Overlooked:
- Telangana cites the Godavari Water Disputes Tribunal award which allocated 968 TMCft to the state out of 1,486 TMCft.
- Telangana argues that “surplus water” claims lack formal quantification or agreement.
4. Potential Impact on Telangana Projects:Telangana fears that Andhra’s diversion plan will affect its own irrigation schemes and reservoirs dependent on Godavari inflows.
Broader Implications
- This dispute underscores the growing tensions over inter-basin water transfers in India, especially in the context of climate variability and regional water stress.
- It highlights the need for:
- Transparent interstate coordination
- Functioning river boards
- Expedited dispute resolution mechanisms
RBI Eases Priority Sector Lending (PSL) Norms for Small Finance Banks (SFBs)

- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major policy shift aimed at enhancing financial flexibility, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has reduced the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) target for Small Finance Banks (SFBs) from 75% to 60% of their Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC).
What Has Changed?
Previous Norms:
- SFBs were required to allocate 75% of ANBC towards PSL.
- An additional 35% PSL requirement applied beyond the standard 40% applicable to universal banks.
- These strict targets led to:
- Difficulty in sourcing quality borrowers.
- Compressed profit margins.
- Limited portfolio diversification.
Revised Norms (2024):
- Overall PSL target reduced to 60% of ANBC.
- Additional PSL requirement brought down from 35% to 20%.
- Sub-sector allocation remains: SFBs must continue to dedicate 40% of ANBC to core PSL sectors such as agriculture, MSMEs, and weaker sections.
Objective of the Reform
- Enhance lending flexibility for SFBs.
- Improve asset quality and profitability by allowing portfolio diversification.
- Align SFB regulations more closely with those of other banks, without compromising on financial inclusion goals.
About Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
Origin and Mandate:
- Conceptualised by the NachiketMor Committee (2013).
- Regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Created to expand financial inclusion by targeting:
- Small and marginal farmers,
- Micro and small enterprises (MSMEs),
- Unbanked and underserved populations.
Key Features:
- Offer basic banking services, including all deposit and small-ticket loan products.
- Operate on a localised model with strong rural and semi-urban outreach.
- Permitted to distribute non-risk sharing financial products like mutual funds and insurance.
Regulatory Requirements:
- At least 25% of branches in rural areas.
- Minimum 50% of loan portfolio must serve the MSME sector.
- Minimum net worth: ?100 crore at inception, to be raised to ?200 crore within 5 years.
- Maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of 15% on risk-weighted assets.
Significance of the Move
- Offers SFBs greater operational autonomy and room to grow sustainably.
- Aims to balance developmental goals with commercial viability.
- Expected to promote credit flow to priority sectors while ensuring sound financial health of these institutions.
UN80 Initiative

- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move towards institutional transformation, UN Secretary-General António Guterres has launched the UN80 Initiative, aimed at overhauling the United Nations system in the run-up to the 80th anniversary of the UN Charter.
What is the UN80 Initiative?
The UN80 Initiative is a system-wide reform agenda designed to align the UN's structures, mandates, and operations with contemporary global challenges, including peacebuilding, sustainable development, and human rights.
Objectives:
- Modernize the UN architecture to improve responsiveness.
- Enhance accountability and reduce inefficiencies.
- Ensure effective delivery of core mandates in peace, development, and human rights.
Key Features of the UN80 Initiative:
1. Three Core Workstreams:
- Efficiency & Cost Reduction: Streamlining operations, eliminating overlaps, cutting administrative costs, and automating services.
- Mandate Implementation Review: Assessing the execution (not content) of over 3,600 UN mandates for effectiveness.
- Structural Reforms: Reorganizing departments and programs, especially in high-cost duty stations.
2. Formation of Thematic UN80 Clusters:
Seven thematic clusters focus on:
- Peace & Security
- Development (UN Secretariat and UN System)
- Humanitarian Affairs
- Human Rights
- Training & Research
- Specialized Agencies
3. Relocation and Rationalization:
- Proposes shifting operations from expensive cities like New York and Geneva.
- Seeks to abolish underperforming and redundant functions.
4. Budget Integration Timeline:
- Initial reforms to be reflected in the 2026 Revised Budget.
- Major structural reforms to be integrated into the 2027 Programme Budget.
Significance of the UN80 Initiative:
- Revitalizes Multilateralism: Supports the broader goals of the Pact for the Future and ensures the UN remains relevant.
- Boosts Operational Efficiency: Reduces waste, overlap, and underutilization of resources.
- Focuses on Results: Transitions from output-heavy reporting to impact-driven outcomes.
India’s Burden of Zero-Dose Children in 2023
- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
According to a recent Lancet study based on Global Burden of Disease data, India ranked second globally in terms of the number of unvaccinated or “zero-dose” children in 2023, trailing only Nigeria.
What Are Zero-Dose Children?
- The term “zero-dose children” refers to those who have not received even a single dose of any routine childhood vaccine.
- In 2023, 1.44 million children in India were identified as zero-dose, highlighting significant immunisation gaps.
Global and National Trends:
- Nigeria topped the list with approximately 2.5 million zero-dose children.
- Eight countries, including India and Nigeria, together accounted for over 50% of the global zero-dose burden.
- Globally, the number of zero-dose children dropped from 58.8 million in 1980 to 14.7 million in 2019, reflecting long-term progress.
Challenges in India:
- Despite the Universal ImmunisationProgramme (UIP) covering 12 vaccine-preventable diseases, several challenges persist:
- COVID-19 pandemic led to significant disruptions in routine immunisation.
- Vaccine hesitancy continues to undermine public health efforts.
- Geographical and socio-economic inequalities limit access to health services in certain regions.
- Between 2010 and 2019, measles vaccine coverage declined in over 100 countries, including India, further exacerbating public health risks.
Sree Narayana Guru

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently attended the centenary celebrations of the historic 1925 conversation between Mahatma Gandhi and Sree Narayana Guru, held at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The event marked the enduring relevance of Guru's message of social equality, spiritual unity, and reform.
Who was Sree Narayana Guru?
- Born: 20 August 1856, in a backward Ezhava community in Kerala
- Died: 20 September 1928
- Role: Spiritual leader, philosopher, poet, yogi, and one of India’s foremost social reformers from Kerala
Historical Context:
- During the 19th century, Kerala society was deeply caste-ridden, and the Ezhava community was subjected to systemic social exclusion.
- Guru revolted against caste oppression, advocating for spiritual liberation without ritual orthodoxy.
Core Philosophy:
- Message of Universal Unity:“OruJathi, OruMatham, OruDaivam, Manushyanu”
(One Caste, One Religion, One God for Mankind) — a powerful call for social harmony, inclusivity, and humanism. - Non-violent transformation:Unlike many radical reform movements, Guru’s approach was inclusive and reformative, rejecting social division without inciting confrontation.
Key Contributions:
- Religious and Spiritual Reforms:
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Consecrated a Shiva idol at Aruvippuram — a direct challenge to Brahmanical dominance and the exclusion of lower castes from temple worship.
- Established over 40 temples in Kerala, allowing unrestricted worship by the marginalized.
- Promoted yoga and meditation, and spent years in hermitage to attain spiritual depth.
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Social Reforms:
- Founded the Sivagiri Mutt (1904) near Varkala — a centre for spiritual and social awakening.
- SNDP Yogam (1903):
-
- Full form: Sri Narayana Guru Dharma ParipalanaYogam
- Aimed at securing education, government access, and political rights for the Ezhavas.
- Guru was the permanent chairman; Kumaran Asan, his disciple, became general secretary.
-
- Vaikom Satyagraha:Played a pivotal role in the anti-untouchability movement, alongside leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Periyar.
- Promoted free education, ashrams, and vocational training for underprivileged children and communities.
- Sivagiri Foundation and Pilgrimage:
- Founded in 1924 to promote values like:Cleanliness, education, devotion, agriculture, handicrafts, and trade
- SivagiriTheerthadanam (pilgrimage):Initiated by his followers to reinforce values of purity, education, and organization
Literary Contributions:
- Guru was a Vedantic scholar and philosopher-poet. His notable works include:
- Advaitha Deepika
- Atmavilasam
- DaivaDasakam
- BrahmavidyaPanchakam
These texts reflected Advaita (non-dualist) philosophy, spiritual self-realization, and social ethics.
Legacy and Recognition:
- Revered as “Gurudevan”by his followers
- His birth and death anniversaries are observed as public holidays in Kerala and some other states
- Celebrated as Sri Narayana Jayanthi
Candida tropicalis
- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
A recent study published in PLoS Biology by researchers from Fudan University, China, has uncovered a disturbing link between the agricultural use of a common fungicide and the emergence of azole-resistant Candida tropicalis, a fungal pathogen responsible for high-mortality infections, especially in India and other tropical regions.
Candida tropicalis and Public Health Risk
- Candida tropicalis is a major fungal pathogen, particularly prevalent in India, associated with mortality rates of 55–60%.
- Azole-class antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole and voriconazole, are frontline treatments.
- Growing drug resistance is being reported in clinics globally, raising serious concerns for treatment efficacy and public health.
Fungicide Link to Drug Resistance
- Tebuconazole, a triazole-based fungicide, widely used in agriculture and gardening, has been found to be the primary driver of cross-resistance to clinical azoles in C. tropicalis.
- Tebuconazole accumulates and persists in the environment, exerting selective pressure on fungal strains.
- Clinical strains exposed to tebuconazole showed cross-resistance to both fluconazole and voriconazole.
Mechanism of Resistance: Ploidy Plasticity and Aneuploidy
- Resistant strains exhibit aneuploidy – a deviation in chromosome number, often with duplications or deletions of chromosome segments.
- This phenomenon, termed ploidy plasticity, is rare in most organisms due to its detrimental effects, but in C. tropicalis, it enables adaptive resistance.
Genetic Changes Observed:
- Duplication of TAC1 gene segment led to overexpression of ABC-transporters, proteins that pump out azoles and reduce their effectiveness.
- Deletion of HMG1 gene segment increased the synthesis of ergosterol, a compound crucial to fungal membranes, thus enhancing azole resistance.
- These adaptations allowed the resistant strains to trade growth rate for survival under antifungal pressure.
Emergence of Stable Haploid Strains
- The study unexpectedly identified haploid strains of C. tropicalis among resistant isolates.
- These haploids were found to be mating-competent, raising concerns over the genetic transfer of resistance traits.
- Further genomic analysis confirmed that naturally occurring haploid strains also exist, such as two clinical isolates from Spain.
Virulence and Resistance in Animal Models
- In mouse models, strains with altered ploidy exhibited greater virulence than their progenitor strains when treated with fluconazole.
- This finding suggests a dual threat: enhanced resistance and increased disease severity.
Implications and Concerns
- The unregulated and widespread use of triazole fungicides like tebuconazole in agriculture is unintentionally selecting for clinically significant drug resistance.
- These resistant fungal strains pose a direct threat to human health, particularly in immunocompromised patients and in settings with limited alternative antifungal therapies.
- Resistant strains can potentially spread and recombine through mating, complicating containment efforts.
State of the Climate in Asia 2024 Report

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its annual State of the Climate in Asia 2024report, highlighting alarming trends in climate change impacts across the Asian continent. The report confirms that Asia is warming at nearly twice the global average, causing severe socio-economic and environmental consequences.
Key Climate Trends and Indicators in Asia (2024)
- Record Heat:The year 2024 was the warmest year in Asia’s history, marked by prolonged and widespread heatwaves across land and oceanic areas.
- Global Comparison:The global mean temperature in 2024 was the highest on record (1850–2024), surpassing the previous record of 1.45°C set in 2023. Each year between 2015 and 2024 ranks among the 10 warmest globally.
- Sea Surface Temperatures & Marine Heatwaves:Sea surface temperatures reached record highs,with Asian waters warming nearly twice as fast as the global average. Most Asian ocean areas experienced strong to extreme marine heatwaves, especially in the northern Indian Ocean, East China Sea, Yellow Sea, and waters near Japan.
- Sea Level Rise:Sea levels rose faster than the global average on both Pacific and Indian Ocean coasts of Asia, exacerbating risks for low-lying coastal areas.
Cryospheric Changes and Glacier Loss
- In Central Himalayas and Tian Shan ranges, 23 out of 24 monitored glaciers experienced mass loss in 2024.
- Consequences included increased risk of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides, and long-term threats to water security.
Scientific Warnings and Observations
The report highlights that the warming trend from 1991 to 2024 in Asia is nearly twice as fast as that between 1961 and 1990, underlining the acceleration of climate risks.
Implications for Asia
- Environmental:Rapid glacier melt, rising sea levels, and extreme weather are disrupting ecosystems, causing habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Economic:Agriculture, fisheries, and coastal infrastructure are suffering massive losses due to droughts, floods, and storms.
- Social:Heatwaves, displacements, and disaster-related fatalities are disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations, including the poor and elderly.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management
- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to develop a Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management (DPIP) under its supervision to curb rising instances of banking frauds in India. This aligns with broader efforts to enhance security and transparency in India’s financial ecosystem.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- Definition: DPI refers to foundational digital systems that are accessible, secure, interoperable, and designed to deliver essential public services.
- Examples in India:
- Aadhaar (Digital ID)
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- DigiLocker, CoWIN, etc.
About DPIP
- Objective:To enhance fraud risk management through real-time intelligence sharing, data gathering, and interbank coordination using advanced technologies.
- Key Features:
- Will strengthen existing fraud detection systems in the banking ecosystem.
- Enables interoperable intelligence sharing between banks and financial institutions.
- Leverages AI/ML tools and data analytics for better predictive fraud detection.
- Institutional Mechanism:
- A committee under Shri A.P. Hota has been constituted to examine various aspects of DPIP’s implementation.
- RBI Innovation Hub (RBIH) is tasked with developing a prototype, in consultation with 5–10 public and private sector banks.
Need for DPIP
- Rise in Bank Frauds:
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
- FY 2024: ?12,230 crore in frauds
- FY 2025: ?36,014 crore — almost 3x increase
- Increasing sophistication of cyber threats and fraud techniques necessitates robust preventive digital infrastructure.
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
Other RBI Initiatives to Combat Bank Frauds
Initiative Description
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Mandatory for all digital/electronic payments to ensure
secure transactions.
Zero Liability Framework Customers are not liable for losses arising from bank’s
negligence or third-party breaches.
bank.in and fin.in domains Reserved for verified bank websites to help customers
avoid phishing and fake sites.
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) is emerging as a novel nature-based carbon removal strategy, gaining global traction from Brazil’s sugar plantations to tea estates in India. It is being explored as a scalable solution to climate change through natural carbon capture mechanisms.
What is Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)?
- Definition: ERW is a geoengineering technique that accelerates the natural chemical process of rock weathering to capture and store atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO?).
- Scientific Basis:
- Natural weathering involves the breakdown of silicate rocks through carbonic acid, formed when CO? dissolves in water, eventually locking the carbon in stable forms like bicarbonate or limestone.
- ERW accelerates this process using fast-weathering rocks like basalt, ground into fine particles to maximize surface area and reactivity.
Effectiveness and Challenges
- Potential Carbon Removal:
- A US-based study found that 50 tonnes of basalt/hectare/year could potentially remove up to 10.5 tonnes of CO?/hectare over four years.
- However, field trials in Malaysia (oil palm) and Australia (sugarcane) have shown lower than expected carbon capture rates.
- Key Variables Affecting Effectiveness:
- Rock type and mineralogy
- Soil characteristics
- Temperature and rainfall patterns
- Land management practices
- Measurement Difficulties:
- Current techniques often overestimate CO? capture due to detection of cations that form even in the absence of carbonic acid reactions.
- Risk: This can lead to inaccurate carbon credit claims, undermining offset integrity.
Co-Benefits of ERW
- Soil Health Improvement:
- Increases soil alkalinity → Improves nutrient availability and crop productivity.
- Contributes to soil formation and resilience.
- Resource Efficiency:Basalt is abundant and often a quarrying by-product, lowering costs and emissions associated with mining.
- Ocean Acidification Mitigation:Even if CO? isn't sequestered directly, rock in the soil can neutralize acidic runoff, preventing CO? release from aquatic systems downstream.
Risks and Concerns
- Health & Safety:
- Finely crushed rock may contain toxic heavy metals (depending on composition).
- Protective equipment is necessary during application.
- Carbon Credit Integrity:Overestimated CO? removal may allow companies to offset emissions inaccurately, leading to net increase in atmospheric carbon.
Global Adoption and Projects
- Countries Involved:Brazil, India, USA, Europe, and Latin America are trialing or implementing ERW.
- India Focus:Trials underway in Darjeeling tea plantations and other agricultural regions through startups like Mati Carbon.
- Global Milestones:
- First verified ERW carbon removal credits issued from a Brazilian project.
- Google signed the largest ERW deal for 200,000 tonnes of CO? removal credits (to be delivered by early 2030s).
- Terradot, an ERW company, sold 90,000 tonnes of carbon credits for $27 million, backed by firms like H&M.
Investor Interest and Innovation Push
- Private Sector Engagement:ERW has attracted big tech, fast fashion, and aviation sectors seeking nature-based offset solutions.
- Prize Recognition:Mati Carbon won the $50 million X Prize for carbon removal, recognizing the potential scalability and innovation of ERW.
India’s Coffee Exports

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
India has emerged as a significant player in the global coffee trade, with its exports witnessing a sharp rise of 125% in the past 11 years, increasing from $800 million in 2014–15 to $1.8 billion in 2023–24, and continuing the momentum with over 25% growth in FY2025–26. This export surge highlights India's expanding footprint in the global premium coffee market, driven by a blend of policy support, sustainable cultivation practices, and global demand for specialty coffee.
Key Drivers of Export Growth
The Coffee Board of India, under the Ministry of Commerce, has played a pivotal role in this transformation through:
- Digitalisation of export permits, RCMC, and certificates of origin.
- Export incentives like freight and transit assistance—?3/kg for value-added exports and ?2/kg for green coffee to distant markets (e.g., US, Canada, Japan, Nordic countries).
- Subsidy support of 40% (up to ?15 lakh) for processing units (roasting, grinding, packaging).
- Global market intelligence and regular industry engagement to remove bottlenecks.
- Promotion via GI tags and digital branding campaigns.
These efforts have enhanced India’s readiness to meet stringent import regulations (e.g., EU deforestation norms) while enabling access to new and emerging markets.
Production and Cultivation
India is the 7th largest producer of coffee globally, accounting for about 3.5% of world production and ranks 5th in global coffee exports with a 5% share. The country produces 3.5–4 lakh tonnes of coffee annually, with Karnataka (70%), Kerala, and Tamil Nadu being major contributors.
- Arabica varieties: Kents, S.795, Cauvery, Selection 9.
- Robusta: High-yielding selections suited to Indian climate.
Climatic Features:
- Grown under two-tier shade canopies with over 50 native tree species.
- Arabica thrives at 1000–1500m, Robusta at 500–1000m altitudes.
- Requires 1600–2500 mm rainfall and 15°C–25°C temperature.
India is unique as the only country that cultivates 100% shade-grown coffee, which promotes biodiversity, soil and water conservation, and ensures a sustainable income for 2 million people, including small and marginal farmers.
Specialty and GI-Tagged Coffee
India’s coffee is known for its mild acidity, full-bodied flavour, and fine aroma. Intercropping with spices like pepper, cardamom, and vanilla further enhances its appeal. The country also boasts five regional and two specialty coffees with Geographical Indication (GI) tags, strengthening brand value in global markets.
The historic legacy of Indian coffee dates back over 400 years to the planting of coffee beans by Baba Budan in Karnataka, making it one of the oldest coffee traditions in Asia.
The Emergency in India (1975–1977)

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
The declaration of Emergency in India from 25 June 1975 to 21 March 1977 marks one of the most debated and transformative chapters in the country’s post-independence history. Proclaimed under Article 352 of the Constitution citing “internal disturbance”, this period had far-reaching legal, political, and social consequences. It served as a stress test for India’s democratic institutions and led to significant constitutional reforms.
Background:
- The early 1970s were marked by growing political discontent. Nationwide protests, especially in Bihar and Gujarat, were spearheaded by Jayaprakash Narayan against issues such as rising unemployment, inflation, corruption, and misuse of political power.
- The immediate provocation came from the Allahabad High Court’s judgment on 12 June 1975, which found Prime Minister Indira Gandhi guilty of electoral malpractice in her 1971 Lok Sabha campaign. The Court disqualified her from contesting elections for six years under the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- Though the Supreme Court granted a conditional stay, political pressure intensified, with mass movements demanding her resignation.
Proclamation of Emergency
On 25 June 1975, President Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed, on the advice of the Prime Minister, declared a national Emergency under Article 352, citing internal disturbance. This was the third Emergency in India — the first two being during external wars (1962 with China and 1971 with Pakistan). However, this was the first peacetime Emergency.
Constitutional Basis
At that time, Article 352 allowed Emergency on three grounds:
- War
- External Aggression
- Internal Disturbance (later amended to “armed rebellion” by the 44th Amendment, 1978)
Suspension of Fundamental Rights
Two days later, on 27 June 1975, the government invoked:
- Article 358: Automatically suspended the freedoms under Article 19 (freedom of speech, assembly, movement, etc.)
- Article 359: Allowed suspension of Articles 14, 21, and 22, stripping protections related to equality before law, life and personal liberty, and protection against preventive detention.
Citizens lost access to courts for constitutional remedies. Prominent opposition leaders, including Jayaprakash Narayan, Morarji Desai, Atal Bihari Vajpayee, and L.K. Advani, were arrested under the Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA). According to the Shah Commission, around 35,000 individuals were detained without trial.
Censorship and Media Suppression
From 26 June 1975, press censorship was imposed. Newspapers were mandated to get clearance from government-appointed censors before publication. International news coverage was also tightly controlled, with telex messages of foreign correspondents placed under surveillance.
Key developments:
- On 20 July 1975, the Board of Film Censors was restructured to impose stricter control over cinema.
- On 1 February 1976, the four national news agencies — PTI, UNI, Samachar Bharati, and Hindustan Samachar — were merged into ‘Samachar’.
- The Press Council of India was dissolved.
Constitutional Amendments and Legislative Overreach
Several constitutional amendments were enacted to consolidate power:
- 38th Amendment (1975): Made the President’s Emergency declaration non-justiciable.
- 39th Amendment (1975): Excluded Prime Minister’s election from judicial review.
- 42nd Amendment (1976) (termed “Mini-Constitution”):
- Gave primacy to Directive Principles over Fundamental Rights
- Extended Lok Sabha and State Assembly terms from 5 to 6 years
- Limited judicial review, centralised authority
- Empowered Parliament to amend the Constitution without court scrutiny
Sterilisation Campaign
One of the most controversial aspects was the forced sterilisationprogramme led by Sanjay Gandhi. While aimed at population control, it resulted in widespread coercion and human rights violations.
- 1975–76: 26.42 lakh sterilisation procedures
- 1976–77: 81.32 lakh
- Total over two years: 1.07 crore
- Many were linked to access to ration cards, housing, loans, and employment
End of Emergency and Democratic Reversal
The Emergency was revoked on 21 March 1977. In the subsequent general elections (March 1977), the Congress party was defeated, and the Janata Party under Morarji Desai assumed power. This marked the first non-Congress government at the Centre
Post-Emergency Reforms: The Shah Commission and 44th Amendment
The Shah Commission (1977–79)
Set up in May 1977, chaired by Justice J.C. Shah, it investigated:
- Illegal arrests and detentions
- Press censorship
- Forced sterilisation
- Bureaucratic misuse and political excesses
44th Constitutional Amendment (1978)
To prevent future misuse:
- Replaced “internal disturbance” with “armed rebellion” as a ground for Emergency
- Restored judicial review of Emergency proclamations
- Safeguarded Fundamental Rights, particularly Articles 20 and 21
- Ensured Cabinet approval was mandatory before Emergency declaration
Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark initiative for tribal inclusion, the Government of India has launched the Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)—India’s largest-ever tribal outreach and empowerment campaign. The programme aims to ensure saturation of welfare schemes and promote tribal pride and participation, covering over 1 lakh tribal villages and PVTG habitations across 31 States and Union Territories.
What is DAJA?
- Full Name: Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan — named in honour of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, a revered tribal freedom fighter.
- Launched by: Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India.
- Nature: A people-centric campaign focused on participatory governance and last-mile delivery of services among Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
Objectives of DAJA
- Saturate government welfare schemes across all tribal settlements.
- Empower over 5.5 crore tribal citizens through Janbhagidari (people’s participation).
- Preserve and promote tribal identity and cultural heritage, invoking the legacy of Birsa Munda.
- Strengthen last-mile governance through technological and administrative convergence.
Key Features:
Feature Description
Geographic Coverage - 1 lakh+ tribal villages, including remote PVTG habitations, across 31 States/UTs.
Scheme Integration - Converges services such as Aadhaar, Ayushman Bharat, PM Kisan, PM
Ujjwala, Jan Dhan, pension schemes, and Forest Rights Act (FRA) claims.
Five Foundational Pillars -
- Janbhagidari (people’s participation)
- Saturation of welfare benefits
- Cultural inclusion
- Convergence of schemes
- Last-mile delivery
Technology-Driven Monitoring - Use of real-time dashboards and data analytics for
transparent tracking and reporting.
Cultural Revival - Celebrates tribal cuisines, folk arts, handicrafts, and oral traditions
during outreach camps to reaffirm cultural identity.
Significance:
- Governance: Represents a shift toward targeted and integrated tribal welfare, reducing administrative fragmentation.
- Inclusion: PrioritisesPVTGs, often the most marginalised and underserved groups.
- Empowerment: Embeds a participatory model, aligning with the spirit of democratic decentralisation.
- Cultural Reaffirmation: Bridges the gap between development and cultural identity, crucial for tribal dignity and preservation.
India’s Data Imperative – The Pivot Towards Quality
- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant policy intervention, NITI Aayog has released the report titled “India’s Data Imperative: The Pivot Towards Quality”, calling for urgent reforms to enhance the integrity, interoperability, and usability of India’s public data systems. The report underscores the critical role of data in governance, welfare delivery, and digital innovation.
Understanding India’s Public Data Ecosystem
India's data ecosystem constitutes a vast digital public infrastructure that powers governance and service delivery across sectors. It integrates identity, finance, health, and welfare through data-centric platforms:
- Aadhaar: Over 27 billion authentications in FY 2024–25; foundational for identity-linked services.
- UPI: Handles transactions worth ?23.9 trillion monthly — the world’s largest real-time digital payment system.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission: 369 million health IDs issued; enhancing interoperability in healthcare.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): ?5.47 lakh crore transferred in FY 2024–25 across 330+ schemes.
- Aadhaar e-KYC: 1.8 billion transactions, significantly reducing onboarding costs and time.
- Digital Inclusion: Over 1.2 billion mobile subscribers and 800 million internet users reflect the scale of India’s digital penetration.
Why India Needs a Quality-Driven Data Ecosystem
- Curb Fiscal Leakage:Inaccurate or duplicate data inflates welfare expenditure by 4–7% annually.
- Enable Evidence-Based Governance:Data-driven insights power AI-led service delivery, improve beneficiary targeting, and strengthen accountability.
- Foster Public Trust:The legitimacy of digital governance depends on accurate, timely, and reliable data systems.
- Strengthen India’s AI & Innovation Ecosystem:Clean, validated data is essential for building AI applications in healthcare, agriculture, and citizen services.
- Enhance Cross-Ministerial Coordination:Interoperable data frameworks help break silos and improve policy coherence across ministries.
Key Challenges in India’s Data Governance Landscape
Challenge Description
Fragmentation Departmental silos with non-standardised data formats hinder seamless integration.
Lack of Ownership Absence of clear data custodians leads to accountability gaps.
Legacy Systems Outdated IT systems impede real-time updates and data sharing.
Incentive Mismatch Existing frameworks reward speed over accuracy, eroding data quality.
Poor Quality Culture A prevailing acceptance of “80% accuracy is good enough” weakens long-term integrity.
NITI Aayog’s Recommendations for Reform
- Institutionalise Data Ownership:Designate dedicated data custodians at national, state, and district levels to oversee quality.
- Incentivise Accuracy:Incorporate data quality metrics into performance appraisals and financial allocations.
- Promote Interoperability:Adopt standards like IndEA (India Enterprise Architecture) and NDGFP (National Data Governance Framework Policy) to ensure consistency.
- Use Practical Tools:Implement tools like the Data Quality Scorecard and Maturity Framework for ongoing assessment.
- Build Capacity:Train field-level personnel and managers to prioritise data fidelity as a core administrative function.
Significance of the Report
This report arrives at a critical juncture when India is rapidly expanding its digital public infrastructure but faces risks from data inaccuracy, siloed systems, and erosion of trust. By shifting focus from quantity to quality, NITI Aayog envisions a resilient, inclusive, and innovation-friendly data regime—essential for achieving Digital India goals and Sustainable Development Objectives.
Total Revolution
- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
India commemorates the 51st anniversary of Jayaprakash Narayan’s (JP) historic call for “Sampoorna Kranti” or Total Revolution, first proclaimed on June 5, 1974, at Gandhi Maidan, Patna. The movement remains a landmark in India's democratic evolution, reflecting enduring concerns over governance, democracy, and civic empowerment.
What is Total Revolution?
- Concept: A holistic, non-violent movement rooted in Gandhian ideals, aimed at comprehensive transformation—political, economic, social, cultural, and spiritual.
- Vision: Building a just and equitable society through decentralised democracy, moral rejuvenation, and participatory governance.
- Leadership: Spearheaded by Jayaprakash Narayan (JP), advocating a “party-less democracy” blending Gandhian ethics, Sarvodaya ideals, and Marxist critique.
Underlying Causes of the Movement
- Electoral Legitimacy Crisis:The 1975 Allahabad High Court judgment disqualified Prime Minister Indira Gandhi for electoral malpractices, eroding her authority and galvanising mass opposition.
- Youth Unrest:Movements like Navnirman Andolan (Gujarat) and Bihar student protests reflected mounting youth dissatisfaction over unemployment and poor governance.
- Economic Distress:The early 1970s saw inflation exceeding 20%, acute unemployment, and food shortages, leading to widespread discontent.
- Democratic Backsliding:Use of draconian laws like MISA, increased centralisation, and suppression of dissent led to civil society mobilisation.
- Charismatic Mobilisation:JP’s appeal for non-violent civic awakening and his ability to unify diverse ideological streams helped launch a broad-based national movement.
Core Components of the Total Revolution
Domain Focus
Political Advocated bottom-up governance, decentralisation, and accountability
to counter bureaucratic authoritarianism.
Economic Promoted land reforms and people-centric development to address inequality.
Social Called for eradication of casteism, gender bias, and dowry to foster egalitarianism.
Educational Suggested reforms emphasisingethics, rural upliftment, and vocational training.
Cultural-Spiritual Encouraged self-discipline, national unity, and moral regeneration.
Impact of Total Revolution
On Society and Citizenry
- Youth Mobilisation: Inspired a generation of political leaders—Lalu Prasad Yadav, Nitish Kumar, Sushil Modi—who reshaped regional politics.
- Civic Engagement: Fostered a deeper culture of public accountability and democratic participation.
- Non-Violent Resistance: Reinforced the efficacy of peaceful protest, a legacy echoed in later movements like Anna Hazare’s anti-corruption crusade.
On Governance and Policy
- Collapse of Congress Monopoly: Led to the formation of the Janata Party, marking a historic electoral defeat for the Congress in 1977.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Triggered the 44th Constitutional Amendment, curbing emergency powers and restoring judicial oversight.
- Democratic Deepening: Inspired Panchayati Raj reforms through the 73rd and 74th Amendments, enhancing grassroots democracy.
Significance and Contemporary Relevance
- Democratic Dissent: Reinvigorated the right to protest as a fundamental democratic tool.
- Leadership Incubation: Nurtured mass-based political leadership, altering India’s political landscape.
- Institutional Vigilance: Exposed systemic vulnerabilities, prompting long-term institutional reforms.
- Civic Awakening: Broadened the role of civil society in governance beyond electoral cycles.
- Modern-Day Lessons: Offers vital insights for addressing centralisation of power, youth alienation, and democratic backsliding in contemporary India.
Haemophilia A
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) has indigenously developed a simple, affordable, and rapid point-of-care test kit for the early diagnosis of Haemophilia A and Von Willebrand Disease (VWD). This development marks a significant step in improving accessible healthcare diagnostics for genetic bleeding disorders in India.
Significance of the Innovation:
- Affordable and accessible: Enables early diagnosis at primary health centres and in low-resource settings.
- Supports Universal Health Coverage: Improves detection and timely treatment, reducing morbidity.
- Make in India in Health Sector: A boost to indigenous biomedical research and diagnostics.
About Haemophilia A
What is it?
- A hereditary bleeding disorder caused by insufficient levels of Factor VIII, a protein essential for blood clotting.
- Part of the broader group of genetic conditions known as inherited coagulopathies.
Causes:
- Deficiency or dysfunction of coagulation Factor VIII in the coagulation cascade.
- Usually inherited through an altered gene passed from parents.
Genetic Transmission:
- X-linked recessive inheritance:
- Males with the defective gene express the disease.
- Females are typically carriers, though they may show mild symptoms.
Symptoms:
- Prolonged bleeding, often seen after circumcision or minor injuries.
- Internal bleeding, particularly into joints, causing pain and swelling.
- Other signs include:
- Nosebleeds
- Blood in stool/urine
- Bruising
- Bleeding after surgery or dental procedures
Treatment:
- Factor VIII replacement therapy: Intravenous infusion of the missing clotting factor.
- Preventive therapy (prophylaxis) to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
About Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
What is it?
- A genetic bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor (VWF), which helps platelets stick together to form blood clots.
Causes:
- Inherited from one or both parents.
- People with VWD have:
- Low levels of VWF, or
- VWF that does not function properly.
Symptoms:
- Often asymptomatic unless triggered by injury or surgery.
- Common symptoms include:
- Easy bruising
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- Heavy or prolonged menstruation (menorrhagia)
- Post-operative bleeding
- Severe cases may show:
- Internal joint bleeding
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Blood in stool (melena)
Treatment:
- No cure, but manageable with:
- Desmopressin (DDAVP) to release stored VWF.
- VWF and Factor VIII concentrates.
- Self-care measures to reduce bleeding risks.
Household Income Survey in 2026

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has announced that India will conduct its first nationwide Household Income Survey in 2026, marking a major milestone in the country’s data-driven policymaking framework.
What is the Household Income Survey?
- A comprehensive, nationwide survey aimed at collecting reliable and robust data on household income distribution across India.
- It is the first standalone survey focused specifically on income estimation, unlike earlier efforts that focused primarily on consumption and employment.
Key Implementing Bodies:
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- National Sample Survey (NSS)
- Technical Expert Group (TEG)
Historical Background:
- 1950: National Sample Survey (NSS) established to conduct large-scale household surveys.
- 1955–1970: Income data attempted in the 9th, 14th, 19th, and 24th NSS rounds but faced challenges such as underreporting.
- 1983–84: A pilot income study failed to produce scalable data due to low income estimates relative to consumption and savings.
- Past difficulties deterred the launch of a dedicated income survey—until now.
Key Features of the 2026 Survey:
- First of its kind: India’s first survey exclusively focused on household income distribution.
- Methodologically robust: Designed by the TEG, incorporating international best practices in conceptual design, sampling, and estimation.
- Use of digital tools: Integration of technology-driven data collection methods to improve precision, timeliness, and reflect the role of digital economy in income generation.
- Built on recent statistical reforms by MoSPI in areas like:
- Unincorporated enterprise surveys
- Services sector data
- Private capital expenditure
- Tourism satellite accounts
Significance of the Survey:
- Addresses a critical data gap in understanding income inequality, disparities, and growth trends.
- Supports evidence-based welfare policies, including targeted subsidies, social protection, and fiscal redistribution.
- Enhances India’s capacity for inclusive growth assessment and SDG tracking.
- Strengthens the country's statistical infrastructure, aligning it with global standards.
Training of Trainers (ToT)Programme

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to strengthen grassroots governance and fiscal autonomy, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has launched a Training of Trainers (ToT)programme in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad and the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA). The initiative aims to enhance the capacity of Panchayats to generate Own Source Revenue (OSR) under the Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA).
Key Objectives:
- Enhance financial self-reliance of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Build a cadre of Master Trainers equipped to train Panchayat-level functionaries.
- Shift local governance from a compliance-based model to proactive planning, innovation, and community engagement.
- Promote a culture of fiscal accountability, transparency, and efficient public service delivery at the grassroots level.
Core Focus Areas of Training
- Fundamentals of Own Source Revenue (OSR)
- Revenue enhancement strategiestailored to rural contexts
- Behavioural insights in tax collectionand compliance
- Revenue utilization for development and service delivery
- Village-level financial planningand Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs)
- Innovative financing mechanisms
- Project management and accountability tools
The training emphasized field orientation, peer learning, and evidence-based practices to ensure real-world applicability and long-term impact.
Institutional Reforms and Digital Integration
As part of the broader reform agenda:
- Model OSR Rules Framework is under development based on state-level legislative reviews.
- A Digital Tax Collection Portal is being created to facilitate:
- Simplified and accountable revenue collection,
- Digital integration with Panchayat-level financial systems.
Case Studies & Best Practices
The training showcased successful Panchayat-level revenue generation models from:Odisha, Gujarat, Goa, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, highlighting scalable models of local innovation.
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA): Background
A Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) launched in 2018 and revamped for 2022–2026, aimed at developing and strengthening the Panchayati Raj System across rural India.
Key Objectives:
- Build governance capacity of PRIs to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Empower Panchayat representatives for effective leadership and participatory governance.
- Enhance OSR generation and financial planning at the Panchayat level.
- Promote inclusive development and convergence of schemes.
- Strengthen Gram Sabhas as platforms for citizen engagement.
Salient Features:
- Emphasis on capacity-building and leadership training.
- Promotes decentralisation and compliance with the PESA Act, 1996.
- Encourages use of technology-driven solutions for governance.
- Recognises and incentiviseshigh-performing Panchayats.
- Facilitates collaboration with international and national institutions.
Ambubachi Mela 2025
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
Thousands of devotees have congregated at the Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati, Assam, to participate in the annual Ambubachi Mela—one of the largest and most significant religious gatherings in Northeast India.
About Ambubachi Mela
- Timing: Celebrated annually during the monsoon season, typically in June.
- Location: Held at the Kamakhya Temple, situated atop Nilachal Hill in Guwahati, Assam.
- Religious Significance:
- Marks the menstrual cycle of Goddess Kamakhya, symbolising the fertility of Mother Earth.
- During this period, the sanctum sanctorum is closed for three days, after which it is ceremonially reopened for darshan.
- Cultural Symbolism:
- Reflects ancient beliefs that associate the Earth with feminine fertility.
- The word ‘Ambubachi’ translates to ‘water flowing’, indicative of both the monsoon rains and the goddess’s fertility.
Kamakhya Temple: Key Facts
- Spiritual Importance:
- Dedicated to Goddess Kamakhya, an incarnation of Shakti.
- Considered one of the most revered sites of Tantric Shaktism in India.
- Recognised as one of the 51 Shakti Peethas, where the yoni (womb) of Sati is believed to have fallen.
- Geographical Location:Located on Nilachal Hill, overlooking the southern bank of the Brahmaputra River.
Architectural Features of Kamakhya Temple
- Architectural Style:
- Combines traditional Nagara style with Saracenic (Mughal) architectural elements, known as the Nilachala Style of Architecture.
- Temple Layout:
- Only temple in Assam with a fully developed ground plan.
- Comprises five main sections:
- Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum)
- Antarala (vestibule)
- Jaganmohan (assembly hall)
- Bhogmandir (offering hall)
- Natmandir (performance hall)
- Distinctive Structural Elements:
- Main dome: Modified Saracenic style.
- Antarala: Features a two-roofed structure.
- Bhogmandir: Crowned with five domes, echoing the central shrine.
- Natmandir: Designed with a shell-shaped roof and apsidal end, similar to the namghars (prayer halls) of Assam.
SDG Index 2025

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
India has ranked 99th out of 193 countries in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index 2025, marking the first time it has entered the top 100. India scored 67 in the index, as per the Sustainable Development Report 2025 released by the U.N. Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
About the Sustainable Development Report 2025
- Publisher: U.N. Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
- Objective: Tracks annual progress on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by all UN member states in 2015.
- Coverage: 193 countries.
- Relevance: Assesses national performance across economic, social, and environmental dimensions of sustainability.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Report
Global Trends
- SDG Progress Stalled Globally: Only 17% of the SDG targets are projected to be met by 2030.
- Barriers to Progress: Conflicts, structural vulnerabilities, and constrained fiscal space are key impediments.
- Top Performers:
- Finland ranks 1st, followed by Sweden (2nd) and Denmark (3rd).
- However, many European nations face serious challenges related to climate change and biodiversity loss, due to unsustainable consumption patterns.
Regional Insights
- East and South Asia have shown the fastest progress since 2015, attributed to rapid socioeconomic development.
- India’s Achievement: Ranked 99th, entering the top 100 for the first time.
Sectoral Progress and Setbacks
- Areas of Strong Progress Globally:
- Access to electricity (SDG 7)
- Use of mobile broadband and internet (SDG 9)
- Reduction in child and neonatal mortality (SDG 3)
- Areas of Reversal Since 2015:
- Rising obesity rates (SDG 2)
- Decline in press freedom (SDG 16)
- Poor sustainable nitrogen management (SDG 2)
- Worsening Red List Index (biodiversity loss – SDG 15)
- Weakening Corruption Perceptions Index (SDG 16)
Commitment to Multilateralism
- Top 3 Countries Committed to UN Multilateralism:
- Barbados
- Jamaica
- Trinidad and Tobago
Notable National Rankings
- Brazil (25): Highest among G20 nations.
- Chile (7): Highest among OECD countries.
NAVYA Initiative

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
In line with the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047 and the government’s focus on women-led development, the Government of India has launched NAVYA—a pilot initiative aimed at vocationally skilling adolescent girls to empower them with future-ready skills and opportunities.
The programme was officially launched in Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh, by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) in collaboration with the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
About Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational Training for Young Adolescent Girls (NAVYA):
- Objective:To provide vocational training to adolescent girls aged 16–18 years (with a minimum qualification of Class 10) in non-traditional job roles.
- Target Areas:Implemented as a pilot project in 27 districts across 19 States, including:
- Aspirational districts
- Districts in the North-Eastern States
This reflects the government's commitment to inclusive development and reaching underserved and vulnerable populations.
- Institutional Collaboration:
- Both ministries will formalize convergence to streamline and institutionalize skilling efforts for adolescent girls.
- NAVYA draws upon existing frameworks like the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) and other flagship skill development schemes.
Significance of NAVYA:
Aspect Importance
Empowerment - Enhances skills, confidence, and self-reliance among young girls
Gender Inclusion - Supports women-led development and economic participation
Employment Readiness - Equips girls with job-oriented skills in non-traditional sectors
Regional Equity - Targets backward and underserved regions to reduce disparities
Demographic Dividend - Harnesses the potential of India’s adolescent population in national development
“NAVYA represents a transformative step in ensuring that every adolescent girl becomes a catalyst for change in India’s journey towards an inclusive, skilled, and developed future.”
Rising Evaporative Demand and Thirstwaves

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
The rising evaporative demand—a measure of how thirsty the atmosphere is—is spotlighting India’s significant data and research gaps related to climate extremes, water stress, and agricultural vulnerability. While global studies are increasingly focusing on "thirstwaves", India lacks adequate research and monitoring frameworks on this critical issue.
What is Evaporative Demand?
- Evaporative demand indicates the near-maximum amount of water that would evaporate from land or vegetation if enough water is available.
- It is not equivalent to actual evaporation, which also depends on water availability.
- Driven by atmospheric factors:
- Temperature
- Wind speed
- Solar radiation
- Humidity
- Cloud cover
High evaporative demand leads to quicker drying of soil and vegetation, increasing drought risk, crop stress, and wildfire susceptibility.
What is a Thirstwave?
- Coined by MeetpalKukal (University of Idaho) and Mike Hobbins (NOAA/University of Colorado).
- Definition: Three or more consecutive days of abnormally high evaporative demand.
- Drivers: Combination of high temperature, low humidity, high solar radiation, and wind speed.
- Impacts:
- Reduces water availability for crops.
- Stresses vegetation.
- Increases fire danger.
- Accelerates drought onset and intensification.
Unlike heatwaves driven by temperature alone, thirstwaves are multi-dimensional and can be more damaging to crops and ecosystems.
Scientific Findings & India-Specific Observations
Global Evidence:
- Kukal& Hobbins’ study (published in Earth’s Future) noted:
- Increased frequency, intensity, and duration of thirstwaves in the U.S.
- Reduced likelihood of zero-thirstwave periods during growing seasons.
India’s Research Gap:
- Chronic shortage of real-time data on evaporative demand and extreme events.
- 1997 Study (Chattopadhyay &Hulme):
- Analyzed 30 years of IMD data.
- Found declining evaporation and potential evapotranspiration, likely due to increased humidity, despite warming.
- Projected future temperature rise would eventually override humidity effects, increasing evaporative demand.
Recent Developments in India:
- IIT Roorkee, NIH & European collaborators (2022):
- Studied 100 river sub-basins.
- Found highest rise in actual evapotranspiration in Northern India, Western Himalayas, and Eastern Himalayan regions.
- Interpreted as signs of increased vegetation or agricultural expansion.
Measurement Techniques:
- Standardised Short-Crop Evapotranspiration:
- A simplified metric to measure water demand of a 12 cm tall, healthy grass under ideal moisture conditions.
- Recommended for crop irrigation planning.
- Rising values signal increasing atmospheric demand and need for adaptive water management.
Implications for India:
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- India’s irrigated crops, especially rice and wheat, are vulnerable to atmospheric water demand.
- Rising thirstwaves threaten to decrease productivity even in well-irrigated regions.
- Water Resource Management:
- Increases soil moisture stress and reduces groundwater recharge.
- Calls for real-time tracking systems for evaporative stress.
- Disaster Preparedness:
- Thirstwaves may precede or exacerbate droughts and wildfires.
- Regions not traditionally drought-prone may still suffer from evaporative shocks.
- Research and Monitoring Needs:
- Lack of indigenous data on thirstwaves.
- Current efforts:Ongoing Indo-U.S. collaboration (University of Idaho & NIT Jalandhar) aims to map South Asian thirstwaves under the Water Advanced Research and Innovation Program.
Way Forward:
- Integrate evaporative demand and thirstwave parameters into IMD's early warning systems.
- Promote region-specific studies on crop sensitivity to evaporative demand.
- Develop adaptive irrigation protocols based on short-crop evapotranspiration trends.
- Sensitise farmers, water managers, and policymakers on atmospheric water demand risks.
- Invest in climate-resilient agriculture and data-driven water governance.
UK’s Terminally Ill Adults (End of Life) Bill
- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark decision, the UK House of Commons has passed the Terminally Ill Adults (End of Life) Bill, which seeks to legaliseassisted dying for terminally ill individuals in England and Wales. The Bill passed with a narrow margin of 314 to 291 votes, and will now proceed to the House of Lords for further deliberation.
Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Applicability: England and Wales.
- Eligibility: Only for patients diagnosed with less than six months to live.
- Safeguards:
- The patient must be mentally competent.
- Approval is required from two doctors, a psychiatrist, a senior lawyer, and a social worker.
- The process ensures the patient’s choice is informed and voluntary.
Understanding Euthanasia:
- Etymology: From Greek “eu” (good) + “thanatos” (death) = “good death”.
- Definition: Intentional act of ending a person’s life to relieve suffering from terminal illness or unbearable pain.
Types of Euthanasia:
Type Description Example
Active Deliberate action to end life Lethal injection
Passive Withdrawal of treatment Removing life support
Voluntary With patient’s consent Terminally ill requesting euthanasia
Involuntary Without consent Considered illegal
Ethical Dimensions:
Arguments in favour
- Right to Autonomy: Upholds personal freedom in deciding life and death.
- Compassionate Exit: Eases intractable suffering.
- Dignity in Death: Ensures control over one’s final moments.
- Relief for Families: Reduces emotional and financial strain.
- Medical Resource Optimization: Redirects care to patients with curable conditions.
Arguments Against
- Sanctity of Life: Human life is sacred and must not be intentionally ended.
- Risk of Coercion: Vulnerable groups may be pressured into opting for death.
- Existence of Palliative Alternatives: Modern hospice care offers non-lethal relief.
- Slippery Slope: May lead to misuse or extension to non-terminal cases.
- Erosion of Medical Ethics: Challenges the healer role of doctors.
Indian Legal Perspective:
India has grappled with the euthanasia debate in various judicial pronouncements:
- Gian Kaur v. State of Punjab (1996): Right to die not included under Article 21.
- Aruna Shanbaug Case (2011): Allowed passive euthanasia under strict conditions.
- Common Cause v. Union of India (2018):Recognised the right to die with dignity and permitted Advance Medical Directives.
UNEP’s NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has released the NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025, aimed at supporting countries in integrating sustainable cooling strategies into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement. The initiative addresses both climate mitigation and adaptation challenges posed by rising global temperatures and energy demand.
About the NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025
- Purpose:Provides a structured global framework for countries to incorporate sustainable cooling into national climate action plans, balancing mitigation, adaptation, and developmental needs.
- Developed by:UNEP’s Cool Coalition NDC Working Group, in collaboration with partners like UNDP.
- Primary Objectives:
- Mainstream sustainable cooling in national NDCs.
- Reduce sectoral emissions by 60% by 2050.
- Improve access to cooling for 1.1 billion vulnerable people.
- Establish robust Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) mechanisms.
- Align with the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol and the Global Cooling Pledge.
Global Cooling Landscape: Key Data Points
- Current Impact:
- Cooling accounts for nearly 7% of global GHG emissions, projected to exceed 10% by 2050.
- Cooling consumes 20% of global building electricity, and up to 50% in countries like UAE.
- Access Challenges:1.1 billion people worldwide lack access to efficient and affordable cooling, threatening lives, food security, and healthcare.
- Efficiency Potential:By doubling appliance efficiency, access can expand sixfold without proportionate emission growth.
Challenges in the Cooling Sector
- Rising Emissions:Without immediate policy interventions, emissions from cooling are expected to double by mid-century, increasing climate and energy pressures.
- Access Inequality:Many low-income and rural populations remain exposed to extreme heat due to lack of sustainable cooling.
- Policy Gaps:Only 27% of updated NDCs currently include specific energy efficiency targets related to cooling.
- Gendered Impacts:Women, especially in vulnerable communities, face greater health risks from inadequate cooling and heat stress.
- Reinforcing Heat-Cooling Loop:Increasing temperatures escalate cooling demand, which if met with inefficient systems, leads to more emissions, exacerbating global warming—a vicious cycle.
Six-Step Framework in the Guidelines
- Baseline Assessment:Measure current energy use and refrigerant emissions in the cooling sector.
- Target Setting:Define clear, time-bound targets aligned with national climate priorities.
- Monitoring, Reporting, Verification (MRV):Develop transparent systems to track and report progress.
- Policy Tools:
- Introduce Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS)
- Phase down high-GWP refrigerants
- Promote urban greening and passive cooling techniques
- Governance & Institutional Support:Establish cross-sectoral coordination, incorporating gender-sensitive planning.
- Financing & Equity:Mobilize investments and develop policies to enable equitable access to sustainable cooling technologies.
Country-Level Initiatives
- Nigeria:Integrated National Cooling Action Plan (NCAP) into its NDC, with a focus on heat-resilient rural infrastructure.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE):Adopted district cooling systems and high-efficiency air conditioning in its updated climate roadmap (NDC 3.0).
- Grenada:Committed to becoming the first HFC-free nation, aiming for complete refrigerant phase-down.
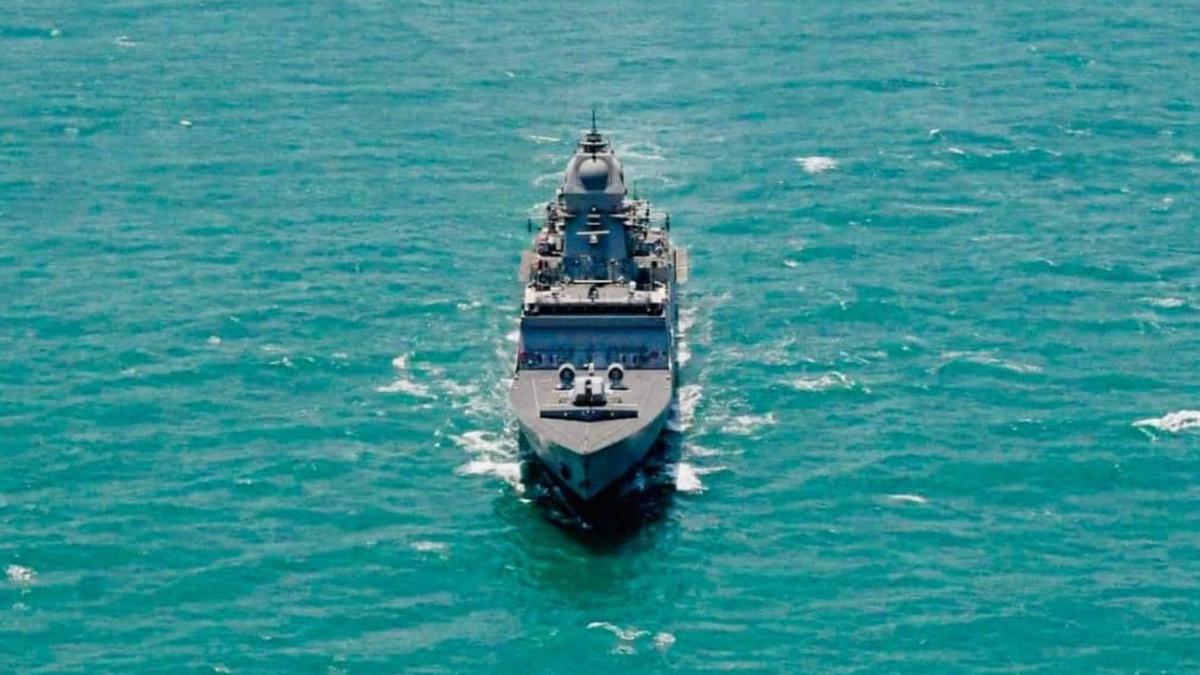
INS Nilgiri

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
INS Nilgiri, the first stealth frigate of the indigenously developed Project 17A series, has recently been inducted into the Eastern Naval Command. It will play a crucial role in the Eastern Sword-Sunrise Fleet.
Key Facts:
- Class and Design:INS Nilgiri belongs to the Nilgiri-class frigates under Project 17A, an advanced stealth warship initiative. It is an improved version of the earlier Shivalik-class (Project 17) frigates.
- Design and Construction:The vessel has been designed by the Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau and constructed by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai.
- Sister Ships Under Construction:Six other frigates of the same class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, Vindhyagiri, and Mahendragiri—are currently being built at MDL, Mumbai and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
Technical Specifications & Capabilities:
- Dimensions & Displacement:
- Length: 149 meters
- Displacement: Approximately 6,670 tonnes
- Propulsion:
- Equipped with a CODAG (Combined Diesel and Gas) propulsion system
- Maximum speed: Up to 28 knots
- Combat Capability:
- Anti-Air Warfare: Armed with 16 Barak-8 surface-to-air missiles
- Surface Warfare: Equipped with 8 BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles for anti-ship and land-attack roles
- Surveillance & Targeting Systems:
- MF-STAR Radar: Offers 360-degree situational awareness
- 3D AESA Radar: Enables tracking of multiple targets simultaneously
- Nishant Radar: Enhances fire control and targeting precision
- Network-Centric Warfare:The onboard Combat Management System (CMS) seamlessly integrates various sensors and weapons, allowing for coordinated operations with other naval platforms.
Significance:
The induction of INS Nilgiri marks a major milestone in India’s pursuit of a modern, self-reliant naval fleet. It enhances the Indian Navy’s blue-water capabilities, contributing to maritime dominance and regional security in the Indo-Pacific.
Tomahawk Missiles
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the Iran-Israel conflict, the United States has reportedly launched precision strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, targeting key sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan. These attacks were carried out using Tomahawk cruise missiles and GBU-57 bunker busters, marking a critical intervention by the US in the unfolding regional crisis. President Donald Trump termed the strikes a “clear warning” to Iran, signalling the potential for intensified military action if diplomatic overtures are rejected.
What Are Tomahawk Missiles?
The Tomahawk missile is a long-range, subsonic, all-weather cruise missile primarily operated by the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It is designed for precision strikes on high-value or heavily defended targets, including hardened or buried infrastructure such as nuclear sites.
- Launch platforms: Ships and submarines
- Flight path: Low-altitude terrain-following flight to evade radar
- Use case: Strategic, surgical strikes in contested or defended environments
Design and Capabilities
- Length: ~5.6 meters (without booster)
- Weight: Up to 1,600 kg
- Speed: ~880 km/h (subsonic)
- Range: Over 1,600 km (varies by variant)
- Flight altitude: As low as 30–50 meters
- Warheads:
- Unitary high-explosive
- Cluster munitions
- Nuclear warheads (retired from use)
Navigation and Guidance Systems
Tomahawk missiles are known for pinpoint accuracy, achieved through a multi-layered guidance system:
- GPS (Global Positioning System) and INS (Inertial Navigation System) for real-time course tracking
- TERCOM (Terrain Contour Matching): Compares terrain under flight path with stored maps
- DSMAC (Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation): Matches live terrain imagery with onboard target data
- Data-link capability: Allows for in-flight re-targeting, mission abort, or loitering over areas
Variants and Modern Upgrades
- Tomahawk Block IV (TLAM-E): Most modern variant, featuring:
- In-flight reprogramming
- Target loitering
- Real-time battle damage assessment
- Two-way satellite communication
Historical Combat Usage
Tomahawk missiles have been extensively used in US military operations:
- Gulf War (1991): ~280 missiles used in the opening strikes
- Operation Infinite Reach (1998): Targeted terrorist camps in Sudan and Afghanistan
- Iraq War (2003): Hundreds used during the initial “shock and awe” campaign
- Libya Intervention (2011): Destroyed air defence infrastructure
- Syria (2017): 59 Tomahawks used against Shayrat Airbase in retaliation for chemical attacks
INS Tamal

- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark development for India's maritime defence, the Indian Navy is set to commission its latest stealth multi-role frigate, INS Tamal, on 1st July 2025 at Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningrad, Russia
Overview:
- Class & Series: INS Tamal is the second ship of the Tushil-class, an upgraded variant of the Talwar and Teg class frigates, forming part of the Krivak class series built under Indo-Russian cooperation.
- Total Induction: With Tamal’s addition, India will operate ten ships with common capabilities across four related classes.
- Construction: Built at Yantar Shipyard with oversight from Indian specialists under the Warship Overseeing Team (WOT), Kaliningrad, under the Embassy of India, Moscow.
Symbolism and Identity
- The name ‘Tamal’ represents the mythical sword of Indra, the King of Gods.
- The ship’s mascot blends India’s Jambavant, the immortal bear king of mythology, with Russia’s Eurasian Brown Bear, symbolising Indo-Russian defence cooperation.
- The ship’s motto: ‘Sarvada Sarvatra Vijaya’ (Victorious Always Everywhere).
Make in India & Indigenous Content
- INS Tamal is the last warship to be inducted from a foreign source, aligning with Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives.
- 26% indigenous content, including:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (anti-ship & land attack roles)
- HUMSA NG Mk II sonar, Indian radars, and communication systems
- Indian OEMs involved: BrahMos Aerospace, BEL, Keltron, Nova Integrated Systems (Tata), Elcome Marine, Johnson Controls India, among others.
- Indigenous components have more than doubled to 33 systems compared to previous imports.
Key Features & Capabilities
- Displacement: 3,900 tonnes | Length: 125 metres
- Top speed: Over 30 knots
- Armament & Combat Systems:
- Vertically Launched Surface-to-Air Missiles (VL-SAM)
- Improved 100 mm main gun, 30 mm CIWS
- Heavyweight torpedoes, anti-submarine rockets
- EO/IR system, fire control radars
- Aviation Support: Flight deck for Air Early Warning & Multi-Role helicopters
- Sensors & Network:
- Surface Surveillance Radar
- Advanced Electronic Warfare suite
- Network Centric Warfare capabilities
- Trials: Successfully completed 3-month sea trials, validating systems and weapons in challenging winter conditions (St. Petersburg & Kaliningrad).
Strategic Importance
- Upon commissioning, INS Tamal will join the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet—the 'Sword Arm' of the Navy under Western Naval Command.
- Reinforces India’s blue water naval ambitions, enhancing operational readiness in multi-threat maritime environments.
- Embodies two decades of Indo-Russian naval cooperation and represents a transition towards domestic warship production.
Gwada Negative
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark discovery for transfusion science, France’s national blood agency (Établissement Français du Sang – EFS), in June 2025, identified a completely new blood group system. Officially recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as the 48th blood group system, it is termed EMM-negative and is informally called “Gwada Negative”, after Guadeloupe, the origin of the only known individual with this blood type.
What is Gwada Negative (EMM-negative)?
- EMM-negative is defined by the absence of the EMM antigen, a high-incidence antigen normally present on red blood cells in nearly all humans.
- High-incidence antigens are so common that individuals lacking them are considered extremely rare and face critical challenges in blood transfusion compatibility.
- The ISBT registered this as ISBT042, making it the latest addition to global blood group systems.
Discovery Timeline
- 2011: A 54-year-old woman from Guadeloupe, living in Paris, underwent pre-surgical blood testing. Her blood showed unidentified antibodies that did not match any known blood group systems.
- 2019: With advancements in Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), researchers led by Dr. Thierry Peyrard (EFS) identified the unique genetic mutation responsible for the absence of the EMM antigen.
- 2025: After peer-reviewed validation, the ISBT officially recognised the EMM-negative system during its Milan meeting.
Why is it So Rare?
- This woman is the only known person in the world with the EMM-negative blood type.
- She inherited the rare gene mutation from both parents, leading to a complete absence of the EMM antigen in her red blood cells.
- Since the EMM antigen is nearly universal, her blood is compatible only with itself, making transfusions extremely high-risk unless a genetically identical donor is found.
Clinical Significance
- Individuals lacking high-incidence antigens like EMM may develop alloantibodies — immune responses against transfused red cells containing those antigens.
- Transfusion of EMM-positive blood into such individuals can cause hemolytic reactions, including life-threatening hemolysis (premature red blood cell breakdown).
- In this case, no donor blood currently available is safe for transfusion into the patient.
Implications for Transfusion Medicine
- Highlights the need for rare blood donor registries, international cooperation, and advanced genetic screening technologies to identify such rare phenotypes.
- Encourages development of precision-matching protocols in complex clinical and emergency situations.
- Expands the understanding of human immunohematological diversity and redefines transfusion compatibility standards.
Kounis Syndrome
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
The recent sudden death of Indian industrialist Sanjay Kapur during a polo match in London has drawn national attention to Kounis Syndrome, a rare but serious medical condition. Reports suggest he may have inhaled a bee, which stung him inside the throat—leading to a cardiac arrest, potentially triggered by an acute allergic reaction. This tragic incident has raised awareness about the interaction between allergic reactions and cardiac emergencies, especially in seemingly healthy individuals.
What is Kounis Syndrome?
Kounis Syndrome is a rare medical condition in which a severe allergic or hypersensitivity reaction triggers a coronary event, such as a heart attack. It is often termed “allergic angina” or “allergic myocardial infarction.”
Mechanism
- Triggered by allergens such as insect stings, drugs, or foods.
- Leads to the activation of mast cells, which release histamine and cytokines.
- These chemicals cause spasms, plaque rupture, or clot formation in coronary arteries.
- Result: Reduced blood flow to the heart, causing ischemia or infarction.
Types of Kounis Syndrome
- Type I: In individuals with normal coronary arteries – allergic reaction causes artery spasm and possible heart attack.
- Type II: In those with existing coronary artery disease – allergic reaction destabilizes plaques, causing infarction.
- Type III: In patients with coronary stents – hypersensitivity leads to thrombosis within stents.
Triggers of Kounis Syndrome
- Insect stings (bee, wasp)
- Medications (NSAIDs, antibiotics)
- Foods (nuts, shellfish, kiwi)
- Environmental allergens (latex, contrast dyes)
- Underlying health conditions (e.g., mastocytosis)
Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Swelling (angioedema), hives, or rash
- Low blood pressure
- ECG changes: ST-segment elevation or depression
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis: Clinical history, ECG, cardiac enzymes, allergy tests.
- Treatment includes:
- For allergy: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, epinephrine
- For cardiac care: Oxygen, nitrates, antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers
Why Mouth/Throat Bee Stings Are Dangerous
- Immediate airway swelling
- Increased absorption of venom into bloodstream
- Enhanced risk of anaphylaxis and cardiac arrest
Even people without a history of allergy can experience severe reactions if stung inside the mouth or throat.
Warning Signs After a Bee Sting
- Difficulty breathing
- Swollen lips, tongue, or throat
- Rash or itching
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid or weak heartbeat
- Nausea or unconsciousness
Immediate emergency care is essential.
Himalayan Brown Bear
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant development for Himalayan biodiversity, a rare sighting of a Himalayan Brown Bear with its family has been reported for the first time in the Dumka region between Nelang and Bhairon Ghati, within Gangotri National Park, Uttarakhand. The sighting has enthused wildlife experts and is viewed as a positive indicator of range expansion and ecosystem resilience in this fragile high-altitude region.
Significance of the Sighting
- This marks the first recorded presence of a brown bear in this specific stretch of the park.
- Previously, sightings were limited to Gomukh (6 bears) and Kedartal (3 bears), both located above 3,000 m.
About the Himalayan Brown Bear
- Scientific Name: Ursus arctos isabellinus
- Common Names: Himalayan Red Bear, Isabelline Bear; known as Denmo in Ladakhi.
- It is believed to be one of the most ancient brown bear lineages and may have inspired the Yeti legend due to its upright gait.
Distribution and Habitat
- Found in the northwestern and central Himalayas: India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, and China (Tibet).
- In India: Exists in fragmented populations in Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Inhabits elevations between 3,000 and 5,500 meters, usually above the timberline in alpine meadows and snow-clad regions.
Ecological Features
- Size: Males average 1.9 m and 135 kg; females 1.6 m and 70 kg.
- Fur: Sandy or reddish-brown; thick to endure high-altitude cold.
- Diet: Omnivorous – consumes roots, berries, nuts, small mammals, fish, and insects.
- Behavior: Solitary, except during mating or a mother with cubs; hibernates during winter in dens.
- Lifespan: 20–30 years in the wild.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
Subarnarekha River
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
A flash flood in the Subarnarekha River affected over 50,000 people in Balasore district, Odisha. The flooding was triggered by heavy rainfall and the release of water from Chandil Dam in Jharkhand.
About Subarnarekha River
Origin:
- Arises near Piska/Nagri, close to Ranchi, in Jharkhand.
- The name "Subarnarekha" means “Streak of Gold”, referring to traces of gold once found in the river’s origin area.
Geographical Course:
- States Covered: Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha.
- Mouth: Empties into the Bay of Bengal near Talsari, in Odisha.
- Total Length: Approx. 395 km.
- Drainage Basin Area: 18,951 sq. km, making it a relatively small multi-state river basin.
- Course Details: Flows through Paschim Medinipur (WB) and Balasore (Odisha) after originating in Jharkhand.
Key Features:
- Hundru Falls: A well-known waterfall on Subarnarekha, located in Jharkhand, with a drop of 98 metres.
- The river system is independent, not a tributary of any larger river.
- Known for its historical and cultural significance due to gold particles in its sands.
Major Tributaries:
- Kharkai (joins at Jamshedpur)
- Kanchi, Roro, Harmu Nadi, Dulunga, Karru, Karakari, Singaduba, Kodia, Dhamra
About Chandil Dam
Location:
- Situated in Chandil, Seraikela Kharsawan district, Jharkhand.
- Built near the confluence of the Subarnarekha River and Karkori River (originating from Hundru Falls).
Purpose:
- Multi-purpose project serving irrigation, flood control, and tourism.
- Plays a significant role in managing water flow in the Subarnarekha basin.
Estimates Committee

- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The Lok Sabha Speaker inaugurated the National Conference of Estimates Committees in Mumbai to mark 75 years of the Parliamentary Estimates Committee.
About the Estimates Committee:
- Type: Parliamentary Financial Standing Committee (Lok Sabha).
- Established in: 1950, under the Rules of Procedure of Lok Sabha, after the adoption of the Constitution.
- Purpose: To examine how public funds are allocated and utilized, and recommend improvements in economy, efficiency, and accountability.
Composition:
- Total Members: 30 Lok Sabha MPs.
- Exclusion: Ministers are not eligible to be members.
- Chairperson: Appointed by the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- Term: One year, renewable annually.
Selection Process:
- Members are elected annually by the Lok Sabha through proportional representation using the single transferable vote system.
Key Functions:
- Examine budget estimates of various ministries and departments.
- Suggest reforms for better economy and efficiency in public expenditure.
- Recommend alternative policies for improved governance and financial management.
- Evaluate effectiveness of spending aligned with policy objectives.
- Suggest improvements in the presentation of budget estimates to Parliament.
Exclusions: Does not examine Public Sector Undertakings — these are dealt with by the Committee on Public Undertakings.
Working Mechanism:
- Selects specific departments or statutory bodies for scrutiny.
- Seeks inputs from government officials and external experts.
- Undertakes study visits and on-ground assessments (with prior approval).
- Holds formal evidence sessions in Parliament.
- Submits findings and recommendations through reports to the Lok Sabha.
- The Government must submit Action Taken Reports (ATR) within six months.
Achievements (as of 2025):
- Total Reports Presented: 1,184
- 656 Original Reports
- 528 Action Taken Reports
- Covered nearly all major ministries and departments.
- Contributed to strengthening Parliamentary financial oversight and ensuring fiscal discipline.
Operation Midnight Hammer
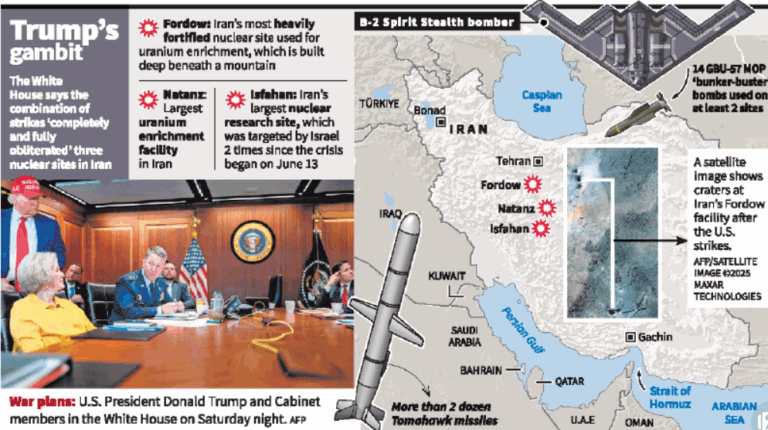
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The United States launched a classified military operation named Operation Midnight Hammer, targeting Iran’s major nuclear sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan, claiming significant damage to its nuclear infrastructure.
About Operation Midnight Hammer:
- A covert US airstrike intended to degrade Iran’s nuclear weapons program.
- Launched by: US Department of Defense.
- Objective: Destruction of fortified nuclear facilities and demonstration of US strategic air power.
Key Assets Deployed:
- B-2 Spirit Stealth Bombers equipped with GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrators (MOPs) – “bunker-buster” bombs designed to penetrate over 200 feet of reinforced concrete.
- Tomahawk Land Attack Cruise Missiles launched from US submarines.
- Support aircraft and decoys for air defence suppression.
B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber:
- Type: Long-range strategic stealth bomber of the US Air Force.
- Developed by: Northrop Grumman (1980s).
- Cost: Approx. $2.1 billion per unit – one of the most expensive aircraft in the world.
- Range: Over 6,000 nautical miles without refuelling.
- Crew: Operated by two pilots.
Weapons and Capabilities:
- Payload Capacity: Over 40,000 pounds.
- Armament Options:
- 2 × GBU-57A/B MOPs
- 16 × B83 nuclear bombs (part of US nuclear triad)
- Precision-guided weapons: JDAM, JSOW, JASSM-ER.
- Stealth Features: Radar cross-section as small as a bird – allows evasion of sophisticated air defences.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances the US’s global precision strike capabilities.
- Reinforces the deterrence role of the B-2 in both conventional and nuclear domains.
- Capable of targeting heavily fortified underground facilities.
- Proven operational effectiveness in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran.
SSLV Technology Transfer
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a historic development for India's space sector, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will, for the first time, completely transfer rocket technology to a domestic firm. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has secured the Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) through a competitive process facilitated by IN-SPACe, marking a new era of private-sector participation in space.
What is the SSLV Technology Transfer?
- Nature of ToT: Complete technology handover of ISRO’s SSLV to HAL.
- Awarded By: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) after a two-stage national selection.
- Winning Bid: HAL won the bid with a ?511 crore offer — the highest among the contenders.
- Other Bidders: Consortia led by Alpha Design (Bengaluru) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (Hyderabad).
- Objective: To empower the private sector to build, market, and launch rockets independently, thus reducing reliance on ISRO for small satellite missions.
Key Features of the SSLV ToT
Parameter Details
Ownership - HAL will own and operate the SSLV, with rights to modify its design and choose commercial partners.
Production Capability - HAL aims to produce 6–10 SSLVs annually, based on demand.
ToT Duration - 2 years of technology handholding by ISRO, during which HAL will manufacture at least two SSLV prototypes.
Post-ToT - HAL will operate independently post-ToT and may enter contracts for commercial launch services.
Contractual Roles - ISRO (technical), IN-SPACe (regulatory + ToT coordination), NSIL (commercial interface), HAL (execution).
About Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- Established: 23 December 1940 (as Hindustan Aircraft Limited).
- HQ: Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Core Role: India’s largest defence and aerospace PSU involved in aircraft, helicopters, engines, and now space systems.
- Key Contributions:
- Manufactured MiG-21, SU-30MKI, LCA Tejas.
- Supplied components for GSLV Mk-III, Mars Orbiter Mission, and Gaganyaan.
- Collaborated with ISRO on cryogenic engines and launch vehicle structures.
- Publicly Listed: On BSE and NSE since 2018.
Significance:
- First Full Rocket ToT in India: Unlike earlier manufacturing contracts (e.g., PSLV), SSLV is entirely owned and operated by HAL.
- Boosts Private Sector Role: Aligns with India’s space sector reforms to commercialize launch services.
- Fosters Innovation & Autonomy: HAL can redesign the SSLV and partner globally, making India more competitive in the small satellite launch market.
- Strategic Diversification: HAL adds space systems to its portfolio, without affecting defence operations.
Green Hydrogen Production
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant scientific milestone, Indian researchers have developed a next-generation, scalable solar-driven device for producing green hydrogen—offering a major boost to clean energy innovation and India’s energy transition goals.
Key Highlights:
- Developed By: Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Bengaluru — an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Publication: The findings were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A (Royal Society of Chemistry).
What Is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced by splitting water molecules using renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind, without any greenhouse gas emissions. It is a clean energy carrier with the potential to decarbonize heavy industries, power vehicles, and store energy.
The Innovation: Solar-Driven Water Splitting Device
- The device uses only solar energy to split water and produce hydrogen.
- It employs a silicon-based photoanode with an n-i-p heterojunction structure:
- n-type TiO?, intrinsic (undoped) Si, and p-type NiO layers.
- This structure enhances charge separation and transport efficiency.
- Fabrication via magnetron sputtering, a scalable, industry-compatible process.
Key Performance Metrics
- Surface photovoltage: 600 millivolts (mV)
- Low onset potential: ~0.11 VRHE
- Stability: Operated continuously for over 10 hours in alkaline medium with only ~4% performance degradation.
- Successfully scaled to a 25 cm² photoanode, showing strong solar-to-hydrogen conversion.
Advantages of the Device
Feature Benefit
Pure solar operation No external power or fossil fuel input
High energy efficiency Better light absorption, reduced recombination loss
Material use Low-cost, earth-abundant materials
Durability Stable under alkaline conditions
Scalability Demonstrated potential for industrial-scale production
Strategic Significance
- Accelerates India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and hydrogen-based economy.
- Supports India’s net-zero emission commitments and climate action.
- Offers a cost-effective, clean energy alternative to fossil fuels in:
- Hard-to-abate sectors like steel and cement
- Clean transport solutions
- Renewable energy storage systems
B-2 Spirit Bomber
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the ongoing US–Iran tensions, the United States deployed the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber to strike Iran’s fortified nuclear infrastructure, including the heavily guarded Fordow enrichment facility, which was described by President Donald Trump as the “crown jewel” of Iran’s nuclear programme. The strikes signal a new phase in the geopolitical standoff, showcasing advanced US airpower and precision capabilities.
What is the B-2 Spirit Bomber?
The B-2 Spirit, developed by Northrop Grumman during the Cold War, is one of the most advanced strategic bombers in the world. Originally built for penetrating heavily defended Soviet airspace, it remains a key asset in the US Air Force due to its stealth capabilities, long range, and precision payload delivery.
Only 21 B-2 bombers were built, each costing an estimated $2.1 billion, making it one of the most expensive aircraft ever developed. Its bat-wing design and radar-absorbent coating significantly reduce its radar cross-section, making it almost invisible to radar and ideal for deep penetration missions in hostile territory. It is operated by a two-person crew and extensively automated to reduce pilot workload.
Why was it used in the Iran strikes?
The B-2 Spirit was chosen for the Iran mission because of its unique combination of stealth, range, and payload capacity. The Fordow facility, built deep within a mountain and protected by sophisticated air defences, required a bomber that could both evade detection and deliver a bunker-busting payload with high precision.
During the mission, the B-2s were reportedly equipped with the GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) — a 30,000-pound bomb specifically designed to destroy deeply buried and fortified targets like Fordow. Due to the weapon’s size and weight, a B-2 can carry only one or two MOPs per sortie. Reports indicate that six MOPs were dropped on Fordow, demonstrating the operational effectiveness of the B-2 for such critical missions.
Capabilities and Strategic Role
The B-2 has an unrefueled range of over 6,000 nautical miles (approximately 11,000 km), enabling it to undertake intercontinental missions directly from the United States. Past missions have seen the B-2 operate from Missouri to targets in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran, demonstrating its global strike capability.
With a total payload capacity exceeding 40,000 pounds (18,000 kg), the B-2 can carry both conventional and nuclear weapons. It forms a crucial part of the US nuclear triad, capable of delivering up to 16 B83 nuclear bombs. Its ability to carry nuclear and precision-guided munitions gives it unmatched strategic versatility.
Weapon Systems Compatible with the B-2
Beyond the MOP, the B-2 can be armed with a variety of precision and standoff weapons, including:
- JDAMs (Joint Direct Attack Munitions): GPS-guided bombs used for high-accuracy strikes on fixed targets.
- JSOW (Joint Standoff Weapons): Glide bombs launched from a distance, allowing engagement of targets outside enemy air defence range.
- JASSM and JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missiles): Long-range cruise missiles, with the extended-range variant capable of striking targets up to 500 miles (805 km) away.
This versatility allows the B-2 to adapt to multiple mission profiles, from conventional warfare to nuclear deterrence.
Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
The deployment of the B-2 in this mission has both tactical and symbolic implications. Tactically, it underscores the US military’s ability to deliver precision strikes on highly protected strategic infrastructure. Strategically, it sends a strong signal to adversaries about the technological edge and operational reach of American military power.
From a geopolitical perspective, the strikes could exacerbate tensions in the already volatile West Asian region, heighten concerns about nuclear proliferation, and potentially provoke retaliatory actions by Iran and its regional allies. It also raises questions about the future of US-Iran relations and the fragility of nuclear diplomacy in the region.
Lenacapavir
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Wednesday approved Lenacapavir (LEN), the most promising HIV prevention medicine to be made so far.
What is Lenacapavir (LEN)?
- Type: Antiretroviral drug used as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV prevention.
- Mechanism: Prevents HIV infection in HIV-negative individuals at high risk.
- Efficacy: Clinical trials show it prevents 99.9% of HIV transmissions.
- Dosage: Injectable form, administered twice a year.
Recent Development
- Approved by: United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) – June 2025.
- Brand name: To be marketed as Yeztugo by Gilead Sciences.
- Described as the most promising HIV prevention drug to date.
Global and Indian Context
Global Need
- LEN could be a game-changer in ending the global HIV/AIDS epidemic.
- However, cost remains a barrier—initially priced at over $40,000 per person/year, now reduced to $28,218.
Indian Reality
- Despite India's 92% contribution to global ART supply, PrEP is yet to be rolled out under India’s National AIDS Control Programme (NACP).
- The National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) has not yet integrated PrEP or LEN into national policy.
India’s Role in Equitable Access
Expert View:
- India must take the lead in making LEN accessible, affordable, and timely.
- Equitable distribution is critical to preventing new infections and achieving AIDS elimination targets.
- Urges Indian regulators and generic companies to fast-track licensing and manufacturing.
Why this matter?
Public Health Impact
- LEN could stop HIV transmission at scale if made widely available in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- Its twice-a-year injectable nature increases adherence, especially in vulnerable populations.
Cost Savings
- Prevention through PrEP like LEN is more cost-effective than providing lifelong ART after infection.
India’s Strategic Position
- India already serves as the global hub for HIV treatment through its generic pharmaceutical capacity.
- India’s leadership is central to global HIV prevention strategies including:
- Treatment as Prevention (TasP)
- Test and Treat
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
Policy Recommendations
- Fast-track regulatory approvals for generic LEN in India.
- Integrate PrEP and injectable LEN into NACO guidelines.
- Ensure price transparency and accessibility through public-private collaboration.
- Collaborate with global health bodies (WHO, UNAIDS, Global Fund) to position India as the equitable access leader.
Samson Option
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The Samson Option, Israel’s controversial and undeclared nuclear deterrence doctrine, has returned to global focus amid escalating military strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure under Operation Rising Lion (June 2025). The rising risk of a multi-front conflict involving Iran, Hezbollah, and Houthi actors has revived global concerns over nuclear escalation in the volatile Middle East.
What is the Samson Option?
- Definition: Israel’s nuclear annihilation doctrine of last resort, based on the principle of massive retaliation in case of an existential threat to the state.
- Doctrine Type: Deterrence-by-retaliation, not first use.
- Strategic Intent: Not to deter routine threats, but to ensure mutual destruction if Israel faces annihilation.
- Named After: Samson, a biblical warrior who destroyed himself and his enemies in a final act of vengeance (Judges 13–16).
Key Features
Feature Details
Ambiguity (Amimut) Israel neither confirms nor denies its nuclear arsenal.
Nuclear Capability Estimated 80–400 nuclear warheads, with delivery via land (Jericho missiles), air, and sea.
Indigenous Development Secret nuclear program began in the 1950s under Ben-Gurion with aid from France & Norway.
Delivery Platforms Multi-platform: land-based missiles (Jericho series), aircraft, and submarines.
Psychological Warfare Operates as a psychological deterrent, not an openly declared policy.
Policy Origin Popularized by Seymour Hersh’s 1991 book, built upon disclosures by whistleblower Mordechai Vanunu (1986).
Historical Evolution
- 1950s–60s: Nuclear ambitions began under PM David Ben-Gurion.
- 1967: Believed to have assembled first nuclear weapon by Six-Day War.
- Public Position: “We will not be the first to introduce nuclear weapons in the Middle East” – Shimon Peres to JFK.
- Doctrinal Continuity: Israel remains outside the NPT (Non-Proliferation Treaty) and follows the policy of opacity to this day.
Why It’s in Focus Now: Operation Rising Lion & 2025 Escalations
- Operation Rising Lion (June 2025): Israel’s largest campaign against Iran’s nuclear sites since the 1981 Osirak raid.
- Iran’s Response: Ballistic missile and drone counterstrikes tested Israel’s air defences (Iron Dome, Arrow-3).
- Multi-Front Threats: Escalations from Hezbollah in Lebanon, Houthi threats in the Red Sea, and tension in Gaza heighten risks of a regional conflagration.
- Red Lines: Any mass-casualty attack involving WMDs (chemical/radiological) may activate Israel’s last-resort nuclear doctrine.
Implications for the Region and the World
- Security and Strategic Balance
- Israel’s nuclear ambiguity complicates strategic planning for adversaries.
- Shapes arms acquisition strategies of regional players like Iran, Saudi Arabia, and UAE.
- Geoeconomic and Business Fallout
- Oil Market Volatility: Brent crude hit $102/barrel after Israeli strike on Natanz.
- Defence Sector Boom: Surge in defence procurement by Gulf States; U.S. firms like Raytheon and Lockheed Martin benefit.
- Investor Uncertainty: Rising nuclear rhetoric rattles financial markets and international investors.
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Challenges
- Israel’s position outside the NPT undermines the credibility of global arms control.
- Inspires double standards debate and pressures nations like Iran to pursue deterrent paths.
- Cyber Deterrence and Intelligence Warfare
- Past cyber ops like Stuxnet (U.S.–Israel malware attack on Iran’s nuclear centrifuges) re-emerging.
- Cyber warfare now considered part of the extended nuclear deterrent architecture.
BSNL Soft Launches Quantum 5G FWA

- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) announced in Hyderabad, the soft launch of BSNL Quantum 5G FWA. This indigenous, SIM-less fixed-wireless-access solution delivers fibre-like speeds over 5G radio.
What is Quantum 5G FWA?
Quantum 5G FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) is an indigenous, SIM-less, 5G broadband solution that offers fibre-like speeds using wireless 5G radio—eliminating the need for traditional fibre connections.
Key Technical Features:
- SIM-less Connectivity: Uses BSNL’s Direct-to-Device (D2D) platform; Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) auto-authenticates without a SIM card.
- Fully Indigenous Tech Stack: Core network, RAN (Radio Access Network), and CPE developed under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- High-Speed Performance:
- Download: Up to 980 Mbps
- Upload: 140 Mbps
- Latency: Under 10 milliseconds
- Plug-and-Play Installation:
- No trenching or fibre required.
- Covers over 85% of Hyderabad households via existing BSNL tower grid.
Significance of the Launch
- India’s First SIM-less 5G FWA solution.
- Marks BSNL as a 5G pioneer in offering 100% made-in-India wireless broadband.
- Showcases Indian R&D strength and self-reliance in advanced telecom under Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Ideal for UHD streaming, cloud gaming, remote work, and smart home services.
- Bridges the digital divide by enabling affordable gigabit-speed internet, even in rural and underserved regions.
Roadmap and Future Expansion
- Pilot Rollouts (By September 2025): Target Cities: Bengaluru, Pondicherry, Visakhapatnam, Pune, Gwalior, Chandigarh
- Tariff Plans:
- ?999/month for 100 Mbps
- ?1499/month for 300 Mbps
- Enterprise Applications: Will support network-sliced, SLA-backed links for MSMEs and smart manufacturing through edge-cloud architecture.
World Investment Report 2025
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Investment Report 2025, released recently by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights critical trends in global foreign direct investment (FDI).
Key Details:
Purpose of the Report:
- To track global trends in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and international production.
- To guide policymakers and investors on aligning investment flows with sustainable development objectives.
- To monitor progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Global Digital Compact through investment trends.
Major Global Trends Identified (2024 Data)
- Overall Decline in Global FDI: FDI declined by 11%, reaching $1.5 trillion, marking the second consecutive year of contraction.
- Digital Economy as a Growth Engine
- Value of digital-sector projects doubled, becoming the primary driver of FDI growth.
- Key growth areas: AI, data centres, cloud computing, semiconductors.
- SDG Investment Crisis: Investment in critical SDG sectors such as renewable energy, water, sanitation, and agrifood fell by 25–33%.
- Regional Divergence
- Africa: FDI surged by 75%, led by Egypt’s $35 billion megaproject.
- ASEAN: Moderate growth of 10% driven by realigned supply chains.
- China: FDI inflows fell by 29%, affected by geopolitical tensions.
- South America: Registered an 18% drop in FDI.
- Collapse in Infrastructure Finance: International Project Finance (IPF) declined by 26%, deepening the infrastructure gap in least developed countries (LDCs).
- Geopolitical Fragmentation
- Rising trade tensions, tariff barriers, and political risks are reshaping FDI flows.
- Emergence of near-shoring and regionalisation as firms relocate to reduce dependence on global supply chains.
Country-Specific Focus: India
- India received $28 billion in FDI inflows in 2024, retaining its rank among top global destinations.
- Key sectors: semiconductors, EV components, digital infrastructure.
- India ranked among top 5 global hubs for greenfield projects.
- Outbound FDI by Indian firms increased by 20%, showing strong outward investment intent.
Assessment of Positive and Negative Trends
Positive Trends:
- Digital FDI Boom: Reflects a global pivot towards a knowledge and tech-driven economy.
- Africa’s Rise: Significant confidence in Africa despite global slowdown.
- Resilient ASEAN & India: Benefitting from global supply chain realignment.
Negative Trends:
- Fall in SDG-Aligned Investments: Threatens progress towards global sustainability targets.
- Infrastructure Finance Crisis: Severely affects LDCs dependent on project finance.
- China’s FDI Decline: Raises concerns about the future of global investment flows amid US-China tensions.
- Geopolitical Fragmentation: Reduces investor appetite for long-term cross-border projects.
Strategic Recommendations
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Scale up investments in broadband, cloud infrastructure, and data hubs through public-private partnerships.
- Bridge SDG Investment Gap: Mobilize development banks, sovereign wealth funds, and climate finance to support SDG sectors.
- Policy Coherence: Align digital, industrial, and sustainability policies at national and international levels.
- De-risking Private Investment: Promote blended finance models to attract global capital to emerging markets.
- Enhance Innovation Governance: Improve IPR frameworks and cross-border data regulations to boost investor confidence in innovation sectors.
- Boost Regional Integration: Strengthen regional trade agreements and infrastructure connectivity to counter global fragmentation.
e-Rakt Kosh

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is set to integrate India’s Rare Donor Registry with e-Rakt Kosh, a centralized national blood bank management platform under the National Health Mission (NHM). This move aims to improve access to rare blood types, enhance donor coordination, and save lives by ensuring timely availability of rare blood groups.
About the Integration
- e-Rakt Kosh: A digital platform developed under NHM for real-time information on blood availability, donation camps, and blood bank locations.
- Rare Donor Registry of India (RDRI): Developed by the ICMR–National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) with four partner institutes. Maintains a database of 4,000 carefully screened rare blood donors, tested for over 300 rare blood markers.
- Objective: To provide a centralized, accessible system for patients needing rare blood and to assist blood banks in managing inventory and donors efficiently.
Key Features and Benefits
- Life-saving Access: Enables patients and hospitals to locate rare blood types like Bombay blood group, Rh-null, and P-null efficiently.
- Safe Transfusions: Helps match blood for patients with multiple antigen deficiencies, common in disorders like thalassemia and sickle cell disease, thus reducing transfusion complications.
- Technological Advancements:
- Use of Multiplex PCR-based DNA testing for rapid identification of rare blood groups.
- Development of a customized blood screening kit tailored for Indian patients.
- Donor Engagement: Aims to ensure a steady, motivated pool of rare blood donors who remain connected to blood banks.
ICMR’s Parallel Work on Hemoglobinopathies and Rare Diseases
- Point-of-Care (POC) Tests Developed For:
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Hemophilia A
- Von Willebrand Disease
- Impact of Innovation:
- Sickle Cell Test Kits cost reduced from ?350 to under ?50 per test through Health Technology Assessment (HTA) led by DHR, ICMR–CRMCH, and NIIH.
- Estimated savings: ?1,857 crore for the government.
- New rapid testing device enables diagnosis even at PHC level.
- International Interest: World Federation for Hemophilia has shown interest in procuring India-developed diagnostic kits for global deployment.
- Commercialization: Technology transferred to Bhat Biotech, which launched the product under the brand Bio-Scan in August 2023.
Significance
- Enhances India’s healthcare infrastructure and emergency response for rare blood groups.
- Aligns with the goals of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and Atmanirbhar Bharat in the field of indigenous diagnostics.
- Showcases India’s growing biotech innovation ecosystem with both national and international relevance.
11th International Day of Yoga (IDY) – 2025

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The 11th International Day of Yoga (IDY) will be observed on June 21, 2025, under the theme “Yoga for One Earth, One Health”. The theme emphasizes the connection between individual well-being and planetary health, aligned with India’s G20 vision of “One Earth, One Family, One Future.”
About the International Day of Yoga
- What it is: An annual global observance promoting yoga as a holistic health practice for physical, mental, and emotional well-being in harmony with nature.
- Adoption: Declared by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) through Resolution 69/131 on December 11, 2014, following India's proposal.
- First Observed: June 21, 2015
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India
Theme for 2025: “Yoga for One Earth, One Health”
- Focuses on the interdependence between human health and environmental sustainability.
- Reinforces yoga’s role in achieving sustainable lifestyles and climate consciousness.
Key Objectives
- Promote mind-body balance, emotional stability, and overall well-being through yoga.
- Raise global awareness on yoga’s health and ecological benefits.
- Encourage adoption of yoga as part of daily life for sustainable living.
- Strengthen India’s soft power and global leadership in wellness traditions.
Highlights and Participation
- Global Reach: Adopted by 175 UN Member States. Global participation has grown from 9 crore in 2018 to 24.53 crore in 2024.
- Mass Events: Celebrated across countries with support from state governments, Indian embassies, UN bodies, and civil society.
- Inclusive Message: Yoga Day’s logo and themes emphasize unity, well-being, and coexistence with nature.
Significance
- Public Health Tool: Promotes a low-cost, accessible, preventive healthcare practice.
- Sustainability Alignment: Advocates for climate-sensitive living and ecological harmony.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Enhances India’s global stature as the birthplace of yoga and a leader in wellness diplomacy.
- Soft Power Projection: Reflects India’s cultural values and promotes its influence through global well-being initiatives.
QS World University Rankings 2026
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
India has recorded its highest representation to date in the QS World University Rankings 2026, with 54 institutions featured—up from 11 in 2015. This marks a five-fold increase in a decade, making India the fourth most represented country, after the US, UK, and China.
Key Highlights
- Total Indian Institutions Ranked (2026): 54
- New Entrants from India: 8
- Top-performing Indian Institution: IIT Delhi (Rank 123)
- Fastest Rising Indian Institution: IIT Madras, up 47 places (from 227 in 2025 to 180 in 2026)
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) Featured: 12
- Debut Institutions in 2026:
- IIT Gandhinagar
- Lovely Professional University (LPU)
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT)
- Ashoka University
- Galgotias University
- Shiv Nadar University
- CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bengaluru
- Manav Rachna International Institute of Research and Studies (MRIIRS)
Significant Trends and Insights
- Global Standing:
- India now ranks 4th globally in terms of number of institutions in the QS Rankings.
- Only the US (192), UK (90), and China (72) rank higher.
- Improvements and Recognition:
- 48% of India’s ranked institutions have improved their positions over last year.
- 6 institutions are in the global top 250.
- 5 Indian universities are among the top 100 globally for Employer Reputation, showing high industry trust.
- 8 institutions rank in the top 100 for Citations per Faculty, with an average score of 43.7—higher than the UK, US, and Germany.
- Diverse Representation:
- Includes central universities, deemed-to-be universities, technical institutions, and private universities, reflecting a balanced and diversified higher education landscape.
QS Ranking Methodology: Key Indicators
Performance Lens Weightage Indicators Weightage
Research & Discovery 50% Academic Reputation 30%
Citations per Faculty 20%
Employability & Outcomes 20% Employer Reputation 15%
Employment Outcomes 5%
Global Engagement 15% International Faculty Ratio 5%
International Research Network 5%
International Student Ratio 5%
Learning Experience 10% Faculty-Student Ratio 10%
Sustainability 5% Sustainability 5%
- New Indicator in 2026: International Student Diversity (tracks number and diversity of international students; non-weighted this cycle)
Significance for India
- The consistent rise highlights the impact of reforms under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, with greater emphasis on research, global collaboration, academic excellence, and employer integration.
- India’s progress makes it the fastest-rising G20 nation in QS rankings.
- Reflects increasing global trust and recognition of India’s higher education system.
Revised Green India Mission (GIM)
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change released the revised roadmap for the National Mission for a Green India (GIM). The updated strategy focuses on restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing forest cover, and addressing climate impacts, especially in vulnerable landscapes like the Aravallis, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangroves.
About Green India Mission (GIM)
- Launched in: 2014
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Core Objectives:
- Increase forest/tree cover by 5 million hectares.
- Improve the quality of forest cover on another 5 million hectares.
- Restore degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Improve the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities.
Achievements So Far
- Afforestation Activities: 11.22 million hectares covered (2015–16 to 2020–21) through central and state schemes.
- Funding: ?624.71 crore released (2019–24) to 18 states; ?575.55 crore utilized.
- Target Areas: Selected based on ecological vulnerability, sequestration potential, and restoration needs.
Key Features of the Revised Roadmap
- Landscape-Specific Restoration:
- Prioritizes Aravalli ranges, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangrove ecosystems.
- Emphasizes regionally adapted best practices for ecosystem restoration.
- Integration with Aravalli Green Wall Project:
- Aims to combat desertification and sandstorm risks in northern India.
- Initial restoration planned across 8 lakh hectares in 29 districts of 4 states.
- Estimated cost: ?16,053 crore.
- Aims to develop a 5 km buffer zone covering 6.45 million hectares around the Aravallis.
- Western Ghats Focus:
- Tackling deforestation, illegal mining, and degradation.
- Measures include afforestation, groundwater recharge, and mining site restoration.
Combating Land Degradation and Climate Change
- Land Degradation (2018–19): Affected 97.85 million hectares (~1/3rd of India’s land), per ISRO data.
- India’s Climate Targets (2030):
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO? equivalent via forest/tree cover.
- Restore 26 million hectares of degraded land.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential (FSI Estimates):
- Restoration of open forests can sequester 1.89 billion tonnes of CO? over 15 million hectares.
- With intensified afforestation and aligned schemes, forest cover could reach 24.7 million hectares—achieving a carbon sink of 3.39 billion tonnes CO? equivalent by 2030.
Significance of the Revised Mission
- Aligns with India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Supports goals under UNCCD and UNFCCC.
- Helps mitigate climate change impacts by creating natural buffers and carbon sinks.
- Promotes ecological sustainability, biodiversity conservation, and community livelihood enhancement.
Bhashini

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Bhashini, the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM), to integrate AI-enabled multilingual tools into rural e-governance platforms.
About Bhashini
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Purpose: Acts as a digital public infrastructure for real-time, AI-powered translation across Indian languages.
Objective of the MoU
- To build an inclusive, multilingual e-governance ecosystem for Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- To bridge language barriers in rural governance and foster participatory democracy.
Key Features of the Initiative
- AI-Driven Language Translation: Offers real-time speech-to-text and text-to-text translation in major Indian languages.
- Platform Integration: Bhashini tools to be integrated with MoPR’s digital platforms like eGramSwaraj, ensuring multilingual access to rural governance services.
- Citizen-Centric Approach: Enables rural citizens to interact with digital governance platforms in their native language, enhancing accessibility and inclusion.
- Promotes Digital Inclusion: Supports rural digital literacy by making digital interfaces linguistically accessible.
- Enhances Transparency and Trust: Facilitates better information dissemination, increasing trust and engagement in local self-governance.
Significance
- Aligns with Digital India goals.
- Empowers Gram Panchayats by ensuring language is not a barrier to governance.
- Sets a precedent for AI-driven, citizen-centric governance reforms.
Predatory Pricing and Competition Law Reform

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has recently proposed the Determination of Cost of Production (DCOP) Regulations, 2025 to replace the older 2009 norms. A major reform introduced is the use of Average Total Cost (ATC) as a key metric to determine pricing in predatory pricing cases, while excluding ‘market value’ as a cost measure in such assessments.
- This development is significant in the context of India's broader competition law landscape, where concerns around market dominance and fair pricing are central to protecting consumer interest and ensuring a level playing field.
Understanding Predatory Pricing
- Predatory pricing refers to the practice of setting prices below cost to eliminate competitors from the market. Although consumers may benefit from low prices in the short term, the long-term consequence is often the emergence of monopolies, leading to higher prices and fewer choices. Due to its anti-competitive nature, this pricing strategy is banned in most jurisdictions globally.
- In India, predatory pricing is classified under ‘abuse of dominance’ as per the Competition Act, 2002, specifically under the broader category of unfair pricing or exclusionary conduct.
Legal Criteria for Establishing Predatory Pricing in India
For any allegation of predatory pricing to hold, three conditions must be satisfied:
- Dominance in the Market: The firm accused must hold a dominant position in the relevant market.
- Pricing Below Cost: The firm must have engaged in below-cost pricing, though defining “cost” has remained contentious. This raises the question—should cost mean fixed, variable, or total?
- Fixed costs are those independent of output (e.g., rent, IT systems).
- Variable costs change with production (e.g., raw materials, logistics).
- Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs.
- Intent to Eliminate Competition: There must be clear evidence that the pricing strategy was intended to exclude competitors from the market.
While dominance is usually straightforward to assess, determining what constitutes “cost” and proving anti-competitive intent remain legally complex.
Regulatory Evolution: From AVC to ATC
- Under existing regulations, the CCI had discretion to choose the cost metric on a case-by-case basis. The norm was to justify the use of any metric other than Average Variable Cost (AVC).
- A notable application was in the MCX vs. NSE case, where the Commission adopted the Long Run Average Incremental Cost (LRAIC) due to the network externalities inherent in stock exchange services, justifying inclusion of fixed costs.
- The new 2025 draft regulations now explicitly include Average Total Cost (ATC) as a valid benchmark for cost evaluation. ATC is widely accepted in industrial economics as a realistic representation of firm cost efficiency. By allowing ATC as a formal benchmark and excluding ‘market value’, the CCI aims to bring clarity and consistency in below-cost pricing investigations.
Why this Reform Matters
This proposed change holds importance for several reasons:
- It allows for a more holistic and realistic cost assessment, especially in industries where fixed costs form a significant part of the cost structure.
- It improves regulatory certainty and empowers the CCI to address anti-competitive practices in both legacy sectors (e.g., oil & gas) and emerging sectors (e.g., artificial intelligence and digital platforms).
- The reform is crucial at a time when the CCI’s budget has been declining year-on-year, limiting its enforcement capability. Simplified legal frameworks can enhance effectiveness without overburdening institutional resources.
Strengthening Inclusive Education for Children with Disabilities in India

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major step towards inclusive education, the Government of India signed a tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in 2025 between the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), and National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). The MoU aims to enhance curriculum reform, institutional coordination, and accessibility for children with disabilities across India’s education system.
What is Inclusive Education?
Inclusive education refers to a model where children with and without disabilities learn together in mainstream classrooms. It is supported by adapted curricula, accessible infrastructure, and individualised support mechanisms. The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016 legally mandates inclusive education environments in India.
Why Inclusive Education Matters
Inclusive education is not merely a policy choice but a constitutional, social, and developmental imperative:
- Right to Education: Under Article 21A of the Constitution and the RTE Act, 2009, every child aged 6–14 has the right to free and compulsory education. This includes children with special needs (CWSN).
- Equity and Access: Reports by UNESCO highlight that 29 million children are out of school in South Asia, many of them with disabilities. Ensuring their inclusion addresses systemic exclusion.
- Social Transformation: Inclusive classrooms reduce stigma, promote empathy, and facilitate social acceptance of persons with disabilities.
- Human Capital Development: Educating CWSN enhances their ability to participate in the economy, contributing to innovation, productivity, and nation-building.
- Global Commitments: India has ratified the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD, 2007) and is committed to SDG 4, which seeks inclusive and equitable quality education for all by 2030. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 also stresses disability inclusion at all education levels.
Key Data Points Highlighting the Need for Intervention
- According to the 2011 Census, around 7% of Indian children (0–19 years) have disabilities. However, data from UDISE+ 2019–20 reveals that less than 1% of children enrolled at the primary level are children with disabilities.
- In 2018–19, around 21 lakh CWSN were covered under Samagra Shiksha, supported by only 27,774 special/resource teachers across the country. This highlights the urgent need for both greater coverage and trained human resources.
Government Initiatives Promoting Inclusive Education
- The 2025 MoU between DEPwD, NIOS, and NCERT is aimed at reforming the curriculum to accommodate diverse learners. It also recognises special schools run under the Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS) as SAIEDs (Schools for Accessible and Inclusive Education for Disabled), expanding academic options for CWSN.
- The National Education Policy 2020 mandates the integration of children with disabilities in regular classrooms and promotes universal access and equity.
- Under Samagra Shiksha, the government provides financial support of ?3,500 per CWSN annually. Additional provisions include stipends for girls (up to Class XII), appointment of special educators, resource rooms, and home-based education for children with severe disabilities.
- NCERT’s Barkha Series, based on the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework, offers accessible reading materials in both print and digital formats, tailored to the diverse needs of learners.
- The RPWD Act 2016 mandates the creation of inclusive learning environments, with accessible buildings, assistive devices, and necessary support services.
UN Oceans Conference 2025

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
The third United Nations Oceans Conference (UNOC) was recently held in France, witnessing major developments in international marine conservation. One of the most significant outcomes was the near-finalisation of the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) agreement, also referred to as the High Seas Treaty.
As of now, 56 countries have ratified the treaty out of the required 60, bringing it close to the threshold for becoming legally binding. Notably, India and the United States have not yet ratified the agreement, although India has officially stated it is in the process of doing so.
About the BBNJ Treaty
- The BBNJ Treaty is a legally binding agreement developed under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Its aim is to regulate the use and protection of biodiversity in areas of the ocean that lie beyond national jurisdictions, also known as the high seas.
- The core objectives of the BBNJ Treaty include the creation of marine protected areas (MPAs) in international waters, regulation of marine genetic resources, enforcement of environmental impact assessments (EIAs) for activities in these regions, and capacity-building and technology transfer to support developing countries.
- The treaty is crucial because the high seas cover about 64% of the ocean’s surface and are largely unregulated.
- The BBNJ aligns with the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) target of conserving 30% of marine and coastal areas by 2030. Once the treaty secures the required number of 60 ratifications, it will enter into force after a 120-day waiting period. This will pave the way for the first Conference of Parties (COP) under the BBNJ to be held by late 2026.
Challenges to Implementation
- A major hurdle to the implementation of the BBNJ is the equitable sharing of benefits from marine genetic resources found in the high seas. These resources include unique life forms from deep-sea ecosystems that could have commercial applications in fields like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
- Since the high seas are global commons and not owned by any single nation, there is no clear consensus on how benefits should be shared.
- Environmental groups have also raised concerns that without a strong ban on resource extraction, the treaty may fall short of its conservation goals and could lead to unchecked exploitation of oceanic biodiversity.
Key Outcomes and Commitments from UNOC 2025
While the treaty itself is still awaiting full ratification, the conference saw a number of voluntary national and institutional commitments toward marine protection and sustainable ocean governance:
- The European Commission pledged €1 billion to support ocean conservation, marine science, and sustainable fisheries.
- French Polynesia committed to creating the world’s largest marine protected area, covering approximately five million square kilometres, equivalent to its entire exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
- New Zealand announced a contribution of $52 million to enhance ocean governance, science, and management in the Pacific Islands region.
- Germany launched an immediate action programme worth €100 million for the recovery and clearance of legacy munitions in the Baltic and North Seas.
- A coalition of 37 countries, led by Panama and Canada, initiated the High Ambition Coalition for a Quiet Ocean, the first global initiative to address ocean noise pollution.
- Italy committed €6.5 million to strengthen surveillance by the Coast Guard in marine protected areas and around oil platforms.
- Canada contributed $9 million to the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance, aiming to help Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and coastal countries build resilience against climate change using nature-based solutions.
- Spain pledged to establish five new marine protected areas, increasing its protected marine territory to 25%.
- A group of UN agencies introduced the One Ocean Finance initiative, which aims to mobilize investment from blue economy sectors to fund ocean sustainability.
Operation Sindhu

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
As tensions escalate in West Asia due to the ongoing Iran-Israel conflict, the Government of India has launched Operation Sindhu to evacuate Indian nationals, particularly students, stranded in conflict-affected regions of Iran.
- The first flight under Operation Sindhu, carrying 110 Indian students, successfully landed in New Delhi, marking the beginning of the evacuation process.
What is Operation Sindhu?
Operation Sindhu is a government-led evacuation mission launched in 2025 to ensure the safe repatriation of Indian citizens from war-hit Iran.
- Launched by: Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India
- Assisted by: Indian Embassies in Iran and Armenia
Objectives:
- To safely evacuate Indian citizens, particularly students, from volatile zones in Iran.
- To coordinate safe land-based exit routes through Armenia, due to restricted or dangerous air routes over Iran.
Key Features of the Operation:
Feature Details
Evacuation Route Northern Iran → Yerevan (Armenia) → New Delhi
Monitoring Real-time updates and continuous monitoring by Indian missions
Coordination Close coordination with governments of Iran and Armenia
Control Room 24/7 MEA Control Room operational in New Delhi
India’s Major Air Evacuation Missions (Chronological Overview):
Mission Name Year Objective
Vande Bharat Mission 2020 Evacuation of Indians stranded abroad during the COVID-19 pandemic
Operation Devi Shakti 2021 Evacuation from Afghanistan after the Taliban takeover
Operation Ganga 2022 Evacuation from Ukraine amid Russia-Ukraine war
Operation Kaveri 2023 Rescue of Indian nationals from conflict-hit Sudan
Operation Ajay 2023 Repatriation of Indians from Israel amid regional conflict
Operation Sindhu 2025 Ongoing evacuation from Iran amid Iran–Israel escalation
Significance for India
- Diaspora Safety: Reinforces India’s commitment to protecting its citizens abroad.
- Diplomatic Efficiency: Reflects India’s growing capabilities in executing rapid and complex evacuation logistics in volatile geopolitical environments.
- Soft Power and Foreign Policy: Enhances India’s global image as a responsible nation ensuring citizen welfare, even beyond borders.
Fattah Hypersonic Missile

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In light of intensifying hostilities between Iran and Israel, Iran has deployed its advanced Fattah hypersonic ballistic missile, marking a significant shift in regional military capabilities and raising concerns over existing air defence systems such as Israel’s Iron Dome.
About Fattah Hypersonic Missile
- Developed by: Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Iran
- Unveiled: November 2022 (on the 11th death anniversary of missile scientist Hassan Tehrani Moghaddam)
- Inducted: 2023
- Name Meaning: “Fattah” translates to “victor” or “conqueror”
Key Capabilities:
Feature Specification
Speed Mach 13–15 (approx. 15,000 km/h)
Range 1,400 km (planned upgrade to 2,000 km)
Mobility Capable of mid-air directional changes
Stealth Forms a plasma shield that blinds radar & blocks radio signals
Deployment Used in attacks against Israeli territory
- A more advanced version, Fattah-2, with a range of 1,500 km, is reportedly under development.
Strategic Significance
- The missile’s ability to evade modern air defence systems—such as Iron Dome and David’s Sling—makes it a potential game-changer.
- Iran claims Fattah is capable of operating within the upper atmosphere with unpredictable trajectory, making interception extremely difficult.
- This hypersonic manoeuvrability marks a leap over traditional ballistic missiles that follow a predictable parabolic trajectory.
Comparative Global Context
Iran claims to be the fourth country globally to possess operational hypersonic missiles, after:
- Russia
- China
- India
Other nations like the USA and North Korea are developing or testing hypersonic systems but have not fielded them in combat as Iran reportedly has.
Operational History
- October 2024: Fattah missiles were reportedly used by Iran in a prior attack on Israeli targets.
- 2025 Escalation: The missile was deployed during “Operation Honest Promise 3,” marking the 11th wave of retaliatory attacks by Iran on Israeli territory.
Iran’s Broader Ballistic Missile Arsenal
In addition to Fattah, Iran possesses a wide range of short-to-long range missiles, including:
- Fateh Series: Short-range solid-fuel missiles (Fateh-110, Fateh-313)
- Zolfaghar and Qasem: Extended versions of Fateh series
- Emad: Long-range liquid-fuel missile with 1,700 km range
- Sejjil: Solid-fuel missile with 2,500 km range, speeds up to 17,000 km/h
- Others: Kheibar, Ghadr-110, Fajr-3, Shahab-3, Ashoura, Haj Qasem, Basir
Implications for India and the Region
- Regional Arms Race: Iran’s hypersonic capability may trigger further military build-up in the Middle East.
- India’s Position: As one of the few nations with hypersonic R&D, India must monitor evolving doctrines and maintain strategic balance.
- Global Security: The usage of such missiles in conflict zones raises concerns over escalation, proliferation, and undermining of existing missile defence systems.
FASTag Annual Pass
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Union Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari announced the launch of a FASTag-based Annual Pass, offering a simplified and cost-effective tolling solution for private vehicle users on National Highways. The initiative is set to be rolled out from August 15, 2025, and aims to improve traffic flow, reduce toll disputes, and enhance ease of travel.
What is the FASTag Annual Pass?
- Cost: ?3,000
- Validity: 1 year from activation or 200 highway trips (whichever comes earlier)
- Eligibility: Only for non-commercial private vehicles (cars, jeeps, vans)
- Coverage: Valid across all National Highways in India
Key Objectives
- Hassle-free highway travel by eliminating repeated toll payments
- Reduce congestion and waiting time at toll plazas
- Simplify toll management with a one-time, prepaid model
- Address concerns regarding toll plazas located in close proximity (within 60 km)
How It Works
- Integrated with the existing FASTag system (uses RFID technology)
- Annual pass will be linked to the user's FASTag account
- Activation and renewal through:
- Rajmarg Yatra App
- NHAI website
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) website
Part of a Broader Reform in Tolling
The Annual Pass complements ongoing toll reforms:
- Introduction of ANPR-FASTag hybrid tolling system:
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) cameras
- RFID-based FASTag readers
- Enables barrier-less tolling, where vehicles are charged without stopping
- Non-compliance may result in:
- e-notices
- Penalties, including FASTag suspension or VAHAN database sanctions
Gharial Conservation

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
On World Crocodile Day (June 17, 2025), Etawah district in Uttar Pradesh marked the 50th anniversary of India’s pioneering Gharial Conservation Programme, commemorating five decades of sustained efforts to protect the endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) along the Chambal River.
About the Gharial Conservation Programme
- Launched in: 1975
- Initiated by: Forest Department of Uttar Pradesh and Society for Conservation of Nature (SCON)
- Supported by: UNDP, FAO, and Government of India
- Location: Primarily focused on Chambal River in Etawah district, Uttar Pradesh
- Breeding Facility: Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre, Lucknow
Why Gharial Conservation Matters
- Species: Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) — endemic, freshwater crocodilian
- Status: Critically Endangered (IUCN Red List)
- Habitat: Prefers deep, fast-flowing rivers with sandy banks and minimal human interference
- Threats: Habitat destruction, sand mining, illegal fishing, entanglement in nets, and declining fish stocks
Programme Objectives
- Protect wild gharial populations in natural river habitats.
- Enhance population through captive breeding and release.
- Study habitat biology and gharial behaviour to inform scientific conservation.
- Promote coexistence between gharials and local fishing communities.
- Create awareness and engage local populations in conservation.
Key Features of the Programme
- Egg Collection: Gharial eggs are safely collected from natural nests on riverbanks.
- Artificial Incubation: Maintained under controlled temperature and humidity to improve hatching success.
- Captive Rearing: Hatchlings are reared for 3–5 years at Kukrail Centre until they are strong enough for survival in the wild.
- Release Strategy: Tagged juveniles are released in protected stretches of the Chambal River.
- Community Involvement: Local fishermen and villagers are involved in conservation-linked livelihoods to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
Impact and Legacy (1975–2025)
- One of India’s earliest species-specific conservation programmes.
- Created a successful model of “rear-and-release” conservation.
- Helped stabilize the gharial population in Chambal, now one of the last strongholds for the species.
- Promoted community-based conservation and scientific habitat management.
Sakura Science High School Programme 2025

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
- In June 2025, 20 Indian school students were officially flagged off by Shri Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL), to participate in the prestigious Sakura Science High School Programme 2025 in Japan.
- The initiative reflects India's growing focus on international educational exposure, scientific collaboration, and experiential learning, in alignment with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
About the Sakura Science Programme
- Launched by: Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) in 2014.
- Objective: To promote science, technology, and innovation through Asia-wide youth exchanges.
- India’s Participation: Since 2016; over 619 students and 91 supervisors have participated till 2025.
- Participants (2025 batch):
- 20 students (7 boys, 13 girls) from Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas and government schools in Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Ladakh, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura.
- Accompanied by 2 supervisors.
- Programme duration: 15–21 June 2025.
- Participating countries (2025): India, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Ukraine.
Key Features of the Programme
- Hands-on Learning: Visits to advanced scientific labs, tech demonstration centres, and universities in Japan.
- Cultural Exposure: Insight into Japanese traditions, societal values, and innovation ecosystem.
- International Peer Exchange: Interaction with students from other Asian nations to foster global scientific thinking.
Relevance to NEP 2020
The NEP 2020 advocates experiential, holistic, and integrated learning. It highlights:
- The need for educational excursions to places of scientific, cultural, and technological relevance.
- Promoting international collaborations that broaden the intellectual horizons of learners.
- Encouraging innovation through interdisciplinary exposure and real-world learning.
The Sakura Programme complements NEP 2020’s goals by offering Indian students a unique platform to explore global advancements in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields.
Strategic Importance
- Science Diplomacy: Strengthens Indo-Japanese relations in education and technology.
- Youth Empowerment: Builds future-ready, globally aware scientific talent.
- Inclusivity: Focuses on students from remote and underserved regions, aligning with India’s equity-focused educational reforms.
Global Drought Outlook 2025
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has released the “Global Drought Outlook 2025”, presenting a stark warning about the increasing frequency, severity, and impact of droughts worldwide.
- The report, titled “Global Drought Outlook: Trends, Impacts and Policies to Adapt to a Drier World”, offers a comprehensive assessment of drought patterns, consequences, and adaptation strategies, making it crucial for policymakers and global environmental governance.
Understanding Drought:
Drought is defined as a hydrological imbalance, characterised by prolonged periods of “drier-than-normal” conditions that deplete soil moisture, surface water, and groundwater. The report identifies three main types:
- Meteorological Drought: Caused by significantly below-average rainfall over an extended period.
- Agricultural Drought: Occurs when soil moisture becomes insufficient for crops and vegetation.
- Hydrological Drought: Involves declining water levels in rivers, lakes, and aquifers, affecting supply for human and ecological needs.
Global Trends and Projections
- Drought-Affected Land: The share of global land experiencing drought has doubled since 1900, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use.
- Current Impact (2023): Nearly 48% of the world’s land experienced at least one month of extreme drought.
- Regional Hotspots: Western USA, South America, Europe, Africa, and Australia are increasingly vulnerable.
- Groundwater Stress: Around 62% of monitored aquifers show declining trends.
- Future Risk: At +4°C global warming, droughts could become 7 times more frequent and severe by 2100, posing systemic global threats to food, water, and economic security.
Multidimensional Impacts of Drought
Ecological:
- 37% of global soils have dried significantly since 1980.
- River and groundwater depletion are threatening biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Economic:
- Drought-related losses are increasing by 3–7.5% annually.
- Modern droughts are twice as costly as in 2000; costs may rise 35% by 2035.
- Agriculture is most affected: crop yields drop up to 22% in drought years.
- Drought causes a 40% drop in river-based trade and a 25% decline in hydropower output.
Social:
- Droughts account for 34% of disaster-related deaths, though only 6% of disasters are droughts.
- It is a major driver of food insecurity, internal displacement, and climate migration, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Political instability and conflict often correlate with drought-induced resource scarcity.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
The OECD emphasizes a multi-sectoral approach to manage drought risks:
- Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM):
- Balancing water use and renewal.
- Promoting efficient and equitable water allocation.
- Nature-based Solutions (NbS):
- Urban de-sealing to enhance groundwater recharge.
- Landscape restoration to improve water retention and ecosystem resilience.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- Adoption of drought-resistant crops and micro-irrigation systems.
- Can reduce water use by up to 76%.
- Urban Planning: Permeable infrastructure restores aquifers (e.g., US examples show 780 million m³/year recovery).
- Early Warning Systems: Enhanced drought monitoring, forecasting, and risk mapping.
- Policy Integration: Embedding climate resilience into national water and land-use policies.
- Cross-Sector Coordination: Engaging sectors like agriculture, energy, transport, construction, and health.
- Economic Benefits: Every $1 invested in drought resilience yields $2–$10 in benefits.
Performance Grading Index (PGI) 2.0
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Education released the Performance Grading Index (PGI) 2.0 for the years 2022–23 and 2023–24, offering a comprehensive assessment of school education across States and Union Territories (UTs). This index, aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 4), serves as a critical evidence-based framework for benchmarking educational performance in India.
About PGI 2.0
- Launched: 2017 (PGI 2.0 is the revised version)
- Published by: Ministry of Education, Government of India
- Purpose: Measures performance in school education using a data-driven approach
- Total Indicators: 73 across 6 domains
- Scoring: Out of 1000 points; graded into 10 performance bands:
- Daksh (951–1000) – Top
- Akanshi-3 (401–460) – Lowest
Domains Assessed
- Learning Outcomes and Quality
- Access to Education
- Infrastructure and Facilities
- Equity
- Governance Processes
- Teacher Education and Training
Key Highlights of PGI 2.0 (2022–24)
- Top Performer: Chandigarh with a score of 703, placed in the fifth band – Prachesta-1.
- Lowest Performer: Meghalaya, with 417 points, in the tenth and lowest band – Akanshi-3.
- No State/UT reached the top four bands (Daksh, Utkarsh, Ati Uttam, Uttam), indicating a national gap in quality education.
State-Wise Band Distribution
- Band 5 (Prachesta-1: 701–760): Chandigarh
- Band 7 (581–640): Punjab, Delhi, Gujarat, Odisha, Kerala, Haryana, Goa, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Dadra & Nagar Haveli & Daman & Diu
- Band 8 (521–580): 14 States/UTs
- Band 9 (461–520): 10 States/UTs
- Band 10 (Akanshi-3: 401–460): Meghalaya (only State in this band)
Performance by Domains
- Learning Outcomes: No State achieved the top four bands. Chandigarh, Punjab, and Puducherry performed relatively better (Prachesta-2).
- Access to Education: Odisha alone achieved the highest band (Daksh), while Bihar and Jharkhand showed notable progress.
- Infrastructure: Only Chandigarh featured in the third band (Ati Uttam), with Delhi and Dadra & Nagar Haveli in the next.
- Equity: All States placed in the top three bands, indicating relatively balanced access among social groups.
- Governance & Monitoring: Chandigarh excelled through digital governance and transparent fund utilization.
Significance for Policy and NEP 2020
- PGI 2.0 is pivotal in monitoring NEP 2020 implementation, especially for early-grade learning, infrastructure enhancement, equity, and governance.
- It identifies strengths and challenges, enabling targeted policy interventions.
- Despite infrastructure and access gains, quality of learning remains the most critical challenge.
PM-JANMAN and Dharti Aaba Initiatives

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has launched a nationwide outreach campaign targeting over 500 districts and 1 lakh tribal-dominated villages and habitations.
- The campaign aims to ensure benefit saturation and last-mile delivery of welfare schemes under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) and the Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan.
- This initiative is part of the ongoing Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh (Tribal Pride Year), a year-long celebration started on November 15, 2024 — the birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, a revered anti-colonial tribal icon.
Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN)
- Launched: 2023 on Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas
- Focus: Holistic development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
- Type: Includes both Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes
- Objectives:
- Safe housing (via PMAY)
- Clean drinking water
- Health, nutrition, and education access
- Road and telecom connectivity
- Electrification of unelectrified households
- Sustainable livelihood opportunities
- Time Frame: 3-year targeted implementation
- Vision: Supports Viksit Gaon, Viksit Bharat, and inclusive development with social justice
Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan
- Launched: October 2, 2024, by PM Modi in Jharkhand
- Named After: Birsa Munda, also known as Dharti Aaba (Father of the Earth)
- Aim: Transform tribal villages into centres of opportunity and dignity
- Approach:
- Multi-sectoral convergence with 17 line ministries
- 25 targeted interventions for integrated rural development
- Welfare activities include: hostel construction, rural electrification, livestock and fisheries support, housing under PMAY, etc.
- Budget Allocation (Union Budget 2025–26):
- Total: ?79,156 crore over 5 years
- Central Share: ?56,333 crore
- State Share: ?22,823 crore
Outreach Campaign (June 2025) Highlights
- Duration: Fortnight-long outreach starting June 15, 2025
- Coverage: 1 lakh tribal villages and habitations across 500+ districts
- Services at Doorstep:
- Aadhaar and Ayushman Bharat card enrollment
- Forest Rights Act (FRA) land title distribution
- Opening of pension and Jan Dhan accounts
- Goal: Awareness generation and saturation of benefits at block and hamlet levels
- Strategy: On-ground ‘benefit saturation camps’ to popularize uptake of the schemes
Significance
- Focus on PVTGs, who are the most marginalized among tribal communities
- Promotes digital inclusion, financial inclusion, and documentation access
- Demonstrates convergent governance through coordination across ministries
- Reinforces India’s tribal empowerment narrative and acknowledges historical contributions through Birsa Munda's legacy
‘Samarth’ Incubation Program

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), an autonomous R&D institution under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India, has launched ‘Samarth’, a cutting-edge incubation program for startups in the Telecom and ICT sectors. In June 2025, C-DOT formally initiated Cohort-I of the program, selecting 18 startups through a competitive national process.
About the Samarth Program
- Objective: To nurture sustainable and scalable startups from ideation to commercialization in high-tech domains.
- Focus Areas:
- Telecom applications
- Cybersecurity
- 5G/6G technologies
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Quantum technologies
Key Features
Feature Details
Financial Support Grant of up to ?5 lakh per startup
Infrastructure Fully furnished office space at C-DOT campuses in Delhi and Bengaluru for 6 months
Technical Access Use of C-DOT’s lab facilities
Mentorship Guidance from C-DOT technologists and external domain experts
Format Hybrid (online + physical) delivery
Program Structure Two cohorts per year, each supporting up to 18 startups (max 36 annually)
Further Opportunities Eligible for extended collaboration and funding under C-DOT Collaborative Research Program (CCRP)
Implementation and Partnerships
- Implementation Partners:
- Software Technology Parks of India (STPI)
- TiE (The Indus Entrepreneurs) – Delhi NCR Chapter
- Evaluation Criteria: Startups were selected based on innovation, team strength, execution capability, problem-solution relevance, and commercialization potential.
- A distinguished Selection Committee from academia, industry, and government oversaw the evaluation.
Significance
- Boosts indigenous R&D in critical emerging tech sectors aligned with national priorities.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat by encouraging homegrown innovation.
- Builds a robust startup ecosystem in the strategic telecom and ICT domains.
- Encourages public-private partnerships and collaboration between startups and research institutions.
Grand Cross of the Order of Makarios III
- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
During his official visit to Cyprus, Prime Minister Narendra Modi was conferred the Grand Cross of the Order of Makarios III, the highest civilian honour of Cyprus. This visit marked the first-ever visit by an Indian Prime Minister to the Mediterranean island nation.
About the Order of Makarios III
- Institution: Established in 1991.
- Named After: Archbishop Makarios III, the first President of the Republic of Cyprus.
- Nature: Cyprus’s highest merit-based honour, awarded to heads of state and individuals of significant global stature.
- Awarded By: The President of Cyprus.
- Grades:
- Grand Collar (highest)
- Grand Cross
- Grand Commander
- Commander
- Officer
- Knight
PM Modi received the Grand Cross, making him one of the few global leaders to be honoured at this level. The Prime Minister dedicated the award to the friendship between India and Cyprus, highlighting shared values and diplomatic ties.
Diplomatic and Economic Significance
- A roundtable interaction with top CEOs from both nations was held, focusing on deepening commercial and strategic engagement.
- Key sectors discussed:
- Innovation
- Energy
- Technology
- Trade and Investment
- PM Modi highlighted India's reform trajectory over the last decade, reinforcing India’s position as a growing economic partner.
Cyprus acknowledged this partnership, stating it was entering a "new era of strategic cooperation" with India, rooted in trust, shared values, and innovation.
Geographical Snapshot: Cyprus
- Region: Eastern Mediterranean
- Status: Eurasian island nation
- Capital: Nicosia
- Major Cities: Limassol, Larnaca, Famagusta, Paphos
- Highest Point: Mount Olympus (1,952 m)
- Size: Third-largest Mediterranean island after Sicily and Sardinia
Rinderpest

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
- India has been officially designated as a Category A Rinderpest Holding Facility (RHF) by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- The recognition was conferred to the ICAR-National Institute of High Security Animal Diseases (NIHSAD) in Bhopal during the 92nd General Session of WOAH held in Paris.
- This makes India one of only six countries globally entrusted with this vital responsibility, marking a major milestone in India’s global leadership in animal health and biosecurity.
What is Rinderpest?
- Also Known As: Cattle Plague
- Pathogen: Caused by a virus from the Paramyxoviridae family, genus Morbillivirus.
- Affected Species: Mainly cattle and buffalo, but also zebus, giraffes, eland, wildebeest, warthogs, and some antelope species.
- Symptoms in Cattle:
- High fever, nasal and eye discharge
- Erosive mouth lesions
- Severe diarrhoea and dehydration
- Death typically within 10–15 days in susceptible herds
- Transmission: Through direct contact; virus present in nasal secretions even before clinical symptoms appear.
- Public Health Risk: None – the virus does not affect humans.
- Geographical Spread: Historically affected Europe, Africa, and Asia.
- Eradication: Officially declared eradicated in 2011, making it the second disease in history to be eradicated after smallpox.
Significance of the Category A RHF Designation
- Background:
- Despite eradication, Rinderpest Virus-Containing Material (RVCM) remains in select laboratories.
- FAO and WOAH limit storage of RVCM to ensure global biosecurity and prevent accidental or intentional release.
- India’s Preparedness:
- In 2012, ICAR-NIHSAD was designated as India’s national repository for RVCM.
- It is a Biosafety Level-3 (BSL-3) facility and a WOAH reference laboratory for avian influenza.
- Recent Developments:
- India submitted its RHF application in 2019.
- In March 2025, FAO-WOAH appointed international experts to inspect the facility.
- Based on strong biosafety, inventory control, and emergency preparedness, ICAR-NIHSAD has now received Category A RHF status for one year.
Implications for India
- Global Recognition: Reinforces India’s commitment to the One Health framework and global biosecurity norms.
- Leadership Role: Positions India among a select global group of only six RHFs, enabling it to contribute to future efforts in disease surveillance, vaccine research, and emergency preparedness.
- Future Prospects:
- Encouraged by WOAH-FAO to contribute to vaccine seed material discussions.
- Paves the way for Category B designation, which allows broader collaborative work on RVCM.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, NASA said the NASA-ISRO SAR mission had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota
What is Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)?
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an advanced remote sensing technology used to generate high-resolution images of Earth's surface, irrespective of weather or lighting conditions.
- Unlike optical sensors that rely on visible light, SAR systems emit microwave pulses and measure the reflected signals (echoes) from the ground, ocean, ice, or structures.
- These echoes are then processed to create detailed images using advanced signal processing techniques.
How SAR Works
- Antenna System: Traditionally, larger antennas yield better resolution, but they are impractical for satellites. SAR overcomes this by using a small antenna mounted on a moving platform (like a satellite), capturing echoes from different positions.
- Through precise timing and phase information, the system simulates a much larger "synthetic" antenna, enhancing image resolution without the need for large hardware.
Advantages of SAR
- All-Weather, All-Time Imaging: SAR can operate day and night and penetrate clouds, smoke, and light rain, ensuring uninterrupted data collection.
- Material Differentiation: Various materials (soil, water, vegetation, buildings) reflect microwaves differently, enabling SAR to detect subtle changes not visible through optical imagery.
- Large Area Mapping: Mounted on satellites, SAR can map swaths of land hundreds of kilometres wide in a single pass.
NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) Mission
- Joint Collaboration: A flagship Earth-observing mission between NASA and ISRO.
- On June 12, 2025, NASA confirmed that the NISAR satellite had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota for its scheduled launch.
Mission Objectives
- NISAR will map nearly all of Earth's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.
- It aims to provide unprecedented data on Earth’s environment, including:
- Ecosystem disturbances
- Land use changes
- Ice sheet dynamics
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, landslides, floods)
Significance
- Will support climate change monitoring, disaster response, and agricultural planning.
- It represents a major step in India’s and the U.S.'s scientific diplomacy and technological cooperation.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The first General Assembly of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was held in New Delhi, marking a significant moment in global biodiversity governance. Chaired by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav, who was unanimously elected President of the IBCA, the event underscored India’s leadership in international wildlife conservation diplomacy.
What is IBCA?
- The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) is a multinational initiative launched by India in March 2024 to conserve the world’s seven major big cat species—Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma—through collective action, knowledge exchange, and capacity building.
- It is coordinated by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The Alliance was conceptualized following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger in April 2023.
Objectives of IBCA
- Promote global collaboration for the protection and conservation of big cats.
- Replicate successful conservation practices across member nations.
- Create a common pool of financial, technical, and institutional resources.
- Address gaps in capacity building, financing, and data sharing.
- Link conservation efforts with livelihood enhancement and climate resilience in big cat habitats.
- Strengthen efforts against poaching and illegal wildlife trade through joint surveillance and data exchange.
Membership
- 95 Range Countries (where the species naturally occur) are eligible to join.
- By September 2024, 25 countries including Bangladesh, Nigeria, Peru, and Ecuador had joined.
- Membership is open to all UN member states through a Note Verbale.
- The IBCA attained legal status after five countries—Nicaragua, Eswatini, India, Somalia, and Liberia—signed the Framework Agreement.
Key Functions of IBCA
- Shared Repository: Compilation of proven conservation strategies for scalable, science-based solutions.
- Training and Capacity Building: Organizes technical workshops and institutional exchanges.
- Scientific and Policy Support: Funds research, drives policy reforms, and raises awareness.
- Technological Innovation: Introduces advanced tools to tackle habitat degradation and prey base decline.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Integrates conservation with community-based development models.
- Anti-Poaching Collaboration: Facilitates real-time data sharing and joint actions against wildlife trafficking.
Highlights from the 2025 General Assembly
- Venue: New Delhi, India
- Participating Nations: Ministerial delegations from nine countries including Bhutan, Cambodia, Kazakhstan, Liberia, Suriname, Somalia, Republic of Guinea, Eswatini, and India.
- Institutional Milestones:
- India ratified as the permanent headquarters of IBCA.
- The Headquarters Agreement was formally ratified, enabling the establishment of IBCA offices in India.
- Leadership: Bhupender Yadav, India’s Environment Minister, was elected as the first President of IBCA.
- Funding Commitment: India pledged ?150 crore (2023–28) to support IBCA’s establishment, coordination, and conservation activities.
Significance for India and the Global South
- Reinforces India’s role as a conservation leader and soft power in environmental diplomacy.
- Positions India as the epicentre for global big cat conservation, akin to its leadership in tiger conservation under Project Tiger.
- Encourages South-South cooperation in biodiversity preservation.
- Aligns with global commitments like CBD, CITES, and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025 began in Bonn, Germany, with over 5,000 delegates from governments, international organisations, civil society, and scientific bodies. It serves as a crucial platform for setting the technical and political groundwork ahead of COP29.
What is the Bonn Climate Conference?
- A mid-year climate summit held annually under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Also referred to as the Sessions of the UNFCCC Subsidiary Bodies (SBs).
- First held in 1995, after the UNFCCC was signed in 1992.
- Hosted in: Bonn, Germany (home of the UNFCCC headquarters).
- Organised by: The UNFCCC Secretariat.
Main Objectives
- Prepare for COP Summits: Provides a platform for technical discussions that shape the COP agenda (COP29 in this case).
- Review of Commitments: Tracks implementation of earlier climate agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Science–Policy Integration: Connects IPCC research with policymaking processes.
- Support for Developing Nations: Discusses climate finance and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Inclusive Participation: Engages Indigenous communities, NGOs, experts, and private stakeholders.
Subsidiary Bodies of the UNFCCC
- SBI (Subsidiary Body for Implementation):
- Reviews how climate commitments are implemented.
- Facilitates support for developing countries.
- SBSTA (Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice):
- Provides scientific guidance.
- Bridges IPCC reports with UNFCCC decision-making.
Key Focus in 2025
Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA)
- Originally mentioned in the Paris Agreement (2015).
- Received major progress only during COP28 (Dubai).
- Aim: Establish a global, measurable, and equitable adaptation framework, similar to the 1.5°C target for mitigation.
- Bonn 2025 focuses on operationalising this goal, especially for climate-vulnerable nations.
Importance of the Bonn Conference
- Pre-COP Platform: Decisions taken here set the tone and agenda for COP summits.
- Technical + Political Dialogue: Encourages cooperation between scientists, policymakers, and climate negotiators.
- Influences Global Climate Action: Outcomes impact the direction of global climate governance.
SIPRI Yearbook 2025
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) has released its 2025 Yearbook, detailing global nuclear trends, armament expansions, and security concerns. The report highlights growing nuclear arsenals and modernisation efforts by all nine nuclear-armed states, including India, which increased its nuclear warhead stockpile in 2024.
India’s Nuclear Arsenal: Key Facts
- Warhead Count (Jan 2025): 180 (up from 172 in Jan 2024)
- India is expanding its nuclear delivery systems, including canisterised missiles that may carry mated or multiple warheads.
- India continues to invest in new-generation weapons and submarine-launched ballistic missiles.
Pakistan and China: Regional Dynamics
- Pakistan: Maintains ~170 warheads; developing new delivery systems and accumulating fissile material.
- China:
- Warheads (2025): 600 (24 deployed).
- Adding ~100 warheads annually since 2023.
- Constructing ~350 new ICBM silos.
- Expected to reach 1,000 warheads by 2032–33, possibly 1,500 by 2035.
Global Nuclear Overview (2025)
- Total nuclear warheads: 12,241
- Military stockpiles (available for use): 9,614
- Deployed warheads (with missiles/aircraft): 3,912
- High-alert warheads (on ballistic missiles): ~2,100 (mostly U.S. & Russia)
Country-wise Inventory Snapshot (2025):
- USA: 5,177 (1,770 deployed, 1,930 stored)
- Russia: 5,459 (1,718 deployed, 2,591 stored)
- China: 600
- India: 180
- Pakistan: 170
- Others: UK, France, Israel, North Korea
Emerging Concerns
- Arms Control Breakdown:
- No major nuclear power is showing full commitment to disarmament.
- New START Treaty (USA-Russia) expires in Feb 2026; no successor yet in sight.
- Potential for increase in deployed strategic warheads post-2026.
- Rising Crisis Risks:
- 2025 saw India-Pakistan tensions escalate to limited armed conflict.
- Strikes on nuclear-related military sites and disinformation increased nuclear risk.
- New Technologies & Doctrines:
- Countries are integrating MIRVs, canisterisation, and AI-based command systems.
- China may now keep warheads mounted during peacetime, like U.S. and Russia.
Military Spending and Arms Trade (2024)
- Global defence spending: $2.7 trillion (↑ 9.4%)
- Top military spenders:
- USA: $997 billion
- China: $314 billion
- Top arms importers: Ukraine, India, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Pakistan
- Top arms exporters:
- USA: 43%
- France: 9.6%
- Russia: 7.8%
About SIPRI
- Founded: 1966, Stockholm, Sweden
- Focus: Independent research on conflict, arms control, nuclear disarmament, and security.
- Funded by: Swedish Parliament (core grant), plus support from global research bodies.
Cyprus & India-EU FTA
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi began his five-day, three-nation tour with a historic visit to Cyprus—the first by an Indian PM in over 20 years. His visit focused on strengthening economic ties and pushing forward the India–European Union Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
Key Highlights of the Visit
- India-EU FTA Commitment: PM Modi announced that India and the EU are committed to concluding a Free Trade Agreement by the end of 2025. Negotiations have gained momentum.
- India–Cyprus Economic Engagement:
- Addressed the India-Cyprus CEO Forum in Limassol, pitching India as a hub for digital innovation and infrastructure.
- Highlighted India’s digital growth: Over 50% of global digital transactions via UPI originate from India. Talks are ongoing to onboard Cyprus into UPI.
- Announced a new shipbuilding policy and noted an annual investment of USD 100 billion in infrastructure.
- Supported the launch of the India–Cyprus–Greece Business and Investment Council, promoting trilateral cooperation.
- Welcomed the NSE–Cyprus Stock Exchange partnership in GIFT City, Gujarat.
- Startup and Innovation Focus: Emphasised India's vibrant startup ecosystem with over 1 lakh startups offering innovative, scalable solutions.
About Cyprus – Key Facts for Prelims
- Location: Eurasian island in the northeastern Mediterranean Sea, south of Turkey and southeast of Greece.
- Capital: Nicosia
- Area: 9,251 sq. km (3rd largest island in the Mediterranean after Sicily and Sardinia)
- Climate: Mediterranean – dry summers and wet winters
- Highest Point: Mount Olympus (1,952 m)
Geopolitical Context
- Divided Island:
- Since 1974, Cyprus has been partitioned between a Turkish-controlled north and a Greek-Cypriot-controlled south.
- Only Turkey recognises Northern Cyprus as an independent state.
- A UN-patrolled Green Line separates the two regions.
- Political System: Presidential republic – the President is both head of state and government.
- Official Languages: Greek and Turkish
- EU Membership: Joined the European Union on May 1, 2004
- Major Cities: Limassol, Larnaca, Famagusta, Paphos
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)

- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
Lucknow has officially submitted its nomination to be recognised as a “City of Gastronomy” under the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), aiming to join Hyderabad as the only other Indian city to hold this title in the gastronomy category.
About the UCCN
- Established: 2004
- Purpose: To promote international cooperation among cities that use creativity as a key element for sustainable urban development.
- Focus Areas: Literature, Music, Crafts & Folk Arts, Design, Film, Media Arts, and Gastronomy.
- Key Goals:
- Leverage the creative economy for sustainable development.
- Encourage cultural diversity and resilience against urban challenges like climate change and inequality.
- Promote collaboration across public, private, and civil society sectors.
UCCN and Sustainable Development
- UCCN supports the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by positioning culture and creativity at the heart of local development policies and planning.
- Member cities are expected to create innovation hubs, support local artists, and preserve cultural heritage.
India and the UCCN
As of 2023, 10 Indian cities are part of the network:
- Hyderabad – Gastronomy
- Jaipur – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Varanasi – Music
- Chennai – Music
- Mumbai – Film
- Srinagar – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Kozhikode – Literature
- Gwalior – Music (Recent entries include Kozhikode and Gwalior)
Lucknow’s Nomination: Highlights
- Nominated Title: City of Gastronomy
- Coordinated by: Department of Tourism and Culture, Lucknow
- Culinary Heritage: Awadhi cuisine, including dishes like nihari, kebabs, biryani, khasta, kulfi, jalebi, and puri-sabzi.
- Cultural Value: The city’s food is not just a tradition but a living culinary ecosystem, passed down through generations and practiced by diverse communities.
- Dossier Preparation: By renowned heritage conservationist Abha Narain Lambah.
- Verification: A field visit by UNESCO is expected as part of the evaluation process.
Global Cities of Gastronomy (Examples)
- Alba (Italy)
- Arequipa (Peru)
- Bergen (Norway)
- Belem (Brazil)
- Bendigo (Australia)
These cities, like Hyderabad, are recognised for their distinctive and sustainable culinary traditions.
Cyber Suraksha Exercise
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
A comprehensive national-level cyber security exercise, Cyber Suraksha, was launched by the Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS).
About Cyber Suraksha
- Type: Multi-phased cybersecurity drill.
- Organised by: Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the aegis of HQ IDS.
- Duration: From 17–27 June 2025.
- Participants: Over 100 experts from national agencies and defence domains.
- Environment: High-paced, gamified simulation of real-world cyber threats.
Objectives
- Enhance national cyber resilience.
- Train personnel in handling advanced cyberattacks.
- Promote a security-first culture across defence institutions.
- Integrate technical proficiency with strategic leadership.
Key Features
- Training capsules: Technical + leadership components.
- CISOs Conclave: Sessions by cybersecurity leaders, culminating in a table-top simulation.
- Hands-on exercises: Real-time attack simulations to test response capabilities.
- Focus on joint operations and decision-making under crisis.
About Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA)
Background
- Established: Announced in 2018, operational from November 2019.
- Origin: Recommended by Naresh Chandra Committee (2012).
- Part of India’s tri-service defence transformation, alongside proposed Aerospace and Special Operations Commands.
Role & Mandate
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- Reports to: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) through Integrated Defence Staff (IDS).
- Location: Based in New Delhi.
Functions
- Conducts cyber defence operations for the armed forces.
- Coordinates incident response, cyber intelligence, and audits.
- Develops capabilities in cyber warfare, AI-driven cyber tools, and joint operations.
- Supports capacity building, certification, and training within the military.
Radio Nellikka

- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan inaugurated Radio Nellikka, an internet radio for children launched by the Kerala State Commission for Protection of Child Rights (KeSCPCR) on June 2025.
What is Radio Nellikka?
- A child-centric internet radio platform launched by KeSCPCR.
- Aims to promote child rights, awareness, and safety through audio content.
- Accessible globally, with 4 hours of programming from Monday to Friday (new content), and repeats on weekends.
- Launch included unveiling of the radio's logo and theme song.
Objectives
- Create a child-friendly Kerala through rights-based literacy.
- Spread awareness on child protection laws, mental health, substance abuse, and cyber safety.
- Empower children with knowledge and build resilience against social challenges.
- Promote responsible parenting and community involvement in child welfare.
Significance
- Addresses rising challenges: social media addiction, cyber threats, child suicides, and mental health issues.
- Provides accessible, engaging content to both children and guardians.
- Acts as a preventive and educational tool against misinformation related to child rights.
- Supports emotional and legal literacy in a format suited for young audiences.
AI and Biomanufacturing in India

- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into India's biomanufacturing sector is gaining momentum with the launch of the BioE3 Policy and the IndiaAI Mission.
What is Biomanufacturing?
- Biomanufacturing involves the use of living cells, enzymes, or biological systems to produce commercial goods such as vaccines, biologics, biofuels, specialty chemicals, biodegradable plastics, and advanced materials.
- The convergence of synthetic biology, industrial biotechnology, and artificial intelligence (AI) has expanded its scope across sectors like healthcare, agriculture, energy, and materials science.
- India, often called the “Pharmacy of the World”, produces over 60% of global vaccines, underlining its industrial strength in biomanufacturing.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Biomanufacturing
AI is revolutionizing biomanufacturing by making it predictive, efficient, and scalable:
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning tools adjust variables like temperature, pH, and nutrient supply in real time to enhance fermentation and reduce batch failure.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of biomanufacturing plants allow engineers to simulate operations, test changes, and foresee potential disruptions without real-world risks.
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AI expedites molecular modeling and screening of drug candidates, reducing time and cost of development.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI forecasts machinery failures, improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
- Smart Supply Chains: AI-driven logistics optimize cold-chain storage and forecast medicine demand, ensuring timely distribution.
Indian Examples and Industrial Applications
- Biocon uses AI to enhance drug screening and fermentation quality.
- Strand Life Sciences applies machine learning in genomics for faster diagnostics.
- Wipro and TCS are developing AI platforms for clinical trials, molecule screening, and treatment prediction.
- AI is also being explored in rural healthcare, using region-specific data for localized diagnostics and advisories.
Key Government Initiatives
- BioE3 Policy (2024):
- Envisions Bio-AI hubs, biofoundries, and next-gen biomanufacturing infrastructure.
- Supports startups with funding and incentives.
- IndiaAI Mission:
- Promotes ethical, explainable AI in sectors like health and biotech.
- Supports bias reduction, machine unlearning, and transparency in AI models.
- Biomanufacturing Mission (2023): Aims to promote R&D and domestic production in bio-based sectors.
- PLI Scheme for Biotech: Incentivizes local production of enzymes, fermentation inputs, and biologics.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023): Lays down principles for lawful data processing, though not tailored for AI-biotech intersection yet.
Challenges in Policy and Regulation
Regulatory Gaps:
- India’s existing drug and biotech laws were designed before the AI era.
- No clear mechanism exists to audit, certify, or govern AI-operated bioreactors or predictive drug systems.
Data and Model Risks:
- AI systems trained on urban datasets may fail in rural or semi-urban manufacturing due to variable water quality, temperature, or power conditions.
- Lack of norms on dataset diversity and model validation raises risk of system failure and reputational damage.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Traditional IP laws do not clarify ownership of AI-generated inventions, molecules, or production protocols.
Workforce and Infrastructure:
- Biomanufacturing needs a workforce skilled in both computational biology and automation.
- India’s AI-bio talent gap and limited high-tech infrastructure outside metro cities hinders inclusive growth.
Ethical & Safety Concerns:
- Without context-specific oversight, AI errors can threaten public safety and product integrity.
- Trust in AI systems requires clear guidelines on explainability, accountability, and redress mechanisms.
Global Best Practices
- EU’s AI Act (2024): Classifies AI applications based on risk levels. High-risk applications (e.g., genetic editing) are subject to strict audits.
- US FDA Guidance (2025):
- Introduces seven-step credibility frameworks for AI in healthcare.
- Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) allow iterative AI updates while ensuring safety.
India lacks similar risk-based, adaptive oversight.
Policy Recommendations
- Establish AI-Biomanufacturing Regulatory Framework:
- Introduce tiered regulation based on context and risk.
- Define use-cases, audit mechanisms, and model validation standards.
- Mandate Dataset Diversity & Safety Audits:
- Ensure AI tools are trained on representative, unbiased, clean data.
- Create regulatory sandboxes to test AI systems in controlled environments.
- Strengthen Public–Private Partnerships:
- Boost industry-academia collaborations.
- Incentivize private investment through R&D credits and de-risking instruments.
- Modernize IP and Licensing Laws:
- Establish clarity on ownership of AI-generated discoveries.
- Develop licensing frameworks for bio-AI algorithms and training data.
- Upskill the Workforce: Promote interdisciplinary training across life sciences, data science, and industrial robotics.
AviList
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the global ornithological and conservation community witnessed a landmark development with the launch of AviList, the first-ever unified global checklist of bird species. This effort is the culmination of four years of work by the Working Group on Avian Checklists, representing leading ornithological and conservation institutions.
About AviList:
- What is it? AviList is a comprehensive, standardized, and freely accessible global bird species checklist.
- Total Entries (2025 Edition):
- Species: 11,131
- Subspecies: 19,879
- Genera: 2,376
- Families: 252
- Orders: 46
- Replacing Previous Lists:
- International Ornithological Committee (IOC) List
- Clements Checklist
- Update Mechanism: To be updated annually
- Access and Formats:
- Available freely at www.avilist.org
- Downloadable in full or short versions in .xlsx and .csv formats.
Developed By:
Working Group on Avian Checklists, comprising representatives from:
- BirdLife International
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- American Ornithologists' Society
- International Ornithologists’ Union
- Avibase (Global Bird Database)
Significance and Benefits:
- Conservation and Research Clarity:
- A unified taxonomy helps prioritize conservation efforts by eliminating taxonomic inconsistencies.
- Scientists can now communicate uniformly on species classification and distribution.
- Global Standardization: Replaces multiple competing checklists, reducing confusion and ensuring consistency across countries and platforms.
- Interdisciplinary Use: Supports birdwatchers, scientists, policymakers, and conservationists in sharing data, linking platforms, and enhancing global collaborations.
- Improved Policy and Decision-Making: Aids in aligning biodiversity policies across nations by ensuring a standardized species concept.
- Technological Integration: Enables harmonization of databases and online tools like eBird, Avibase, and global biodiversity monitoring platforms.
DNA Identification in Mass Fatality Events
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Following the tragic crash of an Air India Boeing 787 Dreamliner from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick (June 2025), authorities have initiated DNA-based identification to match the remains of victims. In mass fatality incidents where bodies are mutilated or decomposed, DNA analysis becomes the gold standard for establishing identity.
What is DNA Identification?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a unique genetic code present in almost every cell of the human body, with the exception of identical twins. It is widely used in forensic science for accurate identification, particularly in disasters where visual identification is impossible.
Sample Collection and Preservation:
- DNA begins degrading post-mortem, and the rate of degradation is influenced by:
- Type of tissue (soft vs hard)
- Environmental conditions (humidity, temperature)
- Hard tissues such as bones and teeth are preferred due to better preservation against decomposition.
- Soft tissues (like skin and muscle) degrade faster and, if used, must be stored in 95% ethanol or frozen at -20°C.
- In large-scale accidents, sample collection from wreckage can take weeks or even months (e.g., 9/11 took 10 months).
Reference Samples:
To match unidentified remains, reference DNA is taken from biological relatives—preferably parents or children of the victims, who share about 50% of their DNA.
Methods of DNA Analysis:
1. Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis:
- Evaluates short, repeating DNA sequences that vary among individuals.
- Requires nuclear DNA, hence not suitable if the DNA is highly degraded.
- Analysis of 15+ hyper-variable STR regions can confirm family relationships with high accuracy.
2. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Analysis:
- Used when nuclear DNA is not recoverable.
- mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother and is present in multiple copies per cell.
- Effective for matching with maternal relatives (e.g., mother, maternal uncles/aunts, siblings).
3. Y-Chromosome Analysis:
- Targets male-specific genetic material.
- Useful for identifying remains using DNA from paternal male relatives (father, brothers, paternal uncles).
- Helpful when direct relatives are unavailable but male-line relatives exist.
4. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Analysis:
- Suitable when DNA is highly degraded.
- Analyzes variations at single base-pair locations in DNA.
- Can also match DNA with personal items like a toothbrush or hairbrush.
- However, less accurate than STR analysis.
Significance for Disaster Management and Forensics:
- DNA-based victim identification ensures scientific accuracy, aiding in closure for families, and upholding legal and humanitarian obligations.
- Modern forensic genetics has become an essential tool in mass disaster response protocols worldwide.
Gyan Post

- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
The Department of Posts, under the Ministry of Communications, launched a new service called ‘Gyan Post’ to facilitate affordable delivery of educational and cultural books across India.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- To bridge the educational divide by improving access to printed educational materials, especially in rural and remote regions.
- Aligned with the goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) to promote inclusive education.
Salient Features:
- Service Availability: All Departmental Post Offices across India.
- Type of Material:
- Only non-commercial printed educational, cultural, social, and religious books.
- Books must not contain advertisements or promotional content.
- Must bear the name of the printer or publisher.
- Delivery Mode: Surface mail (traceable) – enhances transparency and reliability.
- Tariff Structure:
- ?20 for packets up to 300 grams
- ?100 for packets up to 5 kilograms (excluding applicable taxes)
- Tracking: Available to ensure accountability and customer confidence.
Significance:
- Promotes educational equity by supporting learners in under-served areas.
- Complements Digital India and NEP 2020 by reinforcing multi-modal education access (print + digital).
- Encourages the circulation of knowledge, especially in regions with poor digital penetration.
Servants of India Society
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
Tensions have resurfaced between Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics (GIPE) and the Servants of India Society (SIS) over control of a joint bank account and allegations of financial misconduct. This has brought attention back to the legacy and functioning of the historic SIS.
About Servants of India Society (SIS)
- Founded: June 12, 1905
- Founder: Gopal Krishna Gokhale, with G.K. Devadhar, A.V. Patwardhan, and N.A. Dravid
- Location: Fergusson Hill, Pune, Maharashtra
- Headquarters: Pune, with branches in Chennai, Mumbai, Nagpur, Allahabad, etc.
Objectives:
- To train a dedicated cadre of national workers for selfless service to the nation.
- Promote political education, social reform, and public service.
- Work towards upliftment of underprivileged communities, including rural and tribal populations.
- Achieve social change through constitutional and moderate means, not violent agitation.
Membership and Structure:
- Members undergo a five-year training period and vow to serve on modest salaries.
- Considered “young missionaries of Indian nationalism.”
- Notable Members:
- V.S. Srinivasa Sastri (later president after Gokhale’s death in 1915)
- Hriday Nath Kunzru
- A.V. Thakkar
Ideological Basis:
- Strong emphasis on constitutionalism, moderation, and liberalism.
- Aimed to create a disciplined, morally upright civil society to complement political struggle.
About Gopal Krishna Gokhale:
- Born: May 9, 1866 | Died: February 19, 1915
- Moderate leader of the Indian National Congress and a liberal reformer.
- Influenced by Justice M.G. Ranade and Western political thought.
- Advocated for gradual self-governance and saw value in British-initiated modernization.
- Played a pivotal role in the Morley-Minto Reforms (1909).
- Mentor to Mahatma Gandhi and known for his economic insight and powerful oratory.
Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc)
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant medical advancement, a team at the Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. has successfully administered Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc) to treat adenoid cystic carcinoma—a cancer originating in the parotid gland. This marked the first-ever clinical application of this technology. The findings were published in the International Journal of Particle Therapy in June 2025.
What is SPArc Therapy?
SPArc (Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy) is an advanced form of proton beam therapy where proton particles are delivered in a controlled arc across the tumor. It includes two primary modalities:
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc: Follows a pre-programmed dose delivery path.
- Dynamic SPArc: Simulated version where energy levels and targeting points are adjusted in real-time. (Still under regulatory review)
Comparison with Existing Techniques
The study compared three techniques:
- SFO-IMPT (Single-Field Optimized Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy – current standard)
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc (clinical)
- Dynamic SPArc (simulated)
SPArc showed reduced radiation exposure to key organs when compared with SFO-IMPT:
- Brainstem: ↓ 10%
- Optical chiasm: ↓ 56%
- Oral cavity: ↓ 72%
- Spinal canal: ↓ 90%
Treatment Case Study
The first patient treated was a 46-year-old woman with a tumor extending from her parotid gland to the base of her skull. She underwent 33 sessions of SPArc therapy from June to August 2024, reporting only minor skin irritation and no disruptions to eating or daily functioning.
Process & Technology Used:
- Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) was used for real-time imaging before each session.
- A machine learning model converted CBCT to synthetic CT, allowing accurate dose tracking.
- As the patient lost weight, the dose plan was adjusted after two weeks to maintain precision.
- Nine beam angles spanning a 180º arc were used, delivering radiation at 20º intervals.
Each session lasted about 15–18 minutes, enabling nearly continuous dose delivery.
Working Mechanism
- The therapy operates by 'painting' the tumor in energy layers.
- Each energy level targets a specific tissue depth, ensuring maximum precision.
- The system scans dozens of spots in each layer before moving to the next one with increased penetration.
Advantages
- High precision in delivering radiation to deep and complex anatomical regions like the skull base.
- Limits collateral damage to vital organs.
- Effective in large or invasive tumours.
- Better quality of life during treatment (reduced side effects such as fatigue or swallowing issues).
Limitations & Concerns
- Geographical miss risk: Tiny tumors may be missed due to breathing motion or tumor shrinkage over time.
- Cost: High installation and operational costs, making it suitable for a limited patient base.
- Potential for overuse in non-indicated cases, leading to inequitable healthcare delivery.
- Dynamic SPArc still awaits regulatory clearance and integration into oncology systems.
Significance for India
SPArc therapy can be transformative for cancers in anatomically intricate regions and may serve as a benchmark for future precision cancer therapies. However, adoption in India requires cost-reduction, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks.
Spartaeus karigiri
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
A team of researchers has identified a new species of jumping spiders of the Spartaeinae subfamily in southern India, known for their intelligent hunting skills and web-invasion tactics.
Source: European Journal of Taxonomy (June 2025)
Key Facts:
- Species Name: Spartaeus karigiri
- Taxonomy:
- Family: Salticidae (Jumping Spiders)
- Subfamily: Spartaeinae
- Genus: Spartaeus
- Named After: Karigiri (Elephant Hill) in Devarayanadurga, Karnataka.
Significance:
- First recorded presence of Spartaeus and Sonoita genera in India.
- These genera were previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Discovery expands India’s Spartaeinae spider fauna to 15 species across 10 genera.
Features of Spartaeus karigiri:
- Noted for intelligent hunting and web-invasion tactics.
- Possesses keen eyesight and mimics prey to deceive other spiders.
- Males were found in rocky crevices; females guarding egg clutches.
- Found in Karnataka and Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
Other Findings:
- Sonoita cf. lightfooti, previously known from Africa, was also found in Karnataka.
- A taxonomic correction: Marpissa gangasagarensis (2005) is the same as Phaeacius fimbriatus (1900).
Conservation and Research Insight:
- India's arachnid diversity remains under-studied.
- New discoveries indicate rich but undocumented biodiversity in Indian terrains.
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2025
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
The Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2025, published by UNESCO, reveals an alarming surge in the global out-of-school population, now estimated at 272 million—an increase of over 21 million from previous estimates. This setback highlights that by 2025, countries will collectively fall short of their national education targets by 75 million children.
About the GEM Report
- An annual UNESCO publication, originally launched as the Education for All Global Monitoring Report in 2002 and renamed in 2016.
- Provides an evidence-based global assessment of education progress, challenges, and trends.
- Aims to guide policy decisions and strengthen efforts toward achieving SDG 4 (Quality Education).
Key Findings
- The out-of-school population includes:
- 78 million primary school-age children (11%)
- 64 million lower secondary adolescents (15%)
- 130 million upper secondary youth (31%)
- The rise of 21 million in out-of-school children since the last estimate is attributed to:
- New enrolment and attendance data (+8 million): Includes factors like the 2021 ban on girls' education in Afghanistan, which alone accounts for 1.4 million girls.
- Updated UN population projections (+13 million): The 2024 World Population Prospects estimate a 49 million increase in the global school-age population (6–17 years) by 2025.
- The report warns that conflict zones severely hamper data collection, likely underestimating the true number of out-of-school children.
Challenges with Data and Methodology
- The GEM model draws from administrative data, surveys, and census records to estimate schooling trends.
- However, during emergencies and crises, such models may fail to capture sudden drops in attendance, leading to an underreporting of affected populations.
- Conflict-ridden regions face poor data reliability, impacting planning and resource allocation.
Off-Track from Global Targets
- By 2025, countries will be off-track by:
- 4 percentage points for primary and lower secondary levels
- 6 percentage points for upper secondary level
- Even if national targets are met, the world will still have 107 million children out of school by 2030. The GEM report projects a reduction of 165 million if all targets are achieved—but current trajectories suggest this is unlikely.
Kruti and BharatGPT Mini
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
India is witnessing a significant leap in artificial intelligence innovation with the launch of two indigenous AI models — Kruti by Krutrim and BharatGPT Mini by CoRover. These developments aim to democratize AI access across the country by addressing local needs, multilingual capabilities, and infrastructure limitations.
Kruti: India’s First Agentic AI Assistant
Developed by Krutrim, the AI startup co-founded by Bhavish Aggarwal (of Ola fame), Kruti is positioned as India’s first agentic AI, going beyond conventional chatbots. Launched in 2025, Kruti integrates task execution capabilities such as:
- Cab booking
- Food ordering
- Bill payments
- Image generation
- Research assistance
Kruti is powered by Krutrim V2, a locally trained large language model (LLM), and combines open-source AI systems to deliver scalable, cost-effective, and contextualised solutions.
Key Features of Kruti
- Multilingual Support: Understands voice and text in 13 Indian languages
- Personalised AI: Learns user preferences, adapts tone and content
- Human-Centric Design: Supports read-aloud responses, summarised answers, stories, and tables
- SDK for Developers: Offers embeddable tools for LLM orchestration and task automation
- Integrated Assistant: Eliminates app-switching fatigue through contextual task handling
Aggarwal highlighted that Kruti is built for “how Indians live”—mobile-first, intuitive, and multilingual—offering free access to advanced AI tools.
Strategic Investment and Open AI Ecosystem
Krutrim has committed ?12,000 crore in investment (?2,000 crore already, ?10,000 crore by next year), launched Krutrim AI Lab, and published technical resources, with contributions to the open-source community. The company is positioning itself as a competitive force against global giants like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic, and local firms like Sarvam AI.
BharatGPT Mini: Small Language Model for Bharat
On the same day, CoRover, a conversational AI firm, unveiled BharatGPT Mini, a small language model (SLM) with 534 million parameters trained on its proprietary conversational dataset.
- Supports 14 Indian languages
- Designed for low-compute, low-infrastructure environments
- Enables offline and edge deployments for fast, privacy-centric performance
- Ideal for underserved and rural regions with limited internet or device capacity
SLMs like BharatGPT Mini are emerging as viable tools for domain-specific, lightweight, and privacy-respecting AI in India, complementing the role of LLMs in more complex tasks.
Ocean Darkening
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
A recent study titled "Darkening of the Global Ocean", led by researchers from the University of Plymouth, has revealed that over 21% of the global ocean has darkened between 2003 and 2022, marking a significant environmental concern. The phenomenon, known as ocean darkening, is increasingly disrupting marine ecosystems and global climate regulation.
What is Ocean Darkening?
Ocean darkening refers to the reduction in the photic zone — the upper layer of the ocean (up to ~200 meters deep) where sunlight penetrates to support photosynthesis. This zone is foundational to:
- ~90% of marine biodiversity
- Climate regulation
- Ocean productivity
- Global fisheries
The study used satellite data and modeling based on the Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient (Kd 490), which measures how rapidly light fades through seawater. It found:
- 21% of global oceans experienced darkening in two decades.
- 9% saw photic depth decline by over 50 meters.
- 2.6% saw a reduction exceeding 100 meters — an area roughly equal to the size of Africa.
Geographic Distribution
- High darkening: Arctic, Antarctic, Gulf Stream, North Sea, eastern UK coast.
- Lesser darkening or even brightening: Some parts of the English Channel.
- The open ocean and climate-sensitive zones have witnessed the most pronounced declines.
Causes of Ocean Darkening
- Coastal Zones:
- Runoff of agricultural nutrients, organic matter, and sediments.
- Leads to algal blooms that block sunlight.
- Open Ocean:
- Shifts in plankton dynamics
- Rising sea surface temperatures
- Altered ocean circulation patterns
These changes may be linked to climate change, land-use modifications, and increased rainfall-driven erosion.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
Ocean darkening leads to:
- Shrinking habitats for light-sensitive species like Calanus copepods (key zooplankton and food web base).
- Disrupted feeding, migration, and reproduction cycles due to reduced solar and lunar light cues.
- Increased crowding in shallower waters, intensifying competition and predation.
- Collapse of marine food chains, even in areas with minimal fishing pressure.
Experts warn that this could represent one of the largest habitat losses in recent history, with implications for:
- Biodiversity
- Carbon cycling
- Oxygen production
- Ocean buffering against climate change
SEBI’s Verified UPI ID System

- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
To combat rising cyber frauds and impersonation in the securities market, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has announced a verified Unified Payments Interface (UPI) ID system for all SEBI-registered market intermediaries. This mechanism, developed in coordination with the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), will be effective from October 1, 2025, and is part of SEBI’s broader agenda to enhance investor security and transparency.
Key Features:
- Exclusive UPI IDs: Only SEBI-registered intermediaries will be issued validated UPI IDs featuring a structured format: username.category@validBank. For example, a broker ABC Ltd using XYZ Bank would have the UPI ID: abc.brk@validXYZ.
- Category-Specific Suffixes:
- .brk for stock brokers
- .mf for mutual funds
- Authentication Visual Cue: Transactions with verified UPI IDs will display a “thumbs-up inside a green triangle” icon for easy identification by investors.
Role of NPCI
NPCI, which owns and operates the UPI platform, will exclusively allocate the “@valid” handles for payment collection by SEBI-registered intermediaries. This move ensures only authorised entities can use these UPI IDs, significantly reducing risks of fund misdirection.
SEBI Check Tool
To supplement the system, SEBI is also launching ‘SEBI Check’, a verification tool allowing investors to:
- Scan a QR code or enter UPI ID manually to confirm its legitimacy.
- Verify bank details, including account number and IFSC, of registered entities.
Investor and Intermediary Compliance
- Mandatory for Intermediaries: All SEBI-registered intermediaries must adopt the new verified UPI handles and educate investors about them.
- Optional for Investors: While the structured UPI handle is optional, investors must use only the new IDs if opting to pay via UPI.
- Discontinuation of Old IDs: Existing UPI IDs will be discontinued after October 1, 2025, except for ongoing SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans). New and renewed SIPs must use the verified UPI IDs.
Benefits
- Prevents Fraud: Eliminates payments to unauthorised or impersonating entities.
- Enhances Transparency: Clearly distinguishes registered entities from fraudulent ones.
- Boosts Investor Confidence: Assures secure transactions through verified payment channels.
- Supports Cybersecurity: Clamps down on fake UPI handles used for digital scams.
SEBI’s verified UPI ID initiative and the upcoming ‘SEBI Check’ tool are significant steps toward ensuring secure, transparent, and trustworthy digital transactions in India’s securities market. It reflects the regulator’s proactive stance in protecting investor interests in an increasingly digitised financial environment.
Black Boxes in Aviation
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
The tragic crash of an Air India Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick on June 12, 2025, has spotlighted the critical role of black boxes—a key component in aviation safety and accident investigations. Despite their name, these devices are painted bright orange for easy visibility at crash sites.
What are Black Boxes?
Modern aircraft are equipped with two essential flight recorders:
- Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR): Captures pilot and co-pilot conversations, ambient cockpit sounds, alarms, and radio transmissions.
- Flight Data Recorder (FDR): Records up to 25 hours of technical flight data including altitude, speed, engine parameters, flight path, and over 3,500 variables.
These devices operate continuously without interruption, storing vital information that can reconstruct the events leading up to an air crash.
Design and Durability
Black boxes are built to withstand extreme conditions:
- Casing: Made from crash-resistant materials like titanium or steel.
- Survivability: Can endure temperatures up to 1,100°C, high-impact G-forces, and remain underwater for up to 30 days.
- Locator Beacon: Emit signals to help recovery teams locate them, especially in underwater crashes.
Why Are They Called 'Black' Boxes?
The term “black box” originated from early film-based recorders stored in light-tight boxes. However, modern units are painted bright orange with reflective strips to aid visual detection after accidents.
Evolution of Flight Recorders
- 1930s: François Hussenot in France developed early photographic film-based recorders.
- 1953-54: Dr. David Warren in Australia invented the modern FDR while investigating unexplained crashes of the de Havilland Comet.
- 1960: Mandatory installation of CVRs and FDRs in commercial aircraft.
- 1965: Regulators required recorders to be painted in visible colours.
- 1990: Solid-state memory replaced magnetic tapes, increasing durability and storage capacity.
India's Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB), under the Ministry of Civil Aviation, oversees accident probes. In April 2025, it established a dedicated flight recorder laboratory in New Delhi to improve investigation efficiency.
Technological Advancements
- Combined Recorders: Modern systems often integrate CVR and FDR in a single unit to meet ICAO norms for extended recording.
- Deployable Recorders: Automatically ejected during a crash, float on water, and transmit their location using an Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT).
- Satellite-Based Data Streaming: Future technologies aim to stream flight data in real time, minimizing data loss during oceanic crashes.
Black boxes serve as the backbone of aviation accident investigations by providing critical insight into aircraft performance and crew actions before a crash. Their development reflects ongoing efforts to enhance air travel safety and accountability. The Ahmedabad crash investigation led by the AAIB will heavily rely on these devices to determine the exact sequence of events and prevent future tragedies.
RBI Infuses Rs.23,856 Crore into Banking System via Government Securities Buyback
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to bolster liquidity in the financial system, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has infused ?23,856 crore into the banking system through a buyback of government securities (G-Secs) on June 5, 2025. This marks the second such bond buyback by the central bank in the current financial year (FY 2025–26).
What is a Bond Buyback?
A bond buyback refers to the RBI repurchasing existing government securities before their maturity. Conducted on behalf of the central government, such operations aim to inject durable liquidity into the banking system, improve the liquidity position of banks, and influence interest rates. It is part of the RBI's broader Open Market Operations (OMOs) toolkit.
Broader Liquidity Context
The RBI’s intervention is part of a broader liquidity management strategy, aimed at ensuring stable and surplus liquidity conditions. The central bank has employed various tools in recent months:
- Open Market Operations (OMOs)
- USD/INR Buy/Sell swap auctions
- Variable Rate Repo (VRR) auctions
These tools were especially crucial after the banking system faced a liquidity deficit in late 2024. Since then, the RBI’s operations have restored liquidity, with the system now in surplus mode—estimated at around ?3 lakh crore.
Significance
- Monetary Stability: Enhances the transmission of monetary policy by ensuring banks have sufficient funds to lend.
- Market Functioning: Eases pressure in the bond markets, improves demand for new issuances, and helps manage interest rates.
- Fiscal Management: Supports the government's borrowing program by managing the maturity profile of debt and yields.
India’s First INTERPOL Silver Notice

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant development, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has secured India’s first-ever ‘Silver Notice’ from INTERPOL to track the global assets of Shubham Shokeen, a former French Embassy official implicated in a visa fraud case. This move underscores India's enhanced use of international law enforcement mechanisms to combat transnational crimes, particularly financial crimes involving asset concealment abroad.
What is a Silver Notice?
While INTERPOL is globally known for its Red Notice (to arrest or detain fugitives), the Silver Notice is a newer tool designed to help locate, identify, monitor, or seize the criminal assets of individuals or entities under investigation. Issued at the request of India’s National Central Bureau (NCB), the Silver Notice for Shokeen seeks to trace proceeds of crime potentially parked across multiple countries, marking a new phase in India’s international criminal cooperation.
About INTERPOL
INTERPOL (International Criminal Police Organization) is the world’s largest international police organization, comprising 196 member countries, with India being one of the founding members. It facilitates cross-border police cooperation and crime control across jurisdictions. Its genesis lies in the 2nd International Police Congress held in Vienna in 1923, when it was established as the International Criminal Police Commission (ICPC). It adopted the name INTERPOL in 1956 with the adoption of its Constitution during the 25th General Assembly.
- Headquarters: Lyon, France
- National Central Bureau (NCB): Each member state has an NCB that coordinates with INTERPOL. CBI serves as India’s NCB.
- Key Bodies:
- General Assembly: Supreme decision-making body; meets annually.
- Executive Committee: Supervises execution of General Assembly's decisions.
- General Secretariat: Handles operational activities on a daily basis.
INTERPOL Colour-Coded Notices
INTERPOL issues a series of colour-coded notices that serve as international alerts or cooperation requests:
- Red Notice: Request to locate and provisionally arrest a wanted person.
- Blue Notice: To collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities.
- Yellow Notice: For locating missing persons.
- Black Notice: To identify unidentified bodies.
- Silver Notice: To trace, monitor, and seize assets related to criminal proceeds.
These notices are issued by INTERPOL’s General Secretariat upon request from NCBs and are accessible to all member countries, enabling swift global action.
India’s Technological Integration: The BHARATPOL Portal
To streamline international cooperation, the CBI has developed the BHARATPOL portal, a digital interface that connects all Indian law enforcement agencies with INTERPOL. It allows seamless communication and data exchange for tracking fugitives, assets, and criminal networks, thereby enhancing India’s capabilities in combating cross-border financial and cyber crimes.
Significance for India
- Asset Recovery: The Silver Notice is a critical step in tracing and recovering illicit assets abroad, aligning with India’s broader efforts under anti-money laundering frameworks.
- Global Cooperation: Reflects India’s increasing reliance on international institutions for law enforcement, including the UN Convention against Corruption and FATF recommendations.
- Strengthening CBI's International Role: As India’s NCB, the CBI’s proactive role showcases its growing competence in global criminal investigations.
Exercise Shakti 2025

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The 8th edition of Exercise Shakti, a bilateral joint military exercise between India and France, is being held from 18 June to 1 July 2025 at La Cavalerie, France.
About Exercise Shakti
- Type: Joint military exercise between the Indian Army and French Army.
- Edition: 8th edition. The previous edition was hosted by India, as the exercise is biennial and conducted alternately in both countries.
- Venue (2025): La Cavalerie, France.
Objective and Significance
- Primary Aim: To enhance the joint military capability of both nations to conduct Multi-Domain Operations in sub-conventional conflict scenarios.
- Focus Areas:
- Developing interoperability in operations.
- Sharing best practices, tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Strengthening military-to-military cooperation.
- Fostering bonhomie and camaraderie between the two armies.
Strategic Importance
- Exercise Shakti is part of the broader defence partnership between India and France, encompassing counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, and multi-domain coordination.
- It reflects India’s growing strategic engagements with like-minded global partners to address emerging security challenges.
Other India–France Joint Exercises
Name Domain Participants
Garuda Air Indian Air Force – French Air and Space Force
Varuna Naval Indian Navy – French Navy
Desert Knight Air Indo-French air warfare cooperation
Global Gender Gap Report 2025
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The 19th edition of Global Gender Gap Report 2025 was released by World Economic Forum (WEF).
Key Highlights:
Countries Covered: 148
Global Parity Status:
- Overall Gender Gap Closed: 68.8%
- Estimated Time to Full Parity: 123 years (at current pace)
Assessment Criteria (Four Dimensions):
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
The index uses a parity score (0–100%) to quantify gender equality, where 100% indicates full parity.
India’s Performance (Rank: 131/148)
- Parity Score: 64.1%
- South Asia Rank: Among the lowest; only Maldives (138) and Pakistan (148) rank below
- India’s 2024 Rank: 129 (slipped 2 positions in 2025)
Domain-wise Performance:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Improved: Score increased by 0.9 percentage points to 40.7%
- Earned Income Parity: Rose from 28.6% to 29.9%
- Labour Force Participation: Stagnant at 45.9%
- Insight: Despite income parity gains, the gap in actual earnings and participation remains wide.
- Educational Attainment
- Near Parity Achieved: 97.1%
- Driven by rising female literacy and higher tertiary enrolment
- Challenge: Translating education into workforce participation remains limited.
- Health and Survival
- Marginal Gains: Improved parity in sex ratio at birth and healthy life expectancy
- However, overall life expectancy declined for both genders, muting the parity effect.
- Political Empowerment
- Significant Decline:
- Women MPs fell from 14.7% to 13.8%
- Women ministers dropped from 6.5% to 5.6%
- Trend: Continued decline from the 2019 peak of 30% female political representation
- Significant Decline:
South Asia and Global Comparison
- Bangladesh: Best performer in South Asia, ranked 24th globally (up by 75 positions)
- Other Neighbours:
- Bhutan (119),
- Nepal (125),
- Sri Lanka (130),
- Maldives (138),
- Pakistan (148 – last)
- Global Top 5 Countries:
- Iceland (Top for 16th year in a row)
- Finland
- Norway
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
Key Global Insights
- Women in Workforce: 41.2% of global workforce
- Leadership Representation: Only 28.8% of leadership roles are held by women
- Despite post-pandemic recovery in gender parity, leadership gaps and decision-making roles remain major bottlenecks.
Implications for India
- The report underscores that gender parity is not just a social imperative, but also crucial for inclusive and resilient economic growth.
- India’s sluggish progress in political empowerment and gender wage gap highlight the need for institutional reforms, affirmative actions, and gender-sensitive policies in governance, employment, and leadership.
State of World Marine Fishery Resources 2025

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) 2025 Report on the State of World Marine Fishery Resources, released during the UN Ocean Conference (UNOC3) in Nice, France, offers a comprehensive assessment of global fish stock sustainability, regional disparities, and governance challenges.
Key Findings:
- Global Sustainability: 64.5% of marine fishery stocks are fished within biologically sustainable levels, indicating modest improvement. However, 35.5% remain overexploited.
- Deep-Sea Species Vulnerability: Only 29% of deep-sea species are sustainably harvested, largely due to biological traits like slow growth, delayed maturity, and low reproductive rates. These characteristics impair recovery from overfishing.
- Migratory Shark Concerns: Of the 23 shark stocks assessed, 43.5% are overfished, especially in the tropical Indo-Pacific where they frequently become bycatch in tuna fisheries.
- Tuna Success Story: 87% of evaluated tuna and tuna-like species are sustainably fished, a result of effective regulation by Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs).
- Regional Disparities: The northeast and southwest Pacific show high sustainability levels, while areas such as the Mediterranean and Black Sea lag, with only 35.1% of stocks sustainably managed.
- Data Gaps: Despite high reported sustainability (72.7%) in the eastern Indian Ocean, concerns remain due to insufficient species-specific stock assessments.
Governance and Policy Challenges:
- Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Continues to threaten stock sustainability. IUU encompasses:
- Illegal: Breaches of domestic or international laws.
- Unreported: Failure to report or misreport catches.
- Unregulated: Conducted by vessels operating beyond jurisdictional authority, undermining conservation efforts.
- Subsidy Prohibitions (WTO Agreement):
- Bans financial support to vessels engaging in IUU fishing.
- Restricts subsidies for overfished stocks unless recovery measures are implemented.
- Prohibits aid for fishing in unregulated high seas zones.
Critical Analysis:
Positives:
- The rise in sustainable stocks signifies improved management awareness, particularly in regulated regions like the Pacific.
- Tuna fisheries demonstrate successful use of scientific tools—catch reporting and onboard observers—under RFMOs.
- The global survey included over 600 experts across 90 nations, lending credibility and robustness.
Negatives:
- Deep-sea stocks remain acutely overfished and biologically vulnerable.
- Shark species, integral to marine food webs, continue to suffer from bycatch and poor regulatory coverage.
- Monitoring shortfalls in Southeast Asia and African coasts prevent precise biomass estimation and conservation action.
- Weaker implementation and unregulated artisanal practices challenge sustainability in Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
Recommendations for Sustainable Fisheries Governance:
- Empower RFMOs with real-time monitoring systems, electronic catch reporting, and observer programs.
- Adopt Ecosystem-Based Approaches that integrate climate resilience and biodiversity objectives.
- Strengthen Data Infrastructure in data-deficient regions with support from international bodies like the FAO and World Bank.
- Curtail Harmful Subsidies as per WTO protocols to reduce economic incentives driving overfishing.
- Promote Community Participation through co-management strategies and the development of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
Lokpal of India adopts new motto

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Full Bench of the Lokpal of India has officially adopted a new motto — “Empower Citizens, Expose Corruption” — replacing the earlier Sanskrit phrase:
Old Motto: Ma Gridhah Kasyasvid Dhanam (Do not be greedy for anyone’s wealth)
The change aims to improve institutional visibility, enhance public engagement, and reaffirm the Lokpal’s mission to fight corruption by empowering the people.
About Lokpal of India
- Established under: Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
- Came into force: 16 January 2014
- Headquarters: Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
- Nature: Independent statutory anti-corruption body
Composition
- Chairperson: Former Chief Justice of India or SC Judge
- Members: Up to 8 members
- 4 Judicial
- 4 Non-Judicial
- Appointed by: President of India on recommendation of a high-level Selection Committee
Jurisdiction
Lokpal can investigate allegations of corruption against:
- Prime Minister, Union Ministers, and Members of Parliament
- Central Government employees (Group A to D)
- Officials of organizations receiving govt. funding (full/partial)
- Entities receiving foreign donations over ?1 crore annually
Functions & Powers
- Investigates complaints under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- Can:
- Sanction prosecution
- Order attachment of properties
- Recommend suspension or transfer of officials
- Possesses powers of a civil court:
- Summon witnesses
- Seize documents
- Can supervise the CBI in referred cases
- Collaborates with other investigative and enforcement agencies
Why the New Motto Matters
The new motto, “Empower Citizens, Expose Corruption”, reflects:
- A citizen-centric approach to governance
- A renewed commitment to transparency, accountability, and institutional trust
- The evolving role of Lokpal in aligning public participation with anti-corruption efforts
Exercise KHAAN QUEST 2025

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Army contingent has arrived in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, to take part in the 22nd edition of the Multinational Peacekeeping Exercise KHAAN QUEST, scheduled from 14 to 28 June 2025.
About Exercise KHAAN QUEST
- Origin: Launched in 2003 as a bilateral exercise between the USA and Mongolian Armed Forces.
- Multinational Format: Expanded in 2006 to include multiple countries, now recognized as a major UN peacekeeping readiness exercise.
- 2024 Edition: Held from 27 July to 9 August in Mongolia.
- India’s Participation: Contingent Strength: 40 personnel, primarily from a Battalion of the Kumaon Regiment, supported by members from other arms and services.
Aim and Objectives
- Enhance readiness for UN peacekeeping operations under Chapter VII of the UN Charter.
- Promote interoperability, joint tactical planning, and multinational cooperation.
- Share best practices in peace support operations.
Key Tactical Drills
- Static and Mobile Checkpoint Setup
- Cordon and Search Operations
- Patrolling and Evacuation of Civilians from conflict zones
- Counter-IED procedures
- Combat First Aid and Casualty Evacuation
Significance
Exercise KHAAN QUEST serves as a critical platform for building military-to-military cooperation, strengthening international partnerships, and improving operational cohesion among troops from around the world.
International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA)

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
India, as the Vice President of the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA), actively participated in the 2nd Session of the IALA Council, held in Nice, France.
What is IALA?
The International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA) is a global intergovernmental technical body responsible for:
- Standardizing marine navigation aids (AtoN)
- Enhancing maritime safety
- Promoting environmental protection in marine navigation
Key Facts:
- Established: 1957 (as an NGO; became an IGO in 2024)
- Headquarters: Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, France
- Members: 39 countries
- Status: Transitioned to an Intergovernmental Organization in August 2024 after ratification by 30 states
India’s Role in IALA
India has been a Council Member since 1980, and was elected Vice President (2023–2027) during the 1st General Assembly in Singapore in 2023 — a significant recognition of India’s leadership in maritime affairs.
Major Indian Contributions:
- Development of Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) across 12 major ports
- Leadership in digital navigation aids and maritime innovation
- Promoting lighthouse heritage tourism
- Launching global training programs at the Kolkata Marine Navigation Training Institute
Highlights from the 2nd IALA Council Session
- Keynote: Outlined India’s achievements in integrating marine AtoN and future roadmap
- Technical Discussions:
- Standardization of AtoN and VTS systems
- Harmonized IoT protocols for visual AtoN
- Maritime Service Registry development
- Lighthouse heritage conservation
- Planning IALA’s global activity schedule for 2025–2026
India to Host Key IALA Events
- 3rd IALA General Assembly – December 2025, Mumbai
- 21st IALA Conference – 2027, Mumbai
This reflects global confidence in India’s technical capabilities and strategic importance in the maritime domain.
Significance:
- Strategic Leadership: Reinforces India’s influence in international maritime governance.
- Digital Maritime Innovation: India is contributing to cutting-edge technologies like IoT protocols and digital AtoN.
- Global Capacity Building: Hosting and training initiatives bolster the global maritime workforce.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Lighthouse tourism and heritage preservation align technology with history.
India’s Social Security coverage reaches 64.3% in 2025
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
According to the latest data from the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) ILOSTAT database, India’s social security coverage has increased from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, an unprecedented 45 percentage point surge over the past decade.
What is Social Security?
Social security (or social protection) refers to systems and policies that protect individuals and households from:
- Income loss (e.g. old age, unemployment, disability)
- High healthcare costs
- Social vulnerability (e.g. poverty, maternity, sickness)
It is built on three pillars:
- Social Assistance – Non-contributory support (e.g. food, housing)
- Social Insurance – Contributory programs (e.g. pensions, health insurance)
- Labour Market Programs – Employment schemes to build self-reliance
Key Highlights from ILOSTAT 2025
- India’s social security coverage jumped to 64.3%, up from 19% in 2015 – a 45 percentage point increase in 10 years.
- This means over 94 crore (940 million) people are now covered under at least one form of social protection.
- India now ranks 2nd globally in terms of population covered by social security.
- It is also the first country to update its 2025 social protection data in the ILOSTAT global database, showcasing its progress in digital governance and transparency.
Major Social Protection Initiatives Driving the Surge
India’s massive expansion in social coverage is due to a wide range of targeted schemes, including:
Pension & Insurance Schemes
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Pension of ?1,000–?5,000/month for informal workers aged 18–40.
- PM Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-SYM): Contributory pension for unorganized workers with 50% government support.
- PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): ?2 lakh life insurance for people aged 18–50.
- PM Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Accident insurance of ?2 lakh for ages 18–70.
Healthcare & Nutrition
- Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY: ?5 lakh health cover for low-income families.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana: Maternity care for pregnant women.
- PM POSHAN (formerly Mid-Day Meal Scheme): Nutritional support to schoolchildren.
Income, Housing & Food Security
- MGNREGA: Guaranteed 100 days of wage employment annually in rural areas.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: ?6,000/year income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Public Distribution System (PDS) under NFSA: Subsidized food grains to eligible households.
- PM Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G): Pucca homes with basic amenities for rural poor.
Significance
- Poverty Reduction: Enhanced safety net for vulnerable populations.
- Inclusive Growth: Formal inclusion of informal sector workers.
- Digital Governance: Use of technology for efficient delivery (e.g., Aadhaar, DBT).
- Resilience Building: Helps households withstand economic shocks (e.g., pandemics, job loss).
CROPIC: A New AI-Driven Crop Study Scheme
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plans to launch CROPIC, a study to gather crop information using field photographs and AI-based models.
What is CROPIC?
CROPIC stands for Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops. It is a new initiative by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare aimed at studying crops through photographs and artificial intelligence (AI). The core objective is to monitor crop health and assess mid-season losses using images captured at multiple stages of the crop cycle.
Why is CROPIC significant?
CROPIC plays a pivotal role in modernizing and digitizing crop monitoring under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), India’s flagship crop insurance scheme.
Significance:
- Improved Loss Assessment: Traditional methods of crop loss assessment are time-consuming and subjective. CROPIC introduces AI-based analysis for faster and more objective decision-making.
- Automation of Compensation: It will help automate claim processes, ensuring faster payments to farmers in case of crop failure.
- Rich Crop Signature Database: Repeated field observations will build a valuable dataset of crop images over time, useful for future agricultural planning and risk management.
- Farmer Involvement: By crowdsourcing photographs directly from farmers, CROPIC also encourages their direct participation in data collection.
How will CROPIC work on the ground?
- Data Collection via App:
- A mobile app developed by the ministry will be used.
- Farmers and officials will take photos of crops 4–5 times during a crop’s life cycle.
- AI-Based Analysis:
- Photos will be processed on a cloud-based AI platform.
- The model will identify crop type, growth stage, health condition, damage, and loss extent.
- Visualization and Monitoring:
- A web-based dashboard will visualize crop status and damage patterns for stakeholders.
- Use in Insurance Claims:
- The app will also be used by officials to collect photo evidence for PMFBY claims, helping streamline compensation payouts.
Project Timeline:
- Pilot Phase:
- Begins with Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025-26.
- Will cover at least 50 districts per season, spanning various agro-climatic zones and major crops.
- Full Roll-Out: After initial R&D, nationwide implementation is planned from 2026 onwards.
Funding and Support:
- Funded through the Fund for Innovation and Technology (FIAT) under PMFBY.
- FIAT has a total allocation of ?825 crore for various tech-driven agricultural initiatives.
Understanding Tourette Syndrome
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that typically begins in early childhood, often between the ages of 2 and 15, with an average onset around six years. Affecting approximately 0.3% to 1% of the global population, TS is more prevalent among boys than girls. Despite its neurological basis, it remains poorly understood and frequently misdiagnosed, particularly in school settings where symptoms are mistaken for behavioural issues.
Nature and Classification of Tics
Tourette Syndrome is characterised by tics—sudden, repetitive, and involuntary movements or vocalisations. These are classified as:
- Simple tics, such as eye blinking, facial grimacing, throat clearing, or sniffing, involve a single muscle group or sound.
- Complex tics are more coordinated, involving actions like hopping, touching objects, or uttering phrases. Rarely, individuals may display coprolalia, the involuntary use of obscene language.
Tics often intensify with stress or excitement, diminish during calm periods, and usually disappear in deep sleep. External stimuli such as excessive screen exposure have also been linked to an increase in tics, particularly in children.
Causes and Co-morbidities
While the exact cause of TS remains unknown, researchers point to a combination of genetic predisposition and neurobiological factors, including abnormalities in brain regions such as the basal ganglia and frontal lobes. Environmental triggers—like low birth weight, perinatal complications, and post-infectious conditions (e.g., streptococcal infections)—may also contribute.
Tourette’s often coexists with other conditions such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. The presence of these co-morbidities complicates diagnosis and management.
Management and Treatment Approaches
Treatment is individualised and not always pharmacological. Many children with mild, non-disruptive tics do not require medication. Instead, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and behavioural interventions have shown significant efficacy. These therapies help children manage their symptoms while also training families to provide supportive environments that reduce stress and tic frequency.
Medications may be considered in severe cases where tics hinder daily functioning. Importantly, suppression or punishment of tics is counterproductive, often exacerbating symptoms due to built-up tension.
Social Stigma and the Need for Awareness
The primary challenge in managing TS lies not in the disorder itself, but in the societal misunderstanding surrounding it. Children with TS are often labelled as attention-seeking or disruptive, leading to social isolation and emotional distress. As seen in the case of a child from Kochi, delayed diagnosis and stigma worsened his condition until it was recognised as Tourette’s.
Educating teachers, parents, and peers is crucial. Early diagnosis, empathetic engagement, and inclusive school environments are essential to ensuring that children with TS are treated with dignity and compassion.
Rediscovery of the Eurasian Otter in Kashmir
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
After being presumed extinct in the Kashmir Valley for nearly three decades, the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) has been spotted again in the Lidder River in Srigufwara, South Kashmir. This rare sighting rekindles hope for the revival of the Valley’s aquatic biodiversity.
About Eurasian Otter:
- Common Names: Eurasian otter, European otter, Common otter, Old-World otter
- Local Name in Kashmir: Vuder
- Type: Semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal
- Distribution:
- Widely spread across Europe, the Middle East, Northern Africa, and Asia (from Eastern Russia to China).
- In India, found in northern, northeastern, and southern regions.
- In Kashmir, historically abundant in Dal Lake, Dachigam streams, Rambiara stream, and the Lidder River.
Habitat & Features:
- Habitat:
- Occupies diverse freshwater and coastal ecosystems—lakes, rivers, marshes, swamp forests, and mountain streams.
- In the Indian subcontinent, prefers cold hill and mountain waters.
- Physical Traits & Adaptations:
- Sleek brown fur (lighter underneath), long streamlined body, short legs, and thick tail.
- Aquatic adaptations:
- Webbed feet
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense fur trapping air for insulation
- Excellent vision, hearing, and olfactory senses.
- Behavior: Elusive, solitary, and primarily nocturnal.
Conservation Concerns:
- Primary Threats:
- Water pollution degrading habitats
- Hunting for fur, historically significant in Kashmir
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Sant Kabirdas
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
11th June 2025 marked the 648th birth anniversary of Sant Kabirdas, one of India’s most revered 15th-century Bhakti saints.
Place of Birth: Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
Birth Period: Circa 1440 CE, raised in a Muslim weaver family
Philosophy and Teachings
- Nirguna Bhakti: Kabir rejected idol worship and sectarian divisions, instead preaching devotion to a formless, universal God (Nirguna Brahman).
- Social Reform: He denounced casteism, rituals, and blind faith, stressing ethical conduct, humility, and self-realization.
- Inner Divinity: He believed God resides within and taught seekers to seek truth through introspection (Antar-drishti) rather than temple rituals.
- Language and Style:
- Composed in Sant Bhasha, a blend of local dialects understood across religions.
- Created Ulatbansi verses — paradoxical or "upside-down sayings" — challenging conventional wisdom.
Literary Legacy
- Major Works: Bijak, Sakhi Granth, Kabir Granthavali, Anurag Sagar
- Scriptural Inclusion:
- His verses appear prominently in the Adi Granth Sahib compiled by Guru Arjan Dev.
- Adopted by various traditions:
- Kabir Bijak (Kabirpanth, UP)
- Kabir Granthavali (Dadupanth, Rajasthan)
Impact and Influence
- Kabir Panth: A spiritual sect founded on his teachings, still active in North India.
- Sikhism: Deeply influenced Guru Nanak; Kabir’s dohas are integrated into Guru Granth Sahib.
- Cross-Religious Appeal: Respected by both Hindus and Muslims, he is a symbol of India’s syncretic spiritual culture.
- Other Sects: Influenced Dadu Panthis and Nirguna Bhakti traditions across India.
Contemporary Relevance
- Religious Harmony: In a climate of polarization, Kabir’s teachings offer a path of unity and spiritual inclusivity.
- Social Justice: His resistance to caste hierarchy echoes India’s constitutional values of equality and dignity.
- Sustainable Living: His emphasis on simplicity and contentment aligns with ecological and minimalist principles.
- Spiritual Humanism: He stressed conduct over ritual, making his message resonate across belief systems in today’s pluralistic society.
State of the World Population Report 2025
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
According to the United Nations Population Fund’s (UNFPA) State of the World Population Report 2025, India’s population has reached 146.39 crore as of April 2025, surpassing China (141.61 crore) to remain the world’s most populous country. Importantly, India’s Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has declined to 1.9, falling below the replacement level of 2.1.
Key Highlights:
Population Growth and Future Projections
- Current population (2025): 146.39 crore
- Projected peak: 170 crore in the next 40 years, after which population will begin to decline.
- Working-age population (15–64 years): 68%
- Youth population:
- 0–14 years: 24%
- 10–19 years: 17%
- 10–24 years: 26%
- Elderly population (65+ years): 7% (expected to rise steadily)
Fertility Trends and the Real Crisis
What is TFR?
- Total Fertility Rate measures the average number of children a woman is expected to have in her lifetime.
- Replacement level TFR: 2.1 (to maintain population size across generations)
- India’s TFR in 2025: 1.9, marking a demographic shift toward stabilization.
Fertility Divergence Across States:
- High TFR states: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand
- Low TFR states: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Delhi – already below replacement level
The Real Fertility Crisis (UNFPA View):
- The true concern is unmet fertility goals, not overpopulation or underpopulation.
- Barriers to achieving desired family size:
- Financial constraints (40%)
- Job insecurity (21%) and housing issues (22%)
- Lack of childcare (18%)
- Social/family pressures (19%)
- Modern concerns like climate change and shifting gender norms
Structural & Social Challenges
- Persisting inequalities in access to reproductive health across caste, income, and regional lines
- Youth bulge in LMICs (including India) offers demographic dividend but needs skill-building and employment opportunities
- Ageing population calls for future-proof policies on healthcare, pensions, and social security
Life Expectancy & Data Reliability
- Life expectancy (2025):
- Men: 71 years
- Women: 74 years
- Data drawn from: DHS, MICS, World Population Prospects 2024, Family Planning Indicators (2024)
- India’s decennial Census delayed to 2027, limiting official data updates since 2011
UNFPA Recommendations for India:
- Expand SRH (Sexual & Reproductive Health) Services: Universal access to contraception, safe abortion, and infertility care
- Tackle Structural Barriers: Affordable housing, childcare, flexible work policies, and women’s education
- Promote Reproductive Agency: Ensure informed choices on family planning for all, including LGBTQIA+ and unmarried individuals
- Balance Youth & Elderly Policies: Invest in youth employability while preparing for ageing-related challenges
Blue NDC Challenge
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
At the Third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) held in Nice, France (June 9–13, 2025), Brazil and France launched the Blue NDC Challenge — a major international initiative to integrate ocean-based climate solutions into Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, in the lead-up to UNFCCC COP30, to be held in Belem, Brazil.
What is the Blue NDC Challenge?
The Blue NDC Challenge is a multilateral climate action initiative urging countries to incorporate ocean-centric measures into their updated NDCs. It aims to enhance climate mitigation and adaptation by recognizing the vital role of oceans and coastal ecosystems in addressing the climate crisis.
- Launched by: Brazil and France
- Platform: UNOC3 (June 2025)
- Target: Updated NDCs due for 2035 (deadline: February 10, 2025)
Participating Countries (as of June 2025):
- Founding: Brazil, France
- Joined: Australia, Fiji, Kenya, Mexico, Palau, Seychelles
Objectives and Key Features:
- Ocean-Integrated NDCs
- Include marine ecosystems, coastal zones, mangroves, coral reefs, and salt marshes in national climate plans.
- Integrate Marine Spatial Planning (MSP) and Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM).
- Sustainable Blue Economy
- Promote climate-resilient fisheries and carbon-smart aquaculture.
- Expand clean ocean energy: offshore wind, wave, and tidal power.
- Decarbonization and Adaptation
- Phase out offshore oil and gas projects.
- Reduce emissions in shipping, seafood value chains, and coastal infrastructure.
- Boost resilience in maritime sectors vulnerable to climate risks.
- Restoration and Conservation
- Focus on the restoration of mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs—which are effective carbon sinks and natural buffers against sea-level rise.
- Global Partnerships and Support Mechanisms
- Supported by:
- Global Mangrove Alliance
- UN High-Level Climate Champions
- World Resources Institute (WRI)
- Ocean Breakthroughs (Marrakech Partnership for Global Climate Action)
- Supported by:
Significance and Leadership:
- Brazil’s Climate Leadership
- Brazil’s 2035 NDC (submitted in November 2024) includes, for the first time, a dedicated Ocean and Coastal Zones component.
- Brazil is also investing in marine conservation, supported by a $6.8 million fund from Bloomberg Philanthropies (June 8, 2025).
- Expert Insights:
- Mangroves sequester carbon 10 times faster than terrestrial forests.
- Including oceans in NDCs can unlock greater political and financial support, according to Conservation International and WRI.
- Emission Reduction Potential:
- According to WRI, ocean-based solutions can contribute up to 35% of the global emissions reduction needed to stay within the 1.5°C limit.
Relevance for India and the World:
- With India’s vast coastline and diverse marine ecosystems, incorporating ocean-based climate actions into its NDCs could enhance climate resilience, especially for coastal communities.
- Global focus on oceans marks a shift towards holistic climate policy, integrating land, sea, and people-centric approaches.
Discovery of Spathaspina noohi
- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
A significant addition to India's rich biodiversity has emerged from the forests of Meghalaya with the discovery of a new beetle species, Spathaspina noohi. This unique species not only adds to the biological inventory of the region but also necessitated the creation of an entirely new genus, highlighting the ecological and taxonomic uniqueness of the organism.
Location of Discovery
- The beetle was found in the Umran area of Ri Bhoi district, Meghalaya.
- Elevation: 781 metres above sea level.
- The discovery was made by S. S. Anooj, entomologist from Kerala Agricultural University, and formally described by B. Ramesha in the international journal Zootaxa.
Taxonomic Significance
- Spathaspina noohi belongs to the Curculionidae family, commonly known as weevils, which includes over 60,000 species globally.
- Due to a highly distinctive sword-like spine on its back, it was classified under a new genus—Spathaspina, a name derived from Latin:
- Spatha = sword
- Spina = spine
Subfamily and Tribe Characteristics
- The beetle falls under the Ceutorhynchinae subfamily, which includes about 1,300 species worldwide.
- The subfamily is characterized by:
- Compact, robust body
- Ability to tuck their snout (rostrum) between the front legs when resting
- A visible back structure (mesanepimera)
- Within this subfamily, the beetle is linked to the tribe Mecysmoderini, comprising 8 genera and 107 species. This tribe is noted for its thoracic spines and specialized antenna structures, mostly found in South and Southeast Asia.
Ecological Role of Weevils
While many weevils are considered agricultural pests, others, including Spathaspina noohi, play vital ecological roles such as:
- Controlling invasive plant species
- Maintaining ecosystem balance
Geographical Distribution of Ceutorhynchinae
- These beetles are present across most continents except:
- New Zealand
- Oceania
- Antarctica
- Southern parts of South America
- Their highest diversity is noted in the Palaearctic Region (Europe, North Africa, parts of Asia), followed by the Oriental Region (South and Southeast Asia).
Commemorative Naming
The species is named in honour of P. B. Nooh, IAS, Director of Tourism, Government of Kerala. This acknowledges his contribution to eco-tourism and sustainable development, symbolizing the interconnection between biodiversity conservation and responsible tourism.
SEZ Reforms to Promote Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Department of Commerce notified key amendments to the SEZ Rules, 2006, to boost semiconductor and electronics component manufacturing. These reforms address the high capital intensity and import dependency of the sector and aim to attract pioneering investments.
Key Rule Amendments:
Rule 5: Minimum Land Requirement Relaxed
- What Changed: Minimum land required for SEZs dedicated to semiconductor/electronics manufacturing reduced from 50 hectares to 10 hectares.
- Why it matters
- Eases land acquisition
- Makes SEZs more feasible, especially in smaller industrial clusters
- Encourages pioneering investments in land-scarce regions
Rule 7: Encumbrance-Free Land Norm Relaxed
- What Changed: SEZ land no longer required to be entirely encumbrance-free, if it is mortgaged/leased to the Central or State Government or authorized agencies.
- Why it matters
- Removes a major legal hurdle in land approvals
- Accelerates SEZ project clearance and development timelines
Rule 18: Domestic Supply Allowed from SEZ Units
- What Changed: Semiconductor/electronics SEZ units can now sell products in the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) after paying applicable duties.
- Why it matters
- Greater market access
- Enhances revenue and profitability
- Breaks away from traditional export-only SEZ model
Rule 53: Clarity on Free-of-Cost Goods in NFE Calculation
- What Changed: Free-of-cost goods received or supplied will now be included in Net Foreign Exchange (NFE) calculations, using customs valuation rules.
- Why it matters
- Encourages R&D and contract manufacturing
- Promotes transparent reporting of value addition
- Aligns with global manufacturing practices
Significance of Reforms:
- Tailored for High-Tech Sectors: Recognises the long gestation and capital-intensive nature of semiconductor and electronic component industries.
- Encourages Domestic and Global Investment: Makes India an attractive destination for global electronics giants.
- Enables Domestic Market Integration: By allowing DTA sales, it expands market access for SEZ-based units.
- Supports India's Semiconductor Mission: Complements existing initiatives like the Semicon India Programme.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)
- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Finance Minister chaired the 6th Governing Council (GC) meeting of NIIF in New Delhi. The Council urged NIIF to enhance its global presence, diversify funding sources, and attract international investors by leveraging its sovereign-backed model.
About National Investment and Infrastructure Fund
- A government-anchored investment platform to mobilize long-term institutional capital for infrastructure and strategic sectors.
- Operates as a sovereign wealth fund (SWF)-linked asset manager with independent governance.
- Established: 2015 (Union Budget 2015–16)
- Headquarters: Mumbai
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs)
Functions & Objectives:
- Capital Mobilization: Attract domestic & global institutional investors.
- Investment Management: Deploy equity in commercially viable infrastructure.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with global sovereign wealth & pension funds.
- Policy Alignment: Support national initiatives like Make in India, green energy, and digital infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Public-Private Structure:
- 49% Government of India
- 51% Global and domestic institutional investors (e.g., ADIA, Temasek, CPPIB)
- SEBI-Registered AIF: Category II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF)
- Assets Under Management (AUM): ?30,000+ crore
- Capital Catalysed: ?1.17 lakh crore
- CEO & MD: Sanjiv Aggarwal (since Feb 2024)
Funds under NIIF:
- Master Fund: Core infrastructure (ports, airports, data centres, logistics)
- Private Markets Fund (PMF): Fund of funds model
- India-Japan Fund: Focused on climate action and sustainability
- Strategic Opportunities Fund: Growth equity in strategic sectors
Governing Council (GC) of NIIF:
- Chair: Union Finance Minister (currently Nirmala Sitharaman)
- Members include Finance Secretary, DEA/DFS officials, SBI Chairman, private sector leaders.
- Provides strategic guidance on:
- Fundraising
- Global positioning
- Operationalisation of new funds
- Annual review of performance
Key Outcomes of the 6th GC Meeting (2024–25):
- Proactive Global Outreach: GC urged NIIF to enhance its global presence and professionalise international engagement.
- Diversified Fundraising: Encouraged exploring multiple funding sources beyond traditional sovereign investors.
- Private Markets Fund II (PMF II): Target corpus: $1 billion; first closing imminent.
- Bilateral Fund with the USA: Under discussion to foster cross-border infrastructure investments.
- Greenfield Investment Success: Master Fund investments directed toward ports, logistics, airports, data centres.
- Strong Global Partnerships: Includes ADIA, Temasek, Ontario Teachers', CPPIB, AIIB, ADB, JBIC, and NDB.
- Annual Meetings: GC to convene once every year to review and guide NIIF’s evolving role.
Bhagwan Birsa Munda

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
On his 125th death anniversary (Balidan Diwas), the Prime Minister of India paid tribute to Bhagwan Birsa Munda, hailing his pioneering role in tribal empowerment and anti-colonial resistance.
Early Life and Identity
- Born: 15 November 1875, Ulihatu, Chotanagpur Plateau (now in Jharkhand).
- Tribe: Munda.
- Title: Revered as “Dharti Aaba” (Father of the Earth).
- Education: Attended Christian missionary schools in Chaibasa; later rejected colonial influence and converted to Vaishnavism, blending it with tribal spirituality.
- Founder of: The Birsait sect, advocating moral reform and cultural awakening among Adivasis.
Role in Freedom Struggle & Tribal Mobilisation
Resistance Against Exploitation:
- Zamindari System: Opposed British-imposed land systems that dismantled the Khuntkatti tribal land tenure, dispossessing tribals and reducing them to bonded labourers.
- Beth Begari: Led resistance against forced labour and revenue policies.
- Forest Rights: Fought against British encroachment and resource extraction in forests.
Cultural and Spiritual Renaissance:
- Condemned social evils like black magic and alcoholism.
- Mobilised tribals using tribal songs, attire, drums, and community gatherings.
- Advocated tribal self-rule and cultural pride against the oppression by Dikus (outsiders).
Ulgulan Movement (1895–1900): The Great Tumult
- Nature: A widespread anti-colonial rebellion across present-day Jharkhand, Odisha, and Bengal.
- Strategy: Guerrilla warfare, targeting British outposts, churches, and police stations.
- Slogan: “Abua Raj setar jana, Maharani Raj tundu jana” (Let the rule of our people begin, let the Queen’s rule end).
- Emphasized a vision of egalitarian tribal raj rooted in indigenous governance systems.
Arrest, Martyrdom, and Legacy
- Arrested: 1895; Died: 9 June 1900 in Ranchi Jail under mysterious circumstances.
- Though the rebellion was crushed, it led to the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act, 1908, securing tribal land rights.
Recognition and Legacy
- Declared as “Bhagwan” (Lord) by tribal communities for his cultural leadership and resistance.
- Institutions named in his honour: Birsa Agricultural University, Birsa Institute of Technology, etc.
- November 15 (birth anniversary) declared Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (Tribal Pride Day) in 2021 by the Government of India.
- Symbol of tribal assertion, indigenous identity, and early resistance to colonialism in India.
India’s Breakthrough in Heeng Cultivation

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
CSIR-IHBT reported the first flowering and seed setting of heeng in Palampur (1,300 m above sea level). This confirmed the successful acclimatisation and domestication of Ferula assa-foetida in Indian agro-climatic conditions.
This milestone is significant because:
- It proves India’s capability to cultivate heeng domestically.
- It completes the reproductive cycle—a prerequisite for long-term commercial production and sustainability.
- It expands the scope of cold-arid agriculture beyond traditional zones.
Background:
- Heeng or asafoetida (Ferula assa-foetida) is a perennial herb, long revered in Indian culinary and medicinal traditions.
- It is widely mentioned in ancient texts such as the Mahabharata, Charaka Samhita, Pippalada Samhita, and the works of Panini, known for its digestive, aromatic, and therapeutic properties.
- Despite being the world’s largest consumer of heeng, India was entirely import-dependent until the early 2010s, sourcing it mainly from Afghanistan, Iran, and Uzbekistan.
- This was because the species Ferula assa-foetida, the true source of asafoetida, was not found in India—only related species like Ferula jaeschkeana (Himachal Pradesh) and Ferula narthex (Kashmir and Ladakh) existed, which do not yield the culinary resin.
Botanical & Climatic Requirements:
- Plant Type: Perennial, takes about 5 years to mature and flower.
- Soil: Prefers sandy, well-drained soil with low moisture.
- Climate: Thrives in cold, arid environments, requires annual rainfall below 200–300 mm.
- Temperature Range: Grows best in 10–20°C, tolerates up to 40°C, and survives winter lows of –4°C.
- Propagation: The oleo-gum resin (asafoetida) is extracted by making incisions in the plant’s fleshy taproot and rhizome, yielding a latex that hardens into a gum, which is dried into powder or crystal form.
The Indigenous Cultivation Effort:
In a major step toward self-reliance, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research – Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT) in Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, initiated India’s first project for indigenous heeng cultivation.
- Seed Procurement: Between 2018–2020, IHBT coordinated with agencies and suppliers in Iran, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and South Africa. Seeds were finally procured from Iran and Afghanistan with import approvals and quarantine protocols handled by ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- Research and Trials: Researchers developed germination protocols for seeds with low viability and conducted trials at IHBT Palampur and Ribling in Lahaul-Spiti to determine altitude-specific suitability and agronomic practices.
- Milestone Event: On October 15, 2020, the first heeng sapling was planted in a farmer’s field in Kwaring village, Lahaul Valley—marking the start of India’s heeng cultivation journey.
Expansion and Institutional Support:
- New Cultivation Zones: From cold desert areas, cultivation extended to mid-hill regions such as Janjheli in Mandi. Demonstration plots and farmer training programmes were established across Lahaul-Spiti, Kinnaur, Mandi, Kullu, and Chamba.
- Early Adopter Villages:
- Lahaul & Spiti: Madgran, Salgran, Beeling, Keylong
- Mandi: Janjehli, Kataru, Majhakhal, Karsog
- Kinnaur: Kalpa, Hango, Reckong Peo, Maling
- Kullu: Kotla–Banjar, Bagsaid, Dhaugi–Sainj
- Chamba: Pangi, Bharmour, Tooh, Mahala
- Heeng Germplasm Resource Centre: Established at IHBT Palampur in March 2022, this national hub oversees research, conservation, seed production, and propagation of heeng.
- Tissue Culture Innovation: A dedicated lab was developed to scale up propagation using modern techniques, supported by the Government of Himachal Pradesh. Ecological niche modelling using GPS and climate data helped map ideal cultivation areas.
Myotis himalaicus

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A new bat species, the Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus), has been described based on fieldwork in Uttarakhand and historical specimens from Pakistan. Published in Zootaxa journal by a team of Indian and international scientists.
Key Findings of the Study
- Study Area: Western Himalayas – Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand (2017–2021).
- Total Bat Species Documented: 29, including new records and confirmations.
- Raises India's bat species count to 135.
About Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus)
Feature Description
Family/Genus Belongs to the Myotis frater complex
Habitat Deodar, pine, and cedar forests on southern Himalayan slopes
Distribution Found in Uttarakhand (India) and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan)
Size Medium-sized (~3.5 inches, <1 oz)
Morphology Delicate feet, long thumbs with short claws, short ears, fine teeth
Conservation Status Recently described; appears rare
Other Major Additions/Clarifications
- East Asian Free-Tailed Bat (Tadarida insignis):
- First confirmed record in India.
- Extends known range eastward by 2,500 km.
- Earlier misidentified as Tadarida teniotis.
- Babu’s Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus babu):
- Revalidated as a distinct species, not a synonym of Javan pipistrelle.
- Distribution: Pakistan, India, Nepal.
- First specimen-based confirmations in India for:
- Savi’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo savii)
- Japanese greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus nippon)
Ecological Importance of Bats
- Insect Control: Consume pests and mosquitoes.
- Pollination & Seed Dispersal: Important for forest regeneration.
- Fertilizer Contribution: Bat guano rich in Nitrogen & Phosphorous; boosts crop yield.
NASA's Mars Odyssey captures volcano piercing ice cloud belt
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
- Recently, NASA’s 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter captured a stunning image of Arsia Mons, a giant Martian volcano, rising through a morning belt of water-ice clouds.
- First such astronaut-like horizon view of Tharsis Montes volcanoes on Mars.
About Arsia Mons
- Part of Tharsis Montes, a trio of volcanoes near Mars' equator.
- Height: ~20 km (12 miles) – twice the height of Mauna Loa, Earth’s tallest volcano.
- Cloudiest of the Tharsis volcanoes.
- Cloud formation due to orographic uplift and cooling during Mars’ aphelion (farthest point from Sun).
- Featured in the aphelion cloud belt — a seasonal band of water-ice clouds.
Mission Evolution
- Mars Odyssey, launched in 2001, is the longest-operating Mars orbiter.
- In 2023, began a new imaging mode: rotating its THEMIS camera to capture horizon views of Mars’ upper atmosphere.
- These angled images help study seasonal changes in dust and water-ice cloud layers.
Scientific Significance
- Helps track Martian atmospheric evolution, especially cloud behavior and dust storms.
- Valuable for future human missions:
- Assists landing site safety planning.
- THEMIS also detects subsurface water ice, key for astronaut resource use.
Instruments and Collaborators
- THEMIS: Thermal Emission Imaging System, captures both visible and infrared light.
- Managed by NASA’s JPL, designed by Arizona State University, built by Lockheed Martin.
Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A study recently published in the journal Earth’s Future offered an innovative approach to SAI technique that could reduce its costs but also bring it closer to fruition despite the opposition to it.
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)?
- SAI is a proposed solar geoengineering technique to cool the Earth by injecting reflective aerosols (e.g. sulphur dioxide) into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce surface temperatures.
- Inspired by volcanic eruptions, like Mount Pinatubo (1991), which naturally cooled the Earth by emitting aerosols.
Recent Study Highlights (June 2025)
- Published in Earth’s Future journal.
- Led by Alistair Duffey, University College London.
- Used UK Earth System Model 1 (UKESM1) for climate simulations.
Key Findings
- Injecting 12 million tonnes of sulphur dioxide annually at 13 km altitude (spring/summer in each hemisphere) could cool the Earth by ~0.6°C.
- To cool by 1°C, ~21 million tonnes/year are needed at that altitude.
- Only 7.6 million tonnes/year are needed at higher altitudes (subtropics) for the same cooling.
Innovative Proposal
- Low-altitude SAI using modified existing aircraft (e.g. Boeing 777F) instead of specially designed high-altitude aircraft:
- Stratosphere is lower near poles (12–13 km), so current aircraft can reach it.
- Cost-effective and faster to deploy than high-altitude (~20 km) methods.
- Could begin within years, rather than a decade-long wait for new aircraft.
Risks and Concerns
- Tripling aerosol quantity (in low-altitude strategy) raises:
- Ozone depletion
- Acid rain
- Altered weather patterns
- Uneven global effects (benefits poles more, tropics less)
- Moral hazard: may reduce incentives to cut emissions.
- Governance challenge: One country’s action impacts all nations → risk of geopolitical conflict.
Why it matters
- Global GHG emissions are still rising.
- Climate mitigation through decarbonisation is slow and politically vulnerable.
- Technologies like SAI offer a stopgap, but not a substitute for emission cuts.
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
Current Global Progress
- As of May 2025, 56 countries have eliminated at least one NTD, aligned with WHO’s 2030 target (100 countries).
- Between Jan 2023 – May 2025, 17 countries were officially acknowledged by WHO for NTD elimination.
- World NTD Day: Observed annually on 30th January.
What Are NTDs?
- NTDs are a group of infectious diseases affecting over 1 billion people, mainly in tropical and poor regions.
- Caused by parasites, bacteria, viruses, fungi, or toxins.
- Common NTDs include:
- Lymphatic Filariasis (Elephantiasis)
- Onchocerciasis (River Blindness)
- Schistosomiasis
- Soil-transmitted helminths
- Trachoma, Dengue, Kala-azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
Impact of Official Development Assistance (ODA) Cuts
- Major donors like the US and UK have withdrawn NTD funding:
- USAID previously provided US$ 1.4 billion, supporting 3.3 billion treatments across 26 countries, helping 14 of them eliminate at least one NTD.
- UK ended its ‘Ascend’ NTD programme in 2021.
WHO Warning:
- On 10 April 2025, WHO cautioned that over 70% of country offices reported health service disruptions due to ODA cuts.
- NTD services have been disrupted at levels similar to peak COVID-19.
Climate Change & Emerging Threats
- Climate change is worsening the NTD burden:
- Dengue declared a Grade 3 Emergency in 2024:
- 14 million cases, 10,000 deaths across 107 countries.
- Geographical expansion of vector-borne NTDs continues.
- Dengue declared a Grade 3 Emergency in 2024:
Public-Private Partnerships
- Pharma companies have donated US$ 12 billion+ worth of drugs (2011–2025), including: GSK, Pfizer, Sanofi, Merck, Bayer, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, among others.
Recent Global Action
- At the 78th World Health Assembly (May 2025):
- Two NTD-related resolutions adopted:
- Eradication of Dracunculiasis (Guinea Worm)
- Control of Skin-related NTDs
- Two NTD-related resolutions adopted:
Way Forward
- Strengthen nationally owned, sustainable NTD programmes.
- Ensure alternative funding and service delivery mechanisms.
- Prevent reversal of hard-won gains and protect vulnerable communities from deeper health inequities.
Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
The Maharashtra Forest Department partnered with Microsoft and Pune-based CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities) to address the eco-restoration project in the Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary.
Location & Geography:
- Situated in the Western Ghats, about 70 km from Pune, Maharashtra.
- Notified as a Wildlife Sanctuary in January 2013.
- Spread over 49.62 sq. km, comprising:
- 12 forest compartments from Paund and Sinhgad ranges (Pune forest division).
- 8 compartments from Mangaon range (Roha division, Thane).
Vegetation Types:
- Dominated by evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests.
- Rich floral diversity including teak, bamboo, Ain, Shisham, mango, and jamun.
Biodiversity Highlights:
- Mammals (28 species):
- Includes the Indian Giant Squirrel (Shekaru) – state animal of Maharashtra.
- Also hosts Indian pangolin, barking deer, Indian civet, and wild boar.
- Home to the Kondana Soft-furred Rat (Millardia kondana) – an endangered species.
- Birds (150 species):
- Notable species: Malabar whistling thrush, golden oriole, crested serpent eagle, Indian pitta, grey junglefowl.
- Includes 12 species endemic to India.
- Insects & Others:
- 72 species of butterflies, 18 reptile species, and 33 invertebrate species.
Ecological Importance:
- Part of the Western Ghats, a globally recognized biodiversity hotspot.
- Habitat for rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- Supports vital ecosystem services, aiding in climate regulation, water conservation, and pollination.
Recent Conservation Initiative:
- A collaborative eco-restoration project was launched by the Maharashtra Forest Department, Microsoft, and CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities), Pune.
- Aim: Address socio-ecological challenges, promote community engagement, and leverage technology in conservation.
Eco-tourism Potential:
- Features popular trekking and nature spots like Andharban forest, Plus Valley, and Devkund.
- Attracts high tourist footfall, especially during monsoon, including bird watchers and nature enthusiasts.
Raja Bhabhut Singh Honoured
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
In June 2025, the Madhya Pradesh Government held a special Cabinet meeting at Pachmarhi, renaming the Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary after Raja Bhabhut Singh, a lesser-known but formidable tribal freedom fighter of the 1857 revolt.
About Raja Bhabhut Singh
- Lineage: Belonged to the Jagirdar family of Harrakot Raikheri, descended from Thakur Ajit Singh. His grandfather, Thakur Mohan Singh, had allied with Peshwa Appa Saheb Bhonsle of Nagpur during the 1819–20 resistance against the British.
- Role in 1857 Revolt:
- A key Gond tribal leader with control over Jabalpur and the Satpura hills.
- Employed guerrilla warfare tactics in the Satpura forests, using deep geographical knowledge to harass British forces.
- Maintained close ties with Tatya Tope, a prominent national leader.
- Martyrdom:
- British deployed the Madras Infantry to capture him.
- He was executed in 1860, and is remembered in Korku tribal folklore.
- Known as the "Shivaji of Narmadachal" for his resistance strategies.
Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary (Now Raja Bhabhut Singh Sanctuary)
- Located in the Satpura mountain range, central Madhya Pradesh, within the Deccan Peninsula biogeographic zone.
- Highest point: Dhoopgarh (1,352 m).
- Forms part of the Satpura Tiger Reserve, along with:
- Satpura National Park
- Bori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Key Biodiversity Zone in Central India.
Korku Tribe Overview
- Region: Mainly in Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Melghat (Maharashtra).
- Occupation: Traditionally agriculturalists; introduced potato and coffee cultivation.
- Society: Patrilineal communities led by traditional headmen.
- Culture:
- Practice ancestral worship through memorial stones called Munda.
- Rich in oral traditions, which preserve the memory of tribal icons like Raja Bhabhut Singh.
Starlink receives DoT licence to launch Satellite Internet in India

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has granted a licence to Elon Musk’s Starlink to provide satellite-based internet services in India.
- Starlink becomes the third company, after Eutelsat OneWeb and Jio Satellite Communications, to receive such approval. A fourth contender, Amazon’s Kuiper, is still awaiting clearance.
What is Starlink?
- Developer: Starlink is a satellite internet system by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
- Objective: Deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband globally, especially targeting rural and remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Technology:
- Operates a constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites (~550 km altitude).
- Satellites communicate via laser links for inter-satellite data relay, forming a global mesh.
- Ground stations transmit data to satellites, which then beam it to user terminals.
Key Features of Starlink
- Speed: Up to 150 Mbps, with future plans to increase it.
- Latency: As low as 20–25 milliseconds — ideal for video calls and streaming.
- Tech Stack:
- Flat-panel antennas for easy user access.
- Argon-powered ion thrusters for satellite positioning.
- Space lasers for fast inter-satellite communication.
- Deployment: Satellites launched via Falcon 9 rockets with regular updates.
- Scale: Plans to deploy up to 42,000 satellites globally.
Significance for India
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Ensures internet access in rural, remote, and disaster-prone regions.
- Reduced Infrastructure Dependency: Less reliance on fibre optics and mobile towers in hard-to-reach areas.
- Boost to Digital Economy: Enhances competition in India’s broadband sector, especially in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Security Compliance: Starlink must adhere to India’s security norms, including lawful interception requirements, before commercial rollout.
- Next Steps: Will receive trial spectrum within 15–20 days post-application.
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has recently ordered the Rajasthan government to impose an immediate ban on all mining activities within the core area of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, citing concerns over wildlife protection and habitat preservation.
About Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
- Location: Sawai Madhopur district, southeastern Rajasthan.
- Named After: Ranthambore Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, located within the reserve.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- North: Bounded by the Banas River
- South: Bounded by the Chambal River
- Terrain: High rocky plateaus, valleys, rivers, lakes, and historic ruins including forts and mosques.
- Total Area: ~1,411 sq.km, making it one of the largest tiger reserves in northern India.
- Surrounding Ranges: Located at the confluence of the Aravalli and Vindhya hill ranges.
Ecology and Biodiversity
Vegetation: Dominated by dry deciduous forests and open grassy meadows.
- Flora:
- Predominantly Dhok tree (Anogeissus pendula).
- Other species: Acacia, Capparis, Zizyphus, Prosopis, etc.
Water Bodies:
- Important lakes include:
- Padam Talab
- Raj Bagh Talab
- Malik Talab
Fauna:
- Apex predator: Royal Bengal Tiger
- Other mammals:
- Leopard, Caracal, Jungle Cat
- Sambar, Chital, Chinkara, Wild Boar
Historical Significance: Previously served as the royal hunting grounds of the Maharajas of Jaipur.
RBI Revises LTV Ratio for Gold-Backed Loans
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced revised guidelines to enhance formal sector lending and ease credit access for small-ticket gold loan borrowers, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- The new norms focus on raising the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio for gold-backed loans up to ?5 lakh and simplifying appraisal norms for such loans.
What is the Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
- Definition: The LTV ratio is the percentage of a collateral’s value that a lender offers as a loan.
- Formula:
LTV Ratio= (Loan Amount / Appraised Value of Asset) × 100
- A higher LTV indicates greater credit against the same asset but also entails higher risk for the lender.
- Assets like gold, with a stable value and liquid secondary market, are more "desirable" as collateral, often attracting higher LTVs.
Revised RBI Guidelines (June 2025): LTV Ratio for Gold Loans
Loan Amount Revised LTV Ratio Previous LTV (Draft April 2025)
Up to ?2.5 lakh 85% 75%
?2.5 lakh – ?5 lakh 80% 75%
Above ?5 lakh 75% 75%
- The interest component is included in the LTV calculation.
- The move reverses the uniform 75% LTV cap proposed in the April 2025 draft norms.
Additional Key Features
- No credit appraisal required for loans up to ?2.5 lakh.
- End-use monitoring is necessary only if the borrower wishes to qualify the loan under priority sector lending.
- The average ticket size of gold loans (~?1.2 lakh) is expected to increase due to relaxed norms.
- These loans are crucial for middle-class, lower middle-class, self-employed, and small businesses, often lacking formal income proof.
Rationale and Impact
- The revised norms aim to:
- Enhance credit accessibility.
- Prevent migration of borrowers to informal lenders.
- Boost financial inclusion and formalize rural credit ecosystems.
- Industry experts and NBFCs like Muthoot FinCorp and Shriram Finance have welcomed the move, noting it would benefit women, rural borrowers, and small traders.
- Shares of leading gold loan NBFCs like Muthoot Finance, Manappuram Finance, and IIFL Finance witnessed a sharp increase following the announcement.
Index Cards

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has recently upgraded the mechanism for generating Index Cards, making it more technology-driven and automated. Index Cards are a non-statutory, post-election statistical reporting format developed suo moto by the ECI to enhance transparency and accessibility of electoral data at the constituency level.
Purpose and Utility
Index Cards are designed to compile and disseminate election-related data for use by:
- Researchers
- Academia
- Journalists
- Policymakers
- The general public
Scope of Information
The Index Cards provide a wide range of data, including:
- Candidate-wise and party-wise vote share
- Electors and votes polled/counted
- Gender-based voting patterns
- Regional variations in voter turnout
- Performance of:
- National and State parties
- Registered Unrecognised Political Parties (RUPPs)
- Participation of women voters
- Winning candidates' analyses
- State/PC/AC-wise elector details and number of polling stations
Technological Upgrade
Earlier, data was manually filled into physical Index Cards at the constituency level using various statutory formats. These were later digitized for statistical reporting, resulting in delays and inefficiencies.
The 2025 upgrade has:
- Replaced the manual system with an automated, data-integrated mechanism
- Ensured faster and more reliable reporting
- Improved the timeliness of data dissemination
Nature of Data
- Index Cards are based on secondary data used exclusively for academic and research purposes.
- Primary and final electoral data is maintained in statutory forms by the respective Returning Officers.
INS Arnala
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission 'Arnala', the first warship under the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) series at the Naval Dockyard in Visakhapatnam. The commissioning will be presided over by Chief of Defence Staff, General Anil Chauhan.
About INS Arnala
- Type: First in the series of 16 Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW-SWC)
- Builder:
- Primary: Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata
- Partner: L&T Shipbuilders
- Delivery Date: May 8, 2025
- Indigenous Content: Over 80%
- Partners Involved:
- BEL, L&T, Mahindra Defence, MEIL
- 55+ MSMEs involved in the supply chain
Capabilities & Features
- Length: 77 meters
- Displacement: 1,490+ tonnes
- Propulsion: Diesel engine-waterjet system (a first for a warship of this size in India)
- Roles:
- Anti-submarine operations in coastal/shallow waters
- Subsurface surveillance
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Low-intensity maritime operations
Significance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Milestone: Highlights indigenous shipbuilding and defence manufacturing capabilities
- Boost to Coastal Defence: Enhances the Navy’s reach in shallow and strategic coastal zones
- Employment & Industrial Growth: Significant MSME and domestic defence industry involvement
Heritage & Symbolism
- Name Origin: Inspired by Arnala Fort, near Vasai, Maharashtra
- Built by the Marathas in 1737 under Chimaji Appa
- Historically guarded the Vaitarna River mouth and northern Konkan coast
- Design Symbolism:
- Armoured hull reflects the resilient walls of Arnala Fort
- Advanced sensors and weapons echo the fort’s cannons
- Crest:
- Stylised auger shell – precision, strength, vigilance
- Motto: Arnave Shauryam — “Valour in the Ocean”
Rediscovery of Losgna Genus in India

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
At a time when habitat loss and climate change threaten countless species, the discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp - named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
Location of Discovery
- Place: Chandigarh, Union Territory of India
- Habitat: Urban dry scrub forest
- Time: Winter of 2023–24
- Significance: First formal description of any insect species from Chandigarh
Species Description
- Name: Losgna occidentalis
- Genus: Losgna (Ichneumonidae family – Parasitic wasps)
- Group Role: Parasitic wasps known for laying eggs inside/on arthropod hosts
- Ecological Role: Pollinators and biological control agents (important in ecosystems)
Historical Context
- Losgna genus was last recorded in India in 1965, in Heinrich’s monograph
- No Indian records or specimens existed post-1965 in any institution
- Only known specimens (of other Losgna species) are preserved in:
- Natural History Museum, London
- The Hope Collection, Oxford University
- Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany
Naming Rationale
- "Occidentalis" (Latin for "Western")
- Signifies the westernmost known range of the genus
- Earlier Losgna records were only from:
- Northeast India
- Southeast Asia (tropical forests)
- Published in Zootaxa (peer-reviewed journal for animal taxonomy)
Importance & Implications
- Rediscovery highlights India’s hidden and threatened biodiversity
- Emphasizes the critical role of taxonomy in conservation
- Shows potential for citizen-led discoveries and backyard biodiversity
- Demonstrates the need for:
- Responsible specimen collection
- International scientific collaboration
- Support for underfunded taxonomy sectors
Discovery of 800-Year-Old Pandya-Era Shiva Temple

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
An 800-year-old Shiva temple of the later Pandya period has been unearthed at Udampatti, a village in Melur taluk, Madurai district, Tamil Nadu.
Key Highlights:
- Discovery: Foundation of a later Pandya period Shiva temple (dated to 1217–1218 CE) unearthed accidentally by children.
Architectural Insights:
- Only the stone base of the temple (north and south sides) survives.
- Identified as a Shaivite temple using foundation engravings and reference to Silpa Sastram.
Inscriptions & Historical Significance:
- Inscriptions deciphered by C. Santhalingam (Pandya Nadu Centre for Historical Research).
- Temple identified as Thennavanisvaram, located in ancient Attur (present-day Udampatti).
- “Thennavan” was a Pandya royal title, suggesting direct patronage.
Key Inscriptions (1217–18 CE):
- A sale deed records the transfer of a waterbody named Nagankudi along with wet/dry land.
- Seller: Alagaperumal, chieftain of Kalavalinadu
- Buyer: Nambi Perambala Kuthan alias Kangeyan
- Sale amount: 64 kasu (coins)
- Tax revenue from the land assigned to the temple for daily expenses, indicating its financial independence.
Archaeological Relevance:
- Confirms ancient village name (Attur), showcasing socio-economic practices during the Later Pandya period.
- Highlights temple economy, land-water rights, and administrative structures.
Pandya Dynasty
- One of the Three Crowned Tamil Dynasties (alongside Cholas and Cheras).
- Capital: Initially Korkai, later Madurai.
- Early Pandyas active since 4th century BCE; Later Pandyas (1216–1345 CE) saw a golden age under Maravarman Sundara Pandyan.
- Controlled parts of Sri Lanka, Telugu regions, and had trade links with Rome & Southeast Asia.
- Symbol: Fish
Cultural Contributions:
- Patronage of Sangam literature, Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Jainism.
- Temples: Meenakshi Temple (Madurai), Nellaiappar Temple (Tirunelveli).
- Promoted Tamil arts, Bharatanatyam, and education.
Decline:
- Succumbed to Chola, Hoysala conflicts and Delhi Sultanate invasions.
- Madurai Sultanate (1335) and later Madurai Nayak dynasty (1529) succeeded their rule.
National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA)

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Minister of State Dr. L. Murugan will inaugurate the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) for the Puducherry Legislative Assembly.
What is NeVA?
- Full Form: National e-Vidhan Application
- Launched by: Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA)
- Aim: Make legislative functioning paperless across all 37 State/UT legislatures under the idea of “One Nation – One Application.”
Key Features:
- Unified digital platform for legislative work
- Enables real-time document access, online notices, and session management
- Integrates AI/ML-based real-time translation (via partnership with BHASHINI, MeitY)
- Promotes transparency, efficiency, and environmental sustainability
Funding & Implementation:
- Approved by: Public Investment Board (PIB) on 15 January 2020
- Budget: ?673.94 crore
- Model: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
Significance:
- Digital transformation of legislative processes
- Creation of a central data repository
- Enhanced inter-legislature connectivity
- Boosts Digital India and Good Governance goals
4th India–Central Asia Dialogue (2024)
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
India hosted the 4th edition of the India–Central Asia Dialogue in New Delhi, chaired by External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar. The event emphasized regional security, connectivity, critical minerals, counter-terrorism, and economic integration.
What is the India–Central Asia Dialogue?
- Type: Multilateral forum for structured engagement between India and Central Asian republics.
- Initiated in: 2019, Samarkand (Uzbekistan).
- Participants: India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
Key Objectives:
- Strengthen cooperation in trade, connectivity, security, energy, health, and technology.
- Promote regional stability, counter-terrorism collaboration, and sustainable development.
- Enhance people-to-people ties and institutional coordination.
Major Outcomes of the 4th Dialogue:
- Security Cooperation:
- Condemned terror attacks (e.g., Pahalgam).
- Called for early adoption of the UN Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism.
- Critical Minerals & Rare Earths:
- Joint intent for collaboration in exploration and investment.
- Decision to hold the 2nd India–Central Asia Rare Earth Forum soon.
- Connectivity & Trade:
- Focus on using the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and Chabahar Port.
- Supported Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan's inclusion in INSTC.
- Digital & Financial Integration: Agreement to boost digital payments, interbank ties, and trade in local currencies.
- Health and Traditional Medicine: Shared commitment to Universal Health Coverage, medical tourism, and integration of AYUSH systems.
- Clean Energy & Technology: Cooperation on platforms like India Stack, International Solar Alliance, and biofuels.
- Multilateral Support: Reiterated support for India’s permanent seat in UNSC and active role in SCO and UN.
IISc Develops Nanozyme to Prevent Excessive Blood Clotting

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru have developed a novel vanadium-based nanozyme that effectively controls abnormal blood clotting by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). This innovation holds promise for managing life-threatening conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and ischemic stroke.
Scientific Background:
- Normal Blood Clotting: Platelets are specialized blood cells that form clots at injury sites through a process called haemostasis, involving activation by physiological chemicals like collagen and thrombin.
- Problem of Abnormal Clotting: In conditions like COVID-19 and PTE, oxidative stress increases, leading to elevated ROS levels. This causes hyperactivation of platelets, resulting in excessive clot formation (thrombosis) — a leading cause of death globally.
Nanozyme Innovation by IISc:
- What is a Nanozyme?
An engineered nanomaterial that mimics the action of natural enzymes, in this case, glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes ROS.
- Material Used: Vanadium pentoxide (V?O?) nanozymes, particularly those with spherical morphology, were found to be the most efficient.
- Mechanism: The redox-active surface of vanadium nanozymes catalytically reduces ROS, preventing unwanted platelet aggregation.
Testing and Results:
- In vitro testing: Human blood platelets were activated with physiological agonists. Nanozymes were tested for their ability to curb excessive aggregation.
- In vivo testing (mouse model of PTE):
- Nanozyme injection led to reduced thrombosis.
- Improved survival rates without observable toxicity.
- Animals were monitored for 5 days post-treatment for health parameters.
Future Prospects:
- Researchers aim to test the nanozyme's potential against ischemic strokes, which also result from vascular blockages.
- Encouraging results with human platelets indicate the possibility of clinical trials in the near future.
Kerch Strait and Recent Developments
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Ukraine has claimed responsibility for a recent underwater explosion that damaged the Kerch Bridge, a critical transport link connecting mainland Russia to occupied Crimea. The attack underscores the strategic importance of the Kerch Strait in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Kerch Strait: Geographical and Strategic Overview
- Location: The Kerch Strait forms the only maritime passage between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- West: Kerch Peninsula (Crimea)
- East: Taman Peninsula (Russia)
- Width: Narrows to 3–5 km at its tightest point near the Chushka Spit.
- Nearby City: Kerch, located on the Crimean side, lies near the strait’s midsection.
- Strategic Importance:
- A vital shipping lane for transporting goods and military supplies.
- Gained heightened geopolitical importance after Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014.
- Frequently features in Russia–Ukraine maritime tensions.
Kerch Strait Bridge (Crimean Bridge)
- Length: 19 km, making it the longest bridge in Europe.
- Completed: In 2018
- Connectivity: Includes dual road and railway tracks, linking the Russian mainland to Crimea.
- Symbolism: Considered a symbol of Russia’s control over Crimea post-2014 annexation.
- Strategic Use: Facilitates military logistics and civilian transit; crucial for sustaining Russian presence in Crimea.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Western Europe – 2022 Onwards
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Western Europe is experiencing its largest diphtheria outbreak in 70 years, with cases predominantly among vulnerable groups such as migrants and the homeless. The outbreak, which began in 2022, has raised concerns over disease surveillance, migrant healthcare, and immunisation coverage.
Key Facts from the Outbreak
- As per a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, 536 cases and three deaths have been reported across Europe since 2022.
- Most cases were found among young males (average age: 18) who had recently migrated, particularly from Afghanistan and Syria.
- 98% of strains exhibited close genetic similarities, suggesting a common transmission point during migration journeys or in accommodation facilities, not in the countries of origin.
- A genetic match between the 2022 strains and a recent 2025 case in Germany indicates that the bacteria is still circulating silently in the region.
Recommendations from Health Experts
- Enhance vaccination drives, particularly among high-risk and underserved populations.
- Improve awareness among healthcare providers, especially those working with migrants and the homeless.
- Ensure better access to antibiotics and diphtheria antitoxins.
- Strengthen disease surveillance and contact tracing mechanisms.
About Diphtheria
Feature Details
Cause Corynebacterium diphtheriae (produces a potent toxin)
Mode of Spread Respiratory droplets, contact with infected sores or ulcers
Affected Areas Primarily the respiratory tract, but also the skin in some cases
Symptoms Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weakness; grey membrane in throat
Severe Impact Can lead to breathing difficulties, heart and kidney damage, and neurological issues if untreated
Treatment Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT), antibiotics, and supportive care
Fatality Rate Up to 30% in unvaccinated individuals; higher in children
Prevention Vaccination (DPT/DTP) is the most effective preventive measure
Greater Flamingo Sanctuary

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
On the occasion of World Environment Day 2025, the Tamil Nadu government officially declared the Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi, Ramanathapuram district, aiming to protect a vital stopover site for migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Key Highlights
What is it?
A newly notified wildlife sanctuary dedicated to safeguarding migratory wetland birds, especially the greater flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus), in their natural resting and breeding habitat.
Location and Area:
- Located in Rameshwaram taluk, Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Covers approximately 524.7 hectares of revenue and forest land.
- Lies within the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, a globally recognized marine ecosystem.
Ecological Significance
- Functions as a critical site along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the key migratory bird routes.
- As per the 2023–24 Wetland Bird Survey, the region hosts 10,700+ wetland birds representing 128 species, including:
- Flamingos (greater and lesser)
- Herons, egrets, sandpipers, etc.
- The sanctuary harbours diverse ecosystems, such as:
- Mangroves (Avicennia, Rhizophora)
- Mudflats, marshes, sand dunes, and lagoons
- Nesting grounds for sea turtles and marine biodiversity
Conservation and Socioeconomic Benefits
- Strengthens coastal resilience by preventing erosion through natural mangrove buffers.
- Promotes responsible ecotourism, raising awareness of wetland and avian conservation.
- Supports local livelihoods via employment in conservation and tourism activities.
About the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus)
Attribute Details
Size 90–150 cm tall, long necks and legs
Coloration Pink hue from carotenoid-rich diet
Feeding Uses specialized downward-curved bill for filter feeding in shallow waters
Reproduction Builds cone-shaped mud nests, lays 1–2 eggs, both parents incubate
Chick Rearing Chicks are white and fed through regurgitation
Social Traits Highly gregarious, breeds in large colonies and flies in V-formations
Behavioral Note Often seen standing on one leg, possibly to conserve body heat
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for the issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities. This includes instruments such as social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, aiming to boost responsible financing in India.
Understanding ESG Debt Securities
Definition:
ESG debt securities are financial tools designed to raise capital specifically for projects that yield positive environmental, social, or governance (ESG) outcomes. These instruments are a key part of sustainable finance, with categories including:
- Social Bonds: Focused on projects with direct social impact (e.g., affordable housing, education).
- Sustainability Bonds: Target projects with both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Tied to specific ESG performance indicators or targets.
Salient Features:
- Funds raised must be used exclusively for eligible ESG-aligned projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled in line with the project's primary focus.
- Compliance with global ESG norms and standards is mandatory.
- Verification or certification by an independent third-party is required.
- The framework applies to both public and private debt offerings.
Highlights of SEBI’s Framework
1. Classification Guidelines: Issuers are required to categorize their bonds—green, social, or sustainability—based on the core objective of the projects being financed. This ensures transparent communication of the bond's intended impact.
2. Disclosure Norms:
- At the Issuance Stage: Offer documents must detail project eligibility, selection methodology, and a tentative allocation between financing new initiatives and refinancing existing ones.
- Post-Issuance: Issuers must provide annual updates on fund deployment and report impact metrics to demonstrate accountability and transparency.
3. Independent Assurance: Issuers must engage accredited third-party entities to validate the alignment of bonds with ESG principles, thereby enhancing investor confidence and market integrity.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: There is an obligation for ongoing impact assessment. Issuers must ensure the projects funded effectively contribute to reducing environmental degradation or addressing social challenges.
5. Scope and Enforcement: The framework will come into effect from June 5, 2025, and is aligned with international ESG standards to facilitate greater inflow of sustainable and ethical investments.
Significance for India: This move marks a significant step in mainstreaming ESG finance in India. It aims to improve transparency, attract climate-conscious capital, and reinforce India’s commitment to sustainable development.
Waste Picker Enumeration App

- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
On World Environment Day 2025, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) launched the Waste Picker Enumeration App under the NAMASTE Scheme, reaffirming the government’s commitment to environmental justice and the dignity of sanitation workers.
What is the NAMASTE Scheme?
- Full Form: National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem
- Type: Central Sector Scheme (CSS)
- Launched: July 2023
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE)
- Partner Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
- Implementing Agency: National Safai Karamcharis Finance & Development Corporation (NSKFDC)
- Objective: To formalize and rehabilitate sanitation workers and integrate them into formal systems through skilling, social security, and mechanization of hazardous cleaning work.
- Inclusion of Waste Pickers (From June 2024): The NAMASTE Scheme expanded its scope in June 2024 to include Waste Pickers, recognizing their critical role in the circular economy and solid waste management.
Waste Picker Enumeration App – Key Highlights
- Purpose: Digital platform for profiling 2.5 lakh waste pickers across India.
- Recognition: Provides occupational photo ID cards and formal identity to waste pickers.
- Social Security:
- Health coverage under Ayushman Bharat–PM-JAY
- Distribution of PPE kits and seasonal safety gear
- Livelihood & Skilling:
- Skill development programs
- Capital subsidies for waste collection vehicles
- Empowerment:
- Strengthening of Waste Picker Collectives
- Management of 750 Dry Waste Collection Centres (DWCCs) in urban areas
Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL)
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
The Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) is a transformative 272-km railway project aimed at connecting the Kashmir Valley to the Indian Railways network. With Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurating the Chenab Rail Bridge and flagging off Vande Bharat trains in June 2025, the project nears full operationalization.
Key Details:
Chenab Rail Bridge – World’s Highest Railway Arch Bridge
- Height: 359 metres above riverbed (taller than the Eiffel Tower).
- Length: 1,315 metres; Arch span: 467 metres.
- Status: Highest railway arch bridge in the world.
- Engineering feat in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir.
Strategic All-Weather Connectivity
- Reduces dependency on the Srinagar-Jammu highway, which is prone to closure due to snow and landslides.
- Ensures year-round transportation and supply lines.
Enhanced Military Mobility
- Enables rapid movement of troops and equipment to border regions.
- Crucial for national security due to the region's proximity to international borders.
- Designed to withstand blasts and harsh weather.
Anji Bridge – India’s First Cable-Stayed Rail Bridge
- Length: 473 metres; Height: 331 metres.
- Located on the Katra-Banihal section.
- Supported by 48 cables, suitable for rugged Himalayan terrain.
Vande Bharat Connectivity
- High-speed trains introduced on Katra–Srinagar route.
- Improves passenger comfort and reduces travel time.
Economic Boost via Trade
- Improves market access for Kashmiri products: apples, saffron, handicrafts, and dry fruits.
- Facilitates faster freight movement, integrating the region into national trade networks.
Tourism Promotion
- Easier access to religious and scenic sites.
- Expected to boost tourism post disruptions (e.g., Pahalgam incident).
- Cheaper and faster rail travel enhances domestic footfall.
Engineering Resilience
- Chenab Bridge:
- Blast-resistant (withstands up to 40 kg TNT).
- Wind resistant (up to 260 kmph).
- Seismic-resilient with a 120-year design life.
- Symbol of India’s capability in building infrastructure in high-risk zones.
Time Efficiency
- Travel time between Jammu and Srinagar will reduce from 6 hours (by road) to 3–3.5 hours (by rail).
- Facilitates emergency services, logistics, and routine travel.
National Integration and Inclusion
- 943 bridges, 36 tunnels covering 119 km — overcoming Himalayan terrain challenges.
- Integrates remote districts of Jammu & Kashmir into India's railway grid.
- Promotes inclusive development and better governance outreach.
Ayush Nivesh Saarthi
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Government of India launched the ‘Ayush Nivesh Saarthi’ portal—a digital initiative aimed at positioning India as a global hub for traditional medicine investment. The launch took place during the Ayush Stakeholder/Industry Interaction Meet held at Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
- Developed by: Ministry of Ayush in collaboration with Invest India
Objective of the Portal
- To facilitate investment in India’s Ayush sector through a dedicated digital interface.
- To bring together policy frameworks, incentives, investment-ready projects, and real-time facilitation.
- To strengthen India’s position as a global investment destination for traditional systems of medicine.
Portal Features
- Investor-centric platform integrating:
- Investment promotion schemes
- Real-time data and policy information
- Single-window facilitation
- Supports both domestic and foreign investors
- Offers transparency, ease of access, and sectoral insights
Sectoral Significance
- Growth Rate: The Ayush sector recorded an annual growth rate of 17% (2014–2020).
- Medicinal Wealth: India is home to 8,000+ medicinal plant species.
- Global Recognition: Ayush is among the top five health services in India and contributes significantly to the USD 13 billion Medical Value Travel (MVT) sector.
Investment Facilitation
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is permitted in the Ayush sector through the automatic route.
- The portal aims to attract FDI and empower entrepreneurs through digital governance and investment transparency.
EnviStats India 2025
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India's annual mean temperature rise up from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024, Electricity generation from renewable sources increased more than three times in 10 years.
- Released by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) on June 5, 2025, on the occasion of World Environment Day
- Framework Used: UN's Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013)
Key Highlights:
Climate Trends
- Annual Mean Temperature rose from 25.05°C (2001) to 25.74°C (2024).
- 2024 recorded as India’s hottest year since 1901; also, globally the hottest year in 175 years.
- Annual Minimum and Maximum Temperatures (2021–24):
- Minimum: 19.32°C → 20.24°C
- Maximum: 30.78°C → 31.25°C
Rainfall Patterns
- Rainfall shows seasonal concentration between June–September, with signs of shifting patterns such as late onset or extended rains into October.
- No clear long-term trend, reflecting erratic monsoonal behaviour.
Energy Generation
Thermal & Renewable Power (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Thermal: 7.92 lakh GWh → 13.26 lakh GWh
- Renewable: 65,520 GWh → 2.25 lakh GWh, over 3x increase in renewable energy output in a decade.
Biodiversity and Faunal Statistics
Faunal Diversity
- Global Faunal Species: 16,73,627
- India's Share: 1,04,561 species
- Habitat-specific Species in India:
- Soil Ecosystem: 22,404
- Freshwater Ecosystem: 9,436
- Mangrove System: 5,023
- Estuarine Ecosystem: 3,383
- Marine Fauna (India): 20,613 out of global 2,47,605
Fisheries Production
Inland vs. Marine Fish (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Inland Fish Production: 61 lakh tonnes → 139 lakh tonnes
- Marine Fish Production: 34 lakh tonnes → 45 lakh tonnes
Public Expenditure (2021–22)
- Environment Sustainability Sector: ?2,433 crore (highest among sectors)
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Increasing trend
- Agro-Forestry: Lowest allocation
New Data indicators introduced
- Ramsar sites
- Access to sanitation
- Transport infrastructure
- Electricity access
Bar Council of India permits Foreign Lawyers in India

- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
Chief Justice of India (CJI) B.R. Gavai lauded the Bar Council of India (BCI) for amending rules to allow foreign legal professionals and law firms to advise on non-litigious matters in India.
Key Features of BCI’s Reform (2024 Update to 2022 Rules):
- Scope of Practice for Foreign Lawyers:
- Permitted: Advisory roles in foreign law, international law, and arbitration.
- Prohibited: Appearing in Indian courts/tribunals or advising on Indian law.
- Nature of Work Allowed: Only non-litigious activities.
Rationale Behind the Reform:
- Boosting Arbitration Quality:
- India ranks 5th globally in arbitration case volume (ICC 2024 Report).
- Reform aimed at enhancing arbitration standards via foreign expertise.
- Facilitating Legal Reciprocity:
- Enables Indian lawyers to access international legal markets.
- Promotes mutual recognition and cooperation with foreign bar associations.
- Supporting Institutional Arbitration:
- Benefits centres like:
- Mumbai Centre for International Arbitration (MCIA)
- Delhi International Arbitration Centre (DIAC)
- India International Arbitration Centre (IIAC)
- Benefits centres like:
- Filling Talent Gaps:
- Expertise needed in fields such as:
- Climate litigation
- Technology and data law
- Cross-border commercial arbitration
- Expertise needed in fields such as:
Challenges and Concerns:
- Market Displacement Fears: Indian lawyers worry about reduced share in arbitration and consultancy services.
- Reciprocity Barriers: Unequal treatment in countries with restrictive legal entry norms.
- Uneven Playing Field: Foreign firms possess larger capital, advanced tech, and international clientele.
- Regulatory Oversight Needed: BCI must ensure strict compliance to maintain sovereignty of Indian legal framework.
Significance of the Reform:
- Positioning India as an Arbitration Hub: Enhances India's global legal profile, especially in infrastructure and trade.
- Strengthening Indo-UK Legal Cooperation: Reform highlighted during Indo-UK Arbitration Conference, deepening bilateral ties.
- Modernizing Legal Sector: Brings global legal best practices and innovation to India.
- Upholding Indian Legal Integrity: Complies with the Advocates Act, 1961 – no foreign practice in Indian law.
- Opportunities for Indian Lawyers Abroad: Reciprocity clause allows dual practice in India and foreign jurisdictions.
C CARES Version 2.0
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Coal recently launched C CARES Version 2.0, a significant upgrade to the Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization’s (CMPFO) digital platform. The new system aims to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accessibility in provident fund (PF) and pension disbursement for coal sector workers.
Key Features of C CARES Version 2.0
- Developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in collaboration with the State Bank of India (SBI).
- Provides a unified digital interface for coal workers, coal companies, and CMPFO.
- Enables real-time claim tracking, automated ledger updates, and direct benefit transfers to workers’ bank accounts.
- Includes a mobile application for CMPF members, offering:
- PF balance checks
- Profile viewing
- Grievance redressal
- Claim status tracking
- A chatbot assistant for easy navigation
Benefits to Stakeholders
- For Workers: Faster claim settlement, improved access, and reduced delays in PF/pension disbursement.
- For Coal Companies and CMPFO:
- A prescriptive dashboard to generate custom reports.
- Analytics to track settlement trends.
- Support for data-driven decision-making.
About CMPFO
- Full Form: Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization
- Established: 1948
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Coal
- Function: Administration of PF and pension schemes for coal sector employees.
- Coverage:
- Serves around 3.3 lakh PF subscribers
- Supports over 6.3 lakh pensioners
Significance
Union Minister for Coal and Mines G. Kishan Reddy launched the portal on June 4, 2025, stating that it aligns with the Government's vision of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance” under the Digital India initiative. The platform strengthens social security delivery for coal workers and brings administrative reform to a critical sector of the economy.
International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS)

- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
India has secured the Presidency of the International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS) for the term 2025–2028, marking a historic first for the country since becoming a member in 1998. The victory affirms India’s growing influence in the field of global public administration.
About IIAS
- Established: 1930
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium
- Nature: A global federation of 31 Member States, 20 National Sections, and 15 Academic Research Centres, dedicated to collaborative scientific research in public administration.
- Core Objectives:
- Promote collaboration on public governance solutions.
- Accredit academic and professional training programs in public management.
- Disseminate research and best practices in administrative sciences.
Although not formally affiliated with the United Nations, IIAS actively participates in UN mechanisms like the Committee of Experts on Public Administration (CEPA) and the UN Public Administration Network (UNPAN).
India’s Role and Election to Presidency
- India has been a Member State of IIAS since 1998, represented by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- For the 2025–2028 term, Prime Minister Narendra Modi nominated V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG, as India's candidate in November 2024.
- Election Process:
- Hearings were held at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi in February 2025.
- Four countries—India, South Africa, Austria, and Bahrain—submitted nominations.
- The final vote on June 3, 2025, saw India and Austria advance to the final round.
- Out of 141 votes, India secured 87 votes (61.7%), while Austria received 54 votes (38.3%).
Significance for India
- This marks India’s first Presidency of IIAS.
- The victory enhances India's position in global governance and showcases its administrative capabilities on an international platform.
- It also aligns with India’s focus on reforming and modernizing public administration through digital governance and institutional capacity-building.
Kichan and Menar Wetlands
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministry of Environment announced that Kichan (Phalodi) and Menar (Udaipur) wetlands in Rajasthan have been recognized as Ramsar Sites, bringing India’s total to 91 Ramsar-designated wetlands—the highest in Asia.
About Menar Wetland:
- A freshwater monsoon wetland complex in Udaipur district, Rajasthan.
- Formed by three primary ponds: Braham Talab, Dhand Talab, and Kheroda Talab; the latter two are connected by flooded agricultural land during the monsoon.
- Habitat for endangered and migratory birds such as:
- Critically Endangered: White-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis), Long-billed vulture (Gyps indicus)
- Other species: Himalayan griffon, Egyptian vulture, Dalmatian pelican, Ferruginous pochard, Black-tailed godwit
- Home to over 70 plant species, including mango trees (Mangifera indica) that host colonies of Indian flying foxes (Pteropus giganteus).
- Community-led conservation: Menar village residents prevent poaching and fishing, earning it the title "Bird Village".
About Kichan Wetland:
- Located in Phalodi, Jodhpur, in the northern Thar Desert of Rajasthan.
- Comprises:
- Ratri Nadi (river)
- Vijaysagar Talab (pond)
- Riparian and scrub habitats
- Notable for supporting drought-resistant flora and over 150 bird species.
- Globally known for hosting over 22,000 migratory demoiselle cranes (Anthropoides virgo) each winter.
- A hub for birdwatchers, tourists, scientists, and students.
Ramsar Convention Overview:
- An intergovernmental treaty for the conservation of wetlands, signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
- Headquartered in Gland, Switzerland.
- Wetlands listed under the convention are known as Ramsar Sites—of international importance.
- Member countries (Contracting Parties) commit to identifying and protecting these wetlands.
World Wealth Report 2025
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Wealth Report 2025, released by the Capgemini Research Institute, highlights a significant surge in global and Indian high-net-worth individual (HNWI) wealth. The report covers 71 countries, representing over 98% of global Gross National Income (GNI) and 99% of world stock market capitalization.
India’s HNWI Landscape in 2024
- HNWI Wealth Growth: India witnessed an 8.8% increase in HNWI wealth in 2024.
- Total Millionaires: The country had 378,810 HNWIs by the end of 2024, with a cumulative wealth of $1.5 trillion.
- Millionaires Next Door: Among them, 333,340 individuals fell under the "Millionaires Next Door" category (investable assets between $1M–$5M), holding $628.93 billion in wealth.
- Ultra HNWIs: India was home to 4,290 Ultra-HNWIs (assets ≥ $30M), with combined assets worth $534.77 billion.
Global Trends in HNWI Wealth
- Global Growth: HNWI population worldwide rose by 2.6%, driven largely by a 6.2% rise in Ultra-HNWI numbers.
- Investment Trends: Alternative investments (private equity, cryptocurrencies) formed 15% of HNWI portfolios, signaling diversification beyond traditional assets.
- Top Contributors:
- United States added 562,000 millionaires, recording a 7.6% rise, reaching a total of 7.9 million HNWIs.
- The U.S. also holds 36% of centi-millionaires (net worth ≥ $100M) and 33% of the world's billionaires.
- India and Japan saw 5.6% growth, while China recorded a 1.0% decline in HNWI population.
Shifting Dynamics in Wealth Management
- A massive “great wealth transfer” is underway globally.
- 81% of global next-gen HNWIs and 85% of Indian next-gen HNWIs plan to switch wealth management (WM) firms within 1–2 years of inheritance.
- Key reasons include:
- Lack of preferred channel services (51%)
- Ineffective digital transaction tools (41%)
- Digital Transformation Need: The evolving expectations of next-gen clients are pushing firms toward AI-enabled advisory models and advanced digital infrastructure.
Offshore Wealth Allocation
- By 2030, 98% of Indian next-gen HNWIs plan to increase their offshore assets by over 10%.
- Motivations include:
- Superior investment options (55%)
- Better wealth management services (65%)
- Improved market connectivity (54%)
- Tax efficiency and political-economic stability (49%)
- Motivations include:
World Environment Day 2025
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Every year on June 5, people across the globe unite to celebrate World Environment Day, an initiative led by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
Key Highlights:
- Observed on: June 5 annually
- Initiated by: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- First celebrated: 1973 (following the 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment)
- Objective: Promote global awareness and action for environmental protection
Theme for 2025: "Beat Plastic Pollution"
- Focuses on the escalating crisis of plastic pollution and its adverse impact on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
- Highlights the need to transition away from single-use plastics, promote sustainable consumption, and adopt eco-friendly alternatives.
Key Statistics:
- Plastic production: Increased from 2 million tonnes (1950) to 430 million tonnes (2025)
- Marine pollution:19–23 million tonnes of plastic enter aquatic ecosystems annually
- Microplastics detected in oceans, mountains, and the human body
Host Country for 2025: Republic of Korea
- Chosen for its leadership in green innovation and sustainable practices.
- Initiatives include:
- Advanced waste segregation and recycling systems
- Bans on single-use plastics in major outlets
- Promotion of tech-driven eco-solutions
By hosting, South Korea aims to showcase scalable models for combating plastic pollution globally.
Historical Background
- Stockholm Conference 1972 laid the foundation for modern environmental governance.
- UNEP assigns a theme and host country annually to align global action.
- Over 150 countries now participate through:
- Clean-up drives
- Tree plantation campaigns
- Policy forums
- Environmental education programs
Significance
World Environment Day plays a vital role in:
- Raising awareness on climate change, pollution, deforestation, and sustainability
- Encouraging individual and community-level action
- Facilitating policy dialogue and regulatory reform
- Mobilizing youth leadership in environmental movements
UMEED Portal and Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
The Government of India will launch the UMEED Portal to digitize and streamline the registration and management of Waqf properties under the Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025.
What is the UMEED Portal?
- Full Form: Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency, and Development
- Purpose: A centralized digital platform to register, regulate, and monitor Waqf properties nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Minority Affairs, in collaboration with State Waqf Boards and judicial authorities.
Objectives:
- Ensure transparent, efficient, and time-bound registration of Waqf assets.
- Digitally empower stakeholders with access to legal rights, obligations, and procedural information.
- Resolve long-pending disputes and enhance accountability in Waqf administration.
- Provide real-time data, including geo-tagged property mapping, to support policymaking.
Key Features:
- Time-Bound Registration:All Waqf properties must be registered within six months of the portal's launch.
- Geo-Tagging and Digital Mapping:Properties must be geo-tagged and include precise dimensions for registration.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism:Properties not registered by the deadline will be automatically flagged as disputed and referred to Waqf Tribunals for adjudication.
- Legal Support Services:The portal offers awareness tools regarding the amended Act and clarifies legal entitlements.
- Women-Centric Provision:Properties solely in women’s names cannot be declared as Waqf. However, women, children, and the economically weaker sections (EWS) remain eligible beneficiaries.
About Waqf and Recent Legal Reforms:
- What is Waqf?
A Waqf is a permanent charitable endowment under Islamic law, where assets (usually land) are donated for religious or public welfare purposes. Such property is inalienable and cannot be sold, inherited, or transferred.
- Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025:
- Digital Mandate: Mandatory online registration of all Waqf properties within 6 months.
- Judicial Oversight:Introduced provision for appealing Waqf Tribunal decisions in the High Court within 90 days.
- Tribunal Empowerment:Unregistered properties after the deadline will be treated as disputed and decided by Waqf Tribunals.
- Government Monitoring:Enhanced role of State Waqf Boards in ensuring compliance, registration, and dispute handling.
Significance:
- Aims to reduce litigation, encroachments, and opacity in Waqf land management.
- Bridges the gap between community welfare and digital governance.
- Strengthens institutional mechanisms for protecting religious endowments and improves access to justice.
Seva Se Seekhen Campaign
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the ‘Seva Se Seekhen’ (Learn by Doing) campaign to empower youth through hands-on experience at Jan AushadhiKendras (JAKs). Starting from June 1, 2025, this initiative aims to blend experiential learning with public health outreach.
About the Campaign:
- Launched in: 2025
- Nodal Ministries:
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
- Framework:Part of the National Youth Development Framework, aligning youth engagement with grassroots service.
Objectives:
- Provide experiential learning opportunities in real-world public service settings.
- Raise awareness about generic medicines and enhance health literacy.
- Equip youth with technical and soft skills in areas such as inventory, logistics, customer service, and communication.
- Foster values such as discipline, empathy, and civic responsibility among the youth.
Key Features:
- Nationwide Implementation:
- Five youth volunteers per district will be placed across five Jan AushadhiKendras.
- Covers all states and Union Territories.
- Volunteer Sources:Participants are selected from:
- MY Bharat
- National Service Scheme (NSS)
- Pharmacy colleges
- Other youth-focused platforms
- Duration:15-day structured engagement, including guided tasks and learning outcomes.
Roles and Responsibilities of Volunteers:
- Support daily functioning and customer services at JAKs.
- Assist in medicine inventory and logistics management.
- Promote generic medicine awareness among the public.
- Participate in community health outreach activities.
- Observe backend processes like supply chains and stock maintenance.
Key Benefits for Youth:
- Practical exposure to pharmacy operations and public health service.
- Skills in record-keeping, inventory handling, and basic operations.
- Development of employability and customer interaction skills.
- Insights into affordable healthcare delivery under schemes like Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya JanaushadhiPariyojana (PMBJP).
Operation Spider’s Web
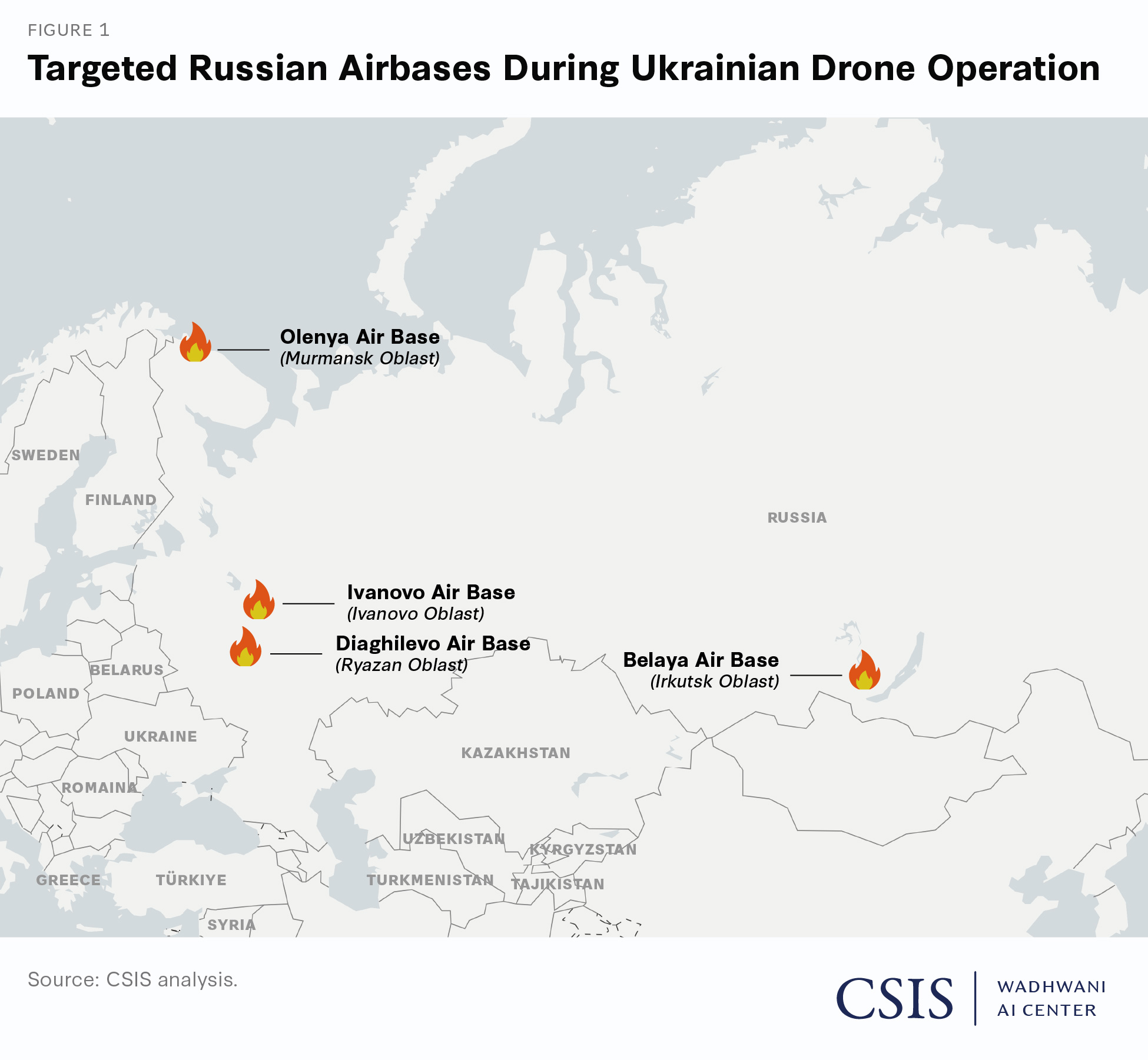
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
On June 1, 2025, Ukraine executed Operation Spider’s Web, its most extensive drone-based military strike against Russia to date. The attack destroyed an estimated $7 billion worth of Russian aircraft, including approximately 34% of Russia’s strategic bomber fleet. The operation occurred just before the second round of peace talks between the two countries in Istanbul.
Key Highlights:
- Nature of Operation:A high-precision, long-range drone strike aimed at crippling Russia’s strategic air power, especially bombers capable of launching cruise missiles and nuclear warheads.
- Planning and Execution:
- Orchestrated over 18 months by the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU).
- 117 explosive-laden drones were deployed simultaneously.
- Drones were concealed in wooden sheds on civilian trucks, enabling stealth transport across vast distances.
- Once positioned, they were remotely launched, surprising Russian air defences.
- Airbases Targeted:The operation struck five major Russian airbases:
- Belaya (Irkutsk)
- Dyagilevo (Ryazan)
- Ivanovo Severny
- Olenya (Murmansk)
- Ukrainka
- Geographic Reach:Some drone targets were over 4,300 km from the front lines, marking the deepest Ukrainian strike inside Russian territory.
Strategic and Political Context:
- The drone strike came hours after Russia's Iskander-M missile attack on a Ukrainian military training centre in Dnipropetrovsk, which killed 12 soldiers and injured over 60.
- Ukrainian Major General MykhailoDrapatyi resigned, accepting personal responsibility for the missile casualties.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy hailed Operation Spider’s Web as a “brilliant success,” showcasing Ukraine’s evolving tactical capabilities.
- The operation served to strengthen Ukraine’s negotiating position ahead of the June 2 Istanbul peace talks.
Peace Negotiation Backdrop:
- The Istanbul talks followed an earlier round that resulted in the largest prisoner exchange since the start of the war but lacked a concrete ceasefire plan.
- Ukraine is expected to propose:
- A 30-day ceasefire
- Mutual prisoner release
- A high-level summit between Presidents Zelenskyy and Putin
- However, Russia has reportedly rejected all ceasefire proposals and has not submitted a formal response.
Wider Conflict Situation:
- As of late May 2025, Ukraine has lost around 18% of its territory to Russian control.
- Meanwhile, Russian forces continue their advance, recently capturing a village in Ukraine’s northern Sumy region.
Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans)

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant ornithological development, the Caspian Gull, one of the rarest gull species to be recorded in India, was positively identified five years after being sighted at Kappad Beach, Kozhikode, Kerala. This marks the first confirmed sighting of the species in Kerala, and only the second in southern India.
Discovery and Identification:
- Ornithologist Abdulla Paleri first spotted the bird in February 2020 but took five years to confirm its identity due to its close resemblance to the more commonly seen Steppe Gull.
- The Caspian Gull differs subtly in features such as head and beak shape, posture, wing pattern, and leg morphology.
- Images were shared with international experts and on the eBird platform, where ornithologists Oscar Campbell and Hans Larsson confirmed the identification. The sighting has remained unchallenged since.
About Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans):
- A monotypic, large, white-headed gull species, considered rare in India.
- Regularly breeds in Central Asia, particularly in steppe and semi-desert habitats with lakes, rivers, and reservoirs.
- Nesting usually occurs on flat, low-lying areas near water bodies, often surrounded by reedbeds.
- The species feeds on fish, insects, molluscs, and other invertebrates.
Migration Pattern:
- It migrates from the Black Sea and Caspian Sea region to southern and eastern Kazakhstan, western China, and parts of South Asia during winter.
- Traditionally winters in the eastern Mediterranean, Persian Gulf, and western India (like Gujarat).
- Increasingly, small populations are dispersing into Europe, including Sweden, Norway, and Denmark.
- The Kozhikode gull is believed to be a straggler—a bird that deviates from its usual migratory route.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern, Despite its rarity in India, the species is not globally threatened.
BharatGen

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh launched BharatGen, India’s first indigenously developed, government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) at the BharatGen Summit 2025, marking a significant step in India’s AI innovation landscape.
About BharatGen:
- BharatGen is a Multimodal LLM designed to support 22 Indian languages and various content formats—text, speech, and image.
- Developed under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) and implemented by the TIH Foundation for IoT and IoE at IIT Bombay.
- Supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), it is a collaborative effort involving premier academic institutions, researchers, and innovators.
Key Features:
- Multilingual and multimodal capabilities (text, voice, image inputs).
- Open-source platform to encourage accessible innovation.
- Trained on Indian datasets to reflect Indian linguistic and cultural diversity.
- Integrated applications across critical sectors like healthcare, education, governance, and agriculture.
- Aims to deliver region-specific AI solutions rooted in Indian values and societal contexts.
Implementation Mechanism:
- Executed through 25 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIHs) across India.
- Four of these TIHs have been upgraded to Technology Translational Research Parks (TTRPs) for real-world deployment.
- Guided by four pillars: technology development, entrepreneurship, human resource development, and international collaboration.
First-Person View (FPV) Drones
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Ukraine conducted a major drone strike on Russia, reportedly destroying over 40 aircraft using First-Person View (FPV) drones—marking one of the deepest strikes into Russian territory since the start of the conflict in 2022. This highlights the growing role of FPV drones in modern asymmetric warfare.
What are FPV Drones?
First-Person View (FPV) drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that allow remote pilots to view the drone’s surroundings through a camera mounted on the drone. The live feed can be transmitted to:
- Specialized goggles
- Smartphones
- Other display screens
This immersive view enables highly precise navigation and control.
Key Features and Technologies
- GPS-Independent Navigation: Operates effectively even when GPS signals are jammed or unavailable.
- SmartPilot System: Uses visual-inertial navigation by interpreting camera data to assess the drone's position and orientation.
- LiDAR Integration: Enhances terrain mapping and obstacle detection in complex environments.
- Low Cost: A functional FPV drone can cost as little as $500, making them highly affordable compared to traditional weapon systems.
Operational Use in Combat
- Reconnaissance First: Typically, a long-range reconnaissance drone is used to identify the target area before deploying FPV drones for strikes.
- Deep Strike Capability: Despite having a short range (a few kilometres), FPV drones offer stealth and precision to strike deeply into enemy territory.
- Combat Strategy: Their agility and affordability make FPV drones a key component of attrition warfare, especially for resource-constrained nations.
Advantages in Warfare
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers high-impact capability at a fraction of the cost of conventional weapons.
- Reduced Human Risk: Limits the need for manned missions in hostile territory.
- Stealth: Smaller size and low acoustic footprint make them harder to detect and intercept.
- High Destructiveness: Able to carry payloads such as explosives, effectively targeting tanks, aircraft, and installations.
Challenges and Limitations
- Limited Range: Operates within a few kilometres, requiring deployment close to target zones.
- Reduced Situational Awareness: Pilots rely solely on camera feed, which may not provide full spatial context.
- Need for Visual Observers: In complex environments, an additional observer may be needed to guide the operator safely.
Ukraine’s Use of FPV Drones
Ukraine has effectively integrated FPV drones into its military strategy:
- In November 2023, FPVs were credited as a low-cost, high-impact method of resisting Russian advances.
- NATO sources indicated that over two-thirds of Russian tanks destroyed recently were hit by FPV drones.
- Ukrainian drone manufacturer Vyriy Drone delivered 1,000 indigenous FPVs in March 2025.
- Ukraine is projected to produce over 4 million drones in 2025, reflecting a significant scaling of domestic capabilities.
Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
- Technological Self-Reliance: Domestic production protects nations from geopolitical supply chain disruptions (e.g., China’s chip exports).
- Global Proliferation: Countries like Israel and Iran have also developed drone systems, including HAROP and Shahed drones respectively.
Jharkhand’s First Tiger Safari
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
The Jharkhand government has proposed setting up its first-ever tiger safari in the fringe area of the Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), located in Latehar district. This initiative aims to promote wildlife education, conservation awareness, and eco-tourism, while also creating employment opportunities.
What is a Tiger Safari?
A tiger safari refers to a tourism model where rescued, conflict-prone, or orphaned tigers are housed in naturalistic enclosures, ensuring sightings for visitors. It differs from traditional wild safaris, where sightings are not guaranteed. The concept was first proposed in the NTCA's 2012 tourism guidelines, refined in 2016, and later aligned with the Supreme Court’s 2024 directive, which mandates that such safaris be located outside core and buffer zones of tiger reserves.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
- Governed by:
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) Guidelines (2012, 2016)
- Central Zoo Authority (CZA) for animal welfare, enclosure design, and project compliance
- Supreme Court Ruling (March 2024):
- Tiger safaris must not be located inside core or buffer zones.
- Intended to protect natural habitats and uphold conservation goals.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR)
- Established: 1974 under Project Tiger
- Location: Chhotanagpur Plateau, Jharkhand
- Rivers: North Koel, Burha (perennial), Auranga
- Vegetation: Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous forest (Sal-dominated)
- Key Fauna: Bengal Tiger, Asiatic Elephant, Sloth Bear, Leopard, Indian Pangolin, Otter
- Historical Note: Site of the world’s first pugmark-based tiger census (1932)
Project Details
- Location: Barwadih Western Forest Range (fringe of PTR, outside core/buffer zones)
- Size: Approx. 150 hectares
- Animals Housed: Only rescued, conflict-prone, or orphaned tigers from reserves/zoos (not wild or zoo-bred tigers unless approved)
- Objectives:
- Promote tourism and conservation education
- Create an experiential learning space for visitors
- Generate employment (~200 local jobs)
The Central Zoo Authority (CZA) will assess the site and species selection. Post Forest Department clearance, the Detailed Project Report (DPR) will be submitted to NTCA and CZA. Approvals may take 5–6 months, followed by a construction period of ~18 months.
Concerns and Challenges
- Tribal and Community Rights:Activists caution that such projects may marginalize forest-dwelling communities and restrict access to traditional forest-based livelihoods (grazing, NTFP collection).
- Consent of Local Communities:As per the Forest Rights Act, projects on forest land must involve Gram Sabha consultation. Activists argue this has yet to be fully addressed.
- State's Clarification:Officials maintain that the site lies on forest land under state management, with no expected displacement.
RBI’s Draft Guidelines on Gold Loans

- 03 Jun 2025
Why is the RBI proposing changes to gold loan regulations?
In April 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released draft guidelines on loans against gold to harmonise regulations across banks and NBFCs and to address irregularities. The move follows an extraordinary surge in gold-backed loans during FY24:
- Gold loan portfolios grew over 50% across banks and NBFCs.
- For banks, the portfolio more than doubled (104% growth).
This rapid growth, amid rising gold prices and lax lending standards, raised regulatory concerns.
What are the key proposals in the draft guidelines?
- LTV Norms:
- The Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio remains capped at 75%.
- For bullet repayment loans for consumption, accrued interest must be included in the LTV calculation, effectively lowering the loan amount disbursed.
- Ownership Proof:Borrowers must furnish proof of ownership for the gold pledged.
- Valuation Standards:
- Gold should be valued based on 22-carat price.
- Uniform procedures must be followed to assess the purity and weight.
- Loan Renewal & Fresh Sanctions:
- Renewals or top-ups are permitted only if:
- The existing loan is standard, and
- It complies with the LTV limit.
- Concurrent loans for both consumption and income-generation are disallowed.
- A fresh loan can only be granted after full repayment (principal + interest) of the previous loan.
- Renewals or top-ups are permitted only if:
- Collateral Return Timeline:If the gold is not returned within 7 working days after repayment, the lender must compensate the borrower at ?5,000/day for each day of delay.
Likely Impact on Borrowers and Lenders
Borrowers:
- May face reduced loan amounts and higher documentation requirements.
- Small and rural borrowers, dependent on gold loans for agriculture and allied sectors, may experience reduced accessibility.
NBFCs and Banks:
- NBFCs that frequently renew or top-up gold loans could lose flexibility.
- Compliance costs will rise due to stringent documentation, valuation, and reporting norms.
- Smaller NBFCs relying on re-pledging of gold may face liquidity issues.
- Interest rates may rise to offset higher operational expenses.
Is a uniform policy suitable?
A one-size-fits-all policy may not be practical. Gold loans are a lifeline for rural households with limited access to formal credit. Experts suggest:
- Differentiated norms for micro gold loans (small-ticket loans) and high-value loans.
- Consideration for the informal nature of ownership in many rural households.
Krishi Nivesh Portal
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
In an effort to streamline and accelerate investments in India’s agriculture and allied sectors, the Government of India has launched the Krishi Nivesh Portal, developed by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
The initiative aligns with the government’s broader goal of promoting the ease of doing business in agriculture by integrating schemes from multiple Central ministries and State governments into a single digital platform.
Key Features of the Portal
- One-Stop Solution: The portal acts as a centralized hub providing real-time access to information on agricultural schemes from various government departments and ministries.
- Multi-Stakeholder Access: It is designed to cater to farmers, entrepreneurs, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), industries, and agri-startups.
- Scheme Integration: As of now, the portal integrates 17 flagship schemes spanning seven Union Ministries, including:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund
- PM KisanSampada Yojana
- PM-KUSUM
- Technological Features: It offers a user-friendly interface, chatbot support, and interactive dashboards for data-driven insights and monitoring.
- Investment Tracking: Users can track application status, explore investment opportunities based on geographical spread, and gain assistance with loan disbursal.
Institutional Integration
- Currently, 14 Union ministries/departments and 9 state government departments are involved in implementing schemes related to agriculture and allied sectors.
- Ministries already integrated include:
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries
- Ministry of Rural Development
- Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
- Ministry of Fertilisers
Efforts are underway to onboard over 300 schemes from various ministries and states, including those related to credit-linked initiatives, PPP models, venture capital projects, and startups.
Significance for Agricultural Sector
- The portal addresses key challenges such as fragmented scheme information, siloed departmental operations, and delays in loan processing.
- It aims to unlock the investment potential of India’s agri-sector, especially for private investors, by offering a consolidated, transparent, and accessible interface.
- According to official estimates:
- The revised budget allocation for FY 2024–25 for agricultural investment schemes stands at ?1.31 lakh crore.
- In FY 2021–22, private sector investment in agriculture amounted to ?2.79 lakh crore.
Sabine’s Gull Spotted at Nalsarovar
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological event, the Sabine’s Gull — a rare Arctic seabird — has been observed at Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary in Gujarat. This marks the species’ first recorded appearance in India since 2013, when it was last sighted in Kerala, underlining the dynamic migratory patterns affecting India’s wetland ecosystems.
About Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary
- Located nearly 64 km west of Ahmedabad, Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary is one of Gujarat’s most prominent wetland ecosystems. Encompassing an area of 120.82 sq km, it comprises a shallow, seasonal lake interspersed with around 360 islets, creating a rich mosaic of aquatic habitats.
- This natural lake traces its origin to the 15th century, following the construction of a check dam on the Sabarmati River. Initially designed to serve irrigation and drinking water needs of nearby villages, the lake gradually evolved into a crucial habitat for avifauna. Recognition of its ecological significance grew over time, prompting colonial authorities in the early 20th century to take protective measures.
- Eventually, in 1969, the Government of Gujarat declared Nalsarovar a bird sanctuary, and it was further accorded the status of a Ramsar wetland site in 2012, signifying its global importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Flora: The sanctuary supports a wide variety of aquatic and wetland plant life, with 48 algae species and 72 flowering plant species recorded. Common plant species include Cyperus, Scirpus, Typha ungustata, Eleocharis palustris, Ruppia, Potamogeton, Vallisneria, Naias, and Chara.
- Fauna:Nalsarovar is home to nearly 250 bird species, making it a haven for bird watchers. Regular sightings include both greater and lesser flamingos, pelicans, ducks, geese, coots, rails, cranes, and a variety of wading and aquatic birds like herons, egrets, storks, spoonbills, and sarus cranes.
- Beyond birds, the sanctuary also supports mammalian fauna. On its southern and southwestern peripheries, species such as the Indian wild ass, mongoose, jungle cat, Indian fox, jackal, wolf, and striped hyena are found.
Sabine’s Gull: Profile
- The Sabine’s Gull (Xemasabini), also known as the fork-tailed gull or xeme, is a small gull species notable for its elegant flight and distinctive wing markings. Adults can be recognized by their pale grey backs, black wingtips, white secondary feathers, and forked white tails.
- This gull breeds in high Arctic and subarctic zones across North America, Russia, Greenland, and Svalbard, and is a rare migrant in South Asia.
- According to the IUCN Red List, it is currently categorized as a species of Least Concern, although sightings in India are extremely uncommon.
ULLAS – Nav Bharat SaakshartaKaryakram and Goa’s Milestone in Literacy

- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Goa became the second state in India to achieve full functional literacy under the ULLAS – Nav Bharat SaakshartaKaryakram (New India Literacy Programme), marking a key achievement in India’s goal of attaining full literacy by 2030, as envisioned in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
About ULLAS
- ULLAS stands for Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented by the Ministry of Education from 2022 to 2027.
- Target Group: Adults aged 15 years and above who missed formal schooling.
- Alignment: The scheme is aligned with NEP 2020, emphasizing inclusive and equitable education.
- Implementation Basis: The programme is built on the spirit of volunteerism and Kartavya Bodh (sense of duty).
Five Components of the ULLAS Scheme:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- Critical Life Skills
- Basic Education
- Vocational Skills Development
- Continuing Education
Digital Outreach
- The ULLAS mobile app facilitates registration of learners and volunteers.
- It also provides access to learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- So far, over 2.40 crore learners and 41 lakh volunteer teachers have been registered on the app.
- Over 1.77 crore learners have taken the Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT).
Goa Achieves Full Literacy
- Declared Fully Literate: On May 30, 2025, during the 39th Goa Statehood Day celebrations at Panaji, Goa was declared fully literate.
- Reported Literacy Rate: As per PLFS 2023–24, Goa had a literacy rate of 93.60%, among the highest in India.
- State Survey Update: A state-led survey confirmed that Goa had crossed the 95% benchmark, qualifying it as fully literate under ULLAS.
Key Factors Behind Goa’s Success
- Adopted a Whole-of-Government approach, involving departments such as:
- Directorate of Panchayats
- Municipal Administration
- Social Welfare
- Planning & Statistics
- Women & Child Development
- Engaged SwayampurnaMitras for grassroots awareness and learning support.
- Played an active role in certification and inclusion of learners into the literacy programme.
- Strong collaboration between SCERT, local administration, school heads, volunteers, and field workers ensured last-mile delivery.
Significance for India
- Goa's achievement underscores the effectiveness of decentralized, people-driven literacy campaigns.
- Demonstrates the potential of tech-enabled platforms, volunteerism, and inter-departmental coordination.
- Sets a model for other states in achieving India’s literacy goal by 2030.
- Reinforces the broader national vision of “Jan-Jan Saakshar” and a Viksit Bharat.
Kawal Tiger Reserve and KumramBheem Conservation Reserve
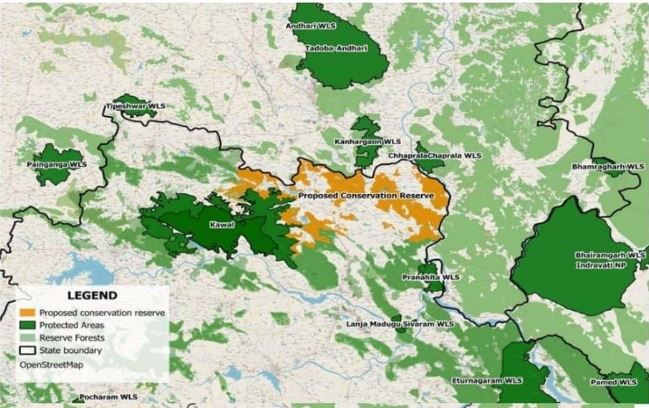
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a recent development, the Telangana government has designated the tiger corridor connecting the Kawal Tiger Reserve (Telangana) with the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) as the KumramBheem Conservation Reserve, under Section 36(A) of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. This move is aimed at preserving critical wildlife corridors in the Central Indian Landscape.
Kawal Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in Telangana, along the Godavari River, forming part of the Deccan Peninsula – Central Highlands.
- Biogeographic Zone: Lies at the southern tip of the Central Indian Tiger Landscape.
- Connectivity: Links with Tadoba-Andhari (Maharashtra), Indravati (Chhattisgarh), and other reserves like Tipeshwar, Chaprala, and Kanhargaon.
- Vegetation Type: Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Flora: Dominated by teak, bamboo, and species like Anogeissuslatifolia, Terminalia arjuna, Boswellia serrata, etc.
- Fauna: Hosts tiger, leopard, nilgai, chinkara, sambar, blackbuck, wild dog, wolf, and jungle cat.
KumramBheem Conservation Reserve: Newly Notified Area
- Legal Basis: Declared under Section 36(A), Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which allows states to notify government-owned land adjacent to or connecting protected areas as conservation reserves.
- Total Area: 1,492.88 sq km (149,288.48 hectares)
- District &Mandals Covered: Spread across KumramBheemAsifabad district, covering parts of Kerameri, Wankidi, Asifabad, Sirpur, Koutala, Bejjur, Kagaznagar, Rebbana, Dahegaon, and Tiryanimandals.
- Forest Blocks Included: 78 blocks including Garlapet, Ada, Manikgarh East & West, Danora, Gudem, Bejjur, Kadamba, and Girali.
Ecological Significance
- Tiger Movement: Over the last decade, more than 45 unique tigers (mostly transient) have been documented in this corridor through camera trapping and surveys.
- Breeding Evidence: Since 2015, 17 tiger cubs born from 3 tigresses have been recorded. The 2022 Tiger Census confirmed 4 adult tigers and 3 cubs in the area.
- Leopard Presence: 8 leopards were recorded during the All India Leopard Estimation, 2022.
- Other Carnivores: Includes sloth bear, hyena, wild dog, wolf, honey badger, and jungle cat.
- Herbivore Diversity: Rich prey base such as gaur, sambar, nilgai, chital, muntjac, four-horned antelope, and Indian gazelle.
- Avifauna: Home to 240+ bird species, including rare species like the Malabar Pied Hornbill and Long-billed Vulture, the latter using the reserve as a nesting site.
- Elephant Movement: Occasional elephant presence has also been reported.
Governance
A Conservation Reserve Management Committee has been established. Members include:
- District Forest Officer (DFO) of KumramBheemAsifabad (Convenor)
- Sarpanches of local panchayats (e.g., Karji, Motlaguda, Murliguda)
- Representatives from NGOs like Hyderabad Tiger Conservation Society, WWF-India, and Wildlife Conservation Trust
- Officials from Veterinary, Agriculture, and Forest Divisions
Ghatampur Thermal Power Project
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently dedicated Unit-1 (660 MW) of the Ghatampur Thermal Power Project, located in Kanpur Nagar, Uttar Pradesh, marking a major step forward in India’s thermal power capacity and energy security goals.
Project Overview
- Location: Ghatampur, Kanpur Nagar District, Uttar Pradesh
- Implementing Agency: Neyveli Uttar Pradesh Power Ltd (NUPPL) — a joint venture between
- NLC India Ltd (51% share)
- Uttar Pradesh Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Ltd (UPRVUNL) (49% share)
- Total Capacity: 3 units × 660 MW = 1,980 MW
- Project Cost: ?21,780.94 crore
Commissioning Timeline
- Unit-1 (660 MW): Commissioned in December 2024, dedicated in May 2025
- Remaining Units: Expected to be operational by December 2025
Power Distribution Agreement
- Uttar Pradesh: Receives 75.12% (1,487.28 MW) of the total power
- Assam: Allocated 24.88% (492.72 MW), subject to transfer of 20% equity from UPRVUNL to Assam Government
Technological and Environmental Features
- Efficient Supercritical Technology:Utilizes supercritical boilers with 88.81% efficiency, reducing fuel usage and emissions.
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD):Ensures no industrial wastewater release, protecting surrounding land and water bodies.
- Air Pollution Control:Equipped with modern pollution mitigation systems:
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) – Controls NOx emissions
- Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) – Reduces SOx emissions
- Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) and Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Stations (AAQMS) – Ensure real-time pollution tracking
- Water Conservation Measures:
- 288 km of canal lining saves approx. 195 million litres/day
- Raw water storage capacity of 46 lakh cubic meters
Fuel Security
- The plant sources coal from its own captive mine, producing 9 million tonnes annually.
- It maintains a 30-day coal stockpile, equivalent to 10.165 lakh tonnes, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
IndiaAI Mission

- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
India has taken a major step toward self-reliance in Artificial Intelligence with the expansion of its national AI compute infrastructure and the selection of three new startups to build indigenous foundation models under the IndiaAI Mission.
Key Highlights
- Compute Infrastructure Boost:India’s total GPU capacity has now surpassed 34,000 units, up from the initial 10,000-target. A fresh addition of 15,916 GPUs to the existing 18,417 empanelled GPUs brings the total to 34,333 GPUs, now available through the IndiaAI Compute Portal (operational since March 2025).
- Subsidised Access:These GPUs are made available at a subsidised rate of ?67/hour, well below the global average of ?115/hour. This has been made possible through private sector empanelment instead of government-built data centres. Service providers receive up to 40% capital subsidy, enabling rapid infrastructure rollout.
- Empanelled Providers:Seven private companies were empanelled for compute provisioning:
- Cyfuture India Pvt. Ltd.
- Ishan Infotech Ltd.
- Locuz Enterprise Solutions Ltd.
- Netmagic IT Services Pvt. Ltd.
- Sify Digital Services Ltd.
- Vensysco Technologies Ltd.
- Yotta Data Services Pvt. Ltd.
Foundation Model Development
Under the IndiaAI Foundation Model initiative, three new startups have joined Sarvam AI (selected earlier in April 2025) to build India-specific Large Language Models (LLMs):
- Soket AI: Will develop a 120-billion parameter open-source model focused on Indian languages and use cases in defence, healthcare, and education.
- Gnani AI: Building a 14-billion parameter Voice AI model for real-time, multilingual speech recognition and reasoning.
- Gan AI: Developing a 70-billion parameter multilingual TTS (text-to-speech) model aiming for "superhuman" capabilities surpassing global benchmarks.
- Sarvam AI: Previously selected to create a 120-billion parameter Sovereign AI model, following the release of Sarvam-1 (2B parameters) and Sarvam-M (24B parameters).
These foundation models will be trained on Indian datasets and tailored for governance, public service delivery, and regional language support.
AI Kosh& Innovation Initiatives
- AI Kosh: A public dataset platform with 367 datasets uploaded, enabling research and model training using India-relevant data.
- IndiaAI I4C CyberGuard Hackathon: In collaboration with the Ministry of Home Affairs, AI models were developed for identifying cybercrime patterns from complex inputs like handwritten FIRs and audio calls on the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal.
- Startup Innovation & Skill Development: Funding support, AI labs in Tier-II cities, and talent development programs are part of a broader push to promote innovation and reverse brain drain.
About IndiaAI Mission
- Launched by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Cabinet Approval: March 2024 with a budget of over ?10,000 crore
- Objectives:
- Develop indigenous AI capabilities and infrastructure
- Democratize AI access for governance, startups, and citizens
- Promote ethical and safe AI use
- Position India among the global AI leaders
India Develops its first indigenous Mechanical Thrombectomy Device for Stroke Treatment
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s medical technology sector, the Technology Development Board (TDB) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has extended support for the development of the country’s first indigenously manufactured mechanical thrombectomy device for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
What is a Mechanical Thrombectomy Device?
The device is a minimally invasive medical tool designed to treat acute ischemic stroke, which occurs due to a blockage in a large blood vessel in the brain. Unlike conventional thrombolytic drugs that dissolve clots chemically, this device physically extracts the clot, thereby restoring blood flow swiftly and reducing the risk of severe brain damage or paralysis.
Development and Manufacturing
This pathbreaking innovation was developed by S3V Vascular Technologies Ltd, based in Mysuru, with financial backing from the TDB. The manufacturing takes place at an advanced, high-precision production facility within the Medical Devices Park in Oragadam, Tamil Nadu.
Key Features and Technological Highlights
- Indigenous Design: S3V is the first Indian company to conceptualize and produce stroke-intervention tools such as microcatheters, aspiration catheters, guidewires, and stent retrievers.
- R&D and Patents: The company has filed multiple patents, particularly for innovations in clot retriever head design and advanced catheter structures.
- Training and Capacity Building: A simulator-based training program has been initiated to train young medical professionals, with a focus on outreach in Tier-II cities.
- Global Compliance: The device aims to meet CE and USFDA standards, paving the way for international exports and aligning with global quality benchmarks.
Significance for India
- Reduces Import Dependency: The device addresses India’s reliance on expensive, imported stroke-care equipment.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare: By making stroke treatment more affordable, it enhances access to quality care for economically weaker sections.
- Supports Public Health Initiatives: It is expected to be integrated into government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, strengthening the country’s universal healthcare mission.
- Boosts MedTech Ecosystem: This innovation is a major stride in positioning India as a global player in the high-end medical devices sector.
DHRUVA(Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address)
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Department of Posts, under the Ministry of Communications, released the policy framework for DHRUVA (Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address) — a key initiative aimed at creating a standardized, geo-coded digital address infrastructure across India.
What is DHRUVA?
DHRUVA is a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) initiative that conceptualizes Address-as-a-Service (AaaS) — a secure, consent-based, and interoperable system for managing and sharing address data. It builds upon the earlier DIGIPIN (Digital Postal Index Number) system, which created a national-level, geo-tagged addressing grid for improved governance and service delivery.
Objectives of DHRUVA
- Transform address information into a digital public good.
- Enable secure, standardized, and interoperable access to address data across sectors.
- Empower users with control and consent over how their address data is shared.
- Promote public-private collaboration in areas like logistics, e-governance, and financial inclusion.
Key Features
- DIGIPIN Backbone: Utilizes the Digital Postal Index Number system, allowing logical and directional naming of addresses with precise geolocation.
- Address-as-a-Service (AaaS): Facilitates seamless address validation, authentication, and sharing across government and private platforms.
- User Autonomy: Individuals can manage and consent to how their address data is used, ensuring privacy and user-centric governance.
- Open & Inclusive Access: The infrastructure is freely accessible, promoting innovation and broad-based adoption.
- Consent Framework: Address data sharing will be user-approved, ensuring a secure and trusted digital ecosystem.
Significance of DHRUVA
- Geospatial Governance: Enhances planning, disaster management, and delivery of public services through precise address mapping.
- Improved Logistics & E-Commerce: Enables more efficient last-mile delivery, reducing ambiguity in address identification.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates smoother KYC, subsidy disbursement, and service access in rural and underserved areas.
- Ease of Living & Digital India: Aligns with broader national goals by supporting smart governance and digital transformation.
- Public-Private Synergy: Encourages co-creation of solutions by government bodies and private enterprises based on shared, trusted digital address data.
India’s Provisional GDP Estimates for FY 2024–25
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the Provisional Estimates (PEs) of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross Value Added (GVA) for the financial year 2024–25 (FY25), providing a comprehensive picture of the country's economic performance.
Understanding GDP and GVA
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures the total expenditure in the economy, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports — representing the demand side.
- GVA (Gross Value Added) evaluates the income generated from the production of goods and services in different sectors — representing the supply side.
- The two are related by the formula:GDP = GVA + Taxes – Subsidies
- Both are reported in nominal terms (current prices) and real terms (adjusted for inflation).
Nature of Provisional Estimates
- The estimates are termed provisional because they include data from all four quarters but are subject to revision:
- First Advance Estimates (FAE): January
- Second Advance Estimates (SAE): February
- Provisional Estimates (PE): May
- Revised Estimates: Finalized over the next two years (in 2026 and 2027 for FY25)
Key Economic Indicators for FY 2024–25
- Nominal GDP
- Estimated at ?330.68 lakh crore, showing a 9.8% growth over FY24.
- In dollar terms (?85.559/USD), India’s economy reached $3.87 trillion.
- However, this 9.8% nominal growth marks the third-slowest since 2014.
- Real GDP
- Rose by 6.5%, reaching ?187.97 lakh crore.
- The real GDP growth slowed from 9.2% in FY24, indicating reduced economic momentum.
- Sectoral GVA Performance
- Overall GVA grew by 6.4%, down from 8.6% in FY24.
- Sector-wise real GVA growth:
- Agriculture & Allied Activities: 4.4% (up from 2.7% last year)
- Industry (including Manufacturing & Construction): 6.1%
- Services: 7.5% (notable growth in public admin, trade, and finance)
- Q4 FY25 Trends
- Real GDP growth: 7.4%
- Nominal GDP growth: 10.8%
- Indicates a strong end-of-year performance.
Structural Insights and Concerns
- Manufacturing Weakness:Since FY20, manufacturing GVA CAGR (4.04%) lags behind agriculture (4.72%), signaling industrial stagnation.
- Employment Implications:Manufacturing’s sluggishness contributes to high urban unemployment and labour migration to rural/agricultural sectors.
- Consumption and Investment Revival:
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE) grew by 7.2%.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) increased by 7.1%, indicating investment momentum.
Significance for Policymaking
- The GDP data serves as a basis for fiscal planning, monetary policy decisions, and public investment.
- It highlights India’s position as one of the fastest-growing major economies, while also revealing structural vulnerabilities — particularly in manufacturing.
- For international comparison, real GDP is crucial as it neutralizes inflationary differences across countries.
Zangezur Corridor
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Zangezur Corridor gained renewed attention following the visit of Armenia’s Security Council Secretary to New Delhi, where he held discussions with India’s National Security Advisor, AjitDoval.
What is the Zangezur Corridor?
The Zangezur Corridor is a proposed transport and transit route that aims to connect mainland Azerbaijan with its exclave, the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, by bypassing Armenia’s Syunik Province. The corridor passes through the Zangezur region, which is currently part of southern Armenia and has been a historically disputed territory since World War I.
Geographical and Strategic Linkages
- On the Azerbaijani side, the corridor integrates with the Horadiz-Agbend highway and railway infrastructure.
- On the Turkish side, it connects with the Nakhchivan-Igdir-Kars railway and highway, creating a direct land route from Azerbaijan to Turkey, and further west to Anatolia and Europe.
- The corridor, therefore, would serve as a critical land bridge across the South Caucasus, improving connectivity between Europe and Asia.
Economic and Strategic Significance
- The corridor is envisioned to:
- Boost regional trade and connectivity across Turkey, Azerbaijan, Iran, Russia, and Central Asia.
- Reduce transportation time and costs between Azerbaijan and Nakhchivan.
- Improve logistics infrastructure and increase supply chain efficiency across the region.
- It has implications for wider Eurasian integration, especially as global trade seeks alternatives to vulnerable chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
India’s Strategic Interest
India's engagement with the Zangezur Corridor gained attention after a meeting between India’s National Security Advisor and Armenia’s Security Council Secretary in New Delhi.
India’s interests in the region include:
- Chabahar Port in Iran: India’s investment here aims to create a secure route to Central Asia and Europe.
- Engagement with Armenia: India has been increasing strategic and defence cooperation with Armenia.
- Alternative Connectivity: The Zangezur Corridor challenges India’s north-south connectivity vision, as it could marginalize the Chabahar route if dominated by Turkish-Azerbaijani interests.
- Geopolitical Balance: India's presence helps counterbalance Turkish-Pakistani influence in the South Caucasus.
Boothapandi Rock Grooves

- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has recently unearthed one of the first known Neolithic rock grooves in Kanniyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, specifically near Boothapandi village. These grooves—estimated to be around 4,000 years old—were likely created by Neolithic people to sharpen tools and weapons used for hunting, agriculture, and digging.
The discovery was made during a field study conducted by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan, ASI Officer (Tirunelveli &Kanniyakumari), and M. Faisal of the Sembavalam Research Centre. The grooves vary in size:
- Length: 8 cm to 15 cm
- Width: 3 cm to 4 cm
Such grooves have also been previously documented in Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram districts of Tamil Nadu. The find strongly suggests the presence of Neolithic human activity in southernmost India and adds a significant layer to our understanding of prehistoric settlements in the region.
Neolithic Age
The Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) marks the final stage of prehistoric human evolution before the emergence of metal tools. Beginning around 10,000 BCE, it coincides with the Holocene Epoch and follows the Paleolithic Age (chipped-stone tools) and precedes the Bronze Age.
Key Features of the Neolithic Age
- Lifestyle Shift: Transition from hunting-gathering to agriculture and animal domestication.
- Permanent Settlements: Emergence of village communities with mud-and-reed houses, both rectangular and circular in design.
- Toolmaking: Development of polished and ground stone tools.
- Crafts and Culture: Rise of pottery, weaving, alcohol production, and early architecture.
- Burial Practices: Use of status objects (e.g., jade, pottery) in burials indicates belief in afterlife and emerging social hierarchies.
- By the end of the Neolithic era, copper metallurgy began, marking the Chalcolithic (Copper-Stone) Age. Eventually, bronze tools replaced stone ones, signaling the end of the Stone Age and the dawn of early civilizations.
Major Neolithic Sites in India
- Burzahom – Kashmir
- Chirand (Chiron) – Bihar
- Uttarapalli – Andhra Pradesh
- Edakkal Caves – Kerala
- Boothapandi (newly identified) – Tamil Nadu
Perito Moreno Glacier

- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Perito Moreno Glacier, often referred to as the ‘White Giant’, is Argentina’s most iconic glacier, located in the Los Glaciares National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Situated in the Andes Mountains, near El Calafate in Santa Cruz province, this glacier spans approximately 250 sq km—about the size of Patna, Bihar—and stretches 30 km in length, with ice walls rising 60 meters above water.
- Formed during the last Ice Age (~18,000 years ago), Perito Moreno has historically remained unusually stable, defying the global trend of rapid glacier retreat. However, this stability changed around 2020, raising alarms among scientists.
Recent Developments and Ice Calving Events
- Perito Moreno is globally renowned for its ice calving events, where massive blocks of ice break off into the lake with thunderous crashes. These events, though natural due to the glacier’s forward motion, have recently become more intense.
- On April 21, 2025, a colossal ice chunk the size of a 20-story building plunged 70 meters into the water—an increasingly frequent occurrence in the past 4–6 years.
- According to local experts and a 2024 government-backed report, the glacier has been retreating steadily since 2015, with an average mass loss of 0.85 meters annually—the fastest in nearly five decades.
- Between 2020 and 2023, the glacier lost over 700 meters of mass, equivalent to around seven large ice blocks.
Causes: Global Warming & Climate Impact
- The primary cause behind this dramatic retreat is climate change. Scientists from IANIGLA (Argentine Institute of Glaciology and Environmental Sciences) and CONICET state that the region has experienced an air temperature rise of 0.06°C per decade and reduced precipitation, leading to less snow accumulation and thinning of the glacier.
Global Perspective on Glacier Retreat
Perito Moreno is now part of a larger, alarming global trend.
- A 2024 study in Nature estimates that glaciers worldwide are losing 273 billion tonnes of ice annually, contributing to a 2 cm rise in global sea levels this century alone.
- A UNESCO report (March 2025) highlighted that glaciers (excluding Greenland and Antarctica) have shed over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1975—comparable to an ice block the size of Germany with 25 meters thickness.
Environmental Significance
- Freshwater Source: Perito Moreno is a major reservoir of freshwater in Argentina.
- Tourism: The glacier attracts global tourists, boosting the local economy.
- Climate Indicator: Its recent retreat reflects the delayed but accelerating impact of global warming, making it a critical environmental bellwether.
