Sakura Science High School Programme 2025

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
- In June 2025, 20 Indian school students were officially flagged off by Shri Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL), to participate in the prestigious Sakura Science High School Programme 2025 in Japan.
- The initiative reflects India's growing focus on international educational exposure, scientific collaboration, and experiential learning, in alignment with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
About the Sakura Science Programme
- Launched by: Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) in 2014.
- Objective: To promote science, technology, and innovation through Asia-wide youth exchanges.
- India’s Participation: Since 2016; over 619 students and 91 supervisors have participated till 2025.
- Participants (2025 batch):
- 20 students (7 boys, 13 girls) from Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas and government schools in Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Ladakh, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura.
- Accompanied by 2 supervisors.
- Programme duration: 15–21 June 2025.
- Participating countries (2025): India, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Ukraine.
Key Features of the Programme
- Hands-on Learning: Visits to advanced scientific labs, tech demonstration centres, and universities in Japan.
- Cultural Exposure: Insight into Japanese traditions, societal values, and innovation ecosystem.
- International Peer Exchange: Interaction with students from other Asian nations to foster global scientific thinking.
Relevance to NEP 2020
The NEP 2020 advocates experiential, holistic, and integrated learning. It highlights:
- The need for educational excursions to places of scientific, cultural, and technological relevance.
- Promoting international collaborations that broaden the intellectual horizons of learners.
- Encouraging innovation through interdisciplinary exposure and real-world learning.
The Sakura Programme complements NEP 2020’s goals by offering Indian students a unique platform to explore global advancements in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields.
Strategic Importance
- Science Diplomacy: Strengthens Indo-Japanese relations in education and technology.
- Youth Empowerment: Builds future-ready, globally aware scientific talent.
- Inclusivity: Focuses on students from remote and underserved regions, aligning with India’s equity-focused educational reforms.
Rinderpest

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
- India has been officially designated as a Category A Rinderpest Holding Facility (RHF) by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- The recognition was conferred to the ICAR-National Institute of High Security Animal Diseases (NIHSAD) in Bhopal during the 92nd General Session of WOAH held in Paris.
- This makes India one of only six countries globally entrusted with this vital responsibility, marking a major milestone in India’s global leadership in animal health and biosecurity.
What is Rinderpest?
- Also Known As: Cattle Plague
- Pathogen: Caused by a virus from the Paramyxoviridae family, genus Morbillivirus.
- Affected Species: Mainly cattle and buffalo, but also zebus, giraffes, eland, wildebeest, warthogs, and some antelope species.
- Symptoms in Cattle:
- High fever, nasal and eye discharge
- Erosive mouth lesions
- Severe diarrhoea and dehydration
- Death typically within 10–15 days in susceptible herds
- Transmission: Through direct contact; virus present in nasal secretions even before clinical symptoms appear.
- Public Health Risk: None – the virus does not affect humans.
- Geographical Spread: Historically affected Europe, Africa, and Asia.
- Eradication: Officially declared eradicated in 2011, making it the second disease in history to be eradicated after smallpox.
Significance of the Category A RHF Designation
- Background:
- Despite eradication, Rinderpest Virus-Containing Material (RVCM) remains in select laboratories.
- FAO and WOAH limit storage of RVCM to ensure global biosecurity and prevent accidental or intentional release.
- India’s Preparedness:
- In 2012, ICAR-NIHSAD was designated as India’s national repository for RVCM.
- It is a Biosafety Level-3 (BSL-3) facility and a WOAH reference laboratory for avian influenza.
- Recent Developments:
- India submitted its RHF application in 2019.
- In March 2025, FAO-WOAH appointed international experts to inspect the facility.
- Based on strong biosafety, inventory control, and emergency preparedness, ICAR-NIHSAD has now received Category A RHF status for one year.
Implications for India
- Global Recognition: Reinforces India’s commitment to the One Health framework and global biosecurity norms.
- Leadership Role: Positions India among a select global group of only six RHFs, enabling it to contribute to future efforts in disease surveillance, vaccine research, and emergency preparedness.
- Future Prospects:
- Encouraged by WOAH-FAO to contribute to vaccine seed material discussions.
- Paves the way for Category B designation, which allows broader collaborative work on RVCM.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
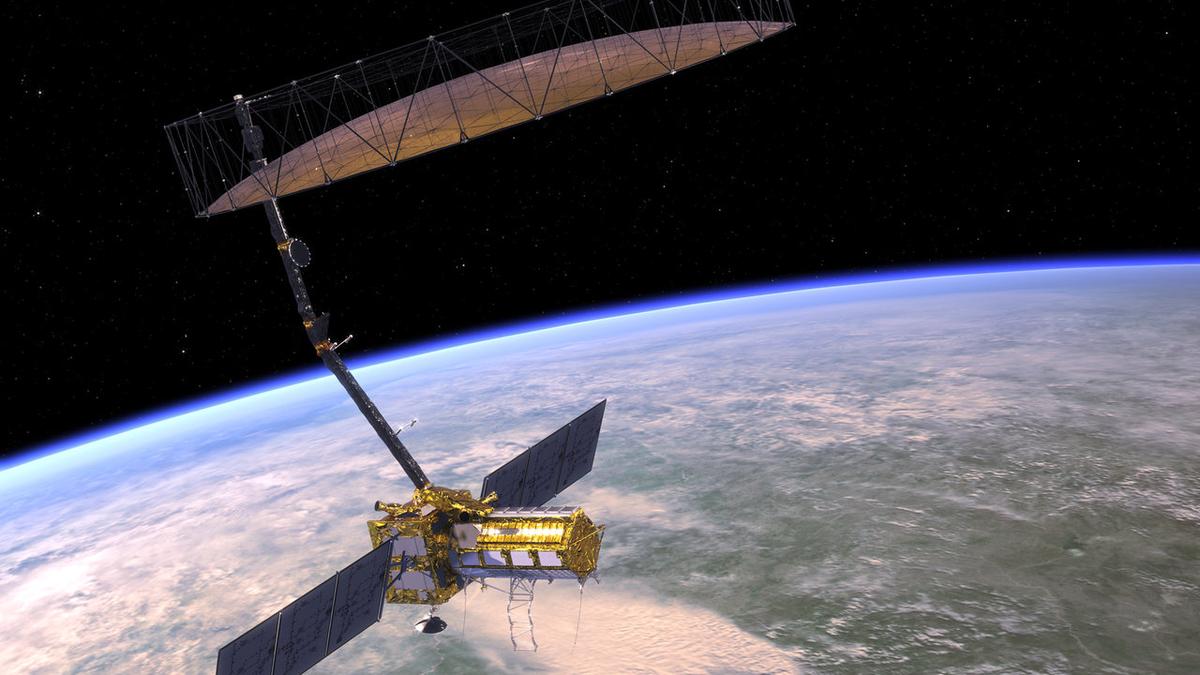
Recently, NASA said the NASA-ISRO SAR mission had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota
What is Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)?
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is an advanced remote sensing technology used to generate high-resolution images of Earth's surface, irrespective of weather or lighting conditions.
- Unlike optical sensors that rely on visible light, SAR systems emit microwave pulses and measure the reflected signals (echoes) from the ground, ocean, ice, or structures.
- These echoes are then processed to create detailed images using advanced signal processing techniques.
How SAR Works
- Antenna System: Traditionally, larger antennas yield better resolution, but they are impractical for satellites. SAR overcomes this by using a small antenna mounted on a moving platform (like a satellite), capturing echoes from different positions.
- Through precise timing and phase information, the system simulates a much larger "synthetic" antenna, enhancing image resolution without the need for large hardware.
Advantages of SAR
- All-Weather, All-Time Imaging: SAR can operate day and night and penetrate clouds, smoke, and light rain, ensuring uninterrupted data collection.
- Material Differentiation: Various materials (soil, water, vegetation, buildings) reflect microwaves differently, enabling SAR to detect subtle changes not visible through optical imagery.
- Large Area Mapping: Mounted on satellites, SAR can map swaths of land hundreds of kilometres wide in a single pass.
NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) Mission
- Joint Collaboration: A flagship Earth-observing mission between NASA and ISRO.
- On June 12, 2025, NASA confirmed that the NISAR satellite had arrived at ISRO’s spaceport in Sriharikota for its scheduled launch.
Mission Objectives
- NISAR will map nearly all of Earth's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.
- It aims to provide unprecedented data on Earth’s environment, including:
- Ecosystem disturbances
- Land use changes
- Ice sheet dynamics
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, landslides, floods)
Significance
- Will support climate change monitoring, disaster response, and agricultural planning.
- It represents a major step in India’s and the U.S.'s scientific diplomacy and technological cooperation.
AI and Biomanufacturing in India

- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into India's biomanufacturing sector is gaining momentum with the launch of the BioE3 Policy and the IndiaAI Mission.
What is Biomanufacturing?
- Biomanufacturing involves the use of living cells, enzymes, or biological systems to produce commercial goods such as vaccines, biologics, biofuels, specialty chemicals, biodegradable plastics, and advanced materials.
- The convergence of synthetic biology, industrial biotechnology, and artificial intelligence (AI) has expanded its scope across sectors like healthcare, agriculture, energy, and materials science.
- India, often called the “Pharmacy of the World”, produces over 60% of global vaccines, underlining its industrial strength in biomanufacturing.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Biomanufacturing
AI is revolutionizing biomanufacturing by making it predictive, efficient, and scalable:
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning tools adjust variables like temperature, pH, and nutrient supply in real time to enhance fermentation and reduce batch failure.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of biomanufacturing plants allow engineers to simulate operations, test changes, and foresee potential disruptions without real-world risks.
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AI expedites molecular modeling and screening of drug candidates, reducing time and cost of development.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI forecasts machinery failures, improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
- Smart Supply Chains: AI-driven logistics optimize cold-chain storage and forecast medicine demand, ensuring timely distribution.
Indian Examples and Industrial Applications
- Biocon uses AI to enhance drug screening and fermentation quality.
- Strand Life Sciences applies machine learning in genomics for faster diagnostics.
- Wipro and TCS are developing AI platforms for clinical trials, molecule screening, and treatment prediction.
- AI is also being explored in rural healthcare, using region-specific data for localized diagnostics and advisories.
Key Government Initiatives
- BioE3 Policy (2024):
- Envisions Bio-AI hubs, biofoundries, and next-gen biomanufacturing infrastructure.
- Supports startups with funding and incentives.
- IndiaAI Mission:
- Promotes ethical, explainable AI in sectors like health and biotech.
- Supports bias reduction, machine unlearning, and transparency in AI models.
- Biomanufacturing Mission (2023): Aims to promote R&D and domestic production in bio-based sectors.
- PLI Scheme for Biotech: Incentivizes local production of enzymes, fermentation inputs, and biologics.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023): Lays down principles for lawful data processing, though not tailored for AI-biotech intersection yet.
Challenges in Policy and Regulation
Regulatory Gaps:
- India’s existing drug and biotech laws were designed before the AI era.
- No clear mechanism exists to audit, certify, or govern AI-operated bioreactors or predictive drug systems.
Data and Model Risks:
- AI systems trained on urban datasets may fail in rural or semi-urban manufacturing due to variable water quality, temperature, or power conditions.
- Lack of norms on dataset diversity and model validation raises risk of system failure and reputational damage.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Traditional IP laws do not clarify ownership of AI-generated inventions, molecules, or production protocols.
Workforce and Infrastructure:
- Biomanufacturing needs a workforce skilled in both computational biology and automation.
- India’s AI-bio talent gap and limited high-tech infrastructure outside metro cities hinders inclusive growth.
Ethical & Safety Concerns:
- Without context-specific oversight, AI errors can threaten public safety and product integrity.
- Trust in AI systems requires clear guidelines on explainability, accountability, and redress mechanisms.
Global Best Practices
- EU’s AI Act (2024): Classifies AI applications based on risk levels. High-risk applications (e.g., genetic editing) are subject to strict audits.
- US FDA Guidance (2025):
- Introduces seven-step credibility frameworks for AI in healthcare.
- Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) allow iterative AI updates while ensuring safety.
India lacks similar risk-based, adaptive oversight.
Policy Recommendations
- Establish AI-Biomanufacturing Regulatory Framework:
- Introduce tiered regulation based on context and risk.
- Define use-cases, audit mechanisms, and model validation standards.
- Mandate Dataset Diversity & Safety Audits:
- Ensure AI tools are trained on representative, unbiased, clean data.
- Create regulatory sandboxes to test AI systems in controlled environments.
- Strengthen Public–Private Partnerships:
- Boost industry-academia collaborations.
- Incentivize private investment through R&D credits and de-risking instruments.
- Modernize IP and Licensing Laws:
- Establish clarity on ownership of AI-generated discoveries.
- Develop licensing frameworks for bio-AI algorithms and training data.
- Upskill the Workforce: Promote interdisciplinary training across life sciences, data science, and industrial robotics.
Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc)
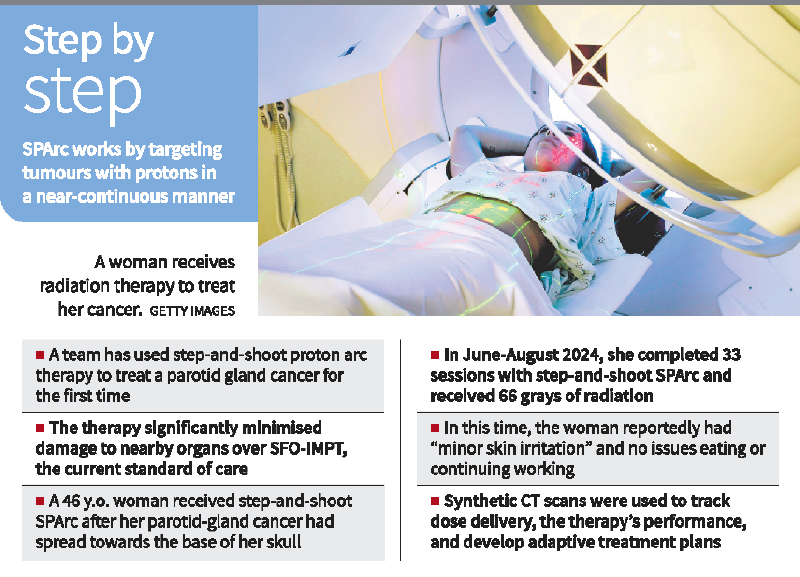
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant medical advancement, a team at the Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. has successfully administered Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc) to treat adenoid cystic carcinoma—a cancer originating in the parotid gland. This marked the first-ever clinical application of this technology. The findings were published in the International Journal of Particle Therapy in June 2025.
What is SPArc Therapy?
SPArc (Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy) is an advanced form of proton beam therapy where proton particles are delivered in a controlled arc across the tumor. It includes two primary modalities:
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc: Follows a pre-programmed dose delivery path.
- Dynamic SPArc: Simulated version where energy levels and targeting points are adjusted in real-time. (Still under regulatory review)
Comparison with Existing Techniques
The study compared three techniques:
- SFO-IMPT (Single-Field Optimized Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy – current standard)
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc (clinical)
- Dynamic SPArc (simulated)
SPArc showed reduced radiation exposure to key organs when compared with SFO-IMPT:
- Brainstem: ↓ 10%
- Optical chiasm: ↓ 56%
- Oral cavity: ↓ 72%
- Spinal canal: ↓ 90%
Treatment Case Study
The first patient treated was a 46-year-old woman with a tumor extending from her parotid gland to the base of her skull. She underwent 33 sessions of SPArc therapy from June to August 2024, reporting only minor skin irritation and no disruptions to eating or daily functioning.
Process & Technology Used:
- Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) was used for real-time imaging before each session.
- A machine learning model converted CBCT to synthetic CT, allowing accurate dose tracking.
- As the patient lost weight, the dose plan was adjusted after two weeks to maintain precision.
- Nine beam angles spanning a 180º arc were used, delivering radiation at 20º intervals.
Each session lasted about 15–18 minutes, enabling nearly continuous dose delivery.
Working Mechanism
- The therapy operates by 'painting' the tumor in energy layers.
- Each energy level targets a specific tissue depth, ensuring maximum precision.
- The system scans dozens of spots in each layer before moving to the next one with increased penetration.
Advantages
- High precision in delivering radiation to deep and complex anatomical regions like the skull base.
- Limits collateral damage to vital organs.
- Effective in large or invasive tumours.
- Better quality of life during treatment (reduced side effects such as fatigue or swallowing issues).
Limitations & Concerns
- Geographical miss risk: Tiny tumors may be missed due to breathing motion or tumor shrinkage over time.
- Cost: High installation and operational costs, making it suitable for a limited patient base.
- Potential for overuse in non-indicated cases, leading to inequitable healthcare delivery.
- Dynamic SPArc still awaits regulatory clearance and integration into oncology systems.
Significance for India
SPArc therapy can be transformative for cancers in anatomically intricate regions and may serve as a benchmark for future precision cancer therapies. However, adoption in India requires cost-reduction, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks.
Kruti and BharatGPT Mini
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
India is witnessing a significant leap in artificial intelligence innovation with the launch of two indigenous AI models — Kruti by Krutrim and BharatGPT Mini by CoRover. These developments aim to democratize AI access across the country by addressing local needs, multilingual capabilities, and infrastructure limitations.
Kruti: India’s First Agentic AI Assistant
Developed by Krutrim, the AI startup co-founded by Bhavish Aggarwal (of Ola fame), Kruti is positioned as India’s first agentic AI, going beyond conventional chatbots. Launched in 2025, Kruti integrates task execution capabilities such as:
- Cab booking
- Food ordering
- Bill payments
- Image generation
- Research assistance
Kruti is powered by Krutrim V2, a locally trained large language model (LLM), and combines open-source AI systems to deliver scalable, cost-effective, and contextualised solutions.
Key Features of Kruti
- Multilingual Support: Understands voice and text in 13 Indian languages
- Personalised AI: Learns user preferences, adapts tone and content
- Human-Centric Design: Supports read-aloud responses, summarised answers, stories, and tables
- SDK for Developers: Offers embeddable tools for LLM orchestration and task automation
- Integrated Assistant: Eliminates app-switching fatigue through contextual task handling
Aggarwal highlighted that Kruti is built for “how Indians live”—mobile-first, intuitive, and multilingual—offering free access to advanced AI tools.
Strategic Investment and Open AI Ecosystem
Krutrim has committed ?12,000 crore in investment (?2,000 crore already, ?10,000 crore by next year), launched Krutrim AI Lab, and published technical resources, with contributions to the open-source community. The company is positioning itself as a competitive force against global giants like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic, and local firms like Sarvam AI.
BharatGPT Mini: Small Language Model for Bharat
On the same day, CoRover, a conversational AI firm, unveiled BharatGPT Mini, a small language model (SLM) with 534 million parameters trained on its proprietary conversational dataset.
- Supports 14 Indian languages
- Designed for low-compute, low-infrastructure environments
- Enables offline and edge deployments for fast, privacy-centric performance
- Ideal for underserved and rural regions with limited internet or device capacity
SLMs like BharatGPT Mini are emerging as viable tools for domain-specific, lightweight, and privacy-respecting AI in India, complementing the role of LLMs in more complex tasks.
Understanding Tourette Syndrome
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that typically begins in early childhood, often between the ages of 2 and 15, with an average onset around six years. Affecting approximately 0.3% to 1% of the global population, TS is more prevalent among boys than girls. Despite its neurological basis, it remains poorly understood and frequently misdiagnosed, particularly in school settings where symptoms are mistaken for behavioural issues.
Nature and Classification of Tics
Tourette Syndrome is characterised by tics—sudden, repetitive, and involuntary movements or vocalisations. These are classified as:
- Simple tics, such as eye blinking, facial grimacing, throat clearing, or sniffing, involve a single muscle group or sound.
- Complex tics are more coordinated, involving actions like hopping, touching objects, or uttering phrases. Rarely, individuals may display coprolalia, the involuntary use of obscene language.
Tics often intensify with stress or excitement, diminish during calm periods, and usually disappear in deep sleep. External stimuli such as excessive screen exposure have also been linked to an increase in tics, particularly in children.
Causes and Co-morbidities
While the exact cause of TS remains unknown, researchers point to a combination of genetic predisposition and neurobiological factors, including abnormalities in brain regions such as the basal ganglia and frontal lobes. Environmental triggers—like low birth weight, perinatal complications, and post-infectious conditions (e.g., streptococcal infections)—may also contribute.
Tourette’s often coexists with other conditions such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. The presence of these co-morbidities complicates diagnosis and management.
Management and Treatment Approaches
Treatment is individualised and not always pharmacological. Many children with mild, non-disruptive tics do not require medication. Instead, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and behavioural interventions have shown significant efficacy. These therapies help children manage their symptoms while also training families to provide supportive environments that reduce stress and tic frequency.
Medications may be considered in severe cases where tics hinder daily functioning. Importantly, suppression or punishment of tics is counterproductive, often exacerbating symptoms due to built-up tension.
Social Stigma and the Need for Awareness
The primary challenge in managing TS lies not in the disorder itself, but in the societal misunderstanding surrounding it. Children with TS are often labelled as attention-seeking or disruptive, leading to social isolation and emotional distress. As seen in the case of a child from Kochi, delayed diagnosis and stigma worsened his condition until it was recognised as Tourette’s.
Educating teachers, parents, and peers is crucial. Early diagnosis, empathetic engagement, and inclusive school environments are essential to ensuring that children with TS are treated with dignity and compassion.
NASA's Mars Odyssey captures volcano piercing ice cloud belt
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
- Recently, NASA’s 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter captured a stunning image of Arsia Mons, a giant Martian volcano, rising through a morning belt of water-ice clouds.
- First such astronaut-like horizon view of Tharsis Montes volcanoes on Mars.
About Arsia Mons
- Part of Tharsis Montes, a trio of volcanoes near Mars' equator.
- Height: ~20 km (12 miles) – twice the height of Mauna Loa, Earth’s tallest volcano.
- Cloudiest of the Tharsis volcanoes.
- Cloud formation due to orographic uplift and cooling during Mars’ aphelion (farthest point from Sun).
- Featured in the aphelion cloud belt — a seasonal band of water-ice clouds.
Mission Evolution
- Mars Odyssey, launched in 2001, is the longest-operating Mars orbiter.
- In 2023, began a new imaging mode: rotating its THEMIS camera to capture horizon views of Mars’ upper atmosphere.
- These angled images help study seasonal changes in dust and water-ice cloud layers.
Scientific Significance
- Helps track Martian atmospheric evolution, especially cloud behavior and dust storms.
- Valuable for future human missions:
- Assists landing site safety planning.
- THEMIS also detects subsurface water ice, key for astronaut resource use.
Instruments and Collaborators
- THEMIS: Thermal Emission Imaging System, captures both visible and infrared light.
- Managed by NASA’s JPL, designed by Arizona State University, built by Lockheed Martin.
Starlink receives DoT licence to launch Satellite Internet in India

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has granted a licence to Elon Musk’s Starlink to provide satellite-based internet services in India.
- Starlink becomes the third company, after Eutelsat OneWeb and Jio Satellite Communications, to receive such approval. A fourth contender, Amazon’s Kuiper, is still awaiting clearance.
What is Starlink?
- Developer: Starlink is a satellite internet system by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
- Objective: Deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband globally, especially targeting rural and remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Technology:
- Operates a constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites (~550 km altitude).
- Satellites communicate via laser links for inter-satellite data relay, forming a global mesh.
- Ground stations transmit data to satellites, which then beam it to user terminals.
Key Features of Starlink
- Speed: Up to 150 Mbps, with future plans to increase it.
- Latency: As low as 20–25 milliseconds — ideal for video calls and streaming.
- Tech Stack:
- Flat-panel antennas for easy user access.
- Argon-powered ion thrusters for satellite positioning.
- Space lasers for fast inter-satellite communication.
- Deployment: Satellites launched via Falcon 9 rockets with regular updates.
- Scale: Plans to deploy up to 42,000 satellites globally.
Significance for India
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Ensures internet access in rural, remote, and disaster-prone regions.
- Reduced Infrastructure Dependency: Less reliance on fibre optics and mobile towers in hard-to-reach areas.
- Boost to Digital Economy: Enhances competition in India’s broadband sector, especially in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Security Compliance: Starlink must adhere to India’s security norms, including lawful interception requirements, before commercial rollout.
- Next Steps: Will receive trial spectrum within 15–20 days post-application.
Neutrino Mass and the KATRIN Experiment
- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
The KATRIN experiment nearly halved the maximum possible mass for the subatomic particles.
What are Neutrinos?
- Neutrinos are electrically neutral fundamental particles under the Standard Model of particle physics.
- They are produced in natural processes such as radioactive decay and nuclear reactions in stars and the Sun.
- Notably, they interact very weakly with matter and possess extremely small mass — less than a millionth the mass of an electron.
- Their exact mass is still not directly known, making them a key area of research in modern physics.
The KATRIN Experiment
- Full Form: Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment
- Location: Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany
- Objective: To determine the mass of the electron antineutrino, a type of neutrino released during beta decay of tritium.
- Method: By observing the energy spectrum of electrons emitted from tritium decay, scientists infer the mass of the associated neutrino — since more massive neutrinos carry away more energy.
Latest Findings (2025)
- KATRIN has now lowered the upper limit of the neutrino mass to less than 0.45 electron volts (eV).
- This marks a ~50% improvement from its previous estimate, demonstrating enhanced precision in measurements.
- The conclusion was drawn from analysis of 36 million electrons emitted during tritium decay.
Legionnaires’ Disease
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
Health authorities in New South Wales (NSW), Australia, have issued a public alert after a spike in Legionnaires’ disease cases in Sydney. The outbreak is suspected to be linked to contaminated air-conditioning systems in the city.
About Legionnaires’ Disease
Aspect Details
Cause Legionella bacteria, found in freshwater and man-made water systems
Type A severe form of pneumonia
Related Disease Pontiac fever – a milder, flu-like respiratory illness caused by the same bacteria
Key Features
- Symptoms:
- High fever, cough, shortness of breath
- Muscle pain, headaches, confusion
- Diarrhoea or nausea in some cases
- Transmission:
- Not person-to-person
- Spread through inhalation of contaminated aerosols (e.g., from cooling towers, air conditioners, hot tubs)
- Risk Factors:
- Elderly individuals
- Smokers
- People with weakened immune systems or chronic lung conditions
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment: Requires antibiotic therapy
- Vaccine: No vaccine currently available
- Prevention:
- Regular maintenance and disinfection of water systems
- Monitoring air-conditioning and cooling systems
Sunbird

- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
British startup Pulsar Fusion is developing Sunbird, a nuclear fusion-powered rocket that could significantly reduce travel time to outer planets like Mars and Pluto. An orbital demonstration is planned for 2027.
Key Features of Sunbird
- Maximum Speed: Up to 805,000 km/h, surpassing the Parker Solar Probe (692,000 km/h), the fastest human-made object to date.
- Travel Efficiency: Could enable missions to Pluto in just 4 years, and cut travel time to Mars by nearly 50%.
- Payload Capacity: Capable of delivering up to 2,000 kg to Mars in six months.
- Functionality: Unlike chemical rockets like SpaceX’s Starship, Sunbird would act as an interplanetary booster, attaching to spacecraft and possibly operating between charging stations in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Mars orbit.
About Nuclear Fusion Propulsion
Nuclear Fusion aims to replicate the process that powers stars — the fusion of atomic nuclei to release energy. Unlike nuclear fission, fusion is cleaner, offers higher energy output, and produces minimal radioactive waste.
Types of Nuclear Propulsion Systems
Propulsion Type Description
Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) Uses a nuclear reactor to heat liquid hydrogen which
turns to plasma and produces thrust. Provides high exhaust
velocity and can increase payload efficiency 2–3 times
over chemical rockets. Ground tests began in the 1950s.
Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NEP) Converts reactor heat into electricity to power ion thrusters,
which gradually reach high speeds. Components include a
compact reactor core, electric generator, heat rejection
system, and electric propulsion system. Unlike solar power,
nuclear sources ensure consistent energy beyond Mars.
Challenges in Fusion Rocket Development
- Fusion systems are currently large and heavy, posing difficulties in miniaturisation for spaceflight.
- Fusion on Earth is hard to replicate due to atmospheric constraints; space offers a more natural environment for fusion reactions.
Global Efforts and Timeline
Apart from Pulsar Fusion, companies like Helicity Space and General Atomics (backed by NASA and Lockheed Martin) are also advancing fusion-powered space propulsion systems, with testing planned around 2027.
IISc Develops Nanozyme to Prevent Excessive Blood Clotting

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru have developed a novel vanadium-based nanozyme that effectively controls abnormal blood clotting by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). This innovation holds promise for managing life-threatening conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and ischemic stroke.
Scientific Background:
- Normal Blood Clotting: Platelets are specialized blood cells that form clots at injury sites through a process called haemostasis, involving activation by physiological chemicals like collagen and thrombin.
- Problem of Abnormal Clotting: In conditions like COVID-19 and PTE, oxidative stress increases, leading to elevated ROS levels. This causes hyperactivation of platelets, resulting in excessive clot formation (thrombosis) — a leading cause of death globally.
Nanozyme Innovation by IISc:
- What is a Nanozyme?
An engineered nanomaterial that mimics the action of natural enzymes, in this case, glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes ROS.
- Material Used: Vanadium pentoxide (V?O?) nanozymes, particularly those with spherical morphology, were found to be the most efficient.
- Mechanism: The redox-active surface of vanadium nanozymes catalytically reduces ROS, preventing unwanted platelet aggregation.
Testing and Results:
- In vitro testing: Human blood platelets were activated with physiological agonists. Nanozymes were tested for their ability to curb excessive aggregation.
- In vivo testing (mouse model of PTE):
- Nanozyme injection led to reduced thrombosis.
- Improved survival rates without observable toxicity.
- Animals were monitored for 5 days post-treatment for health parameters.
Future Prospects:
- Researchers aim to test the nanozyme's potential against ischemic strokes, which also result from vascular blockages.
- Encouraging results with human platelets indicate the possibility of clinical trials in the near future.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Western Europe – 2022 Onwards
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Western Europe is experiencing its largest diphtheria outbreak in 70 years, with cases predominantly among vulnerable groups such as migrants and the homeless. The outbreak, which began in 2022, has raised concerns over disease surveillance, migrant healthcare, and immunisation coverage.
Key Facts from the Outbreak
- As per a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, 536 cases and three deaths have been reported across Europe since 2022.
- Most cases were found among young males (average age: 18) who had recently migrated, particularly from Afghanistan and Syria.
- 98% of strains exhibited close genetic similarities, suggesting a common transmission point during migration journeys or in accommodation facilities, not in the countries of origin.
- A genetic match between the 2022 strains and a recent 2025 case in Germany indicates that the bacteria is still circulating silently in the region.
Recommendations from Health Experts
- Enhance vaccination drives, particularly among high-risk and underserved populations.
- Improve awareness among healthcare providers, especially those working with migrants and the homeless.
- Ensure better access to antibiotics and diphtheria antitoxins.
- Strengthen disease surveillance and contact tracing mechanisms.
About Diphtheria
Feature Details
Cause Corynebacterium diphtheriae (produces a potent toxin)
Mode of Spread Respiratory droplets, contact with infected sores or ulcers
Affected Areas Primarily the respiratory tract, but also the skin in some cases
Symptoms Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weakness; grey membrane in throat
Severe Impact Can lead to breathing difficulties, heart and kidney damage, and neurological issues if untreated
Treatment Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT), antibiotics, and supportive care
Fatality Rate Up to 30% in unvaccinated individuals; higher in children
Prevention Vaccination (DPT/DTP) is the most effective preventive measure
BharatGen

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh launched BharatGen, India’s first indigenously developed, government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) at the BharatGen Summit 2025, marking a significant step in India’s AI innovation landscape.
About BharatGen:
- BharatGen is a Multimodal LLM designed to support 22 Indian languages and various content formats—text, speech, and image.
- Developed under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) and implemented by the TIH Foundation for IoT and IoE at IIT Bombay.
- Supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), it is a collaborative effort involving premier academic institutions, researchers, and innovators.
Key Features:
- Multilingual and multimodal capabilities (text, voice, image inputs).
- Open-source platform to encourage accessible innovation.
- Trained on Indian datasets to reflect Indian linguistic and cultural diversity.
- Integrated applications across critical sectors like healthcare, education, governance, and agriculture.
- Aims to deliver region-specific AI solutions rooted in Indian values and societal contexts.
Implementation Mechanism:
- Executed through 25 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIHs) across India.
- Four of these TIHs have been upgraded to Technology Translational Research Parks (TTRPs) for real-world deployment.
- Guided by four pillars: technology development, entrepreneurship, human resource development, and international collaboration.
IndiaAI Mission

- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
India has taken a major step toward self-reliance in Artificial Intelligence with the expansion of its national AI compute infrastructure and the selection of three new startups to build indigenous foundation models under the IndiaAI Mission.
Key Highlights
- Compute Infrastructure Boost:India’s total GPU capacity has now surpassed 34,000 units, up from the initial 10,000-target. A fresh addition of 15,916 GPUs to the existing 18,417 empanelled GPUs brings the total to 34,333 GPUs, now available through the IndiaAI Compute Portal (operational since March 2025).
- Subsidised Access:These GPUs are made available at a subsidised rate of ?67/hour, well below the global average of ?115/hour. This has been made possible through private sector empanelment instead of government-built data centres. Service providers receive up to 40% capital subsidy, enabling rapid infrastructure rollout.
- Empanelled Providers:Seven private companies were empanelled for compute provisioning:
- Cyfuture India Pvt. Ltd.
- Ishan Infotech Ltd.
- Locuz Enterprise Solutions Ltd.
- Netmagic IT Services Pvt. Ltd.
- Sify Digital Services Ltd.
- Vensysco Technologies Ltd.
- Yotta Data Services Pvt. Ltd.
Foundation Model Development
Under the IndiaAI Foundation Model initiative, three new startups have joined Sarvam AI (selected earlier in April 2025) to build India-specific Large Language Models (LLMs):
- Soket AI: Will develop a 120-billion parameter open-source model focused on Indian languages and use cases in defence, healthcare, and education.
- Gnani AI: Building a 14-billion parameter Voice AI model for real-time, multilingual speech recognition and reasoning.
- Gan AI: Developing a 70-billion parameter multilingual TTS (text-to-speech) model aiming for "superhuman" capabilities surpassing global benchmarks.
- Sarvam AI: Previously selected to create a 120-billion parameter Sovereign AI model, following the release of Sarvam-1 (2B parameters) and Sarvam-M (24B parameters).
These foundation models will be trained on Indian datasets and tailored for governance, public service delivery, and regional language support.
AI Kosh& Innovation Initiatives
- AI Kosh: A public dataset platform with 367 datasets uploaded, enabling research and model training using India-relevant data.
- IndiaAI I4C CyberGuard Hackathon: In collaboration with the Ministry of Home Affairs, AI models were developed for identifying cybercrime patterns from complex inputs like handwritten FIRs and audio calls on the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal.
- Startup Innovation & Skill Development: Funding support, AI labs in Tier-II cities, and talent development programs are part of a broader push to promote innovation and reverse brain drain.
About IndiaAI Mission
- Launched by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Cabinet Approval: March 2024 with a budget of over ?10,000 crore
- Objectives:
- Develop indigenous AI capabilities and infrastructure
- Democratize AI access for governance, startups, and citizens
- Promote ethical and safe AI use
- Position India among the global AI leaders
India Develops its first indigenous Mechanical Thrombectomy Device for Stroke Treatment
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s medical technology sector, the Technology Development Board (TDB) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has extended support for the development of the country’s first indigenously manufactured mechanical thrombectomy device for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
What is a Mechanical Thrombectomy Device?
The device is a minimally invasive medical tool designed to treat acute ischemic stroke, which occurs due to a blockage in a large blood vessel in the brain. Unlike conventional thrombolytic drugs that dissolve clots chemically, this device physically extracts the clot, thereby restoring blood flow swiftly and reducing the risk of severe brain damage or paralysis.
Development and Manufacturing
This pathbreaking innovation was developed by S3V Vascular Technologies Ltd, based in Mysuru, with financial backing from the TDB. The manufacturing takes place at an advanced, high-precision production facility within the Medical Devices Park in Oragadam, Tamil Nadu.
Key Features and Technological Highlights
- Indigenous Design: S3V is the first Indian company to conceptualize and produce stroke-intervention tools such as microcatheters, aspiration catheters, guidewires, and stent retrievers.
- R&D and Patents: The company has filed multiple patents, particularly for innovations in clot retriever head design and advanced catheter structures.
- Training and Capacity Building: A simulator-based training program has been initiated to train young medical professionals, with a focus on outreach in Tier-II cities.
- Global Compliance: The device aims to meet CE and USFDA standards, paving the way for international exports and aligning with global quality benchmarks.
Significance for India
- Reduces Import Dependency: The device addresses India’s reliance on expensive, imported stroke-care equipment.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare: By making stroke treatment more affordable, it enhances access to quality care for economically weaker sections.
- Supports Public Health Initiatives: It is expected to be integrated into government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, strengthening the country’s universal healthcare mission.
- Boosts MedTech Ecosystem: This innovation is a major stride in positioning India as a global player in the high-end medical devices sector.
Quantum Supremacy Demonstrated via Simple Game
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
Researchers from the University of Oxford and Universidad de Sevilla have demonstrated quantum supremacy using a simple mathematical game based on the odd-cycle graph colouring problem. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, marks a significant milestone in quantum computing.
What is Quantum Supremacy?
Quantum supremacy refers to the ability of a quantum computer to perform a task that is practically impossible for classical computers to solve efficiently. This advancement showcases the unique capabilities of qubits, which leverage two core principles:
- Superposition: Qubits can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- Entanglement: Measurement of one qubit instantly affects another, even over a distance.
These principles enable exponential scaling of computational power. For instance, a 50-qubit quantum computer could potentially outperform the most powerful classical supercomputers.
The Odd-Cycle Game: A Novel Approach
The team implemented a game inspired by graph theory:
- Players (Alice and Bob) are tasked with colouring an odd-numbered cycle (e.g., triangle) using only two colours such that adjacent points differ in colour.
- Mathematically, this is impossible in classical terms for odd cycles due to inevitable repetition of colours.
In the experiment:
- Two strontium atoms placed 2 meters apart were entangled using lasers.
- A referee sent each atom a "question" (mapped to a point on the cycle).
- Players performed quantum operations based on the questions and returned either 0 or 1 (representing colours).
The experiment was repeated 101,000 times, covering circles from 3 to 27 points.
Results and Significance
- Classical win rate: 83.3% for 3-point cycles.
- Quantum win rate: 97.8%, clearly surpassing classical limits.
- Quantum supremacy was evident up to 19-point circles.
- The entanglement correlation was the strongest ever recorded between two separated quantum systems.
Comparison with Previous Demonstrations
- Google’s Sycamore (2019): Used 53 superconducting qubits for a complex problem called random circuit sampling.
- China’s Jiuzhang: Used Gaussian boson sampling.
- In contrast, this new approach used just two entangled qubits, making it simpler, efficient, and easier to verify.
Practical Implications
This simplified game-based model of quantum advantage could have real-world applications in problems where coordination is needed without communication—such as the "rendezvous problem". Quantum systems can dramatically reduce search steps compared to classical ones (e.g., Grover’s algorithm can reduce 1 million steps to 1,000).
ESA Biomass Satellite Mission
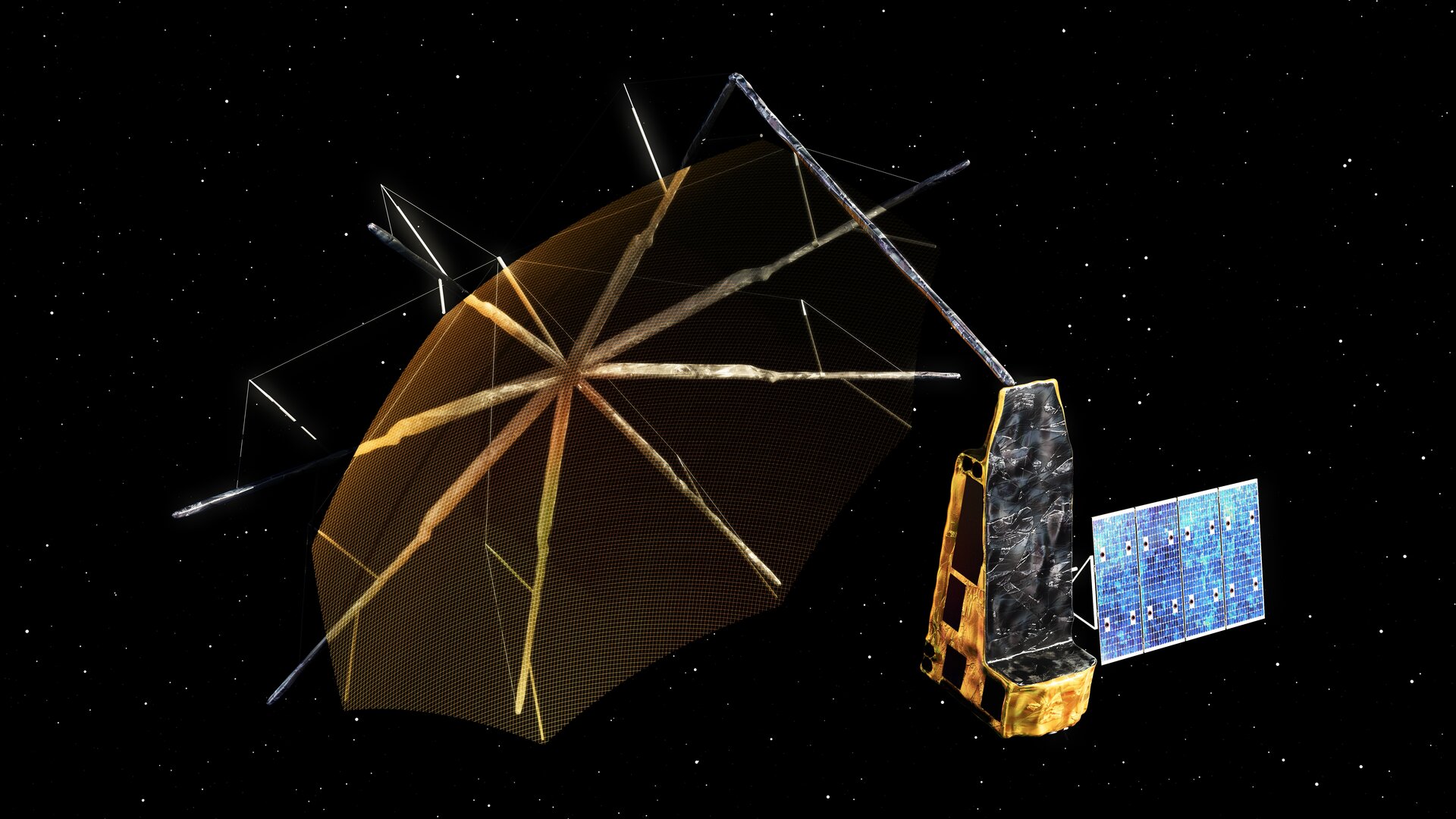

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Biomass Mission is a new Earth observation mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) aimed at enhancing our understanding of the global carbon cycle through accurate forest biomass measurements.
Launch Details:
- Rocket: Vega-C
- Launch Site: Europe’s Spaceport, French Guiana
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of ~666 km
- Scheduled Launch Date: 29 April 2025 (subject to final checks)
Key Features:
- First satellite to use P-band radar (long-wavelength synthetic aperture radar).
- Capable of penetrating dense forest canopies to scan tree trunks, branches, and stems — where most of a tree’s carbon is stored.
- Will generate 3D maps of the world’s tropical forests.
Mission Objectives:
- Measure above-ground forest biomass and forest height.
- Create five global biomass maps over its five-year mission.
- Monitor changes in forests to assess their role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
Scientific Importance:
- Forests absorb ~8 billion tonnes of CO? annually and are often referred to as "Earth’s green lungs."
- By analyzing forest carbon storage and changes, the mission will contribute significantly to:
- Monitoring climate change
- Supporting carbon accounting
- Improving air quality assessments
Phases of the Mission:
- Initial Phase: Produces detailed 3D forest maps globally.
- Second Phase: Generates global estimates of forest height and biomass.
Relevance to Climate Action:
- Helps in quantifying carbon uptake and release.
- Supports global climate models and carbon budgeting.
- Aids in policy-making for sustainable forest management.
De-Extinction
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A US biotech company, Colossal Biosciences, claims to have genetically engineered three grey wolf pups to carry traits of the extinct dire wolf, calling it a de-extinction.
What is De-Extinction?
De-extinction is the process of reviving extinct species using advanced biotechnological methods such as:
- Gene editing (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9),
- Cloning (e.g., somatic cell nuclear transfer),
- Ancient DNA sequencing and genome reconstruction,
- Synthetic biology to reintroduce key traits of extinct organisms.
Colossal Biosciences and the Dire Wolf Project
In late 2024, a U.S.-based biotechnology firm, Colossal Biosciences, announced the birth of three genetically engineered wolf pups—Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi—claimed to be the world’s first successful case of "functional de-extinction."
About the Dire Wolf
- Scientific name: Aenocyon dirus
- Habitat: Grasslands and forests of North America during the Pleistocene Epoch
- Extinction: ~12,500–13,000 years ago
- Characteristics: 25% larger than modern grey wolves; strong jaws to hunt megafauna like bison and horses; light-colored dense fur; social, pack-hunting predators.
Scientific Process Involved
- DNA Extraction: Ancient DNA was recovered from dire wolf fossils (13,000 to 72,000 years old).
- Genome Reconstruction: Sequencing and comparative analysis showed ~99.5% similarity between dire wolves and modern grey wolves.
- Gene Editing: Scientists edited 20 genes in grey wolves to replicate dire wolf traits like:
- White, thick fur
- Increased body mass
- Enhanced musculature and coat pattern
- Cloning: Modified DNA was used to create embryos via somatic cell nuclear transfer.
- Surrogacy: Embryos were implanted in large domestic dogs. Of several attempts, three pups survived.
Scientific and Ethical Concerns
- Experts argue these are not true dire wolves but genetically edited grey wolves with some dire wolf-like traits.
- Critics highlight the absence of peer-reviewed publication, limited understanding of epigenetic and behavioral factors, and the artificial environment in which the pups are raised.
- Colossal terms the process "functional de-extinction", meaning re-creating genetically and ecologically similar organisms, not exact replicas.
Ecological and Conservation Relevance
- Colossal claims the technology could help endangered species like the red wolf (native to the southeastern U.S.), threatened by habitat loss and hybridization with coyotes.
- Four clones of red wolf–coyote hybrids have been produced with potential use in restoring genetic diversity.
- The company aims to democratize conservation biotechnology, pledging to share tools with global conservationists and working with Native American communities.
Contemporary Debates
- Over 60 environmental groups have protested proposed U.S. legislation to delist grey wolves from the Endangered Species Act, warning of ecological consequences.
- Scientists urge caution, stressing that true resurrection of extinct species requires more than gene editing, as behavior, evolutionary context, and environmental adaptation cannot be synthetically replicated.
India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST-Kashmir) has successfully developed India’s first gene-edited sheep, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of animal biotechnology.
Key Highlights:
- Institution Involved: Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST), Srinagar.
- Technology Used:
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing — a precision genome editing tool that won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
- Gene editing was conducted without insertion of foreign DNA, thus the sheep is non-transgenic and differs from traditional GMOs.
- Gene Targeted: The myostatin gene, which regulates muscle growth, was edited to enhance muscle mass.
- Result: Muscle mass increased by 30%, a trait absent in Indian sheep breeds but seen in select European breeds like the Texel.
- Significance:
- Improved meat yield and quality in sheep.
- Potential for disease-resistant and higher-reproduction-rate livestock in the future.
- Supports India’s evolving biotech policy by promoting non-transgenic, gene-edited organisms that are more likely to receive regulatory acceptance.
- Aligns with goals of sustainability and food security by enhancing productivity per animal.
- Regulatory & Safety Aspects:
- Research adhered to international biosafety protocols.
- Sponsored by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Legacy & Research Background:
- Developed after 4 years of dedicated research.
- Led by Prof. Riaz Ahmad Shah, also known for creating India’s first cloned Pashmina goat, Noori, in 2012, and contributing to the world’s first cloned buffalo at NDRI, Karnal.
Implications for the Future:
- Opens doors for precision breeding in livestock to boost India’s animal husbandry sector.
- Strengthens India’s position in advanced genomic research and supports the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat in biotechnology.
- Awaits comprehensive regulatory framework for gene-edited animals, currently under government consideration.
Semi-Transparent Perovskite Solar Cell Technology
- 28 May 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have developed an advanced semi-transparent perovskite solar cell (PSC) layered over a traditional silicon solar cell. This results in a 4-terminal (4T) tandem solar cell that significantly boosts power conversion efficiency (PCE) to ~30%, compared to the current average of ~20% in conventional solar panels.
Key Features and Technology
- Structure: Tandem architecture using a bottom silicon sub-cell and a top layer of indigenously developed halide perovskite semiconductor.
- Material Efficiency: Halide perovskite is one of the most efficient light-absorbing materials and can be locally produced using available chemical resources.
- Cost & Efficiency Gains:
- Potential to reduce solar power cost to ?1/kWh, down from ?2.5–4/kWh.
- Offers 25–30% more efficiency compared to standard solar panels.
- Stability Improvements: Previously, PSCs degraded quickly. The new configuration extends lifespan up to 10 years, enhancing durability under heat and low-light conditions.
Strategic Significance for India
- Indigenous Manufacturing: Reduces dependence on imported raw materials, especially those dominated by China.
- Commercialization Plan:
- Maharashtra government and MAHAGENCO exploring large-scale implementation.
- ART-PV India Pvt. Ltd., a start-up from IIT Bombay's SINE, aims to deliver a commercial wafer-size solution by December 2027 using indigenous equipment.
- Applications:
- Rooftop solar installations
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Vehicle-integrated photovoltaics (VIPV)
Clean Energy Linkage: IIT Bombay is also working with the Maharashtra government to develop green hydrogen solutions. The PSC’s high open-circuit voltage makes it suitable for solar-to-hydrogen (STH) applications, offering performance comparable to costly compound semiconductors but at lower cost and with locally accessible materials.
Google’s AI Matryoshka Strategy
- 26 May 2025
In News:
At its 2025 I/O Developer Conference, Google unveiled AI Matryoshka, a multi-layered artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem powered by its latest Gemini 2.5 models. This marks a fundamental restructuring of Google’s platforms around AI, affecting users, developers, and enterprises.
What is AI Matryoshka?
- Concept: Named after the Russian nesting dolls, AI Matryoshka is a layered AI architecture where each outer application or interface draws intelligence from a core AI “brain.”
- Objective: To embed AI deeply and uniformly across Google’s services, enabling agentic, intelligent, and autonomous interactions.
Core AI Models: Gemini 2.5
- Gemini 2.5 Pro:
- Advanced reasoning and mathematics capabilities.
- Achieved high scores on USAMO 2025 (a premier U.S. math olympiad).
- Features a mode called Deep Think for complex problem-solving.
- Gemini 2.5 Flash:
- A more efficient, lightweight model using 20–30% fewer tokens.
- Supports natural audio output and multi-speaker TTS in 24 languages.
- Set to become the default model in Gemini applications.
Foundational Hardware: Ironwood TPUs
- Ironwood (7th Gen TPUs):
- Delivers 42.5 exaFLOPS of compute power per pod.
- Offers 10x performance boost over previous TPUs.
- Supports large-scale training and deployment of generative AI models.
Generative Media Models
- Imagen 4: Advanced image generation.
- Veo 3: High-quality video generation.
- Lyria 2: Music creation using AI.
- Copyright Tools:
- SynthID (watermarking) and SynthID Detector (verification) aim to address copyright concerns over the training data.
Developer Ecosystem
- Gemini API & Vertex AI:
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Enables agent-to-agent communication.
- Thinking Budgets: Let developers allocate compute resources wisely.
- Project Mariner: Tool for automating complex tasks.
- Thought Summaries: Improves transparency of AI decisions.
- Coding Agent – Jules:
- Beta launched globally.
- Integrates with code repositories to write tests, build features, and fix bugs using Gemini 2.5 Pro.
User-Centric Features
- Search Integration (AI Mode):
- Rolls out first in the U.S. with Deep Search generating cited, multimodal answers.
- Offers virtual shopping try-ons and agentic checkout, raising privacy and data security concerns.
- Gemini App:
- Available on Android and iOS with Live and image generation features.
- Deep Research allows analysis of private documents and images, necessitating strong data protection protocols.
- Integrated into Chrome (for Pro and Ultra users) for webpage summarization.
- Canvas Feature: A creative workspace for interactive infographics, quizzes, and audio content in 45 languages.
Subscription Tiers and Privacy Concerns
- Google AI Ultra Tier:
- Offers premium access to advanced capabilities, including video generation with native audio.
- Raises questions about "privacy premium" – whether better AI safety features will be available only to paying users.
Tamil Nadu’s Space Industrial Policy and IN-SPACe

- 26 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Tamil Nadu Cabinet approved its Space Industrial Policy, becoming the third state after Karnataka and Gujarat to adopt a dedicated strategy to stimulate investments and innovation in the space sector. This move aligns with the national framework set by the Indian Space Policy 2023 and supports India's growing space economy.
IN-SPACe and its Role:
- IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre) is an autonomous, single-window agency under the Department of Space (DoS).
- Created as part of India’s space sector reforms, it promotes and authorises the participation of Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs) in space activities.
- Functions include:
- Supporting private entities in the development of launch vehicles, satellites, and space-based services.
- Facilitating access to ISRO infrastructure and co-development initiatives.
- Providing support for research, innovation, and educational collaboration.
- Headquartered at Bopal, Ahmedabad, it serves as the bridge between ISRO and private sector stakeholders.
- IN-SPACe encouraged Tamil Nadu to formulate the Space Industrial Policy to promote the state’s role in India’s space mission.
Tamil Nadu’s Strategic Space Assets:
- ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC), Mahendragiri (Tirunelveli): Engaged in testing cryogenic engines, liquid propulsion systems, and R&D activities.
- Second Spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam (Thoothukudi): Enhances satellite launch capacity, especially for small satellites and polar launches.
- Presence of space-tech startups in areas like:
- Reusable launch vehicles
- In-space manufacturing
- In-orbit refuelling
- Satellite data analytics
- Space Technology Incubation Centre (STIC) at NIT Trichy supports southern-region ISRO projects and academia-industry collaboration.
- Over 250 ISRO vendors operate in the state, creating a robust supply chain ecosystem.
Objectives of Tamil Nadu's Space Industrial Policy:
- Target investment: ?10,000 crore over the next 5 years.
- Employment generation: Estimated 10,000 direct and indirect jobs.
- Strengthens Tamil Nadu’s capabilities in:
- Electronics and precision manufacturing
- Strategic electronics and space-grade components
- Promotes integration of space technologies in governance (e.g., disaster management, fisheries, agriculture, health, transport).
Policy Incentives:
- Payroll subsidy for companies engaged in R&D or setting up Global Capability Centres.
- Space Bays: Select regions will be designated to offer structured incentive packages for investments below ?300 crore.
- Industrial housing incentive: 10% subsidy (capped at ?10 crore) for building residential facilities in space industrial parks.
- Green initiatives: 25% capital subsidy (capped at ?5 crore) for environmentally sustainable developments.
Institutional Support:
- TIDCO (Tamil Nadu Industrial Development Corporation) signed an MoU with IN-SPACe to facilitate:
- Manufacturing activities
- Strategic collaborations with private companies
- R&D and design-based projects in the space domain
Technology and Innovation Report 2025

- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
India has been ranked 10th globally in terms of private sector investments in Artificial Intelligence (AI) in 2023, according to the Technology and Innovation Report 2025, released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). The report highlights the evolving global AI landscape and underscores India's growing role in frontier technologies.
About the Technology and Innovation Report
- Published by: UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development).
- Objective: To provide policy-relevant insights on emerging issues in science, technology, and innovation (STI), especially from the perspective of developing countries.
- Theme of the 2025 Edition: “Inclusive Artificial Intelligence for Development”.
- Purpose: Aims to assist policymakers in formulating inclusive and equitable STI policies amid the rapid expansion of AI technologies.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Report
- India’s Position:
- Ranked 10th globally for private AI investments, amounting to $1.4 billion in 2023.
- Among developing countries, only India and China feature prominently in global AI investments.
- India’s growing prominence reflects its rising technological capacity and startup ecosystem.
- Global Investment Trends:
- The United States led global AI investment with $67 billion (70% of global private investment).
- China ranked second with $7.8 billion.
- The report reveals that just 100 companies, mainly from the US and China, account for 40% of global private R&D investment in AI, signifying a concentration of technological power.
- AI and Global Employment:
- The report warns that up to 40% of global jobs could be influenced by AI-driven automation, necessitating adaptive policies, especially in the Global South.
- Governance Gaps:
- 118 countries, mostly from the Global South, are not participating meaningfully in global AI governance dialogues, highlighting a digital divide in international policy spaces.
- Recommendations for Developing Countries:
UNCTAD urges developing nations to strengthen three critical areas, termed “key leverage points”:- Infrastructure: Improve digital and physical infrastructure.
- Data Ecosystems: Ensure data accessibility, quality, and sovereignty.
- Human Capital and Skills: Invest in AI-related education and skilling.
- India’s Broader Performance:
- Ranked 36th out of 170 countries on the Readiness for Frontier Technologies Index 2024, an improvement from 48th in 2022.
Antimony Discovery in Balochistan, Pakistan
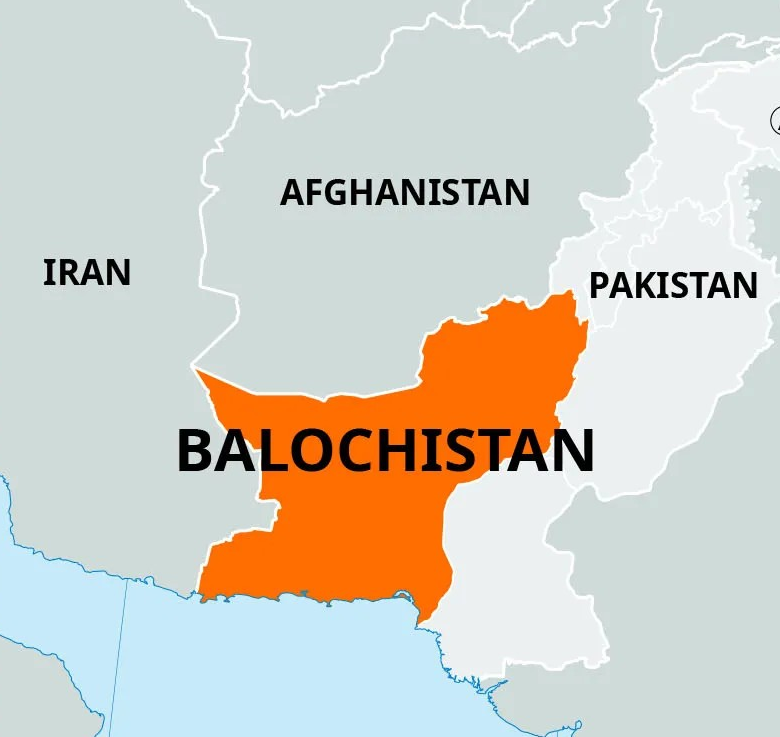
- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
In a recent geopolitical development, Pakistan has reportedly discovered a significant deposit of Antimony in the Balochistan region — an area marred by conflict and instability. This finding holds both economic and strategic significance, given the growing global demand for rare and critical minerals.
About Antimony
- Chemical Element: Antimony (Symbol: Sb, Atomic Number: 51) is a metalloid, meaning it exhibits properties of both metals and non-metals.
- Physical Properties:
- Solid at room temperature.
- Poor conductor of heat and electricity.
- Found in commercial forms such as ingots, broken pieces, granules, and cast cakes.
Geological Occurrence
- Primary Ore: The chief ore of Antimony is Stibnite (Sb?S?).
- Mode of Occurrence: Found in volcanic-associated deposits and deep-seated veins, formed under moderate to high temperature and pressure.
- Also commonly obtained as a byproduct from lead-zinc-silver mining operations.
Global Production Landscape
- China is the dominant global producer, accounting for over 88% of world production.
- Other notable producers include Russia, Bolivia, and Tajikistan.
- India currently does not have significant reserves or production of Antimony, making it dependent on imports for industrial use.
Key Industrial and Strategic Uses
- Electronics Industry:Used in manufacturing semiconductors, infrared detectors, and diodes.
- Alloys:
- Alloyed with lead and other metals to increase hardness and strength.
- Lead-antimony alloys are extensively used in lead-acid batteries.
- Defense and Printing:Utilized in the production of bullets, type metal for printing, and cable sheathing.
- Flame-Retardants and Ceramics:Antimony compounds are key ingredients in flame-retardant materials, as well as in paints, enamels, glass, and pottery.
Hansa-3 Trainer Aircraft
- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s indigenous aviation sector, the Hansa-3 trainer aircraft has recently been approved for training aircrew for pilot licences. Notably, the production of this aircraft will now be undertaken by private industry, marking a step forward in India’s push for self-reliance in aviation technology and defence manufacturing.
About Hansa-3 Trainer Aircraft
- India’s First Indigenous Flying Trainer: The Hansa-3 is the country’s first indigenously developed light trainer aircraft.
- Developed by: The aircraft was designed and developed by the CSIR–National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), Bengaluru, under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- Intended Use: Specifically designed for flying clubs in India, it is well-suited for Commercial Pilot Licensing (CPL) training, owing to its cost-effectiveness and low fuel consumption.
Key Features and Technological Advancements
- Configuration: It is a two-seater, low-wing monoplane, optimized for pilot training missions.
- Engine: Powered by a Rotax Digital Control Engine, known for high efficiency and performance.
- Advanced Airframe: Incorporates Just-In-Time Prepreg (JIPREG) composite lightweight material, enhancing aerodynamic efficiency and reducing fuel use.
- Modern Cockpit: Equipped with a glass cockpit and bubble canopy, offering a wide panoramic view — critical for pilot situational awareness.
- Electronic Systems:
- Electric Flaps for improved handling.
- Advanced Electronic Fuel Injection System for automatic adjustment of fuel-air mixture across varying altitudes, enhancing performance and fuel economy.
Significance for India
- Promotes Atmanirbhar Bharat: The transition to private manufacturing aligns with the government’s vision of strengthening the domestic aerospace ecosystem under the Make in India initiative.
- Reduces Dependency: Reduces reliance on imported aircraft for pilot training, supporting India’s goal of strategic autonomy in aviation technology.
- Skill Development: Enhances the capacity of Indian flying schools and contributes to the growth of the civil aviation sector by producing more trained pilots domestically.
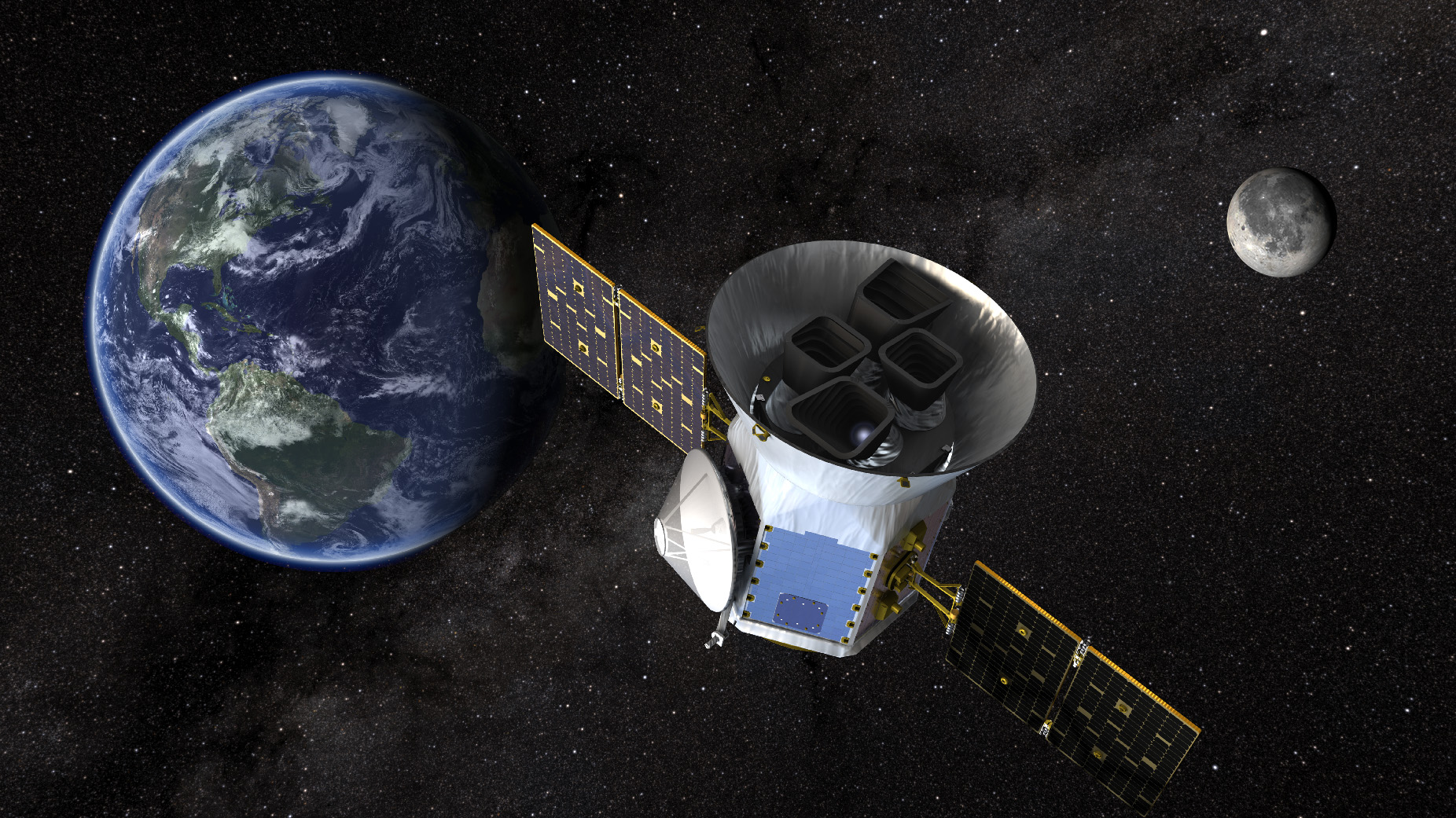
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)

- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
- An international team of astronomers, using NASA’s TESS mission, has discovered a new warm Jupiter-type exoplanet located over 1,000 light-years away.
- “Warm Jupiters” are gas giants that orbit their stars at moderate distances, experiencing higher temperatures than Jupiter but cooler than “hot Jupiters”.
About TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite)
- Launched: March 2018 by NASA.
- Objective: To discover thousands of exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) by observing the brightest dwarf stars in the sky.
- Successor to: NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope, which pioneered large-scale exoplanet discovery (2009–2018).
Working Principle:
- TESS uses the transit method:
- It monitors periodic dips in star brightness, caused when a planet crosses (or transits) in front of its host star.
- This reveals the size (diameter) of the exoplanet and helps estimate its orbital characteristics.
- Helps identify habitable zone planets, where liquid water may exist on Earth-like worlds.
Mission Highlights:
- Prime Mission Duration: Two years, completed on July 4, 2020.
- Covered nearly 75% of the sky, divided into 26 sectors.
- Discovered 66 confirmed exoplanets during the prime mission.
- Now operating under an extended mission, continuing to explore distant planetary systems.
- Finds planets of varied sizes and compositions, from rocky Earth-like bodies to gas giants.
Saturn becomes undisputed 'Moon King' of Solar System
- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
In a major astronomical breakthrough, scientists have discovered 128 new moons orbiting Saturn, raising its total confirmed moon count to 274—the highest for any planet in the solar system. This discovery has been officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
About the Discovery
- The moons were detected using the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope with a method called “shift and stack”, which enhances the visibility of faint objects moving across the sky.
- Most of the newly identified moons are irregular, small, and non-spherical, indicating a likely origin as captured asteroids or remnants of larger celestial bodies.
- Their clustered orbits suggest a history of violent collisions or fragmentation, possibly linked to the chaotic early evolution of the solar system.
Significance
- Confirms Saturn’s status as the planet with the most known moons, overtaking Jupiter (95 moons as of 2024).
- Enhances understanding of planetary formation, orbital dynamics, and the evolution of ring and satellite systems.
- May contribute to refining the scientific definition of a moon and deepen knowledge of irregular satellite formation in gas giants.
Key Facts about Saturn
- Position: Sixth planet from the Sun.
- Size: Second-largest planet after Jupiter.
- Type: Gas giant composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with traces of methane and ammonia.
- Density: Approximately 0.69 g/cm³, the only planet less dense than water.
- Shape: Oblate due to rapid rotation—flattened at poles, bulging at the equator.
- Rings: Made of ice, dust, and rocky debris.
- Orbit: About 9.59 AU (1,434 million km) from the Sun; orbital period ~29.45 Earth years.
- Weather: Hosts extreme storms like the Great White Spot, recurring roughly once every Saturnian year (~29 Earth years).
Important Moons of Saturn
Titan
- Largest moon of Saturn and second-largest in the solar system, larger than Mercury.
- Only moon with a dense atmosphere, rich in nitrogen and methane.
- Features liquid hydrocarbon lakes near the poles.
- Explored by Cassini-Huygens mission; lander touched down in 2005.
Enceladus
- An icy moon with a subsurface liquid ocean.
- Known for its highly reflective surface and water-ice geysers.
- Cassini (2005) observed plumes of water vapor ejecting at ~400 m/s.
- Discovery of silica nanograins suggests hydrothermal activity, making it a prime target in the search for extraterrestrial life.
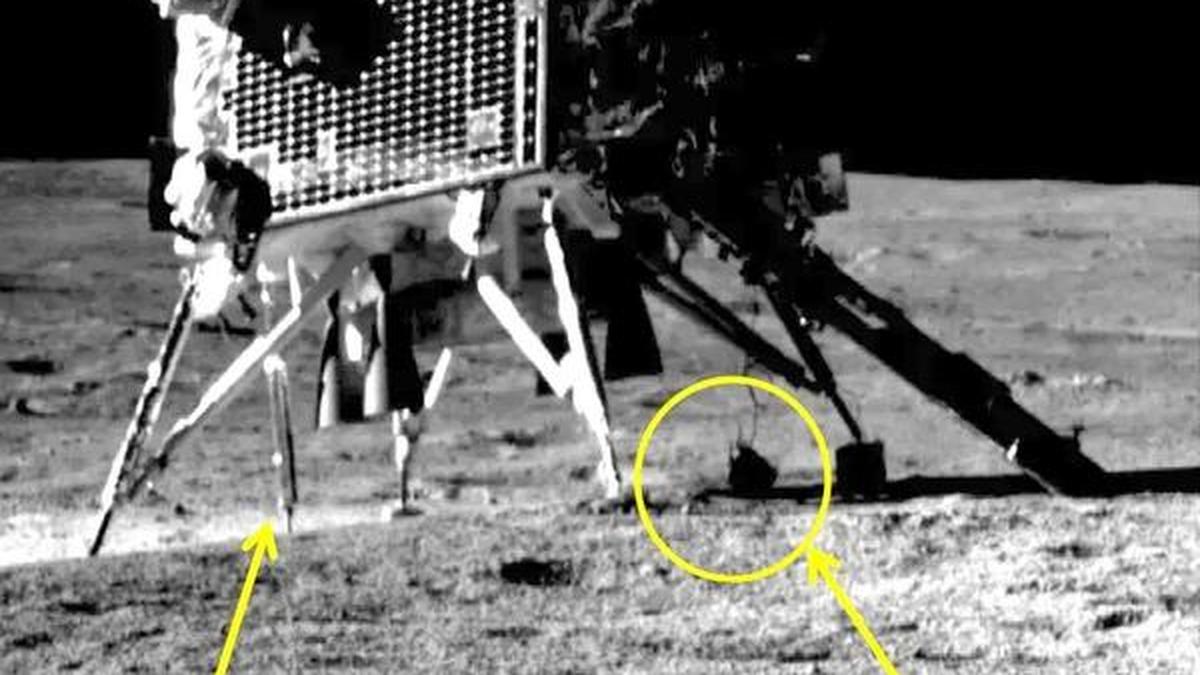
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)

- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission, which successfully landed on the Moon’s south polar region on August 23, 2023, achieved a global first with its Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) — the first thermal probe to successfully penetrate the soil of a celestial body and measure subsurface temperatures in situ.
About ChaSTE:
- Full form: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment.
- Part of: Vikram lander (Chandrayaan-3).
- Depth achieved: Successfully tunnelled10 cm into the lunar regolith.
- Duration of operation: From August 23 to September 2, 2023.
- Significance: First successful deployment of a thermal probe into extraterrestrial soil.
Key Features:
- Temperature sensors: 10 sensors spaced 1 cm apart near the probe’s tip.
- Deployment mechanism: Unique rotation-based system — unlike previous missions that used hammering mechanisms.
- Measurement technique: Monitored changes in motor resistance and tip temperature to determine soil contact and depth.
Scientific Outcomes:
- Provided direct temperature profiles of lunar subsurface near the south pole.
- Enabled insights suggesting greater-than-expected presence of water ice beneath the surface.
Comparison with Previous Attempts:
Mission Agency Celestial Body Instrument Outcome
Rosetta – Philae (2014) ESA Comet 67P MUPUS Deployment failed due to
landing bounce
InSight (2018) NASA Mars HP3 ("The Mole") Could not collect data;
probe failed to burrow
as intended
Chandrayaan-3 (2023) ISRO Moon ChaSTE Successful soil
penetration and
temperature measurement
- Innovation Edge: Unlike ESA’s and NASA’s hammer-based devices, ChaSTE used a rotating drill, allowing steady penetration despite lunar soil resistance.
- Developed by the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
- Ranchi, Jharkhand, is poised to become the first district in the state to launch a comprehensive campaign for the screening and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), now redefined as Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
- The initiative will be carried out under the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD).
- The campaign will begin on April 19, marking World Liver Day, and aims to raise awareness and strengthen early detection and treatment of liver disorders in the population.
About NAFLD/MASLD:
- NAFLD refers to fat accumulation in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption.
- It includes two types:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL) – mild form.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) – severe form, can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or cancer.
- It is increasingly prevalent in individuals with obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
- NAFLD is asymptomatic in early stages but can elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and diabetes-related complications.
- Affects all age groups, including children.
Key Features of the Ranchi NAFLD Initiative:
- Two-phase Screening Drive:
- Phase 1 (April–June): Focus on 30,000 high-risk individuals—those with obesity, diabetes, or hypertension.
- Phase 2 (July–November): Screening expanded to all adults over 18 years in the district.
- Technical Support: Provided by the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi.
- Mobile Screening Vans:
- Each van costs approx. ?1 crore.
- Equipped with FibroScan, an advanced, non-invasive liver diagnostic tool.
- Services provided free of cost in both urban and rural areas.
- Capacity Building:
- 30–40 district-level officers to be trained as master trainers.
- Frontline healthcare workers will be trained to conduct screenings and data collection.
- Health System Strengthening:
- Referral mechanisms to ensure patients receive specialised care.
- Data tracking system to maintain records until integration with the national NCD portal.
Public Health Significance:
- As per the district's civil surgeon, 50% of OPD cases are liver-related.
- On average, 25 patients/day are diagnosed with liver disease; five require hospitalisation.
- Early detection through such initiatives can help prevent disease progression and mortality.
Treatment & Prevention of NAFLD:
- No specific drug currently exists for NAFLD.
- Weight loss remains the primary treatment—shown to reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis.
- Management of comorbidities like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes is also recommended.
Carbon Dioxide (CO?) Lasers
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
A team of physicists in the United States has developed a novel method for remotely detecting radioactive substances using carbon dioxide (CO?) lasers. This advancement offers significant implications for national security, nuclear safety, and emergency response, where safe, long-distance detection is essential.
About CO? Lasers:
- Inventor: Prof. C.K.N. Patel, an Indian-American physicist.
- Laser Type: Four-level molecular gas laser.
- Active Medium: A gas mixture of CO?, nitrogen (N?), and helium (He).
- Wavelengths: 9.6 µm and 10.6 µm (Infrared region).
- Power Output: Can reach up to 10 kW, delivering continuous or pulsed beams.
- Mechanism: Operates through transitions between vibrational energy states of CO? molecules, facilitated by energy transfer from excited N? molecules.
Structure and Vibrational Modes of CO? Molecule:
- Composed of one carbon atom flanked by two oxygen atoms.
- Exhibits three vibrational modes:
- Symmetric Stretching – oxygen atoms move in tandem.
- Bending Mode – atoms move perpendicular to the axis.
- Asymmetric Stretching – oxygen and carbon atoms move in opposite directions.
Detection Principle: Avalanche Breakdown and Plasma Formation
- Radioactive decay emits charged particles (e.g., alpha particles) that ionize air, forming plasma.
- Seed electrons in this plasma gain energy via the CO? laser and initiate avalanche breakdown, causing further ionization.
- This chain reaction forms microplasmas, which produce optical backscatter detectable through sensors.
Key Experimental Insights:
- Laser Used: Long-wave infrared CO? laser at 9.2 µm, ideal for minimizing unwanted ionization.
- Alpha particle detection: Achieved from 10 meters, a tenfold improvement over previous techniques.
- Gamma ray detection (e.g., from Cs-137): Potential detection range of up to 100 meters, scalable with improved laser optics.
- Fluorescence imaging: Employed to analyze plasma dynamics and map seed electron distributions.
- Mathematical modeling: Successfully predicted backscatter based on plasma characteristics, validating the method.
Advantages of the Technique:
- Enhanced sensitivity to weak radioactive sources.
- Long-range detection without direct contact.
- Reduced risk for personnel during radiation monitoring.
- Scalability: Theoretically extendable to ~1 km with high-energy lasers and larger optics.
Challenges Ahead:
- Extended range detection requires larger optical systems and higher laser power.
- Signal degradation due to atmospheric interference and background noise at longer distances.
- Trade-off between detection range and signal clarity remains a critical engineering hurdle.
The use of CO? lasers for radioactive detection marks a significant leap in remote sensing technologies. While currently limited to tens or hundreds of meters, future developments may push detection ranges further, making it a valuable tool in defense, nuclear safety, and disaster management.
ISRO’s CARTOSAT-3

- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
Recently, a 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck Myanmar near the Sagaing-Mandalay border, causing severe damage in key cities such as Mandalay and Sagaing. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) used its advanced Earth observation satellite CARTOSAT-3 to assess the destruction via high-resolution post-disaster imagery.
CARTOSAT-3: An Overview
- Developer: ISRO
- Launched by: PSLV-C47
- Mission Type: Third-generation agile Earth observation satellite
- Successor to: IRS (Indian Remote Sensing) series
Key Specifications:
Feature Details
Resolution Panchromatic: 0.25 metres (sharpest civilian)
Orbit Altitude 509 km (Sun-synchronous orbit)
Inclination 97.5°
Weight 1,625 kg
Technologies Agile cameras, advanced onboard computers, high-speed data transmission
Commercial Use
- First commercial order executed by NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL), ISRO’s commercial arm.
Applications of CARTOSAT-3
- Disaster Management: Monitoring and assessing damage from earthquakes, floods, and landslides
- National Security & Strategic Operations: Surveillance and intelligence (used in 2016 LoC surgical strikes and 2015 Myanmar-Manipur ops)
- Urban & Rural Planning: Infrastructure development, land-use mapping, and road networks
- Environmental Monitoring: Coastal regulation and land-use changes
- Cartography and Remote Sensing: High-precision geospatial mapping and terrain analysis
Cartosat and Other ISRO Satellite Series
Satellite Series Focus Area
Cartosat-1 to 3 High-resolution Earth imaging for urban/rural planning
RISAT Radar-based imaging (all-weather surveillance)
Oceansat Oceanography, weather, and marine research
INSAT &Megha-Tropiques Atmospheric and climate monitoring
Understanding "Vibe Coding"
- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The concept of “vibe coding” gained traction after an OpenAI co-founder demonstrated how modern AI tools can translate intuitive prompts into working code—eliminating the need for in-depth technical expertise.
What is Vibe Coding?
Vibe coding is an intuition-driven, casual approach to programming where users describe what they want to build, and AI generates the code accordingly. Instead of relying on traditional programming logic, this method focuses on the user’s "feel" or intent—making it well-suited for low-stakes, creative, or personal projects.
How It Works:
- Users give natural language prompts describing their desired output (e.g., a simple game, utility, or web page).
- AI models like ChatGPT, Cursor, or Sonnet generate the corresponding code.
- The user then runs or copies the code without necessarily understanding its structure or logic.
Key Features of Vibe Coding:
- Prompt-first, logic-second: Relies on describing functionality rather than coding step-by-step.
- Low technical barrier: No deep knowledge of syntax, algorithms, or frameworks required.
- Trial-and-error approach: Users often accept AI-generated suggestions without critical review.
- Heavy dependence on AI: Debugging and improvements rely primarily on AI assistance.
- Limited focus on performance/security: Generated code may lack optimization or safeguards.
Why Vibe Coding Matters:
- Democratizes coding: Makes programming accessible to those without formal training.
- Fuels creativity: Encourages playful experimentation and rapid prototyping.
- Saves time for developers: Ideal for automating small, repetitive tasks.
- Inspires new learners: Attracts non-traditional audiences into tech through approachable tools.
- Useful for quick builds: Ideal for weekend hacks, personal utilities, or mock-ups.
Irula Tribe of Tamil Nadu
- 21 May 2025
In News:
In Tamil Nadu’s Kunnapattu, Irula families who have lived on the land for generations face eviction and denial of rights, as nearly half remain without legal ownership or recognition.
Who are the Irulas?
- Ethnic Group: Indigenous Dravidian community, primarily in Tamil Nadu and parts of Kerala.
- Constitutional Status: Recognized as a Scheduled Tribe and classified under Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Tamil Nadu.
- Population: Second largest Adivasi group in Tamil Nadu.
- Language: Speak Irula, a Dravidian language related to Tamil and Kannada.
- Traditional Occupations: Snake-catching, healing, collection of forest produce, cattle rearing, and agricultural labour.
- Religious Beliefs: Pantheistic with reverence for spirits; worship Kanniamma (virgin goddess associated with cobras).
- Living Structures: Reside in small clusters called mottas, typically located on hill edges near forests.
Irulas and Snake Venom Economy
- The Irula Snake Catchers’ Cooperative Society supplies nearly 80% of venom for the production of anti-snake venom (ASV) in India.
- The community uses traditional knowledge to locate and capture snakes humanely, extract venom, and release them safely.
The Crisis in Kunnapattu and Beyond
Core Issue: Denial of Land Rights
- In Kunnapattu village, near Mamallapuram, ~40 Irula families have lived for generations. However, nearly 20 families lack legal land documents (pattas).
- The land is classified as meikalporamboke (grazing land), making it ineligible for patta allocation under current policies.
- Without pattas, families are denied access to electricity, government housing, and welfare schemes.
Government Response
- Officials proposed relocation with promised housing and legal ownership, but Irulas resist displacement due to ancestral ties, rituals, and local livelihoods.
- Affected families submitted multiple petitions, seeking in-situ recognition rather than relocation.
Broader Pattern across Tamil Nadu
Similar Issues in Other Villages
- Ottiyambakkam, Iyankulam, Keerapakkam, Chinnakayar, and Nemmeli show the same trend: ancestral tribal settlements without legal tenure, facing:
- Forced or incentivized relocation.
- Inadequate or delayed infrastructure (roads, electricity, water).
- Joint pattas that complicate individual welfare access.
Urbanization vs Indigenous Habitat
- Irula hamlets are increasingly surrounded or displaced by real estate developments.
- Some families resist high-rise housing due to loss of space, cultural disconnect, and impracticality for community rituals.
Notable Success: Senneri Model Village
- Near Chengalpattu, Senneri-Hanumantapuram-Dargesh is a model Irula settlement:
- Home to Padma Shri awardees in snake-catching.
- Over 10 active SHGs working in traditional medicine.
- Gender-inclusive education and organized habitation.
- However, even here, funding and timely housing construction remain challenges.
Challenges and Needs
- Lack of individual pattas limits access to electricity, housing schemes (e.g., PMAY-G), water, sanitation, and health services.
- Infrastructural gaps persist even in relocated areas.
- Traditional knowledge and community bonds are under threat from urban pressures and displacement.
Titan’s Dynamic Atmosphere
- 21 May 2025
In News:
In a significant breakthrough, NASA scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Hawaii’s W. M. Keck Observatory have captured first-ever evidence of convective cloud activity in the northern hemisphere of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. The observations were conducted in November 2022 and July 2023.
About Titan:
- Second-largest moon in the Solar System (after Jupiter’s Ganymede).
- Only moon known to have a dense atmosphere and liquid hydrocarbon bodies (methane and ethane lakes/seas).
- Exhibits Earth-like weather, including clouds, rainfall, and seasonal cycles, making it unique among planetary satellites.
Key Findings:
- Clouds were observed in the mid- and high-latitudes of Titan’s northern hemisphere, the region where most of its methane seas (e.g., Kraken Mare, Ligeia Mare) are located.
- This marks the first confirmed evidence of convection-driven weather in Titan’s north, suggesting active atmospheric dynamics during Titan’s summer season.
- These findings expand our understanding of Titan’s methane cycle, which parallels Earth’s hydrological cycle, though methane replaces water.
- The JWST also detected a key organic molecule — the methyl radical, a reactive compound with an unpaired electron, involved in complex hydrocarbon chemistry.
- This is significant because sunlight and Saturn’s charged particles break apart methane in Titan’s atmosphere, initiating prebiotic chemical reactions.
Scientific Significance:
- Offers a rare opportunity to study active chemical processes in real time — likened by scientists to seeing "a cake rising in the oven" instead of just its ingredients or finished form.
- Enhances understanding of prebiotic chemistry and the potential for habitability on icy celestial bodies.
- Builds on the legacy of the Cassini–Huygens mission (2004–2017), which studied Titan’s southern hemisphere.
Dragonfly Mission: The Next Leap
- NASA's Dragonfly, a nuclear-powered octocopter, is scheduled for launch in 2028 (on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy) and expected to reach Titan in 2034.
- Aims to conduct in-situ analysis of Titan’s surface, hopping between locations to study chemistry, weather, and possible signs of life.
- Recently passed the Critical Design Review, moving into the manufacturing phase.
About the W.M. Keck Observatory:
- Located at Mauna Kea, Hawaii, at 4,200 m elevation — ideal for infrared astronomy.
- Houses two 10-meter telescopes (Keck I and II), the world’s largest optical/infrared system.
- Features segmented mirrors and real-time computer-actuated adjustments for precision imaging.
- Uses stressed mirror polishing, a major advancement in off-axis mirror technology.
GRAIL Mission
- 19 May 2025
In News:
The Moon, Earth's only natural satellite, exhibits a striking hemispheric contrast. The nearside, visible from Earth, is dominated by dark, flat basaltic plains (mare), while the farside is rugged, heavily cratered, and lacks these features. This asymmetry has long puzzled scientists.
Recent findings from NASA's GRAIL (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) mission, launched in 2011, have provided critical insights into this phenomenon.
GRAIL Mission: An Overview
- Objective: To map the Moon’s gravitational field in unprecedented detail.
- Spacecraft: Two identical probes named Ebb and Flow.
- Method: By measuring the tiny variations in the distance between the probes as they orbited the Moon, scientists could infer differences in crust thickness, interior composition, and subsurface structures.
Key discoveries:
- The Moon’s crust is more porous and thinner than previously thought.
- Detection of long, linear features called dikes, indicating early lunar expansion.
Reasons for Lunar Asymmetry
- Tidal Deformation and Gravitational Asymmetry
- The nearside flexes more than the farside during the Moon’s elliptical orbit, a result of tidal deformation caused by Earth’s gravity.
- The increased internal heat and flexibility on the nearside suggest it is warmer and more geologically active at depth.
- Volcanic Activity and Heat Distribution
- The nearside experienced intense volcanic activity billions of years ago, forming the large mare regions.
- This activity led to the concentration of radioactive, heat-producing elements (like thorium and titanium) in the nearside mantle.
- The nearside mantle is 100–200°C hotter than the farside, establishing a long-term thermal imbalance.
- Crustal Thickness and Surface Composition
- The nearside crust is significantly thinner, allowing magma to reach the surface more easily, contributing to extensive lava flows.
- The thicker farside crust restricted such activity, preserving its rugged, cratered appearance.
Implications for Space Science and Earth
- The findings aid in developing precise lunar navigation and positioning systems, essential for future human missions.
- The methodology can be applied to other celestial bodies like Enceladus (Saturn) and Ganymede (Jupiter), both candidates in the search for life.
- Understanding the Moon's structure enhances our grasp of Earth-Moon gravitational dynamics, which affect tides and planetary stability.
India assembles first Chromosome-Level Genome of the Yak

- 16 May 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant breakthrough in livestock genomics with the successful assembly of the first-ever chromosome-level genome of the Indian yak (Bos grunniens). The initiative was led by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) through collaboration among four of its premier institutes.
Key Institutions Involved:
- ICAR-National Research Centre on Yak (NRC-Yak), Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh
- ICAR-Indian Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology (IIAB), Ranchi
- ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cattle (CIRC), Meerut
- ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cattle (CIRC), Nagpur
Importance of the Indian Yak:
- Known as the “Ship of the Himalayas,” the domestic yak is crucial to the livelihoods of high-altitude pastoral communities.
- Provides meat, milk, fibre, dung for fuel, and is used for transport in rugged terrain.
- Found at elevations above 7,000 feet in regions like Ladakh, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Exhibits extraordinary cold tolerance, making it a valuable model for studying climate adaptation.
Scientific Achievement:
- Researchers used long-read sequencing technology and advanced bioinformatics tools to develop a chromosome-level genome assembly.
- This allows precise gene mapping, facilitating identification of genes related to:
- Cold tolerance
- Disease resistance
- Milk and meat quality
- Reproductive traits
Benefits and Applications:
- Conservation: Helps counter threats like genetic erosion, climate change, and loss of grazing lands.
- Livestock Improvement: Enables targeted breeding programs for improved productivity and adaptability.
- Scientific Research: Offers comparative insights into bovine genetics and facilitates allele mining for key traits.
- Sustainable Development: Aids in the socio-economic upliftment of yak herders by improving livestock performance.
About ICAR-NRC on Yak:
- Established in 1989, located in Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Premier institution for research on yak husbandry, health, nutrition, and genetics.
- Works to preserve the unique genetic resources of Himalayan livestock.
Desalination Technology
- 16 May 2025
The Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, has successfully developed a high-pressure, nanoporous, multilayered polymeric membrane for seawater desalination.
Developing Agency:
- The technology was developed by the Defence Materials Stores Research & Development Establishment (DMSRDE), Kanpur, a DRDO laboratory.
- It addresses the Indian Coast Guard's (ICG) operational needs aboard Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPVs), especially to counter instability caused by chloride ions in saline water.
Salient Features of the Technology:
- Indigenous development completed in a record time of 8 months.
- Successfully tested in existing desalination plants aboard ICG vessels.
- Undergoing 500-hour operational testing before final clearance by ICG.
- Can be adapted for use in coastal areas for civilian desalination purposes as well.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances onboard freshwater self-reliance for maritime security forces.
- Reduces dependency on imported technologies.
- Contributes to India’s self-reliance in critical defence and water technologies.
Desalination Technology: Key Concepts
What is Desalination?
Desalination is the process of removing dissolved salts and minerals from seawater or brackish water to produce potable or industrial-grade water.
Main Technologies Used:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO):
- Pressure-driven membrane filtration.
- Uses semi-permeable membranes to separate salts from water.
- Thermal Desalination:Involves evaporation followed by condensation to obtain fresh water.
Working of RO Desalination:
- In osmosis, water naturally moves from low solute to high solute concentration across a membrane.
- In reverse osmosis, external pressure is applied to force water from high solute (saline) to low solute (freshwater) side.
- RO membranes allow only water molecules to pass, filtering out salts and impurities.
- Seawater with ~35,000 ppm Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is reduced to 200–500 ppm, making it drinkable.
Axions and the HAYSTAC Experiment
- 15 May 2025
In News:
A recent study published inPhysical Review Letters reports that while the HAYSTAC experiment did not detect axions, it achieved a major technological milestone. The experiment significantly broadened the search range for axion masses and their interaction strengths, marking substantial progress in the hunt for dark matter.
What are Axions?
Axions are theoretical subatomic particles proposed in the late 1970s as a solution to the strong CP (Charge-Parity) problem in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). This problem involves the puzzling absence of CP violation in strong nuclear interactions, contrary to expectations.
- Axions were introduced to dynamically neutralize CP-violating effects by adjusting the QCD theta (θ) parameter to nearly zero.
- Over time, they have also gained prominence as a leading candidate for dark matter, the elusive form of matter believed to make up the bulk of the universe’s mass.
Why Axions matter in Dark Matter Research
Axions are particularly attractive as Cold Dark Matter (CDM) candidates due to their theoretical and cosmological properties:
- Electromagnetically neutral
- Extremely low mass
- Very weak interactions with ordinary matter and radiation
Foundational work by physicists like Sikivie, Wilczek, Dine, and Preskill demonstrated that axions produced in the early universe could account for the observed dark matter density—roughly 85% of the universe's matter content.
The HAYSTAC Experiment: A Precision Tool for Axion Detection
HAYSTAC (Haloscope At Yale Sensitive To Axion Cold Dark Matter) is a collaborative project led by Yale, Berkeley, and Johns Hopkins University, designed to detect axions by converting them into detectable photons using a haloscope.
Key Features:
- Haloscope Design: A microwave cavity placed in a strong magnetic field, following a design originally proposed by Pierre Sikivie.
- Quantum Squeezing: HAYSTAC is one of the few experiments—alongside Advanced LIGO—that uses quantum squeezing to reduce quantum noise, thereby enhancing measurement precision.
What is Quantum Squeezing?
Quantum squeezing is a technique that manipulates quantum uncertainty to minimize noise in one variable while tolerating increased uncertainty in another. This helps:
- Suppress random fluctuations, and
- Improve the signal-to-noise ratio—vital for detecting rare, weak signals like those possibly produced by axions.
Phase II Highlights of HAYSTAC
- Conducted the widest frequency sweep to date in the axion mass range.
- Marked a technical breakthrough in detection sensitivity.
- Although axions were not detected, the results helped rule out certain mass-coupling combinations, narrowing the parameter space for future searches.
Crohn’s Disease
- 15 May 2025
In News:
A former SpaceX employee has filed a lawsuit against the company, alleging wrongful termination. According to the claim, the individual was fired due to frequent restroom visits linked to Crohn’s disease, a chronic medical condition. The case has drawn attention to the difficulties faced by individuals managing long-term illnesses in demanding work environments.
Key Details:
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. It is a lifelong condition that can significantly impact quality of life and daily functioning.
Key Features:
- Nature of the Disease:A persistent and often progressive condition marked by inflammation in different sections of the digestive tract, most frequently affecting the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
- Extent of Inflammation:Inflammation may penetrate deep into the bowel wall, leading to pain, damage, and complications over time.
- Common Symptoms:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Weight loss
- Fatigue and sometimes malnutrition
Symptoms can vary in severity and may appear intermittently, often referred to as “flare-ups.”
Complications and Impact
Crohn’s disease can be debilitating and may result in serious complications, including:
- Intestinal blockages
- Fistulas (abnormal connections between body parts)
- Abscesses
- Nutritional deficiencies
Treatment and Management
- No Cure Available:While there is currently no cure for Crohn’s disease, medical therapies can effectively manage symptoms and inflammation.
- Goals of Treatment:
- Inducing and maintaining remission
- Healing affected intestinal tissues
- Improving overall quality of life
- Treatment Approaches:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Immune system suppressors
- Dietary changes
- In severe cases, surgery may be required
Many individuals with Crohn’s can lead productive lives with appropriate treatment and support.
ALICE Experiment
- 13 May 2025
In News:
The ALICE collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has experimentally observed the conversion of lead nuclei into gold nuclei through a rare nuclear transmutation process. This discovery, reported in Physical Review C, marks the first systematic detection of gold production via electromagnetic dissociation at the LHC.
Historical Context: The Dream of Chrysopoeia
The idea of turning lead, a common base metal, into gold—a precious metal—dates back to medieval alchemy and is known as chrysopoeia. Alchemists were motivated by the similarity in density between lead and gold, but modern chemistry has established that chemical reactions cannot change one element into another since elements differ by their number of protons.
With the advent of nuclear physics in the 20th century, scientists learned that nuclear reactions could transmute elements, either naturally (radioactive decay) or artificially (particle accelerators). However, the ALICE experiment at CERN has revealed a novel mechanism of such transmutation involving near-miss collisions of lead nuclei.
Mechanism of Transmutation at the LHC
The LHC, located on the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator. It accelerates two beams of lead nuclei (each containing 82 protons) to velocities close to the speed of light (about 99.999993% of the speed of light) inside a 27-kilometre ring.
During ultra-peripheral or near-miss collisions, lead nuclei pass close by each other without direct contact. The intense electromagnetic fields generated by the 82 protons in each lead nucleus compress into a short-lived pulse of photons, producing a process called electromagnetic dissociation.
This photon-induced excitation causes the nucleus to oscillate internally and emit a small number of protons and neutrons. When a lead nucleus (Pb-208) ejects three protons and two neutrons, it effectively becomes a gold nucleus (Au-203).
Role of ALICE Detector and Zero Degree Calorimeters (ZDCs)
The ALICE detector uses Zero Degree Calorimeters (ZDCs) to detect and count these nuclear dissociation events by measuring the number of emitted protons and neutrons. The emission of zero, one, two, or three protons corresponds to the creation of lead, thallium, mercury, and gold nuclei, respectively.
This capability allows ALICE to distinguish rare electromagnetic transmutations from the usual high-energy head-on collisions producing thousands of particles.
Key Findings and Quantitative Data
- The LHC produces gold nuclei at a rate of about 89,000 nuclei per second during lead–lead collisions.
- During LHC Run 2 (2015–2018), approximately 86 billion gold nuclei were generated.
- This corresponds to a mass of only 29 picograms (2.9 × 10?¹¹ grams), far too little for any practical use like jewelry.
- Run 3, with increased luminosity, has nearly doubled the amount of gold produced.
- The gold nuclei exist only for a fraction of a second before fragmenting into protons, neutrons, and other particles upon hitting the LHC’s beam pipe or collimators.
Significance
This discovery:
- Demonstrates a new pathway for nuclear transmutation via electromagnetic interactions at ultra-relativistic speeds.
- Provides experimental data that helps refine theoretical models of electromagnetic dissociation.
- Aids in understanding and predicting beam losses, which are critical for improving the performance of the LHC and future particle colliders.
About CERN and the LHC
- CERN (European Organisation for Nuclear Research), established in 1954, is Europe’s premier high-energy physics research organization with 23 member states and 10 associate members (including India).
- The LHC accelerates particles to nearly light speed in a 27-km circular tunnel under the Franco-Swiss border, facilitating collisions studied by four major experiments: ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, and LHCb.
- These experiments aim to probe fundamental particles and forces, test the Standard Model of particle physics, and explore conditions of the early universe.
Discovery of Chirality in KV?Sb?
- 12 May 2025
In News:
In a major advancement in condensed matter physics, researchers have identified a chiral quantum state in KV?Sb?, a topological material with a Kagome lattice structure. This discovery is significant as the material was earlier thought to be non-chiral, making this the first observation of intrinsic chirality in a bulk topological quantum system.
What is Chirality?
- Chirality refers to the geometric property of an object not being superimposable on its mirror image—a concept known as "handedness".
- It is common in nature, observed in:
- Amino acids
- The double helical structure of DNA
- Spiral patterns in biological systems
- Molecules often exist in left-handed (L) and right-handed (D) forms, a feature crucial to both biochemistry and quantum physics.
About KV?Sb? and the Kagome Lattice
- KV?Sb? is a bulk quantum material characterized by a Kagome lattice—a structure formed by corner-sharing triangles.
- The Kagome pattern, originating from Japanese basket-weaving, serves as a fertile platform for investigating topological and quantum phenomena like superconductivity, charge ordering, and now, chirality.
Scientific Technique Used
- Researchers employed a novel tool called the Scanning Photocurrent Microscope (SPCM).
- Unlike Scanning Tunnelling Microscopy (STM), which offers atomic-resolution images, SPCM is designed to detect nonlinear electromagnetic responses in materials.
- The SPCM detected handedness in the photocurrent, confirming the circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE)—a definitive marker of chirality.
Key Findings
- The material exhibited spontaneous symmetry breaking, particularly the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
- At 4 Kelvin, KV?Sb? responded differently to right- and left-handed circularly polarized light, demonstrating the breaking of mirror and inversion symmetries.
- This confirms the presence of intrinsic chiral charge order, marking the first such observation in a bulk topological material.
Kosmos 482
- 11 May 2025
In News:
A 500-kg fragment of the Soviet-era Kosmos 482 spacecraft, launched in 1972 as part of the Venera programme, is expected to make an uncontrolled re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere around May 10, 2025, after over 53 years in orbit.
What was the Kosmos 482 Mission?
- Launched: March 31, 1972, by the Soviet Union.
- Objective: To land a probe on Venus and collect atmospheric and surface data.
- Programme: Part of the Venera series (1961–1984), which launched 28 probes to Venus.
- 13 entered the Venusian atmosphere.
- 10 successfully landed on the surface.
- Twin Mission:Venera 8, launched on March 27, 1972, successfully landed on Venus and transmitted data for 50 minutes.
Mission Failure and Orbit Status
- The mission failed due to a timer malfunction in the rocket's upper stage, which shut down prematurely, leaving the spacecraft stranded in low Earth orbit instead of heading to Venus.
- The main spacecraft eventually burned up in the atmosphere, but a lander module (approx. 500 kg) remained in orbit.
Expected Re-entry (May 2025)
- The lander module is currently being dragged down by atmospheric friction.
- No precise location or time of impact is known due to the uncontrolled nature of its descent.
- Expected re-entry corridor lies between 52° North and 52° South latitude, covering:
- Africa, Australia
- Most of the Americas
- Much of southern and mid-latitude Europe and Asia
Is it a risk to Earth?
- The lander is made of titanium, with a melting point of ~1,700°C, higher than typical atmospheric re-entry temperatures (~1,600°C).
- This increases the likelihood of survival through re-entry.
- Possible outcomes as per space debris experts:
- “A splash” (ocean impact) — least dangerous
- “A thud” — impact on uninhabited land
- “An ouch” — impact on populated area (least desired scenario)
- If intact, the object could impact Earth at a speed of ~242 km/h, similar to a high-speed train.
Lagrangian Growth-Advection Model
- 09 May 2025
In News:
In a significant advancement for climate science, researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) and Florida State University have developed a novel method to more accurately estimate oceanic carbon export using satellite data. This method, called the Lagrangian Growth-Advection Model, enhances our understanding of the ocean’s role in sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO?).
What is the Lagrangian Growth-Advection Model?
The model integrates Lagrangian tracking (which follows individual fluid parcels in motion) with advection (the horizontal movement of water) and biological growth processes. This innovative framework allows scientists to trace the journey of phytoplankton and the associated carbon flux as they move with ocean currents—particularly in dynamic regions such as the California Current upwelling system.
Key Innovations:
- Captures Spatial and Temporal Lags: Unlike conventional models, this approach accounts for delays between carbon production at the surface and its eventual export to deeper waters.
- Incorporates Biological Complexity: The model factors in zooplankton activity, biological succession, and advection of plankton communities, offering a more comprehensive representation of the carbon cycle.
- Beyond Ocean Colour: Traditional models rely heavily on ocean colour data, which is limited to surface chlorophyll concentration. The new model goes beyond this by incorporating additional ecological and physical processes.
Validation and Performance:
The model’s predictions were validated against deep-sea carbon flux measurements, particularly at Station M—a long-term ocean floor observatory operated by MBARI. Remarkably, it explained episodic pulses of carbon export previously unaccounted for by older models, marking a significant improvement in understanding carbon dynamics.
Why this Matters:
The biological pump—the process by which marine organisms convert dissolved CO? into organic carbon that eventually sinks to the deep ocean—is a crucial mechanism for long-term carbon sequestration. The ocean currently absorbs a substantial share of anthropogenic CO? emissions, helping mitigate global warming. Accurate estimates of this process are vital for climate modelling and carbon budgeting.
Existing satellite-based models fall short in capturing the subsurface processes and time-lagged carbon fluxes that significantly impact overall carbon export. The Lagrangian Growth-Advection Model addresses these limitations, offering a more realistic and dynamic understanding of the ocean’s carbon cycle.
Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) 2025

- 09 May 2025
In News:
India is set to host the 12th edition of the Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) 2025 from 7th to 9th May 2025 in New Delhi, marking a significant milestone in the nation's emergence as a key global player in space exploration.
Key Highlights of GLEX 2025:
- Theme: “Reaching New Worlds: A Space Exploration Renaissance”
- The conference theme underscores a renewed global commitment to innovation, inclusivity, and international collaboration in space science and technology.
- Organisers:
- International Astronautical Federation (IAF) – The world’s foremost space advocacy organisation.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) – Serving as the primary host, reflecting India’s growing stature in the global space ecosystem.
- Astronautical Society of India (ASI) – Acting as the co-host and supporting India's role in global space diplomacy.
GLEX 2025 is expected to bring together global experts, policymakers, scientists, and industry leaders to discuss cutting-edge advancements, collaborative missions, and the future of space exploration. It will also highlight India's evolution from a regional space power to a central figure in the international space community.
About the International Astronautical Federation (IAF):
- Established: 1951
- Membership: Over 500 organisations from 78 countries, including major space agencies, private companies, academic institutions, and research bodies.
- Vision: “A space-faring world cooperating for the benefit of humanity”
- Motto: “Connecting @ll Space People”
- The IAF promotes global space cooperation and knowledge exchange. Through platforms like GLEX, it fosters dialogue on programmatic, technical, and policy aspects of space missions.
Significance for India:
GLEX 2025 reflects India’s growing prominence in the global space domain, reaffirming its commitment to peaceful space exploration and international collaboration. The event offers a valuable opportunity for India to showcase its achievements, build new partnerships, and contribute to shaping the future of global space policy and science.
Metal-Free Catalyst for Hydrogen Fuel Production
- 08 May 2025
In News:
In a significant breakthrough for clean energy technology, Indian scientists have engineered a metal-free catalyst capable of generating hydrogen fuel by harnessing mechanical energy. This innovation marks a major step forward in sustainable hydrogen production, aligning closely with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and its goal to lead in green energy solutions.
What is the Metal-Free Catalyst?
The catalyst is a specially designed donor-acceptor covalent organic framework (COF) that functions as a piezocatalyst without relying on any metal components. It can efficiently split water molecules to produce hydrogen gas (H?) when subjected to mechanical forces such as vibrations or pressure.
Development and Collaboration
This pioneering catalyst was developed at the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) in Bengaluru, under the leadership of Professor Tapas K. Maji. The project was carried out in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Pune and Wroc?aw University of Science and Technology in Poland.
Key Features of the Catalyst
- Metal-Free Composition: Made entirely from organic molecules, specifically TAPA (donor) and PDA (acceptor), connected through stable imide bonds.
- Ferrielectric Ordering (FiE): This internal property creates strong electric fields within the material, driving the catalytic water-splitting process.
- Porous, Sponge-like Structure: Enhances water permeability and promotes efficient separation of charges generated during the reaction.
- Mechanically Activated: The catalyst produces electron-hole pairs when exposed to mechanical pressure, enabling effective hydrogen generation.
Significance and Impact
- Environmentally Friendly: Eliminates the need for expensive and potentially harmful metal-based catalysts by using sustainable organic materials.
- Energy-Efficient: Utilizes ambient mechanical energy sources, such as vibrations or applied pressure, to power hydrogen production.
- Supports India’s Clean Energy Goals: Advances the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, strengthening India’s position in global clean energy innovation and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Scalable and Cost-Effective: Offers a practical and affordable alternative to conventional metal-based hydrogen production technologies, making it suitable for widespread adoption.
DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala) &Pusa DST Rice 1
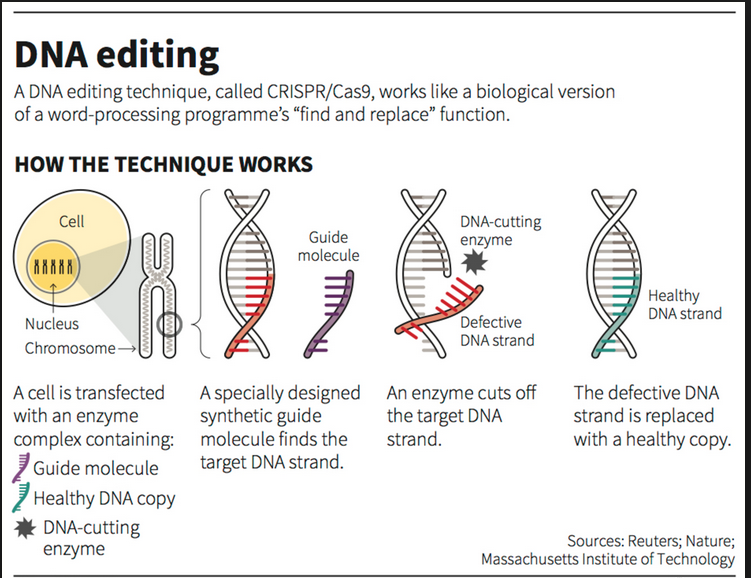
- 06 May 2025
In News:
- Recently, the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare launched India’s first genome-edited rice varieties—DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala) and Pusa DST Rice 1.
- Developed by ICAR-IIRR (Hyderabad) and ICAR-IARI (New Delhi) using CRISPR-Cas9 technology under SDN1/SDN2 methods.
About the Varieties
DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala)
- Developed by: ICAR-Indian Institute of Rice Research (IIRR), Hyderabad
- Parent variety: Samba Mahsuri (BPT 5204)
- Features:
- 19% increase in yield
- Matures in ~130 days (20 days earlier than parent)
- Stronger stem – reduces lodging
- Saves ~7,500 million cubic meters of irrigation water
- Lower methane emissions
- Edited gene: CKX2 (Gn1a) – increases grain number per panicle
Pusa DST Rice 1
- Developed by: ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi
- Parent variety: MTU 1010 (Cotton Dora Sannalu)
- Features:
- Improved tolerance to drought and salinity
- Yield increase: Up to 30.4% in saline/alkaline soils
- Edited gene: DST gene
- Developed using SDN1 genome editing – no foreign DNA inserted
Technology Used
- CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system:
- Enables precise editing of native genes without inserting foreign DNA
- SDN1/SDN2 methods approved by India’s biosafety regulations
- Genome editing vs GMOs:
- Genome editing makes internal gene alterations
- GMOs involve insertion of foreign genetic material
- GM crops are banned for cultivation/import in India (except Bt cotton)
Benefits Claimed
- Increased agricultural productivity:
- 19% increase in yield (DRR Dhan 100)
- Up to 30.4% increase in saline soils (Pusa DST Rice 1)
- Environmental benefits:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions (~20%)
- Lower methane release due to early maturation
- Major water conservation
- Target states: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Puducherry
Concerns and Criticisms
Biosafety and Unintended Effects
- Unintended mutations: CRISPR-Cas enzymes may cause off-target gene edits, potentially resulting in unknown protein formations.
- Lack of global standardisation on enzyme concentration and specificity.
- Some scientists warn of genetic instability in SDN1-based edits.
Seed Sovereignty & Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- Genome editing tools are IPR-protected, raising concerns over farmers' seed sovereignty.
- Activist groups like Coalition for a GM-Free India demand transparency on IPR ownership and oppose reliance on proprietary technologies.
- Risk of monoculture, loss of rice genetic diversity, and trade barriers for India’s non-GM rice exports.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
- India’s biosafety guidelines (2022) permit SDN1 and SDN2 genome editing for general crops.
- The Union Budget 2023–24 allocated ?500 crore for advancing genome editing in agriculture.
- ICAR expanding genome editing to oilseeds and pulses.
Pulsar G359 and Galactic ‘Bone’
- 06 May 2025
In News:
Astronomers have discovered a likely explanation for a fracture in a huge cosmic "bone" in the Milky Way galaxy, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and radio telescopes.
About G359.13-0.20005 ("The Snake")
- G359.13 is a non-thermal filament in the Milky Way, resembling a "galactic bone."
- It stretches about 230 light-years and is located ~26,000 light-years from Earth, near the Galactic Center.
- These filaments are visible primarily in radio waves and aligned with galactic magnetic field lines.
- Emissions result from charged particles spiraling along magnetic fields, producing synchrotron radiation.
Key Discovery
- A fracture has been observed in the continuous structure of G359.13.
- This fracture aligns with the location of a pulsar, identified using:
- Chandra X-ray Observatory (X-ray data)
- MeerKAT and VLA (radio data)
About the Pulsar
- A highly magnetized, fast-moving neutron star formed by a supernova explosion.
- Estimated speed: 1–2 million miles per hour.
- The pulsar likely collided with G359.13, causing:
- Distortion in the magnetic field
- Fracture in the radio filament
- Chandra data revealed blue-colored X-ray emissions from the pulsar.
- Nearby X-ray sources may be from electrons and positrons accelerated to high energies.
Scientific Significance
- Provides insights into:
- High-energy astrophysical processes
- Pulsar interactions with galactic magnetic structures
Chandra X-ray Observatory – Key Facts
- Launched: July 23, 1999, aboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93)
- Function: Detects X-ray emissions from hot cosmic objects (e.g., black holes, supernova remnants)
- Orbit: High Earth orbit (~139,000 km altitude) to avoid atmospheric X-ray absorption
- Part of NASA’s “Great Observatories” (with Hubble, Spitzer, Compton)
- Capabilities:
- 8x better resolution than previous X-ray missions
- Detects X-ray sources 20 times fainter than predecessors
- Managed by: NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center
Amazon’s Project Kuiper
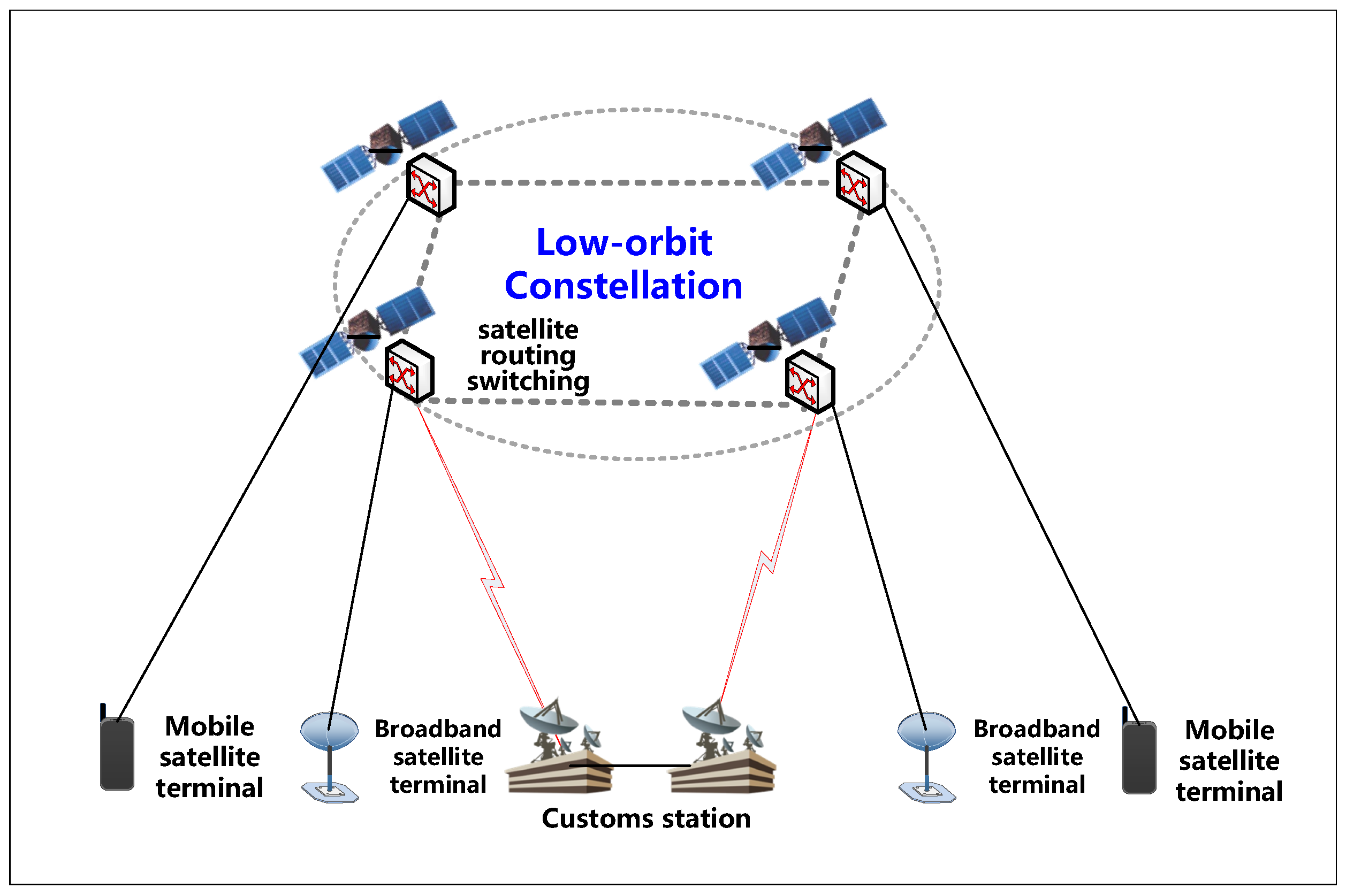
- 02 May 2025
In News:
Amazon successfully launched the first 27 satellites of Project Kuiper aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. This marks the beginning of a large-scale effort to deploy a global satellite internet network to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink.
What is Project Kuiper?
Project Kuiper is Amazon’s satellite-based broadband project aimed at delivering high-speed internet across the globe, especially in underserved and remote regions, using Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
- Implementing Agency: Amazon
- FCC License: Approved in July 2020 by the US Federal Communications Commission
- Launch Name: KA-01 (Kuiper Atlas 1)
- Total Satellites Planned: 3,232 satellites in LEO (~630 km altitude)
- Current Launch: 27 satellites deployed; over 80 launches are planned to build the full constellation.
Objectives
- Provide affordable, high-speed internet to users across the globe.
- Support education, healthcare, disaster response, rural connectivity, and government services.
- Serve sectors requiring resilient communications in low-connectivity areas.
Internet Speed Tiers
Terminal Type Speed
Compact (Home Use) Up to 100 Mbps
Standard (Schools/Hospitals) Up to 400 Mbps
Large (Govt/Enterprise) Up to 1 Gbps
Comparison with Starlink and Other Satellite Internet Systems
Network Organisation Satellites Planned Current Status
Starlink SpaceX 40,000+ ~7,200 operational satellites; 5M+ users
OneWeb UK/India 648 Hundreds in orbit
Telesat Lightspeed Canada 298 In development
Guowang China 13,000+ Under planning
Project Kuiper Amazon 3,232 First 27 launched (May 2025)
How Satellite Internet Works
- Constellation: A network of satellites working in coordination to provide continuous global coverage.
- LEO Orbit: Satellites operate between 500–2,000 km altitude, offering low latency (20–40 ms).
- Ground Stations: Transmit and receive data to and from satellites.
- Inter-satellite Links: Use lasers/radio waves to relay data between satellites.
- AI-based Routing: Manages network traffic and reduces lag.
Technical Features
- Frequency Bands Used:
- Ka-band: High speed, weather-sensitive
- Ku-band: Balanced speed and reliability
- C-band: Slower, good in poor weather
- V-band: Experimental, ultra-fast but obstructed easily
- ACM Technology: Adjusts signal strength dynamically during adverse weather conditions.
Challenges
- High Cost: Satellite launches and user equipment are expensive.
- Weather Sensitivity: Rain and storms disrupt signals, especially in Ka/V bands.
- Space Debris Risk: Dense constellations increase chances of satellite collisions.
- Astronomical Interference: Bright satellite trails obstruct telescopic observations.
Strategic and Commercial Implications
- Project Kuiper marks Amazon’s entry into a growing space-based internet economy, competing with SpaceX’s Starlink.
- Expected to play a commercial and strategic role, including possible defence applications.
- With over 80 launches planned, Amazon will use various launch providers including ULA, Arianespace, Blue Origin, and SpaceX.
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Breakthrough
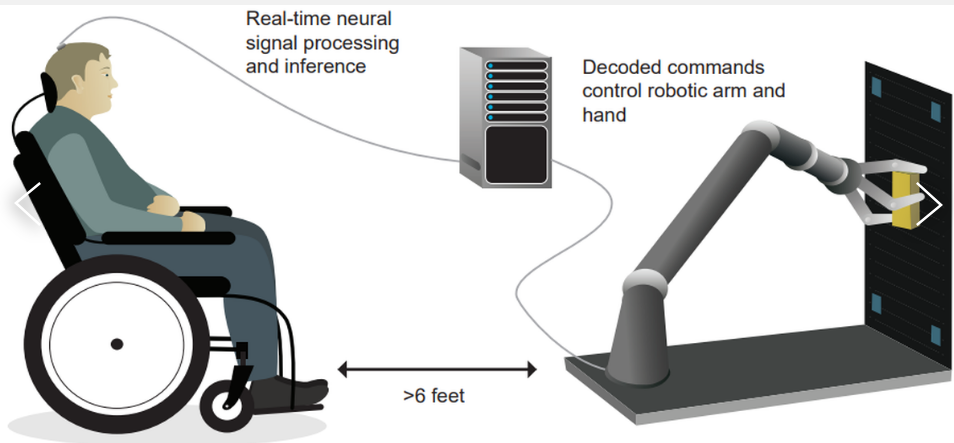
- 01 May 2025
In News:
In a pioneering advancement in neurotechnology and assistive healthcare, scientists at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)have developed a stable Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) system that enables a paralysed individual to control a robotic arm using only brain signals. This innovation holds transformative potential for people with paralysis, significantly enhancing autonomy and quality of life.
What is Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)?
A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a neurotechnological system that establishes direct communication between the brain and external devices, bypassing damaged neural pathways. It decodes neural signals related to intended movements and translates them into actionable commands to control robotic limbs, computers, or speech systems.
Key Technological Achievements
- Long-Term Stability: The developed BCI system allowed continuous and accurate control of a robotic arm for over 7 months with minimal recalibration, overcoming a major limitation of earlier BCI systems.
- Sensor Implantation: Tiny electrodes were implanted in the motor cortex, the region of the brain that governs movement.
- AI-Powered Signal Decoding: The system used machine learning algorithms to decode brain activity and adapt to daily shifts in neural signals, ensuring consistent performance.
- Virtual to Real Transition: The participant underwent virtual training with a robotic arm before controlling a real-world robotic limb, aiding in precision and neural calibration.
Functionality Demonstrated
The paralysed participant, who had lost all movement and speech abilities due to a stroke, could:
- Pick up and rotate blocks
- Open cabinets
- Retrieve and position a cup under a water dispenser
These basic actions, enabled purely by imagined movement, highlight the immense real-world utility of the BCI system.
Scientific Insights
- High-Dimensional Neural Mapping: Although neural signals shifted slightly each day, their overall structure remained consistent. This allowed researchers to create a dynamic AI framework that predicted and compensated for signal changes.
- No Direct Brain Stimulation: The system only read signals and did not send any electrical impulses to the brain.
- End-to-End Signal Processing Pipeline: From capturing brain signals to executing robotic arm movement, a seamless pipeline was established for fluid, real-time motion.
Broader Applications
The implications of this BCI research go beyond limb movement:
- Restoration of Speech: In cases of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) and brainstem stroke, BCIs can decode intended speech from neural activity and render it as text, synthesized voice, or avatar speech.
- Faster Communication: A recent trial showed an ALS patient using BCI technology to communicate at 62 words per minute, nearly 3.4 times faster than earlier systems.
Future Prospects & Challenges
- Scalability: More work is needed to generalize this system for diverse forms of paralysis.
- Complex Environments: Future BCIs must function in real-world environments filled with distractions, like grocery stores or public spaces.
- Ethical and Regulatory Oversight: Given the invasive nature of electrode implantation, ethical considerations around consent, privacy, and long-term effects must be addressed.
CAG and BISAG-N collaborate to enhance auditing through advanced Geo-spatial Technologies

- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has entered into a significant partnership with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) to leverage advanced technologies in geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and satellite image analytics for strengthening audit processes.
About BISAG-N
- Institution Profile: BISAG-N is an autonomous scientific society under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India, located in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. It operates under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Core Domains: The institute specializes in satellite communication, geo-informatics, and geo-spatial technologies.
- Functions: BISAG-N develops and manages GIS databases, creates and updates maps, conducts data migration and format translation, provides software customization and systems integration, and offers technical consulting for large-scale GIS implementations.
- Applications: It delivers comprehensive geo-spatial solutions including photogrammetry, cartography, remote sensing applications for agriculture (crop monitoring), watershed management, forest fire mapping, and environmental resource management.
- Collaborations: BISAG-N works closely with central ministries and state government agencies to support planning and development activities using space and geo-spatial technologies.
Details of the CAG-BISAG-N Partnership
- Objective: The partnership aims to integrate cutting-edge geo-spatial tools such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data Analytics into the CAG's audit methodologies. This will enhance audit accuracy, efficiency, and accountability.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Developing customized geo-spatial solutions and platforms for audit analysis.
- Utilizing data available from government initiatives like PM GatiShakti for comprehensive audit evaluations.
- Conducting joint research in geo-spatial analysis, remote sensing, and satellite image analytics.
- Organizing training and capacity-building programs to equip CAG officials with skills in geo-spatial technologies.
- Significance: This collaboration reflects the CAG’s commitment to adopting digital public infrastructure and technological innovation, enhancing governance, and reinforcing financial accountability in India’s public institutions.
Gaia Space Observatory
- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The European Space Agency (ESA) has officially retired its Gaia space observatory after over nine years of pioneering work in astrometry. Launched in December 2013, Gaia was designed to create the most detailed three-dimensional map of the Milky Way galaxy, transforming our understanding of its structure, evolution, and constituents.
About Gaia
- Mission Objective: Gaia aimed to precisely measure the positions, distances, motions, and physical properties of over 2 billion stars within the Milky Way. Its data helps scientists study the galaxy’s formation, predict its future evolution, and explore celestial phenomena.
- Orbit & Technology: Stationed at the second Lagrange point (L2), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, Gaia operated beyond the disturbances of Earth’s atmosphere, sun, and moon. Equipped with twin telescopes focusing light onto a nearly one-billion-pixel digital camera—the largest ever deployed in space—the observatory had three key instruments: an astrometer, photometer, and spectrometer to measure stellar positions, brightness, and compositions.
Major Contributions and Discoveries
- 3D Galactic Map: Gaia revealed the warped and wobbling nature of the Milky Way’s disc, mapped its spiral arms and central bulge, and detailed its dynamic evolution shaped by ancient galactic collisions. These findings shed light on events influencing the formation of stars including our Sun.
- New Black Holes: The mission identified previously unseen black holes detectable only by their gravitational influence, marking a first in astronomical observations.
- Asteroid Cataloguing: Gaia tracked the paths of over 150,000 asteroids, enabling better prediction of their trajectories and potential threats to Earth.
- Legacy and Data: Although Gaia has mapped approximately 2% of the galaxy’s stars so far, its extensive data sets continue to be processed and released, promising decades of future scientific breakthroughs.
End of Mission and Legacy
In March 2025, ESA safely deactivated Gaia by draining its energy and shifting it to a retirement orbit around the Sun, ensuring it does not interfere with upcoming missions. While the spacecraft’s active observations have ended, Gaia’s rich data legacy remains invaluable to astronomers worldwide.
Lyme Disease
- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. These ticks become carriers when they feed on infected animals, such as rodents. Importantly, Lyme disease does not spread from person to person, nor through food, water, air, pets, or other insects like mosquitoes and flies.
The disease is primarily reported in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, particularly in wooded and grassy regions during the warmer months. In the United States, it is most prevalent in the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and upper Midwestern states.
Symptoms and Progression
Lyme disease often begins with a characteristic red, expanding rash called erythema migrans, which may appear in a bull’s-eye pattern. Early symptoms also include fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches, headache, and swollen lymph nodes. If untreated, it can progress to cause:
- Neurological issues: meningitis, facial palsy (Bell’s palsy), nerve pain, and brain inflammation.
- Cardiovascular problems: irregular heartbeat and heart block.
- Musculoskeletal symptoms: arthritis, joint pain (especially in the knees), and swelling.
- Other effects: dizziness, vision problems, memory issues, and concentration difficulties (often referred to as “brain fog”).
Treatment Protocol
Lyme disease is primarily treated with antibiotics, especially when diagnosed early. Common antibiotics include doxycycline (for adults and children over 8 years), amoxicillin (for younger children and pregnant women), cefuroxime, and azithromycin (for those allergic to other options). The treatment duration varies:
- Localized skin infections: 14 days
- Early disseminated infections: 21 days
- Lyme arthritis: 28 to 60 days
- Severe or neurological cases may require intravenous antibiotics like ceftriaxone
In some cases, symptoms may persist even after treatment, a condition known as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS). While the exact cause is unknown, continued antibiotic use does not improve outcomes, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
Recent Scientific Breakthrough
In a major scientific advancement, researchers have identified a crucial enzyme—lactate dehydrogenase specific to Borrelia burgdorferi (BbLDH)—which plays a vital role in the bacterium's survival and infectivity. Unlike most organisms that rely on thiamin-dependent metabolism, B. burgdorferi uniquely depends on BbLDH to convert pyruvate to lactate, maintaining its NADH/NAD+ balance.
The research, conducted at Virginia Commonwealth University and published in mBio, demonstrated through genetic, biochemical, and structural analysis that BbLDH is essential for the growth and infection capability of the Lyme disease bacterium. Loss-of-function studies confirmed its indispensability, both in laboratory and in vivo models.
High-throughput screening of chemical compounds led to the identification of several promising BbLDH inhibitors. These inhibitors could form the basis for future, highly targeted treatments against Lyme disease. Moreover, the findings have broader implications for tackling other tick-borne illnesses.
Coeliac Disease
- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) may significantly accelerate the diagnosis of coeliac disease, an inherited autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption. Researchers at the University of Cambridge have developed an AI-based tool capable of diagnosing the disease swiftly and accurately, potentially transforming current diagnostic practices.
What is Coeliac Disease?
- Nature: An inherited autoimmune disorder.
- Cause: Triggered by consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
- Mechanism: Gluten intake causes an immune reaction in the small intestine, damaging the intestinal lining (villi), leading to malabsorption of nutrients.
Key Symptoms:
- Gastrointestinal: Diarrhoea, bloating, stomach cramps, weight loss
- Systemic: Fatigue, anaemia, skin rashes
- In children: Impaired growth and development
- Long-term complications: Malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, anaemia, and increased risk of autoimmune diseases and certain cancers
Prevalence and Risk Factors:
- Affects approximately 1 in 100 people worldwide
- About 700,000 people in the UK live with the disease
- Individuals with a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) with coeliac disease have a 1 in 10 risk
- It can develop at any age after gluten consumption begins
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Current Diagnostic Method:
- Blood tests to detect gluten antibodies
- Duodenal biopsy to assess damage to villi (requires analysis by pathologists)
- Treatment: No cure; managed through a strict lifelong gluten-free diet
AI-Based Diagnostic Advancement:
- Development: By University of Cambridge researchers
- Function: The AI model analyses biopsy images to detect villous damage
- Training: Based on 4,000+ biopsy images from five hospitals using scanners from four manufacturers
- Efficiency: Matches the accuracy of expert pathologists, with diagnosis in under a minute
- Impact: Could eliminate delays caused by backlog in pathology labs and speed up diagnosis for patients
Significance of AI in Healthcare:
- Benefits:
- Faster diagnosis for patients
- Reduces burden on pathologists and NHS waiting lists
- Frees up time for pathologists to focus on more critical cases (e.g., cancer)
- Expert Support:Recognised by the Royal College of Pathologists as a tool with the potential to transform diagnostic pathology
- Future Requirements:
- Investment in digital pathology
- Integrated IT systems across health organisations
- Training for medical professionals in AI-based diagnostic tools
Parker Solar Probe

- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, the NASA’s Parker Solar Probe made another close approach to the Sun, reaching within 6 million km of its surface. It continues to break records as the closest any human-made object has come to the Sun, aiming to improve our understanding of solar activity and space weather.
Key Highlights:
- Background:Launched on August 12, 2018, by NASA from Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Parker Solar Probe is designed for in-situ study of the Sun's outer atmosphere (corona), solar wind, and magnetic field. It was named after physicist Eugene Parker, who first theorized the existence of the solar wind in the late 1950s.
- Mission Objectives:
- Investigate the structure and dynamics of the solar corona
- Understand the origin and evolution of solar wind
- Study energetic particles responsible for solar storms
- Examine the mechanisms that heat the corona to over a million degrees Celsius while the Sun’s surface remains relatively cooler at ~6,000°C
- Orbital Details & Speed:The Parker Probe moves in a highly elliptical orbit using Venus' gravity for repeated assists to get closer to the Sun. It is the fastest human-made object, reaching speeds of up to 692,000 km/hr. Its closest planned approach is 6.16 million km (3.83 million miles) from the Sun—about seven times closer than any previous spacecraft.
- Heat Protection Technology:To withstand extreme solar radiation, the probe uses an 8-foot-wide, 4.5-inch-thick carbon-carbon composite heat shield capable of resisting temperatures up to 1,377°C. The shield’s sun-facing side is coated with white ceramic paint to reflect sunlight, and its design ensures that just behind the shield, temperatures drop to a manageable 29°C, protecting the onboard instruments.
- Scientific Instruments Onboard:
- FIELDS – Measures electric and magnetic fields in the corona.
- ISoIS (Integrated Science Investigation of the Sun) – Studies high-energy solar particles.
- SWEAP (Solar Wind Electrons, Alphas, and Protons) – Captures data on solar wind particles.
- WISPR (Wide-Field Imager) – Takes images of the solar corona and heliosphere.
- Faraday Cup – An external device made of molybdenum alloy (melting point: 2,349°C), measures ion and electron densities in solar wind.
- Key Discoveries:
- First ‘Touch’ of the Sun (April 2021): The probe crossed the Sun’s Alfvén surface — the boundary where solar wind escapes the Sun’s influence — thus officially entering the solar corona.
- Magnetic Switchbacks: Detected sudden reversals in the Sun’s magnetic field direction, providing clues about how solar wind accelerates.
- Dust-Free Zones: Found regions near the Sun unexpectedly devoid of dust, challenging earlier theories about uniform dust distribution in the solar system.
- Corona Heating Mystery: Parker’s data, especially on Alfvén waves and magnetic switchbacks, may help solve why the corona is vastly hotter than the Sun’s surface
- Challenges Overcome:Contrary to expectations, the Sun’s gravity, not heat, posed a significant challenge. High speeds needed careful navigation to avoid crashing into the Sun. The mission used Earth and Venus flybys to gradually spiral inward for closer approaches rather than the initial, longer route via Jupiter.
- Mission Timeline:The Parker Solar Probe is scheduled to make 24 close passes of the Sun, continuing into the 2030s. Each pass provides new insights into solar activity and its potential impacts on Earth.
- Comparison with India’s Aditya-L1 Mission:While the Parker Solar Probe performs in-situ analysis by flying into the corona, ISRO’s Aditya-L1, launched in 2023, is stationed at the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), 1.5 million km from Earth. Aditya-L1 remotely observes solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and magnetic storms using seven payloads, including a coronagraph.
India’s First Frozen Zoo

- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
In a pioneering conservation step, Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP) in Darjeeling, West Bengal, has become India’s first zoo to launch a DNA cryogenic conservation project—popularly known as a “frozen zoo”.
About the DNA Cryogenic Conservation Initiative
- Objective: Preserve genetic material of endangered Himalayan species for future research, assisted reproduction, and biodiversity conservation in case of extinction threats.
- Launched in:2023, with 60 DNA samples already collected.
- Collaborators:
- PNHZP, Darjeeling
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad
- Species covered: Red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan black bears, and other native animals.
- Source of Samples: Tissue collected from animals deceased in captivity or road accidents.
- Storage Method:
- DNA samples stored in liquid nitrogen at –196°C.
- A dedicated in-zoo laboratory with steel cryo-containers established.
About the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB)
- Established: 1977; full national lab status in 1981–82.
- Location: Hyderabad, Telangana.
- Affiliation: Under Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- Recognition: Designated a “Center of Excellence” by UNESCO’s Global Molecular and Cell Biology Network.
- Mandate: Advanced research and training in frontier areas of modern biology.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park
Feature Description
Location Darjeeling, West Bengal
Altitude 2,150 metres (7,050 feet) – India’s highest-altitude zoo
Area 67.8 acres
Established 14 August 1958
Renamed 1975 in memory of Padmaja Naidu, former Governor of West Bengal
Transferred to State 1993; now under Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
Focus Areas Ex-situ conservation, education, research, and captive breeding
Notable Species Red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan wolves, gorals, Siberian tigers
India’s First Indigenous MRI Scanner Installed at AIIMS
- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
AIIMS New Delhi is set to install India’s first indigenously developed MRI scanner for clinical evaluation by October 2025. This marks a major milestone under the government's push for import substitution and promotion of ‘Make in India’ in the medical device sector.
Key Highlights:
- MRI Type: 1.5 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) system.
- Developed by: SAMEER (Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research), an autonomous R&D institution under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Initiative under: National Mission SCAN-ERA (Swadeshi Chumbakiya Anu-naadChitran – EkRashtriyaAbhiyaan), launched in December 2014.
- Purpose: Clinical evaluation and performance feedback at AIIMS to refine the system for wide-scale clinical use.
- Objective: Reduce dependence on imported diagnostic equipment and lower treatment costs.
Significance:
- Currently, 80–85% of India's medical devices are imported.
- In FY 2023–24, India’s medical device import bill rose by 13% to ?69,000 crore.
- The initiative aligns with the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for medical devices, under which 7 critical devices (including MRI machines, CT scanners, LINACs, heart valves, etc.) are now being domestically manufactured.
- 19 PLI-supported projects have been commissioned to manufacture 46 medical devices.
MRI: How It Works
- Principle: Uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to align protons in tissues. As protons return to their original alignment, they emit signals that are captured to create detailed 3D anatomical images.
- Applications:
- Imaging soft tissues, brain, spinal cord, joints, and internal organs.
- Detecting tumors, strokes, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Functional MRI (fMRI) maps brain activity during cognitive tasks.
Safety & Limitations:
- Magnetic interference: Risky for patients with implants (e.g., pacemakers).
- Noise: Loud clicking sounds may cause discomfort.
- Claustrophobia: May cause anxiety in closed spaces; open MRI designs mitigate this.
- Contrast agents: Use of gadolinium-based agents can pose risks to dialysis patients.
Audible Enclaves

- 20 Mar 2025
Context:
Audible enclaves are highly localized zones of sound that remain undisturbed by ambient noise. These allow only specific individuals—usually within a defined space—to hear the sound, even in crowded or noisy environments.
Science Behind the Concept
- Nature of Sound:Sound travels as waves through a medium, causing its particles to vibrate back and forth.
- Frequency: The rate of this vibration determines the pitch of the sound.
- Higher frequency = Higher pitch.
- Diffraction: As sound propagates, it naturally spreads out. Higher-frequency waves tend to diverge more.
- Frequency: The rate of this vibration determines the pitch of the sound.
How Audible Enclaves are created
- Parametric Array Loudspeakers:These devices emit high-frequency ultrasonic waves modulated with an audio signal. As they move through air, the waves undergo self-demodulation, converting into audible sound in a narrow, focused beam. This beam is heard only by those directly in its path.
- Advanced Audible Enclaves (New Research – 2024):A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (March 17, 2024) demonstrated a more precise technique:
- Two ultrasonic waves of slightly different frequencies are emitted.
- These are inaudible on their own.
- When they intersect, non-linear acoustic interactions occur at that point.
- This generates an audible sound wave only at the intersection point, creating an enclave audible only to nearby individuals.
Applications and Relevance
- Private Communication in public places.
- Augmented Reality and targeted advertising.
- Assistive technology for the hearing-impaired.
- Security and military operations, where discreet communication is required.
NASA’s Curiosity Rover
- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA's Curiosity Rover has made a significant breakthrough by detecting carbon-bearing minerals on Mars, offering the first direct evidence of a potential carbon cycle on the planet. This finding adds a crucial piece to the puzzle of Mars' climatic and geological history.
Curiosity Rover: Mission Overview
- Launch Date: 26 November 2011
- Landing Date: 5 August 2012 (via sky crane system)
- Mission: Part of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) initiative
- Power Source:Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG) using plutonium-238, unlike solar-powered predecessors
- Size and Capabilities: Approximately 3 meters long and 900 kg in weight, equipped with an onboard chemical laboratory for rock analysis
Scientific Objectives
- Investigate whether Mars ever supported microbial life
- Analyze the planet’s climatic history
- Study Martian geology, especially sedimentary layers
- Contribute data for future human missions to Mars
Key Scientific Discovery
- The finding occurred while Curiosity was exploring an ancient lakebed region in Gale Crater, over an 89-meter-long stretch.
- It drilled into sulfate-rich rocks and discovered siderite (a carbonate mineral composed of iron, carbon, and oxygen), marking the first detection of this mineral on Mars.
- Rocks containing 5–10% siderite by weight imply that substantial amounts of ancient atmospheric CO? may have been locked within the Martian crust, rather than being lost to space.
- The presence of iron oxyhydroxides in the same rocks suggests that acidic water interactions could have dissolved siderite, potentially releasing carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere—indicating a slow and limited carbon cycle on Mars.
India’s Space Docking Capability

- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, ISRO successfully demonstrated autonomous space docking and undocking with its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx), making India the fourth country—after the USA, Russia, and China—to achieve this advanced space capability.
Two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), were launched into a 470 km orbit. From a starting separation of 20 km, they were autonomously maneuvered, docked using an indigenous androgynous docking mechanism, and later undocked after two months of in-orbit operation.
What is Space Docking and Why It Matters?
Docking is the process where two spacecraft in orbit are brought together and joined. Undocking is the controlled separation of these joined vehicles. These procedures are vital for:
- Assembling large structures (e.g., space stations) in orbit, bypassing launch weight limits.
- Orbital servicing of satellites (repairs, refueling).
- Interplanetary missions requiring in-space assembly and resupply.
- Crewed missions to space stations and planetary bodies (e.g., Moon, Mars).
Historical Context
- 1966 (USA): First manual docking by NASA’s Gemini VIII (Neil Armstrong with Agena).
- 1967 (USSR): First autonomous docking using Kosmos 186 & 188.
- 2011–12 (China): First unmanned and then crewed docking.
- 2025 (India): Successful autonomous docking and undocking via SpaDEx.
Strategic and Technological Significance for India
Future Missions:
- BharatiyaAntariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and Human Moon Mission by 2040 will rely heavily on in-orbit docking and assembly.
- Chandrayaan-4, aiming to return lunar samples, will use docking systems for orbital rendezvous and return modules.
Global Space Economy
- Positions ISRO as a leader in modular satellite design, orbital assembly, and international collaborations.
- Enables NewSpace India Ltd. (NSIL) to attract commercial contracts for space stations, satellite servicing, and deep-space ventures.
Domestic Technological Advancements
- Promotes indigenous innovation in docking systems, AI-driven autonomous navigation, robotics, and in-space power sharing.
- Supports R&D in microgravity, space manufacturing, and even space agriculture (e.g., orbital seed germination experiments).
Strategic and Diplomatic Impact
- Enhances India’s soft power and strengthens ties with space agencies like NASA and ESA.
- Contributes to space security by enabling orbital refueling and satellite servicing during emergencies.
- Offers collaborative platforms for BRICS and developing countries through BAS.
Capacity Building
- Encourages STEM education and youth engagement via initiatives like YUVIKA.
- Expands India’s aerospace industrial base, creating skilled jobs and fostering innovation.
Birefringence

- 17 Mar 2025
Context:
Birefringence, or double refraction, is an optical phenomenon observed in certain anisotropic materials where a single light ray splits into two rays upon entering the material. Each ray travels at a different speed and experiences a different refractive index based on the direction of light propagation and its polarization.
Refraction vs Birefringence
- Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another due to a change in speed. It is governed by the refractive index, defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the medium.
- Birefringence occurs when a material has multiple refractive indices in different directions, causing light to split into two rays.
Key Terms
- Refractive Index:
- Vacuum: 1
- Air: ≈1.0003
- Glass: ≈1.5
- Diamond: ≈2.4
- Polarization: The direction in which the light’s electric field oscillates. It influences how light behaves in birefringent media.
Types of Materials
- Isotropic Materials:
- Structure is uniform in all directions.
- Refractive index is the same regardless of direction.
- Examples: Glass, Sodium Chloride (NaCl).
- Anisotropic Materials:
- Structure varies along different crystal axes.
- Show different refractive indices in different directions.
- Exhibit birefringence.
- Examples: Calcite, Quartz, Mica, Tourmaline.
Sources of Birefringence
- Natural Birefringent Materials: Calcite, Mica, Quartz.
- Synthetic Birefringent Materials: Barium borate, Lithium niobate.
- Induced Birefringence: Can be generated by applying mechanical stress, electric, or magnetic fields to otherwise non-birefringent materials.
Applications of Birefringent Materials
- Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs)
- Medical and Polarising Microscopes
- Optical Switches and Waveplates
- Laser Technology
- Nonlinear Optics (e.g., Frequency Converters)
India’s First CAR T-Cell Therapy
- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant milestone in cancer treatment with the successful clinical trials of its first CAR T-cell therapy, marking a crucial step in indigenous biomedical innovation. The findings were recently published in The Lancet, making it the first CAR T-cell clinical trial from India to appear in an international journal.
What is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
- CAR T-cell therapy (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy) is a form of immunotherapy where a patient’s own T-cells are genetically modified to identify and destroy cancer cells.
- Primarily used for blood cancers, especially those unresponsive to first-line treatments, such as:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Large B-cell Lymphoma
Indian Breakthrough
- Developed by ImmunoAct, a start-up incubated at IIT Bombay.
- 73% response rate recorded in Phase I and II clinical trials.
- Approved by India’s drug regulator in 2023, bypassing Phase III trials under conditional approval due to the urgent need and novelty.
- Therapy is now available in major hospitals like Apollo, Fortis, Max, and Amrita.
Key Findings (Lancet Report)
- Median progression-free survival:
- 6 months for ALL patients
- 4 months for lymphoma patients
- Therapy costs approx. ?25 lakh, about 1/20th of global CAR T-cell therapy prices (?8–10 crore abroad).
Side Effects
- Severe immune reaction (Haemophagocyticlymphohistiocytosis) in 12% patients, leading to at least one death.
- Other adverse effects:
- Neutropenia (96%) – Low white blood cells
- Thrombocytopenia (65%) – Low platelet count
- Anemia (61%) – Low red blood cell count
- Febrile neutropenia (47%) – Infection risk due to low immunity
Significance
- Makes advanced cancer care more accessible and affordable within India.
- Positions India among a select group of countries with indigenous CAR T-cell therapy capabilities.
- Marks progress towards self-reliance in high-end medical technologies.
Supersolid Light
- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
In a groundbreaking achievement, Italian scientists have successfully created the world’s first ‘supersolid’ made from light, marking a new milestone in quantum physics. This discovery demonstrates that light, traditionally understood as pure energy, can be manipulated into a rare state of matter that combines the order of a solid with the frictionless flow of a superfluid.
What Is a Supersolid?
A supersolid is an exotic quantum phase of matter exhibiting dual characteristics:
- Solid-like structure: Maintains a periodic, lattice-like spatial arrangement.
- Liquid-like behavior: Flows without internal resistance (zero viscosity), like a superfluid.
Previously, supersolidity was observed in Bose-Einstein condensates (BECs)—ultracold atomic systems cooled near absolute zero (–273.15°C), where quantum effects dominate.
How was Supersolid Light created?
Researchers used semiconductor nanostructures (gallium arsenide with micro-ridges) to create polaritons—hybrid quasiparticles formed by coupling photons (light) with excitons (matter).
- When cooled and stimulated with a laser, these polaritons condensed into a coherent quantum fluid arranged in a regular pattern, exhibiting both superfluid and solid-like properties.
Key Features of Supersolid Light:
- Quantum Coherence: Particles move in a synchronized, wave-like manner due to shared quantum states.
- Frictionless Flow: Can move through obstacles without energy loss.
- Crystalline Order: Particles maintain a rigid spatial configuration.
- Symmetry Breaking: Demonstrates both spatial order and dynamic fluidity.
Significance and Applications:
- Quantum Computing: Enhances qubit stability and coherence, essential for error-free quantum operations.
- Photonics and Optical Devices: Enables development of light-based circuits with high efficiency.
- Energy Technologies: Potential applications in superconductors and frictionless systems.
- Fundamental Research: Offers insights into non-equilibrium quantum systems and phase transitions.
Why it matters for Science & Technology?
This marks the first time light has been shown to form a supersolid, expanding the boundaries of material science. It provides a new experimental platform for studying quantum behavior in light-matter systems, bridging the gap between theoretical physics and practical innovation.
Woolly Mice

- 12 Mar 2025
In News:
Scientists at Colossal Biosciences, a US-based biotechnology company, have genetically engineered mice with mammoth-like traits, dubbed “woolly mice”, as part of a broader project aiming to revive the extinct woolly mammoth.
What are Woolly Mice?
Woolly mice are genetically modified laboratory mice that express specific traits observed in woolly mammoths, such as thick, wavy fur and cold adaptation features. These traits were introduced to validate the feasibility of editing multiple genes for the potential de-extinction of the woolly mammoth.
How Were Woolly Mice Created?
- Methodology:
- Scientists compared ancient DNA of woolly mammoths with modern Asian elephants (their closest living relatives) to identify unique cold-adaptation genetic variants.
- Selected 10 mammoth-associated gene variants related to hair length, thickness, color, and fat metabolism were mapped to their equivalents in lab mice.
- Using CRISPR gene-editing technology, seven key genes were edited across eight changes in mouse embryos.
- Key Gene Edits:
- FGF5: Regulated hair cycle, producing hair three times longer than normal.
- MC1R: Altered coat color to golden, similar to mammoths.
- FABP2: Modified lipid metabolism for potential cold resistance.
- Additional genes affected hair texture, follicle structure, and whisker curling.
Significance of the Experiment
- Proof of Concept: Demonstrates that mammoth-like traits can be recreated in living organisms through targeted gene editing.
- Model for Cold Adaptation Studies: Offers insights into thermoregulation and climate resilience, useful for biodiversity research.
- Potential for Conservation: Highlights the emerging role of gene editing in preventing extinctions and enhancing species’ adaptability.
Scientific and Ethical Concerns
- Some experts argue that the research lacks conclusive evidence that the mice are truly cold-adapted.
- Critics note that while physical traits were achieved, this does not equate to reviving a mammoth, but rather mimicking select features in a different organism.
- There are broader debates on whether such de-extinction efforts are beneficial or divert resources from conserving existing endangered species.
AI Kosha

- 12 Mar 2025
In News
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has launched AI Kosha, a secure platform to catalyze Artificial Intelligence (AI) innovation by providing centralized access to high-quality datasets, models, and development tools. This initiative is part of the broader IndiaAI Mission, which has an outlay of ?10,371 crore and aims to democratize AI access and boost research and governance applications.
Key Features and Infrastructure
- Datasets & Models: AI Kosha hosts 316 datasets and over 80 AI models, covering areas such as Indian language translation, health, census, meteorology, pollution, and satellite imagery.
- AI Sandbox Environment: Offers integrated development tools, tutorials, and an IDE for training AI models.
- Security Protocols: Implements encryption, secure API-based access, real-time threat filtering, and tiered permissions for users (researchers, startups, government bodies).
- AI-readiness Scoring: Aids users in selecting relevant and usable datasets.
Compute Capacity Boost
Under the Compute Capacity pillar of the IndiaAI Mission, the government has commissioned 14,000 GPUs (up from 10,000 announced earlier in 2025) to support shared access for startups and academic institutions. This infrastructure is vital for training large AI models, particularly foundational models tailored for Indian needs.
Policy and Data Governance Background
- AI Kosha complements earlier government efforts like data.gov.in, which already hosts 12,000+ public datasets.
- A 2018 committee, led by Infosys co-founder Kris Gopalakrishnan, proposed access to non-personal data from private firms to promote innovation—a proposal that faced resistance from industry stakeholders.
- The platform promotes ethically sourced and consent-based datasets, aligning with responsible AI practices.
Challenges
- Limited Dataset Diversity: Current datasets are mostly government or research-based, limiting private-sector applicability.
- Access Barriers: Strong security protocols, while crucial, may hinder ease of access for some innovators.
- Early Stage Evolution: Wider participation from industry is essential to expand dataset variety and utility.
PUNCH Mission

- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA is set to launch the PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission on March 6, 2025, from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. It will be the third major solar mission launched globally in the past 18 months.
About the PUNCH Mission:
Aspect Details
Agency NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
Launch Date March 6, 2025
Mission Objective Study the Sun’s corona (outer atmosphere) and how solar wind evolves as it moves
into the heliosphere
Unique Features - First dedicated mission to image the transition from the corona to the heliosphere
- Will use four identical suitcase-sized satellites for continuous imaging of the inner corona
Importance - Improves understanding of space weather
- Helps predict solar storms, safeguarding satellites, astronauts, and
communication networks
What is the Solar Cycle?
- The solar cycle is an ~11-year periodic change in the Sun’s magnetic field, where the north and south poles flip positions.
- This cycle governs the level of solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- Solar Maximum: Period of peak activity with increased sunspots and solar eruptions.
- Solar Minimum: Period of least activity.
The current solar cycle began gaining momentum around May 2022, and solar activity remained above normal through 2024. The solar maximum is anticipated around 2025, offering an ideal window for solar observation.
Why the Surge in Solar Missions?
- Solar maximum periods offer the best conditions to observe high-energy events like flares and CMEs.
- Scientists aim to maximize data collection before the next solar minimum (next solar max expected ~2035–36).
- Monitoring solar activity is crucial because solar storms can disrupt satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Recent Major Solar Missions (2023–25):
Mission Agency Launch Date Purpose
Aditya-L1 ISRO (India) Sept 2, 2023 India’s first solar observatory; studies solar flares, solar winds, and magnetic fields
Proba-3 ESA (Europe) Dec 4, 2024 Dual-satellite mission to study solar corona and space weather
PUNCH NASA (USA) Mar 6, 2025 First mission to study continuous evolution from solar corona to heliosphere
‘One Day as a Scientist’ Initiative

- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
In response to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s call during his Mann Ki Baat address, the Ministry of Ayush has launched the ‘One Day as a Scientist’ initiative. This program offers students an immersive experience in scientific research, providing them hands-on exposure to advanced laboratory equipment and modern research methodologies. The initiative aims to nurture the scientific temperament among young minds and encourage them to explore the integration of traditional medicine with modern science.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Hands-on Lab Experience: Students visit Ayush research institutions where they explore cutting-edge scientific tools and technologies, gaining firsthand insight into the research process.
- Mentorship by Experts: Scientists and researchers guide students, offering valuable insights into research methodologies and the potential of Ayush systems in mainstream healthcare.
- Integration of Traditional and Modern Sciences: The initiative emphasizes the role of Ayush therapies, including Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, and Homeopathy, combined with modern scientific advancements.
- Nationwide Participation: The program is implemented across various institutions such as the National Institute of Ayurveda, Central Council for Research in Homoeopathy (CCRH), and the Central Research Institute for Yoga & Naturopathy (CRIYN), facilitating student engagement in scientific exploration.
Objectives of the Initiative:
- Encouraging Youth Participation: By providing direct exposure to scientific research, the initiative aims to inspire students to pursue careers in research and innovation.
- Bridging the Gap Between Traditional and Modern Medicine: The program focuses on scientifically validating and innovating traditional medicine, making it an integral part of India’s healthcare system.
- Fostering a Scientific Temperament: Students gain a deeper understanding of scientific processes, enhancing their curiosity and critical thinking, key traits for future leaders in research and innovation.
Alignment with National Science Day:
The National Science Day 2025 theme, “Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science and Innovation for Viksit Bharat,” aligns perfectly with the goals of this initiative. The program aims to inspire students to become future leaders in science and innovation, contributing to India’s vision of becoming a developed nation.
Giloy (Tinosporacordifolia)
- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
Giloy, also known as Guduchi and referred to as Amrita in Sanskrit—meaning the "herb of immortality"—is gaining global attention for its therapeutic potential, with scientific research on the herb witnessing a remarkable surge.
Surge in Scientific Publications
According to PubMed, a globally recognised biomedical database, there has been a 376.5% increase in research publications on Giloy between 2014 and 2024:
- 2014: 243 studies
- 2024: 913 studies
This significant rise reflects growing interest in natural and plant-based therapies, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic, which intensified focus on immunity boosters and holistic healthcare.
Therapeutic Properties and Uses
- Giloy is used in Ayush systems for:
- Fever management
- Gouty arthritis
- Autoimmune diseases
- Inflammatory disorders
- Cancer therapy (emerging evidence)
- Bioactive compounds in Giloy have shown:
- Immunomodulatoryeffects
- Anti-inflammatoryaction
- Adaptogenicandantiviralproperties
Botanical & Agricultural Features
- Scientific name: Tinosporacordifolia
- Distribution: Widely found across India
- Growth conditions:
- Grows in most soil types
- Propagated via stem cuttings (May–June)
- Large climber with corky, grooved stems
Recent Research Highlights
- Feb 2025 (Gujarat University): Giloy extracts showed promise in HPV-positive cervical cancer treatment through immunomodulation.
- Jan 2025 (Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai): Giloy-based phytopharmaceuticals were effective in managing Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis (IGM), offering a safe, steroid-free, and cost-effective alternative to surgery.
Government Initiatives
- The Ministry of Ayush has launched a technical dossier on Giloy, compiling scientific research and therapeutic insights.
- Aim: Promote evidence-based integration of Ayurveda with modern healthcare systems.
- Emphasis on global collaboration, research funding, and mainstreaming traditional medicine.
Blue Ghost Mission

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander successfully achieved a stable, upright landing on the Moon's Mare Crisium region on March 2, 2025, marking it as the second private spacecraft to land on the Moon and the first to do so upright. This mission is a part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative.
Key Details of the Blue Ghost Mission
- Developer: Firefly Aerospace, Texas-based private aerospace firm
- Launch Date: January 15, 2025
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon 9
- Landing Site: Near Mons Latreille, a volcanic formation in the Mare Crisium
- Descent & Duration: 16-day lunar orbit followed by powered descent; operates for one lunar day (14 Earth days)
Mission Objectives
- Scientific Research:
- Study heat flow from the Moon’s interior to understand its thermal history
- Analyze plume-surface interactions to refine lunar landing techniques
- Collect data on magnetic and electric fields to infer geological evolution
- Conduct X-ray imaging of Earth's magnetosphere
- Examine lunar dust dynamics, particularly its levitation due to solar radiation
- Investigate soil adhesion for improved lunar hardware design
- Technology Demonstration:
- Test radiation-hardened systems
- Evaluate the use of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals on the Moon
Payload and Instruments
- Number of Payloads: 10 NASA scientific payloads
- Notable Tools:
- Vacuum device for soil collection
- Subsurface drill measuring temperature up to 3 meters deep
Significant Observations
- Eclipse Imaging: Scheduled to capture a total lunar eclipse (March 14)
- Lunar Sunset: Will image lunar horizon glow during sunset (March 16), a phenomenon first noted during Apollo 17
- Firsts Achieved:
- First commercial lander to land upright on the Moon
- First of three major private lunar missions scheduled in 2025
Relevance for India and the World
- Demonstrates the viability of public-private partnerships in deep space missions
- Advances NASA’s Artemis program by developing cost-effective lunar logistics
- Paves the way for international lunar commerce and exploration
Why Mars is Red?

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
Mars, often called the Red Planet, owes its distinctive hue to the iron-rich mineral ferrihydrite, according to a recent multi-agency study published in Nature Communications. This research offers significant insights into Mars’ ancient climate, the possibility of past water, and the planet’s habitability.
Key Discoveries:
- Primary Cause of Red Color:
- Ferrihydrite, a water-formed iron oxide, has been identified as the main source of Mars’ red dust.
- Previously, hematite—an iron oxide that forms in dry conditions—was believed responsible. The new evidence suggests cooler, water-rich conditions prevailed when ferrihydrite formed.
- Martian dust, dispersed globally by winds, contains ferrihydrite, giving Mars its iconic red appearance.
- Significance of Ferrihydrite:
- It forms only in the presence of liquid water and oxygen, implying that ancient Mars had a more temperate and moist environment.
- Hydrogen bound to ferrihydrite suggests past interactions between water and iron.
- Methodology:
- The study used data from NASA and ESA missions, including:
- Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
- Mars Express
- Trace Gas Orbiter
- Ground-level data from rovers like Perseverance, Curiosity, and Opportunity
- Lab simulations recreated Martian conditions to study how ferrihydrite interacts with light and other minerals.
- The study used data from NASA and ESA missions, including:
Role of NASA’s Perseverance Rover:
- Launched in 2020, landed in 2021, Perseverance is collecting soil and rock samples.
- These samples will help validate the presence of ferrihydrite and the climatic conditions required for its formation.
Climatic Evolution of Mars:
- Mars once likely supported liquid water and a mild climate, possibly suitable for life.
- Over billions of years, the solar wind stripped away its atmosphere due to the absence of a strong magnetic field.
- This led to a transition to today's cold, dry, and barren landscape.
Facts about Mars:
- Position: 4th planet from the Sun
- Size: Radius ~3,390 km (~half of Earth’s)
- Moons: 2 – Phobos and Deimos (likely captured asteroids)
- Day (Sol): 24.6 hours
- Year: 687 Earth days
- Tilt: 25° (similar to Earth’s 23.4° → seasonal changes)
- Temperature Range: +20°C to -153°C
- Surface Features:
- Olympus Mons: Largest volcano in the solar system
- Valles Marineris: Giant canyon system, 10x longer than Grand Canyon
- Atmosphere: Thin, mostly CO?; lacks global magnetic field
- Dust Storms: Frequent and planet-wide, lasting months
Key Mars Missions:
- NASA: Perseverance, Curiosity, Spirit, Opportunity
- India: Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan)
- UAE: Hope Mission
- China: Tianwen-1
HeroRATS and the Future of Tuberculosis Detection

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the deadliest infectious diseases globally, with over 10 million new cases annually. India carries the highest TB burden, accounting for about 28% of global cases and recording nearly five lakh TB-related deaths each year—roughly one death every minute. Despite progress under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), which aims to eliminate TB by 2025 (ahead of the global 2030 target), early and accurate diagnosis remains a major hurdle, especially in children, low bacillary load cases, and underserved regions.
A Novel Solution: HeroRATS in TB Diagnosis
In a groundbreaking initiative, APOPO, a Tanzanian non-profit, has trained African giant pouched rats (HeroRATS) to detect TB by sniffing sputum samples. These rats have highly sensitive olfactory receptors, enabling them to detect TB cases that conventional diagnostics often miss.
Key Features of HeroRATS:
- Can screen 100 samples in 20 minutes, compared to 3–4 days by sputum-smear microscopy.
- Trained through operant conditioning, rewarded with food after accurate detection.
- Detect twice as many TB cases in children and six times more in low-bacillary-load patients than traditional methods.
- Confirmatory tests: Ziehl-Neelsen and fluorescent microscopy.
A 2023 study involving over 35,000 patients in Tanzania showed that HeroRATS detected over 2,000 additional TB cases, particularly among smear- or Xpert-negative patients. The method offers a fast, cost-effective, and scalable secondary diagnostic tool.
Relevance to India
With India facing challenges like poor health infrastructure in rural areas and reluctance to seek re-testing after a negative result, integrating HeroRATS into the NTEP could boost case detection. Experts suggest a phased rollout in high-burden states like Maharashtra and West Bengal. The Central TB Division’s collaboration with APOPO could help accelerate TB diagnosis and reduce transmission.
About Tuberculosis
- Cause: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mainly affects the lungs, spread via airborne droplets.
- Prevalence: One-fourth of the global population is infected; only 5–10% show symptoms.
- Risk Factors: Weakened immunity, malnutrition, diabetes, tobacco and alcohol use.
- Diagnosis: WHO recommends rapid molecular tests like Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra.
- Prevention: BCG vaccine at birth.
- Treatment: Standard 4–6 month antibiotic course.
- Drug-Resistant TB:
- MDR-TB: Resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin.
- XDR-TB: Resistant to multiple drug classes, harder to treat.
- TB-HIV Link: HIV patients are 16 times more likely to develop TB.
Bio-detection Beyond Rats: Macrosmatic Species in Medicine
Several animals with heightened olfactory senses are being used in disease detection:
- Dogs: Detect Parkinson’s, cancers, and diabetes using their 125–300 million olfactory receptors and Jacobson’s organ.
- Ants: Trained to detect cancer cells within three days using chemical signals.
- Honeybees: Can differentiate between types of lung cancer with 88% accuracy using synthetic biomarkers.
NASA’s Lunar Trailblazer and IM-2 Mission

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA launched the Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy Space Center to enhance understanding of water distribution on the Moon—crucial for long-term human exploration under the Artemis program.
Lunar Trailblazer Mission:
- Type: Small satellite (orbiter); part of NASA’s Small, Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEX) program.
- Developed by: NASA in collaboration with Lockheed Martin.
- Objective:
- Map and analyze the presence of water, particularly in permanently shadowed craters near the Moon’s poles.
- Study the lunar water cycle and evaluate water as a potential resource for future missions.
- Instruments:
- Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM): Measures surface temperature to track water movement.
- High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM3): Detects spectral signatures of water molecules.
- Timeline:
- Fuel-efficient trajectory to reach the Moon in 4 months.
- Mission duration: At least 2 years of mapping operations.
- Significance:
- Supports Artemis program objectives—long-term human presence on the Moon.
- Identifies potential water sources for drinking, fuel, and oxygen.
- Enhances understanding of water on airless planetary bodies and may offer clues to Earth’s water origins.
IM-2 Mission and Intuitive Machines’ Lunar Lander:
- Landing Site:Mons Mouton, near the Moon’s south pole (landing scheduled for March 6).
- Under: NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) and Artemis campaign.
Key Scientific Objectives and Instruments:
- Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1):
- TRIDENT Drill: Extracts lunar soil samples.
- MSolo Spectrometer: Detects volatile compounds in samples (e.g., water vapor).
- Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA): Provides a precise, passive reference point for future orbiters using laser ranging.
- Micro Nova Hopper (“Grace”):
- Autonomous drone developed under NASA’s Tipping Point initiative.
- Capable of hopping into shadowed craters to collect and transmit data.
- Nokia Lunar Surface Communications System (LSCS):
- 4G/LTE system for high-definition video, telemetry, and command messaging.
- Supports inter-device connectivity between the lander, rover, and hopper.
Strategic Importance:
- Pioneers in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) demonstrations.
- Tests surface communications and autonomous mobility systems.
- Lays groundwork for sustainable human presence and commercial space infrastructure.
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
A recent study on the Tra2b gene in mice has revealed a potential reason why certain segments of the genome called Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) have remained unchanged for over 80 million years across species like humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish.
What are Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)?
- Definition:DNA sequences at least 200 base pairs long that have remained perfectly identical across diverse species for tens of millions of years.
- Number in Human Genome:Around 500 UCEs have been identified in the human genome.
- Location:Found in both coding regions (genes) and non-coding regulatory regions like enhancers and silencers.
- Species Overlap:Identical UCEs are shared by humans, mice, rats, chickens, and fish, reflecting their evolutionary conservation.
Key Findings from the Tra2b Gene Study
- Research Insight:A UCE embedded in the first intron of the Tra2b gene acts as a “poison exon” to regulate production of the Tra2β protein, which is involved in RNA splicing.
- Mechanism:
- When Tra2β levels rise, the UCE is included as an extra exon in the mRNA.
- This exon contains multiple stop codons, halting protein synthesis.
- The mRNA is then degraded, preventing excess Tra2β protein.
- Experimental Result:
- Deleting this UCE in mouse sperm-producing cells led to overproduction of Tra2β, causing cell death and infertility.
- This implies that any mutation in the UCE that disrupts its function would lead to infertility and thus prevent its transmission, explaining its evolutionary stability.
Significance of UCEs
- Evolutionary Importance:Their intolerance to mutation suggests they are critical for basic survival and reproductive success.
- Functional Role:
- Do not typically code for proteins.
- Regulate gene expression, often during early development, fertility, and immune response.
- Act as enhancers, silencers, or splice regulators (as in the case of poison exons).
- Medical Relevance:
- Help understand gene regulation and disease mechanisms.
- Their conservation across species makes them valuable for comparative genomics and biomedical research.
- Mice are used as model organisms due to ~85% genetic similarity with humans.
Aditya-L1 Mission
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission has made a significant breakthrough by capturing the first-ever image of a solar flare 'kernel' using the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) payload.
Key Highlights:
- Captured Phenomenon:
- An X6.3-class solar flare (among the most intense categories) was observed on February 22, 2024.
- SUIT detected localized brightening in the Near Ultraviolet (NUV) wavelength (200–400 nm), a range never before observed in such detail.
- Scientific Significance:
- Observation occurred in the lower solar atmosphere (photosphere and chromosphere).
- Confirmed energy transmission from the flare through multiple solar atmospheric layers.
- Demonstrated a direct link between flare energy deposition and plasma temperature increase in the solar corona.
- Validated longstanding theories while offering new insights into solar flare physics.
About Aditya-L1 Mission:
- Launch Date: September 2, 2023
- Orbit: Placed in a halo orbit around the first Earth-Sun Lagrange Point (L1) on January 6, 2024.
- Objective: Study solar activities and their impact on space weather.
- Significance: India’s first space-based solar observatory, and ISRO’s second astronomy mission after AstroSat (2015).
Solar Flares – Quick Facts:
- Solar flares are massive explosions on the Sun's surface that release energy, light, and high-speed charged particles.
- Often associated with Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) that can affect Earth's magnetosphere and satellites.
- Classification: A, B, C, M, and X — with X-class being the most powerful, increasing tenfold in energy per class.
Amazon’s Ocelot Quantum Chip
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has unveiled its first in-house quantum computing chip, Ocelot, aimed at significantly reducing the development time for commercially viable quantum computers.
Key Highlights:
- Developed By: AWS Center for Quantum Computing at the California Institute of Technology.
- Objective: To accelerate the development of scalable and error-resilient quantum computers using novel architecture.
What is Ocelot?
- Type: Prototype quantum computing chip.
- Technology: Utilizes “cat” qubits—named after Schrödinger’s cat paradox—to suppress certain types of quantum errors intrinsically.
- Efficiency: Achieves 1 logical qubit using only 9 physical qubits, compared to the industry norm of ~1 million physical qubits for similar output.
Technical Features:
- Chip Design:
- Dual silicon microchips (~1 sq. cm each) stacked together.
- 14 core components:
- 5 cat qubits (for data storage),
- 5 buffer circuits (for qubit stabilization),
- 4 ancillary qubits (for error detection).
- Material Used: Standard chip fabrication techniques with tantalum.
Significance:
- Developmental Impact:
- Expected to reduce quantum computer development timelines by 5–10 years.
- Enables building practical quantum systems with around 100,000 qubits instead of the previously assumed 1 million.
- Potential Applications:
- Advanced drug discovery,
- New material development (e.g., batteries),
- Financial modeling, and
- Climate simulations.
- Strategic Implication: Strengthens Amazon’s position in the global quantum computing race alongside rivals like Google, Microsoft, and PsiQuantum.
Understanding Quantum Chips:
- Qubits vs Classical Bits:
- Classical bits = 0 or 1;
- Qubits = 0 and 1 simultaneously (superposition).
- Entanglement:Interlinked qubits can influence each other instantly, enhancing computational capacity.
- Quantum Gates:Operations are performed via gates like Hadamard, CNOT, and Pauli.
- Error Correction:Quantum systems are fragile; Ocelot’s built-in cat qubit architecture enhances stability and reliability.
National Science Day 2025
- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
National Science Day to be celebrated with theme ‘Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science & Innovation for Viksit Bharat’.
Key Details:
- Observed On: February 28 annually
- Purpose: To commemorate the discovery of the Raman Effect by Sir C.V. Raman in 1928. The day highlights the importance of science and promotes scientific temper among the public.
- Theme 2025:“Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science & Innovation for Viksit Bharat”
- This theme reflects the vision of building a developed India (Viksit Bharat) by nurturing youth-led scientific innovation and aligning with India’s S&T ambitions for 2047.
About Sir C.V. Raman and Raman Effect:
- Born: 7 November 1888, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu
- Major Contributions:
- Discovered the Raman Effect (1928), for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, becoming the first Asian Nobel Laureate in science.
- Founded: Indian Journal of Physics (1926), Indian Academy of Sciences (1934), Raman Research Institute (1948).
- First Indian Director of IISc, Bangalore (1933).
- Awarded Bharat Ratna in 1954.
Raman Effect:A phenomenon where light passing through a substance changes in wavelength due to interaction with molecular vibrations. This principle is used in Raman Spectroscopy, widely applied in material science, chemistry, forensics, and even nuclear waste analysis.
National Science Day – History & Celebrations:
- Established: 1986 by the Government of India
- First Observed: 1987
- Organisedby:National Council for Science & Technology Communication (NCSTC) under the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- Celebrations include lectures, open labs, science fairs, and awareness drives across the country, especially for students.
Key Developments in Science & Technology (2024-25):
- Innovation & IP Rankings:
- 39th in Global Innovation Index 2024 (WIPO)
- 6th in Global IP Filings
- Major Initiatives:
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF): Boosts R&D and supports innovation in EVs, materials, and emerging technologies.
- National Quantum Mission (NQM): ?6003.65 crore mission to advance quantum computing, communication, and sensing.
- National Supercomputing Mission (NSM):
- Deployed 33 supercomputers, capacity: 32 PetaFlops.
- Target: 77 PetaFlops using indigenous technology.
- Artificial Intelligence:
- BharatGen: India’s first multilingual, multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) for Generative AI.
- STEM Inclusivity:
- Programs like WISE-KIRAN support women in science.
- PM Early Career Research Grant nurtures young researchers.
- INSPIRE continues to attract school and college students to science careers.
- Geospatial & Climate Research:
- Expansion of spatial thinking programs in schools (116 schools across 7 states).
- Establishment of 4 Centres of Excellence for climate risk mapping to enhance disaster preparedness.
NASA’s SPHEREx Telescope

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA is set to launch the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer (SPHEREx) aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The telescope is megaphone-shaped, infrared-based, and is designed for a 2-year mission to scan the entire sky in infrared and optical light.
Key Details:
Mission Objectives
- Cosmic Inflation: SPHEREx will investigate the phenomenon of cosmic inflation, the ultra-rapid expansion of the universe that occurred a fraction of a second after the Big Bang (~13.8 billion years ago). By mapping the 3D positions of nearly 450 million galaxies, the mission aims to refine theories about the universe’s earliest moments.
- Spectroscopic Mapping: It will divide light into 96–102 spectral bands, creating a 3D map of the sky. It will collect 8 million spectroscopic images, allowing the study of the composition and distribution of celestial objects on an unprecedented scale.
- Biogenic Molecules Detection: The telescope will identify life-forming (biogenic) molecules like water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and methanol in cold molecular clouds of the Milky Way. These icy particles are essential for understanding the chemical preconditions for life.
- Cosmic Glow & New Phenomena: SPHEREx will also measure the collective glow from intergalactic space, which could help uncover previously unknown cosmic events and structures.
Comparison with Other Telescopes
Unlike the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) or the Hubble Space Telescope, which focus on high-resolution, narrow field observations, SPHEREx is designed to scan the entire sky. The full-sky mapping capability makes it a complementary tool for large-scale statistical cosmology.
Significance for Astronomy and Astrobiology
- It provides a comprehensive sky census of galaxies, stars, and asteroids (around 1 billion galaxies, 100 million stars, and 10,000 asteroids).
- By locating regions rich in life-bearing molecules, it enhances our understanding of how life-essential chemistry emerges in the galaxy.
- It lays the groundwork for future targeted studies of exoplanets and habitable environments in space.
HKU5-CoV-2 (Bat Virus)

- 27 Feb 2025
In News:
A newly discovered bat coronavirus named HKU5-CoV-2 has been identified in China by a research team led by Shi Zhengli (Wuhan Institute of Virology), known for her work on bat coronaviruses.
About HKU5-CoV-2
- Type: Bat coronavirus
- Subgenus: Merbecovirus
- This group includes MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome virus).
- Similarity: Shares traits with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19 virus).
- Discovery Location: China
Virological Features
- ACE2 Receptor Binding:
- HKU5-CoV-2 can bind to the human ACE2 receptor, the same one used by SARS-CoV-2 for cell entry.
- Binding Affinity: Lower than SARS-CoV-2, indicating weaker infectivity in current form.
- Intermediate Hosts:Can bind to ACE2 receptors in multiple mammalian species → possible spread through intermediate animals (like SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV).
- Laboratory Studies:The virus could infect lab-grown human lung and gut tissues, suggesting potential zoonotic transmission.
- Pandemic Potential:
- No immediate threat of a pandemic.
- Requires ongoing surveillance for possible mutations enhancing transmission.
Transmission Pathways
- Direct Transmission:From bats to humans through contact with bodily fluids (saliva, urine, feces).
- Zoonotic Transmission via Intermediate Host:Could jump species before infecting humans, similar to MERS and SARS-CoV.
Symptoms (Speculative)
- No confirmed human cases so far.
- Possible respiratory symptoms (based on similarity to MERS and COVID-19):
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Body aches
Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP)
- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
Launched under the Create in India Challenge Season 1, the Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP) is a flagship initiative aimed at promoting India’s gaming and interactive entertainment ecosystem on the global stage.
Key Highlights
- Launch Year: 2025
- Ministry Involved: Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Organizing Partner: Interactive Entertainment and Innovation Council (IEIC)
Objectives:
- Identify and showcase Indian gaming talent internationally.
- Support the growth of the gaming, animation, visual effects, and immersive technology (AR/VR/Metaverse) sectors.
- Boost the 'Create in India' initiative in the media and entertainment domain.
- Enable Indian developers and startups to create globally competitive digital products.
Program Features:
- Eligibility:
Open to developers, studios, startups, and tech companies with working prototypes in:- Game development
- Esports
- Business solutions for gaming ecosystem
- Selection Process:
- Game Submission
- Expert Evaluation – Based on product, pitch, and team viability
- Final Showcase – Winners selected by a jury
Global Exposure Platforms:
- Game Developers Conference (GDC) 2025
- Location: San Francisco
- Dates: March 17–21, 2025
- World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025
- Location: Mumbai
- Dates: May 1–4, 2025
- Venue: Jio World Convention Centre &Jio World Gardens
- Focus Areas: Broadcasting, AVGC-XR, Digital Media, Innovation, and Films
Relevance of WAVES Summit:
- WAVES acts as a global convergence point for the Media & Entertainment (M&E) sector.
- AVGC-XR (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics + AR/VR/Metaverse) is a central pillar, aligning with TTP’s goals.
Significance for India:
- Positions India as a global hub for innovation in digital entertainment.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat in the tech and creative economy sectors.
- Encourages cross-border collaborations and export of Indian intellectual property in the gaming domain.
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy in North East India

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The North Eastern Region (NER) of India, endowed with rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and indigenous knowledge, is undergoing a transformation through biotechnology-led initiatives. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology is spearheading this change to harness the region’s biological resources for inclusive and sustainable development.
Biotechnology: Definition and Types
Biotechnology involves the use of biological systems or organisms to develop products and technologies that improve healthcare, agriculture, industry, and the environment.
Types of Biotechnology:
- Medical Biotechnology – Vaccines, gene therapy, diagnostics.
- Agricultural Biotechnology – Pest-resistant crops, high-yield seeds, and sustainable agriculture.
- Industrial Biotechnology – Biofuels, biodegradable plastics, enzyme-based processes.
- Environmental Biotechnology – Waste treatment, pollution control, and bioremediation.
Why North East India is Ideal for Biotech Development
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Home to 8,000+ plant species, including 850+ medicinal plants and agro-climatic diversity.
- Indigenous Knowledge: Rich traditional practices in herbal medicine and organic farming.
- Agri-Biotech Potential: Ideal for medicinal crops, essential oils, and organic produce.
- Industrial Opportunity: Scope for biofuel production, value-added food processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
Key DBT Programmes and Initiatives in the North East
- DBT North Eastern Programme
- Since 2010, 10% of DBT’s annual budget is dedicated to NER.
- Focus: R&D, education, infrastructure, entrepreneurship, and employment generation in biotechnology.
- Twinning R&D Programme (2010–11)
- Promotes collaborative biotech research between NER and national institutes.
- Over 65 institutional partnerships, supporting 650+ projects and benefiting ~2,500 researchers/students.
- Biotech Hubs Network (Since 2011)
- 126 Biotech Hubs established across universities and colleges.
- Phase II supports 54 hubs for focused research on local issues.
- BLiSS (Biotech Labs in Senior Secondary Schools): Started in 2014 to introduce biotechnology at the school level.
- Visiting Research Professorship (VRP) Programme:Launched in 2015 to utilize the expertise of top scientists for NER biotechnology development.
- Chemical Ecology Programme (2015): Collaborative training by NCBS, UAS, and IISc for Ph.D. scholars in the field of chemical ecology.
- Genomics Training Programme (2016):Conducted by DBT-NIBMG, Kalyani, for biomedical researchers in the region.
Agri-Biotech and Livelihood-Oriented Initiatives
- DBT-NECAB (Phase III): Enhancing biotech applications in agriculture.
- Citrus Research: Disease-free scion material of Khasi mandarin and sweet orange developed at IHT, Assam.
- Medicinal Crop Cultivation: 64.1 acres under Curcuma caesia and lemongrass cultivation; 649 farmers trained.
- Essential Oil Distillation: Facility set up in Mudoi village, Arunachal Pradesh, for revenue support.
- Value-Addition in Wild Fruits: Docynia indica (Assam apple) processed into products like jam, pickles, and candy.
Technology-Driven Achievements
- Bacterial Blight-Resistant Rice (Patkai): Developed by Assam Agricultural University; notified by CVRC.
- Brucellosis Detection Kit: Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) to detect anti-Brucella antibodies in livestock.
- Pig Disease Diagnosis Expert System (PDDES): Mobile app for livestock disease detection and management (available on Google Play Store).
Challenges in NER’s Biotech Growth
- Limited infrastructure for biotech R&D and production.
- High cost of commercial biotech projects.
- Shortage of trained professionals in advanced biotech fields.
- Vulnerability to climate change and poor connectivity with markets.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Infrastructure: Develop biotech parks, R&D centers, and incubators.
- Skill Development: Train local youth, researchers, and farmers.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster industrial collaboration for startups and innovation.
- Eco-friendly Technologies: Promote sustainable and low-impact biotech industries.
- Digital Integration: Use AI and data analytics for agricultural and healthcare biotech solutions.
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 Quantum Chip
- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Microsoft has unveiled Majorana 1, a new quantum chip that marks a significant advancement in quantum computing, suggesting that scalable quantum systems could be achieved in years rather than decades.
What is Majorana 1?
- It is the world’s first quantum chip built on a topological architecture, using Majorana fermions, exotic subatomic particles that are both particles and antiparticles.
- The chip is designed to be more stable and error-resistant than current quantum technologies developed by competitors like Google and IBM.
Core Technology & Innovation:
- Material Composition: Made from indium arsenide (a semiconductor) and aluminum (a superconductor).
- Topological Superconductivity: When cooled near absolute zero and exposed to magnetic fields, it enables the formation of Majorana Zero Modes, which serve as building blocks for stable qubits.
- Topoconductor Architecture: A new class of materials creating a topological state, offering enhanced fault tolerance.
Quantum Advantage:
- Qubit Efficiency: Majorana 1 reduces the number of physical qubits needed to generate logical (error-corrected) qubits.
- Error-Resistance: Its design addresses two major quantum computing limitations — qubit instability (decoherence) and high error rates.
- Scalability Potential: The chip includes eight topological qubits, with future potential to scale up to a million-qubit system.
Why This Matters:
- Improved Reliability: Lower error rates enhance the practical applicability of quantum systems.
- Accelerated Development: Brings the world closer to realizing commercially viable quantum computers.
- Wide Applications: Potential use in drug discovery, material science, clean energy solutions, and more.
- AI Integration: May combine with artificial intelligence to tackle global challenges like microplastic degradation.
Quantum Computing in Brief:
- Quantum Computers use qubits and properties like superposition and entanglement to perform highly complex calculations.
- Major Challenges: Qubit instability and error correction.
- Significance: Quantum computing could revolutionize fields by solving problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Technology Adoption Fund (TAF)

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
IN-SPACe, India’s space sector regulator under the Department of Space, has launched the Technology Adoption Fund (TAF) to accelerate the commercialization of indigenous space technologies.
About TAF:
- Objective: To bridge the gap between early-stage innovation and market-ready space solutions developed by Indian startups, MSMEs, and industries.
- Goal: Reduce dependence on imported technologies and strengthen India's position in the global space sector.
Key Features:
- Financial Support:
- Startups/MSMEs: Up to 60% of project cost.
- Larger industries: Up to 40%.
- Funding cap: ?25 crore per project.
- Eligibility: Open to all non-government entities (NGEs) with commercially viable space innovations.
- Support Provided:
- Partial funding for development and commercialization.
- Technical mentoring and guidance.
- Focus Areas: Launch vehicles, satellites, space-based applications, and related services.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Development of new space products.
- Intellectual property generation.
- Enhanced production capabilities.
- Economic growth and job creation.
About IN-SPACe:
- Established: 2020
- Ministry: Department of Space
- Location: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- Role: Single-window agency promoting private participation in India's space ecosystem.
- Functions:
- Authorizes and monitors private sector space activities.
- Facilitates access to ISRO infrastructure.
- Collaborates with academia, industry, and research bodies.
Significance:
- Encourages private innovation in space tech.
- Aligns with the larger vision of making India a hub for space entrepreneurship.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance and competitiveness in global space technology.
WEST Tokamak Reactor

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
The WEST Tokamak reactor in southern France has set a new world record by sustaining a nuclear fusion plasma for 1,337 seconds (22 minutes and 17 seconds), surpassing the previous record of 1,066 seconds held by China’s EAST reactor by 25%. This achievement is a major milestone in the global quest for clean, limitless energy through nuclear fusion.
About Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei (typically deuterium and tritium) to form a heavier nucleus, releasing vast amounts of energy.
- The mass defect (loss of mass) in the fusion process converts into energy, as per Einstein’s equation E=mc2E = mc^2E=mc2.
- This reaction occurs in the plasma state—a hot, ionized gas consisting of free electrons and atomic nuclei.
How Tokamak Reactors Work
- A Tokamak is a doughnut-shaped (toroidal) magnetic confinement device that replicates the Sun’s fusion process.
- It uses superconducting magnetic coils to confine and heat the plasma to temperatures exceeding 50 million°C, about three times hotter than the Sun's core.
- Fusion reactors inject external power (WEST used 2 MW) to maintain the plasma and prevent it from touching reactor walls.
WEST Reactor: Key Highlights
- Operated by the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA).
- Aims to simulate long-duration, high-temperature plasma conditions.
- Reached a plasma state sustained for over 22 minutes at 50 million°C.
- Contributes critical insights and validation to the ongoing ITER project, the world’s largest nuclear fusion experiment also based in southern France.
Significance of the Achievement
To make fusion viable for electricity generation, three key conditions must be met:
- High temperature – to overcome electrostatic repulsion between nuclei.
- Sustained confinement time – achieved by WEST.
- Sufficient plasma density – to ensure high collision rates.
Maintaining plasma for extended durations is crucial for transitioning from experimental reactors to commercial fusion energy systems.
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion
- High Energy Output: Produces 4x more energy per kg of fuel than fission, and nearly 4 million times more than fossil fuels.
- Environmentally Clean: Emits no greenhouse gases or long-lived radioactive waste. Only byproducts are inert helium and neutrons.
- Abundant Fuel Supply: Fusion uses deuterium (from seawater) and tritium, eliminating the need for uranium mining.
- Inherent Safety: Fusion reactions are inherently safe as they cannot trigger uncontrolled chain reactions, unlike fission.
Fusion vs. Fission: A Comparison
Aspect Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Fission
Process Combines light nuclei Splits heavy nuclei
Fuel Deuterium and Tritium Uranium or Plutonium
Energy Output Extremely high Moderate
Waste Minimal and short-lived Long-lived radioactive waste
Emissions No greenhouse gases Potential radiation hazards
Safety No risk of meltdown Risk of runaway reactions/meltdowns
Global Perspective
- Over 200 tokamaks are operational globally.
- The ITER project is set to become the centerpiece of global fusion research.
- Recent breakthroughs like those at WEST provide a technical roadmap for future commercial reactors.
Nvidia's Evo 2

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Nvidia, in collaboration with the Arc Institute and Stanford University, has launched Evo 2 — the world’s largest publicly available AI model for genomic data — aiming to revolutionize genetic research and biomedical innovation.
About Evo 2
- Type: Foundation AI model for genomics.
- Function: Understands and designs genetic code across all domains of life.
- Scale: Trained on ~9 trillion nucleotides from 128,000+ organisms, including bacteria, plants, animals, and humans.
- Platform: Built using 2,000 Nvidia H100 processors on Amazon Cloud, through the NVIDIA DGX Cloud platform.
- Access: Freely available on Nvidia’s BioNeMo research platform.
Key Features
- Accuracy in Mutation Detection:Accurately identified 90% of harmful mutations in BRCA1 — a gene linked to breast cancer.
- Speed and Efficiency:Enables rapid pattern recognition in vast genomic datasets — research that would otherwise take years.
- Collaborative Development:Created by Nvidia in partnership with Arc Institute (nonprofit research body founded in 2021 with $650 million funding) and Stanford University.
Applications
- Healthcare & Medicine:
- Predicts form and function of proteins.
- Identifies gene mutations and their impact.
- Facilitates precision medicine and gene therapy development.
- Agricultural Biotechnology:
- Aids in designing climate-resilient crops.
- Industrial & Environmental Science:
- Assists in creating enzymes to break down pollutants.
- Supports development of new bio-materials.
Significance for India & Global Science
- Accelerates biomolecular research and biotech innovation.
- Contributes to scientific self-reliance and the bioeconomy.
- Enhances capability in combating diseases like cancer and improving food security.
Meta’s Project Waterworth
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
Meta has launched Project Waterworth, its most ambitious subsea cable initiative to date, aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity. The project involves the deployment of AI-driven subsea cable infrastructure, with India being a key beneficiary.
Key Features:
- Massive Scale:A multi-billion dollar, multi-year global initiative, the project will lay over 50,000 km of undersea cables, connecting five continents, including India, the USA, Brazil, South Africa, and others.
- AI Integration:The project leverages advanced machine learning models to predict and mitigate network disruptions, ensuring greater resilience and reliability of global internet infrastructure.
- Deep Water Deployment:The cable will operate at depths reaching 7,000 meters, using enhanced burial techniques in high-risk areas to prevent damage from ship anchors and other maritime hazards.
- Digital Backbone:Subsea cables like those in Project Waterworth currently carry over 95% of global internet traffic, forming the backbone of international digital communication, video streaming, e-commerce, and cloud-based AI services.
Strategic Relevance for India:
- India’s Digital Push:The project supports India’s growing digital economy by ensuring faster, more reliable internet connectivity and fostering digital inclusion and innovation.
- AI and Infrastructure Synergy:With AI-driven maintenance and deployment, the initiative complements India's vision of becoming a global hub for AI, data centers, and digital services.
- Economic and Strategic Benefits:Enhanced connectivity is expected to boost economic cooperation, cross-border trade, and participation in global digital platforms.
UNESCO’s “Imagine a World with More Women in Science” Campaign

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 11, 2025, to mark the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, UNESCO, with support from Canada’s International Development Centre (IDRC), launched the global campaign titled “Imagine a World with More Women in Science.”
Campaign Highlights
- Objective: Promote gender equality in science and innovation by encouraging the active participation and leadership of women in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine).
- Social Media Drive: The campaign uses the hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience to amplify diverse voices and encourage global engagement.
- Focus: Emphasizes the real-world impact of gender disparities in science, including missed innovations, biased artificial intelligence, and inequitable scientific opportunities.
Background
- The UN General Assembly (UNGA) declared February 11 as the International Day of Women and Girls in Science in 2015 to foster female participation in scientific research and innovation globally.
Current Status of Women in Science
Global Trends
- Representation: Women comprise only one-third of the global scientific workforce.
- Leadership Gap: Merely 10% of STEM leadership positions are held by women.
India-Specific Data
- STEMM Enrolment: Women account for 43% of enrolment in STEMM disciplines.
- Women Scientists: Only 18.6% of scientists in India are women.
- R&D Projects: About 25% of R&D projects are led by women researchers.
Challenges Faced by Women in Science
Challenge Description
Restrictive Social Norms Traditional gender roles hinder women’s
scientific pursuits.
Lack of Role Models Few visible female leaders discourage young women from
aspiring to scientific careers.
Workplace Inequality Gender biases, hostile work environments, and lack of inclusive
policies create barriers.
Educational Gaps Gender-biased teaching content and insufficient support systems
limit girls’ access to science education.
Recommended Measures
Dismantle Gender Stereotypes
- Remove gender biases from teaching and learning materials.
- Include contributions of female scientists in textbooks with visuals.
- Promote equitable representation of women in boards, panels, and decision-making bodies.
Enhance Visibility of Women Role Models
- Highlight discoveries by female scientists.
- Increase media and curriculum exposure to successful women in science.
Open Educational Pathways
- Promote inclusive teaching practices and gender-neutral curricula.
- Encourage CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives to support girls in science education.
Create Inclusive Work Environments
- Enforce policies for diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Take strong action against gender-based violence, including sexism and harassment in the workplace.
- Advance women into leadership roles in scientific institutions.
mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine
- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has announced the development of an mRNA-based personalized cancer vaccine, expected to be available free of cost to patients by early 2025. It is being developed under the Russian Ministry of Health, with pre-clinical trials showing promising results in suppressing tumour growth and metastasis.
What is an mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine?
- mRNA (Messenger RNA) vaccines deliver genetic instructions to the body’s cells to produce antigens—proteins that trigger an immune response.
- In the case of cancer, these vaccines train the immune system to recognize and destroy tumor-specific antigens, thereby attacking cancer cells.
- Unlike conventional vaccines, these are therapeutic, not preventive, and are used in existing cancer patients.
How Does It Work?
- The vaccine prompts the body to produce proteins that mimic tumor markers.
- These markers stimulate the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- The treatment is personalized, with the mRNA sequence tailored to match the unique antigens of a patient’s tumour, enhancing precision and efficacy.
- It can potentially target multiple antigens simultaneously, unlike standard mRNA vaccines such as those for COVID-19.
Advantages Over Conventional Therapies
- Selective Action: Targets only cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
- Fewer Side Effects: Compared to chemotherapy, the side effects are significantly reduced.
- Customizable: Can be adapted to target various cancers through tumor-specific markers.
- Boosts Immunity: Enhances the body’s natural defense mechanisms for long-term protection.
mRNA Technology – Core Concepts
- mRNA is a single-stranded RNA transcribed from DNA.
- It delivers genetic instructions to ribosomes (protein factories) in cells to produce specific proteins.
- In mRNA vaccines, this mechanism is harnessed to make the body generate target antigens, which the immune system learns to combat.
India and mRNA Vaccines
- India has approved two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Gennova Biopharmaceuticals with DBT-BIRAC support:
- GEMCOVAC-OM(Omicron-specific)
- GEMCOVAC-19
- Features include needle-free delivery and thermostability, marking India’s entry into mRNA-based immunotherapy platforms.
Cautions and Limitations
- Not Preventive: These are not preventive like HPV or Hepatitis B vaccines, which protect against cancers linked to viruses.
- Limited Data: Russian vaccine data is not yet publicly available; clinical validation is pending.
- Not Universally Effective: Immunotherapy may not work for all types or stages of cancer.
- Time-Consuming Trials: New treatments must undergo phased trials, often spanning years, before general approval.
Surge in Colorectal Diseases in India
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
In recent years, India has witnessed a marked increase in colorectal diseases, including colorectal cancer, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and other related disorders. This surge is closely linked to urbanization, dietary transitions, sedentary lifestyles, and improved diagnostic practices.
What are Colorectal Diseases?
Colorectal diseases affect the colon and rectum and encompass a spectrum of conditions:
- Colorectal Cancer: Originates from polyps in the colon or rectum. If untreated, these polyps can turn malignant. The incidence of colorectal cancer is rising rapidly in Indian urban centers, now ranking among the top cancers in cities.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A chronic condition involving inflammation of the digestive tract, especially the colon and small intestine. Subtypes include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Once rare in India, IBD is now on the rise due to industrialization, Western diets, and enhanced medical diagnostics.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A non-inflammatory, functional bowel disorder marked by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea) without visible bowel damage. IBS is highly prevalent in India.
- Diverticular Disease: Characterized by the formation of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon wall. Inflammation or infection of these pouches leads to complications and discomfort.
- Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures: Swollen veins or tears in the rectal region, leading to pain, bleeding, and itching—often caused by hard stools or chronic constipation.
Why are these diseases increasing?
- Dietary Shifts: Increased intake of processed foods, red meat, and low-fiber diets (lacking fruits and vegetables) have significantly raised the risk of colorectal cancer and other digestive disorders.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary behavior, especially in urban populations, heightens susceptibility to these conditions.
- Rising Obesity: Obesity, closely associated with lifestyle disorders, is a contributing factor for colorectal cancer and IBS.
- Ageing Population: Risk increases with age, and India’s growing elderly demographic intensifies disease burden.
- Genetic and Lifestyle Factors: A family history of colorectal conditions, coupled with habits like smoking and alcohol consumption, further elevate risk levels.
- Gut Microbiota Disruption: Imbalance in gut bacteria and possible infections are emerging as factors in the etiology of IBD; ongoing research aims to establish clearer links.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent changes in bowel habits: constipation, diarrhea, or narrow stools.
- Rectal bleeding: presence of bright red or dark blood in the stool.
- Abdominal pain, bloating, or cramps.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue and weakness.
- Sensation of incomplete bowel emptying.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination and clinical history evaluation.
- Stool Tests for blood, infections, or abnormalities.
- Colonoscopy (gold-standard diagnostic tool) to inspect the colon and collect biopsies.
- Sigmoidoscopy for lower colon and rectum.
- Imaging: CT, MRI, or X-rays to detect abnormalities.
- Blood Tests to assess inflammation and exclude other conditions.
Treatment Modalities
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs (for IBD), antibiotics, pain relief, and symptom-specific treatments.
- Lifestyle Interventions: High-fiber diets (for IBS, diverticulitis), regular physical activity, and stress reduction.
- Surgery: Required in advanced cases of colorectal cancer or severe IBD/diverticular disease.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: Used post-operatively or in advanced malignancies.
- Targeted Biological Therapies: Including monoclonal antibodies for immune modulation in IBD.
Einstein Ring Discovered by ESA’s Euclid Telescope
- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
- The European Space Agency’s (ESA) Euclid space telescope has recently discovered a rare Einstein ring around the galaxy NGC 6505, located nearly 590 million light-years from Earth.
- This ring was formed by the light of a distant unnamed galaxy situated 4.42 billion light-years away, distorted and amplified due to gravitational lensing by NGC 6505.
What is an Einstein Ring?
- It is a circular ring of light that appears around a massive celestial object such as a galaxy, dark matter concentration, or cluster of galaxies.
- Caused due to strong gravitational lensing, it occurs when a massive foreground object (gravitational lens) bends and amplifies the light from a background object, resulting in a circular or arc-like appearance.
- The phenomenon only results in a full ring when the observer, lensing object, and background galaxy are almost perfectly aligned.
Theoretical Basis
- Named after Albert Einstein, who in his General Theory of Relativity predicted that massive objects warp space-time, thereby bending the path of light.
- The phenomenon of gravitational lensing, and by extension Einstein rings, was first theoretically anticipated by Einstein and empirically confirmed much later.
Scientific Importance
- Extremely rare phenomena: Occur in less than 1% of galaxies.
- Serve as natural cosmic magnifying lenses that allow scientists to study:
- Dark Matter: Helps trace the invisible distribution of dark matter through gravitational effects.
- Dark Energy: Supports understanding of dark energy’s role in accelerating the universe’s expansion.
- Distant Galaxies: Reveals otherwise invisible galaxies by amplifying their light.
- Universe Expansion: Provides data on how space between galaxies stretches over cosmic time.
Gravitational Lensing: Explained
- Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive body (galaxy, cluster, black hole) creates a gravitational field that bends and magnifies light from objects behind it.
- This leads to multiple outcomes — arcs, double images, or full rings (Einstein rings).
- The lensing object in the recent case is NGC 6505, a galaxy first observed in the 19th century.
Observation and Imaging
- Einstein rings are not visible to the naked eye and require powerful space telescopes like Euclid for detection.
- Euclid captured images showing a bright central galaxy (NGC 6505) with a distinctive, cloudy ring formed by the bent light from the background galaxy.
About the Euclid Space Telescope
- Launched in 2023 by ESA using a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
- Operates from Lagrangian Point 2 (L2), located 1.5 million km from Earth.
- Designed for a six-year mission to study the dark universe.
- Key Objectives:
- Create the largest 3D map of the cosmos.
- Observe billions of galaxies across 10 billion light-years.
- Understand the distribution of dark matter and the influence of dark energy in the early universe.
- Study light emitted from galaxies up to 10 billion years ago to trace cosmic evolution.
Quipu Superstructure

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
Astronomers have discovered the largest known cosmic structure, named Quipu, in a study led by Hans Bohringer of the Max Planck Institute. The findings are part of efforts to map matter distribution in the universe using redshift data between 0.3 to 0.6, revealing some of the most distant known objects.
Key Features of Quipu:
Attribute Description
Type Superstructure (clusters of galaxy superclusters)
Length ~1.3 billion light-years (Over 13,000 times the Milky Way’s size)
Mass ~200 quadrillion (2 × 10¹?) solar masses
Components ~70 galactic superclusters
Shape Central filament with multiple branching filaments (named after the Incan “Quipu” cord system)
Cosmic Significance:
- Gravitational Lensing (GL): Due to its enormous mass, Quipu bends light from background objects, distorting sky images.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): Its gravitational field causes fluctuations in the CMB—the relic radiation from the Big Bang.
- Hubble Constant Impact: Quipu and similar structures distort measurements of the Universe’s expansion rate.
Scientific Context:
- Superstructures: Extremely large arrangements of matter including groups of galaxy clusters and superclusters.
- Quipu is hundreds of thousands of times more massive than a single galaxy.
- Discovered at a distance of 425 to 815 million light-years from Earth.
Other Superstructures Identified:
Alongside Quipu, astronomers identified four other massive structures:
- Shapley Supercluster
- Serpens-Corona Borealis Superstructure
- Hercules Supercluster
- Sculptor-Pegasus Superstructure
Together, these five structures:
- Contain ~45% of all galaxy clusters
- Include ~30% of galaxies
- Hold ~25% of the matter in the universe
- Occupy ~13% of the universe’s volume
Future Evolution:
- Scientists consider Quipu a "transient configuration".
- It is expected to break into smaller collapsing units in the future, altering cosmic structures over time.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- Natco Pharma, a Hyderabad-based generic drug manufacturer, has received final approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) for its generic version of Bosentan tablets for oral suspension (32mg).
- This drug, a generic version of Actelion Pharmaceuticals’ Tracleer, is used to treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs.
- The approval comes after Natco's successful submission of an abbreviated new drug application (ANDA), which was jointly developed with its marketing partner, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Natco believes that it holds the sole first-to-file status for the product, which qualifies it for a 180-day exclusivity period upon launch. The exclusivity period would allow Natco to be the only supplier of the generic product in the U.S. market for a limited time, which could offer significant market share before generic competition arrives.
- Bosentan, the active ingredient in Tracleer, is prescribed for patients suffering from PAH, a progressive condition that raises the blood pressure in the lungs and causes strain on the heart.
- The treatment helps to improve pulmonary vascular resistance and is indicated for patients aged three years and above, including those with idiopathic or congenital PAH. The product is expected to improve exercise capacity and overall quality of life for these patients.
- In the U.S., Bosentan 32mg oral suspension generated an estimated $11 million in sales for the 12 months ending September 2024.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Overview
- It is a specific type of pulmonary hypertension in which the small arteries in the lungs become thickened and narrowed. This results in obstructed blood flow and increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the lungs.
- The exact cause of PAH remains unclear, though it is believed to result from injury to the cells lining the blood vessels in the lungs, leading to long-term vascular disease.
- PAH can develop in association with several medical conditions, including congenital heart disease, liver disease, HIV, and autoimmune diseases like scleroderma and lupus. It can also be triggered by past or current drug use, such as the abuse of methamphetamine or the use of certain diet pills.
Symptoms of PAH include:
- Shortness of breath that worsens over time
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Chest pain
- Cyanosis (blue fingers or lips)
- Fainting episodes
While there are treatment options available for PAH, including medications that help manage the symptoms and slow disease progression, there is currently no known cure. PAH remains a significant area of concern in pulmonary healthcare, and the introduction of generic Bosentan by Natco Pharma offers a more affordable treatment option for patients in the U.S.
Gaia Black Holes

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, launched in 2013, continues to redefine our understanding of the Milky Way by detecting celestial phenomena through precise astrometry.
One of its most significant contributions has been the discovery of dormant stellar-mass black holes that are not associated with X-ray emissions—previously the main detection method. These discoveries represent a paradigm shift in black hole detection and open new avenues for astrophysical research.
Gaia BH Series: Discovery and Significance
Gaia BH1
- Discovery Year: 2022
- Location: ~1,560 light years from Earth in the Ophiuchus constellation
- Significance:
- Closest known black hole to Earth
- Detected via a yellow star orbiting a dark mass, whose high orbital velocity implied the presence of a black hole nearly nine times the mass of the Sun
- Validated using data from LAMOST (China) and Magellan Clay Telescope (Chile)
Gaia BH2
- Discovery Year: 2023
- Location: ~3,800 light years away in the Centaurus constellation
- Mass: Around nine solar masses
- Observation Method: Tracked motion of a luminous star orbiting an unseen massive companion
Gaia BH3 – A Landmark Discovery
- Discovery Year: 2024
- Distance from Earth: ~1,926 light years (~2,000 light years), making it the second closest black hole
- Location:Aquila constellation, in the Milky Way’s outer regions
- Mass: ~33 times the mass of the Sun, making it the largest known stellar-mass black hole in the Milky Way
- Orbital Partner: A yellow giant star orbiting every 11.6 years, with an average separation similar to the Sun-Uranus distance
- Special Traits:
- It is a dormant or passive black hole, not actively accreting matter
- Lacks X-ray emissions, suggesting a scarcity of surrounding material
- Its companion star’s chemical composition indicates ancient origins, hinting that such massive black holes were formed early in the universe
Scientific Implications:
- Detection Technique Innovation:Gaia uses astrometric mapping to track the apparent motion of stars across the sky. When a star appears to orbit "empty space," astronomers infer the presence of a massive object—typically a black hole—using Kepler’s laws and the Doppler effect.
- Redefining Black Hole Census:Most black holes were previously detected through X-ray emissions. Gaia has revealed non-emitting black holes, indicating a possibly larger hidden black hole population in our galaxy.
- Historical Linkage:Black holes with masses above 30 solar masses were previously only observed through gravitational waves (LIGO/VIRGO, 2015). Gaia BH3 now provides a local, observable counterpart.
Ranikhet Disease in India

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
Brucellosis Outbreak in Kerala
- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
An eight-year-old girl, Shasa Fathima, from Kottakkal in Malappuram district, Kerala, recently died after undergoing nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis at the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode. This tragic incident has renewed public health concerns regarding zoonotic infections in India.
What is Brucellosis?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), brucellosis is a bacterial disease caused by various species of the genus Brucella. The bacteria primarily infect: cattle, swine, goats, sheep & dogs.
Humans typically contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected animals or their secretions (blood, placenta, fetus, uterine fluids)
- Ingestion of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurised milk and cheese
- Inhalation of airborne bacteria (e.g., in lab or farm environments)
Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare, as per WHO guidelines.
Symptoms and Incubation Period
- The disease presents a wide spectrum of symptoms: fever, weakness, weight loss, general discomfort or malaise.
- In many cases, symptoms may be mild or go undiagnosed. The incubation period ranges from one week to two months, most commonly between two to four weeks.
At-Risk Populations
- Brucellosis can affect individuals of all age groups. However, certain occupational groups are at higher risk, including: farmers and dairy workers, butchers, hunters, veterinarians, laboratory personnel. These individuals are often exposed to animal blood and reproductive fluids, which are primary modes of transmission.
Status in Kerala
Kerala has reported sporadic cases of brucellosis in recent years. In 2023, cases emerged from Kollam (July) and Thiruvananthapuram (October). While the disease is not new to the state, fatalities remain rare.
In response, the Department of Animal Husbandry has initiated awareness campaigns for dairy farmers and conducted milk sample testing across cooperative societies to monitor possible sources of infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics:
- Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days)
- Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days)
Effective preventive measures include:
- Vaccination of livestock (cattle, goats, sheep)
- Pasteurisation of milk and dairy products before human consumption
- Public awareness campaigns on the dangers of consuming unpasteurised animal products
- Regulatory policies on the sale of raw milk
Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Union Finance Minister announced a five-year Cotton Mission to boost productivity, sustainability, and promotion of Extra-Long Staple (ELS) cotton in India, aiming to reduce import dependency and strengthen the high-end textile sector.
What is Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton?
- Definition: ELS cotton refers to cotton varieties with fibre lengths of 30 mm or more, renowned for their superior softness, strength, durability, and premium quality.
- Botanical Origin: Derived primarily from the species Gossypium barbadense, commonly known as Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Distinguishing Cotton Types by Fibre Length
Type Fibre Length Species Quality Uses Yield per Acre
Short Staple < 25 mm Gossypium hirsutum Coarser Low-cost textiles High
Medium Staple 25–28.6 mm Gossypium hirsutum Moderate Everyday fabrics 10–12 quintals
Extra-Long 30 mm & above Gossypium barbadense Superior Luxury textiles 7–8 quintals
Staple (ELS)
Special Characteristics of ELS Cotton
- Softer & Smoother: Ideal for premium, luxury clothing.
- Stronger & More Durable: Resistant to wear and tear.
- Resistant to Pilling: Maintains smoothness over time.
- Luxurious Finish: Produces fine yarns with a natural sheen.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Retains natural texture and quality.
Global and Indian Production Landscape
- Origin: Native to South America.
- Globally Grown In:
- Egypt, China, Australia, Peru – leading producers.
- In India:
- Cultivated in Atpadi Taluka (Sangli, Maharashtra), around Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), and in parts of Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Grown mostly in rain-fed areas with warm climates and fertile soil, aiding fibre quality.
Challenges in ELS Cotton Cultivation in India
- Low Yield: ELS cotton yields 7–8 quintals/acre, significantly lower than medium staple varieties (10–12 quintals/acre).
- Market Linkage Deficit: Farmers struggle to fetch premium prices for ELS cotton due to weak market access and lack of dedicated procurement infrastructure.
- Technological Gaps: Limited access to improved seed varieties, agronomic practices, and technologies like HtBT (Herbicide-tolerant Bt) cotton.
- Import Dependency: India imports 20–25 lakh bales annually, accounting for ~90% of its ELS cotton requirements, to meet demand from the premium textile industry.
Significance of the Five-Year Cotton Mission
- Aimed at:
- Enhancing productivity and sustainability of ELS cotton.
- Reducing import dependence through indigenous development.
- Strengthening high-value textile exports by ensuring reliable ELS supply.
- Supports:
- Farmer income enhancement through value-added cultivation.
- Research and development in ELS cotton seed technology.
- Improved extension services, supply chain development, and market support mechanisms.
Henipavirus

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
A henipavirus, specifically the Camp Hill virus, has been detected in North America for the first time. This discovery in northern short-tailed shrews—a small mammal species found commonly in Canada and the U.S.—raises concerns over a potential zoonotic disease outbreak.
About Henipavirus
- Virus Type: Henipaviruses are zoonotic, negative-sense RNA viruses.
- Family: Paramyxoviridae.
- Natural Hosts: Pteropid fruit bats (commonly known as flying foxes).
- Other Hosts: Capable of infecting various mammals, including humans, horses, pigs, and shrews.
Notable Henipaviruses:
- Hendra virus (HeV):
- First identified in Australia.
- Mortality rate: Up to 70%.
- Nipah virus (NiV):
- Found in Southeast Asia, including Malaysia and Bangladesh.
- Case fatality rate ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on surveillance and clinical care.
Symptoms and Disease Progression
- Initial symptoms: Fever, dizziness, headache, and muscle pain (myalgias).
- Advanced symptoms: Respiratory issues, encephalitis (brain inflammation), confusion, abnormal reflexes, seizures, and coma.
- Relapsing encephalitis may occur months or years after apparent recovery.
- Fatality Risk: High, primarily due to encephalitis and multi-organ failure caused by damage to small blood vessels (microinfarction) in organs like the brain, liver, and kidney.
Why are Henipaviruses so dangerous?
- Henipaviruses produce proteins that:
- Suppress the innate immune system.
- Block interferon-stimulated antiviral responses, aiding viral replication.
- Act as virulence factors, allowing widespread infection and severe outcomes.
Modes of Transmission
- Animal-to-human:
- Direct contact with infected animals (e.g., fruit bats, pigs, horses, shrews).
- Consumption of contaminated food or water (e.g., raw date palm sap in Nipah outbreaks).
- Human-to-human: Via bodily fluids, close contact, or respiratory droplets during caregiving.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment:
- No specific vaccine or antiviral currently exists.
- Management is symptomatic and supportive (respiratory support, ICU care).
- Prevention:
- Vaccination of horses (in HeV-risk regions like Australia).
- Avoiding contact with fruit bats and sick animals.
- Isolating infected individuals and animals to prevent spread.
GARBH-INi-DRISHTI

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
India has made a significant stride in biomedical research and public health with three major developments led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) in Faridabad, Haryana.
Key Highlights:
India’s First Ferret Research Facility
- Inaugurated by: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.
- Location: NCR Biotech Science Cluster, Faridabad.
- Purpose: To bolster India's capacity in:
- Vaccine development
- Therapeutic testing
- Research on emerging infectious diseases like influenza, COVID-19, and tuberculosis.
- Significance:
- Strengthens India’s pandemic preparedness.
- Positions India among the select nations with advanced biosafety labs using ferrets—ideal models due to respiratory systems similar to humans.
Launch of GARBH-INi-DRISHTI Data Repository
- Platform: DBT Data Repository and Information Sharing Hub under the GARBH-INi program.
- Dataset Size: Over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers.
- Developed by: THSTI with collaboration from top Indian research institutions and hospitals.
- Features:
- Comprehensive clinical data, medical images, and biospecimens.
- Secure, controlled access promoting ethical research.
- Facilitates predictive tools for preterm birth and maternal health complications.
- Utility:
- Empowers both national and global researchers.
- Informs maternal and neonatal health interventions.
- Supports evidence-based policymaking in public health.
- Program Genesis:
- GARBH-INi (2014): Interdisciplinary initiative to understand preterm birth risks—biological and non-biological.
- Part of: Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission under the UNaTI initiative.
Technology Transfer Agreement with Industry
- Agreement Between: THSTI and Sundyota Numandis Probioceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
- Technology Transferred:
- Lactobacillus crispatus, a genetically defined synthetic microbial consortium.
- Isolated from reproductive tracts of Indian women enrolled in GARBH-INi.
- Applications:
- Nutraceuticals and probiotics for reproductive health.
- Potential treatments for vaginal infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Significance:
- Promotes microbiome-based interventions.
- Bridges lab-to-market gap, boosting the biomanufacturing ecosystem.
Strategic Implications for India
- Scientific Diplomacy & Global Standing: With cutting-edge facilities and open data-sharing platforms, India emerges as a key player in global biomedical research.
- Public Health Impact: Supports targeted, data-driven maternal health policies and pandemic response frameworks.
- Innovation Ecosystem: Reflects the convergence of academic research, industry collaboration, and translational science.
Shubhanshu Shukla

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla of the Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to become the first Indian astronaut to travel to the International Space Station (ISS) on a private mission, marking a significant milestone in India’s space diplomacy and international collaboration in human spaceflight.
Mission Details:
- Mission Name: Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4)
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft
- Launch Site: Kennedy Space Center, Florida, USA
- Tentative Timeline: Spring 2025
- Duration on ISS: Up to 14 days
- Mission Objectives: Conduct scientific experiments, educational outreach, and commercial activities, in collaboration with NASA and ISRO.
International Collaboration:
- The mission includes astronauts from India, Poland, and Hungary—the first such trilateral collaboration in over four decades.
- Marks the return of human spaceflight for Poland and Hungary after a hiatus of more than 40 years.
- Demonstrates Axiom Space’s emerging role in redefining access to low-Earth orbit and supporting national space programs through private missions.
About Shubhanshu Shukla:
- Born: October 10, 1985, in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- Commissioned into IAF: June 2006, Fighter Wing
- Promoted to Group Captain: March 2024
- Current Role: Astronaut-designate for India’s Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission
- Flight Experience: Over 2,000 hours across multiple aircraft including Su-30 MKI, MiG-21, MiG-29, Jaguar, Hawk, Dornier, and An-32
- Astronaut Training: Trained at Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center, Star City, Moscow (1-year program)
Historical Context:
- Rakesh Sharma remains the first Indian to travel to space (1984) aboard Soviet Soyuz T-11, under the Interkosmos program.
- Shukla’s upcoming mission marks a new era of Indian participation in international human space missions, particularly through private partnerships.
F11 Bacteria

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study has identified a bacterial strain, Labrys portucalensis F11 (commonly referred to as F11), capable of degrading per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — popularly known as “forever chemicals” — by breaking their strong carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds.
About F11 Bacteria:
- Scientific Name: Labrys portucalensis F11
- Family: Xanthobacteraceae
- Nature: Aerobic and pollutant-resistant bacterium
- Origin: Isolated from industrially contaminated soil in Portugal
- Significance:
- Adapted to thrive in toxic environments
- Uses environmental contaminants as an energy source
- Capable of degrading at least three types of PFAS and certain toxic byproducts
What Are Forever Chemicals (PFAS)?
- Definition: A group of synthetic, man-made chemicals known for their extremely strong C-F bonds, making them persistent and non-biodegradable.
- Why Called 'Forever':
- Resistant to natural breakdown
- Found in air, rainwater, and soil for decades or longer
- Health & Environmental Hazards:
- Linked to cancer, hormonal disorders, immune dysfunction, and environmental toxicity
- Migrate into soil, water, and air during production and use
- Regulation: Certain PFAS are listed under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Relevance for India and the World:
- Global Impact:
- PFAS are used in a wide range of consumer products such as non-stick cookware, firefighting foams, and food packaging.
- Their persistence poses long-term risks to public health, groundwater contamination, and biodiversity.
- India's Concern:
- Increasing industrialization and waste mismanagement heighten PFAS exposure risks.
- No comprehensive PFAS regulation in place yet; calls for adopting stringent environmental safety norms.
WHO Guidelines on Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued new guidelines promoting the use of Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS) to tackle the global burden of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and stroke, which are largely driven by excessive sodium consumption. This is especially relevant for countries like India, with a high prevalence of high blood pressure and salt consumption.
What Are Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)?
- LSSS are alternatives to regular table salt, where sodium chloride (NaCl) is partially replaced by potassium chloride (KCl), magnesium sulphate, or calcium chloride.
- They are designed to retain the taste of regular salt while significantly reducing sodium intake and improving heart health.
- LSSS can help lower blood pressure, thanks to the potassium content, which helps balance fluid levels and offset sodium’s harmful effects.
Key WHO Recommendations:
- Daily sodium intake should be restricted to less than 2 grams per day, equivalent to about 5 grams of salt.
- Avoid regular table salt, and replace it, wherever safe, with LSSS for household use.
- LSSS use is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women
- Children
- Individuals with kidney impairments or those requiring low-potassium diets
- The guidelines do not apply to packaged or restaurant foods, which are major contributors to overall sodium intake.
Why Is This Important or India?
- Salt Intake in India: Average salt consumption is 10.4 grams/day, over double the WHO recommendation.
- Hypertension Prevalence: Over 35.5% of India’s population (approx. 315 million people) suffers from hypertension (INDIAB Study).
- CVD Burden: Cardiovascular diseases accounted for 28.1% of all deaths in India (2016) – Global Burden of Disease Study.
- Dietary Impact: Globally, 8 million deaths annually are diet-related, with 1.9 million directly linked to high sodium intake.
Implementation and Policy Measures:
- India’s Response:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has initiated sodium reduction policies.
- Edible salt must contain 97% sodium chloride, with anticaking agents limited to 2.2%.
- New labelling norms enforce accurate “low sodium” and “sodium-free” claims.
Public Health and Safety Considerations:
- While LSSS are safe and beneficial for most adults, excess potassium can cause hyperkalemia, especially dangerous for those with kidney disease.
- WHO guidelines aim to maximize benefits and minimize risks by promoting regulated, evidence-based usage.
- Governments, policymakers, and health professionals are urged to integrate LSSS into public health strategies, especially in high-risk populations.
About WHO:
- Established in 1948, the World Health Organization is the UN agency dedicated to promoting global health, preventing disease, and coordinating international health responses.
- It leads efforts for universal health coverage and responds to global health emergencies.
DeepSeek AI
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup based in Hangzhou, has emerged as a major player in the global AI race with the release of its models DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1.
These models are designed to rival top-tier Western counterparts such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Bard, and Meta’s LLaMA, but at a fraction of the cost.
Key Developments and Technological Edge
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek-V3 was trained at a cost of under $6 million, using older Nvidia H800 chips, compared to the estimated $100 million cost of GPT-4. Its subscription fee is significantly lower—$0.50/month versus $20/month for ChatGPT.
- Model Performance:
- DeepSeek-R1, a “reasoning model,” reportedly matches OpenAI’s o1 model in mathematics, coding, and contextual processing, while using fewer resources through incremental reasoning.
- Models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, reinforcement learning, and self-improvement loops, making them more memory-efficient and scalable.
- Advanced Models Released:
- DeepSeek Coder / Coder-V2 (for coding tasks).
- DeepSeek LLM (67B parameters), V2, V3 (671B parameters), and R1-Distill (fine-tuned using synthetic data).
Global Impact and Market Disruption
- App Success & Outages: The DeepSeek AI app topped the U.S. App Store, surpassing ChatGPT. This success triggered large-scale cyberattacks and caused temporary service disruptions.
- Market Reaction: The launch reportedly led to a historic $600 billion drop in Nvidia's market value, highlighting the disruptive potential of cost-efficient AI innovation.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: The rise of DeepSeek is seen as a technological parallel to the 1957 Sputnik moment, which shocked the U.S. and triggered the space race.
DeepSeek has reignited US-China AI rivalry, intensifying great-power competition in frontier technologies.
Strategic Lessons for India
- Bipolar AI Landscape: The U.S. and China dominate AI due to massive investment and infrastructure. Middle powers like India and France face the challenge of staying relevant without matching this scale.
- Doing More with Less: DeepSeek’s success underscores how innovation with limited resources can be effective—providing a model for India to emulate via Small Language Models (SLMs) and cost-efficient AI strategies.
- Sovereign AI & Global Governance:
- India advocates for “Sovereign AI”, balancing independence and strategic alliances, especially with France and the U.S.
- Future cooperation between U.S. and China on AI governance, similar to Cold War-era nuclear agreements, is a possibility.
- India must learn from past exclusions (e.g., nuclear governance) and proactively shape global AI governance frameworks.
- Policy Implications:
- DeepSeek's rise may lead to stricter U.S. chip export restrictions to China.
- It presents both security risks (censorship, pro-China bias) and opportunities (cost-effective models, domestic self-reliance).
Ethical Concerns and Limitations
- Censorship: DeepSeek complies with Chinese state censorship, refusing responses on politically sensitive topics (e.g., Tiananmen Square), raising concerns about bias and lack of transparency.
Security & Privacy: Experts have flagged potential data privacy and AI ethics issues, emphasizing the need for robust global standards and accountability mechanisms.
Paraquat Poisoning

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
- In a landmark ruling, a Thiruvananthapuram court sentenced a 24-year-old woman to death for the murder of her boyfriend by poisoning him with paraquat, a highly toxic herbicide.
- The incident, which occurred in 2022, has brought the spotlight back on paraquat's widespread availability, extreme toxicity, and the lack of regulatory enforcement in India.
What is Paraquat?
- Paraquat, chemically known as paraquat dichloride or methyl viologen, is one of the most widely used herbicides globally.
- It is primarily used for:
- Weed control
- Crop desiccation, especially in crops like cotton before harvest
- Despite its toxicity, India and the United States continue to permit its usage, unlike over 70 countries, including China, Brazil, and the European Union, which have banned it.
WHO Classification
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies paraquat as a Category 2 chemical, meaning it is moderately hazardous and irritating to the skin and eyes.
- It has a narrow margin between a safe and lethal dose, making accidental or intentional poisoning common and often fatal.
Routes and Effects of Exposure
- Ingestion is the most common method of poisoning.
- It may also occur through inhalation or skin contact, especially if the exposure is prolonged or the skin is broken.
Symptoms Vary by Dosage and Exposure Time:
Exposure Level Symptoms and Organ Damage
Small Quantity Gradual damage to lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart over days/weeks
Large Quantity Immediate symptoms such as:
- Acute kidney failure
- Liver and heart failure
- Seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nausea
- Mouth and throat swelling |
Treatment and Challenges
- No known antidote exists for paraquat poisoning.
- Treatment options include:
- Immunosuppressive therapy
- Charcoal hemoperfusion (a blood-purification technique)
- However, these treatments offer limited efficacy, especially in cases of large-dose ingestion.
Regulatory and Public Health Implications in India
- Despite paraquat’s well-documented toxicity, it remains:
- Legally available in India
- Easily accessible in rural markets
- The lack of regulation increases the risks of:
- Occupational exposure
- Accidental poisoning
- Use in crimes or suicides
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent study conducted by Assam Medical College and Hospital has revealed a high prevalence of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) among tuberculosis (TB) survivors in Assam’s tea garden communities. Published in the PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases journal, the research underscores a significant public health concern in a region already burdened by TB.
What is Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)?
- CPA is a severe, life-threatening fungal infection caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, a filamentous fungus commonly found in soil, decaying vegetation, and humid organic matter.
- It predominantly affects individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, especially those who have recovered from or are currently battling TB.
- CPA is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation:
CPA shares many clinical features with TB, making diagnosis challenging:
- Chronic cough
- Haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Persistent respiratory symptoms
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Key Findings from Assam:
- Study Area: Conducted in Dibrugarh district, covering tea workers and their dependents from four major tea estates.
- Sample Size: 128 patients with prolonged respiratory symptoms (>3 months).
- Prevalence:
- CPA prevalence: 17.18% overall
- Seropositivity in active TB patients: 18.5%
- Seropositivity in post-TB patients: Spiked to 48.9%, indicating a strong link between CPA and previous TB infections.
- Demographic Insights:
- Mean age: 41.9 years
- Higher incidence among middle-aged male workers
- Comparison with Global Trends:
- Assam’s CPA prevalence (60 per 1,00,000) exceeds the global average (42 per 1,00,000)
- Worse than several African nations including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (20–50 per 1,00,000)
Contributing Risk Factors in Assam’s Tea Belt:
- High TB burden: 217 per 1,00,000 (National TB Prevalence Survey 2019–2021)
- Poverty and malnutrition
- Kitchen smoke exposure
- Congested living conditions
- Delayed or inadequate TB treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosis:
- Serological testing for Aspergillus antibodies
- Radiological imaging to identify fungal growth in lung cavities
- Treatment:
- Antifungal therapy (e.g., itraconazole or voriconazole)
- Surgical removal in severe cases with fungal mass
Public Health Recommendations:
- Routine screening of post-TB patients for CPA in high-risk zones like tea estates
- Awareness campaigns targeting healthcare providers and workers to improve recognition and response
- Education on nutrition, respiratory hygiene, and early symptom detection
- Inclusion of fungal diseases like CPA in broader national TB and occupational health programs
Additional Context: Epidemic Dropsy in Assam’s Tea Belt
- A 2019 study had previously flagged the prevalence of epidemic dropsy, a condition caused by contaminated edible oils with Argemone mexicana oil, adding to the health risks in tea-growing regions.
ISRO’s NVS-02 Satellite Launch

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully launched the NVS-02 satellite aboard GSLV-F15, placing it into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). This marks ISRO’s 100th mission, reinforcing India’s space and navigation capabilities under the NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) program.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC is India’s indigenous regional satellite navigation system, developed for both civilian and strategic use.
- Offers accurate positioning over India and up to 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- Comparable to GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China).
About NVS-02 Satellite:
Feature Description
Series Second satellite in the next-gen NVS series (after NVS-01 in 2023)
Mission Role Replaces aging IRNSS-1E satellite
Mass 2,250 kg
Power Capacity ~3 kW
Orbit Final orbital slot at 111.75°E in geosynchronous orbit (~36,000 km)
Life Span 12 years
Developed by URSC (U R Rao Satellite Centre), Bengaluru
Technological Advancements:
- Equipped with navigation payloads across L1, L5, and S-bands for enhanced accuracy and broader coverage.
- Features the Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard (RAFS) – an indigenously developed atomic clock for precision timekeeping.
- Includes C-band ranging payload, similar to NVS-01.
Significance of NVS-02:
- Enhances NavIC’s positioning accuracy for civilian, commercial, and strategic applications:
- Disaster management
- Fleet tracking
- Precision agriculture
- Emergency response
- Mobile navigation
- L1 signal inclusion makes NavIC-compatible with international GNSS systems, improving global device integration.
- Demonstrates India’s technological self-reliance, particularly in atomic clock development.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
Vehicle First Flight Notable Use
SLV 1980 Launched Rohini satellite
ASLV 1987 Five-stage solid rocket, retired in 1990s
PSLV 1994 Reliable, used for Mars Orbiter, LEO missions
GSLV 2001 Used for heavier payloads, INSAT/GSAT
GSLV 2014 Heavy-lift, Chandrayaan-2/3, Gaganyaan crew module
Mk III (LVM3)
SSLV 2022 Affordable launches for nano/micro satellites
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
India is set to deploy its first human-operated deep-sea submersible as part of the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), marking a significant leap in the country’s marine research and technological capability.
Key Highlights:
- Submersible Deployment (2024):
- India will operate its first human submersible at a depth of 500 meters this year.
- The goal is to reach a depth of 6,000 meters by 2025.
- The project aligns with the timelines of Gaganyaan, India’s first human space mission—showcasing parallel progress in marine and space technology.
- Indigenous Technology:
- The mission is powered by 100% indigenous technology, underlining India’s growing self-reliance in high-end scientific infrastructure.
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM):
- Launched: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Budget: ?4,077 crore over five years
- Framework: One of nine key missions under PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council)
Core Objectives:
- Develop deep-sea technologies, including a manned submersible for ocean exploration.
- Explore and harness ocean resources such as: Polymetallic nodules, Hydrothermal sulphides & Rare earth metals
- Study marine biodiversity for sustainable fisheries and conservation.
- Support India’s blue economy through innovation and research.
- Monitor ocean climate change and develop advisory services.
- Promote marine biology and biotechnology via dedicated marine research stations.
- Harvest renewable energy and freshwater from ocean sources.
Key Components and Technologies:
Matsya6000 Submersible:
- India’s first manned deep-sea vehicle.
- Designed to reach 6,000 meters depth.
- Crew Capacity: Three members
- Developed by: National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai
- Structure: Made of titanium alloy, withstanding 6,000 bar pressure
- Equipped with: Scientific sensors, tools for sampling, viewports, propellers, and acoustic communication systems.
- Combines capabilities of ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) and AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles).
Varaha Deep-Ocean Mining System:
- Developed by NIOT
- Successfully conducted trials at 5,270 meters
- Key to India’s future in deep-sea mining of critical minerals
Strategic Importance:
- Scientific Advancement: DOM places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France, Japan) with human-crewed deep-ocean exploration capacity.
- Economic Potential: Unlocks access to underwater mineral wealth, critical for electronics, defense, and energy sectors.
- Environmental Sustainability: Supports marine biodiversity conservation and promotes sustainable use of oceanic resources.
- Geopolitical Significance: Enhances India’s presence and influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Technological Leap: Strengthens India’s capabilities in underwater robotics, materials engineering, and ocean sciences.
Mission SCOT

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India praised Indian space startup Digantara for the successful launch of Mission SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) — the world’s first commercial SSA satellite, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
What is Mission SCOT?
Feature Description
Developer Digantara (Indian space startup), supported by Aditya Birla Ventures & SIDBI
Launched on SpaceX Transporter-12 mission (rideshare platform)
Type First commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite
Orbit Sun-Synchronous Orbit – ideal for consistent Earth observation
Function Tracks Resident Space Objects (RSOs) as small as 5 cm in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
What is Space Situational Awareness (SSA)?
- SSA involves the detection, tracking, cataloging, and prediction of natural and man-made objects in Earth's orbit (like satellites, debris, etc.).
- Ensures safe and sustainable operations by minimizing collision risks.
- Critical due to increasing congestion in LEO, especially with rising numbers of small satellites and mega-constellations.
Key Features of Mission SCOT
Feature Advantage
High Revisit Rate More frequent observations of objects in orbit
Precision Tracking Can track debris ≥ 5 cm in size
All-Weather Monitoring Overcomes limitations of ground-based systems like cloud cover, FoV
Space-based System Unhindered by geography, providing continuous global surveillance
Supports SSA Infrastructure Aids in collision avoidance, space traffic management, and defence preparedness
???????? India’s SSA Ecosystem
Initiative Role
ISRO’s IS4OM Provides Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR); enables safe & sustainable space operations
NETRA Project Network for Space Objects Tracking & Analysis – aims to build a dedicated SST (Space Surveillance & Tracking) network using radars & optical telescopes
Multi-Object Tracking Radar Operated at Sriharikota – limited range, being augmented
Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAMs) Regularly performed by ISRO to protect its satellites from debris threats
Global Context: Transporter-12 Rideshare
- A SpaceX program providing low-cost access to space by allowing multiple customers to launch small payloads on a single rocket.
- Enhances global commercial space activity, democratizes space access.
Significance for India
Strategic:
- Strengthens national space defence by enabling indigenous tracking of space threats.
- Reduces reliance on foreign SSA data (e.g., NORAD/US Space Command).
Technological:
- Demonstrates India’s capability in space-based surveillance tech.
- Positions India as a global contributor in the emerging SSA domain.
Economic:
- Boosts private sector space innovation aligned with India’s NewSpace Policy.
- Attracts venture capital and international collaboration.
LID-568
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, an international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory discovered a low-mass supermassive black hole, LID-568, showing super-Eddington accretion—a rare and extreme feeding process—just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
About LID-568
Feature Description
Type Low-mass supermassive black hole
Age Formed ~1.5 billion years after Big Bang (Universe’s “youth”)
Discovery Observed via Chandra (X-ray) & JWST (infrared)
Location In a distant galaxy with very low star formation
Feeding Rate Accreting at ~40× the Eddington limit (super-Eddington accretion)
Key Concepts
Eddington Limit
- Theoretical upper limit on how fast matter can fall into a black hole before radiation pressure balances gravitational pull.
- Exceeding this limit (super-Eddington) is thought to be unstable and short-lived.
Super-Eddington Accretion
- Observed in LID-568, feeding at 40× Eddington rate.
- Suggests rapid, short bursts of black hole growth, not the slow, steady model previously assumed.
Why is LID-568 Important?
Challenges Current Theories
- Traditional black hole growth models require:
- Long periods (hundreds of millions of years).
- Seed black holes formed from:
- Death of first stars (light seeds: 10–100 solar masses).
- Collapse of primordial gas clouds (heavy seeds: 1,000–100,000 solar masses).
- LID-568 suggests brief, intense growth spurts could create supermassive black holes faster than previously thought.
Impact on Host Galaxy
- Powerful outflows prevent gas accumulation → suppresses star formation.
- Indicates black holes can regulate galaxy evolution, even when young.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
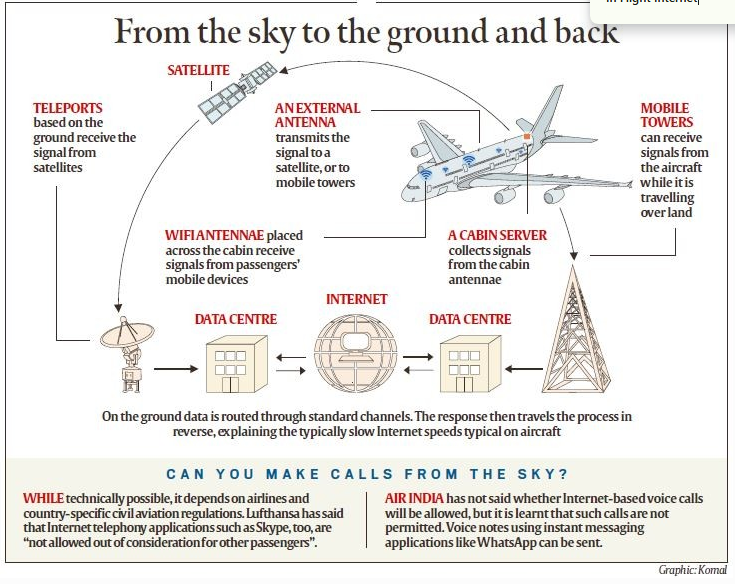
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
GenCast AI
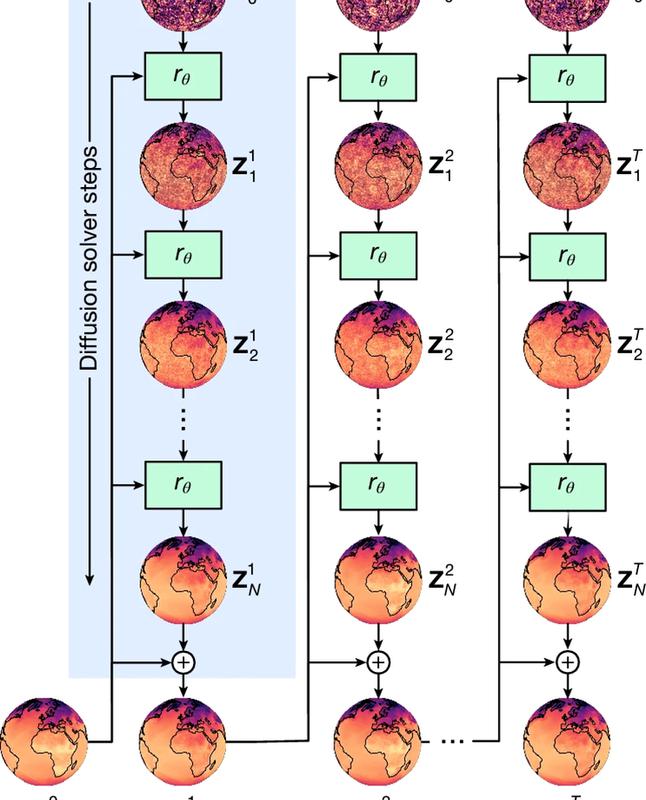
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
AgeXtend
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
Black holes in Webb data allay threat to cosmology’s standard model

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched almost three years ago, has provided unprecedented insights into the early universe. Astronomers were surprised to find large, fully-developed galaxies when the universe was only 400-650 million years old, a timeframe previously thought to be too early for such structures.
The Challenge to the Standard Model:
- Cosmological Expectations: According to the standard model of cosmology, the first stars formed around 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, and galaxies began to form within the first billion years.
- Unexpected Findings: JWST observations seemed to show that galaxies were already large and well-formed much earlier than expected, raising questions about the timeline of galaxy formation.
New Study's Contribution:
- The Study: A study published in the Astrophysical Journal in August 2024, examined JWST data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey. They focused on galaxies from 650 to 1,500 million years after the Big Bang.
- Key Findings: One explanation for the unexpected size and number of early galaxies is that these galaxies formed stars much more efficiently than those in the modern universe. This could account for the larger-than-expected galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes:
- Impact of Black Holes: The study also explored the presence of black holes at the centers of early galaxies. These black holes, which emit significant light, were previously unaccounted for in the star mass estimations of galaxies. When the researchers removed the light from black holes (referred to as "little red dots"), they found that the galaxies were not as massive as initially thought.
- Correction to Previous Estimates: This adjustment in calculations helped align the data with the standard model of cosmology, sparing it from a major revision.
Implications for the Standard Model:
- Star Formation Efficiency: The study suggests that extreme conditions in the early universe, including abundant gas and less disruptive stellar events, could explain the higher efficiency of star formation.
- Cosmology's Stability: Despite earlier challenges to the standard model, the new findings support its predictions, showing that more efficient star formation and the role of black holes could explain the rapid growth of galaxies in the early universe.
Future Research Directions:
- Expanding Data Sets: The team plans to incorporate more data from JWST to study even earlier galaxies, which could help refine our understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe.
- Further Observations: As the team continues to explore galaxies from even earlier periods (around 400 million years after the Big Bang), they aim to strengthen their findings and provide further evidence to either support or challenge the current cosmological models.
Heat Shock Protein 70
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
JNU scientists make big discovery that could change malaria, Covid-19 treatment.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Institution: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Special Centre for Molecular Medicine.
- Key Discovery: Identification of human protein Hsp70 as a critical factor in the spread of malaria and COVID-19.
- Research Collaboration: Involvement of Indian and Russian researchers.
- Outcome: Development of a small molecule inhibitor of Hsp70 that could act as a broad-spectrum treatment for multiple infections.
About Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70):
- Definition: Hsp70 is a type of molecular chaperone protein.
- Function:
- Helps other proteins fold into their proper shapes.
- Prevents protein misfolding.
- Regulates protein synthesis and protects proteins from stress.
- Elevates during cellular stress to shield cells from damage.
- Role in Cellular Processes:
- Prevents protein aggregation and assists in protein transport across membranes.
- Plays a critical role in protein homeostasis and cell survival during stress conditions.
Hsp70's Role in Disease Spread:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Interaction:
- Hsp70 interacts with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptors.
- Facilitates viral entry into human cells by stabilizing this interaction during fever (when Hsp70 levels rise).
- Malaria:Pathogens like malaria parasites rely on the host's machinery for survival, including Hsp70.
Research Findings and Implications:
- Published in: International Journal for Biological Macromolecules.
- Inhibition of Hsp70:
- Targeting Hsp70 can disrupt viral replication.
- In lab tests, Hsp70 inhibitor (PES-Cl) blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication at low doses.
- Potential for Broad-Spectrum Treatment:
- Hsp70 could be a target for treating multiple infections, not limited to COVID-19 or malaria.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance:
- Host-targeting antivirals are less prone to resistance as the virus cannot mutate the host protein (Hsp70).
- This approach could be especially beneficial for combating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (e.g., Omicron).
Host-Targeting Approach vs. Traditional Drugs:
- Host-Targeting: Targets the host cell machinery (e.g., Hsp70) rather than the virus itself.
- Reduces the likelihood of viral mutation-induced resistance.
- Traditional Drugs: Target the virus directly, which can lead to resistance, especially with rapidly mutating viruses.
Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness:
- Universal Tool for Infectious Diseases: The discovery could serve as a universal tool for managing infections during health emergencies.
- Collaboration and Importance: Highlights the significance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges (e.g., Dr. Pramod Garg of AIIMS, Ph.D. scholar Prerna Joshi).
- Future Implications:Preparation for future pandemics, as the world must remain vigilant even post-COVID-19.
SheSTEM 2024
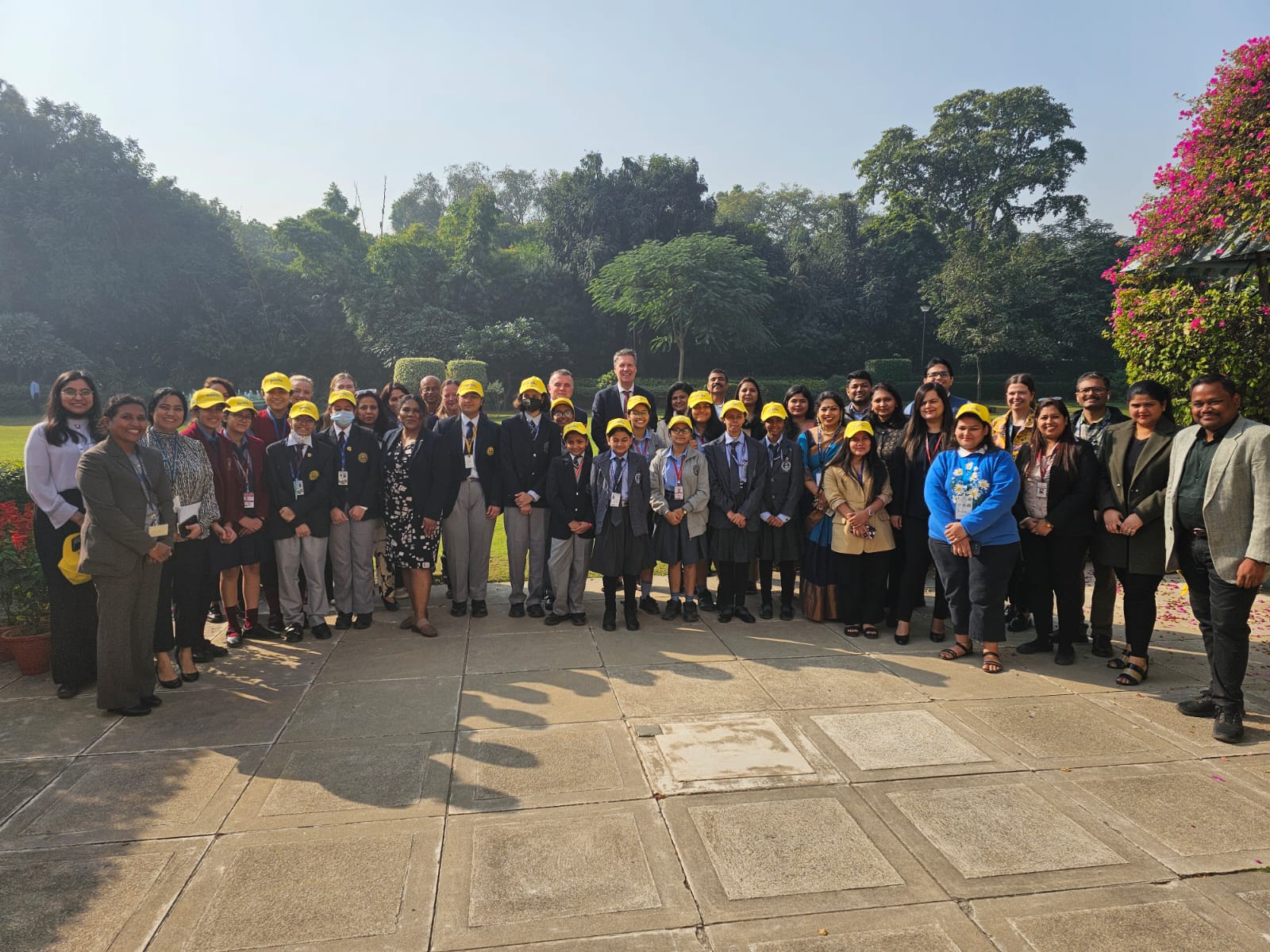

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
Proba-3 mission

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission on its PSLV rocket to study the solar corona, the outermost and hottest part of the Sun’s atmosphere, from Sriharikota on December 4.
Key Highlights:
- Mission Objective:The mission will study the Sun’s outermost and hottest atmosphere, the solar corona. The mission will also demonstrate the first-ever precision formation flying with two satellites working in tandem.
- Satellite Formation:Proba-3 consists of two satellites that will fly together, maintaining a fixed formation to study the Sun's corona.
What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3 is a solar mission developed by ESA, with an estimated cost of 200 million euros. The mission involves launching two satellites that will separate after launch, but fly in precise formation. The satellites will create a solar coronagraph, which blocks the Sun’s bright light to observe the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
- Orbit: Proba-3 will orbit in a highly elliptical path (600 x 60,530 km) with an orbital period of 19.7 hours.
- Mission Duration: The expected mission life is two years.
What will Proba-3 Study?
The Sun's corona is extremely hot (up to 2 million degrees Fahrenheit), making it difficult to observe with conventional instruments. However, studying the corona is essential because it generates space weather phenomena such as solar storms and solar winds, which can impact satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Proba-3 will use three main instruments for its mission:
- ASPIICS (Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun):This coronagraph will observe the Sun’s outer and inner corona, similar to how the corona is visible during a solar eclipse. It features a 1.4-meter occulting disk to block the Sun’s light and facilitate close-up observations.
- DARA (Digital Absolute Radiometer):This instrument will measure the Sun’s total energy output (total solar irradiance).
- 3DEES (3D Energetic Electron Spectrometer):It will study electron fluxes as they pass through Earth's radiation belts, providing valuable data on space weather.
Why is Proba-3 Unique?
- Proba-3 is designed to mimic a natural solar eclipse, allowing continuous study of the Sun’s corona. Typically, solar scientists observe the corona for only about 10 minutes during an eclipse, occurring around 1.5 times a year. Proba-3 will provide up to six hours of data per day, equivalent to 50 eclipse events annually.
- The two satellites will maintain a precise formation, with one acting as an occulting spacecraft to cast a shadow, while the other (the coronagraph) stays in the shadow and observes the Sun’s corona. They will be positioned 150 meters apart, maintaining their formation autonomously.
- This artificial eclipse will enable scientists to study the corona and its less-understood features more effectively.
Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
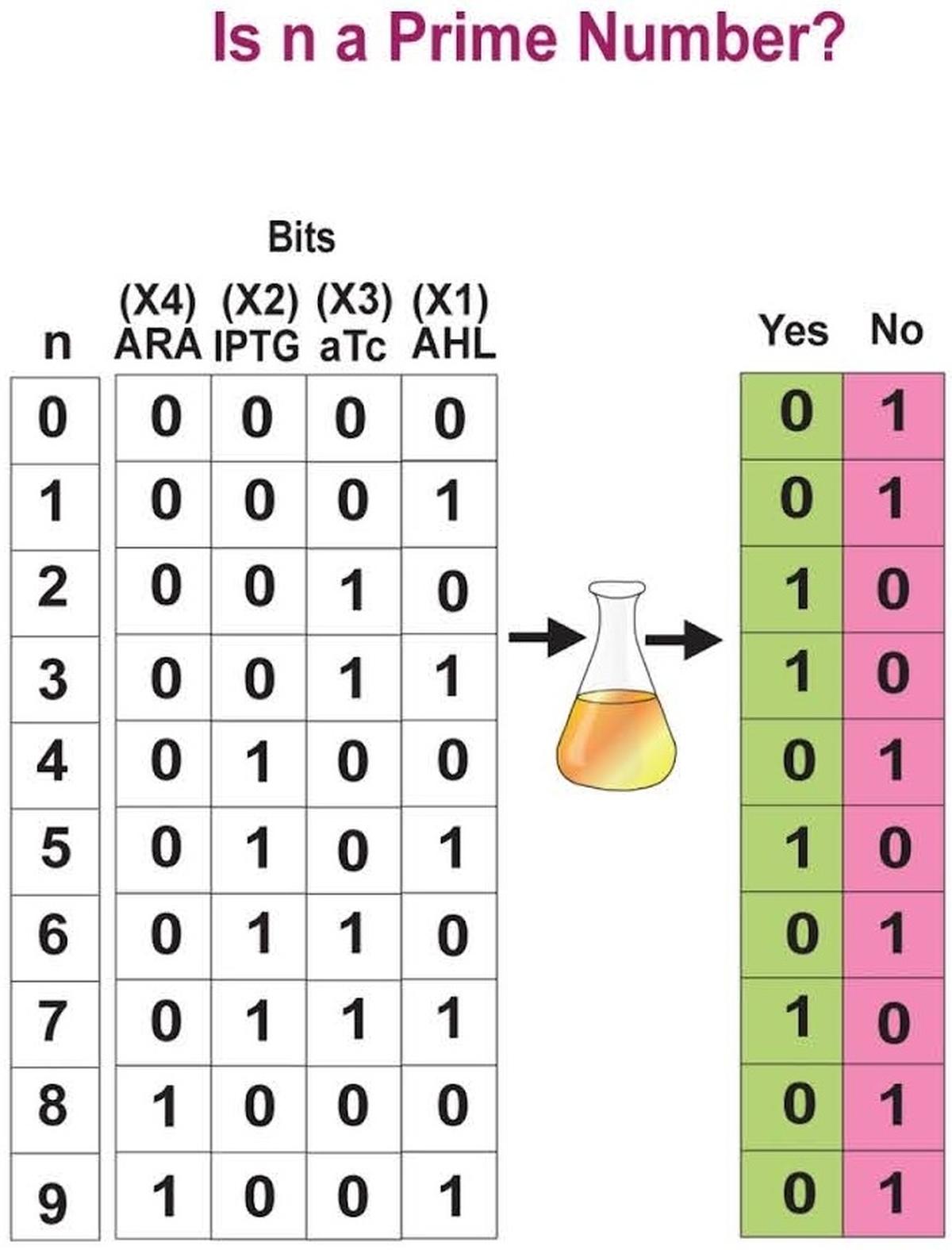
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
Chagas Disease
- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
A recent study by Texas A&M University has uncovered a concerning new risk for dogs in Texas related to Chagas disease—the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), which causes the disease, can survive in dead kissing bugs (Triatominae). This discovery was published in the Journal of Medical Entomology in October 2024 and has raised alarms about how dead insects, which might be found in insecticide-treated dog kennels, could still pose a transmission risk for dogs.
Key Findings:
- Chagas Disease is primarily spread by kissing bugs, which carry T. cruzi in their gut. Dogs can contract the parasite by ingesting the bug's feces, especially when they lick their bite wounds.
- The study shows that even dead kissing bugs, which are often discarded in kennels, can still carry viable T. cruzi. This is particularly worrying in areas where insecticides are used to control the insects but dead bugs remain accessible to dogs.
- Researchers collected live and dead triatomines from six Texas kennels between June and October 2022, using both genetic testing and culture methods to assess whether the bugs were carrying live T. cruzi.
- 28% of the collected bugs tested positive for T. cruzi.
- A dead kissing bug (Paratriatomalecticularia) was found to still harbor live T. cruzi cultures, demonstrating that the parasite can survive even after the insect has died.
Transmission and Risks:
- Kissing bugs typically feed on the blood of animals like dogs, rodents, and raccoons, defecating near the bite site. If the dog licks the contaminated area, they can ingest the parasite-laden feces and become infected.
- The new discovery suggests that dead kissing bugs may pose a secondary transmission route for T. cruzi. Dogs that ingest these dead bugs, either in insecticide-treated areas or natural environments, could still contract the parasite.
- Researchers noted that dead bugs with intact gut contents showed a higher rate of infection than desiccated ones, which suggests that the condition of the bug after death impacts how long the parasite survives.
Implications for Management:
- The findings challenge current insecticide-based control methods. While insecticides kill the bugs, dead insects could still serve as a source of infection, necessitating new approaches for managing Chagas disease transmission in dog kennels.
- The study underscores the importance of regularly removing dead insects in kennels and reconsidering control strategies beyond just using insecticides.
About Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease is caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, commonly found in the feces of kissing bugs. It can cause long-term heart and digestive issues if left untreated.
- The disease is common in parts of South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it has been increasingly reported in the southern United States.
- Treatment focuses on killing the parasite in the acute phase, but once it progresses to the chronic phase, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research:
- The Texas A&M team plans to explore how long T. cruzi survives in dead triatomines and whether insecticides affect the parasite’s ability to persist. They are also looking into developing integrated pest management strategies for environments with high kissing bug activity.
- The study also forms part of a broader "One Health" approach, recognizing that both human and animal health are interconnected, and research on Chagas disease in animals can help inform public health strategies.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Green World Awards 2024

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Coal India Limited (CIL) under the aegis of the Ministry of Coal, has been conferred with the esteemed Green World Environment Award in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category along with the distinguished tile of Green World Ambassador.
Key Highlights:
- Reason for the Award:
- The award was granted to CIL for its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna, a CSR initiative aimed at providing permanent curative treatment for Thalassemia through Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT).
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?10 lakh for BMT and has helped over 600 Thalassemia patients across India.
- Background of the Award:
- The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group, conferred the award.
- The organization has been recognizing and promoting environmental best practices and CSR initiatives globally since its establishment in 1994.
- CIL’s Role in CSR:
- CIL has been a pioneer in CSR, with its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna being the first of its kind among public sector undertakings in India.
- The initiative partners with 17 prominent hospitals across India to provide stem cell transplants for Thalassemia patients.
- CIL’s Contribution to India's Energy Sector:
- CIL is responsible for producing over 80% of India's coal and contributes to 70% of the total coal-based power generation in the country.
- CIL accounts for 55% of India’s total power generation and meets 40% of the primary commercial energy requirements.
- Environmental Initiatives by CIL:
- CIL has adopted various measures to improve environmental sustainability, including:
- Expanding green cover over mined areas.
- Creating eco-parks and tourism spots.
- Providing mine water for domestic and agricultural use to surrounding villages.
- About Coal India Limited (CIL):
- Established: November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Status: A Maharatna company and the largest coal-producing company in the world.
- Subsidiaries: CIL has seven producing subsidiaries and is a major corporate employer in India.
- About the Green Organization:
- Founded: 1994.
- Nature: Independent, non-political, non-profit organization.
- Objective: To recognize, reward, and promote environmental and CSR best practices worldwide.
- Initiatives: The Green World Awards are part of global efforts to encourage sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Significance of the Award:
- The Green World Environment Award highlights CIL’s commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability while maintaining its core role as an energy provider.
- The recognition underscores CIL’s leadership in integrating CSR initiatives with corporate operations to contribute to national development.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
3rd Indian Space Conclave
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd Indian Space Conclave, held in New Delhi, was a significant event for India's growing role in global space exploration and strategic partnerships.
- Organized by the Indian Space Association (ISPA), the conclave brought together key stakeholders from the government, industry, academia, and space agencies to discuss India’s space ambitions and the transformative role of space technologies.
Key Highlights:
Satcom as a Transformative Force for Digital India
- Emphasis on Satellite Communication (Satcom) is more than a mere tool—it's a transformative force driving Digital India by connecting every household, village, and remote area of the country.
- Satcom has a wide array of applications that extend across essential sectors such as telecommunications, disaster management, healthcare, education, and agriculture, particularly in underserved regions.
Indo-EU Space Collaboration
- The event also showcased India’s growing space partnerships, particularly with the European Union (EU). The EU Ambassador recognized India as a dynamic space power and highlighted shared goals in Earth observation, space security, and human spaceflight.
- Proposed joint initiatives include training programs, collaborative research, and satellite missions, such as the Proba-3 satellite launch by ISRO, focusing on observing the Sun.
- India’s trustworthiness as a partner in space was underscored by its role in the successful launch of the Proba-1 and Proba-2 missions for the EU, with Proba-3 marking India’s third contribution to EU space exploration.
Space Startups and Innovation
- The rise of space-focused startups in India, spurred by the 2020 space sector reforms, was another key highlight. India now has over 300 space startups, contributing to both economic growth and innovation in the space industry.
- These reforms have helped curb brain drain, with many talented Indian professionals returning from global agencies like NASA to join the expanding Indian space ecosystem.
India’s Long-Term Space Goals
- The Indian space program has ambitious long-term goals, including:
- Gaganyaan, India’s human spaceflight mission.
- A crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- The establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040.
- These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technological innovation.
Space Sector Reforms (2020)
- The Space Sector Reforms 2020 were designed to increase the participation of private players in India’s space activities. The creation of agencies like the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) and the strengthening of New Space India Limited (NSIL) have been pivotal in boosting India’s global space market share.
- IN-SPACe serves as an autonomous body fostering industry, academia, and startups, while NSIL handles commercial activities and promotes high-tech space-related ventures.
India's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission
- ISRO's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission was inaugurated in Leh, Ladakh. This mission simulates the conditions of space habitats, specifically focusing on Mars and Moon environments.
- Ladakh's unique climate—high altitude, low oxygen levels, and extreme temperature fluctuations—makes it an ideal location for testing life support systems, space habitat technologies, and sustainable resource utilization.
Key Aspects of the Analog Mission:
- Life support systems like hydroponics (space farming) and standalone solar power systems to support sustainable food production and renewable energy in space habitats.
- Circadian lighting to simulate daylight cycles, maintaining astronaut health and well-being.
- The mission’s goal is to understand the psychological and operational challenges of living in isolation and extreme conditions, preparing India for future interplanetary exploration.
AntarikshaAbhyas 2024

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- ‘AntarikshaAbhyas – 2024’ is a three-day space exercise held from November 11-13, 2024, hosted by the Defence Space Agency (DSA), Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff.
- The exercise is the first of its kind and focuses on war-gaming the growing threats to space-based assets and services.
Objective of the Exercise:
- Enhance understanding of space-based assets and their operational dependencies.
- Identify vulnerabilities in military operations in case of denial or disruption of space services.
- Integrate India's space capabilities in military operations to secure national strategic objectives.
Participants:
- Defence Space Agency (DSA) and its allied units.
- Personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Specialist agencies under Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff, including:
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCA)
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Representatives from ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research & Development Organisation).
Focus Areas:
- Space-based asset and service operational dependency.
- Securing national interests in space through technological innovation and development.
- Assessing space service vulnerabilities and impacts on military operations.
Zhurong Rover

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
Spraying Diamond Dust to cool the Earth

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- A new study in Geophysical Research Letters suggests that diamond dust could be more effective than any other material in reflecting solar radiation.
- Objective: The goal is to reduce global temperatures by 1.6°C by spraying approximately 5 million tonnes of diamonds annually into the atmosphere.
Background of Geoengineering Solutions:
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions aimed at altering Earth's natural climate system to counteract global warming.
- One proposed solution involves spraying diamond dust in the Earth's upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- This approach is part of Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which seeks to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby reducing global temperatures.
- Previous Materials Considered: Sulphur, calcium, aluminium, silicon, and other compounds have been studied to perform a similar function.
Context of Geoengineering and Climate Crisis:
- Inadequate Progress: Current efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have been insufficient. Global temperatures have continued to rise, and targets like the Paris Agreement's 1.5°C are increasingly out of reach.
- Rising Global Temperatures:
- 2023: Global temperatures were approximately 1.45°C higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Projected Challenge: To meet the Paris goal, global emissions must be reduced by at least 43% by 2030. However, current actions will likely result in only a 2% reduction by 2030.
Geoengineering Technologies:
- Geoengineering Methods:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): Reflects sunlight to cool Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): Involves capturing and storing CO?.
- SRM Techniques:
- SRM draws inspiration from natural events like volcanic eruptions, where large amounts of sulphur dioxide form particles that reflect sunlight.
- Mount Pinatubo (1991): One of the largest eruptions, which temporarily reduced global temperatures by 0.5°C due to the sulphur dioxide released.
Diamond Dust vs Other Materials:
- Study Comparison: Diamonds were found to be the most effective material compared to other compounds (sulphur, calcium, etc.) for reflecting solar radiation.
- Quantity Needed: To achieve a cooling of 1.6°C, 5 million tonnes of diamonds would need to be dispersed into the upper atmosphere each year.
Broader Geoengineering Context:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS is already in practice, where CO? emissions from industries are captured and stored underground to reduce atmospheric carbon.
- However, CCS faces high costs and scalability issues, and safe storage sites for CO? are limited.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): A more advanced method where CO? is directly removed from ambient air, but it faces even greater challenges in terms of infrastructure and cost.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
LignoSat
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
The world's first wooden satellite, LignoSat, is set to launch from the Kennedy Space Center aboard a SpaceX rocket. This pioneering satellite is a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry Co., marking a significant step towards exploring more sustainable materials in space exploration.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:The primary goal of LignoSat is to test the viability of using wood in space technology, with a focus on the eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness of using renewable materials in satellite construction. The satellite will be tested aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assess its durability, strength, and ability to withstand extreme space conditions.
- Material:The satellite is crafted from magnolia wood, chosen for its durability and adaptability. Magnolia was selected for its strength, making it a suitable candidate to endure the harsh conditions of space travel and the intense environmental factors faced in space exploration.
- Mission Details:Once launched, LignoSat will be sent to the ISS, where it will be released from the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo). Researchers will collect data on the satellite’s performance, examining its ability to handle the challenges of space, including temperature fluctuations and physical strain.
- Environmental Benefits:One of the key advantages of wooden satellites is their environmental impact. Traditional metal satellites, when re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, can generate metal particles that contribute to air pollution. In contrast, wooden satellites like LignoSat are designed to be eco-friendly during reentry. Wood is a natural material that burns up more cleanly during reentry, reducing the potential for harmful atmospheric pollution.
First Science Result from India's Aditya-L1 Mission

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Aditya-L1 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 2, 2023, is India's first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Primary Payload: The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru, is the spacecraft's main instrument.
Key Highlights:
- First Science Outcome:The first scientific result from the mission, involving VELC, has been released. It successfully estimated the onset time of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred on July 16, 2023.
- CMEs are massive solar eruptions that can disrupt electronics in satellites and communications on Earth.
- Key Findings:
- VELC's Role: The VELC payload was crucial in observing the CME close to the solar surface, providing a detailed understanding of its onset.
- CMEs are typically observed in visible light after they have traveled far from the Sun. However, VELC’s unique spectroscopic observations allowed scientists to study the CME much closer to the Sun's surface.
- Publication:The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Future Significance:
- As the Sun approaches the maximum phase of its current solar cycle (No. 25), CMEs are expected to become more frequent. Continuous monitoring with VELC will provide valuable data for understanding these events.
- Monitoring the thermodynamic properties of CMEs near the Sun is essential to understand their source regions and behavior.
- Mission Details:
- The spacecraft is in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Mission Lifetime: 5 years.
Centre for Science and Environment

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Centre for Science and Environment release a report on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastic Packaging
Key Findings:
- EPR Guidelines (2022) were a step towards enforcing the "polluter pays" principle, but the system faces significant issues in its implementation and registration processes.
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) report, released on October 29, 2024, highlights gaps in the EPR system for plastic packaging and suggests corrective actions.
EPR Guidelines Overview:
- Issued by: Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective: Hold producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and plastic waste processors (PWPs) responsible for managing plastic packaging waste.
- Key Requirements:
- PIBOs must register on a centralized portal and set targets for collection, recycling, and reuse of plastic packaging.
- Registration involves compliance with targets on end-of-life recycling and recycled content usage.
Problems Identified in the Current EPR System:
- Low Registration and Enrollment:
- 41,577 registrations on the EPR portal, but a significant discrepancy in the type of stakeholders registered.
- 83% of registered entities are importers, 11% are producers, and only 6% are brand owners.
- Producers contribute 65% of the plastic packaging in the market but have low registration.
- Absence of Key Polluters:
- Manufacturers of virgin plastics are notably absent from the portal, despite being required to register.
- Fraudulent Practices:
- 700,000 fake certificates were generated by plastic recyclers, far exceeding the actual certificate generation capacity.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that such fraudulent activities are undermining the integrity of the system.
- For example, end-of-life co-processing units (e.g., cement plants) claimed to have processed 335.4 million tonnes per annum of plastic waste, while their actual capacity is just 11.4 million tonnes per annum.
- Underreporting and Mismanagement:
- Despite 23.9 million tonnes of plastic packaging being introduced into the market, the CPCB’s estimation of plastic waste generation (4.1 MT annually) is underestimated.
- Lack of Stakeholder Representation:
- Urban local bodies and informal waste collectors—key contributors to plastic waste management—are not included in the EPR framework, which limits their incentives and support.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Incorporate the Informal Sector:
- Recognize informal waste collectors and waste management agencies in the EPR framework to improve traceability and ensure better waste management.
- Eliminate Fraudulent Practices:
- Strict actions need to be taken against fraudulent recyclers and fake certificate issuers to restore credibility to the EPR system.
- Establish Fair Pricing for EPR Certificates:
- Undertake baseline cost studies to determine the true costs of plastic waste management, ensuring fair pricing for recycling certificates and preventing undervaluation.
- Standardize Packaging:
- Focus on product standardization to ensure that packaging materials are uniform and easily recyclable.
- Strengthen Monitoring:
- Improve oversight on the registration process and ensure that all polluters (producers, importers, brand owners) comply with the system’s guidelines.
EPR and Plastic Waste Management: Context and Importance
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach where the responsibility of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products (from production to disposal) lies with the producer.
- It is an essential part of India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), which mandate the recycling and proper disposal of plastic packaging waste.
Key Elements of EPR:
- Producer Accountability: Producers are responsible for the take-back, recycling, and final disposal of plastic packaging.
- Waste Minimization: Encourages reducing waste at the source by promoting sustainable packaging designs.
- Lifecycle Approach: Considers the entire lifecycle of the product, focusing on sustainability from production to disposal.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Ensures that the cost of waste management is borne by those responsible for generating the waste.
Discovery of the First "Black Hole Triple" System

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have discovered a "black hole triple" system, which is a rare configuration in space involving one black hole and two stars.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Location: The system is located 8,000 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Cygnus.
- Key Features:
- A black hole at the center, currently consuming a star that is spiraling very close to it.
- A second, more distant star that orbits the black hole every 70,000 years, and another star that orbits it every 6.5 days.
What is a Black Hole Triple System?
- Black Hole and Two Stars: Unlike typical binary systems (comprising a black hole and one other object), this system contains a black hole surrounded by two stars, one nearby and one far away.
- V404 Cygni: The central black hole in the system is the V404 Cygni, one of the oldest known black holes, roughly 9 times the mass of the Sun.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Questions on Black Hole Formation: The discovery raises new questions about how black holes are formed. Traditionally, black holes are thought to form after the explosion of a massive star (supernova), but this system does not follow that model.
- New Formation Theory: Researchers suggest the black hole may have formed via a "direct collapse" process, where a star collapses into a black hole without undergoing a supernova explosion. This is referred to as a "failed supernova".
- In a failed supernova, the star's collapse happens too quickly for the explosive outer layers to be ejected, leading to the formation of a black hole without the typical violent explosion.
Implications for Other Binary Systems:
- The black hole’s gradual consumption of one of its stars may imply that some binary black hole systems could have originally been triple systems, with one star eventually being consumed by the black hole.
Research and Collaboration:
- Study: The discovery was made by researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- Published in: The findings were published in Nature in October 2024.
Additional Context:
- Distance: The system is about 8,000 light years away, which is vast but still observable with advanced telescopes.
- Mystery of the "Failed Supernova": The concept of a failed supernova offers new insights into the life cycle of massive stars and their transformation into black holes.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
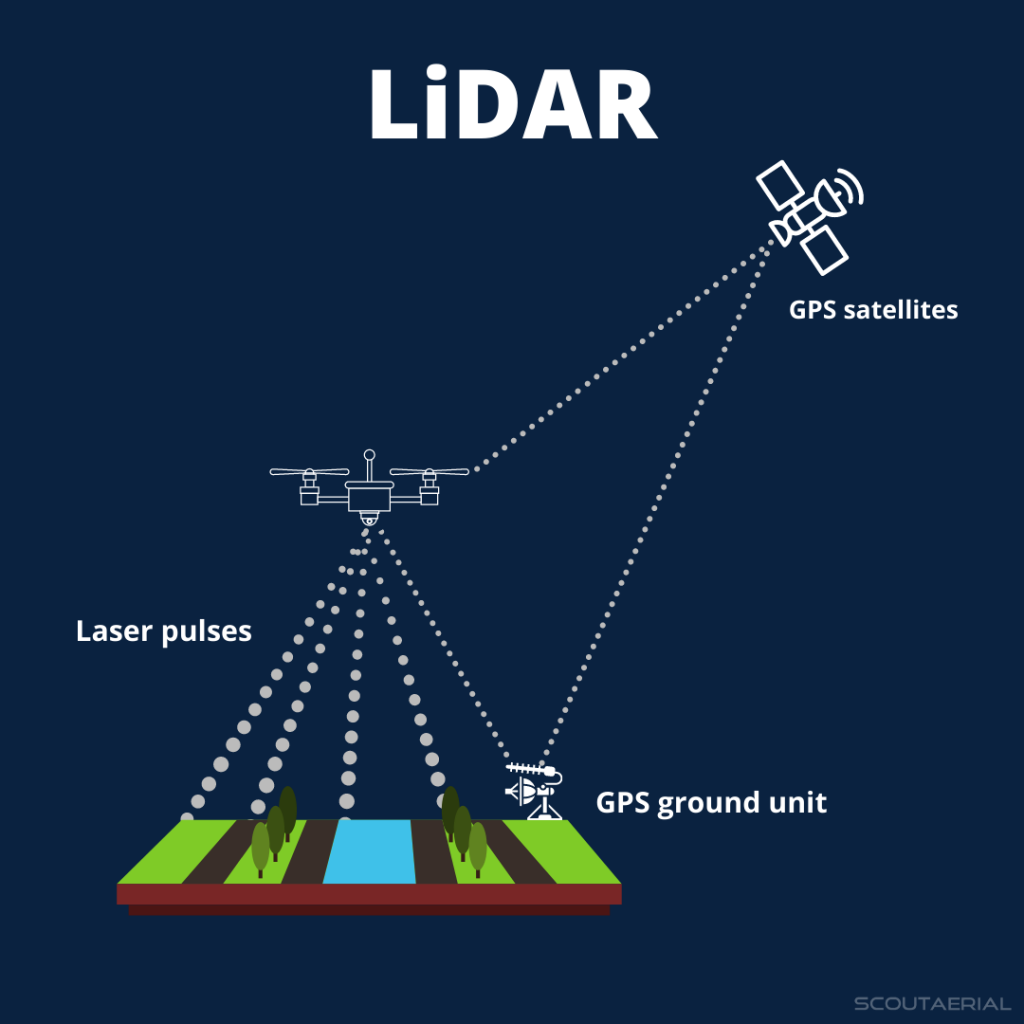
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
ISRO’s First Electric Propulsion-Led Spacecraft (TDS-1)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India's first home-grown electric propulsion satellite to be launched in Dec.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of TDS-1:
- Purpose: To demonstrate electric propulsion technology for satellite steering, using solar-powered ionized gas.
- Goal: Reduce reliance on chemical fuel, making satellites lighter and more efficient.
- Key Benefits of Electric Propulsion:
- Weight Reduction: The technology can significantly cut down satellite mass. For example, a satellite weighing 4 tonnes could be reduced to around 2 tonnes.
- Fuel Efficiency: By using electric propulsion, the need for chemical fuel is minimized, allowing for a more efficient journey to geostationary orbit.
- Technology Details:
- Fuel Used: Gases like Argon are ionized using solar power to create propulsion.
- Process: The ionized gas is expelled at high speeds to generate thrust, pushing the satellite towards its desired orbit.
- Historical Context:
- The technology was first used in GSAT-9 (South Asia Satellite) in 2017 but with imported Russian components.
- TDS-1 marks the first fully indigenous development of electric propulsion technology by ISRO, highlighting India’s increasing space autonomy.
- Significance for India’s Space Program:
- Self-Reliance: TDS-1 reflects ISRO’s growing capacity to develop advanced space technologies domestically.
- Future Prospects: This breakthrough is expected to lead to more efficient satellite designs, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global space industry.
New Space Missions and Developments

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Space Commission also approved a joint moon mission with Japan called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission. For LUPEX, ISRO is developing a different moon lander than the one it used for Chandrayaan-3
New Space Missions and Developments
- Chandrayaan-4 (Moon Mission):
- Type: Sample-return mission.
- Launch: Expected by 2027.
- Cost: ?2,104 crore.
- Objective: Sample collection of moon soil and rock to return to Earth.
- Mission Details: Two LVM-3 launch vehicles will launch components that will dock in Earth orbit before heading to the moon. The samples will be sent back using a bespoke canister.
- Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX):
- Collaboration: Joint mission with Japan.
- Objective: Exploration of lunar poles with a new lander design, intended for potential crewed missions in future.
- Venus Orbiter Mission:
- Launch Window: March 2028.
- Cost: ?1,236 crore.
- Objective: Study Venus' surface and atmosphere to understand planetary evolution in the Solar System.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):
- Development Budget: ?8,240 crore for first three development flights.
- Objective: A new launcher developed with private sector collaboration for future space missions.
Cabinet Approvals for Space Initiatives
- Human Spaceflight Programme (Gaganyaan):
- Four new missions under Gaganyaan, including an uncrewed Gaganyaan flight.
- Focus on developing technologies for India’s first space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), planned by 2028.
- Space-Based Surveillance (SBS) Missions:
- Phase 3: Approval for building 21 ISRO satellites, with 31 additional satellites by private companies.
- Total Cost: ?26,968 crore.
- Development of a Third Launch Pad:
- To support the NGLV and additional space missions at Sriharikota.
Upcoming Satellite Missions
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar):
- Launch: Early 2025 on a GSAT launch vehicle.
- Purpose: Earth observation using advanced radar technology.
- Issue: Protective coating added due to high temperatures during testing.
- Proba-3 (European Space Agency):
- Launch: November 29, 2024, aboard PSLV-XL.
- Objective: Study the Sun’s corona using two satellites in formation, mimicking an eclipse to capture unique solar data.
Private Sector Involvement
- Manastu Space & Dhruva Space:
- Collaboration: Testing green propulsion technology for the LEAP-3 mission.
- Technology: Hydrogen-peroxide-based green propulsion system.
- Launch: LEAP-3 mission in 2025.
- Bellatrix Aerospace:
- Project: Prototype satellite for ultra-low earth orbit at 200 km altitude.
- Ananth Technologies:
- Achievement: First private company to assemble, integrate, and test Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx) satellites for ISRO.
Space Science and Research Updates
- Chandrayaan-3:
- Findings: The crater where Chandrayaan-3 landed is older than the South Pole-Aitken Basin (4.2-4.3 billion years old).
- Data Source: Optical High-Resolution Camera (Chandrayaan-2) and Pragyaan rover (Chandrayaan-3).
- Astrosat (India’s First Space Observatory):
- Mission Life: Expected to last two more years (originally planned for 5 years).
- Significance: Contributed to over 400 published papers based on multi-wavelength space observatory data.
ISRO-DBT Agreement for Biotechnology Experiments in Space

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to conduct biotechnology experiments on the upcoming Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
- Timeline for BAS:
- The BAS is expected to be operational from 2028-2035, with the initial module launches slated for 2028 and full expansion by 2035.
- It will be located at an altitude of 400 km above Earth and will support 15–20-day missions in space.
Focus Areas of Research
- Health Impact:
- Weightlessness & Muscle Health: Studying the effects of zero-gravity on muscle loss during space missions.
- Radiation Effects: Investigating how space radiation impacts astronaut health over long durations.
- Bio-Manufacturing:
- Algae Studies: Exploring algae for potential use in nutrient-rich, long-lasting food sources and biofuel production.
- Food Preservation: Identifying algae varieties that can help preserve food for longer periods in space.
- Integration with Gaganyaan Mission:
- Experiments may also be conducted during uncrewed test flights for the Gaganyaan mission (India’s first crewed mission to space, scheduled for 2025-2026).
BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Objective: The BioE3 policy aims to boost bio-manufacturing in India, which is projected to contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030.
- Key Focus Areas:
- High-Value Bio-Based Products: Promotes the development of bio-based chemicals, biopolymers, enzymes, and smart proteins.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture & Carbon Capture: Aims to strengthen agricultural practices to withstand climate change and promote carbon capture technologies.
- Healthcare & Nutrition: Focuses on advancements in biotherapeutics, functional foods, and regenerative medicine.
- Marine & Space Biotechnology: Encourages research in space and marine biotechnology for new applications.
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Supports R&D-driven entrepreneurship through the establishment of bio-manufacturing hubs, bio-AI centers, and biofoundries.
- Employment Growth: Aims to create skilled jobs in the growing bioeconomy, promoting green growth and sustainable industries.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) Overview
- Structure: The station will consist of:
- Command Module
- Habitat Module
- Propulsion Systems
- Docking Ports
- Objective: To support long-term research in space life sciences and bio-manufacturing, with a focus on human health, food sustainability, and biotechnology innovations.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The tiny nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has played an outsized role in scientific discovery, contributing to four Nobel Prizes over the years.
Key Discoveries from C. elegans Research
- C. elegans and Cellular Processes:
- The worm has helped scientists understand programmed cell death (apoptosis), a vital process in development and disease. This work contributed to the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, addressing how cells are instructed to kill themselves and how this process goes awry in conditions like AIDS, strokes, and degenerative diseases.
- Gene Silencing and RNA Interference:
- In 2006, a Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi), a process first explored using C. elegans. This discovery led to the development of a new class of RNA-based drugs.
- Cellular Imaging Techniques:
- In 2008, C. elegans contributed to breakthroughs in cellular imaging, as its use helped invent cellular “lanterns” that allowed scientists to visualize the inner workings of cells, earning a Chemistry Nobel.
- Gary Ruvkun’s 2024 Nobel:
- Gary Ruvkun’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 was the fourth in a series of Nobel recognitions stemming from C. elegans research, reinforcing its role in fundamental biological discoveries.
Key Facts About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
- Size: 1 millimeter long.
- Life Cycle: Completes in 3-5 days.
- Cell Count: 959 cells.
- Genome: First multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced in 1998.
- Sexual Reproduction: Hermaphroditic (self-fertilizing) and male.
- Scientific Role: Used to study genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and cell biology.
- Nobel Prize Contributions: Four Nobel Prizes, including those in Physiology, Medicine, and Chemistry, for advancements in cell death, gene silencing, and imaging.
Funga Taxonomic Kingdom

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
- Chile and the United Kingdom have prepared a proposal to recognize fungi as an independent kingdom, termed "Funga", alongside flora (plants) and fauna (animals).
- This will be presented at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), to be held in Cali, Colombia in October 2024.
- Why Funga?
- Fungi (e.g., mushrooms, moulds, yeast, lichen) play crucial ecological roles, but have historically been overlooked in conservation strategies.
- Fungi contribute significantly to decomposition, forest regeneration, carbon sequestration, and the global nutrient cycle.
- The recognition aims to strengthen fungal conservation by integrating fungi into global legislation and policies.
- Ecological Importance of Fungi:
- Decomposition: Fungi break down organic matter, facilitating nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Many fungi form crucial symbiotic relationships with plants (e.g., mycorrhizal associations) and animals.
- Climate Mitigation: Boreal forest fungi absorb large amounts of carbon through symbiosis with plants, playing a role in mitigating climate change.
- Pollution Remediation: Fungi can help clean polluted soils by breaking down toxins.
- Food Production: Fungi are essential for producing common foods like bread, cheese, wine, beer, and chocolate.
- Health: Fungi produce antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) and aid in mammalian digestion.
- Scientific Recognition:
- In August 2021, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) recognized fungi as one of the three kingdoms of life, alongside plants and animals.
- The 3F initiative (Flora, Fauna, and Funga), led by Giuliana Furci, aims to promote the international recognition and protection of fungi.
- Diversity and Research Gaps:
- Only 8% of the estimated 2.2 to 3.8 million fungal species have been formally described.
- Approximately 2,000 new fungal species are discovered annually, indicating the vast underexplored diversity of fungi.
- Threats to Fungi:
- Fungi face significant threats from deforestation, climate change, pollution, overharvesting, and fungicide use.
- These threats disrupt the symbiotic relationships fungi share with plants and animals, leading to ecosystem instability.
- Nitrogen enrichment in soils and habitat loss further exacerbate these risks.
Key Facts About Fungi
- Biological Characteristics:
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with rigid cell walls made of chitin (distinct from the cellulose found in plant cell walls).
- They are heterotrophic, meaning they absorb nutrients from their environment through external digestion (secreting enzymes to break down organic material before absorption).
- Reproductive Strategies:
- Fungi reproduce both asexually (via spores) and sexually, ensuring their proliferation across ecosystems.
- Growth Form:
- Fungi grow primarily as mycelium, a network of hyphae (filamentous structures) that helps in nutrient absorption and environmental interaction.
- Symbiotic Relationships:
- Fungi form mycorrhizal relationships with plants, enhancing nutrient exchange, and lichen associations with algae, providing mutual benefits in extreme environments.
Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi is organising its first-ever international conference - Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024.
Key Details:
- Theme: "Advancements in Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda"
- Conference Goals
- Position Ayurveda as a key pillar of global health and wellness.
- Facilitate dynamic exchanges among scholars, industry leaders, and practitioners.
- Explore the integration of traditional Ayurvedic wisdom with modern scientific advancements.
- Agenda Highlights
- Topics Covered:
- Ayurveda and ethnomedicine
- Quality control and standardization
- Diagnosis and drug delivery
- Evidence-based understanding and globalization
- Topics Covered:
- Institute Background
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA): Apex institute for Ayurveda with NAAC A++, NABH, and ISO accreditations.
- Facilities: 200-bed referral hospital, 44 specialty departments.
- Global Collaborations: Partnerships with institutions in 17 countries, including London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and Western Sydney University.
- Innovations: Focus on research, drug development, and scientific validation of Ayurvedic practices.
- Participant Benefits
- Networking Opportunities: Engage with experts in Ayurveda and holistic healthcare.
- Learning Experiences: Attend plenary sessions, round table discussions, and exhibitions on medicinal plants and startups in Ayurveda.
- Recognition: Awards for contributions to Ayurveda.
- Research and Innovation Focus: Discussions on technology integration, including AI and bioinformatics.
Announcement of AI Centres of Excellence

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, announced the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence (CoE) focused on Healthcare, Agriculture, and Sustainable Cities in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Establishment of Three AI-CoEs:
- Focus Areas:
- Healthcare: Led by AIIMS and IIT Delhi.
- Agriculture: Led by IIT Ropar, Punjab.
- Sustainable Cities: Led by IIT Kanpur.
- Collaboration: CoEs will work with industry partners and start-ups.
- Focus Areas:
- Financial Commitment:
- Total Approved Budget: ?990 crore for FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Purpose: Support the establishment and operation of the CoEs.
- Vision and Impact:
- Pradhan emphasized the CoEs' role as solution providers for global public good.
- Expected to create a new generation of job and wealth creators.
- Aims to strengthen India's credentials in the global AI landscape.
- Leadership and Implementation:
- Apex Committee: Co-chaired by Shri Sridhar Vembu (Zoho CEO).
- Committee includes industry leaders and academic heads.
- Shri K. Sanjay Murthy highlighted the importance of interdisciplinary research and collaboration.
- Future Prospects:
- Dr. Vembu noted the CoEs will enhance the health of villages and cities, nurture talent, and generate opportunities.
- The initiative aligns with India's vision of "Viksit Bharat" (Developed India).
- Presentation and Film:
- Insights into the development of AI-CoEs presented by Smt. Saumya Gupta.
- A short film titled "Make AI in India and Make AI work for India" was showcased.
The establishment of these Centres of Excellence in AI signifies a major step toward fostering an effective AI ecosystem in India, aimed at developing scalable solutions and enhancing human resources in critical sectors.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has officially launched its first two initiatives: the Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG) and the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s research landscape and support innovation in critical sectors.
Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- Objective: The PMECRG is designed to empower early career researchers by providing flexible funding and support for high-quality innovative research. It aims to foster creativity and drive technological progress, positioning India as a global leader in science and technology (S&T).
- Significance: This grant recognizes the essential role of young researchers in advancing India's scientific agenda. By investing in their development, ANRF aims to cultivate a vibrant research ecosystem that encourages groundbreaking discoveries.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission
- Focus: The MAHA-EV Mission targets the development of key technologies for electric vehicles, specifically in areas such as tropical EV batteries, power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD), and charging infrastructure.
- Goals:
- Reduce Import Dependency: By fostering domestic innovation in EV components.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the electric vehicle sector, aligning with the government's Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Collaboration: The mission is designed to encourage multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary collaboration to address critical scientific challenges, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of India's EV sector.
Significance of Both Initiatives
- Bridging Gaps: Both initiatives aim to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial applications, a key goal of ANRF. This alignment is crucial for translating research into practical applications that benefit society.
- Strategic Interventions: These programs reflect the discussions held during the ANRF's Governing Board meeting, which emphasized global positioning in key sectors, capacity building, and fostering an innovation ecosystem.
- Long-term Vision: The initiatives contribute to India's goal of achieving a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047, accelerating the country's progress toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The launch of the PMECRG and MAHA-EV Mission marks a significant step in enhancing India's research ecosystem. By supporting early career researchers and advancing electric vehicle technologies, ANRF is poised to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and strengthen India’s position on the global scientific stage. These initiatives reflect a commitment to sustainable development and technological leadership, paving the way for transformative advancements in various sectors.
ITU World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2024

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ITU WTSA 2024 and India Mobile Congress 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- First Time in India: WTSA hosted for the first time in India and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Participants: Over 3,000 industry leaders, policy-makers, and tech experts from more than 190 countries expected.
ITU WTSA 2024
- Significance: Governing conference for the standardization work of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), held every four years.
- Focus Areas: Discussion on standards for next-generation technologies including:
- 6G
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Opportunities for India: Enhances India’s role in shaping the global telecom agenda; insights into Intellectual Property Rights and Standard Essential Patents for startups and research institutions.
India Mobile Congress 2024
- Theme: "The Future is Now"
- Technological Focus: Highlight advancements in:
- Quantum Technology
- Circular Economy
- 6G and 5G use cases
- Cloud and Edge Computing
- IoT and Semiconductors
- Cybersecurity
- Green Technology
- Satellite Communication and Electronics Manufacturing
Importance for India
- Showcase of Innovation: A platform for India’s innovation ecosystem, demonstrating advancements in digital technology.
- Global Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address global telecommunication challenges.
New Cancer Therapy Target
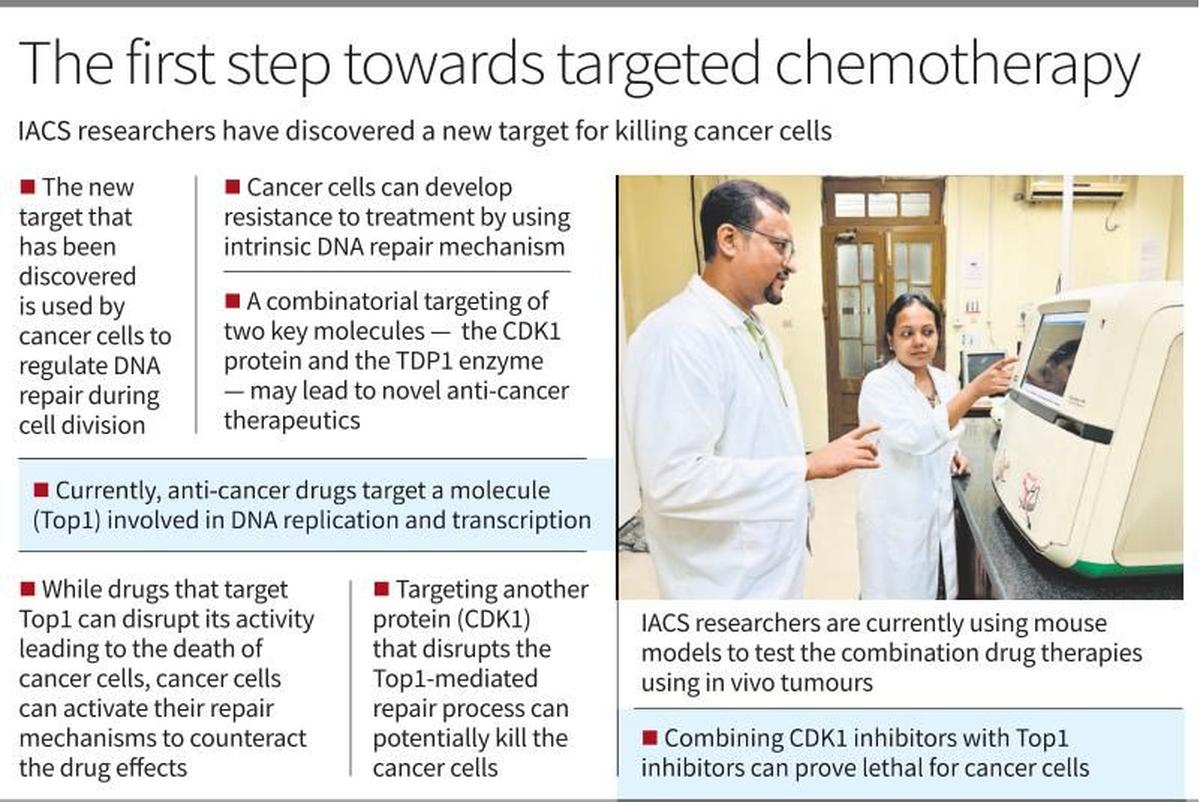
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
U.S. Scientists David Baker and John Jumper and Britain’s Demis Hassabis won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, for their work on understanding the protein structures.
Prize Distribution
- David Baker: Awarded half of the Prize for pioneering work in computational protein design.
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper: Jointly awarded the other half for their revolutionary contributions to protein structure prediction using artificial intelligence.
Significance of Achievements
- The advancements in protein science represent a major milestone for healthcare and biotechnology.
- These innovations have unlocked new possibilities for designing proteins, potentially leading to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and more.
David Baker's Innovations
- Baker has achieved the significant feat of creating entirely new types of proteins, enhancing our understanding of protein functionality.
- In 2003, he designed a novel protein using amino acids and custom software methods, which opened avenues for rapid protein creation.
- Applications include pharmaceuticals, vaccines, nanomaterials, and tiny sensors.
AI Contributions by Hassabis and Jumper
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper employed advanced artificial intelligence to address the challenge of predicting complex protein structures.
- In 2020, they introduced the AI model AlphaFold2, which can predict the structure of nearly all identified proteins (approximately 200 million).
Notable Facts about the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded 116 times to 197 laureates from 1901 to 2024.
- Frederick Sanger and Barry Sharpless are the only recipients to have won the Prize twice.
- The inaugural Prize was awarded in 1901 to Jacobus H. van ‘t Hoff for his work on chemical dynamics and osmotic pressure.
- Marie Curie became the first woman to win the Prize in 1911 for her discovery of radium and polonium.
- Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, a citizen of Indian origin, received the Prize in 2009 for his research on ribosomes.
2024 Nobel Prize in Physics

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton won the 2024 Nobel Prize for physics “for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks”. Their work lies at the roots of a large tree of work, the newest branches of which we see today as artificially intelligent (AI) apps like ChatGPT.
Significance of ANNs
- Definition: ANNs are collections of interconnected nodes that mimic the networks of neurons in animal brains, enabling machines to process data, recognize patterns, and learn.
- Applications: Integral to AI applications such as facial recognition, language translation, and numerous fields including physics, chemistry, and medicine.
Historical Context
- Hopfield Network:
- Developed by John Hopfield in 1983.
- Based on Donald Hebb's neuropsychological theory of learning, emphasizing how connections between neurons strengthen through repeated interactions.
- Capable of storing and reconstructing images by adjusting node connections to achieve a low-energy state, effectively denoising input.
- Boltzmann Machine:
- Geoffrey Hinton's work on deep-learning machines, building on Ludwig Boltzmann's statistical mechanics.
- Introduced the concept of generative AI through networks that differentiate between probable outcomes.
- Developed Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) in the 2000s, enhancing learning efficiency through layered networks.
Evolution and Current State of ANNs
- Technological Progress: ANNs have evolved significantly, transitioning from individual computers to distributed networks like the cloud.
- Current Variants: Innovations include transformers, backpropagation, and long short-term memory techniques, making ANNs more capable and widely accessible.
Concerns and Risks
- Ethical Considerations: Rapid advancements in AI raise concerns about safety, misinformation, and job displacement.
- Expert Opinions: Both Hopfield and Hinton have expressed worries about the implications of AI systems surpassing human intelligence and the potential for misuse.
MACE Observatory

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The MACE Observatory was recently inaugurated by the Secretary of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission in Hanle, Ladakh.
About MACE Observatory
- Name: Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory.
- Significance:
- Largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
- Highest imaging Cherenkov observatory in the world.
- Location: Situated at approximately 4,300 meters altitude in Hanle, Ladakh.
- Indigenous Development:
- Built by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Supported by the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, and other Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- Research Focus:
- Enhances understanding in astrophysics, fundamental physics, and particle acceleration mechanisms.
- Observes high-energy gamma rays to investigate cosmic phenomena like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- Global Impact:
- Aims to foster international collaborations in space research.
- Strengthens India’s position in the global scientific community.
Socio-Economic Role
- Local Impact: Contributes to the socio-economic development of Ladakh, promoting scientific awareness and opportunities.
Understanding Cherenkov Radiation
- Definition: A blue glow emitted when charged particles (e.g., electrons and protons) travel faster than light in a specific medium.
- Historical Note: Named after Pavel Cherenkov, who, along with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for his work in demonstrating and explaining this phenomenon.
Marburg Virus
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
- Definition:
- Marburg virus is one of the deadliest pathogens known to infect humans, causing severe hemorrhagic fever.
- Current Situation in Rwanda:
- Rwanda reported its first Marburg case late last month.
- At least 46 individuals have been infected, with 12 reported deaths.
- Approximately 80% of infections are among medical workers.
- The outbreak poses a significant threat to Rwanda’s fragile healthcare system, which has only 1,500 doctors for over 13 million people.
Characteristics of Marburg Virus
- Deadliness:
- Marburg virus disease (MVD) has case fatality rates ranging from 24% to 88%, depending on the strain and case management.
- The first outbreak occurred in Marburg, Germany, in 1967, with subsequent outbreaks primarily in Africa.
- Family:
- Marburg belongs to the filovirus family, which includes Ebola.
- Both viruses are clinically similar and can cause high-fatality outbreaks.
Transmission
- Initial Infection:
- Human infections initially occurred through prolonged exposure to mines or caves inhabited by Rousettus bats (notably the Egyptian fruit bat).
- Human-to-Human Transmission:
- MVD spreads directly through contact with blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
- Indirect transmission can occur via contaminated surfaces and materials (bedding, clothing).
- Risk for Medical Workers:
- Medical workers treating MVD cases are frequently infected, especially when infection control measures are inadequate.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)
- Incubation Period: Symptoms can appear 2 to 21 days after infection.
- Initial Symptoms: High fever, Severe headache, Muscle ache, Watery diarrhea, Abdominal pain and cramping, Vomiting
- Hemorrhagic Symptoms:
- Many patients develop bleeding from various sites, including the digestive system (fresh blood in feces and vomit), nose, gums, and vagina.
- Fatalities often occur due to severe blood loss and shock, typically 8 to 9 days after symptom onset.
Prevention and Treatment
- Current Status:
- No approved vaccines or specific treatments exist for MVD.
- Supportive Care:
- Rehydration (oral or intravenous fluids) and symptom management improve survival rates.
- Experimental Treatments:
- Rwanda is seeking experimental vaccines and treatments to address the outbreak.
- The US-based Sabin Vaccine Institute provided 700 doses of an experimental Marburg vaccine for healthcare professionals on the frontlines.
Genome Editing and Hereditary Cancers
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Agency for Research on Cancer’s estimates of the burden of 36 cancers in 185 countries suggest one in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer.
- Impact of CRISPR on Cancer Research:
- CRISPR screens have revolutionized the study of BRCA genes through high-throughput functional genetic analysis.
- Researchers use CRISPR-Cas9 to create specific mutations in BRCA genes, studying their effects on DNA repair and cancer development.
- Cancer Statistics:
- One in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer (International Agency for Research on Cancer).
- In 2022, there were approximately 20 million new cancer cases and 9.74 million cancer-related deaths; projections suggest these could rise to 32 million new cases and 16 million deaths by 2045, with Asia potentially accounting for half of the cases.
- Genetic Mutations and Inheritance:
- All cancers stem from genetic mutations; about 10% of cancer cases may involve inherited mutations.
- Specific inherited mutation prevalence:
- 20% in ovarian cancer patients.
- 10% in breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers.
- 6% in cervical cancer.
- BRCA Genes Overview:
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, discovered in 1994 and 1995, are crucial for understanding hereditary cancer syndromes.
- Mutations in BRCA genes significantly increase the risk of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers.
- BRCA mutations are estimated to occur in 1 in 400 individuals, with higher prevalence (1 in 40) among Ashkenazi Jews due to genetic bottlenecks and founder effects.
- Importance of Genetic Testing:
- Testing for BRCA mutations helps identify individuals at higher risk, enabling personalized prevention strategies such as increased surveillance or preventive surgery.
- The American Society of Clinical Oncology recommends testing for 15 genes related to breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Targeted Therapies:
- PARP inhibitors represent a new class of chemotherapy drugs effective for cancers with BRCA mutations.
- Clinical trials show promising results, especially when combined with platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Advancements in Understanding Cancer Genes:
- CRISPR technology has improved our understanding of cancer-related genes, enabling researchers to study the effects of specific mutations.
- Studies have identified how different mutations influence responses to therapies like PARP inhibitors.
- Recent Research Findings:
- Research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute identified over 3,000 genetic changes in the RAD51C gene that could significantly increase breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Variants disrupting RAD51C function can increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and aggressive breast cancer risk four-fold.
- Risk Spectrum:
- Genetic risk is a spectrum based on how mutations affect protein function.
- Large-scale variant analysis is vital for personalized medicine and cancer prevention.
- Role of Population Studies:
- Population prevalence studies help identify hereditary cancer risks and inform genetic screening for at-risk individuals.
- Early cancer detection allows for better healthcare decisions and potential preventive therapies.
- Goals for Cancer Management:
- The ultimate aim is to reduce cancer morbidity and mortality, leading to healthier lives for individuals and families.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
BharatGen Initiative
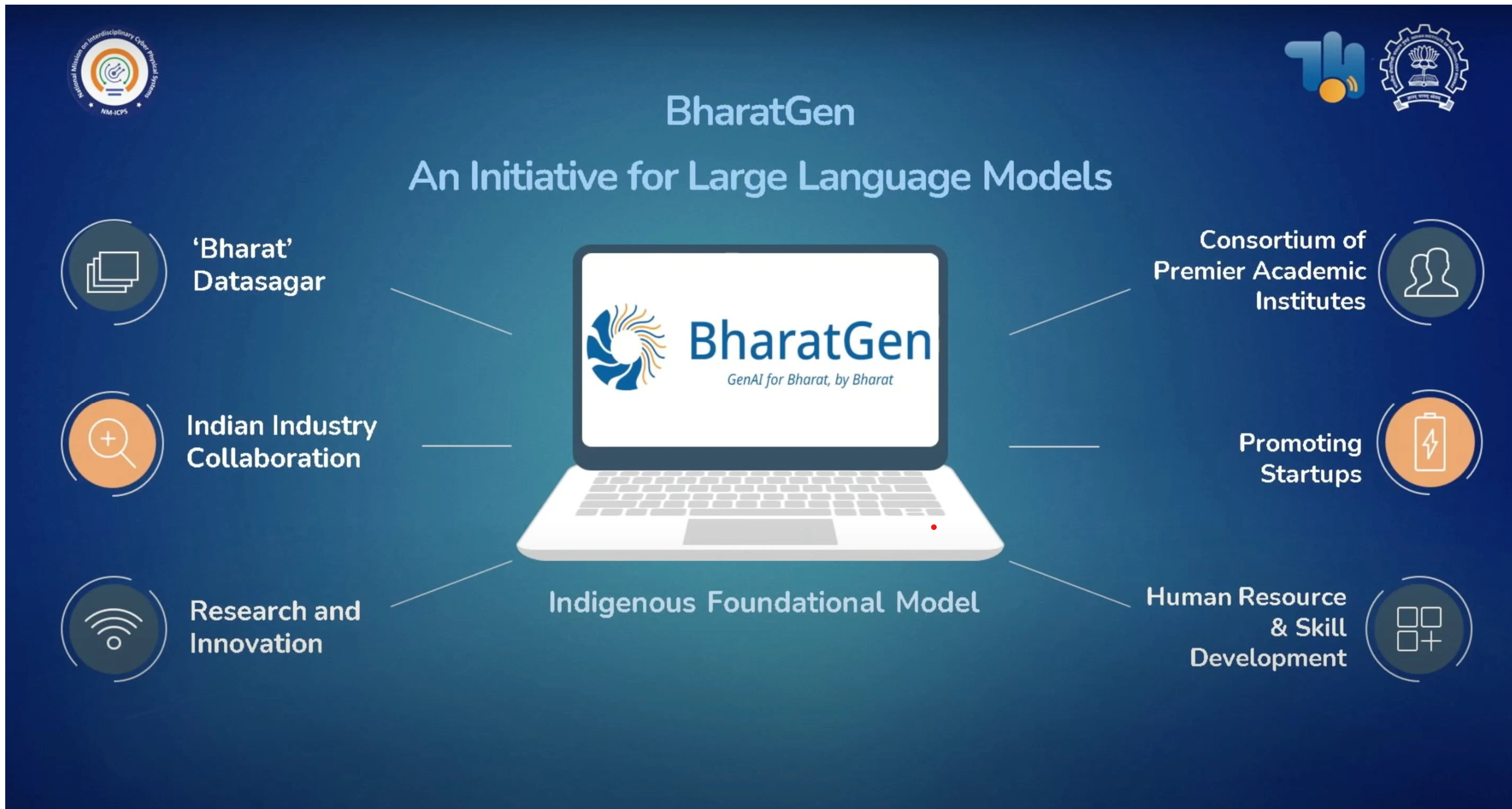
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
BharatGen is a pioneering generative AI initiative launched in New Delhi, aimed at revolutionizing public service delivery and enhancing citizen engagement, with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State, in virtual attendance.
- Significance
- Represents India's commitment to advancing homegrown technologies.
- Positions India as a global leader in generative AI, similar to achievements with UPI and other innovations.
- Marks the world's first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model project focusing on Indian languages.
- Leadership and Implementation
- Spearheaded by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Collaboration with the TIH Foundation for IoT and various academic partners, including IITs and IIMs.
- Key figures involved include Prof. Shireesh Kedare (Director, IIT Bombay) and Prof. Ganesh Ramakrishnan (consortium leader).
- Core Objectives
- Deliver generative AI models as a public good, prioritizing socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Address broader needs such as social equity, cultural preservation, and inclusivity.
- Make AI accessible for industrial, commercial, and national priorities.
- Key Features
- Multilingual and Multimodal Models: Capable of handling text and speech in multiple languages.
- Bhartiya Data Sets: Focus on India-centric data collection and training.
- Open-Source Platform: Promotes collaboration and innovation in AI research.
- Ecosystem Development: Fosters a robust AI research community.
- Project Timeline and Impact
- Expected completion in two years, with benefits for government, private, educational, and research institutions.
- Ensures coverage of India’s diverse linguistic landscape through multilingual datasets.
- Emphasis on data sovereignty to strengthen control over digital resources.
- Alignment with National Goals
- Supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
- Aims to strengthen the domestic AI ecosystem for startups, industries, and government agencies.
- Focuses on democratizing access to AI for innovators and researchers.
- Research and Community Engagement
- Data-efficient learning for languages with limited digital presence.
- Development of effective models with minimal data through research collaborations.
- Initiatives to foster an AI research community, including training programs and hackathons.
- Future Roadmap
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
- Extensive AI model development and experimentation.
- Establishment of AI benchmarks tailored to India’s needs.
- Scaling AI adoption across industries and public initiatives.
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD)

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- Establishment of Disease-Free Zones:
- The Union government plans to create FMD-free zones in eight states: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Uttarakhand, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
- Aim: Expand export opportunities for Indian animal products and enhance global market presence.
- Vaccination Efforts:
- Advanced vaccination initiatives are underway in the identified states, as stated by Alka Upadhyaya, Secretary of the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Collaborative Workshop:
- A workshop on ‘Animal Infectious Disease Prioritisation’ was held in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organisation.
- Focus: Prioritized 20 major animal infectious diseases based on severity, transmissibility, and national importance.
- Action Plan:
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Coordination
- Communication
- Monitoring and surveillance
- Prevention and control
- Therapeutics and socio-economic planning
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Regional Disease Prioritization:
- Strengthening regional-level prioritization of animal diseases for tailored control strategies.
- Overview of FMD:
- Highly contagious viral disease affecting cloven-hoofed animals like cattle, swine, sheep, and goats, but not horses or cats.
- Significant economic impact due to its effect on livestock production and trade.
Key Characteristics of FMD:
- Transmission:
- Virus present in excretions and secretions; aerosolized virus can infect other animals via respiratory or oral routes.
- Symptoms:
- Fever, blister-like sores on the tongue, lips, and hooves.
- High mortality in young animals, with production losses noted even post-recovery.
- Vaccination:
- Available vaccines must be matched to specific virus types/subtypes.
India's Biotech Revolution

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian Cabinet has recently approved the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) proposal, a significant move to advance the country’s biotechnology sector.
Scheduled to take effect on April 1, 2025, the BioE3 policy aims to capitalize on India's biotechnology potential by focusing on six key areas: bio-based chemicals, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research.
Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector
India ranks among the top 12 biotechnology destinations globally and is the third-largest in the Asia-Pacific region. As of 2024, India's Bioeconomy is valued at an estimated USD 130 billion. The sector is integral to India’s goal of becoming a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024, with biotechnology contributing about 3% to the global market share.
Biotechnology Categories in India:
- Biopharmaceuticals: India is a major supplier of low-cost drugs and vaccines, leading in biosimilars with the highest number of approvals.
- Bio-Agriculture: India dedicates approximately 55% of its land to agriculture, holding the fifth-largest area of organic agricultural land worldwide. The sector's contribution to the Bioeconomy is expected to grow from USD 10.5 billion to USD 20 billion by 2025.
- Bio-Industrial: Biotechnology is enhancing industrial processes, manufacturing, and waste disposal.
- Bio IT & BioServices: India excels in contract manufacturing, research, and clinical trials, hosting the highest number of US FDA-approved plants outside the US.
Government Initiatives:
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) is permitted in greenfield pharma and medical devices.
- The National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2021-25 aims to make India a global leader in biotechnology, targeting a USD 150 billion Bioeconomy by 2025.
- The Department of Biotechnology has established 51 Biotech-KISAN hubs to connect farmers with scientific advancements.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 includes INR 10,000 crore for 500 ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan scheme.
- The GenomeIndia Project focuses on sequencing and analyzing the Indian population’s genomes to aid public health.
Challenges and Recommendations
Challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex approval process for GMOs and overlapping regulatory bodies slow down progress.
- Funding Issues: Limited funding and high risks deter investment. The biotechnology sector receives only 0.05% of India's GDP from the Central Government.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate research facilities and cold chain infrastructure hamper progress.
- IP Concerns: Intellectual property protection remains weak, affecting innovation.
- Global Competition: Indian firms face stiff competition from established global players.
- Talent Shortages: A brain drain and skills mismatch impede growth.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical issues related to GMOs and gene editing pose challenges.
Recommendations:
- Regulatory Streamlining: Establish a unified Biotechnology Regulatory Authority and adopt a risk-based assessment approach.
- Innovative Funding: Create a Biotechnology Investment Fund with public-private partnerships.
- Talent Development: Launch skill development programs and integrate biotech training into various disciplines.
- Infrastructure Investment: Develop shared high-end research facilities and upgrade cold chain infrastructure.
- IP Strengthening: Enhance the IPR regime and establish a Biotech Patent Pool.
- Leverage Make in India: Expand the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to cover more biotech products and establish specialized manufacturing corridors.
New Target for Cancer Treatment Discovered by IACS Scientists

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant breakthrough, scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) in Kolkata have identified a new target for cancer therapy. Their study, recently published in The EMBO Journal, focuses on how cancer cells manage DNA repair during cell division, potentially paving the way for more effective treatments.
Key Findings
The researchers explored how cancer cells respond to topoisomerase 1 (Top1)-targeted chemotherapy. Top1 inhibitors, such as camptothecin, topotecan, and irinotecan, disrupt DNA replication and transcription, causing damage that usually leads to cell death. However, cancer cells can sometimes develop resistance by employing internal DNA repair mechanisms, primarily involving a protein called TDP1.
Mechanism of Action
Top1 is crucial for relaxing DNA supercoils during cell division, a process necessary for accurate chromosome segregation. Drugs targeting Top1 can kill cancer cells by preventing this relaxation. Nonetheless, cancer cells counteract this damage with TDP1, which repairs the DNA and promotes cell survival.
The IACS team discovered that TDP1's function is influenced by its phosphorylation status, which changes during the cell cycle and drug treatment. This modification helps TDP1 detach from chromosomes during cell division, a mechanism that helps cells survive despite the presence of chemotherapy drugs.
Novel Therapeutic Approach
The researchers propose a novel approach that combines inhibitors of two key molecules: CDK1 protein and TDP1 enzyme. CDK1 plays a critical role in regulating the cell cycle, while TDP1 is involved in repairing DNA damage. By inhibiting both, the researchers aim to disrupt the cancer cell's ability to repair DNA damage caused by Top1 inhibitors.
This combinatorial targeting strategy could enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatments. While Top1 inhibitors induce DNA damage, CDK1 inhibitors could prevent the repair of this damage or halt the cell cycle, making it difficult for cancer cells to survive. This dual-target approach may also help overcome resistance mechanisms that cancer cells develop against single-agent therapies.
Clinical Implications
CDK1 inhibitors, including avotaciclib, alvocidib, roniciclib, riviciclib, and dinaciclib, are currently in various stages of clinical trials. These drugs can be used alone or in combination with other DNA-damaging agents. Combining CDK1 inhibitors with Top1 inhibitors holds promise for significantly improving cancer treatment outcomes by targeting different aspects of the cell cycle and DNA replication.
Although the study was conducted using human breast cancer cells, the findings suggest potential benefits for patients with other types of cancer, such as ovarian, colorectal, and small cell lung cancers (SCLC). SCLC, in particular, is associated with tobacco smoking and could potentially benefit from this new combinatorial approach.
Conclusion
The IACS study opens new possibilities for cancer treatment by targeting DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. By combining CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors, the researchers aim to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and overcome resistance. Further research, including clinical trials, will be essential to validate these findings and develop personalized cancer therapies that could improve patient outcomes across various cancer types.
Recent Announcement on Dark Matter Research
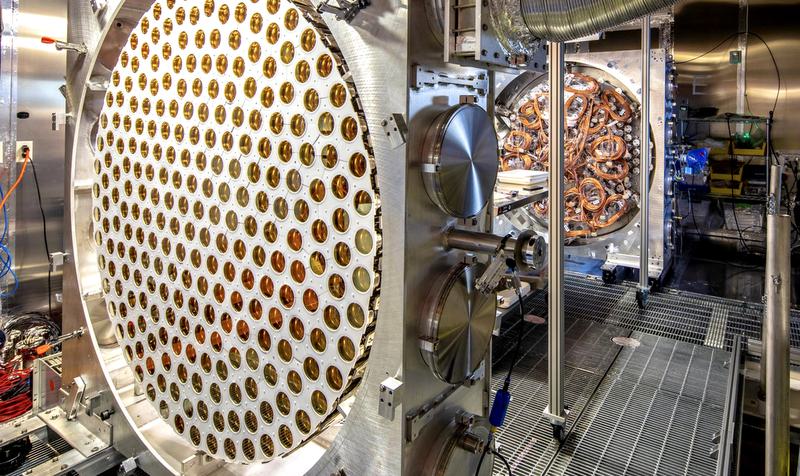

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently two representatives from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, working 1.5 km underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, announced that they had placed the tightest restrictions yet on the identities of dark matter particles, resulting in a null finding that clarified which identities these particles could not have, leading to a sense of resignation rather than disappointment among the physics community, as similar experiments like XENON-nT in Italy and PandaX-4T in China have yielded empty results for decades despite significant efforts.
Background on Dark Matter
- Definition: Dark matter makes up most of the universe's mass, contributing to its structure.
- Composition: Likely consists of previously unknown particles that:
- Do not interact with photons.
- Remain stable over billions of years.
- Key Question: Can dark matter interact with atomic nuclei and electrons?
Experimental Strategies
- Proposed Method:
- Introduced by physicists Mark Goodman and Ed Witten in 1985.
- Concept: Use a “sail” (a chunk of metal) deep underground to detect dark matter interactions.
- Objective: Measure unknown mass and interaction rate (cross-section) of dark matter particles.
Scattering Cross-Section
- Concept:
- Similar to light interaction with different media (vacuum, glass, rock).
- Cross-sections indicate how readily a particle can scatter.
- Previous Limits: Proposed limits as small as 10−38cm210^{-38} text{cm}^210−38cm2.
- Current Achievements: Recent experiments have ruled out cross-sections as small as 10−44cm210^{-44} text{cm}^210−44cm2.
Challenges Ahead
- Neutrino Interference:
- As detectors increase in size, they also detect more noise from neutrinos, complicating dark matter detection.
- Both PandaX-4T and XENONnT report issues with neutrino signals.
- Resignation in Community:
- Scientists had hoped for clearer results before facing the challenge of distinguishing dark matter from neutrinos.
Alternative Research Avenues
- Focus on Lighter Particles:
- Exploring dark particles lighter than atomic nuclei for easier detection.
- Technological Development:
- Advancing technologies to measure minimal energy transfers using special materials.
Conclusion
- Ongoing Effort: The search for dark matter continues to unite scientific disciplines and require innovative approaches.
- Human Ingenuity: The pursuit reflects a broader effort to understand the universe, drawing on collective expertise and creativity.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Prime Minister of India launched three Param Rudra Supercomputing Systems and a High-Performance Computing (HPC) system for weather and climate research via a virtual event.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers
- Development: Indigenously developed under the National Supercomputing Mission.
- Deployment Locations:
- Delhi: Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) focuses on material science and atomic physics.
- Pune: Giant Metre Radio Telescope (GMRT) will explore Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) and other astronomical phenomena.
- Kolkata: S N Bose Centre drives advanced research in physics, cosmology, and earth sciences.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) System
- Purpose: Tailored for weather and climate research.
- Location:
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- National Center for Medium Range Weather Forecast (NCMRWF), Noida.
- System Names: 'Arka' and 'Arunika', reflecting their solar connection.
Significance of the HPC System
- Enhanced Predictive Capabilities:
- High-resolution models improve accuracy and lead time for: Tropical cyclones, Heavy precipitation, Thunderstorms, Hailstorms, Heat waves, Droughts and Other critical weather phenomena
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- Launch and Goals
- Launched in 2015 to position India among world-class computing power nations.
- Aims to connect national academic and R&D institutions with a network of over 70 high-performance computing (HPC) facilities.
- Implementation
- Managed by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Government of India.
- Estimated cost: Rs 4,500 crore over 7 years.
- Supports initiatives like 'Digital India' and 'Make in India'.
- Current Status
- India ranks 74th globally in supercomputing, with only 9 supercomputers out of more than 500 worldwide.
- The mission addresses the growing computing demands of the scientific community and aligns with international technology trends.
- Infrastructure and Networking
- Envisions a supercomputing grid with over 70 HPC facilities networked via the National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- NKN connects academic institutions and R&D labs through a high-speed network.
INDIA’s FIRST MISSION TO VENUS

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
India is set to launch its first mission to Venus in March 2028, following the recent approval from the Union Cabinet. This mission, led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), marks India’s second interplanetary endeavor after the successful Mars Orbiter Mission in 2013.
Importance of Studying Venus
- Earth's Twin: Venus is often referred to as Earth’s twin due to its similar mass, density, and size. Understanding Venus can provide insights into Earth’s own evolution.
- Extreme Conditions: The planet has a surface temperature around 462°C and an atmospheric pressure similar to that found deep under Earth’s oceans. Its atmosphere consists primarily of 96.5% carbon dioxide and features clouds of sulfuric acid.
- Historical Water Presence: Venus may have had water in the past, leading scientists to explore how it transitioned to its current hostile environment, likely due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Mission Overview
- Launch Timeline: The mission will utilize a strategic launch window when Earth and Venus are closest, occurring every 19 months. It was initially planned for 2023 but is now set for 2028.
- Payload: The mission will carry around 100 kg of scientific instruments, including 17 Indian and 7 international experiments.
- Journey to Venus: After exiting Earth's orbit, the spacecraft will take about 140 days to reach Venus.
Aero-Braking Technique
- First-time Use: This mission will employ aero-braking, a technique to adjust the spacecraft’s orbit by skimming through Venus's atmosphere, creating drag that reduces altitude.
- Target Orbit: The satellite will initially be in a highly elliptical orbit of 500 km x 60,000 km and will be gradually lowered to an orbit of either 300 x 300 km or 200 x 600 km over about six months.
Scientific Payloads
- Synthetic Aperture Radar: For imaging the surface of Venus.
- Thermal Camera: To study temperature variations.
- Interplanetary Dust Analysis: Investigating dust particle flow.
- High-Energy Particle Studies: Examining particles entering the atmosphere and their ionization effects.
- Atmospheric Composition Study: Assessing the structure, variability, and thermal state of Venus’s atmosphere.
Which countries are trying to study Venus?
- There have been several missions to Venus in the past by the United States, the erstwhile USSR, Japan, and a collaborative mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) with Japan.
- The US has planned at least two more missions to Venus in the future — DaVinci in 2029 and Veritas in 2031 — and the ESA has planned the EnVision mission for 2030.
EUROPA CLIPPER MISSION

- 21 Sep 2024
In news:
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which aims to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Key Details:
- Objective: This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa, focusing on its potential habitability.
- Significance: Europa Clipper will be NASA's first mission specifically designed to explore an ocean world beyond Earth. Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy surface, which raises the possibility of supporting life.
- Spacecraft Specifications:
- The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end and 58 feet (17.6 meters) across, making it the largest NASA spacecraft ever built for a planetary mission.
- Mission Plan:
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of Europa to gather critical data regarding its environment and potential habitability.
- Instrumentation:
- Equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that leverages its telecommunications system, the spacecraft will maximize data collection by operating all instruments simultaneously during each flyby. This approach will allow scientists to compile comprehensive data layers, creating an in-depth understanding of Europa.
- Power Source:
- The spacecraft is outfitted with large solar arrays to harness sunlight for its energy needs while operating in the challenging environment of the Jupiter system.
Solar Array
A solar array is a collection of solar panels interconnected to generate electrical power. When combined with other components like an inverter and battery, it forms a complete solar energy system.
GLOBAL CYBERSECURITY INDEX 2024

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), with an impressive score of 98.49 out of 100.
Role-Modeling Country: This accomplishment places India among ‘role-modeling’ countries, reflecting a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices globally.
Assessment Criteria: The GCI 2024 evaluates national efforts based on five pillars:
-
- Legal Measures
- Technical Measures
- Organizational Measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
- Evaluation Methodology: The index utilized a comprehensive questionnaire comprising 83 questions, which cover 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators, ensuring a thorough assessment of each country's cybersecurity landscape.
- Tier Classification: The GCI 2024 report categorized 46 countries in Tier 1, the highest tier, indicating a strong commitment across all five cybersecurity pillars. Most countries fall into lower tiers, either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4) their cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Achievements
- Global Standing: India ranks at the top level of global cybersecurity rankings, showcasing its dedication to enhancing cyber resilience and securing its digital infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives:
- Robust Frameworks: Establishment of comprehensive frameworks for cybersecurity and cybercrime laws.
- Sectoral Support: Implementation of Sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) that provide technical support and incident reporting across various industries.
- Educational Integration: Cybersecurity has been integrated into primary and secondary education curricula to foster informed digital citizens.
- Public Awareness: Targeted campaigns have promoted secure online practices across multiple sectors, including private industry and academia.
- Skill Development and Innovation: The government has provided incentives and grants to enhance skill development and promote research within the cybersecurity sector.
- International Collaborations: India has engaged in numerous bilateral and multilateral partnerships to strengthen its capacity-building and information-sharing efforts.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Overview: Established in 1865, the ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies, becoming a UN agency in 1947.
- Membership: ITU has 193 member countries and over 1,000 associated organizations, including companies and universities.
- Functions: ITU coordinates global radio spectrum allocation, sets technical standards for telecommunication, and works to improve ICT access in underserved communities.
- India's Involvement: India has been an active ITU member since 1869 and a regular participant in the ITU Council since 1952.
EARTH TO EXPERIENCE A TEMPORARY 'MINI-MOON' IN SEPTEMBER

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
In late September, Earth will temporarily capture a small asteroid known as 2024 PT5. This phenomenon, where an asteroid becomes a "mini-moon," will last for about two months before the asteroid escapes back into space. While Earth has gained mini-moons before, such occurrences are quite rare; most asteroids either miss the planet entirely or burn up upon entering the atmosphere.
What Is a 'Mini-Moon'?
Mini-moons are small asteroids that get temporarily captured by Earth's gravity, orbiting the planet for a limited time. These asteroids are typically small and difficult to detect—only four mini-moons have been identified in Earth's history, and none remain in orbit today. Some objects previously thought to be mini-moons were later determined to be space debris, including rocket stages and satellites.
Details About 2024 PT5
Discovered on August 7 through the NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), 2024 PT5 measures approximately 33 feet in length, making it invisible to the naked eye and standard amateur telescopes. However, it is detectable by professional astronomical equipment.
According to Carlos de la Fuente Marcos, a professor at the Complutense University of Madrid, 2024 PT5 originates from the Arjuna asteroid belt, which consists of space rocks that share similar orbits with Earth. There is also speculation that it could be a fragment resulting from an impact on the moon, as noted by Paul Chodas from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
However, some experts argue that 2024 PT5 may not fully qualify as a mini-moon. For an asteroid to be classified as such, it must complete at least one full orbit around Earth. Instead, 2024 PT5 will follow a horseshoe-shaped path, leading Lance Benner, a principal investigator at JPL, to express skepticism about its classification as a mini-moon.
Significance of the Event
Studying 2024 PT5 will provide valuable insights into asteroids that pass near Earth and their potential for future collisions. Additionally, many asteroids are believed to contain precious minerals and water, which could be harvested for future space missions and resource utilization. Observing this mini-moon will enhance our understanding of these celestial bodies and their behavior in Earth's vicinity.
TRISHNA MISSION

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
During a recent event, the President of the French Space Agency, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), addressed various topics, celebrating 60 years of collaboration between France and India in space exploration, alongside discussions on the Gaganyaan and TRISHNA missions.
Overview of the TRISHNA Mission
The Thermal Infrared Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) is a joint initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and CNES.
Mission Objectives
TRISHNA aims to provide high-resolution, timely observations of Earth's surface temperature, monitor vegetation health, and analyze water cycle dynamics. It will facilitate:
- Assessment of urban heat islands
- Detection of thermal anomalies related to volcanic activity and geothermal resources
- Monitoring of snowmelt runoff and glacier behavior
- Collection of data on aerosol optical depth, atmospheric water vapor, and cloud cover
Satellite Payloads
TRISHNA is equipped with two main payloads:
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) Payload: Supplied by CNES, this payload includes a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor that enables high-resolution mapping of surface temperature and emissivity.
- Visible-Near Infra-Red-ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this payload consists of seven spectral bands aimed at detailed mapping of surface reflectance, which is crucial for calculating biophysical and radiation budget variables.
The data retrieved from both payloads will aid in solving surface energy balance equations to estimate heat fluxes.
Operational Details
- TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km, with a scheduled overpass time of 12:30 PM at the equator.
- This orbit will achieve a spatial resolution of 57 meters for land and coastal regions, and 1 km for oceanic and polar areas.
- The mission is expected to have an operational lifespan of five years.
PROJECT 200

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
At the Bengaluru Space Expo 2024, Bengaluru-based start-up Bellatrix Aerospace launched Project 200, a pioneering satellite designed to operate in the Ultra-Low Earth Orbit (ULEO) range of 180 km to 250 km.
Revolutionary Capabilities
Bellatrix Aerospace claims that operating in this orbit dramatically enhances satellite capabilities and redefines their connection to Earth. The satellite's launch is part of a technology demonstration mission, showcasing an innovative propulsion system tailored for this low altitude.
Breakthrough Propulsion Technology
Traditionally, satellites are positioned above 450 km to minimize atmospheric interference. However, deploying at 200 km can significantly enhance capabilities, which has been hindered by propulsion technology limitations until now.
Enhanced Performance Metrics
The new propulsion system allows satellites to maintain their orbits for years, avoiding rapid deorbiting due to atmospheric drag. Key benefits of Project 200 include:
- Reduced Communication Latency: Halves the delay in satellite communication.
- Improved Image Resolution: Enhances clarity threefold.
- Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers overall satellite costs.
Bellatrix's innovative approach not only addresses current limitations but also positions its satellite as a transformative solution for applications in high-resolution Earth observation, telecommunications, and scientific research.
Cabinet approves Chandrayaan-4 mission, first module of Bharatiya Antariksh Station, Venus mission, next-gen launcher

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The PM Modi-led Union Cabinet has approved several ambitious space initiatives, marking a significant leap for India's lunar and space exploration programs.
Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Objective: The fourth lunar mission aims to collect lunar samples, return them safely to Earth, and analyze them.
- Timeline: Expected completion within 36 months post-approval, with a budget of ?2,104 crore.
- Significance: This mission will build foundational technological capabilities for a manned Moon landing planned by 2040.
- Remarks: ISRO Chairman S. Somanath emphasized that the mission's highlight is its low-cost execution and the step-by-step approach to developing the necessary technology.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) and Gaganyaan
- BAS Development: Approval for the first module of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, targeted for launch by 2028, with full completion by 2035.
- Gaganyaan Program: The program’s budget has been revised to ?20,193 crore, with an additional funding of ?11,170 crore to enhance its scope and include precursor missions for BAS.
- Mission Plan: Eight missions are envisaged by 2028, including four under the ongoing Gaganyaan program, development of BAS-1, and four additional missions for technology demonstration and validation.
Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for March 2028, VOM will explore Venus's atmosphere, geology, and generate extensive scientific data.
- Budget: The Cabinet approved ?1,236 crore for VOM, with ?824 crore allocated for the spacecraft.
- Research Focus: The mission will provide insights into Venus's transformation and how different planetary environments evolve.
Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
- Development Approval: A reusable NGLV has been greenlit with a budget of ?8,240 crore.
- Capabilities: The new rocket will have three times the payload lifting capability compared to existing vehicles (10 tonnes to 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit) and will be cost-effective and commercially viable.
- Features: The NGLV will include reusability options and modular green propulsion systems, enhancing India's capacity for satellite launches.
Chamran-1 satellite

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
Iran successfully launched its Chamran-1 research satellite into orbit, utilising the Qaem-100 rocket developed by the paramilitary Revolutionary Guard.
Key Highlights:
- Satellite Details: Chamran-1, a research satellite, was designed and manufactured by Iranian engineers at Iran Electronics Industries (SAIran) in collaboration with the Aerospace Research Institute and private firms. It weighs approximately 60 kilograms.
- Launch Vehicle: The satellite was launched into orbit using the Ghaem-100, Iran's first three-stage solid-fuel space launch vehicle (SLV), developed by the Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Mission Objectives: The primary mission of Chamran-1 is to test hardware and software systems for validating orbital maneuver technology. Additionally, it aims to assess the performance of cold gas propulsion subsystems and evaluate navigation and attitude control subsystems.
- Orbit Details: The satellite was placed into a 550-kilometer (341 miles) orbit above Earth.
What are Intercontinental ballistic missiles?
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are a type of ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometers and are primarily designed to deliver nuclear warheads.
- They can carry conventional, chemical, and biological weapons, although the latter types have rarely been deployed on ICBMs.
- The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are known to possess operational ICBMs, with Pakistan being the only nuclear-armed state that does not have them.
RHUMI-1

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
India recently celebrated the launch of its first reusable hybrid rocket, RHUMI-1, developed by the Tamil Nadu-based start-up Space Zone India in collaboration with the Martin Group. The launch took place on August 24, 2024, from Thiruvidandhai in Chennai. This innovative rocket was propelled into a suborbital trajectory using a mobile launcher, carrying three Cube Satellites and fifty Pico Satellites designed to gather data on global warming and climate change.
Key Features of RHUMI-1:
- Hybrid Propulsion System: RHUMI-1 utilizes a combination of solid and liquid propellants, which enhances efficiency and lowers operational costs.
- Adjustable Launch Angle: The rocket's engine allows for precise trajectory control with adjustable angles ranging from 0 to 120 degrees.
- Electrically Triggered Parachute System: Equipped with an advanced and eco-friendly descent mechanism, this system ensures safe recovery of rocket components, offering both cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits.
- Environmentally Friendly: RHUMI-1 is entirely free of pyrotechnics and TNT, underlining its commitment to sustainability.
Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLVs):
Reusable Launch Vehicles are spacecraft designed to be launched, recovered, and reused multiple times. They offer several advantages:
- Cost Savings: RLVs can be up to 65% cheaper than constructing a new rocket for every launch.
- Reduced Space Debris: By minimizing discarded rocket components, RLVs help reduce space debris.
- Increased Launch Frequency: Shorter turnaround times allow for more frequent use of the rocket.
Unlike traditional multi-stage rockets, where the first stage is discarded after fuel depletion, RLVs recover and reuse the first stage. After separation, the first stage returns to Earth using engines or parachutes for a controlled landing.
Background on Space Zone India and Recent Missions:
Space Zone India is an aero-technology company based in Chennai, focusing on providing cost-effective, long-term solutions in the space industry. They offer hands-on training in aerodynamic principles, satellite technology, drone technology, and rocket technology while raising awareness about careers in the space sector. In 2023, Space Zone India conducted the "Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam Students Satellite Launch Mission," involving over 2,500 students from various schools across India. This mission resulted in the creation of a student satellite launch vehicle capable of carrying a payload of 150 Pico Satellites for research experiments.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the proposal of Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd to setup a semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat, with an investment of Rs 3,300 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The proposed unit, under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), will produce nearly 60 lakh chips per day.
- The chips produced in this unit will cater to a wide variety of applications which include segments such as industrial, automotive, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, telecom and mobile phones, etc.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of developing indigenous semiconductor capabilities.
- As per the reports, India’s semiconductor market is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, positioning the country as a major global semiconductor hub.
- The first indigenously-developed chip is set to arrive in the country by the end of this year.
- In March, PM Modi laid the foundation stone of three semiconductor projects worth Rs 1.25 lakh crore.
- Tata Electronics is setting up a semiconductor fab in Dholera, Gujarat and one semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- CG Power is setting up one semiconductor unit in Sanand. These units will produce lakhs of direct and indirect jobs.
- These four units will bring an investment of almost Rs 1.5 Lakh crore. The cumulative capacity of these units is about 7 crore chips per day, according to the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- The Programme for Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem in India was notified in 2021 with a total outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
About India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- It is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation that aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- ISM has all the administrative and financial powers and is tasked with the responsibility of catalysing the India Semiconductor ecosystem in manufacturing, packaging, and design.
- ISM has an advisory board consisting of some of the leading global experts in the field of semiconductors.
- ISM has been working as a nodal agency for the schemes approved under the Semicon India Programme.
Semicon India Programme:
- Launched in 2021 with a total budget of Rs. 76,000 crore, the ISM is overseen by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), Government of India. This initiative is part of a broad effort to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem within the country.
- The programme is designed to offer financial support to companies involved in semiconductor and display manufacturing and design. It also aims to foster the creation of domestic Intellectual Property (IP), and to promote and incentivize the Transfer of Technologies (ToT).
- Under this programme, four key schemes have been introduced:
- Scheme for establishing Semiconductor Fabs in India.
- Scheme for establishing Display Fabs in India.
- Scheme for setting up Compound Semiconductors/Silicon Photonics/Sensors Fabs and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP)/OSAT facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
Centre gives clearance for ‘Mission Mausam’

- 13 Sep 2024
The Union Cabinet approved 'Mission Mausam,' a groundbreaking initiative with an investment of ?2,000 crore over the next two years. The mission, spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to significantly advance India's capabilities in atmospheric sciences and climate resilience.
Objectives and Key Focus Areas
Mission Mausam is designed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of weather forecasting and climate management through several critical components:
- Advanced Technology Deployment: The mission will focus on deploying next-generation radars and satellite systems equipped with advanced sensors. These technologies are crucial for enhancing weather surveillance and prediction accuracy.
- Research and Development: A key objective of Mission Mausam is to bolster research and development in atmospheric sciences. This will include the development of enhanced Earth system models and advanced weather forecasting techniques.
- GIS-Based Decision Support System: An automated decision support system based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS) will be developed to facilitate real-time data sharing and improve decision-making processes.
Institutional Framework and Implementation
The Ministry of Earth Sciences will oversee the implementation of Mission Mausam. The following institutions will play central roles in the mission:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
- National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting
Additional support will come from other MoES bodies:
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research
- National Institute of Ocean Technology
Sectoral Benefits
Mission Mausam is expected to bring significant improvements across various sectors:
- Agriculture: Enhanced agromet forecasts will aid farmers in optimizing crop management and increasing resilience to climatic variability.
- Disaster Management: Improved monitoring and early warning systems will enhance disaster preparedness and response, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
- Defence: Accurate weather forecasting will support strategic planning and operational efficiency within the defence sector.
- Energy and Water Resources: Better weather predictions will lead to more efficient management of energy and water resources.
- Aviation: Safer aviation will be supported by more reliable weather information, reducing risks and improving travel safety.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism will benefit from accurate weather forecasting, contributing to safer and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Mission Mausam represents a significant investment in India’s ability to manage and mitigate the impacts of climate change and extreme weather events, ultimately aiming to enhance the resilience of communities and support sustainable development.
NEUROMORPHIC COMPUTING
- 14 Sep 2024
Indian Researchers Advance Neuromorphic Computing with Innovative Molecular Film
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have made a groundbreaking development in neuromorphic computing, creating an analog computing system that leverages molecular films. This new system can store and process data across 16,500 different states, a significant leap from conventional binary computing methods.
Understanding Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic computing is an advanced computing paradigm designed to emulate the structure and function of the human brain. By using artificial neurons and synapses, this approach marks a departure from traditional binary computing, enabling systems to learn and adapt from their environments.
How Neuromorphic Computing Works
Neuromorphic computing relies on Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), which consist of millions of artificial neurons similar to those found in the human brain. These neurons communicate through electrical spikes or signals, following the principles of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). This setup allows the system to replicate the brain’s neuro-biological networks, performing tasks such as visual recognition and data interpretation with high efficiency.
Key Features of Neuromorphic Systems
- Brain-Inspired Architecture: Neuromorphic systems mimic the brain's structure, particularly the neocortex, which is involved in higher cognitive functions like sensory perception and motor commands.
- Spiking Neural Networks: These networks use spiking neurons that interact through electrical signals, mirroring the behavior of biological neurons. This design facilitates parallel processing and real-time learning.
- Integrated Memory and Processing: Unlike traditional von Neumann architecture, which separates memory and processing functions, neuromorphic systems combine these functions, leading to improved computational efficiency.
Advantages of Neuromorphic Computing
- Enhanced Efficiency: Neuromorphic computing enables faster problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making compared to conventional systems.
- Revolutionizing AI Hardware: It holds the potential to transform AI hardware, allowing for complex tasks, such as training Large Language Models (LLMs), to be performed on personal devices. This advancement addresses current limitations related to hardware resources and energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency: Current AI tools are confined to data centers due to their high energy demands. Neuromorphic computing could overcome these constraints by providing energy-efficient hardware solutions.
Integration with Molecular Films
Molecular films, ultrathin layers engineered with specific electrical and optical properties, are central to this new advancement. These films act as neuromorphic accelerators, enhancing data storage and processing capabilities. They simulate brain-like parallel processing, improving performance in tasks such as matrix multiplication.
The recent development involves a molecular film that supports 16,500 possible states, a significant advancement over traditional binary systems. This film uses molecular and ionic movements to represent memory states, mapped through precise electrical pulses, creating what can be described as a "molecular diary" of states.
Comparison with Traditional Computing
- Parallel Processing: Neuromorphic computers can handle multiple streams of information simultaneously, unlike traditional computers that process data sequentially.
- Energy Efficiency: These systems consume less power by computing only when relevant events occur, making them suitable for real-time data processing applications.
- Analog vs. Binary: Traditional binary computing operates with bits that are either 0 or 1, akin to a light switch being on or off. In contrast, analog computing involves continuous values, similar to a dimmer switch with varying brightness levels.
This breakthrough by IISc researchers signifies a major step forward in neuromorphic computing, potentially transforming the way we approach data processing and artificial intelligence.
What is Helium & why is it used in rockets?

- 14 Sep 2024
The Crucial Role of Helium in Space Missions and the Challenges It Presents
Two NASA astronauts aboard Boeing’s Starliner will extend their stay on the International Space Station (ISS) due to issues with the spacecraft’s propulsion system, which includes problematic helium leaks. Meanwhile, SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission, which successfully launched on Tuesday, experienced delays due to similar helium-related issues with ground equipment.
The Importance of Helium in Spacecraft
Helium plays a critical role in space missions for several reasons. As an inert gas, it does not react with other substances or combust, which is crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of rocket systems. With an atomic number of 2, helium is the second lightest element after hydrogen. Its lightweight nature is essential for reducing the overall mass of rockets, which in turn minimizes fuel consumption and the need for more powerful (and costly) engines.
A key property of helium is its extremely low boiling point of –268.9 degrees Celsius. This allows it to remain in a gaseous state even in the super-cold environments where many rocket fuels are stored.
How Helium Is Utilized in Spacecraft
In spacecraft, helium is primarily used for:
- Pressurizing Fuel Tanks: Helium ensures that fuel flows smoothly to the rocket’s engines. As fuel and oxidizer are consumed during launch, helium fills the empty space in the tanks, maintaining consistent pressure.
- Cooling Systems: Helium is also used in cooling systems to manage the temperature of various components, preventing overheating and ensuring the proper functioning of the spacecraft.
Due to its non-reactive nature, helium can safely interact with the residual contents of the tanks without causing adverse reactions.
The Challenge of Helium Leaks
Despite its advantages, helium is prone to leakage. Its small atomic size and low molecular weight allow helium atoms to escape through even minor gaps or seals in storage tanks and fuel systems. This characteristic poses a significant challenge for space missions.
On Earth, helium leaks are easier to detect due to the gas’s rarity in the atmosphere. This makes helium a valuable tool for identifying potential faults in rocket or spacecraft fuel systems. The frequency of these leaks across various space missions, including those by ISRO and ESA, underscores a broader industry need for improved valve designs and more precise tightening mechanisms.
OpenAI’s powerful new AI model o1

- 14 Sep 2024
OpenAI Unveils New AI Model: Key Features and Implications
OpenAI has introduced its latest AI model, a significant advancement that aims to elevate the capabilities of artificial intelligence. This new model, part of the enigmatic ‘Project Strawberry,’ is designed to think more like a human when solving complex problems, offering a glimpse into the future of AI reasoning.
Introduction of OpenAI o1
The new OpenAI o1 model marks the beginning of a series of "reasoning" models intended to address intricate tasks in fields such as science, coding, and mathematics. This model, released as part of a preview in both ChatGPT and the API, represents a major leap forward in AI technology. OpenAI has announced that this is just the start, with regular updates and enhancements expected. Additionally, evaluations for the next model update, currently under development, are included in this release.
How It Works
The o1 model is designed to approach queries with a level of careful consideration similar to human problem-solving processes. It learns to tackle problems from various angles, verify its outputs, and improve through feedback. According to OpenAI, this model performs at a level comparable to PhD students in disciplines such as physics, chemistry, and biology. It is particularly adept in mathematics and coding, solving 83% of problems in a challenging math contest— a notable improvement from previous versions that only managed 13%. In coding, it has outperformed 89% of participants.
Sub-Models and Their Features
Alongside the main o1 model, OpenAI has also launched the o1-Mini. This version is a more cost-effective alternative, being 80% cheaper than the o1-preview. The o1-Mini is designed to offer fast and efficient reasoning, particularly beneficial for developers focused on coding tasks.
Implications for Jobs and Research
The advanced problem-solving capabilities of the o1 model are expected to impact various job sectors, particularly those involving routine coding, data analysis, and mathematical modeling. While this could reduce the need for human intervention in some tasks, it may also create new roles in AI safety and maintenance. For researchers, the model offers a powerful tool for accelerating breakthroughs in fields like physics, chemistry, biology, and healthcare. Its ability to generate formulas and analyze large datasets positions it as a valuable asset for advancing scientific research.
Access and Usage
The OpenAI o1 model is now accessible to ChatGPT Plus and Team users. The o1-preview and o1-mini can be selected using the model picker, with weekly message limits set at 30 for o1-preview and 50 for o1-mini. This rollout marks a new era in AI capabilities, showcasing OpenAI’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence.
Key Points to Note
1. Not Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Despite its advanced capabilities, o1-preview is not a step towards AGI, which aims for AI systems to perform cognitive tasks as well as or better than humans. The o1 models, while more adept at reasoning, still fall short of human-level intelligence.
2. Impact on Competition: While o1 gives OpenAI a temporary edge, it is expected to prompt competitors like Google, Meta, and others to accelerate their development of similar advanced models. These companies have the expertise to quickly develop models that could rival or surpass o1's capabilities.
3. Unknowns About Model Operations: Details on how o1 operates remain limited. It combines various AI techniques, including "chain of thought" reasoning and reinforcement learning, but specifics about its training data and internal mechanisms are not fully disclosed.
4. Cost Considerations: Using o1-preview comes at a higher cost compared to previous models. OpenAI charges $15 per million input tokens and $60 per million output tokens for corporate customers, compared to $5 and $15, respectively, for GPT-4o. The model’s complex reasoning requires more tokens, potentially making it more expensive to use.
5. Chain of Thought Transparency: OpenAI has chosen not to reveal the chain of thought process used by o1, citing safety and competitive reasons. This decision may cause issues for enterprise customers who lack visibility into their usage and billing accuracy.
6. New Scaling Laws: OpenAI's o1 models reveal new "scaling laws" suggesting that longer inference times can improve accuracy. This could increase the computing power and costs required to run these models effectively.
7. Potential Risks: o1 models could enable powerful AI agents, but they also present risks. Instances of “reward hacking” and unintended actions suggest that companies must carefully manage these agents to avoid ethical, legal, or financial issues.
8. Safety Assessments: OpenAI reports that o1 is generally safer than previous models, though it still poses a "medium risk" of assisting in biological attacks. This rating has raised concerns among AI safety and national security experts.
9. Concerns About Persuasion and Deceptive Alignment: AI safety experts are wary of o1’s persuasive capabilities and the potential for “deceptive alignment,” where a model might deceive users to achieve hidden goals. These concerns highlight the ongoing challenges in ensuring AI safety and transparency.
Overall, while the o1 models represent a significant leap forward in AI reasoning and problem-solving, they also introduce new complexities and risks that will need to be managed as they become more integrated into various applications.
Polaris Dawn Mission: First Private Spacewalk Attempt

- 11 Sep 2024
Recently, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched from Florida, carrying American billionaire Jared Isaacman and three other astronauts into orbit for the Polaris Dawn mission. This five-day mission marks a milestone as it aims to achieve the world’s first private spacewalk. Polaris Dawn is the inaugural flight of the Polaris Program, a collaborative effort between Isaacman and SpaceX, led by Elon Musk. The program's goal is to develop innovative technologies for future Mars missions.
What is a Spacewalk?
A spacewalk, or “extravehicular activity” (EVA), involves an astronaut conducting activities outside a spacecraft while in space. The concept of a spacewalk dates back to March 18, 1965, when Soviet cosmonaut Alexei Leonov performed the first EVA during the Space Race. Leonov's spacewalk lasted just 10 minutes.
Modern spacewalks typically occur outside the International Space Station (ISS) and can last between five and eight hours. Astronauts conduct spacewalks for various purposes, such as performing scientific experiments, testing new equipment, or repairing satellites and spacecraft.
During a spacewalk, astronauts wear specially designed spacesuits and use safety tethers to prevent floating away into space. These tethers have one end attached to the astronaut and the other secured to the spacecraft. An alternative safety device is the SAFER (Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue), a backpack with small jet thrusters controlled by a joystick, which helps astronauts maneuver in space.
Objectives of the Polaris Dawn Mission
The Polaris Dawn mission, utilizing SpaceX’s Dragon capsule, aims to reach an altitude of approximately 1,400 km from Earth. This altitude exceeds the previous record set by NASA’s Gemini XI mission in 1966, which reached 1,372 km. At this height, the mission will be deep within the Van Allen radiation belts, which start around 1,000 km altitude and are known for their high levels of radiation. The crew will study the effects of spaceflight and radiation on human health.
Following this high-altitude phase, the Dragon capsule will descend to a lower orbit to facilitate the spacewalk scheduled for the third day of the mission, Thursday. During the spacewalk, the capsule will be depressurized, and the hatch will open, exposing the interior to the vacuum of space. Only two crew members, Isaacman and Gillis, will exit the capsule, while Poteet and Menon will remain inside to manage safety tethers and monitor the mission’s status.
The primary objective of the spacewalk is to test SpaceX’s newly developed EVA spacesuits. These suits, designed specifically for this mission, feature built-in cameras and heads-up displays to provide real-time information about the suit's condition. They also incorporate advanced thermal management systems.
After the spacewalk, Isaacman and Gillis will return to the capsule, which will then be repressurized before resuming its mission activities.
Additional Mission Activities
Throughout the mission, the crew will conduct 40 scientific experiments. These include attempting to capture X-ray images using natural space radiation instead of traditional X-ray equipment. The mission will also test SpaceX’s Starlink satellite network for laser-based communication, allowing satellite-to-satellite communication without relying on ground-based infrastructure.
National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing innovations (NIDHI) program
- 08 Sep 2024
- NIDHI is an umbrella programme conceived and developed by the Technology Translation and Innovation (TTI) Division/ National Science and Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board, of Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, for nurturing ideas and innovations (knowledge-based and technology-driven) into successful startups.
- The NIDHI programme works in line with the current national priorities and goals and its focus would be to build an innovation driven entrepreneurial ecosystem with an objective of national development through wealth and job creation.
- NIDHI aims to nurture Startups through scouting, supporting and scaling of innovations by providing them with a series of programme components tailored towards the critical initial phases of the Startup journey.
- The key stakeholders of NIDHI include Science & Technology based entrepreneurs, Startup Incubators, academic and R&D institutions, Startup mentors, financial institutions, angel investors, venture capitalists, relevant government & industry bodies and associations.
- NIDHI has been developed to suit the national aspirations and on the basis of DST’s three-decade long experience in propelling Startup Incubation centres and Science & Technology based entrepreneurs.
- The key components of NIDHI are :-
- NIDHI PRAYAS: Promotion and Acceleration of Young and Aspiring technology entrepreneurs – Support from Idea to Prototype
- NIDHI – EIR: Entrepreneur In Residence – Support system to reduce risk for entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI – TBI : Technology Business Incubator (NIDHI-TBI) – Converting Innovations to start-ups.
- NIDHI – iTBI : Inclusive- Technology Business Incubator – A new variant of the NIDHI-TBI launched in 2022-’23.
- NIDHI – Accelerator : Startup Acceleration Programme – Fast tracking a start-up through focused intervention.
- NIDHI – SSS : Seed Support System – Providing early stage investment
- NIDHI – COE : Centres of Excellence – Globally competitive facilities to help startups go global.
- While NSTEDB is the funding agency, the NIDHI programmes are implemented through Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) available around the country.
- Note: All the NIDHI-Startup funds and offerings are disbursed to eligible startups only through eligible NSTEDB associated incubators across India
Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- 08 Sep 2024
The Government of India has recently introduced several significant initiatives to advance blockchain technology and its applications.
1. Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- Purpose: The Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack is designed to offer Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) with a geographically distributed infrastructure. This stack supports various permissioned blockchain-based applications, enhancing the security and efficiency of digital services.
2. NBFLite
- Description: NBFLite is a lightweight blockchain platform intended as a sandbox for startups and academic institutions. It allows for rapid prototyping, research, and capacity building, fostering innovation in blockchain applications.
3. Praamaanik
- Purpose: Praamaanik is a blockchain-enabled solution for verifying the origin of mobile apps. This ensures that users can trust the source of their applications, contributing to enhanced digital security.
4. National Blockchain Portal
- Function: The National Blockchain Portal serves as a central hub for accessing blockchain technologies and services developed under the National Blockchain Framework (NBF).
5. National Blockchain Framework (NBF)
- Overview: The NBF is designed to promote secure, transparent, and trusted digital service delivery. It includes:
- Distributed Infrastructure: Hosted across NIC Data Centers in Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Hyderabad.
- Core Framework Functionality: Provides the backbone for various blockchain applications.
- Smart Contracts & API Gateway: Facilitates interactions with blockchain-based systems.
- Security, Privacy & Interoperability: Ensures robust security and privacy while supporting integration with other systems.
- Applications Development: Supports the creation and deployment of blockchain applications.
- Goals: The NBF aims to address challenges such as the need for skilled manpower, vendor lock-in, and issues related to security, interoperability, and performance.
6. Strategic Objectives
- Digital Trust and Service Delivery: The framework is part of the government's effort to create trusted digital platforms and improve service delivery to citizens.
- Global Leadership: The initiative seeks to position India as a global leader in blockchain technology, driving economic growth, social development, and digital empowerment.
- Governance Transformation: Blockchain technology is envisioned to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability in public services.
7. Collaborative Efforts
- Development: The technologies have been developed through the collaborative efforts of organizations including C-DAC, NIC, IDRBT Hyderabad, IIT Hyderabad, IIIT Hyderabad, and SETS Chennai, with support from MeitY.
- Research and Patents: The NBF project has already resulted in several patents and research publications, reflecting its innovative and research-driven approach.
8. Future Directions
- Scaling Applications: There is an emphasis on scaling blockchain applications across various states and departments.
- Exploring New Innovations: Efforts will continue to onboard new applications and innovative components on the NBF stack.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
Maillard Reaction

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maillard Reaction elucidates the intricate chemical processes responsible for the diverse array of flavours, aromas, and textures found in foods.
What is Maillard's Reaction?
- The Maillard reaction is a complex chain of chemical reactions that occurs when heat is exposed to amino acids and reducing sugars.
- The Maillard Reaction, named after the French scientist Louis-Camille Maillard, is a chemical phenomenon observed when amino acids, essential components of proteins, and sugars undergo heating.
- This reaction influences the taste, scent, and consistency of food items.
- It characterizes a non-enzymatic browning process in food, where colour alterations manifest without the involvement of enzymes.
How does the Maillard Reaction Induce Browning in Food?
- The Maillard reaction initiates a complex chemical process that yields various products. Chemist J.E. Hodge first delineated its steps in 1953 to simplify its understanding.
- An array of foods, from meats to bread to vegetables and coffee beans, contain both sugars and protein components.
- When subjected to heat, these sugars and proteins undergo a condensation reaction, forming an unstable compound known as Schiff base.
- This Schiff base undergoes rearrangement and dehydration, yielding diverse intermediate compounds.
- These intermediates further react to generate essential flavour components, enriching the food's aroma.
- Some intermediates undergo rearrangement, resulting in a more stable product. These products serve as vital precursors to melanoidins, pivotal in imparting the food's characteristic brown hue.
- Continued transformation, including condensation and polymerization, culminates in the formation of melanoidins—nitrogen-containing compounds responsible for the food's distinctive brown colouration.
What are the Factors Affecting the Reaction?
- The pace and magnitude of the Maillard reaction hinge on various elements, including temperature, acidity, moisture levels, and the composition of proteins and sugars in the food.
- Optimal Temperature: Temperatures typically fall within the range of 110 to 170 degrees Celsius, with levels surpassing this threshold potentially resulting in food burning and imparting bitter flavours.
- Elevated temperatures generally expedite the reaction, whereas acidic environments and moisture content can impede it.
- Hence, foods tend to brown more rapidly at higher temperatures, and dry items like bread crusts often acquire a rich brown hue during baking.
A first in 100 years, the Indian Science Congress was postponed amid a tussle between organisers, Govt (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Science Congress, the largest gathering of scientists and students of science in the country and a permanent annual fixture in the calendar of the participant group for more than a century has been postponed.
Postponement of the Indian Science Congress:
- Unprecedented Interruption: The postponement of the Indian Science Congress holds unprecedented significance.
- Since its inception in 1914, the Congress has been an annual event, except for the years immediately following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022).
- Tradition and Prime Ministerial Engagement: A cornerstone of scientific tradition, the Indian Science Congress is inaugurated by the Prime Minister, making it a fixture on the PM's calendar.
- Typically, it stands as the Prime Minister's first public engagement of the new year.
Why has the Science Congress Been Postponed This Year?
- This year's postponement stems from a protracted dispute between the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), the organizing body, and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) within the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The DST, a key funding entity, withdrew support in September 2023, citing financial irregularities.
- The ISCA refuted the allegations and contested the DST's directive prohibiting government funds for Science Congress-related expenses, leading to an impasse that has resulted in the postponement.
- A legal challenge to the DST's decision is currently pending.
What is the Indian Science Congress (ISC)?
- The Indian Science Congress (ISC) is a unique event in the country that serves as a platform for scientific communities to interact with students and the general public on science-related matters.
- Organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), an independent body supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government, the Science Congress is an annual five-day event from January 3 to 7, considered a permanent fixture on the Prime Minister’s calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
- In recent years, the Indian Science Congress (ISC) has faced criticism due to issues such as a lack of substantial discussions, the promotion of pseudoscience, and outlandish claims by certain speakers.
- This has led to concerns among prominent scientists, with some advocating for the discontinuation of the event or, at the very least, the withdrawal of government support.
- While the government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, it does not play a direct role in its organization.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
Pontus Tectonic Plate: Geologist Unexpectedly Finds Remnants of a Lost Mega-Plate (Science Daily)
- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Geologists have reconstructed a massive and previously unknown tectonic plate that was once one-quarter the size of the Pacific Ocean.
About Pontus Tectonic Plate:
- Recently discovered in the west Pacific Ocean, the Pontus Tectonic Plate is a long-lost geological plate that holds significance in Earth's history.
- Believed to have measured about 15 million square miles at its zenith, roughly equivalent to one-quarter of the Pacific Ocean, this massive tectonic plate dates back as far as 160 million years, with more recent traces extending to approximately 20 million years ago.
- Over millions of years, the Pontus Plate underwent a gradual subduction process, pulled downward beneath a neighbouring plate by the force of gravity.
How was this Discovery Made?
- The subducting process involves the plate sinking into Earth's mantle due to its higher density compared to the surrounding mantle.
- Traces of a subducted plate are discernible in the form of rock fragments concealed in mountain belts.
- During subduction, upper portions of the plate are occasionally scraped off.
- Researchers employed geological data and computer modelling to reconstruct the movements of current plates, revealing a substantial area potentially vacated by the subducted Pontus Plate.
- Utilizing magnetic techniques, scientists identified basalt remnants in Borneo as Pontus relics, suggesting that this fragmentary evidence was left behind during the plate's subduction some 85 million years ago.
What is Plate Tectonics?
- Tectonic plates are large, rigid pieces of Earth's lithosphere, the outer shell comprising the crust and uppermost part of the mantle.
- These plates, which vary in size and shape, constantly move and interact, shaping the Earth's dynamic surface.
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several major plates, such as the Pacific, North American, and Eurasian plates, among others.
- The interactions at plate boundaries result in various geological phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Plate tectonics, the theory explaining these movements, underscores how heat-driven convective currents in the Earth's mantle cause plates to diverge, converge, or slide past each other.
- Tectonic plate movements influence the planet's topography, seismic activity, and the distribution of continents and oceans, playing a fundamental role in Earth's geological evolution.
India International Science Festival (PIB)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 9th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023 will be held at Faridabad, Haryana from January 17th-20th, 2024.
About the India International Science Festival (IISF):
- The India International Science Festival (IISF) is an annual science festival organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Earth Science, and Vijnana Bharati in India.
- The festival aims to promote science and technology in India and to showcase the latest advancements in these fields.
- The IISF has been held every year since 2007.
- The festival typically lasts for four days and features a variety of events, including exhibitions, seminars, workshops, and competitions.
- The exhibitions feature displays of scientific and technological innovations from India and around the world.
- The seminars and workshops provide opportunities for scientists and technologists to share their knowledge with the public.
- The competitions encourage students to participate in science and technology.
- The IISF is a major event in the Indian scientific community and has been praised for its role in promoting science education and public awareness of science.
- The festival has also been successful in attracting international participation, with scientists and technologists from around the world attending the event.
- The 2022 IISF was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, from January 21 to 24.
India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023:
- It will be held at the Campus of Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) and Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB) of the Department of Biotechnology in Faridabad.
- Theme: 'Science and Technology Public Outreach in Amrit Kaal'.
- IISF 2023 will have a total of 17 themes to showcase scientific achievements, offering diverse benefits to participants and the general public.
Mines Ministry to Launch National Geoscience Data Repository Portal To Foster Innovation in Exploration (PIB)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines is to launch the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) Portal on 19th December 2023 in a ceremony in New Delhi.
What is the National Geoscience Data Repository Portal?
- This extensive online platform facilitates the retrieval, exchange, and examination of geospatial information nationwide.
- Spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), the NGDR initiative marks a notable advancement in democratizing crucial geoscience data.
- It empowers stakeholders in various industries and academia by providing unparalleled access to invaluable resources.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) originated in 1851 with the primary objective of identifying coal deposits for the Railways.
- Since its inception, GSI has transformed into a repository of geo-scientific information, achieving international recognition for its contributions.
- The organization is dedicated to creating and updating national geoscientific data, conducting mineral resource assessments, and providing impartial geological expertise crucial for policy decisions, commercial ventures, and socio-economic needs.
- GSI focuses on comprehensive documentation of geological processes, employing state-of-the-art techniques in geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys.
- As an attached office of the Ministry of Mines, GSI operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, with six regional offices in Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong, and Kolkata, along with state unit offices across India.
About BISAG (N):
- Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) operates as an Autonomous Scientific Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, falling under the MeitY, Government of India.
- Its multifaceted mission encompasses technology development and management, research and development, fostering national and international collaboration, capacity building, and facilitating technology transfer and entrepreneurship development in the realm of geospatial technology.
- BISAG-N has played a pivotal role in implementing GIS and geospatial technologies for major ministries and nearly all states, integrating diverse technological domains such as geo-spatial science, information science systems, and mathematics science systems.
- The institute operates as a state agency under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of Gujarat, situated in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Euclid Mission (NASA)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Euclid mission, which will investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, released its first five science images recently.
About Euclid Mission:
- Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by European Space Agency (ESA), with contributions from NASA.
- Euclid is designed to give important new insights into the "dark side" of the universe -- namely dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
- It was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, (USA) on 1 July 2023 and the launch vehicle used was ‘SpaceX Falcon 9’.
- The mission derives its name from Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician from around 300 BC, who laid the foundations of geometry.
- Euclid Mission Objective: The primary goal of the Euclid mission is to create a three-dimensional map of the universe, with time as the third dimension.
- This will be achieved by observing billions of galaxies, extending up to 10 billion light-years away, and covering over a third of the celestial sphere.
- Euclid will explore how the Universe has expanded and how structure has formed over cosmic history, revealing more about the role of gravity and the nature of dark energy and dark matter.
- The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2,000 scientists from 300 institutes in 13 European countries, the U.S., Canada, and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis.
- NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP.
- Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
