Antimony Discovery in Balochistan, Pakistan
- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
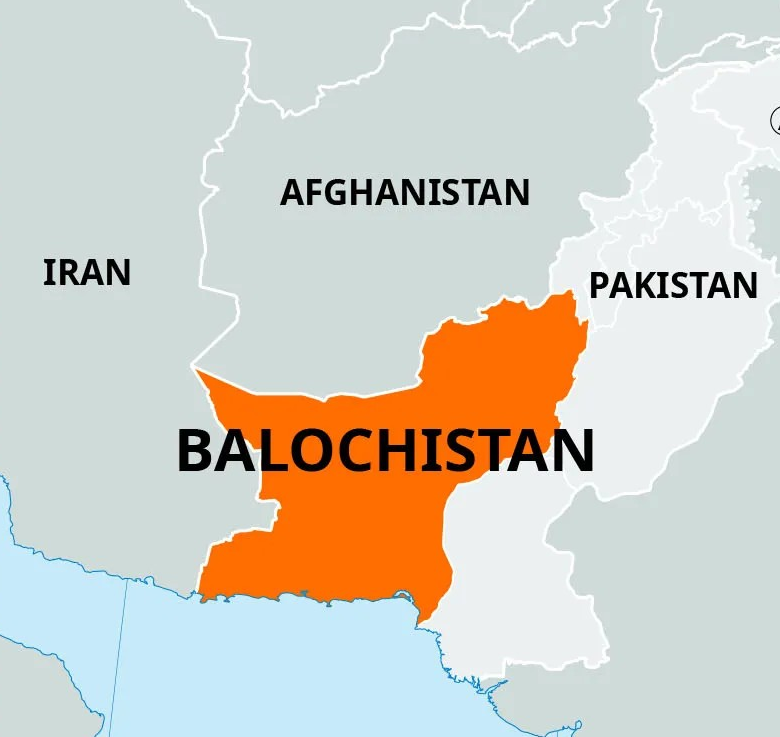
In a recent geopolitical development, Pakistan has reportedly discovered a significant deposit of Antimony in the Balochistan region — an area marred by conflict and instability. This finding holds both economic and strategic significance, given the growing global demand for rare and critical minerals.
About Antimony
- Chemical Element: Antimony (Symbol: Sb, Atomic Number: 51) is a metalloid, meaning it exhibits properties of both metals and non-metals.
- Physical Properties:
- Solid at room temperature.
- Poor conductor of heat and electricity.
- Found in commercial forms such as ingots, broken pieces, granules, and cast cakes.
Geological Occurrence
- Primary Ore: The chief ore of Antimony is Stibnite (Sb?S?).
- Mode of Occurrence: Found in volcanic-associated deposits and deep-seated veins, formed under moderate to high temperature and pressure.
- Also commonly obtained as a byproduct from lead-zinc-silver mining operations.
Global Production Landscape
- China is the dominant global producer, accounting for over 88% of world production.
- Other notable producers include Russia, Bolivia, and Tajikistan.
- India currently does not have significant reserves or production of Antimony, making it dependent on imports for industrial use.
Key Industrial and Strategic Uses
- Electronics Industry:Used in manufacturing semiconductors, infrared detectors, and diodes.
- Alloys:
- Alloyed with lead and other metals to increase hardness and strength.
- Lead-antimony alloys are extensively used in lead-acid batteries.
- Defense and Printing:Utilized in the production of bullets, type metal for printing, and cable sheathing.
- Flame-Retardants and Ceramics:Antimony compounds are key ingredients in flame-retardant materials, as well as in paints, enamels, glass, and pottery.
R-37M Missile

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has recently offered the R-37M missile, a state-of-the-art, long-range air-to-air missile, to India. This missile, one of the world’s most advanced, has the potential to transform India's aerial defense capabilities. The offer also comes with the opportunity for India to license the production of this missile domestically. However, the acquisition of such a potent weapon is raising tensions in the region, particularly with Pakistan, China, and Bangladesh, and has broader strategic implications.
Overview of R-37M Missile:
The R-37M, also known by its NATO reporting name AA-13 Axehead, is a hypersonic, long-range air-to-air missile developed by Russia.
It is designed to target high-value assets, such as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control Systems), tanker aircraft, and other support platforms, beyond visual range (BVR).
Evolved from the R-33 missile, the R-37M significantly enhances air combat capabilities due to its range, speed, and precision.
- Speed and Range: The missile can travel at speeds of up to Mach 6 (approximately 7,400 km/h), enabling it to intercept fast-moving aerial threats. It has an operational range of 300-400 km (160-220 nautical miles), making it one of the longest-reaching air-to-air missiles.
- Weight: The missile weighs 510 kg, with a 60 kg warhead.
- Guidance System: It uses an advanced combination of inertial navigation with mid-course updates, active radar homing, and semi-active radar guidance for the terminal phase.
- Combat Advantage: The R-37M can target beyond visual range, enabling the launching aircraft to engage enemy targets while remaining outside the reach of enemy missiles.
Impact on the Indian Air Force (IAF):
The R-37M missile could replace the current R-77 missile used by India’s Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighter jets. This acquisition will bolster India's air defense by providing enhanced capabilities to intercept aerial threats at greater distances. Additionally, the offer to license the local production of the missile is a significant step toward strengthening India’s defense industry and reducing its dependence on foreign weapon systems. This move can also contribute to India's strategic autonomy in military engagements.
Strategic Implications for Pakistan:
Pakistan’s Air Force (PAF) primarily relies on F-16 fighter jets for its aerial superiority. However, these aircraft are vulnerable to interception beyond the Line of Control (LoC) by the R-37M, which has an engagement range of up to 400 kilometers. This could significantly alter Pakistan's defense posture, as its aircraft would be exposed to threats from Indian aircraft even before crossing the LoC.
Potential Effects on China:
China, which already possesses advanced air-to-air missiles such as the PL-15 and PL-21, will closely monitor India’s acquisition of the R-37M missile. While China is not directly threatened by the missile due to its own advanced defense systems, India’s missile capabilities could alter the balance of air superiority in the region. The acquisition could prompt China to accelerate the development of counter-hypersonic technologies, potentially altering the trajectory of military developments in the region.
Impact on Bangladesh:
Bangladesh, which shares friendly relations with India, could find itself caught in the strategic competition between India and Pakistan, despite its own military capabilities not directly challenging India. The regional military dynamics, influenced by India’s acquisition of advanced weapons like the R-37M, may push Bangladesh to enhance its defense capabilities, either through regional alliances or by procuring advanced defense technologies.
India-Russia Defense Relations:
India’s defense cooperation with Russia has been longstanding and substantial. Between 2015 and 2020, India’s defense imports from Russia were valued at approximately $10 billion, making Russia one of India’s largest defense suppliers. Around 70% of India's defense equipment is of Russian origin. Key joint defense projects include:
- BrahMos Missile: A joint venture to develop a supersonic cruise missile.
- S-400 Triumph: A $5.4 billion deal for five S-400 air defense systems.
- AK-203 Assault Rifles: A project for the local manufacturing of over 700,000 rifles.
- Military Exercises: India and Russia conduct joint military exercises, such as the INDRA (focused on counter-terrorism) and AVIAINDRA (aerial exercises between the Indian Air Force and Russian Aerospace Forces).
Iskander-M

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant defense development with wide-ranging geopolitical implications, the Russian Federation is preparing to mass-produce the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missile, a new-generation weapon system with enhanced range and destructive capabilities. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to upgrade its missile arsenal amid ongoing tensions with NATO, especially in the context of the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features and Strategic Purpose
The 9K720 Iskander-M, developed by the Machine-Building Design Bureau (Kolomna), is a medium-range tactical ballistic missile with an effective range of up to 1,000 kilometers. It is capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads, making it a versatile and high-impact weapon in regional conflict scenarios.
- The missile is precision-targeted and designed to neutralize high-value enemy assets, including NATO’s military infrastructure in Eastern Europe, especially in Ukraine.
- The production of the upgraded missile, unofficially referred to as the Iskander-1000, is expected to begin in full swing by 2025.
- The missile is reported to be highly destructive, with the ability to conduct deep strikes with minimal detection, offering Russia a tactical advantage in asymmetric warfare.
Deployment of Oreshnik Missile Systems in Belarus
In a parallel development, Russia has confirmed the deployment of Oreshnik medium-range ballistic missile systems in Belarus, a strategic ally. This decision follows agreements between the Russian and Belarusian leadership, reinforcing the military integration under their collective defense pact.
- The Oreshnik system, though less publicly detailed than the Iskander, is designed for tactical use and contributes to enhancing Russia’s regional defense shield.
- According to Russian foreign ministry officials, Belarus already hosts a joint Regional Forces Group, non-strategic nuclear weapons, and modern Russian defense systems.
- The positioning of these systems near NATO’s eastern borders heightens tensions with Western powers, particularly the United States, Poland, the Baltic States, and the European Union.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The Iskander-M and Oreshnik missile programs are part of Russia’s strategic doctrine to deter NATO's influence and reassert its military dominance in Eastern Europe. These deployments are:
- Likely to escalate NATO-Russia tensions, increasing the risk of a regional arms race.
- Expected to complicate European security dynamics, especially in Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states, which are seen as potential frontlines.
- Raising the prospect of further military escalation in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Prompting NATO countermeasures, including deployment of missile defense systems and increased troop presence near Eastern borders.
Hwasong-19

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- North Korea recently announced the successful test-firing of its latest intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), the ‘Hwasong-19’.
- Claims by North Korea: The missile was described as ‘the world’s strongest strategic missile’ and a ‘perfected weapon system’ by North Korean state media.
Key Features of the Hwasong-19:
- Solid-Fuel Propulsion: The Hwasong-19 reportedly uses solid-fuel propulsion, which enables quicker launches and greater secrecy. This contrasts with liquid-fuel missiles, which take longer to prepare and are more visible.
- Enhanced Performance: The missile is said to have improved altitude and flight duration compared to previous North Korean ICBMs, marking significant progress in missile technology.
- Size: The Hwasong-19 is estimated to be 28 meters long (92 feet), which is notably larger than many other ICBMs, including those from the U.S. and Russia, which are typically under 20 meters (66 feet).
Strategic Implications:
- Reach and Targeting: The Hwasong-19 is believed to have a range of over 13,000 kilometers, which is sufficient to target the U.S. mainland, signaling a significant advancement in North Korea’s missile capabilities.
- Nuclear Capability: While specific details on the missile’s payload remain undisclosed, the Hwasong-19 could potentially be equipped with a nuclear warhead, enhancing North Korea's strategic deterrence.
Impact on Regional and Global Security:
- US-North Korea Tensions: The launch occurred against the backdrop of ongoing U.S.-North Korea tensions, particularly over North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs. The missile could potentially alter the regional security dynamics, especially in East Asia.
What is an ICBM?
- ICBM Definition: An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range missile capable of carrying nuclear warheads (or other payloads) across continents.
- Range and Speed: ICBMs typically have a minimum range of 5,500 km (3,400 miles), with some capable of reaching up to 16,000 km or more, making them far faster and more capable than other ballistic missiles.
- Launch Mechanism: ICBMs are launched from land or submarine platforms, traveling through space before re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere and targeting distant objectives.
- Comparison with India's Agni-V: India’s Agni-V ICBM, which has a range of over 5,000 km, is often compared to North Korea’s missile systems.
