Asiatic Caracal
- 20 Nov 2025
In News:
The elusive Asiatic Caracal was recently sighted at Ramgarh in Jaisalmer, marking a significant wildlife record for Rajasthan. Once widespread across India’s grasslands and semi-arid regions, the species had nearly disappeared from public consciousness due to its extremely low numbers and elusive behaviour.
About the Caracal
- Scientific Name:Caracal caracal
- Common Names: Desert lynx (misnomer); Siya gosh in India (Persian for “black ear”)
- Taxonomy: More closely related to the African golden cat and serval than to lynxes
- Type: Medium-sized wild cat, shy and predominantly nocturnal
Distribution
- Global: Africa, Central Asia, the Middle East, arid regions of Pakistan, and north-western India
- India: Extremely rare; estimated population of ~50 individuals, mainly confined to Rajasthan and Gujarat
Habitat
- Occupies semi-deserts, savannahs, shrublands, steppes, dry forests, and woodlands
- Strong preference for dry areas with low rainfall
Key Physical & Behavioural Features
- Solid build, long legs, short face, and distinctive black ear tufts
- Coat colour ranges from red-tan to sandy, with occasional black individuals
- Dark facial markings near eyes and nose; short, dense fur
- Back legs longer than front, aiding agility
- Exceptional leaper: can jump up to 3 metres (10 feet) to catch birds mid-air
- Speed: up to 80 km/h (50 mph) in short bursts
- Largely nocturnal and elusive, making sightings rare
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern (globally)
- Indian Context: Despite global status, the species is locally threatened due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and very small population size
Amoebic meningoencephalitis
- 29 Oct 2025
In News:
Kerala has reported yet another fatal case of amoebic meningoencephalitis in 2025, deepening public health concerns in the state. With this incident, Kerala’s cases linked to amoebic meningoencephalitis in 2025 have risen to 27, highlighting an emerging disease surveillance challenge. Health authorities are still investigating the exact source of infection in the latest case, as environmental exposure remains the primary risk factor.
Understanding Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
- Nature of the Disease: Amoebic meningoencephalitis, or Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), is a rare but rapidly progressing and typically fatal brain infection. It occurs when a free-living amoeba invades the central nervous system, causing severe inflammation and extensive brain tissue damage.
- Causative Organism: The infection is caused by Naegleria fowleri, often referred to as the “brain-eating amoeba.” This thermophilic organism is naturally present in warm freshwater bodies and moist soil.
Transmission and Environmental Factors
- The disease is not transmitted person-to-person.
- Infection occurs when contaminated water enters the nasal cavity, allowing the amoeba to migrate through the olfactory nerve into the brain.
- Naegleria fowleri proliferates in warm freshwater, particularly during summer months, in environments such as:
- Lakes
- Ponds
- Hot springs
- Poorly chlorinated swimming pools
- Warm freshwater streams and rivers
Kerala’s warm and humid climate, combined with widespread freshwater sources, may create favourable conditions for the organism, necessitating stronger environmental monitoring and public awareness.
Clinical Presentation
Early Symptoms (1–9 days after exposure):
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Advanced Symptoms:
- Stiff neck
- Seizures
- Confusion
- Loss of balance
- Hallucinations
- Progressive neurological deterioration
The disease often leads to coma and death within days, making it one of the deadliest infections of the central nervous system.
Treatment and Mortality
Treatment remains highly challenging, with over 95% mortality. Some survival cases have been associated with:
- Early diagnosis
- Rapid initiation of drugs like amphotericin B and miltefosine
- Aggressive supportive care in intensive settings
However, the overall prognosis remains extremely poor due to the fast progression of the infection.
Preventive Measures
Given the absence of person-to-person transmission, prevention focuses on reducing environmental exposure:
- Avoid swimming or diving in untreated freshwater bodies, especially during warmer months.
- Use nose clips while entering freshwater.
- Ensure proper chlorination and maintenance of swimming pools.
- Avoid stirring mud or sediment in shallow freshwater areas where amoebae thrive.
UNESCO’s New Director-General

- 10 Oct 2025
In News:
The Executive Board of UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) has elected Egypt’s Khaled El-Enany as its new Director-General for a four-year term (2025–2029), succeeding Audrey Azoulay of France. His election marks a significant moment for African and Arab representation within the United Nations system.
About the Election Process
- Nomination: Candidates are nominated by member states and evaluated by UNESCO’s 58-member Executive Board.
- Voting: The Board conducts a secret ballot, requiring an absolute majority to select a nominee.
- Approval: The selected candidate’s name is then forwarded to the General Conference—comprising 194 member states—for formal confirmation.
About the Director-General’s Role
The Director-General serves as the chief executive officer and spokesperson of UNESCO, responsible for implementing the policies and decisions of the General Conference and Executive Board.
Key Functions
- Leadership & Administration:
- Oversees UNESCO’s global programmes across education, culture, science, and communication.
- Manages the World Heritage Sites framework and educational cooperation initiatives.
- Policy Implementation:Translates strategic resolutions of the General Conference into operational programmes.
- Global Representation:Acts as the face of UNESCO in international diplomacy, fostering partnerships for cultural and educational cooperation.
- Financial Stewardship:Mobilizes funding, particularly important after the U.S. withdrawal, which caused an 8% cut in UNESCO’s annual budget.
About UNESCO
- Founded: 1945
- Headquarters: Paris, France
- Membership: 194 member states
- Mandate: To promote peace, education, science, and cultural understanding through international collaboration.
UNESCO’s global initiatives include:
- The World Heritage Convention (1972)
- The Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) framework
- The Man and the Biosphere (MAB)Programme
- Promotion of freedom of expression and media pluralism
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- 10 Sep 2025
In News:
Odisha’s Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary has recently been approved by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) to become India’s newest tiger reserve. This marks a significant ecological achievement rooted in community participation, innovative eco-tourism, and conservation success.
Location and Geography
- Situated in western Odisha, near Sambalpur and Bargarh district, Debrigarh is bordered by the Hirakud Reservoir—a Ramsar-tagged wetland and part of the Mahanadi River system.
- The Hirakud Dam, the world’s longest earthen dam, lies adjacent to the sanctuary.
- Spread over 804 sq km, it includes around 347 sq km of core area, encompassing forests, grasslands, and wetlands, making it a unique amphi-terrestrial ecosystem.
Historical Significance
- The rugged terrain of Debrigarh was a strategic base for freedom fighter Veer Surendra Sai during his armed resistance against British colonial rule.
- Sites like Bara Bakra/Barapathara remain important heritage landmarks within the sanctuary.
Flora and Fauna
- Vegetation: Dominated by mixed and dry deciduous forests, with species such as Sal, Asana, Bija, Aanla, and Dhaura.
- Mammals: Indian bison (gaur), sambar deer, wild boar, chousingha (four-horned antelope), leopards, sloth bears, and wild dogs.
- Avifauna: Over 300 bird species, including 120 migratory species such as crested serpent eagle, drongo, tree pie, flower peckers, and white-eye oriental.
Eco-Tourism and Innovation
- Debrigarh is home to India’s first dark sky tourism hub, offering stargazing facilities.
- Adventure tourism includes safaris (53 vehicles), kayaking, cycling, and birding trails, designed with minimal ecological footprint.
Conservation and Community Model
- Declared a sanctuary in 1985 and upgraded to a tiger reserve in 2025.
- A community-led model: Over 400 families voluntarily relocated with rehabilitation packages; 155 villages actively participate in conservation and eco-tourism activities.
- Wildlife success: Expansion of prey base, increase in gaur population, and nearly 40% of herds comprising newborns, reflecting ecosystem recovery.
Significance
Debrigarh exemplifies a national model of integrated conservation, blending:
- Biodiversity protection (tiger reserve status, prey base recovery).
- Cultural heritage (legacy of Veer Surendra Sai).
- Sustainable eco-tourism (dark sky hub, water- and land-based safaris).
- Community participation (relocation and livelihood integration).
Its success offers a replicable blueprint for wildlife conservation across India, highlighting how ecological protection, heritage, and rural livelihoods can be balanced under one framework.
Strait of Malacca
- 01 Sep 2025
In News:
India and Singapore have recently elevated their Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) by signing multiple agreements across defence, space, trade, skills, and sustainability.
A key highlight was Singapore’s support for India’s interest in joint patrolling of the Malacca Strait, one of the world’s most critical maritime chokepoints. This development has both bilateral and regional strategic implications.
The Malacca Strait: Geography and Importance
- Location: Between Sumatra (Indonesia) and Peninsular Malaysia–Thailand, linking the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) with the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Significance:
- One of the busiest shipping lanes globally, handling ~60% of India’s seaborne trade and nearly all its LNG imports.
- A vital energy artery for China, making it a strategic vulnerability (“Malacca Dilemma”).
- Historically named after the Malacca Sultanate (1400–1511).
Malacca Straits Patrols (MSP)
- Launched in 2004 by Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore; Thailand joined later.
- Aimed at curbing piracy, terrorism, and trafficking.
- Three coordinated layers:
- Sea Patrols: Regular joint naval patrolling.
- Eyes-in-the-Sky: Combined aerial surveillance.
- Intelligence Exchange Group: Real-time information sharing.
- India’s interest in joining the MSP reflects its commitment to freedom of navigation, regional stability, and maritime security.
India–Singapore Bilateral Cooperation (2025 Roadmap)
During PM Narendra Modi’s meeting with Singapore PM Lawrence Wong (2025), a roadmap was adopted identifying eight priority areas:
- Trade and Economy
- Skills Development – MoU to establish a National Centre of Excellence for Advanced Manufacturing Skilling in Chennai.
- Digitalisation& AI
- Sustainability – MoU for a Green and Digital Shipping Corridor and collaboration on green maritime fuel.
- Connectivity– Deepening maritime links.
- Healthcare & Medicine
- People-to-People and Cultural Exchanges
- Defence and Security – including space collaboration.
Key Agreements
- Space Cooperation: MoU between IN-SPACe (India) and Singapore’s Office for Space Technology and Industry for commercial and research linkages.
- Green Shipping Corridor: To promote sustainable maritime trade.
- Skill Development: Centre of Excellence for advanced manufacturing skilling.
Strategic Implications
- For India:
- Securing energy and trade routes through the Strait.
- Expanding its role in regional security architecture.
- Strengthening defence and space cooperation with ASEAN.
- For Singapore:
- Reinforces its position as a hub for maritime and digital connectivity.
- Gains from India’s manufacturing, space, and green energy initiatives.
- Regional Balance:
- Counters China’s strategic dominance in the South China Sea.
- Enhances multilateral security frameworks in the Indo-Pacific.
Guryul Ravine Fossil Site
- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has raised an alarm over a serious threat to the Guryul Ravine fossil site located in Khonmoh, on the outskirts of Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir. The site holds immense geological significance and is facing the risk of degradation due to human activity.
About the Site
The Guryul Ravine is situated near Khonmoh in Jammu & Kashmir, close to the Dachigam National Park. Geologically, the area is part of the Vihi district. It falls within the ecologically sensitive Khonmoh Conservation Reserve.
- This fossil site is globally significant because it contains sedimentary layers that preserve evidence of the Permian–Triassic mass extinction event. These geological layers date back around 260 million years and represent one of the most catastrophic periods in Earth’s biological history.
- Remarkably, the site also shows signs of what is believed to be the world’s earliest recorded tsunami, with the imprint still visible in the exposed strata.
Significance of the Permian–Triassic Extinction Event
- Also referred to as the “Great Dying,” the Permian–Triassic extinction event occurred around 251.9 million years ago. It marks a major boundary between the Permian and Triassic geological periods and also separates the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras.
- This event was the most severe extinction episode in Earth’s history. It led to the loss of nearly 90–95% of marine species and about 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species. The extinction dramatically reshaped life on Earth and paved the way for the rise of dinosaurs in the subsequent Mesozoic era.
Conservation Concerns
- The GSI has warned that this invaluable geo-heritage site is under threat due to encroachment and unregulated activities. It has recommended urgent steps to protect the fossil-rich area to preserve its scientific and educational value.
Motor Vehicle Aggregator Guidelines (MVAG) 2025
- 05 Jul 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has released the Motor Vehicle Aggregator Guidelines (MVAG), 2025, updating the 2020 norms to accommodate evolving urban transport trends — including bike taxis, electric vehicles (EVs), and app-based autorickshaws.
Overview
- Legal Basis: Formulated under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, MVAG provides the regulatory foundation for digital ride-hailing platforms such as Ola, Uber, and Rapido.
- Issuing Authority: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Government of India
Key Provisions of MVAG 2025
Driver Welfare and Remuneration
- Revenue Sharing:
- Drivers using own vehicles must receive minimum 80% of the fare.
- For aggregator-owned vehicles, the share must be at least 60%.
- Insurance Requirements:
- Health cover of ?5 lakh
- Term life insurance of ?10 lakh for each driver
- Skill Enhancement: Drivers in the lowest 5% rating bracket to undergo quarterly training
Passenger Safety and Accountability
- Travel Insurance: Mandatory coverage of ?5 lakh per passenger
- Complaint Resolution:
- Issues must be addressed within 3 working days
- Aggregators must notify passengers of outcomes
- Fare Transparency: Charges apply only from pick-up to drop-off location
Fare Regulation and Surge Pricing
- Base Fare Governance: State governments to decide base fare for each vehicle type
- Dynamic Pricing Limits:
- Aggregators may charge as low as 50% below base fare or up to 2x the base fare cap
- Designed to curb excessive surge pricing and ensure fare predictability
Cancellation Penalties
- Symmetrical Accountability:
- 10% penalty (capped at ?100) for riders or drivers cancelling without valid reason
- Acceptable cancellation grounds must be clearly listed on platforms
Legitimisation of Bike Taxis
- Policy Recognition:
- For the first time, private two-wheelers (non-transport motorcycles) may be used for commercial ride services, pending state-level approval
- Legal clarity for platforms operating in regulatory grey zones
EV Integration and Inclusivity
- EV Adoption Targets: States may enforce annual targets for aggregator fleets to switch to electric vehicles
- Accessible Vehicles Mandate: Aggregators must include vehicles equipped to serve persons with disabilities (Divyangjan)
Enhanced Driver Onboarding Standards
- Screening and Health Protocols: Mandatory police verification, medical fitness, and psychological evaluation before onboarding
- Training Mandates: Induction training for new drivers and annual refresher programs for all
Grievance Redressal & Licensing
- Mandatory Officer Appointment: A Grievance Redressal Officer must be designated with contact details published on the platform
- Centralised Licensing Portal: A unified digital portal to streamline aggregator licensing, renewals, and deposit management
Enforcement and Penalties
- Penalty Range: Fines for non-compliance range from ?1 lakh to ?1 crore
- Escalation for Repeat Offences: Repeat violations can lead to license suspension (up to 3 months) and possible revocation
Significance of MVAG 2025
- Aligns India’s mobility ecosystem with sustainable transport goals, passenger safety, and driver welfare
- Encourages EV transition, inclusive access, and regulated digital transport economy
- Brings regulatory clarity for emerging services like bike taxis
Predatory Pricing and Competition Law Reform

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has recently proposed the Determination of Cost of Production (DCOP) Regulations, 2025 to replace the older 2009 norms. A major reform introduced is the use of Average Total Cost (ATC) as a key metric to determine pricing in predatory pricing cases, while excluding ‘market value’ as a cost measure in such assessments.
- This development is significant in the context of India's broader competition law landscape, where concerns around market dominance and fair pricing are central to protecting consumer interest and ensuring a level playing field.
Understanding Predatory Pricing
- Predatory pricing refers to the practice of setting prices below cost to eliminate competitors from the market. Although consumers may benefit from low prices in the short term, the long-term consequence is often the emergence of monopolies, leading to higher prices and fewer choices. Due to its anti-competitive nature, this pricing strategy is banned in most jurisdictions globally.
- In India, predatory pricing is classified under ‘abuse of dominance’ as per the Competition Act, 2002, specifically under the broader category of unfair pricing or exclusionary conduct.
Legal Criteria for Establishing Predatory Pricing in India
For any allegation of predatory pricing to hold, three conditions must be satisfied:
- Dominance in the Market: The firm accused must hold a dominant position in the relevant market.
- Pricing Below Cost: The firm must have engaged in below-cost pricing, though defining “cost” has remained contentious. This raises the question—should cost mean fixed, variable, or total?
- Fixed costs are those independent of output (e.g., rent, IT systems).
- Variable costs change with production (e.g., raw materials, logistics).
- Total cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs.
- Intent to Eliminate Competition: There must be clear evidence that the pricing strategy was intended to exclude competitors from the market.
While dominance is usually straightforward to assess, determining what constitutes “cost” and proving anti-competitive intent remain legally complex.
Regulatory Evolution: From AVC to ATC
- Under existing regulations, the CCI had discretion to choose the cost metric on a case-by-case basis. The norm was to justify the use of any metric other than Average Variable Cost (AVC).
- A notable application was in the MCX vs. NSE case, where the Commission adopted the Long Run Average Incremental Cost (LRAIC) due to the network externalities inherent in stock exchange services, justifying inclusion of fixed costs.
- The new 2025 draft regulations now explicitly include Average Total Cost (ATC) as a valid benchmark for cost evaluation. ATC is widely accepted in industrial economics as a realistic representation of firm cost efficiency. By allowing ATC as a formal benchmark and excluding ‘market value’, the CCI aims to bring clarity and consistency in below-cost pricing investigations.
Why this Reform Matters
This proposed change holds importance for several reasons:
- It allows for a more holistic and realistic cost assessment, especially in industries where fixed costs form a significant part of the cost structure.
- It improves regulatory certainty and empowers the CCI to address anti-competitive practices in both legacy sectors (e.g., oil & gas) and emerging sectors (e.g., artificial intelligence and digital platforms).
- The reform is crucial at a time when the CCI’s budget has been declining year-on-year, limiting its enforcement capability. Simplified legal frameworks can enhance effectiveness without overburdening institutional resources.
Indian Star Tortoise
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant conservation achievement under the Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP), 340 Indian Star Tortoises were successfully released into the wild at Jogapur Reserve Forest, located in Chandrapur district, Maharashtra.
Indian Star Tortoise (Geochelone elegans)
- IUCN Status:Vulnerable
- CITES Listing:Appendix I
- Protection under Indian Law:Schedule I, Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
Habitat & Range:
- Native to Northwest India, Southern India, and Sri Lanka
- Prefers arid and semi-arid ecosystems including scrublands, dry forests, grasslands, and semi-deserts
Key Characteristics:
- Recognizable by the radiating star-like patterns on its domed shell
- Faces high poaching pressure due to demand in the illegal exotic pet trade
- Exhibits crepuscular behavior (most active during dawn and dusk)
- Primarily herbivorous, consuming grasses, flowers, and leafy vegetation
Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP): A Conservation Initiative
- Launched: Late 2024; witnessed a major release event in April 2025
- Implemented By: Maharashtra Forest Department in collaboration with RESQ Charitable Trust
Objectives:
- Rescue and rehabilitate illegally trafficked tortoises and turtles
- Facilitate safe reintroduction into natural habitats through:
- Medical treatment
- Acclimatization to wild conditions
- Biometric tracking for post-release monitoring
- Raise public awareness via community engagement and school outreach
NaBFIDsigns strategic MoU with New Development Bank (NDB)
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) has entered into a strategic Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the New Development Bank (NDB) to strengthen cooperation in long-term infrastructure financing and promote clean energy development in India.
About NaBFID (National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development)
- Type: Development Finance Institution (DFI)
- Established Under:NaBFID Act, 2021
- Regulated By: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI)
Objectives:
- Bridge the gap in long-term, non-recourse infrastructure finance
- Support the development of India’s bond and derivatives markets
- Foster sustainable economic growth
- Enable project financing in clean energy, transport, and water infrastructure
Key Features:
- Capital base to be scaled up to ?1 trillion
- Focuses on medium to long-term financing (1–5+ years)
- Promotes Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) and financial viability of projects
- Engages in joint research, capacity building, and knowledge-sharing with global institutions like NDB
About the New Development Bank (NDB)
- Type: Multilateral Development Bank formed by BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
- Proposed: BRICS Summit, New Delhi (2012)
- Established By:Fortaleza Declaration, 15 July 2014
- Became Operational: 21 July 2015
Mandate:
- Mobilize funds for infrastructure and sustainable development
- Finance projects in emerging and developing economies (EMDCs)
- Promote green, inclusive, and resilient growth, particularly in clean energy, transport, and water sectors
Key Features:
- Authorized Capital: $100 billion
- India’s Contribution: $2 billion (paid in 7 tranches, 2015–2022)
- Engagement in India: As of December 2024, NDB has financed 20 projects worth $4.867 billion
Accommodative Stance of Monetary Policy
- 11 Apr 2025
In News:
In its latest Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, the RBI decided to retain the accommodative stance amid signs of moderating inflation and sluggish economic growth. This was intended to support the ongoing recovery and ensure credit availability in key sectors.
Definition:
An accommodative stance is a monetary policy approach adopted by central banks, such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), to stimulate economic activity. It generally involves:
- Keeping interest rates low
- Injecting liquidity into the financial system
This stance signals that the central bank is open to reducing rates further or maintaining low rates for an extended period to support growth and demand.
When is it Adopted?
The RBI typically adopts an accommodative stance during:
- Slowing or below-potential economic growth
- Low or stable inflation within the RBI’s target range
- Need to revive consumption, investment, and employment
- Response to domestic or global financial shocks and uncertainties
Objectives
The main aims of an accommodative stance include:
- Boosting credit flow and private investment
- Encouraging borrowing and spending
- Supporting aggregate demand revival
- Providing liquidity relief to stressed sectors
- Promoting employment generation
Key Monetary Tools Used by RBI
To implement an accommodative stance, the RBI uses several instruments:
- Repo Rate Reduction:
- Lowers the cost of borrowing for commercial banks.
- Encourages banks to lend more to businesses and consumers.
- Open Market Operations (OMOs):RBI buys government securities to infuse liquidity into the market.
- Long-Term Repo Operations (LTROs):Provides long-term funding to banks at low interest rates.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) Adjustments:Temporarily lowering CRR increases the funds available for lending.
- Moral Suasion & Regulatory Forbearance:RBI encourages banks to maintain or enhance credit flow, especially to priority and stressed sectors.
Zangezur Corridor
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Zangezur Corridor gained renewed attention following the visit of Armenia’s Security Council Secretary to New Delhi, where he held discussions with India’s National Security Advisor, AjitDoval.
What is the Zangezur Corridor?
The Zangezur Corridor is a proposed transport and transit route that aims to connect mainland Azerbaijan with its exclave, the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, by bypassing Armenia’s Syunik Province. The corridor passes through the Zangezur region, which is currently part of southern Armenia and has been a historically disputed territory since World War I.
Geographical and Strategic Linkages
- On the Azerbaijani side, the corridor integrates with the Horadiz-Agbend highway and railway infrastructure.
- On the Turkish side, it connects with the Nakhchivan-Igdir-Kars railway and highway, creating a direct land route from Azerbaijan to Turkey, and further west to Anatolia and Europe.
- The corridor, therefore, would serve as a critical land bridge across the South Caucasus, improving connectivity between Europe and Asia.
Economic and Strategic Significance
- The corridor is envisioned to:
- Boost regional trade and connectivity across Turkey, Azerbaijan, Iran, Russia, and Central Asia.
- Reduce transportation time and costs between Azerbaijan and Nakhchivan.
- Improve logistics infrastructure and increase supply chain efficiency across the region.
- It has implications for wider Eurasian integration, especially as global trade seeks alternatives to vulnerable chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
India’s Strategic Interest
India's engagement with the Zangezur Corridor gained attention after a meeting between India’s National Security Advisor and Armenia’s Security Council Secretary in New Delhi.
India’s interests in the region include:
- Chabahar Port in Iran: India’s investment here aims to create a secure route to Central Asia and Europe.
- Engagement with Armenia: India has been increasing strategic and defence cooperation with Armenia.
- Alternative Connectivity: The Zangezur Corridor challenges India’s north-south connectivity vision, as it could marginalize the Chabahar route if dominated by Turkish-Azerbaijani interests.
- Geopolitical Balance: India's presence helps counterbalance Turkish-Pakistani influence in the South Caucasus.
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
Ahilyabai Holkar
- 31 May 2025
In News:
On the 300th birth anniversary of Maharani Ahilyabai Holkar, the Prime Minister will participate in the Mahila Sashaktikaran Maha Sammelan in Bhopal to honour her enduring legacy.
Historical Background
- Born: 31 May 1725
- Ruled: Malwa region (1767–1795) as part of the Maratha Confederacy
- Dynasty: Holkar
- Capital: Maheshwar (now in Madhya Pradesh)
Initially serving as a regent, Ahilyabai Holkar became the sovereign ruler after her husband and father-in-law’s deaths. Her rule is widely regarded as the golden age of the Holkar dynasty.
Governance and Administrative Reforms
- Ahilyabai was known for her equitable justice system, exemplified by the sentencing of her own son for a capital crime.
- She abolished discriminatory practices, such as the law confiscating property from childless widows.
- Courts for dispute resolution were established, and she remained accessible to the public, holding daily audiences.
- She broke gender norms by not observing purdah, a rare move for female rulers of the time.
Military Leadership
- Trained under Malhar Rao Holkar, she led her forces in battle.
- Appointed Tukoji Rao Holkar (Malhar Rao’s adopted son) as army commander.
- In 1792, she engaged a French officer, Chevalier Dudrenec, to modernize her army by establishing four battalions.
Cultural and Architectural Contributions
- A patron of literature and arts, she invited scholars like Moropant, Ananta Gandhi, and Khushali Ram to her court.
- Promoted craft and industry, notably founding the Maheshwar textile industry—famous today for Maheshwari sarees.
- Commissioned the construction and restoration of hundreds of Hindu temples and dharamshalas across India.
- Her most iconic act was the renovation of the Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Varanasi in 1780.
- Also contributed to infrastructure development, including roads, wells, forts, and rest houses.
Titles and Recognition
- Referred to as ‘Punyashlok’, meaning one as pure as sacred chants.
- British historian John Keay called her the ‘Philosopher Queen’.
Demise and Succession
Ahilyabai passed away on 13 August 1795 at the age of 70. She was succeeded by Tukoji Rao Holkar, who later abdicated in favour of Jaswant Rao Holkar. Jaswant Rao remained the last Holkar to rule independently until 1804.
India’s Agri-Export Regime

- 17 May 2025
In News:
India has recently inked free trade agreements (FTAs) with the United Kingdom, a trade and economic partnership agreement with the EFTA bloc, and concluded terms of reference for an India-US trade agreement. It is also negotiating with the European Union. In short, India is racing to plug itself into shifting global supply chains. Yet amid all the flashbulbs and photo?ops, India’s agriculture sector remains conspicuously absent.
Definition:
India’s agricultural export regime comprises the policies, institutions, and infrastructure that regulate and promote the export of farm produce.
Present Status:
- In 2023–24, India’s agricultural exports declined to $48 billion, down from $52 billion in 2022–23.
- Basmati rice accounts for approximately 21% of the total agri-export value.
- Bodies such as APEDA and branding tools like ODOP-GI tags play a role in market promotion.
- Agricultural products have been kept largely outside recent FTAs due to concerns over food security, rural employment, and political sensitivity.
Key Challenges in India’s Agri-Export Ecosystem
- Limited FTA Coverage:Agriculture is often excluded or granted extended transition periods in trade agreements, limiting access to foreign markets.
- High Rejection Rates:Several Indian agri-products face export rejections due to non-compliance with Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) norms and pesticide residue limits (e.g., mangoes, groundnuts).
- Governance Gaps:With agriculture under the State List and trade under the Union List, there is often a disconnect in policy coordination, affecting timely decisions.
- Lack of Value Addition:A significant share of exports is in the form of raw produce, with insufficient emphasis on processed or brandedagri-goods.
- Infrastructure Deficits:Inadequate cold storage, pre-cooling facilities, and container depots—particularly in landlocked states like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh—hinder export readiness.
- Subsidy Distortions:Input subsidies on power, water, and fertilizers disincentivize farmers from diversifying to export-oriented, high-value crops.
Strategic Roadmap for Agri-Export Growth
- Boost Value Addition:
- Establish agro-processing zones near APMCs.
- Incentivize processed exports through output-linked schemes.
- Strengthen Policy Coordination:Form a National Agri Trade Council involving the Centre, States, APEDA, FSSAI, and industry stakeholders to harmonize regulations and streamline decision-making.
- Reform Subsidy Framework:Transition to Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT) instead of input-based subsidies to encourage crop diversification and resource efficiency.
- Leverage Agri-Tech Solutions:Expand use of AI tools for crop health monitoring, promote vernacular advisories, and enhance access to real-time market data.
- Upgrade Infrastructure:
- Deploy GIS-based mapping for tracking surplus zones and export potential.
- Develop pre-cooling chains, inland ports, and container hubs in the hinterlands.
- Improve Connectivity in Interior States:Focus on building logistics networks in non-coastal states like UP and MP to integrate them with export supply chains.
Recent ASI Discoveries in Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary

- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) recently made significant archaeological findings in the Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kadapa district of Andhra Pradesh. During an epigraphical survey, ASI discovered three rock shelters, rock paintings, and 30 inscriptions, highlighting the region’s historical and cultural significance.
Key Facts:
- Location: Kadapa district, Andhra Pradesh.
- Water bodies:
- The sanctuary forms the catchment area of the Pennar River.
- The Telugu Ganga Canal flows through the eastern part and drains into the Pennar.
Biodiversity:
- Vegetation types:
- Southern tropical dry deciduous forests (hills)
- Scrub forests (plains)
- Southern dry mixed deciduous forests
- Tropical thorn forests
- Tropical dry evergreen forests
- Flora:
- Rare and endangered species: Red Sanders, Sandalwood
- Riparian vegetation: Terminalia spp., Syzygium spp. (Jamun), Wild Mangoes, Anogeissuslatifolia, Phoenix spp., Bamboo, Hardwickiabinata
- Fauna:
- Notable species: Common toad, Bullfrog, Common Indian skink, Green vine snake
- Critically endangered species: Jerdon’s Courser — this sanctuary is the only known habitat of this bird.
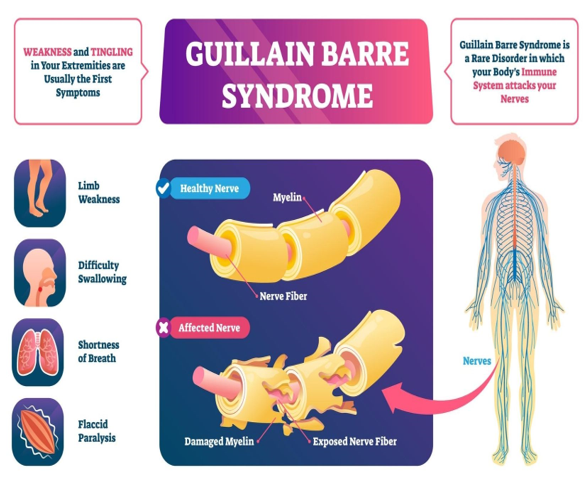
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
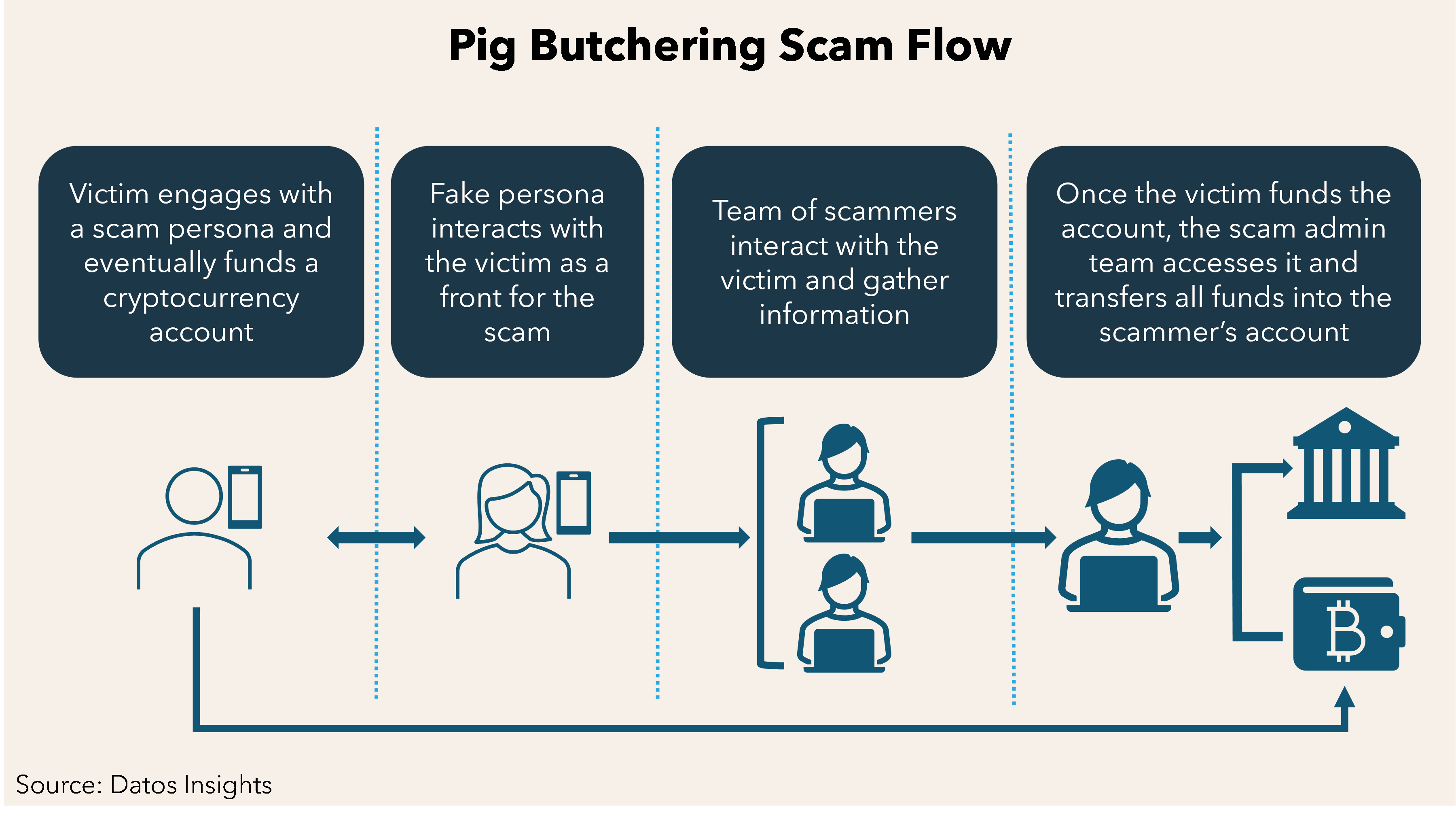
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
Financial Action Task Force (Deccan Herald)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has suggested to all G20 nations to actively cooperate to deal comprehensively and efficiently with fugitive economic offenders as part of the action against them and recovery of the assets.
Facts About:
- The FATF is an international organization made up of governments that focuses on creating policies and standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Objective: Its main goal is to establish global standards and encourage the development of policies at both national and international levels to prevent money laundering and the financing of terrorism.
- The FATF provides recommendations to combat financial crimes, assesses its member countries' policies and procedures, and strives to promote the adoption of anti-money laundering regulations worldwide.
- Formation: The FATF was established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris with the initial aim of addressing money laundering. In 2001, its scope expanded to include combating terrorism financing.
- Headquarters: Its headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- Membership: The FATF comprises 39 member countries, including the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Britain, Germany, France, and the European Union.
- India became a member in 2010.
- As part of its efforts, the FATF maintains two lists: the blacklist and the greylist.
Black List:
- The blacklist contains countries referred to as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs). These are countries known for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF regularly updates this list, adding or removing countries as needed.
Grey List:
- The grey list includes countries considered to be safe havens for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering. Placement on this list serves as a warning that a country may eventually be placed on the blacklist.
- Currently, three countries on the FATF blacklist are North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar.
Consequences of Being on the FATF Blacklist:
- Countries on the FATF blacklist do not receive financial aid from organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank (ADB), and the European Union (EU).
- Additionally, they face various international economic and financial restrictions and sanctions.
