‘CHAKRA’ – Centre of Excellence (CoE)
- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
In a significant move to align banking with India’s future economic priorities, the State Bank of India (SBI) has launched ‘CHAKRA’ – Centre of Excellence (CoE). The initiative is designed to support financing for sunrise sectors that are expected to play a decisive role in India’s transition toward a technology-driven, sustainable, and globally competitive economy.
This step signals a shift in institutional finance from traditional asset-heavy industries toward innovation-led and climate-aligned growth sectors.
What is CHAKRA?
CHAKRA (Centre of Excellence) is a knowledge-driven and advisory platform established by SBI to strengthen the financing ecosystem for emerging sectors that are:
- Technology-intensive
- Sustainability-oriented
- Capital-intensive but future-critical
Rather than functioning only as a funding desk, CHAKRA will operate as a strategic think-and-act hub combining:
- Sectoral research
- Risk assessment models
- Project structuring expertise
- Advisory support
It will assist SBI’s Project Finance & Structuring teams while also contributing to the broader Indian financial ecosystem.
Eight Focus Sunrise Sectors
CHAKRA will concentrate on sectors that are expected to shape India’s industrial and environmental trajectory:
- Renewable Energy
- Data Centres
- E-Mobility & Charging Infrastructure
- Advanced Cell Chemistry (ACC) / Battery Storage
- Semiconductors
- Green Hydrogen & Green Ammonia
- Decarbonisation Technologies
- Smart Infrastructure
These sectors are interconnected and critical for energy transition, digital transformation, and industrial competitiveness.
Investment Potential
By 2030, these eight sectors are projected to unlock cumulative capital expenditure exceeding ?100 lakh crore.
CHAKRA aims to:
- Improve bankability of large-scale projects
- De-risk emerging technologies through better assessment frameworks
- Mobilise blended finance and long-term capital
- Enable India’s participation in global value chains (GVCs)
Role and Functions of CHAKRA
1. Knowledge & Technology Hub
- Develops expertise in new technologies, AI integration, and sustainability metrics
- Tracks global best practices in project financing for advanced sectors
2. Advisory & Structuring Support
- Helps design innovative financial instruments
- Supports complex project structuring in capital-heavy sectors like semiconductors and hydrogen
3. Ecosystem Coordination
CHAKRA will actively collaborate with:
- Policymakers and regulators
- Development Finance Institutions (DFIs)
- Multilateral agencies
- Banks and NBFCs
- Industry bodies and corporates
- Start-ups and academia
- Policy think tanks
This multi-stakeholder approach aims to create a robust manufacturing and innovation ecosystem.
Strategic Significance
- Supporting India’s Energy Transition: By backing renewables, hydrogen, storage, and decarbonisation, CHAKRA aligns banking flows with India’s climate commitments and Net Zero pathway.
- Strengthening Technological Sovereignty: Financing for semiconductors, batteries, and data centres reduces import dependence and enhances strategic autonomy.
- Enabling Digital & Infrastructure Growth: Smart infrastructure and data centres are essential for Digital India, AI adoption, and Industry 4.0.
- Financial Sector Innovation: The CoE model marks a transition from collateral-based lending to knowledge-based financing, especially for technology-driven sectors where risks are complex but long-term returns are high.
Sanchar Saathi App
- 04 Dec 2025
In News:
The DoT has mandated that all newly manufactured or imported smartphones sold in India from March 2026 must come with the Sanchar Saathi app pre-installed. This ensures that users have access to security tools and awareness features from the outset.
However, Union Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia clarified that the app is not mandatory for continued use; users can delete it if they choose. The mandatory aspect applies only to pre-installation by manufacturers, not compulsory retention by users.
What is Sanchar Saathi?
Sanchar Saathi is a telecom security and awareness platform developed by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India. It is available both as a mobile application and a web portal, designed to empower users to manage their digital identity, report frauds, and safeguard mobile devices against misuse.
The initiative addresses rising concerns over phone theft, cyber fraud, cloning of devices, phishing scams, and unauthorised use of SIM connections, which have become widespread with increased mobile penetration.
Objectives of Sanchar Saathi
The app is designed to:
- Enhance digital safety and awareness among mobile users.
- Prevent telecom and cyber frauds by providing tools to report and track suspicious activities.
- Empower users to manage digital identity linked to mobile connections.
- Strengthen security mechanisms against phone theft and misuse.
These aims support broader national priorities on cybersecurity, consumer protection, and trust in digital services.
Key Features of the Sanchar Saathi Platform
- Fraud & Scam Reporting (‘Chakshu’):Users can report suspicious calls, SMS, or WhatsApp messages, including fake KYC alerts, impersonation scams, phishing links, and fraudulent content. This helps authorities identify and analyse fraud patterns.
- SIM and Identity Protection:Displays all mobile connections linked to a user’s identity, enabling detection of unauthorised or unknown SIMs registered without consent.
- Lost or Stolen Phone Blocking:Users can block the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) of a lost or stolen device, rendering it unusable on any network. Devices can be unblocked if recovered.
- Device Authenticity Verification:Helps verify whether a handset is genuine or blacklisted, particularly useful in India’s large second-hand phone market.
- Reporting Illegally Masked International Calls:Enables reporting of international calls disguised as local (+91) calls, which are often used in scams.
- Spam & Malicious Link Reporting:Users can report spam calls and messages, unsafe APKs, phishing websites, and fraudulent apps that violate Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) rules.
- Local ISP Locator:Helps users identify local wired internet service providers by entering a PIN code, address, or provider name.
- Trusted Contact & Helpline Directory:Provides a repository of verified customer-care numbers, emails, and websites for major institutions, aiding in authentic communication.
Significance and Impact
Sanchar Saathi strengthens India’s defence against digital fraud and mobile misuse by combining security functions with user awareness. Its features help:
- Reduce incidence of cloned or tampered devices.
- Protect users from identity misuse and financial scams.
- Assist authorities in curbing mobile theft and unauthorised network access.
- Provide safeguards to consumers, especially in the pre-owned smartphone market.
Since its launch, the platform has contributed to blocking more than 7 lakh lost or stolen devices, indicating its utility and reach.
Implementation and Accessibility
- For newly sold smartphones, Sanchar Saathi will be pre-installed by manufacturers and appear as a system app.
- Users with existing devices can install the app from official app stores.
- Manufacturers may also push it through software updates to existing devices.
Upon installation, users can log in with their mobile number and access the app’s features through a simple interface.
Revised Income Tax Bill, 2025

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Income Tax (No. 2) Bill, 2025 was passed in the Lok Sabha in August 2025, replacing the Income Tax Act, 1961 after nearly six decades. The earlier draft of the Bill was withdrawn to incorporate recommendations of the Parliamentary Select Committee and stakeholder feedback. The revised Bill consolidates, simplifies, and modernises India’s direct tax framework.
Background
- Old Act (1961): Complex language, overlapping provisions, and compliance burden.
- New Bill (2025):
- Contains 536 sections and 16 schedules.
- Incorporates over 285 recommendations of the Select Committee, which examined the draft for four months and submitted a 4,500-page report.
- Aims to make the law simpler, clearer, and more aligned with the digital era.
Key Features
- Simplification of Tax Framework
- Single “Tax Year” concept replaces “Previous Year” and “Assessment Year”.
- Outdated and contradictory provisions removed to reduce litigation.
- Clear drafting, structured numbering, and improved terminology for easier interpretation.
- Taxpayer-Friendly Provisions
- Refunds allowed even if returns are filed after the due date.
- NIL-TDS certificates available for taxpayers with no liability.
- Relief on vacant house property – no taxation on notional rent.
- 30% standard deduction (post municipal tax) and interest deduction allowed on rented property.
- Corporate and MSME Reforms
- ?80M deduction on inter-corporate dividends reintroduced.
- MSME definition aligned with the MSME Act for uniformity.
- Institutional & Governance Reforms
- CBDT empowered for flexible, digital-era rule-making.
- Simplified compliance for TDS, PF withdrawals, advance rulings, and penalties.
- Relief to Specific Sectors
- Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) on LLPs abolished.
- Charitable Trusts – compliance relaxations and reduced regulatory burden.
- Transfer Pricing & Associated Enterprise definitions rationalised.
- Extension of pension benefits – commuted pension deduction available even for non-employee individuals.
RBI’s New Policy on Pre-Payment Charges
- 05 Jul 2025
In News:
In a move aimed at enhancing fair lending practices and improving access to affordable credit, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has prohibited pre-payment penalties on floating-rate loans availed by individuals and Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs). The new norms will come into effect from January 1, 2026, and will apply to all loans and credit facilities sanctioned or renewed on or after this date.
Key Provisions of the RBI Guidelines
Ban on Pre-Payment Charges:
- Applicable to:
- Individuals taking floating-rate loans for non-business purposes, even with co-borrowers.
- Individuals and MSEs availing business loans.
- Individuals taking floating-rate loans for non-business purposes, even with co-borrowers.
- Lenders prohibited from imposing pre-payment penalties include:
- Commercial Banks (except SFBs, RRBs, Local Area Banks)
- Tier 4 Urban Cooperative Banks
- NBFCs in the Upper Layer (NBFC-UL)
- All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs)
- For smaller institutions like Small Finance Banks, RRBs, Tier 3 Urban Cooperative Banks, State and Central Co-op Banks, and NBFCs in the Middle Layer (NBFC-ML), the exemption from pre-payment charges applies to loans up to ?50 lakh.
Early Closure of Overdraft/Cash Credit:
- If the borrower informs in advance and closes the account on time, no pre-closure charges can be levied.
- If the lender requests prepayment, no charges are permitted in such cases either.
Transparency and Disclosure Requirements
- Lenders must clearly disclose the applicability or non-applicability of pre-payment charges in:
- Sanction letters
- Loan agreements
- Key Facts Statement (KFS) (where applicable)
- Any charges not explicitly disclosed as per these guidelines cannot be imposed.
Pre-Payment Without Lock-in
- Pre-payment (partial or full) can be made without any lock-in period, and irrespective of the source of funds.
Rationale Behind the Move
- The RBI noted that inconsistent practices regarding pre-payment fees have led to customer disputes.
- Ensuring easy and affordable finance for MSEs is “of paramount importance,” the central bank emphasized.
Policy Continuity and Legal Update
- All earlier RBI circulars and guidelines regarding pre-payment charges stand repealed.
- The final guidelines were issued after considering public feedback on the draft circular (February 2025).
Significance for MSEs and Borrowers
- Enhances credit mobility and refinancing freedom for borrowers.
- Prevents penalty-driven disincentives for early loan closure.
- Aligns with the RBI’s broader goal of financial consumer protection and MSME support.
Kounis Syndrome
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
The recent sudden death of Indian industrialist Sanjay Kapur during a polo match in London has drawn national attention to Kounis Syndrome, a rare but serious medical condition. Reports suggest he may have inhaled a bee, which stung him inside the throat—leading to a cardiac arrest, potentially triggered by an acute allergic reaction. This tragic incident has raised awareness about the interaction between allergic reactions and cardiac emergencies, especially in seemingly healthy individuals.
What is Kounis Syndrome?
Kounis Syndrome is a rare medical condition in which a severe allergic or hypersensitivity reaction triggers a coronary event, such as a heart attack. It is often termed “allergic angina” or “allergic myocardial infarction.”
Mechanism
- Triggered by allergens such as insect stings, drugs, or foods.
- Leads to the activation of mast cells, which release histamine and cytokines.
- These chemicals cause spasms, plaque rupture, or clot formation in coronary arteries.
- Result: Reduced blood flow to the heart, causing ischemia or infarction.
Types of Kounis Syndrome
- Type I: In individuals with normal coronary arteries – allergic reaction causes artery spasm and possible heart attack.
- Type II: In those with existing coronary artery disease – allergic reaction destabilizes plaques, causing infarction.
- Type III: In patients with coronary stents – hypersensitivity leads to thrombosis within stents.
Triggers of Kounis Syndrome
- Insect stings (bee, wasp)
- Medications (NSAIDs, antibiotics)
- Foods (nuts, shellfish, kiwi)
- Environmental allergens (latex, contrast dyes)
- Underlying health conditions (e.g., mastocytosis)
Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Swelling (angioedema), hives, or rash
- Low blood pressure
- ECG changes: ST-segment elevation or depression
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis: Clinical history, ECG, cardiac enzymes, allergy tests.
- Treatment includes:
- For allergy: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, epinephrine
- For cardiac care: Oxygen, nitrates, antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers
Why Mouth/Throat Bee Stings Are Dangerous
- Immediate airway swelling
- Increased absorption of venom into bloodstream
- Enhanced risk of anaphylaxis and cardiac arrest
Even people without a history of allergy can experience severe reactions if stung inside the mouth or throat.
Warning Signs After a Bee Sting
- Difficulty breathing
- Swollen lips, tongue, or throat
- Rash or itching
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid or weak heartbeat
- Nausea or unconsciousness
Immediate emergency care is essential.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)

- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
Lucknow has officially submitted its nomination to be recognised as a “City of Gastronomy” under the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), aiming to join Hyderabad as the only other Indian city to hold this title in the gastronomy category.
About the UCCN
- Established: 2004
- Purpose: To promote international cooperation among cities that use creativity as a key element for sustainable urban development.
- Focus Areas: Literature, Music, Crafts & Folk Arts, Design, Film, Media Arts, and Gastronomy.
- Key Goals:
- Leverage the creative economy for sustainable development.
- Encourage cultural diversity and resilience against urban challenges like climate change and inequality.
- Promote collaboration across public, private, and civil society sectors.
UCCN and Sustainable Development
- UCCN supports the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by positioning culture and creativity at the heart of local development policies and planning.
- Member cities are expected to create innovation hubs, support local artists, and preserve cultural heritage.
India and the UCCN
As of 2023, 10 Indian cities are part of the network:
- Hyderabad – Gastronomy
- Jaipur – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Varanasi – Music
- Chennai – Music
- Mumbai – Film
- Srinagar – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Kozhikode – Literature
- Gwalior – Music (Recent entries include Kozhikode and Gwalior)
Lucknow’s Nomination: Highlights
- Nominated Title: City of Gastronomy
- Coordinated by: Department of Tourism and Culture, Lucknow
- Culinary Heritage: Awadhi cuisine, including dishes like nihari, kebabs, biryani, khasta, kulfi, jalebi, and puri-sabzi.
- Cultural Value: The city’s food is not just a tradition but a living culinary ecosystem, passed down through generations and practiced by diverse communities.
- Dossier Preparation: By renowned heritage conservationist Abha Narain Lambah.
- Verification: A field visit by UNESCO is expected as part of the evaluation process.
Global Cities of Gastronomy (Examples)
- Alba (Italy)
- Arequipa (Peru)
- Bergen (Norway)
- Belem (Brazil)
- Bendigo (Australia)
These cities, like Hyderabad, are recognised for their distinctive and sustainable culinary traditions.
Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL)
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
The Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) is a transformative 272-km railway project aimed at connecting the Kashmir Valley to the Indian Railways network. With Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurating the Chenab Rail Bridge and flagging off Vande Bharat trains in June 2025, the project nears full operationalization.
Key Details:
Chenab Rail Bridge – World’s Highest Railway Arch Bridge
- Height: 359 metres above riverbed (taller than the Eiffel Tower).
- Length: 1,315 metres; Arch span: 467 metres.
- Status: Highest railway arch bridge in the world.
- Engineering feat in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir.
Strategic All-Weather Connectivity
- Reduces dependency on the Srinagar-Jammu highway, which is prone to closure due to snow and landslides.
- Ensures year-round transportation and supply lines.
Enhanced Military Mobility
- Enables rapid movement of troops and equipment to border regions.
- Crucial for national security due to the region's proximity to international borders.
- Designed to withstand blasts and harsh weather.
Anji Bridge – India’s First Cable-Stayed Rail Bridge
- Length: 473 metres; Height: 331 metres.
- Located on the Katra-Banihal section.
- Supported by 48 cables, suitable for rugged Himalayan terrain.
Vande Bharat Connectivity
- High-speed trains introduced on Katra–Srinagar route.
- Improves passenger comfort and reduces travel time.
Economic Boost via Trade
- Improves market access for Kashmiri products: apples, saffron, handicrafts, and dry fruits.
- Facilitates faster freight movement, integrating the region into national trade networks.
Tourism Promotion
- Easier access to religious and scenic sites.
- Expected to boost tourism post disruptions (e.g., Pahalgam incident).
- Cheaper and faster rail travel enhances domestic footfall.
Engineering Resilience
- Chenab Bridge:
- Blast-resistant (withstands up to 40 kg TNT).
- Wind resistant (up to 260 kmph).
- Seismic-resilient with a 120-year design life.
- Symbol of India’s capability in building infrastructure in high-risk zones.
Time Efficiency
- Travel time between Jammu and Srinagar will reduce from 6 hours (by road) to 3–3.5 hours (by rail).
- Facilitates emergency services, logistics, and routine travel.
National Integration and Inclusion
- 943 bridges, 36 tunnels covering 119 km — overcoming Himalayan terrain challenges.
- Integrates remote districts of Jammu & Kashmir into India's railway grid.
- Promotes inclusive development and better governance outreach.
Krishi Nivesh Portal
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
In an effort to streamline and accelerate investments in India’s agriculture and allied sectors, the Government of India has launched the Krishi Nivesh Portal, developed by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
The initiative aligns with the government’s broader goal of promoting the ease of doing business in agriculture by integrating schemes from multiple Central ministries and State governments into a single digital platform.
Key Features of the Portal
- One-Stop Solution: The portal acts as a centralized hub providing real-time access to information on agricultural schemes from various government departments and ministries.
- Multi-Stakeholder Access: It is designed to cater to farmers, entrepreneurs, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), industries, and agri-startups.
- Scheme Integration: As of now, the portal integrates 17 flagship schemes spanning seven Union Ministries, including:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund
- PM KisanSampada Yojana
- PM-KUSUM
- Technological Features: It offers a user-friendly interface, chatbot support, and interactive dashboards for data-driven insights and monitoring.
- Investment Tracking: Users can track application status, explore investment opportunities based on geographical spread, and gain assistance with loan disbursal.
Institutional Integration
- Currently, 14 Union ministries/departments and 9 state government departments are involved in implementing schemes related to agriculture and allied sectors.
- Ministries already integrated include:
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries
- Ministry of Rural Development
- Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
- Ministry of Fertilisers
Efforts are underway to onboard over 300 schemes from various ministries and states, including those related to credit-linked initiatives, PPP models, venture capital projects, and startups.
Significance for Agricultural Sector
- The portal addresses key challenges such as fragmented scheme information, siloed departmental operations, and delays in loan processing.
- It aims to unlock the investment potential of India’s agri-sector, especially for private investors, by offering a consolidated, transparent, and accessible interface.
- According to official estimates:
- The revised budget allocation for FY 2024–25 for agricultural investment schemes stands at ?1.31 lakh crore.
- In FY 2021–22, private sector investment in agriculture amounted to ?2.79 lakh crore.
India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)
- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
To meet its climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, India is moving towards a market-based mechanism for emissions reduction through the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023. The scheme was made possible by amending the Energy Conservation Act, 2021 and replaces the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) scheme operational since 2012.
What is the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)?
- CCTS is India’s version of an emissions trading system (ETS) designed to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions intensity — emissions per unit of output — rather than absolute emissions.
- It introduces Carbon Credit Certificates (CCC), each representing one tonne of CO? equivalent (tCO?e) reduction.
- Managed by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) and coordinated by a National Steering Committee, the scheme involves various regulatory bodies including electricity exchanges, MoEFCC, and the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission.
Key Features of the CCTS
Aspect Description
Transition from PAT - Shifts focus from energy efficiency (PAT) to emission intensity (CCTS).
Coverage - Initially targets energy-intensive sectors: Iron & Steel, Cement, Aluminium,
Fertilisers, Refineries, Pulp & Paper, and Textiles (~16% of national
GHG emissions). Power sector (~40%) may be included later.
Dual Mechanisms - 1. Compliance: Mandates targets for large emitters. 2. Offset:
Voluntary participants earn credits by reducing emissions.
Implementation Timeline - Expected to launch fully by mid-2026, in a phased manner.
Global Context of Carbon Pricing
- As of June 2024, 89 countries operate carbon pricing mechanisms, covering 12.8 Gt CO?e (25% of global emissions).
- Carbon pricing methods:
- ETS (Cap-and-Trade / Baseline-and-Credit): Companies trade allowances or credits based on performance.
- Carbon Tax: Fixed price on emissions; provides cost certainty but not emissions certainty.
- Crediting Mechanism: Projects generating verified emission reductions earn tradable carbon credits.
Challenges in Implementing CCTS
- Target Setting: Overly lenient targets may cause credit oversupply, reducing prices; overly strict ones risk high compliance costs.
- Compliance Gaps: Under PAT, over half the required energy certificates were never purchased, with no penalties imposed.
- Delays: Credit issuance under PAT (Phase IV onwards) has been delayed since 2021, affecting market confidence.
- Transparency: Lack of public access to data on actual performance undermines accountability.
- Monitoring and Verification (MRV): Requires robust systems to prevent double counting and ensure credible reporting.
Steps to Strengthen India’s Carbon Market
- Align with global practices: Learn from the EU ETS — implement strict monitoring, gradual tightening of caps, and price stability mechanisms.
- Robust MRV Framework: Ensure accuracy in emission data to boost trust.
- Digital Trading Platform: Track and authenticate credit transactions; avoid fraud.
- Industry Incentives: Encourage early compliance via tax benefits and access to green finance.
- Trade Compatibility: Prepare for global measures like the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) by ensuring transparency and comparability.
India’s CCTS represents a significant shift in climate governance by institutionalizing carbon pricing. While it brings India in line with evolving global practices, the success of the Indian carbon market will depend on credible enforcement, transparent functioning, and strong regulatory architecture. If implemented effectively, it can drive low-carbon growth and support India’s target of reducing emissions intensity by 45% by 2030.
Cayman Islands
- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake recently struck the Caribbean Sea southwest of the Cayman Islands, as reported by the U.S. Geological Survey. While no tsunami warning was issued, tremors were felt across the region, and assessments of damage are ongoing.
Geographical and Geopolitical Overview
- The Cayman Islands is a British Overseas Territory located in the western Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica.
- It comprises three islands:
- Grand Cayman (largest and most populous)
- Cayman Brac
- Little Cayman
- The islands are part of the Cayman Ridge, an underwater mountain range, with the islands themselves being the emergent peaks of this ridgeline.
- Area: Only 264 sq. km
- Capital: George Town, located on Grand Cayman
- Official Language: English
- Currency: Cayman Islands Dollar (KYD)
- Ethnic Composition:
- Afro-European: 40%
- African: 20%
- European: 20%
- Other: 20%
Seismic and Climatic Features
- The islands are near the Cayman Trench, a deep subduction zone formed by the interaction between the North American and Caribbean Plates.
- Although major earthquakes are rare, the region is seismically active, and moderate to high seismic events are possible, such as the recent 7.6 magnitude quake.
- Climate: Tropical marine with a distinct wet and dry season; vulnerable to hurricanes, especially during the Atlantic hurricane season (June–November).
Ecological Significance
- Known for crystal-clear waters, coral reefs, and white sand beaches, the Cayman Islands are a global hub for marine biodiversity.
- Key ecological features include:
- Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves
- Famous dive sites like the Great Blue Hole and Bloody Bay Wall
- Terrestrial biodiversity is limited due to the islands’ small limestone-based land area, but they are home to endemic species such as the Grand Cayman Blue Iguana, which has recovered from critical endangerment through conservation efforts.
Economic Importance: A Global Financial Hub
- The Cayman Islands is renowned as a major offshore financial center and global tax haven.
- Zero taxation: No corporate, income, or capital gains tax
- Home to:
- Offshore banks
- Hedge funds
- Multinational corporations
- The islands offer a favorable regulatory environment and strict financial confidentiality laws, although they now comply with international transparency norms.
Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF)

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
India is actively exploring the creation of a Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF) or The Bharat Fund (TBF) to harness the untapped wealth embedded within its public sector ecosystem. This fund aims to unlock and strategically manage dormant capital, estimated at ?40 lakh crore ($450–500 billion), primarily held in equity stakes of around 80 listed public sector enterprises (PSEs) and banks.
What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF)?
A Sovereign Wealth Fund is a state-owned investment vehicle that manages national savings or surplus revenues—often derived from foreign exchange reserves, natural resource exports, or trade surpluses.
According to the Santiago Principles (2008), SWFs:
- Are owned by the general government (central or sub-national),
- Invest primarily in foreign financial assets, and
- Aim to achieve financial objectives rather than monetary policy.
Types of SWFs include:
- Stabilization Funds: Cushion fiscal shocks from revenue volatility.
- Future Generation Funds: Preserve wealth for long-term national benefit.
- Strategic Development Funds: Support priority sectors and national growth.
- Reserve Investment Funds: Enhance returns on foreign currency reserves.
Examples include:
- Norway’s Government Pension Fund Global ($1.7 trillion),
- China Investment Corporation ($1.35 trillion),
- Abu Dhabi Investment Authority ($993 billion).
India’s SWF Landscape and the BSWF Proposal
India previously explored SWF models in 2007–08 and again in 2010–11. While the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) was launched in 2015, it remains sector-specific and limited in scale. The proposed BSWF envisions a comprehensive and transformational fund akin to global best practices.
Key features of the BSWF proposal:
- Consolidation of government equity in PSEs and PSU banks under a professionally managed umbrella.
- Strategic divestment—e.g., reducing government stake from 51% to 40%—without losing operational control.
- Leveraging this pooled equity to attract global co-investors, potentially unlocking tens or hundreds of billions in foreign capital.
Why India Needs the Bharat SWF
- Wealth Unlocking: Potential monetization of over ?40 lakh crore in dormant government equity assets.
- Fiscal Prudence: Even a modest 2% annual divestment could yield $10+ billion, narrowing the fiscal deficit from 4.9% to ~4.6% of GDP.
- Strategic Sector Investment: Deployment into high-potential sectors—AI, semiconductors, electric vehicles, hydrogen energy, biotechnology—to drive innovation and economic leadership.
- Attracting Global Capital: Enhanced investor confidence, especially from established SWFs like those of Singapore, Norway, and Abu Dhabi, which are already increasing exposure in Indian equities and infrastructure.
- Social Sector Funding: Generate non-debt financial resources for welfare programs and national development missions.
- Soft Power Projection: Fund ventures, disaster relief, and advocacy efforts, strengthening India’s international standing.
Governance and Reform Imperatives
For the BSWF to succeed, it must:
- Be governed by a clear legal and regulatory framework aligned with Santiago Principles.
- Operate independently, with professional asset managers, market-based remuneration, and arm’s length oversight.
- Transition PSEs to function with autonomy and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic delays and enabling innovation.
- Foster joint ventures to turn around non-performing PSEs—among the 1,830 PSEs, around 400 remain non-functional, demanding nearly ?9 lakh crore annually in budgetary support.
Challenges and Concerns
- Macroeconomic Constraints: India faces a current account deficit and substantial fiscal pressures—conditions unlike traditional SWF-rich nations.
- Geopolitical and Market Risks: Global uncertainty and decoupling trends could impact cross-border investment strategies.
- Environmental and Technological Vulnerabilities: Investment risks in carbon-heavy sectors and exposure to data fraud or tech disruptions.
- Institutional Resistance: Political and bureaucratic inertia may delay implementation unless national interest is prioritized.
SWF Investments in India: A Growing Trend
Foreign SWFs are already deepening their footprint in India:
- $6.7 billion in direct investments in 2022 (up from $4.3 billion in 2021).
- Preferred sectors: healthcare, entertainment, renewables, infrastructure.
- Beneficiaries of tax exemptions on direct infrastructure investments via InVITS (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) and AIFs (Alternative Investment Funds), valid for investments made before March 31, 2024.
These incentives have encouraged foreign SWFs to explore establishing physical presence in India’s financial hubs, especially GIFT City, Gandhinagar.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
Ramesh Chand Panel
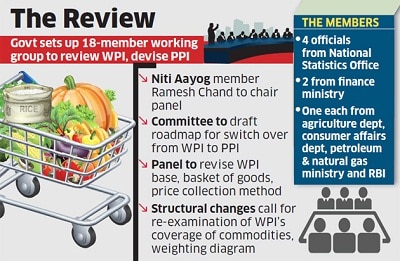
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
