1st Blind Women’s T20 World Cup 2025
- 01 Dec 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, met and felicitated the Indian Women’s Blind Cricket Team after their historic victory in the first-ever Blind Women’s T20 World Cup 2025, where India defeated Nepal in the final.
Key Details:
- The Blind Women’s T20 World Cup 2025 is the first global cricket championship exclusively for women cricketers with visual impairment.
- A landmark initiative promoting inclusivity, representation, and international recognition for blind women athletes.
Organising Body
- Organised by World Blind Cricket Ltd. (WBC)
- Hosted jointly with:
- Cricket Association for the Blind in India (CABI)
- Cricket Association for the Blind in Sri Lanka
Hosts & Venues
- Co-hosts: India and Sri Lanka
- Venues:
- Delhi (India)
- Bengaluru (India)
- Colombo (Sri Lanka)
- Final Venue: P. Sara Oval Stadium, Colombo
Tournament Structure & Format
- Participating Nations (6): India, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Australia, USA
- Format:
- Round-robin league
- Semi-finals
- Final
Unique Playing Features (Blind Cricket Rules)
- Player Categories:
- B1: Totally blind
- B2 & B3: Partially sighted
- Mandatory mix of all categories in the playing XI
- Equipment & Rules:
- White plastic ball with metal bearings to produce sound
- Underarm bowling along the ground
- B1 batters use runners
- Each run scored by a B1 batter is counted double
Results & Indian Team Highlights
- Champion: India (Unbeaten throughout the tournament)
- Final Result: India defeated Nepal by 7 wickets
- Player of the Final: Phula Saren
- Captain of India: Deepika TC (Deepika Gaonkar)
State of Social Justice 2025
- 10 Oct 2025
In News:
The International Labour Organization (ILO) released its landmark report, “The State of Social Justice: A Work in Progress (2025)”, ahead of the Second World Summit for Social Development. The report marks three decades since the historic 1995 Copenhagen Summit and evaluates global efforts towards achieving justice, equality, and inclusion in a rapidly transforming world.
I. Purpose and Framework
The report assesses progress over 30 years in advancing social justice—defined as fair and equitable access to opportunities, rights, and resources—through four foundational pillars:
- Fundamental Human Rights and Capabilities – promoting freedom, equality, and universal social protection.
- Equal Access to Opportunities – removing barriers to education, employment, and fair wages.
- Fair Distribution – ensuring equitable sharing of the gains from economic growth.
- Fair Transitions – managing environmental, digital, and demographic shifts inclusively.
II. Global Progress: Achievements and Trends
1. Poverty and Labour Improvements
- Extreme Poverty fell sharply from 39% (1995) to 10% (2023).
- Working Poverty declined from 27.9% (2000) to 6.9% (2024).
- Labour Productivity per worker increased by 78% globally and by 215% in upper-middle-income countries, indicating narrowing productivity gaps between nations.
- Child Labour dropped from 20.6% (1995) to 7.8% (2024), driven by education access and monitoring systems.
2. Education and Skills
- Secondary school completion rates rose by 22 percentage points since 2000, underscoring significant human capital development.
3. Social Protection Expansion
- Over half of the global population is now covered by at least one form of social protection—pensions, healthcare, or income support—up from a marginal share in 1995.
III. Persistent Challenges
Despite these gains, the report warns that social justice remains “a work in progress,” with stark inequalities continuing to undermine inclusive growth.
1. Inequality and Wealth Concentration
- The top 1% of the global population controls 20% of income and 38% of total wealth.
- 800 million people still survive on less than US$3 per day, and one in four lacks access to safely managed drinking water.
2. Gender and Birth Inequalities
- Women earn 78% of men’s wages, and gender parity in labour participation has improved by only three percentage points since 1995.
- Nearly 71% of income outcomes globally are influenced by birth circumstances, reflecting entrenched structural inequities.
3. Informality and Job Quality
- 58% of workers remain in the informal economy, with limited access to labour rights and social protection.
- Collective bargaining rights have weakened globally, as reflected in declining compliance scores across income groups.
4. Declining Trust in Institutions
Confidence in governments, corporations, and unions has steadily eroded since the 1980s due to perceptions of unfair reward systems, corruption, and widening wealth gaps—posing risks to democratic stability.
IV. India in the Global Context
India mirrors many global patterns highlighted by the ILO but also shows unique progress in certain areas:
1. Poverty and Human Development
- Multidimensional poverty reduced from 29% (2013–14) to 11% (2022–23).
- Education: Secondary school completion rate reached 79% (2024), and female literacy stands at 77%.
- Digital Empowerment: The JAM trinity (Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile) enhanced direct benefit delivery and reduced leakages.
2. Social Protection and Welfare
Schemes such as PM-KISAN, Ayushman Bharat, and e-Shram have significantly extended coverage to over 55 crore unorganised workers. The Social Security Code (2020) further streamlined pension and maternity benefits.
3. Labour Market and Gender Gaps
- Informality remains high—over 80% of India’s workforce operates outside formal contracts.
- Female labour force participation has improved to 37% (PLFS 2024–25) but remains below the global average.
V. Managing Emerging Transitions
The ILO identifies three ongoing societal transitions that must be managed fairly to sustain progress:
- Climate Transition – Ensuring green jobs and protecting workers displaced by decarbonisation.
- Technological Transition – Bridging the digital divide through skills, reskilling, and inclusive access.
- Demographic Transition – Addressing challenges of ageing populations while leveraging youth dividends in developing countries.
To navigate these, the ILO recommends:
- Applying existing labour institutions to emerging contexts.
- Adapting them to specific transition challenges.
- Amplifying them by integrating labour concerns into climate, digital, and fiscal policies.
VI. ILO’s Key Recommendations
- Embed Social Justice Across Policies – Integrate equity into finance, trade, climate, and healthcare governance.
- Rebuild Trust in Institutions – Enhance transparency, accountability, and participatory policymaking.
- Invest in People – Expand education, skills, and lifelong learning to bridge gender and digital gaps.
- Strengthen Social Protection Systems – Aim for universal and portable coverage, backed by fair minimum wages.
- Promote Fair Transitions – Ensure environmental and technological shifts generate decent work.
- Enhance Global Cooperation – Reinforce multilateralism to manage migration, inequality, and global shocks.
UK’s Terminally Ill Adults (End of Life) Bill
- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark decision, the UK House of Commons has passed the Terminally Ill Adults (End of Life) Bill, which seeks to legaliseassisted dying for terminally ill individuals in England and Wales. The Bill passed with a narrow margin of 314 to 291 votes, and will now proceed to the House of Lords for further deliberation.
Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Applicability: England and Wales.
- Eligibility: Only for patients diagnosed with less than six months to live.
- Safeguards:
- The patient must be mentally competent.
- Approval is required from two doctors, a psychiatrist, a senior lawyer, and a social worker.
- The process ensures the patient’s choice is informed and voluntary.
Understanding Euthanasia:
- Etymology: From Greek “eu” (good) + “thanatos” (death) = “good death”.
- Definition: Intentional act of ending a person’s life to relieve suffering from terminal illness or unbearable pain.
Types of Euthanasia:
Type Description Example
Active Deliberate action to end life Lethal injection
Passive Withdrawal of treatment Removing life support
Voluntary With patient’s consent Terminally ill requesting euthanasia
Involuntary Without consent Considered illegal
Ethical Dimensions:
Arguments in favour
- Right to Autonomy: Upholds personal freedom in deciding life and death.
- Compassionate Exit: Eases intractable suffering.
- Dignity in Death: Ensures control over one’s final moments.
- Relief for Families: Reduces emotional and financial strain.
- Medical Resource Optimization: Redirects care to patients with curable conditions.
Arguments Against
- Sanctity of Life: Human life is sacred and must not be intentionally ended.
- Risk of Coercion: Vulnerable groups may be pressured into opting for death.
- Existence of Palliative Alternatives: Modern hospice care offers non-lethal relief.
- Slippery Slope: May lead to misuse or extension to non-terminal cases.
- Erosion of Medical Ethics: Challenges the healer role of doctors.
Indian Legal Perspective:
India has grappled with the euthanasia debate in various judicial pronouncements:
- Gian Kaur v. State of Punjab (1996): Right to die not included under Article 21.
- Aruna Shanbaug Case (2011): Allowed passive euthanasia under strict conditions.
- Common Cause v. Union of India (2018):Recognised the right to die with dignity and permitted Advance Medical Directives.
India’s Social Security coverage reaches 64.3% in 2025
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
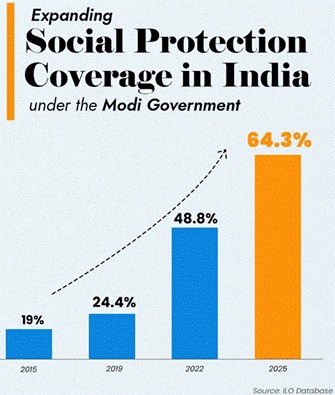
According to the latest data from the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) ILOSTAT database, India’s social security coverage has increased from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, an unprecedented 45 percentage point surge over the past decade.
What is Social Security?
Social security (or social protection) refers to systems and policies that protect individuals and households from:
- Income loss (e.g. old age, unemployment, disability)
- High healthcare costs
- Social vulnerability (e.g. poverty, maternity, sickness)
It is built on three pillars:
- Social Assistance – Non-contributory support (e.g. food, housing)
- Social Insurance – Contributory programs (e.g. pensions, health insurance)
- Labour Market Programs – Employment schemes to build self-reliance
Key Highlights from ILOSTAT 2025
- India’s social security coverage jumped to 64.3%, up from 19% in 2015 – a 45 percentage point increase in 10 years.
- This means over 94 crore (940 million) people are now covered under at least one form of social protection.
- India now ranks 2nd globally in terms of population covered by social security.
- It is also the first country to update its 2025 social protection data in the ILOSTAT global database, showcasing its progress in digital governance and transparency.
Major Social Protection Initiatives Driving the Surge
India’s massive expansion in social coverage is due to a wide range of targeted schemes, including:
Pension & Insurance Schemes
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Pension of ?1,000–?5,000/month for informal workers aged 18–40.
- PM Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-SYM): Contributory pension for unorganized workers with 50% government support.
- PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): ?2 lakh life insurance for people aged 18–50.
- PM Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Accident insurance of ?2 lakh for ages 18–70.
Healthcare & Nutrition
- Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY: ?5 lakh health cover for low-income families.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana: Maternity care for pregnant women.
- PM POSHAN (formerly Mid-Day Meal Scheme): Nutritional support to schoolchildren.
Income, Housing & Food Security
- MGNREGA: Guaranteed 100 days of wage employment annually in rural areas.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: ?6,000/year income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Public Distribution System (PDS) under NFSA: Subsidized food grains to eligible households.
- PM Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G): Pucca homes with basic amenities for rural poor.
Significance
- Poverty Reduction: Enhanced safety net for vulnerable populations.
- Inclusive Growth: Formal inclusion of informal sector workers.
- Digital Governance: Use of technology for efficient delivery (e.g., Aadhaar, DBT).
- Resilience Building: Helps households withstand economic shocks (e.g., pandemics, job loss).
Chenchu Tribe and Indiramma Housing Scheme

- 17 May 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Telangana government announced the sanctioning of 10,000 Indiramma houses to Chenchu tribal families under a saturation approach in four Integrated Tribal Development Agencies (ITDA)—Utnur, Bhadrachalam, Munnanur, and EturuNagaram. An additional 700 units per ST assembly constituency have also been approved within these ITDA areas.This move aligns with the state’s commitment to improving housing infrastructure in tribal areas.
About Chenchu Tribe
Classification:
- Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Andhra Pradesh
- Also found in Telangana, Karnataka, and Odisha
Habitat:
- Primarily inhabit the Nallamalai forests (Eastern Ghats)
- Chenchu settlements are called “Penta”, consisting of kin-based scattered huts
Language:
- Native Chenchu language (Dravidian family)
- Many also speak Telugu
Social Structure:
- Small conjugal families with gender equality
- Village elder, known as “Peddamanishi”, serves as the community authority
Livelihood:
- Forest-based subsistence lifestyle
- Depend on collection of non-timber forest produce (NTFPs) such as:
- Roots, tubers, fruits, beedi leaves, honey, gum, mohua flowers, tamarind
- Some serve as forest laborers, but mostly rely on traditional hunting and gathering
Religion & Culture:
- Worship local deities; blend of indigenous and Hindu practices
- Hold deep spiritual ties with the Srisailam Temple (dedicated to Lord Shiva and Devi Brahmaramba), which lies at the heart of their region
- Chenchus enjoy customary privileges at the Srisailam shrine
World Happiness Report 2025
- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Happiness Report (WHR) 2025 was released on 20th March (World Happiness Day) by the Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford, in collaboration with Gallup and the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (UNSDSN).
India’s Performance:
- India’s Rank (2025):118th out of 147 countries (Improved from 126th in 2024).
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Donations: 57th
- Volunteering: 10th
- Helping a Stranger: 74th
- Wallet Return Probability:
- 115th (by neighbor)
- 86th (by stranger)
- 93rd (by police)
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Happiness Score: Increased from 4.054 (2021–23) to 4.389 (2022–24).
- Rank among Neighbors:
- Nepal: 92nd
- Pakistan: 109th
- Myanmar: 126th
- Sri Lanka: 133rd
- Bangladesh: 134th
Top 10 Happiest Countries (2025):
- Finland (8th consecutive year)
- Denmark
- Iceland
- Sweden
- Israel
- Costa Rica (new entrant)
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Luxembourg
- Mexico(new entrant)
Least Happy Countries (Bottom 5):
- 147th: Afghanistan (4th consecutive year as lowest)
- 146th: Sierra Leone
- 145th: Lebanon
- 144th: Malawi
- 143rd: Zimbabwe
About the Report:
- Purpose: Measures global well-being through life evaluations and promotes policy focus on happiness, mental health, and quality of life over mere economic growth.
- Methodology:
- Based on Gallup World Poll (2022–2024 data).
- Uses Cantril Ladder Scale (0–10) for life evaluation.
- Six Key Indicators:
- GDP per capita
- Healthy life expectancy
- Social support
- Freedom to make life choices
- Generosity
- Perception of corruption
Global Trends in Happiness (2025):
- Nordic Dominance: Finland, Denmark, Iceland, and Sweden occupy top ranks.
- Decline in Western Countries:
- USA: 24th (down from 11th in 2012)
- UK: 23rd (lowest since 2017)
- Rising loneliness and social isolation major causes.
- Israel (5th): Maintained high rank despite ongoing conflict.
- Social Support Decline: 19% of young adults globally report having no one to rely on.
Special Focus: India vs Pakistan – The Paradox
Despite India’s:
- Higher GDP per capita ($2,480.8 vs Pakistan’s $1,365.3),
- Better health indicators (life expectancy: 58.1 vs 56.9),
- Better corruption perception rank (India: 96th, Pakistan: 135th),
India still ranks lower in happiness.
Reason: Low scores in perceived freedom and individual life satisfaction.
World Happiness Day:
- Observed on: 20th March
- Initiated by: Bhutan, which pioneered the concept of Gross National Happiness (GNH).
- Adopted by UNGA: July 2012
- Theme 2025:"Caring and Sharing"
UNESCO’s “Imagine a World with More Women in Science” Campaign

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 11, 2025, to mark the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, UNESCO, with support from Canada’s International Development Centre (IDRC), launched the global campaign titled “Imagine a World with More Women in Science.”
Campaign Highlights
- Objective: Promote gender equality in science and innovation by encouraging the active participation and leadership of women in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine).
- Social Media Drive: The campaign uses the hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience to amplify diverse voices and encourage global engagement.
- Focus: Emphasizes the real-world impact of gender disparities in science, including missed innovations, biased artificial intelligence, and inequitable scientific opportunities.
Background
- The UN General Assembly (UNGA) declared February 11 as the International Day of Women and Girls in Science in 2015 to foster female participation in scientific research and innovation globally.
Current Status of Women in Science
Global Trends
- Representation: Women comprise only one-third of the global scientific workforce.
- Leadership Gap: Merely 10% of STEM leadership positions are held by women.
India-Specific Data
- STEMM Enrolment: Women account for 43% of enrolment in STEMM disciplines.
- Women Scientists: Only 18.6% of scientists in India are women.
- R&D Projects: About 25% of R&D projects are led by women researchers.
Challenges Faced by Women in Science
Challenge Description
Restrictive Social Norms Traditional gender roles hinder women’s
scientific pursuits.
Lack of Role Models Few visible female leaders discourage young women from
aspiring to scientific careers.
Workplace Inequality Gender biases, hostile work environments, and lack of inclusive
policies create barriers.
Educational Gaps Gender-biased teaching content and insufficient support systems
limit girls’ access to science education.
Recommended Measures
Dismantle Gender Stereotypes
- Remove gender biases from teaching and learning materials.
- Include contributions of female scientists in textbooks with visuals.
- Promote equitable representation of women in boards, panels, and decision-making bodies.
Enhance Visibility of Women Role Models
- Highlight discoveries by female scientists.
- Increase media and curriculum exposure to successful women in science.
Open Educational Pathways
- Promote inclusive teaching practices and gender-neutral curricula.
- Encourage CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives to support girls in science education.
Create Inclusive Work Environments
- Enforce policies for diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Take strong action against gender-based violence, including sexism and harassment in the workplace.
- Advance women into leadership roles in scientific institutions.
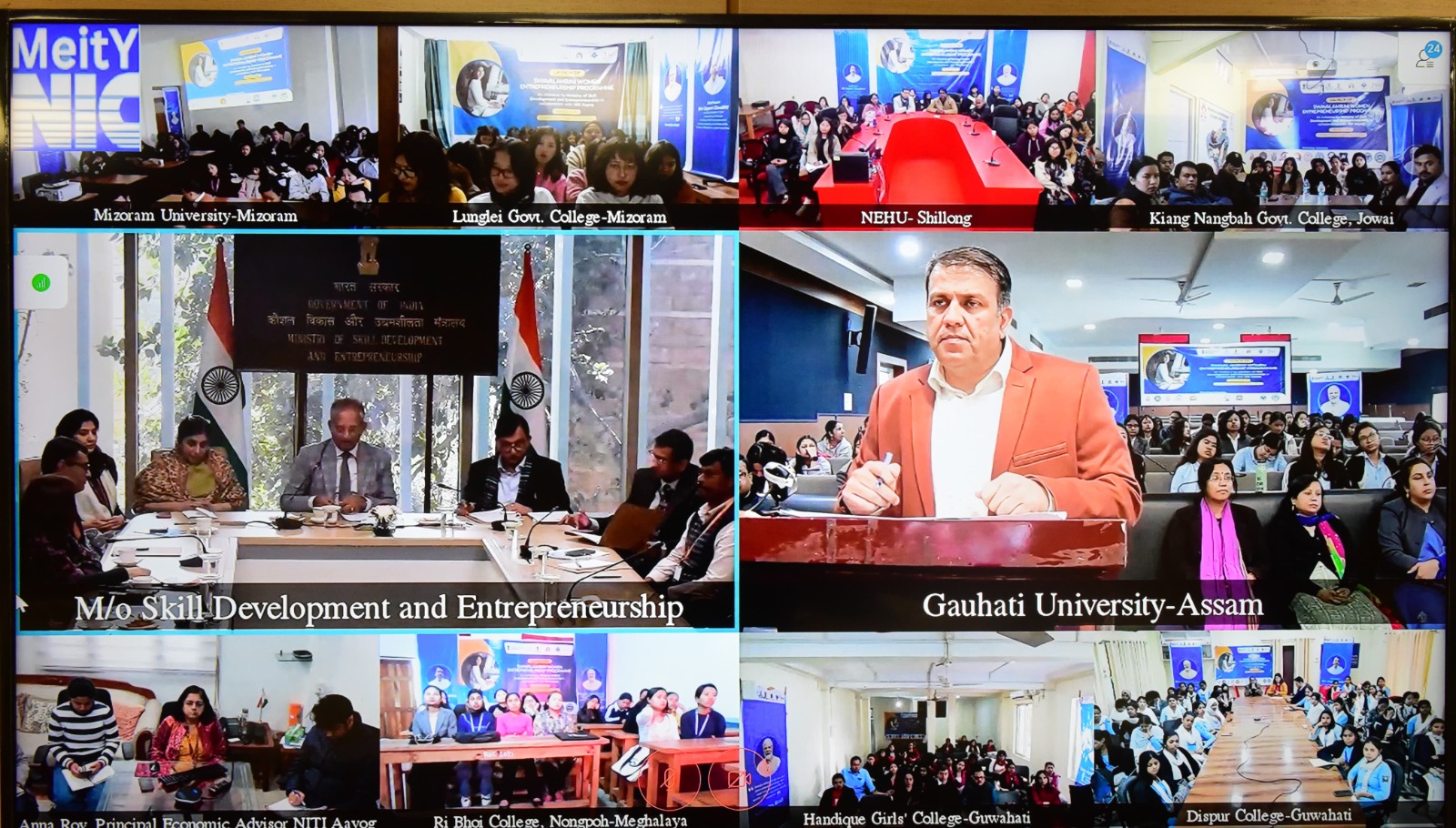
SwavalambiniProgramme

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The SwavalambiniProgramme, launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) in collaboration with NITI Aayog, is a pioneering initiative aimed at empowering women in the Northeast.
This programme targets female students in select Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, providing them with an entrepreneurial mindset, essential resources, and ongoing mentorship to ensure their success in entrepreneurial ventures.
Programme Structure and Implementation
The programme follows a structured, stage-wise entrepreneurial process to guide participants through the various phases of business creation, from awareness to development, mentorship, and funding. It includes the following key components:
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP): Introduces 600 female students to entrepreneurship as a viable career option. The programme involves a 2-day session covering foundational entrepreneurial concepts and opportunities.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): This intensive 40-hour training is offered to 300 selected students, covering crucial aspects of business, including:
- Business training and skilling
- Access to finance and market linkages
- Compliance and legal support
- Networking opportunities
- Mentorship: After completing the training, participants receive six months of mentorship to help them translate their ideas into sustainable business ventures.
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP): A 5-day FDP will upskill faculty members in HEIs, enabling them to effectively mentor students in entrepreneurship. The training focuses on industry insights, business incubation strategies, and coaching techniques.
- Award to Rewards Initiative: Successful ventures will be recognized and awarded, inspiring others and fostering a culture of women-led enterprises.
Expected Outcomes and Impact
- The SwavalambiniProgramme aims to promote entrepreneurship among women, with an expectation that 10% of EDP trainees will successfully launch their businesses.
- It strives to establish a clear framework for nurturing and scaling women-led enterprises in India.
- The initiative contributes to economic transformation by making entrepreneurship a viable career path for women, particularly in the Northeast, a region brimming with untapped entrepreneurial potential.
Alignment with National Policies
The SwavalambiniProgramme aligns with several national initiatives and policies aimed at promoting women entrepreneurship:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The programme complements the NEP’s vision by integrating skill development, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-driven education within HEIs.
- Women Entrepreneurship Schemes: It strengthens existing initiatives like Start-Up India, Stand-Up India, PM Mudra Yojana, and the Women Entrepreneurship Platform, providing financial and mentorship support to emerging women entrepreneurs.
- Union Budget 2025: The ?10,000 crore start-up fund and the extension of the 100% tax exemption on start-up profits for five years in the Union Budget 2025 offer crucial financial backing for women-led enterprises.
Launch and Regional Focus
The programme was officially launched across nine colleges and universities in the Northeast, including Gauhati University, North-Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Mizoram University, and others.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, being the Nodal Department for the welfare of senior citizens, develops and implements programmes and policies for these groups in close collaboration with State Governments, Non-Governmental Organisations and civil society.
About the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens.
- The project is implemented by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Aims and Objectives:
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
The components of the AVYAY Scheme are as under:-
-
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC)
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC)
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY)
- Elderline – National Helpline for Senior Citizens
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE)
- Geriatric Caregivers Training
Components of the AVYAY Scheme:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): Grant aid is provided to Non-Governmental/ Voluntary Organizations for running and maintenance of Senior Citizens' Homes (old age homes), continuous care homes, etc.
- Facilities like shelter, nutrition, medicare and entertainment are provided free of cost to indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC): Grant in aid is released to States/ UTs for the creation of a pool of trained Geriatric Caregivers for senior citizens, for carrying a special drive for Cataract Surgeries for Senior Citizens and State Specific Activities for the welfare of senior citizens, especially who are indigent in the States/UTs.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): To provide for senior citizens, suffering from any age-related disability/infirmity such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- The eligible senior citizens under this component are those who are in the BPL Category or have monthly income up to Rs.15000/.
- Generic and non-generic devices are distributed to the senior citizens through the camps.
- Elderline: National Helpline for Senior Citizens (14567): The Ministry has set up the National Helpline for Senior Citizens to provide free information, Guidance, Emotional Support and field intervention in cases of abuse and rescues.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): To promote out-of-the-box and innovative solutions for commonly faced problems, innovative start-ups are identified and encouraged to develop products, processes and services for the welfare of the elderly under this initiative.
- The initiative is implemented through IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd. (Investment Manager).
- Geriatric Caregivers Training: To bridge the gap in supply and increasing demand in the field of geriatric caregivers and also to create a cadre of professional caregivers in the field of geriatrics.
- The component is implemented through the National Institute of Social Defence and at present 3,180 geriatric caregivers have been trained.
