Deepavali inscribed on UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage List

- 14 Dec 2025
In News:
Deepavali (Diwali) has been officially inscribed on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO during the 20th Session of the Intergovernmental Committee held in New Delhi. It becomes the 16th Indian element on the list.
About Deepavali
- Also known as Diwali, meaning “row of lights”
- Celebrated on Kartik Amavasya (October–November)
- A multi-regional, multi-faith festival symbolising light over darkness, renewal, hope and harmony
- Observed across India and the global diaspora
Cultural and Mythological Significance
Deepavali is associated with multiple traditions across regions:
- Return of Lord Rama to Ayodhya after exile
- Victory of Lord Krishna over Narakasura (Naraka Chaturdashi)
- Worship of Goddess Lakshmi for prosperity
- Mahavira’s Nirvana for Jains
- Kali Puja in eastern India
- Govardhan Puja linked to Krishna traditions
- King Bali’s return celebrated in parts of western India
These diverse narratives reflect India’s cultural pluralism.
Key Features as Living Heritage
- Social practices: Lighting diyas, rangoli, rituals, gift exchange, sweets, community feasts
- Five-day celebration: Dhanteras - Naraka Chaturdashi - Lakshmi Puja - Govardhan/Bali Pratipada - Bhai Dooj
- Livelihood linkages: Potters, artisans, sweet-makers, florists, farmers, jewellers, textile workers benefit economically
- Diaspora dimension: Celebrated across Southeast Asia, Africa, Europe, Gulf countries, Caribbean
- Values embodied: Inclusivity, unity, generosity, wellbeing, moral ideal of “Tamso Ma Jyotirgamaya” (darkness to light)
Environmental & Social Dimensions
- Promotion of eco-friendly celebrations (e.g., green crackers)
- Cleaning rituals reinforce hygiene and wellbeing
- Strengthens family bonds and community cohesion
- Supports charity, food distribution, and care for vulnerable groups
About Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH)
Definition: ICH includes living traditions, rituals, performing arts, craftsmanship, oral traditions, and knowledge systems that communities recognise as part of their cultural identity.
UNESCO Framework
- Governed by the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Came into force in 2006
- India ratified in 2005
Five Domains of ICH
- Oral traditions & expressions
- Performing arts
- Social practices, rituals & festivals
- Knowledge concerning nature & the universe
- Traditional craftsmanship
Representative List
Highlights cultural practices that showcase humanity’s diversity and encourage dialogue.
Exercise MILAN
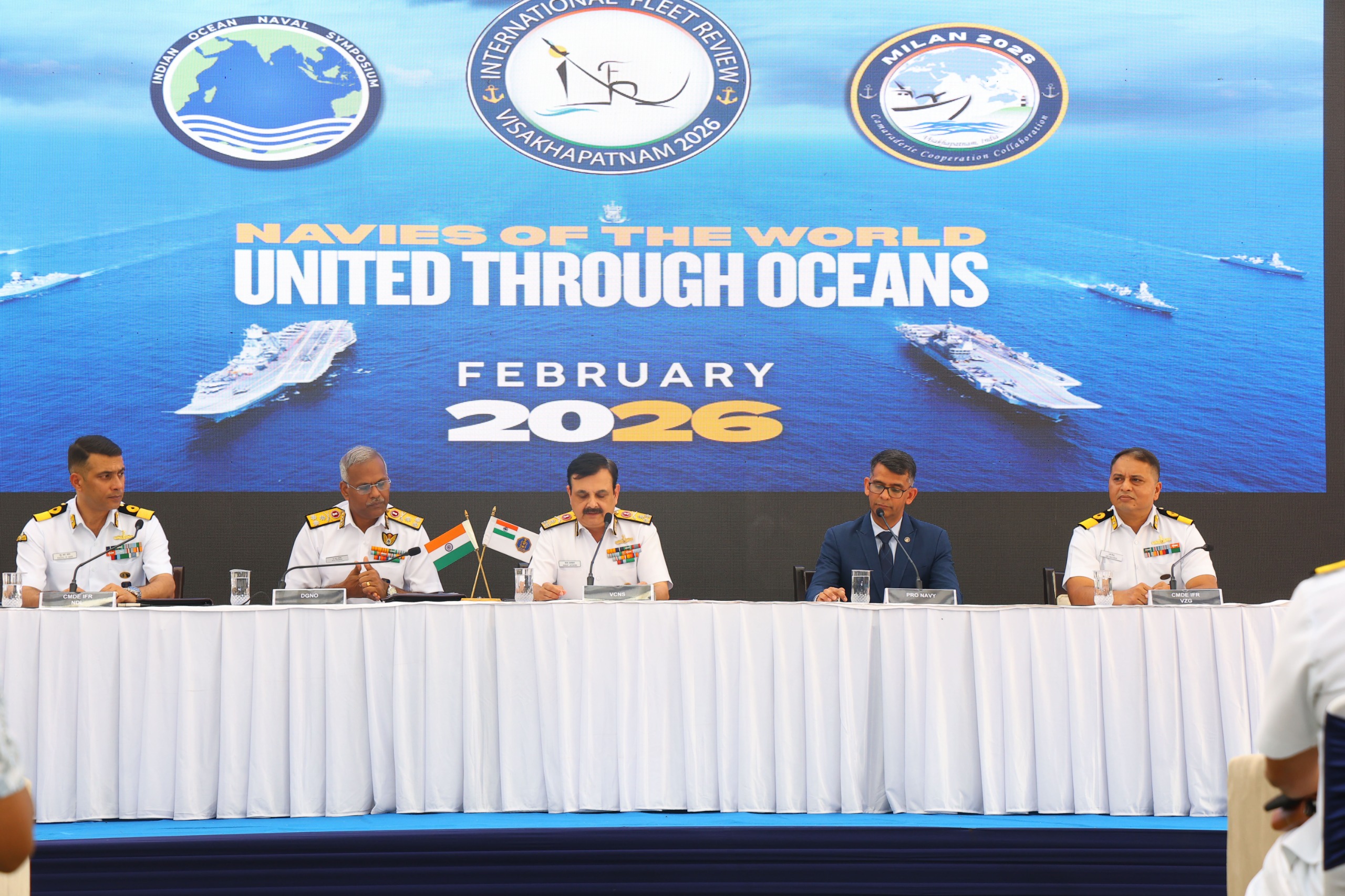

- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
India will host a historic maritime convergence from 15–25 February 2026 at Visakhapatnam, featuring three major international naval events conducted simultaneously for the first time:
- International Fleet Review (IFR) 2026
- Exercise MILAN 2026
- IONS Conclave of Chiefs (2025–27 Chairmanship)
The event operationalises the MAHASAGAR vision (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions), announced in 2025, extending India's SAGAR doctrine from the Indian Ocean to wider maritime regions.
About Exercise MILAN
Background
- Biennial multilateral naval exercise launched in 1995 at Port Blair.
- Started with four participants — Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka & Thailand.
- Has evolved into India’s largest naval exercise, reflecting the Act East Policy and SAGAR/MAHASAGAR frameworks.
Objectives
- Strengthen interoperability, maritime domain awareness, and naval diplomacy.
- Promote cooperation on maritime security, HADR, and regional stability.
MILAN 2026 Features
- Dual-phase format:
- Harbour Phase: Briefings, professional exchanges, cultural events.
- Sea Phase:
- Anti-submarine warfare (ASW)
- Air defence drills
- Search and rescue (SAR)
- Maritime domain awareness operations
- International City Parade at RK Beach with contingents from:
- Participating navies
- Indian Army & Indian Air Force
International Fleet Review (IFR) 2026
- A Presidential Fleet Review at sea showcasing India’s indigenous naval platforms, including:
- INS Vikrant (India’s first indigenously built aircraft carrier)
- Visakhapatnam-class destroyers
- Nilgiri-class stealth frigates
- Arnala-class ASW corvettes
- Participation expected from navies across the globe, alongside ships from:
- Indian Navy
- Indian Coast Guard
- Merchant Marine
- Demonstrates India’s transformation into a “Builder’s Navy”.
IONS Conclave of Chiefs (2026)
Overview
- Platform under the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) for promoting:
- Maritime cooperation
- Information sharing
- HADR coordination
- Regional security
- India will hold the IONS Chairmanship (2025–27) for the second time.
The Conclave will deliberate on maritime security, operational synergy, and emerging threats.
MAHASAGAR Vision
- Announced in 2025.
- Expands the earlier SAGAR doctrine to emphasise:
- Sustainability
- Collective regional responsibility
- Secure, open and inclusive maritime commons
- Supports India’s role as a Preferred Security Partner in the Indo-Pacific and beyond.
Significance of the 2026 Maritime Convergence
- First time India is hosting IFR, MILAN & IONS together.
- Strengthens India’s position as a responsible maritime power.
- Enhances India's role in Indo-Pacific cooperation through frameworks such as:
- Act East Policy
- MAHASAGAR
- SAGAR
- Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)
- IONS
- Showcases India’s indigenous shipbuilding capacity and India’s Navy as a driver of regional security architecture.
- Expected to generate significant economic benefits for Visakhapatnam through tourism and services.
National Narcotics Helpline MANAS
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India launched the National Narcotics Helpline MANAS (Madak-PadarthNishedAsoochna Kendra) to strengthen citizen participation in the fight against the drug menace. The initiative, spearheaded by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), functions as a secure, bilingual, and citizen-centric platform to enable anonymous reporting of drug trafficking, illicit cultivation, and related crimes, while also providing counselling and rehabilitation support.
Key Features of MANAS
- Helpline Number: 1933 (Toll-Free)
- Digital Access: Web portal (www.ncbmanas.gov.in), Email (info.ncbmanas@gov.in), and UMANG Mobile App
- Integration: Direct transfer to the MoSJE De-addiction Helpline (14446) for rehabilitation guidance
- Awareness Outreach: Posters, videos, contests, and citizen engagement through MyGov platform under the Drug-Free Bharat campaign
India’s Legal & Policy Framework Against Drug Abuse
- Constitutional Backing: Article 47 directs the State to prohibit intoxicating substances except for medicinal purposes.
- Legislation:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985
- Prevention of Illicit Traffic in NDPS Act, 1988
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
- International Conventions: India is party to the
- Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (amended 1972)
- Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988
- Other Initiatives: NIDAAN Portal (for drug law offenders), NashaMukt Bharat Abhiyan (community-based de-addiction programme).
Significance for Governance & Society
The MANAS helpline marks a shift from enforcement-centric approaches to a citizen-participatory, tech-enabled model. It bridges law enforcement, rehabilitation, and public awareness, reflecting India’s commitment to a balanced supply and demand reduction strategy against narcotics.
India’s Joint Doctrines on Cyberspace and Amphibious Operations

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
Recently, the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan released thedeclassified versions of India’s Joint Doctrines for Cyberspace Operations and Amphibious Operations. This step reflects India’s effort to enhance jointness, interoperability, and transparency in military operations while strengthening preparedness for multi-domain warfare.
Cyberspace Operations Doctrine
What is Cyberspace?
- A global domain comprising information systems, communication networks, satellites, and data infrastructures.
- It is borderless, dual-use (civilian and military), and subject to rapidly evolving threats.
Components of Cyberspace Operations
- Defensive Cyber Operations – Protects national and military networks against malware, hacking, and data breaches.
- Offensive Cyber Operations – Targets adversary systems to disrupt communications, disable command networks, or damage infrastructure.
- Cyber Intelligence & Reconnaissance – Collects and analyses data to detect vulnerabilities and anticipate attacks.
- Cyber Support Operations – Provides digital tools and assistance to land, maritime, air, and space operations.
- Resilience & Recovery – Ensures continuity through backup systems, redundancies, and rapid restoration measures.
Operational Principles
- Threat-informed Planning – Based on real-time intelligence.
- Interoperability – Seamless coordination across the three Services and with civil agencies.
- Layered Defence – Multi-tiered cyber security protocols.
- Legal & Ethical Compliance – Operates within Indian law and global cyber norms.
- Real-time Response – Swift counteraction to minimise damage.
Significance:
- Shields critical infrastructure (power grids, defence networks, communication systems).
- Acts as a force multiplier, enhancing conventional operations.
- Prepares India for hybrid warfare, where cyber, land, sea, and air threats are interlinked.
Amphibious Operations Doctrine
What are Amphibious Operations?
- Coordinated actions by naval, air, and land forces launched from the sea to secure objectives onshore.
- Applications range from combat missions to humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR).
Key Features
- Tri-service Integration – Combines maritime, aerial, and ground assets.
- Rapid Response – Enables swift deployment from sea to shore.
- Strategic Reach – Expands influence over island territories and littoral regions.
- Flexible Missions – Suitable for both warfare and non-war operations (e.g., disaster relief).
- Maritime–Land Linkage – Strengthens the sea–land operational continuum.
Significance:
- Enhances maritime superiority in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Secures India’s island territories, trade routes, and coastal areas.
- Strengthens India’s blue-water navy aspirations and capacity for overseas contingencies.
- Provides options for HADR missions, vital in the Indo-Pacific where natural disasters are frequent.
Strategic Importance of Doctrines
The release of these doctrines marks a major step in joint military planning and multi-domain operations. They:
- Promote synergy among the Army, Navy, and Air Force, reducing duplication of efforts.
- Build resilience against hybrid threats, including cyber-attacks and maritime conflicts.
- Signal India’s intent to safeguard its national security and global strategic interests.
- Provide policymakers and military planners with a common framework and lexicon.
Further, the CDS has initiated work on new doctrines covering Military Space Operations, Special Forces Operations, Airborne/Heliborne Operations, Integrated Logistics, and Multi-Domain Operations. These will ensure India remains prepared for the emerging spectrum of modern warfare.
Notary Portal

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the Notary Portal, a dedicated digital platform designed to modernize services under the Notaries Act, 1952 and the Notaries Rules, 1956. The initiative, led by the Ministry of Law and Justice, aims to create a faceless, paperless, transparent, and efficient system for notarial services.
Key Features
- Online Interface: Connects notaries appointed by the Central Government with the Ministry for seamless service delivery.
- Services Offered:
- Submission of applications for appointment as notaries.
- Verification of eligibility for appointment.
- Issuance of digitally signed Certificates of Practice.
- Renewal of certificates, change of practice area, and submission of annual returns.
- Current Status: Modules for verification of documents, eligibility checks, and issuance of digitally signed certificates are operational.
Significance
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in legal certification processes.
- Reduces paperwork, delays, and physical interface, thereby minimizing scope for corruption.
- Aligns with the government’s broader agenda of Digital India and modernization of legal services.
SheLeadsProgramme

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Minister for Women and Child Development, inaugurated the second edition of UN Women’s flagship capacity-building programme — SheLeads II: Workshop for Women Leaders in New Delhi (August 2025). The initiative seeks to strengthen women’s political leadership, a crucial step towards women-led development and the vision of a Viksit Bharat.
Key Highlights:
- The workshop comes in the backdrop of the Women’s Reservation Act, 2023, mandating 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Despite this landmark reform, only 14% of seats in the 18th Lok Sabha are currently occupied by women, highlighting the urgent need for leadership training and political empowerment.
About SheLeadsProgramme
- Flagship Initiative: Launched by the UN Women India Country Office.
- Aim: Advance gender equality in public and political leadership, equipping women with skills, confidence, and networks to contest elections and participate effectively in governance.
- Scope: Supports women leaders in shaping policies, governance structures, and electoral narratives that reflect the aspirations of all citizens.
- Participation: In 2025, over 260 applications from 22 states were received; 36 participants were selected for the two-day workshop.
- Engagement: Interactive sessions with MPs, policy experts, and media strategists on electoral campaigning, governance, narrative building, and media engagement.
About UN Women
- Established in 2010 by the UN General Assembly, consolidating resources and mandates under one entity.
- Mandate:
- Support intergovernmental bodies (e.g., Commission on the Status of Women) in framing global standards.
- Assist member states in implementing gender equality commitments through technical and financial support.
- Partner with civil society to advance women’s rights and empowerment.
‘Matri Van’ initiative
- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the ‘Matri Van’ initiative in Gurugram under the ‘Ek Ped MaaKe Naam’ programme, symbolizing ecological preservation and community participation. The project was inaugurated by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Shri Bhupender Yadav, and the Union Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs and Power, Shri Manohar Lal, during Van Mahotsav 2025.
About the Initiative
- Location & Scale: Spread over 750 acres in the Aravalli hill area along the Gurugram-Faridabad road.
- Concept: A theme-based urban forest aimed at nurturing generations through mother-nature-inspired green efforts.
- Vision: To enhance biodiversity, public well-being, and urban sustainability, while serving as the “heart and lung of Delhi-NCR.”
- Collaboration: Developed through multi-stakeholder participation, including CSR partners, Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs), NGOs, MNCs, school children, and government bodies.
Ecological and Social Significance
- Restoration of degraded land by removing invasive Kabuli Kikar (Prosopis juliflora).
- Plantation of native Aravalli species such as Dhak, Amaltash, Neem, Bargad, Peepal, Gullar, Pilkhan, Khair, Semal, and bamboo.
- Development of theme-based groves, including:
- Bodhi Vatika (sacred fig species like Bargad, Peepal),
- Bamboosetum (bamboo species),
- Aravalli Arboretum,
- PushpVatika (flowering trees),
- Sugandh Vatika (fragrant species),
- Medicinal Plants Vatika,
- Nakshatra and RashiVatika,
- Cactus Garden,
- Butterfly Garden.
Facilities and Infrastructure
- Eco-tourism and community spaces: nature trails, cycle tracks, yoga zones, gazebos, and sitting areas.
- Environmental safeguards: treated water irrigation systems, sprinklers, and waterbodies to aid water conservation and urban flood prevention.
- Urban amenities: parking spaces, public facilities, and accessibility features.
Broader Environmental Vision
- Linked to Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) with components like:
- Saving food, water, and energy,
- Solid waste and e-waste management,
- Ban on single-use plastics,
- Promotion of healthy lifestyles.
- Complements India’s renewable energy transition, with non-fossil fuel power now accounting for over 50% of the national energy mix.
- Supports Prime Minister’s vision of rejuvenating the Aravalli ecosystem through plantation of native species.
Significance for Delhi-NCR
- Acts as a natural carbon sink to counter rising emissions.
- Provides a green lung to improve air quality in a highly polluted urban region.
- Promotes eco-tourism and environmental education through biodiversity parks, wildlife safaris, and thematic groves.
- Offers citizens a serene, stress-free environment, strengthening the image of Gurugram as a model “Millennium City.”
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), established in 2016 under the Companies Act, 2013, functions under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) with the mandate of safeguarding investor interests, refunding unclaimed financial assets, and promoting financial literacy across India.
Mandate and Fund Structure
The Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF) consists of amounts that remain unclaimed for seven years, including:
- Unpaid dividends,
- Application money due for refund,
- Matured deposits and debentures,
- Accrued interest on investments,
- Grants and donations received from government or other entities.
The fund is utilized to refund unclaimed shares/dividends to rightful investors and to spread financial awareness among citizens.
Recent Developments: Integrated Portal
IEPFA is in the final phase of testing its Integrated Portal, a unified digital platform aimed at:
- Streamlining claim processes for unclaimed shares/dividends,
- Enhancing accessibility for both investors and companies,
- Integrating stakeholders such as depositories and the Public Financial Management System (PFMS).
Companies have been urged to upload their IEPF-1/7 SRNs with prescribed templates to enable smooth data verification and claim processing.
Key Features of the New System
- Simplified claims for low-value refunds through reduced documentation.
- Integrated Call Center to strengthen grievance redressal and ensure responsive communication with stakeholders.
- Temporary disruptions may occur during transition, but the reforms promise faster, transparent, and investor-friendly outcomes.
Investor Awareness Initiatives
IEPFA also undertakes extensive financial literacy campaigns through programs like:
- Niveshak Didi,
- Niveshak Panchayat,
- NiveshakShivir.
These initiatives empower citizens, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, to make informed financial decisions and protect themselves from fraud and mismanagement.
Significance
- For Investors: Easier access to unclaimed assets and improved grievance redressal.
- For Companies: Structured compliance framework and digital integration with regulators.
- For Governance: Strengthens India’s financial ecosystem by combining investor protection with financial literacy.
A New Approach to Treating Liver Cirrhosis
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
A team of Indian scientists may have found a way to improve the drainage capacity of lymphatic vessels in the liver and intestine that fails in case of cirrhosis, by using nanocarriers filled with a powerful protein called VEGF-C.
Understanding Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of chronic liver disease where healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue due to prolonged inflammation. This structural distortion affects both blood and lymphatic vessels in the liver and intestine, impairing circulation and fluid balance.
Causes:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steato-Hepatitis)
- Chronic viral infections such as Hepatitis B and C
Symptoms (often in advanced stages): extreme fatigue, loss of appetite, easy bruising or bleeding, swelling in legs/ankles (edema), and abdominal fluid accumulation (ascites).
The Problem of Lymphatic Dysfunction
In cirrhosis, lymphatic vessels (mesenteric lymphatic vessels or mLVs) become dilated and dysfunctional. Normally, these vessels drain interstitial fluid, proteins, and immune cells back into venous blood.
- In cirrhosis, lymph production increases nearly 30-fold due to portal hypertension and liver congestion.
- Dysfunctional lymph flow leads to ascites (abdominal fluid buildup), one of the most serious complications of decompensated cirrhosis.
- Currently, there is no effective therapy to correct this lymphatic dysfunction.
The VEGF-C Based Breakthrough
A joint team from the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi and the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), Guwahati has developed a novel therapy using Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C (VEGF-C).
- Role of VEGF-C: A key pro-lymphangiogenic factor that binds to VEGFR-3 receptors, stimulating the growth of new lymphatic vessels and enhancing drainage.
- Challenge: VEGF-C has a short half-life, is hydrophilic, and can cause systemic side effects.
The Innovation: Nanocarriers
- Scientists at NIPER designed reverse micelle-based nanocarriers to encapsulate VEGF-C, ensuring targeted delivery to gut lymphatic vessels.
- These nanocarriers specifically bind to VEGFR-3 homodimers, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- The formulation was delivered orally in animal models, ensuring uptake by intestinal lymphatic vessels.
Findings (Animal Studies)
- Significant increase in mesenteric lymph drainage
- Reduction in ascites and portal hypertension
- Enhanced cytotoxic T-cell immunity in lymph nodes
- Reduction in local and systemic bacterial load
Significance and Future Prospects
- This is the first study to demonstrate that therapeutic lymphangiogenesis using VEGF-C can reconstruct fragmented lymphatic networks and restore function in advanced cirrhosis.
- Funded by the DST Nano Mission and published in JHEP Reports, it marks a major step in translational medicine.
- Next steps: Preclinical studies in larger animals, followed by human clinical trials to establish safety, dosage, and efficacy.
Piprahwa Relics

- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
The recent return of the sacred Piprahwa relics of Lord Buddha to India marks a landmark moment in India’s cultural diplomacy, heritage preservation, and spiritual history. Orchestrated by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Godrej Industries Group, this event prevented the relics’ auction in Hong Kong (May 2025) and instead restored them to their rightful home. For India, the land where the Buddha attained enlightenment and preached, this repatriation is more than a matter of archaeology—it reaffirms India’s role as the civilizational custodian of global heritage.
What are the Piprahwa Relics?
- Association: Believed to be the mortal remains of Lord Buddha, enshrined by the Sakya clan (his kinsmen) in the 3rd century BCE.
- Discovery: Excavated in 1898 by William Claxton Peppé, a British civil engineer and estate manager, from a stupa at Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, located just south of Lumbini (Buddha’s birthplace, now in Nepal).
- Contents:
- Bone fragments of the Buddha
- Caskets: soapstone, crystal, and sandstone coffer
- Offerings: gold ornaments, gemstones, and other ritual objects
- Inscription: A Brahmi script engraving on one of the caskets confirmed the relics’ identity, noting they were deposited by the Sakya clan.
Historical Journey of the Relics
- Colonial Appropriation (1898–1899)
- Following their discovery, the British Crown claimed the artefacts under the Indian Treasure Trove Act, 1878.
- The bone and ash relics were gifted to King Chulalongkorn of Siam (Thailand), reflecting colonial practices of cultural transfer.
- The majority of the remaining relics were placed in the Indian Museum, Kolkata (1899).
- Legal Protection
- Classified as ‘AA’ antiquities under Indian law, these relics cannot be sold, exported, or removed—underscoring their sacred and national significance.
- Attempted Auction in 2025
- The relics resurfaced in Hong Kong for an intended auction.
- Through timely diplomatic and legal intervention, supported by public-private partnership with the Godrej Group, the Ministry of Culture secured their return.
Significance of the Repatriation
1. Spiritual and Cultural Significance
- Buddhism, which spread from India across Asia, regards relics of the Buddha as sacred embodiments of peace, compassion, and enlightenment.
- The return reaffirms India as the spiritual homeland of Buddhism, strengthening cultural linkages with Buddhist-majority nations like Thailand, Myanmar, Japan, and Sri Lanka.
2. Archaeological and Historical Importance
- Piprahwa is one of the earliest archaeologically verified stupa sites.
- The discovery provides rare material evidence of Buddhist practices of relic veneration, confirming textual accounts in Buddhist scriptures.
3. Diplomatic and Soft Power Dimensions
- The move highlights cultural diplomacy as a tool of India’s foreign policy.
- India positions itself as a global guardian of Buddhist heritage, enhancing ties with Southeast Asian nations where Buddhism is deeply rooted.
4. Model of Public–Private Partnership
- The collaboration between the Government of India and the Godrej Industries Group sets a precedent for safeguarding heritage.
- It reflects how corporate social responsibility (CSR) can extend beyond business to civilizational legacy.
SIMBEX-25
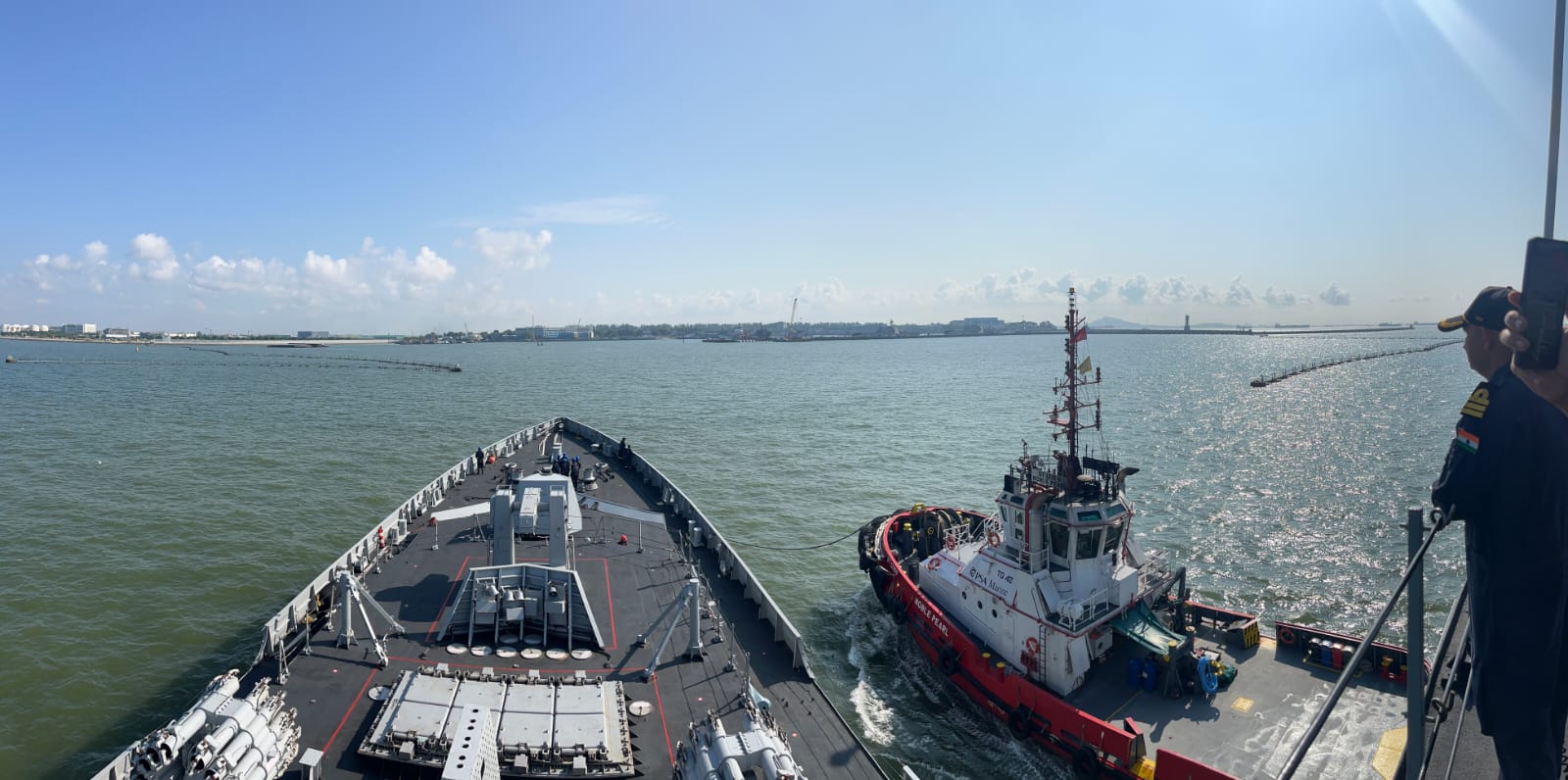

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
- The 32nd edition of SIMBEX—India’s longest continuously conducted maritime bilateral exercise—was held from 28 July to 1 August 2025, hosted by Singapore. It included a Harbour Phase at Changi Naval Base and a Sea Phase in the southern South China Sea.
- Indian participation: INS Satpura, alongside INS Delhi, INS Kiltan, and the support vessel INS Shakti.
- Singapore Navy elements: RSN Vigilance and RSN Supreme, supported by MV Mentor and aerial units—S-70B Seahawk, Fokker-50 aircraft, and F-15SG fighters.
Objectives & Activities
Harbour Phase
- Featured Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEEs), professional presentations, and strategic interactions.
- Conducted deck familiarisation visits aboard respective ships to foster doctrinal alignment
Sea Phase
- Encompassed advanced drill sequences, including:
- Air defence exercises, cross-deck helicopter operations
- Precision targeting, complex manoeuvres, and VBSS operations (Visit, Board, Search, and Seizure)
- Concluded with a ceremonial sail-past, symbolising professionalism and unity.
Geopolitical Landscape
- Strategic Reach: Deployment of Indian vessels to Philippines and Vietnam — alongside participation in SIMBEX—demonstrates India’s extended operational posture in Southeast Asia amidst regional tensions, notably with China’s maritime assertiveness.
- Broader Continuity: The Indian Navy, operating via the Andaman and Nicobar Command, employs SIMBEX as part of a broader matrix of maritime outreach in the region, including CORPAT and MILAN exercises
Mera Gaon Mera Dharohar Programme

- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
The Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar (MGMD) initiative is a nationwide cultural mapping project launched by the Ministry of Culture on 27th July 2023 as part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav. It operates under the National Mission on Cultural Mapping (NMCM) and is implemented by the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To digitally document and preserve the intangible cultural heritage of all 6.5 lakh villages across India through a comprehensive virtual cultural portfolio.
- Current Status (as of 2025):
- Over 4.7 lakh villages have been culturally mapped.
- The data is accessible on the MGMD web portal.
- Thematic Categories: Each village is documented based on one or more of seven cultural themes:
- Arts and Crafts Villages
- Ecologically Oriented Villages
- Scholastic Villages (linked to texts and scriptural traditions)
- Epic Villages (associated with Ramayana, Mahabharata, Puranas, and oral epics)
- Historical Villages (linked to local or national history)
- Architectural Heritage Villages
- Other culturally significant villages (e.g., fishing, horticulture, pastoral communities)
Significance:
- Preservation of Heritage: Helps safeguard India’s diverse village-level traditions and practices.
- Cultural Inclusion: Recognizes lesser-known cultural narratives and identities.
- Rural Development: Encourages economic and artistic growth through cultural awareness.
- Digital Cultural Infrastructure: Enables access to cultural data via online platforms.
About National Mission on Cultural Mapping (NMCM)
Launched in 2017, the NMCM is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Culture aimed at documenting and promoting India’s cultural diversity with a focus on grassroots-level heritage.
Key Components:
- Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar (MGMD) – Mapping of village-level cultural assets.
- Sanskritik Pratibha Khoj – Campaigns to discover artistic talent and promote folk and tribal arts.
- National Cultural Workplace (NCWP) – A digital platform and mobile app to create databases of artists, art forms, and cultural services.
This initiative strengthens India’s commitment to heritage conservation, digital documentation, and self-reliant cultural development, in line with Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Exercise Bold Kurukshetra 2025

- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
The 14th edition of Exercise Bold Kurukshetra was commenced in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, reinforcing India–Singapore military ties. This bilateral military exercise is a key component of both countries’ growing defence cooperation.
About Exercise Bold Kurukshetra:
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Type |
Bilateral joint military exercise |
|
First Initiated |
2005 |
|
Edition |
14th edition (2025) |
|
Location (2025) |
Jodhpur, Rajasthan |
|
Duration |
28 July – 4 August 2025 |
|
Format |
Tabletop Exercise and Computer-Based Wargame |
|
Objective |
Enhance interoperability, validate mechanised warfare tactics, and simulate UN peacekeeping operations |
Participating Contingents:
|
Country |
Unit/Regiment |
|
India |
Mechanised Infantry Regiment |
|
Singapore |
42nd Armoured Regiment, 4th Singapore Armoured Brigade |
Key Features:
- Mechanised Warfare Focus: Validates joint operational tactics in modern armoured and mechanised operations.
- UN Mandate Simulation: Exercises conducted under simulated Chapter VII of the UN Charter, preparing both armies for peacekeeping and peace enforcement missions.
- Ceremonial Traditions: Enhances military camaraderie through shared symbolism and operational command handovers.
- Equipment Display: The exercise concludes with a display of Indian Army equipment, highlighting India's indigenous defence capabilities.
Strategic Significance:
|
Domain |
Contribution |
|
Defence Diplomacy |
Deepens bilateral military cooperation with Singapore |
|
Indo-Pacific Stability |
Enhances India’s strategic role in maintaining peace in the Indo-Pacific |
|
UN Peacekeeping |
Builds joint operational readiness for multinational UN-mandated missions |
|
Capacity Building |
Boosts joint planning and execution skills for mechanised combat environments |
Sohrai Art of Jharkhand

- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
Sohrai Art from Jharkhand was prominently showcased during Kala Utsav 2025 held at Rashtrapati Bhavan, where President Droupadi Murmu hailed it as reflecting the “soul of India.” The event marked a significant national recognition for this traditional tribal art.
About Sohrai Art:
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Tribal Origins |
Practised by Santhal, Munda, and Oraon tribes in Jharkhand. |
|
Region |
Predominantly in Hazaribagh, Santhal Parganas, and parts of eastern Bihar. |
|
Occasion |
Ritual wall-painting during Diwali and harvest festivals. |
|
Purpose |
Thanksgiving for livestock and land fertility; linked to agrarian rituals and spiritual ecology. |
|
Artists |
Traditionally women; passed down through generations orally and practically. |
Key Features of Sohrai Art:
- Motifs: Stylized animals, birds, trees, and rural life, symbolizing harmony with nature.
- Materials: Uses natural pigments such as red ochre, white kaolin, yellow clay, and black manganese.
- Tools: Made with bamboo twigs, chewed sticks, and cloth instead of synthetic brushes.
- Cultural Essence: Embodies a blend of mythology, agrarian life, womanhood, and sustainability.
Kala Utsav 2025: National Recognition
- Held at Rashtrapati Bhavan as part of the Artists in Residence Programme.
- Ten tribal artists from Hazaribagh showcased their work to a national audience.
- President Murmu lauded the art as a symbol of India’s cultural depth and ecological consciousness.
Institutional Support: IGNCA’s Role
- Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) and its Regional Centre in Ranchi coordinated artist participation.
- IGNCA continues to promote indigenous art forms, ensuring cultural preservation and artist recognition.
Cultural and Policy Relevance:
- Art & Culture: Highlights India’s rich tribal and folk heritage.
- Women Empowerment: Female-centric art practice promoting rural livelihoods.
- Sustainable Development: Use of eco-friendly materials and community-led traditions.
- Tribal Development Schemes: Aligns with objectives of schemes like TRIFED, GI tagging, and cultural promotion under Tribal Affairs Ministry.
Environmental Flow (E-Flow) in Indian Rivers
- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
Union Jal Shakti Minister Shri C.R. Patil recently chaired a crucial meeting focused on the Environmental Flow (E-Flow) of the Ganga River and its tributaries, with particular attention to the Yamuna River. This initiative is a part of the broader effort to ensure the ecological sustainability of India’s river systems.
What is Environmental Flow (E-Flow)?
Environmental Flow refers to the quantity, timing, and quality of water flow necessary to sustain freshwater ecosystems and the livelihoods dependent on them. It ensures that rivers maintain their ecological integrity, supporting aquatic life, estuarine health, and human usage in a sustainable manner.
Why is E-Flow Important?
- Maintains ecological balance in rivers and estuaries.
- Supports aquatic biodiversity, especially key fish species.
- Provides long-term ecological and economic benefits.
- Balances human needs and environmental sustainability, especially in overexploited river basins.
Challenges in Maintaining E-Flow:
- Construction of dams and barrages.
- Pollution and urban encroachments.
- Over-extraction of water for agriculture and industry.
These interventions disrupt natural flow patterns, threatening riverine ecosystems and dependent communities.
Government Initiatives and Studies:
Environmental Flow Notification (2018):
- Introduced by the government to regulate minimum required flows in the Ganga. However, a review of its impact is now being undertaken to determine its effectiveness and the need for improvements.
Recent Meeting Outcomes:
- Emphasis on strengthening the e-flow framework, especially for the Yamuna River, which faces severe pollution and over-extraction issues.
- Need for a robust, inclusive, and scientific approach to water management.
Studies Approved Under National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
|
Institution |
Rivers/Sub-Basins Assigned |
|
NIH Roorkee |
Chambal, Son, Damodar |
|
IIT Roorkee |
Ghaghara, Gomti |
|
IIT Kanpur |
Kosi, Gandak, Mahananda |
These studies aim to assess current flow conditions and recommend sustainable flow levels.
Way Forward:
- Expedite assessments under NMCG and ensure multi-stakeholder participation.
- Develop comprehensive water flow strategies for heavily impacted rivers like the Yamuna.
- Strengthen decision-making frameworks to balance ecological and human needs.
ICJ Declares Clean Environment a Human Right
- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
In a historic advisory opinion delivered on 23rd July 2025, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) recognized the right to a clean, healthy, and sustainable environment as a fundamental human right. The opinion was issued at the request of the UN General Assembly (2023) following lobbying by Vanuatu and supported by over 130 countries, mainly small island developing states (SIDS) vulnerable to climate change.
Key Legal Questions Addressed:
- What are states’ obligations under international law to mitigate climate change?
- What are the legal consequences of failing to act on climate commitments?
Major Highlights of the ICJ Advisory Opinion:
1. Environment as a Human Right
- The Court affirmed that access to a clean, healthy, and sustainable environment is inherent to the enjoyment of other human rights.
- Based on customary international law, UNGA Resolution 76/300 (2022), and international human rights treaties.
2. Binding Legal Duties
- States are bound under UNFCCC, Kyoto Protocol, and Paris Agreement to:
- Implement mitigation and adaptation policies.
- Submit and update Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- Facilitate technology transfer and climate finance.
3. Due Diligence and Liability
- States must prevent significant transboundary environmental harm and regulate both public and private actors (e.g., fossil fuel companies).
- Failure to act amounts to an internationally wrongful act, triggering:
- Cessation,
- Guarantees of non-repetition,
- Compensation or restitution.
4. Historical Emissions & Responsibility
- The ICJ accepted that cumulative emissions can be legally attributed to specific states.
- Supports legal claims for reparations and accountability based on historic contributions to climate change.
5. Climate Obligations as Erga Omnes
- These duties are owed to the entire international community.
- Any state can seek enforcement, regardless of direct injury.
6. Scientific Attribution Accepted
- Climate science was admitted as legal evidence.
- Allows courts to establish causal links between emissions and environmental harm.
Geopolitical & Legal Implications:
- Empowers SIDS and developing nations in climate negotiations.
- Opens doors to domestic and international litigation based on environmental rights.
- Highlights inadequacy of current global agreements in ensuring timely climate action.
- Major emitters like USA and Russia have resisted legally binding obligations through courts.
Relevance for India:
- Reinforces Article 21 (Right to Life) and Article 48A (Protection of Environment) of the Indian Constitution.
- Can influence Indian courts and tribunals (e.g., NGT, Supreme Court) in:
- Air and water pollution cases,
- Waste management,
- Climate adaptation litigation.
This ruling marks a critical shift in international environmental law, signaling greater legal accountability for climate action and strengthening the legal foundation for future climate justice claims.
National Cooperation Policy 2025

- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
- The National Cooperation Policy (NCP) 2025 marks a strategic roadmap for revitalizing India’s cooperative sector to meet the nation’s goal of becoming “Viksit” by 2047.
- Rooted in the ethos of Sahkar-se-Samriddhi, this policy aims to build on the unique strengths of India’s cooperative tradition, promote economic democratization, and uplift rural economies through collective participation.
- Mission: To create an enabling legal, economic, and institutional framework that will strengthen and deepen the cooperative movement at the grassroots level and facilitate the transformation of cooperative enterprises into professionally managed, transparent, technology-enabled, vibrant, and responsive economic entities to support production by the masses.
What is a Cooperative?
A cooperative is an autonomous association of persons, united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically member-controlled enterprise.
Difference between Credit & Non-Credit Cooperatives
|
Aspect |
Credit Cooperatives |
Non-Credit Cooperatives |
|
Function |
Provide financial services like loans and savings |
Provide goods/services like farming inputs, housing, etc. |
|
Examples |
PACS, Urban Cooperative Banks |
Dairy, Marketing, Consumer, Housing Cooperatives |
The Indian cooperative movement has been the flag bearer of a participatory, people-led development model aimed at socio-economic upliftment at the grassroots level for more than a century.
Strategic Pillars:
The policy is structured around six mission pillars and 16 objectives:
- Strengthening the Foundation – Legal reforms, better governance, access to finance, digitalization.
- Promoting Vibrancy – Creating business ecosystems, expanding exports and rural clusters.
- Making Cooperatives Future-Ready – Technology integration, professional management, cooperative stack.
- Promoting Inclusivity and Deepening Reach – Promoting cooperative-led inclusive development and cooperatives as a people’s movement.
- Entering New and Emerging Sectors – Biogas, clean energy, warehousing, healthcare, etc.
- Shaping Young Generation for Cooperative Growth – Courses, training, employment exchanges.
Key Highlights of the Policy
Legislative and Institutional Reforms
- Encourage States to amend cooperative laws (Cooperative Societies Acts and Rules) to enhance transparency, autonomy and the ease of doing business.
- Promote digitalization of registrar offices and real-time cooperative databases.
- Revive sick cooperatives with institutional mechanisms.
Financial Empowerment
- Preserve and promote the three-tier Primary Agriculture Credit Societies - District Central Cooperative Bank - State Cooperative Bank credit structure.
- Promote cooperative banks and umbrella organizations (like National Urban Cooperative Finance & Development Corporation).
- Enable cooperative banks to handle government businesses.
Business Ecosystem Development
- Model cooperative villages with multipurpose PACS as growth engines.
- Encouraging States/UTs to develop at least one model cooperative village.
- Develop rural economic clusters (e.g., honey, spices, tea).
- Support branding under the ‘Bharat’ brand.
Model Cooperative Village
A Model Cooperative Village is a self-reliant rural unit developed through a cooperative-led, household-focused approach to enhance livelihoods and productivity.
Future-Readiness & Technology
- Develop a national ‘Cooperative Stack’ integrating with Agri-stack and databases.
- Promote Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) and Government e-marketplace (GeM) platform integration.
- Encourage research and innovation through cooperative incubators and Centres of Excellence.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
The ONDC is a transformative initiative by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce, Government of India aimed at democratizing digital commerce. Launched in April 2022, ONDC aims at promoting open networks for all aspects of exchange of goods and services over digital or electronic networks.
Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
GeM is an online platform for public procurement in India. The initiative was launched on August 09, 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry with the objective to create an open and transparent procurement platform for government buyers.
Inclusivity Measures
- Active participation of youth, women, SC/STs, and differently-abled in cooperatives.
- Model bye-laws for gender representation and transparent governance.
- Cooperative awareness campaigns in schools and colleges.
Model Bye-Laws
The Model Bye-laws are simply a representative sample and a guide to frame bye-laws of a multi-state cooperative society.
Sectoral Diversification
- Promote cooperatives in new and emerging sectors such as:
- Renewable energy,
- Waste management,
- Health and education,
- Mobile-based aggregator services (e.g., for plumbers, taxi drivers),
- Organic and natural farming,
- Biogas and ethanol production, etc.
Youth-Oriented Capacity Building
- Develop cooperative-focused courses in higher education institutions (HEIs).
- Build a national digital cooperative employment exchange.
- Promote financial and digital literacy among youth.
- Recruit quality cooperative teachers and resource persons.
Implementation and Monitoring
A robust multi-tier implementation structure is proposed:
- Implementation Cell within the Ministry of Cooperation with technical Project Management Unit support for effective and timely implementation of the policy.
- National Steering Committee on Cooperation Policy chaired by the Union Cooperation Minister will be constituted for overall guidance, inter-ministerial coordination, periodic policy review, etc.
- Policy Implementation and Monitoring Committee headed by the Union Cooperation Secretary for coordination with States, troubleshooting implementation bottlenecks, periodic monitoring and evaluation, etc.
India Skills Accelerator Initiative

- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with the World Economic Forum (WEF), deliberated on the “India Skills Accelerator” initiative.
Key Highlights:
- Launched by: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE)
- Collaborating Partner: World Economic Forum (WEF)
- Announced on: 8th April 2025 during a high-level roundtable at Kaushal Bhawan, New Delhi
- Objective: To strengthen India's skilling ecosystem through inclusive upskilling and reskilling, enhanced government-industry collaboration, and investment in lifelong learning, particularly in high-growth sectors such as Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and clean energy.
- Key Features:
- Public-Private Collaboration: Structured as a national platform bringing together government and private sector stakeholders; notably, 2 of the 4 co-chairs are from the private sector.
- Focus Areas:
- Promotes scalable and adaptive training models
- Facilitates agile career transitions for the workforce
- Aligns education and training with evolving industry demands
- Strategic Approach:
- Raising awareness and changing perceptions about future skills
- Encouraging cross-sectoral collaboration and sharing of best practices
- Reforming institutional frameworks to support a responsive and dynamic skilling system
- Significance: The initiative is aligned with India’s goal of building a future-ready workforce by addressing skill mismatches and preparing youth for rapidly transforming industries. It contributes to the broader national missions like Skill India, Digital India, and Make in India.
AI for India 2.0 Programme

- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
The Minister of State (Independent Charge), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), informed the Rajya Sabha about AI for India 2.0 Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Launched: 15th July 2023, on the occasion of World Youth Skills Day
- Implementing Bodies: Joint initiative by Skill India and GUVI (an ed-tech platform incubated by IIT Madras and IIM Ahmedabad)
- Accreditation: Recognized by NCVET and IIT Madras
- Objective: To democratize access to emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), especially among youth from non-English-speaking and rural backgrounds.
- Key Features:
- Free Online Training: Offers no-cost courses in AI and ML.
- Vernacular Focus: Educational content provided in 9 Indian languages including Hindi, Telugu, and Kannada, enhancing accessibility for non-English speakers.
- Target Audience: College students, recent graduates, and early-career professionals, with a focus on learners from rural regions.
- Course Content: Includes expert-curated Python programming courses designed to enhance technical proficiency.
- National Recognition: The programme is nationally accredited, ensuring quality and credibility.
- Significance: This initiative aims to empower the Indian youth by equipping them with industry-relevant digital skills, thus aligning with the broader goals of digital inclusion and skilling under Digital India and Skill India missions.
National Critical Mineral Mission
- 26 Jul 2025
In News:
The National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM), launched by the Government of India in 2025, represents a strategic initiative to secure India's access to essential critical minerals, vital for clean energy, advanced electronics, defence, and emerging technologies. It aims to address India’s dependence on imports, strengthen domestic capacity, and build resilient supply chains.
What are Critical Minerals?
Critical minerals are those essential to economic development and national security, often marked by limited domestic availability and a high risk of supply disruption. These include lithium, cobalt, nickel, rare earth elements (REEs), graphite, and silicon, which are central to electric vehicles (EVs), solar panels, semiconductors, wind turbines, and defence applications.
Why NCMM? Strategic Context
- Energy Transition: India is 100% import-dependent for lithium, cobalt, and rare earths—crucial for EVs and energy storage.
- Tech Sovereignty: Strategic autonomy in AI, defence, and semiconductors depends on secure mineral access.
- Geopolitical Concerns: China controls 70–90% of global critical mineral processing. Diversifying supply chains is essential.
- Industrial Push: Schemes like PLI for EVs, electronics, and solar energy require a reliable mineral base.
- Climate Commitments: India aims to reduce emissions intensity by 45% (from 2005 levels) and reach net-zero by 2070.
Components of the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM)
Key Features of NCMM
1. Legal and Policy Framework
- Enacted under the Ministry of Mines in 2025.
- 30 critical minerals identified (24 inserted into Part D of the First Schedule of the MMDR Act, 1957).
- The Centre now has exclusive authority to auction mining leases for these minerals.
2. Domestic and Foreign Sourcing Targets (2024–2030)
|
Objective |
Target |
|
Domestic Exploration Projects |
1,200 |
|
Overseas Projects by PSUs |
26 |
|
Overseas Projects by Private Sector |
24 |
|
Recycling Incentive Scheme (in kilotons) |
400 |
|
Strategic Mineral Stockpile |
5 |
3. Capacity Building and Innovation
|
Objective |
Target |
|
Patents in Critical Mineral Tech |
1,000 |
|
Workforce Trained |
10,000 |
|
Processing Parks |
4 |
|
Centres of Excellence |
3 |
Sectoral Applications of Critical Minerals
- Solar Energy: Silicon, tellurium, indium, and gallium in photovoltaic cells; India’s solar capacity is 64 GW.
- Wind Energy: Neodymium and dysprosium in turbine magnets; target capacity: 140 GW by 2030.
- EVs: Lithium, nickel, cobalt in batteries; goal: 6–7 million EVs by 2024.
- Energy Storage: Lithium-ion battery storage systems; key for grid balancing and renewables.
Implementation Highlights
Exploration and Domestic Production
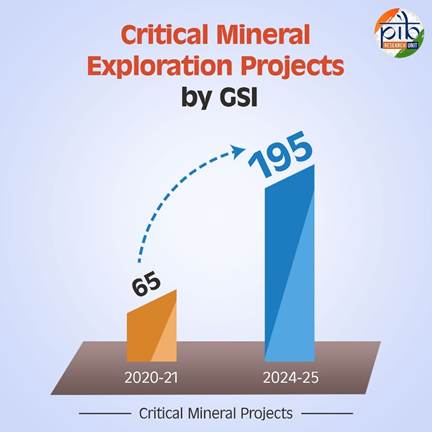
- 195 GSI projects launched in 2024–25, including 35 in Rajasthan.
- Over 100 mineral blocks identified for auction.
- Offshore exploration for polymetallic nodules (cobalt, REEs, nickel, manganese) underway.
- UNFC classification and MEMC Rules, 2015, guide the exploration methodology.
Asset Acquisition Abroad
- KABIL (Khanij Bidesh India Ltd):
- MoU with CAMYEN (Argentina) for lithium over 15,703 hectares.
- Ties with Australia for cobalt/lithium via Critical Mineral Office (CMO).
- Public–Private Partnership support via funding, MEA coordination, and guidelines for overseas investments.
Recycling and Circular Economy
- Incentives for mineral recovery from e-waste, fly ash, and tailings.
- Emphasis on building a formal recycling infrastructure.
- Current battery and electronics recycling sector is informal and lacks scale.
Processing and Midstream Infrastructure
- Development of dedicated Mineral Processing Parks.
- Encourage public–private partnerships and offer PLI-style incentives for refining technologies.
Challenges in India’s Critical Mineral Ecosystem
- High Import Dependence: 100% for lithium, cobalt, REEs.
- Underdeveloped Infrastructure: Lack of domestic refining, separation, and conversion capacity.
- Low Private Sector Participation: Technical and financial barriers deter participation.
- ESG Concerns: Mining zones often overlap with ecologically or tribally sensitive regions.
- Legal Bottlenecks: Environmental clearance delays due to weak ESG compliance.
- Informal Recycling Ecosystem: Fragmented, unregulated battery/e-waste recovery systems.
Strategic Roadmap Ahead
- Strengthen Exploration: Expand GSI capabilities; fund viability gap to attract investment.
- Diversify Global Sources: Engage in “friendshoring” with Australia, Argentina, U.S., etc.
- Build Midstream Capacity: Set up refining zones, mineral parks, and conversion units.
- Sustainable and Inclusive Mining: Implement ESG mandates and tribal welfare frameworks.
- Enhance Circular Economy: Provide tax breaks and subsidies for high-efficiency recovery systems.
Institutional Support
- IREL (India) Limited:
- Produces ilmenite, zircon, sillimanite, and rare earths.
- Operates Rare Earth Extraction Plant (Chatrapur, Odisha) and Refining Unit (Aluva, Kerala).
- Profitable PSU with ?14,625 million turnover (2021–22), including ?7,000 million exports.
Conclusion
India's National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) is pivotal for achieving strategic autonomy, industrial growth, and clean energy goals. By integrating domestic exploration, international partnerships, midstream processing, recycling, and regulatory reform, NCMM lays the foundation for a resilient and self-reliant mineral ecosystem. Its success is critical for India’s leadership in green technologies, manufacturing, and strategic geopolitics—making it a cornerstone initiative under Atmanirbhar Bharat and India's 21st-century industrial vision.
India–UK Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA)
- 26 Jul 2025
In News:
India and the United Kingdom signed the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) in July 2025, marking a landmark Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and a major developed economy. The agreement is part of the broader India–UK Vision 2035, aiming to strengthen bilateral ties across trade, technology, defence, climate, and education.
Key Features of CETA
1. Trade in Goods
- Zero-duty access for 99% of Indian exports to the UK, covering major sectors:
- Labour-intensive: textiles, leather, footwear, gems & jewellery, toys, marine products.
- High-growth: auto components, engineering goods, organic chemicals.
- Improved access for Indian agricultural products (tea, spices, coffee, fruits, meats) to UK’s $63.4 billion agri-market (dairy excluded).
2. Trade in Services
- First-of-its-kind comprehensive services commitment by the UK.
- Expands Indian access in: IT/ITeS, financial & legal services, architecture, education, telecom, consulting, and engineering.
3. Labour Mobility
- Liberalised visa norms for:
- Contractual Service Suppliers
- Intra-Corporate Transferees
- Independent Professionals (e.g. chefs, yoga instructors, musicians)
- Double Contribution Convention (DCC):
- Exempts Indian professionals and their employers from UK social security contributions for up to 3 years.
4. Inclusive Growth
- Benefits designed for MSMEs, women entrepreneurs, artisans, farmers, and startups.
- Provisions include:
- Dedicated SME contact points
- Digital trade facilitation
- Paperless customs
India–UK Vision 2035: 5 Strategic Pillars
1. Growth and Jobs
- Target: Double bilateral trade from USD 56 bn to USD 112 bn by 2030.
- Initiatives:
- New Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)
- UK–India Infrastructure Financing Bridge
- British International Investment (BII)
- Regulatory harmonisation in legal and financial services.
2. Technology and Innovation
- Focus Areas: AI, 6G, semiconductors, biotech, cybersecurity, biomaterials.
- Key Initiatives:
- Joint AI research centre
- India–UK Critical Minerals Guild
- Startup collaboration via incubators and biofoundries.
3. Defence and Security
- Launch of 10-Year Defence Industrial Roadmap: R&D in electric propulsion, underwater warfare, directed energy weapons.
- Deepening:
- 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
- Military exercises, intelligence sharing
- Indian Ocean logistics cooperation
4. Climate and Clean Energy
- Areas of Collaboration: Offshore wind, small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs), carbon markets, blue carbon research.
- Joint commitment to:
- International Solar Alliance (ISA)
- One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG)
- Net Zero Innovation Partnership
5. Education and People-to-People Ties
- UK universities allowed to open campuses in India.
- Launch of dual degree programmes, mutual qualification recognition.
- Young Professionals Scheme for career mobility.
- Green Skills Partnership to bridge climate tech skill gaps.
Strategic Importance for India
|
Sector |
Impact |
|
Economy |
Enhances export potential, promotes Make in India, and attracts FDI. |
|
Employment |
Boosts jobs in textiles, IT, food processing, and engineering. |
|
Mobility |
Facilitates professional migration and global exposure. |
|
Technology |
Drives domestic innovation in AI, semiconductors, climate tech. |
|
Defence |
Supports self-reliance in high-tech military R&D. |
|
Climate Action |
Aids India’s Net Zero goals via access to green finance and clean energy tech. |
|
Global Positioning |
Strengthens India’s influence in WTO, UN, IMF, and other multilateral fora. |
Palna Scheme

- 25 Jul 2025
In News
Launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) under the Samarthya vertical of Umbrella Mission Shakti, the Palna Scheme aims to provide safe, accessible, and quality day care (crèche) facilities for children aged 6 months to 6 years across all States and Union Territories, effective from 1st April 2022.
Key Features:
- Objective: To support working mothers by providing crèche services ensuring:
- Safety and well-being of children
- Nutritional support
- Early childhood care and cognitive development
- Health check-ups, growth monitoring, and immunization
- Target Beneficiaries: All children aged 6 months to 6 years. Services are irrespective of mothers' employment status, covering both organized and unorganized sectors.
- Types of Crèches:
- Standalone Crèches
- Anganwadi-cum-Crèches (AWCCs)
Anganwadi-cum-Crèche (AWCC) Model
- Utilizes existing Anganwadi Centres, the world’s largest public childcare infrastructure, to provide full-day childcare services.
- Ensures last-mile delivery of services in a safe and secure environment.
- Supports women’s workforce participation by relieving unpaid childcare burden.
Timings & Flexibility
- Crèches to operate for 26 days/month and 7.5 hours/day, with timings adapted to local needs.
- States/UTs may adjust timings under Standard Operating Procedures based on community work patterns.
Funding Pattern
|
Category |
Centre:State Funding Ratio |
|
General States |
60:40 |
|
North Eastern & Special Category States |
90:10 |
|
UTs with Legislature |
60:40 |
|
UTs without Legislature |
100% Central Assistance |
Integrated Services Offered
- Day care and sleeping facilities
- Early stimulation for children below 3 years
- Pre-school education for 3–6 years
- Supplementary nutrition (locally sourced)
- Growth monitoring, health check-ups & immunization
Implementation Status (As of July 2025)
- Total Envisioned AWCCs (FY 2022–26): 17,000
- AWCCs Approved by MoWCD (as of July 2025): 14,599
- Implemented based on proposals from States/UTs with cost-sharing as per applicable funding norms.
Significance
- Addresses the rising need for formal childcare due to:
- Increasing nuclear families
- Greater women’s participation in the workforce
- Migration, urbanization, and limited informal support structures
- Aligns with SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) by formalizing care work and supporting inclusive economic participation.
Fungus-Resistant Pineapple
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
- Pineapple (Ananas comosus L. Merr.), the most economically significant fruit of the Bromeliaceae family, plays a crucial role in nutrition and agriculture across tropical regions.
- In India, pineapple cultivation contributes significantly to rural livelihoods, particularly in northeastern and southern states. However, the productivity of this high-value fruit is severely impacted by Fusariosis, a destructive fungal disease caused by Fusarium moniliforme.
- A recent breakthrough by Indian scientists promises a potential game-changer in combating this challenge using indigenous genetic innovation.
Fusariosis
- Fusariosis is a devastating fungal infection that warps the stem, blackens the leaves, and rots the fruit internally, leading to heavy crop losses.
- Traditional breeding methods have struggled to provide effective resistance due to the rapid evolution of fungal pathogens. For farmers, this translates into unreliable harvests and financial instability.
The Biotechnological Solution: AcSERK3 Gene Overexpression
Researchers from the Bose Institute, an autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have successfully identified and overexpressed a gene in pineapple that significantly enhances resistance to Fusariosis.
- The gene, AcSERK3 (Somatic Embryogenesis Receptor Kinase 3), is part of the pineapple’s natural genome.
- It is known to regulate somatic embryogenesis and strengthen plant responses to biotic and abiotic stress.
- By genetically overexpressing this gene in pineapple plants, the researchers were able to trigger enhanced internal defence mechanisms.
- The transgenic lines exhibited increased production of stress-associated metabolites and antioxidant enzyme activity, enabling them to survive fungal attacks that severely damaged wild-type plants.
This is the first documented instance of overexpression of an indigenous pineapple gene to impart fungal disease tolerance while simultaneously improving regenerative capacity.
Significance of the Research
- The study, published in In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plants, lays the foundation for developing multi-fungal tolerant pineapple varieties.
- These genetically enhanced lines are not dependent on foreign genes, thereby addressing biosafety concerns.
- Field trials, if successful, could lead to the commercial deployment of these varieties using conventional propagation methods like slips and suckers.
- This offers a sustainable, farmer-friendly solution, especially for smallholder pineapple growers in India.
Pineapple Cultivation in India: Key Facts
- Climatic Conditions: Grows well in 15–30°C temperature range and 600–2500 mm annual rainfall (optimum: 1000–1500 mm).
- Soil: Requires well-drained soils; intolerant to waterlogging.
- Tolerant to Drought: Possesses water-storing tissues making it suitable for rainfed cultivation.
- Cultivation Pattern: Can be grown as a monocrop or intercropped with coconut.
- Major Producing States: Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Manipur, West Bengal, Kerala, Karnataka, and Goa.
- Global Producers: Thailand, Philippines, Brazil, China, Nigeria, Mexico, Indonesia, Colombia, and the USA.
Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX)
- 23 Jul 2025
In News:
The Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) has completed ten successful years since its launch in 2015. Initiated at the Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA), New Delhi, WiFEX has emerged as a pioneering long-term scientific initiative aimed at understanding and mitigating the impact of dense winter fog over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP) — one of the most fog-prone regions in the world.
What is WiFEX?
- Launched in Winter 2015 at IGIA, New Delhi.
- Led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Supported by:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF).
- One of the world’s few open-field long-term experiments exclusively dedicated to studying winter fog.
Objectives of WiFEX
- To develop accurate now-casting (up to 6 hours) and forecasting systems for fog events over North India.
- To reduce the adverse impact of fog on:
- Aviation (flight delays, diversions, safety).
- Surface transport (road and rail accidents).
- Economy and public safety.
How it was Conducted
Observational Framework
WiFEX deployed cutting-edge scientific equipment, including:
- Micrometeorology towers
- Ceilometers
- High-frequency sensors
- Radiometers
- Wind profilers
These were installed at multiple locations including:
- IGIA, Delhi
- Jewar Airport, Noida
- Hisar, Haryana
Key Parameters Studied
- Atmospheric temperature stratification
- Relative humidity and soil heat flux
- Wind speed and turbulence
- Aerosol concentration
- Urban heat island effects
- Land-use changes
This comprehensive data helped scientists decode how dense fog forms, persists, and disperses.
Major Achievements of WiFEX
High-Resolution Forecasting Model
- A 3-km resolution probabilistic fog prediction model was developed.
- Achieved over 85% accuracy in forecasting very dense fog (visibility <200 meters).
- Provides insights on:
- Onset and dissipation timing
- Fog density
- Duration of fog events
Operational Impact
- Significantly reduced flight diversions and delays at IGIA.
- Enhanced airport safety and efficiency in fog conditions.
- Helped airlines and transport authorities activate timely contingency plans.
Scientific Contributions
- Showcased how air pollution, aerosols, urbanization, and land-use changes influence fog behavior.
- Facilitated improvements in early warning systems for North India.
- Informed urban planning and air quality policies for fog-prone areas.
Meri Panchayat App

- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s digital governance model received global recognition as the Meri Panchayat mobile application won the prestigious WSIS Prizes 2025 Champion Award under the category Cultural Diversity and Identity, Linguistic Diversity and Local Content. The award was presented during the WSIS+20 High-Level Event 2025 held in Geneva, Switzerland.
Key Highlights:
- The award was conferred by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) as part of the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) initiative.
- The WSIS+20 event commemorated 20 years of WSIS, providing a platform to assess digital progress, address new challenges, and promote inclusive information societies.
- The event was co-hosted by ITU and the Swiss Confederation, and co-organized by UNESCO, UNDP, and UNCTAD.
About the “Meri Panchayat” App:
- A flagship m-Governance platform developed by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj in collaboration with National Informatics Centre (NIC) under the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY).
- Designed to empower 2.65 lakh Gram Panchayats, the app caters to over 950 million rural residents and 25 lakh elected Panchayat representatives.
Key Features:
- Real-time Access: Budgets, receipts, payments, and Panchayat-level development plans.
- Transparency & Accountability: Social audit tools, geo-tagged fund utilization, and grievance redressal mechanisms.
- Participatory Governance: Enables citizens to propose projects, rate completed works, and view Gram Sabha decisions.
- Multilingual Support: Interface available in 12+ Indian languages, enhancing local inclusivity.
- Weather and Civic Info: Gram Panchayat-level weather forecasts, civic services, and infrastructure details.
Significance:
- The app strengthens participatory democracy by digitally integrating rural citizens into governance.
- It aims to bridge the digital divide and promote linguistic and cultural inclusivity in rural India.
- Recognized globally for promoting citizen-centric governance and local content diversity.
Allographa effusosoredica
- 20 Jul 2025
In News:
A team of Indian scientists from MACS-Agharkar Research Institute, Pune (under the Department of Science & Technology) has discovered a new species of lichen named Allographa effusosoredica in the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and biodiversity hotspot. This crustose lichen exhibits effuse soredia and contains norstictic acid, a rare secondary metabolite within its genus.
Scientific and Molecular Significance
- The species was examined through polyphasic taxonomy, integrating:
- Morphological traits
- Chemical profiling
- Molecular sequencing using genetic markers:
- Fungal DNA markers: mtSSU, LSU, RPB2
- Algal symbiont marker: ITS
- The lichen’s photobiont was identified as a species of Trentepohlia, advancing the understanding of tropical algal diversity in lichens.
- Though morphologically similar to Graphis glaucescens, it is phylogenetically closest to Allographa xanthospora.
Symbiosis in Lichens
- Lichens are composite organisms, formed by a symbiotic association between:
- A fungal partner (mycobiont) — provides structure and protection.
- A photosynthetic partner (photobiont), such as green algae or cyanobacteria — produces nutrients via photosynthesis.
- This discovery supports the concept of locally adapted symbiosis, emphasizing co-evolution in tropical ecosystems.
Ecological Importance of Lichens
- Lichens are vital for:
- Soil formation
- Feeding insect populations
- Acting as bioindicators of air quality and ecosystem health.
Conservation and Biodiversity Impact
- Allographa effusosoredica is:
- The 53rd Allographa species reported from India.
- The 22nd species of this genus documented in the Western Ghats.
- The first Indian Allographa species validated using molecular tools.
- The study was supported by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) and contributes to the growing inventory of India’s cryptic biodiversity.
88th Executive Committee Session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC88)

- 21 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s contributions were widely appreciated at the 88th Executive Committee Session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC88) held at FAO Headquarters, Rome.
What is the Codex Alimentarius?
- A collection of internationally recognized food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice.
- Promotes consumer health protection, food safety, and fair-trade practices.
- Recognized under the WTO Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures as a global reference point.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC)
|
Feature |
Detail |
|
Established |
1963 by FAO and WHO |
|
Type |
Intergovernmental food standards body |
|
Headquarters |
Rome, Italy |
|
Objectives |
To protect consumer health and ensure fair practices in the food trade |
|
Members |
189 members: 188 countries + European Union |
|
India’s Membership |
Since 1964 |
Structure of CAC:
- Codex Commission
- Executive Committee (CCEXEC)
- Codex Secretariat
- Subsidiary Bodies and Committees
Meetings alternate between Geneva and Rome annually. Funded by regular budgets of FAO and WHO.
India’s Contributions at CCEXEC88 (2025):
1. Millet Standards: India chaired the development of Codex group standards for whole millet grains, alongside Mali, Nigeria, and Senegal. These standards are up for final approval at CAC48.
2. Strategic Planning (2026–2031):
- India led discussions on SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) indicators for monitoring Codex outcomes.
- These KPIs will guide Codex’s strategic direction and will be adopted at CAC48.
3. Regional Capacity Building:
- India mentored Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Timor Leste under the Codex Trust Fund (CTF).
- Urged other developing countries to use the CTF for mentorship and twinning programs.
Other Leadership Roles by India in Codex:
|
Domain |
India's Role |
|
Spices & Herbs |
Chairs Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH) since 2014 |
|
Fresh Produce |
Led standard development for dates, co-chaired for turmeric and broccoli |
|
Digital Participation |
Promotes transparent, inclusive discussions in Codex committees |
National Codex Contact Point (NCCP), India
- Constituted by: Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Role:
- Liaison with the Codex Secretariat
- Coordinate India’s input via National Codex Committee
- Facilitate domestic stakeholder consultation for Codex decisions
Kashi Declaration

- 21 Jul 2025
In News:
The Youth Spiritual Summit 2025 concluded at the Rudraksh International Convention Centre, Varanasi, with the formal adoption of the Kashi Declaration — a landmark roadmap to combat drug abuse through youth and spiritual leadership.
- Organised by: Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Theme: "Drug-Free Youth for Developed India"
What is the Kashi Declaration?
The Kashi Declaration is a national action plan to counter substance abuse in India. It integrates spiritual wisdom, youth empowerment, and institutional coordination to establish a Nasha Mukt Yuva (Drug-Free Youth) by 2047, aligning with the vision of Viksit Bharat @2047.
Key Objectives:
- Eradicate Drug Abuse: Mobilise youth to build a drug-free society by 2047.
- Spiritual Mobilisation: Leverage India’s spiritual heritage as a tool for transformation and healing.
- Whole-of-Society Approach: Involve families, schools, communities, and institutions in prevention and rehabilitation.
- Empower Youth Volunteers: Enable MY Bharat clubs to conduct awareness, outreach, and de-addiction drives.
- Institutional Coordination: Establish a Joint National Committee for multi-ministerial convergence and periodic reporting.
Major Features:
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Plenary-Driven Agenda |
Covered themes of psychology, drug trafficking, awareness, and spiritual rehabilitation. |
|
Multi-Ministerial Action |
Involves Ministries of Youth Affairs, Social Justice, Home Affairs, Labour, and Culture. |
|
Annual Review Mechanism |
Progress tracked via the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2026. |
|
Digital Monitoring |
Measures proposed to curb online targeting of schoolchildren for drugs. |
|
Community Outreach |
Grassroots campaigns, pledge drives, and support services launched through the MY Bharat platform. |
Institutional Mechanisms Proposed:
- Joint National Committee: For inter-ministerial coordination and implementation oversight.
- Annual Progress Reporting: Ensures transparent monitoring and accountability.
- National Platform: To connect affected youth with rehabilitation and support services.
Green Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
- 19 Jul 2025
In News:
Indian scientists at the S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS) have developed a novel, eco-friendly method to synthesize hydrogen peroxide (H?O?) directly from sunlight and water using a photocatalyst called Mo-DHTA COF. This innovation marks a significant advancement in green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
What is Hydrogen Peroxide (H?O?)?
- A colorless, bitter-tasting liquid with powerful oxidizing properties.
- Environmentally friendly: Decomposes into water and oxygen without leaving harmful residues.
- Naturally present in trace amounts in the atmosphere.
- Unstable and decomposes readily, releasing heat.
- Found in household use (3–9% concentration) for disinfection, bleaching, and wound cleaning.
Applications
- Medical: Disinfectant, wound cleaner.
- Industrial: Textile and paper bleaching, foam rubber production, and rocket propellant.
- Environmental: Wastewater treatment, green sterilization.
- Energy & Chemistry: Fuel cells, chemical synthesis, and potentially in CO? reduction and water splitting.
Limitations of Conventional H?O? Production
- Energy-intensive and environmentally hazardous.
- Costly and not sustainable for large-scale, decentralized applications.
The Innovation: Mo-DHTA COF
What is it?
- Mo-DHTA COF stands for dimolybdenum paddlewheel-embedded Covalent Organic Framework.
- Developed by a DST-supported research team at SNBNCBS.
- Published in the journal Small.
Photocatalytic Mechanism
- Made from α-hydroquinone-based organic linkers and dimolybdenum units.
- Upon visible light exposure, the material generates excitons (electron-hole pairs).
- Electrons reduce oxygen to superoxide radicals, which then convert to H?O? through further reactions.
- Functions in various media (ethanol, benzyl alcohol, and even pure water).
Advantages of Mo-DHTA COF
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Eco-Friendly |
Uses only water and sunlight—no harmful by-products. |
|
High Photocatalytic Efficiency |
Effective even in pure water, not just organic solvents. |
|
Stability |
Structurally stable and recyclable, suitable for long-term use. |
|
Enhanced Performance |
Overcomes limitations of earlier photocatalysts like metal oxides, g-C?N?, and MOFs. |
|
Scalable |
Promising for industrial upscaling and decentralized chemical production. |
Significance and Future Potential
- Green Chemistry: Sets a foundation for cleaner chemical production methods.
- Healthcare & Pharma: Enables low-cost production of disinfectants.
- Environmental Remediation: Supports sustainable water purification and sterilization.
- Energy & Materials Science: Potential use in CO? reduction, water splitting, and fuel cell technologies.
- Research Outlook: Future focus includes optimization of metal-embedded COFs and exploring other catalytic systems for broader applications.
Akash Prime Missile System

- 19 Jul 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted a high-altitude trial of the Akash Prime surface-to-air missile system in Ladakh, marking a major step in strengthening indigenous air defence capabilities, particularly for mountainous and high-altitude terrains.
What is Akash Prime?
Akash Prime is an upgraded variant of the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It is designed to operate efficiently in high-altitude, low-oxygen environments—ideal for India’s sensitive border regions like Ladakh and Sikkim.
Developers
- DRDO – Lead developer
- In collaboration with:
- Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL)
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
Key Features
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Purpose |
Neutralizes aerial threats like enemy aircraft, drones, and cruise missiles |
|
Altitude Performance |
Successfully tested at 15,000 ft; engineered for deployment above 4,500 metres |
|
Seeker Technology |
Equipped with an indigenous Radio Frequency (RF) seeker for precise target acquisition during terminal phase |
|
Guidance System |
Hybrid: Command guidance + terminal active homing |
|
Range & Speed |
Operates within 25–30 km range; travels at Mach 2.5 |
|
Mobility |
Mounted on mobile platforms for rapid deployment across terrains |
|
All-Weather Capability |
Functions in extreme cold and low-density atmospheric conditions |
|
Kill Probability |
88% (single missile); up to 98.5% in dual-salvo mode |
Operational Significance
- High-Altitude Readiness: Specifically tailored for mountainous regions such as the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Versatile Deployment: Protects mobile, semi-mobile, and fixed military installations.
- Strategic Feedback Integration: Incorporates enhancements based on feedback from armed forces for use in vital installations.
Strategic Importance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat: Fully indigenous system contributing to self-reliance in defence manufacturing.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces dependency on imported air defence systems.
- Force Multiplier: Strengthens India’s layered air defence network against modern aerial threats.
ADEETIE Scheme

- 18 Jul 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Power launched the Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments (ADEETIE) scheme to promote energy efficiency in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
Key Details:
- Objective: To reduce energy consumption by 30–50%, enhance the power-to-product ratio, and facilitate the creation of green energy corridors in MSME industrial sectors.
- Implementing Agency:
- o Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), under the Ministry of Power
- o Legislative backing: Energy Conservation Act, 2001
- Duration & Funding
- o Period: FY 2025–26 to 2027–28 (3 years)
- o Budgetary Outlay: ?1000 crore
- Target Beneficiaries
- Eligible Enterprises: MSMEs with Udyam ID
- Must demonstrate a minimum 10% energy savings using implemented technologies
- Sectoral Coverage: Targets 14 energy-intensive sectors, including: Brass, Bricks, Ceramics, Chemicals, Fisheries, Food Processing, etc.
- Implementation Strategy Phased Roll-out:
- Phase 1: 60 industrial clusters
- Phase 2: Additional 100 clusters
Scheme Components
|
Component |
Details |
|
Interest Subvention |
- 5% for Micro & Small Enterprises |
|
Technical Assistance |
- Investment Grade Energy Audits (IGEA) |
|
Financial Support |
- Incentives for adoption of efficient technologies |
Other BEE Initiatives for MSMEs
|
Initiative |
Purpose |
|
BEE-SME Programme |
Promote energy efficiency in MSMEs |
|
National Programme on Energy Efficiency & Technology Upgradation |
Modernize and reduce energy intensity |
|
SIDHIEE Portal |
Digital tool providing energy efficiency insights and handholding support |
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- The Government of India set up the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) on March 1, 2002 under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- The mission of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency is to assist in developing policies and strategies with a thrust on self-regulation and market principles, within the overall framework of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 with the primary objective of reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy.
- BEE coordinates with designated consumers, designated agencies and other organizations and recognises, identifies and utilises the existing resources and infrastructure, in performing the functions assigned to it under the Energy Conservation Act.
- The Energy Conservation Act provides for regulatory and promotional functions.
Quantum Noise and Intraparticle Entanglement
- 18 Jul 2025
In News:
A collaborative study led by the Raman Research Institute (RRI), Bengaluru, in association with Indian and international institutions, has made a groundbreaking discovery: quantum noise, often seen as a disruptive factor in quantum systems, may facilitate or even revive quantum entanglement under specific conditions.
Key Scientific Concept: Quantum Entanglement
- Quantum Entanglement: A quantum phenomenon where particles remain interconnected such that the state of one particle instantly influences the state of another, regardless of distance.
- Intraparticle Entanglement: A lesser-known form of entanglement occurring between different properties (degrees of freedom) of a single particle, as opposed to interparticle entanglement (between two or more particles).
The Discovery
- Contrary to long-held assumptions, quantum noise, specifically amplitude damping, can:
- Revive lost intraparticle entanglement
- Generate entanglement in initially unentangled intraparticle systems
- In contrast, interparticle entanglement under similar noise conditions only decays without revival.
Types of Quantum Noise Studied
- Amplitude Damping: Simulates energy loss, akin to an excited state relaxing to a ground state.
- Phase Damping: Disrupts phase relationships, impacting quantum interference.
- Depolarizing Noise: Randomizes the quantum state in all directions.
- Key Finding: Intraparticle entanglement is more robust and less susceptible to decay across all three noise types.
- Scientific Tools Used
- Derived an analytical formula for concurrence (a measure of entanglement)
- Developed a geometric representation of how entanglement behaves under noise
Institutions Involved
- Raman Research Institute (RRI) – Lead Institute (Autonomous under DST)
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc)
- Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Kolkata
- University of Calgary
- Funded by:
- India-Trento Programme on Advanced Research (ITPAR)
- National Quantum Mission (NQM), Department of Science and Technology (DST)
Applications and Significance
- Could lead to more stable and efficient quantum systems
- Implications for Quantum Communication and Quantum Computing
- Results are platform-independent (applicable to photons, trapped ions, neutrons)
- Provides a realistic noise model (Global Noise Model) for practical quantum technologies
Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK)
- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
The Union Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment has recently inaugurated the 75th Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK) at the Government Medical College, Badaun, Uttar Pradesh, marking a significant milestone in India's efforts toward inclusive social welfare.
About PMDK
The Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India aimed at delivering integrated rehabilitation and assistive services under one roof. It caters primarily to:
- Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), as identified under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- Senior Citizens, especially those from economically weaker sections (EWS).
These centres offer comprehensive services including:
- Assessment and evaluation
- Counselling
- Distribution of assistive devices
- Post-distribution follow-up care
Institutional Framework
PMDKs operate under the aegis of the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, and are implemented by the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO), a Central Public Sector Undertaking under the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD).
Schemes Implemented through PMDKs
- Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase/Fitting of Aids and Appliances (ADIP Scheme): Aims to assist Divyangjan with suitable, durable, and scientifically manufactured aids and appliances.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): Focuses on providing free-of-cost assistive devices to senior citizens from BPL or economically weaker backgrounds.
Beneficiary-Oriented Impact
- With the inauguration of the latest centre in Badaun, the total number of operational PMDKs in the country has reached 75.
- These centres have collectively benefited over 1.4 lakh individuals, distributing assistive devices worth ?179.15 lakh.
- Devices offered include:
- Tricycles, wheelchairs, walkers
- Hearing aids and artificial limbs
- Other mobility and sensory support equipment
Significance and Relevance
The PMDK initiative plays a crucial role in addressing the accessibility gap in health and welfare services for Divyangjan and elderly citizens. By establishing these centres at regional medical hubs, the government is:
- Reducing the travel burden and logistical challenges for beneficiaries.
- Ensuring dignified, timely, and localised support.
- Strengthening the implementation of constitutional and legal mandates under Articles 41 and 46, which call for state support to the vulnerable sections of society.
Sanchar Mitra Scheme

- 15 Jul 2025
In News:
The Sanchar Mitra Scheme, launched by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications, is a nationwide volunteer-based initiative aimed at promoting digital literacy, telecom safety, and cybersecurity awareness among citizens.
Initially piloted in select institutions, the scheme has now been scaled up nationally due to its successful outreach and impact.
Key Highlights:
- Who are Sanchar Mitras?
- Selected university student volunteers from streams such as telecom, electronics, computer science, and cybersecurity who act as digital ambassadors to spread awareness at the grassroots level.
- Core Objectives:
- Promote digital safety and cyber hygiene
- Raise awareness on cyber frauds, EMF radiation concerns, and responsible mobile usage
- Bridge the communication gap between telecom services and citizens
- Training & Exposure: Sanchar Mitras receive specialized training from:
- National Communications Academy–Technology (NCA-T)
- DoT Media Wing: Training covers topics such as 5G, 6G, Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity, and telecom technologies.
- Community Engagement: Volunteers organize awareness campaigns, collaborate with NGOs, and engage in door-to-door outreach to promote informed digital behavior.
- Assessment & Incentives: Participants are evaluated on innovation, consistency, and outreach impact. Top performers receive:
- Internship opportunities
- Involvement in national telecom projects
- Invitations to forums like the India Mobile Congress
- Participation in International Telecommunication Union (ITU) events
Recent Developments:
- The first expanded rollout was initiated in Assam, where DoT partnered with 18 top engineering institutions including IIT, IIIT, and NIT.
- Chaired by senior DoT officials, sessions in BSNL Bhawan, Guwahati, introduced the scheme and invited collaboration from academic institutions.
Significance for India:
- Digital Inclusion: Empowers citizens to participate securely in the digital ecosystem.
- Youth Engagement: Mobilizes Yuva Shakti as a force for nation-building and technological awareness.
- Cybersecurity Shield: Acts as a grassroots defense against increasing cyber threats and misinformation.
- Alignment with National Priorities: Supports India’s vision of leadership in the 4 Ds – Democracy, Demography, Digitization, and Delivery.
TALASH Initiative

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS), under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, in collaboration with UNICEF India, has launched TALASH — Tribal Aptitude, Life Skills and Self-Esteem Hub — a first-of-its-kind national initiative aimed at fostering the holistic development of tribal students enrolled in Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs).
Launched in July 2025, TALASH reflects a focused effort to promote self-awareness, life skills, and career clarity among tribal youth across India. The initiative aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, emphasizing inclusive, equitable, and holistic education.
Key Objectives:
- Support all-round development of over 1.38 lakh EMRS students across 28 States and 8 Union Territories.
- Strengthen academic learning, while building life skills, self-esteem, and career readiness.
- Bridge educational and psychological gaps for tribal youth, especially in remote and underprivileged areas.
Core Features of TALASH
- Digital Self-Discovery Platform: TALASH is an innovative digital portal that equips students with tools for career planning, aptitude assessment, and personal development.
- Psychometric Assessments: Inspired by NCERT’s Tamanna initiative, it offers a standardized aptitude test to identify students’ strengths, interests, and potential career paths.
Students are provided with Career Cards based on test results. - Career Counselling Support: Helps students make informed choices by aligning their aspirations with personal aptitude and career opportunities.
- Life Skills & Self-Esteem Modules: Includes interactive content to build problem-solving abilities, emotional intelligence, communication skills, and self-confidence.
- E-Learning for Educators: Offers a dedicated teacher portal for capacity building, enabling educators to mentor and support students effectively.
Implementation and Outreach
- The program is being rolled out in phases, starting in select EMRSs for smooth execution.
- So far, 189 teachers from 75 EMRSs have been trained as master trainers.
- By the end of 2025, TALASH aims to be active in all EMRSs nationwide.
Institutional Backing and Vision
- NESTS: An autonomous body under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, responsible for the establishment and administration of EMRSs to ensure quality education for tribal students.
- UNICEF India: Brings global expertise in child development, focusing on equitable access, well-being, and digital empowerment.
Broadcasting Infrastructure and Network Development (BIND) Scheme

- 12 Jul 2025
In News:
The Government of India has proposed the establishment of a new Akashvani Kendra in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, under the Broadcasting Infrastructure and Network Development (BIND) Scheme.
About BIND Scheme
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Implementing Agency: Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Beneficiary: Prasar Bharati (All India Radio and Doordarshan)
- Objective: To provide financial support for:
- Expansion and modernization of broadcasting infrastructure
- Content development for domestic and international audiences
- Civil works related to Prasar Bharati’s operations
Key Features
- Facilitates technological upgradation of All India Radio (AIR) and Doordarshan (DD)
- Enhances reach in border, Left-Wing Extremism (LWE)-affected, and strategic regions
- Focuses on high-quality and diverse content
- Expands the capacity of the DTH platform, enabling more channels for viewers
- Aims to boost AIR FM coverage from 59% to 66% of India's geographical area and from 68% to 80% of the population
Significance
- Supports regional broadcasting, especially in underserved and aspirational districts
- Promotes cultural preservation and grassroots-level development narratives
- Expected to create indirect employment in manufacturing and broadcast services sectors
- Aids in ensuring last-mile delivery of public communication and information services
The proposed Akashvani Kendra in Ujjain aligns with the broader vision of ‘Viksit Bharat’, focusing on inclusive media access and robust public broadcasting infrastructure. It underscores the growing synergy between the Centre and States to enhance media penetration and communication outreach.
Miniature Plasma Loops

- 11 Jul 2025
In News:
A significant discovery by Indian and international astronomers has unveiled the existence of miniature plasma loops in the lower layers of the Sun’s atmosphere, shedding new light on how the Sun stores and releases magnetic energy—a long-standing mystery in solar physics.
- These loops are tiny in scale, measuring 3,000–4,000 km in length and less than 100 km in width, making them difficult to detect with earlier instruments. Despite their short lifespan of only a few minutes, they offer crucial insights into magnetic reconnection—a process where tangled magnetic field lines snap and realign, releasing immense energy.
- The research was led by scientists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), in collaboration with global institutions including NASA, the Max Planck Institute, and the Big Bear Solar Observatory (BBSO).
Key Findings and Instruments Used
- The team used high-resolution imaging and multi-wavelength spectroscopy, combining data from the Goode Solar Telescope (BBSO), NASA’s IRIS, and the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
- The loops were observed in the H-alpha spectral line from hydrogen atoms—crucial for studying the solar chromosphere.
- Spectroscopic data from IRIS revealed non-thermal broadening of spectral lines, indicating explosive magnetic activity.
- Plasma jets erupting from the tops of these loops point to reconnection-driven events, similar to those that cause large-scale solar eruptions.
- Using Differential Emission Measure (DEM) analysis, the plasma inside these tiny loops was found to reach temperatures of several million degrees, which is unexpectedly high for regions in the dense chromosphere.
Why It Matters
- Although coronal loops in the outer solar atmosphere have been studied for decades, these miniature loops offer a unique window into the fine-scale dynamics of the Sun's magnetic environment. Understanding them is crucial for grasping the mechanisms behind solar flares, coronal heating, and space weather phenomena that impact Earth.
Future Prospects
- The findings highlight the need for next-generation solar observatories. India’s upcoming National Large Solar Telescope (NLST)—a 2-meter aperture facility proposed near Pangong Lake, Ladakh—aims to provide sharper images of the Sun’s chromosphere and better magnetic field data.
C-FLOOD

- 06 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant advancement in disaster risk management, Union Minister of Jal Shakti Shri C.R. Patil inaugurated C-FLOOD, a Unified Inundation Forecasting System. Developed under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM), C-FLOOD marks a pivotal step toward strengthening India's flood preparedness and mitigation strategy.
What is C-FLOOD?
C-FLOOD is a web-based, real-time flood forecasting platform designed to deliver two-day advance inundation forecasts at village-level resolution. It provides:
- Flood inundation maps
- Water level predictions
- Localized early warnings to support disaster response and planning.
Developing Agencies:
- Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune
- Central Water Commission (CWC)
- National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)
Developed in collaboration with the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY), and Department of Science & Technology (DST).
Key Features:
- 2-Day Village-Level Forecasts: Localized and high-resolution predictions up to the gram panchayat level.
- Advanced 2-D Hydrodynamic Modelling: Simulations run on High-Performance Computing (HPC) systems under NSM.
- Multi-Basin Coverage: Initially operational in the Mahanadi, Godavari, and Tapi river basins, with future expansion planned.
- Unified Data Integration: Combines outputs from national and regional flood models into one platform.
- Disaster Portal Linkage: Designed for integration with the National Disaster Management Emergency Response Portal (NDEM).
- Climate-Adaptive Governance: Supports flood forecasting in regions vulnerable to climate-induced extreme weather events.
Strategic Importance:
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Enables timely warnings, efficient evacuations, and minimizes loss of life and property.
- Scientific & Operational Integration: Bridges hydrological modelling with on-ground responses.
- Supports Viksit Bharat @2047 Vision: Contributes to climate-resilient water governance.
- Promotes Inter-Agency Synergy: Encourages coordination among CWC, C-DAC, NRSC, and disaster management bodies.
Government Directions and Future Path:
During the inauguration, the Union Minister emphasized:
- Wide dissemination of C-FLOOD to enhance public awareness.
- Expansion to all major river basins through comprehensive inundation studies.
- Improved accuracy via satellite data validation and ground-truthing.
- Integration with NDEM for real-time emergency response.
The minister lauded the collaborative spirit of CWC, C-DAC, and NRSC, and reaffirmed the government's commitment to proactive and technology-driven disaster management.
CRISPR-Based Gene Switch for Climate-Resilient Agriculture
- 03 Jul 2025
In News:
Scientists at the Bose Institute, Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed a modified CRISPR-based molecular tool to enhance plant resilience against heat stress and bacterial infections. The research is published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
What is the Innovation?
- The tool is a modified version of the CRISPR system called dCas9 (dead Cas9), which does not cut DNA.
- Instead, it functions as a stress-responsive gene switch, turning defense and heat-tolerance genes on or off only when the plant is under stress (e.g., high temperature or pathogen attack).
How Does It Work?
- The switch is held outside the plant cell’s nucleus using a tomato-derived protein domain (NACMTF3 TM domain).
- Under stress conditions, such as heat waves or bacterial infection, the tether is released.
- The dCas9 switch then enters the nucleus, activating genes that help the plant combat the stress.
Key Functional Genes Activated:
|
Gene |
Function |
|
CBP60g, SARD1 |
Activate immune response to bacterial infection (e.g., Pseudomonas syringae) |
|
NAC2, HSFA6b |
Enhance heat tolerance, retain water, and improve overall health |
Salient Features of the Tool:
- Non-invasive: Unlike traditional CRISPR, this version does not edit the DNA, making it safer and more acceptable.
- Energy-efficient: The switch is activated only when needed, minimizing unnecessary energy use by the plant.
- Dual Protection: Shields plants from both heat stress and pathogenic infections.
- Eco-friendly and crop-compatible: Based on naturally occurring proteins, tested successfully in tomato, potato, and tobacco.
Significance and Impact:
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Helps plants survive in rising temperatures and unpredictable weather.
- Food Security: Boosts productivity in solanaceous crops like tomato, potato, brinjal, and chilli.
- Smart Farming Solution: Offers a model for sustainable and precision agriculture globally.
- Global Applicability: Can be adapted to other food crops affected by climate change and disease outbreaks.
Cell Broadcast System

- 03 Jul 2025
In News:
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT), in collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), is piloting a Cell Broadcast (CB) system to enhance emergency communication and deliver real-time disaster alerts across India.
What is the Cell Broadcast System?
Cell Broadcasting is a telecommunication technology that enables mobile network operators to send geographically targeted text alerts to all mobile devices in a specific area. Unlike traditional SMS, CB messages are broadcast simultaneously to all phones within a cell tower’s coverage, ensuring instant delivery even during network congestion.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Instantaneous alerts during emergencies like earthquakes, tsunamis, lightning strikes, and industrial disasters.
- Indigenously developed by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT).
- Language inclusivity: Messages can be broadcast in multiple Indian languages.
- Particularly effective in high-density areas and during network overloads.
Integration with Existing Systems:
This CB system complements the existing Integrated Alert System (SACHET), which:
- Has delivered over 6,899 crore SMS alerts.
- Covers all 36 States and Union Territories.
- Supports 19 Indian languages.
- Is based on the Common Alerting Protocol (CAP) as recommended by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Once fully deployed, the Cell Broadcast system will strengthen India’s disaster preparedness, ensuring wider, faster, and more inclusive dissemination of critical alerts.
India Energy Stack (IES)

- 02 Jul 2025
In News:
In a transformative move aimed at digitising India’s power sector, the Ministry of Power has announced the conception of the India Energy Stack (IES) — a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) initiative designed to build a unified, secure, and interoperable digital ecosystem across the energy value chain.
This effort aligns with India’s goals of achieving a $5 trillion economy and meeting its Net Zero commitments, while addressing the growing complexities of a rapidly evolving energy landscape marked by renewables, electric vehicles, and consumer-centric markets.
What is India Energy Stack (IES)?
The India Energy Stack is envisioned as a standardised, open, and secure digital infrastructure to:
- Streamline operations in the power sector
- Empower consumers with access to real-time, consent-based data
- Integrate renewable energy into the national grid
- Enhance the efficiency of Distribution Companies (DISCOMs)
The initiative is spearheaded by the Ministry of Power, drawing inspiration from successful DPI models like Aadhaar (identity) and UPI (digital payments).
Core Features of IES
- Unique IDs: Assigned to consumers, assets, and energy transactions
- Real-time Data Sharing: Consent-based access for secure and accountable data exchange
- Open APIs: Enabling seamless integration across utility systems and third-party applications
- Consumer Empowerment Tools: Market access platforms, billing transparency, demand response options, and innovation support
- Interoperability: Standardised protocols for all stakeholders in the electricity ecosystem
Implementation Strategy
1. Proof of Concept (PoC) – 12 Months
A year-long pilot phase will test the India Energy Stack using real-world scenarios in partnership with selected utilities and DISCOMs.
2. Utility Intelligence Platform (UIP)
The UIP is a modular, analytics-driven application built on the India Energy Stack. It aims to:
- Provide real-time insights to utilities, policymakers, and regulators
- Enable smart energy management
- Enhance decision-making for grid operations and consumer services
3. Pilot Regions
The PoC will be conducted in collaboration with DISCOMs in:
- Mumbai
- Gujarat
- Delhi
Institutional Framework
- A dedicated Task Force has been established by the Ministry of Power.
- It includes experts from:
- Technology domain
- Power sector operations
- Regulatory bodies
- The Task Force will guide:
- System architecture design
- Pilot implementation
- National scale-up strategy
Expected Outcomes
- India Energy Stack White Paper for public consultation
- UIP deployment in pilot cities
- National roadmap for phased rollout of IES across all states and UTs
- Improved grid stability, energy access, and transparency in service delivery
- Enhanced integration of renewable energy sources into the mainstream grid
Significance for India’s Power Sector
The India Energy Stack has the potential to be a game-changer for the power sector, enabling:
- Modernisation of legacy systems
- Digital empowerment of consumers
- Efficient energy trading and billing
- Decentralised and democratised power governance
As India undergoes its green energy transition, IES will serve as the digital spine supporting clean, accountable, and consumer-centric power distribution.
At Sea Observer Mission

- 02 Jul 2025
In News:
In a major milestone for regional security, the QUAD nations — India, Japan, the United States, and Australia — have launched their first-ever 'At Sea Observer Mission'. This cross-embarkation initiative, conducted under the Wilmington Declaration, seeks to deepen maritime interoperability, operational coordination, and domain awareness in the Indo-Pacific region.
This move signifies the QUAD’s growing shift from diplomatic coordination to practical maritime collaboration, in line with the vision outlined at the QUAD Leaders’ Summit in September 2024.
Key Features of the At Sea Observer Mission
- Participating Nations: India, Japan, USA, and Australia — the four QUAD countries.
- Agencies Involved:
- Indian Coast Guard (ICG)
- Japan Coast Guard (JCG)
- United States Coast Guard (USCG)
- Australian Border Force (ABF)
- Vessel Involved:USCGC Stratton (US Coast Guard Cutter) currently en route to Guam.
- Observer Teams: Two officers from each country, including women officers, embarked for the mission.
- Format:Cross-embarkation, where officers from different countries are hosted on board a partner nation's ship to enable firsthand operational learning.
Objectives and Strategic Relevance
- Strengthening Maritime Security
- Promotes collective surveillance, intelligence sharing, and maritime law enforcement.
- Enhances preparedness against common threats such as illegal fishing, piracy, smuggling, and disaster response.
- Boosting Interoperability and Coordination
- Lays groundwork for real-time joint operations and coordinated patrols.
- Encourages standardization of practices and communication protocols across QUAD navies and coast guards.
- Upholding the Rules-Based Order: Reinforces commitment to a Free, Open, Inclusive, and Rules-Based Indo-Pacific, countering unilateral actions and grey-zone threats in the region.
Indian Perspective: SAGAR and IPOI
India’s participation in the mission reflects its broader strategic vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region). It also aligns with India’s leadership in the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), particularly in the pillars of:
- Maritime Security
- Capacity Building and Resource Sharing
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Management
- Maritime Ecology and Maritime Resources
India's active role demonstrates its commitment to multilateral maritime cooperation, gender inclusivity, and regional stability.
Long-Term Implications: Toward a 'QUAD Coast Guard Handshake'
The ‘At Sea Observer Mission’ represents a foundation for the future institutionalisation of QUAD maritime security cooperation, informally dubbed the ‘QUAD Coast Guard Handshake.’ This aims to:
- Foster trust and operational familiarity
- Improve collective resilience against emerging maritime challenges
- Create a responsive, inclusive, and rule-abiding Indo-Pacific maritime domain
Eight Years of GST
- 02 Jul 2025
In News:
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) was implemented on 1st July 2017, aiming to unify India’s fragmented indirect tax system into a single, nation-wide tax. It replaced multiple central and state levies such as excise duty, service tax, VAT, and others.
By simplifying the tax structure and improving transparency, GST aimed to enhance compliance, remove tax cascading, and create a common national market. As of 1st July 2025, GST has completed eight years.
Key Highlights of 2024–25
- In the financial year 2024–25, GST collections reached an all-time high of ?22.08 lakh crore, representing a growth of 9.4% over the previous year. The average monthly collection was ?1.84 lakh crore. The number of active GST taxpayers crossed 1.51 crore.
- According to the Deloitte GST@8 survey, 85% of respondents across industries reported a positive experience with GST, highlighting improvements in compliance, transparency, and ease of doing business.
Structure of the GST System
Components of GST
GST operates under a dual model:
- Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) for intra-state transactions.
- Integrated GST (IGST) for inter-state transactions and imports.
Rate Structure
The GST Council has approved a multi-tier rate structure:
- Standard slabs of 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28% apply to most goods and services.
- Special lower rates include 0.25% on rough diamonds, 1.5% on cut and polished diamonds, and 3% on gold, silver, and jewellery.
- A Compensation Cess is levied on select goods such as tobacco, aerated drinks, and luxury cars to compensate states for revenue loss during the transition.
Key Features of GST
- Destination-Based Tax: GST is levied at the place of consumption, rather than origin. This ensures equitable revenue distribution and smooth credit flow across the supply chain.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Businesses can claim credit for taxes paid on inputs. This eliminates the cascading effect of taxes and reduces overall costs.
- Threshold Exemption: Small businesses with turnover below ?40 lakh for goods and ?20 lakh for services are exempt from GST, reducing the compliance burden on micro-enterprises.
- Composition Scheme: Businesses with turnover up to ?1.5 crore (goods) and ?50 lakh (services) can opt for a simplified tax scheme with fixed rates and minimal paperwork.
- Digital Compliance: All processes—from registration to return filing and payments—are conducted online through the GSTN portal. This digital-first approach enhances transparency and efficiency.
- Sector-Specific Exemptions: Essential sectors such as healthcare and education are either exempt or taxed at concessional rates to ensure affordability.
- Revenue Sharing: GST enables seamless credit transfers and transparent revenue sharing between the Centre and States, strengthening cooperative fiscal federalism.
Impact of GST
On MSMEs
- GST has provided major relief to micro, small, and medium enterprises by raising exemption thresholds and simplifying compliance. The introduction of the composition scheme allows them to pay tax at a flat rate with simplified filing.
- The Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) has also expanded access to credit. As of May 2024, four digital platforms were operational, with over 5,000 buyers and 53 banks and 13 NBFCs registered as financiers.
- Other initiatives include quarterly return filing for businesses with turnover up to ?5 crore and SMS-based NIL return filing, reducing administrative hassle for small taxpayers.
On Consumers
- GST has benefited consumers by lowering tax rates on essential goods such as cereals, edible oils, sugar, and snacks. A study by the Finance Ministry found that GST led to an average household saving of 4% in monthly expenses.
- The expansion of the tax base from 60 lakh registered taxpayers in 2017 to over 1.51 crore in 2025 has enabled the government to rationalize rates further.
On the Logistics Sector
- The removal of inter-state check posts and the introduction of e-way bills have significantly improved logistics efficiency. Transport time has reduced by over 33%, and businesses no longer need to maintain warehouses in every state. This has facilitated the creation of centralized, tech-enabled supply chains.
Revenue Performance Over Time
Since its launch, GST collections have shown consistent growth. In 2020–21, collections stood at ?11.37 lakh crore. They rose to ?14.83 lakh crore in 2021–22, ?18.08 lakh crore in 2022–23, ?20.18 lakh crore in 2023–24, and finally to ?22.08 lakh crore in 2024–25. This reflects improved compliance, economic recovery, and digital enforcement.
GST Council and Its Role
Constitutional Basis: The GST Council was constituted under Article 279A of the Constitution following the passage of the 122nd Constitutional Amendment Act. The Council was formally set up after Presidential assent on 8th September 2016.
Composition: The Council includes:
- Union Finance Minister as Chairperson
- Union Minister of State (Finance/Revenue)
- State Finance Ministers
- Special representation in case of constitutional emergency (Article 356)
Major Decisions: Since its inception, the GST Council has met 55 times and taken several reform-oriented decisions:
- Introduced e-way bills, e-invoicing, and the QRMP scheme
- Reduced GST on under-construction affordable housing from 8% to 1%
- Lowered GST on electric vehicles from 12% to 5%, and exempted large EV buses
- Streamlined compliance through auto-populated returns and QR codes
- Rationalized GST slabs, reducing items in the 28% slab from 227 to 35
- Set up GST Appellate Tribunals with Principal Bench in New Delhi
- Rolled out Aadhaar-based biometric authentication and clarified rules for vouchers
- Recommended full GST exemption on gene therapy and a legal framework for Invoice Management System
Skills for the Future

- 01 Jul 2025
In News:
Recently, theUnion Minister Jayant Chaudhary (MoS, Independent Charge – Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, and MoS – Ministry of Education) unveiled the report "Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Workforce Landscape", prepared by the Institute for Competitiveness (IFC). This data-driven report critically analyses India’s skilling ecosystem using PLFS 2023–24 and other datasets.
Significance of Skilling for India’s Development
- Demographic Dividend: India has one of the world’s youngest populations. Skilling is crucial to leverage this before population ageing sets in (by 2047).
- Economic Growth: A 1% rise in Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) at the tertiary level increases GDP by 0.511% (Parika, 2020).
- Employment Creation: India needs to create 5 lakh non-farm jobs annually till 2030 (Economic Survey 2023–24).
- Global Competitiveness: Leadership in EVs, AI, biotechnology, and green energy demands a future-ready workforce.
Key Findings from the Report (PLFS 2023–24 Based)
1. Skill Distribution
- 88% of India’s workforce is in low-competency jobs (Skill Levels 1 & 2).
- Only 10–12% are employed in high-skill roles (Skill Levels 3 & 4).
- Only 4.5% of the workforce has received formal vocational training.
2. Education-Skill Mismatch
- Only 8.25% of graduates are in roles matching their skill level.
- Over 50% of graduates are employed in lower-skill jobs.
- Severe case of overqualification and underutilization of educational capital.
3. TVET and Sectoral Gaps
- Top 5 Sectors (66% of vocational enrolment):
- Electronics
- IT & ITeS
- Textiles & Apparel
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Beauty & Wellness
- Skill Deficits are critical in high-growth sectors like green tech, AI, biotech, and EVs.
4. Wage Inequality by Skill Level
Skill Level Avg. Annual Wage
Level 1 Rs.98,835
Level 2 Rs.1.26 lakh
Level 3 Rs.2.81 lakh
Level 4 Rs.3.94 lakh
46% of the workforce earns less than ?1 lakh/year, highlighting a major economic disparity.
5. Regional Disparities
- Low-Skilled States: Bihar, Assam (95% in Skill Levels 1 & 2)
- Higher-Skill States: Kerala, Chandigarh
- Migration and brain drain observed in low-skill, low-growth regions
Challenges Identified
- Skill-Education Mismatch: Graduates in low-skill jobs; vocational roles filled by underqualified informal workers.
- Weak TVET-Industry Linkage: Existing courses not aligned with Industry 4.0 or green economy needs.
- Low GER and Transition Dropout: Higher secondary GER at 57.56%, tertiary GER still below 30%.
- Gender & Social Exclusion: Low skilling access for women, SC/STs, rural youth.
- Data & Outcome Gaps: No central skill repository or real-time job-skill tracking.
Recommendations from the Report
- Institutional Reforms
- Launch a National Skill Gap Survey
- Establish a Central Skill Data Repository for real-time, evidence-based policymaking
- Curriculum & TVET Overhaul
- Update NCO codes (National Classification of Occupations)
- Integrate vocational training in schools
- Scale up PMKVY, NAPS, and credit-linked certifications
- Industry & Market Linkages
- Incentivise hiring of certified skilled labour
- Link industry wage structures to skill certifications
- Encourage industry-led training programs
- Targeted Inclusion & Regional Empowerment
- Empower State Skill Missions
- Prioritise high-potential regions and sectors
- Target women, SC/STs, informal sector workers
- Education Pipeline Strengthening
- Raise GER at higher secondary and tertiary levels
- Promote flexible, modular skilling programs for working populations and school dropouts
Digital Initiatives for Maritime Sector

- 01 Jul 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, launched a series of digital and sustainability-driven initiatives aimed at modernising India’s maritime sector. These reforms are aligned with the Maritime India Vision 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
Major Digital and Policy Initiatives Launched
1. Digital Centre of Excellence (DCoE)
- MoU signed between: MoPSW and Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC)
- Objective: Accelerate digital transformation across Indian ports
- Key Features:
- Application of AI, IoT, Blockchain to optimize maritime logistics
- Drive real-time operational upgrades
- Support green and sustainable port operations
- Strategic Alignment: Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat, Viksit Bharat @2047
2. SAGAR SETU Platform
- Type: Unified digital interface for maritime trade and EXIM operations
- Go-Live Date: 26th June 2025
- Integration: Connects 80+ ports and 40+ stakeholders
- Objective:
- Streamline cargo and vessel documentation
- Enable paperless, seamless, and transparent logistics
- Improve Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Linked with: PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan
3. DRISHTI Framework
- Full Form: Data-driven Review Institutional System for Tracking Implementation
- Purpose: Real-time monitoring of projects under Maritime India Vision 2030
- Key Pillars:
- KPI Monitoring
- Progress & Achievements Tracking
- Organisational Oversight
- Functional Cell Coordination
- Strategic Value: Informed decision-making, faster project delivery
4. Standardised Scale of Rates (SOR) Template for Major Ports
- Objective: Standardise port tariffs to remove inconsistencies and improve transparency
- Features:
- Uniform structure for port tariffs
- Digitally comparable rates across ports
- Ports retain flexibility for local economic conditions
- Expected Impact:
- Enhances investor confidence
- Improves user experience
- Aligns with global maritime practices
Sustainability & Clean Energy: Hydrogen Transition Roadmap
Gateway to Green Report
Title: Gateway to Green — Assessing Port Readiness for Green Hydrogen Transition in India
- Released by: Ministry of Ports in collaboration with the Indian Ports Association (IPA)
- Objective: Transform Indian ports into green hydrogen hubs by 2030
- Strategic Goals:
- Produce 5 million tonnes of Green Hydrogen by 2030
- Develop infrastructure for production, storage, and export
- Leverage India’s maritime geography for clean energy leadership
- Targeted Ports for Hydrogen Transition:
- V.O. Chidambaranar Port
- Paradip Port
- Deendayal Port
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port
- Mumbai Port
- Cochin Port
- Key Action Areas:
- Land allocation for hydrogen projects
- Demand stimulation and investor facilitation
- International collaborations for knowledge and finance
- Shared infrastructure models
Strategic Relevance for India
- Economic Impact:
- Enhances trade competitiveness and reduces logistics cost
- Modernises infrastructure to global benchmarks
- Boosts Make in India and port-led development
- Digital Governance:
- Promotes data-driven decision-making
- Enables real-time monitoring and performance tracking
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Aligns with India’s National Hydrogen Mission
- Ports act as catalysts for clean energy transition
NAVYA Initiative

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
In line with the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047 and the government’s focus on women-led development, the Government of India has launched NAVYA—a pilot initiative aimed at vocationally skilling adolescent girls to empower them with future-ready skills and opportunities.
The programme was officially launched in Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh, by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) in collaboration with the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
About Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational Training for Young Adolescent Girls (NAVYA):
- Objective:To provide vocational training to adolescent girls aged 16–18 years (with a minimum qualification of Class 10) in non-traditional job roles.
- Target Areas:Implemented as a pilot project in 27 districts across 19 States, including:
- Aspirational districts
- Districts in the North-Eastern States
This reflects the government's commitment to inclusive development and reaching underserved and vulnerable populations.
- Institutional Collaboration:
- Both ministries will formalize convergence to streamline and institutionalize skilling efforts for adolescent girls.
- NAVYA draws upon existing frameworks like the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) and other flagship skill development schemes.
Significance of NAVYA:
Aspect Importance
Empowerment - Enhances skills, confidence, and self-reliance among young girls
Gender Inclusion - Supports women-led development and economic participation
Employment Readiness - Equips girls with job-oriented skills in non-traditional sectors
Regional Equity - Targets backward and underserved regions to reduce disparities
Demographic Dividend - Harnesses the potential of India’s adolescent population in national development
“NAVYA represents a transformative step in ensuring that every adolescent girl becomes a catalyst for change in India’s journey towards an inclusive, skilled, and developed future.”
India’s Automotive Industry and Global Value Chains

- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog has recently released a comprehensive report titled “Automotive Industry: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains”. It offers a roadmap to boost India’s role in the global automotive sector by enhancing competitiveness, production capacity, and export potential.
India’s Current Position
India is the world’s fourth-largest automobile producer, with nearly 6 million vehicles manufactured annually. However, its share in the global automotive component trade remains modest at 3%, primarily due to limited penetration in high-precision segments like engine components and drive transmission systems. The country exports auto components worth $20 billion, with major strengths in small cars and utility vehicles.
Global Landscape and Emerging Trends
Globally, 94 million vehicles were produced in 2023, with the automotive components market valued at $2 trillion, of which $700 billion was exported. The industry is witnessing rapid transformation through:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Rising demand, regulatory shifts, and battery innovations are reshaping manufacturing.
- Battery Ecosystems: Hubs in Europe and the US are altering global supply chains, focusing on lithium and cobalt.
- Industry 4.0: AI, IoT, robotics, and machine learning are revolutionizing automotive manufacturing through smart factories and digital supply chains.
Challenges to India’s GVC Participation
Despite a strong production base, India faces several hurdles in climbing the Global Value Chain (GVC):
- Low R&D spending and limited innovation
- High operational costs and infrastructural gaps
- Weak IP ecosystem and low brand visibility
- Inadequate skilling and moderate digital adoption
Strategic Interventions Proposed
NITI Aayog recommends a combination of fiscal and non-fiscal measures to address these gaps and strengthen India’s automotive ecosystem.
Fiscal Measures:
- Opex support to scale up production and infrastructure
- Skilling initiatives to build a trained workforce
- R&D incentives and IP transfer support for MSMEs
- Cluster development for shared R&D and testing facilities
Non-Fiscal Measures:
- Promoting Industry 4.0 adoption and quality manufacturing
- Ease of Doing Business reforms in labour, logistics, and regulations
- Global tie-ups and Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) to boost exports
Vision for 2030
By 2030, the report envisions:
- Auto component production to grow from ~$60 billion to $145 billion
- Exports to increase from $20 billion to $60 billion
- GVC share to rise from 3% to 8%
- Trade surplus of around $25 billion
- Employment generation of 2–2.5 million additional jobs
DRDO’s Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’

- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted release trials of the indigenously developed Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’ from a Su-30 MKI aircraft.
About LRGB ‘Gaurav’
- Type: Air-launched, precision-guided munition.
- Purpose: Designed for accurate strikes on land targets from stand-off distances, i.e., beyond enemy air defence range.
- Indigenously developed by DRDO under the Ministry of Defence.
Key Features
- Range:
- Demonstrated precision strike at nearly 100 km.
- Operational range: 30–150 km.
- Variants by Weight:
- Gaurav (winged): 1,000 kg
- Gautham (non-winged): 550 kg
- Guidance Systems:
- Inertial Navigation System (INS)
- Satellite-based navigation (e.g., GPS/IRNSS)
- Digital control for enhanced accuracy
Significance
- Boosts India’s precision strike capability.
- Promotes self-reliance in defence technology under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Related Concepts
Glide Bomb:
- A precision-guided munition that travels significant distances without powered propulsion.
- Uses aerodynamic lift to glide toward the target.
- Navigation via INS, GPS, or laser guidance.
Su-30 MKI Aircraft:
- A twin-engine, multirole fighter aircraft.
- Developed jointly by Sukhoi Design Bureau (Russia) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Backbone of the Indian Air Force (IAF) combat fleet.
Seva Se Seekhen Campaign
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the ‘Seva Se Seekhen’ (Learn by Doing) campaign to empower youth through hands-on experience at Jan AushadhiKendras (JAKs). Starting from June 1, 2025, this initiative aims to blend experiential learning with public health outreach.
About the Campaign:
- Launched in: 2025
- Nodal Ministries:
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
- Framework:Part of the National Youth Development Framework, aligning youth engagement with grassroots service.
Objectives:
- Provide experiential learning opportunities in real-world public service settings.
- Raise awareness about generic medicines and enhance health literacy.
- Equip youth with technical and soft skills in areas such as inventory, logistics, customer service, and communication.
- Foster values such as discipline, empathy, and civic responsibility among the youth.
Key Features:
- Nationwide Implementation:
- Five youth volunteers per district will be placed across five Jan AushadhiKendras.
- Covers all states and Union Territories.
- Volunteer Sources:Participants are selected from:
- MY Bharat
- National Service Scheme (NSS)
- Pharmacy colleges
- Other youth-focused platforms
- Duration:15-day structured engagement, including guided tasks and learning outcomes.
Roles and Responsibilities of Volunteers:
- Support daily functioning and customer services at JAKs.
- Assist in medicine inventory and logistics management.
- Promote generic medicine awareness among the public.
- Participate in community health outreach activities.
- Observe backend processes like supply chains and stock maintenance.
Key Benefits for Youth:
- Practical exposure to pharmacy operations and public health service.
- Skills in record-keeping, inventory handling, and basic operations.
- Development of employability and customer interaction skills.
- Insights into affordable healthcare delivery under schemes like Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya JanaushadhiPariyojana (PMBJP).
BharatGen

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh launched BharatGen, India’s first indigenously developed, government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) at the BharatGen Summit 2025, marking a significant step in India’s AI innovation landscape.
About BharatGen:
- BharatGen is a Multimodal LLM designed to support 22 Indian languages and various content formats—text, speech, and image.
- Developed under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS) and implemented by the TIH Foundation for IoT and IoE at IIT Bombay.
- Supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), it is a collaborative effort involving premier academic institutions, researchers, and innovators.
Key Features:
- Multilingual and multimodal capabilities (text, voice, image inputs).
- Open-source platform to encourage accessible innovation.
- Trained on Indian datasets to reflect Indian linguistic and cultural diversity.
- Integrated applications across critical sectors like healthcare, education, governance, and agriculture.
- Aims to deliver region-specific AI solutions rooted in Indian values and societal contexts.
Implementation Mechanism:
- Executed through 25 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIHs) across India.
- Four of these TIHs have been upgraded to Technology Translational Research Parks (TTRPs) for real-world deployment.
- Guided by four pillars: technology development, entrepreneurship, human resource development, and international collaboration.
ULLAS – Nav Bharat SaakshartaKaryakram and Goa’s Milestone in Literacy

- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Goa became the second state in India to achieve full functional literacy under the ULLAS – Nav Bharat SaakshartaKaryakram (New India Literacy Programme), marking a key achievement in India’s goal of attaining full literacy by 2030, as envisioned in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
About ULLAS
- ULLAS stands for Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented by the Ministry of Education from 2022 to 2027.
- Target Group: Adults aged 15 years and above who missed formal schooling.
- Alignment: The scheme is aligned with NEP 2020, emphasizing inclusive and equitable education.
- Implementation Basis: The programme is built on the spirit of volunteerism and Kartavya Bodh (sense of duty).
Five Components of the ULLAS Scheme:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- Critical Life Skills
- Basic Education
- Vocational Skills Development
- Continuing Education
Digital Outreach
- The ULLAS mobile app facilitates registration of learners and volunteers.
- It also provides access to learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- So far, over 2.40 crore learners and 41 lakh volunteer teachers have been registered on the app.
- Over 1.77 crore learners have taken the Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT).
Goa Achieves Full Literacy
- Declared Fully Literate: On May 30, 2025, during the 39th Goa Statehood Day celebrations at Panaji, Goa was declared fully literate.
- Reported Literacy Rate: As per PLFS 2023–24, Goa had a literacy rate of 93.60%, among the highest in India.
- State Survey Update: A state-led survey confirmed that Goa had crossed the 95% benchmark, qualifying it as fully literate under ULLAS.
Key Factors Behind Goa’s Success
- Adopted a Whole-of-Government approach, involving departments such as:
- Directorate of Panchayats
- Municipal Administration
- Social Welfare
- Planning & Statistics
- Women & Child Development
- Engaged SwayampurnaMitras for grassroots awareness and learning support.
- Played an active role in certification and inclusion of learners into the literacy programme.
- Strong collaboration between SCERT, local administration, school heads, volunteers, and field workers ensured last-mile delivery.
Significance for India
- Goa's achievement underscores the effectiveness of decentralized, people-driven literacy campaigns.
- Demonstrates the potential of tech-enabled platforms, volunteerism, and inter-departmental coordination.
- Sets a model for other states in achieving India’s literacy goal by 2030.
- Reinforces the broader national vision of “Jan-Jan Saakshar” and a Viksit Bharat.
DHRUVA(Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address)
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Department of Posts, under the Ministry of Communications, released the policy framework for DHRUVA (Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address) — a key initiative aimed at creating a standardized, geo-coded digital address infrastructure across India.
What is DHRUVA?
DHRUVA is a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) initiative that conceptualizes Address-as-a-Service (AaaS) — a secure, consent-based, and interoperable system for managing and sharing address data. It builds upon the earlier DIGIPIN (Digital Postal Index Number) system, which created a national-level, geo-tagged addressing grid for improved governance and service delivery.
Objectives of DHRUVA
- Transform address information into a digital public good.
- Enable secure, standardized, and interoperable access to address data across sectors.
- Empower users with control and consent over how their address data is shared.
- Promote public-private collaboration in areas like logistics, e-governance, and financial inclusion.
Key Features
- DIGIPIN Backbone: Utilizes the Digital Postal Index Number system, allowing logical and directional naming of addresses with precise geolocation.
- Address-as-a-Service (AaaS): Facilitates seamless address validation, authentication, and sharing across government and private platforms.
- User Autonomy: Individuals can manage and consent to how their address data is used, ensuring privacy and user-centric governance.
- Open & Inclusive Access: The infrastructure is freely accessible, promoting innovation and broad-based adoption.
- Consent Framework: Address data sharing will be user-approved, ensuring a secure and trusted digital ecosystem.
Significance of DHRUVA
- Geospatial Governance: Enhances planning, disaster management, and delivery of public services through precise address mapping.
- Improved Logistics & E-Commerce: Enables more efficient last-mile delivery, reducing ambiguity in address identification.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates smoother KYC, subsidy disbursement, and service access in rural and underserved areas.
- Ease of Living & Digital India: Aligns with broader national goals by supporting smart governance and digital transformation.
- Public-Private Synergy: Encourages co-creation of solutions by government bodies and private enterprises based on shared, trusted digital address data.
Seaweed Farming in India
- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
With growing attention on sustainable marine resources and coastal livelihood enhancement, the Government of India is promoting seaweed cultivation as part of its broader Blue Economy strategy. Recognized for its nutritional, economic, and ecological value, seaweed farming is emerging as a viable livelihood and environmental solution for India's coastal communities.
What is Seaweed?
Seaweed is a nutrient-rich marine plant that grows in shallow ocean waters. It is:
- Rich in vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and 54 trace elements.
- Known to aid in managing non-communicable diseases such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular ailments, and hypertension.
- Used in food, cosmetics, fertilizers, medicines, and industrial gelling agents like agar, alginate, and carrageenan.
Global Significance and Industry Potential
- The global seaweed market is valued at US$ 5.6 billion and projected to reach US$ 11.8 billion by 2030 (World Bank).
- Major consumers: Japan, China, and South Korea.
- India possesses vast untapped potential with over 7,500 km of coastline and 844 identified seaweed species, of which ~60 are commercially viable.
Seaweed and the Blue Economy in India
Government Initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) (launched in 2020):
- Total Outlay: ?20,050 crore.
- ?640 crore allocated for seaweed development (2020–25).
- Goal: Increase seaweed production to 1.12 million tonnes in five years.
- Projects funded:
- Multipurpose Seaweed Park in Tamil Nadu.
- Seaweed Brood Bank in Daman & Diu.
- Provision of 46,095 rafts and 65,330 monocline tubenets to farmers.
Supportive Regulatory Measures:
- Seaweed-based biostimulants regulated under the Fertilizer (Control) Order, 1985.
- Integrated with Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) and MOVCDNER to promote organic farming.
Economic, Environmental & Social Benefits
Economic:
- Seaweed farming offers high returns — e.g., farming Kappaphycusalvarezii may yield up to ?13.28 lakh/hectare/year.
- Generates foreign exchange through exports of seaweed-based bio-products.
Environmental:
- Requires no land, freshwater, fertilizers, or pesticides.
- Absorbs CO?, combats ocean acidification, and enhances marine biodiversity.
Social:
- Provides alternative livelihoods for fishers.
- Particularly beneficial for women and youth, promoting inclusive growth in coastal regions.
Success Stories and Innovations
Women Empowerment in Tamil Nadu:
Four women from Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, trained under PMMSY, successfully cultivated seaweed, producing 36,000 tonnes despite cyclones and market challenges. Their venture created employment and inspired other women.
Tissue Culture Innovation:
The CSIR-Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute (CSIR-CSMCRI)developed tissue-cultured Kappaphycusalvareziiseedlings, leading to:
- 20–30% higher growth rates.
- Better carrageenan quality.
- Enhanced farmer productivity in Tamil Nadu’s coastal districts.
Challenges and Way Forward
Challenges:
- Vulnerability to climatic shocks (cyclones, salinity changes).
- Limited market access and value chain infrastructure.
- Need for increased awareness and skill-building in coastal areas.
Recommendations:
- Strengthen public-private partnerships and R&D for better cultivars.
- Expand seaweed farming cooperatives with financial inclusion mechanisms.
- Promote Blue Economy integration in coastal development policies.
Acharya Charaka and Sage Sushruta

- 25 May 2025
In News:
The Vice-President of India recently inaugurated the statues of Acharya Charaka and Sage Sushruta at Raj Bhavan, Goa, to honour India's ancient medical heritage rooted in Ayurveda and surgery.
Acharya Charaka – Father of Indian Medicine
- Period: Circa 100 BCE – 200 CE
- Region: Associated with Taxila, under the Kushan emperor Kanishka.
- Key Contribution:
- Originally based on the Agnivesha Samhita, later revised and compiled by Charaka.
- Focused on internal medicine (Kayachikitsa).
- Discussed physiology, disease pathology, diagnosis, and therapeutic techniques.
- Introduced the concept of three doshas: Vata, Pitta, Kapha—the basis for diagnosis and treatment in Ayurveda.
- Provided early insights into embryology (Garbha Vigyan) and preventive healthcare.
- Stressed medical ethics, such as confidentiality, non-maleficence, and the moral duties of a physician.
- Emphasized the importance of diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors in health.
- The Charaka Samhita is part of the B?hatTrayi (Great Trilogy) of Ayurveda and was expanded by D??habala.
- Translated into Arabic, Latin, and other languages, reflecting its global medical influence.
Sage Sushruta – Father of Surgery
- Period: Circa 600–700 BCE
- Region:Practised in Kashi (Varanasi), likely under King Divodasa.
- Key Contribution:
- A pioneering treatise in surgery and medical science.
- Detailed 300+ surgical procedures and over 100 surgical instruments.
- Innovations include rhinoplasty (nasal reconstruction), skin grafts, cataract surgery, and caesarean sections.
- Explained fractures, dislocations, use of anaesthesia, and surgical training.
- Emphasized dissection-based anatomy, practical education, and simulation for surgical learning.
- Covered areas like public health, toxicology, pediatrics (Kaumarbhritya), and neonatal care.
- Integrated scientific observation, hygiene, and evidence-based methods long before modern systems.
Collective Significance:
- Both are part of the B?hatTrayi (Charaka Samhita, Sushruta Samhita, and Ashtanga Hridaya), forming the backbone of Ayurvedic literature.
- Their work laid the foundation for:
- Holistic medicine and ethical healthcare practice.
- Advanced understanding of human physiology and embryology.
- Scientific surgery, centuries ahead of global developments.
- Contributions to child health (Kaumarbhritya) and public hygiene.
- Their texts influenced Arab and European medicine through translations such as Kitab-i-Susrud.
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR)
- 24 May 2025
In News:
To mark its 25th anniversary, the Union Minister of Earth Sciences inaugurated two landmark facilities—Polar Bhavan and Sagar Bhavan—at the NCPOR campus in Vasco da Gama, Goa.
About NCPOR
- Established: 25 May 1998 (originally as the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research – NCAOR).
- Status: Autonomous R&D institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Headquarters: Vasco da Gama, Goa.
- Governing Body: Includes 13 members; the Secretary of MoES serves as the ex-officio Chairman.
Mandate and Key Functions
- Polar Research Leadership:
- Manages India's scientific stations:
- Antarctica: Maitri and Bharati
- Arctic: Himadri
- Himalayas: Himansh
- Coordinates India’s Antarctic, Arctic, Southern Ocean, and Himalayan expeditions.
- Manages India's scientific stations:
- Oceanic Research:
- Implements projects under the Deep Ocean Mission.
- Conducts Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) mapping and continental shelf surveys.
- Explores deep-sea minerals, gas hydrates, and metal sulphides.
- Policy Implementation:
- Supports India’s Arctic Policy (2022) and Indian Antarctic Act (2022):
- Antarctic Act: Provides legal framework for governance and environmental protection via CAG-EP (Committee on Antarctic Governance and Environmental Protection).
- Arctic Policy: Based on six pillars—science, environment, development, connectivity, governance, and capacity building.
- Supports India’s Arctic Policy (2022) and Indian Antarctic Act (2022):
- Scientific Logistics and Collaboration:
- Operates research vessels (e.g., ORV Sagar Kanya).
- Engages in international polar networks and climate monitoring programs.
- Maintains India’s Antarctic Data Centre and conducts climate modelling.
New Facilities at NCPOR
Polar Bhavan:
- Area: 11,378 sq. m | Cost: ?55 crore
- Features:
- Advanced polar and ocean research laboratories
- Science on Sphere (SOS) 3D visualization platform
- Accommodation for 55 scientists
- Conference halls, library
- Home to India’s first Polar and Ocean Museum
Sagar Bhavan:
- Area: 1,772 sq. m | Cost: ?13 crore
- Features:
- Two -30°C ice core laboratories
- +4°C storage units for biological and sediment samples
- Class 1000 clean room for trace metal and isotope studies
Significance for India
- Strengthens India’s strategic presence in polar regions.
- Enhances research capacity in ocean and climate sciences.
- Enables India to fulfill international obligations under polar treaties.
- Promotes science diplomacy and public outreach through the upcoming museum.
Sagar Mein Samman (SMS) Initiative

- 24 May 2025
In News:
The Government of India launched the Sagar Mein Samman (SMS) initiative on International Day for Women in Maritime (18 May), observed by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). The 2025 theme is “An Ocean of Opportunities for Women.”
About the Initiative:
- Objective: To build a gender-equitable maritime workforce by promoting inclusivity, safety, skill development, leadership, and equal opportunities for women across seafaring and shore-based maritime operations.
- Alignment:
- IMO’s gender inclusion mandate.
- UN SDG-5 (Gender Equality).
- India’s Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) framework.
- Maritime India Vision 2030 and Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
Key Features:
- Structured Policy Roadmap covering:
- Planning & strategy.
- Training & development.
- Research & innovation.
- Governance & compliance.
- Outreach & communications.
- Financial Support: ~2,989 women received assistance since 2014.
- Incentives for Industry: Shipping companies are incentivized to hire women; scholarships support training.
Achievements:
- 649% growth in women seafarers:From 341 in 2014 to 2,557 in 2024.
- Rise in financial aid beneficiaries:From 45 in 2014-15 to 732 in 2024-25.
- Female representation target:12% in technical maritime roles by 2030.
- Increasing employment of Indian women on Indian and foreign-flagged ships.
Recognition and Outreach:
- Women Leaders Honoured: Ten outstanding women were felicitated for their contributions to maritime.
- Focus on awareness campaigns, onshore job facilitation, and leadership opportunities.
Significance:
- Aims to dismantle gender-based barriers and promote inclusive economic growth.
- Reinforces India’s commitment to gender equity as a strategic enabler of maritime sustainability and national development.
- Aligns with global maritime norms and India’s broader commitment to SDGs.
Other Key Maritime Initiatives:
- SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region): Maritime security and regional cooperation.
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Long-term strategy for port-led development and gender inclusion.
Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)

- 23 May 2025
In News:
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT), under the Ministry of Communications, has launched the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) to counter the growing menace of cyber-enabled financial frauds, especially those involving mobile numbers.
What is FRI?
The Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) is a multi-dimensional analytical tool developed under the Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP). It classifies mobile numbers based on their risk level—Medium, High, or Very High—of being associated with financial fraud.
Purpose:
- To provide advance risk intelligence to financial institutions.
- To serve as a pre-transaction validation tool, flagging suspicious mobile numbers involved in digital transactions.
How It Works:
- The classification is based on data inputs from:
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP)
- DoT’s Chakshu facility
- Intelligence from banks and NBFCs
- Risk-tagged mobile numbers are flagged in real-time to stakeholders, including banks, UPI platforms, and payment service providers.
- Acts as a cyber shield, preventing fraudulent digital payments before they occur.
Implementation and Use Cases:
- PhonePe, an early adopter, uses FRI to:
- Block transactions involving "Very High" risk numbers.
- Warn users during transactions with "Medium" risk numbers via its "PhonePe Protect" feature.
- Other UPI giants like Google Pay and Paytm (collectively handling 90% of UPI traffic) are integrating FRI-based alerts.
- Banks have begun introducing transaction delays and alerts to curb cyber fraud using FRI data.
Why FRI is Crucial:
- India lost over ?3,207 crore to approximately 5.82 lakh cyber fraud cases between FY 2020–2024.
- The short operational window of fraudulent mobile numbers makes advance detection vital.
- Common cyber frauds include:KYC scams, UPI frauds, investment scams, digital arrest frauds, and get-rich-quick schemes.
Supporting Mechanisms:
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP): Facilitates real-time intelligence sharing between law enforcement and financial institutions.
- Chakshu on Sanchar Saathi: Enables citizens to report suspicious communication.
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting System: Part of I4C, it allows real-time fraud reporting via the 1930 helpline or cybercrime.gov.in.
- E-Zero FIR: Automatically registers FIRs for cybercrime complaints involving more than ?10 lakh.
- Mulehunter (RBI): AI-based tool to identify and track money mule accounts.
Blue Talks
- 23 May 2025
In News:
Recently, India successfully hosted the Second Blue Talks in New Delhi, organised by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) in collaboration with the Embassies of France and Costa Rica. This high-level consultation platform aims to contribute to the upcoming 3rd United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) scheduled from June 9–13, 2025 in Nice, France.
About Blue Talks
- Purpose: A multilateral platform for dialogue among governments, scientists, civil society, and stakeholders to promote the sustainable use of ocean resources and accelerate progress on Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14 – Life Below Water.
- Key Objectives:
- Promote marine sustainability, research, and education.
- Facilitate global scientific cooperation on ocean-related challenges.
- Share best practices and strategic knowledge tools.
- Strengthen consensus and policy alignment in the lead-up to UNOC3.
- Thematic Focus Areas of 2nd Blue Talks:
- Conservation and Restoration of Marine and Coastal Ecosystems.
- Scientific Cooperation, Marine Technology, and Ocean Literacy.
- Reduction of Marine Pollution from land and sea-based sources.
- Interlinkages among Oceans, Climate, and Biodiversity.
Highlights of the Event:
- White Paper Released: Transforming India’s Blue Economy: Investment, Innovation, and Sustainable Growth.
- Aim: To align government action, mobilize investments, and promote sustainable ocean development.
- Notable Themes:
- Mapping of marine resources.
- Promotion of offshore wind and deep-sea exploration.
- Technology and data-sharing gaps.
- Women-led seaweed farming, smart ports, and green ship recycling as success models.
About the 3rd United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3)
Feature Details
Host Countries France and Costa Rica
Venue & Dates Nice, France; June 9–13, 2025
Organiser United Nations
Theme “Accelerating action and mobilizing all actors to conserve and
sustainably use the ocean.”
Goal Strengthen global efforts under SDG 14
Key Outcome Nice Ocean Action Plan – a non-binding but politically influential declaration.
Focus Areas Marine conservation, pollution reduction, global partnerships, and
BBNJ ratification.
UN Ocean Conference Series
- 1st UNOC (2017): New York, USA – Raised awareness and voluntary commitments.
- 2nd UNOC (2022): Lisbon, Portugal – Focused on innovation and science-driven approaches.
- 3rd UNOC (2025): Nice, France – Aims to intensify action and collaboration.
India’s Blue Economy Vision
- India's Blue Economy is a critical pillar of the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
- MoES is the nodal agency for national ocean governance.
- The white paper integrates efforts from 25 ministries and all coastal states/UTs.
- Builds on India’s G20 Presidency and Chennai High-Level Principles for a Sustainable and Resilient Blue Economy.
e-Zero FIR System
- 22 May 2025
IN News:
In a significant stride toward modernizing cybercrime response mechanisms, Union Home Minister Amit Shah unveiled the e-Zero FIR system. This initiative ensures that complaints involving financial cyber frauds exceeding ?10 lakh—submitted via the 1930 helpline or the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP)—are automatically registered as FIRs, eliminating the need for the complainant to visit a police station.
Objective and Operational Rollout
The project, developed under the guidance of the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), is aimed at accelerating the registration and investigation of high-value cybercrime cases.
- Pilot Implementation: Initiated in Delhi as a testbed.
- National Expansion: Plans are underway to replicate the model across India.
Concept of Zero FIR
The Zero FIR mechanism permits the filing of an FIR at any police station, regardless of the location of the offence. This removes jurisdictional constraints and ensures prompt registration of cases.
- Legal Backing: Incorporated under Section 173 of the BharatiyaNagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023.
- Historical Context: Introduced following recommendations from the Justice Verma Committee post the 2012 Nirbhaya case, to address delays caused by jurisdictional rigidities.
Salient Features of Zero FIR
- No Jurisdictional Restrictions: Victims may file complaints at any police station or via electronic means.
- Initial Registration: The complaint is logged as a Zero FIR and then forwarded to the relevant jurisdictional police unit for investigation.
- Primary Goal: To facilitate timely intervention and prevent procedural delays for the complainant.
Integration with National Digital Systems
To enhance responsiveness and coordination, the e-Zero FIR system integrates with several key digital platforms:
- NCRP (National Cybercrime Reporting Portal) – Administered by I4C.
- Delhi Police’s e-FIR mechanism
- Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS) – Maintained by theNational Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
This digital infrastructure enables real-time complaint registration at Delhi’s e-Crime Police Station, which then redirects the FIR to the appropriate jurisdiction.
Alignment with New Criminal Legislation
The initiative is fully aligned with India’s revised criminal justice framework effective from July 1, 2024, which includes:
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023
- BharatiyaNagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023
- BharatiyaSakshyaAdhiniyam (BSA), 2023
Under the BNSS provisions:
- Mandatory Zero FIR registration under Section 173.
- Victim must visit a cybercrime police station within 72 hours to convert a Zero FIR into a formal FIR.
- Free copy of FIR to be provided to the complainant, ensuring transparency and empowering victims.
Vision for a Cyber-Secure India
The launch of the e-Zero FIR system underscores the government’s resolve to build a secure and digitally empowered India by:
- Ensuring easy and immediate access to justice for victims of cyber fraud.
- Facilitating quick action by investigative agencies without procedural bottlenecks.
- Strengthening citizen trust through digital governance and victim-friendly policing.
58thJnanpith Award Conferred

- 20 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the President of India, presented the 58thJnanpith Award to renowned Sanskrit scholar Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Ji at a function held at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi. She also extended congratulations to celebrated writer Gulzar, a fellow recipient who could not attend due to health reasons.
About Jagadguru Rambhadracharya
- A prominent Sanskrit scholar, spiritual leader, poet, and educationist.
- Despite being visually challenged, he has made significant literary and social contributions.
- Recognized for his multi-faceted excellence in Sanskrit literature and devotion to nation-building through literary and cultural service.
Highlights from the President’s Address
- Emphasized that literature unites and awakens society, playing a key role in movements from 19th-century social reform to the freedom struggle.
- Referenced the literary legacy of figures like Valmiki, Vyas, Kalidas, and Rabindranath Tagore as embodiments of India’s civilizational essence.
- Praised the BharatiyaJnanpith Trust for honoring literary excellence since 1965 across various Indian languages.
- Celebrated the contributions of women Jnanpith awardees such as Ashapurna Devi, Amrita Pritam, Mahasweta Devi, and Pratibha Ray, urging young women to draw inspiration from their works.
About the Jnanpith Award
Feature Details
Established 1961
First Awarded 1965 to Malayalam poet G. SankaraKurup for Odakkuzhal
OrganisedBy BharatiyaJnanpith, a literary and cultural organization founded in 1944
Eligibility Indian citizens writing in Schedule VIII languages of the Constitution or
in English
Award Components Cash prize, citation, and a bronze replica of Vagdevi (Saraswati)
Nature Annual, but may be withheld if no suitable candidate is found
One-Time Recognition A writer can receive the award only once
Language Rotation Rule A language that has received the award is ineligible for the next two years
Operation Olivia

- 20 May 2025
In News:
Operation Olivia is an annual conservation initiative launched by the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) in collaboration with the Odisha Forest Department, aimed at protecting the nesting habitats of Olive Ridley turtles along the Odisha coastline. It is conducted from November to May, aligning with the turtles’ mass nesting (Arribada) season.
Key Features of Operation Olivia (as of 2025)
- In February 2025, a record 6.98 lakh Olive Ridley turtles nested at the Rushikulya river mouth.
- Since inception, the ICG has conducted:
- 5,387 surface patrol sorties
- 1,768 aerial surveillance missions
- 366 boats involved in illegal fishing were detained, ensuring effective protection of the turtles' breeding grounds.
- 225 ship days and 388 aircraft hours were dedicated to Operation Olivia during a recent season.
- Focus areas include Gahirmatha Beach, Rushikulya, and Dhamra river mouths in Odisha—home to over 8 lakh nesting turtles annually.
Conservation Measures
- Fishing ban within 20 km of nesting coasts (Devi, Dhamra, and Rushikulya rivers), enforced under:
- Orissa Marine Fishing Regulation Act, 1982
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Promotion of Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs) to reduce accidental bycatch.
- Community awareness campaigns and MoUs with NGOs to ensure local participation and education on marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles
- Scientific Name:Lepidochelysolivacea
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Legal Protection:
- Schedule I, Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Appendix I, CITES
- Habitat: Warm tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans
- India’s Nesting Sites:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary – world’s largest rookery
- Rushikulya and Devi river mouths in Odisha
- Unique Feature: Mass nesting behavior known as Arribada, where thousands of females lay eggs on the same beach.
- Behavior: Omnivorous and solitary; migrate thousands of kilometers annually between feeding and breeding grounds.
Viksit Krishi Sankalp Abhiyan

- 20 May 2025
In News:
The Viksit Krishi Sankalp Abhiyan is a nationwide agricultural outreach and awareness initiative being launched by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare from May 29 to June 12, 2025.
The campaign is part of the government’s vision of “Viksit Bharat” and seeks to empower farmers through the dissemination of modern agricultural knowledge, technologies, and innovations across India.
Key Objectives and Vision
- Enhance agricultural productivity, improve farmer incomes, and ensure national food security.
- Promote modern, sustainable, and scientific farming practices aligned with the Prime Minister’s Lab-to-Land vision.
- Strengthen agriculture’s contribution to making India the “Food Basket of the World.”
Campaign Features
- Coverage: 700+ districts, 65,000+ villages, targeting 1.3–1.5 crore farmers
- Organized by: Ministry of Agriculture, ICAR, agricultural universities, and state governments
- Teams Deployed: ~2,170 expert teams with scientists, officials, FPOs, and progressive farmers
- Sessions Held: Morning, afternoon, and evening village-level meetings daily
- Format: Two-way interaction for knowledge dissemination and farmer feedback
Strategic Focus Areas
- Lab-to-Land Technology Transfer:Dissemination of ICAR research, advanced seed varieties, scientific sowing practices, and balanced fertilizer use through 731 Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs).
- Farm Productivity and Resource Use Efficiency:Recommendations based on Soil Health Cards, agro-climatic conditions, water availability, and rainfall data to reduce input costs and promote sustainable practices.
- Farmer Empowerment and Inclusivity:Addressing field-level challenges like pest infestation, enabling participatory feedback loops for future agricultural research.
- Six-Point Strategy by Ministry:
- Increase agricultural output
- Lower production costs
- Ensure fair pricing for farmers
- Compensate disaster-related losses
- Promote crop diversification and value addition
- Encourage natural and organic farming
Notable Achievements and Data
- Record Agricultural Output (2024–25):
- Foodgrains: 3309.18 lakh tonnes (up from 3157.74 lakh tonnes in 2023–24)
- Pulses: 230.22 lakh tonnes
- Oilseeds: 416 lakh tonnes
- Kharif Rice: 1206.79 lakh tonnes
- Wheat: 1154.30 lakh tonnes
- Maize: 248.11 lakh tonnes
- Groundnut: 104.26 lakh tonnes
- Soybean: 151.32 lakh tonnes
- Over 16,000 agricultural scientists are contributing to real-time research translation to the field.
Desalination Technology
- 16 May 2025
The Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, has successfully developed a high-pressure, nanoporous, multilayered polymeric membrane for seawater desalination.
Developing Agency:
- The technology was developed by the Defence Materials Stores Research & Development Establishment (DMSRDE), Kanpur, a DRDO laboratory.
- It addresses the Indian Coast Guard's (ICG) operational needs aboard Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPVs), especially to counter instability caused by chloride ions in saline water.
Salient Features of the Technology:
- Indigenous development completed in a record time of 8 months.
- Successfully tested in existing desalination plants aboard ICG vessels.
- Undergoing 500-hour operational testing before final clearance by ICG.
- Can be adapted for use in coastal areas for civilian desalination purposes as well.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances onboard freshwater self-reliance for maritime security forces.
- Reduces dependency on imported technologies.
- Contributes to India’s self-reliance in critical defence and water technologies.
Desalination Technology: Key Concepts
What is Desalination?
Desalination is the process of removing dissolved salts and minerals from seawater or brackish water to produce potable or industrial-grade water.
Main Technologies Used:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO):
- Pressure-driven membrane filtration.
- Uses semi-permeable membranes to separate salts from water.
- Thermal Desalination:Involves evaporation followed by condensation to obtain fresh water.
Working of RO Desalination:
- In osmosis, water naturally moves from low solute to high solute concentration across a membrane.
- In reverse osmosis, external pressure is applied to force water from high solute (saline) to low solute (freshwater) side.
- RO membranes allow only water molecules to pass, filtering out salts and impurities.
- Seawater with ~35,000 ppm Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is reduced to 200–500 ppm, making it drinkable.
NiveshakShivir

- 13 May 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, in collaboration with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), convened a strategic preparatory meeting at SEBI’s Mumbai office to launch the “NiveshakShivir” initiative. This nationwide investor outreach program aims to facilitate the reclamation of unclaimed dividends and shares by investors across India.
Key Features of “NiveshakShivir”
- Investor Helpdesks: Physical helpdesks will be set up to enable investors to interact directly with company representatives and Registrars and Transfer Agents (RTAs) for end-to-end assistance in recovering unclaimed assets.
- Digital Search Facility: IEPFA provides an online portal (https://iepfa.gov.in/login) where shareholders can check if their shares have been transferred to the IEPF and file claims using Form IEPF-5.
- Streamlined Process: Clear guidance is provided for shareholders holding shares in dematerialized or physical form to verify and reclaim their unclaimed dividends and shares efficiently.
- Coverage: The initiative is set to launch first in Mumbai and Ahmedabad, with plans to expand to other cities with high volumes of unclaimed investor assets.
Actions for Shareholders
- Demat Shareholders: Are encouraged to directly contact respective companies for clarification regarding shares liable for transfer to IEPFA.
- Physical Shareholders: Should verify share status on the IEPFA website and claim refunds if shares have been transferred.
- The initiative reduces dependence on intermediaries and improves transparency and efficiency in the recovery process.
About the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)
- Legal Basis: Established under Section 125 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Function: Operates under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs to protect investor interests, promote financial literacy, and manage the corpus of unclaimed dividends, matured deposits, and shares transferred by companies.
- Objective: To foster a transparent, investor-friendly financial ecosystem through outreach and education programs like “NiveshakShivir.”
India and Chile Sign Terms of Reference for CEPA Negotiations

- 13 May 2025
In News:
Recently, India and Chile signed the Terms of Reference (ToR) to initiate negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), marking a significant step toward deepening bilateral economic ties.
Background and Significance
- The CEPA aims to expand and build upon the existing Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) between the two countries by covering a broader range of sectors including digital services, investment promotion, MSMEs, and critical minerals.
- India and Chile share warm, strategic bilateral relations strengthened over years through high-level exchanges. The economic partnership began with a Framework Agreement in 2005, followed by a PTA in 2006, an expanded PTA effective from 2017, and further discussions towards CEPA since 2019.
- A Joint Study Group report finalized in April 2024 laid the foundation for advancing to a CEPA to unlock the full trade and investment potential between the two nations.
- The recent State visit of Chile’s President Gabriel Boric Font to India in April 2025 reaffirmed both countries’ commitment to enhancing trade frameworks and fostering a balanced, ambitious, and mutually beneficial economic agreement.
About Chile: Geopolitical and Economic Profile
- Chile is a long, narrow South American country bordered by Peru and Bolivia to the north, Argentina to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
- It shares the longest border in South America with Argentina, which is also the third-longest international border worldwide.
- Key geographical features include the Andes Mountains (the world’s longest continental mountain range), the Atacama Desert (driest non-polar desert globally), the Loa River (Chile’s longest river, approx. 440 km), and Ojos del Salado volcano (world’s highest active volcano at 6,880 meters).
- Situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Chile is prone to frequent earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Chile is the world’s largest producer of copper and a significant member of the “Lithium Triangle” (alongside Argentina and Bolivia), holding over 75% of global lithium reserves found in salt flats.
- Other important resources include molybdenum, iron ore, timber, hydropower, and precious metals.
Importance for India
- The CEPA negotiations with Chile are expected to enhance trade and investment flows, promote MSMEs, and strengthen cooperation in critical sectors such as minerals and digital services.
- This move aligns with India’s broader strategy to diversify economic partnerships globally and deepen ties with Latin American countries.
- Enhanced economic integration with Chile will boost employment, trade balance, and strategic cooperation between the two nations.
Arnala

- 13 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy received Arnala, the first of eight indigenously designed and built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWCs). The vessel was constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in partnership with M/s L&T Shipyard, Kattupalli, under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP), exemplifying the growing collaboration in India’s defence manufacturing sector.
Key Features and Significance
- Arnala is named after the historic Arnala Fort located off Vasai, Maharashtra, symbolizing India’s rich maritime heritage.
- The ship measures 77 metres in length and is the largest Indian Naval warship powered by a Diesel Engine-Waterjet propulsion system.
- Designed and built according to the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) classification rules, the vessel adheres to domestic naval architecture standards.
- Over 80% of the ship’s components are sourced indigenously, marking a significant stride toward the Government’s vision of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ in defence production.
Operational Roles
The Arnala class ASW SWCs are specialized for:
- Underwater surveillance in coastal and littoral zones
- Conducting search and rescue (SAR) operations
- Engaging in Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO)
- Performing coastal Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) missions
- Advanced mine-laying activities
The induction of these vessels enhances India’s capabilities in shallow water ASW, critical for safeguarding maritime security in near-shore environments and ensuring dominance in the strategically vital littoral areas.
Strategic Importance
The delivery of Arnala signifies a major milestone in the Indian Navy’s ongoing efforts to promote indigenous shipbuilding and strengthen domestic defence manufacturing. It highlights successful public-private collaboration in advanced warship construction and contributes directly to India’s broader strategic goal of self-reliance in defence technology.
20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20)

- 13 May 2025
In News:
India actively participated in the 20th session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20) held from May 5 to 9, 2025, at the United Nations Headquarters, New York. UNFF, established in 2000 by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), is the sole intergovernmental platform dedicated to global forest policy dialogue and coordination, aiming to promote sustainable forest management (SFM) and strengthen political commitment worldwide.
Key Objectives and Functions of UNFF
- Promotes conservation, management, and sustainable development of all forest types.
- Supports the implementation of Agenda 21, Rio Forest Principles, and the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030.
- Oversees six voluntary Global Forest Goals (GFGs) and 26 targets, including reversing deforestation and enhancing forest governance.
- Facilitates cooperation through technical exchanges, policy development, financing mechanisms like the Global Forest Financing Facilitation Network, and advocacy linking forests with climate, biodiversity, and sustainable development.
India’s Highlights at UNFF20
India reaffirmed its commitment to the Voluntary National Contributions (VNCs) under the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030, reporting progress in increasing its forest and tree cover, which now constitutes 25.17% of the country’s geographical area, as per the latest India State of Forest Report. Major achievements include:
- Restoration efforts under the Aravalli Green Wall project.
- A 7.86% increase in mangrove cover over the past decade.
- Afforestation of over 1.55 lakh hectares through the Green India Mission.
- Plantation of 1.4 billion seedlings under the “Ek Ped MaaKe Naam” (Plant4Mother) campaign.
Global Contributions and Initiatives
India extended an invitation to all UN member states to join the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)—a global platform launched by India to conserve seven big cat species through collaborative research, knowledge exchange, and capacity-building.
India also emphasized the importance of incorporating the outcomes of the Country-Led Initiative (CLI) on forest fire management and forest certification—hosted by India in Dehradun in October 2023—into formal global mechanisms. It acknowledged contributions from other countries such as the Republic of Congo, Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, and Austria in this initiative.
Policy and Technical Engagements
India hosted a side event titled “Restoring Degraded Forest Landscapes: India’s Approach to Sustainable Forest Management and Climate Resilience”, showcasing integrated forest restoration strategies combining policy innovation, resource convergence, community participation, and technology.
In a high-level panel on “Valuing Forest Ecosystems in National Policy and Strategy,” India shared pilot study findings from Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, and tiger reserves that quantified ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation. India stressed the need to incorporate ecosystem valuation into national planning to enhance forest governance and ecological sustainability.
Significance of UNFF20
The session focused on advancing three Global Forest Goals:
- Reversing forest cover loss.
- Increasing protected and sustainably managed forests.
- Promoting forest governance and legal frameworks.
UNFF20 aimed to strengthen global dialogue following the 2024 midterm review of the international arrangement on forests and set the agenda for future policy deliberations in 2026. It underscored the critical role forests play in climate resilience, biodiversity, livelihoods, and sustainable development.
International Maritime Defence Exhibition (IMDEX) Asia 2025

- 10 May 2025
In News:
The International Maritime Defence Exhibition (IMDEX) Asia is a leading biennial maritime and defence event in the Asia-Pacific region, held since 1997 in Singapore at the Changi Exhibition Centre. It serves as a key global platform for navies, coast guards, and maritime defence industries to showcase advanced naval platforms, cutting-edge technologies, and engage in strategic dialogue.
Indian Navy’s Participation
- In May 2025, the Indian Naval Ship INS Kiltan arrived in Singapore to participate in IMDEX Asia 2025.
- This deployment forms part of the Indian Navy’s operational commitments and highlights the strong maritime partnership between India and Singapore.
- During the exhibition, the Indian Navy crew engaged in multiple bilateral and multilateral activities, including professional exchanges with the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and other participating navies.
- Activities included guided tours for schoolchildren, cross-deck visits with other navies, and curated visits for defence industry representatives to promote awareness of maritime security and India’s naval heritage.
Key Features of IMDEX Asia
- Platform for Defence Collaboration: IMDEX Asia facilitates showcasing of naval systems and debut of advanced maritime technologies.
- Strategic Dialogue: The event hosts high-level policy discussions and strategic dialogues on maritime security.
- International Maritime Security Conference (IMSC):
- Established in 2009, IMSC is a crucial component of IMDEX.
- Jointly organised by the Republic of Singapore Navy and the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies (RSIS).
- It convenes navy chiefs, coast guard leaders, policymakers, and strategic analysts.
- The conference aims to enhance mutual maritime security, improve maritime domain awareness, and foster cooperative responses to challenges in the global maritime commons.
Significance
- The Indian Navy’s participation in IMDEX Asia underlines its commitment to regional maritime security and stability.
- It also reinforces the longstanding friendly ties between India and Singapore and highlights the importance of naval interoperability and defence cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) 2025

- 09 May 2025
In News:
India is set to host the 12th edition of the Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) 2025 from 7th to 9th May 2025 in New Delhi, marking a significant milestone in the nation's emergence as a key global player in space exploration.
Key Highlights of GLEX 2025:
- Theme: “Reaching New Worlds: A Space Exploration Renaissance”
- The conference theme underscores a renewed global commitment to innovation, inclusivity, and international collaboration in space science and technology.
- Organisers:
- International Astronautical Federation (IAF) – The world’s foremost space advocacy organisation.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) – Serving as the primary host, reflecting India’s growing stature in the global space ecosystem.
- Astronautical Society of India (ASI) – Acting as the co-host and supporting India's role in global space diplomacy.
GLEX 2025 is expected to bring together global experts, policymakers, scientists, and industry leaders to discuss cutting-edge advancements, collaborative missions, and the future of space exploration. It will also highlight India's evolution from a regional space power to a central figure in the international space community.
About the International Astronautical Federation (IAF):
- Established: 1951
- Membership: Over 500 organisations from 78 countries, including major space agencies, private companies, academic institutions, and research bodies.
- Vision: “A space-faring world cooperating for the benefit of humanity”
- Motto: “Connecting @ll Space People”
- The IAF promotes global space cooperation and knowledge exchange. Through platforms like GLEX, it fosters dialogue on programmatic, technical, and policy aspects of space missions.
Significance for India:
GLEX 2025 reflects India’s growing prominence in the global space domain, reaffirming its commitment to peaceful space exploration and international collaboration. The event offers a valuable opportunity for India to showcase its achievements, build new partnerships, and contribute to shaping the future of global space policy and science.
INS Sharda
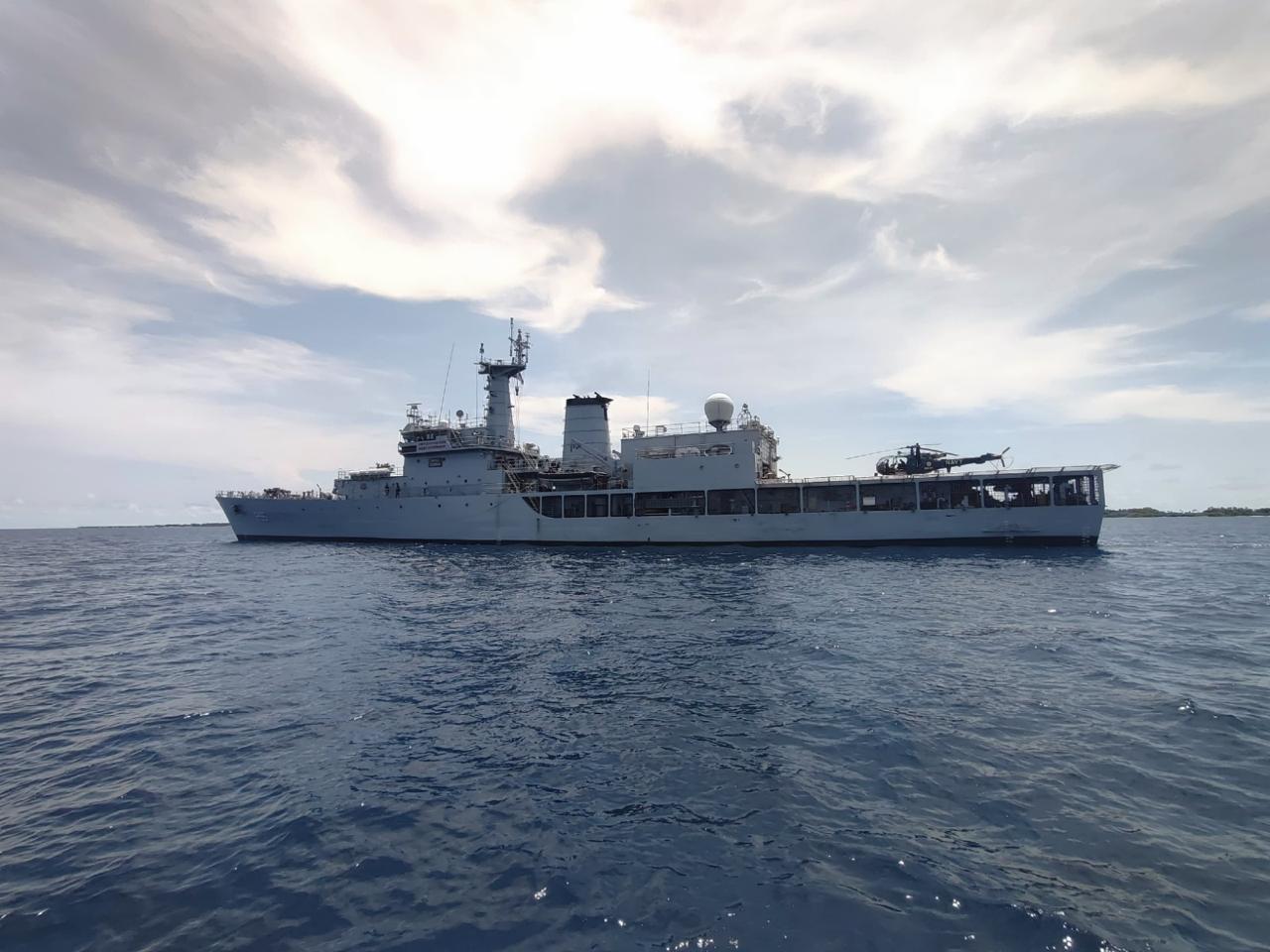

- 08 May 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s offshore patrol vessel, INS Sharda, has reached Maafilaafushi Atoll in the Maldives to participate in its first-ever Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) exercise, scheduled from May 4 to May 10, 2025.
Strengthening Regional Maritime Cooperation and Disaster Preparedness
This exercise is a key part of India’s strategic efforts to enhance regional maritime cooperation and bolster disaster readiness within the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). It underscores India’s steadfast commitment to its “Neighbourhood First” Policy, which recognizes the Maldives as a close maritime neighbour with deep strategic and cultural ties.
Aligning with the MAHASAGAR Vision
The HADR exercise supports the recently unveiled MAHASAGAR vision—Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions—introduced by the Prime Minister during the Mauritius visit. MAHASAGAR reaffirms India’s role as a net security provider and first responder in the Indian Ocean, building on the earlier SAGAR doctrine (Security and Growth for All in the Region). Both frameworks emphasize inclusive security, regional cooperation, and disaster resilience.
Objectives of the HADR Exercise
According to the Indian Navy, the exercise aims to:
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian Navy and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF).
- Conduct joint drills focusing on Search and Rescue (SAR), disaster response coordination, logistical support, and medical aid.
- Facilitate training programs for capacity building among personnel.
- Engage with local communities to raise awareness and strengthen disaster preparedness.
This maiden HADR exercise by INS Sharda marks a significant step toward deepening India-Maldives maritime collaboration and regional disaster management capabilities.
Annual Survey of Services Sector Enterprises (ASSSE)
- 05 May 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) recently released findings from a pilot study on the Annual Survey of Services Sector Enterprises (ASSSE). This initiative aims to fill a crucial data gap regarding India’s incorporated service sector, which is not currently covered by regular surveys like the Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE).
Significance of the Services Sector
- Contribution to Economy: The services sector contributed ~55% of India's Gross Value Added (GVA) in FY 2024–25, up from 50.6% in FY14.
- Employment: It employs around 30% of India’s workforce, spanning industries like IT, finance, education, tourism, and healthcare.
- Trade: India’s services exports stood at USD 280.94 billion (April–Dec 2024). In ICT services, India is the 2nd-largest global exporter, accounting for 10.2% of global exports.
- FDI Magnet: The sector attracted USD 116.72 billion in FDI (April 2000–Dec 2024)—about 16% of total FDI inflows.
- Support to Digital India & Urbanization: The sector underpins the Digital India initiative and Smart Cities Mission by enabling digital payments, urban mobility, e-governance, and waste management.
About the ASSSE Pilot Study
Purpose & Objectives
- To test the suitability of the GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network) database as a sampling frame.
- To develop robust survey instruments and methodology for a full-scale annual survey starting January 2026.
- To gather data on economic characteristics, employment, and financial indicators from incorporated enterprises under:
- Companies Act, 1956/2013
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act, 2008
Survey Coverage
- Conducted in two phases:
- Phase I (May–Aug 2024): Verified enterprise data for 10,005 units.
- Phase II (Nov 2024–Jan 2025): Collected detailed data from 5,020 enterprises under the Collection of Statistics Act, 2008.
- Data collected for FY 2022–23 using CAPI (Computer-Assisted Personal Interviewing).
Key Findings:
Enterprise Type Distribution
- Private Limited Companies: 82.4%
- Public Limited Companies and LLPs: ~8% each
Size-Class Analysis (FY 2022–23)
Output Class (?) % Share of Gross Value Added (GVA) % Share of Fixed Assets % Share of Employment
< 10 crore 1.19% 2.64% 9.28%
10–100 crore 9.45% 9.58% 20.03%
100–500 crore 19.90% 25.00% 33.73%
> 500 crore 69.47% 62.77% 36.96%
- Large enterprises (output > ?500 crore) dominate in assets, value addition, and compensation paid, but smaller units employ over 63% of the total workforce in the sample.
Additional Establishments
- 28.5% of enterprises reported having additional business locations within the state.
- Highest in the Trade sector (41.8%).
Insights and Challenges from the Pilot
- Suitability of GSTN as Sampling Frame: Confirmed.
- Challenges Faced:
- Data retrieval from enterprises with headquarters in other states.
- Centralized data (CIN-based) posed difficulty in disaggregating state-level data.
- Positive Outcomes:
- High response rate and cooperation.
- Survey instruments found largely clear and functional.
Challenges Faced by the Services Sector
- Skill Gaps:
- Only 51.25% of youth are employable (Economic Survey 2023–24).
- Merely 5% of workforce is formally skilled (WEF).
- Informality:
- About 78% of service jobs were informal in 2017–18.
- Gig workers lack social protection.
- Global Competition:
- Visa restrictions (e.g., H-1B in the US).
- Competing hubs: Philippines, Vietnam.
- Rising IT wage costs in India.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:
- Inadequate AI/ML adoption.
- Digital divide persists in rural and marginalized MSMEs.
- Post-COVID Recovery:
- Inbound tourism yet to reach pre-pandemic levels (90% of 2019 arrivals in H1 2024).
Way Forward
- Upskilling Initiatives:
- Expand Skill India Digital and PMKVY 4.0.
- Promote Prime Minister Internship Scheme (PMIS) for bridging academia-industry gap.
- Boosting Global Competitiveness:
- Negotiate FTAs with EU, UK, Australia.
- Expand Global Capability Centres (GCCs).
- Digital Infrastructure & Security:
- Strengthen cybersecurity frameworks and promote secure cloud adoption.
- Improve digital literacy, especially in financial services.
- Decentralized Growth:As per NITI Aayog, promote services sector in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities with better infrastructure and connectivity.
Exercise DUSTLIK

- 05 May 2025
In News:
The 6th edition of Exercise DUSTLIK, a bilateral joint military exercise between India and Uzbekistan, was recently held at the Foreign Training Node in Aundh, Pune. The previous edition (2024) was conducted in Termez, Uzbekistan.
Key Highlights:
- Exercise Theme: Joint Multi-Domain Sub-Conventional Operations in Semi-Urban Terrain.
- Aimed at simulating counter-terrorism operations, especially in scenarios involving territorial capture by terrorist groups.
- Indian contingent: 60 personnel from the JAT Regiment and the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Uzbek contingent: Personnel from the Uzbekistan Army.
Core Activities:
- Establishment of a Joint Operations Centre at the battalion level.
- Execution of population control, raids, search-and-destroy operations.
- Use of air assets: drones, helicopters for reconnaissance, Special Heliborne Operations (SHBO), Small Team Insertion and Extraction (STIE).
- Focus on counter-UAS (unmanned aerial systems) measures and logistics support in hostile conditions.
Objectives:
- Enhance interoperability, tactical coordination, and operational synergy between the two armies.
- Promote defence cooperation and strengthen bilateral relations between India and Uzbekistan.
- Exchange of best practices in conducting joint sub-conventional operations.
About Uzbekistan:
- Doubly landlocked country in Central Asia, located between the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers.
- Borders: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Turkmenistan.
Caste Census in India
- 03 May 2025
In News:
The Cabinet Committee on Political Affairs (CCPA) has recently approved the inclusion of caste enumeration in the forthcoming national Population Census. This marks a significant policy shift from its 2021 position, where the idea was set aside.
Understanding the Caste Census
A caste census involves the systematic recording of individuals' caste affiliations during a national population count. This exercise aims to generate detailed socio-economic profiles of various caste groups, facilitating better policy planning, especially in the context of welfare schemes and affirmative action.
Legal and Constitutional Framework
- No Direct Provision: The Constitution does not expressly mandate a caste census.
- Permissibility Under Article 340: The government is empowered to investigate the conditions of socially and educationally backward classes, which provides scope for caste-based data collection.
- Union Subject: As per Entry 69 of the Union List (Seventh Schedule), the Census falls within the legislative jurisdiction of the Union Government under Article 246.
Historical Context
- Colonial Era (1881–1931): The British administration included caste enumeration in decennial censuses, the last being in 1931.
- Post-Independence Practice (1951 onwards): Independent India has only counted Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) in its censuses.
- Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) 2011: Though it aimed to gather caste-related data, the caste-specific findings remain unpublished due to concerns over accuracy.
Why a Caste Census is Relevant Today
- Evidence-Based Policy Making:Reliable data on Other Backward Classes (OBCs) is absent. For example, the Mandal Commission (1980) estimated OBCs at 52%, but this figure lacks empirical validation. Recent data from Bihar's 2023 caste survey pegged the OBC+EBC population at 63%.
- Restructuring Reservation:A caste census can guide rationalisation of quotas and potential sub-categorisation within OBCs, ensuring benefits reach the most deprived segments.
- Social Welfare Targeting:Caste-disaggregated data allows for focused delivery of healthcare, education, and livelihood schemes.
- Women’s Political Representation:Accurate population data is necessary for delimitation, a precursor to implementing the recently passed Women’s Reservation Act, which reserves seats for women in legislatures.
- Constitutional Backing:Article 15(4) enables the state to provide for the advancement of backward classes, but this requires reliable data for identification.
WAVES 2025 & WAM!
- 01 May 2025
In News:
In line with the vision of “Create in India, Create for the World,” the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, in partnership with the Media & Entertainment Association of India (MEAI), is hosting WAVES 2025—India’s largest summit for the Media & Entertainment (M&E) sector. A major highlight of this summit is the WAM! (WAVES Anime & Manga Contest)—India’s first national initiative to promote original Indian IPs in anime, manga, webtoons, and cosplay.
What is WAM!?
- Full Form: WAVES Anime & Manga Contest.
- Nature: India’s first national initiative focused on discovering and nurturing original Indian creative intellectual properties (IPs) in:Anime, Manga, Webtoons&Cosplay
- Organisers: Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, in collaboration with MEAI.
- Finale: To be held at WAVES 2025, from May 1–4, 2025, at the Jio World Convention Centre, Mumbai.
- Participants: Finalists from 11 cities selected through regional contests.
Global Support & Incentives
- Crunchyroll, a global anime platform (a joint venture of Sony Pictures Entertainment and Aniplex, Japan), is the Title Sponsor of WAM! 2025.
- It has introduced a Creator Development Grant to support Indian talent and foster global-ready original content.
Grant Details
Category Student (INR) Professional (INR)
Manga 25,000 25,000
Webtoon 25,000 25,000
Anime 50,000 50,000
- Winners of WAM! 2025 will represent India at Anime Japan 2026 in Tokyo—one of the world's leading anime conventions—marking India’s presence on the global animation stage.
About WAVES 2025
- Full Form: World Audio-Visual & Entertainment Summit.
- Objective: Showcase India's capabilities in content creation, technological innovation, and media & entertainment IP development.
- Hosted by: Government of India.
- Venue: Jio World Convention Centre, Mumbai
Key Pillars of WAVES 2025
- AVGC-XR Sector Focus:Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics&Extended Reality (XR) including AR, VR, and Mixed Reality.
- "Create in India" Challenges (CIC):
- Season 1 witnessed over 1 lakh registrations, including 1,100 international participants.
- 750+ finalists selected through 32 unique creative challenges.
- Thematic Focus Areas:
- Broadcasting, Films, Television, Radio
- Print & Digital Media, Advertising, Social Media Platforms
- Sound & Music
- Generative AI, Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Extended Reality (XR)
- Target Audience: Content creators, industry professionals, investors, technology innovators, and global studios.
National Technical Textiles Mission
- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
India’s textile sector plays a vital role in the country’s economy, contributing nearly 2% to GDP and ranking as the world’s 6th largest textile exporter with a 3.9% share of global textile exports. The sector is projected to grow to USD 350 billion by 2030, generating around 3.5 crore jobs. Alongside traditional textiles, technical textiles—specialized fabrics designed for specific industrial and functional uses—are emerging as a major growth driver.
What are Technical Textiles?
Technical textiles are fabrics engineered for performance rather than aesthetics. They serve diverse sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, construction, automotive, and safety by providing solutions like protective gear, medical textiles, geotextiles, and industrial fabrics. The industry segments technical textiles into 12 categories based on application.
National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM)
To capitalize on this potential, the Ministry of Textiles launched the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM) in 2020, with an outlay of ?1,480 crore running through 2025-26. The mission aims to position India as a global leader in technical textiles by focusing on innovation, research, market expansion, export promotion, and skill development.
Four Pillars of NTTM:
- Research, Innovation, and Development: Funding and supporting R&D projects to develop new materials and processes.
- Promotion and Market Development: Facilitating wider adoption of technical textiles domestically and internationally.
- Export Promotion: Establishing dedicated export councils to enhance global market access.
- Education, Training, and Skill Development: Training 50,000 individuals, from students to professionals, through specialized courses and industry internships.
Since its inception, NTTM has approved 168 research projects worth ?509 crore and allocated ?517 crore towards mission activities. So far, ?393.39 crore has been utilized for research, market promotion, export, and skill training.
Key Initiatives under NTTM
- GIST 2.0 (Grant for Internship Support in Technical Textiles): Bridges academia and industry by providing hands-on learning and internships, fostering innovation and supporting the Make in India initiative.
- GREAT Scheme (Grant for Research & Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles): Funds startups and educational institutions to commercialize innovative technical textile products. For example, 8 startups received ?50 lakh each to develop medical, industrial, and protective textiles. IIT Indore and NIT Patna were awarded ?6.5 crore to launch specialized courses in geotextiles and sports textiles.
- Skill Development: Courses developed by premier textile research associations like SITRA, NITRA, and SASMIRA train workers in sectors such as medical, protective, mobile, and agricultural textiles.
- Technotex 2024: A platform showcasing cutting-edge projects under the NTTM Innovation Zone, featuring 71 innovations to attract global investments.
Impact and Success Stories
India is witnessing rapid innovation in technical textiles. For instance, Eicher Goodearth’s “Mahina” is India’s first bonded leak-proof period underwear, providing 12-hour protection using natural materials and reusable up to 100 washes.
Several states are prioritizing technical textiles growth through policy support. Tamil Nadu’s budget highlights include establishing the PM MITRA Park in Virudhunagar and a textile park in Salem, along with increased subsidies for machinery modernization in spinning units—from 2% to 6%—to lower costs and boost competitiveness.
Baalpan ki Kavita Initiative

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
To fulfil the vision of NEP 2020, the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education has launched “Baalpan ki Kavita initiative: Restoring Bhartiya rhymes/poems for young children” for preparing a compendium of nursery rhymes/poems in all Bhartiya Bhasha and also in English, focusing on content relevant to the Indian context.
Key Highlights:
Objective:To compile a national-level compendium of nursery rhymes and poems in all Bhartiya Bhashas (Indian languages) and English, with a focus on culturally relevant content for early childhood learning.
Key Features:
- Encourages multilingual and mother-tongue based education, in line with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Aims to make foundational learning joyful, relatable, and rooted in Indian ethos.
- Invites existing folklore rhymes and newly composed poems across three age-based categories:
- Pre-primary: Ages 3–6
- Grade 1: Ages 6–7
- Grade 2: Ages 7–8
- Open to submissions in all Indian languages and English.
Significance:
- Reinforces foundational literacy through culturally contextual content.
- Promotes regional literature, creativity, and early multilingualism.
- Strengthens identity and connection to Indian culture from an early age.
Baalpan ki Kavita Initiative

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
To fulfil the vision of NEP 2020, the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education has launched “Baalpan ki Kavita initiative: Restoring Bhartiya rhymes/poems for young children” for preparing a compendium of nursery rhymes/poems in all Bhartiya Bhasha and also in English, focusing on content relevant to the Indian context.
Key Highlights:
Objective:To compile a national-level compendium of nursery rhymes and poems in all Bhartiya Bhashas (Indian languages) and English, with a focus on culturally relevant content for early childhood learning.
Key Features:
- Encourages multilingual and mother-tongue based education, in line with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Aims to make foundational learning joyful, relatable, and rooted in Indian ethos.
- Invites existing folklore rhymes and newly composed poems across three age-based categories:
- Pre-primary: Ages 3–6
- Grade 1: Ages 6–7
- Grade 2: Ages 7–8
- Open to submissions in all Indian languages and English.
Significance:
- Reinforces foundational literacy through culturally contextual content.
- Promotes regional literature, creativity, and early multilingualism.
- Strengthens identity and connection to Indian culture from an early age.
Delhi Joins National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA)

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
The Delhi Legislative Assembly has become the 28th legislature in India to sign a tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA) and the Government of NCT of Delhi for implementing the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA). This move marks a significant advancement in India's push for paperless, transparent, and efficient legislative processes.
About NeVA:
- Developed by: Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs
- Hosted on:Meghraj 2.0, India’s national cloud infrastructure
- Objective: To digitize legislative operations across State Legislatures and Union Territory Assemblies
- Vision: Aligned with the “One Nation, One Application” initiative
Key Features:
Feature Description
Device-Neutral Accessible via smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktops
Real-Time Access Legislators can view agendas, bills, questions, committee reports, and proceedings anytime
Digital Repository Secure storage for legislative documents with confidentiality and integrity
Multilingual Support Facilitates linguistic inclusivity across India
Member-Centric Tools Access to member directories, notices, starred/unstarred Q&A, digital bulletins, and
house business
Public Interface Allows citizens and media to access legislative documents and updates
Smart Legislative Tools Aids Speakers/Chairs in conducting proceedings smoothly
Stakeholders Benefiting from NeVA:
- Members of Legislative Assemblies and Councils
- Government Ministers and Department Staff
- Assembly Secretariat Officials
- Media and General Public
Delhi’s Onboarding Highlights:
- Signed By: Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs, Delhi Legislative Assembly, and GNCTD
- Purpose: To empower Delhi MLAs with digital tools and reduce paper-based procedures
- Significance: Part of Delhi’s 100-day governance agenda aimed at modernization and transparency
World Water Day 2025

- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
Marking World Water Day, the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change and the Government of Haryana, launched the much-anticipated sixth edition of Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain - 2025 in Panchkula, Haryana.
World Water Day 2025
- Observed On: 22nd March 2025
- 2025 Theme: ‘Glacier Preservation’
- Global Context: Declared by the United Nations General Assembly in 1993, conceptualized at the 1992 Rio Earth Summit.
- Linked SDG: Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG-6) – Clean Water and Sanitation for All by 2030.
- Purpose: To raise global awareness on water conservation and promote sustainable water use.
India's Observance: Launch of Jal Shakti Abhiyan – Catch the Rain 2025
- Launched by: Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and Government of Haryana.
- Launch Venue: Panchkula, Haryana (first time outside Delhi).
- Theme: “????????????????: ??????????????” (People’s Action for Water Conservation – Towards Intensified Community Connect).
- Focus Areas:
- Rainwater harvesting
- Groundwater recharge
- Community-led water conservation
- Ecological restoration (forests, rivers, springs)
Key Campaigns & Initiatives
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2025 (JSA:CTR)
- Targeted Districts: 148 water-stressed districts across India.
- Tagline: “Catch the Rain where it falls, when it falls.”
- Objective: Promote localized water conservation through people’s participation and decentralized planning.
“Jal-Jangal-Jan” Abhiyan
- Aim: Restore ecological connectivity between water, forests, and communities.
- Collaborators: MoEFCC and Jal Shakti Ministry.
- Tools Used: Awareness videos, AV content, best practice compilations.
State-Level Innovations: Haryana Model
- Launched:
- Mukhyamantri Jal Sanchay Yojana – Enhancing water harvesting through community participation.
- Water Resources Atlas – Scientific mapping of water availability.
- Online Canal Water Management System – Real-time irrigation data for efficiency.
- E-booklet on Integrated Water Resources Management.
- Infrastructure Projects under SBM-G & JSA:
- Community Sanitary Complexes
- Solid & Liquid Waste Management
- Gobardhan (Biogas) Projects
- Borewell Recharge Systems
- Micro-irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting Projects
Key Government Schemes Related to Water
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) – Time-bound, mission-mode campaign for water conservation.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana – Participatory groundwater management in critical areas.
- AMRUT 2.0 – Urban water supply and sewerage services improvement.
RBI’s 6th Remittance Survey (2023–24)
- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
India remains the world’s top recipient of remittances, with total inward remittances doubling from USD 55.6 billion in 2010–11 to USD 118.7 billion in 2023–24, as per the Reserve Bank of India’s Sixth Round of the Remittances Survey.
Shift in Sources of Remittances
- A significant trend in 2023–24 is the growing dominance of Advanced Economies (AEs) over traditional Gulf sources.
- The United States emerged as the largest contributor with a 27.7% share, followed by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at 19.2%.
- AEs including the UK, Singapore, Canada, and Australia now account for over 50% of India’s total remittance inflows.
- The UK’s share increased notably from 3.4% (2016–17) to 10.8% (2023–24).
- Australia contributed 2.3%, reflecting rising skilled migration.
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain) collectively contributed 38%, a decline from 47% in 2016–17.
Reasons for the Shift
- Robust Job Markets in AEs: High-paying jobs for skilled Indian migrants in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
- UK-India Migration and Mobility Partnership (MMP) tripled Indian migration to the UK from 76,000 in 2020 to 250,000 in 2023.
- Favorable immigration policies in Canada (Express Entry) and Australia boosted skilled migration.
- Declining Opportunities in GCC:
- Post-pandemic return of Indian migrants and reduced demand for low-skilled labor due to automation and economic diversification.
- Nationalization policies (e.g., Nitaqat in Saudi Arabia, Emiratization in UAE) favor local employment.
- Changing Migration Patterns:
- Southern states (Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana) now prefer AEs due to higher education levels.
- Northern states (Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan) still send migrants to GCC, but limited by lower skill levels.
- Rise in Education-Driven Migration:
- Many Indian students pursue higher education abroad and stay back for employment.
- Indian students abroad: Canada (32%), US (25.3%), UK (13.9%), Australia (9.2%).
State-Wise Remittance Distribution (2023–24)
- Maharashtra: 20.5%
- Kerala: 19.7%
- Tamil Nadu: 10.4%
- Telangana: 8.1%
- Karnataka: 7.7%
- Notable increases observed in Punjab and Haryana.
Mode of Transfers
- The Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA) remains the dominant channel.
- Other channels include direct Vostro transfers and fintech platforms.
- Digital transactions account for 73.5% of remittance flows.
Shaheed Diwas

- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
On Shaheed Diwas (23rd March), the nation commemorates the supreme sacrifice of three iconic freedom fighters—Bhagat Singh, Shivaram Rajguru, and Sukhdev Thapar. Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tribute to these martyrs, remembering their unwavering resolve and courageous efforts in the struggle for India's independence. This day marks the execution of these three revolutionaries by British colonial authorities in Lahore Jail in 1931.
Background of the Martyrs
The trio was convicted for their involvement in the 1928 Lahore Conspiracy Case, which revolved around the killing of J.P. Saunders, a British officer. The incident occurred after Saunders was mistakenly identified as Superintendent James Scott, who was blamed for the death of Lala Lajpat Rai during a protest against the Simon Commission. The execution of these freedom fighters on 23rd March 1931 became a symbol of their sacrifice for the cause of India’s freedom.
The three were members of the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA), a revolutionary group that sought to overthrow British rule through armed struggle. Their fearless actions continue to inspire the nation to this day.
Brief Profiles of the Martyrs
- Bhagat Singh (1907–1931): Born in Punjab, Bhagat Singh was a prominent revolutionary who played a key role in the fight against British rule. He is remembered for his bold actions, such as the bombing of the Central Legislative Assembly in 1929, and his fearless stand against colonial oppression. His execution at the age of 23 became a catalyst for the freedom struggle.
- Shivaram Rajguru (1908–1931): Born in Maharashtra, Rajguru was a committed revolutionary who, along with Bhagat Singh, was involved in the assassination of J.P. Saunders. He was known for his dedication to the cause of armed resistance and his determination to fight colonial oppression. Rajguru was executed at the age of 23.
- Sukhdev Thapar (1907–1931): A key figure in mobilizing youth for the freedom struggle, Sukhdev was born in Punjab. He played a significant role in the activities of the HSRA and was instrumental in organizing protests and revolutionary activities. His execution, like that of his fellow revolutionaries, became a symbol of the ultimate sacrifice for India's freedom.
Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture
- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Culture has implemented several schemes aimed at supporting the growth and preservation of India's rich art and cultural heritage. One of the key initiatives is the ‘Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture’ Scheme, a Central Sector Scheme that provides financial support to eligible cultural organizations across the country. Below is an overview of the scheme, its components, and eligibility criteria.
Eligibility Criteria for Organizations
To be eligible for assistance under this scheme, cultural organizations must meet the following criteria:
- Registered as a society, trust, or not-for-profit company for at least three years.
- Registered on the NGO Darpan Portal of NITI Aayog.
- Have a primary focus on cultural activities.
- Submit audited financial statements for the last three years.
- Have filed Income Tax returns during the last three years.
Sub-Components of the Scheme
The scheme consists of eight sub-components, each designed to support different aspects of art and culture across India.
- Financial Assistance to Cultural Organizations with National Presence
- Objective: To support large cultural organizations with a nationwide presence.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 1 crore (may increase to Rs. 5 crore in exceptional cases).
- Cultural Function & Production Grant (CFPG)
- Objective: Provides financial aid for cultural events like seminars, conferences, research, workshops, festivals, exhibitions, and productions of dance, drama, and music.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 5 lakh (may increase to Rs. 20 lakh in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Cultural Heritage of the Himalayas
- Objective: To promote and preserve the cultural heritage of the Himalayan region, including Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 10 lakh per year (may increase to Rs. 30 lakh in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Buddhist/Tibetan Organizations
- Objective: To support Buddhist/Tibetan organizations, including monasteries, in preserving and developing Buddhist/Tibetan culture and traditions.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 30 lakh per year (may increase to Rs. 1 crore in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for Building Grants including Studio Theatres
- Objective: To provide financial support for creating cultural infrastructure, such as studio theatres, auditoriums, and rehearsal halls, along with providing essential facilities like lighting, acoustics, and sound systems.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 50 lakh in metro cities and Rs. 25 lakh in non-metro cities.
- Financial Assistance for Allied Cultural Activities
- Objective: To assist in the creation of assets that enhance the audio-visual spectacle for live performances and cultural activities.
- Grant Amount:
- Audio: Up to Rs. 1 crore.
- Audio + Video: Up to Rs. 1.5 crore (includes 5 years of operation and maintenance costs).
- Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Objective: To safeguard and promote India’s intangible cultural heritage, supporting institutions, groups, and NGOs involved in relevant activities.
- Grant Amount: Varies based on specific activities.
- Domestic Festivals and Fairs
- Objective: To assist in organizing RashtriyaSanskritiMahotsavs (National Culture Festivals) across India, engaging artists and showcasing various cultural traditions.
- Grant Amount: Event-based assistance; Rs. 38.67 crore was released in the last three years for these events.
Implementation and Monitoring
The Ministry of Culture closely monitors the effective utilization of funds under this scheme through:
- Utilization Certificates and audited financial statements.
- On-site physical inspections to assess the progress and impact of the funded projects.
- Regular oversight ensures that the assistance is used for its intended purpose and meets the objectives of cultural promotion and preservation.
Support for Individual Artists and Cultural Research
In addition to the above schemes, the Ministry of Culture also supports individual artists and cultural researchers through the ‘Scheme of Scholarship and Fellowship for Promotion of Art and Culture’. This scheme includes the following components:
- Award of Scholarships to Young Artists (SYA)
- Objective: To support young artists aged 18-25 years in various cultural fields.
- Duration: 2 years.
- Eligibility: Applicants should have undergone at least 5 years of training under a recognized guru or institution.
- Award of Senior/Junior Fellowships
- Senior Fellowship: For individuals 40 years and above to support cultural research.
- Junior Fellowship: For individuals 25-40 years for cultural research.
- Up to 400 Fellowships are awarded annually.
- Tagore National Fellowship for Cultural Research
- Objective: To provide funding for cultural research under two categories: Tagore National Fellowship and Tagore Research Scholarship.
- Selection: Fellows and scholars are selected by the National Selection Committee.
- Project Grants for Research in Performing Arts
- Objective: To provide financial assistance to individuals conducting research in performing arts.
Exercise Sea Dragon 2025

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
India successfully concluded its participation in Exercise Sea Dragon 2025, a two-week multinational anti-submarine warfare (ASW) drill conducted in the Indo-Pacific region, hosted by the United States Navy’s 7th Fleet.
About Exercise Sea Dragon 2025
- Type: Annual Multinational Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) Exercise
- Duration: Two weeks
- Location:Andersen Air Force Base, Guam, Western Pacific
- Host: U.S. Navy’s 7th Fleet
- Inception: Started as a bilateral US-Australia exercise in 2019; expanded to include more Indo-Pacific allies.
- India’s Participation: Since 2021; SD25 marks India’s 4th consecutive participation.
Objectives of Sea Dragon 2025
- Enhance Maritime Security and regional naval cooperation
- Strengthen anti-submarine warfare capabilities
- Improve interoperability and coordination among Indo-Pacific allies
- Promote a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific
- Address undersea threats, particularly in light of China’s growing maritime presence
Key Features of Sea Dragon 2025
- Live ASWEX: Tracking of real U.S. Navy submarines
- Mobile Drills: Use of MK-30 ‘SLED’ (Submarine Launch Expendable Device) as training targets
- Competitive Phase: Crews evaluated and graded based on ASW tactics and effectiveness
- Theoretical + Practical Training: Included tactical discussions, submarine detection, and neutralization scenarios
- Deployment of Advanced MPRA (Maritime Patrol and Reconnaissance Aircraft): Equipped with sonobuoys and sensors for submarine tracking
Significance for India
- Improves ASW Readiness and operational capabilities of the Indian Navy
- Strengthens ties with Quad members (U.S., Australia, Japan) and other Indo-Pacific partners
- Supports India’s broader strategy of naval modernization
- Aligns with India’s efforts to safeguard its interests in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and maintain regional stability.
Outcome
- RAAF (Australia) emerged as the top-performing team in the competitive phase.
- India successfully demonstrated its capabilities and reaffirmed commitment to Indo-Pacific security cooperation.
Samarth Incubation Programme

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The ‘Samarth’ Incubation Programme is a strategic initiative launched by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) to foster startup-driven innovation in India’s rapidly evolving telecommunications and IT sectors. This programme aligns with the goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat and Digital India, aiming to build indigenous capabilities in cutting-edge technologies.
Key Highlights:
- Launched By:Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), an autonomous R&D centre under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India.
- Implementation Partner:Software Technology Parks of India (STPI), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), which promotes IT/ITES innovation, startups, and R&D.
- Launch Date:19th March 2025.
- Objective:To support DPIIT-recognized startups developing next-generation technologies in the fields of:
- Telecom Software
- Cybersecurity
- 5G/6G Communications
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Quantum Technologies
- Program Structure:
- Two cohorts, each of six months duration.
- 18 startups per cohort (Total of 36 startups).
- Hybrid mode of delivery (virtual + physical support).
Support and Benefits Provided
- Financial Assistance:Grant of up to ?5 lakh per selected startup.
- Infrastructure Access:
- Fully furnished office space for 6 months at the C-DOT campus.
- Access to C-DOT’s lab and testing facilities.
- Mentorship & Networking:
- Guidance from C-DOT technical experts and industry leaders.
- Connection with investors, stakeholders, and potential collaborators.
- Future Opportunities:Eligible startups may be offered continued collaboration under the C-DOT Collaborative Research Program, based on their performance and innovation outcomes.
Selection Process
- Eligibility:Open to startups recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- Screening:Applications are evaluated through a structured selection process:
- Screening of applications based on innovation potential.
- Pitch presentation before an expert selection committee.
- Final cohort selection.
Significance for India’s Tech Ecosystem
- Promotes self-reliance in telecom and IT hardware/software innovation.
- Encourages the commercialization of research and ideas in emerging technology domains.
- Creates a supportive ecosystem for startups to thrive through structured mentorship and funding.
- Contributes to job creation and skill development in advanced digital sectors.
SansadBhashini Initiative

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The SansadBhashini Initiative is a collaborative project between the Lok Sabha Secretariat and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), launched to enhance digital and linguistic accessibility in India's parliamentary functioning.
About SansadBhashini
- Objective:To provide real-time AI-powered translation and transcription of parliamentary proceedings and documents across multiple Indian languages, ensuring greater transparency, inclusivity, and accessibility.
- Associated Platform:It is built on MeitY’sBhashini platform, a part of the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM), focused on democratizing access to digital content in Indian languages.
Key Features and Technologies Used
- AI-Powered Real-Time Translation: Enables instantaneous multilingual translation of legacy debates, legislative documents, and committee reports.
- Speech-to-Text Transcription System
- Converts spoken parliamentary debates into text with features such as:
- Background noise reduction
- Customizable vocabulary suited for legislative discourse
- High transcription accuracy
- Converts spoken parliamentary debates into text with features such as:
- Automatic Summarization: Generates concise and coherent summaries of long parliamentary discussions, aiding in faster decision-making and better public understanding.
- AI-Driven Chatbot Support
- Assists MPs, researchers, and officials with quick access to:
- Procedural rules
- Parliamentary archives
- Legislative documents
- Assists MPs, researchers, and officials with quick access to:
- Multilingual Accessibility and Inclusivity: Enhances linguistic diversity in governance by making proceedings available in multiple regional languages, thereby fostering greater public engagement.
Significance
- Strengthens e-Governance and digital democracy by making Parliament more accessible to citizens, especially non-Hindi/English speakers.
- Enhances documentation, transparency, and archiving through digitization and AI tools.
- Empowers MPs and legislative staff with real-time information and language tools, improving efficiency.
- Supports India’s Digital India mission and promotes linguistic equity in democratic institutions.
SagarmalaProgramme

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The SagarmalaProgramme, launched by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW) in 2015, aims to revolutionize India’s maritime sector by focusing on port-led development, logistics optimization, and coastal economic growth. With a 7,500 km coastline and strategic positioning on global trade routes, India is set to leverage its maritime potential for sustainable economic development.
Key Components of the SagarmalaProgramme
- Port Modernization & New Port Development: Upgrading existing ports and constructing new ones to enhance operational capacity, reduce bottlenecks, and improve efficiency.
- Port Connectivity Enhancement: Fostering seamless multi-modal logistics, including inland waterways and coastal shipping, to optimize time and cost of cargo transportation.
- Port-Led Industrialization: Establishing industrial clusters near ports, boosting economic growth while minimizing logistics costs.
- Coastal Community Development: Focusing on the sustainable development of coastal communities, through skill development, livelihood generation, and fisheries enhancement.
- Coastal Shipping & Inland Waterways Transport: Promoting eco-friendly cargo transportation via coastal and inland waterways to alleviate road and rail congestion.
Key Achievements and Outcomes
- Project Implementation: 839 projects worth ?5.79 lakh crore have been identified, with 272 projects already completed, amounting to ?1.41 lakh crore in investments.
- Growth in Coastal Shipping: Coastal shipping has surged by 118% over the last decade, significantly reducing logistics costs and emissions.
- Increased Inland Waterway Cargo: A 700% increase in inland waterway cargo, reducing congestion on roadways and railways.
- Improved Global Maritime Standing: Nine Indian ports now rank among the world’s top 100, with Vizag among the top 20 container ports globally.
Sagarmala 2.0 and Strategic Initiatives
- Sagarmala 2.0, launched with a ?40,000 crore budgetary support, aims to position India among the top five shipbuilding nations by 2047.
- It introduces a focus on shipbuilding, repair, recycling, and further port modernization, which will help India become a global maritime hub.
- The initiative targets a shipbuilding capacity of 4 million GRT and an annual port handling capacity of 10 billion metric tons.
- Additionally, the Sagarmala Startup Innovation Initiative (S2I2), launched in March 2025, seeks to promote innovation, research, and startups in the maritime sector.
- The program emphasizes green shipping, smart ports, and sustainable coastal development, providing funding, mentorship, and industry partnerships to boost technological advancement in the sector.
Funding and Project Implementation
- The SagarmalaProgramme follows a strategic and stakeholder-driven approach, involving central ministries, state governments, major ports, and other agencies.
- The funding structure utilizes a combination of public-private partnerships (PPP), internal resources of MoPSW agencies, and grant-in-aid for high-social-impact projects.
- The establishment of the Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL) facilitates equity participation in key projects.
Future Outlook and Alignment with Vision 2047
Sagarmala 2.0 and its strategic initiatives are aligned with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047 (MAKV), which aims to make India a leader in global maritime affairs. By enhancing port efficiency, expanding shipbuilding capacity, and fostering innovation, these initiatives will support India's vision of a Viksit Bharat (developed India) and Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) by 2047.
Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM)

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the implementation of the Revised Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) for 2024–25 and 2025–26, with an enhanced financial outlay.
Background:
- Launched: December 2014
- Type: Central Sector Scheme under the Development Programmes
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying
- Primary Aim: Conservation and development of indigenous bovine breeds and enhancement of milk productivity through advanced breeding technologies.
Revised Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?3,400 crore
- Additional Allocation: ?1,000 crore for 2024–25 and 2025–26
- Finance Commission Cycle: 15th (2021–22 to 2025–26)
Objectives of Revised RGM:
- Enhance productivity of bovines and sustainable milk production.
- Promote scientific breeding using high genetic merit (HGM) bulls.
- Expand Artificial Insemination (AI) coverage across India.
- Conserve indigenous cattle and buffalo breeds through genomic and reproductive technologies.
Key New Initiatives (2024–26):
- Heifer Rearing Centres:
- One-time assistance of 35% of capital cost.
- To establish 30 housing facilities with a total of 15,000 heifers.
- Interest Subvention Scheme:
- 3% interest subsidy on loans for purchasing HGM IVF heifers.
- Applicable to farmers borrowing from milk unions, banks, or financial institutions.
Major Achievements (as of 2023–24):
- Milk Production Increase: 63.55% rise in 10 years.
- Per Capita Milk Availability:
- 2013–14: 307 grams/day
- 2023–24: 471 grams/day
- Productivity Increase: 26.34% over the last decade.
Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme (NAIP):
- Coverage: 605 districts with <50% baseline AI coverage.
- Animals Covered: 8.39 crore
- Farmers Benefitted: 5.21 crore
- Service: Free AI at farmer's doorstep.
Technological Interventions:
- IVF Labs: 22 labs set up across States and Universities.
- HGM Calves Born: 2,541 through IVF.
- Indigenous Technologies Developed:
- Gau Chip &Mahish Chip: Genomic chips by NDDB & ICAR-NBAGR.
- Gau Sort: Indian-developed sex-sorted semen technology by NDDB.
Significance:
- Strengthens Atmanirbhar Bharat in livestock genomics and AI.
- Enhances livelihoods of 8.5 crore dairy farmers.
- Preserves India’s indigenous bovine biodiversity.
- Promotes scientific cattle rearing and milk self-sufficiency.
BHIM-UPI Incentive Scheme 2024–25

- 20 Mar 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, approved the Incentive Scheme for Promotion of Low-Value BHIM-UPI Transactions (Person-to-Merchant or P2M) for FY 2024–25 to encourage digital payment adoption, particularly among small merchants and in rural and remote areas.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Duration: 1 April 2024 to 31 March 2025
- Outlay: ?1,500 crore
- Coverage: UPI (P2M) transactions up to ?2,000 for small merchants only
- Incentive Rate:0.15% per transaction value
- MDR (Merchant Discount Rate):
- Zero MDR for all UPI P2M transactions
- Incentive applicable only for small merchants on transactions ≤ ?2,000
Incentive Disbursement Conditions:
- 80% of claim amount: Paid upfront each quarter
- Remaining 20%: Conditional on:
- 10%: If acquiring bank’s technical decline < 0.75%
- 10%: If acquiring bank’s system uptime > 99.5%
Objective:
- Promote adoption of indigenous BHIM-UPI platform
- Achieve ?20,000 crore P2M transaction volume in FY 2024–25
- Expand UPI in Tier 3 to Tier 6 cities, especially rural areas
- Promote inclusive tools: UPI 123PAY (for feature phones), UPI Lite/LiteX (offline payments)
Expected Benefits:
- Cost-free UPI usage for small merchants (encouraging cashless transactions)
- Enhanced digital footprint helps merchants access formal credit
- Ensures round-the-clock availability of payment systems
- Strengthens financial inclusion and less-cash economy
- Balanced fiscal support from the government while encouraging systemic efficiency
Digital Payments Background:
- Since January 2020, MDR has been made zero for BHIM-UPI and RuPay Debit Cards via amendments to:
- Payments and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (Section 10A)
- Income-tax Act, 1961 (Section 269SU)
- Previous incentive outlays (in ? crore):
Financial Year RuPay Debit Card BHIM-UPI Total
2021–22 432 957 1,389
2022–23 408 1,802 2,210
2023–24 363 3,268 3,631
What is BHIM-UPI?
- UPI: Real-time payment system developed by NPCI; allows instant money transfer between bank accounts via mobile apps.
- BHIM-UPI: Government-promoted UPI app launched in 2016.
- NIPL, NPCI’s international arm, is expanding UPI globally. UPI is accepted in Singapore, UAE, France, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and more.
NECTAR to Lead Agri-Tech Revolution
- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
In a major policy and scientific initiative, the Government of India is transforming the Northeast into the country’s next saffron cultivation hub, following the successful model of Jammu & Kashmir’s Pampore. The development is being led by the North East Centre for Technology Application and Reach (NECTAR), an autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
Mission Saffron and the Saffron Bowl Project
Originally launched in 2010–11 for Jammu and Kashmir, Mission Saffron was expanded to the Northeast in 2021 through the Saffron Bowl Project. The initiative now promotes saffron cultivation in Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Meghalaya, with further expansion planned for Nagaland and Manipur.
Saffron, derived from the stigmas of Crocus sativus, requires high-altitude (approx. 2000m), well-drained loamy or calcareous soils, and a dry to temperate climate. These agro-climatic conditions are present in parts of the Northeast, making it a viable region for saffron farming.
NECTAR’s Role in Agri-Tech and Regional Development
Established in 2014, NECTAR is driving technology-based interventions in agriculture, infrastructure, and economic development across the Northeastern states. The foundation stone for its permanent campus in Shillong was laid in March 2025 by Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh, marking a significant boost for scientific infrastructure in the region.
NECTAR's notable initiatives include:
- Saffron cultivation under the Saffron Bowl Project.
- Use of drone technology for land mapping under the Swamitva Yojana.
- Promotion of bamboo-based industries and honey production.
- Supporting indigenous technologies for sustainable rural development.
The Shillong campus is envisioned as a Centre of Excellence for advanced technological demonstrations and skill development, helping bridge last-mile gaps in technology adoption.
Significance for India’s Development
The Northeast is integral to India's aim of becoming a developed nation by 2047. Improvements in connectivity—roads, railways, and air links—have laid the groundwork for economic and scientific transformation in the region. The government sees the Northeast as a key growth frontier to unlock the country’s untapped potential.
5th Edition of Lineman Diwas

- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA), in partnership with Tata Power Delhi Distribution Ltd (Tata Power-DDL), organized the 5th Edition of Lineman Diwas on March 4, 2025, in New Delhi. The event commemorates the invaluable service of linemen and ground maintenance staff—frontline workers vital to ensuring uninterrupted power supply across India.
Key Highlights:
- Theme: Seva, Suraksha, Swabhiman (Service, Safety, Self-respect).
- Over 180 linemen from 45+ state and private utilities attended.
- Recognized 5 linemen and 4 DISCOMs for exemplary safety and service standards.
- Special Anthem on linemen launched by CEA Chairperson Ghanshyam Prasad.
- Safety videos and demonstrations of modern equipment were showcased.
- Participants visited the Distribution Operations & Safety Excellence Center (DOSEC) for exposure to training modules and tools.
The event highlighted the importance of Hotline Maintenance Training, which enables linemen to safely work on live power lines, improving both worker safety and power grid reliability.
About Central Electricity Authority (CEA):
- Statutory Body under the Ministry of Power, Govt. of India.
- Established: Originally under Electricity (Supply) Act, 1948; reconstituted under Electricity Act, 2003.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Functions:
- Advises government on electricity policy, planning, and technical standards.
- Monitors power generation, transmission, and distribution efficiency.
- Promotes safety, training, and regulatory compliance.
- Key Divisions:
- Power Planning & Monitoring
- Grid Operations & Transmission
- Distribution & Regulatory Affairs
- Safety & Training
‘One Day as a Scientist’ Initiative

- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
In response to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s call during his Mann Ki Baat address, the Ministry of Ayush has launched the ‘One Day as a Scientist’ initiative. This program offers students an immersive experience in scientific research, providing them hands-on exposure to advanced laboratory equipment and modern research methodologies. The initiative aims to nurture the scientific temperament among young minds and encourage them to explore the integration of traditional medicine with modern science.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Hands-on Lab Experience: Students visit Ayush research institutions where they explore cutting-edge scientific tools and technologies, gaining firsthand insight into the research process.
- Mentorship by Experts: Scientists and researchers guide students, offering valuable insights into research methodologies and the potential of Ayush systems in mainstream healthcare.
- Integration of Traditional and Modern Sciences: The initiative emphasizes the role of Ayush therapies, including Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, and Homeopathy, combined with modern scientific advancements.
- Nationwide Participation: The program is implemented across various institutions such as the National Institute of Ayurveda, Central Council for Research in Homoeopathy (CCRH), and the Central Research Institute for Yoga & Naturopathy (CRIYN), facilitating student engagement in scientific exploration.
Objectives of the Initiative:
- Encouraging Youth Participation: By providing direct exposure to scientific research, the initiative aims to inspire students to pursue careers in research and innovation.
- Bridging the Gap Between Traditional and Modern Medicine: The program focuses on scientifically validating and innovating traditional medicine, making it an integral part of India’s healthcare system.
- Fostering a Scientific Temperament: Students gain a deeper understanding of scientific processes, enhancing their curiosity and critical thinking, key traits for future leaders in research and innovation.
Alignment with National Science Day:
The National Science Day 2025 theme, “Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science and Innovation for Viksit Bharat,” aligns perfectly with the goals of this initiative. The program aims to inspire students to become future leaders in science and innovation, contributing to India’s vision of becoming a developed nation.
India–Nepal MoU on WASH Sector Cooperation

- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, India and Nepal signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to strengthen bilateral cooperation in the Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) sector, including waste management. The signing ceremony took place at Sushma Swaraj Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Objectives and Components of the MoU
- Capacity Building: Training programs for Nepali personnel in water resource management.
- Technology and Knowledge Transfer: Exchange of best practices and innovations in WASH.
- Groundwater Management: Joint efforts on:
- Groundwater quality monitoring
- Artificial recharge
- Rainwater harvesting and conservation practices
Strategic Significance
- Promotes regional cooperation and sustainability in public health and water management.
- Nepal seeks to learn from India’s successful initiatives under the Jal Jeevan Mission and Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
- The agreement includes official visits, site inspections, and regular bilateral meetings to monitor progress.
Sashakt Panchayat-Netri Abhiyan

- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj launched the “Sashakt Panchayat-Netri Abhiyan” at a National Workshop held in Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The initiative is a significant step toward gender-sensitive governance and enhancing the role of Women Elected Representatives (WERs) in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
Key Features of the Initiative
- Objective: Capacity-building of WERs to strengthen their leadership, decision-making, and active participation in local governance.
- Scale: Over 1,200 WERs from across India participated.
- Representation: Women from all three tiers of PRIs took part, marking a first-of-its-kind national gathering.
Model Women-Friendly Gram Panchayats (MWFGPs)
- Launched alongside the Abhiyan.
- Aim: Establish at least one Model Women-Friendly Gram Panchayat in each district.
- Purpose: Promote gender-sensitive, inclusive, and girl-friendly local governance models.
Primer on Gender-Based Violence
- A "Primer on Law Addressing Gender-Based Violence and Harmful Practices" was released.
- Targeted at elected representatives to raise awareness and promote legal literacy regarding women's safety and rights.
Context and Background
- India has over 1.4 million women elected representatives in PRIs.
- Some states, like Bihar, report over 50% representation, surpassing the 33% constitutional mandate.
- The campaign also addresses the elimination of "Sarpanch Pati" culture, emphasizing the independent authority of WERs.
Panel Discussions and Sectoral Themes
- Themes included:
- Women’s participation and leadership in PRIs
- Health, education, safety, digital empowerment, and economic opportunities for women
Cultural Integration and Recognition
- Cultural performances by UNFPA celebrated women’s achievements.
- Outstanding WERs from various states/UTs were felicitated for contributions to rural governance.
Significance
- Aligns with PM Narendra Modi’s “Mann Ki Baat” (119th episode) highlighting Nari Shakti in nation-building.
- Reinforces commitment to inclusive, safe, and socially just Gram Panchayats.
Giloy (Tinosporacordifolia)
- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
Giloy, also known as Guduchi and referred to as Amrita in Sanskrit—meaning the "herb of immortality"—is gaining global attention for its therapeutic potential, with scientific research on the herb witnessing a remarkable surge.
Surge in Scientific Publications
According to PubMed, a globally recognised biomedical database, there has been a 376.5% increase in research publications on Giloy between 2014 and 2024:
- 2014: 243 studies
- 2024: 913 studies
This significant rise reflects growing interest in natural and plant-based therapies, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic, which intensified focus on immunity boosters and holistic healthcare.
Therapeutic Properties and Uses
- Giloy is used in Ayush systems for:
- Fever management
- Gouty arthritis
- Autoimmune diseases
- Inflammatory disorders
- Cancer therapy (emerging evidence)
- Bioactive compounds in Giloy have shown:
- Immunomodulatoryeffects
- Anti-inflammatoryaction
- Adaptogenicandantiviralproperties
Botanical & Agricultural Features
- Scientific name: Tinosporacordifolia
- Distribution: Widely found across India
- Growth conditions:
- Grows in most soil types
- Propagated via stem cuttings (May–June)
- Large climber with corky, grooved stems
Recent Research Highlights
- Feb 2025 (Gujarat University): Giloy extracts showed promise in HPV-positive cervical cancer treatment through immunomodulation.
- Jan 2025 (Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai): Giloy-based phytopharmaceuticals were effective in managing Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis (IGM), offering a safe, steroid-free, and cost-effective alternative to surgery.
Government Initiatives
- The Ministry of Ayush has launched a technical dossier on Giloy, compiling scientific research and therapeutic insights.
- Aim: Promote evidence-based integration of Ayurveda with modern healthcare systems.
- Emphasis on global collaboration, research funding, and mainstreaming traditional medicine.
Obesity in India: A Public Health Challenge

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
Obesity has emerged as a critical public health issue in India, with rising prevalence across age groups and socio-economic strata. It is a key risk factor for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension. Recognizing its growing burden, the Government of India has adopted a multi-ministerial, community-driven, and policy-integrated strategy to promote healthier lifestyles.
What is Obesity?
- Definition (WHO): Abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health.
- Measurement: Body Mass Index (BMI = kg/m²)
- Body Mass Index (BMI), previously known as the Quetelet index, is a simple way to check if an adult has a healthy weight. It is calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared (kg/m²). To find BMI, take a person’s weight (kg) and divide it by their height (m) squared.
- WHO Standard:
- Overweight: BMI ≥ 25
- Obese: BMI ≥ 30
- Indian Criteria (lower threshold):
- Overweight: BMI 23–24.9 kg/m²
- Obese: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m²
- Morbid Obesity: BMI ≥ 35
Prevalence of Obesity
Global Trends (1990–2022):
- Children (5–19 yrs) with obesity: ↑ from 2% to 8%
- Adults with obesity: ↑ from 7% to 16%
India-Specific Data (NFHS-5, 2019–21):
- Overweight/obese: 24% women, 23% men
- Obese (15–49 yrs): 6.4% women, 4.0% men
- Children under 5 (overweight): ↑ from 2.1% (NFHS-4) to 3.4%
Causes of Obesity
- Increased consumption of processed, calorie-dense foods
- Sedentary lifestyle and urbanization
- Reduced physical activity
- Environmental and socio-economic factors
- Excessive use of edible oil, salt, and sugar in Indian diets
Key Government Initiatives to Combat Obesity
1. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- NP-NCD (National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases):
- Integrated under Ayushman Bharat Health & Wellness Centres
- Focus: Screening, early diagnosis, IEC/BCC awareness, and NCD clinics
- Facilities: 682 District NCD Clinics, 191 Cardiac Units, 5408 CHC Clinics
2. Ministry of AYUSH
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA): Specialized treatments (Panchakarma, diet, yoga)
- Ayurswasthya Yojana (2021–22): Funds projects tackling obesity, diabetes, and NCDs
- Research by CCRAS: Validating Ayurvedic lifestyle interventions (Dincharya, Ahara, Yoga)
- Collaboration with CSIR for integrating Ayurveda with modern science
3. Ministry of Women and Child Development
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (2018):
- Focus: Nutrition for children, adolescent girls, pregnant/lactating women
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi &Poshan 2.0 (2021): Combines nutrition, health, wellness
- Use of PoshanVatikas, millet promotion, and fortified food
- Jan Andolan for community-level awareness
4. Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Fit India Movement (2019):
- Fitness pledges, Fit India School certification, community fitness programs
- Khelo India Programme (2016–17):
- Sports infrastructure and talent development
- Promotes sports culture and active lifestyles in youth
5. Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Eat Right India Movement:
- Supply-Side Reforms:FoSTaC, hygiene ratings, food fortification
- Demand-Side Awareness: Eat Right Schools/Campus, DART Book, Magic Box
- Aaj Se Thoda Kam Campaign: Reduce fat, salt, and sugar intake
- RUCO Initiative: Repurposing Used Cooking Oil into biodiesel
- HFSS Food Labelling: Front-of-pack labels for High Fat, Salt, Sugar foods
Innovative Tools
Tool Description
DART Book Simple home tests for food adulteration
Magic Box 102 school-level food safety experiments
Food Safety on Wheels Mobile food testing & awareness vans
Fit India App Daily fitness tracking and motivation
India’s Way Forward: Towards Amrit Kaal
- Whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach
- Emphasis on lifestyle change, preventive healthcare, and regulation
- Stronger public health infrastructure and education
- Leveraging traditional wellness systems (Ayurveda & Yoga)
- Community empowerment via awareness drives and behavior change
Dholavira
- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
President DroupadiMurmu recently visited Dholavira, a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Gujarat, India. She expressed appreciation for the Archaeological Survey of India’s (ASI) meticulous conservation efforts to preserve this ancient site, despite its remote location.
Location and Significance:
Dholavira is situated on Khadir Bet Island in the Great Rann of Kutch, Gujarat, within the Kutch Desert Wildlife Sanctuary and along the Tropic of Cancer. It was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2021 due to its remarkable contributions to understanding the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization, one of the world's earliest urban cultures.
Key Features:
- City Layout and Construction:Dholavira is distinct from other Harappan sites in its layout, divided into three main sections: the Citadel, the Middle Town, and the Lower Town. The city is unique for its extensive use of stone in construction, unlike the brick-built cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro. It also featured multi-purpose grounds, including a marketplace and a festive area.
- Water Conservation System:The site is renowned for its sophisticated water management techniques, which included 16 massive reservoirs, stepwells, check dams, and underground water storage systems. This advanced water conservation system earned it the name "Jal Durga" or "Water Fort." The engineering skills of the Harappans, especially in water harvesting, were far ahead of their time and continue to be admired today.
- Trade and Cultural Exchange:Dholavira was a significant trade hub, connected to regions such as Magan (modern Oman) and Mesopotamia. It is believed to have been involved in the trade of copper, jewelry, and timber. The site yielded a variety of artifacts, including terracotta pottery, seals, ornaments, and evidence of metallurgy, along with inscriptions in the Indus Valley script.
- Archaeological Discoveries:The site was first discovered by Jagat Pati Joshi in 1967 and excavated systematically between 1990 and 2005 under Dr. Ravindra Singh Bisht of ASI. It is the fifth-largest site of the Indus Valley Civilization and provides evidence of habitation over seven cultural phases from 3000 to 1500 BCE. Notably, no human remains have been found, but the presence of architectural structures, artifacts, and inscriptions gives a rich understanding of the ancient civilization's culture and economy.
- Technological Advancements:The President, during her visit, highlighted the technological advancements of the Harappans, particularly in urban planning and water management, which were superior in many respects to the technology of modern times.
Historical Context:
The Harappan Civilization, flourishing from around 3300 to 1300 BCE along the Indus River, was an urban society known for its advanced city planning, sanitation systems, and trade networks. Dholavira stands out as a crucial link in understanding the broader scope of this civilization. Other key Harappan sites include Harappa, Mohenjo-Daro, Banawali, Lothal, and Ropar.
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025 was a high-intensity Tri-Service Special Forces military drill conducted by the Indian Air Force at Air Force Station Jodhpur, Rajasthan, from 24 to 28 February 2025.
Participating Forces
- Indian Army: Para (Special Forces)
- Indian Navy: Marine Commandos (MARCOS)
- Indian Air Force: Garud Special Forces
Objective
- To enhance interoperability, coordination, and operational synergy among the Special Forces of the three services.
- To ensure swift and effective responses to emerging security threats through joint operations.
Key Activities
- Airborne insertion and combat free-fall
- Precision strikes and counter-terrorism drills
- Hostage rescue operations
- Urban warfare simulations
- Validation of joint operational doctrines under realistic combat conditions
Significance
- Strengthens tri-service integration and fosters inter-service cooperation.
- Reinforces the commitment of the Indian Armed Forces to national security.
- Provides a platform for doctrinal validation and operational readiness.
All-India Consumer Price Index for Agricultural and Rural Labourers
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
The Labour Bureau, Ministry of Labour& Employment released the All-India Consumer Price Index (CPI) for Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL) and Rural Labourers (CPI-RL) for January 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Inflation Rates:
- CPI-AL: 4.61%
- CPI-RL: 4.73%
- Marked a decline from January 2024, when rates were 7.52% (CPI-AL) and 7.37% (CPI-RL).
- Also lower than December 2024: 5.01% (CPI-AL) and 5.05% (CPI-RL), indicating easing rural inflation.
- Index Levels:
- CPI-AL: 1316 (down by 4 points from 1320 in December 2024)
- CPI-RL: 1328 (down by 3 points from 1331 in December 2024)
Group-wise Index Comparison (Dec 2024 vs Jan 2025):
Group CPI-AL (Dec → Jan) CPI-RL (Dec → Jan)
General Index 1320 → 1316 1331 → 1328
Food 1262 → 1255 1269 → 1261
Pan, Supari, etc. 2093 → 2103 2100 → 2111
Fuel & Light 1382 → 1390 1372 → 1380
Clothing, Bedding, Footwear 1329 → 1332 1392 → 1396
Miscellaneous 1376 → 1385 1377 → 1385
About CPI-AL and CPI-RL:
- CPI-AL: Measures cost-of-living changes for agricultural labourers; used for revising minimum wages in agriculture.
- CPI-RL: Captures cost-of-living changes for rural labourers (includes CPI-AL as a subset).
- Compiled monthly for 20 states and at the All-India level.
- Base Year: 1986–87=100 (used to measure price change over time).
Significance:
- Declining CPI reflects lower rural price pressure, beneficial for wage policy formulation, poverty analysis, and rural development planning.
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
A recent study on the Tra2b gene in mice has revealed a potential reason why certain segments of the genome called Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) have remained unchanged for over 80 million years across species like humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish.
What are Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)?
- Definition:DNA sequences at least 200 base pairs long that have remained perfectly identical across diverse species for tens of millions of years.
- Number in Human Genome:Around 500 UCEs have been identified in the human genome.
- Location:Found in both coding regions (genes) and non-coding regulatory regions like enhancers and silencers.
- Species Overlap:Identical UCEs are shared by humans, mice, rats, chickens, and fish, reflecting their evolutionary conservation.
Key Findings from the Tra2b Gene Study
- Research Insight:A UCE embedded in the first intron of the Tra2b gene acts as a “poison exon” to regulate production of the Tra2β protein, which is involved in RNA splicing.
- Mechanism:
- When Tra2β levels rise, the UCE is included as an extra exon in the mRNA.
- This exon contains multiple stop codons, halting protein synthesis.
- The mRNA is then degraded, preventing excess Tra2β protein.
- Experimental Result:
- Deleting this UCE in mouse sperm-producing cells led to overproduction of Tra2β, causing cell death and infertility.
- This implies that any mutation in the UCE that disrupts its function would lead to infertility and thus prevent its transmission, explaining its evolutionary stability.
Significance of UCEs
- Evolutionary Importance:Their intolerance to mutation suggests they are critical for basic survival and reproductive success.
- Functional Role:
- Do not typically code for proteins.
- Regulate gene expression, often during early development, fertility, and immune response.
- Act as enhancers, silencers, or splice regulators (as in the case of poison exons).
- Medical Relevance:
- Help understand gene regulation and disease mechanisms.
- Their conservation across species makes them valuable for comparative genomics and biomedical research.
- Mice are used as model organisms due to ~85% genetic similarity with humans.
One Nation-One Port Initiative

- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) has launched the ‘One Nation, One Port Process (ONOP)’, a transformative initiative aimed at standardizing port operations across India to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and bolster India’s position in global trade. This move aligns with PM Gati Shakti, the National Logistics Policy, and India’s ambition to become a leading maritime and logistics hub under Viksit Bharat@2047.
Key Components of the Maritime Reform Package:
1. One Nation, One Port Process (ONOP):
- Seeks uniform documentation and standardized customs procedures across all Indian ports.
- Reduced container operation documents by 33% (from 143 to 96) and bulk cargo documentation by 29% (from 150 to 106).
- Aims to eliminate procedural inconsistencies, boost ease of doing business, and cut logistics delays.
2. Sagar Ankalan – Logistics Port Performance Index (LPPI):
- Evaluates performance of major and non-major ports under Bulk (Dry & Liquid) and Container categories.
- Assesses indicators like cargo handling, turnaround time, berth idle time, and container dwell time.
- Encourages data-driven port benchmarking and fosters transparency in maritime logistics.
- Supports India’s improvement in the World Bank’s LPI (International Shipments) – from rank 44 to 22 in 2023.
3. MAITRI (Master Application for International Trade and Regulatory Interface):
- A digital platform using AI and Blockchain to automate trade clearances and enable Virtual Trade Corridors (VTC).
- Initial linkage with UAE, to expand towards BIMSTEC and ASEAN nations.
- Reduces bureaucratic redundancies, improves supply chain integration, and enhances trade resilience.
4. Bharat Ports Global Consortium:
- A collaborative body combining IPGL (operations), SDCL (finance), and IPRCL (infrastructure).
- Focuses on port development, global trade connectivity, and supporting the Make in India initiative.
- Strengthens India's presence in global logistics networks.
5. Financial and Policy Support:
- Launch of a ?25,000 crore Maritime Development Fund to facilitate long-term port and shipping investments.
- Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy 2.0 to aid Indian shipyards in competing globally.
- Customs duty exemptions on shipbuilding inputs extended for 10 years.
- Inclusion of large ships in the Infrastructure Harmonised Master List (HML) to ease access to funding.
6. Sustainability and Green Shipping:
- Launch of the National Centre of Excellence in Green Port and Shipping (NCoEGPS).
- Focus on carbon footprint reduction, cleaner fuels, and eco-friendly port operations.
7. Promotion and Maritime Diplomacy:
- Announcement of India Maritime Week (Oct 27–31, 2025) in Mumbai to showcase India’s Maritime Virasat (Heritage) and Vikaas (Development).
- Will host the 4th Global Maritime India Summit and the 2nd Sagarmanthan Dialogue, with representation from 100 countries and over 1 lakh delegates.
Strategic Significance:
- Aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat, Blue Economy, and India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
- Boosts domestic manufacturing and export potential through better port infrastructure and trade facilitation.
- Reflects India’s push toward a digital, green, and globally competitive maritime sector.
Make the World Wear Khadi Campaign

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
The “Make the World Wear Khadi” campaign is a strategic initiative launched to globalize Khadi, India’s iconic hand-spun fabric, by integrating it with contemporary fashion trends. It is part of the inaugural World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES), scheduled from 1–4 May 2025at theJio World Convention Centre, Mumbai.
Key Highlights:
Organizers
- Advertising Agencies Association of India (AAAI)
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India
Objectives
- Elevate Khadi as a global, aspirational brand.
- Celebrate and modernize India's textile heritage.
- Engage creative professionals in branding and marketing of Khadi through various media.
- Showcase India’s soft power in the global Media & Entertainment (M&E) space.
Campaign Highlights
- Part of the broader Create in India Challenges under WAVES.
- Participants: Open to advertising professionals and freelancers globally.
- Format: Creative entries in digital, print, video, and experiential marketing.
- Total Registrations for Create in India Challenges: 73,000+
- Registrations for Khadi Challenge (as of Feb 15, 2025): 112
Khadi – Key Facts
- What is Khadi?
- A traditional Indian fabric made from hand-spun and hand-woven cotton, silk, or wool.
- Historical Significance:
- Promoted by Mahatma Gandhi during the freedom movement as a symbol of swadeshi, self-reliance, and economic independence.
- Key Characteristics:
- Hand-spun using a charkha (spinning wheel).
- Woven on traditional looms.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable, made from natural fibers.
- Supports rural employment and cottage industries.
WAVES Summit 2025 – Snapshot
- A flagship Media & Entertainment event with a hub-and-spoke model.
- Four thematic pillars:
- Broadcasting & Infotainment
- AVGC-XR (Animation, VFX, Gaming, Comics, Extended Reality)
- Digital Media & Innovation
- Films
- The Khadi campaign falls under the Broadcasting & Infotainment category.
Plastic Parks in India

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
The Department of Chemicals and Petro-Chemicals is implementing the Scheme for Setting up of Plastic Parks under the umbrella scheme of New Scheme of Petrochemicals, to support setting up need-based Plastic Parks, with requisite state-of-the-art infrastructure, enabling common facilities through cluster development approach, to consolidate the capacities of the domestic downstream plastic processing industry.
What is a Plastic Park?
- A Plastic Park is a dedicated industrial zone for plastic-related industries.
- Aims to synergize capacities of the plastic processing sector and promote investment, production, export, and employment.
- Encourages sustainable development through waste management and recycling.
Plastic Parks Scheme
- Implemented by the Department of Chemicals and Petro-Chemicals under the New Scheme of Petrochemicals.
- Financial Support: 50% of project cost, up to ?40 crore per park.
- Focus: Common infrastructure, cluster development, employment generation, and environmental sustainability.
Plastic Parks Approved (as of April 2025):
Location State Year Approved Grant Sanctioned (? crore) Amount Released (? crore)
Tamot Madhya Pradesh 2013 40.00 36.00
Jagatsinghpur Odisha 2013 40.00 36.00
Tinsukia Assam 2014 40.00 35.73
Bilaua Madhya Pradesh 2018 34.36 30.92
Deoghar Jharkhand 2018 33.67 30.30
Tiruvallur Tamil Nadu 2019 40.00 22.00
Sitarganj Uttarakhand 2020 33.93 30.51
Raipur Chhattisgarh 2021 21.04 11.57
Ganjimutt Karnataka 2022 31.38 6.28
Gorakhpur Uttar Pradesh 2022 34.79 19.13
Objectives
- Boost competitiveness, polymer absorption, and value addition.
- Support R&D-led growth and enhance exports.
- Promote eco-friendly practices like plastic recycling, effluent treatment, and hazardous waste management.
- Encourage cluster-based industrial growth.
Process of Setting up
- States submit proposals → In-principle approval by Scheme Steering Committee → Submission of DPR → Final approval.
- Implementation via Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) formed by states.
Other Government Measures
13 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) established at premier institutions (IITs, CSIR labs, CIPET) for:
- Sustainable polymers
- Bio-engineered polymer systems
- Advanced polymeric materials
- Wastewater management in petrochemical industries
Skill Development:
- CIPET offers short- and long-term training in plastic processing technology.
Sustainability Measures
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mandates recycling targets, use of recycled content.
- Hazardous Waste Management Rules enforce safe disposal practices.
- Ban on certain single-use plastics.
- Promotion of circular economy and biodegradable alternatives.
- Active engagement with WTO, UNEP, ISO for global compliance.
India in Global Plastic Trade
- 12th largest plastic exporter globally (World Bank, 2022).
- Exports increased from USD 8.2 million (2014) to USD 27 million (2022).
Prelims Facts to Remember
- Scheme launched under Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals.
- Max central grant per park = ?40 crore.
- Plastic Park = cluster-based industrial zone for plastic processing industries.
- Gorakhpur (UP) &Ganjimutt (Karnataka) approved in 2022.
- India is actively integrating sustainability and innovation in the plastic sector.
National Science Day 2025
- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
National Science Day to be celebrated with theme ‘Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science & Innovation for Viksit Bharat’.
Key Details:
- Observed On: February 28 annually
- Purpose: To commemorate the discovery of the Raman Effect by Sir C.V. Raman in 1928. The day highlights the importance of science and promotes scientific temper among the public.
- Theme 2025:“Empowering Indian Youth for Global Leadership in Science & Innovation for Viksit Bharat”
- This theme reflects the vision of building a developed India (Viksit Bharat) by nurturing youth-led scientific innovation and aligning with India’s S&T ambitions for 2047.
About Sir C.V. Raman and Raman Effect:
- Born: 7 November 1888, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu
- Major Contributions:
- Discovered the Raman Effect (1928), for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, becoming the first Asian Nobel Laureate in science.
- Founded: Indian Journal of Physics (1926), Indian Academy of Sciences (1934), Raman Research Institute (1948).
- First Indian Director of IISc, Bangalore (1933).
- Awarded Bharat Ratna in 1954.
Raman Effect:A phenomenon where light passing through a substance changes in wavelength due to interaction with molecular vibrations. This principle is used in Raman Spectroscopy, widely applied in material science, chemistry, forensics, and even nuclear waste analysis.
National Science Day – History & Celebrations:
- Established: 1986 by the Government of India
- First Observed: 1987
- Organisedby:National Council for Science & Technology Communication (NCSTC) under the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- Celebrations include lectures, open labs, science fairs, and awareness drives across the country, especially for students.
Key Developments in Science & Technology (2024-25):
- Innovation & IP Rankings:
- 39th in Global Innovation Index 2024 (WIPO)
- 6th in Global IP Filings
- Major Initiatives:
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF): Boosts R&D and supports innovation in EVs, materials, and emerging technologies.
- National Quantum Mission (NQM): ?6003.65 crore mission to advance quantum computing, communication, and sensing.
- National Supercomputing Mission (NSM):
- Deployed 33 supercomputers, capacity: 32 PetaFlops.
- Target: 77 PetaFlops using indigenous technology.
- Artificial Intelligence:
- BharatGen: India’s first multilingual, multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) for Generative AI.
- STEM Inclusivity:
- Programs like WISE-KIRAN support women in science.
- PM Early Career Research Grant nurtures young researchers.
- INSPIRE continues to attract school and college students to science careers.
- Geospatial & Climate Research:
- Expansion of spatial thinking programs in schools (116 schools across 7 states).
- Establishment of 4 Centres of Excellence for climate risk mapping to enhance disaster preparedness.
PRAKRITI 2025

- 28 Feb 2025
In News:
- The International Conference on Carbon Markets – PRAKRITI 2025 was inaugurated by the Minister of Power and Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Organized by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power, the event served as a major platform for global dialogue on carbon markets, climate finance, and sustainability strategies.
Key Highlights:
PRAKRITI 2025 (Promoting Resilience, Awareness, Knowledge, and Resources for Integrating Transformational Initiatives) aimed to:
- Understand the functioning of Indian and global carbon markets.
- Discuss challenges, dynamics, and opportunities in carbon trading.
- Strengthen carbon credits, offset mechanisms, and compliance systems.
- Promote renewable energy, green innovations, and ecosystem-based interventions.
- Foster collaboration between governments, industries, and citizens.
Insights from PRAKRITI 2025
- Global Linkages:India’s carbon market will increasingly be influenced by global policies such as the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which imposes carbon pricing on imports like steel and aluminium. Indian industries must prepare to maintain competitiveness.
- Carbon Market Mechanisms:
- Under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, carbon trading allows entities to buy carbon credits to offset emissions.
- Carbon credit = reduction of 1 metric ton of CO? or equivalent GHGs.
- India’s Progress:
- India ranks second globally in Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project registrations.
- The Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, regulated by BEE, has saved over 106 million tonnes of CO? since 2015.
- Development of a domestic carbon market is a priority to align with global standards and leverage international finance.
- Challenges Highlighted:
- Need for robust Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) frameworks.
- Ensuring fair benefit distribution among stakeholders.
- Developing policies tailored to India’s economic and social realities.
- Increasing private sector engagement and incentivizing renewable energy developers.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- Established: 1 March 2002 under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Mandate: Develop policies and programmes to promote energy efficiency, coordinate with stakeholders, and promote self-regulation within market principles to reduce India's energy intensity.
- Role in Carbon Market: BEE is the nodal agency regulating India’s carbon trading schemes and energy conservation initiatives.
First Regional Dialogue and ESIC Foundation Day

- 27 Feb 2025
In News:
- India hosted the first-ever Regional Dialogue on Social Justice under the Global Coalition for Social Justice in New Delhi (Feb 2025).
- Event coincided with the 74th Foundation Day of Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC), established in 1952.
Global Coalition for Social Justice (GCSJ)
- Launched by ILO in 2023, GCSJ aims to address social justice deficits globally, aligned with SDGs.
- Membership: Open to governments, businesses, academia; India is a key member.
- Promotes inclusive, sustainable development, responsible business conduct, and labor rights.
- India leads the Asia-Pacific Coordinating Group and spearheads responsible business initiatives.
India’s Achievements in Social Protection
- As per ILO’s World Social Protection Report 2024-26:
- India’s social protection coverage (excluding health) has doubled from 24.4% (2021) to 48.8% (2024).
- India contributed 5% of the global increase in social protection coverage.
- Employability of Indian graduates rose from 33.95% (2013) to 54.81% (2024).
Key Government Initiatives
- e-Shram Mobile App launched to improve access to welfare schemes, curated job listings, and multilingual support.
- Focus on extending coverage to:
- Informal sector (unorganized, gig, platform, construction, agricultural workers).
- Women and youth, with targets like 70% female workforce participation by 2047.
- Emphasis on AI and the Future of Work, living wages, and Global Value Chains through the Decent Work Country Programme.
Constitutional Provisions Supporting Social Justice
Provision
Focus
Preamble
Social, economic, and political justice
Art. 23 & 24
Prohibit trafficking, forced and child labour
Art. 38
Reduce social and economic inequalities
Art. 39 & 39A
Fair wages, legal aid, livelihood opportunities
Art. 46
Promote education and welfare of weaker sections
About Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
- Statutory body under the ESI Act, 1948, Ministry of Labour& Employment.
- Eligibility: Employees earning ≤ ?21,000/month.
- Coverage: Establishments with ≥10 employees (or <10 in hazardous sectors).
- Benefits: Medical care, maternity, sickness, disability, dependent benefits, and unemployment allowance.
Significance of the Dialogue
- Platform for global best practices exchange from countries like Germany, Brazil, Australia, Philippines, and Namibia.
- Showcased India’s leadership in technology-driven social security, gender-responsive policies, and youth skilling.
- Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS) and CII-EFI signed a Joint Statement on Responsible Business Conduct.
- Publications released include:
- Best Practices on Responsible Business Conduct
- Compendium on Social Protection in India
- Social Security for Informal Workers
Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP)
- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
Launched under the Create in India Challenge Season 1, the Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP) is a flagship initiative aimed at promoting India’s gaming and interactive entertainment ecosystem on the global stage.
Key Highlights
- Launch Year: 2025
- Ministry Involved: Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Organizing Partner: Interactive Entertainment and Innovation Council (IEIC)
Objectives:
- Identify and showcase Indian gaming talent internationally.
- Support the growth of the gaming, animation, visual effects, and immersive technology (AR/VR/Metaverse) sectors.
- Boost the 'Create in India' initiative in the media and entertainment domain.
- Enable Indian developers and startups to create globally competitive digital products.
Program Features:
- Eligibility:
Open to developers, studios, startups, and tech companies with working prototypes in:- Game development
- Esports
- Business solutions for gaming ecosystem
- Selection Process:
- Game Submission
- Expert Evaluation – Based on product, pitch, and team viability
- Final Showcase – Winners selected by a jury
Global Exposure Platforms:
- Game Developers Conference (GDC) 2025
- Location: San Francisco
- Dates: March 17–21, 2025
- World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025
- Location: Mumbai
- Dates: May 1–4, 2025
- Venue: Jio World Convention Centre &Jio World Gardens
- Focus Areas: Broadcasting, AVGC-XR, Digital Media, Innovation, and Films
Relevance of WAVES Summit:
- WAVES acts as a global convergence point for the Media & Entertainment (M&E) sector.
- AVGC-XR (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics + AR/VR/Metaverse) is a central pillar, aligning with TTP’s goals.
Significance for India:
- Positions India as a global hub for innovation in digital entertainment.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat in the tech and creative economy sectors.
- Encourages cross-border collaborations and export of Indian intellectual property in the gaming domain.
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy in North East India

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The North Eastern Region (NER) of India, endowed with rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and indigenous knowledge, is undergoing a transformation through biotechnology-led initiatives. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology is spearheading this change to harness the region’s biological resources for inclusive and sustainable development.
Biotechnology: Definition and Types
Biotechnology involves the use of biological systems or organisms to develop products and technologies that improve healthcare, agriculture, industry, and the environment.
Types of Biotechnology:
- Medical Biotechnology – Vaccines, gene therapy, diagnostics.
- Agricultural Biotechnology – Pest-resistant crops, high-yield seeds, and sustainable agriculture.
- Industrial Biotechnology – Biofuels, biodegradable plastics, enzyme-based processes.
- Environmental Biotechnology – Waste treatment, pollution control, and bioremediation.
Why North East India is Ideal for Biotech Development
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Home to 8,000+ plant species, including 850+ medicinal plants and agro-climatic diversity.
- Indigenous Knowledge: Rich traditional practices in herbal medicine and organic farming.
- Agri-Biotech Potential: Ideal for medicinal crops, essential oils, and organic produce.
- Industrial Opportunity: Scope for biofuel production, value-added food processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
Key DBT Programmes and Initiatives in the North East
- DBT North Eastern Programme
- Since 2010, 10% of DBT’s annual budget is dedicated to NER.
- Focus: R&D, education, infrastructure, entrepreneurship, and employment generation in biotechnology.
- Twinning R&D Programme (2010–11)
- Promotes collaborative biotech research between NER and national institutes.
- Over 65 institutional partnerships, supporting 650+ projects and benefiting ~2,500 researchers/students.
- Biotech Hubs Network (Since 2011)
- 126 Biotech Hubs established across universities and colleges.
- Phase II supports 54 hubs for focused research on local issues.
- BLiSS (Biotech Labs in Senior Secondary Schools): Started in 2014 to introduce biotechnology at the school level.
- Visiting Research Professorship (VRP) Programme:Launched in 2015 to utilize the expertise of top scientists for NER biotechnology development.
- Chemical Ecology Programme (2015): Collaborative training by NCBS, UAS, and IISc for Ph.D. scholars in the field of chemical ecology.
- Genomics Training Programme (2016):Conducted by DBT-NIBMG, Kalyani, for biomedical researchers in the region.
Agri-Biotech and Livelihood-Oriented Initiatives
- DBT-NECAB (Phase III): Enhancing biotech applications in agriculture.
- Citrus Research: Disease-free scion material of Khasi mandarin and sweet orange developed at IHT, Assam.
- Medicinal Crop Cultivation: 64.1 acres under Curcuma caesia and lemongrass cultivation; 649 farmers trained.
- Essential Oil Distillation: Facility set up in Mudoi village, Arunachal Pradesh, for revenue support.
- Value-Addition in Wild Fruits: Docynia indica (Assam apple) processed into products like jam, pickles, and candy.
Technology-Driven Achievements
- Bacterial Blight-Resistant Rice (Patkai): Developed by Assam Agricultural University; notified by CVRC.
- Brucellosis Detection Kit: Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) to detect anti-Brucella antibodies in livestock.
- Pig Disease Diagnosis Expert System (PDDES): Mobile app for livestock disease detection and management (available on Google Play Store).
Challenges in NER’s Biotech Growth
- Limited infrastructure for biotech R&D and production.
- High cost of commercial biotech projects.
- Shortage of trained professionals in advanced biotech fields.
- Vulnerability to climate change and poor connectivity with markets.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Infrastructure: Develop biotech parks, R&D centers, and incubators.
- Skill Development: Train local youth, researchers, and farmers.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster industrial collaboration for startups and innovation.
- Eco-friendly Technologies: Promote sustainable and low-impact biotech industries.
- Digital Integration: Use AI and data analytics for agricultural and healthcare biotech solutions.
Jhumoir Binandini (Jhumur) Dance

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to attend the Jhumoir Binandini (Mega Jhumoir) 2025, a grand cultural event featuring around 8,600 performers showcasing the traditional Jhumur dance. This event highlights the rich cultural contributions of the tea tribe community of Assam.
About Jhumoir (Jhumur) Dance
- Jhumur, also known as Jhumoir, is a traditional folk dance performed predominantly by the Adivasi tea tribes of Assam.
- It is typically showcased during the harvest season, as well as on occasions like weddings and community festivals.
- The dance was introduced to Assam by the tea garden workers, who originally migrated from regions like Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal in the 19th century under British colonial rule.
Cultural Origins and Community
- The dance traces its roots to the Sadan ethnolinguistic group from the Chotanagpur plateau (present-day Jharkhand).
- The tea tribe community is a multi-ethnic group comprising descendants of migrant tea garden laborers.
- These communities have significantly shaped Assam’s socio-cultural landscape.
Performance Style and Attire
- Jhumur is performed in a circular formation, with dancers often holding each other's waists.
- The performance features rhythmic footwork, swaying movements, and energetic music.
- Women typically wear colorful sarees, often in red and white, while men dress in dhotis and kurtas.
- The musical accompaniment includes traditional instruments like the Madal, Dhol, Dhak, Taal (cymbals), and Flute.
Themes and Social Significance
- Jhumur songs blend liveliness with social commentary, often highlighting the struggles, exploitation, and migration experiences of the tea plantation workers.
- Major tea garden festivals where Jhumur is performed include Tushu Puja and Karam Puja, both celebrating the harvest.
- The dance fosters community bonding, promotes cultural pride, and represents Assam’s syncretic cultural heritage.
- It stands as a symbol of inclusivity, unity, and the resilience of the tea tribe community.
SWARBICA Executive Body Meeting 2025

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Executive Body Meeting of the South and West Asian Regional Branch of the International Council on Archives (SWARBICA) was held on 20–21 February 2025 at the India International Centre, New Delhi.
- It was inaugurated by Union Minister for Culture and Tourism, Gajendra Singh Shekhawat, and hosted by the National Archives of India.
- This is the second time India has hosted the SWARBICA meeting, the last being in Colombo, Sri Lanka, in 2017.
Key Highlights
- The event marked the first SWARBICA Executive Meeting in eight years.
- Participating nations included Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
- Pakistan joined the meeting virtually, while Iran could not attend due to visa-related issues.
- The meeting provided a platform for regional cooperation in archival development, emphasizing shared cultural and religious heritage.
Agenda and Focus Areas
- Digital Preservation & Archives Digitization:
- Arun Singhal, Director General of the National Archives of India (NAI) and Treasurer of SWARBICA, presented NAI’s ongoing efforts in the digitization of archival records.
- Emphasis was placed on training programs, technical exchange, and conservation practices.
- AI in Digital Archiving:
- Aseminar titled "Using AI for Digital Preservation in Archives" was organized.
- Experts from India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and SAMHiTA (India International Centre) discussed the potential of artificial intelligence in archival science.
About SWARBICA
- It functions as a regional arm of the International Council on Archives (ICA), fostering collaboration among archival institutions in South and West Asia.
- Established: The idea was proposed in 1973 at an ICA meeting in Brussels and officially launched on 11th December 1976 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
- SWARBICA promotes professional networking, training, resource sharing, and advancement in archival practices among member countries.
Significance for India
- Reflects India’s leadership in regional cultural cooperation.
- Aligns with national goals of digital governance, knowledge preservation, and heritage conservation.
- Strengthens India's cultural diplomacy in South and West Asia.
India–Qatar Strategic Partnership

- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
In February 2025, His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani, Amir of Qatar, paid a State Visit to India, during which India and Qatar elevated their bilateral relations to a Strategic Partnership.
Major Outcomes of the 2025 Summit
- Strategic Partnership Agreement:Formalized multifaceted cooperation across sectors—trade, investment, energy, security, technology, and people-to-people ties.
- Trade and Economic Engagement:
- Target set to double bilateral trade to $30 billion by 2030 (from $14 billion in FY 2023–24).
- Joint Commission on Trade and Commerce established to monitor economic ties.
- Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) pledged $10 billion in Indian infrastructure, green energy, and startups.
- Revised Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement signed.
- Energy Cooperation:
- A landmark 20-year LNG supply deal (2028–2048) between QatarEnergy and Petronet LNG.
- Collaboration in renewable energy including green hydrogen, solar energy, and AI-based efficiency solutions.
- Investment and Digital Integration:
- QIA to open an office in India; Qatar National Bank to set up presence in GIFT City.
- India’s UPI system operationalized in Qatar's POS infrastructure; nationwide rollout planned.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Cooperation in AI, semiconductors, IoT, robotics and digital governance.
- Indian startups to participate in Web Summits in Doha (2024–25).
People-to-People and Cultural Ties
- Over 830,000 Indians reside in Qatar, forming the largest expatriate community.
- MoUs signed on youth, sports, education, archives, and cultural cooperation.
- Agreement to celebrate India-Qatar Year of Culture, Friendship and Sports.
Security and Counter-Terrorism
- Strong condemnation of terrorism in all forms, including cross-border terrorism.
- Commitment to enhanced cooperation in intelligence sharing, cybercrime, anti-money laundering, and countering transnational crimes.
- Emphasis on regular meetings of the Joint Committee on Security and Law Enforcement.
Labour and Health Cooperation
- Agreement to hold regular Joint Working Group on Labour and Employment to address expatriate welfare and mobility.
- Collaboration in the health sector, including pharma exports, device registration, and pandemic response mechanisms.
Geopolitical and Multilateral Cooperation
- Exchange of views on Middle East stability, UN reforms, and India-GCC engagement.
- Appreciation for Qatar’s Chairmanship of the India-GCC Strategic Dialogue (Sept 2024).
- Agreement on UN Security Council reform and advancing SDG goals through multilateralism.
Challenges Ahead
- Trade Imbalance: Imports of LNG/LPG ($12B) far exceed exports (<$2B).
- Labour Rights Concerns: Working conditions of Indian laborers in Qatar remain under scrutiny.
- Legal and Judicial Issues: Over 600 Indians in Qatari jails; need for agreement on transfer of sentenced persons.
- Geopolitical Complexities: Qatar’s involvement in West Asian diplomacy presents nuanced challenges.
- Naval Veterans Case: Pending resolution affects diplomatic sentiment.
Way Forward
- Boost Indian exports in pharmaceuticals, IT, engineering goods.
- Expedite India-Qatar Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) to streamline FDI.
- Expand collaboration in green hydrogen, carbon capture, and energy diversification.
- Strengthen ministerial-level engagements, labor welfare frameworks, and regional security dialogue.
NAKSHA Programme
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Ministry of Rural Development has launched a pilot project titled NAKSHA(National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations) in 152 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across 26 States and 3 Union Territories, with the inauguration taking place in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
Objective of NAKSHA
The NAKSHA initiative aims to:
- Create and update urban land records for accurate, reliable documentation of property ownership.
- Empower citizens by improving ease of access to land records.
- Facilitate urban planning and reduce land-related disputes.
- Promote transparency, efficiency, and sustainable development through an IT-based system.
Key Features
- Technical Partner: The Survey of India will carry out aerial surveys and provide orthorectified imagery via third-party vendors.
- Implementation Partners:
- Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation (MPSEDC) will develop a web-based GIS platform.
- National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI) will provide data storage facilities.
- Execution at State Level: States and UTs will conduct field surveys and ground truthing, leading to the final publication of urban and semi-urban land records.
Exercise Komodo
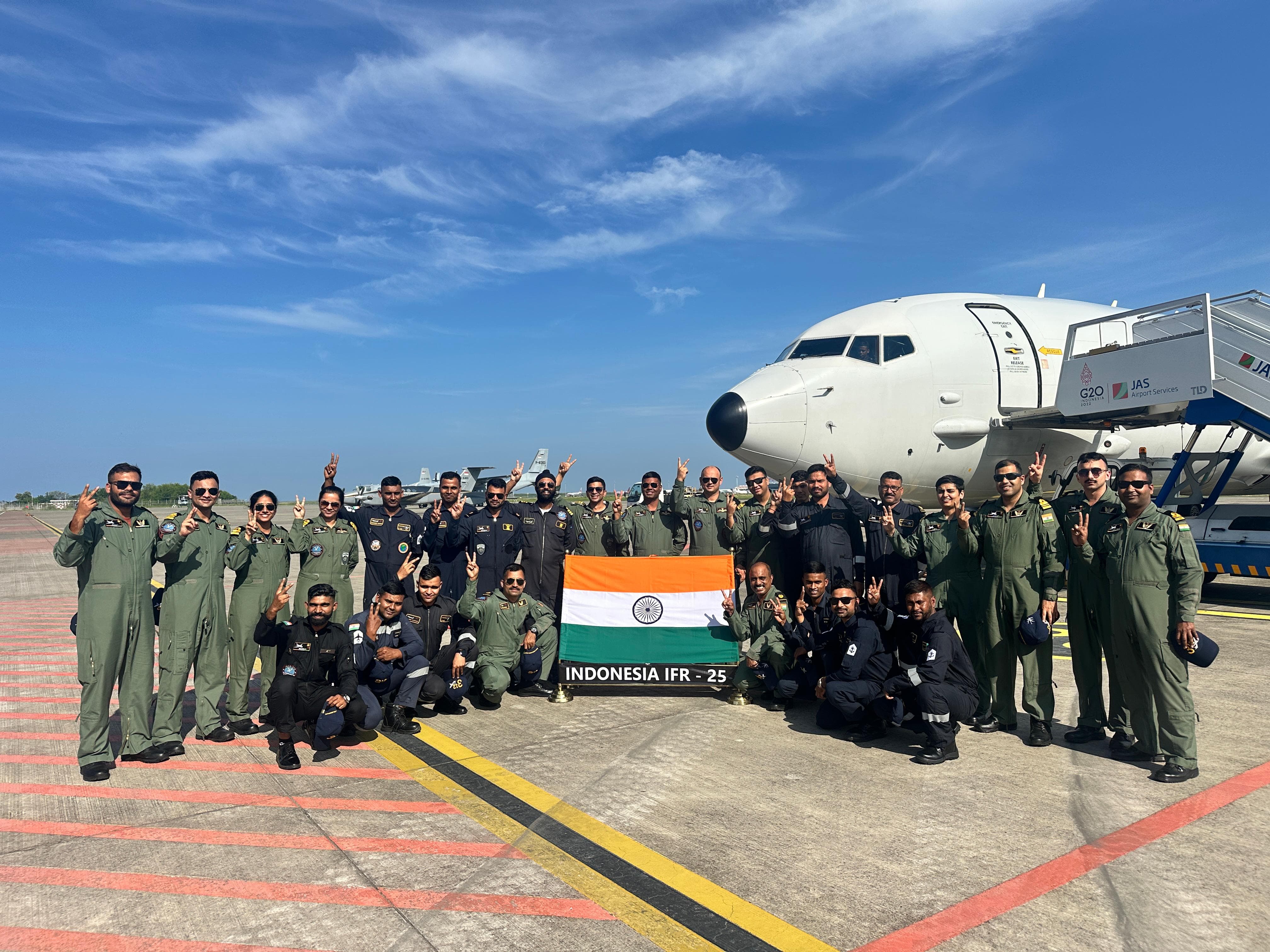

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy's platforms—INS Shardul, an amphibious warfare ship, and the P-8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft—participated in the International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025 and the 5th edition of the Multilateral Naval Exercise Komodo held in Bali, Indonesia, from 15 to 22 February 2025.
International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025
- IFR 2025 is a prestigious multinational naval event reviewed by the President of Indonesia.
- Participating nations showcased naval assets including warships, helicopters, and maritime aircraft.
- The Indian Navy took part in:
- International Maritime Security Symposium
- Tactical floor games
- City parade
- Coral and mangrove plantation
- Beach cleaning activities
- Baby turtle release, promoting environmental and maritime sustainability.
Exercise Komodo 2025
- Initiated in 2014, Exercise Komodo is a non-combat multilateral naval exercise hosted by the Indonesian Navy.
- The 2025 edition had the theme: "Maritime Partnership for Peace and Stability".
- Objectives:
- Promote maritime cooperation
- Enhance interoperability
- Foster regional security cooperation
- Key Features:
- Participation from 39 countries
- Involvement of 34 foreign and 18 Indonesian Navy warships
- Included:
- Naval exercises
- Officer exchange forums
- Bilateral naval meetings
- Defense exhibition
- Cultural parades
Strategic Context and Bilateral Engagements
- The participation builds upon the Indian Navy’s involvement in the La Pérouse exercises in Indonesia (January 2025) involving INS Mumbai and a P-8I aircraft.
- It coincided with the visit of Admiral Muhammad Ali, Chief of Staff of the Indonesian Navy, to India during the Republic Day 2025, accompanying President Prabowo Subianto as the Chief Guest.
Significance for India
- The participation reaffirms India’s commitment to SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- It strengthens India-Indonesia defense ties and underscores India's proactive role in regional maritime diplomacy and environmental stewardship.
Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ayush has officially opened nominations for the Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards 2025, which will be conferred on the occasion of the International Day of Yoga (IDY) 2025. These prestigious awards aim to honour individuals and organizations that have made exceptional and sustained contributions to the promotion and development of Yoga at both national and international levels.
Background and Objective
Instituted by the Government of India and endorsed by the Hon’ble Prime Minister, the awards recognize Yoga’s vital role in:
- Health promotion
- Disease prevention
- Management of lifestyle-related disorders
The initiative reflects the government’s broader vision to acknowledge and encourage meaningful contributions in advancing Yoga as a holistic system of well-being and preventive healthcare.
Award Categories and Benefits
The awards will be presented in the following four categories:
- National Individual
- National Organization
- International Individual
- International Organization
Each awardee will receive:
- A Trophy
- A Certificate of Recognition
- A Cash Prize of ?25 lakh
Eligibility Criteria
- Individual applicants must be 40 years or older.
- They should possess a minimum of 20 years of committed work in promoting Yoga.
- Organizations must have a proven track record in the field of Yoga development and outreach.
Applicants or nominees can apply for only one category (either National or International) in a given year. Applications can be submitted directly by individuals/entities or through nominations made by recognized Yoga institutions.
Application and Submission Process
- Nominations and applications are to be submitted through the MyGov platform:
https://innovateindia.mygov.in/pm-yoga-awards-2025/ - The link is also accessible on the Ministry of Ayush website and those of its autonomous bodies.
- The deadline for submission is March 31, 2025.
Selection Procedure
The award process involves two key stages:
- A Screening Committee formed by the Ministry of Ayush will evaluate all entries and recommend a maximum of 50 nominations per category.
- These shortlisted names will be reviewed by a high-level Evaluation Jury comprising eminent personalities from diverse fields, which will serve as the final decision-making body.
Significance of the Initiative
The Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards not only celebrate excellence in Yoga but also further the objectives of initiatives like Fit India Movement, Ayushman Bharat, and the mainstreaming of traditional Indian wellness systems.
The awards are a key element of the Ministry of Ayush’s broader mandate to integrate traditional systems such as Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa, and Homeopathy into the healthcare ecosystem of India.
Exercise Dharma Guardian 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The 6th edition of Exercise Dharma Guardian, a joint annual military exercisealternately hosted in India and Japan since 2018is scheduled from February 25 to March 9, 2025, at Mount Fuji, Japan.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Strengthen Bilateral Defence Relations: Enhances military diplomacy under the India–Japan Special Strategic and Global Partnership.
- Promote Interoperability: Develops joint operational capabilities and tactical synergy in line with UN peacekeeping mandates (Chapter VII).
- Urban and Semi-Desert Warfare: Trains troops in counter-terrorism operations and urban combat scenarios.
- Regional Stability: Supports the Indo-Pacific security architecture and complements Quad defence objectives (India, Japan, US, Australia).
Key Features of Dharma Guardian 2025
- Advanced Tactical Training: Close-quarter battle drills, live-fire exercises, battlefield medical evacuation.
- Joint Counter-Terror Operations: Conducted under UN charter guidelines for multinational cooperation.
- 48-hour Validation Exercise: Simulated real-time combat for assessing operational readiness and coordination.
- ISR and Tactical Mobility Drills: Involves establishing temporary operating bases, ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance) grids, mobile vehicle checkpoints, and heliborne insertions.
- House Intervention & Search Operations: Practical training for securing urban areas against militant threats.
- Weapons & Equipment Display: Demonstrates India’s growing defence manufacturing under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Mount Fuji – Host Site
- Geographical Significance: Japan’s highest peak at 3,776.24 meters, located 100 km southwest of Tokyo.
- Cultural Importance: Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2013) and revered as one of Japan’s “Three Holy Mountains.”
- Training Terrain: Its stratovolcanic landscape provides a realistic backdrop for high-altitude and rugged terrain operations.
Related India-Japan Military Exercises
India and Japan conduct a wide spectrum of bilateral and multilateral defense exercises across all services:
Exercise Name Service Branch Focus Area
Dharma Guardian Army Land-based counter-terror and urban warfare
JIMEX Navy Naval interoperability and maritime security
Malabar (Quad) Navy (Multilateral) Naval drills with US and Australia
Veer Guardian Air Force Air combat tactics and coordination
ShinyuuMaitri Air Force Air mobility and humanitarian operations
NAMASTE Scheme

- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme, launched by the Government of India, aims to empower sanitation workers, particularly Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs), also known as SafaiMitras.
Key Highlights:
- It focuses on ensuring their dignity, safety, and economic empowerment, while promoting the mechanization of sanitation processes.
- The scheme is designed to address the challenges faced by these workers, who are often exposed to hazardous conditions.
Objectives of the NAMASTE Scheme
The primary objectives of the NAMASTE scheme include:
- Formalization of sanitation work and enhancing occupational safety.
- Promotion of mechanized cleaning techniques to reduce manual interventions.
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and other safety devices to workers.
- Ensuring economic and social empowerment of sanitation workers.
Implementing Agencies and Timeline
- The NAMASTE Scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The scheme is executed by the National SafaiKaramcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC), under MoSJE.
- The scheme is scheduled for implementation from FY 2023-24 to 2025-26, with a target group comprising sewer workers, septic tank workers, and waste pickers (the latter being added in 2024).
Key Initiatives Under NAMASTE
- Distribution of PPE Kits: Under the scheme, PPE kits are provided to sanitation workers to safeguard them from health hazards, especially while working in unsafe environments like sewer lines and septic tanks. These kits include masks, gloves, goggles, face shields, gowns, and shoe covers.
- Ayushman Health Cards: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) health cards are distributed to SSWs under the scheme. These cards enable workers to access cashless healthcare at empaneled hospitals, ensuring that sanitation workers receive timely medical attention without financial burden.
- Capacity Building and Training: The scheme promotes capacity building for SSWs through training programs on safety protocols, mechanized cleaning processes, and the use of modern sanitation technologies. This helps improve the efficiency and safety of their work, while also reducing manual handling.
- Promoting Mechanization: To reduce the hazardous practice of manual scavenging, the scheme focuses on providing mechanized equipment to enhance sanitation operations and create safer working conditions for workers.
14th Asian Fisheries and Aquaculture Forum (14AFAF)

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
India is set to host the 14th Asian Fisheries and Aquaculture Forum (14AFAF) from February 12–14, 2025, at the ICAR Convention Centre, Pusa Campus, New Delhi.
Key Highlights
- This triennial international event—organized by the Asian Fisheries Society (AFS), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Department of Fisheries (DoF), and AFS Indian Branch (AFSIB)—is themed "Greening the Blue Growth in Asia-Pacific".
- It aims to promote sustainable, inclusive, and innovation-driven development in the fisheries and aquaculture sector.
- Previous Indian Host: India is hosting the AFAF for the second time, the first being the 8th AFAF in Kochi (2007).
- Legacy: AFAF, headquartered in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, has been a leading platform for fostering global cooperation in fisheries and aquaculture since its inception.
India's Role and Significance
- India ranks second globally in total fish production and aquaculture output, underlining its emerging leadership in the blue economy.
- The forum presents a strategic opportunity to:
- Showcase India’s technological and policy advancements.
- Strengthen international collaborations.
- Promote sustainable, resilient, and globally competitive aquaculture systems.
Forum Structure and Thematic Sessions
The event will feature 20+ technical sessions and keynote presentations by international experts, focusing on priority areas such as:
- Sustainable Fisheries Management:Emphasis on responsible fishing, biodiversity preservation, and efficient resource utilization.
- Climate Change and Fisheries:Addressing climate impacts on aquatic ecosystems and developing adaptive strategies.
- Smart Aquaculture & Technology:Integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance fish farming efficiency and monitoring.
- Fish Genetics & Biotechnology:Innovations for disease resistance, improved yields, and genetic advancements.
- Post-Harvest and Value Addition:Improving fish quality, market access, and export competitiveness through better processing techniques.
Devolution Index Report 2024

- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister of State Prof. S. P. Singh Baghel released the Devolution Index Report at the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), New Delhi.
Titled “Status of Devolution to Panchayats in States – An Indicative Evidence-Based Ranking 2024”, the report assesses the extent of autonomy and empowerment of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) across Indian States and UTs.
Context and Constitutional Framework
The initiative is anchored in the vision of Article 243G of the Constitution and the 73rd Constitutional Amendment, which mandates the devolution of powers, authority, and responsibilities to Panchayats over 29 subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule. It reflects the spirit of grassroots democracy and aims to realize the vision of "Local Self-Government".
Core Objectives and Dimensions of the Index
The Devolution Index provides an evidence-based evaluation of decentralization and self-governance in rural India. It assesses PRIs across six critical dimensions:
- Framework – Legal and institutional setup for decentralization.
- Functions – Scope of responsibilities devolved to Panchayats.
- Finances – Fiscal powers and resource autonomy.
- Functionaries – Availability and control over human resources.
- Capacity Building – Training and skill development mechanisms.
- Accountability – Transparency, audit mechanisms, and citizen participation.
Significance and Policy Implications
- Strengthening Cooperative Federalism: By highlighting inter-state comparisons, the Index fosters competitive federalism in the spirit of collaborative governance.
- Multi-Stakeholder Utility:
- Citizens: Increases transparency in Panchayat functioning and fund utilization.
- Elected Representatives: Offers a data-driven basis for decentralization advocacy.
- Officials & Policymakers: Acts as a policy instrument for reform and targeted capacity building.
- Aligns with National Vision:
- Supports Viksit Bharat goals through ??????????????????????????????? (developed and empowered PRIs).
- Contributes to inclusive rural development and grassroots democratization.
Income-tax Bill, 2025
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
The Income-tax Bill, 2025, tabled in Parliament on February 13, 2025, seeks to repeal and replace the Income-tax Act, 1961, marking a landmark step in tax law simplification.
It reflects the government's commitment to ease of doing business, legal clarity, and tax compliance, without altering the core tax policy or rate structure.
Guiding Principles
- Textual and structural simplification for better clarity.
- Policy continuity—no major tax policy changes.
- Preservation of existing tax rates for predictability.
Approach and Methodology
- Three-pronged strategy:
- Simplify language and eliminate legalese.
- Remove obsolete, redundant, and repetitive provisions.
- Reorganize the Act for logical and easier navigation.
- Consultative process:
- 20,976 online suggestions received.
- Stakeholder consultations with taxpayers, professionals, and industry bodies.
- International best practices reviewed, notably from Australia and the UK.
Quantitative Simplification
Parameter Income-tax Act, 1961 Income-tax Bill, 2025 Change
Words 5,12,535 2,59,676 ↓ 2,52,859
Chapters 47 23 ↓ 24
Sections 819 536 ↓ 283
Tables 18 57 ↑ 39
Formulae 6 46 ↑ 40
Key Features and Improvements
- Qualitative Enhancements:
- Use of simplified and accessible language.
- Consolidation of amendments to reduce fragmentation.
- Enhanced readability via structured use of tables and formulae.
- Elimination of outdated provisions.
- Introduction of "Tax Year":Defined as the 12-month period beginning April 1, providing better uniformity.
- Crypto as Capital Asset:Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) such as cryptocurrencies included in the definition of "property", now taxable as capital assets.
- Dispute Resolution Clarity:Improved transparency in Dispute Resolution Panel (DRP) procedures by including points of determination and reasoning—addressing a key criticism of ambiguity in the earlier framework.
- Removal of Obsolete Exemptions:Section 54E, providing capital gain exemptions for transfers before April 1992, has been scrapped.
- Expected Timeline:Once enacted, the Income-tax Act, 2025 is proposed to come into effect from April 1, 2026.
Gender Budgeting

- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
The Gender Budget allocation for FY 2025-26 has increased to ?4.49 lakh crore, accounting for 8.86% of the total Union Budget, up from 6.8% in FY 2024-25. This represents a 37.25% increase compared to the ?3.27 lakh crore allocated in the previous year.
Key Highlights:
- Expansion Across Ministries:
- A total of 49 Ministries/Departments and 5 Union Territories (UTs) have reported allocations in the Gender Budget Statement (GBS) for 2025-26, marking the highest participation since the inception of the Gender Budget.
- Twelve new Ministries have been included in the GBS this year, signaling a broader inclusion of gender considerations in sectors such as animal husbandry, biotechnology, water resources, food processing, and railways.
- Gender Budget Allocation Breakdown:
- Part A (100% Women-specific schemes): ?1,05,535.40 crore (23.5% of total GBS).
- Part B (30-99% allocation for women): ?3,26,672 crore (72.75% of total GBS).
- Part C (Below 30% allocation for women): ?16,821.28 crore (3.75% of total GBS).
- Top Ministries reporting high percentages in gender-focused allocations include the Ministry of Women & Child Development (81.79%), Department of Rural Development (65.76%), and Department of Health & Family Welfare (41.10%).
- Focus on Women’s Economic Participation:
- The Union Budget aims to boost women’s participation in economic activities, targeting 70% by 2047.
- Women’s Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) rose to 42% in 2023-24 from 33% in 2021-22.
- Efforts to close the gender gap involve increased allocations to programs like Skill India, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM), and PM Vishwakarma, with 52% of the ?1.24 lakh crore allocated for these programs earmarked for women and girls.
- Support for Women Entrepreneurs:
- Women own 20.5% of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India, employing approximately 27 million people.
- The Budget focuses on empowering women entrepreneurs by advocating for collateral-free loans, alternative credit scoring models, and financial literacy programs.
- Establishing 30 million additional women-owned businesses could generate 150-170 million jobs by 2030, contributing significantly to India's employment needs.
- Gig Economy and Informal Sector:
- The Budget introduces measures to formalize gig workers, 90% of whom are women. By issuing identity cards and registering gig workers on the e-Shram portal, the Budget aims to provide them with access to social security and financial inclusion benefits.
- This addresses the challenges faced by women in the informal sector, including low wages, job insecurity, and lack of maternity benefits.
- Gender Inclusivity in Technology:
- A dedicated ?600 crore allocation under the India AI Mission aims to promote gender inclusivity in the technology sector. This includes the establishment of a Centre of Excellence on Artificial Intelligence (AI) for education and skill development, ensuring women’s participation in high-growth technological fields.
- Gender Budgeting Components:
- Part A: Gender-specific expenditure, directly benefiting women (e.g., BetiBachaoBetiPadhao).
- Part B: Pro-women general expenditure, benefiting both men and women but focusing on women’s advancement (e.g., MGNREGA).
- Part C: Gender-neutral budgets that may require gender-sensitive planning (e.g., Har GharNal project, which reduces women’s time spent fetching water).
- Policy Vision and Challenges:
- The Union Budget for 2025-26 is part of the government’s vision for a "Viksit Bharat" with zero poverty, universal education, 100% skilled labor, and 70% female participation in the workforce by 2047.
- While the Budget lays a strong foundation, addressing persistent challenges like gender pay gaps, occupational segregation, and cultural barriers will require sustained policy interventions, gender-sensitive workplace reforms, and effective implementation of gender-disaggregated data for monitoring outcomes.
India’s Indigenous Shakti Semiconductor Chip
- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant milestone in semiconductor technology with the development of the indigenous Shakti semiconductor chip. Developed by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), the Shakti chip is a crucial component of India’s push for technological self-reliance under the Digital India RISC-V (DIRV) initiative.
Overview of Shakti Semiconductor Chip
- The Shakti chip is an indigenous microprocessor based on the RISC-V open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
- Its primary objective is to meet the high-performance computing, security, and reliability needs of India’s defense, aerospace, and space industries.
- It was specifically designed to support applications in satellite missions, avionics, embedded systems, and command-and-control operations.
- The chip is the third in the Shakti series, following the earlier RIMO (2018) and MOUSHIK (2020) chips, which served as technology demonstrators.
Key Features:
- Indigenous Development: Fully developed, fabricated, and tested in India, ensuring complete control over the design and manufacturing process.
- RISC-V Architecture: The Shakti chip utilizes the RISC-V open-source architecture, offering flexibility for customization and adaptation to various hardware and application needs.
- Fault Tolerant and Reliable: Designed to endure the harsh conditions of space and defense applications, making it highly reliable for mission-critical functions.
- High-Performance Computing: Supports complex functions like AI-based operations, real-time control systems, and sensor integration, essential for space missions and advanced defense technologies.
- Advanced Security: Aimed at providing robust security measures for critical sectors, including defense and aerospace, ensuring protection against cyber threats.
- Expandable and Scalable: The chip supports multiple boot modes and hybrid memory extensions, allowing for future upgrades and expansions, especially for space exploration.
Applications of the Shakti Chip
- Space Missions: The Shakti chip plays a vital role in powering ISRO's command-and-control systems, satellite avionics, and embedded systems used in various space missions.
- Defense & Aerospace: It enhances India’s strategic autonomy by reducing reliance on foreign semiconductor technology for military-grade electronics.
- IoT & AI Applications: The chip’s high-performance computing capabilities are ideal for smart systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and AI applications.
- Research and Development: The chip contributes significantly to India’s semiconductor ecosystem, providing a foundation for further R&D in indigenous chip fabrication.
The Digital India RISC-V (DIRV) Initiative
- Launched in April 2022 by MeitY, the DIRV initiative aims to strengthen India’s semiconductor ecosystem by promoting the development of indigenous RISC-V-based microprocessors.
- The initiative emphasizes reducing dependency on foreign semiconductor solutions and fostering self-reliance in the digital sector.
- DIRV also focuses on high-performance computing for emerging technologies such as 5G, AI, and cloud computing. Through collaborations with IITs, ISRO, C-DAC, and private industry partners, the program aims to create a robust ecosystem for scalable microprocessor solutions.
IRIS: A Key Development from Shakti
- One of the most notable outputs of the Shakti chip initiative is the IRIS (Indigenous RISC-V Controller for Space Applications).
- Developed for ISRO’s space missions, the IRIS chip is a high-performance, fault-tolerant, 64-bit processor based on the Shakti microprocessor.
- It has been designed to meet the specific needs of space missions, such as satellite command-and-control systems, by integrating custom modules like watchdog timers and advanced serial buses.
- The IRIS chip also features multiple boot modes and hybrid memory extensions for future scalability and expansion in line with upcoming space missions.
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
To enhance the efficacy and wider adoption of MIS, the Government of India revised the guidelines in 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It aims to provide price support for perishable agricultural and horticultural commodities not covered under the Minimum Support Price (MSP) regime. It prevents distress sales during periods of excessive production and sharp price declines.
- Implementing Authority:The scheme is under the Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and is now a component of the PM-AASHA (Pradhan Mantri AnnadataAaySanrakshan Abhiyan) umbrella scheme.
- Eligibility & Activation:
- Implemented on the request of State/UT Governments.
- Triggered when market prices fall by at least 10% compared to the average price of the previous normal year.
- Nature of the Scheme:
- Ad-hoc price support mechanism operational during sudden market crashes.
- Cost-sharing pattern between Centre and States is 50:50, and 75:25 for North-Eastern states.
- Procurement Provisions (Revised 2025):
- Procurement limit increased from 20% to 25% of total production of the crop.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode introduced: States may directly compensate farmers for the price difference between Market Intervention Price (MIP) and actual selling price.
- Physical procurement is optional under the revised scheme.
- Authorized Procurement Agencies:
- Central Nodal Agencies like NAFED (National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India) and NCCF (National Cooperative Consumers’ Federation of India).
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs), and state-nominated agencies can also participate in procurement, storage, and transportation.
- Support for Transportation and Storage:
- Reimbursement of storage and transport costs is provided by Central Nodal Agencies for TOP crops (Tomato, Onion, Potato).
- This provision helps balance regional price disparities between producing and consuming states.
- Significance:
- The revamped MIS strengthens market resilience for perishable crop producers.
- Enhances State participation, reduces post-harvest losses, and ensures remunerative returns through institutional and technological support mechanisms.
NITI Aayog Policy Report on Expanding Quality Higher Education
- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog released a comprehensive policy report titled ‘Expanding Quality Higher Education through States and State Public Universities (SPUs)’, focusing on the development of higher education institutions, particularly public universities in India.
The report aims to enhance the quality, funding, governance, and employability outcomes within SPUs, which contribute to around 80% of the country's higher education system.
The document, the first of its kind in India, presents a detailed analysis of vital indicators like quality, funding, financing, governance, and employability over the last decade, supported by stakeholder consultations with over 20 states and Union Territories, Vice Chancellors, academicians, and State Higher Education Council Chairs. The report includes nearly 80 policy recommendations, along with 125 performance indicators, aiming to address long-standing challenges within SPUs.
Key Findings from the Report
- Funding:
- Maharashtra leads in funding for higher education, with Bihar and Tamil Nadu following closely behind.
- On the other hand, states like Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland have the lowest funding for higher education, highlighting regional disparities.
- University Density:
- The national average university density is 0.8 universities per lakh population. However, states such as Sikkim, with a density of 10.3, and Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, Meghalaya, and Uttarakhand have significantly higher densities. In contrast, states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Maharashtra have lower densities compared to the national average.
- Female Enrolment:
- Kerala, Chhattisgarh, and Himachal Pradesh have achieved higher female enrolment rates than males, which reflects positive gender inclusivity trends in certain regions.
- Challenges:
- Infrastructure deficits, including a lack of quality facilities and resources.
- A shortage of faculty and staff, particularly in advanced fields such as MTech and Ph.D. levels.
- Insufficient investment in research and development (R&D).
- Outdated courses, syllabi, and curricula, which are not aligned with industry needs.
- Financial constraints due to over-reliance on traditional revenue sources like admission fees and state grants.
- Administrative delays in fund sanctioning and the absence of frameworks for securing loans through financial institutions.
Policy Recommendations
The report proposes several reforms to address the aforementioned challenges, with a focus on improving educational quality, securing better funding, enhancing governance, and boosting employability:
- Funding and Investment:
- Increase the combined investment in education to 6% of GDP, as recommended in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Increase R&D investment (both public and private) to 2% of GDP, as recommended in the Economic Survey 2017-18.
- Creating Centers of Excellence:
- SPUs should form clusters and focus on addressing local challenges by establishing Centres of Excellence. These centres should focus on region-specific issues to drive academic and practical advancements.
- Governance Reforms:
- Enhance governance structures at SPUs, empowering Vice Chancellors, faculty, and staff through targeted capacity-building initiatives.
- States may consider setting up dedicated finance agencies, similar to the Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA), to fund infrastructure and research development specifically for SPUs.
- Financial Innovations:
- Develop financial frameworks to increase investment in education, ensuring access to timely funds, and reducing dependency on state grants or admission fees.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration:
- Strengthen the link between academia and industry to ensure that the curricula are relevant and prepare students for the job market. This can be achieved through increased partnerships, internships, and practical learning opportunities.
Restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM)

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Bamboo Mission (NBM) was initially launched in 2006 under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare to promote bamboo-based development. Between 2014–2016, it was subsumed under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
In 2018-19, it was restructured under the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) to revamp bamboo cultivation, processing, and value chain integration.
A key reform was the 2017 amendment to the Indian Forest Act, 1927, which removed bamboo grown outside forests from the definition of “tree.” This de-regulated its felling and transit, boosting private bamboo farming and easing trade.
Objectives
- Increase the availability of quality planting materials and expand area under bamboo cultivation, especially in non-forest land.
- Promote post-harvest management, primary treatment, seasoning, and preservation technologies.
- Develop market infrastructure, incubation centers, and tools & equipment for value addition.
- Encourage value-added product development, skill development, and entrepreneurship.
- Reduce import dependency on bamboo and bamboo-based products.
Funding Pattern
- General States: 60% Central and 40% State funding.
- Northeastern & Hilly States: 90% Central and 10% State.
- Union Territories, BTSGs & National Level Agencies: 100% Central funding.
Implementation Framework
- Implemented through the State Nodal Departments, nominated by respective State/UT governments.
- Notable example: Bareilly Bamboo Cluster operational in Shahjahanpur district, Uttar Pradesh, since 2019-20, with activities like nursery establishment, bamboo plantation, skill development, and bamboo product demonstration.
Bamboo – Ecological & Economic Significance
- Botanical Classification: Grass (Family: Poaceae, Subfamily: Bambusoideae), ~115 genera and ~1,400 species globally.
- Native to tropical, subtropical, and mild temperate zones, with highest concentration in East and Southeast Asia.
Properties & Applications:
- Carbon Sequestration: Produces 35% more oxygen than comparable vegetation; acts as a natural carbon sink.
- Climate Adaptability: Thrives in degraded lands; prevents soil erosion; vital for land restoration.
- Alternative Energy Source: Among the fastest-growing plants (up to 90 cm/day); can substitute fossil fuels.
- Food & Medicine: Bamboo shoots are consumed in Northeast India; roots and parts used in traditional medicine.
- Livelihood Support: Flexible harvest cycles provide year-round income for farmers.
Bamboo Production Status in India
- 18,000+ inventoried grids reported bamboo presence between 2016–17 to 2019–20.
- Estimated total bamboo culms: 53,336 million.
- 35.19% increase in bamboo culms from ISFR 2019 to ISFR 2021 (an increase of 13,882 million culms).
Restructured Skill India Programme (2022–2026)

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation and restructuring of the Skill India Programme (SIP) till March 2026, with a financial outlay of ?8,800 crore.
The revamped programme consolidates three flagship schemes under a composite Central Sector Scheme—Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and Jan ShikshanSansthan (JSS)—with the aim to build a skilled, future-ready workforce.
Objectives and Vision
- Strengthen workforce development through industry-aligned, technology-enabled, and demand-driven skill training.
- Enhance global competitiveness, promote international mobility, and align with India's economic priorities such as Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and Digital India.
- Enable lifelong learning, skilling, reskilling, and upskilling through inclusive, flexible, and community-based training.
Beneficiaries and Coverage
- Over 2.27 crore individuals have benefited so far.
- Targeted age groups vary across schemes:
- PMKVY 4.0: 15–59 years
- PM-NAPS: 14–35 years
- JSS: 15–45 years
- Emphasis on marginalized sections, women, rural youth, aspirational districts, and the North-East Region.
Key Components of the Restructured Programme
1. Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0)
- Offers NSQF-aligned training via:
- Short-Term Training (STT)
- Special Projects (SP)
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
- Introduces 400+ new courses in emerging fields:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI), 5G, Cybersecurity, Green Hydrogen, Drone Technology.
- Establishment of Skill Hubs in premier institutions (IITs, NITs, JNVs, KendriyaVidyalayas, etc.).
- Focus on international mobility:
- Mobility Partnership Agreements (MMPAs), joint certifications, and language proficiency training.
- Blended learning models with digital delivery and regional language content.
- Integration with schemes such as PM Vishwakarma, PM Surya GharMuft Bijli Yojana, National Green Hydrogen Mission, and NAL JAL Mitra.
- Adoption of an Ease of Doing Business framework to reduce compliance burdens.
2. Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS)
- Promotes earn-while-you-learn through industry-specific apprenticeships.
- Government support of 25% stipend (up to ?1,500/month per apprentice) via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Focus on both traditional and emerging sectors like AI, robotics, blockchain, green energy, and Industry 4.0.
- Encourages participation of MSMEs and enterprises in underserved regions.
3. Jan ShikshanSansthan (JSS) Scheme
- Community-based skilling for economically disadvantaged, rural youth, and women.
- Offers low-cost, flexible, doorstep training for both self-employment and wage-based livelihoods.
- Linked with initiatives such as PM JANMAN, ULLAS, and financial literacy campaigns.
- Also promotes awareness in health, hygiene, gender equality, and education.
Certification and Digital Integration
- All certifications are aligned with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- Integrated with DigiLocker and the National Credit Framework (NCrF), ensuring:
- Formal recognition of skills.
- Horizontal and vertical mobility in education and employment.
- Micro-credential courses (7.5 to 30 hours) and National Occupational Standards (NoS)-based training introduced.
Supporting Schemes and Initiatives
- SANKALP(Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion).
- TEJAS (Skilling for international placement).
- Model Skill Loan Scheme.
Significance of Skill India Programme
- Demographic Dividend: With over 65% of India’s population below 35, the programme is pivotal in transforming potential into productivity.
- Employment & Entrepreneurship: Reduces unemployment through structured training, apprenticeships, and encourages skill-based startups.
- Global Workforce Readiness: Aligns with international standards, enabling Indian workers to access global job markets.
- Technological Preparedness: Equips the youth with skills in futuristic technologies.
- Inclusive Growth: Ensures urban-rural and gender-based equity in skilling access.
- Economic Impact: Supports India's manufacturing, IT, and services sectors, driving GDP growth.
India Achieves 100 GW Solar Power Capacity

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
India has officially surpassed 100 GW of installed solar power capacity as of January 31, 2025, marking a historic milestone in its clean energy journey. This achievement strengthens India’s position as a global leader in renewable energy and signifies major progress toward its ambitious target of 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, as outlined by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Union Minister of New and Renewable Energy, highlighted this milestone as a testament to India’s energy self-reliance, driven by key initiatives such as solar parks, rooftop solar schemes, and domestic solar manufacturing.
Growth Trajectory and Achievements
- Installed Capacity Growth:
- From 2.82 GW in 2014 to 100.33 GW in 2025 – a growth of 3450% over a decade.
- Solar energy now accounts for 47% of India’s total installed renewable energy capacity.
- Capacity Pipeline:
- 84.10 GW of solar under implementation.
- 47.49 GW under tendering.
- Including hybrid and RTC renewable projects, India has 296.59 GW of solar and hybrid projects in total.
- Record Additions in 2024:
- 24.5 GW solar capacity added, more than double from 2023.
- 18.5 GW utility-scale installations – a 2.8 times increase from 2023.
- 4.59 GW of rooftop solar added, a 53% increase over 2023.
- Top States in utility-scale solar growth:Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh.
Solar Manufacturing Boom
- Solar module production capacity has grown from 2 GW (2014) to 60 GW (2024).
- With continued policy support, India is targeting 100 GW of manufacturing capacity by 2030.
- This shift makes India a global hub for solar technology and reduces reliance on imports.
Major Government Initiatives Driving Solar Growth
- National Solar Mission (NSM) (2010):Set long-term targets, with 280 GW of solar capacity by 2030 under its ambit.
- PM SuryaGharMuft Bijli Yojana (2024):
- A game-changing rooftop solar scheme aiming to empower households with free, clean electricity.
- Nearly 9 lakh rooftop installations as of early 2025.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme:Promotes solar irrigation pumps and supports farmers with grid-connected solar systems.
- Solar Parks Scheme:Facilitates development of large-scale solar clusters in states to boost capacity.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:Incentivizes domestic manufacturing of solar PV modules.
- Net Metering Policy:Allows consumers to generate and export surplus solar power to the grid.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA):India-led global initiative fostering solar energy cooperation among solar-rich countries.
Benefits of Solar Energy for India
- Energy Security: Reduces dependence on fossil fuel imports.
- Environmental Gains: Cuts GHG emissions and combats climate change.
- Economic Boost: Millions of jobs created across installation, manufacturing, and maintenance.
- Affordability: Declining PV costs make solar a cost-effective energy source.
- Rural Electrification: Powers remote and off-grid regions, improving livelihoods.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Land Acquisition: Scarcity of land hinders large-scale solar deployment.
- Grid Integration: Intermittency of solar power stresses the existing power grid.
- Finance & Investment: Scaling up infrastructure and storage requires sustained capital inflow.
- Storage Solutions: Affordable battery storage is essential for reliability and round-the-clock supply.
TROPEX-25

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s biennial TROPEX-25is currently underway in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) from January to March 2025.
It is the Indian Navy’s largest maritime exercise, aimed at testing combat readiness and integrated warfighting capabilities across all domains.
About TROPEX
- Full Form: Theatre Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX)
- Frequency: Biennial (every two years)
- Lead Agency: Indian Navy
- Participants:
- Indian Navy (all operational units)
- Indian Army (IA)
- Indian Air Force (IAF)
- Indian Coast Guard (ICG)
Purpose and Strategic Objectives
TROPEX-25 aims to:
- Validate core warfighting skills of the Indian Navy.
- Ensure a synchronised, integrated response across services to defend India’s maritime interests.
- Simulate real-time operations in a contested maritime environment, including conventional, asymmetric, and hybrid threats.
- Enhance jointness, interoperability, and combat synergy among the three armed forces and the Coast Guard.
Duration and Operational Scope
- Timeline: January to March 2025 (Three months)
- Location: Various sectors across the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Phases:
- Harbour Phase: Planning and coordination activities.
- Sea Phase: Execution of complex naval and joint operations.
- Joint Work-Up Phase: Includes cyber and electronic warfare, and live weapon firings.
- AMPHEX (Amphibious Exercise): Integrated amphibious operations.
Key Features
- Integrated Combat Operations: Real-time execution of multi-domain missions
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare: Tactical simulations of modern non-kinetic threats
- Live Weapon Firings: Enhancing target precision and battle readiness
- Inter-Service Jointness: High-level coordination across the Navy, Army, Air Force, and Coast Guard
- Maritime Domain Awareness: Surveillance and security operations over vast maritime stretches
Strategic Significance
- Reinforces India’s commitment to safeguarding maritime sovereignty and strategic interests in the Indian Ocean.
- Enhances forward-deployment strategies, logistics, and sustained operations far from the mainland.
- Demonstrates India’s ability to operate “Anytime, Anywhere, Anyhow” in support of national security.
Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme for Minorities
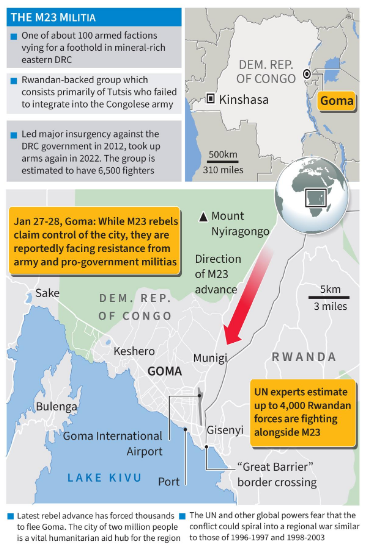
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister’s New 15 Point Programme for welfare of Minorities is a programme which covers various schemes/initiatives of the participating Ministries/Departments with an aim to ensure that the underprivileged and weaker sections of six centrally notified minority communities have equal opportunities for availing the various Government welfare Schemes and contribute to the overall socio-economic development of the Country.
Key Highlights:
The programme has the following broad objectives:
- Enhancing opportunities for education
- Ensuring an equitable share for minorities in economic activities and employment, through existing and new schemes, enhanced credit support for self-employment, and recruitment to State and Central Government jobs
- Improving the conditions of living of minorities by ensuring an appropriate share for them in infrastructure development schemes
- Prevention and control of communal disharmony and violence.
The schemes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs covered under the Prime Minister’s 15 Point Programme are exclusively meant for notified minorities. However, 15% of the outlays and targets, to the extent possible, of schemes/initiatives implemented by other participating Ministries/Departments are earmarked for notified minorities.
The welfare schemes, including initiatives for education and skill development of minorities, being implemented by Ministry of Minority Affairs and other participating ministries under the programme, are as under:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Merit-cum- Means based Scholarship Scheme
- National Minorities Development Finance Corporation (NMDFC) Loan Schemes
- Samagra Shiksha Abhiyaan (M/o Education)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana (DAY-NRLM)- (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayal Upadhyay – GraminKaushalya Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana - National Urban Livelihoods Mission (M/o Housing & Urban Affairs)
- Priority Sector Lending by Banks (Department of Financial Services)
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (Department of Financial Services)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (Ministry of Women & Child Development)
- National Health Mission (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- Ayushman Bharat (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- National Rural Drinking Water Programme (Jal Jeevan Mission), (Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation)
The Schemes are being implemented by the respective Ministries/Departments under the saturation approach of Government. Under the saturation approach of the Government many of the components have achieved mainstreaming.
PM Young Achievers’ Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM YASASVI)

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
With a vision of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas", the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has implemented the PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM-YASASVI).
- Objective of PM-YASASVI:
- The scheme aims to provide financial support and educational opportunities to students from Other Backward Classes (OBC), Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and Denotified Tribes (DNT).
- The goal is to help these students overcome financial barriers and pursue quality education, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Consolidation of Earlier Schemes:
- PM-YASASVI integrates multiple previous scholarship schemes:
- Dr. Ambedkar Post-Matric Scholarship for EBCs.
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs.
- This consolidation aims to streamline the process and increase the impact on vulnerable groups.
- Key Components of the Scheme:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: For students in Class 9-10 with annual family income below ?2.5 lakh. Provides ?4,000 annually.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: For students pursuing higher education, with academic allowances ranging from ?5,000 to ?20,000 based on course type.
- Top Class School Education: For meritorious students, offering ?1.25 lakh annually for students from OBC, EBC, and DNT categories in Classes 9-12.
- Top Class College Education: Covers tuition, living expenses, and educational materials for students in top institutions.
- Construction of Hostels for OBC Boys and Girls: Provides hostel facilities to socially and educationally backward students near government institutions.
- Scope and Financial Allocation (2023-24):
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: ?32.44 crore allocated to states and UTs for the year 2023-24, benefiting 19.86 lakh students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: ?387.27 crore allocated for the year, benefiting 27.97 lakh students.
- Top Class School Education: ?6.55 crore for 2,602 students.
- Top Class College Education: ?111.18 crore for 4,762 students.
- Hostel Construction: ?14.30 crore allocated for the construction of hostels, accommodating 1,146 students.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Assistance: Reduces the financial burden on students from marginalized communities, enabling them to continue their education without financial stress.
- Inclusive Education: Supports students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they can access quality education from school through to higher education.
- Promotion of Merit: Focuses on meritorious students, ensuring that academic excellence is supported at all levels, from school to top-class institutions.
- Selection Process:
- The YASASVI Entrance Test (YET) is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for candidate selection under the scheme.
- Eligible students must appear for this test, and the results determine scholarship awards.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The scheme is open to OBC, EBC, and DNT students with a family income not exceeding ?2.5 lakh annually.
- Additional specific eligibility criteria may apply for different scholarships under the scheme.
- Application Process:
- Interested students can apply for scholarships via the National Scholarship Portal (scholarships.gov.in), which is the official platform for application submission.
National Water Awards 2023

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
The Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 on October 22nd 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
Organizing Body:
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Department: Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR)
- Purpose: To recognize and honor individuals, organizations, and bodies that have made significant contributions to water conservation and management.
Award Categories
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (other than school or college)
- Best Civil Society Organization
Winners
- Best State:
- 1st Prize: Odisha
- 2nd Prize: Uttar Pradesh
- 3rd Prize (joint): Gujarat & Puducherry
- Other Awards: Winners in the remaining categories have been recognized, with citations, trophies, and cash prizes provided in certain categories.
Objectives of the National Water Awards
- Promote Water Conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of water and encourage effective water usage practices.
- Recognize Efforts: Celebrate the work of individuals, institutions, and organizations contributing to the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat’ (Water-rich India).
- National Campaign: Under the guidance of Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has been working to spread awareness on water management and conservation through extensive national campaigns.
History and Background
- The National Water Awards (NWAs) were launched in 2018 by the DoWR, RD & GR to foster awareness and action on water-related issues.
- Awards were given for 2019, 2020, and 2022, but there were no awards in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The awards aim to inspire best practices in water usage, conservation, and management across India, involving government bodies, industries, communities, and civil society.
Significance
- The National Water Awards serve as a platform to recognize the innovative initiatives taken by various stakeholders in addressing water challenges.
The awards contribute to furthering the government’s mission of achieving sustainable water management practices across the nation.
Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto.
About Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC):
- The Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC) is a national forum established in 1919, comprising creators, custodians, and users of records.
- Its primary purpose is to advise the Government of India on matters related to record management and their utilization for historical research.
Secretariat:
- The National Archives of India, New Delhi, serves as the Secretariat for the IHRC, formerly known as the Indian Historical Records Committee since 1911.
Leadership and Membership:
- Led by the Union Minister of Culture, the IHRC consists of 134 members, including government agencies, government-appointed nominees, representatives from State/UT Archives, universities, and learning institutions.
- Over the years, the IHRC has convened 62 sessions.
Committee Structure: The IHRC operates with two adjunct bodies:
- Editorial Committee: Responsible for reviewing and approving papers based on archival sources for presentation at committee sessions.
- Standing Committee: Tasked with reviewing the implementation of committee recommendations and providing input on meeting agendas.
- The Secretary of the Ministry of Culture chairs the Standing Committee of IHRC.
- The Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto recently.
- The logo signifies the theme and uniqueness of IHRC entirely.
- The pages in the shape of lotus petals represent IHRC as the resilient nodal institution for maintaining historical records.
- The Sarnath pillar in the middle represents India's glorious past.
- Brown as the colour theme reinforces the organization's mission of preserving, studying, and honouring India's historical records.
- The motto translates as "Where history is preserved for the future."
- The IHRC plays a vital role in identifying, collecting, cataloging, and maintaining historical documents, manuscripts other sources of historical information.
- By doing so the Commission ensures that valuable historical knowledge is conserved for future generations.
- The motto, therefore, reflects the Commission's commitment to ensuring the safeguarding of historical documents and making these accessible for the benefit of present and future generations.
Panchayat Development Index (PIB)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj recently informed Lok Sabha about the Panchayat Development Index.
About the Panchayat Development Index:
- The Panchayat Development Index serves as a comprehensive and versatile metric designed to actively evaluate the holistic advancement, efficacy, and ongoing progress of panchayats.
- This index actively considers a spectrum of socio-economic indicators and parameters, offering an actively nuanced understanding of the well-being and developmental status of local communities within the panchayat's jurisdiction.
- Objectives: The primary objective is to actively play a pivotal role in assessing performance and progress towards actively achieving Sustainable Development Goals at the grassroots level.
- An active component of this initiative is the Local Indicators Framework, which encompasses nine key themes for actively localising Sustainable Development Goals.
- These themes actively encompass creating poverty-free and thriving livelihoods, ensuring health and actively child-friendly environments, actively promoting water sufficiency, actively fostering clean and green spaces, actively developing self-sufficient infrastructure, actively establishing socially just and secure communities, actively promoting good governance, and actively creating women-friendly villages.
How Ranking Works?
- Ranks within the index are actively assigned based on scores, actively categorising panchayats into four grades.
- Those actively scoring below 40 percent are actively classified as Grade D,
- 40-60 percent as Grade C,
- 60-75 percent as Grade B
- 75-90 percent as Category A
- and those actively surpassing 90 percent are actively designated as A+.
- Significance of this Index: The significance of this index lies in its ability to actively offer valuable insights into areas requiring attention and improvement within rural areas under panchayat jurisdiction.
- It actively aids in identifying disparities, gauging the achievement of development goals, and actively crafting targeted policies and interventions to elevate the overall well-being and quality of life in rural communities.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Kati Bihu (PIB)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi recently extended best wishes on the auspicious occasion of KatiBihu to the people of Assam.
About Kati Bihu:
- Kati Bihu is an annual celebration observed in the state of Assam, signifying the relocation of rice saplings.
- The term "Kati" translates to cutting, representing the agricultural activity during this period.
- Also known as Kongali Bihu, with "Kongali" connoting a state of poverty, the festival holds cultural significance in Assam alongside two other Bihu festivals—Bhogali or Magh Bihu in January and Rongali or Bohag Bihu in April.
Significance:
- In this month, food resources are scarce, prompting people to celebrate by illuminating their homes with earthen lamps or candles.
- Lighting lamps near the Tulsi plant are a central aspect of the festival, signifying devotion and auspiciousness.
- People light a special lamp known as "Akash Banti" (Sky candle) in their paddy fields. Fueled by mustard oil, these lamps are elevated on bamboo poles.
- The belief prevails that the illuminated lamps guide the spirits of ancestors toward their heavenly abode.
Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” Portal Launched (PIB)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Development of the North-East Region virtually launched the “MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” portal at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi recently.
About Poorvottar Sampark Setu Portal:
- The Poorvottar Sampark Setu portal is a robust tool designed to streamline and improve the monitoring of Union Ministers' fortnightly visits to the North Eastern Region (NER)
Key features include:
- Insightful Dashboard: The portal offers a comprehensive dashboard presenting valuable insights and graphical information on state-wise/district-wise visits to NER by Union Ministers, serving as a centralized resource for stakeholders.
- Curated Minister List: It generates a curated list of Ministers eligible for nomination for visits to NER in the upcoming months, facilitating efficient planning.
- Online Tour Reporting: After their visit, Ministers can conveniently submit tour reports and recommendations online, streamlining the reporting process.
- Recommendation Analysis: MDoNER (Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region) can analyze and forward the received recommendations to respective line Ministries, Departments, and State Governments for prompt action.
- Summary Report Generation: The portal offers a one-click summary report generation feature, simplifying the overview of visits for effective decision-making.
What is the MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard?
- The MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard is a comprehensive platform integrating data from 112 schemes across 55 Departments and Ministries.
Its key benefits include:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowers stakeholders with data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow.
- Centralized Monitoring: Provides a centralized hub for monitoring diverse schemes and initiatives.
- Policy-Level Decision Tool: Functions as a valuable tool for crafting policies based on robust data analysis.
- Information Integration: Integrates information seamlessly, fostering coherence and accessibility.
- Focused Monitoring: Keeps a vigilant eye on NER Aspirational districts, North East border districts, and the most backward districts in NER for targeted interventions.
INS Sumedha Visits Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (PIB)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Naval Ship INS Sumedha recently made a port visit at Lagos, Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (GoG).
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is the third vessel among the indigenously crafted Saryu-class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV).
- Constructed and designed domestically, Goa Shipyard Limited played a pivotal role in the indigenous creation of INS Sumedha.
- The vessel officially joined the Indian Navy's fleet on March 7, 2014.
- Operational Base: A key asset of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet, INS Sumedha operates from its base in Visakhapatnam.
- Primary Functions: The vessel is tasked with a diverse range of functions, including EEZ surveillance, anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations, maritime security provision to offshore assets, and execution of escort operations for high-value assets.
- Features:
- With a displacement of 2,230 tonnes, INS Sumedha boasts dimensions of 105 meters in length and 12.9 meters in beam.
- Equipped with a cutting-edge weapon and sensor package, the vessel ensures enhanced operational capabilities.
- Designed to carry an Advanced Light Combat Helicopter onboard, adding to its versatility in maritime operations.
- Powered by two of the largest diesel engines deployed in the Indian Navy, INS Sumedha attains a top speed of 25 knots.
- Featuring a remarkable range of 6,000 nautical miles (11,000 km) at 16 knots (30 km/h), the offshore patrol vessel is well-suited for prolonged missions and operations.
About the Gulf of Guinea:
- Location: Situated as the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Guinea is positioned off the western coast of the African continent.
- The Gulf lies at the confluence of the Prime Meridian and the Equator, specifically at 0°0’N and 0°0'E.
- Extent and Coastline: Encompassing an area of 2.3 million square kilometres, the Gulf features an extensive coastline stretching approximately 6,000 kilometres.
- Characterized by a narrow continental shelf, it boasts a distinctive coastal landscape.
- Oceanic Conditions: The Gulf of Guinea experiences warm tropical waters characterized by relatively low salinity, influenced by the inflow of rivers and high regional rainfall.
- Notable tributaries include the Volta and Niger rivers.
- Coastal Countries: 16 countries border the Gulf of Guinea, including Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic of Congo, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Nigeria, Ghana, São Tomé and Principe, Togo, and Sierra Leone.
- Topography: The coastal region is predominantly low-lying, featuring mangrove swamps, marshes, and lagoons.
- Geological Significance: The Gulf's coastline bears a striking resemblance to the continental margin of South America, affirming the theory of continental drift.
- Holding over 35% of the world’s petroleum reserves, the Gulf of Guinea is a significant global repository of petroleum.
- Security Challenges: Regrettably, the Gulf of Guinea has gained notoriety as one of the world’s most perilous gulfs due to widespread piracy, significantly impacting West African countries and attracting international concern.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of an Autonomous Body Mera Yuva Bharat (PIB)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of an autonomous body Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat).
About Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat):
- Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat), an autonomous body will benefit the youth in the age group of 15-29 years, in line with the definition of ‘Youth’ in the National Youth Policy.
- In the case of programme components specifically meant for adolescents, the beneficiaries will be in the age group of 10-19 years.
- It will help in Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and to make the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- It will be launched on 31st October 2023 on National Unity Day.
Objective:
- The primary objective of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) is to make it a whole of Government platform for youth development.
- With access to resources & connection to opportunities, youth would become community change agents and nation builders allowing them to act as the Yuva Setu between the Government and the citizens.
- It seeks to harness the immense youth energy for nation-building.
The establishment of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) would lead to:
- Leadership Development in the Youth:
- Improve leadership skills through experiential learning by shifting from isolated physical interaction to programmatic skills.
- Investing more in youth to make them social innovators, and leaders in the communities.
- Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and making the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- Better alignment between youth aspirations and community needs.
- Enhanced efficiency through Convergence of existing programmes.
- Act as a one-stop shop for young people and Ministries.
- Create a centralized youth database.
- Improved two-way communication to connect youth government initiatives and activities of other stakeholders that engage with youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem.
Why There is a Need for Such Initiative?
- India’s youth are to play a critical role in defining the future of the nation.
- There is a need to establish a new contemporary technology-led platform for the Government to engage with the present-day youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem
- Mera Yuva Bharat supported by a technology platform would help to increase the Youth outreach efforts of the Department of Youth Affairs.
SUGAM REC Mobile App for 54EC Bonds Investors (PIB)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, REC Limited, the Maharatna Central Public Sector Enterprise launched a SUGAM REC mobile application.
What is the SUGAM REC App?
- The SUGAM REC App caters exclusively to current and prospective investors in REC's 54EC Capital Gain Tax Exemption Bonds.
- Users can conveniently download e-bond certificates, apply for new investments, access essential forms for KYC updates, and connect with REC's Investor Cell through call, email, or WhatsApp.
What are 54EC Bonds?
- Also known as Capital Gain Bonds, these fixed-income instruments offer capital gains tax exemption under section 54EC.
- Investors can save on income tax for long-term capital gains by investing in these bonds within six months of the gain.
- With a fixed lock-in period of 5 years, the bonds can be held in either Physical or Demat form.
- Issued by government-managed institutions, they fund specific capital projects and derive their name from the relevant section of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Key Facts about REC Limited:
- A 'Maharatna' company under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- Registered with RBI as a non-banking finance company (NBFC), Public Financial Institution (PFI), and Infrastructure Financing Company (IFC).
- Established in 1969 to address severe drought and famine, focusing on energizing agricultural pump sets for irrigation and reducing reliance on monsoons.
- Provides long-term loans and financing products to State, Centre, and Private Companies for infrastructure asset creation.
- It is the nodal agency for initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGAYA), Deen Dayal Upadhaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), and National Electricity Fund (NEF) Scheme.
Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) (PIB)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, GoI is organizing the 19th Working Party on Data Collection and Statistics (WPDCS19) of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) from 28th November to 2nd December 2023.
About the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission:
- The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for the management of tuna and tuna-like species in the Indian Ocean.
- It works to achieve this by promoting cooperation among its Contracting Parties (Members) and Cooperating Non-Contracting Parties in order to ensure the conservation and appropriate utilisation of fish stocks and encouraging the sustainable development of fisheries.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations adopted the Agreement for the Establishment of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission during its 105th Session in Rome on 25 November 1993.
- The Indian Ocean holds the position as the second-largest tuna fishery globally, making it a crucial focus for the IOTC.
- Currently, the IOTC boasts 31 contracting parties, including countries and two cooperating non-contracting parties, Liberia and Senegal.
- Membership is open to Indian Ocean coastal countries, countries or regional economic integration organizations that are UN members, countries that are members of UN special organizations, and countries involved in tuna fishing in the Indian Ocean.
- India is an active member of the IOTC, with its headquarters located in Victoria, Seychelles.
