Global Environment Outlook–7 (GEO-7), 2025

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The 7th edition of the Global Environment Outlook (GEO-7) was released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) during its session in Nairobi, warning that the world is far off track in meeting climate and environmental goals.
About Global Environment Outlook (GEO)
- The Global Environment Outlook is UNEP’s flagship assessment of the state of the global environment, future risks, and policy solutions. It provides scientific evidence for international environmental decision-making.
Key Findings of GEO-7
Rising Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Global GHG emissions have grown ~1.5% annually since 1990
- 2024 recorded temperatures around 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels
- Intensifying heatwaves, floods, droughts, and extreme events
Biodiversity Loss
- 1 million species (out of ~8 million) face extinction
- 20–40% of global land is degraded
- Over 3 billion people are affected by land degradation
Economic Costs of Environmental Damage
- Climate-related disasters cost ~USD 143 billion annually
- Air pollution caused USD 8.1 trillion in health damages in 2019 (≈6% of global GDP)
- 9 million deaths per year linked to pollution
Plastic Pollution Crisis
- About 8 billion tonnes of plastic waste pollute ecosystems
- Toxic chemical exposure leads to ~USD 1.5 trillion annual health losses
Projected Impacts if Current Trends Continue
- Temperature thresholds: Likely to exceed 1.5°C in early 2030s and 2°C by 2040s
- Economic decline: Global GDP may fall 4% by 2050 and 20% by 2100
- Loss of fertile land: Equivalent to losing a country-sized fertile area annually
- Food insecurity: Per capita food availability may drop 3.4% by 2050
- Rising hunger, poverty, displacement, and conflict risks
GEO-7 Recommended Transformative Actions
Economy & Finance
- Move beyond GDP to wealth-based indicators
- Price environmental externalities
- Invest in decarbonization, ecosystem restoration, sustainable agriculture
- USD 8 trillion/year investment needed till 2050
- Could generate USD 20 trillion annual benefits by 2070
Materials & Waste
- Promote circular economy models
- Transparent product design and recycling chains
- Shift from linear consumption to regenerative systems
Energy Transition
- Rapid decarbonization of energy
- Improve energy efficiency
- Secure sustainable critical mineral supply chains
- Reduce air pollution → 9 million premature deaths avoidable by 2050
Food Systems
- Promote sustainable diets
- Reduce food loss and waste
- Improve agricultural efficiency
- Could reduce undernourishment by ~200 million people
Ecosystem Protection
- Scale up ecosystem restoration
- Use Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for adaptation
- Stronger mitigation and biodiversity conservation policies
Collaborative & Integrated Governance
- Solutions must involve governments, private sector, civil society, academia, Indigenous communities
- Policies across sectors must be implemented together, not in isolation
About UNEP
- Established in 1972 after the Stockholm Conference
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
- Leading global authority on environmental issues
- Major reports include:
- Emissions Gap Report
- Adaptation Gap Report
- Global Environment Outlook
- Frontiers Report
Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)

- 09 Dec 2025
In News:
Recent large-scale flight cancellations by a major Indian airline led the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) to grant a one-time exemption from the newly implemented Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) rules. These rules are designed to reduce pilot fatigue by regulating maximum duty hours and ensuring mandatory rest periods. The decision has highlighted DGCA’s critical role in balancing aviation safety with operational realities.
About DGCA
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is India’s statutory civil aviation regulator responsible for ensuring aviation safety, airworthiness, and regulatory compliance in line with international standards.
- Established: 1927 (as a government organisation)
- Statutory Status: Granted under the Aircraft (Amendment) Act, 2020
- Administrative Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA)
- Mandate: Promote safe, efficient, and reliable air transport through regulatory oversight and alignment with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards.
Key Functions of DGCA
1. Safety Regulation & Oversight
- Frames and enforces Civil Aviation Requirements (CARs)
- Conducts surveillance, audits, and inspections of airlines, airports, MROs, and training institutes
2. Aircraft & Aerodrome Certification
- Registers civil aircraft
- Issues Certificates of Airworthiness
- Certifies aerodromes for operational safety
3. Licensing & Training
- Issues licences to pilots, Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs), Air Traffic Controllers (ATCOs), cabin crew, and flight dispatchers
- Approves flying schools, AME institutes, and simulator training centres
4. Accident & Incident Investigation
- Investigates incidents and serious incidents (aircraft up to 2,250 kg All-Up Weight)
- Implements aviation safety programmes
5. Air Transport Regulation
- Grants Air Operator Certificates (AOCs)
- Regulates scheduled and non-scheduled domestic and international operations
6. ICAO Coordination
- Aligns Indian aviation standards with ICAO norms
- Participates in global aviation safety audits (USOAP)
7. Dangerous Goods & Air Navigation Oversight
- Certifies operators transporting dangerous goods
- Coordinates civil–military airspace usage
Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL)
FDTL rules regulate:
- Maximum flying and duty hours for pilots
- Minimum mandatory rest periods
- Fatigue risk management
These are crucial for aviation safety, as pilot fatigue is a significant risk factor in accidents.
Significance of DGCA
- Ensures Passenger Safety: Through strict oversight of aircraft airworthiness, pilot training, and crew rest norms
- Maintains Operational Discipline: Enforces compliance with technical and safety regulations
- Balances Safety & Industry Needs: The recent FDTL exemption shows DGCA’s role in managing real-time operational disruptions while upholding safety standards
- Global Compliance: Ensures India meets international aviation obligations under ICAO
Bharat NCAP 2.0
- 26 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has released the draft Bharat NCAP 2.0, significantly upgrading India’s vehicle safety assessment framework by introducing new crash-test categories, higher benchmarks, and pedestrian safety norms.
What is Bharat NCAP 2.0?
- Nature: Revised vehicle safety rating programme for passenger cars sold in India.
- Background: Updates the Bharat NCAP guidelines notified in 2023.
- Objective:
- Align India’s crash-safety standards with global NCAP norms.
- Protect vehicle occupants as well as pedestrians and other vulnerable road users (VRUs).
- Push manufacturers to adopt advanced safety technologies.
Implementing & Testing Agency
- Certification & Testing: Central Institute of Road Transport (CIRT), Pune
- Nodal Ministry: MoRTH
Key Features of Bharat NCAP 2.0
1. Five Safety Assessment Verticals
- Safe Driving
- Accident Avoidance
- Crash Protection
- Vulnerable Road User (VRU) Protection (New)
- Post-Crash Safety (New)
2. Expanded Crash-Test Regime
- Existing Tests:
- Frontal impact
- Side impact
- Oblique pole impact
- New Tests Added:
- Full-width frontal crash test
- Rear impact test
3. Advanced Injury Evaluation: Use of Advanced Test Dummies (ATDs) to assess injury risks to different body regions under multiple crash scenarios.
4. Vulnerable Road User (VRU) Protection
- Pedestrian Safety Tests:
- Legform impact test
- Adult and child head impact tests
- Optional Safety Tech: Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) for pedestrians and motorcyclists earns additional points.
5. Accident-Avoidance Technologies
- Mandatory: Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- Optional (Extra Score): Autonomous Emergency Braking System (AEBS)
6. Post-Crash Safety Assessment
- Fire and electrical safety checks
- Ease of occupant escape (functioning doors, seat-belt buckles after crash)
Revised Star Rating System
- Stricter thresholds for higher star ratings.
- A vehicle cannot receive a 5-star rating if:
- Any assessment vertical scores zero, or
- There is evidence of severe or life-threatening injury risk.
Significance of Bharat NCAP 2.0
- Moves India closer to global vehicle safety benchmarks.
- Addresses pedestrian safety—pedestrians account for over 20% of road accident deaths in India.
- Supports India’s target to reduce road fatalities by 50% by 2030.
- Encourages safety-led competition among automobile manufacturers.
Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
- 06 Nov 2025
In News:
NASA astronomers have confirmed the chemical fingerprint of water on the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS using ultraviolet data from the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory. This marks a major advance in understanding the chemistry of planetary systems beyond the Sun.
What is 3I/ATLAS?
- Designation: 3I/ATLAS
- Discovery: 1 July 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in Hawaii.
- Category: Third confirmed interstellar object after 1I/‘Oumuamua (2017) and 2I/Borisov (2019).
- Origin: Formed in another planetary system, possibly 7 billion years old, older than Earth.
Trajectory & Motion
- Travels on a hyperbolic orbit—meaning it is not gravitationally bound to the Sun and will exit the Solar System permanently.
- Speed relative to Sun: 57–68 km/s.
Physical Characteristics
- An active comet with a visible coma of dust and icy particles.
- Expected to form a cometary tail as it approaches the Sun.
- Surface hue: Slightly reddish, indicating the presence of complex organics or water ice.
- Nucleus size: Estimated 10–30 km wide.
- Age: Nearly twice as old as Earth, making it one of the oldest comets ever observed.
Breakthrough Discovery: Water Signature Detected
How was it detected?
- Swift Observatory captured faint ultraviolet emissions from hydroxyl (OH).
- OH forms when sunlight breaks apart water molecules → indirect but strong evidence of water ice sublimation.
Why is it important?
- First chemical confirmation of water activity on an interstellar comet at such a large distance from the Sun.
- Indicates that protoplanetary systems outside the Solar System may share similar chemical building blocks.
Unusual Behaviour
- 3I/ATLAS was losing water at ~40 kg per second even when far beyond the usual frost line where comets become active.
- Suggests:
- Presence of small icy grains being heated by sunlight,
- Complex physical and chemical processes not seen in typical comets.
Scientists noted its activity “defies our models”, indicating new insights into comet evolution.
Significance for Planetary Science & Astrobiology
- Strengthens the idea that organic chemistry and water—key ingredients for life—are common across the Galaxy.
- Provides clues on:
- Composition of ancient planetary systems,
- How water and organics travel between stars,
- Early stages of planet formation.
3I/ATLAS acts as a “messenger” from another star, preserving primordial material from its home system.
Interstellar Objects:
- Formed outside the Solar System and travel through it.
- Not gravitationally bound → follow open-ended hyperbolic trajectories.
- Have a perihelion (closest approach to Sun) but no aphelion.
- Often ejected from their home systems due to collisions or gravitational slingshot events.
Port of Pasni
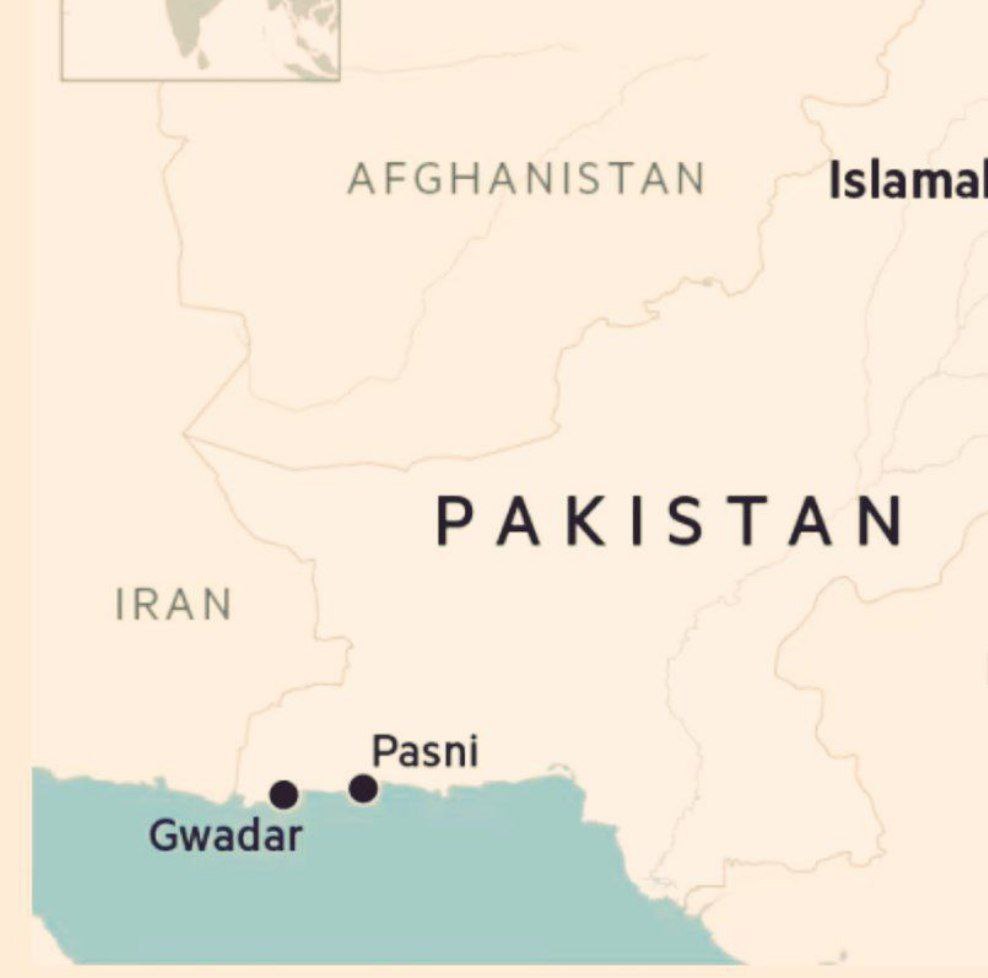
- 12 Oct 2025
In News:
Pakistan’s recent diplomatic engagements indicate a marked shift in its foreign policy priorities. The country, traditionally aligned with China under the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) framework, is now attempting to re-engage with the United States. Central to this emerging realignment is Islamabad’s reported proposal to allow the US to develop a new port at Pasni in Balochistan — a move that carries significant geopolitical and strategic ramifications.
The Pasni Port Proposal: Redefining Strategic Partnerships
Pakistan has reportedly offered the United States the opportunity to build and operate a port at Pasni, a deep-water harbour located on the Arabian Sea in Balochistan’s Gwadar district.
- The proposed port is around 70 miles east of China-operated Gwadar Port and approximately 100 miles from Iran’s border.
- The initiative aims to reduce Pakistan’s dependence on China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), attract American investment, and open access to critical mineral exports from Balochistan.
- Plans for a railway linkage between Pasni and the hinterland have also been discussed to enhance trade connectivity.
If realised, this project would grant Washington a strategic maritime foothold in the region — an area of growing competition among global powers.
The Emerging Maritime Triangle: Pasni–Gwadar–Chabahar
Pasni’s location gives rise to a new maritime triangle involving:
- Gwadar Port – a China–Pakistan venture central to the CPEC framework;
- Chabahar Port – a joint India–Iran initiative providing access to Afghanistan and Central Asia; and
- Pasni Port – potentially linked to US–Pakistan cooperation.
This triad places China, the US, and India in close operational proximity, turning the northern Arabian Sea into a strategic hotspot where economic corridors overlap with geopolitical rivalries.
Economic Drivers: The Mineral Dimension
Balochistan is rich in rare earth elements and critical minerals, crucial for high-tech manufacturing and green technologies.
- During recent engagements in Washington, Pakistan’s leadership reportedly showcased samples of these minerals to US officials in an attempt to secure American investment.
- The proposal reflects a shift in Pakistan’s economic diplomacy — reoffering projects once promised to China now to the United States.
This “resource diplomacy” underlines Islamabad’s efforts to diversify partnerships amid economic distress and debt dependence on China.
Domestic Political Motivations
The overtures toward Washington also have domestic political undertones.
- The civil–military establishment, led by Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif and Army Chief General Asim Munir, faces questions of legitimacy and stability at home.
- Closer ties with the US are seen as a way to gain international backing and financial relief.
- However, the leadership’s willingness to reconsider Pakistan’s stance on issues like recognition of Israel under the Abraham Accords has invited domestic criticism for allegedly compromising national principles and Palestinian solidarity without parliamentary approval.
Regional Reactions and Strategic Fallout
China’s Concerns
- Beijing views the Pasni initiative as undermining CPEC and encroaching upon its sphere of influence.
- A potential US presence near Gwadar and close to Xinjiang’s western frontier could be perceived as a strategic encirclement.
Iran’s Apprehensions
- Pasni’s proximity to the Iranian border raises concerns in Tehran, which already faces tensions with the US.
- The project could alter the regional balance and complicate Iran’s trade interests via Chabahar.
India’s Calculations
- India’s Chabahar Port project could lose strategic relevance if the Pasni initiative attracts significant US investment and attention.
- The US’s ambiguous stance on the Chabahar sanctions waiver further limits India’s operational space in the region.
Afghanistan’s Position
- The Taliban government may cautiously welcome US economic engagement but will resist any renewed American military presence, such as at Bagram Airbase.
Security Implications: Risk of Regional Instability
Balochistan already faces persistent challenges, including:
- Baloch insurgency,
- Militant violence in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and
- Ethnic and sectarian tensions.
Introducing American infrastructure and personnel into this volatile setting could exacerbate local grievances and trigger a new phase of proxy competition between the US and China.
Such dynamics risk turning Balochistan into a geostrategic flashpoint and further destabilising Pakistan’s internal security landscape
Super Typhoon Ragasa
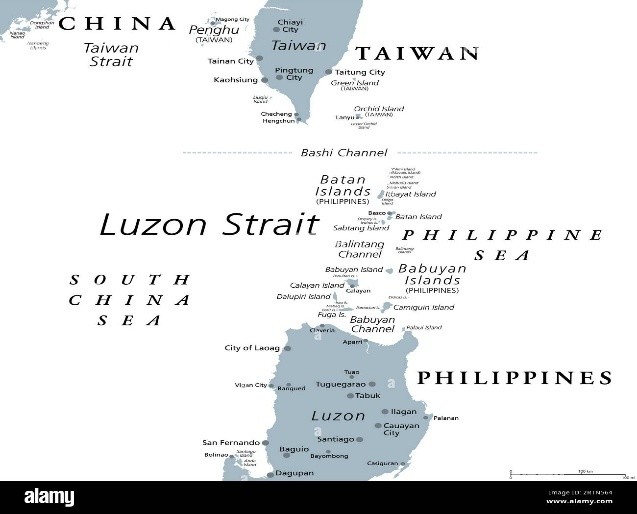
- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
Super Typhoon Ragasa—locally known as Nando—has emerged as one of the most powerful storms to strike Southeast Asia in recent years. With sustained winds exceeding 200 km/h and gusts up to 250 km/h, it has prompted large-scale shutdowns across the Philippines and Hong Kong, highlighting the region’s vulnerability to climate-induced extreme weather events.
About Super Typhoon Ragasa
- Category: 5 (the highest on the Saffir-Simpson scale)
- Wind Speed: Sustained winds of around 205 km/h, gusting up to 250 km/h.
- Origin: Formed over the western Pacific Ocean, where warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear facilitated rapid intensification.
- Track: Moving northwestward across the Luzon Strait, impacting the Babuyan Islands in northern Philippines before heading toward southern China, including Hong Kong.
Regional and Environmental Significance
- The increasing intensity of storms like Ragasa reflects the broader pattern of climate change-driven extreme weather in the western Pacific region.
- Rising sea surface temperatures and shifting atmospheric circulation patterns have led to more frequent and severe typhoons, posing long-term challenges to disaster preparedness and coastal infrastructure resilience in densely populated regions like Luzon and Hong Kong.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Early Warning Systems: Enhanced forecasting and community-based alert dissemination can save lives in coastal and island regions.
- Climate Adaptation Infrastructure: Investment in storm-resilient housing, flood barriers, and sustainable urban planning is critical for mitigating recurring damage.
- Regional Cooperation: Shared meteorological data and coordinated disaster response among ASEAN nations, China, and Pacific island states can improve resilience.
MERITE Scheme

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the Multidisciplinary Education and Research Improvement in Technical Education (MERITE) Scheme with a total outlay of ?4,200 crore (2025–26 to 2029–30). This includes ?2,100 crore World Bank loan assistance. The scheme seeks to transform India’s technical education landscape in line with the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
Coverage
- Institutions: 275 government/government-aided technical institutions (175 engineering institutions + 100 polytechnics).
- Beneficiaries: Around 7.5 lakh students across all States and Union Territories.
- Stakeholders: National Institutes of Technology (NITs), State Engineering Institutions, Affiliating Technical Universities (ATUs), with implementation support from IITs, IIMs, AICTE, and NBA.
Objectives
- Improve quality, equity, and governance in technical education.
- Align curricula with labour market requirements.
- Strengthen the research and innovation ecosystem.
- Support State/UT technical education departments in digitalization and quality assurance.
Key Focus Areas
- Digital Transformation: ICT-enabled learning, blended teaching models.
- Multidisciplinary Programs: Introduction of NEP-2020 aligned technical courses.
- Skill & Employability Enhancement: Internships, industry-linked curricula, language labs, skill/maker labs.
- Research and Innovation: Establishing research hubs, incubation centres, innovation labs.
- Faculty & Governance: Faculty development programs, creation of academic administrators with focus on women leadership.
- Accreditation & Quality Assurance: Strengthening institutional governance and accountability.
Expected Outcomes
- Increased student employability and higher placement rates.
- Improved research output and innovation ecosystem.
- Greater equity and inclusion in technical education, with emphasis on reducing gender gaps and digital divide.
- Enhanced global competitiveness of Indian technical institutions.
Employment Generation Impact
By modernising technical education and strengthening linkages with industry, MERITE is expected to:
- Improve fresh graduates’ placement prospects.
- Foster entrepreneurship through incubation and innovation centres.
- Contribute to reducing unemployment among engineering graduates.
Background and Significance
India’s sustainable and inclusive growth hinges on technological advancement, which demands upgraded academic and research standards. MERITE builds upon NEP-2020 reforms such as curriculum revamp, skill development, interdisciplinary learning, and enhanced governance. Importantly, it integrates global expertise through the World Bank partnership.
The scheme also ensures participatory governance, incorporating feedback from States/UTs during policy design, thereby strengthening cooperative federalism in higher education reform.
Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR)

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently carried out a 7-day Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) auction worth ?1 lakh crore. This measure was taken to manage the surplus liquidity in the banking system, which had surged to approximately ?3.75 lakh crore.
What is VRRR?
The Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) is a liquidity management tool employed by the RBI to absorb excess funds from commercial banks for a specified period. Unlike the fixed reverse repo rate, the VRRR rate is determined through an auction mechanism, allowing market forces to decide the interest rate.
Key Characteristics:
- Auction-Based Interest Rate: Interest is not fixed but discovered through competitive bidding.
- Time-Bound Operation: Typically conducted for durations like 7, 14, or 28 days.
- Liquidity Management Tool: Helps the RBI withdraw excess liquidity from the financial system.
- Repo Rate Ceiling: The interest rate in VRRR operations cannot exceed the current repo rate.
- Flexible Tenor: RBI may modify the duration of VRRR auctions based on prevailing liquidity conditions.
Objective of VRRR
- To mop up surplus liquidity from the banking system.
- To help regulate short-term interest rates and support effective transmission of monetary policy.
- To foster a market-driven interest rate environment in the short-term interbank market.
How VRRR Functions
- Auction Announcement: RBI declares the amount and duration of the VRRR operation.
- Bid Submission: Banks submit bids with the amount and the interest rate at which they are willing to park funds with RBI.
- Rate Determination: RBI accepts bids at or above the cut-off rate, determined by the auction.
- Interest Earnings: Banks earn interest at the accepted rate over the auction tenure.
Implications of VRRR Operations
- On the Money Market: Tightens liquidity, leading to an uptick in short-term rates such as the call money rate and TREPS.
- On the Bond Market: May cause short-term government and corporate bond yields to rise, increasing borrowing costs.
- On Banks:
- Offers an avenue to earn returns on idle funds, improving short-term profitability.
- Temporarily locks up funds, which may reduce immediate availability for lending or investment.
This mechanism is a vital part of the RBI's toolkit to maintain financial stability and ensure efficient transmission of monetary policy.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management
- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to develop a Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management (DPIP) under its supervision to curb rising instances of banking frauds in India. This aligns with broader efforts to enhance security and transparency in India’s financial ecosystem.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- Definition: DPI refers to foundational digital systems that are accessible, secure, interoperable, and designed to deliver essential public services.
- Examples in India:
- Aadhaar (Digital ID)
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- DigiLocker, CoWIN, etc.
About DPIP
- Objective:To enhance fraud risk management through real-time intelligence sharing, data gathering, and interbank coordination using advanced technologies.
- Key Features:
- Will strengthen existing fraud detection systems in the banking ecosystem.
- Enables interoperable intelligence sharing between banks and financial institutions.
- Leverages AI/ML tools and data analytics for better predictive fraud detection.
- Institutional Mechanism:
- A committee under Shri A.P. Hota has been constituted to examine various aspects of DPIP’s implementation.
- RBI Innovation Hub (RBIH) is tasked with developing a prototype, in consultation with 5–10 public and private sector banks.
Need for DPIP
- Rise in Bank Frauds:
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
- FY 2024: ?12,230 crore in frauds
- FY 2025: ?36,014 crore — almost 3x increase
- Increasing sophistication of cyber threats and fraud techniques necessitates robust preventive digital infrastructure.
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
Other RBI Initiatives to Combat Bank Frauds
Initiative Description
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Mandatory for all digital/electronic payments to ensure
secure transactions.
Zero Liability Framework Customers are not liable for losses arising from bank’s
negligence or third-party breaches.
bank.in and fin.in domains Reserved for verified bank websites to help customers
avoid phishing and fake sites.
Haemophilia A
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) has indigenously developed a simple, affordable, and rapid point-of-care test kit for the early diagnosis of Haemophilia A and Von Willebrand Disease (VWD). This development marks a significant step in improving accessible healthcare diagnostics for genetic bleeding disorders in India.
Significance of the Innovation:
- Affordable and accessible: Enables early diagnosis at primary health centres and in low-resource settings.
- Supports Universal Health Coverage: Improves detection and timely treatment, reducing morbidity.
- Make in India in Health Sector: A boost to indigenous biomedical research and diagnostics.
About Haemophilia A
What is it?
- A hereditary bleeding disorder caused by insufficient levels of Factor VIII, a protein essential for blood clotting.
- Part of the broader group of genetic conditions known as inherited coagulopathies.
Causes:
- Deficiency or dysfunction of coagulation Factor VIII in the coagulation cascade.
- Usually inherited through an altered gene passed from parents.
Genetic Transmission:
- X-linked recessive inheritance:
- Males with the defective gene express the disease.
- Females are typically carriers, though they may show mild symptoms.
Symptoms:
- Prolonged bleeding, often seen after circumcision or minor injuries.
- Internal bleeding, particularly into joints, causing pain and swelling.
- Other signs include:
- Nosebleeds
- Blood in stool/urine
- Bruising
- Bleeding after surgery or dental procedures
Treatment:
- Factor VIII replacement therapy: Intravenous infusion of the missing clotting factor.
- Preventive therapy (prophylaxis) to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
About Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
What is it?
- A genetic bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor (VWF), which helps platelets stick together to form blood clots.
Causes:
- Inherited from one or both parents.
- People with VWD have:
- Low levels of VWF, or
- VWF that does not function properly.
Symptoms:
- Often asymptomatic unless triggered by injury or surgery.
- Common symptoms include:
- Easy bruising
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- Heavy or prolonged menstruation (menorrhagia)
- Post-operative bleeding
- Severe cases may show:
- Internal joint bleeding
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Blood in stool (melena)
Treatment:
- No cure, but manageable with:
- Desmopressin (DDAVP) to release stored VWF.
- VWF and Factor VIII concentrates.
- Self-care measures to reduce bleeding risks.
Household Income Survey in 2026

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has announced that India will conduct its first nationwide Household Income Survey in 2026, marking a major milestone in the country’s data-driven policymaking framework.
What is the Household Income Survey?
- A comprehensive, nationwide survey aimed at collecting reliable and robust data on household income distribution across India.
- It is the first standalone survey focused specifically on income estimation, unlike earlier efforts that focused primarily on consumption and employment.
Key Implementing Bodies:
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- National Sample Survey (NSS)
- Technical Expert Group (TEG)
Historical Background:
- 1950: National Sample Survey (NSS) established to conduct large-scale household surveys.
- 1955–1970: Income data attempted in the 9th, 14th, 19th, and 24th NSS rounds but faced challenges such as underreporting.
- 1983–84: A pilot income study failed to produce scalable data due to low income estimates relative to consumption and savings.
- Past difficulties deterred the launch of a dedicated income survey—until now.
Key Features of the 2026 Survey:
- First of its kind: India’s first survey exclusively focused on household income distribution.
- Methodologically robust: Designed by the TEG, incorporating international best practices in conceptual design, sampling, and estimation.
- Use of digital tools: Integration of technology-driven data collection methods to improve precision, timeliness, and reflect the role of digital economy in income generation.
- Built on recent statistical reforms by MoSPI in areas like:
- Unincorporated enterprise surveys
- Services sector data
- Private capital expenditure
- Tourism satellite accounts
Significance of the Survey:
- Addresses a critical data gap in understanding income inequality, disparities, and growth trends.
- Supports evidence-based welfare policies, including targeted subsidies, social protection, and fiscal redistribution.
- Enhances India’s capacity for inclusive growth assessment and SDG tracking.
- Strengthens the country's statistical infrastructure, aligning it with global standards.
Training of Trainers (ToT)Programme

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to strengthen grassroots governance and fiscal autonomy, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has launched a Training of Trainers (ToT)programme in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad and the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA). The initiative aims to enhance the capacity of Panchayats to generate Own Source Revenue (OSR) under the Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA).
Key Objectives:
- Enhance financial self-reliance of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Build a cadre of Master Trainers equipped to train Panchayat-level functionaries.
- Shift local governance from a compliance-based model to proactive planning, innovation, and community engagement.
- Promote a culture of fiscal accountability, transparency, and efficient public service delivery at the grassroots level.
Core Focus Areas of Training
- Fundamentals of Own Source Revenue (OSR)
- Revenue enhancement strategiestailored to rural contexts
- Behavioural insights in tax collectionand compliance
- Revenue utilization for development and service delivery
- Village-level financial planningand Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs)
- Innovative financing mechanisms
- Project management and accountability tools
The training emphasized field orientation, peer learning, and evidence-based practices to ensure real-world applicability and long-term impact.
Institutional Reforms and Digital Integration
As part of the broader reform agenda:
- Model OSR Rules Framework is under development based on state-level legislative reviews.
- A Digital Tax Collection Portal is being created to facilitate:
- Simplified and accountable revenue collection,
- Digital integration with Panchayat-level financial systems.
Case Studies & Best Practices
The training showcased successful Panchayat-level revenue generation models from:Odisha, Gujarat, Goa, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, highlighting scalable models of local innovation.
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA): Background
A Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) launched in 2018 and revamped for 2022–2026, aimed at developing and strengthening the Panchayati Raj System across rural India.
Key Objectives:
- Build governance capacity of PRIs to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Empower Panchayat representatives for effective leadership and participatory governance.
- Enhance OSR generation and financial planning at the Panchayat level.
- Promote inclusive development and convergence of schemes.
- Strengthen Gram Sabhas as platforms for citizen engagement.
Salient Features:
- Emphasis on capacity-building and leadership training.
- Promotes decentralisation and compliance with the PESA Act, 1996.
- Encourages use of technology-driven solutions for governance.
- Recognises and incentiviseshigh-performing Panchayats.
- Facilitates collaboration with international and national institutions.
Strengthening Inclusive Education for Children with Disabilities in India

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major step towards inclusive education, the Government of India signed a tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in 2025 between the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), and National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). The MoU aims to enhance curriculum reform, institutional coordination, and accessibility for children with disabilities across India’s education system.
What is Inclusive Education?
Inclusive education refers to a model where children with and without disabilities learn together in mainstream classrooms. It is supported by adapted curricula, accessible infrastructure, and individualised support mechanisms. The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016 legally mandates inclusive education environments in India.
Why Inclusive Education Matters
Inclusive education is not merely a policy choice but a constitutional, social, and developmental imperative:
- Right to Education: Under Article 21A of the Constitution and the RTE Act, 2009, every child aged 6–14 has the right to free and compulsory education. This includes children with special needs (CWSN).
- Equity and Access: Reports by UNESCO highlight that 29 million children are out of school in South Asia, many of them with disabilities. Ensuring their inclusion addresses systemic exclusion.
- Social Transformation: Inclusive classrooms reduce stigma, promote empathy, and facilitate social acceptance of persons with disabilities.
- Human Capital Development: Educating CWSN enhances their ability to participate in the economy, contributing to innovation, productivity, and nation-building.
- Global Commitments: India has ratified the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD, 2007) and is committed to SDG 4, which seeks inclusive and equitable quality education for all by 2030. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 also stresses disability inclusion at all education levels.
Key Data Points Highlighting the Need for Intervention
- According to the 2011 Census, around 7% of Indian children (0–19 years) have disabilities. However, data from UDISE+ 2019–20 reveals that less than 1% of children enrolled at the primary level are children with disabilities.
- In 2018–19, around 21 lakh CWSN were covered under Samagra Shiksha, supported by only 27,774 special/resource teachers across the country. This highlights the urgent need for both greater coverage and trained human resources.
Government Initiatives Promoting Inclusive Education
- The 2025 MoU between DEPwD, NIOS, and NCERT is aimed at reforming the curriculum to accommodate diverse learners. It also recognises special schools run under the Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS) as SAIEDs (Schools for Accessible and Inclusive Education for Disabled), expanding academic options for CWSN.
- The National Education Policy 2020 mandates the integration of children with disabilities in regular classrooms and promotes universal access and equity.
- Under Samagra Shiksha, the government provides financial support of ?3,500 per CWSN annually. Additional provisions include stipends for girls (up to Class XII), appointment of special educators, resource rooms, and home-based education for children with severe disabilities.
- NCERT’s Barkha Series, based on the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework, offers accessible reading materials in both print and digital formats, tailored to the diverse needs of learners.
- The RPWD Act 2016 mandates the creation of inclusive learning environments, with accessible buildings, assistive devices, and necessary support services.
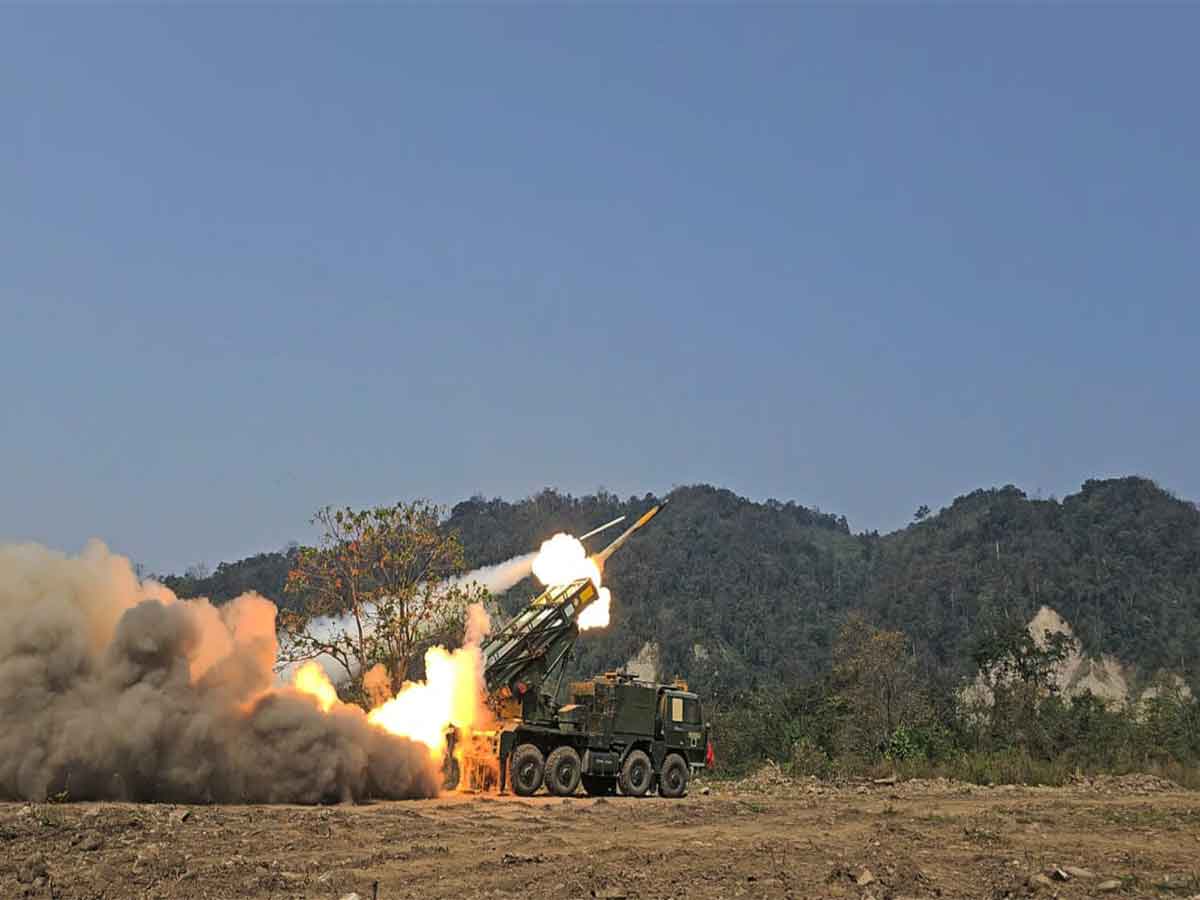
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
4th India–Central Asia Dialogue (2024)
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
India hosted the 4th edition of the India–Central Asia Dialogue in New Delhi, chaired by External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar. The event emphasized regional security, connectivity, critical minerals, counter-terrorism, and economic integration.
What is the India–Central Asia Dialogue?
- Type: Multilateral forum for structured engagement between India and Central Asian republics.
- Initiated in: 2019, Samarkand (Uzbekistan).
- Participants: India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
Key Objectives:
- Strengthen cooperation in trade, connectivity, security, energy, health, and technology.
- Promote regional stability, counter-terrorism collaboration, and sustainable development.
- Enhance people-to-people ties and institutional coordination.
Major Outcomes of the 4th Dialogue:
- Security Cooperation:
- Condemned terror attacks (e.g., Pahalgam).
- Called for early adoption of the UN Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism.
- Critical Minerals & Rare Earths:
- Joint intent for collaboration in exploration and investment.
- Decision to hold the 2nd India–Central Asia Rare Earth Forum soon.
- Connectivity & Trade:
- Focus on using the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and Chabahar Port.
- Supported Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan's inclusion in INSTC.
- Digital & Financial Integration: Agreement to boost digital payments, interbank ties, and trade in local currencies.
- Health and Traditional Medicine: Shared commitment to Universal Health Coverage, medical tourism, and integration of AYUSH systems.
- Clean Energy & Technology: Cooperation on platforms like India Stack, International Solar Alliance, and biofuels.
- Multilateral Support: Reiterated support for India’s permanent seat in UNSC and active role in SCO and UN.
Amrit Bharat Scheme
- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS), launched to transform railway stations across India into world-class travel hubs, has achieved a key milestone. Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw announced the completion of redevelopment work at 104 stations out of the planned 1,300 stations under the scheme.
About the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme
- Launched: 2023
- Objective: Comprehensive redevelopment of railway stations to:
- Upgrade passenger amenities
- Enhance multi-modal connectivity
- Modernize infrastructure with sustainable and accessible design
Key Updates (As of April 2025)
- Total stations under ABSS: 1,300
- Stations with completed redevelopment: 104
- Stations in Maharashtra: 132 (significant progress reported)
Major Highlights
Feature Details
Notable Station Project Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus (CSMT), Mumbai
CSMT Redevelopment Cost ?1,800 crore
Modern Facilities Planned Waiting lounges, food courts, clean restrooms, lifts, escalators,
digital signage
International Comparison CSMT post-redevelopment projected to surpass
London’s Kings Cross station
Additional Infrastructure Developments in Maharashtra
- Gondia–Ballarshah Railway Line Doubling:
- Length: 240 km
- Region: Vidarbha
- Approved Investment: ?4,819 crore
- Strategic Importance: Enhances connectivity and freight movement
Centre–State Collaboration
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Government of India and Government of Maharashtra for railway project implementation and coordination.
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for the issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities. This includes instruments such as social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, aiming to boost responsible financing in India.
Understanding ESG Debt Securities
Definition:
ESG debt securities are financial tools designed to raise capital specifically for projects that yield positive environmental, social, or governance (ESG) outcomes. These instruments are a key part of sustainable finance, with categories including:
- Social Bonds: Focused on projects with direct social impact (e.g., affordable housing, education).
- Sustainability Bonds: Target projects with both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Tied to specific ESG performance indicators or targets.
Salient Features:
- Funds raised must be used exclusively for eligible ESG-aligned projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled in line with the project's primary focus.
- Compliance with global ESG norms and standards is mandatory.
- Verification or certification by an independent third-party is required.
- The framework applies to both public and private debt offerings.
Highlights of SEBI’s Framework
1. Classification Guidelines: Issuers are required to categorize their bonds—green, social, or sustainability—based on the core objective of the projects being financed. This ensures transparent communication of the bond's intended impact.
2. Disclosure Norms:
- At the Issuance Stage: Offer documents must detail project eligibility, selection methodology, and a tentative allocation between financing new initiatives and refinancing existing ones.
- Post-Issuance: Issuers must provide annual updates on fund deployment and report impact metrics to demonstrate accountability and transparency.
3. Independent Assurance: Issuers must engage accredited third-party entities to validate the alignment of bonds with ESG principles, thereby enhancing investor confidence and market integrity.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: There is an obligation for ongoing impact assessment. Issuers must ensure the projects funded effectively contribute to reducing environmental degradation or addressing social challenges.
5. Scope and Enforcement: The framework will come into effect from June 5, 2025, and is aligned with international ESG standards to facilitate greater inflow of sustainable and ethical investments.
Significance for India: This move marks a significant step in mainstreaming ESG finance in India. It aims to improve transparency, attract climate-conscious capital, and reinforce India’s commitment to sustainable development.
C CARES Version 2.0
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Coal recently launched C CARES Version 2.0, a significant upgrade to the Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization’s (CMPFO) digital platform. The new system aims to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accessibility in provident fund (PF) and pension disbursement for coal sector workers.
Key Features of C CARES Version 2.0
- Developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in collaboration with the State Bank of India (SBI).
- Provides a unified digital interface for coal workers, coal companies, and CMPFO.
- Enables real-time claim tracking, automated ledger updates, and direct benefit transfers to workers’ bank accounts.
- Includes a mobile application for CMPF members, offering:
- PF balance checks
- Profile viewing
- Grievance redressal
- Claim status tracking
- A chatbot assistant for easy navigation
Benefits to Stakeholders
- For Workers: Faster claim settlement, improved access, and reduced delays in PF/pension disbursement.
- For Coal Companies and CMPFO:
- A prescriptive dashboard to generate custom reports.
- Analytics to track settlement trends.
- Support for data-driven decision-making.
About CMPFO
- Full Form: Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization
- Established: 1948
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Coal
- Function: Administration of PF and pension schemes for coal sector employees.
- Coverage:
- Serves around 3.3 lakh PF subscribers
- Supports over 6.3 lakh pensioners
Significance
Union Minister for Coal and Mines G. Kishan Reddy launched the portal on June 4, 2025, stating that it aligns with the Government's vision of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance” under the Digital India initiative. The platform strengthens social security delivery for coal workers and brings administrative reform to a critical sector of the economy.
Exercise PrachandPrahar (2025)

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
Exercise PrachandPrahar was a tri-service integrated multi-domain military exercise conducted by the Indian Armed Forces in the high-altitude terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, along the Northern Borders, specifically under the Eastern Army Command.
Timeline:
- Held: March 25–27, 2025
- Preceded by:Exercise PoorviPrahar (November 2024), which focused on integrated aviation asset application.
Objective:
To validate integrated operational capabilities of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, and enhance India's preparedness for future warfare scenarios along the 3,488-km long Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Key Highlights:
- Location: High-altitude Himalayan terrain, eastern sector of the LAC in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Forces Involved:
- Indian Army (including Special Forces)
- Indian Air Force (IAF)
- Indian Navy
Major Components:
- Surveillance and Domain Awareness:
- Long-range surveillance aircraft (IAF)
- Maritime domain awareness aircraft (Navy)
- Helicopters and UAVs
- Space-based assets
- Precision Strike Capabilities:
- Fighter aircrafts
- Long-range rocket systems
- Medium artillery
- Armed helicopters
- Swarm drones
- Loitering munitions
- Kamikaze drones
- Operational Environment:
- Simulated electronic warfare and contested conditions.
- Focus on jointness, precision, and rapid response.
Strategic Importance:
- Demonstrated seamless command, control, and coordination among the three services.
- Validated the ability to conduct multi-domain operations (MDO) in challenging terrain.
- Reinforced India’s technological edge and combat readiness along strategic frontiers.
Ayurveda Day

- 18 May 2025
In News:
The Government of India has officially fixed September 23 as Ayurveda Day, replacing the earlier practice of celebrating it on Dhanteras, which follows a variable lunar calendar. This change, notified through a Gazette notification in March 2025, aims to bring uniformity and global visibility to Ayurveda observance.
About Ayurveda Day:
- Purpose:Ayurveda Day is observed to honour India’s ancient medicinal heritage and promote Ayurveda as a scientific, evidence-based, and holistic healthcare system rooted in preventive and sustainable wellness practices.
- New Fixed Date:Starting 2025, Ayurveda Day will be celebrated every year on 23rd September, coinciding with the autumnal equinox, a day when day and night are nearly equal, symbolizing balance—a core concept in Ayurvedic philosophy.
- Why the Shift?The previous observance on Dhanteras created logistical challenges due to its annual date fluctuation (between mid-October and mid-November). The new fixed date allows for better planning and consistent global celebrations.
- Symbolism of Autumnal Equinox:The equinox represents cosmic balance and harmony, aligning with Ayurveda’s emphasis on equilibrium between mind, body, spirit, and environment.
Ayurveda: Key Facts for UPSC
- Definition:Ayurveda, meaning the “Science of Life” (from Sanskrit Ayu = life, Veda = knowledge), is a traditional Indian medical system dating back over 5,000 years, with roots in the Atharva Veda.
- Core Principles:
- SwasthasyaSwasthyaRakshanam: Maintaining the health of the healthy
- AturasyaVikaraPrashamanam: Treating diseases in the sick
- Emphasis on natural healing, diet, seasonal routines, and mind-body balance
- Key Features:
- Focus on preventive healthcare
- Use of herbal medicines, detox therapies, yoga, and meditation
- Personalised treatment based on individual constitution (Prakriti)
Significance for Global Health:
The Ministry of AYUSH envisions Ayurveda Day as a global platform to promote India’s traditional knowledge system as a part of the international wellness movement. Health professionals, researchers, academic institutions, and global partners are encouraged to participate in its observance to integrate Ayurveda into broader healthcare dialogues.
India’s First Geothermal Production Well in Northeast

- 18 May 2025
In News:
In a significant advancement for clean energy in Northeast India, Dirang in Arunachal Pradesh has become the site of the region’s first operational geothermal production well. This marks a pivotal step in utilizing Earth’s internal heat for sustainable energy generation in the eastern Himalayas.
Project Details
- Location:Dirang, West Kameng district, Arunachal Pradesh
- Terrain: Eastern Himalayan region
Technology Used
- The project employs a closed-loop binary Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system, which captures subsurface geothermal heat for applications such as:
- Electricity generation
- Space heating
- Agricultural processing
- Reservoir Temperature: Approx. 115°C — optimal for direct-use geothermal systems.
- Drilling Approach: Low-impact precision drilling aimed at fault zones between quartzite and schist rock formations.
Institutional Collaboration
- Implementing Agency:Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS), Itanagar
- Supported by:
- Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India
- Government of Arunachal Pradesh
- International partners from Norway, Iceland, and Guwahati research institutes
Significance
- First-of-its-kind in the entire Northeast region
- Potential to make Dirang energy self-reliant through clean geothermal power
- Helps replace diesel and firewood in cold climates, reducing emissions
- Can enhance agricultural productivity and living standards in high-altitude areas
- Strengthens India’s geothermal potential (~10,600 MW), offering reliable base-load renewable energy unlike solar or wind
Stagflation and Banking Sector Risks in the U.S.

- 18 May 2025
In News:
In 2025, economic analysts are raising alarms over growing signs of stagflation in the United States and its potential to trigger a renewed banking crisis similar to the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in 2023.
Unrealized Losses in U.S. Banks
As of early 2025, U.S. banks are grappling with $482.4 billion in unrealized losses from securities investments, according to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). This marks a 32.5% rise from the previous quarter. The figure is approaching the $515 billion mark observed during the SVB crisis and could rise to $600–700 billion if interest rates hit 5%.
These losses are primarily linked to long-term securities like government bonds, whose prices have fallen due to rising benchmark 10-year Treasury yields, now exceeding 4.5%.
What is Stagflation?
Stagflation is a rare and difficult economic condition marked by:
- High inflation
- Stagnant or negative economic growth
- High unemployment
It complicates policymaking because:
- Tightening monetary policy (raising interest rates) to control inflation can worsen unemployment and slow growth.
- Loosening policy to boost growth can further fuel inflation.
Causes of Stagflation in 2025:
- Supply Shocks – Rising input costs (e.g., energy or tariffs).
- Tariff Hikes – New U.S. tariffs on imports have raised production costs.
- Policy Missteps – Uncoordinated fiscal and monetary measures.
Impacts on the Financial Sector
- Reduced Bond Values: High interest rates lower the market value of banks’ bond holdings.
- Risk of Bank Runs: Diminished asset values can trigger depositor panic.
- Credit Losses: Particularly in sectors like tech and venture capital where firms have weak earnings and poor debt coverage.
- Liquidity Crisis: A sudden negative news cycle could lead to another SVB-like collapse.
Experts warn that continued high interest rates could deepen banking stress and prolonged stagflation could amplify credit defaults.
International Labour Day (May Day)
- 02 May 2025
In News:
International Labour Day, also known as May Day, is observed annually on May 1 to honor the dedication and contributions of workers across the globe.
Key Highlights:
- Observed On: May 1
- Also Known As: International Workers’ Day, May Day
- Purpose: To commemorate the contributions of workers and honor the global labor movement's struggles and achievements.
Historical Background
- Origin: The roots of International Labour Day trace back to Chicago, USA, where on May 1, 1886, workers launched a strike demanding an 8-hour workday.
- The protest culminated in the Haymarket Affair on May 4, 1886, when a bomb explosion led to the deaths of six police officers and several civilians, marking a major milestone in labor rights activism.
- In 1889, the Second International (Paris) declared May 1 as a day of international workers’ solidarity.
Global Observance
- Observed in over 160 countries, including India, China, Cuba, France, Germany, Brazil, South Africa, Russia, Vietnam, among others.
- Celebrated through parades, union meetings, and public demonstrations advocating workers’ rights and social justice.
Country-wise Observance Differences
- India: First observed in 1923 in Chennai by the LabourKisan Party of Hindustan. It is a public holiday, widely recognized across the country.
- United States: Despite its historical origin, the U.S. celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, officially declared in 1894 after the Pullman Strike. The shift was made to distance the holiday from socialist and communist affiliations.
- Canada: Also celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, following U.S. traditions, though May 1 has some informal recognition by trade unions.
- United Kingdom: Celebrates a related holiday called the Early May Bank Holiday on the first Monday of May, which may or may not fall on May 1. It is not explicitly labor-themed like in other countries.
Significance
- Serves as a global reminder of workers’ rights, the historical fight for humane working conditions, and the ongoing struggles of labor communities.
- Symbolizes solidarity among workers across nations, cutting across political ideologies and economic systems.
Sahkar Taxi

- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The government has announced the upcoming introduction of ‘Sahkar Taxi’, a cooperative-based ride-hailing platform designed to directly benefit drivers by eliminating intermediary commissions.
What is ‘Sahkar Taxi’?
‘Sahkar Taxi’ is a ride-hailing service supported by the government, operated through cooperative societies. Unlike conventional app-based services such as Ola and Uber, this platform allows drivers to retain their full earnings, without deductions by middlemen or aggregators. It draws inspiration from existing app-based models but is fundamentally driven by cooperative principles.
Why is ‘Sahkar Taxi’ Needed?
- Concerns Over Commission Charges: Leading ride-hailing apps have faced criticism for imposing high commission fees, reducing the take-home earnings of drivers.
- Pricing Transparency Issues: Allegations of differential pricing based on the type of user device (e.g., iPhone versus Android) have sparked doubts regarding fairness and transparency.
- Driver Challenges: Centralized control by large platforms often leaves drivers with limited negotiation power and inadequate income security.
Importance and Impact of ‘Sahkar Taxi’
- Driver Empowerment: By establishing a cooperative ownership model, drivers gain a stronger stake in the business, leading to improved financial stability.
- Decentralized Economic Participation: The initiative encourages local involvement and collective growth, aligning with the government’s vision of ‘Sahkar Se Samriddhi’ (Prosperity through Cooperation).
- Sustainable Alternative: It presents a viable, inclusive option to the dominant profit-driven ride aggregator market, focusing on equitable benefit sharing.
- Enhanced Consumer Confidence: The cooperative framework promotes transparent pricing and greater accountability in digital service delivery, fostering trust among users.
India’s First Indigenous MRI Scanner Installed at AIIMS
- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
AIIMS New Delhi is set to install India’s first indigenously developed MRI scanner for clinical evaluation by October 2025. This marks a major milestone under the government's push for import substitution and promotion of ‘Make in India’ in the medical device sector.
Key Highlights:
- MRI Type: 1.5 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) system.
- Developed by: SAMEER (Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research), an autonomous R&D institution under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Initiative under: National Mission SCAN-ERA (Swadeshi Chumbakiya Anu-naadChitran – EkRashtriyaAbhiyaan), launched in December 2014.
- Purpose: Clinical evaluation and performance feedback at AIIMS to refine the system for wide-scale clinical use.
- Objective: Reduce dependence on imported diagnostic equipment and lower treatment costs.
Significance:
- Currently, 80–85% of India's medical devices are imported.
- In FY 2023–24, India’s medical device import bill rose by 13% to ?69,000 crore.
- The initiative aligns with the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for medical devices, under which 7 critical devices (including MRI machines, CT scanners, LINACs, heart valves, etc.) are now being domestically manufactured.
- 19 PLI-supported projects have been commissioned to manufacture 46 medical devices.
MRI: How It Works
- Principle: Uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to align protons in tissues. As protons return to their original alignment, they emit signals that are captured to create detailed 3D anatomical images.
- Applications:
- Imaging soft tissues, brain, spinal cord, joints, and internal organs.
- Detecting tumors, strokes, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Functional MRI (fMRI) maps brain activity during cognitive tasks.
Safety & Limitations:
- Magnetic interference: Risky for patients with implants (e.g., pacemakers).
- Noise: Loud clicking sounds may cause discomfort.
- Claustrophobia: May cause anxiety in closed spaces; open MRI designs mitigate this.
- Contrast agents: Use of gadolinium-based agents can pose risks to dialysis patients.
India to Host FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum 2025 in Mumbai
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
- India will host the FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum (PSCF) 2025 in Mumbai from March 25-27, 2025. This event will focus on global priorities such as payment transparency, financial inclusion, and the digital transformation of financial systems.
- The forum will be a critical platform for addressing the evolving challenges of money laundering and terrorist financing through the use of digital tools and enhanced transparency.
Key Agenda
The discussions at PSCF 2025 will revolve around tackling contemporary financial crimes, including those linked to cryptocurrency-related laundering. Key topics will include:
- Strengthening Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) compliance mechanisms.
- Promoting financial inclusion through risk-based supervision of regulated entities.
- Enhancing transparency in beneficial ownership and using digital tools to bolster AML/CFT measures.
- Addressing emerging risks, including terrorist financing and proliferation financing.
The forum will also assess how the private sector can enhance information-sharing practices to address these threats more effectively.
About FATF
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris, is an intergovernmental body that sets international standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF’s mission is to develop policies, establish guidelines, and promote global cooperation to mitigate the financial risks associated with these crimes.
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Membership: FATF has 39 member countries, including major economies such as the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Germany, and theEuropean Union.
- Regional Bodies: In addition to its direct members, FATF affiliates over 180 countries through FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs) like the Asia Pacific Group (APG) and the Eurasian Group.
- FATF Recommendations are recognized as the global standard for AML/CFT measures.
FATF evaluates countries' efforts to comply with these standards, providing assessments and promoting policy changes to counteract financial crimes. Countries that fail to comply may be placed on the grey list or blacklist.
FATF Grey and Black Lists
Countries that fail to meet FATF standards are placed on one of two lists:
- Black List: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs), which directly support terrorist financing and money laundering. North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar are currently on this list.
- Grey List: Countries considered at risk of supporting financial crimes but not yet fully engaging in those activities. Being on the grey list serves as a warning, with the risk of moving to the blacklist if improvements are not made.
Countries on the blacklist face severe international sanctions, including restrictions on financial aid and economic interactions from organizations like the IMF, World Bank, and Asian Development Bank.
India's Role in FATF
India became a member of FATF in 2010 and has made significant strides in improving its AML/CFT frameworks. In 2024, FATF acknowledged India’s efforts towards anti-money laundering and countering terrorist financing, placing it in the "regular follow-up" category for continued compliance.
The upcoming PSCF 2025 will be a milestone in India’s ongoing commitment to global financial security, as it seeks to enhance international collaboration and discuss innovative ways to address evolving threats in financial crimes.
Open Market Operations
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a liquidity injection of ?1.9 lakh crore into the banking system through Open Market Operations (OMOs) and USD/INR forex swaps, in response to tightening liquidity conditions observed since December 2024.
What are Open Market Operations (OMOs)?
- Open Market Operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities in the open market by the central bank to regulate liquidity in the banking system.
- It is a monetary policy tool used to manage inflation and ensure financial stability.
How OMOs Work:
- To inject liquidity: RBI purchases government securities from banks, increasing their cash reserves, which lowers interest rates, encourages lending, and boosts economic activity.
- To absorb liquidity: RBI sells government securities, reducing cash reserves in the system, which raises interest rates, discourages excessive lending, and cools inflation.
RBI’s Recent Measures (March 2025):
- OMO Purchase Auctions:Government securities worth ?1 lakh crore to be bought in two tranches of ?50,000 crore each on March 12 and March 18.
- Forex Swap Auction:
- A USD/INR Buy/Sell Swap worth $10 billion with a 36-month tenor, scheduled for March 24, to inject long-term dollar liquidity.
- A similar $10 billion swap was conducted on February 28, which saw strong demand.
T-72 Tanks
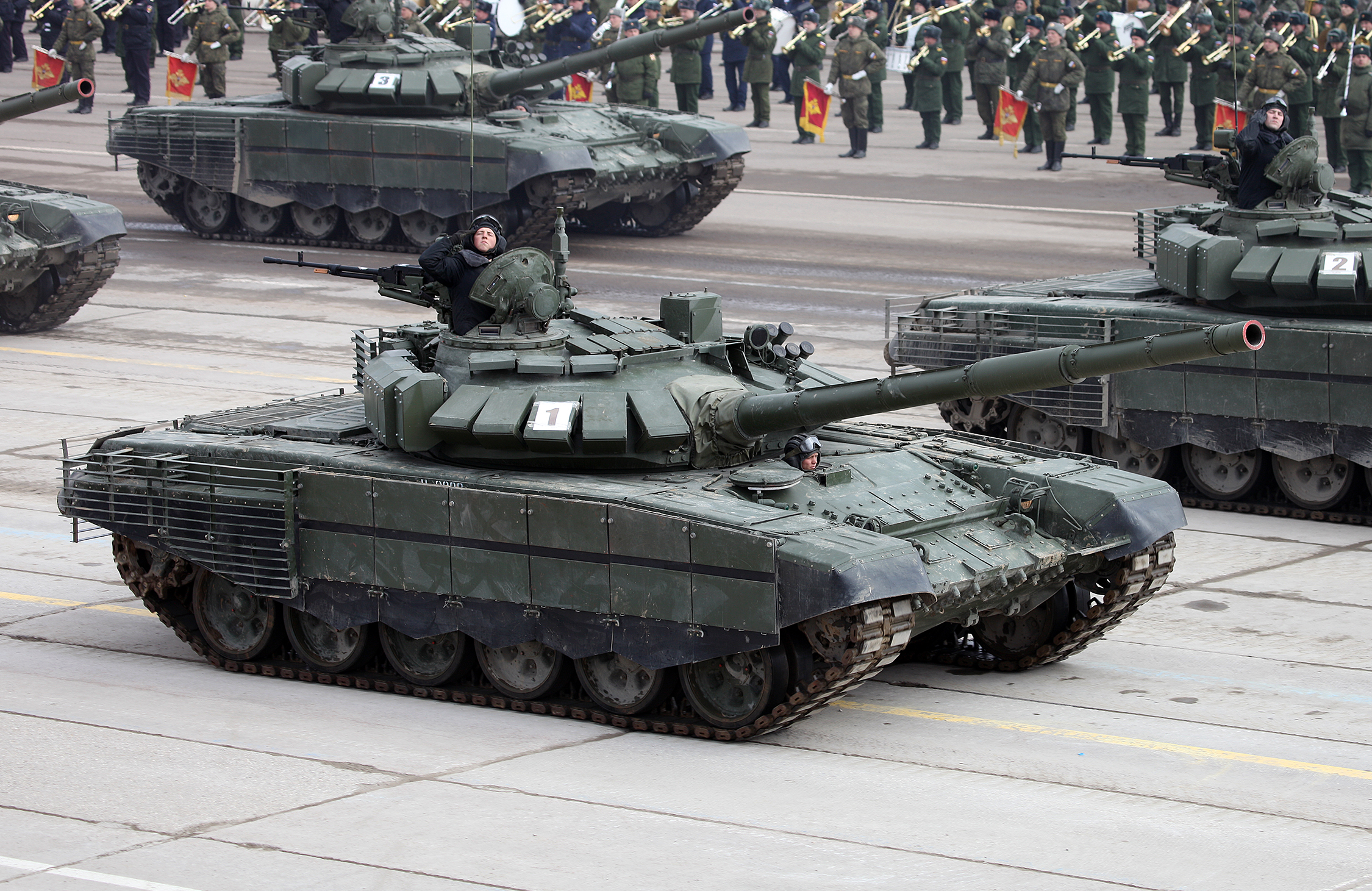

- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
India has signed a $248 million contract with Russia’s Rosoboronexport for the procurement of 1,000 horsepower (HP) engines to upgrade its fleet of T-72 main battle tanks (MBTs). This marks a significant step in enhancing the Indian Army's offensive and mobility capabilities.
Key Features of the Deal
- Engines to replace existing 780 HP ones in T-72 tanks.
- Delivered in fully formed, completely knocked down (CKD), and semi-knocked down (SKD) formats.
- Includes Transfer of Technology (ToT) to Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVNL) at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi (Chennai).
- Boosts the ‘Make in India’ initiative in the defence sector through local assembly and licensed production.
About T-72 Tanks
- Origin: Developed by the Soviet Union in the 1970s; designed by Uralvagonzavod.
- India’s Usage: Operates over 2,400 units, making it the backbone of India’s armored forces.
- Manufacturing in India: Locally produced and upgraded at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi.
Specifications
- Armament:
- 125 mm smoothbore main gun
- 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun
- 12.7 mm anti-aircraft machine gun
- Mobility: With new 1,000 HP engines, improves maneuverability and combat speed.
- Protection: Equipped with composite and reactive armour.
- Night Capability: Advanced thermal imaging systems.
- Operational Range:
- ~460 km on-road
- ~300 km off-road (with auxiliary fuel)
Strategic Significance
- Combat Readiness: Enhances battlefield performance in high-altitude and desert environments like Ladakh.
- Cost Efficiency: Upgrading older platforms is more economical than procuring new MBTs.
- India-Russia Defence Ties: Reinforces long-standing military cooperation between the two countries.
Gravehawk Hybrid Air Defense System
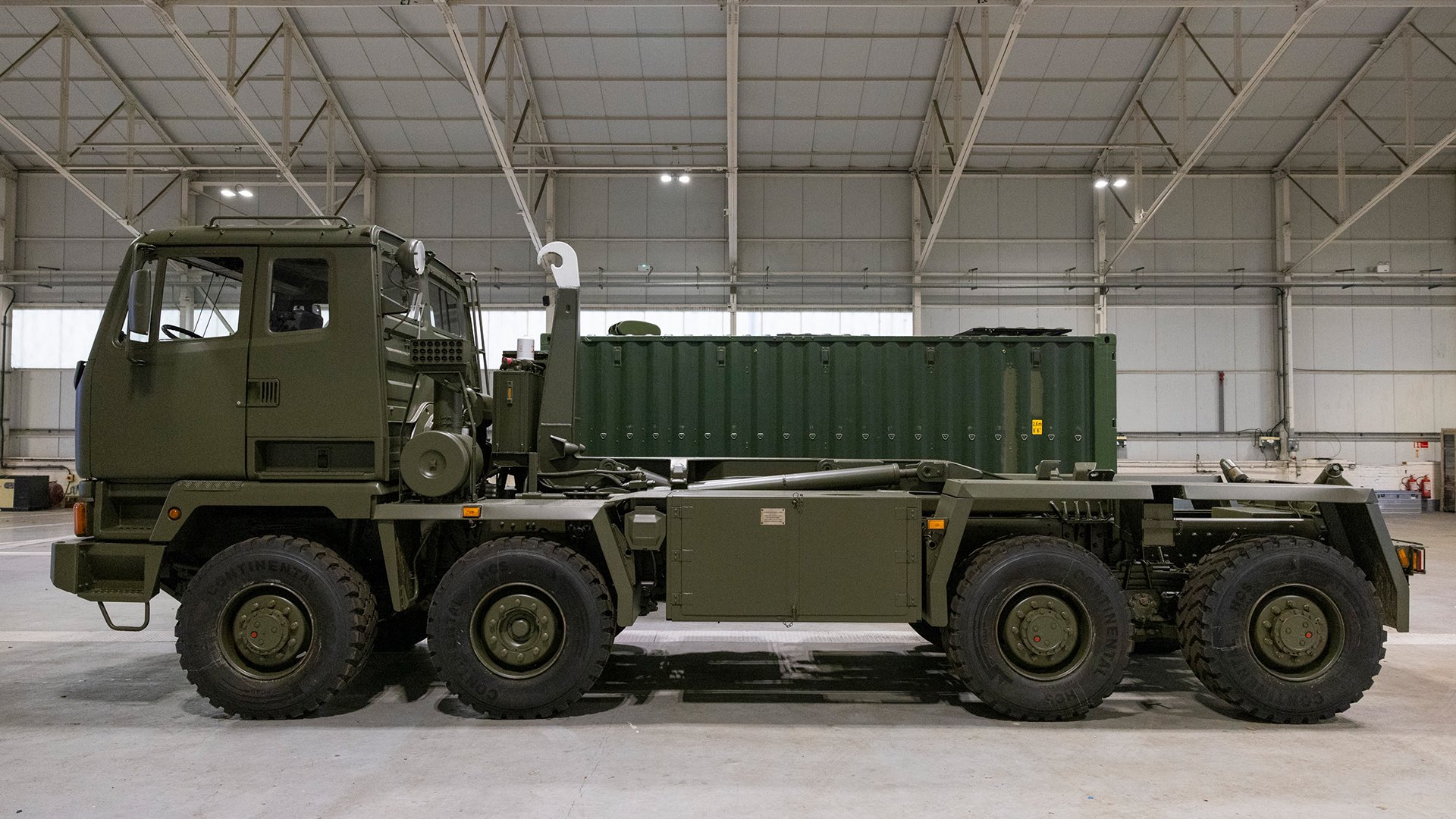

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The Gravehawk is a newly developed mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, introduced by the United Kingdom in collaboration with Denmark, to bolster Ukraine's defenses against Russian aerial threats. This innovative hybrid system exemplifies the modern trend in NATO of repurposing existing missile technology to build flexible, cost-effective, and rapidly deployable air defense platforms.
Overview and Development
- The Gravehawk system is designed to counter short-range aerial threats such as drones, cruise missiles, and low-flying aircraft.
- It combines Western and Soviet-era missile technologies, providing Ukraine with a unique edge in a contested aerial environment.
- The United Kingdom, in partnership with Denmark, is actively delivering these systems to Ukraine, with 15 additional units expected in the coming months.
- The cost per system is approximately USD 1.25 million, with Denmark covering 50% of the expense.
Key Features and Technical Capabilities
- Missiles Used: The system utilizes infrared-guided missiles including the AIM-132 ASRAAM (Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile) and the Soviet-origin R-73 (AA-11 Archer).
- Guidance System: Both missiles employ passive infrared (IR) seekers, allowing them to track heat signatures of targets without emitting radar signals, thereby reducing vulnerability to electronic warfare (EW) detection.
- Speed and Range: Missiles can reach speeds of up to Mach 2.5 and engage targets at distances of approximately 12 miles (about 19 km).
- R-73 Specifics: Originally developed for close-range dogfights, the R-73 is highly maneuverable, capable of tracking targets up to 40 km ahead and 300 meters behind, with off-boresight targeting up to 40 degrees.
- Mobility: Mounted on all-terrain Drops vehicles, the system offers rapid ground mobility and deployment flexibility.
- Containerized Launch Platform: Housed in ISO-standard shipping containers, the system’s roof rolls back to expose two missile rails—repurposed from Soviet-era fighters like the Sukhoi Su-27.
- Crew and Operation: Operated by a five-member crew, the system incorporates electro-optical and infrared targeting cameras, enabling remote operation and safe standoff missile launches.
Strategic Relevance for Ukraine
- Ukraine’s acquisition of the Gravehawk system marks a significant advancement in its air defense capabilities, particularly in the face of persistent Russian air and missile attacks.
- It enhances short-range interception capacity, allows for quick reaction deployment, and reduces dependence on continuous NATO resupplies. Additionally, the system’s use of widely available R-73 missiles ensures operational sustainability.
- The Gravehawk is part of a broader effort to field "hybrid systems", where older missile stocks are integrated into modern platforms.
- Other such initiatives include FrankenSAM programs developed by the U.S. and UK, where systems like ASRAAM have been adapted to ground-based launchers.
- Ukraine has also employed R-73 missiles on drone boats and unmanned surface vessels to target Russian air assets, showcasing the multi-domain applicability of these munitions.
Pradhan Mantri AnusuchitJaatiAbhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY)

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
It is a 100% Centrally Sponsored Scheme initiated by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. The scheme aims at the socio-economic upliftment of the Scheduled Caste (SC) communities, particularly targeting the reduction of poverty through various initiatives that focus on skill development, infrastructure, and income-generating projects.
Key Highlights:
- Launch and Funding: Launched in 2021, the scheme is fully funded by the central government, though states and Union Territories (UTs) have the option to contribute additional funds from their own resources. PM-AJAY is the consolidation of three pre-existing schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY)
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP)
- BabuJagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY)
- Objectives of PM-AJAY: The scheme is focused on improving the overall well-being of SC communities by:
- Reducing poverty through income-generating schemes, skill development, and infrastructure projects.
- Promoting social and economic development by improving literacy rates, educational enrolment, and providing better livelihood opportunities.
- Transforming SC-majority villages into model villages with integrated development, enhancing socio-economic indicators like education, healthcare, and financial inclusion.
- Eligibility Criteria
- Scheduled Caste (SC) persons living below the poverty line (BPL) are eligible for benefits.
- For infrastructure development, villages with 50% or more SC population are prioritized for grants.
- Key Components of PM-AJAY: The scheme comprises three core components:
- Adarsh Gram Development (formerly PMAGY): Aims to develop SC-majority villages into model villages with holistic improvements in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and skill development.
- Grants-in-Aid for District/State-Level Projects (formerly SCA to SCSP): Financial assistance is provided for livelihood development projects, including skill development programs and infrastructure projects, to generate sustainable income for SC communities.
- Construction of Hostels in Higher Educational Institutions (formerly BJRCY): Focuses on promoting higher education among SC students by constructing hostels in top-ranked institutions according to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF). This aims to reduce dropout rates and enhance access to quality education.
Special Provisions under the Grants-in-Aid Component
- 15% of the total grants are exclusively allocated for income-generating schemes for SC women.
- 30% of the grants are allocated for infrastructure development in SC-dominated areas.
- 10% of funds are reserved for skill development programs.
- The scheme encourages the formation of SC women cooperatives for producing and marketing consumer goods and services.
Achievements (2022-23)
- 1,260 villages were declared as Adarsh Gram in the financial year 2023-24 under the Adarsh Gram component.
- Nine new hostels were sanctioned under the Hostel Construction component.
- Perspective plans for seven states were approved under the Grants-in-Aid component.
Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Government, under the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, has introduced the Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global diamond trade, promote exports, and protect employment, especially in the MSME sector.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Boost value addition and export growth in the diamond sector.
- Support MSME exporters to compete globally.
- Retain India’s position as a global hub for diamond processing and exports.
- Mitigate recent challenges like export decline, job losses, and global demand shifts.
Key Features of the Scheme:
Feature Details
Type of Diamonds Allowed Natural cut and polished diamonds less than ¼ carat (25 cents)
Eligibility Exporters with Two Star Export House status and minimum $15 million annual exports
Export Obligation 10% value addition on imported diamonds
Duty Exemptions Exempts Basic Customs Duty, Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, etc.
Effective Date April 1, 2025
Exclusion Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs) not covered
Monitoring Agency Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC)
Why the Scheme Was Introduced:
Challenges in the Diamond Sector:
- Global: Falling demand in US, Europe, China; rise in lab-grown diamonds.
- Domestic: High unsold inventory, rising operational costs, reduced credit flow, and high corporate tax.
- Employment Impact: Job losses in the diamond cutting and polishing segment.
International Context:
- Inspired by beneficiation policies in diamond-producing countries like Botswana and Namibia, which mandate local value addition.
Significance:
- Enhances India’s role in the global diamond value chain.
- Provides ease of doing business through duty relief.
- Promotes employment generation, especially for diamond assorters and processors.
- Facilitates inclusive growth by supporting MSMEs in a traditionally export-driven industry.
Way Forward:
- Regulate Lab-Grown Diamonds to prevent market distortion.
- Extend export credit period and consider tax exemptions for foreign diamond sellers.
- Ensure technology upgradation and skill training to sustain global leadership.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
Urea Gold (ET)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent event held in Rajasthan's Sikar, the Prime Minister unveiled "Urea Gold," a novel type of Urea fertilizer.
About Urea Gold:
- Urea Gold is an advanced variety of Urea that features a Sulphur coating.
- Its primary purpose is to address soil Sulphur deficiency while also offering cost-saving benefits to farmers.
- In comparison to the existing Neem-coated urea, Urea Gold stands out due to its superior economic viability and efficiency.
- The gradual release of nitrogen facilitated by its Sulphur coating enhances crop uptake, and the inclusion of humic acid extends its fertilizing lifespan.
- Notably, Urea Gold not only acts as a substitute for traditional urea but also contributes to a reduction in overall fertilizer usage.
- According to a report, using 15 kg of Urea Gold can provide comparable benefits to 20 kg of conventional urea, making it a more efficient and effective choice for farmers.
INDIAai (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, INDIAai and Meta India entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to create a collaborative framework for cooperation and partnership in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About INDIAai:
- INDIAai, the National artificial intelligence Portal of India, was launched on 28th May 2020 as a comprehensive platform.
- It serves as a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative.
- Its primary aim is to foster unity and encourage collaborations within India's AI ecosystem by bringing together various entities.
- This joint initiative is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
- NeGD, established in 2009 under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY), plays a crucial role in this venture.
- NASSCOM, a prominent not-for-profit industry association, serves as the apex body for India's IT and IT-enabled products and services sector.
- INDIAai functions as the central knowledge hub for artificial intelligence and related fields, catering to aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and all other stakeholders in the domain.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science: It involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
- Machine Learning and Algorithms: AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data, learn from it, and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Applications in various fields: AI finds applications in diverse domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, robotics, healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles, among others. Its goal is to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making.
Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The synchronization of the 660-MW unit-2 of the 1,320-MW Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) with the electricity grid in Bangladesh was recently announced by the state-owned engineering firm Bharat Heavy Electricals.
- Location:
- It is situated in Rampal, in the Bagerhat district of Bangladesh's Khulna division.
- It will be one of the biggest coal-fired power plants in Bangladesh, along with the Payra Power Plant in Pataukhali, which commenced test production in January 2020.
- Capacity and Cost:
- The power station has a capacity of 1320 MW (2x660 MW) and is estimated to cost around $2 billion.
- Financing Plan:
- The project is being developed under India's tax concessions finance plan, aiming to enhance Bangladesh's national grid by an additional 1320 MW.
- Financed through a £1.3bn ($1.6bn) loan from the Export-Import (EXIM) Bank of India.
- Implementing Entity:
- India’s Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is responsible for constructing the power plant on behalf of Bangladesh-India Friendship Electricity Company Private Limited (BIFPCL).
- Commercial Operation:
- The first unit of the super thermal power plant is expected to commence commercial operation in early October, representing a significant milestone in the growing cooperation between India and Bangladesh in the power industry.
- Future Expansion:
- In the subsequent year, the power plant's Unit-II, also known as the Rampal coal-fired power project, is scheduled for implementation.
