Gwada Negative
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark discovery for transfusion science, France’s national blood agency (Établissement Français du Sang – EFS), in June 2025, identified a completely new blood group system. Officially recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as the 48th blood group system, it is termed EMM-negative and is informally called “Gwada Negative”, after Guadeloupe, the origin of the only known individual with this blood type.
What is Gwada Negative (EMM-negative)?
- EMM-negative is defined by the absence of the EMM antigen, a high-incidence antigen normally present on red blood cells in nearly all humans.
- High-incidence antigens are so common that individuals lacking them are considered extremely rare and face critical challenges in blood transfusion compatibility.
- The ISBT registered this as ISBT042, making it the latest addition to global blood group systems.
Discovery Timeline
- 2011: A 54-year-old woman from Guadeloupe, living in Paris, underwent pre-surgical blood testing. Her blood showed unidentified antibodies that did not match any known blood group systems.
- 2019: With advancements in Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), researchers led by Dr. Thierry Peyrard (EFS) identified the unique genetic mutation responsible for the absence of the EMM antigen.
- 2025: After peer-reviewed validation, the ISBT officially recognised the EMM-negative system during its Milan meeting.
Why is it So Rare?
- This woman is the only known person in the world with the EMM-negative blood type.
- She inherited the rare gene mutation from both parents, leading to a complete absence of the EMM antigen in her red blood cells.
- Since the EMM antigen is nearly universal, her blood is compatible only with itself, making transfusions extremely high-risk unless a genetically identical donor is found.
Clinical Significance
- Individuals lacking high-incidence antigens like EMM may develop alloantibodies — immune responses against transfused red cells containing those antigens.
- Transfusion of EMM-positive blood into such individuals can cause hemolytic reactions, including life-threatening hemolysis (premature red blood cell breakdown).
- In this case, no donor blood currently available is safe for transfusion into the patient.
Implications for Transfusion Medicine
- Highlights the need for rare blood donor registries, international cooperation, and advanced genetic screening technologies to identify such rare phenotypes.
- Encourages development of precision-matching protocols in complex clinical and emergency situations.
- Expands the understanding of human immunohematological diversity and redefines transfusion compatibility standards.
Subarnarekha River
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
A flash flood in the Subarnarekha River affected over 50,000 people in Balasore district, Odisha. The flooding was triggered by heavy rainfall and the release of water from Chandil Dam in Jharkhand.
About Subarnarekha River
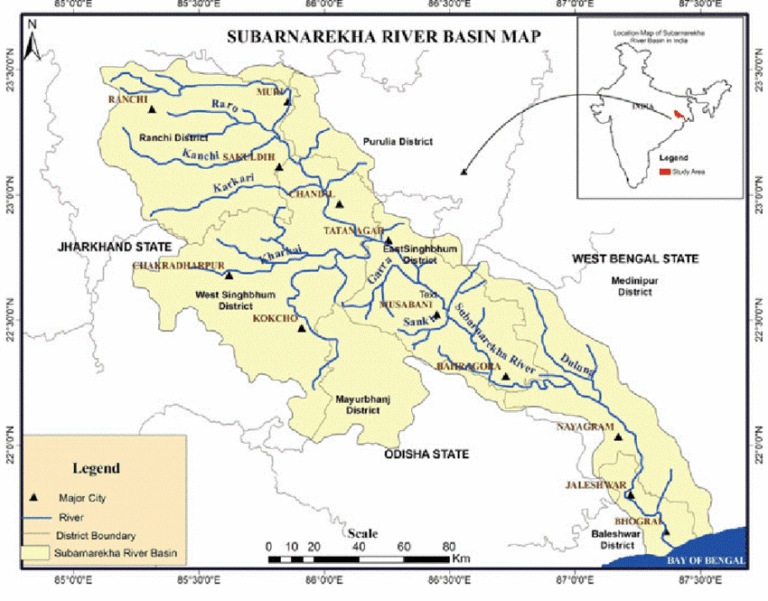
Origin:
- Arises near Piska/Nagri, close to Ranchi, in Jharkhand.
- The name "Subarnarekha" means “Streak of Gold”, referring to traces of gold once found in the river’s origin area.
Geographical Course:
- States Covered: Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha.
- Mouth: Empties into the Bay of Bengal near Talsari, in Odisha.
- Total Length: Approx. 395 km.
- Drainage Basin Area: 18,951 sq. km, making it a relatively small multi-state river basin.
- Course Details: Flows through Paschim Medinipur (WB) and Balasore (Odisha) after originating in Jharkhand.
Key Features:
- Hundru Falls: A well-known waterfall on Subarnarekha, located in Jharkhand, with a drop of 98 metres.
- The river system is independent, not a tributary of any larger river.
- Known for its historical and cultural significance due to gold particles in its sands.
Major Tributaries:
- Kharkai (joins at Jamshedpur)
- Kanchi, Roro, Harmu Nadi, Dulunga, Karru, Karakari, Singaduba, Kodia, Dhamra
About Chandil Dam
Location:
- Situated in Chandil, Seraikela Kharsawan district, Jharkhand.
- Built near the confluence of the Subarnarekha River and Karkori River (originating from Hundru Falls).
Purpose:
- Multi-purpose project serving irrigation, flood control, and tourism.
- Plays a significant role in managing water flow in the Subarnarekha basin.
e-Rakt Kosh

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is set to integrate India’s Rare Donor Registry with e-Rakt Kosh, a centralized national blood bank management platform under the National Health Mission (NHM). This move aims to improve access to rare blood types, enhance donor coordination, and save lives by ensuring timely availability of rare blood groups.
About the Integration
- e-Rakt Kosh: A digital platform developed under NHM for real-time information on blood availability, donation camps, and blood bank locations.
- Rare Donor Registry of India (RDRI): Developed by the ICMR–National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) with four partner institutes. Maintains a database of 4,000 carefully screened rare blood donors, tested for over 300 rare blood markers.
- Objective: To provide a centralized, accessible system for patients needing rare blood and to assist blood banks in managing inventory and donors efficiently.
Key Features and Benefits
- Life-saving Access: Enables patients and hospitals to locate rare blood types like Bombay blood group, Rh-null, and P-null efficiently.
- Safe Transfusions: Helps match blood for patients with multiple antigen deficiencies, common in disorders like thalassemia and sickle cell disease, thus reducing transfusion complications.
- Technological Advancements:
- Use of Multiplex PCR-based DNA testing for rapid identification of rare blood groups.
- Development of a customized blood screening kit tailored for Indian patients.
- Donor Engagement: Aims to ensure a steady, motivated pool of rare blood donors who remain connected to blood banks.
ICMR’s Parallel Work on Hemoglobinopathies and Rare Diseases
- Point-of-Care (POC) Tests Developed For:
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Hemophilia A
- Von Willebrand Disease
- Impact of Innovation:
- Sickle Cell Test Kits cost reduced from ?350 to under ?50 per test through Health Technology Assessment (HTA) led by DHR, ICMR–CRMCH, and NIIH.
- Estimated savings: ?1,857 crore for the government.
- New rapid testing device enables diagnosis even at PHC level.
- International Interest: World Federation for Hemophilia has shown interest in procuring India-developed diagnostic kits for global deployment.
- Commercialization: Technology transferred to Bhat Biotech, which launched the product under the brand Bio-Scan in August 2023.
Significance
- Enhances India’s healthcare infrastructure and emergency response for rare blood groups.
- Aligns with the goals of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and Atmanirbhar Bharat in the field of indigenous diagnostics.
- Showcases India’s growing biotech innovation ecosystem with both national and international relevance.
AI and Biomanufacturing in India

- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into India's biomanufacturing sector is gaining momentum with the launch of the BioE3 Policy and the IndiaAI Mission.
What is Biomanufacturing?
- Biomanufacturing involves the use of living cells, enzymes, or biological systems to produce commercial goods such as vaccines, biologics, biofuels, specialty chemicals, biodegradable plastics, and advanced materials.
- The convergence of synthetic biology, industrial biotechnology, and artificial intelligence (AI) has expanded its scope across sectors like healthcare, agriculture, energy, and materials science.
- India, often called the “Pharmacy of the World”, produces over 60% of global vaccines, underlining its industrial strength in biomanufacturing.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Biomanufacturing
AI is revolutionizing biomanufacturing by making it predictive, efficient, and scalable:
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning tools adjust variables like temperature, pH, and nutrient supply in real time to enhance fermentation and reduce batch failure.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of biomanufacturing plants allow engineers to simulate operations, test changes, and foresee potential disruptions without real-world risks.
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AI expedites molecular modeling and screening of drug candidates, reducing time and cost of development.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI forecasts machinery failures, improving equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
- Smart Supply Chains: AI-driven logistics optimize cold-chain storage and forecast medicine demand, ensuring timely distribution.
Indian Examples and Industrial Applications
- Biocon uses AI to enhance drug screening and fermentation quality.
- Strand Life Sciences applies machine learning in genomics for faster diagnostics.
- Wipro and TCS are developing AI platforms for clinical trials, molecule screening, and treatment prediction.
- AI is also being explored in rural healthcare, using region-specific data for localized diagnostics and advisories.
Key Government Initiatives
- BioE3 Policy (2024):
- Envisions Bio-AI hubs, biofoundries, and next-gen biomanufacturing infrastructure.
- Supports startups with funding and incentives.
- IndiaAI Mission:
- Promotes ethical, explainable AI in sectors like health and biotech.
- Supports bias reduction, machine unlearning, and transparency in AI models.
- Biomanufacturing Mission (2023): Aims to promote R&D and domestic production in bio-based sectors.
- PLI Scheme for Biotech: Incentivizes local production of enzymes, fermentation inputs, and biologics.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (2023): Lays down principles for lawful data processing, though not tailored for AI-biotech intersection yet.
Challenges in Policy and Regulation
Regulatory Gaps:
- India’s existing drug and biotech laws were designed before the AI era.
- No clear mechanism exists to audit, certify, or govern AI-operated bioreactors or predictive drug systems.
Data and Model Risks:
- AI systems trained on urban datasets may fail in rural or semi-urban manufacturing due to variable water quality, temperature, or power conditions.
- Lack of norms on dataset diversity and model validation raises risk of system failure and reputational damage.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Traditional IP laws do not clarify ownership of AI-generated inventions, molecules, or production protocols.
Workforce and Infrastructure:
- Biomanufacturing needs a workforce skilled in both computational biology and automation.
- India’s AI-bio talent gap and limited high-tech infrastructure outside metro cities hinders inclusive growth.
Ethical & Safety Concerns:
- Without context-specific oversight, AI errors can threaten public safety and product integrity.
- Trust in AI systems requires clear guidelines on explainability, accountability, and redress mechanisms.
Global Best Practices
- EU’s AI Act (2024): Classifies AI applications based on risk levels. High-risk applications (e.g., genetic editing) are subject to strict audits.
- US FDA Guidance (2025):
- Introduces seven-step credibility frameworks for AI in healthcare.
- Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) allow iterative AI updates while ensuring safety.
India lacks similar risk-based, adaptive oversight.
Policy Recommendations
- Establish AI-Biomanufacturing Regulatory Framework:
- Introduce tiered regulation based on context and risk.
- Define use-cases, audit mechanisms, and model validation standards.
- Mandate Dataset Diversity & Safety Audits:
- Ensure AI tools are trained on representative, unbiased, clean data.
- Create regulatory sandboxes to test AI systems in controlled environments.
- Strengthen Public–Private Partnerships:
- Boost industry-academia collaborations.
- Incentivize private investment through R&D credits and de-risking instruments.
- Modernize IP and Licensing Laws:
- Establish clarity on ownership of AI-generated discoveries.
- Develop licensing frameworks for bio-AI algorithms and training data.
- Upskill the Workforce: Promote interdisciplinary training across life sciences, data science, and industrial robotics.
Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc)
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
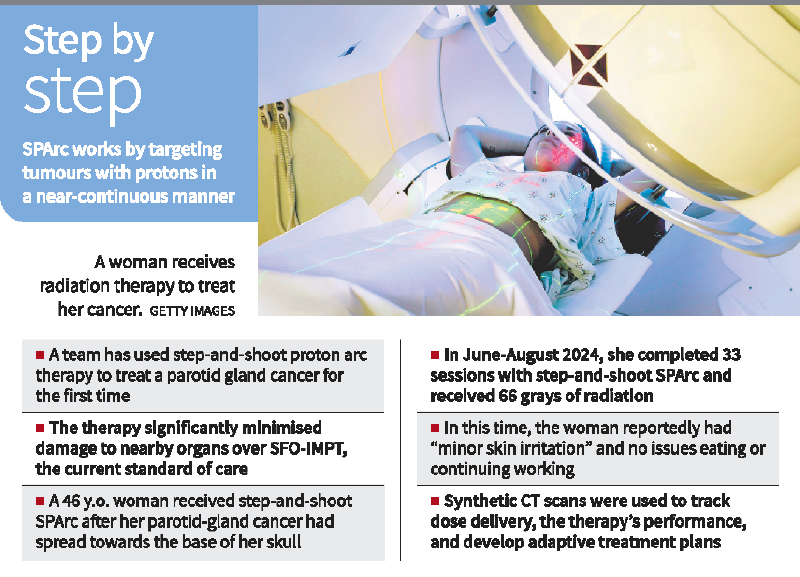
In a significant medical advancement, a team at the Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. has successfully administered Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc) to treat adenoid cystic carcinoma—a cancer originating in the parotid gland. This marked the first-ever clinical application of this technology. The findings were published in the International Journal of Particle Therapy in June 2025.
What is SPArc Therapy?
SPArc (Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy) is an advanced form of proton beam therapy where proton particles are delivered in a controlled arc across the tumor. It includes two primary modalities:
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc: Follows a pre-programmed dose delivery path.
- Dynamic SPArc: Simulated version where energy levels and targeting points are adjusted in real-time. (Still under regulatory review)
Comparison with Existing Techniques
The study compared three techniques:
- SFO-IMPT (Single-Field Optimized Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy – current standard)
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc (clinical)
- Dynamic SPArc (simulated)
SPArc showed reduced radiation exposure to key organs when compared with SFO-IMPT:
- Brainstem: ↓ 10%
- Optical chiasm: ↓ 56%
- Oral cavity: ↓ 72%
- Spinal canal: ↓ 90%
Treatment Case Study
The first patient treated was a 46-year-old woman with a tumor extending from her parotid gland to the base of her skull. She underwent 33 sessions of SPArc therapy from June to August 2024, reporting only minor skin irritation and no disruptions to eating or daily functioning.
Process & Technology Used:
- Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) was used for real-time imaging before each session.
- A machine learning model converted CBCT to synthetic CT, allowing accurate dose tracking.
- As the patient lost weight, the dose plan was adjusted after two weeks to maintain precision.
- Nine beam angles spanning a 180º arc were used, delivering radiation at 20º intervals.
Each session lasted about 15–18 minutes, enabling nearly continuous dose delivery.
Working Mechanism
- The therapy operates by 'painting' the tumor in energy layers.
- Each energy level targets a specific tissue depth, ensuring maximum precision.
- The system scans dozens of spots in each layer before moving to the next one with increased penetration.
Advantages
- High precision in delivering radiation to deep and complex anatomical regions like the skull base.
- Limits collateral damage to vital organs.
- Effective in large or invasive tumours.
- Better quality of life during treatment (reduced side effects such as fatigue or swallowing issues).
Limitations & Concerns
- Geographical miss risk: Tiny tumors may be missed due to breathing motion or tumor shrinkage over time.
- Cost: High installation and operational costs, making it suitable for a limited patient base.
- Potential for overuse in non-indicated cases, leading to inequitable healthcare delivery.
- Dynamic SPArc still awaits regulatory clearance and integration into oncology systems.
Significance for India
SPArc therapy can be transformative for cancers in anatomically intricate regions and may serve as a benchmark for future precision cancer therapies. However, adoption in India requires cost-reduction, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks.
Spartaeus karigiri
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
A team of researchers has identified a new species of jumping spiders of the Spartaeinae subfamily in southern India, known for their intelligent hunting skills and web-invasion tactics.
Source: European Journal of Taxonomy (June 2025)
Key Facts:
- Species Name: Spartaeus karigiri
- Taxonomy:
- Family: Salticidae (Jumping Spiders)
- Subfamily: Spartaeinae
- Genus: Spartaeus
- Named After: Karigiri (Elephant Hill) in Devarayanadurga, Karnataka.
Significance:
- First recorded presence of Spartaeus and Sonoita genera in India.
- These genera were previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Discovery expands India’s Spartaeinae spider fauna to 15 species across 10 genera.
Features of Spartaeus karigiri:
- Noted for intelligent hunting and web-invasion tactics.
- Possesses keen eyesight and mimics prey to deceive other spiders.
- Males were found in rocky crevices; females guarding egg clutches.
- Found in Karnataka and Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
Other Findings:
- Sonoita cf. lightfooti, previously known from Africa, was also found in Karnataka.
- A taxonomic correction: Marpissa gangasagarensis (2005) is the same as Phaeacius fimbriatus (1900).
Conservation and Research Insight:
- India's arachnid diversity remains under-studied.
- New discoveries indicate rich but undocumented biodiversity in Indian terrains.
Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2025
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
The Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2025, published by UNESCO, reveals an alarming surge in the global out-of-school population, now estimated at 272 million—an increase of over 21 million from previous estimates. This setback highlights that by 2025, countries will collectively fall short of their national education targets by 75 million children.
About the GEM Report
- An annual UNESCO publication, originally launched as the Education for All Global Monitoring Report in 2002 and renamed in 2016.
- Provides an evidence-based global assessment of education progress, challenges, and trends.
- Aims to guide policy decisions and strengthen efforts toward achieving SDG 4 (Quality Education).
Key Findings
- The out-of-school population includes:
- 78 million primary school-age children (11%)
- 64 million lower secondary adolescents (15%)
- 130 million upper secondary youth (31%)
- The rise of 21 million in out-of-school children since the last estimate is attributed to:
- New enrolment and attendance data (+8 million): Includes factors like the 2021 ban on girls' education in Afghanistan, which alone accounts for 1.4 million girls.
- Updated UN population projections (+13 million): The 2024 World Population Prospects estimate a 49 million increase in the global school-age population (6–17 years) by 2025.
- The report warns that conflict zones severely hamper data collection, likely underestimating the true number of out-of-school children.
Challenges with Data and Methodology
- The GEM model draws from administrative data, surveys, and census records to estimate schooling trends.
- However, during emergencies and crises, such models may fail to capture sudden drops in attendance, leading to an underreporting of affected populations.
- Conflict-ridden regions face poor data reliability, impacting planning and resource allocation.
Off-Track from Global Targets
- By 2025, countries will be off-track by:
- 4 percentage points for primary and lower secondary levels
- 6 percentage points for upper secondary level
- Even if national targets are met, the world will still have 107 million children out of school by 2030. The GEM report projects a reduction of 165 million if all targets are achieved—but current trajectories suggest this is unlikely.
RBI Infuses Rs.23,856 Crore into Banking System via Government Securities Buyback
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to bolster liquidity in the financial system, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has infused ?23,856 crore into the banking system through a buyback of government securities (G-Secs) on June 5, 2025. This marks the second such bond buyback by the central bank in the current financial year (FY 2025–26).
What is a Bond Buyback?
A bond buyback refers to the RBI repurchasing existing government securities before their maturity. Conducted on behalf of the central government, such operations aim to inject durable liquidity into the banking system, improve the liquidity position of banks, and influence interest rates. It is part of the RBI's broader Open Market Operations (OMOs) toolkit.
Broader Liquidity Context
The RBI’s intervention is part of a broader liquidity management strategy, aimed at ensuring stable and surplus liquidity conditions. The central bank has employed various tools in recent months:
- Open Market Operations (OMOs)
- USD/INR Buy/Sell swap auctions
- Variable Rate Repo (VRR) auctions
These tools were especially crucial after the banking system faced a liquidity deficit in late 2024. Since then, the RBI’s operations have restored liquidity, with the system now in surplus mode—estimated at around ?3 lakh crore.
Significance
- Monetary Stability: Enhances the transmission of monetary policy by ensuring banks have sufficient funds to lend.
- Market Functioning: Eases pressure in the bond markets, improves demand for new issuances, and helps manage interest rates.
- Fiscal Management: Supports the government's borrowing program by managing the maturity profile of debt and yields.
India’s First INTERPOL Silver Notice

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant development, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has secured India’s first-ever ‘Silver Notice’ from INTERPOL to track the global assets of Shubham Shokeen, a former French Embassy official implicated in a visa fraud case. This move underscores India's enhanced use of international law enforcement mechanisms to combat transnational crimes, particularly financial crimes involving asset concealment abroad.
What is a Silver Notice?
While INTERPOL is globally known for its Red Notice (to arrest or detain fugitives), the Silver Notice is a newer tool designed to help locate, identify, monitor, or seize the criminal assets of individuals or entities under investigation. Issued at the request of India’s National Central Bureau (NCB), the Silver Notice for Shokeen seeks to trace proceeds of crime potentially parked across multiple countries, marking a new phase in India’s international criminal cooperation.
About INTERPOL
INTERPOL (International Criminal Police Organization) is the world’s largest international police organization, comprising 196 member countries, with India being one of the founding members. It facilitates cross-border police cooperation and crime control across jurisdictions. Its genesis lies in the 2nd International Police Congress held in Vienna in 1923, when it was established as the International Criminal Police Commission (ICPC). It adopted the name INTERPOL in 1956 with the adoption of its Constitution during the 25th General Assembly.
- Headquarters: Lyon, France
- National Central Bureau (NCB): Each member state has an NCB that coordinates with INTERPOL. CBI serves as India’s NCB.
- Key Bodies:
- General Assembly: Supreme decision-making body; meets annually.
- Executive Committee: Supervises execution of General Assembly's decisions.
- General Secretariat: Handles operational activities on a daily basis.
INTERPOL Colour-Coded Notices
INTERPOL issues a series of colour-coded notices that serve as international alerts or cooperation requests:
- Red Notice: Request to locate and provisionally arrest a wanted person.
- Blue Notice: To collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities.
- Yellow Notice: For locating missing persons.
- Black Notice: To identify unidentified bodies.
- Silver Notice: To trace, monitor, and seize assets related to criminal proceeds.
These notices are issued by INTERPOL’s General Secretariat upon request from NCBs and are accessible to all member countries, enabling swift global action.
India’s Technological Integration: The BHARATPOL Portal
To streamline international cooperation, the CBI has developed the BHARATPOL portal, a digital interface that connects all Indian law enforcement agencies with INTERPOL. It allows seamless communication and data exchange for tracking fugitives, assets, and criminal networks, thereby enhancing India’s capabilities in combating cross-border financial and cyber crimes.
Significance for India
- Asset Recovery: The Silver Notice is a critical step in tracing and recovering illicit assets abroad, aligning with India’s broader efforts under anti-money laundering frameworks.
- Global Cooperation: Reflects India’s increasing reliance on international institutions for law enforcement, including the UN Convention against Corruption and FATF recommendations.
- Strengthening CBI's International Role: As India’s NCB, the CBI’s proactive role showcases its growing competence in global criminal investigations.
Exercise Shakti 2025

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The 8th edition of Exercise Shakti, a bilateral joint military exercise between India and France, is being held from 18 June to 1 July 2025 at La Cavalerie, France.
About Exercise Shakti
- Type: Joint military exercise between the Indian Army and French Army.
- Edition: 8th edition. The previous edition was hosted by India, as the exercise is biennial and conducted alternately in both countries.
- Venue (2025): La Cavalerie, France.
Objective and Significance
- Primary Aim: To enhance the joint military capability of both nations to conduct Multi-Domain Operations in sub-conventional conflict scenarios.
- Focus Areas:
- Developing interoperability in operations.
- Sharing best practices, tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Strengthening military-to-military cooperation.
- Fostering bonhomie and camaraderie between the two armies.
Strategic Importance
- Exercise Shakti is part of the broader defence partnership between India and France, encompassing counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, and multi-domain coordination.
- It reflects India’s growing strategic engagements with like-minded global partners to address emerging security challenges.
Other India–France Joint Exercises
Name Domain Participants
Garuda Air Indian Air Force – French Air and Space Force
Varuna Naval Indian Navy – French Navy
Desert Knight Air Indo-French air warfare cooperation
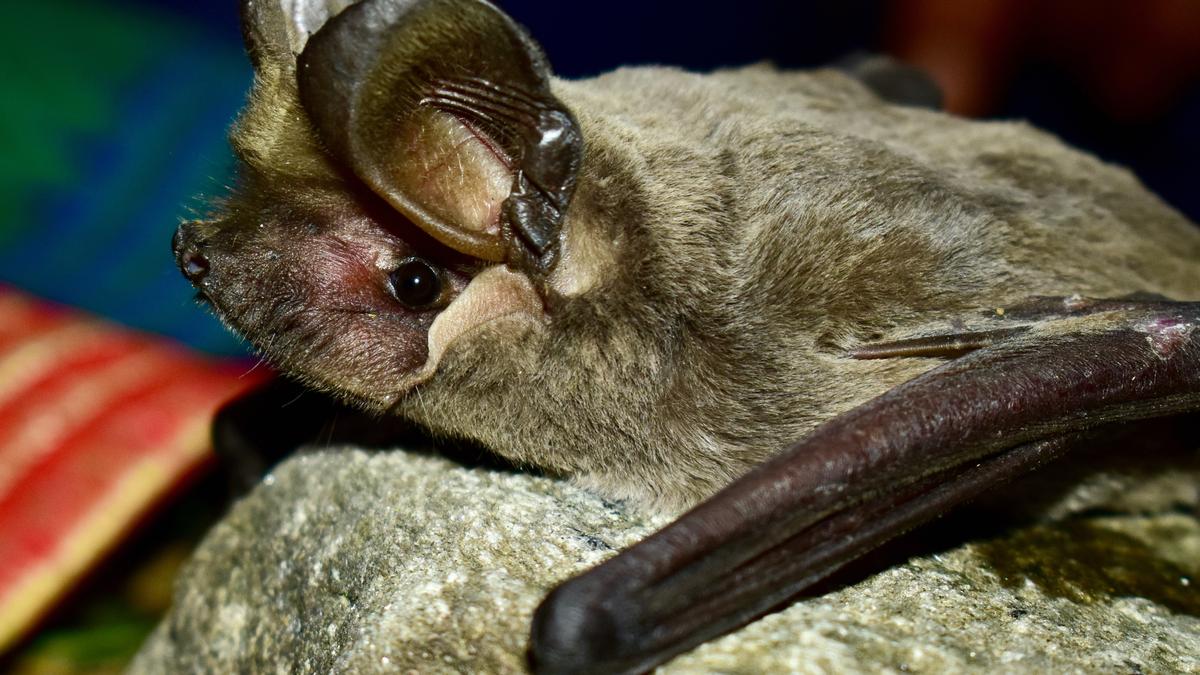
Myotis himalaicus

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A new bat species, the Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus), has been described based on fieldwork in Uttarakhand and historical specimens from Pakistan. Published in Zootaxa journal by a team of Indian and international scientists.
Key Findings of the Study
- Study Area: Western Himalayas – Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand (2017–2021).
- Total Bat Species Documented: 29, including new records and confirmations.
- Raises India's bat species count to 135.
About Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus)
Feature Description
Family/Genus Belongs to the Myotis frater complex
Habitat Deodar, pine, and cedar forests on southern Himalayan slopes
Distribution Found in Uttarakhand (India) and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan)
Size Medium-sized (~3.5 inches, <1 oz)
Morphology Delicate feet, long thumbs with short claws, short ears, fine teeth
Conservation Status Recently described; appears rare
Other Major Additions/Clarifications
- East Asian Free-Tailed Bat (Tadarida insignis):
- First confirmed record in India.
- Extends known range eastward by 2,500 km.
- Earlier misidentified as Tadarida teniotis.
- Babu’s Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus babu):
- Revalidated as a distinct species, not a synonym of Javan pipistrelle.
- Distribution: Pakistan, India, Nepal.
- First specimen-based confirmations in India for:
- Savi’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo savii)
- Japanese greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus nippon)
Ecological Importance of Bats
- Insect Control: Consume pests and mosquitoes.
- Pollination & Seed Dispersal: Important for forest regeneration.
- Fertilizer Contribution: Bat guano rich in Nitrogen & Phosphorous; boosts crop yield.
RBI Revises LTV Ratio for Gold-Backed Loans
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced revised guidelines to enhance formal sector lending and ease credit access for small-ticket gold loan borrowers, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- The new norms focus on raising the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio for gold-backed loans up to ?5 lakh and simplifying appraisal norms for such loans.
What is the Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
- Definition: The LTV ratio is the percentage of a collateral’s value that a lender offers as a loan.
- Formula:
LTV Ratio= (Loan Amount / Appraised Value of Asset) × 100
- A higher LTV indicates greater credit against the same asset but also entails higher risk for the lender.
- Assets like gold, with a stable value and liquid secondary market, are more "desirable" as collateral, often attracting higher LTVs.
Revised RBI Guidelines (June 2025): LTV Ratio for Gold Loans
Loan Amount Revised LTV Ratio Previous LTV (Draft April 2025)
Up to ?2.5 lakh 85% 75%
?2.5 lakh – ?5 lakh 80% 75%
Above ?5 lakh 75% 75%
- The interest component is included in the LTV calculation.
- The move reverses the uniform 75% LTV cap proposed in the April 2025 draft norms.
Additional Key Features
- No credit appraisal required for loans up to ?2.5 lakh.
- End-use monitoring is necessary only if the borrower wishes to qualify the loan under priority sector lending.
- The average ticket size of gold loans (~?1.2 lakh) is expected to increase due to relaxed norms.
- These loans are crucial for middle-class, lower middle-class, self-employed, and small businesses, often lacking formal income proof.
Rationale and Impact
- The revised norms aim to:
- Enhance credit accessibility.
- Prevent migration of borrowers to informal lenders.
- Boost financial inclusion and formalize rural credit ecosystems.
- Industry experts and NBFCs like Muthoot FinCorp and Shriram Finance have welcomed the move, noting it would benefit women, rural borrowers, and small traders.
- Shares of leading gold loan NBFCs like Muthoot Finance, Manappuram Finance, and IIFL Finance witnessed a sharp increase following the announcement.
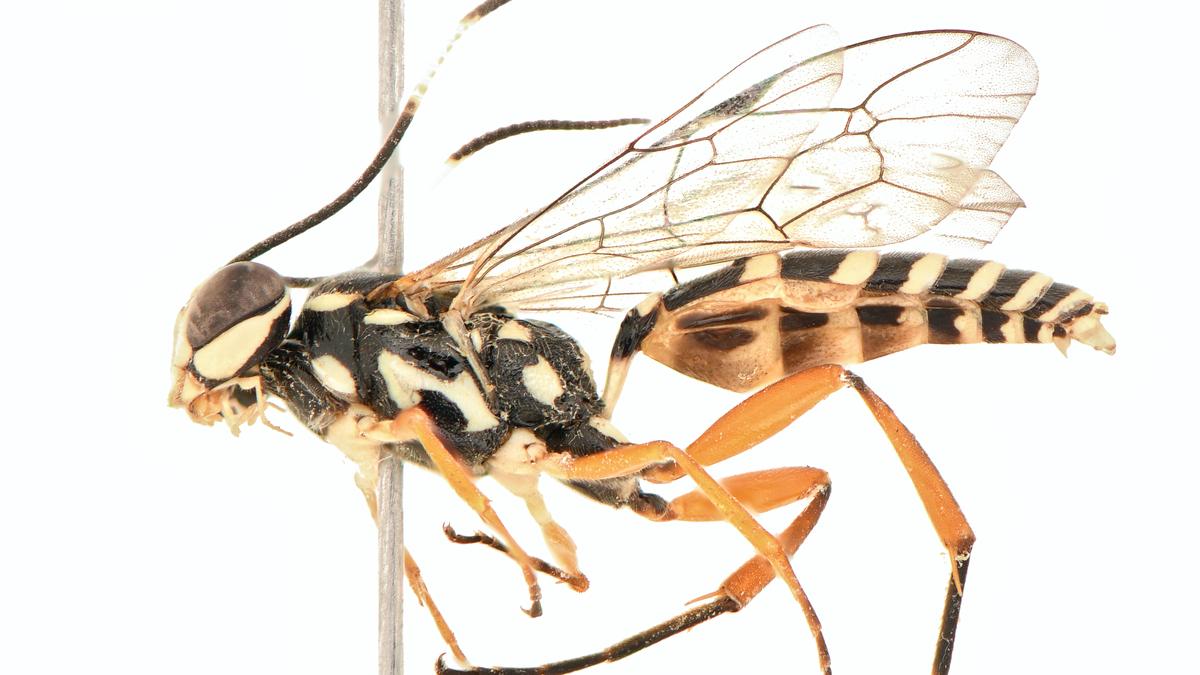
Rediscovery of Losgna Genus in India

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
At a time when habitat loss and climate change threaten countless species, the discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp - named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
Location of Discovery
- Place: Chandigarh, Union Territory of India
- Habitat: Urban dry scrub forest
- Time: Winter of 2023–24
- Significance: First formal description of any insect species from Chandigarh
Species Description
- Name: Losgna occidentalis
- Genus: Losgna (Ichneumonidae family – Parasitic wasps)
- Group Role: Parasitic wasps known for laying eggs inside/on arthropod hosts
- Ecological Role: Pollinators and biological control agents (important in ecosystems)
Historical Context
- Losgna genus was last recorded in India in 1965, in Heinrich’s monograph
- No Indian records or specimens existed post-1965 in any institution
- Only known specimens (of other Losgna species) are preserved in:
- Natural History Museum, London
- The Hope Collection, Oxford University
- Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany
Naming Rationale
- "Occidentalis" (Latin for "Western")
- Signifies the westernmost known range of the genus
- Earlier Losgna records were only from:
- Northeast India
- Southeast Asia (tropical forests)
- Published in Zootaxa (peer-reviewed journal for animal taxonomy)
Importance & Implications
- Rediscovery highlights India’s hidden and threatened biodiversity
- Emphasizes the critical role of taxonomy in conservation
- Shows potential for citizen-led discoveries and backyard biodiversity
- Demonstrates the need for:
- Responsible specimen collection
- International scientific collaboration
- Support for underfunded taxonomy sectors
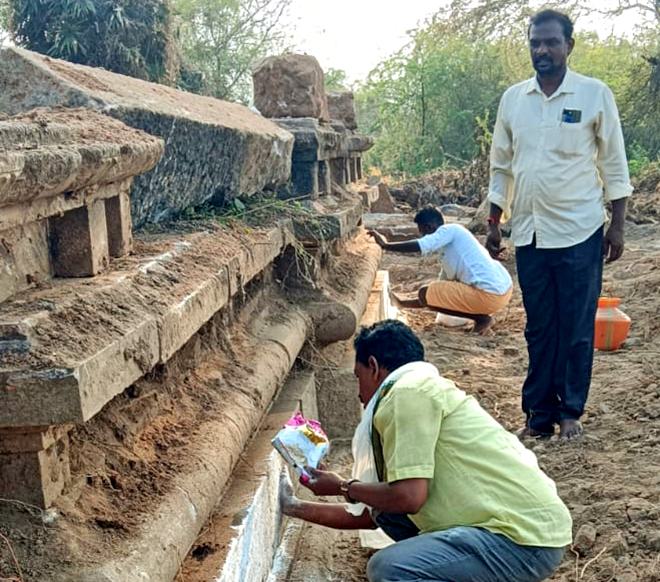
Discovery of 800-Year-Old Pandya-Era Shiva Temple

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
An 800-year-old Shiva temple of the later Pandya period has been unearthed at Udampatti, a village in Melur taluk, Madurai district, Tamil Nadu.
Key Highlights:
- Discovery: Foundation of a later Pandya period Shiva temple (dated to 1217–1218 CE) unearthed accidentally by children.
Architectural Insights:
- Only the stone base of the temple (north and south sides) survives.
- Identified as a Shaivite temple using foundation engravings and reference to Silpa Sastram.
Inscriptions & Historical Significance:
- Inscriptions deciphered by C. Santhalingam (Pandya Nadu Centre for Historical Research).
- Temple identified as Thennavanisvaram, located in ancient Attur (present-day Udampatti).
- “Thennavan” was a Pandya royal title, suggesting direct patronage.
Key Inscriptions (1217–18 CE):
- A sale deed records the transfer of a waterbody named Nagankudi along with wet/dry land.
- Seller: Alagaperumal, chieftain of Kalavalinadu
- Buyer: Nambi Perambala Kuthan alias Kangeyan
- Sale amount: 64 kasu (coins)
- Tax revenue from the land assigned to the temple for daily expenses, indicating its financial independence.
Archaeological Relevance:
- Confirms ancient village name (Attur), showcasing socio-economic practices during the Later Pandya period.
- Highlights temple economy, land-water rights, and administrative structures.
Pandya Dynasty
- One of the Three Crowned Tamil Dynasties (alongside Cholas and Cheras).
- Capital: Initially Korkai, later Madurai.
- Early Pandyas active since 4th century BCE; Later Pandyas (1216–1345 CE) saw a golden age under Maravarman Sundara Pandyan.
- Controlled parts of Sri Lanka, Telugu regions, and had trade links with Rome & Southeast Asia.
- Symbol: Fish
Cultural Contributions:
- Patronage of Sangam literature, Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Jainism.
- Temples: Meenakshi Temple (Madurai), Nellaiappar Temple (Tirunelveli).
- Promoted Tamil arts, Bharatanatyam, and education.
Decline:
- Succumbed to Chola, Hoysala conflicts and Delhi Sultanate invasions.
- Madurai Sultanate (1335) and later Madurai Nayak dynasty (1529) succeeded their rule.
Index of Industrial Production (IIP)

- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP), a key barometer of industrial activity in India, registered a growth of just 2.9% in February 2025, the slowest pace in six months. This was below market expectations of around 4% and reflects broad-based slowdown across sectors.
About the IIP
- Published by: Central Statistics Office (CSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- Base Year: 2011–12
- Purpose: Measures the short-term changes in volume of production in industrial sectors.
Sectoral Composition and Weights
Sector Weight in IIP No. of Items
Manufacturing 77.63% 809
Mining 14.37% 29
Electricity 7.99% 1
Sector-wise Performance (YoY in February 2025)
Sector Feb 2025 Growth Feb 2024 Growth
Mining 1.6% 8.1%
Manufacturing 2.9% 4.9%
Electricity 3.6% 7.6%
Use-Based Classification Performance
Category Feb 2025 Growth Feb 2024 Growth
Capital Goods 8.2% 1.7%
Intermediate Goods 1.5% —
Consumer Non-Durables -2.1% -3.2%
Observation: Capital goods were the only category to show robust growth. All other segments registered deceleration.
Eight Core Industries (Weight in IIP: 40.27%)
In decreasing order of weight:
- Refinery Products
- Electricity
- Steel
- Coal
- Crude Oil
- Natural Gas
- Cement
- Fertilisers
Key Concerns Highlighted
- Slowing growth across mining, manufacturing, and electricity sectors
- A high base effect from the previous year
- A decline in month-on-month output after five months of sustained growth
- Consumer non-durables in continued contraction, indicating weak rural/household demand
Beijing+30 India Report

- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
India’s official submission on the Beijing+30 Report marks three decades since the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995), a landmark framework advancing gender equality across 12 key areas such as education, health, economy, and political participation.
While the report acknowledges past progress—including enactment of laws like the Domestic Violence Act (2005) and the POSH Act (2013)—it lacks an integrated climate-gender perspective, an urgent gap given rising climate vulnerabilities affecting women disproportionately.
Climate Change and Gender Inequality: A Dual Challenge
- Rural women, particularly in agrarian and forest-dependent regions, face acute consequences of climate change—loss of livelihood, food insecurity, and health risks.
- India’s rural women often bear the brunt of extreme weather events, droughts, and resource scarcity.
- According to reports:
- 33% loss of income occurs due to climate-induced productivity disruption, especially from non-farm sources.
- Women perform over 8 hours of daily work, of which 71% is unpaid.
- By 2050, unpaid care work is projected to rise to 8.3 hours/day without mitigation.
Key Data and Impacts
Indicator Insight
Pregnant women (India) 50%+ are anaemic; worsened by food insecurity
Temperature–Violence Link +1°C rise → 8% rise in physical violence, 7.3% rise in sexual violence
Climate policies (FAO) Only 6% mention women; 1% mention poor people
Agriculture Potential Closing gender gap in agri-inputs could raise yields by 20–30%
Women as Agents of Climate Resilience
- Women contribute to 50% of global food production and lead community efforts in seed preservation, sustainable farming, and disaster response.
- Indigenous and rural women prioritize livelihood security (Mahua), safety (Mao), and managing migration—termed the three M's.
- Informal women’s collectives are key in disaster resilience, ecosystem protection, and productivity gains.
Recommendations for Climate-Gender Integration
- Policy Interventions:
- Introduce gender-responsive climate budgeting to prevent greenwashing and ensure equitable allocation.
- Incorporate gender in NAPCC, SAPCC, and ensure percolation to local governance and disaster planning.
- Address emerging risks—trafficking, migration, health, and geriatric safety in disaster zones.
- Data and Monitoring:
- Establish indicators and research on gendered climate impacts.
- Conduct inclusive climate consultations to enable community-driven planning.
- Private Sector & Green Finance:
- Encourage women-led green enterprises, climate-resilient technologies, and inclusive innovations.
- Allocate climate adaptation funds to skill-building, non-farm livelihoods, and local resilience-building.
- Partnership Model:
- Promote collaboration between government, civil society, research institutions, private sector, and international organisations.
- Foster knowledge exchange, capacity building, and public recognition of women climate leaders.
Kerala Researchers win International Grant for Hornbill Conservation
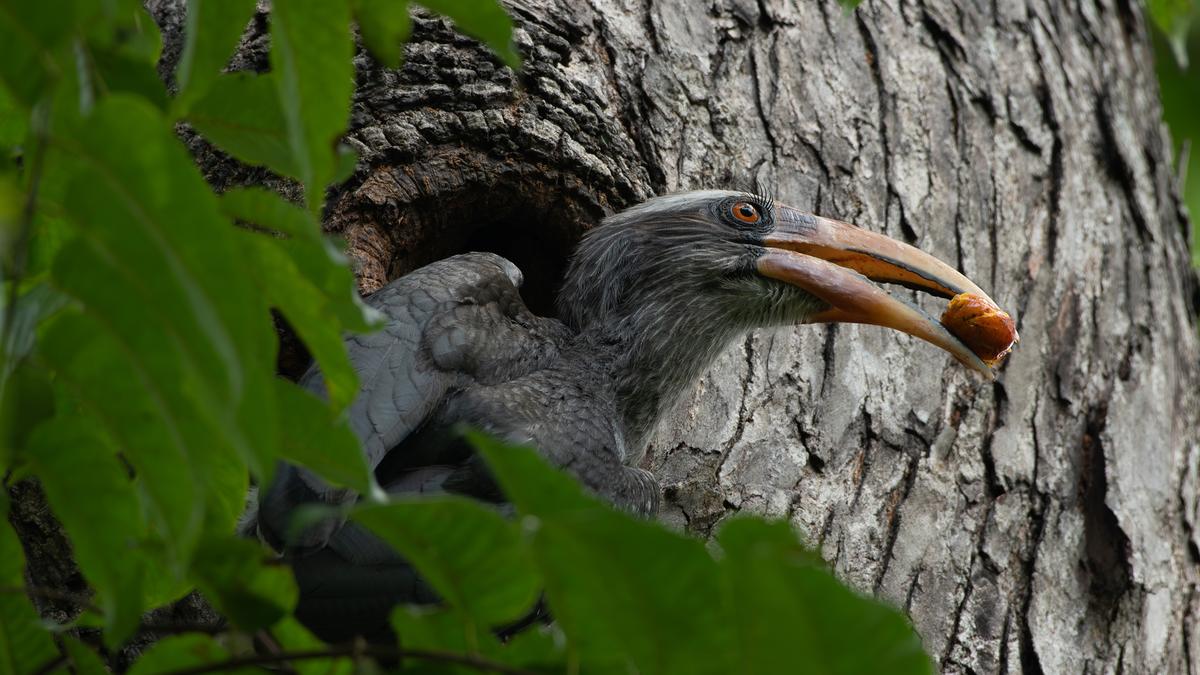

- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A team of young researchers from Kerala has won the prestigious Future Conservationist Award by the Conservation Leadership Programme (CLP) for their community-driven project on conserving the Malabar Grey Hornbill in Wayanad.
About Malabar Grey Hornbill (Ocyceros griseus)
- Status: Vulnerable (IUCN Red List)
- Legal Protection: Schedule IV of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Endemic to: Western Ghatsand parts of the Nilgiris, Wayanad, and Anamalai Hills in Southern India.
- Habitat: Evergreen forests, plantations, and agricultural landscapes
- Ecological Importance: Cavity-nesting frugivore, plays a key role in seed dispersal
- Nesting Behavior:
- Nests in secondary cavities (e.g., old woodpecker hollows)
- Reuses the same nesting cavity for years
- Dependent on cavity-bearing trees, often outside protected areas
About the Future Conservationist Award (CLP)
- Awarded By:
- Fauna & Flora International
- BirdLife International
- Wildlife Conservation Society
- Purpose: Supports early-career conservationists with funding and mentorship
- Focus Areas: Field conservation, community engagement, biodiversity monitoring
Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023

- 11 Apr 2025
In News:
A recent United Nations report titled ‘Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023’, released by the Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (MMEIG), highlights global progress and setbacks in maternal health. While acknowledging India's significant gains, the report places India second in global maternal deaths, behind Nigeria.
India’s Maternal Mortality Statistics (2023)
- Maternal deaths in India: 19,000(7.2% of global total)
- Rank: Second globally, tied with the Democratic Republic of Congo
- MMR: Reduced from 362 per 1 lakh live births (2000) to 80 in 2023 — a 78% decline
- Global average decline: 40% (2000–2023), but India achieved 86% decline
- Comparison with Nigeria:
- Nigeria: 75,000 deaths, contributing 28.7% of global maternal deaths
- India's Health Ministry deemed the comparison unfair given population differences (India: 145 crore, Nigeria: 23.26 crore)
Definition and Importance of MMR
According to WHO, Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) refers to:
“The death of a woman during pregnancy or within 42 days of termination, from pregnancy-related causes excluding accidental ones.”
MMR is a critical indicator for assessing healthcare quality and maternal well-being.
UN Global Findings
- Estimated maternal deaths globally (2023): 260,000
- Daily deaths: Over 700 women; about one death every two minutes
- Leading causes: Post-partum haemorrhage, hypertensive disorders, infections
- SDG 3.1 Target: Reduce MMR to <70 per 1 lakh live births by 2030
India-Specific Causes of Maternal Deaths
- Medical reasons:
- Post-partum haemorrhage
- Hypertensive disorders (e.g. pre-eclampsia)
- Infections related to pregnancy
- Co-morbidities: Anaemia, diabetes, hypertension
- Systemic challenges:
- Inadequate emergency obstetric care at Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and Community Health Centres (CHCs)
- Lack of infrastructure, trained personnel, and referral systems
- Socio-economic backwardness and poor access to healthcare in northern India
Concerns Highlighted in the Report
- Slowing progress post-2016 despite early improvements
- Humanitarian funding cuts impacting:
- Health worker retention
- Facility operations
- Availability of essential drugs (for haemorrhage, malaria, pre-eclampsia)
- Disruption in maternal care supply chains, especially in low-resource regions
India’s Stand
The Union Health Ministry has contested comparisons with smaller nations like Nigeria, asserting that India's maternal health progress is notable given its large population. The Ministry emphasized the 86% decline in MMR since 1990, as opposed to a global decline of 48% in the same period.
Arctic Biome: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 11 Apr 2025
Context:
- The Arctic biome, primarily a treeless tundra, spans approximately 11.5 million km² and includes regions in Canada, Greenland, Iceland, and Eurasia.
- It is characterized by permafrost (permanently frozen ground) close to the surface, limiting plant root growth.
- Vegetation consists of grasses, lichens, mosses, and low shrubs, while fauna includes polar bears, arctic foxes, caribou, musk ox, and migratory birds like snow geese.
- Climatic conditions are harsh, with temperatures ranging from -60°C in winter to 15.5°C in summer, and annual precipitation between 150–250 mm, mostly as snow.
- Despite nutrient-poor soils, the biome has functioned as a major carbon sink by storing carbon in peat and humus.
The Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ) and Carbon Dynamics
The Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ), which includes tundra, coniferous forests, and wetlands, has historically played a crucial role in global carbon sequestration. Its coniferous forests form the largest land-based biome on Earth.
However, recent studies, including one in Nature Climate Change (2025), indicate that over 30% of the ABZ has shifted from being a carbon sink to a carbon source. This reversal is primarily driven by:
- Permafrost thawing: Warmer topsoil temperatures lead to decomposition of organic matter, releasing CO? and methane.
- Frequent and intense wildfires: These burn organic-rich soils, releasing large volumes of carbon.
This transition creates a positive feedback loop: Wildfires release carbon → global temperatures rise → permafrost thaws → more emissions → more fires.
Fire Trends and Global Impact
Data from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) reveal that wildfires released 800,000 tonnes of carbon in January 2025 alone, nearly 4 times more than in the same period a decade ago.
Key wildfire incidents include:
- Texas and Oklahoma (USA): Destroyed 14,000+ structures, burned 16,000 hectares, and displaced thousands.
- Ofunato City (Japan): One of the country’s largest fires in 50 years, affecting nearly 2,900 hectares.
According to the India State of Forest Report (Dec 2024):
- Uttarakhand recorded the highest number of forest fires (5,315 fires) between Nov 2022–June 2023.
- However, fire hotspots are declining: 2.23 lakh (2021–22) → 2.12 lakh (2022–23) → 2.03 lakh (2023–24).
India’s Changing Fire and Climate Profile
Research by IIT Kharagpur and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology shows that land temperatures in northwest, northeast, and central India are rising by:
- 0.1–0.3°C/decade (pre-monsoon)
- 0.2–0.4°C/decade (post-monsoon)
This trend has led to earlier, longer, and slower-moving heatwaves, increasing wildfire vulnerability. India emits an estimated 69 million tonnes of CO? annually from forest fires.
Key Findings from the 2024 Arctic Report Card (NOAA)
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) confirms that the Arctic tundra is becoming a carbon source, exacerbated by fossil fuel pollution and recurrent wildfires. According to NOAA, this shift reflects persistent, long-term climate trends, not mere variability.
A global study of 200 monitoring sites (1990–2020) found:
- Alaska contributed 44% of the ABZ’s new carbon emissions.
- Northern Europe and Siberia added 25% and 13%, respectively.
- Non-summer months now emit more carbon than the entire summer absorption.
Historical fire events like the 2003 Siberian fires and the 2012 Timmins fire (Canada) significantly accelerated this trend.
IISc Develops Nanozyme to Prevent Excessive Blood Clotting

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru have developed a novel vanadium-based nanozyme that effectively controls abnormal blood clotting by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). This innovation holds promise for managing life-threatening conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and ischemic stroke.
Scientific Background:
- Normal Blood Clotting: Platelets are specialized blood cells that form clots at injury sites through a process called haemostasis, involving activation by physiological chemicals like collagen and thrombin.
- Problem of Abnormal Clotting: In conditions like COVID-19 and PTE, oxidative stress increases, leading to elevated ROS levels. This causes hyperactivation of platelets, resulting in excessive clot formation (thrombosis) — a leading cause of death globally.
Nanozyme Innovation by IISc:
- What is a Nanozyme?
An engineered nanomaterial that mimics the action of natural enzymes, in this case, glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes ROS.
- Material Used: Vanadium pentoxide (V?O?) nanozymes, particularly those with spherical morphology, were found to be the most efficient.
- Mechanism: The redox-active surface of vanadium nanozymes catalytically reduces ROS, preventing unwanted platelet aggregation.
Testing and Results:
- In vitro testing: Human blood platelets were activated with physiological agonists. Nanozymes were tested for their ability to curb excessive aggregation.
- In vivo testing (mouse model of PTE):
- Nanozyme injection led to reduced thrombosis.
- Improved survival rates without observable toxicity.
- Animals were monitored for 5 days post-treatment for health parameters.
Future Prospects:
- Researchers aim to test the nanozyme's potential against ischemic strokes, which also result from vascular blockages.
- Encouraging results with human platelets indicate the possibility of clinical trials in the near future.
Kerch Strait and Recent Developments
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Ukraine has claimed responsibility for a recent underwater explosion that damaged the Kerch Bridge, a critical transport link connecting mainland Russia to occupied Crimea. The attack underscores the strategic importance of the Kerch Strait in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Kerch Strait: Geographical and Strategic Overview
- Location: The Kerch Strait forms the only maritime passage between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- West: Kerch Peninsula (Crimea)
- East: Taman Peninsula (Russia)
- Width: Narrows to 3–5 km at its tightest point near the Chushka Spit.
- Nearby City: Kerch, located on the Crimean side, lies near the strait’s midsection.
- Strategic Importance:
- A vital shipping lane for transporting goods and military supplies.
- Gained heightened geopolitical importance after Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014.
- Frequently features in Russia–Ukraine maritime tensions.
Kerch Strait Bridge (Crimean Bridge)
- Length: 19 km, making it the longest bridge in Europe.
- Completed: In 2018
- Connectivity: Includes dual road and railway tracks, linking the Russian mainland to Crimea.
- Symbolism: Considered a symbol of Russia’s control over Crimea post-2014 annexation.
- Strategic Use: Facilitates military logistics and civilian transit; crucial for sustaining Russian presence in Crimea.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Western Europe – 2022 Onwards
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Western Europe is experiencing its largest diphtheria outbreak in 70 years, with cases predominantly among vulnerable groups such as migrants and the homeless. The outbreak, which began in 2022, has raised concerns over disease surveillance, migrant healthcare, and immunisation coverage.
Key Facts from the Outbreak
- As per a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, 536 cases and three deaths have been reported across Europe since 2022.
- Most cases were found among young males (average age: 18) who had recently migrated, particularly from Afghanistan and Syria.
- 98% of strains exhibited close genetic similarities, suggesting a common transmission point during migration journeys or in accommodation facilities, not in the countries of origin.
- A genetic match between the 2022 strains and a recent 2025 case in Germany indicates that the bacteria is still circulating silently in the region.
Recommendations from Health Experts
- Enhance vaccination drives, particularly among high-risk and underserved populations.
- Improve awareness among healthcare providers, especially those working with migrants and the homeless.
- Ensure better access to antibiotics and diphtheria antitoxins.
- Strengthen disease surveillance and contact tracing mechanisms.
About Diphtheria
Feature Details
Cause Corynebacterium diphtheriae (produces a potent toxin)
Mode of Spread Respiratory droplets, contact with infected sores or ulcers
Affected Areas Primarily the respiratory tract, but also the skin in some cases
Symptoms Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weakness; grey membrane in throat
Severe Impact Can lead to breathing difficulties, heart and kidney damage, and neurological issues if untreated
Treatment Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT), antibiotics, and supportive care
Fatality Rate Up to 30% in unvaccinated individuals; higher in children
Prevention Vaccination (DPT/DTP) is the most effective preventive measure
Greater Flamingo Sanctuary
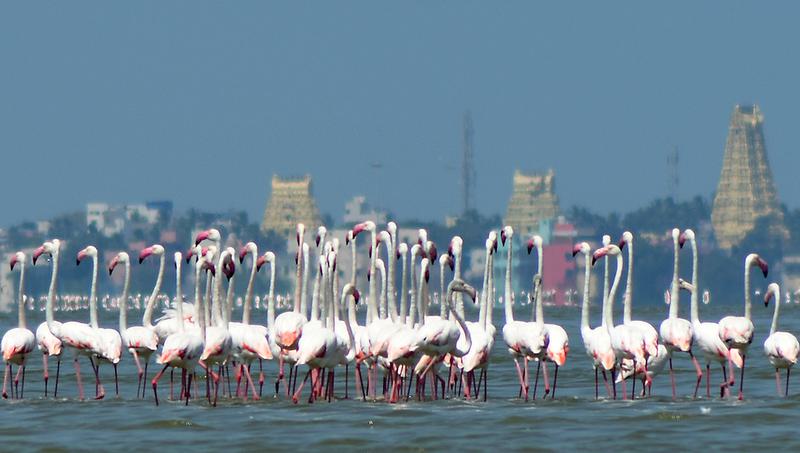

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
On the occasion of World Environment Day 2025, the Tamil Nadu government officially declared the Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi, Ramanathapuram district, aiming to protect a vital stopover site for migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Key Highlights
What is it?
A newly notified wildlife sanctuary dedicated to safeguarding migratory wetland birds, especially the greater flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus), in their natural resting and breeding habitat.
Location and Area:
- Located in Rameshwaram taluk, Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Covers approximately 524.7 hectares of revenue and forest land.
- Lies within the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, a globally recognized marine ecosystem.
Ecological Significance
- Functions as a critical site along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the key migratory bird routes.
- As per the 2023–24 Wetland Bird Survey, the region hosts 10,700+ wetland birds representing 128 species, including:
- Flamingos (greater and lesser)
- Herons, egrets, sandpipers, etc.
- The sanctuary harbours diverse ecosystems, such as:
- Mangroves (Avicennia, Rhizophora)
- Mudflats, marshes, sand dunes, and lagoons
- Nesting grounds for sea turtles and marine biodiversity
Conservation and Socioeconomic Benefits
- Strengthens coastal resilience by preventing erosion through natural mangrove buffers.
- Promotes responsible ecotourism, raising awareness of wetland and avian conservation.
- Supports local livelihoods via employment in conservation and tourism activities.
About the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus)
Attribute Details
Size 90–150 cm tall, long necks and legs
Coloration Pink hue from carotenoid-rich diet
Feeding Uses specialized downward-curved bill for filter feeding in shallow waters
Reproduction Builds cone-shaped mud nests, lays 1–2 eggs, both parents incubate
Chick Rearing Chicks are white and fed through regurgitation
Social Traits Highly gregarious, breeds in large colonies and flies in V-formations
Behavioral Note Often seen standing on one leg, possibly to conserve body heat
International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS)

- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
India has secured the Presidency of the International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS) for the term 2025–2028, marking a historic first for the country since becoming a member in 1998. The victory affirms India’s growing influence in the field of global public administration.
About IIAS
- Established: 1930
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium
- Nature: A global federation of 31 Member States, 20 National Sections, and 15 Academic Research Centres, dedicated to collaborative scientific research in public administration.
- Core Objectives:
- Promote collaboration on public governance solutions.
- Accredit academic and professional training programs in public management.
- Disseminate research and best practices in administrative sciences.
Although not formally affiliated with the United Nations, IIAS actively participates in UN mechanisms like the Committee of Experts on Public Administration (CEPA) and the UN Public Administration Network (UNPAN).
India’s Role and Election to Presidency
- India has been a Member State of IIAS since 1998, represented by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- For the 2025–2028 term, Prime Minister Narendra Modi nominated V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG, as India's candidate in November 2024.
- Election Process:
- Hearings were held at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi in February 2025.
- Four countries—India, South Africa, Austria, and Bahrain—submitted nominations.
- The final vote on June 3, 2025, saw India and Austria advance to the final round.
- Out of 141 votes, India secured 87 votes (61.7%), while Austria received 54 votes (38.3%).
Significance for India
- This marks India’s first Presidency of IIAS.
- The victory enhances India's position in global governance and showcases its administrative capabilities on an international platform.
- It also aligns with India’s focus on reforming and modernizing public administration through digital governance and institutional capacity-building.
Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans)
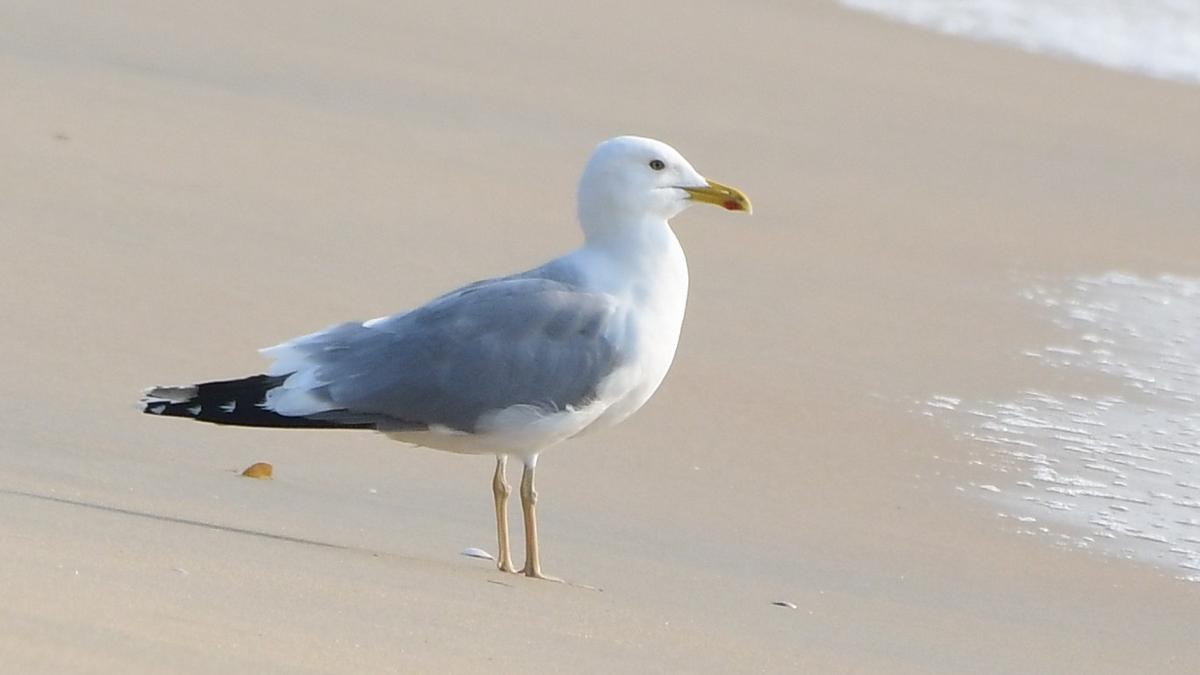

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant ornithological development, the Caspian Gull, one of the rarest gull species to be recorded in India, was positively identified five years after being sighted at Kappad Beach, Kozhikode, Kerala. This marks the first confirmed sighting of the species in Kerala, and only the second in southern India.
Discovery and Identification:
- Ornithologist Abdulla Paleri first spotted the bird in February 2020 but took five years to confirm its identity due to its close resemblance to the more commonly seen Steppe Gull.
- The Caspian Gull differs subtly in features such as head and beak shape, posture, wing pattern, and leg morphology.
- Images were shared with international experts and on the eBird platform, where ornithologists Oscar Campbell and Hans Larsson confirmed the identification. The sighting has remained unchallenged since.
About Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans):
- A monotypic, large, white-headed gull species, considered rare in India.
- Regularly breeds in Central Asia, particularly in steppe and semi-desert habitats with lakes, rivers, and reservoirs.
- Nesting usually occurs on flat, low-lying areas near water bodies, often surrounded by reedbeds.
- The species feeds on fish, insects, molluscs, and other invertebrates.
Migration Pattern:
- It migrates from the Black Sea and Caspian Sea region to southern and eastern Kazakhstan, western China, and parts of South Asia during winter.
- Traditionally winters in the eastern Mediterranean, Persian Gulf, and western India (like Gujarat).
- Increasingly, small populations are dispersing into Europe, including Sweden, Norway, and Denmark.
- The Kozhikode gull is believed to be a straggler—a bird that deviates from its usual migratory route.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern, Despite its rarity in India, the species is not globally threatened.
RBI’s Draft Guidelines on Gold Loans

- 03 Jun 2025
Why is the RBI proposing changes to gold loan regulations?
In April 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released draft guidelines on loans against gold to harmonise regulations across banks and NBFCs and to address irregularities. The move follows an extraordinary surge in gold-backed loans during FY24:
- Gold loan portfolios grew over 50% across banks and NBFCs.
- For banks, the portfolio more than doubled (104% growth).
This rapid growth, amid rising gold prices and lax lending standards, raised regulatory concerns.
What are the key proposals in the draft guidelines?
- LTV Norms:
- The Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio remains capped at 75%.
- For bullet repayment loans for consumption, accrued interest must be included in the LTV calculation, effectively lowering the loan amount disbursed.
- Ownership Proof:Borrowers must furnish proof of ownership for the gold pledged.
- Valuation Standards:
- Gold should be valued based on 22-carat price.
- Uniform procedures must be followed to assess the purity and weight.
- Loan Renewal & Fresh Sanctions:
- Renewals or top-ups are permitted only if:
- The existing loan is standard, and
- It complies with the LTV limit.
- Concurrent loans for both consumption and income-generation are disallowed.
- A fresh loan can only be granted after full repayment (principal + interest) of the previous loan.
- Renewals or top-ups are permitted only if:
- Collateral Return Timeline:If the gold is not returned within 7 working days after repayment, the lender must compensate the borrower at ?5,000/day for each day of delay.
Likely Impact on Borrowers and Lenders
Borrowers:
- May face reduced loan amounts and higher documentation requirements.
- Small and rural borrowers, dependent on gold loans for agriculture and allied sectors, may experience reduced accessibility.
NBFCs and Banks:
- NBFCs that frequently renew or top-up gold loans could lose flexibility.
- Compliance costs will rise due to stringent documentation, valuation, and reporting norms.
- Smaller NBFCs relying on re-pledging of gold may face liquidity issues.
- Interest rates may rise to offset higher operational expenses.
Is a uniform policy suitable?
A one-size-fits-all policy may not be practical. Gold loans are a lifeline for rural households with limited access to formal credit. Experts suggest:
- Differentiated norms for micro gold loans (small-ticket loans) and high-value loans.
- Consideration for the informal nature of ownership in many rural households.
Kawal Tiger Reserve and KumramBheem Conservation Reserve
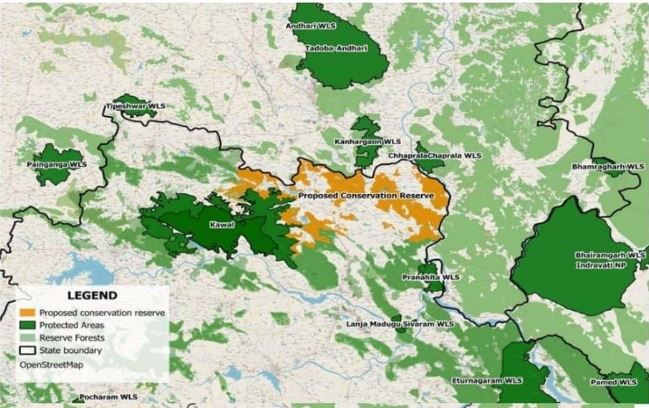
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a recent development, the Telangana government has designated the tiger corridor connecting the Kawal Tiger Reserve (Telangana) with the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) as the KumramBheem Conservation Reserve, under Section 36(A) of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. This move is aimed at preserving critical wildlife corridors in the Central Indian Landscape.
Kawal Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in Telangana, along the Godavari River, forming part of the Deccan Peninsula – Central Highlands.
- Biogeographic Zone: Lies at the southern tip of the Central Indian Tiger Landscape.
- Connectivity: Links with Tadoba-Andhari (Maharashtra), Indravati (Chhattisgarh), and other reserves like Tipeshwar, Chaprala, and Kanhargaon.
- Vegetation Type: Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Flora: Dominated by teak, bamboo, and species like Anogeissuslatifolia, Terminalia arjuna, Boswellia serrata, etc.
- Fauna: Hosts tiger, leopard, nilgai, chinkara, sambar, blackbuck, wild dog, wolf, and jungle cat.
KumramBheem Conservation Reserve: Newly Notified Area
- Legal Basis: Declared under Section 36(A), Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which allows states to notify government-owned land adjacent to or connecting protected areas as conservation reserves.
- Total Area: 1,492.88 sq km (149,288.48 hectares)
- District &Mandals Covered: Spread across KumramBheemAsifabad district, covering parts of Kerameri, Wankidi, Asifabad, Sirpur, Koutala, Bejjur, Kagaznagar, Rebbana, Dahegaon, and Tiryanimandals.
- Forest Blocks Included: 78 blocks including Garlapet, Ada, Manikgarh East & West, Danora, Gudem, Bejjur, Kadamba, and Girali.
Ecological Significance
- Tiger Movement: Over the last decade, more than 45 unique tigers (mostly transient) have been documented in this corridor through camera trapping and surveys.
- Breeding Evidence: Since 2015, 17 tiger cubs born from 3 tigresses have been recorded. The 2022 Tiger Census confirmed 4 adult tigers and 3 cubs in the area.
- Leopard Presence: 8 leopards were recorded during the All India Leopard Estimation, 2022.
- Other Carnivores: Includes sloth bear, hyena, wild dog, wolf, honey badger, and jungle cat.
- Herbivore Diversity: Rich prey base such as gaur, sambar, nilgai, chital, muntjac, four-horned antelope, and Indian gazelle.
- Avifauna: Home to 240+ bird species, including rare species like the Malabar Pied Hornbill and Long-billed Vulture, the latter using the reserve as a nesting site.
- Elephant Movement: Occasional elephant presence has also been reported.
Governance
A Conservation Reserve Management Committee has been established. Members include:
- District Forest Officer (DFO) of KumramBheemAsifabad (Convenor)
- Sarpanches of local panchayats (e.g., Karji, Motlaguda, Murliguda)
- Representatives from NGOs like Hyderabad Tiger Conservation Society, WWF-India, and Wildlife Conservation Trust
- Officials from Veterinary, Agriculture, and Forest Divisions
India Develops its first indigenous Mechanical Thrombectomy Device for Stroke Treatment
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s medical technology sector, the Technology Development Board (TDB) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has extended support for the development of the country’s first indigenously manufactured mechanical thrombectomy device for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
What is a Mechanical Thrombectomy Device?
The device is a minimally invasive medical tool designed to treat acute ischemic stroke, which occurs due to a blockage in a large blood vessel in the brain. Unlike conventional thrombolytic drugs that dissolve clots chemically, this device physically extracts the clot, thereby restoring blood flow swiftly and reducing the risk of severe brain damage or paralysis.
Development and Manufacturing
This pathbreaking innovation was developed by S3V Vascular Technologies Ltd, based in Mysuru, with financial backing from the TDB. The manufacturing takes place at an advanced, high-precision production facility within the Medical Devices Park in Oragadam, Tamil Nadu.
Key Features and Technological Highlights
- Indigenous Design: S3V is the first Indian company to conceptualize and produce stroke-intervention tools such as microcatheters, aspiration catheters, guidewires, and stent retrievers.
- R&D and Patents: The company has filed multiple patents, particularly for innovations in clot retriever head design and advanced catheter structures.
- Training and Capacity Building: A simulator-based training program has been initiated to train young medical professionals, with a focus on outreach in Tier-II cities.
- Global Compliance: The device aims to meet CE and USFDA standards, paving the way for international exports and aligning with global quality benchmarks.
Significance for India
- Reduces Import Dependency: The device addresses India’s reliance on expensive, imported stroke-care equipment.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare: By making stroke treatment more affordable, it enhances access to quality care for economically weaker sections.
- Supports Public Health Initiatives: It is expected to be integrated into government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, strengthening the country’s universal healthcare mission.
- Boosts MedTech Ecosystem: This innovation is a major stride in positioning India as a global player in the high-end medical devices sector.
Boothapandi Rock Grooves

- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has recently unearthed one of the first known Neolithic rock grooves in Kanniyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, specifically near Boothapandi village. These grooves—estimated to be around 4,000 years old—were likely created by Neolithic people to sharpen tools and weapons used for hunting, agriculture, and digging.
The discovery was made during a field study conducted by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan, ASI Officer (Tirunelveli &Kanniyakumari), and M. Faisal of the Sembavalam Research Centre. The grooves vary in size:
- Length: 8 cm to 15 cm
- Width: 3 cm to 4 cm
Such grooves have also been previously documented in Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram districts of Tamil Nadu. The find strongly suggests the presence of Neolithic human activity in southernmost India and adds a significant layer to our understanding of prehistoric settlements in the region.
Neolithic Age
The Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) marks the final stage of prehistoric human evolution before the emergence of metal tools. Beginning around 10,000 BCE, it coincides with the Holocene Epoch and follows the Paleolithic Age (chipped-stone tools) and precedes the Bronze Age.
Key Features of the Neolithic Age
- Lifestyle Shift: Transition from hunting-gathering to agriculture and animal domestication.
- Permanent Settlements: Emergence of village communities with mud-and-reed houses, both rectangular and circular in design.
- Toolmaking: Development of polished and ground stone tools.
- Crafts and Culture: Rise of pottery, weaving, alcohol production, and early architecture.
- Burial Practices: Use of status objects (e.g., jade, pottery) in burials indicates belief in afterlife and emerging social hierarchies.
- By the end of the Neolithic era, copper metallurgy began, marking the Chalcolithic (Copper-Stone) Age. Eventually, bronze tools replaced stone ones, signaling the end of the Stone Age and the dawn of early civilizations.
Major Neolithic Sites in India
- Burzahom – Kashmir
- Chirand (Chiron) – Bihar
- Uttarapalli – Andhra Pradesh
- Edakkal Caves – Kerala
- Boothapandi (newly identified) – Tamil Nadu
Kannadippaya

- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
The traditional tribal mat Kannadippaya from Kerala has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, marking a significant milestone in the protection and promotion of India’s tribal handicraft heritage.
About Kannadippaya
- Origin and Craftsmanship:Kannadippaya (literally, mirror mat) is a unique handicraft made by various tribal communities of Kerala, notably the Oorali, Mannan, Muthuvan, Malayan, Kadar, Ulladan, Malayarayan, and Hill Pulaya tribes. The craft is predominantly practiced in Idukki, Thrissur, Ernakulam, and Palakkad districts.
- Raw Material:The mat is woven using the soft inner layers of reed bamboo (Teinostachyumwightii) and other bamboo species such as Ochlandra sp., known locally by various names including Njoonjileetta and Kanjoora.
- Functional and Aesthetic Value:The mat’s reflective design gives it a mirror-like appearance. It offers thermal comfort by providing warmth during winter and cooling during summer, showcasing traditional ecological knowledge.
- Historical Significance:Historically, these mats were offered by tribal communities as a token of honour to kings, reflecting the cultural and symbolic value attached to the craft.
Significance of the GI Tag
- Cultural Recognition:Kannadippaya becomes Kerala’s first tribal handicraft to receive a GI tag, acknowledging its cultural uniqueness and heritage value.
- Economic Empowerment:The GI tag is expected to:
- Provide market protection for tribal artisans.
- Enable branding and certification, enhancing the product's authenticity.
- Open national and international markets, especially for eco-friendly, sustainable products.
- Encourage entrepreneurship among tribal communities, reducing dependency on intermediaries.
- Institutional Support:
- The Kerala Forest Research Institute (KFRI) played a pivotal role in securing the GI tag, along with contributions from experts.
- The application was supported by tribal cooperatives like UnarvuPattikavarghaVividodeshaSahakarana Sangam and Vanasree Bamboo Craft, Idukki.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Lack of Structured Market:Artisans have highlighted the absence of a robust marketing ecosystem. There is a need for State and Central government interventions to:
- Facilitate marketing infrastructure and e-commerce platforms.
- Provide training and capacity-building for artisans.
- Encourage younger generations to take up the craft through incentives and education.
- Sustainability and Global Demand:Given the rising demand for eco-friendly and sustainable products globally, Kannadippaya has the potential to become a symbol of India’s green and inclusive development model.
Domestically Manufactured Iron & Steel Products (DMISP) Policy – 2025
- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
To address the rising steel imports and strengthen domestic industry under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the Government of India has notified the DMISP Policy – 2025, mandating the exclusive use of Indian steel in government procurement and incorporating a reciprocity clause against non-cooperative foreign countries.
About the DMISP Policy – 2025
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Steel
- Aim:To promote the use of domestically produced iron and steel in government-funded projects, thereby reducing import dependence, enhancing self-reliance, and safeguarding the interests of the Indian steel industry.
- Key Objectives
- Promote Self-Reliance: Advance the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by boosting domestic steel production and consumption.
- Curb Imports: Mitigate the adverse impact of rising steel imports on Indian steelmakers.
- Support Domestic Industry: Provide a level playing field to Indian steel manufacturers in public procurement.
- Encourage Value Addition: Increase domestic sourcing and manufacturing of capital goods used in steel production.
Salient Features of the Policy
- Mandatory Use of Indian Steel:
- Applicable across all Union Ministries, PSUs, statutory bodies, and trusts.
- Covers products such as flat-rolled steel, rods, bars, and rails.
- Steel must meet the “Melt and Pour” condition — i.e., must be melted and solidified in India.
- Reciprocity Clause:
- Nations that restrict Indian firms from participating in their public procurement (e.g., China) are barred from Indian government tenders.
- Exceptions can be made only with the approval of the Ministry of Steel.
- Ban on Global Tenders (GTE):
- GTEs for steel products are prohibited.
- GTEs for capital goods (e.g., furnaces, rolling mills) are permitted only for contracts above ?200 crore, with prior clearance.
- Domestic Value Addition Requirement:
- Capital goods used in steel production must have at least 50% local value addition.
- Certification by statutory or cost auditors is mandatory.
- Procurement Applicability:
- Mandatory for all government procurement above ?5 lakh.
- Also extends to centrally funded but state-executed projects.
- Monitoring and Enforcement:
- A Standing Committee chaired by the Secretary (Steel) will:
- Oversee compliance and redress grievances.
- Grant exemptions in case of non-availability of Indian products.
- A Standing Committee chaired by the Secretary (Steel) will:
- Penalties for Non-Compliance:False declarations may result in blacklisting of suppliers and forfeiture of earnest money deposits.
Euphaeawayanadensis
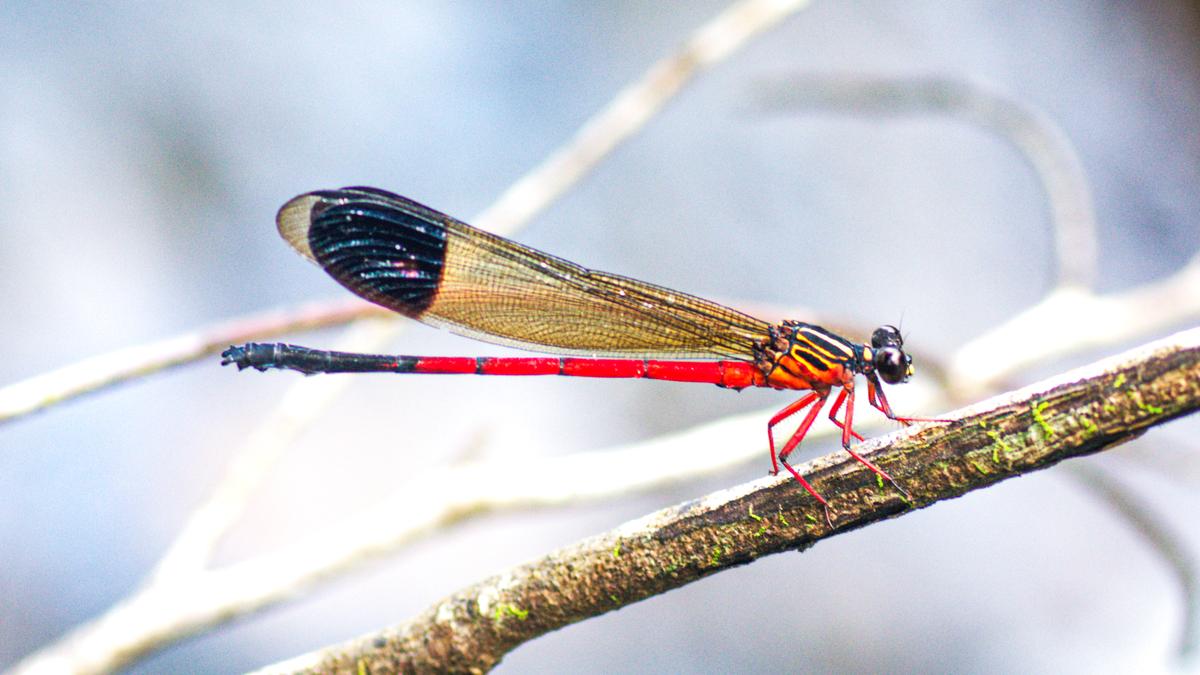

- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
A new species of damselfly, Euphaeawayanadensis, has been discovered in the Wayanad region of Kerala, marking a significant addition to India’s odonate diversity.
Key Details:
- Taxonomy:
- Belongs to the family Euphaeidae.
- Officially recognized as Kerala’s 191stodonate species (including damselflies and dragonflies).
- 223rd species recorded from the Western Ghats.
- Discovery and Research:
- First observed in 2013 at Kalindi River, Thirunelli, Wayanad.
- Confirmed after field studies conducted until 2023 across Wayanad, Aralam (Kannur), and western Coorg slopes (Karnataka).
- Discovery published in the peer-reviewed journal ENTOMON.
- Research Contributors:Collaborative effort involving scientists from Kerala Agricultural University, Alphonsa College, and conservation groups like Warblers and Waders, Travancore Nature History Society.
- Identification Process:
- Initially mistaken for Euphaeapseudodispar (from Maharashtra).
- Declared a distinct species based on morphological traits and genetic analysis.
Distinct Morphological Features
- Hind wing: Longer black patch compared to similar species.
- Stripes: Broader, uninterrupted humeral and antehumeral stripes in males.
- Male genital vesicle: Structurally unique from related species.
Habitat & Distribution
- Inhabits fast-flowing rocky streams with aquatic vegetation.
- Found in evergreen and semi-evergreen forests along stream banks.
- Active throughout the year except March–April (dry season).
- Shows restricted distribution, making it ecologically vulnerable.
Conservation Importance
- The discovery underlines the biodiversity richness of the Western Ghats.
- Highlights the need for targeted conservation of aquatic invertebrates in fragile ecosystems like Wayanad.
- Emphasised by experts from the IUCN Dragonfly Specialist Group.
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)

- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission, which successfully landed on the Moon’s south polar region on August 23, 2023, achieved a global first with its Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) — the first thermal probe to successfully penetrate the soil of a celestial body and measure subsurface temperatures in situ.
About ChaSTE:
- Full form: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment.
- Part of: Vikram lander (Chandrayaan-3).
- Depth achieved: Successfully tunnelled10 cm into the lunar regolith.
- Duration of operation: From August 23 to September 2, 2023.
- Significance: First successful deployment of a thermal probe into extraterrestrial soil.
Key Features:
- Temperature sensors: 10 sensors spaced 1 cm apart near the probe’s tip.
- Deployment mechanism: Unique rotation-based system — unlike previous missions that used hammering mechanisms.
- Measurement technique: Monitored changes in motor resistance and tip temperature to determine soil contact and depth.
Scientific Outcomes:
- Provided direct temperature profiles of lunar subsurface near the south pole.
- Enabled insights suggesting greater-than-expected presence of water ice beneath the surface.
Comparison with Previous Attempts:
Mission Agency Celestial Body Instrument Outcome
Rosetta – Philae (2014) ESA Comet 67P MUPUS Deployment failed due to
landing bounce
InSight (2018) NASA Mars HP3 ("The Mole") Could not collect data;
probe failed to burrow
as intended
Chandrayaan-3 (2023) ISRO Moon ChaSTE Successful soil
penetration and
temperature measurement
- Innovation Edge: Unlike ESA’s and NASA’s hammer-based devices, ChaSTE used a rotating drill, allowing steady penetration despite lunar soil resistance.
- Developed by the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad.
INSV Tarini at Cape Town

- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
The Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Tarini, crewed by women officers Lt CdrDilna K. and Lt Cdr Roopa A., reached Cape Town, South Africa, marking the final international port in the Navika Sagar Parikrama II — a global circumnavigation mission by the Indian Navy.
About INSV Tarini:
- Type: 56-foot indigenously built sailing vessel.
- Commissioned: February 2017.
- Builder:Aquarius Shipyard Ltd., Goa, under the Make in India initiative.
- Features:
- Equipped with Raymarine navigation suite, satellite communication systems, and emergency steering.
- Designed to operate in extreme maritime conditions.
- Name Origin: Named after the Tara-Tarini hill shrine in Odisha; ‘Tarini’ in Sanskrit means “boat” and “saviour.”
Navika Sagar Parikrama II:
- Flagged off from Goa: October 2, 2024, by Admiral Dinesh K. Tripathi, Chief of the Naval Staff.
- Duration: ~8 months.
- Total distance: Approx. 23,400 nautical miles (43,300 km).
- Route across three oceans, rounding three major capes.
- Ports of call before Cape Town:
- Fremantle (Australia)
- Lyttelton (New Zealand)
- Port Stanley (Falkland Islands, UK)
Challenges Faced:
- Extreme weather: Winds > 50 knots (93 km/h), waves up to 7 metres.
- Rough seas and cold temperatures posed significant navigational challenges.
Significance:
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to women-led maritime expeditions.
- Strengthens India–South Africa naval cooperation:
- October 2024: INS Talwar participated in Exercise IBSAMAR.
- January 2025: INS Tushil made a port call at Durban.
Carbon Dioxide (CO?) Lasers
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
A team of physicists in the United States has developed a novel method for remotely detecting radioactive substances using carbon dioxide (CO?) lasers. This advancement offers significant implications for national security, nuclear safety, and emergency response, where safe, long-distance detection is essential.
About CO? Lasers:
- Inventor: Prof. C.K.N. Patel, an Indian-American physicist.
- Laser Type: Four-level molecular gas laser.
- Active Medium: A gas mixture of CO?, nitrogen (N?), and helium (He).
- Wavelengths: 9.6 µm and 10.6 µm (Infrared region).
- Power Output: Can reach up to 10 kW, delivering continuous or pulsed beams.
- Mechanism: Operates through transitions between vibrational energy states of CO? molecules, facilitated by energy transfer from excited N? molecules.
Structure and Vibrational Modes of CO? Molecule:
- Composed of one carbon atom flanked by two oxygen atoms.
- Exhibits three vibrational modes:
- Symmetric Stretching – oxygen atoms move in tandem.
- Bending Mode – atoms move perpendicular to the axis.
- Asymmetric Stretching – oxygen and carbon atoms move in opposite directions.
Detection Principle: Avalanche Breakdown and Plasma Formation
- Radioactive decay emits charged particles (e.g., alpha particles) that ionize air, forming plasma.
- Seed electrons in this plasma gain energy via the CO? laser and initiate avalanche breakdown, causing further ionization.
- This chain reaction forms microplasmas, which produce optical backscatter detectable through sensors.
Key Experimental Insights:
- Laser Used: Long-wave infrared CO? laser at 9.2 µm, ideal for minimizing unwanted ionization.
- Alpha particle detection: Achieved from 10 meters, a tenfold improvement over previous techniques.
- Gamma ray detection (e.g., from Cs-137): Potential detection range of up to 100 meters, scalable with improved laser optics.
- Fluorescence imaging: Employed to analyze plasma dynamics and map seed electron distributions.
- Mathematical modeling: Successfully predicted backscatter based on plasma characteristics, validating the method.
Advantages of the Technique:
- Enhanced sensitivity to weak radioactive sources.
- Long-range detection without direct contact.
- Reduced risk for personnel during radiation monitoring.
- Scalability: Theoretically extendable to ~1 km with high-energy lasers and larger optics.
Challenges Ahead:
- Extended range detection requires larger optical systems and higher laser power.
- Signal degradation due to atmospheric interference and background noise at longer distances.
- Trade-off between detection range and signal clarity remains a critical engineering hurdle.
The use of CO? lasers for radioactive detection marks a significant leap in remote sensing technologies. While currently limited to tens or hundreds of meters, future developments may push detection ranges further, making it a valuable tool in defense, nuclear safety, and disaster management.
ISRO’s CARTOSAT-3

- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
Recently, a 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck Myanmar near the Sagaing-Mandalay border, causing severe damage in key cities such as Mandalay and Sagaing. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) used its advanced Earth observation satellite CARTOSAT-3 to assess the destruction via high-resolution post-disaster imagery.
CARTOSAT-3: An Overview
- Developer: ISRO
- Launched by: PSLV-C47
- Mission Type: Third-generation agile Earth observation satellite
- Successor to: IRS (Indian Remote Sensing) series
Key Specifications:
Feature Details
Resolution Panchromatic: 0.25 metres (sharpest civilian)
Orbit Altitude 509 km (Sun-synchronous orbit)
Inclination 97.5°
Weight 1,625 kg
Technologies Agile cameras, advanced onboard computers, high-speed data transmission
Commercial Use
- First commercial order executed by NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL), ISRO’s commercial arm.
Applications of CARTOSAT-3
- Disaster Management: Monitoring and assessing damage from earthquakes, floods, and landslides
- National Security & Strategic Operations: Surveillance and intelligence (used in 2016 LoC surgical strikes and 2015 Myanmar-Manipur ops)
- Urban & Rural Planning: Infrastructure development, land-use mapping, and road networks
- Environmental Monitoring: Coastal regulation and land-use changes
- Cartography and Remote Sensing: High-precision geospatial mapping and terrain analysis
Cartosat and Other ISRO Satellite Series
Satellite Series Focus Area
Cartosat-1 to 3 High-resolution Earth imaging for urban/rural planning
RISAT Radar-based imaging (all-weather surveillance)
Oceansat Oceanography, weather, and marine research
INSAT &Megha-Tropiques Atmospheric and climate monitoring
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum Portal

- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The NITI NCAER States Economic Forum portal, jointly developed by NITI Aayog and the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER), was launched on April 1, 2025, by the Union Finance Minister.
Key Highlights:
The portal serves as a comprehensive digital repository offering over 30 years (1990-91 to 2022-23) of state-wise data on social, economic, and fiscal parameters, promoting evidence-based policymaking and fiscal transparency.
Purpose and Significance
- Objective: To enable policymakers, researchers, and academics to access, compare, and analyze long-term trends in State finances and socio-economic indicators.
- Promotes data-driven governance, facilitates inter-State comparisons, and strengthens cooperative federalism.
- Addresses persistent demands for transparent, centralized, and accessible fiscal data, especially amid concerns of fiscal imbalance between Centre and States.
Core Features of the Portal
The portal is structured around four main components:
- State Reports:
- Covers all 28 Indian States.
- Summarizes macroeconomic and fiscal landscapes based on key indicators—demography, economic structure, social indicators, and fiscal metrics.
- Data Repository:
- Offers access to extensive datasets organized into five verticals:
- Demography
- Economic Structure
- Fiscal
- Health
- Education
- Offers access to extensive datasets organized into five verticals:
- Fiscal and Economic Dashboard:
- Interactive dashboards with graphical representations of vital statistics.
- Enables visualization of trends and download of datasets.
- Research and Commentary:Features expert analyses, research papers, and commentary on fiscal policies and State-level financial management.
Benefits and Policy Implications
- Enhances transparency and informed public debate.
- Supports benchmarking of States' performance against national averages and peer States.
- Aids in planning reforms, improving public finance management, and addressing regional disparities.
- A vital tool for academicians, policy analysts, and government officials working on State-level governance and development planning.
Arctic Geopolitics
- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The Arctic region, traditionally isolated due to its extreme climate and thick ice cover, is rapidly emerging as a global geopolitical hotspot. Accelerated melting of ice caps due to climate change has unlocked access to untapped resources and new shipping routes, intensifying competition among major powers.
Resource Wealth and Strategic Significance
- The Arctic holds an estimated 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil and 30% of untapped natural gas (USGS, 2009).
- Rich in rare earth elements, phosphates, and copper, particularly in areas like Greenland.
- Melting ice is opening access to valuable fishing grounds and enabling commercial navigation.
Emerging Shipping Routes
- Northeast Passage (Northern Sea Route): Along Russia’s Arctic coast, connecting Europe and Asia. Reduces distance by ~8,000 km compared to the Suez Canal.
- Northwest Passage: Through Canada’s Arctic Archipelago. Disputed between Canada (claims internal waters) and the U.S. (asserts international strait).
These routes offer significant economic and strategic advantages, including reduced dependency on traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
Governance: The Arctic Council
The Arctic Council, established by the 1996 Ottawa Declaration, is the key intergovernmental forum for Arctic affairs.
Members (8 Arctic States):
- Canada, Denmark (via Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States
These countries:
- Control Arctic land territories
- Have sovereign rights over resources within their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs)
Permanent Participants:
- Six Indigenous groups representing Arctic communities.
Observers:
- Includes India, China, Japan, UK, among others.
- 13 countries, 13 intergovernmental, and 12 non-governmental organisations.
- All decisions require consensus of member states and consultation with Indigenous groups.
Legal Framework and Territorial Claims
- Governed primarily by UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea).
- Allows Arctic states to extend claims beyond their 200-nautical-mile EEZ if they prove natural extension of the continental shelf.
- Russia, Canada, and Denmark have submitted overlapping claims to the Arctic seabed.
Unlike Antarctica, which is demilitarised under international treaties, the Arctic has no such binding legal framework, allowing military infrastructure and territorial claims.
Geopolitical Tensions in the Arctic
Russia’s Military Build-up:
- Largest fleet of Arctic icebreakers, including nuclear-powered vessels.
- Maintains Soviet-era Arctic military bases.
- Planted a flag on the Arctic seabed at the North Pole in 2007.
- In 2022, conducted naval exercises with China, signaling deepening strategic ties.
U.S. Interests:
- Renewed interest in Greenland, citing national security.
- Operates the Pituffik Air Base in Greenland.
- Dispute with Canada over Northwest Passage navigation rights.
NATO’s Arctic Response:
- All Arctic Council members except Russia are NATO allies.
- NATO has increased its Arctic presence post-Ukraine conflict.
- Strategic focus on GIUK (Greenland-Iceland-UK) Gap, a critical naval chokepoint for Russian submarines.
China’s Arctic Aspirations:
- Declared itself a "Near-Arctic State" in 2018.
- Investing in Arctic research and building its first nuclear-powered icebreaker.
- Interested in Russia’s Northeast Passage for trade under the proposed “Polar Silk Road”.
India and the Arctic
India, an observer in the Arctic Council, is closely monitoring developments. It has an Arctic Policy focusing on:
- Scientific research
- Climate and environmental protection
- International cooperation
Strength of Cloud Bands and their role in Indian Monsoon

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
A recent study by the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has shed new light on the role of equatorial cloud bands in determining the movement and intensity of monsoon rainfall over India. These insights could enhance the accuracy of seasonal and sub-seasonal climate models.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Importance of Cloud Band Strength:
- The northward movement of monsoon cloud bands—crucial for triggering wet spells in India—is not guaranteed. Only strong cloud bands originating near the equator successfully propagate northward.
- Weak cloud bands fail to initiate wet spells, countering earlier assumptions that all cloud bands move north regardless of strength.
- Role of BSISO:
- The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO) governs alternating wet and dry spells during the monsoon. It helps transport convection (cloud activity and heat) from the Indian Ocean towards the Indian subcontinent.
- The size and strength of the cloud band influenced by BSISO determine the duration and intensity of wet phases.
- Air-Sea Interaction:
- Moisture buildup and wind strength, both vital for rain formation, are heavily influenced by air-sea interaction in the equatorial Indian Ocean.
- Strong coupling between the ocean and atmosphere enhances atmospheric moisture, aiding cloud formation and monsoon intensity.
- Impact of Climate Change:
- With rising global temperatures, background atmospheric moisture is expected to increase.
- This is projected to lead to a 42%–63% rise in rainfall during wet spells across India and surrounding seas in the future.
- Modeling and Forecasting:
- The study's findings help address gaps in current climate models, improving forecasts for monsoon rains at both seasonal and sub-seasonal scales.
What is BSISO?
- A large-scale monsoon phenomenon active between June and September.
- Alternates between active (rainy) and break (dry) spells.
- Modulated by global oceanic phenomena such as:
- El Niño: Weakens northward propagation of BSISO.
- La Niña: Enhances BSISO movement towards India.
Key Facts About Indian Monsoon:
- Monsoon Etymology: Derived from Arabic "mausim", meaning season.
Types of Monsoons in India:
- Southwest Monsoon (June–September):
- Also called the advancing monsoon.
- Brings 80% of India's annual rainfall.
- Driven by low pressure over the Indian subcontinent and high pressure over the Indian Ocean.
- Northeast Monsoon (October–December):
- Known as the retreating monsoon.
- Affects southeastern coastal regions, especially Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh.
Key Influencing Factors:
- Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): Moves northward in summer, attracting moisture-laden winds.
- Tibetan Plateau Heating: Generates the Tropical Easterly Jet, enhancing monsoon inflow.
- Somali Jet: Strengthens monsoon winds from the Arabian Sea.
- Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD):
- Positive IOD (warmer west): Enhances monsoon.
- Negative IOD (warmer east): Weakens it.
- ENSO (El Niño–Southern Oscillation):
- El Niño: Linked with weaker monsoons and droughts.
- La Niña: Associated with stronger and prolonged monsoon spells.
India–Myanmar Free Movement Regime (FMR)

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
In February 2024, Union Home Minister Amit Shah announced the scrapping of the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the India–Myanmar border, citing national security concerns. The decision is reportedly influenced by the former Manipur Chief Minister, who blamed unregulated cross-border movement for ethnic violence in Manipur. However, the decision has not yet been implemented, and no formal notification or bilateral agreement has been issued. Mizoram and Nagaland have opposed the move, highlighting socio-cultural concerns.
What is the Free Movement Regime (FMR)?
- Introduced: 1968
- Current Limit: Movement up to 16 km on either side of the 1,643 km-long India–Myanmar border
- Eligibility: Members of hill tribes on both sides with a border pass valid for one year, allowing stay for up to 2 weeks per visit
- Purpose:
- Preserve historical, cultural, and familial ties between border communities
- Facilitate local trade and people-to-people exchanges
- Complement India’s Act East Policy by promoting cross-border cooperation
- Regulations: Initially 40 km (1968), reduced to 16 km (2004), with tighter checks from 2016
- Formal Implementation: 2018
Impact on Border Communities:
- Deep Ethnic and Familial Ties: Many communities across Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh share ancestry and cultural links with communities in Myanmar, such as the Chin and Mizo peoples.
- Local Trade & Livelihoods: FMR supports livelihoods through informal trade. Its removal could disrupt economic dependence in these remote areas.
- Perceived as Redundant: Locals report that cross-border interaction predates FMR and continues with or without official sanction.
Security Concerns and Contraband Issues:
- Despite increased military presence post the Border Area Development Programme (BADP) in the 1980s, smuggling of contraband such as drugs, gold, and areca nuts continues unabated.
- Centre’s View: FMR allegedly facilitates illegal migration, drug trafficking, and infiltration contributing to internal instability.
- Local View: Scrapping the FMR alone won’t stop cross-border crime without comprehensive border management and community engagement.
Challenges with Border Fencing:
- Difficult Terrain: The mountainous and forested landscape makes border fencing logistically and financially challenging.
- Social Sensitivity: Fencing may provoke protests as the border cuts across ethnically unified communities.
- Unified Homeland Demand: Risk of reviving separatist sentiments, especially in regions like Eastern Nagaland, where demands for Frontier Nagaland exist.
Legal and Strategic Concerns:
- The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023 allows the use of forest land within 100 km of international borders for strategic projects, raising concerns about displacement and loss of ancestral lands.
Way Forward:
- Balanced Approach Needed:
- Any changes must consider security needs as well as local sensitivities.
- Community engagement and consultation are crucial to avoid unrest.
- Alternatives to Fencing:
- Strengthen customs and intelligence units along the border.
- Promote legal trade channels to formalize economic activities.
- Enhance monitoring mechanisms without disrupting historical ties.
- Long-Term Strategy:
- Address instability in Myanmar, Chinese influence, and Golden Triangle drug trade through coordinated regional efforts.
- Align border governance with India’s Act East Policy, focusing on connectivity and cultural diplomacy.
Keezhadi Excavations
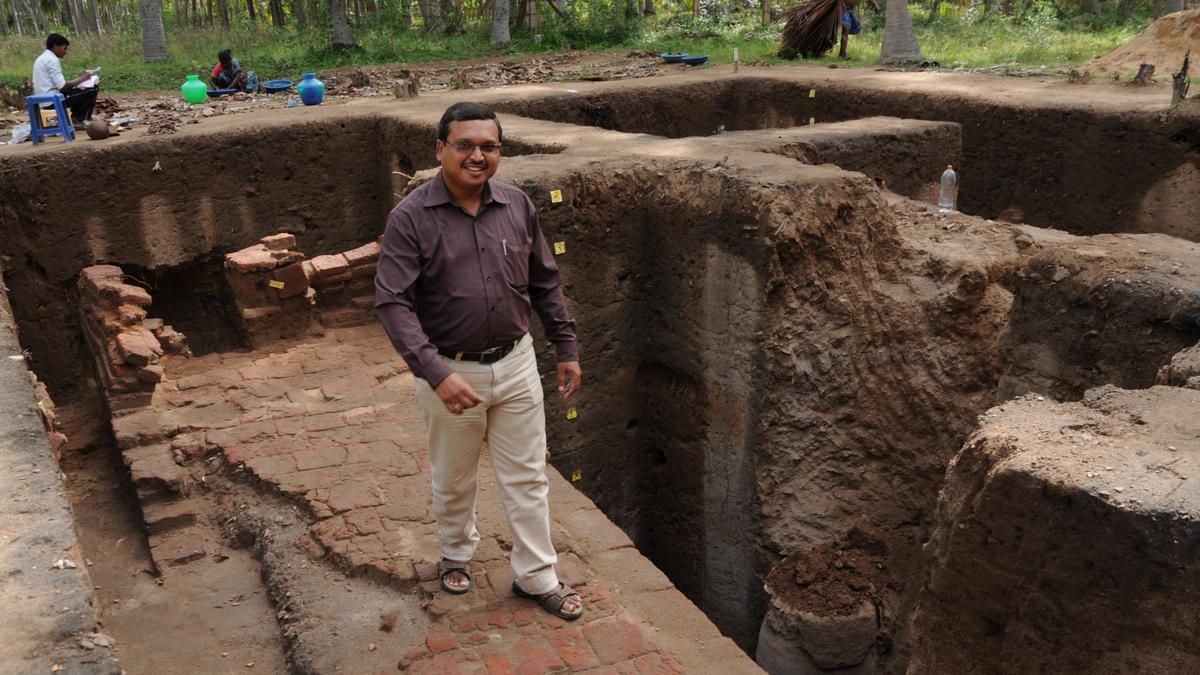

- 24 May 2025
In News:
The Keezhadi archaeological site, located near Madurai along the Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu’s Sivaganga district, is a major site of cultural and historical significance. It offers compelling evidence of an urban, literate, and industrialized Tamil civilization dating back to the Sangam Age.
Background and Discovery
- Discovered: Surveys in 2013–14; Excavations began in 2015.
- Excavating Agencies: Initially conducted by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and later by the Tamil Nadu State Archaeology Department.
- Excavated Area: Only 1 out of 100 acres has been explored; over 4,000 artefacts recovered.
Significant Findings
- Carbon Dating (AMS) of charcoal: Indicates urban habitation existed by 200 BCE.
- Key Discoveries: Brick structures, ring wells, pottery with Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions, beads, graffiti, water storage facilities, and a large decorative pot unique to the region.
- Artefacts suggest links with North India and Western trade networks.
Cultural and Historical Significance
- Suggests early urbanization in South India, independent of northern influence.
- Supports theories of a pre-Sangam urban Tamil culture.
- Establishes Keezhadi as a centre of literacy, trade, and craftsmanship.
- Mention of nearby settlements like Manalur and Konthagai in Tamil classics such as Tiruvilayadal Puranam strengthens the site's literary links.
Sangam Period Context
- Spanned approximately 3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE.
- Tamil academies or ‘Sangams’ under the Pandya dynasty produced extensive literature.
- Notable texts: Tolkappiyam, Ettuthogai, Pattupattu, Padinenkilkanakku, and epics like Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, and CivakaCintamani.
- Literature depicts advanced socio-political systems, agriculture, trade, and maritime activities.
Current Issues and ASI Involvement
- The excavation report prepared by archaeologist Amarnath Ramakrishna (submitted in January 2023) has been returned by ASI for revision to ensure:
- Accurate period classification.
- Better stratigraphic and cartographic details.
- Consistency in scientific dating and layer mapping.
- ASI has flagged the need for clearer mapping, missing illustrations, and precise scientific justification for dating claims, especially for Period I (8th to 5th century BCE).
Controversy and Criticism
- Concerns have been raised over delays in publishing excavation reports.
- Critics highlight a perceived bias in the handling of southern archaeological sites, pointing to similar delays with the Adichanallur site report.
- Experts stress the importance of transparent and timely reporting to enhance historical understanding.
Guttala Inscription
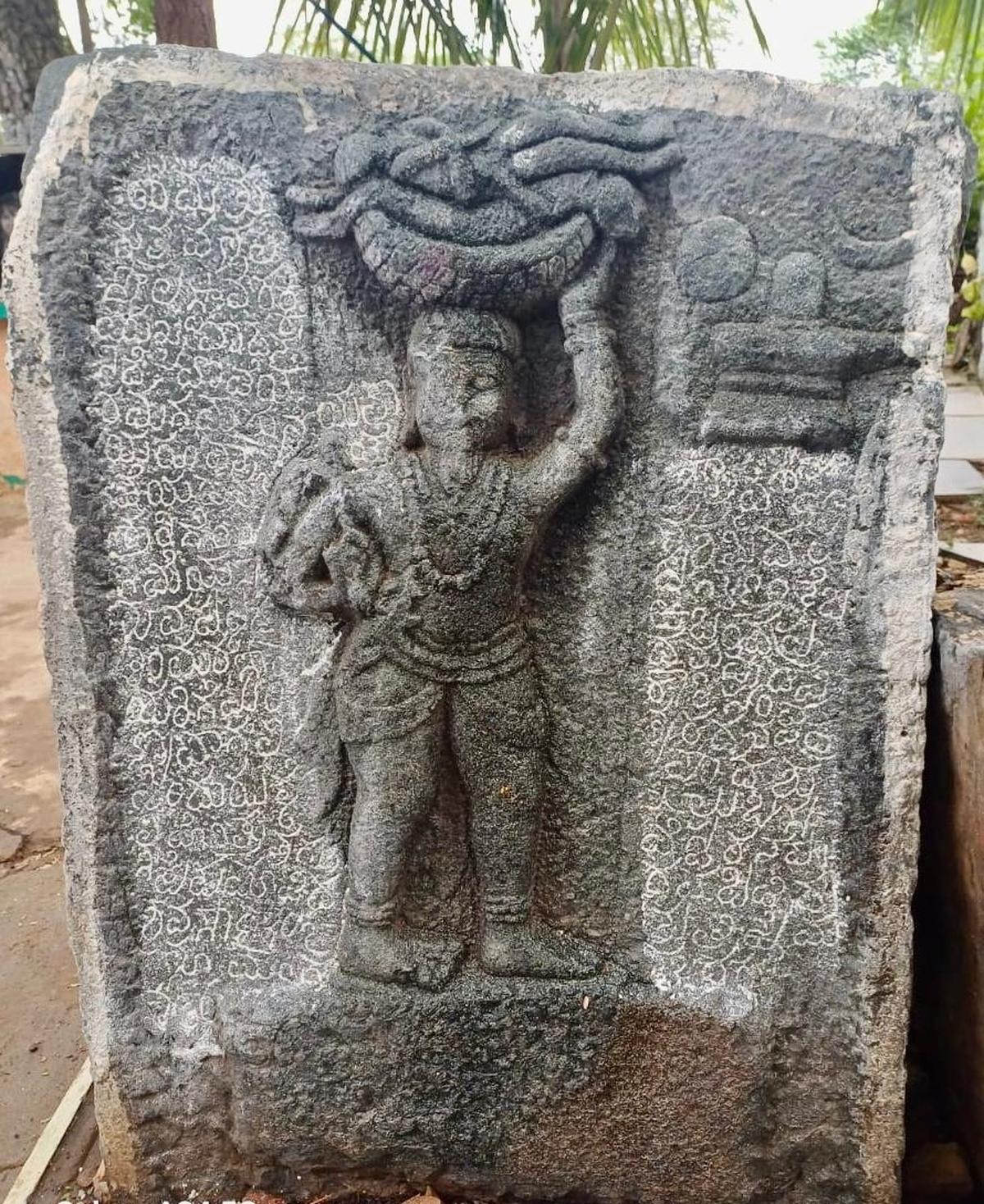

- 24 May 2025
In News:
A rare 16th-century sculptural inscription discovered near the Chandrashekara temple in Guttala village, Haveri district, Karnataka, marks the earliest known epigraphic evidence in India of a large-scale humanitarian disaster caused by a natural calamity—a drought (bara) that claimed 6,307 lives in 1539 CE (Saka 1461, August 18).
Key Features of the Inscription:
- Language and Script: Kannada.
- Medium: Stone slab.
- Depiction: A sculpture showing MarulaihOdeya, the son of NanidevaOdeya, carrying a basket containing dead bodies—representing his act of burying the deceased to earn religious merit for the regional ruler, TimmarasaSvami.
- Religious Context: The burial was conducted after paying homage to Basaveshwara, reflecting the spiritual and ritualistic practices of the time.
- Territorial Reference: Mentions the term "seeme", indicating the existence of local administrative divisions.
Significance:
- First explicit historical record in India of deaths caused by a natural disaster, making it an important source for disaster history and epigraphic heritage.
- Offers textual and visual representation of community response to drought.
- Provides insights into local governance, religious customs, and socio-economic conditions of 16th-century Karnataka.
- Adds depth to the study of historical climate events, with potential to track past climatic patterns and their impact on populations.
Broader Context:
- Inscriptions in India, typically engraved on stone or metal, serve as valuable primary sources for understanding royal decrees, battles, donations, and societal events.
- Other notable Karnataka inscriptions include:
- Maski Edict (3rd Century BCE) – First mention of Emperor Ashoka as "Devanampriya".
- Halmidi Inscription (c. 450 CE) – Oldest Kannada inscription referencing Kadamba king Kakusthavarma.
- Aihole Inscription (634 CE) – Chronicles the military achievements of Pulakeshin II.
Recent Epigraphic Developments:
- The Epigraphy Branch of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered and documented over 1,000 inscriptions across India during 2024–25, including more than 100 new finds this year alone.
- These discoveries reinforce the role of epigraphy in reconstructing Indian history, especially in areas lacking detailed literary sources.
BrahMos-NG and Extended Range BrahMos

- 23 May 2025
In News:
India is advancing its supersonic missile capabilities with the development of two significant assets:
- The BrahMos-NG (Next Generation) missile—lighter, stealthier, and more versatile.
- The extended-range BrahMos, which pushes the missile’s reach up to 800 km, enhancing India’s strategic depth.
About BrahMos:
- Joint Venture: BrahMos Aerospace (DRDO of India and Russia’s NPO Mashinostroyenia).
- First Induction: 2005 (anti-ship version).
- Name Origin: Combines names of Brahmaputra (India) and Moskva (Russia) rivers.
- Capabilities: Launch from land, sea, sub-sea, and air against land and sea targets.
BrahMos-NG (Next Generation):
A miniaturized, next-gen supersonic cruise missile designed for enhanced operational flexibility and platform compatibility.
Key Features:
- Size & Weight: ~1.33–1.5 tonnes, nearly half the current air-launched BrahMos (2.5–2.65 tonnes).
- Speed: Mach 2.8.
- Range: ~400–450 km; potential for 800 km with future trials.
- Stealth: Lower radar cross-section and advanced stealth design.
- Platforms: Compatible with Su-30MKI, LCA Tejas, Rafale, MiG-29, naval ships, and submarines.
- Launch Options: From air, land vehicles, surface warships, and submarine torpedo tubes.
- Advanced ECCM: Improved resistance against electronic warfare/jamming.
- Precision Targeting: Ideal for land-attack, anti-ship, and underwater combat scenarios.
Strategic Benefits:
- Higher platform density: E.g., a Su-30MKI can carry up to 4 BrahMos-NG missiles; Tejas can carry 2.
- Faster deployment and reload cycles due to reduced size and logistics burden.
- Future-ready design: Modular, stealthy, and agile—ideal for modern warfare.
Extended-Range BrahMos:
- Background: Initial range capped at 290 km under Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
- Post-MTCR Membership: India joined MTCR in 2016, enabling range extension.
- Current Status: Successfully extended to 450 km; testing ongoing for 800 km version.
- Trial Update: Initial flight trial of the 800 km version conducted; more planned.
Operational Highlights:
- Combat Proven: BrahMos was used by the IAF for precision strikes on Pakistani airbases during the 2024 confrontation, demonstrating effective penetration of enemy air defence.
- Deterrence Capability: Former Air Chief Marshal V.R. Chaudhari called BrahMos-NG the IAF’s "primary deterrent weapon".
- Squadron Integration: 222 ‘Tiger Sharks’ squadron in Thanjavur equipped with BrahMos-armed Su-30MKIs.
SPICED Scheme
- 22 May 2025
In News:
The Spices Board of India, under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, has introduced the SPICED Scheme (Sustainability in Spice Sector through Progressive, Innovative and Collaborative Interventions for Export Development) for the financial year 2025–26.
Key Objectives
The SPICED initiative is designed to:
- Promote sustainability and innovation in spice farming.
- Enhance productivity and quality of major spices like small and large cardamom.
- Encourage organic cultivation, GI-tagged spice production, and value addition.
- Improve post-harvest processing standards.
- Ensure compliance with international food safety and phytosanitary regulations.
- Strengthen the export ecosystem and support spice stakeholders, including farmers, SHGs, and MSMEs.
Major Components and Interventions
The scheme extends financial assistance and capacity-building support across the spice value chain, including:
1. Agricultural Support
- Rejuvenation and replanting of cardamom plantations.
- Development of water sources and micro-irrigation systems.
- Promotion of organic farming and Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs).
2. Post-Harvest Infrastructure
- Installation of modern processing machinery such as dryers, dehullers, slicers, and grading systems.
- Assistance to farmers and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) for acquiring spice-specific equipment like:
- Turmeric boilers
- Spice polishers
- Mint distillation units
- Threshers
3. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Establishment of Spice Incubation Centres to promote product development and branding.
- Support for startups and MSMEs in accessing markets and improving competitiveness.
4. Capacity Building
- Training and extension activities to disseminate knowledge on best practices and technical know-how.
- Skill enhancement for Self-Help Groups (SHGs), farmers, and FPOs.
5. Export Promotion
- Facilitation of participation in international trade fairs, buyer-seller meets, and market linkage events.
- Financial aid prioritised for:
- First-time exporters
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
- Registered exporters with a valid CRES (Certificate of Registration as Exporter of Spices).
Governance and Transparency
- All scheme activities will be geo-tagged.
- Status of applications, fund allocation, and beneficiary details will be made available on the Spices Board's website to ensure transparency and accountability.
INSV Kaundinya

- 22 May 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy formally inducted and named an ‘ancient stitched sail ship’ as the INSV Kaundinya at a ceremonial event held at the Naval Base in Karwar. INSV Kaundinya has been built based on a 5th century ship depicted in paintings seen in the Ajanta Caves.
What is INSV Kaundinya?
The INSV Kaundinya is a reconstructed ancient stitched ship, modeled after maritime imagery found in the Ajanta Cave murals. It represents India’s historical naval engineering capabilities and cultural exchanges across the Indian Ocean.
Construction and Origins
- The project was initiated in July 2023 as a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Culture, the Indian Navy, and Hodi Innovations.
- The ship was built using traditional stitched shipbuilding methods, where wooden planks are lashed with coir ropes and coconut fibre, sealed with natural resin—a method that avoids the use of nails or metal fasteners.
- The design took inspiration from 5th-century depictions in the Ajanta caves, interpreted through archaeological analysis, hydrodynamics, and naval architecture, as no original ship designs from that era have survived.
Planned Expedition
- INSV Kaundinya is slated to retrace an ancient maritime trade route in 2025, sailing from Gujarat to Oman, highlighting India's historical seafaring ties with West Asia.
Cultural Symbolism
- The ship’s sails are embellished with traditional motifs such as the Gandabherunda (a two-headed mythical eagle) and Sun iconography, symbolizing resilience and energy.
- A SimhaYali (lion-dragon hybrid) figure adorns the bow, a nod to Dravidian maritime symbolism.
- The deck features a Harappan-style stone anchor, linking the vessel to India’s ancient Indus Valley maritime practices.
- Named after Kaundinya, an ancient Indian voyager known for establishing early trade and cultural links with Southeast Asia, the ship reflects India's historic role in transoceanic interaction.
Ajanta Cave Paintings: Artistic Reference
- Located in Maharashtra, the Ajanta Caves date from the 2nd century BCE to the 6th century CE, renowned for some of the oldest surviving Indian mural art.
- These murals use the tempera technique—painting on dry plaster with natural dyes such as red ochre and black.
- They largely portray Buddhist narratives, including Jataka Tales, and scenes from the Buddha’s life, interwoven with nature and decorative elements.
- The paintings emphasize emotional expression, spiritual depth, and distinctive anatomical stylization.
India’s Climate Physical Risk (CPR)

- 21 May 2025
In News:
Amid rising climate-induced disasters—floods, heatwaves, droughts—the Union Home Minister recently called for proactive climate risk assessments. India, however, lacks a comprehensive and standardised system to assess Climate Physical Risks (CPR), exposing critical gaps in preparedness.
What is Climate Physical Risk (CPR)?
Definition: CPR refers to the potential damage from:
- Acute events: Floods, cyclones, heatwaves.
- Chronic stresses: Changing monsoon patterns, droughts.
IPCC Formula:
CPR = Hazard × Exposure × Vulnerability
- Hazard: Climate threats like floods or wildfires.
- Exposure: Presence of people/assets in risk-prone areas.
- Vulnerability: System's capacity to withstand and recover.
Why CPR Assessment Matters for India
- High Risk: Over 80% of Indians reside in districts exposed to climate disasters (World Bank).
- Systemic Threat: Affects not just the environment, but public health, agriculture, economy, and national security.
- Future-proofing Development: Long-term planning must consider CPR for sustainable infrastructure and financial stability.
Challenges in India’s CPR Management
- Fragmented Efforts: Multiple agencies (IMD, IITs, NIDM) conduct isolated studies with no integration.
- Lack of Standardised Data: No central repository for CPR metrics at the district or panchayat level.
- Modelling Limitations: Global models like RCPs and SSPs fail to capture India's hyper-local climate variations.
- Private Sector Constraints: Businesses lack tools to evaluate climate risks across supply chains.
Global Best Practices
- Mandatory Climate Disclosures: Global frameworks like ISSB S2 and EU Taxonomy require companies to report CPRs.
- Adaptation as Priority: Nations, including the Global North, are investing in adaptation infrastructure, recognizing its economic returns.
- UNEP estimates: $1 in adaptation = $4 saved in disaster recovery.
Initiatives by India
- Adaptation Communication (2023): India’s first report to the UNFCCC under Article 7 of the Paris Agreement.
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP): In progress; covers 9 thematic sectors with district-level focus.
- RBI Framework: Climate risk integrated into financial supervision and regulatory assessments.
New Calcedonia
- 20 May 2025
In News:
For decades, New Caledonia, a French island territory of approximately 2,71,400 people in the southwest Pacific Ocean, has been on a complex journey regarding its status.
Geography and Strategic Significance
- Location: South Pacific Ocean, ~1,500 km east of Australia.
- Status: French overseas territory; part of EU’s Overseas Countries and Territories (OCTs), but outside the Euro and Schengen zones.
- Key Resources: Holds ~25% of the world’s nickel reserves.
- UNESCO Heritage: Lagoons and coral reefs recognized in 2008.
- Capital: Nouméa
Demographics (2019 Census)
- Population: ~2,71,400
- Indigenous Kanaks: ~39%
- Others: European, Polynesian, Vietnamese, Indonesian, Algerian descent.
Historical Timeline
- 1853: France annexes the islands; becomes a penal colony.
- 1957: French citizenship granted to all residents.
- 1980s: Ethnic tensions escalate; near civil war.
- 1988: Matignon Agreements signed.
- 1998: Nouméa Accord grants wide autonomy, New Caledonian citizenship, and promised three referendums on independence.
Independence Referendums
- 2018 & 2020: Majority voted against independence.
- 2021: Final vote boycotted by pro-independence groups (FLNKS) citing COVID-19 and customary mourning; outcome rejected as illegitimate.
Recent Crisis (2024)
- Trigger: French proposal to “unfreeze” electoral rolls to include newer residents.
- Consequence: Violent riots, 14 deaths, and widespread unrest.
- Talks Collapse: May 2024 negotiations failed due to rejection of the “sovereignty in partnership” proposal by loyalists.
Sovereignty-in-Partnership Proposal
- Envisioned enhanced self-rule with international recognition.
- Power would be delegated back to France in certain domains (e.g., judiciary).
- Rejected by loyalists as “disguised independence”.
Alternate Proposal by Loyalists
- Partition Model:
- Pro-independence North & Loyalty Islands – special status
- Wealthier, loyalist South Province – remain French
- Rejected by all sides:
- France – violates territorial integrity.
- FLNKS – compared it to apartheid.
What Lies Ahead?
- Provincial Elections due by November 2025.
- No political consensus on institutional status raises concerns of prolonged instability.
Gyan Bharatam Mission

- 19 May 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will launch the revamped National Manuscripts Mission, which was announced in the Union Budget earlier this year, on June 9.
Key Highlights:
- Implementing Body: Ministry of Culture, Government of India
- Earlier Version: National Manuscripts Mission (est. 2003), under Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA)
- Objective:To survey, document, conserve, and digitize over one crore (10 million) Indian manuscripts located in academic institutions, libraries, museums, and private collections.
Key Features
- Massive Coverage: Targets over 1 crore manuscripts, making it India’s largest manuscript preservation project.
- Digital Repository: Creation of a National Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems to ensure accessibility for researchers and the public. Includes AI-powered tools for metadata tagging, translation, and archiving.
- Modern Techniques: Uses advanced scientific conservation methods, including AI and 3D imaging.
- Collaborative Model: Engages academic institutions, libraries, museums, private collectors, and international bodies.
- Budgetary Support: Budget raised from ?3.5 crore to ?60 crore, with a total outlay of ?482.85 crore for 2024–31.
Background and Need
- The earlier NMM (2003) made limited progress. Out of 52 lakh manuscripts surveyed, only 3 lakh titles were digitized, and only 70,000 are currently viewable due to lack of access policy.
- 80% of manuscripts in India are privately owned, underscoring the need for public-private collaboration.
- Over 9 crore folios have been conserved (preventive and curative) in the last two decades.
What is a Manuscript?
A manuscript is a handwritten document (on paper, palm leaf, birch bark, etc.), at least 75 years old, and of historical, scientific, or artistic significance.
Example: The Bakhshali Manuscript (3rd–4th century BCE) is a key Indian text on mathematics, featuring the earliest known use of the symbol for zero.
India assembles first Chromosome-Level Genome of the Yak

- 16 May 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant breakthrough in livestock genomics with the successful assembly of the first-ever chromosome-level genome of the Indian yak (Bos grunniens). The initiative was led by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) through collaboration among four of its premier institutes.
Key Institutions Involved:
- ICAR-National Research Centre on Yak (NRC-Yak), Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh
- ICAR-Indian Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology (IIAB), Ranchi
- ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cattle (CIRC), Meerut
- ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cattle (CIRC), Nagpur
Importance of the Indian Yak:
- Known as the “Ship of the Himalayas,” the domestic yak is crucial to the livelihoods of high-altitude pastoral communities.
- Provides meat, milk, fibre, dung for fuel, and is used for transport in rugged terrain.
- Found at elevations above 7,000 feet in regions like Ladakh, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Exhibits extraordinary cold tolerance, making it a valuable model for studying climate adaptation.
Scientific Achievement:
- Researchers used long-read sequencing technology and advanced bioinformatics tools to develop a chromosome-level genome assembly.
- This allows precise gene mapping, facilitating identification of genes related to:
- Cold tolerance
- Disease resistance
- Milk and meat quality
- Reproductive traits
Benefits and Applications:
- Conservation: Helps counter threats like genetic erosion, climate change, and loss of grazing lands.
- Livestock Improvement: Enables targeted breeding programs for improved productivity and adaptability.
- Scientific Research: Offers comparative insights into bovine genetics and facilitates allele mining for key traits.
- Sustainable Development: Aids in the socio-economic upliftment of yak herders by improving livestock performance.
About ICAR-NRC on Yak:
- Established in 1989, located in Dirang, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Premier institution for research on yak husbandry, health, nutrition, and genetics.
- Works to preserve the unique genetic resources of Himalayan livestock.
Indian Grey Wolf
- 15 May 2025
In News:
The Indian grey wolf, a keystone predator crucial to maintaining the ecological balance of India’s grasslands, is facing a sharp population decline. The primary threat stems from increasing encounters with feral (free-ranging) dogs, which pose risks of disease transmission, competition, and hybridization.
Profile:
- Scientific Classification:A subspecies of the grey wolf (Canis lupus), native to the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southwest Asia.
- Habitat:Inhabits scrublands, semi-arid grasslands, and pastoral agro-ecosystems, often overlapping with human-dominated landscapes.
- Physical Traits:Intermediate in size between the Tibetan and Arabian wolves, the Indian grey wolf is adapted to warmer climates and lacks the dense winter coat of its colder-climate relatives.
- Behavioral Characteristics:
- Primarily nocturnal
- Hunts in small packs
- Less vocal than other wolf subspecies
- Geographical Range:Extends from Israel in the west to the Indian subcontinent in the east.
Legal and Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern globally, but considered locally endangered in India due to habitat loss and increasing threats.
- CITES Listing:Appendix I – Species facing extinction, with trade subject to strict regulation.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I, ensuring maximum legal protection within India.
Conservation Dilemma: Feral Dogs
- The Maharashtra Forest Rules, 2014 permit the removal of non-wild species, like dogs, from protected forest areas if they pose a threat to native wildlife.
- Despite this provision, forest officials often refrain from culling dogs due to ethical and animal rights concerns.
- Vaccination programs are proposed as alternatives to mitigate disease risks like canine distemper virus (CDV), but implementation remains logistically challenging.
Key Threats
- Disease Transmission: Feral dogs carry zoonotic diseases such as CDV, which can infect and decimate wolf populations.
- Hybridization: Interbreeding with dogs leads to genetic dilution, threatening the purity and survival of the species.
- Competition: Feral dogs compete with wolves for food and territory.
Case Study: Kadbanwadi Grassland, Maharashtra
- Location: Situated in Indapur tehsil, Pune district, this grassland spans over 2,000 hectares.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Home to species like the Bengal fox, striped hyena, Brahminy kite, and the Indian grey wolf.
- Cultural Coexistence: The local shepherd communities have shared a mutually respectful relationship with wolves over generations, reflecting a model of harmonious coexistence.
Geotubing

- 14 May 2025
In News:
A joint study conducted by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) and the Kerala State Coastal Area Development Corporation (KSCADC) has confirmed the effectiveness of geotubing-based offshore breakwaters in managing coastal erosion at Poonthura, Kerala. The installation not only mitigated shoreline erosion but also contributed to sustainable beach formation—highlighting the method's potential for broader coastal protection strategies.
What is Geotubing?
Geotubing involves the use of large geotextile tubes, filled with sand or slurry, which are strategically placed underwater to reduce wave energy and prevent shoreline erosion. At Poonthura, three vertical layers of 15-meter circumference geotubes were installed perpendicular to the coast, forming submerged breakwaters that trap sediment and promote natural sand deposition.
Materials and Construction
- Geotubes Composition:Constructed from high-performance woven geotextiles, typically made of polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET).
- Material Properties:These fabrics are designed to be permeable, durable, and resistant to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and microbial degradation, making them well-suited for long-term marine use.
Key Functional Features
- Wave Energy Dissipation:Submerged geotubes act as barriers that absorb and deflect wave energy before it reaches the shoreline.
- Beach Nourishment Support:By slowing wave action, the geotubes encourage natural sand accumulation, supporting beach regeneration.
Advantages of Geotubing
- High Durability:Withstands tensile stress and harsh environmental conditions, including chemical and biological exposure.
- Environmentally Friendly:Geotubing is non-toxic and contributes to coastal and wetland restoration without polluting ecosystems.
- Cost-Effective:More economical than traditional concrete or steel structures and easier to install, particularly in remote or variable terrains.
- Customizable Design:Geotubes can be tailored in size and configuration to suit specific project requirements and geographical conditions.
- Multi-Functional Utility:Beyond coastal defense, geotubes are effective in flood management, riverbank stabilization, sludge dewatering, and landfill containment.
Broader Applications of Geotubing
- Coastal Protection:Used in breakwaters, seawalls, and dune reinforcement projects.
- River and Lake Management:Effective for stabilizing riverbanks and controlling sedimentation.
- Wastewater Treatment:Applied in industrial and municipal dewatering processes.
- Infrastructure Support:Utilized in the construction of roads, railways, ports, and reservoirs.
- Environmental Remediation:Useful for site isolation, pollution control, and ecosystem restoration.
Thalassemia Burden in West Bengal higher than National Average

- 12 May 2025
In News:
On World Thalassemia Day, health experts in West Bengal highlighted the state’s significantly higher prevalence of Thalassemia carriers, ranging from 6% to 10%, compared to the national average of 3% to 4% (2011 Census). The elevated rate is mainly attributed to low awareness, intra-community marriages, and inadequate genetic screening.
What is Thalassemia?
- Definition: Thalassemia is a hereditary blood disorder marked by the body’s inability to produce adequate or normal haemoglobin, impairing oxygen transport in the blood.
- Genetic Cause:It arises from mutations or deletions in genes responsible for haemoglobin chains (alpha or beta globin), inherited from both parents.
- Types:
- Alpha Thalassemia: Involves up to four gene deletions; severity varies with number of deletions; common in Southeast Asian, Middle Eastern, and African populations.
- Beta Thalassemia: Caused by mutations in the beta-globin gene; prevalent in Mediterranean, South Asian, and Chinese communities. Includes:
- Thalassemia Minor: Carrier state with mild or no symptoms.
- Thalassemia Major (Cooley’s Anaemia): Severe form requiring lifelong blood transfusions.
- Symptoms:Fatigue, weakness, jaundice, facial deformities, stunted growth, enlarged spleen and liver, and breathlessness.
Thalassemia in India and West Bengal
- India sees about 10,000 to 15,000 babies born annually with Thalassemia Major (National Health Mission, 2016).
- Certain communities like Bengalis, Sindhis, Punjabis, and Gujaratis have higher carrier frequencies.
- West Bengal reports over 18,000 transfusion-dependent Thalassemia patients with a patient positivity rate of 2.5%.
Challenges in West Bengal
- Low Awareness: Many remain uninformed about genetic transmission and implications.
- Intra-community Marriages: Increase risk of two carriers marrying, leading to affected children.
- Insufficient Screening: Inadequate prenatal and adolescent screening limits early detection and prevention.
- No Legal Framework: India lacks laws to prevent marriages between carriers; awareness is the key preventive strategy.
Government Efforts and Recommendations
- West Bengal has established 36 Thalassemia Control Units (TCUs) across districts focusing on screening pregnant women (especially in the first trimester) and adolescents to reduce future disease incidence.
- Experts emphasize early parental screening, informed counseling, and timely medical care.
- Supportive care includes regular blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, vaccinations, nutritional balance (low iron diet), infection prevention, and mental health counseling.
23rd South Asia Press Freedom Report (2024–25)

- 12 May 2025
In News:
The 23rd Annual South Asia Press Freedom Report 2024–25, titled “Frontline Democracy: Media and Political Churn”, flags a concerning decline in media freedom across South Asia, including India. Published by the Asia Press Freedom group, the report assesses press conditions in eight countries: India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives.
Key Findings
- Over 250 violations of media rights recorded.
- 69 journalists were jailed or detained; 20 killed in the line of duty.
- India ranked 151st globally in press freedom; Bhutan dropped to 152nd—its lowest ever.
- Pakistan witnessed its most violent year for journalists in two decades, with eight killed.
India-Specific Observations
Legal and Institutional Suppression
- Increasing use of stringent laws like UAPA, PMLA, defamation, and sedition against journalists.
- Media organizations critical of the government have faced IT raids, ED investigations, and denial of government advertising.
- These actions have led to widespread self-censorship and a chilling effect on critical reporting.
Disinformation and Political Interference
- Political IT Cells play a key role in spreading fake news and hate speech, deepening the trust deficit in mainstream media.
- The Global Risks Report 2024 identifies “manipulated information” as the world’s most serious short-term threat.
Digital & Economic Challenges
- AI-generated content undermines journalistic credibility and originality.
- Media workforce faces challenges from:
- Declining advertisement revenue
- Contractualisation under new labour codes
- Mergers and corporate restructuring
- Precarity of gig and freelance journalists
Gender Inequality
- Poor representation of women in newsroom leadership roles.
- Pervasive gender-based harassment remains unaddressed.
Impacts of Eroding Media Freedom
- Democratic Deficit: Weakens the role of the press as the fourth pillar of democracy.
- Public Mistrust: Rising perception of media bias and loss of credibility.
- Reduced Information Access: Laws like the DPDP Act 2023 and changes to RTI provisions hinder public transparency.
India–U.S. Energy Cooperation
- 09 May 2025
In News:
U.S. Vice-President J.D. Vance recently reaffirmed strong bilateral engagement with India in the domains of energy and defence. In parallel, India underscored the need to prioritiseenergy security, technology transfer, and collaboration on critical minerals as pillars of this strategic partnership.
Major India–U.S. Energy Initiatives
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP):Facilitates cooperation across bioenergy, solar power, hydrogen fuels, and energy efficiency measures.
- Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET):Focused on advanced technologies such as clean energy, Artificial Intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
- Civil Nuclear Cooperation:Aims to enhance technology exchange and investments aligned with India’s goal of achieving 100 GW of nuclear capacity by 2047.
- Critical Minerals MoU (2024):Establishes a framework for resilient and transparent supply chains for rare earth elements and critical minerals, along with potential third-country investment opportunities.
Rationale for Strengthening the Energy Partnership
- Energy Security:India’s transition to a $5 trillion economy requires uninterrupted, affordable energy access.
?Example: India's energy import bill reached $153 billion in FY 2023–24, highlighting the need for long-term partnerships. - Climate Commitments:To achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, India must scale up investments in low-carbon technologies, including nuclear, renewables, and green hydrogen.
- Mineral Supply Chain Diversification:With China dominating over 90% of rare earth processing, India seeks reliable and democratic supply partnerships to support its clean energy transition.
- Infrastructure and Financing Needs:Developing nuclear energy infrastructure alone could demand over $180 billion by 2047, requiring foreign capital, joint ventures, and technology collaboration.
Proposed Roadmap for Enhancing Bilateral Energy Ties
- Legal Reform:Revisit the Civil Liability Act to facilitate private sector participation in India's nuclear sector.
?Example: Proposed transfer of SMR technology from Holtec to Indian companies (e.g., L&T, Tata Consulting) requires legal assurances. - Strategic Mineral Reserves Collaboration:Joint stockpiling via India’s Strategic Petroleum Reserves and the U.S. National Defense Stockpile can buffer supply shocks.
- India–U.S. Mineral Exchange Platform:Launch a digital trade and traceability platform using blockchain technology to enhance transparency and co-investment.
- Leverage the Quad Partnership:Deepen trilateral mineral partnerships with Australia and Japan, focusing on processing facilities, R&D hubs, and outreach to resource-rich African nations.
- Accelerate Nuclear Rollout:Standardise nuclear reactor designs, streamline regulatory approvals, and aim to install 5–6 GW of new nuclear capacity annually by the early 2030s.
- Green Financing Mechanisms:Develop innovative funding frameworks such as green bonds, blended finance, and leverage multilateral funding for clean energy and mineral projects.
Stratospheric Airship Platform by DRDO

- 07 May 2025
In News:
India successfully conducted the maiden flight trial of its indigenous Stratospheric Airship Platform, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The trial took place at Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh, and marked a significant milestone in India’s pursuit of advanced high-altitude surveillance technologies.
About the Stratospheric Airship Platform
- Nature: A lighter-than-air, high-altitude airship designed to operate at stratospheric heights (~17 km altitude).
- Developer: Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), Agra under DRDO.
- Purpose: To provide extended surveillance and real-time observation capabilities for military and civilian applications.
Key Features and Flight Trial Details
- Successfully reached an altitude of about 17 km (stratosphere).
- Carried an instrumental payload for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) tasks.
- Flight duration: Approximately 62 minutes.
- Tested crucial systems such as envelope pressure control and emergency deflation mechanisms.
- Data from onboard sensors will aid in developing simulation models for future flights.
- The platform was recovered post-mission for further analysis.
Strategic and Operational Significance
- Enhanced ISR: Boosts India’s military surveillance over borders, coastal regions, and conflict zones.
- Earth Observation: Supports disaster management, environmental monitoring, and communication relays.
- Cost-Effective: Provides persistent coverage at a fraction of the cost of satellite launches.
- Technological Edge: Places India among a select group of nations with indigenous high-altitude airship capabilities, crucial amid rising regional security challenges.
- Dual-Use Potential: Suitable for both defence and civilian applications, including atmospheric sensing.
Operation Hawk 2025

- 04 May 2025
In News:
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has launched Operation Hawk in 2025 to combat international cybercrime networks involved in online child sexual exploitation (OCSE). The operation led to arrests in Delhi and Mumbai, following inputs from foreign agencies including the United States.
About Operation Hawk
Feature Details
Launched By CBI’s International Operations Division
Year of Launch 2025
Main Objective Target and dismantle cybercriminal networks engaged in OCSE
Scope International cooperation, digital forensics, and prosecution
Key Objectives
- Disrupt organized cyber-pedophile networks.
- Enhance coordination with agencies like Interpol, FBI, and foreign governments.
- Strengthen legal action under IPC, IT Act, and POCSO Act.
- Address complaints involving Indian nationals from foreign jurisdictions.
- Boost cross-border digital evidence collection and swift response systems.
Previous Related Operations
- Operation CARBON (2021):Targeted dark web CSAM (Child Sexual Abuse Material) users globally.
- Operation MEGH CHAKRA (2022):Pan-India action based on Interpol alerts; resulted in large-scale arrests and digital data seizures.
Digital Access now a Fundamental Right

- 03 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India, in the case of Amar Jain v. Union of India &Ors., declared that inclusive digital access to e-governance and welfare systems is an integral part of the fundamental right to life and liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution. The Court issued a set of 20 binding directions to enhance the accessibility of digital services, especially the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, for persons with disabilities (PwDs) and other marginalized groups.
Background of the Case
The ruling arose from petitions filed which highlighted that digital KYC processes, which rely heavily on visual and facial inputs, were discriminatory and inaccessible to individuals with visual impairments or facial disfigurements. This impeded their access to banking, welfare schemes, and essential services.
Key Supreme Court Observations
- Digital access is part of Article 21: The right to life and liberty must now be interpreted to include meaningful digital access, particularly as governance, education, and financial services shift online.
- Constitutional mandate, not policy choice: Bridging the digital divide is not discretionary but a constitutional obligation under Articles 14, 15, 21, and 38.
- Substantive Equality: Digital services must be inclusive and equitable, particularly for:
- Persons with Disabilities (PwDs)
- Rural and remote communities
- Linguistic minorities
- Senior citizens
- Economically weaker sections
- Exclusion through technology: Digital platforms, in their current form, further alienate historically disadvantaged groups rather than empowering them.
Key Directives Issued by the Court
- Revise digital KYC norms to be PwD-inclusive.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulators must ensure universal accessibility.
- Mandate accessibility audits by certified professionals.
- Appoint nodal officers in each department to monitor compliance.
- Include PwDs in digital platform design processes.
- Ban discriminatory design features that rely solely on facial inputs.
Relevant Constitutional Provisions
Article Provision
Article 14 Equality before law
Article 15 Prohibition of discrimination
Article 21 Right to life and personal liberty
Article 38 Directive for securing social justice and reducing inequalities
Precedents in Digital Rights Jurisprudence
- Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India (1978): Expanded Article 21 to include fair, just, and reasonable procedures.
- Faheema Shirin v. State of Kerala (2019): First Indian case to recognize right to internet access as part of Right to Life and Right to Education (Article 21A).
- Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India (2020): Held that freedom of speech (Article 19(1)(a)) and right to trade (Article 19(1)(g)) apply to the internet.
Barriers to Digital Empowerment of PwDs
- Digital Literacy Gap: PwDs are underrepresented in programs like PMGDISHA.
- Weak Enforcement: Accessibility mandates under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 are poorly implemented.
- Limited Assistive Technology (AT): Lack of affordable tools for facially disfigured or visually impaired individuals.
- Design Exclusion: Platforms that depend on facial cues (e.g., blinking, alignment) exclude acid attack survivors and visually impaired users.
Way Forward: Recommendations for Inclusive Digital Access
- Accessible Digital Infrastructure:
- Promote screen readers, voice commands, haptic navigation, and AI-based assistive tech under Digital India.
- Adhere to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
- Disability-Focused Digital Literacy:
- Collaborate with tech giants like Google/Microsoft to provide training in assistive technologies.
- Expand schemes like PMGDISHA to include PwD-specific modules.
- Disability-Sensitive Urban Planning:
- Incorporate assistive tech into Smart City projects.
- Public infrastructure should have Braille, audio, and sign language-based digital signage.
- Inclusive Innovation Lab:
- Establish Public-Private Innovation Hubs for developing affordable accessibility tech.
- Encourage startups and NGOs to co-create need-based digital solutions for PwDs.
India’s First Certified Green Municipal Bond
- 03 May 2025
In News:
The Ghaziabad Nagar Nigam has become the first municipal body in India to issue a certified Green Municipal Bond, successfully raising ?150 crore to construct a Tertiary Sewage Treatment Plant (TSTP) — a major step toward sustainable urban water management.
What is a Green Municipal Bond?
A Green Municipal Bond is a financial instrument issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) to finance projects with environmental benefits, such as:
- Renewable energy
- Water and wastewater treatment
- Pollution control
- Solid waste management
These bonds are aligned with international Green Bond Principles and require sustainability certification through independent third-party audits.
Key Features
- Targeted Use of Funds: Capital raised is exclusively allocated to environmentally certified projects.
- Independent Certification: Must meet Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards.
- Investor Confidence: Appeals to climate-focused investors, ESG funds, and global financial institutions.
- Municipal Creditworthiness: Encourages better financial management and credit ratings for ULBs.
Significance of the Initiative
- Supports SDGs: Contributes to UN Sustainable Development Goals, especially SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- Promotes Green Infrastructure: Enables low-emission urban development and enhances climate resilience.
- Enhances Water Security: Facilitates wastewater recycling, reducing dependence on freshwater sources.
- Replicable Model: Serves as a template for other municipalities to mobilize green capital for eco-projects.
Natural Hydrogen

- 03 May 2025
In News:
Governments and private players globally are increasingly exploring natural hydrogen as a low-cost, zero-emission energy source. Recent discoveries in France’s Moselle region and growing interest in countries like India and the U.S. signal a new frontier in clean energy exploration.
What is Natural Hydrogen?
Natural hydrogen, or geologic hydrogen, refers to free molecular hydrogen (H?) naturally present underground due to geological processes. Unlike manufactured hydrogen (grey, blue, or green), it occurs naturally and can be extracted directly from the Earth.
Key Geological Sources:
- Serpentinisation: Water reacts with ultramafic rocks.
- Radiolysis: Water splits due to radioactive decay of rocks.
- Organic decomposition: Deep-seated carbon-rich matter releases hydrogen.
- Co-existence with helium: Indicates deep crustal origins.
Extraction Process
- Exploration: Detection of hydrogen seeps using geophysical tools.
- Drilling: Boreholes drilled in hydrogen-rich zones (e.g., Mali, U.S., France).
- Capture & Compression: Hydrogen is purified and compressed.
- Distribution: Delivered for use in fuel cells, refineries, or industries.
Why is it Important?
- Zero Emissions: Burns to produce only water vapor — no CO?.
- Cost-Effective: Estimated cost ~$1/kg, cheaper than green hydrogen.
- Renewable & Sustainable: Can replenish naturally in rock formations.
- High Efficiency: Hydrogen fuel cells are 3x more efficient than gasoline.
Historical Background
- 1987, Mali: Accidental discovery of a hydrogen-rich well during water drilling.
- 2012: Confirmed to be 98% pure hydrogen, sparking interest in natural reserves.
- Once viewed as a geological oddity, it is now recognized for its energy potential.
Global Exploration Trends
- Over 40 companies exploring hydrogen in Australia, U.S., Spain, France, Albania, Colombia, South Korea, Canada.
- USGS model (2022): Suggests potential to meet global hydrogen demand for ~200 years.
- France (2025): Moselle region found to contain ~92 million tonnes of natural hydrogen — worth ~$92 billion.
India’s Natural Hydrogen Potential
India has favourable geology for natural hydrogen generation:
- Ophiolite belts: Himalayas, Andaman.
- Cratons: Dharwar, Singhbhum greenstone belts.
- Sedimentary basins: Vindhyan, Cuddapah, Gondwana.
- Hydrothermal systems: Hot spring regions.
- Basement rocks: With deep fractures and mafic/ultramafic content.
A comprehensive geological survey is needed to assess extractable reserves.
Challenges in Adoption
- Lack of Mapping: Global hydrogen reserves are poorly explored.
- Scattered Deposits: Difficult to commercialize if reserves are dispersed.
- Storage & Transport: Requires high-pressure systems due to low density.
- Safety Risks: Odourless and flammable — hard to detect leaks.
- Infrastructure Deficit: Refuelling stations and pipelines still underdeveloped.
Way Forward
- National Hydrogen Mapping: Focus on cratonic belts and ophiolites in India.
- Policy Framework: Integrate natural hydrogen into the National Hydrogen Mission.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Offer PPPs, tax breaks, and R&D incentives.
- Global Partnerships: Collaborate with USGS, France, U.S. on exploration models.
- Infrastructure Investment: Build hydrogen hubs, refuelling stations, and pipelines.
Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect
- 01 May 2025
In News:
With accelerating urbanization and climate change, the Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon has emerged as a significant public health and environmental concern. Recent studies, including one published in Nature Climate Change, highlight that while UHIs elevate heat-related mortality, they simultaneously reduce cold-related deaths, especially in colder regions. This dual impact has major implications for urban planning and climate adaptation strategies.
What is Urban Heat Island (UHI)?
- Definition: UHI refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural regions due to human activities and urban infrastructure.
- Cities Affected: Notable examples include New Delhi, Moscow, New York, Paris, and London, where dense infrastructure and limited vegetation intensify urban heat.
Key Causes of UHI
- Impervious Surfaces: Materials like asphalt and concrete absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night due to low albedo.
- Lack of Vegetation: Reduced greenery limits evapotranspiration, curbing natural cooling.
- Anthropogenic Heat: Heat from vehicles, air conditioners, and industries raises ambient temperatures.
- Air Pollution: Black carbon and particulates absorb solar radiation, compounding heat effects.
- Urban Morphology: Dense construction and narrow streets create a canyon effect, trapping heat and reducing airflow.
Dual Impact on Mortality
A 2025 study led by Dr. Wenfeng Zhan analyzed temperature-related mortality across 3,000+ cities globally using remote sensing and socioeconomic data:
- Cold-related Deaths Reduced: In 2018, the decline in cold-related fatalities was 4.4 times higher than the rise in heat-related deaths due to UHI.
- High-Latitude Cities: In cities like Moscow, cold-related deaths decreased 11.5 times more than heat-related deaths increased.
- Key Insight: The UHI effect's net mortality impact can vary significantly by region and season.
Consequences of UHI
- Increased Energy Demand: Higher temperatures raise demand for air conditioning, increasing fossil fuel use and emissions.
- Health Risks: Elevated risks of heat stroke, dehydration, and cardiovascular stress, especially among the elderly and urban poor.
- Deterioration of Air Quality: Heat-induced formation of ground-level ozone exacerbates respiratory ailments.
- Water Stress: Faster evaporation and increased demand for cooling water pressure urban water resources.
- Biodiversity Decline: Excessive heat and lack of green spaces threaten urban flora and fauna.
Mitigation Strategies
- Cool Roofs (Los Angeles):Mandates reflective roofing in new buildings and renovations to reduce heat absorption.
- Smart Cooling Systems (Dubai):Centralized chilled water systems reduce cooling energy by 30–50% compared to individual AC units.
- Cool Streets Initiative (Paris):Converts streets to pedestrian zones, replaces asphalt with vegetation, and expands urban greenery.
India and the USTR Special 301 Report
- 01 May 2025
In News:
India has once again been placed on the Priority Watch List(PWL) in the United States Trade Representative (USTR) Special 301 Report, alongside countries such as China, Russia, and Venezuela. The report has raised concerns over India's Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) regime, prompting debates on the implications for India's trade and innovation environment.
What is the USTR Special 301 Report?
- Mandate & Purpose: The Special 301 Report is an annual review mandated under Section 182 of the US Trade Act of 1974, identifying countries that the US believes do not offer "adequate and effective" protection of IPR or deny fair and equitable market access to US IPR holders.
- Designations:
- Priority Foreign Country (PFC): Most severe classification; can trigger investigations and trade sanctions.
- Priority Watch List (PWL): Countries with serious IPR concerns requiring close monitoring and bilateral engagement.
- Watch List: Countries with moderate IPR issues.
- Historical Context: India has been consistently listed under the Priority Watch List in the report, including in the years 2020, 2021, and 2024.
Concerns Raised by the USTR Regarding India
- IP Enforcement Deficiencies:
- Weak enforcement mechanisms against online piracy.
- Backlogs in trademark opposition proceedings.
- Lack of a strong legal framework for protecting trade secrets.
- Pharmaceutical Patents:
- Alleged lack of transparency and delays in resolving pre-grant patent disputes.
- Absence of effective mechanisms for early resolution of disputes in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Copyright Issues:The report criticizes India for not fully aligning with WIPO Internet Treaties, especially regarding the protection of content in interactive transmissions like streaming and downloads.
- Market Access Concerns:The US claims that India imposes high tariffs on IP-intensive products and creates procedural barriers for foreign firms seeking patent protection.
India’s Response and Position
- India maintains that its IPR laws fully comply with the WTO’s TRIPS Agreement, which sets minimum standards for IP protection globally.
- India rejects unilateral pressure to conform to IP standards beyond TRIPS, asserting its right to balance IP protection with public health, access to medicines, and developmental needs.
- Progress has been acknowledged in areas like trademark investigation reforms and IP policy transparency through bilateral platforms such as the US-India Trade Policy Forum.
US Measures to Push IPR Standards
- The USTR uses a mix of bilateral negotiations, WTO forums, and technical assistance to persuade countries to adopt stricter IP regimes.
- It also undertakes anti-counterfeiting initiatives, capacity-building programs, and trade diplomacy to influence global IPR enforcement.
India's Arbitration Ecosystem

- 01 May 2025
In News:
India's growing stature as a global economic powerhouse has led to an upsurge in commercial transactions—both domestic and international. With the traditional litigation system overburdened (nearly 50 lakh cases pending for over 10 years), arbitration is increasingly viewed as a faster and more efficient alternative for dispute resolution. However, despite legislative reforms, the effectiveness of India’s arbitration landscape remains hindered by structural flaws, especially concerning arbitrator quality and institutional credibility.
What is Arbitration?
Arbitration is a quasi-judicial mechanism of Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) wherein a neutral third party (arbitrator) delivers a binding decision outside the court system. It is governed by the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, which aligns with the UNCITRAL Model Law. Amendments in 2015, 2019, and the draft Bill of 2024 aim to promote institutional arbitration, reduce delays, and enhance credibility.
Historical and Institutional Evolution
- 1899: Indian Arbitration Act introduced (limited to Presidency towns).
- 1940: Comprehensive domestic arbitration law enacted.
- 1996: Post-liberalization, India adopted UNCITRAL-compliant Arbitration and Conciliation Act.
- 2019: Establishment of India International Arbitration Centre (IIAC) to offer cost-effective and globally competitive arbitration services.
- Arbitration Council of India (ACI): Set up under 2019 Amendment to regulate and promote quality arbitration, headed by a retired SC/HC judge or expert.
Why Arbitration is Gaining Importance in India
- Judicial Backlog: With only 21 judges per million people, courts are overwhelmed. Arbitration offers a time-bound alternative (mandated 12-month timeline for award delivery).
- Economic Growth and FDI Surge: India attracted $1 trillion in FDI (2024), heightening cross-border disputes that demand specialized, swift dispute resolution.
- Confidentiality and Expertise: Arbitration provides procedural flexibility and protects sensitive commercial data—key for tech, pharma, and IP-driven sectors.
- Global Recognition: India is a signatory to the New York Convention, making its arbitral awards globally enforceable.
- Policy Push: Civil Procedure Code and National Litigation Policy (2010) encourage ADR to reduce court burden.
Core Challenges in India’s Arbitration Framework
- Judicial Dominance in Arbitrator Appointments:
- Retired judges dominate arbitration panels.
- Their court-centric mindset leads to lengthy, costly, and rigid processes, often mimicking litigation.
- The Ministry of Finance (2024) criticized these arbitrations as lacking efficiency and innovation.
- Narrow Arbitrator Pool:
- Predominantly comprises legal professionals and ex-judges.
- Lacks subject-matter experts like engineers, economists, and technologists, crucial for technical or industry-specific disputes.
- Insufficient Training and Accreditation:
- No mandatory certification or capacity-building for arbitrators.
- Skills like cross-cultural communication, financial analysis, and evidence handling are often underdeveloped.
- Low Global Representation:
- Indian arbitrators are rarely appointed in international disputes without an Indian party.
- As highlighted by former CJI D.Y. Chandrachud (2024), this points to gaps in credibility, visibility, and networking.
Reforms Needed to Build a Robust Arbitration Ecosystem
- Diversify and Professionalize Arbitrator Pool:
- Move beyond reliance on retired judges.
- Include professionals from fields like law, finance, engineering, and management.
- Accreditation and Skill Development:
- Establish a National Accreditation Board for Arbitrators under the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- Mandate rigorous training via institutions like IIAC or professional bodies.
- Encourage soft-skills and exposure to global best practices.
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Boost the functioning of IIAC and ACI for better standards, accountability, and case management.
- Promote institutional arbitration over ad hoc arbitration.
- Awareness and Capacity Building:
- Launch a National Arbitration Awareness Mission targeting MSMEs and Tier-2/3 cities.
- Integrate with existing platforms like Startup India, Skill India, and MSME Sambandh.
- Limit Judicial Interference:
- Strict adherence to the “minimum judicial intervention” principle (as per the 1996 Act).
- Establish dedicated commercial courts with arbitration-specialist judges for related matters.
- International Engagement and Visibility:
- Partner with global arbitral institutions (e.g., SIAC, ICC).
- Organize International Arbitration Summits to showcase Indian capabilities.
- Use forums like UN, IBA, and G20 to promote Indian arbitrators globally.
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Breakthrough
- 01 May 2025
In News:
In a pioneering advancement in neurotechnology and assistive healthcare, scientists at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)have developed a stable Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) system that enables a paralysed individual to control a robotic arm using only brain signals. This innovation holds transformative potential for people with paralysis, significantly enhancing autonomy and quality of life.
What is Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)?
A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a neurotechnological system that establishes direct communication between the brain and external devices, bypassing damaged neural pathways. It decodes neural signals related to intended movements and translates them into actionable commands to control robotic limbs, computers, or speech systems.
Key Technological Achievements
- Long-Term Stability: The developed BCI system allowed continuous and accurate control of a robotic arm for over 7 months with minimal recalibration, overcoming a major limitation of earlier BCI systems.
- Sensor Implantation: Tiny electrodes were implanted in the motor cortex, the region of the brain that governs movement.
- AI-Powered Signal Decoding: The system used machine learning algorithms to decode brain activity and adapt to daily shifts in neural signals, ensuring consistent performance.
- Virtual to Real Transition: The participant underwent virtual training with a robotic arm before controlling a real-world robotic limb, aiding in precision and neural calibration.
Functionality Demonstrated
The paralysed participant, who had lost all movement and speech abilities due to a stroke, could:
- Pick up and rotate blocks
- Open cabinets
- Retrieve and position a cup under a water dispenser
These basic actions, enabled purely by imagined movement, highlight the immense real-world utility of the BCI system.
Scientific Insights
- High-Dimensional Neural Mapping: Although neural signals shifted slightly each day, their overall structure remained consistent. This allowed researchers to create a dynamic AI framework that predicted and compensated for signal changes.
- No Direct Brain Stimulation: The system only read signals and did not send any electrical impulses to the brain.
- End-to-End Signal Processing Pipeline: From capturing brain signals to executing robotic arm movement, a seamless pipeline was established for fluid, real-time motion.
Broader Applications
The implications of this BCI research go beyond limb movement:
- Restoration of Speech: In cases of ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) and brainstem stroke, BCIs can decode intended speech from neural activity and render it as text, synthesized voice, or avatar speech.
- Faster Communication: A recent trial showed an ALS patient using BCI technology to communicate at 62 words per minute, nearly 3.4 times faster than earlier systems.
Future Prospects & Challenges
- Scalability: More work is needed to generalize this system for diverse forms of paralysis.
- Complex Environments: Future BCIs must function in real-world environments filled with distractions, like grocery stores or public spaces.
- Ethical and Regulatory Oversight: Given the invasive nature of electrode implantation, ethical considerations around consent, privacy, and long-term effects must be addressed.
Nag Anti-Tank Missile System (NAMIS)

- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed contracts worth approximately ?2,500 crore for procuring advanced anti-tank missile systems and light vehicles to enhance the Indian Army's operational capabilities.
Nag Anti-Tank Missile System (NAMIS)
- Development and Production:Developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and produced by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- System Overview:NAMIS is a tracked, third-generation anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system mounted on a BMP-2 chassis (Nag Missile Carrier or NAMICA). It features a ‘fire-and-forget’ capability, employing an Imaging Infrared (IIR) seeker to lock on to heavily armored targets before launch.
- Key Features:
- Range: 500 meters to 4 kilometers.
- Attack Modes:
- Top Attack Mode: Missile climbs and strikes the target from above to penetrate weaker top armor.
- Direct Attack Mode: Missile flies directly to strike the target.
- Night Capability: Operates effectively under low visibility.
- Mobility: Based on the amphibious BMP-2, NAMIS can operate across varied terrains.
- Significance:The tracked NAMIS enhances the anti-tank capabilities of mechanized infantry, marking a crucial step in modernizing the Indian Army’s battlefield readiness.
- Other Nag Variants:The Helina is a helicopter-launched version designed for deployment on Rudra and Light Combat Helicopters (LCH), successfully tested in 2018.
Light Vehicles Procurement
- The MoD signed contracts with Force Motors Limited and Mahindra & Mahindra Limited for around 5,000 light vehicles.
- These vehicles are equipped with enhanced engine power and designed to carry payloads of up to 800 kg, ensuring mobility across diverse terrains and operational conditions.
Additional Defence Contract
- Zen Technologies Limited secured a contract worth approximately ?152 crore for supplying Integrated Air Defence Combat Simulators (IADCS) for the Army’s L70 air defence guns.
- The IADCS is a virtual training system developed under the Make-II category to provide realistic simulation-based training for air defence operations.
New Pamban Rail Bridge

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the newly constructed Pamban Rail Bridge on April 6, 2025, coinciding with Ram Navami. The bridge connects Mandapam (mainland Tamil Nadu) to Rameswaram Island, replacing the century-old Pamban bridge.
Key Highlights:
- Total Project Cost: ?531 crore
- Constructed by:Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL)
- Bridge Type:Vertical-lift railway bridge – thefirst of its kind in India
- Total Length:2.2 km
- Lift Span:72 metres, enabling automated vertical clearance for ships
- Technology: Fully automated lift mechanism (unlike manual operation in the old bridge)
- Materials: Constructed with corrosion-resistant materials for improved longevity
- Sustainability:Solar-compatible design for future energy efficiency
Significance:
- Enhances rail connectivity to Rameswaram, a major religious and tourist destination.
- Improves maritime navigation safety by enabling faster ship movement through the lift span.
- Strengthens coastal infrastructure in Tamil Nadu, supporting economic and strategic interests.
Old Pamban Bridge (1914–2022): A Legacy
- Inaugurated: 1914 by British India (under Madras Railway)
- Length: 2.065 km with 143 piers
- Mechanism:Double-leaf bascule (Scherzer lift) manually operated for ship passage
- Structure Height: 12.5 m above sea level
- Distinction: India’s first sea bridge; remained operational for over 108 years
- Reason for Closure: Severe corrosion led to decommissioning in 2022
Safety and Commissioning Notes:
- The Commissioner of Railway Safety (CRS) conducted a statutory inspection in November 2024.
- CRS had flagged structural and planning lapses; rectification was completed before inauguration.
- Parts of the old bridge will be preserved due to its historical value, though full relocation is not feasible.
Additional Developments:
- New Train Flagged Off: PM Modi flagged a new train service between Tambaram and Rameswaram.
- Rameswaram Station Redevelopment: Work is underway and expected to be completed by September 2025.
Great White Sharks

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
A 20-year study in South Africa reveals that the decline of Great White Sharks disrupted marine ecosystems, causing cascading food web imbalances.
Key Highlights:
- Scientific Name:Carcharodon carcharias
- IUCN Red List Status:Vulnerable
- Habitat and Distribution:
- Commonly found in temperate coastal waters, including regions off the USA, South Africa, Australia, and Japan.
- Highly migratory, often venturing into tropical waters but returning to temperate zones for feeding.
- Key Biological Features:
- Endothermic Adaptation: Capable of maintaining body temperature higher than surrounding waters (regional endothermy).
- Body Structure: Streamlined, torpedo-shaped body with serrated teeth for efficient hunting.
- Feeding Behavior: Ambush predator – uses a "bite-and-wait" strategy to hunt seals, dolphins, and large fish.
- Reproduction:
- Viviparous: Gives birth to live young.
- Gestation Period: Around 12 months.
- Maturity:
- Females: Mature at 15–16 feet, around 12–18 years of age.
- Males: Mature at 11–13 feet, around 10 years of age.
- Ecological Importance:
- Apex Predator: Plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems by regulating populations of prey such as seals and mid-level predators.
- Indicator Species: Their presence signals the health and stability of marine ecosystems.
- Ecological Disruption in South Africa – Key Findings:
- A 20-year study in False Bay, South Africa, revealed a significant decline in Great White Shark numbers.
- This led to:
- A surge in seal populations and sevengill sharks.
- A corresponding collapse in populations of smaller sharks and fish, showcasing a trophic cascade and food web imbalance.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
Karnataka Forest Department has initiated a "soft release" strategy to address the escalating human-elephant conflict in the districts of Hassan, Chikkamagaluru, and Kodagu. The strategy involves the phased rehabilitation of captured elephants into the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS).
Soft Release Strategy – Key Highlights
- Objective: To rehabilitate conflict-prone wild elephants and reduce human-elephant encounters.
- Implementation Site:Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS), Chikkamagaluru district.
- Initial Step: Captured elephants will be placed in a 20 sq. km enclosure within the sanctuary.
- Purpose of Enclosure:
- Acclimatisation to the wild.
- Health monitoring and behavioural assessment.
- Final Release: Once deemed fit, elephants will be released into one of four pre-identified zones in BWS, chosen based on:
- Availability of water and forage.
- Absence of human activity.
- Road connectivity.
Monitoring & Management
- The enclosure will be fenced using railway barricades.
- A dedicated team of veterinarians will supervise the elephants from a nearby veterinary centre.
- Minimal human interaction will be ensured during the acclimatisation period.
- Expert guidance is being provided by Prof. R. Sukumar (Indian Institute of Science) and senior forest officials.
About Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS)
- Location: Western Ghats, Karnataka.
- Area: 492.30 sq. km.
- Also Known As:Muthodi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Named After: Bhadra River.
- Status: A designated Project Tiger Reserve.
Ecological Significance
- Forest Types:
- Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous Forests.
- Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Shola Forests.
- Wildlife Diversity:
- Mammals: Tigers, leopards, elephants, gaurs, dholes, and deer.
- Birds: ~250 species, including endemic birds like Hornbills, Malabar Trogon, and Hill Myna.
Significance of the Initiative
- Biodiversity Conservation: Enhances protection of endangered species and habitats in the Western Ghats.
- Conflict Mitigation: Aims to provide a sustainable solution to frequent elephant incursions, crop damage, and human casualties.
- Model Strategy: Draws upon similar practices implemented in West Bengal and tailors them to Karnataka’s ecological conditions.
IEA Global Energy Review 2025

- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
The world's energy demand grew at 2.2% in 2024, a pace described as "faster than average" by the International Energy Agency (IEA) in its Global Energy Review.
Key Highlights:
Global Energy Demand
- Global energy demand grew by 2.2% in 2024, faster than the average of the past decade.
- Emerging and developing economies accounted for over 80% of the increase, with Asia leading the growth.
- Electricity demand rose 4.3%, nearly double the past decade's average.
Rise of Renewables
- Renewables were the fastest-growing energy source, contributing 38% of global energy growth.
- A record 700 GW of renewable power capacity was added globally in 2024 (22nd consecutive annual record).
- Low-emission sources (renewables + nuclear) accounted for 80% of the increase in electricity generation.
Key Country Contributions:
- China added:340 GW solar and 80 GW wind (≈ two-thirds of global additions).
- India added:30 GW solar, triple the previous year's addition.
Global Renewable Generation (2024):
- Solar: +480 TWh
- Wind: +180 TWh
- Hydropower: +190 TWh (mainly due to favorable weather, not capacity increase)
Coal Trends:
- Coal demand rose 1%, reaching a record high in 2024.
- China derives 60% of its electricity from coal; India, about 75%.
- Coal’s global electricity share dropped to 35% – the lowest since the IEA's inception in 1974.
- The seaborne coal market is shrinking as top consumers are also top producers with domestic-use policies.
Natural Gas Outlook
- Natural gas demand rose 2.7%, hitting a record 115 billion cubic metres in 2024.
- Driven by:
- China's adoption of LNG trucks
- Heatwaves increasing power demand
- However, demand fell in late 2024 due to rising LNG spot prices, indicating price sensitivity in Asia.
Crude Oil Demand Slows
- Oil demand grew just 0.8%, mainly from the petrochemical sector.
- Transport-related oil use declined due to:
- Growth in electric vehicles (EVs) (especially in China)
- Expansion of LNG trucks and high-speed rail networks
About the International Energy Agency (IEA)
- Founded: 1974 (post-1973 oil crisis) by OECD nations.
- HQ: Paris, France.
- Members: 31 countries (only OECD nations can be full members); India is an association country.
- Mandate: Energy security, sustainability, and global cooperation.
- Key Reports: World Energy Outlook, India Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, Global Energy Review.
IISc Study on Monsoon Cloud Bands and Rainfall Intensity
- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
A recent study by the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has challenged the conventional understanding of monsoon dynamics by highlighting the critical role of cloud band strength in determining the movement and intensity of rainfall during the Indian monsoon season.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Strength Determines Propagation: Only strong equatorial cloud bands are capable of northward movement, initiating wet spells over the Indian subcontinent. Weak cloud bands fail to propagate, contradicting earlier models that assumed uniform northward movement.
- Role of BSISO: The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO) governs alternating wet and dry spells by transporting cloud bands from the equator to India. The duration and intensity of wet spells are influenced by the size and strength of these cloud bands.
- Air-Sea Interaction: Interaction between the equatorial Indian Ocean’s sea surface and atmosphere significantly influences moisture buildup and wind strength. A stronger ocean-atmosphere coupling enhances moisture transport, intensifying the monsoon.
- Impact of Climate Change:
- Warmer atmosphere → Increased background moisture.
- Future wet spells may see 42%–63% more rainfall over India and adjoining seas.
- Improving Forecast Models: These insights will enhance the accuracy of seasonal and sub-seasonal monsoon prediction models, crucial for agriculture and disaster preparedness.
Understanding BSISO (Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation)
- A dominant monsoon variability pattern active from June to September.
- Modulates ‘active’ (rainy) and ‘break’ (dry) phases of the monsoon.
- Moves cloud activity and convection from the Indian Ocean towards the Western Pacific.
- ENSO link:
- La Niña enhances BSISO propagation → stronger monsoon.
- El Niño suppresses it → weaker monsoon.
Key Facts about the Indian Monsoon
Aspect Details
Definition “Monsoon” comes from Arabic mausim meaning season.
Southwest Monsoon June–September; moist winds from Indian Ocean bring ~80% of India’s
annual rainfall.
Northeast Monsoon October–December; brings rain to Tamil Nadu, coastal Andhra Pradesh.
Key Drivers ITCZ shift, Tibetan heating, Tropical Easterly Jet, Somali Jet.
Oceanic Influences IOD (positive enhances, negative weakens monsoon), ENSO (El Niño
weakens,La Niña strengthens monsoon).
Monsoon Importance Critical for agriculture, water supply, economy; affects ~50% of India’s
population directly.
Rushikonda Beach Regains prestigious Blue Flag Certification

- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
Rushikonda Beach, located in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, has successfully regained its Blue Flag certification after a temporary withdrawal due to non-compliance issues. It remains the only Blue Flag-certified beach in Andhra Pradesh and one of 13 such beaches in India.
What is the Blue Flag Certification?
- Administered by: Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), Denmark.
- National Operator in India: Blue Flag India under the Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM).
- Purpose: Recognizes beaches meeting strict standards of environmental management, safety, cleanliness, and facilities.
- Criteria: Beaches must comply with 33 environmental and safety criteria, including water quality, waste management, safety measures, and environmental education.
- Control Visits: National Operator conducts scheduled and surprise inspections.
Reasons for Temporary Withdrawal
- The Blue Flag tag was withdrawn after complaints of poor maintenance and non-compliance with amenities.
- Non-compliance types:
- Minor issues require rectification within 10 days.
- Multiple or major issues can lead to temporary or season-long withdrawal.
- Rushikonda Beach lost the tag for about two weeks before corrective measures were implemented.
Measures Taken for Regaining the Blue Flag
- Repair and upgrade of beach amenities.
- Plans to install bamboo fencing around the premises to protect the area.
- Public appeals to avoid littering and misuse.
- Education drives for local fisherfolk on beach cleanliness.
- Plans to promote tourism with new beach shacks and regulated alcohol sales, awaiting government approval.
- Identification of 10 other beaches in Andhra Pradesh for upgradation and Blue Flag certification.
Importance of the Blue Flag Tag for Rushikonda Beach
- Tourism Impact: The Blue Flag is internationally recognized by tourists as a mark of safety, cleanliness, and eco-friendliness.
- Environmental Awareness: Promotes responsible tourism and protects coastal ecosystems.
- Local Economy: Supports livelihoods of petty vendors and fisherfolk by attracting visitors.
Key Facts About Rushikonda Beach
- Location: Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- Awarded Blue Flag: First awarded in 2020.
- Features: Golden sands, clear waters, and well-maintained recreational amenities.
- Significance: The only Blue Flag beach in Andhra Pradesh and among 13 in India.
India’s First Frozen Zoo

- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
In a pioneering conservation step, Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP) in Darjeeling, West Bengal, has become India’s first zoo to launch a DNA cryogenic conservation project—popularly known as a “frozen zoo”.
About the DNA Cryogenic Conservation Initiative
- Objective: Preserve genetic material of endangered Himalayan species for future research, assisted reproduction, and biodiversity conservation in case of extinction threats.
- Launched in:2023, with 60 DNA samples already collected.
- Collaborators:
- PNHZP, Darjeeling
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad
- Species covered: Red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan black bears, and other native animals.
- Source of Samples: Tissue collected from animals deceased in captivity or road accidents.
- Storage Method:
- DNA samples stored in liquid nitrogen at –196°C.
- A dedicated in-zoo laboratory with steel cryo-containers established.
About the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB)
- Established: 1977; full national lab status in 1981–82.
- Location: Hyderabad, Telangana.
- Affiliation: Under Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- Recognition: Designated a “Center of Excellence” by UNESCO’s Global Molecular and Cell Biology Network.
- Mandate: Advanced research and training in frontier areas of modern biology.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park
Feature Description
Location Darjeeling, West Bengal
Altitude 2,150 metres (7,050 feet) – India’s highest-altitude zoo
Area 67.8 acres
Established 14 August 1958
Renamed 1975 in memory of Padmaja Naidu, former Governor of West Bengal
Transferred to State 1993; now under Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
Focus Areas Ex-situ conservation, education, research, and captive breeding
Notable Species Red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan wolves, gorals, Siberian tigers
Abolition of Equalisation Levy on Online Advertisements
- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
The Indian government has proposed to abolish the Equalisation Levy (digital tax) on online advertisements, effective April 1, 2025. This move is set to benefit digital advertisers on platforms like Google, Meta (formerly Facebook), and X (formerly Twitter), reducing their tax burden.
Overview of Equalisation Levy
- Introduction:
- The Equalisation Levy was introduced by the Finance Act of 2016. Its primary objective was to tax foreign digital service providers (such as Google, Meta, etc.) for income generated from digital transactions in India, ensuring these businesses contribute fairly to India’s tax system, despite having no physical presence.
- Coverage:
- Initially, the levy applied to online advertising services, imposing a 6% tax on payments made to non-resident providers. This was later expanded in 2020 to include e-commerce transactions, imposing a 2% levy on revenues from e-commerce operations. The e-commerce levy was abolished in August 2024.
- Conditions: The levy is applicable if:
- The payment is made to a non-resident service provider.
- The annual payment to the service provider exceeds Rs. 1 lakh in a financial year.
- Exclusions:
- If the non-resident service provider has a permanent office in India or if the income qualifies as royalties or technical services fees, it is not subject to the levy.
- Transactions under Rs. 1 lakh or involving exempt income under Section 10(50) are not taxed under the Equalisation Levy.
Key Reasons for Abolishing the Equalisation Levy
- Improved Tax Relations with the US: The levy has been a point of contention, particularly with the US, which threatened retaliatory tariffs. The move to abolish the 6% levy is seen as a step to improve trade relations and avoid escalation of trade disputes.
- Simplification of Tax Laws: Experts believe that removing the levy aligns with India’s broader efforts to simplify and streamline its tax legislation, making it easier for digital service providers to operate within the country.
- Addressing Global Concerns: The proposal to remove the levy is also in response to concerns raised by partner nations, like the US, about the unilateral nature of the tax. This step aims to reduce friction and maintain smoother diplomatic and trade ties.
Implications of the Abolition of the Equalisation Levy
- Reduced Costs for Advertisers: The removal of the 6% tax will lower the financial burden on advertisers in India who use platforms like Google, Meta, and X. This is expected to encourage more investment in digital advertising and benefit the broader digital economy.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: By removing the levy, India aims to create a more level playing field for both domestic and foreign companies involved in digital advertising, fostering fairer competition.
- Impact on International Relations: The decision could help defuse trade tensions, particularly with the US, and might avoid reciprocal tariffs that could affect Indian companies operating internationally.
- Tax Revenue Implications: While the abolition may result in short-term revenue loss from the digital services sector, it is anticipated that the long-term benefits from increased digital advertising spending and improved international relations will outweigh the initial loss.
Future Outlook
- Monitoring and Adjustments: While the government has moved to abolish the Equalisation Levy, experts suggest that further monitoring and analysis of digital taxation might be required, especially considering global trends and the evolving digital economy. The impact of this abolition on India’s digital tax landscape will need to be observed closely.
- Diplomatic Measures: Along with the abolition of the levy, the government continues to pursue diplomatic efforts to ensure fair trade practices and avoid potential retaliatory measures by foreign nations.
Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) Sagar & AIKEYME

- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
India’s Maiden India-Africa Naval Exercise: Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) Sagar & AIKEYME.
Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) Sagar
- Launched: April 5 – May 8, 2025
- Vessel: INS Sunayna (Offshore Patrol Vessel)
- Objective: Maritime security cooperation in the Southwest Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Participants:India + 9 African & IOR nations:Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, and South Africa
- Activities:
- Port Visits: Dar-es-Salaam (Tanzania), Nacala (Mozambique), Port Louis (Mauritius), Port Victoria (Seychelles), Male (Maldives)
- Joint EEZ Surveillance: With Tanzania, Mozambique, Mauritius, and Seychelles
- Training: Personnel from participating countries trained at Indian naval institutions in Kochi on operations, navigation, and maritime security
AIKEYME (Africa-India Key Maritime Engagement)
- Meaning: "Unity" (from Sanskrit)
- Type: First Multilateral Naval Exercise between India and African nations
- Duration: Six days in mid-April 2025
- Co-hosts: Indian Navy and Tanzania People's Defence Force (TPDF)
- Inauguration: By Indian Defence Minister at Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania
- Participants:India + 10 African nations:Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, South Africa, Tanzania
- Exercise Phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Table-top exercises
- Command post exercises on piracy and information sharing
- Training in Seamanship and Visit, Board, Search & Seizure (VBSS)
- Sea Phase:
- Maritime security drills
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Small arms firing
- Helicopter operations
- Harbour Phase:
Strategic Context & Broader Framework
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) – 2015
- Aim: Promote a free, open, inclusive and secure Indo-Pacific
- Key Pillars:
- Countering China's influence in the region
- Enhancing maritime security (anti-piracy, anti-terrorism)
- Capacity building in disaster management and infrastructure
- Promoting regional economic and connectivity projects
MAHASAGAR Initiative
- Announced by PM Modi in Mauritius
- Stands for Advancement for Security Across the Regions
- Focuses on bolstering maritime security partnerships across the Indian Ocean
Key Supporting Indian Initiatives
- Mission SAGAR: Delivered COVID-19 aid to Indian Ocean nations
- Vaccine Maitri: Supplied vaccines to neighbours like Maldives and Bhutan
- South Asia Satellite: Enhanced communication & disaster response
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Project: Boosted India-Myanmar-Southeast Asia connectivity
India and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
Charting a route for IORA under India’s chairship
What is IORA?
The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) is a regional inter-governmental organization established on 7 March 1997 to promote economic cooperation, regional integration, and sustainable development among countries bordering the Indian Ocean. The idea was initiated during Nelson Mandela’s visit to India in 1995, leading to the Indian Ocean Rim Initiative (IORI).
- Membership: 23 Member States and 10 Dialogue Partners
- Geographical Reach: Connects Asia, Africa, and Oceania via the Indian Ocean
- Secretariat: Based in Mauritius
Importance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Geopolitical Relevance: Subset of the Indo-Pacific but with unique characteristics
- Demographics: Home to two-thirds of the global population
- Economic Significance:
- Handles 75% of global trade volume
- Accounts for 50% of global daily oil consumption
- Generates USD 1 trillion worth of goods/services annually
- Intra-IORA trade: USD 800 billion (2023)
India’s Chairship of IORA (2025–27)
India is set to take over as Chair of IORA in November 2025 (currently Vice-Chair). It aims to enhance the organization’s governance and effectiveness by focusing on:
- Strengthening IORA’s Budget:
- Promote public-private partnerships
- Encourage investments from key maritime industries (shipping, oil & gas, marine tourism)
- Learn from other models like the Indian Ocean Commission ($1.3 billion budget for 2020–25)
- Technology Integration:
- Adopt digital tools for data governance
- Enable faster policy analysis and decision-making
- Reduce inefficiencies in record-keeping
- Maritime Education and Capacity Building:
- Collaborate with academic and research institutions
- Launch maritime-ready and interdisciplinary courses (e.g., marine accounting)
- Develop a skilled workforce to support the blue economy
Strategic Synergy with India’s SAGAR Vision
India’s Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) vision aligns with IORA’s objectives:
- Enhancing maritime safety and security
- Fostering economic growth and sustainable development
- Promoting regional peace and cooperation
India is expected to leverage its diplomatic ties with member states and encourage collaborative problem-solving across the region.
India-ASEAN and EU Cooperation on Counter-Terrorism
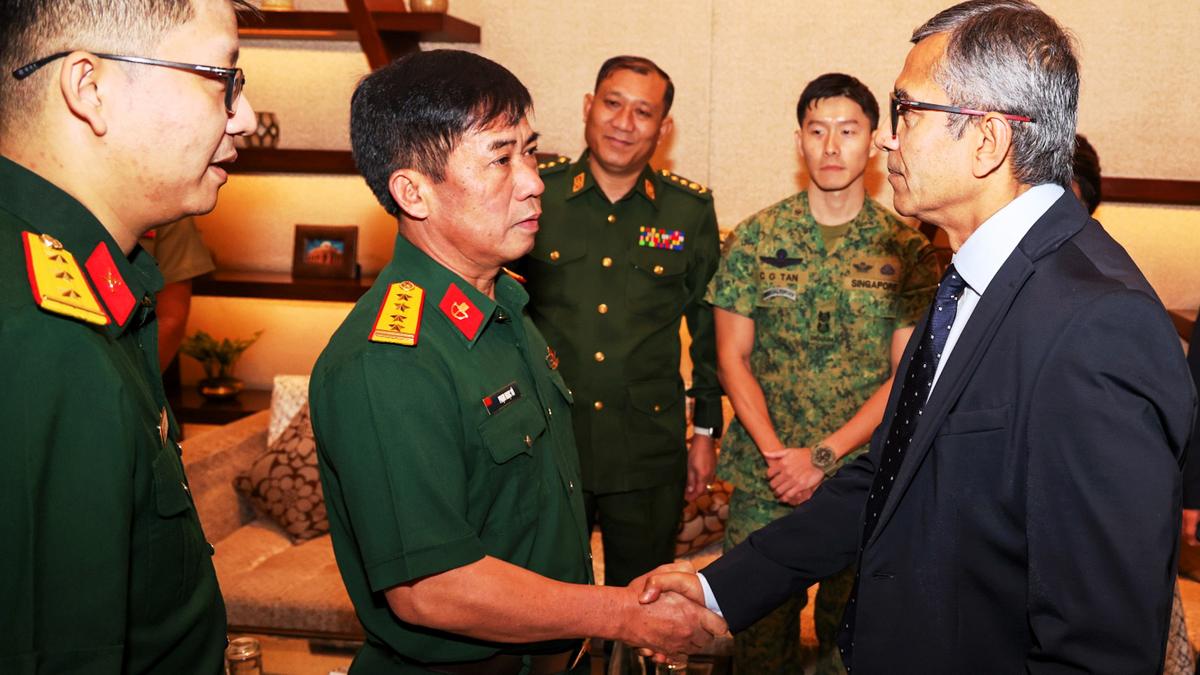

- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
- 14th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) Experts’ Working Group on Counter-Terrorism (EWG on CT) was held in New Delhi.
- India and Malaysia took over as co-chairs for the 2024–2027 cycle, succeeding Myanmar and Russia (2021–2024).
- Two major exercises were announced:
- Table-top Exercise in Malaysia – 2026
- Field Training Exercise in India – 2027
- These are part of the EWG on CT 2024–2027 Work Plan.
Purpose and Agenda:
- To devise a comprehensive and coordinated counter-terrorism strategy.
- To share on-ground experiences of ASEAN and partner nations’ defence forces.
- Focus on evolving threats like violent extremism, radicalisation, and terrorism financing.
Participants in ADMM-Plus EWG on CT:
- ASEAN Member States: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia.
- Dialogue Partners: India, China, U.S., Russia, Japan, South Korea, Australia.
- ASEAN Secretariat also participated.
India-EU Counterterrorism Engagement:
- On the sidelines of the Raisina Dialogue, the European Union (EU) conducted a technical workshop in New Delhi on preventing and countering violent extremism.
- Organized with the Embassy of the Netherlands and attended by security experts from EU states like Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, and the Netherlands, as well as the Strong Cities Network (SCN).
- Discussions focused on:
- De-radicalisation strategies
- Rehabilitation of extremists
- Whole-of-government approaches
- Risk evaluation and reintegration
- Reinforced the India-EU commitment made during the EU College of Commissioners' visit to India and in the Joint Leaders' Statement.
About ASEAN:
- Established: August 8, 1967 (Bangkok Declaration)
- Headquarters: Jakarta, Indonesia
- Motto: "One Vision, One Identity, One Community"
- Members (10):
- Founding (1967): Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand
- Later: Brunei (1984), Vietnam (1995), Laos & Myanmar (1997), Cambodia (1999)
- Population: ~662 million (2022)
- Combined GDP: $3.2 trillion (2022)
ASEAN Institutional Mechanisms:
- ASEAN Summit – Annual heads-of-state meeting.
- ASEAN Coordinating Council (ACC) – Implements decisions and agreements.
- ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) – India joined in 1996; focuses on regional security dialogue.
- ASEAN Secretariat – Administrative support to ASEAN initiatives.
India-ASEAN Relations:
- Sectoral Dialogue Partner since 1992; Full Dialogue Partner since 1996.
- India-ASEAN FTA:
- Goods (2009)
- Services & Investments (2014)
- Strategic Partnership: Established in 2012.
- India in ADMM-Plus: Actively participates in defence and security cooperation mechanisms.
- ASEAN Future Forum: Proposed by Vietnam (2023); India is a founding member.
GPS Interference and Spoofing in Indian Airspace

- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
Between November 2023 and February 2025, 465 incidents of GPS interference and spoofing were reported, predominantly in the Amritsar and Jammu border regions. This was disclosed by Minister of State for Civil Aviation MurlidharMohol in a written reply to the Lok Sabha.
What is GPS/GNSS Spoofing?
- GPS (Global Positioning System) and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) spoofing involves broadcasting false GPS signals that deceive receivers into calculating incorrect locations.
- It is a form of cyberattack exploiting weak satellite signal strength to override legitimate GPS data.
- It can mislead aircraft navigation systems, creating flight safety risks in sensitive regions like international borders.
How GPS Spoofing Works:
- GPS satellites transmit weak signals to Earth.
- Spoofers broadcast stronger fake signals mimicking these satellites.
- Receivers (like those in aircraft) pick up false data, resulting in mislocation or navigation errors.
Types of Spoofing Attacks:
- GPS Spoofing – False location data.
- IP Spoofing – Hides origin of data, often used in DDoS attacks.
- SMS/Caller ID Spoofing – Disguises identity to deceive users.
Government Response:
DGCA Circular (Nov 2023):
- Mandated reporting of GPS interference.
- Issued mitigation guidelines for:
- Aircraft operators
- Pilots
- Air Traffic Controllers
- Air Navigation Service Providers (ANSP)
Use of International Best Practices:
- Guidelines align with ICAO and EASA standards.
- NOTAMs (Notice to Airmen) are issued in affected areas.
- Airlines implement Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to manage spoofing incidents.
Navigation Redundancy Measures:
- Retention of ground-based navigation systems as backups.
- Ensures continued navigation in the event of GPS disruption.
Role of AAI (Airports Authority of India):
- Sole Air Navigation Service Provider (ANSP) in India.
- Continuously upgrading air navigation infrastructure to counter emerging threats like spoofing.
APAAR ID

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The Centre and several State governments are pushing for large-scale adoption of the APAAR ID, leading to concerns over privacy, data security, and its voluntary status.
What is APAAR?
APAAR stands for Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, a 12-digit unique student identification number. It is a central digital record system introduced under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and is part of the broader ‘One Nation, One Student ID’ initiative. The ID consolidates students’ academic and co-curricular achievements across school and higher education, accessible via DigiLocker and generated through the UDISE+ portal.
Objectives and Benefits:
- Seamless Academic Mobility: Enables smooth transfers between schools and institutions.
- Permanent Record Keeping: Stores marksheets, qualifications, and affiliations in one place.
- Career and Skill Support: Facilitates use in entrance exams, job applications, skill training, and admissions.
- Data for Policymaking: Helps track educational outcomes and inform targeted interventions.
- Integration with Other Platforms:
- DigiLocker: Cloud-based certificate storage recognized under IT Rules, 2016.
- Academic Bank of Credits (ABC): Links credit transfers with APAAR ID.
Is APAAR Mandatory?
- Legally Voluntary: The Union Government clarified in Parliament (Dec 2024) that APAAR registration is not compulsory.
- Implementation Pressure: CBSE and states like Uttar Pradesh have aggressively pushed for 100% coverage, leading to confusion.
- Opt-Out Provision: Parents can submit a written refusal to schools. Templates are available from digital rights organizations like the Software Freedom Law Centre (SFLC).
Generation Process:
- School verifies student’s demographic details.
- Parent/guardian provides consent (especially for minors).
- ID is generated post-authentication.
Key Challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: Collection of children's personal data without a dedicated legal framework raises constitutional questions.
- Section 9(3) of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 prohibits tracking and profiling of children.
- Risk of data exposure due to open APIs and lack of cybersecurity safeguards.
- Lack of Transparency: No clear policy document; RTI applications have been redirected multiple times without clear answers.
- Administrative Burden: Teachers duplicate data already recorded under UDISE+, leading to extra workload.
- Technical Glitches: Issues in Aadhaar linking and data mismatches delay generation. Example: Only 24% APAAR generation in Bengaluru Urban South due to such errors.
Way Forward:
- Clear Communication: Government must ensure schools inform parents about the voluntary nature.
- Legal Safeguards: A robust data protection mechanism should be mandated before full-scale rollout.
- Capacity Building: Train school authorities on secure data handling and informed consent procedures.
- Monitoring and Accountability: States should report progress and resolve grievances via helplines and grievance redress mechanisms.
Hmar-Zomi Clashes and Peace Efforts

- 20 Mar 2025
In News:
Following inter-community clashes between the Hmar and Zomi tribes in Churachandpur district of Manipur, efforts have been initiated by tribal leaders to restore peace. These communities are constituents of the larger Kuki-Zo ethnic group, which has been in conflict with the non-tribal Meitei community since May 2023.
Key Developments:
- Peace Initiative:Leaders of the Hmar Inpui and Zomi Council, apex bodies of the two communities, issued a joint statement on March 18, 2025, expressing concern over the violence and agreed to:
- Lift the shutdown in Churachandpur.
- Resolve disputes through customary laws.
- Work jointly for peace and normalcy.
- Government Response:
- Restrictions under Section 163 of BNSS (BharatiyaNagarik Suraksha Sanhita) were imposed as a preventive measure.
- President’s Rule was imposed in Manipur on February 13, 2025, and the State Assembly was placed under suspended animation following Chief Minister N. Biren Singh's resignation.
Ethnographic Background
Zomi Tribe:
- Ethnic Affiliation: Tibeto-Burman (Mongoloid race).
- Distribution: Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Assam; also in Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Language: Belong to the Kuki-Chin (Kukish) group of languages.
- Religion: Predominantly Christian (Baptist, Presbyterian); formerly animistic.
- Features: Short stature, straight black hair, dark brown eyes.
Hmar Tribe:
- Ethnic Affiliation: Part of the Chin-Kuki-Mizo group, Mongoloid stock.
- Distribution: Manipur, Assam, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Tripura.
- Language: Hmar language under Kuki-Chin group (Tibeto-Burman family).
- Traditional Beliefs: Animism; now mostly Christian.
- Social Structure: Clan-based; village led by a chief called “Lal”.
- Occupation: Mainly slash-and-burn (jhum) cultivators.
- Migration History: Folk traditions trace origin to Sinlung, believed to be in China.
Audible Enclaves

- 20 Mar 2025
Context:
Audible enclaves are highly localized zones of sound that remain undisturbed by ambient noise. These allow only specific individuals—usually within a defined space—to hear the sound, even in crowded or noisy environments.
Science Behind the Concept
- Nature of Sound:Sound travels as waves through a medium, causing its particles to vibrate back and forth.
- Frequency: The rate of this vibration determines the pitch of the sound.
- Higher frequency = Higher pitch.
- Diffraction: As sound propagates, it naturally spreads out. Higher-frequency waves tend to diverge more.
- Frequency: The rate of this vibration determines the pitch of the sound.
How Audible Enclaves are created
- Parametric Array Loudspeakers:These devices emit high-frequency ultrasonic waves modulated with an audio signal. As they move through air, the waves undergo self-demodulation, converting into audible sound in a narrow, focused beam. This beam is heard only by those directly in its path.
- Advanced Audible Enclaves (New Research – 2024):A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (March 17, 2024) demonstrated a more precise technique:
- Two ultrasonic waves of slightly different frequencies are emitted.
- These are inaudible on their own.
- When they intersect, non-linear acoustic interactions occur at that point.
- This generates an audible sound wave only at the intersection point, creating an enclave audible only to nearby individuals.
Applications and Relevance
- Private Communication in public places.
- Augmented Reality and targeted advertising.
- Assistive technology for the hearing-impaired.
- Security and military operations, where discreet communication is required.
Colossal Squid

- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
In a landmark moment for marine biology, scientists have captured the first-ever footage of a colossal squid in its natural deep-sea habitat. The sighting was made by an international research team using a remotely operated submersible in the South Atlantic Ocean, near the South Sandwich Islands, and was announced by the Schmidt Ocean Institute in April 2025.
About the Colossal Squid
- Scientific Name:Mesonychoteuthishamiltoni
- Distribution: Found in the cold, deep waters of the Southern Ocean near Antarctica
- IUCN Status:Least Concern
The colossal squid is among the largest and most elusive invertebrates on Earth. The filmed specimen was a juvenile about 30 cm (1 foot) long, observed at a depth of 600 meters. However, fully grown adults can reach up to 7 meters (23 feet) in length and weigh around 500 kg.
Key Features
- Body: Tube-shaped and soft-bodied, similar to octopuses but far more massive
- Arms & Tentacles: Equipped with suckers and sharp, swivelling hooks — a feature unique to the species
- Eyes: Possess the largest eyes known in the animal kingdom, aiding visibility in the pitch-dark ocean depths
- Coloration:
- Juveniles are nearly transparent, giving them a glassy, ghost-like appearance
- Adults become opaque, with dark red or purple hues and muscular limbs
Scientific Importance & Recent Discovery
- This deep-sea sighting comes almost a century after the species was first identified, and confirms long-standing hypotheses based on carcasses found in the stomachs of whales and seabirds.
- The team is now testing improved camera systems to attempt capturing footage of an adult colossal squid in action.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) is an innovative energy solution that allows Electric Vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid (charging) but also send excess stored electricity back to the grid (discharging) when not in use. This bi-directional energy flow creates a unique opportunity to support grid stability, especially when renewable energy (RE) sources like solar and wind are intermittent. When connected via bi-directional chargers, EV batteries can act as decentralized storage systems, offering a potential solution to address the challenges posed by renewable energy integration and peak demand periods.
Global Adoption and Benefits of V2G
V2G technology has gained significant traction in developed EV markets like Europe and the U.S., where it is seen as a cost-effective solution for distributed energy storage.
- In the U.K. and the Netherlands, EV owners are compensated for supplying excess energy to the grid, particularly during peak hours.
- In California, EVs are integrated into the ancillary services market, helping improve grid reliability.
- Additionally, V2G technologies have shown promise in offering emergency power during natural disasters and grid failures, proving to be an essential tool for enhancing grid resilience.
V2G in India: Current Status and Challenges
In India, V2G technology is still in its nascent stages. While there is a growing adoption of EVs and charging infrastructure, integrating these vehicles into the national grid remains a challenge. The electricity market in India is not yet fully equipped to support decentralized energy solutions like V2G. The current grid structure, characterized by variable RE generation and mismatches in supply and demand, requires significant regulatory and structural changes for successful V2G integration.
The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) and the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) have launched a pilot V2G project to assess the feasibility of this technology in the state. This project will explore how EVs can help support grid demand during peak hours, particularly when solar energy generation is low, as Kerala experiences both rapid EV adoption and increasing rooftop solar installations.
Key Features of V2G
- Charging (G2V): When an EV is charged, it functions as a load on the grid. This process can be managed through Time of Use (ToU) electricity tariffs, which incentivize charging during off-peak hours to reduce grid stress.
- Discharging (V2G): When EV batteries discharge power back to the grid, they act as distributed energy resources. This is especially valuable during periods of high demand or when renewable energy generation is insufficient.
- Decentralized Energy Storage: V2G enables EVs to serve as decentralized storage units, reducing the dependency on centralized storage systems and making the grid more resilient and efficient.
Advantages for the Indian Power Sector
- Grid Stability: V2G can help modulate the power flow in the grid by reducing the impact of variable RE generation. It also helps to stabilize grid operations during peak demand periods.
- Support for Renewable Energy: By enabling EVs to store excess solar energy during the day, V2G can assist in using this stored power during nighttime or when renewable energy generation is low, contributing to true decarbonization.
- Smart Charging: Integrating V2G with smart charging systems can help optimize energy use, ensuring that EVs charge during periods of high renewable energy generation and discharge during peak demand.
Potential for Wider Adoption
The Kerala pilot project is expected to pave the way for broader V2G implementation across India. The project aims to test how EVs can provide support during peak demand, particularly when solar power generation is unavailable. The integration of smart charging solutions and V2G will help mitigate concerns about increasing electricity demand due to the growing number of EVs. Additionally, incentives for EV owners to participate in V2G systems can lead to cost-effective solutions for grid management.
The Indian government, through the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), has already initiated steps to frame guidelines for reverse charging (V2G). With the increasing adoption of EVs and solar power, V2G has the potential to become a cornerstone of India's energy future.
Shishtachar Squads

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
To enhance women's safety in public spaces, Delhi Police has launched district-wise Shishtachar Squads, a dedicated initiative to curb eve-teasing and harassment. The move comes in line with the Bharatiya Janata Party’s pre-poll promise and is inspired by Uttar Pradesh’s Anti-Romeo Squads.
Key Features:
- Purpose: To prevent, intervene, and assist in cases of sexual harassment against women in public areas.
- Deployment: 30 squads have been formed across Delhi, with at least two squads in each district.
- Composition: Each 12-member squad includes:
- 1 Inspector (Head)
- 1 Sub-Inspector
- 4 Female Constables
- 5 Male Constables
- 1 Constable from the Anti-Auto Theft Squad (technical support)
- Supervision: Squads function under the ACP of the district's Crime Against Women (CAW) Cell.
Operational Strategy:
- Patrolling: Daily drives in at least two vulnerable spots identified by District DCPs.
- Surprise Checks: Plainclothes officers inspect public transport and engage with DTC staff, market associations, and RWAs.
- Victim-Centric Approach: Emphasis on sensitive handling of cases, ensuring swift action under relevant provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (e.g., Sections 74 for molestation and 78 for stalking).
- Monitoring:
- Weekly Reports by ACP-CAW submitted to the DCP of the Special Police Unit for Women and Children (SPUWAC).
- Monthly Evaluations based on feedback from schools, RWAs, MWAs, and control rooms.
Birefringence

- 17 Mar 2025
Context:
Birefringence, or double refraction, is an optical phenomenon observed in certain anisotropic materials where a single light ray splits into two rays upon entering the material. Each ray travels at a different speed and experiences a different refractive index based on the direction of light propagation and its polarization.
Refraction vs Birefringence
- Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another due to a change in speed. It is governed by the refractive index, defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the medium.
- Birefringence occurs when a material has multiple refractive indices in different directions, causing light to split into two rays.
Key Terms
- Refractive Index:
- Vacuum: 1
- Air: ≈1.0003
- Glass: ≈1.5
- Diamond: ≈2.4
- Polarization: The direction in which the light’s electric field oscillates. It influences how light behaves in birefringent media.
Types of Materials
- Isotropic Materials:
- Structure is uniform in all directions.
- Refractive index is the same regardless of direction.
- Examples: Glass, Sodium Chloride (NaCl).
- Anisotropic Materials:
- Structure varies along different crystal axes.
- Show different refractive indices in different directions.
- Exhibit birefringence.
- Examples: Calcite, Quartz, Mica, Tourmaline.
Sources of Birefringence
- Natural Birefringent Materials: Calcite, Mica, Quartz.
- Synthetic Birefringent Materials: Barium borate, Lithium niobate.
- Induced Birefringence: Can be generated by applying mechanical stress, electric, or magnetic fields to otherwise non-birefringent materials.
Applications of Birefringent Materials
- Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs)
- Medical and Polarising Microscopes
- Optical Switches and Waveplates
- Laser Technology
- Nonlinear Optics (e.g., Frequency Converters)
U.S. airstrikes in Yemen

- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
In March 2025, the United States launched a series of airstrikes on Houthi-controlled areas in Yemen, targeting bases, missile defenses, and key leadership. The operation aimed to neutralize threats to international shipping and assert freedom of navigation through the vital Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. The Houthis, backed by Iran, vowed retaliation, intensifying tensions in an already volatile region.
Who are the Houthis?
- Sect and Origin: Houthis belong to the Zaidi Shia sect, primarily based in Yemen’s northwestern Sa’dah province. The movement originated in the 1990s as a sociopolitical rebellion against President Ali Abdullah Saleh’s regime.
- Role in Yemen’s Civil War: Since 2014, the Houthis have controlled large parts of Yemen, including the capital, Sana’a. They are one of the main belligerents in the civil war, opposing the internationally recognized Yemeni government (backed by Saudi Arabia and the U.S.).
- Foreign Links: The Houthis are aligned with Iran and are considered part of the Iran-led "Axis of Resistance" opposing Israel and Western interests in West Asia.
Geopolitical Importance of Yemen
- Strategic Location: Yemen borders Saudi Arabia and Oman and has coastlines along the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, and Arabian Sea.
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait: This narrow maritime chokepoint between Yemen and Djibouti is a crucial link between the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea (via the Suez Canal and Red Sea).
- It is essential for global oil shipments and international maritime trade.
- Disruptions here threaten energy security and commercial shipping routes.
U.S. Justification and Objectives
- Freedom of Navigation: The U.S. stated that the strikes aimed to protect commercial and naval vessels from attacks and ensure navigational freedom.
- Military Goal: According to U.S. officials, the campaign will continue until the Houthis lose the capability to threaten global shipping.
Regional Reactions
- Iran: Strongly condemned the U.S. airstrikes, asserting that Washington had no authority to dictate West Asian security dynamics.
- Houthi Response: Warned of retaliation, indicating a potential escalation in the Red Sea and Arabian Peninsula.
India's Foreign Exchange Reserves witness sharpest rise in two years

- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
In a notable economic development, India’s foreign exchange (forex) reserves rose sharply by $15.267 billion to reach $653.966 billion during the week ending March 7, 2025. This marks the largest weekly increase in over two years, as per data released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Key Reason for the Surge
- The jump is attributed primarily to a $10 billion forex swap conducted by the RBI on February 28, 2025, where the central bank purchased US dollars in exchange for rupees.
- The objective was to inject liquidity into the domestic financial system while strengthening forex reserves.
Component-wise Breakdown
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): Increased by $13.993 billion to $557.282 billion.
(FCAs are held in major currencies like USD, Euro, Pound, Yen and are affected by their exchange rate fluctuations.) - Gold Reserves: Decreased by $1.053 billion to $74.325 billion.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): Rose by $212 million to $18.21 billion.
- Reserve Tranche Position (RTP) with IMF: Declined by $69 million to $4.148 billion.
Understanding Forex Reserves
- Foreign Exchange Reserves are external assets held by a country's central bank, used to support its monetary and exchange rate policies.
- These reserves include:
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA)
- Gold
- SDRs (with the International Monetary Fund)
- RTP (Reserve capital with the IMF)
Purpose and Importance
- Ensure external stability and maintain confidence in the currency.
- Help manage the exchange rate and balance of payments (BoP).
- Act as a buffer against external shocks, such as volatile capital flows or currency crises.
- Strengthen India’s international creditworthiness.
Global Context
- RBI is the custodian of India’s forex reserves.
- China holds the largest forex reserves globally.
Uniyalakeralensis
- 15 Mar 2025
In News:
Researchers have confirmed the discovery of a new flowering plant species named Uniyalakeralensis (family: Asteraceae) in the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve (ABR), located in the southern Western Ghats of Kerala. Endemic to southwest India, the species is named in honour of the state of Kerala.
Key Features:
- Plant Type: Dense shrub with light purple flowers, growing 1–3 metres tall.
- Distinctive Traits: Larger leaves, longer petioles (leaf stalks), and fewer lateral veins compared to related species like U. comorinensis and U. salviifolia.
- Flowering & Fruiting Period: August to April.
- Habitat: Open areas on western mountain slopes of ABR, at elevations between 700–1,400 metres.
- Distribution: Around 5,000 individuals across four subpopulations, covering an estimated area of 250 km².
- IUCN Status (2024): Data Deficient (DD) due to limited information on long-term population trends.
The plant was first collected in 1998 and initially misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata. Later taxonomic revisions led to the recognition of Uniyala as a separate genus, named after botanist B.P. Uniyal, with this species formally described as new.
About Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve (ABR):
- Location: Spans parts of Kerala and Tamil Nadu in the southern Western Ghats.
- UNESCO Status: Recognized under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme in 2016.
- Biodiversity Highlights: Home to over 2,254 higher plant species, including 405 endemics; key fauna includesNilgiriTahr, Lion-tailed Macaque, Bengal Tiger, and Indian Elephant.
- Indigenous Communities: Inhabited by the Kani tribes in both states.
Mission Amrit Sarovar

- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
Launched in April 2022, Mission Amrit Sarovar is a Government of India initiative aimed at addressing water scarcity, particularly in rural areas, by constructing or rejuvenating 75 water bodies in every district, targeting over 50,000 ponds nationwide. As of October 2024, over 68,000 ponds have been completed.
Key Features:
- Minimum Pond Size: 1 acre with a water holding capacity of ~10,000 cubic metres.
- Community Participation: Sites approved by special Gram Sabha, with a Panchayat Pratinidhi supervising development.
- Multi-Ministerial Collaboration: Involves the Ministries of Rural Development, Jal Shakti, Panchayati Raj, Culture, Environment, and others.
- Technical Support: BISAG-N (Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics) is the technical partner, offering a dedicated portal and mobile app for tracking progress.
- Whole-of-Government Approach: Ensures coordinated implementation across ministries.
Railways' Involvement (2025 Initiative):
- Under Phase II of the mission, Indian Railways is tasked with:
- Desilting existing water bodies or constructing new ponds near railway tracks.
- Using excavated soil for railway embankments, where suitable.
- Coordinating with district authorities and the Ministry of Rural Development to identify appropriate sites.
- The goal is to complete a significant number of ponds by August 15, 2025.
- Promotes climate resilience, ecological balance, and sustainable water resource management.
Japan’s Largest Wildfire in Decades
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
Japan is currently battling its most extensive wildfire in over three decades, with flames spreading across approximately 1,200 hectares of forest in Ofunato, a coastal city in Iwate Prefecture, located in northern Honshu Island. This is Japan's largest wildfire since the 1992 Kushiro fire in Hokkaido, which burned 1,030 hectares.
The cause remains unknown, and the situation is worsened by record-low rainfall (2.5 mm in February) and the hottest year on record in 2023, highlighting the growing impact of climate change. The region is also vulnerable due to its dense forests, dry winter winds, and limited precipitation during February–April, a peak season for wildfires in Japan.
About Ofunato and Iwate Prefecture
- Location: Ofunato is in Iwate Prefecture, northern Japan, along the Pacific coast.
- Ecological Importance: It features mountainous terrain, coastal forests, and is known for fisheries, tourism, and biodiversity.
Japan – Geographical Context
- Location: East Asia, surrounded by the Pacific Ocean.
- Capital: Tokyo.
- Neighbouring Countries (via maritime boundaries): China, South Korea, North Korea, Russia, Taiwan.
- Geological Features:
- Over 80% mountainous terrain; part of the Pacific Ring of Fire (earthquake and volcanic activity-prone).
- Major Islands: Honshu (location of Ofunato), Hokkaido, Kyushu, Shikoku.
- Climate: Ranges from humid subtropical (south) to cold continental (north).
- Major Rivers: Shinano, Tone, Kiso.
Colossal A23a Iceberg
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
The colossal iceberg A23a -- which is more than twice the size of Greater London and weighs nearly one trillion tonnes -- has been drifting north from Antarctica towards South Georgia island since 2020.
What is A23a?
A23a is currently the world’s largest iceberg, covering an area of approximately 3,672 sq. km—more than twice the size of Greater London—and weighing nearly one trillion tonnes. It calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf (Antarctica) in 1986 and remained grounded in the Weddell Sea for over 30 years before breaking free in 2020 and drifting northward.
Current Status:
As of March 2025, A23a appears to have run aground about 70–73 km from South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean. This grounding may spare the island’s rich wildlife, particularly penguins and seals, from disruption in feeding routes and breeding patterns.
Ecological Implications:
- If it had drifted closer, it could have blocked access to feeding grounds, leading to increased mortality of chicks and pups.
- In its current position, nutrients released by its melting and grounding may enhance marine food availability, supporting the local ecosystem.
- This comes as a relief after a difficult season caused by an avian flu outbreak among local wildlife.
Geopolitical Context:
- South Georgia Island is a British Overseas Territory administered by the UK but also claimed by Argentina.
- There is no permanent human population on the island, minimizing direct human impact.
Iceberg Dynamics & Climate Change Link:
- Icebergs such as A23a are natural parts of the Antarctic ice sheet lifecycle, calving from glaciers or ice shelves.
- They are made of freshwater ice, with around 90% submerged below the surface.
- While large icebergs are not new, the rate of calving and ice loss has accelerated, with Antarctic ice shelves losing ~6,000 billion tonnes of mass since 2000.
- Scientists warn that a global temperature rise of 1.5–2°C above pre-industrial levels may trigger irreversible melting, potentially causing sea-level rise of several metres.
Navigation and Fishing Impact:
- The iceberg currently poses no danger to shipping due to its visibility and size.
- However, as it breaks into smaller fragments (bergy bits), it may pose navigation hazards and force commercial fishing vessels to avoid the area.
Colossal A23a Iceberg
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
The colossal iceberg A23a -- which is more than twice the size of Greater London and weighs nearly one trillion tonnes -- has been drifting north from Antarctica towards South Georgia island since 2020.
What is A23a?
A23a is currently the world’s largest iceberg, covering an area of approximately 3,672 sq. km—more than twice the size of Greater London—and weighing nearly one trillion tonnes. It calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf (Antarctica) in 1986 and remained grounded in the Weddell Sea for over 30 years before breaking free in 2020 and drifting northward.
Current Status:
As of March 2025, A23a appears to have run aground about 70–73 km from South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean. This grounding may spare the island’s rich wildlife, particularly penguins and seals, from disruption in feeding routes and breeding patterns.
Ecological Implications:
- If it had drifted closer, it could have blocked access to feeding grounds, leading to increased mortality of chicks and pups.
- In its current position, nutrients released by its melting and grounding may enhance marine food availability, supporting the local ecosystem.
- This comes as a relief after a difficult season caused by an avian flu outbreak among local wildlife.
Geopolitical Context:
- South Georgia Island is a British Overseas Territory administered by the UK but also claimed by Argentina.
- There is no permanent human population on the island, minimizing direct human impact.
Iceberg Dynamics & Climate Change Link:
- Icebergs such as A23a are natural parts of the Antarctic ice sheet lifecycle, calving from glaciers or ice shelves.
- They are made of freshwater ice, with around 90% submerged below the surface.
- While large icebergs are not new, the rate of calving and ice loss has accelerated, with Antarctic ice shelves losing ~6,000 billion tonnes of mass since 2000.
- Scientists warn that a global temperature rise of 1.5–2°C above pre-industrial levels may trigger irreversible melting, potentially causing sea-level rise of several metres.
Navigation and Fishing Impact:
- The iceberg currently poses no danger to shipping due to its visibility and size.
- However, as it breaks into smaller fragments (bergy bits), it may pose navigation hazards and force commercial fishing vessels to avoid the area.
Carbon Intensity

- 08 Mar 2025
What is Carbon Intensity?
Carbon intensity refers to the amount of carbon dioxide (CO?) emitted per unit of output in a particular sector or economy. It integrates environmental accountability into performance metrics across industries and nations.
- Sectoral Carbon Intensity: For example, in the steel sector, it is measured as tonnes of steel produced per tonne of CO? emitted.
- National Carbon Intensity: At the country level, it is calculated by dividing GDP per capita by CO? emissions, offering insights into how efficiently a nation grows economically while managing emissions.
Why is Carbon Intensity Important?
- It allows for the tracking of emissions relative to economic or production output, highlighting whether growth is becoming cleaner over time.
- It enables comparison across sectors and geographies by normalizing emissions data.
Relevance for India and Global Commitments:
- Under the Paris Agreement (2015), India has committed to reducing the emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
- Monitoring carbon intensity helps India evaluate progress toward this Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) goal while ensuring sustainable development.
Global Context:
- China recently reported a 3.4% reduction in carbon intensity in 2024, although it fell short of its 3.9% target.
- Such data underscores the challenge of balancing economic growth with climate responsibility, especially for large emitters.
New Species of Jumping Spiders Discovered in Western Ghats
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
Two new species of jumping spiders belonging to the genus Epidelaxia have been discovered from the Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary in Kollam, Kerala, marking the first recorded presence of this genus in India. Previously, Epidelaxia was considered endemic to Sri Lanka.
Details of the Discovery
- Species: Epidelaxiafalciformis sp. nov. and Epidelaxiapalustris sp. nov.
- Discovered during field studies in December 2022 and April 2023.
- Conducted by researchers from:
- University of Kerala
- Saveetha Medical College, Chennai
- Bharata Mata College, Kochi
- Published in Zootaxa (Feb 2025), a peer-reviewed journal.
Physical Features
- Females: Yellow triangular mark on the prosoma (front body) and white orbital setae around the eyes.
- Males of E. falciformis: Brown carapace with a yellow-brown stripe.
- Males of E. palustris: Pale brown band along the side of the body.
- Size:
- E. falciformis: 4.39 mm
- E. palustris: 4.57 mm (males), 3.69 mm (females)
Ecological Context
- These species are highly adapted to dense foliage in the Western Ghats, a recognized global biodiversity hotspot.
- The discovery extends the known geographical range of the genus and highlights the rich, yet underexplored, arachnid diversity of the Western Ghats.
State of India’s Digital Economy Report 2025

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
The Indian digital economy is growing twice as fast as the overall economy and is projected to contribute 20% of India’s GDP by 2029, according to the State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) 2025 Report released by the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER) and its Prosus Centre for Internet and Digital Economy (CIDE).
Key Highlights:
- Global Standing:
- India is the 3rd largest economy globally.
- However, it ranks only 28th in digital user spending, reflecting a significant per capita digital adoption gap.
- In terms of a combined ranking of economic size and digital user economy, India stands 8th globally.
- CHIPS Framework for Digitalisation:The report uses the CHIPS framework to assess digital development:
- Connect: Internet access, affordability, and quality.
- Harness: Usage intensity, fintech adoption.
- Innovate: Start-up ecosystem, AI readiness.
- Protect: Cybersecurity and digital rights.
- Sustain: Green energy investments in the digital sector.
Strengths:
- Harnessing Digital Potential:
- India performs strongly in ICT service exports.
- The Indian IT sector has the third-highest global market capitalisation, after the U.S. and China.
- High levels of fintech usage and a robust start-up ecosystem contribute to digital growth.
- Digital Growth Rate:
- The digital economy is expanding at twice the pace of the broader economy.
Challenges:
- Low Per Capita Spending:Despite high internet penetration, digital service usage and spending are low, particularly among the average user.
- Regional Digital Divide:Southern and Western states are significantly ahead in digital adoption compared to Northern and Eastern states, pointing to the need for region-specific policy support.
- Weakness in Emerging Technologies:
- India ranks 11th in AI research and 16th in AI infrastructure.
- It lags behind countries like the U.S., China, Singapore, South Korea, and the Netherlands in AI and advanced tech innovation.
- Adoption of Consumer IoT and the metaverse remains well below global medians.
Way Forward:
To bridge the digital usage gap and fully harness the potential of the digital economy:
- Policies must focus on increasing affordability, especially in under-served regions.
- There is a need to strengthen AI infrastructure and research.
- Investment in emerging technologies, decentralised finance, and digital skilling is vital.
- A targeted approach to address regional disparities will ensure inclusive digital growth.
HeroRATS and the Future of Tuberculosis Detection

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the deadliest infectious diseases globally, with over 10 million new cases annually. India carries the highest TB burden, accounting for about 28% of global cases and recording nearly five lakh TB-related deaths each year—roughly one death every minute. Despite progress under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), which aims to eliminate TB by 2025 (ahead of the global 2030 target), early and accurate diagnosis remains a major hurdle, especially in children, low bacillary load cases, and underserved regions.
A Novel Solution: HeroRATS in TB Diagnosis
In a groundbreaking initiative, APOPO, a Tanzanian non-profit, has trained African giant pouched rats (HeroRATS) to detect TB by sniffing sputum samples. These rats have highly sensitive olfactory receptors, enabling them to detect TB cases that conventional diagnostics often miss.
Key Features of HeroRATS:
- Can screen 100 samples in 20 minutes, compared to 3–4 days by sputum-smear microscopy.
- Trained through operant conditioning, rewarded with food after accurate detection.
- Detect twice as many TB cases in children and six times more in low-bacillary-load patients than traditional methods.
- Confirmatory tests: Ziehl-Neelsen and fluorescent microscopy.
A 2023 study involving over 35,000 patients in Tanzania showed that HeroRATS detected over 2,000 additional TB cases, particularly among smear- or Xpert-negative patients. The method offers a fast, cost-effective, and scalable secondary diagnostic tool.
Relevance to India
With India facing challenges like poor health infrastructure in rural areas and reluctance to seek re-testing after a negative result, integrating HeroRATS into the NTEP could boost case detection. Experts suggest a phased rollout in high-burden states like Maharashtra and West Bengal. The Central TB Division’s collaboration with APOPO could help accelerate TB diagnosis and reduce transmission.
About Tuberculosis
- Cause: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, mainly affects the lungs, spread via airborne droplets.
- Prevalence: One-fourth of the global population is infected; only 5–10% show symptoms.
- Risk Factors: Weakened immunity, malnutrition, diabetes, tobacco and alcohol use.
- Diagnosis: WHO recommends rapid molecular tests like Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra.
- Prevention: BCG vaccine at birth.
- Treatment: Standard 4–6 month antibiotic course.
- Drug-Resistant TB:
- MDR-TB: Resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin.
- XDR-TB: Resistant to multiple drug classes, harder to treat.
- TB-HIV Link: HIV patients are 16 times more likely to develop TB.
Bio-detection Beyond Rats: Macrosmatic Species in Medicine
Several animals with heightened olfactory senses are being used in disease detection:
- Dogs: Detect Parkinson’s, cancers, and diabetes using their 125–300 million olfactory receptors and Jacobson’s organ.
- Ants: Trained to detect cancer cells within three days using chemical signals.
- Honeybees: Can differentiate between types of lung cancer with 88% accuracy using synthetic biomarkers.
Agritourism in Himachal Pradesh

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
With a public debt exceeding ?1 lakh crore, Himachal Pradesh (HP) is actively exploring sustainable and innovative ways to boost its economy. Tourism contributes around 7% to the state's GDP, and the state is now integrating agriculture with tourism through agritourism to enhance rural livelihoods and extend tourist engagement.
What is Agritourism?
Agritourism is a form of tourism where visitors are engaged in agricultural activities such as farm stays, crop tours, and interactive farming experiences. It provides farmers with additional income, promotes sustainable tourism, and preserves agricultural and cultural heritage.
Opportunities and Features in Himachal Pradesh
Crop and Farm-Based Tourism
- Tulip farming in Kangra has already attracted tourist interest.
- Scope for cultivation of high-value crops like saffron and Himalayan medicinal herbs.
- Promotion of nutraceutical farming to tap into the growing demand for preventive health-based tourism.
Educational Tourism
- Farm visits can be organized for school and college students to raise awareness about food systems and sustainability.
- Farmers can charge nominal fees, benefiting financially while educating the younger generation.
Cultural and Experiential Engagement
- Local youth can be involved in storytelling, showcasing unique farming practices and regional traditions.
- Farm stays, panchayat-level fairs, and cultural activities (folk music, traditional cuisine) can enrich tourist experiences.
Economic and Employment Benefits
- Diversifies farmer income beyond conventional crops like apples.
- Creates jobs for local guides, cooks, transport providers, and artisans, particularly empowering rural women and youth.
Market Integration
- Organizing crop fairs and displaying agricultural products in urban spaces (e.g., malls) can help secure pre-orders and boost local brands.
- Encourages direct farmer-consumer connections.
Environmental and Social Impact
- Promotes organic farming, eco-friendly practices, and water conservation.
- Builds social capital by fostering urban-rural understanding and collaboration.
- Requires visitor sensitization and capacity building among locals to ensure respectful, responsible tourism.
Learning from Other States
- Maharashtra: First state to promote agritourism (Agro-Tourism Development Corporation, 2005); successful models include Baramati's pilot farm and Nashik’s vineyards.
- Kerala: Agro-Tourism Network for spice cultivation experiences.
- Sikkim: Organic farming tourism in the first organic state of India.
- Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Bihar, NE States: Promote local heritage, farming traditions, and eco-tourism (e.g., Ziro Valley’s wet rice farming, Amul’s dairy tourism).
Policy and Government Support
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: Develops thematic rural and tribal tourism circuits.
- DekhoApnaDesh: Encourages domestic tourism in lesser-known destinations.
- PMJUGA: Focus on tribal homestays and livelihood promotion.
- National Strategy for Promotion of Rural Homestays (2022): Supports agritourism under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund: Helps build infrastructure and marketing support for farm-based tourism.
Way Forward for Himachal Pradesh
- Develop a dedicated agritourism policy, like Goa’s, focusing on farm diversification and long-term returns.
- Promote public-private partnerships (PPP) for integrated agritourism models in each district.
- Leverage the nutraceutical potential of Himalayan herbs to attract health-conscious visitors.
- Institutionalize farm festivals, crop exhibitions, and story-driven agritourism to diversify Himachal’s tourism landscape.
NASA’s SPHEREx Telescope

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA is set to launch the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer (SPHEREx) aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The telescope is megaphone-shaped, infrared-based, and is designed for a 2-year mission to scan the entire sky in infrared and optical light.
Key Details:
Mission Objectives
- Cosmic Inflation: SPHEREx will investigate the phenomenon of cosmic inflation, the ultra-rapid expansion of the universe that occurred a fraction of a second after the Big Bang (~13.8 billion years ago). By mapping the 3D positions of nearly 450 million galaxies, the mission aims to refine theories about the universe’s earliest moments.
- Spectroscopic Mapping: It will divide light into 96–102 spectral bands, creating a 3D map of the sky. It will collect 8 million spectroscopic images, allowing the study of the composition and distribution of celestial objects on an unprecedented scale.
- Biogenic Molecules Detection: The telescope will identify life-forming (biogenic) molecules like water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and methanol in cold molecular clouds of the Milky Way. These icy particles are essential for understanding the chemical preconditions for life.
- Cosmic Glow & New Phenomena: SPHEREx will also measure the collective glow from intergalactic space, which could help uncover previously unknown cosmic events and structures.
Comparison with Other Telescopes
Unlike the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) or the Hubble Space Telescope, which focus on high-resolution, narrow field observations, SPHEREx is designed to scan the entire sky. The full-sky mapping capability makes it a complementary tool for large-scale statistical cosmology.
Significance for Astronomy and Astrobiology
- It provides a comprehensive sky census of galaxies, stars, and asteroids (around 1 billion galaxies, 100 million stars, and 10,000 asteroids).
- By locating regions rich in life-bearing molecules, it enhances our understanding of how life-essential chemistry emerges in the galaxy.
- It lays the groundwork for future targeted studies of exoplanets and habitable environments in space.
India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA)

- 28 Feb 2025
In News:
India and the United Kingdom (UK) have resumed negotiations for a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) after an eight-month gap, with the latest round of talks marking the continuation of discussions that began in January 2022. To date, 14 rounds of talks have been held. The FTA aims to strengthen bilateral economic relations by reducing tariff and non-tariff barriers, enhancing market access, and increasing investments between the two nations.
What is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
An FTA is a trade pact between two or more countries that aims to eliminate or reduce import duties on goods traded between them. It also seeks to minimize non-tariff barriers, enhance services trade, and foster investments. By reducing tariffs, FTAs make goods more competitive in foreign markets, which can help boost exports, create jobs, and enhance diplomatic ties.
India’s Trade Strategy and Focus
India has signed 13 FTAs and six preferential trade agreements with various countries and regional blocs, with a recent emphasis on Western nations, particularly the UK, the European Union (EU), and the United States (US). These agreements are part of India’s strategy to diversify its export markets, expand trade, and attract more foreign direct investment (FDI). FTAs with the UK and EU are seen as vital steps in this direction, given the opportunities they present in key sectors such as technology, healthcare, and education.
Key Objectives of the India-UK FTA
The India-UK FTA aims to:
- Boost Trade and Investment: By reducing tariffs and addressing non-tariff barriers, the FTA seeks to facilitate smoother trade between India and the UK.
- Market Access for Services: India is looking to expand its services exports, particularly in sectors like IT, healthcare, and education.
- Enhance Mobility: India aims to secure greater access for students and professionals in the UK, addressing visa and mobility challenges.
- Investment Opportunities: The agreement includes a Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT), which will safeguard investments and create a more favorable environment for foreign investment.
Benefits of the India-UK FTA
For India, the FTA presents opportunities in both merchandise trade and services:
- Merchandise Trade: India's exports to the UK totaled $12.9 billion in FY24. The FTA is expected to provide tariff reductions on Indian goods, including textiles, apparel, footwear, cars, marine products, and agricultural exports such as grapes and mangoes. These goods currently face relatively low to moderate tariffs in the UK, and the FTA would make them even more competitive.
- Services: Indian sectors like IT, healthcare, and education are poised to benefit significantly from the FTA due to greater market access.
- Investments: The BIT will promote UK investments in India by providing a more stable and transparent investment environment, including mechanisms for dispute resolution.
For the UK, the FTA would reduce high import tariffs on certain goods, making UK products more competitive in the Indian market. Key UK exports such as automobiles, whisky, and machinery, which currently face high tariffs in India, would benefit from reduced duties.
Key Demands and Challenges
While both nations stand to gain from the FTA, several challenges and demands need to be addressed:
- India’s Demands: India seeks greater access for its students and professionals in the UK, alongside more favorable market access for key goods. It also wants to ensure that its domestic industries are protected from a surge in imports, particularly in sensitive sectors.
- UK’s Demands: The UK is pushing for significant cuts in import duties on products like scotch whisky, electric vehicles, and lamb meat. Additionally, the UK seeks improved market access for its services in India, particularly in telecommunications, legal, and financial sectors.
- Dispute Resolution: One of the key areas of negotiation is the dispute resolution mechanism in the BIT. India prefers foreign firms to exhaust local judicial remedies before seeking international arbitration, while the UK has concerns about the efficiency of India’s judicial system.
Sectoral Gains
- Technology: Both countries can collaborate on digital trade, innovation, and technology transfer, fostering mutual growth in the tech sector.
- Green Energy: The FTA could also serve as a platform for enhanced cooperation in renewable energy, aligning with both countries' commitments to climate goals.
- Education and Healthcare: Increased opportunities for educational exchanges and professional mobility in these sectors would enhance bilateral cooperation.
Way Forward
To successfully conclude the FTA, both India and the UK need to:
- Balance Tariff Reductions: Ensure that tariff reductions are fair and that sensitive domestic industries are adequately protected.
- Enhance Market Access: Address concerns related to visa and mobility, ensuring that professionals and students from both countries can benefit from easier movement.
- Finalize Investment Protections: Ensure that the BIT offers clear and mutually beneficial terms for dispute resolution and investment safeguards.
- Strengthen Sector-Specific Cooperation: Focus on areas such as technology, green energy, and digital trade to drive innovation and growth.
AI in Indian Agriculture

- 28 Feb 2025
In News:
Microsoft Chairman Satya Nadella recently showcased the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Indian agriculture through Project Farm Vibes in Baramati, Maharashtra, where AI-driven techniques led to a 40% increase in crop yields while reducing resource consumption significantly.
What is Project Farm Vibes?
Developed by Microsoft Research in collaboration with the Agricultural Development Trust, Baramati, Project Farm Vibes is an open-sourced AI suite aimed at making farming more data-driven, efficient, and sustainable.
Key Technologies:
- Azure Data Manager for Agriculture: Aggregates satellite imagery, weather data, and sensor inputs for a complete view of field conditions.
- FarmVibes.AI: Analyzes soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and pH to offer precise, AI-driven farming recommendations.
- Agripilot.AI: Provides real-time, localized, and personalized farming advice, including in regional languages.
Impact:
- 40% increase in crop production with healthier crops.
- 25% reduction in fertilizer costs through precision spot fertilization.
- 50% decrease in water usage, promoting sustainable irrigation.
- 12% reduction in post-harvest wastage, improving profitability.
- Environmental gains through reduced chemical runoff, soil erosion, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
How is AI Revolutionizing Indian Agriculture?
- Smart Irrigation:
- AI-based soil and climate analysis optimizes irrigation.
- Schemes like "Per Drop More Crop" are integrating AI with drip and sprinkler systems.
- IoT-driven irrigation systems by ICAR automate water supply based on real-time data.
- Pest and Weed Control:
- The National Pest Surveillance System uses AI to detect pests early and issue real-time alerts.
- AI-enabled computer vision distinguishes between crops and weeds, minimizing herbicide use.
- Economic Impact:
- The AI in agriculture market is projected to grow from USD 1.7 billion (2023) to USD 4.7 billion (2028) at a CAGR of 23.1%.
- Tools like Kisan e-Mitra, an AI chatbot, are improving farmer access to government schemes like PM-Kisan.
Challenges in AI Adoption
- Lack of Awareness: Limited digital literacy in rural areas hampers effective use.
- High Costs: Expensive AI tools like drones and IoT devices are unaffordable for small and marginal farmers (85% of farming community).
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor internet connectivity; over 25,000 villages lack mobile/internet access.
- Data Issues: AI needs accurate, real-time agricultural data, which is often missing or unreliable.
- Limited Customization: Generic AI models fail to address India's diverse agro-climatic conditions, requiring localized solutions.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Data Frameworks: Utilize platforms like AgriStack and IDEA for integrated farm data management.
- Develop Region-Specific Solutions: Leverage National AI Centres of Excellence to create localized AI applications.
- Improving Digital Infrastructure: Expand PM-WANI and BharatNet to enhance rural connectivity.
- Farmer Skilling and Awareness: Scale initiatives like NeGPA and FutureSkills PRIME for farmer education in digital technologies.
- Financial Support: Promote subsidized loans and investments through the Digital Agriculture Mission (2021-2025) to empower agri-tech startups and farmer cooperatives.
Soliga Tribe and Tiger Conservation

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
In the 119th edition of Mann Ki Baat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded the Soliga tribe of the BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve in Karnataka for their significant role in tiger conservation and sustainable forest practices.
Who are the Soligas?
- Location: Indigenous, forest-dwelling tribe residing primarily in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka, and parts of Tamil Nadu, especially around Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara Hills.
- Meaning of the Name: "Soliga" translates to “children of bamboo”, symbolizing their deep ecological ties.
- Language: They speak Sholaga (a Dravidian language), along with Kannada and Tamil.
- Lifestyle:Soligas live in bamboo-and-mud huts, practice shifting cultivation, and depend on non-timber forest produce (NTFP) for sustenance.
- Diet & Livelihood:Honey is a staple in their diet; they extensively forage and harvest forest produce like amla, gooseberries, and medicinal herbs, leaving a portion for wildlife—a reflection of their conservation ethos.
Religious and Cultural Practices:
- Soligasworship wildlife, especially the tiger, locally called “DoddaNayi” (Great Dog). They have even built temples dedicated to tigers.
- Their belief system includes Hindu customs, animism, and naturism, highlighting their spiritual connection with nature.
- They produce eco-friendly artifacts like ‘jottai’ (leaf cups), showcasing sustainable craftsmanship.
Recognition of Forest Rights:
- In 2011, Soligas became the first tribal community in India to receive legal recognition of their forest rights within a tiger reserve, under the Forest Rights Act (FRA).
- This ruling allowed them to reside within the BRT Tiger Reserve and sustainably collect forest produce without displacing wildlife.
Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Soligas’ traditional knowledge of forest ecology helps them coexist peacefully with wildlife, minimizing human-animal conflict.
- They assist the Forest Department in fire prevention, wildlife tracking, and ecological management.
- Their cultural practices ensure minimal disturbance to wildlife. For instance, during harvest, they intentionally leave 25–33% of the produce in the forest for animals.
BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka; lies at the confluence of the Western and Eastern Ghats, forming a critical wildlife corridor.
- Ecosystem: Rich in biodiversity with forest types including:
- Southern Tropical Evergreen
- Semi-Evergreen
- Moist Deciduous
- Flora:Axlewood, Rosewood, Terminalia spp., Indian Gooseberry, Ceylon Oak, Golden Shower Tree.
- Fauna: Tigers, Wild Dogs, Sloth Bears, Sambars, Bison, and endangered species like the Icthyophisghytinosus (Caecilian).
- Cultural Site: Named after Lord Rangaswamy, the reserve houses the Biligiri Temple atop mist-covered hills.
USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced its largest-ever USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction worth $10 billionfor a tenor of three years. This strategic move is aimed at addressing the persistent liquidity deficit in the banking system and stabilizing the Rupee-Dollar exchange rate.
What is a USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction?
A Dollar/Rupee Buy-Sell Swap Auction is a foreign exchange (forex) tool used by RBI to manage domestic liquidity and curb currency volatility. It is a two-leg transaction:
- First Leg (Buy Phase):Banks sell US dollars to the RBI and receive rupee liquidity.
- Reverse Leg (Sell Phase):RBI sells back the same amount of US dollars to banks at a future date (here, after 3 years), along with a swap premium.
Key Features of the February 2025 Swap Auction:
- Auction Size: USD 10 billion
- Tenor: 3 years (long-term)
- Rupee Liquidity Injected: Approx. ?86,000 crore
- Auction Date: 28 February 2025
- Spot Settlement Date: 4 March 2025
- Far-leg Settlement Date: 6 March 2028
- Reference Rate: Based on FBIL (Financial Benchmarks India Pvt Ltd) benchmark
Objectives and Benefits:
- Liquidity Management:
- Addresses durable liquidity needs; helps ease banking system deficit (estimated at ?1.7 lakh crore).
- Supports credit flow to businesses, aiding economic growth.
- Exchange Rate Stability:
- Reduces volatility in the USD/INR rate (expected to stabilize around ?86.30).
- Mitigates pressure from foreign fund outflows.
- Efficient Forex Reserve Utilization:
- Uses RBI’s reserves productively to manage monetary conditions.
- Enhances Policy Transmission:
- Aligns money market interest rates with RBI’s monetary policy stance.
- Supports Inflation Control:
- Infuses liquidity without directly adding to inflationary pressures.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Impact on Forex Reserves:Large-scale swaps temporarily tie up reserves.
- Global Dependencies:Effectiveness may be affected by global interest rate differentials, capital flows, and external shocks.
- Market Speculation Risks:Poor timing or execution could trigger speculative activity in the forex market.
- Temporary Measure:Swap auctions offer short- to medium-term relief; structural reforms are needed for long-term liquidity management.
Northern White Rhino
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Northern White Rhino (NWR) is on the brink of extinction, with only two females—Najin and Fatu—remaining at the Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Kenya. However, a breakthrough in In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has rekindled hope for reviving this subspecies, with 36 lab-created embryos ready for implantation. This effort is part of an international project named BioRescue.
About the White Rhino
- Scientific Name: Ceratotherium simum
- Common Name: Square-lipped rhinoceros (due to broad upper lip)
- Subspecies:
- Northern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum cottoni)
- Southern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum simum)
- Habitat:
- Southern White Rhino: South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Kenya
- Northern White Rhino: Historically central and eastern Africa; now only in captivity
- IUCN Status:
- White Rhino (overall): Near Threatened
- Northern White Rhino: Critically Endangered
- Southern White Rhino: Near Threatened
Biological Features
- Second-largest land mammal after elephants
- Square upper lip adapted for grazing on short grasses
- Two horns, with the front horn being larger
- No actual color difference between black and white rhinos
Social & Dietary Behavior
- Diet: Pure herbivores; feed almost exclusively on short grasses
- Behavior:
- Semi-social and territorial
- Males mark territories with dung
- SWRs form larger social herds; NWRs were found in smaller groups
Threats to Survival
- Poaching for horns
- Habitat loss due to human encroachment
- Civil unrest, particularly in their native range
- Low genetic diversity, especially critical in the NWR
- Climate change, affecting habitat and water sources
Conservation Through Reproductive Technology
BioRescue Initiative
- An international scientific effort launched in 2015 to save the NWR using advanced reproductive technologies.
- Uses frozen sperm from deceased males and eggs from Najin and Fatu to create embryos in the lab.
- 36 embryos have been successfully created and are stored for future implantation.
IVF and Surrogacy
- First-ever rhino pregnancy via lab-made embryo announced recently.
- Southern white rhinos are used as surrogate mothers due to genetic similarity and higher population.
- IVF and embryo transfers are the only options since the last male NWR, Sudan, died in 2018, and both remaining females are non-reproductive due to age and health.
Challenges & Concerns
- Limited gene pool restricts genetic variability.
- Loss of unique traits if crossbred with southern white rhinos.
- Behavioral imprinting: IVF calves must learn from remaining NWR females before they pass away.
- Ethical and ecological concerns: Critics argue conservation must also address root causes like poaching, habitat destruction, and lack of genetic diversity, not just focus on “test-tube” solutions.
Indian Rhinoceros
- Scientific Name: Rhinoceros unicornis (Greater One-Horned Rhino)
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Habitat: Indian subcontinent (Assam, West Bengal, UP, Nepal)
- It is distinct from African rhinos, both genetically and ecologically.
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 Quantum Chip
- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Microsoft has unveiled Majorana 1, a new quantum chip that marks a significant advancement in quantum computing, suggesting that scalable quantum systems could be achieved in years rather than decades.
What is Majorana 1?
- It is the world’s first quantum chip built on a topological architecture, using Majorana fermions, exotic subatomic particles that are both particles and antiparticles.
- The chip is designed to be more stable and error-resistant than current quantum technologies developed by competitors like Google and IBM.
Core Technology & Innovation:
- Material Composition: Made from indium arsenide (a semiconductor) and aluminum (a superconductor).
- Topological Superconductivity: When cooled near absolute zero and exposed to magnetic fields, it enables the formation of Majorana Zero Modes, which serve as building blocks for stable qubits.
- Topoconductor Architecture: A new class of materials creating a topological state, offering enhanced fault tolerance.
Quantum Advantage:
- Qubit Efficiency: Majorana 1 reduces the number of physical qubits needed to generate logical (error-corrected) qubits.
- Error-Resistance: Its design addresses two major quantum computing limitations — qubit instability (decoherence) and high error rates.
- Scalability Potential: The chip includes eight topological qubits, with future potential to scale up to a million-qubit system.
Why This Matters:
- Improved Reliability: Lower error rates enhance the practical applicability of quantum systems.
- Accelerated Development: Brings the world closer to realizing commercially viable quantum computers.
- Wide Applications: Potential use in drug discovery, material science, clean energy solutions, and more.
- AI Integration: May combine with artificial intelligence to tackle global challenges like microplastic degradation.
Quantum Computing in Brief:
- Quantum Computers use qubits and properties like superposition and entanglement to perform highly complex calculations.
- Major Challenges: Qubit instability and error correction.
- Significance: Quantum computing could revolutionize fields by solving problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Nvidia's Evo 2

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Nvidia, in collaboration with the Arc Institute and Stanford University, has launched Evo 2 — the world’s largest publicly available AI model for genomic data — aiming to revolutionize genetic research and biomedical innovation.
About Evo 2
- Type: Foundation AI model for genomics.
- Function: Understands and designs genetic code across all domains of life.
- Scale: Trained on ~9 trillion nucleotides from 128,000+ organisms, including bacteria, plants, animals, and humans.
- Platform: Built using 2,000 Nvidia H100 processors on Amazon Cloud, through the NVIDIA DGX Cloud platform.
- Access: Freely available on Nvidia’s BioNeMo research platform.
Key Features
- Accuracy in Mutation Detection:Accurately identified 90% of harmful mutations in BRCA1 — a gene linked to breast cancer.
- Speed and Efficiency:Enables rapid pattern recognition in vast genomic datasets — research that would otherwise take years.
- Collaborative Development:Created by Nvidia in partnership with Arc Institute (nonprofit research body founded in 2021 with $650 million funding) and Stanford University.
Applications
- Healthcare & Medicine:
- Predicts form and function of proteins.
- Identifies gene mutations and their impact.
- Facilitates precision medicine and gene therapy development.
- Agricultural Biotechnology:
- Aids in designing climate-resilient crops.
- Industrial & Environmental Science:
- Assists in creating enzymes to break down pollutants.
- Supports development of new bio-materials.
Significance for India & Global Science
- Accelerates biomolecular research and biotech innovation.
- Contributes to scientific self-reliance and the bioeconomy.
- Enhances capability in combating diseases like cancer and improving food security.
UNESCO’s “Imagine a World with More Women in Science” Campaign

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 11, 2025, to mark the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, UNESCO, with support from Canada’s International Development Centre (IDRC), launched the global campaign titled “Imagine a World with More Women in Science.”
Campaign Highlights
- Objective: Promote gender equality in science and innovation by encouraging the active participation and leadership of women in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine).
- Social Media Drive: The campaign uses the hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience to amplify diverse voices and encourage global engagement.
- Focus: Emphasizes the real-world impact of gender disparities in science, including missed innovations, biased artificial intelligence, and inequitable scientific opportunities.
Background
- The UN General Assembly (UNGA) declared February 11 as the International Day of Women and Girls in Science in 2015 to foster female participation in scientific research and innovation globally.
Current Status of Women in Science
Global Trends
- Representation: Women comprise only one-third of the global scientific workforce.
- Leadership Gap: Merely 10% of STEM leadership positions are held by women.
India-Specific Data
- STEMM Enrolment: Women account for 43% of enrolment in STEMM disciplines.
- Women Scientists: Only 18.6% of scientists in India are women.
- R&D Projects: About 25% of R&D projects are led by women researchers.
Challenges Faced by Women in Science
Challenge Description
Restrictive Social Norms Traditional gender roles hinder women’s
scientific pursuits.
Lack of Role Models Few visible female leaders discourage young women from
aspiring to scientific careers.
Workplace Inequality Gender biases, hostile work environments, and lack of inclusive
policies create barriers.
Educational Gaps Gender-biased teaching content and insufficient support systems
limit girls’ access to science education.
Recommended Measures
Dismantle Gender Stereotypes
- Remove gender biases from teaching and learning materials.
- Include contributions of female scientists in textbooks with visuals.
- Promote equitable representation of women in boards, panels, and decision-making bodies.
Enhance Visibility of Women Role Models
- Highlight discoveries by female scientists.
- Increase media and curriculum exposure to successful women in science.
Open Educational Pathways
- Promote inclusive teaching practices and gender-neutral curricula.
- Encourage CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives to support girls in science education.
Create Inclusive Work Environments
- Enforce policies for diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Take strong action against gender-based violence, including sexism and harassment in the workplace.
- Advance women into leadership roles in scientific institutions.
India–U.S. Underwater Domain Awareness Cooperation

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
India and the United States have deepened their defense partnership by launching the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA), a landmark initiative focused on co-producing Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) technologies in India.
Understanding Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA)
- UDA refers to the ability to monitor, detect, and evaluate activities beneath the surface of oceans and seas. It plays a vital role in ensuring maritime security, enabling anti-submarine warfare (ASW), managing marine resources, responding to disasters, and protecting the underwater environment.
- In the backdrop of China’s rapid naval expansion and its increasing footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), enhancing UDA has become imperative for India, both at the bilateral level and as part of the Quad framework (India, U.S., Japan, and Australia).
Strategic Significance and Geopolitical Relevance
The UDA collaboration marks a significant step in Indo-U.S. strategic relations. As the maritime domain becomes increasingly contested, especially in the Indo-Pacific, India’s need for robust submarine detection, surveillance, and underwater intelligence capabilities has become critical. The joint initiative aligns with broader strategic goals such as:
- Enhancing Quad cooperation to maintain a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
- Countering threats arising from Chinese submarine activities and naval assertiveness.
- Enabling shared maritime patrols and airlift capacity for disaster response across the region.
Key Technologies Identified for Co-Production
Several high-end underwater surveillance systems have been identified for co-production or co-development in India under the ASIA framework:
- Sea Picket: An autonomous sonar surveillance platform developed by Thayer Mahan.
- Wave Glider Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs): Discussions are underway between Boeing’s Liquid Robotics and Sagar Defence Engineering for the co-production of 60 platforms in India.
- Low-Frequency Active Towed Sonar: Negotiations involve L3 Harris and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for co-development.
- Multistatic Active (MSA) Sonobuoys: A sophisticated submarine-tracking technology, to be co-produced in India by Ultra Maritime and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), with a production line expected by 2027.
- Large-Diameter Autonomous Undersea Vehicles: Produced by Anduril, these offer deep-sea monitoring capabilities.
- Triton Autonomous Underwater and Surface Vehicle: Developed by Ocean Aero, integrates underwater and surface operations.
Existing and Emerging ASW Platforms
India’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities have already been bolstered through U.S. defense acquisitions, including:
- 12 P-8I Poseidon maritime patrol aircraft currently in service.
- 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters, being inducted to enhance ASW and surveillance.
- 15 MQ-9B Sea Guardian UAVs, part of a 31-unit contract with deliveries beginning from 2029.
- An additional six P-8I aircraft were cleared during the recent bilateral talks.
These platforms significantly improve maritime interoperability among Quad nations and provide India with a strategic edge in underwater operations.
Make-in-India and Technological Sovereignty
The UDA initiative strongly supports India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by fostering indigenous manufacturing of advanced underwater systems. It introduces a first-of-its-kind co-production framework in sensitive defense technologies, thus catalyzing innovation and industrial capability within the Indian defense sector.
The initiative also aims to strengthen logistics, intelligence-sharing, and force mobility between the Indian and U.S. armed forces. Enhanced training, joint operations, and technological exchanges will help sustain forward deployments and enable humanitarian and disaster relief missions across the Indo-Pacific.
Aero India 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of Asia's largest biennial airshow, is scheduled to take place from February 10 to 14, 2025, at the Air Force Station, Yelahanka, in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Organized by the Defence Exhibition Organisation under the Ministry of Defence, with support from HAL, DRDO, and the Indian Air Force, the event showcases India's growing prowess in aerospace, aviation, and defense technologies.
Key Highlights:
Edition: 15th (First held in 1996; originally Avia India in 1993)
Theme: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities”
Conclave Theme: “BRIDGE – Building Resilience through International Defence and Global Engagement”
Objectives and Significance
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: In alignment with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, the show promotes domestic aerospace and defense production.
- Showcase Technological Advancements: Cutting-edge systems including fighter jets, helicopters, UAVs, and AI-integrated defense solutions will be exhibited.
- Encourage Global Partnerships: Facilitates joint ventures, MoUs, and technology transfers between Indian and foreign defense firms.
- Boost Strategic Diplomacy: A platform for global defense ministers, CEOs, and military leaders to foster bilateral and multilateral defense ties.
- Stimulate Investment: Attracts FDI and international contracts in India’s defense sector.
Key Events
- Live Aerial Displays: Aerobatic performances by combat aircraft, helicopters, and elite teams like Surya Kiran.
- Defense Ministers’ Conclave: Deliberations on enhancing international defense cooperation.
- CEO Roundtable: Industry leaders discuss emerging trends and investment prospects.
- Manthan/iDEX Pavilion: Showcasing start-up innovations in defense and aerospace.
- India Pavilion: A dedicated zone for indigenous defense production and capabilities.
- International Seminar (Feb 8–9): Focused on Futuristic Aerospace Technologies and related R&D challenges.
Strategic Role of Aero India
Aero India plays a pivotal role in:
- Supporting Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) procurements.
- Demonstrating India's readiness as a global defense manufacturing hub.
- Enhancing India’s geopolitical standing by fostering defense diplomacy through multilateral engagement.
India–US TRUST Initiative

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
India and the United States launched the Transforming Relationship Utilizing Strategic Technology (TRUST) initiative during the Indian Prime Minister’s 2025 visit to the US. This landmark partnership aims to strengthen bilateral cooperation across critical and emerging technology sectors, diversify global supply chains, and reduce dependence on China in strategic industries.
Key Objectives and Scope of the TRUST Initiative
The TRUST initiative is a comprehensive framework focused on:
- Critical Minerals and Advanced Materials
- Establishing resilient supply chains for critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements (REEs)—vital for sectors like defense, semiconductors, clean energy, and electric vehicles (EVs).
- Launch of the Strategic Mineral Recovery Programme to recover and process critical minerals from industrial waste.
- Joint R&D and investment under the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and Minerals Security Finance Network (MSFN).
- India to scale up exploration, processing, and recycling of critical minerals under the National Critical Minerals Mission (2025–31) with a ?16,300 crore outlay.
- Pharmaceutical Sector Collaboration
- Reducing India’s reliance on China for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) through alternative supply chains and expanded API manufacturing.
- Encouraging investment in Indian pharma production, including facilities in the US.
- Pharma formed 21.9% of India’s $20 billion consumer goods exports to the US in 2023.
- High-Tech and Emerging Technologies
- Joint R&D in semiconductors, AI, quantum computing, space, defense, biotechnology, and energy.
- U.S.-India AI Roadmap to be finalized by 2025, including data center infrastructure, processor access, and AI applications.
- Facilitating innovation through academic, industrial, and government collaboration.
- Technology Transfer and Trade Facilitation
- Easing export controls and restrictions to foster high-tech trade.
- Enabling smoother cross-border technology flows and investment under mechanisms like the CHIPS Act (ITSI Fund).
Associated Initiatives Enhancing TRUST
- iCET (Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies) – Launched in 2022, focuses on bilateral cooperation in semiconductors, AI, quantum, and wireless tech with defense applications.
- INDUS-X – Defense innovation initiative involving India’s iDEX and the US Defense Innovation Unit (DIU), emphasizing secure chip designs and green energy.
- CHIPS Act Collaboration – ITSI Fund supports India's semiconductor capacity through funding for R&D and infrastructure.
Strategic Significance
- Reducing China Dependence:China dominates ~70% of global REE production. TRUST helps India and the US build alternative, secure supply chains.
- Boosting Atmanirbhar Bharat:TRUST supports India’s goals under the National Critical Minerals Mission to become self-reliant in key strategic sectors.
- Enhancing Tech and Defense Capability:Ensures timely access to rare materials essential for missiles, radars, fighter jets, AI hardware, and quantum computing.
- Strengthening Pharma and Health Security:Addresses global API shortages and reduces vulnerability in critical drug manufacturing.
- Promoting Clean Energy Transition:Secures supply of minerals like lithium and cobalt essential for battery production and renewable energy tech.
- Fostering Innovation and Investment:Encourages private sector collaboration and US investments in India’s tech, mineral, and pharma sectors.
Current Status of India’s Critical Minerals Ecosystem
- Imports: India is a net importer of most critical minerals; import bill (FY24) stood at approx. ?30,000 crore.
- Exports: India remains a net exporter in rare earths.
- Budgetary Allocation (2025–31):
- ?7,000 crore for exploration.
- ?1,500 crore for recycling incentives.
MITRA Platform

- 18 Feb 2025
ecosystem, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has launched a new digital platform—MITRA (Mutual Fund Investment Tracing and Retrieval Assistant).
Key Features:
- Objective:MITRA aims to help investors trace, identify, and reclaim inactive or unclaimed mutual fund folios, while ensuring KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance under prevailing regulatory norms.
- Developed by:The platform has been developed at an industry level by the two Qualified Registrar and Transfer Agents (QRTAs) —
- Computer Age Management Services Ltd. (CAMS)
- KFIN Technologies Ltd.
These firms serve as agents of Asset Management Companies (AMCs).
- Hosted by:The platform is hosted jointly by CAMS and KFIN Technologies to serve as a centralized, searchable database for inactive and unclaimed mutual fund folios across the industry.
- Functions:
- Enables investors to search for overlooked investments or investments made in their name by others.
- Facilitates rightful legal claims by heirs or nominees.
- Encourages KYC compliance, thus reducing the number of non-KYC compliant folios.
- Aims to minimize the risks of fraudulent redemptions linked to dormant folios.
- Supports the creation of a transparent financial ecosystem by reducing unclaimed investments.
Definition of Inactive Folio:
- A mutual fund folio is considered inactive when no investor-initiated financial or non-financial transactions have occurred for ten consecutive years, even though the folio holds units.
Institutional Measures:
- Unit Holder Protection Committee (UHPC):SEBI has broadened the role of the UHPC under mutual fund regulations. The committee is now tasked with monitoring inactive folios, unclaimed dividends, and pending redemptions, ensuring proactive steps are taken for investor protection.
- Stakeholder Involvement:SEBI has directed AMCs, RTAs, Registered Investment Advisers (RIAs), the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI), and mutual fund distributors to actively promote awareness regarding MITRA among investors.
India Gas Market Report: Outlook to 2030

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The International Energy Agency (IEA), in its report “India Gas Market Report: Outlook to 2030”, has highlighted the transformative potential of natural gas in India’s energy transition.
As India aims to raise the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix from ~6% to 15% by 2030, the report outlines a roadmap for achieving this goal through policy reforms, infrastructure expansion, and market liberalization.
Current Status and Future Outlook
- Demand Growth: India's natural gas consumption is projected to increase by 60%, reaching 103 billion cubic meters (bcm) by 2030. The City Gas Distribution (CGD) sector, which supplies gas to households, transport, and industries, will drive this growth.
- Domestic Production: India produced 35 bcm in 2023, with the Krishna-Godavari deepwater fields contributing a quarter. Production is expected to reach just under 38 bcm by 2030, a modest 8% increase.
- Import Dependency: With domestic supply growth lagging behind demand, LNG imports are expected to more than double, from ~30 bcm in 2023 to around 65 bcm by 2030. India is already the fourth-largest LNG importer globally.
Infrastructure Expansion
India’s natural gas infrastructure has undergone rapid growth:
- Since 2019, the number of CNG stations quadrupled and residential gas connections more than doubled.
- The gas transmission pipeline network expanded by 40%, with another 50% expansion expected by 2030.
- CGD infrastructure is poised for a further boom, supporting increased consumption in urban areas.
Sectoral Trends
- Industry: Heavy industry and manufacturing are expected to add 15 bcm to gas demand by 2030.
- Refining: Gas use in refineries will rise by over 4 bcm as more refineries get connected.
- Transport: Greater CNG adoption, if incentivized, could significantly reduce vehicular emissions.
Challenges Hindering Growth
- Price Distortion: Prices from legacy fields are capped (e.g., USD 6.5–10 per MMBtu), limiting true market-based discovery.
- Monopoly in Transport & Marketing: GAIL’s dominance in both gas marketing and pipeline ownership creates potential conflicts of interest.
- Storage Limitations: India lacks underground gas storage (UGS) and has limited LNG storage capacity, affecting supply security.
- Policy and Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate third-party access and fragmented pricing/taxation systems reduce investor confidence.
Policy Recommendations by IEA
- Gas Pricing Freedom:
- Implement full pricing freedom, in line with Kirit Parekh Committee (2022) recommendations.
- Initially lift ceilings on high-cost deepwater and ultra-deepwater projects.
- Allow producers to sell more output on platforms like the Indian Gas Exchange (IGX).
- Unbundling Supply and Transmission:
- Establish independent gas transmission system operators (TSOs).
- Legally separate marketing from pipeline operations to ensure fair, non-discriminatory access.
- Standardize Gas Sales Agreements (GSAs) and Gas Transmission Agreements (GTAs).
- Infrastructure and Market Development:
- Ensure transparent, regulated third-party access to pipelines.
- Develop strategic gas reserves and expand LNG terminal capacity.
- Improve data transparency on pipeline capacities and tariffs.
- Tax and Regulatory Reforms:
- Harmonize taxes across fuels to create a level playing field.
- Rationalize GST on CNG vehicles and revise import duties on natural gas.
- Offer tax benefits to natural gas similar to electric vehicles to promote adoption.
- Secure Long-Term LNG Contracts:
- With legacy contracts expiring post-2028, proactive procurement is essential to avoid spot market volatility.
Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024

- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
India ranked 96th out of 180 countries in the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) for 2024, with a score of 38, a decline from 39 in 2023 and 40 in 2022. This indicates a worsening perception of corruption within India’s public sector.
Global Context:
- The CPI, compiled annually by Transparency International, is a widely recognized global ranking system that evaluates the perceived levels of corruption in public sectors.
- It uses a scale of 0 to 100, where 0 indicates highly corrupt and 100 signifies very clean.
- The CPI is based on expert assessments and surveys, drawing from at least three data sources out of 13 recognized corruption assessments from organizations like the World Bank and the World Economic Forum.
- Top Ranking Countries: Denmark topped the 2024 CPI, followed by Finland and Singapore, indicating strong governance systems with minimal corruption. These countries are recognized for their effective public sector governance, transparency, and low corruption levels.
- Regional Comparison: Among India’s neighbors, Pakistan ranked 135th, Sri Lanka at 121st, Bangladesh at 149th, and China ranked 76th, performing relatively better than India. The Asia-Pacific region, in general, saw a decline in its average CPI score, dropping by one point to 44.
- Global Trends: The CPI 2024 reveals troubling global trends, with corruption being a persistent issue worldwide. While 32 countries have significantly improved their corruption scores since 2012, 148 countries have either stagnated or worsened in the same period.
- The global average score remains at 43, with more than two-thirds of countries scoring below 50, signaling a widespread corruption problem.
- Corruption’s Impact on Climate Action: One of the significant findings in 2024 is the link between corruption and climate action. Corruption undermines efforts to combat climate change by misappropriating funds meant for emission reduction and climate adaptation projects.
- The report warns that such corruption obstructs effective policies and hinders climate change mitigation, leading to environmental degradation. Furthermore, it highlights that corruption in high-CPI countries often serves the interests of fossil fuel companies, complicating global climate efforts.
- Corruption and Human Rights: The report underscores that corruption not only impedes economic development but also contributes to the erosion of democracy, human rights violations, and instability. Corruption, particularly in the form of misallocation of resources, exacerbates the vulnerability of populations already affected by climate change, poverty, and human rights abuses.
- Financial Hubs and Illicit Funds: Many countries with high CPI scores, despite their lower domestic corruption levels, serve as financial hubs that attract illicit funds stemming from corruption and environmental damage. This "dirty money" exacerbates corruption on a global scale and has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond national borders.
- The Call for Action: Transparency International’s report stresses the need for global cooperation in tackling corruption. It warns that corruption is a major contributor to the rise of authoritarianism and calls for urgent, concrete action to address global corruption. The report emphasizes that combating corruption is crucial for achieving a peaceful, sustainable, and democratic world.
NITI Aayog Policy Report on Expanding Quality Higher Education
- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog released a comprehensive policy report titled ‘Expanding Quality Higher Education through States and State Public Universities (SPUs)’, focusing on the development of higher education institutions, particularly public universities in India.
The report aims to enhance the quality, funding, governance, and employability outcomes within SPUs, which contribute to around 80% of the country's higher education system.
The document, the first of its kind in India, presents a detailed analysis of vital indicators like quality, funding, financing, governance, and employability over the last decade, supported by stakeholder consultations with over 20 states and Union Territories, Vice Chancellors, academicians, and State Higher Education Council Chairs. The report includes nearly 80 policy recommendations, along with 125 performance indicators, aiming to address long-standing challenges within SPUs.
Key Findings from the Report
- Funding:
- Maharashtra leads in funding for higher education, with Bihar and Tamil Nadu following closely behind.
- On the other hand, states like Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland have the lowest funding for higher education, highlighting regional disparities.
- University Density:
- The national average university density is 0.8 universities per lakh population. However, states such as Sikkim, with a density of 10.3, and Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, Meghalaya, and Uttarakhand have significantly higher densities. In contrast, states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Maharashtra have lower densities compared to the national average.
- Female Enrolment:
- Kerala, Chhattisgarh, and Himachal Pradesh have achieved higher female enrolment rates than males, which reflects positive gender inclusivity trends in certain regions.
- Challenges:
- Infrastructure deficits, including a lack of quality facilities and resources.
- A shortage of faculty and staff, particularly in advanced fields such as MTech and Ph.D. levels.
- Insufficient investment in research and development (R&D).
- Outdated courses, syllabi, and curricula, which are not aligned with industry needs.
- Financial constraints due to over-reliance on traditional revenue sources like admission fees and state grants.
- Administrative delays in fund sanctioning and the absence of frameworks for securing loans through financial institutions.
Policy Recommendations
The report proposes several reforms to address the aforementioned challenges, with a focus on improving educational quality, securing better funding, enhancing governance, and boosting employability:
- Funding and Investment:
- Increase the combined investment in education to 6% of GDP, as recommended in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Increase R&D investment (both public and private) to 2% of GDP, as recommended in the Economic Survey 2017-18.
- Creating Centers of Excellence:
- SPUs should form clusters and focus on addressing local challenges by establishing Centres of Excellence. These centres should focus on region-specific issues to drive academic and practical advancements.
- Governance Reforms:
- Enhance governance structures at SPUs, empowering Vice Chancellors, faculty, and staff through targeted capacity-building initiatives.
- States may consider setting up dedicated finance agencies, similar to the Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA), to fund infrastructure and research development specifically for SPUs.
- Financial Innovations:
- Develop financial frameworks to increase investment in education, ensuring access to timely funds, and reducing dependency on state grants or admission fees.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration:
- Strengthen the link between academia and industry to ensure that the curricula are relevant and prepare students for the job market. This can be achieved through increased partnerships, internships, and practical learning opportunities.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- Natco Pharma, a Hyderabad-based generic drug manufacturer, has received final approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) for its generic version of Bosentan tablets for oral suspension (32mg).
- This drug, a generic version of Actelion Pharmaceuticals’ Tracleer, is used to treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs.
- The approval comes after Natco's successful submission of an abbreviated new drug application (ANDA), which was jointly developed with its marketing partner, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Natco believes that it holds the sole first-to-file status for the product, which qualifies it for a 180-day exclusivity period upon launch. The exclusivity period would allow Natco to be the only supplier of the generic product in the U.S. market for a limited time, which could offer significant market share before generic competition arrives.
- Bosentan, the active ingredient in Tracleer, is prescribed for patients suffering from PAH, a progressive condition that raises the blood pressure in the lungs and causes strain on the heart.
- The treatment helps to improve pulmonary vascular resistance and is indicated for patients aged three years and above, including those with idiopathic or congenital PAH. The product is expected to improve exercise capacity and overall quality of life for these patients.
- In the U.S., Bosentan 32mg oral suspension generated an estimated $11 million in sales for the 12 months ending September 2024.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Overview
- It is a specific type of pulmonary hypertension in which the small arteries in the lungs become thickened and narrowed. This results in obstructed blood flow and increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the lungs.
- The exact cause of PAH remains unclear, though it is believed to result from injury to the cells lining the blood vessels in the lungs, leading to long-term vascular disease.
- PAH can develop in association with several medical conditions, including congenital heart disease, liver disease, HIV, and autoimmune diseases like scleroderma and lupus. It can also be triggered by past or current drug use, such as the abuse of methamphetamine or the use of certain diet pills.
Symptoms of PAH include:
- Shortness of breath that worsens over time
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Chest pain
- Cyanosis (blue fingers or lips)
- Fainting episodes
While there are treatment options available for PAH, including medications that help manage the symptoms and slow disease progression, there is currently no known cure. PAH remains a significant area of concern in pulmonary healthcare, and the introduction of generic Bosentan by Natco Pharma offers a more affordable treatment option for patients in the U.S.
Exercise Cyclone 2025

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- The third edition of the India-Egypt Joint Special Forces Exercise CYCLONE is being conducted from February 10–23, 2025 at the Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan.
- The previous edition (2nd) was held in Egypt in January 2024, and the first edition was conducted in India in 2023.
About Exercise CYCLONE
- It is a bilateral joint special forces military exercise between India and Egypt.
- Annual exercise, held alternatively in India and Egypt.
- The 2025 edition is focused on:
- Counter-terrorism operations
- High-intensity combat training
- Survival techniques in desert/semi-desert terrain
- Tactical drills and real-world combat scenarios
- Motto of the exercise: “Together we train, together we excel.”
Objectives
- Enhance military-to-military cooperation.
- Strengthen interoperability and joint operational capabilities.
- Exchange of special warfare tactics and combat strategies.
- Operate under frameworks aligned with Chapter VII of the UN Charter (pertaining to threats to peace, breaches of peace, and acts of aggression).
Strategic Importance
- The exercise reflects deepening India-Egypt defence cooperation.
- Aimed at enhancing readiness for evolving security challenges in the region.
- Enables both forces to operate together in simulated combat situations, improving coordination and adaptability.
India-Egypt Relations: Defence and Beyond
- Strategic Partnership established in 2023, covering:
- Political, defence, security, energy, and economic cooperation.
- Bilateral Trade Agreement (1978): Based on Most Favored Nation (MFN) clause.
- India is one of Egypt’s key trading partners in Africa.
National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, on February 7, 2025, approved the extension of the tenure of the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK) for three years beyond March 31, 2025, i.e., up to March 31, 2028.
The move is aimed at sustaining efforts to eradicate manual scavenging, improve the welfare of sanitation workers, and achieve zero fatalities in hazardous cleaning activities. The extension involves a financial outlay of ?50.91 crore.
Background and Legal Status
- Constitution: NCSK was established in August 1994 under the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis Act, 1993 as a statutory body.
- Post-2004 Status: The statutory Act lapsed in 2004, and since then, NCSK has functioned as a non-statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, with periodic extensions.
- Current Demand: The current Chairperson, M. Venkatesan, has welcomed the extension but stressed the need for granting statutory status to the commission to enhance its authority and effectiveness.
Mandate and Functions
As per Government Notification and MS Act, 2013:
- Policy Recommendations:Recommend specific programmes of action to eliminate inequalities in the status, facilities, and opportunities of SafaiKaramcharis.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Study and evaluate implementation of welfare schemes and programmes.
- Monitor working conditions, including health, safety, and wages of sanitation workers.
- Grievance Redressal:
- Investigate specific complaints and take suomotu cognizance of non-implementation of policies or schemes related to SafaiKaramcharis.
- Report to governments on issues affecting SafaiKaramcharis.
- Role under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013:
- Monitor the implementation of the Act.
- Enquire into violations, and convey findings with recommendations to authorities.
- Advise the Centre and States on effective implementation.
- Take suomotu notice of non-compliance.
- Data Collection:
- NCSK remains the only national body tracking sewer and septic tank deaths.
Significance of the Extension
- Aims to improve working conditions in the sanitation sector.
- Supports the socio-economic upliftment of one of the most marginalized communities in India.
- Enhances implementation of manual scavenging prohibition laws.
- Facilitates rehabilitation and dignity for sanitation workers.
- Aligns with the broader vision of inclusive development and social justice.
Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards modernizing India's artillery capabilities, the Union Ministry of Defence signed contracts worth ?10,147 crore on February 6, 2025, for the procurement of advanced ammunition for the Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS).
These agreements were concluded with Economic Explosives Limited (EEL) and Munitions India Limited (MIL) for the acquisition of Area Denial Munition (ADM) Type-1 and High Explosive Pre-Fragmented (HEPF)-Mk-1 (enhanced) rockets, respectively.
Pinaka MRLS: An Overview
- Type: All-weather, battle-proven, indirect fire Artillery Weapon System.
- Developer: Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) of DRDO.
- Combat History: First used effectively during the Kargil War, neutralising enemy positions on mountain tops.
- Mobility: Mounted on Tatra trucks, providing high mobility and quick deployment.
- Payload & Firing Capacity:
- Each launcher: 12 rockets.
- Each battery: 6 launchers = 72 rockets.
- Capable of delivering a full salvo in 44 seconds.
- Range:
- Initial range: 60–75 km.
- Guided Pinaka (Pinaka-G) extends range to 75 km, with future plans to extend up to 120 km and eventually 300 km.
- Precision: The guided version uses INS/GPS navigation, allowing high accuracy against critical and time-sensitive targets.
- Warhead Types: High-explosive and submunitions, suitable for a wide variety of targets.
New Ammunition Contracts: Enhancing Lethality
The contracts include the procurement of:
- ADM Type-1: Equipped with specialised warheads designed to disperse sub-munitions over wide areas. These are effective in targeting mechanised formations, vehicles, and personnel, thereby denying area access to the enemy. These are similar to Dual Purpose Improved Conventional Munitions (DPICM).
- HEPF-Mk-1 (Enhanced): An advanced variant of the currently used HEPF rockets with extended range and improved lethality, capable of deep precision strikes in enemy territory.
In addition, a contract was signed with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for upgrades to the Shakti software, which supports artillery operations.
Operational & Strategic Significance
- The upgraded Pinaka system will be the mainstay of long-range rocket artillery in the Indian Army.
- Four Pinaka regiments are already operational, with six more on order.
- The system’s development and expansion are a testament to India’s defenceindigenisation drive.
- The DRDO successfully completed flight tests of the guided Pinaka rocket with a range of 75 km, doubling its earlier reach. Future versions aim for up to 120 km and 300 km range.
Employment and MSME Impact
Besides enhancing strategic deterrence, the ?10,147 crore investment is expected to:
- Generate direct and indirect employment, particularly in the defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Promote the Indian MSME sector, which contributes components and subsystems for the rockets and launchers.
- Support the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing dependency on imported artillery systems.
Rhododendron wattii

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
A recent study has highlighted the alarming decline of the rare Rhododendron wattii, a species endemic to Nagaland and Manipur, especially in the Dzukou Valley, Nagaland. The species is now on the brink of extinction due to severe threats to its survival, raising serious conservation concerns.
Botanical Profile
- Taxonomy and Discovery:
- First collected by Sir George Watt during his 1882–85 survey in the Japfu Hill range, Nagaland.
- Belongs to the Rhododendron genus, which has over 1,000 species worldwide.
- India hosts 132 taxa, of which 129 are found in the northeastern region.
- Growth and Habitat:
- Grows as a small tree or shrub in the temperate biome.
- Attains a maximum height of 25 feet.
- Endemic to Manipur and Nagaland, predominantly in the Dzukou Valley at ~2,600 metres altitude.
- Phenological Features:
- Evergreen plant with year-round leaf renewal.
- Flowering: Late February to April.
- Fruiting:April to December.
- Produces trusses of 18–25 pink flowers with dark flecks and purplish basal blotches.
- Pollinated by the Fire-tailed Sunbird (Aethopygaignicauda) and bumble bees.
Conservation Concerns:
- Conservation Status:
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Severe population fragmentation.
- Area of occupancy less than 500 sq. km.
- Botanists at the Botanical Survey of India consider it Critically Endangered in its natural habitat.
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Threats to Survival:
- Poor seedling survivability despite abundant seed production.
- Anthropogenic pressures such as:
- Deforestation
- Habitat destruction
- Use of trees for firewood by local communities.
- Wildfires: A major fire incident in 2020–21 severely impacted the Dzukou Valley.
- The lone surviving Rhododendron wattii tree was recorded far from human trails during a recent field study.
Recent Study Highlights:
- Conducted by Imtilila Jing and S.K. Chaturvedi of Nagaland University.
- Published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa.
- Found only one living tree in the surveyed area of 27 sq. km of Dzukou Valley.
- The last previously reported tree in Nagaland (2012–13) was cut down.
Additional Botanical Development in the Region:
While the situation of Rhododendron wattii is grim, the region also witnessed a positive botanical development:
- Discovery of Phalaenopsis wilsonii, a new orchid species in Manipur’s Senapati district.
- Identified by researchers from the Institute of Bioresources and Sustainable Development (IBSD), Imphal.
- It is the ninth species of the Phalaenopsis genus recorded in Manipur.
Grameen Credit Score

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 introduced the Grameen Credit Score (GCS) framework as a targeted initiative to enhance access to formal credit for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and the rural population. It reflects the government’s commitment to financial inclusion, rural empowerment, and inclusive development.
What is the Grameen Credit Score?
- The Grameen Credit Score is a rural-specific credit evaluation framework being developed by Public Sector Banks.
- It aims to formalize the credit behavior and transaction history of SHG members and rural individuals, especially women entrepreneurs, and integrate them into India’s central credit ecosystem.
- Unlike conventional credit scores (like CIBIL or CRIF Highmark), GCS is tailored to assess creditworthiness based on local financial behavior, such as SHG repayment records, informal lending history, and community participation.
Key Features and Objectives:
- Improved Credit Assessment:
- Bridges the gap in the current credit bureau systems, which often overlook rural borrowers and SHG members.
- Uses digital records and behavioral insights to provide a customized and accurate credit profile.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Targets women-led SHGs to provide better access to loans, credit cards, and microfinance products.
- Encourages rural borrowers to understand and monitor credit scores, EMIs, and repayment cycles.
- Customized Financial Products:
- Linked with the introduction of custom credit cards for micro-enterprises with credit limits of up to ?5 lakh.
- Facilitates product innovation for grassroots entrepreneurs in agriculture, MSMEs, and allied sectors.
- Support for Broader Rural Ecosystems:
- Integrated with initiatives like the SVAMITVA Scheme for property records digitization.
- Complements reforms like the transformation of India Post into a rural logistics backbone and support for cooperative sectors via the NCDC.
- Economic Empowerment:
- By expanding credit access and improving repayment discipline, GCS is expected to:
- Boost rural entrepreneurship
- Strengthen economic resilience of rural households
- Support the long-term development of the rural economy
- By expanding credit access and improving repayment discipline, GCS is expected to:
Impact on Rural Development and SHGs:
- Empowers rural women through financial independence and enterprise development.
- Enhances formal credit linkage of SHGs, reducing reliance on informal moneylenders.
- Promotes financial literacy and long-term economic stability in villages.
- Aims to be a catalyst for poverty alleviation and inclusive growth.
Gaia Black Holes

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, launched in 2013, continues to redefine our understanding of the Milky Way by detecting celestial phenomena through precise astrometry.
One of its most significant contributions has been the discovery of dormant stellar-mass black holes that are not associated with X-ray emissions—previously the main detection method. These discoveries represent a paradigm shift in black hole detection and open new avenues for astrophysical research.
Gaia BH Series: Discovery and Significance
Gaia BH1
- Discovery Year: 2022
- Location: ~1,560 light years from Earth in the Ophiuchus constellation
- Significance:
- Closest known black hole to Earth
- Detected via a yellow star orbiting a dark mass, whose high orbital velocity implied the presence of a black hole nearly nine times the mass of the Sun
- Validated using data from LAMOST (China) and Magellan Clay Telescope (Chile)
Gaia BH2
- Discovery Year: 2023
- Location: ~3,800 light years away in the Centaurus constellation
- Mass: Around nine solar masses
- Observation Method: Tracked motion of a luminous star orbiting an unseen massive companion
Gaia BH3 – A Landmark Discovery
- Discovery Year: 2024
- Distance from Earth: ~1,926 light years (~2,000 light years), making it the second closest black hole
- Location:Aquila constellation, in the Milky Way’s outer regions
- Mass: ~33 times the mass of the Sun, making it the largest known stellar-mass black hole in the Milky Way
- Orbital Partner: A yellow giant star orbiting every 11.6 years, with an average separation similar to the Sun-Uranus distance
- Special Traits:
- It is a dormant or passive black hole, not actively accreting matter
- Lacks X-ray emissions, suggesting a scarcity of surrounding material
- Its companion star’s chemical composition indicates ancient origins, hinting that such massive black holes were formed early in the universe
Scientific Implications:
- Detection Technique Innovation:Gaia uses astrometric mapping to track the apparent motion of stars across the sky. When a star appears to orbit "empty space," astronomers infer the presence of a massive object—typically a black hole—using Kepler’s laws and the Doppler effect.
- Redefining Black Hole Census:Most black holes were previously detected through X-ray emissions. Gaia has revealed non-emitting black holes, indicating a possibly larger hidden black hole population in our galaxy.
- Historical Linkage:Black holes with masses above 30 solar masses were previously only observed through gravitational waves (LIGO/VIRGO, 2015). Gaia BH3 now provides a local, observable counterpart.
PRASHAD Scheme

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture has raised concerns over delays in the completion of projects under the Spiritual Tourism Circuits and the PRASHAD Scheme.
It has recommended the establishment of a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and emphasized obtaining prior clearances to ensure timely execution of future projects.
About PRASHAD Scheme
- Full Form: Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spirituality Augmentation Drive.
- Launched: 2014–15 by the Ministry of Tourism, Government of India.
- Objective: To promote, develop, and enhance spiritual tourism infrastructure at important pilgrimage sites across India.
Aims and Objectives:
- Improve infrastructure (roads, water supply, sanitation, waste management).
- Enhance connectivity (road, rail, and air) to pilgrimage destinations.
- Preserve and conserve religious and cultural heritage sites.
- Promote eco-friendly and sustainable tourism practices.
- Increase domestic and international tourist footfall through spiritual tourism.
- Generate local employment through skill development and livelihood programmes.
Funding Model:
- 100% centrally funded for eligible components.
- Also includes voluntary contributions through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Public-Private Partnership (PPP) initiatives.
Implementation Challenges and Parliamentary Findings
Spiritual Tourism Circuits under Swadesh Darshan Scheme:
- Launched to promote thematic tourism circuits, including 23 Spiritual Circuits across India.
- Of these, five circuits remain incomplete, with two key circuits in Kerala—
- Sabarimala–Erumeli–Pampa–Sannidhanam Circuit
- Sivagiri Sree Narayana Guru Ashram Circuit
- Progress Status (as of September 2023):
- Sabarimala Circuit: 76% complete
- Sivagiri Circuit: 51% complete
- Original target completion dates: June 2023 and October 2023, respectively.
Reasons for Delay:
- Lack of timely clearances from Temple Authorities.
- Administrative and coordination issues across agencies.
Committee Recommendations:
- Formulate a clear-cut SOP for the execution of spiritual tourism projects.
- Ensure pre-approval and coordination with all concerned stakeholders before initiating construction.
- Strengthen planning at the Detailed Project Report (DPR) stage to anticipate implementation challenges and avoid delays and cost overruns.
PRASHAD Scheme Performance:
- Out of 45 sanctioned projects, only 21 have been completed as of the latest report.
- The committee noted this performance as unsatisfactory, even accounting for disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India-U.S. defence cooperation is advancing with the proposed co-production of the Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV). This deal represents a significant leap in bilateral defence industrial collaboration and aligns with India's strategic goal of military modernization and indigenisation under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
About Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV):
- Origin: Jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and U.S., it is the first new military vehicle inducted into U.S. Army service since the 1980s.
- Type: Eight-wheeled armoured infantry combat vehicle designed for rapid deployment and battlefield mobility.
- Variants: Includes Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), reconnaissance vehicle, medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, and Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrier.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Top speed of ~100 km/h and an operational range of 483 km. Can be airlifted using C-17 and C-130 aircraft (both in IAF’s fleet) or Chinook helicopters, enhancing deployment in remote terrains.
- Firepower: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: V-hull structure for blast protection; composite armour reinforced with ceramic tiles offers increased survivability against IEDs and small arms.
- Capacity: Operated by a 2-member crew and can transport a 9-member infantry squad.
Operational Evaluation in India:
- High-Altitude Trials: Conducted in Ladakh (13,000–18,000 feet) during September–October 2024. Evaluation reports were shared with Army Headquarters for further review.
- Javelin ATGM Demonstration: Conducted alongside Stryker trials; however, the performance was sub-optimal due to the vintage system used. Repeat trials have been requested by India.
Strategic Importance for India:
- Tactical Advantage: Enhanced mobility and survivability in high-altitude warfare make it suitable for regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Border Security: Bolsters India's defence posture along sensitive frontiers with China and Pakistan.
- Force Modernization: Meets the Indian Army’s requirement for ICVs with integrated ATGM capabilities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Push: The proposed model includes initial direct imports followed by large-scale license production in India, potentially by Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML).
Defence Diplomacy and Industrial Cooperation:
- The deal is being advanced under the India-U.S. Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap, focusing on co-development and co-production.
- In November 2023, Indian Defence Secretary confirmed discussions under this framework.
- The U.S. has reiterated the importance of India enhancing procurement of U.S.-made defence equipment, aiming at a balanced trade partnership.
- The Stryker deal is expected to feature in high-level bilateral dialogues, including the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Washington DC and during engagements at Aero India.
Challenges and Reservations:
- Some Indian defence officials have flagged concerns, noting that similar ICVs have been developed by Indian private companies.
- Delays in previous U.S. defence exports (e.g., F-404 jet engines for LCA-Mk1A) have also raised caution regarding timelines and reliability.
Fort William Renamed Vijay Durg

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards decolonising the Indian Armed Forces and aligning with indigenous historical consciousness, Fort William, the headquarters of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army in Kolkata, has been renamed Vijay Durg. This renaming is part of a broader initiative to remove colonial-era symbols and practices and restore Indian military heritage.
Historical Background of Fort William
- Construction: The original Fort William was constructed in 1696 by the English East India Company. It was later attacked and captured by Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in 1756.
- The Black Hole Incident: The original fort had an inner bastion used for imprisoning captives, leading to the infamous “Black Hole of Calcutta” narrative.
- Reconstruction: After the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the defeat of Siraj-ud-Daulah, Robert Clive initiated the construction of a new fort, which was completed in 1773 or 1781 (sources differ).
- Naming: It was named Fort William in honour of King William III of England.
Architectural Features
- Design: The fort is octagonal in shape with a massive structure made of brick and mortar.
- Area: Spread across 70.9 acres on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, it features hundreds of arched windows and lush green surroundings.
- Aesthetics: Its walls are adorned with intricate stonework, reflecting colonial military architecture.
Recent Changes and Renaming
- New Name: Vijay Durg – Inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, a prominent naval base of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Other Changes:
- Kitchener House has been renamed Manekshaw House, after Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw.
- St. George’s Gate has been renamed Shivaji Gate.
- Implementation: According to the Defence Public Relations Office in Kolkata, the name change was decided in mid-December 2024, and internal communications have already adopted the new nomenclature, though an official notification is awaited.
Broader De-Colonisation Drive in Indian Defence
The renaming of Fort William is part of a larger movement initiated by the Government of India to eliminate colonial vestiges in the armed forces. Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a 2022 speech at Kevadia, Gujarat, urged the forces to discard “legacy systems” and move towards “freedom from the mentality of slavery (gulami ki mansikta se mukti)”.
Key Initiatives:
- Indianisation of military music during the Beating Retreat ceremony.
- Adoption of a new naval ensign (2022) inspired by the seal of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, moving away from British colonial symbols.
- Renaming of military establishments and symbols rooted in colonial heritage.
- Review publication (2024) titled “Colonial Practices and the Armed Forces – A Review”, released at the Joint Commanders’ Conference in Lucknow by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
Brucellosis Outbreak in Kerala
- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
An eight-year-old girl, Shasa Fathima, from Kottakkal in Malappuram district, Kerala, recently died after undergoing nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis at the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode. This tragic incident has renewed public health concerns regarding zoonotic infections in India.
What is Brucellosis?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), brucellosis is a bacterial disease caused by various species of the genus Brucella. The bacteria primarily infect: cattle, swine, goats, sheep & dogs.
Humans typically contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected animals or their secretions (blood, placenta, fetus, uterine fluids)
- Ingestion of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurised milk and cheese
- Inhalation of airborne bacteria (e.g., in lab or farm environments)
Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare, as per WHO guidelines.
Symptoms and Incubation Period
- The disease presents a wide spectrum of symptoms: fever, weakness, weight loss, general discomfort or malaise.
- In many cases, symptoms may be mild or go undiagnosed. The incubation period ranges from one week to two months, most commonly between two to four weeks.
At-Risk Populations
- Brucellosis can affect individuals of all age groups. However, certain occupational groups are at higher risk, including: farmers and dairy workers, butchers, hunters, veterinarians, laboratory personnel. These individuals are often exposed to animal blood and reproductive fluids, which are primary modes of transmission.
Status in Kerala
Kerala has reported sporadic cases of brucellosis in recent years. In 2023, cases emerged from Kollam (July) and Thiruvananthapuram (October). While the disease is not new to the state, fatalities remain rare.
In response, the Department of Animal Husbandry has initiated awareness campaigns for dairy farmers and conducted milk sample testing across cooperative societies to monitor possible sources of infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics:
- Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days)
- Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days)
Effective preventive measures include:
- Vaccination of livestock (cattle, goats, sheep)
- Pasteurisation of milk and dairy products before human consumption
- Public awareness campaigns on the dangers of consuming unpasteurised animal products
- Regulatory policies on the sale of raw milk
Dhimsa Dance

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant development, tribal families from Neelabandha, a remote hilltop hamlet in Anakapalli district, Andhra Pradesh, received electricity for the first time since Independence. In celebration, they performed the Dhimsa dance, a vibrant expression of tribal culture.
About Dhimsa Dance:
- Origin & Region:
- Dhimsa is a traditional tribal dance predominantly performed in Andhra Pradesh, especially in the tribal belts of the Eastern Ghats.
- Its origin can be traced to the Koraput region (present-day Odisha and bordering Andhra Pradesh), primarily home to the Gond tribe.
- Communities Performing Dhimsa:
- Tribes such as Bagata, Valmiki, Poraja, Khond, Gadaba, Kondadora, Mukadora, and Kotia actively perform this dance.
- Occasions:
- Commonly performed during festivals, weddings, and the hunting festival in April.
- Celebratory, spiritual, and social in nature, symbolizing unity and joy.
- Dance Formation and Movements:
- Performed in circular formations with dancers holding each other's arms.
- Emphasis on synchronized hand and leg movements.
- Troupes usually consist of 20 or more dancers.
- Themes:
- Dhimsa is a narrative dance that expresses tribal mythologies, folktales, cultural mores, economic activities, kinship, and marital life.
- Musical Instruments Used:
- Dappu, Tudumu, Mori, Kidgi, Gilka, and Jodukommulu.
- A combination of percussion and wind instruments drives the rhythm and variation in the dance.
- Varieties:
- There are 12 known types of Dhimsa dances, each varying in pace, rhythm, and purpose.
Rural Electrification of Neelabandha Village:
- Background:
- Neelabandha is located in Arla Panchayat of Rolugunta Mandal in Anakapalli district.
- Consists of four households (approximately 20 individuals) who had been living without electricity since Independence.
- Implementation:
- The electrification was part of the Andhra Pradesh government’s rural development drive to provide basic infrastructure to underdeveloped tribal villages.
- Under the directions of District Collector Vijaya Krishnan, and CMD of APEPDCL, Prithvi Tej, the Eastern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh (EPDCL) carried out the electrification.
- Challenges Overcome:
- The hamlet lacked motorable roads, making it difficult to transport materials.
- Electricity poles had to be carried manually for over 6 km to reach the village.
- Outcome:
- Free electricity was provided to the villagers, marking a major milestone in tribal welfare.
- In a heartfelt celebration, the villagers performed Dhimsa under electric lights for the first time.
Issues Still Persisting:
- Infrastructure Deficits:
- The village still lacks road connectivity, educational access, and healthcare facilities.
- These gaps hinder children's ability to attend school and access essential services.
- Community Response:
- Local leaders, including CPI(M) district committee member K. Govind, welcomed the electrification but urged the government to address remaining developmental needs.
Kolleru Lake
- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Southern Zonal Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently restrained the Andhra Pradesh government from proceeding with six proposed infrastructure projects in the Kolleru wetland area, citing violations of environmental protocols and lack of statutory clearances.
About Kolleru Lake
- Location: Northeastern Andhra Pradesh, between the Krishna and Godavari river deltas, near Eluru city.
- Type: One of Asia’s largest shallow freshwater lakes, covering an area of 308 sq. km.
- Hydrology:
- Fed by Budameru and Tammileru rivers.
- Drains into the Bay of Bengal via Upputeru river (a tidal water channel).
- Acts as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the Krishna and Godavari river systems.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1999 and a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- Designated as an Important Bird Area (IBA) due to the presence of over 50,000 waterfowl annually.
- Lies on the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), a major migratory bird route.
- Key Avian Species:
- Grey Pelican (indicator species), Siberian Cranes, Glossy Ibis, Open-billed Stork, Purple Moorhen, Painted Storks.
Kolleru Bird Sanctuary
- A protected wetland marsh habitat within the Kolleru Lake region.
- Supports diverse aquatic flora and fauna, serving as a crucial ecosystem for migratory and resident bird species.
Infrastructure Projects and Legal Challenges
- The projects were proposed under the entity "A.P. Krishna – Kolleru Salinity Mitigation Projects Corporation Limited" with a total capital outlay of approximately ?2,952 crore.
- The plans included construction of three regulators-cum-roads across the Upputeru river and other barrages, regulators, and sluices, falling within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ).
- The Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Department (WRD) issued G.O. Ms. No. 63 (dated 2nd December 2020) authorizing the project.
Grounds for NGT Intervention
- Key objections included:
- Absence of scientific or ecological studies.
- Lack of consultations with wetland experts, wildlife conservationists, and hydrologists.
- No clearances obtained from:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- A.P. Coastal Zone Management Authority (CZMA)
- A.P. Pollution Control Board (PCB)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
NGT Observations and Ruling
- The tribunal emphasized the need for comprehensive evaluation of ecological and hydrological impacts before proceeding.
- It cited potential threats to the lake’s ecosystem, including:
- Disruption to natural hydrology.
- Loss of biodiversity and eco-sensitive habitats.
- The NGT ruled that the projects should not proceed unless fully compliant with environmental laws and backed by appropriate expert assessments.
- The ruling reinforced India's obligations under the Ramsar Convention and domestic environmental legislation, stressing the urgent need to protect the integrity of the Kolleru ecosystem.
Golden-headed Cisticola

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
- Recently, the Union Government has introduced the PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana which aims at enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Objective: To boost agricultural productivity, modernize farming practices, and enhance rural prosperity by addressing region-specific challenges in backward agricultural districts.
Key Features:
- Integrated Approach:
- Consolidates multiple existing agricultural schemes under one umbrella for greater synergy and implementation efficiency.
- Draws inspiration from the Aspirational Districts Programme, which has improved socio-economic outcomes in backward regions.
- District-Specific Interventions:
- Focuses on districts with:
- Low crop productivity
- Moderate crop intensity
- Limited institutional credit access
- Implements customized strategies based on the unique challenges of each region.
- Focuses on districts with:
- Core Focus Areas:
- Enhancing farm productivity through modern technology.
- Improving irrigation infrastructure.
- Increasing formal credit availability to reduce dependence on informal moneylenders.
- Promoting crop diversification and sustainable agriculture.
- Strengthening post-harvest infrastructure like storage at Panchayat and block levels.
- Technology-Driven Solutions:
- Encourages adoption of climate-resilient and precision farming.
- Supports digital access to credit and advisory services.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Strengthens linkages with government financial programs, microfinance institutions, and banks.
- Aims to reduce rural indebtedness and promote formal financial participation.
- State and Centre Collaboration: Implementation will involve both central and state governments, ensuring localized solutions with national support.
- Reducing Distress Migration: By improving rural livelihoods and opportunities, the scheme aims to make migration a choice rather than a compulsion.
Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme
- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
Announced in the Union Budget 2025–26, the Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme is a major initiative to provide digital textbooks and learning materials in multiple Indian languages for school and university students.
Key Features:
- Digital Access: Study resources will be made available in digital formats via platforms such as DIKSHA, e-PG Pathshala, and the National Digital Library of India.
- Target Groups: Students in schools, colleges, and universities affiliated with UGC, AICTE, and other regulatory bodies.
- Focus Areas: STEM, social sciences, humanities, and commerce; with a special emphasis on technical education in Indian languages.
- Use of Technology: AI-based tools will support automated translation, voice-assisted learning, and customized content.
- Alignment with NEP 2020: Promotes multilingualism and regional language education, as envisioned in the National Education Policy.
Complementary Initiative – ASMITA (Augmenting Study Materials in Indian Languages)
- Aims to develop 22,000 textbooks in Indian languages over the next five years.
- Jointly led by UGC and the Bharatiya Bhasha Samiti under the Ministry of Education.
- Thirteen nodal universities will coordinate content development, supported by regional institutions.
- SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) have been developed for translation, writing, editing, review, plagiarism checks, and publication.
Budgetary Allocations and Educational Infrastructure
Highest-Ever Allocation for School Education: ?78,572 crore
- 16.28% rise over revised estimates of 2024–25.
- ?9,503 crore allocated to Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (?776 crore hike).
- Plan to set up 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in government schools to foster innovation and scientific thinking.
- BharatNet Project to ensure broadband access in all government secondary schools within three years.
Higher Education Allocation: ?50,077.95 crore
- Covers central universities, IITs, and centrally sponsored schemes.
- Budget for centrally sponsored schemes like PM-USHA and RUSA increased to ?1,815 crore.
- Student financial aid raised to ?2,160 crore.
Boost to IIT Infrastructure:
- Additional infrastructure for five IITs established after 2014, accommodating 6,500 more students.
- Expansion of hostel and academic facilities at IIT Patna.
Artificial Intelligence in Education
- Announcement of a Centre of Excellence in AI for Education with an outlay of ?500 crore.
- Objective: Reduce disparities, improve efficiency, and ensure equitable access to high-quality education using AI technologies.
Microplastics detected in Delhi’s Groundwater

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
A first-of-its-kind study, commissioned by the Delhi government and conducted by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), has revealed the presence of microplastics in groundwater across all 11 districts of Delhi. The interim findings, submitted in November 2024, also reported microplastics in Yamuna River water and soil samples along its banks.
Key Findings:
- Widespread Contamination: Microplastics were found in groundwater samples across Delhi, indicating potential contamination due to leaching from the Yamuna River.
- Additional Contamination: Microplastics were also detected in the Yamuna's water and riverbank soil, suggesting environmental pervasiveness.
- Water Usage Impact: Since Delhi relies on borewells and treated groundwater for drinking and domestic purposes, this contamination raises serious public health concerns.
- No Objection by Authorities: The Delhi government has not disputed the study’s interim findings; further post-monsoon analysis is underway, and a final report is expected later in 2025.
What Are Microplastics?
According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Definition: Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size
- Types:
- Primary Microplastics: Manufactured for use in cosmetics (e.g., microbeads) and textiles (e.g., microfibers from clothing, nets)
- Secondary Microplastics: Result from breakdown of larger plastics (e.g., bottles) due to sunlight, abrasion, and ocean waves
Environmental & Health Impacts:
- Persistence: Microplastics are non-biodegradable, mobile, and difficult to eliminate from natural ecosystems.
- Toxicity:
- Can adsorb harmful chemicals, making them more toxic
- Known to bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains
- Human Exposure: Microplastics can enter the human body via:
- Inhalation (air)
- Ingestion (water and seafood)
- Dermal absorption (through skin)
- Health Risks (UNEP Report – From Pollution to Solution, 2021):
- Potential effects on genetics, brain development, respiration, and placental health in newborns
- No global standard exists for safe microplastic limits in drinking water
Saffron Reedtail Damselfly
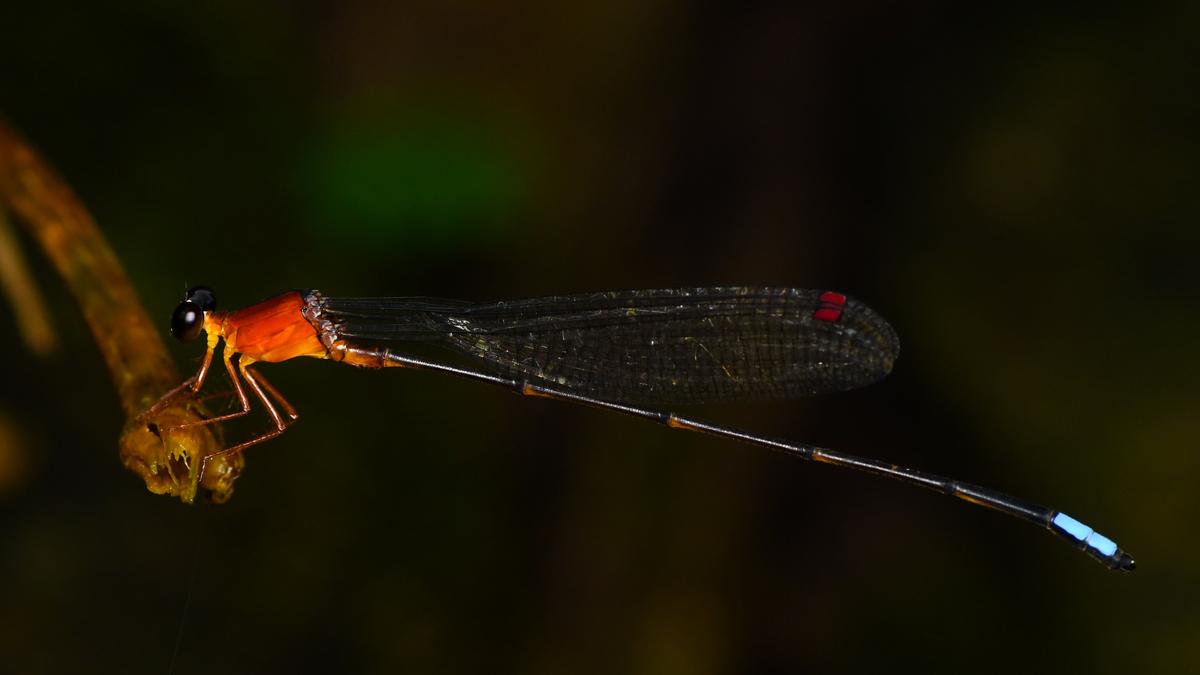

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Saffron Reedtail Damselfly, a rare and endemic species of the Western Ghats, has been recorded in Karnataka.
This significant discovery was made in Madhugundi village, Chikkamagaluru district, along the Nethravati River. The findings were published in the journal Entomon.
Key Facts:
- Scientific Name: Indosticta deccanensis
- Common Name: Saffron Reedtail
- Family: Platystictidae (commonly known as shadow damselflies)
- Appearance: Slender, delicate body with a characteristic saffron coloration
- Habitat: Prefers slow-moving forest streams surrounded by thick vegetation; requires pristine water quality
Ecological Significance:
- Indicator Species: Highly sensitive to environmental changes and pollution, indicating a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Implication:
- Previously recorded only in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The first sighting in Karnataka (northern Western Ghats) extends the known range of the species, suggesting it may be more widely distributed than earlier believed.
Conservation Relevance:
- The discovery underscores the ecological richness of the Madhugundi forests, which were severely affected by floods and landslides in 2019.
- Highlights the urgency to protect fragile ecosystems from deforestation, water pollution, and climate change, especially in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats.
About Damselflies (Order: Odonata):
- General Features:
- Predatory, aerial insects
- Slender bodies with net-veined wings
- Fly weakly compared to dragonflies
- Mostly inhabit freshwater habitats
DeepSeek AI
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup based in Hangzhou, has emerged as a major player in the global AI race with the release of its models DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1.
These models are designed to rival top-tier Western counterparts such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Bard, and Meta’s LLaMA, but at a fraction of the cost.
Key Developments and Technological Edge
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek-V3 was trained at a cost of under $6 million, using older Nvidia H800 chips, compared to the estimated $100 million cost of GPT-4. Its subscription fee is significantly lower—$0.50/month versus $20/month for ChatGPT.
- Model Performance:
- DeepSeek-R1, a “reasoning model,” reportedly matches OpenAI’s o1 model in mathematics, coding, and contextual processing, while using fewer resources through incremental reasoning.
- Models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, reinforcement learning, and self-improvement loops, making them more memory-efficient and scalable.
- Advanced Models Released:
- DeepSeek Coder / Coder-V2 (for coding tasks).
- DeepSeek LLM (67B parameters), V2, V3 (671B parameters), and R1-Distill (fine-tuned using synthetic data).
Global Impact and Market Disruption
- App Success & Outages: The DeepSeek AI app topped the U.S. App Store, surpassing ChatGPT. This success triggered large-scale cyberattacks and caused temporary service disruptions.
- Market Reaction: The launch reportedly led to a historic $600 billion drop in Nvidia's market value, highlighting the disruptive potential of cost-efficient AI innovation.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: The rise of DeepSeek is seen as a technological parallel to the 1957 Sputnik moment, which shocked the U.S. and triggered the space race.
DeepSeek has reignited US-China AI rivalry, intensifying great-power competition in frontier technologies.
Strategic Lessons for India
- Bipolar AI Landscape: The U.S. and China dominate AI due to massive investment and infrastructure. Middle powers like India and France face the challenge of staying relevant without matching this scale.
- Doing More with Less: DeepSeek’s success underscores how innovation with limited resources can be effective—providing a model for India to emulate via Small Language Models (SLMs) and cost-efficient AI strategies.
- Sovereign AI & Global Governance:
- India advocates for “Sovereign AI”, balancing independence and strategic alliances, especially with France and the U.S.
- Future cooperation between U.S. and China on AI governance, similar to Cold War-era nuclear agreements, is a possibility.
- India must learn from past exclusions (e.g., nuclear governance) and proactively shape global AI governance frameworks.
- Policy Implications:
- DeepSeek's rise may lead to stricter U.S. chip export restrictions to China.
- It presents both security risks (censorship, pro-China bias) and opportunities (cost-effective models, domestic self-reliance).
Ethical Concerns and Limitations
- Censorship: DeepSeek complies with Chinese state censorship, refusing responses on politically sensitive topics (e.g., Tiananmen Square), raising concerns about bias and lack of transparency.
Security & Privacy: Experts have flagged potential data privacy and AI ethics issues, emphasizing the need for robust global standards and accountability mechanisms.
Indian Squid

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi, have successfully decoded the gene expression pattern of the Indian squid (Uroteuthis duvaucelii), marking a major scientific advancement with wide-ranging implications for neuroscience, environmental studies, and sustainable marine resource management.
About Indian Squid
- Common Name: Indian Calamari
- Scientific Classification: Cephalopod
- Size: Typically 20–30 cm; can grow up to 50 cm
- Appearance: Light pinkish-grey body with two large fins, eight arms, and two longer tentacles used for capturing prey
- Key Abilities:
- Camouflage
- Jet propulsion for rapid movement
- Advanced nervous system
- Problem-solving skills and behavioral intelligence
Habitat & Distribution
- Preferred Habitat: Coastal and open sea regions of the Indian Ocean
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to 500 meters, some even up to 1,500 meters
- Requires high dissolved oxygen levels for respiration
- Geographic Distribution:
- Widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific
- Found in Indian Ocean, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, from Mozambique to the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, and northward to Taiwan
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Scientific Significance of Genetic Research
- Key Findings:
- Revealed genetic similarities with higher vertebrates like fish and humans, suggesting deep evolutionary links
- Indicates that Indian squid could serve as a model organism to study brain evolution, intelligence, and neurobiological functions
- Potential to inform research in neural circuits, memory, learning, and even neurological diseases
- Findings may also explain squid's adaptive success, such as evading predators and fishing pressures due to high cognitive ability
Institutional Background: CMFRI
- Established: 1947
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) since 1967
- Headquarters: Kochi, Kerala
- Mandate: Research on sustainable marine fisheries and ecosystem conservation
CMFRI’s Broader Recommendations for Sustainable Marine Management
- Enactment of Sea Fishing Act to regulate fishing beyond territorial waters
- Institutionalization of ecological stock assessments for sustainable exploitation
- Simplification and promotion of open mariculture with focus on environmental sustainability
- Use of AI-based systems to estimate landings and monitor fishing vessels
- Deep-sea resource exploration and alternative fishing methods
- Institutional mechanism for supervising deep-sea fishing
- Strengthening insurance coverage for marine fishers
Is Poverty Being Underestimated in India?

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The recent 2023-24 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed a decline in poverty across rural and urban India. However, questions have emerged about whether poverty is being underestimated, due to changes in methodologies, definitions, and data availability.
Evolution of Poverty Measurement in India
- 1970s to 2005: Poverty was defined based on minimum calorie intake; updated every 5 years using NSSO data.
- Tendulkar Committee introduced in response to divergence between NSSO and National Accounts data.
- Post-2011-12: No official poverty estimates or surveys; alternative indices like Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) were used.
Current Data Issues
- Different recall periods in surveys (7-day, 30-day, 365-day) create non-comparability.
- Modified Mixed Recall Period (MMRP) introduced in 2017-18 and improved upon in recent years with three household visits, enhancing recall and thus raising reported expenditures.
- Result: Using older poverty lines on newer, higher expenditure data underestimates poverty.
Diverging Poverty Estimates
- Dr. C. Rangarajan (2022-23): Estimated poverty at around 10%.
- Recent factsheet (2023-24) suggests poverty may have declined to single digits.
- A paper using Rangarajan’s methodology on 2022-23 HCES data estimated 25% poverty, but this is debated.
Reasons for Poverty Reduction
- High GDP growth, increased public expenditure, and improved public delivery systems.
- National Food Security Act covers nearly 80 crore people.
- Broadened definition of poverty now includes non-food items and essential services.
- Decline in poverty estimated around 17-18% between 2011-12 and 2023-24.
Rural-Urban Trends
- Consumption gap between rural and urban areas is narrowing.
- Rural consumption patterns becoming more urban-like.
- 2011 Census definitions outdated — many rural areas are peri-urban in character.
Need for Poverty Line Revision
- Lack of consensus and official backing on methodology hinders creation of a new poverty line suited to current data.
- UNDP’s global poverty line is $2.15/day; India’s poverty was 12.9% in 2019 by that metric.
- NITI Aayog’s estimates do not support 25% poverty claim.
Debate on Multidimensional Poverty Index
- India’s MPI (12 indicators) differs from UNDP’s 10-indicator framework.
- Additions like bank accounts and maternal health are India-specific.
- Criticism: Once indicators (e.g., electricity, bank accounts) are met, they remain met — poverty appears to decline permanently, while income vulnerability is not captured.
LID-568
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, an international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory discovered a low-mass supermassive black hole, LID-568, showing super-Eddington accretion—a rare and extreme feeding process—just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
About LID-568
Feature Description
Type Low-mass supermassive black hole
Age Formed ~1.5 billion years after Big Bang (Universe’s “youth”)
Discovery Observed via Chandra (X-ray) & JWST (infrared)
Location In a distant galaxy with very low star formation
Feeding Rate Accreting at ~40× the Eddington limit (super-Eddington accretion)
Key Concepts
Eddington Limit
- Theoretical upper limit on how fast matter can fall into a black hole before radiation pressure balances gravitational pull.
- Exceeding this limit (super-Eddington) is thought to be unstable and short-lived.
Super-Eddington Accretion
- Observed in LID-568, feeding at 40× Eddington rate.
- Suggests rapid, short bursts of black hole growth, not the slow, steady model previously assumed.
Why is LID-568 Important?
Challenges Current Theories
- Traditional black hole growth models require:
- Long periods (hundreds of millions of years).
- Seed black holes formed from:
- Death of first stars (light seeds: 10–100 solar masses).
- Collapse of primordial gas clouds (heavy seeds: 1,000–100,000 solar masses).
- LID-568 suggests brief, intense growth spurts could create supermassive black holes faster than previously thought.
Impact on Host Galaxy
- Powerful outflows prevent gas accumulation → suppresses star formation.
- Indicates black holes can regulate galaxy evolution, even when young.
Rupee Depreciation

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian rupee has recently experienced sharp devaluation against the US dollar after a period of relative stability. This shift is attributed to several factors, including capital outflows, rising import costs, and RBI’s evolving policy stance.
Understanding Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange rates are classified into:
- Fixed Exchange Rate: The central bank maintains a constant exchange rate by actively managing reserves.
- Floating Exchange Rate: Market-driven rates with minimal intervention.
- Managed-Floating Exchange Rate: A blend of market forces and central bank intervention.
India has largely pursued a managed-floating exchange rate regime. The RBI has historically responded to excess demand by depreciating the rupee while selling forex reserves and, under excess supply conditions, resisted rupee appreciation to maintain export competitiveness.
Post-COVID Exchange Rate Shift
Between 2022 and November 2024, the RBI temporarily adopted a strategy resembling a fixed exchange rate regime to stabilize the rupee. However, amid rising capital outflows and increased import costs, the RBI recently reverted to its managed-float approach, allowing the rupee to depreciate.
Causes of Rupee Depreciation
- Internal Factors:
- Rising inflation reduced the rupee's real value and increased production costs.
- A widening trade deficit due to higher crude oil imports heightened demand for foreign currency.
- Persistent fiscal imbalances further pressured the rupee.
- Policy ambiguity in the RBI’s stance added market uncertainty.
- External Factors:
- Capital outflows driven by global uncertainties and rising US interest rates.
- Geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) increased India’s import bill.
- The US dollar's strength amid aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes further weakened the rupee.
Implications of Rupee Devaluation
- Positive Effects:
- Boost to Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian goods cheaper, enhancing export competitiveness if supported by real exchange rate depreciation.
- Adverse Effects:
- Inflationary Pressures: Higher import costs increase consumer prices.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Increased costs are often passed on to consumers.
- Foreign Debt Servicing: A depreciated rupee raises debt repayment costs for Indian firms and the government.
- Investor Sentiment: Currency instability diminishes foreign investor confidence, triggering further capital outflows.
Structural Constraints in the Indian Economy
- Divergence between NEER and REER:
- Since the mid-2010s, India's Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) depreciated while the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) appreciated. This divergence undermines export competitiveness, as rising domestic prices offset nominal depreciation benefits.
- Rising Markups:
- Non-financial firms increased their markups on variable costs, contributing to inflation and nullifying the advantages of currency depreciation for exports.
Policy Responses and Recommendations
- RBI Interventions:
- Forex market interventions to manage demand-supply imbalances.
- Interest rate adjustments to attract capital inflows and stabilize the rupee.
- Enhanced forex reserve management to mitigate excessive volatility.
- Fiscal Strategies:
- Reducing Import Dependency: Boost domestic production of high-demand goods like crude oil substitutes.
- Export Incentives: Strengthen export sectors through subsidies, incentives, and improved infrastructure.
- Encouraging Long-Term FDI: Promoting stable investment environments for sustained capital inflows.
- Structural Reforms:
- Policies that enhance domestic production, reduce reliance on volatile foreign portfolio investments (FPIs), and maximize remittances can stabilize the rupee in the long term.
Eighth Pay Commission

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union government has approved the constitution of the Eighth Pay Commission, benefiting 50 lakh central government employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defence personnel. The decision, taken ahead of the Delhi Assembly elections, aims to address long-standing demands from trade unions and employee organizations.
Key Features of the 8th Pay Commission
- Early Constitution: Although the Seventh Pay Commission's term ends in 2026, the early establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission ensures timely recommendations and implementation.
- Composition: The commission will have a Chairperson and two members, typically led by a retired Supreme Court judge.
- Terms of Reference (ToR):
- Revision of Pay: Recommend updates to salary structures and allowances.
- Addressing Pay Disparities: Resolve wage differences across various cadres.
- Market Parity: Align pay structures with industry standards.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits: Improve pension schemes and adjust them for inflation.
- Economic Impact Analysis: Assess how salary hikes contribute to economic growth.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Engage with governments and other stakeholders before finalizing recommendations.
Economic Implications of the 8th Pay Commission
- Employee Well-being: Higher wages will enhance the quality of life for government employees.
- Boost to Consumption: Increased salaries are expected to stimulate demand and support economic expansion.
- Ripple Effect on PSUs & States: Many public sector undertakings and state governments follow the central pay commission’s recommendations, potentially leading to wider economic benefits.
- Fiscal Considerations: The implementation of the Seventh Pay Commission in 2016-17 led to an expenditure increase of ?1 lakh crore. A similar rise in 2026-27 could impact fiscal space for capital expenditures.
Challenges and Concerns
- Implementation Delays: Past commissions have taken two years to submit recommendations, which could push implementation beyond 2027.
- Living Wage & Pension Issues: Existing formulas for minimum wage and pension calculations may need revision to reflect rising healthcare, education, and digital access costs.
- Financial Burden on the Exchequer: A significant increase in revenue expenditure could limit the government’s ability to invest in infrastructure and development projects.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
Flamingo Festival 2025
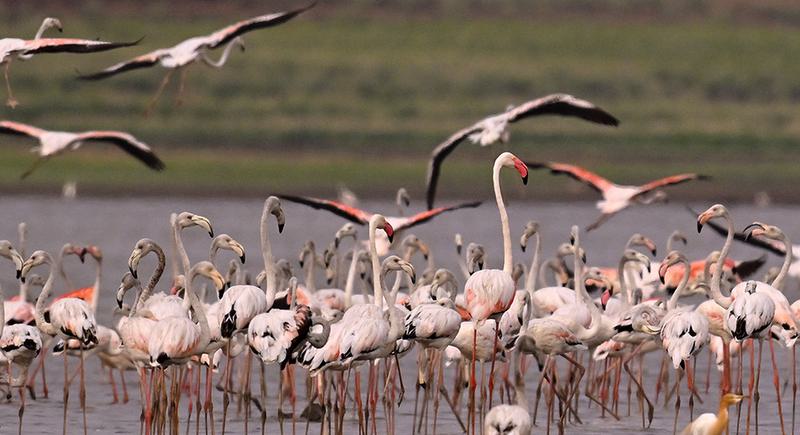

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
GenCast AI
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
2024 World Chess Championship

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
D. Gukesh became the youngest world chess champion after defeating Ding Liren of China in the final game of their match.
Key Facts about the 2024 World Chess Championship:
- Held At: Singapore, from November 25 to December 12, 2024.
- Players: Reigning champion Ding Liren (China) vs. Challenger D. Gukesh (India).
- Significance: This was the first-ever World Championship match contested by two Asian players. Gukesh became the third Asian to win the World Championship after Viswanathan Anand (India) and Ding Liren (China).
- Historical Context: The World Chess Championship was first established in 1886 with Wilhelm Steinitz as the first official World Champion.
- Governing Body: Organized by FIDE (Fédération Internationale des Échecs), which has been responsible for the event since 1948.
- Selection Process: Gukesh earned his spot through his victory in the 2024 Candidates Tournament in Toronto, while Ding Liren was the reigning champion after Magnus Carlsen declined to defend his title.
D. Gukesh: Key Details
- Birth: May 29, 2006, in Chennai, India.
- Grandmaster Title: Achieved at age 12 years, 7 months, and 17 days, making him the third-youngest Grandmaster in history.
- Chess Rating: He is the youngest player to reach a 2750 FIDE rating.
- Significant Wins:
- Gold medals in both team and individual events at the 2024 Chess Olympiad.
- Bronze medal in team events at the 2024 Asian Games.
- Remarkable Fact: Gukesh is four years younger than Garry Kasparov was when he won the World Championship in 1985.
FIDE World Chess Championship Overview:
- Founded: 1924 in Paris; headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- Governing Body: The International Chess Federation (FIDE) is recognized by the International Olympic Committee and governs global chess competitions. FIDE has 201 member countries.
Indian Chess Achievements:
- Viswanathan Anand: First Indian to win the World Chess Championship (5-time World Champion).
- D. Gukesh: Second Indian to win the World Chess Championship.
Indian Scientists Develop Novel Gene Therapy for Haemophilia
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian scientists have developed a successful gene therapy treatment for severe haemophilia A, a rare inherited blood disorder causing spontaneous, potentially fatal bleeding episodes.
Key Highlights:
Trial Success:
- The trial, conducted at Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore, involved five patients from Tamil Nadu.
- Results: None of the five patients reported bleeding episodes for over a year after receiving the treatment. The follow-up period averaged 14 months.
- This marks a significant improvement, as haemophilia patients typically experience frequent bleeding episodes requiring regular treatment.
Gene Therapy as a One-Time Solution:
- Traditional treatments involve frequent injections of clotting factors to prevent bleeding.
- The new gene therapy offers a one-time solution, teaching the body to produce enough clotting factor to prevent hemorrhages.
Haemophilia A - Overview:
- Caused by the absence of Factor VIII, a critical blood-clotting protein.
- Hemophilia A primarily affects males (since it's an X-linked disorder), though some females with two defective X chromosomes can also develop the condition.
- Symptoms include prolonged bleeding from minor injuries or internal bleeding in joints and muscles.
Current Treatment Challenges:
- Haemophilia treatments can be expensive and require lifelong care, costing up to ?2.54 crore over a 10-year period.
- The therapy requires repeated infusions of clotting factors or synthetic alternatives, which can be burdensome.
Gene Therapy Details:
- The gene therapy used in this trial involves fusing stem cells with the gene for Factor VIII using a lentivirus vector (safer than other vectors like adenovirus).
- This therapy eliminates the need for repeated Factor VIII infusions, providing a more cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Global Context:
- India has one of the world’s largest haemophilia populations, with an estimated 40,000 to 100,000 patients.
- The success of this gene therapy in India could lead to localized production, reducing treatment costs and increasing accessibility to gene therapy in resource-constrained settings.
Comparison with Roctavian:
- Roctavian, the only FDA-approved gene therapy for haemophilia A, also uses gene delivery to produce Factor VIII, but requires immunosuppressive therapy and is not approved for children.
- In contrast, the Vellore trial's lentivirus-based approach is considered safer, especially for children, with the potential for broader application.
Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was passed in the Lok Sabha on December 20, 2024, aiming to enhance the functioning and autonomy of Indian Railways.
Key Provisions:
- Repeal of the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905: The Bill repeals the 1905 Act and incorporates its provisions into the Railways Act, 1989, simplifying the legal framework by reducing the need to refer to two separate laws.
- Statutory Backing for Railway Board: The Bill provides statutory backing to the Railway Board, which previously lacked such a legal mandate. It grants the Union government the authority to determine the number of members, their qualifications, terms, and conditions of service.
- Decentralization of Power: The Bill aims to decentralize decision-making, granting greater autonomy to regional railway zones. This shift will allow more independence in budgeting, infrastructure projects, and recruitment, addressing long-standing calls for improved regional empowerment.
- Independent Regulator: The Bill proposes the creation of an independent regulator for overseeing tariffs, safety, and private sector participation. This idea has been supported by previous expert committees to encourage greater competition and transparency in the sector.
- Fast-Tracking Infrastructure and Services: The Bill will streamline approvals for new train services and infrastructure projects, helping meet demands from underserved regions, particularly in states like Bihar.
Objectives:
- Modernization of the Legal Framework: By incorporating the provisions of the 1905 Act into the 1989 Act, the Bill aims to simplify and modernize the legal architecture governing the railways.
- Empowerment of Railway Zones: Autonomy for railway zones is seen as a key step towards improving efficiency and accountability in operations.
- Private Sector Participation: The establishment of an independent regulator is expected to promote private participation in the railway sector, aligning with international standards.
Historical Context:
- The Indian Railways Act, 1890 established the foundations for Indian Railways as a government entity, which was further refined with the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905.
- This Bill aligns with recommendations from previous committees, including the Sreedharan Committee (2014) and the Committee on Restructuring Railways (2015), which have called for greater decentralization and autonomy for railway zones, as well as an independent regulatory body.
Challenges and Proposed Reforms:
- Financial Sustainability: The railways face challenges such as high operating costs, particularly from salaries and pensions, and losses in the passenger segment. Suggestions to improve finances include rationalizing passenger fares, enhancing freight revenue, and attracting private investment in infrastructure.
- Efficient Freight Operations: The Bill also addresses concerns about network congestion, especially for freight operations, and aims to increase the competitiveness of freight transport by improving infrastructure and reducing cross-subsidies from passenger fares.
Recommendations of various Committees on reforming the Railways
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
World Malaria Report 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Malaria Report 2024 released by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights significant progress in malaria control, particularly in India, but underscores the continued burden of malaria in Southeast Asia, where India accounts for half of all malaria cases.
About Malaria:
- Cause: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, primarily P. falciparum and P. vivax, transmitted through bites from infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Transmission: Non-contagious; transmitted via mosquito bites.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, and headaches appear 10–15 days after the mosquito bite. In some individuals, the symptoms may be mild.
- Prevention: Includes vector control strategies like insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor spraying. Malaria is treatable with early diagnosis and prompt medication.
India’s Malaria Status:
- Progress:
- India has made significant strides in reducing malaria, with cases decreasing from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023, a reduction of 82.4%.
- Similarly, malaria-related deaths dropped by 82.9%, from 35,000 in 2000 to 6,000 in 2023.
- Exit from High-Burden-High-Impact (HBHI) Group:
- India exited this group in 2024, signaling its success in reducing malaria burden.
- Cases dropped by 69% (from 6.4 million in 2017 to 2 million in 2023), and deaths fell by 68% (from 11,100 to 3,500 in the same period).
Key Strategies Behind India's Success:
- Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (ACT): Used to treat malaria effectively.
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLIN): Widely deployed to control mosquito populations.
- Targeted Interventions: Focused on forested and tribal areas where malaria transmission is higher, particularly in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, and the North-East.
- Effective Monitoring: Ensures proper implementation of strategies and interventions.
WHO's Global Malaria Report 2024 Highlights:
- Global Burden: In 2023, there were 263 million malaria cases globally and 597,000 deaths. The African region remains the hardest hit, accounting for 95% of malaria deaths.
- Progress Since 2000: Malaria incidence and deaths have significantly decreased. The global number of malaria cases and deaths dropped substantially, with over 2.2 billion cases and 12.7 million deaths averted.
- Malaria-Free Countries: As of November 2024, 44 countries and one territory, including Egypt, have been certified malaria-free.
- Emerging Threats: Drug resistance (especially to Artemisinin) and insecticide resistance are growing concerns, affecting control efforts.
India and Southeast Asia:
- India contributes nearly half of the malaria cases in Southeast Asia, while Indonesia accounts for about one-third. Despite progress, India and Indonesia together accounted for 88% of malaria deaths in the region.
- South-East Asia Progress: The region reduced malaria cases by 82.4% from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023. Timor-Leste and Bhutan reported zero indigenous malaria cases in 2023.
Global Recommendations:
- WHO stresses the need for continued investment, innovative strategies, and targeted actions, especially in high-burden areas like Africa, to sustain progress and tackle remaining challenges, such as drug resistance, insecticide resistance, and new vector species like Anopheles stephensi, which thrives in urban areas.
Ayush Visa

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Recently, the government introduced a separate category of Ayush Visa for foreigners seeking treatment under the Ayush systems of medicine (Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy).
- The Ayush Visa is available in four sub-categories:
- Ayush Visa: For foreigners visiting India for therapeutic care and wellness treatment in accredited hospitals/wellness centers.
- Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients seeking Ayush treatment.
- e-Ayush Visa: An electronic version of the Ayush Visa for convenience.
- e-Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients on an e-Ayush Visa.
- Visa Statistics (as of December 4, 2024):
- 123 regular Ayush visas have been issued.
- 221 e-Ayush visas issued.
- 17 e-Ayush attendant visas issued.
- Advantage Healthcare India Portal:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the Advantage Healthcare India portal, an official platform for Medical Value Travel (MVT).
- The portal facilitates information for international patients seeking medical treatment and wellness services in India.
- The website for accessing the portal is www.healinindia.gov.in.
- Government's Objectives: The government aims to sensitize stakeholders involved in MVT, including Ayush facility providers, to ensure smooth services for international patients.
AgeXtend
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced the appointment of Sanjay Malhotra as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He replaces Shaktikanta Das, whose six-year tenure ends on December 10, 2024.
Background of Sanjay Malhotra:
- Education & Early Career: Sanjay Malhotra is a 1990-batch IAS officer from the Rajasthan cadre. He holds a degree in Computer Science Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and a Master’s in Public Policy from Princeton University.
- Professional Experience: Malhotra has over 33 years of experience in various sectors including power, finance, taxation, information technology, and mines. He is currently serving as the Revenue Secretary in the Ministry of Finance, a position he has held since October 2022. Prior to this, he was Secretary of the Department of Financial Services.
- Monetary Policy and Challenges: As RBI Governor, Malhotra will inherit the responsibility of steering India's monetary policy, especially as inflation has been a persistent issue and economic growth has slowed. His first monetary policy review is expected in February 2025.
About the Appointment Process:
RBI Governors are appointed by the Government of India, and the appointment process involves the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointment Search Committee, which includes the Cabinet Secretary, the current RBI Governor, the Financial Services Secretary, and two independent members. The committee prepares a list of eligible candidates, interviews them, and the final decision is made by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments, chaired by the Prime Minister.
RBI Governors Eligibility Criteria
- The RBI Act, 1934 does not mention any specific qualification for the governor. People with different educational backgrounds were selected to head the institution. However, the governor traditionally is either a civil services personnel or an economist.
- Candidates should have prior experience in areas such as:
- Working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank.
- Serving as Chairman or General Manager of a bank.
- Holding significant positions in reputable financial or banking organizations.
- Working in the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- The candidate must be an Indian citizen aged 35 years or older.
- The candidate cannot be a member of Parliament, State Legislature, or hold any other office for profit
Key Responsibilities of the RBI Governor:
- Monetary Policy: The RBI Governor chairs the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which is responsible for setting benchmark interest rates and managing inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Institutions: The Governor oversees the regulation of banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
- Currency Management: The Governor ensures the proper issuance of currency and the withdrawal of unfit notes.
- Crisis Management and Policy Execution: The Governor is pivotal in managing financial crises and ensuring the execution of policies related to foreign exchange and financial inclusion.
Reforms in Merchant Shipping

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The Government is preparing to introduce several significant bills aimed at driving much-needed reforms in the shipping industry. Key among them are the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 and the Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024, both of which promise to bring transformative changes to boost the sector.
Context and Need for Reforms:
- Outdated Framework: The Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838, fail to address the current needs of the shipping sector, particularly offshore vessels.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate regulation of offshore vessels, maritime training institutions, and welfare provisions for seafarers on foreign-flagged ships.
- Global Alignment: Need to align with international maritime conventions and modernize administration for competitiveness and better governance.
- Investment and Growth: Outdated laws hinder foreign investment and ease of doing business, necessitating a regulatory overhaul.
Key Features of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Ease of Vessel Registration:
- Reduces ownership threshold for Indian entities from 100% to 51%, enabling NRIs, OCIs, and foreign entities to invest.
- Facilitates registration of vessels chartered by Indian entities under the "bareboat charter-cum-demise" system, promoting capital-deficient entrepreneurs.
- Temporary registration provisions for vessels destined for demolition, boosting India's ship recycling industry.
- Expansion of Vessel Scope:
- Broadens the definition of "vessel" to include all types of mechanized and non-mechanized crafts, such as submersibles, hydrofoils, and Mobile Offshore Units (MOUs).
- Ensures comprehensive regulatory oversight, particularly in the offshore sector, enhancing transparency and safety.
- Coastal Security:
- Strengthens coastal security by empowering authorities to issue instructions to all types of vessels, addressing vulnerabilities highlighted by incidents like the 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Marine Pollution Measures:
- Incorporates global standards like the MARPOL convention to address marine pollution.
- Introduces measures such as reducing sulphur content in marine fuel and banning single-use plastics on Indian ships.
- Launch of the ‘Swachh Sagar’ portal to ensure proper disposal of ship-generated waste.
- Seafarer Welfare:
- Expands welfare provisions to include Indian seafarers working on foreign-flagged ships, offering protections under the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
- Ensures better working conditions and safety standards for a growing workforce of Indian seafarers abroad.
- Maritime Training Regulations:
- Establishes a legal framework to regulate maritime training institutions, addressing the rise of unauthorized institutes post-liberalization.
- Ensures standardized, high-quality education and eliminates fraudulent practices.
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Focus on Commercial Utilization of Coastal Waters:
- Distinguishes between the technical regulation of ships and the commercial utilization of Indian coastal waters.
- Aims to streamline licensing, operations, and coastal planning, enhancing the integration of inland and coastal shipping.
- Alignment with ‘Sagarmala’ Program: Supports the promotion of coastal shipping through better infrastructure and connectivity, in line with the government's ‘Sagarmala’ initiative, which boosts port connectivity and coastal trade.
International Conventions India Has Ratified:
- MARPOL: Focuses on preventing ship-based pollution.
- Maritime Labour Convention (MLC): Protects seafarers' rights and ensures fair working conditions.
- Bunker Convention: Addresses liability for oil pollution damage.
- Wreck Removal Convention: Mandates safe removal of shipwrecks.
- Civil Liability Convention: Establishes liability for oil pollution incidents.
Significance of the Reforms:
- Modernized Framework: Aligns India’s maritime laws with global standards for enhanced competitiveness.
- Economic Growth: Encourages foreign investment and entry into the shipping sector by removing regulatory barriers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on combating marine pollution and ensuring sustainable shipping practices.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Strengthens coastal security and ensures stringent safety regulations for vessels.
- Seafarers’ Welfare: Extends benefits and protections to Indian seafarers working globally, ensuring better working conditions.
- Maritime Education: Provides a robust regulatory framework to ensure high-quality, standardized maritime training.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, is once again in focus, albeit in a context in which its objectives are being ignored. Civil suits questioning the religious character of mosques at Varanasi and Mathura are progressing apace. These developments show that legislation freezing the status of places of worship is inadequate to stop Hindu claimants from making determined legal efforts to achieve their goal of replacing them with temples.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991:
- Objective: To preserve the religious character of places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947, and prevent changes in religious identity.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 3: Prohibits conversion of a place of worship from one religion to another.
- Section 4(1): Ensures the religious character remains unchanged from August 15, 1947.
- Section 4(2): Terminates ongoing or future legal proceedings seeking to alter the religious character of a place of worship.
- Exemptions:
- Ayodhya dispute: Exempted, allowing ongoing litigation.
- Ancient monuments & archaeological sites: Not covered by the Act.
- Already settled disputes or those agreed upon before the Act came into force.
- Penalties: Violators can face up to 3 years of imprisonment or fines.
- Criticism: The Act has been challenged for limiting judicial review, imposing a retrospective cutoff date, and restricting religious rights.
Recent Legal Disputes:
- Gyanvapi Mosque (Varanasi):
- Claim: Hindu worshippers assert the right to worship deities (e.g., Ma Sringar Gauri, Lord Vishweshwar) within the mosque premises.
- Legal Basis: Claim that the mosque was built over an ancient Hindu temple.
- Court's Ruling: The court allows the case to proceed, stating that the aim is to assert worship rights, not change the mosque’s status.
- Archaeological Survey: ASI report confirms the existence of a temple before the mosque’s construction.
- Key Legal Outcome: The Places of Worship Act does not bar these suits as they aim to ascertain the religious character of the site, not alter it.
- Shahi Idgah Mosque (Mathura):
- Claim: Hindu groups assert the mosque was built over Lord Krishna’s birthplace.
- Historical Context: The dispute was settled by a compromise in 1968, which was implemented in 1974, where part of the land was given to the mosque.
- Current Legal Dispute: New suits challenge the 1968 agreement as ‘fraudulent’ and seek the entire land to be transferred to the deity.
- Court's Ruling: The Act is not applicable as the 1968 agreement predates the 1991 Act, and the dispute pertains to the compromise, not the religious character.
- Shahi Jama Masjid (Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh):
- Claim: Allegation that the mosque was built over a Hindu temple (Hari Har Mandir).
- Survey Request: Petitioners seek a survey to verify the site’s historical and religious character.
- Legal Context: The mosque is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904.
Key Legal Interpretations:
- Court’s Role: Courts have ruled that the Places of Worship Act does not prohibit suits related to the religious character of a site if they are aimed at determining, not altering, that character.
- Interpretation of ‘Religious Character’: The Allahabad High Court stated that a structure can’t have dual religious character (both Hindu and Muslim), and the religious character of a place must be determined through evidence.
Political and Social Implications:
- Ongoing Controversy: The Gyanvapi and Mathura mosque disputes continue to fuel political and religious debates, as Hindu organizations seek to assert their claims, while mosque committees and Muslim groups resist changes.
- Public and Legal Attention: The legal and political landscape surrounding the Places of Worship Act remains contentious, with several legal suits challenging its applicability.
1984 Bhopal disaster

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Forty years after the Bhopal disaster on December 2-3, 1984, several hundred tonnes of toxic waste still remain around the ill-fated Union Carbide plant.
Overview of the incident:
The 1984 Bhopal disaster, one of the world’s worst industrial accidents, was caused by the release of methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas, which was a key component in the production of pesticides at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) plant. However, the toxic legacy of the disaster extends far beyond MIC, with a range of other harmful substances lingering in the environment. These include:
- Methyl Isocyanate (MIC):Primary toxic agent: MIC is a highly toxic, volatile compound. Exposure can cause severe respiratory distress, eye irritation, pulmonary edema, and even death.
- Heavy Metals:The site of the plant is contaminated with various heavy metals, including:
- Mercury: Known to accumulate in the body and affect the nervous system, kidneys, and liver. Even small doses over time can lead to chronic health problems.
- Chromium: Exposure to high levels of chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, is associated with lung cancer and damage to the respiratory system.
- Lead: A potent neurotoxin, lead can cause developmental delays, memory problems, and damage to the kidneys.
- Nickel: Can cause respiratory and lung cancers when inhaled in significant quantities.
- Copper: High levels of copper exposure can damage the liver and kidneys.
- Organic Compounds:Several organic chemicals were found at the site, including:
- Hexachlorobutadiene: A suspected carcinogen that can cause liver damage, kidney damage, and neurological issues upon exposure.
- Chloroform (Trichloromethane): Known for its effects on the central nervous system, exposure can lead to dizziness, loss of consciousness, and even death at high concentrations. It is also a possible carcinogen.
- Carbon Tetrachloride: A potent liver toxin, exposure can result in liver damage, cancer, and nervous system toxicity.
- Trichlorobenzene: These compounds are volatile and can spread through air and water, accumulating in fatty tissues and causing damage to organs like the liver and kidneys.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):Some of the contaminants, particularly the organic compounds, are classified as persistent organic pollutants, which do not degrade easily in the environment. These can lead to:
- Cancer: Several of these compounds are carcinogenic.
- Neurological damage: Prolonged exposure can affect both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Reproductive and developmental disorders: Exposure has been linked to adverse effects on fertility and developmental health in humans.
- Environmental and Long-term Health Effects:
- Even decades later, contamination continues to affect the health of people living around the site, with high rates of cancers, birth defects, respiratory diseases, and other health issues. Water sources in the region remain unsafe due to heavy contamination with toxic chemicals. Persistent organic pollutants have been identified in local communities, indicating that the contamination continues to spread.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
MahaKumbh Mela 2025

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- On December 1, 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government declared the MahaKumbh Mela area as a temporary district for four months.
- The new district will be known as the MahaKumbh Mela District, to streamline management for the 2025 MahaKumbh.
- Over 5,000 hectares of land will be part of this district, including 66 revenue villages from four tehsils: Sadar, Sorav, Phulpur, and Karchana.
Key Administrative Changes:
- Mela Adhikari (Kumbh Mela Officer) will act as the District Magistrate (DM) and will hold powers of Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate.
- The Mela Adhikari will have authority under the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023, and the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006.
- The Mela Adhikari can appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
MahaKumbh Mela Overview:
- The Kumbh Mela is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims, with participants bathing in sacred rivers at locations including Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain, and Nashik.
- The PrayagrajKumbh takes place at the Sangam, the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers.
- The event spans over a month and includes religious, cultural, and social activities, along with massive infrastructural setup including tented townships, civic facilities, and security measures.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
U.N. Peacebuilding Commission

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been re-elected to the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) for the term 2025–2026, continuing its strong commitment to global peace and stability.
UN Peacebuilding Commission (PBC)
It is an advisory body established by the UN General Assembly and UN Security Council in 2005. It is tasked with supporting peace efforts in conflict-affected countries by advising and recommending strategies for post-conflict recovery and long-term peacebuilding.
Composition of PBC:
- The PBC is composed of 31 member states, elected from the General Assembly, Security Council, and Economic and Social Council.
- It includes key financial and troop-contributing countries, which play a central role in shaping global peacebuilding initiatives.
Key Mandates of the PBC
- Coordination of Resources and Strategies:The Commission brings together all relevant actors to propose integrated strategies for post-conflict recovery and peacebuilding.
- Reconstruction and Development:It focuses on rebuilding conflict-affected countries through institution-building and supporting sustainable development efforts.
- Improving Coordination:The PBC ensures better coordination within and outside the UN, develops best practices, and secures predictable financing for early recovery initiatives.
- Sustaining Peace:The Commission promotes sustained international attention to peacebuilding efforts and offers political support to countries emerging from conflict, with their consent.
- Integrated Approach:The PBC advocates for an integrated approach that links security, development, and human rights as interrelated and mutually reinforcing.
- Bridging Role:It serves as a platform to connect UN bodies, Member States, national authorities, civil society, and other stakeholders, sharing good practices in peacebuilding.
India’s Contributions to UN Peacebuilding and Peacekeeping
India has been at the forefront of UN peacebuilding initiatives due to its long-standing commitment to international peace and stability.
- Largest Contributor of Personnel:India is one of the largest contributors of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping. Currently, around 6,000 Indian military and police personnel are deployed across multiple missions in Abyei, Central African Republic, Cyprus, Democratic Republic of Congo, Lebanon, Middle East, Somalia, South Sudan, and Western Sahara.
- Sacrifices in Service:India holds the tragic distinction of having lost over 180 peacekeepers, the highest number from any troop-contributing nation. These sacrifices reflect India's enduring commitment to global peace.
- Financial Support:India contributes to the Peacebuilding Fund, the primary financial instrument for conflict prevention and peacebuilding, which supports countries transitioning from conflict to peace.
- Championing South-South Cooperation:India has actively promoted South-South cooperation, a model for post-conflict recovery that emphasizes shared learning and capacity-building among developing nations.
- Women in UN Peacekeeping:India has led efforts for gender parity in UN peacekeeping. In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN peacekeeping mission. It has since deployed Female Engagement Teams (FETs) and Female Formed Police Units (FFPUs) in Lebanon and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Training and Capacity Building:India has invested in capacity development for both the UN and host nations. The Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in New Delhi, established by the Indian Army, trains over 12,000 troops annually in peacekeeping operations. India also deploys Mobile Training Teams to share best practices with other countries.
India’s Pledges at the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial (2023)
At the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial held in Accra, Ghana (December 2023), India made significant pledges:
- To contribute an Infantry Battalion Group, along with various sub-groups and pre-deployment training courses, for the next two years.
- India’s ongoing commitment to strengthening peacekeeping efforts and supporting the UN’s peacebuilding agenda was reaffirmed.
Socialist and Secular in Preamble

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
Supreme Court upholds ‘secular, socialist’ in Preamble of the Constitution.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Judgment Overview:
- Supreme Court's Ruling: The Court upheld the inclusion of the terms ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976.
- Challenge: Petitioners, including BJP leader Subramanian Swamy, challenged the retrospective application of these terms, arguing they were not part of the original Preamble adopted in 1949.
- Court's Explanation:
- Socialist: The term represents a welfare state aimed at reducing inequality and ensuring social, political, and economic justice, but does not prescribe a specific economic policy (left or right).
- Secular: Denotes a state that treats all religions equally, ensuring religious freedom and neutrality in religious matters. It is linked to Articles 14, 15, and 16, which ensure equality and non-discrimination.
- Retrospective Application:The Court affirmed that Parliament’s amendment power under Article 368 extends to the Preamble, and the retrospective application of the terms was valid.
- Constitution as a ‘Living Document’:The Court emphasized that the Constitution is adaptable to societal changes and evolving needs. The inclusion of 'secular' and 'socialist' reflects India’s evolving democratic and social framework.
- Interpretation of Secularism and Socialism:
- Secularism in India refers to the state's neutral stance towards all religions, promoting religious harmony.
- Socialism signifies India’s commitment to ensuring equality of opportunity and promoting welfare policies, such as social justice and economic welfare.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 368: Grants Parliament the authority to amend the Constitution, including the Preamble. The Court affirmed that this power is unquestionable.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): Established the ‘basic structure doctrine,’ which means certain fundamental features of the Constitution cannot be altered. The inclusion of ‘secular’ and ‘socialist’ is in line with this basic structure.
- S.R. Bommai Case (1994): Reinforced the secular nature of the Indian state.
Preamble to the Constitution
- Definition: The Preamble is an introductory statement that outlines the fundamental values and goals of the Indian Constitution.
- Key Objectives: Justice (social, economic, political), Liberty (thought, expression, belief), Equality (status and opportunity), and Fraternity (national unity and dignity).
- Terms in the Preamble:
- Sovereign: India's independence in all matters.
- Socialist: Commitment to social justice and welfare.
- Secular: Equal respect for all religions.
- Democratic: Governance by the people, through elected representatives.
- Republic: Head of state elected, not hereditary.
42nd Amendment Act, 1976:
- Context: Introduced during the Emergency under Indira Gandhi's government.
- Key Changes: Added 'socialist' and 'secular' to the Preamble, revised 'Unity of the Nation' to 'Unity and Integrity of the Nation.'
- Significance: Strengthened constitutional values like inclusivity, equality, and justice.
Socialist and Secular Initiatives by Government
- Socialist Programs:
- MGNREGA: Rural employment guarantee.
- PDS: Food security system.
- Right to Education (RTE): Free, compulsory education.
- Housing Schemes: Awas Yojana for the economically weaker sections.
- Secular Programs:
- Minority Welfare: Scholarships and skill development.
- Religious Protection Laws: Protection of places of worship.
- Communal Violence Laws: Special courts for violence-related cases.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Equal rights for all religions under Articles 25-28.
Significance of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Reaffirmation of Constitutional Values: The inclusion of ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ reinforces India’s commitment to equality, justice, and democratic principles.
- Legitimacy of Amendments: Affirms Parliament's constitutional power to amend the Preamble.
- Evolving Interpretation: Recognizes that the Constitution must evolve in response to societal and political changes.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
Access to Medicine Index Report 2024

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Access to Medicine Index Report 2024 was released by the Access to Medicine Foundation. The report evaluates 20 leading pharmaceutical companies on their efforts to expand access to medicines in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).The biennial report has been published since 2008.
- Key Highlights:
- Key Areas of Evaluation
- Governance of Access: Companies’ leadership in addressing access issues.
- Research & Development (R&D): Focus on innovations for diseases prevalent in LMICs.
- Product Delivery: Efforts to ensure medicines and vaccines are accessible.
- Findings from the 2024 Report
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Many pharmaceutical companies are adopting ‘inclusive business models,’ but outcomes are mixed, with transparent reporting still lacking.
- 61% of products lack specific access strategies for low-income countries.
- Exclusion from Clinical Trials:Only 43% of clinical trials take place in LMICs, despite these countries representing 80% of the global population.
- Limited Technology Transfers & Local Availability:
- Technology transfers and voluntary licensing are concentrated in countries like Brazil, China, and India.
- Sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) remains largely overlooked.
- Decline in R&D for Priority Diseases:
- Pharmaceutical companies are moving away from diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which disproportionately affect LMICs.
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Key Issues in Accessing Medicines in LMICs
- Economic Barriers:
- High costs of essential medicines, including patented drugs, limit access for patients in LMICs with low purchasing power.
- Out-of-pocket expenditures lead to catastrophic financial consequences for families.
- Infrastructure Challenges:
- Poor transportation and cold chain infrastructure hamper the efficient distribution of medicines, especially in rural areas.
- Disruptions in supply chains (e.g., during pandemics) exacerbate medicine shortages.
- Regulatory Issues:Weak enforcement of regulatory frameworks results in the proliferation of substandard and counterfeit medicines, compromising treatment efficacy.
- Workforce Limitations:
- A shortage of trained healthcare professionals restricts appropriate prescription and management of medicines.
- Cultural beliefs and low health literacy further complicate adherence to treatments.
- Economic Barriers:
- Challenges Specific to LMICs
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- LMICs face both infectious diseases and non-communicable diseases (NCDs), putting strain on fragile healthcare systems.
- 17 million people die from NCDs before age 70 annually, with 86% of these deaths occurring in LMICs.
- Need for Local Manufacturing:
- Strengthening local pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution networks is crucial to ensure a reliable supply of essential medicines and reduce dependence on imports.
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- Recommendations for Improving Access
- Companies should scale up efforts to bridge the health equity gap and use innovative approaches and local partnerships to improve access.
- Focus on increasing transparency in access reporting and addressing the lack of strategies for low-income countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies should refocus on diseases prevalent in LMICs, such as malaria and tuberculosis, and ensure that their R&D addresses the needs of these regions.
- Key Areas of Evaluation
Chagas Disease
- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
A recent study by Texas A&M University has uncovered a concerning new risk for dogs in Texas related to Chagas disease—the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), which causes the disease, can survive in dead kissing bugs (Triatominae). This discovery was published in the Journal of Medical Entomology in October 2024 and has raised alarms about how dead insects, which might be found in insecticide-treated dog kennels, could still pose a transmission risk for dogs.
Key Findings:
- Chagas Disease is primarily spread by kissing bugs, which carry T. cruzi in their gut. Dogs can contract the parasite by ingesting the bug's feces, especially when they lick their bite wounds.
- The study shows that even dead kissing bugs, which are often discarded in kennels, can still carry viable T. cruzi. This is particularly worrying in areas where insecticides are used to control the insects but dead bugs remain accessible to dogs.
- Researchers collected live and dead triatomines from six Texas kennels between June and October 2022, using both genetic testing and culture methods to assess whether the bugs were carrying live T. cruzi.
- 28% of the collected bugs tested positive for T. cruzi.
- A dead kissing bug (Paratriatomalecticularia) was found to still harbor live T. cruzi cultures, demonstrating that the parasite can survive even after the insect has died.
Transmission and Risks:
- Kissing bugs typically feed on the blood of animals like dogs, rodents, and raccoons, defecating near the bite site. If the dog licks the contaminated area, they can ingest the parasite-laden feces and become infected.
- The new discovery suggests that dead kissing bugs may pose a secondary transmission route for T. cruzi. Dogs that ingest these dead bugs, either in insecticide-treated areas or natural environments, could still contract the parasite.
- Researchers noted that dead bugs with intact gut contents showed a higher rate of infection than desiccated ones, which suggests that the condition of the bug after death impacts how long the parasite survives.
Implications for Management:
- The findings challenge current insecticide-based control methods. While insecticides kill the bugs, dead insects could still serve as a source of infection, necessitating new approaches for managing Chagas disease transmission in dog kennels.
- The study underscores the importance of regularly removing dead insects in kennels and reconsidering control strategies beyond just using insecticides.
About Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease is caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, commonly found in the feces of kissing bugs. It can cause long-term heart and digestive issues if left untreated.
- The disease is common in parts of South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it has been increasingly reported in the southern United States.
- Treatment focuses on killing the parasite in the acute phase, but once it progresses to the chronic phase, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research:
- The Texas A&M team plans to explore how long T. cruzi survives in dead triatomines and whether insecticides affect the parasite’s ability to persist. They are also looking into developing integrated pest management strategies for environments with high kissing bug activity.
- The study also forms part of a broader "One Health" approach, recognizing that both human and animal health are interconnected, and research on Chagas disease in animals can help inform public health strategies.
Imperial Eagle(Aquila heliaca)

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
- A rare Imperial Eagle (Aquila heliaca) was spotted in the PulluzhiKole wetlands. This marks a significant event as the species was last reported in Kannur in 2003.
Key Highlights:
- Habitat and Migration:
- The Imperial Eagle primarily breeds in southeastern Europe, west, and central Asia.
- During the winter months, it migrates to regions including northeastern Africa, West Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Conservation Status:The IUCN Red List lists the Imperial Eagle as a vulnerable species, indicating its potential risk of extinction, underscoring the need for its conservation efforts.
- Importance of Conservation:
- The Kole fields are a Ramsar-protected area, emphasizing their critical role in preserving migratory bird habitats.
- Ongoing conservation and observation efforts in these wetlands are essential for protecting the diverse bird species that use the area.
Features of the Imperial Eagle:
- Scientific Name: Aquila heliaca
- Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Length ranges from 68 to 90 cm, with a wingspan between 1.76 to 2.2 meters.
- Color: It has a pale golden crown and nape, with a grey base extending to the tail. Its wings feature prominent white "braces" on the scapulars.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are typically smaller than females.
- Habitat: Prefers old forests, mountainous regions, and riverside forests.
- Feeding: It has strong legs and curved talons for capturing and killing prey, and exceptional eyesight to spot prey from high altitudes.
- Conservation Efforts: Continued monitoring and protection of the Kole wetlands and other vital habitats are crucial for the survival of this vulnerable species and other at-risk birds.
Minke Whale

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have directly measured the hearing range of minke whales for the first time, finding that they can detect high-frequency sounds up to 90 kHz.
Key Highlights:
- Implication for Ocean Noise: The study suggests that baleen whales, including minke whales, may be more affected by anthropogenic ocean noise (e.g., naval sonar) than previously recognized, as their hearing range had been underestimated.
- Research Method: A novel catch-and-release technique was used to temporarily hold adolescent minke whales in Norway for auditory evoked potential (AEP) tests to measure their hearing sensitivity.
- Findings: Contrary to the belief that baleen whales are low-frequency specialists, minke whales can detect frequencies between 45 kHz to 90 kHz.
- Impact of Findings: The results could affect future regulations on ocean noise and its impact on marine mammals, as better hearing data is now available for baleen whales.
Minke Whale Overview:
- Family: Minke whales are members of the baleen or "great" whale family and are the smallest of the rorquals.
- Species: There are two recognized species:
- Common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), found in various ocean basins.
- Antarctic minke whale (B. bonaerensis), found in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Subspecies:
- Dwarf minke whale: An unnamed subspecies of the common minke whale, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- North Atlantic (B. a. acutorostrata) and North Pacific (B. a. scammoni) subspecies of common minke whales.
- Distribution: Minke whales are widely spread across tropical, temperate, and polar regions (65°S to 80°N), with common minke whales in all ocean basins and dwarf minke whales mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Feeding Areas: They feed in cooler waters at higher latitudes and can be found both inshore and offshore.
- Conservation Status (IUCN):
- Common minke whale: Least Concern.
- Antarctic minke whale: Data Deficient.
Cicada

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
North American cicadas have life cycles that last for prime numbers of years, putting pressure on the idea that humans created mathematics.
What are Cicadas?
- Classification: Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Physical Features: Hemipteran insects (also known as true bugs) have piercing-sucking mouthparts and two pairs of wings.
- Life Span: Cicadas spend the majority of their life underground, feeding on plant sap. Once they emerge from the soil, they have a short adult life span of about 2 to 4 weeks.
Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Cicadas are typically found in natural forests with large trees and are considered canopy dwellers.
- Global Distribution: Cicadas are found on every continent except Antarctica. The highest genetic diversity of cicadas is found in India and Bangladesh, followed by China.
Cicada Emergence and Life Cycle:
- Life Cycle: Cicadas have a complex life cycle, involving long periods of underground development followed by brief adult emergence.
- Periodical Cicadas: There are species of cicadas that emerge in 13-year and 17-year cycles.
- Broods: Initially, 30 broods were categorized based on geography and emergence times, but currently, only about 15 broods remain active due to some broods becoming extinct.
- Unique Phenomenon: In April 2024, a rare event is expected where a trillion cicadas from two different broods will emerge simultaneously in the Midwest and Southeast regions of the United States.
Cicada's underground Development:
- Feeding on Sap: During their underground phase, cicadas feed on the sap of plants.
- Purpose of Long Development: Researchers believe the long development period helps cicadas evade above-ground predators by keeping them hidden in the soil.
Vulnerability after Emergence:
- Emergence Behavior: Once cicadas emerge, they construct a "cicada hut" to shed their nymphal skins, then climb onto nearby trees or vegetation.
- Predator Vulnerability: Adult cicadas are vulnerable to predators such as turtles and other forest creatures because they are clumsy and defenseless, making them easy prey for predators.
Significance of the 2024 Emergence:
- The coinciding emergence of cicadas from different broods (13-year and 17-year cycles) is a rare event that highlights the complexity and mathematical precision behind the cicada life cycle.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
Rare Leucistic Peacock

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu Forest Department staff and members of a non-governmental organisation rescued a rare peacock with white feathers, caused by a genetic condition called leucism, in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
Incident Details:
- Species: Indian peacock (Pavocristatus), known for its beautiful plumage.
- Condition: The peacock was rescued due to a leg injury and its rare white plumage.
- Cause of White Plumage: The bird's white feathers are caused by leucism, a genetic condition that reduces pigmentation in feathers while leaving eye color unaffected.
Expert Insights:
- Leucism: It causes partial loss of pigmentation in animals. A leucistic animal retains normal eye color but has pale or white coloration.
- Distinction from Albinism: Unlike albinism, which results in a complete lack of melanin and often causes red or pink eyes, leucistic animals retain normal eye pigmentation.
- Identification of Leucism in Peacock: The bird’s dark eyes and pink bill and feet confirmed it as fully leucistic.
Peacock Species:
- Indian Peacock (Pavocristatus): The National Bird of India, native to India and Sri Lanka. It belongs to the Phasianidae family, which also includes pheasants, quails, and jungle fowl.
- Green Peacock (Pavomuticus): Found from Myanmar to Java.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Listed as Least Concern.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: The Indian peacock is listed under Schedule I, offering it the highest level of legal protection in India.
Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report was released at the annual UN climate conference in Baku.
Key Highlights:
- It is published by think tanks German watch, New Climate Institute, and Climate Action Network International.It was first published in 2005.
- It tracks the progress of the world’s largest emitters in terms of emissions, renewables, and climate policy.
India's Ranking in Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- India's Rank: 10th (Dropped two places from the previous year).
- Key Factors for India's High Rank:
- Low per capita emissions: 2.9 tons of CO2 equivalent (global average: 6.6 tons).
- Rapid deployment of renewables: India is a leader in solar energy projects, including large-scale solar and rooftop solar schemes.
- Renewable energy targets: Aims for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Energy efficiency standards: Introduced, but coverage remains inadequate.
- Electric vehicle (EV) deployment: Significant progress, especially in two-wheelers.
- Challenges for India:
- Heavy reliance on coal: India remains one of the top 10 countries with the largest developed coal reserves.
- Growth-oriented approach: Economic growth and energy demand continue to drive climate action, with limited change in climate policy expected.
- Future Pledges:
- Net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Global leadership in green energy.
CCPI 2025 Rankings Overview
Rank
Country
Key Points
1-3
Empty
No country performed well enough to achieve a "very high" rating.
4
Denmark
Leading climate actions but ranks 4th technically.
5
Netherlands
Strong climate performance, follows Denmark.
6
U.K.
Notable improvement due to coal phase-out and halting new fossil fuel licenses.
10
India
High performer, despite challenges like reliance on coal.
55
China
Largest emitter, heavily reliant on coal, ranks 55th despite promising plans.
57
U.S.
Second-largest emitter, ranks 57th with insufficient climate targets.
59
Argentina
Major climate policy setbacks, including potential exit from Paris Agreement.
64-67
Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Russia
Lowest-ranked, major oil and gas producers with weak climate policies.
General Findings of the Report
- CCPI Methodology: Assesses 63 countries (plus the EU) responsible for 90% of global emissions based on their emissions, renewable energy efforts, and climate policies.
- Global Trends:
- No country has been able to secure a "very high" rating across all categories.
- Denmark and Netherlands are among the top performers.
- The U.K. shows significant progress with its coal phase-out and fossil fuel policies.
UNICEF’s State of the World’s Children 2024 (SOWC-2024) Report
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
The world is facing an unprecedented crisis with nearly half of all children – about 1 billion – living in countries that face a high risk of climate and environmental hazards, the UNICEF’s State of the World’s Children 2024 (SOWC-2024) report, said.
Key Highlights:
Environmental Hazards and Children’s Health:
- Children face an increasingly unpredictable and hazardous environment due to climate change, environmental crises, and frontier technologies.
- Nearly 1 billion children live in countries facing high risks from climate and environmental hazards.
- Children’s developing bodies are especially vulnerable to pollution, extreme weather, and environmental hazards.
- Air pollution, rising temperatures, and extreme weather events harm children's respiratory health, increase the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue, and impact food security and access.
Impact of Climate Change:
- Climate destabilization, biodiversity loss, and pollution are intensifying globally.
- Climate-related disasters (e.g., floods) affect water supplies, causing waterborne diseases, a leading cause of death in children under five.
- Extreme weather events, such as floods, can cause trauma, anxiety, and displacement for children.
- By the 2050s, more children will be exposed to extreme climate hazards compared to the 2000s.
- School closures, affecting 400 million children since 2022 due to extreme weather, disrupt education and hinder economic growth.
Projections for Child Survival and Life Expectancy:
- Newborn survival rates: Projected to rise by nearly 4 percentage points to over 98% globally by the 2050s.
- Probability of surviving to age 5: Expected to increase to 99.5%.
- Life expectancy: Expected to rise to 81 years for girls and 76 years for boys by the 2050s.
Child Population Trends by 2050:
- Global child population expected to stabilize at 2.3 billion by the 2050s.
- South Asia, Eastern/Southern Africa, and West/Central Africa will have the largest child populations, facing significant challenges in meeting children’s basic needs.
- These regions also face climate risks, inadequate digital infrastructure, and socio-economic challenges.
Technological Advancements:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI), neurotechnology, renewable energy, and vaccine breakthroughs could significantly improve childhood well-being.
- Digitalization: While it can empower children, it also exposes them to online risks, including sexual exploitation and abuse.
Socio-Economic Conditions and Inequality:
- 23% of children projected to live in low-income countries by 2050, a significant increase from 11% in the 2000s.
- GDP per capita in East Asia, Pacific, and South Asia expected to more than double from the 2020s to the 2050s.
- Growing inequalities between high- and low-income countries, particularly in terms of digital access and infrastructure.
Urbanization and Child Welfare:
- By the 2050s, nearly 60% of children globally will live in urban areas, up from 44% in the 2000s.
- Ensuring healthier and more secure urban environments is critical for improving future childhoods.
- Over 95% of people in high-income countries are connected to the internet, compared to just 26% in low-income countries, exacerbating inequalities.
Key Takeaways:
- Children are facing a more hazardous environment than ever before, influenced by climate change, technological developments, and demographic shifts.
- Proactive measures are needed to mitigate environmental risks, promote digital inclusion, and ensure equitable access to resources and opportunities for children globally.
High-Altitude Sickness

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
In September, a trekker from Idukki, Kerala, died in Uttarakhand while attempting to scale Garur Peak due to respiratory failure. Every year, numerous tourists like this succumb to the effects of high-altitude sickness in the pristine but challenging inner Himalayas. These regions present hidden dangers due to their extreme altitudes, where thinner air and reduced oxygen can lead to potentially fatal conditions.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
- Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) occurs when the body struggles to acclimatize to high altitudes, typically above 8,000 feet (2,400 meters), where oxygen levels are lower.
- As altitude increases, oxygen levels decrease, leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). Early symptoms include:Headache, Nausea, Fatigue&Shortness of breath
- If untreated, AMS can develop into:
- High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE): Fluid accumulation in the lungs, leading to severe breathing problems.
- High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE): Fluid in the brain causing confusion, hallucinations, or coma.
- Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate descent to lower altitudes.
Infrastructural Issues
- Many Himalayan regions lack adequate healthcare facilities beyond major towns like Shimla.
- Leh is an exception, with specialized facilities for high-altitude ailments, but most areas lack preventive health measures.
- Implementing health screenings at entry points to high-altitude zones (like Kinnaur or Lahaul-Spiti) could significantly improve prevention and response to AMS.
Mandatory Registration System for Tourists
- Tourist Registration: A system where tourists must register before entering remote mountain areas would allow authorities to monitor movements and provide timely medical assistance.
- Benefits:
- Quick emergency responses by having data on tourists' locations.
- Research support: Tracking demographic patterns and risk factors to better understand how altitude impacts different populations.
Early Intervention for High-Altitude Sickness
- Gradual Ascent: To allow the body to acclimatize, gradual ascent is crucial. Every 3-4 days, take a rest day and avoid increasing sleeping altitude by more than 500 meters/day.
- Medications: Doctors recommend:
- Acetazolamide to promote better oxygenation.
- Dexamethasone for reducing inflammation in severe cases.
- For those with a history of HAPE, Nifedipine may be used preventively.
- However, no medication guarantees immunity from AMS. Travelers with pre-existing conditions should consult a doctor before traveling.
Treatment Strategies
- Descent: The best treatment for AMS is to descend to lower altitudes (300-1,000 meters), where symptoms improve rapidly.
- Additional Measures: If available, supplemental oxygen or a portable hyperbaric chamber can help in emergencies.
- Medications like acetazolamide and dexamethasone can provide short-term relief but are not substitutes for descent.
Policy Recommendations
- Medical Infrastructure: Establish state-of-the-art medical facilities in high-altitude regions of the Himalayas.
- Research: Set up research centers to study high-altitude illnesses.
- Air-ambulance Services: Equip states with air-ambulance services for rapid medical evacuation in emergencies.
- Health and Safety Information: Provide accessible information on government websites and at check-in points to educate tourists on preventing and managing AMS.
Preventive Measures Before Scaling the Himalayas
- Acclimatization: Gradual ascent is essential for preventing AMS.
- Health Checks: Get a medical check-up to assess risk factors before travel.
- Medications: Consult a doctor for potential preventive medications.
- Hydration and Rest: Stay hydrated and take ample rest during the ascent.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be aware of early symptoms like headaches or nausea and stop ascending if they occur.
By addressing these measures, the risks associated with high-altitude sickness can be mitigated, improving safety for tourists and trekkers in the Himalayas.
Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
PM Modi receives Nigeria’s second-highest national award.
Key Events and Achievements
- Award Conferred:
- Award Name: Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger (GCON).
- Significance: Nigeria’s second-highest national award, conferred on Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Historical Context: Modi becomes the second foreign dignitary to receive this award, after Queen Elizabeth in 1969.
Strategic and Developmental Ties Between India and Nigeria
- First Visit in 17 Years: Modi’s visit is the first by an Indian PM to Nigeria in 17 years, underscoring the significance of strengthening bilateral ties.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Over 200 Indian companies have invested around $27 billion in Nigeria across key sectors, making India a major economic partner.
- India has provided $100 million in development assistance through concessional loans and is actively involved in capacity-building training programs in Nigeria.
- MoUs Signed:
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Cultural Exchange.
- Customs Cooperation.
- Survey Cooperation.
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Relief Aid: Modi announced the dispatch of 20 tonnes of relief supplies to help Nigeria recover from the devastating floods that affected the country last month.
Diplomatic Discussions and Initiatives
- Strategic Partnership: Modi described the India-Nigeria partnership as one with immense potential in sectors like defence, energy, technology, trade, health, and education.
- Indian Expatriate Community: Modi acknowledged the 60,000-strong Indian diaspora in Nigeria, recognizing their role as a pillar of bilateral ties.
- Support for Africa:
- Modi highlighted India’s support for the African Union’s membership in the G20, an outcome of the India-hosted G20 summit in 2023.
- Nigeria’s Role: He noted Nigeria’s positive influence on Africa and its importance as a key partner in India’s Africa engagement.
Broader Implications for International Relations
- India-Nigeria Security Cooperation:
- The National Security Advisors (NSA) of India and Nigeria held in-depth discussions on counter-terrorism, extremism, and cybersecurity challenges.
- India and Nigeria are committed to jointly addressing global threats such as arms smuggling and international crime.
- India's Role as a Development Partner:
- India’s growing role as a development partner for African nations is becoming increasingly important, exemplified by Nigeria’s close ties with India.
- Global Diplomacy and Soft Power:
- Modi’s award and visit reflect India’s growing influence in Africa and its emphasis on fostering ties with resource-rich and strategically located nations like Nigeria.
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger is also a reflection of the soft power India is wielding globally.
Key Facts about Nigeria:
- Location: Nigeria is located in West Africa, bordering Niger, Chad, Cameroon, and Benin, with access to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Significance:
- Known as the “Giant of Africa” due to its large population and economic power.
- It has the largest economy in Africa, largely driven by its oil reserves.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV)

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
As Delhi’s AQI worsened, the Commission for Air Quality Management issued the order to activate Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan.
Restrictions Under GRAP-IV in Delhi-NCR
- Truck Movement:
- Banned except for essential goods and trucks using clean fuels (LNG, CNG, BS-VI diesel, or electric).
- Non-essential light commercial vehicles registered outside Delhi are also banned unless they are CNG or BS-VI diesel or electric vehicles (EVs).
- Delhi-registered BS-IV or older diesel vehicles (medium and heavy goods vehicles) are banned, except for those in essential services.
- Construction Activities:Suspension of all construction work, including public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power lines, pipelines, etc.
- Schools and Work:
- Online classes for students of Classes 6 to 9 and Class 11.
- Work from home (WFH) recommendations for 50% office capacity in NCR.
- Central government employees may also be asked to work from home.
- Offline classes for Classes 10 and 12 continue, but schools for other classes must shift to online mode.
- Other Measures:
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
- Closure of colleges.
- Odd-even vehicle scheme.
- Restrictions on non-essential commercial activities.
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
About GRAP (Graded Response Action Plan)
- Purpose: A plan to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region based on AQI levels.
- Approved By: Supreme Court in 2016 (M.C. Mehta v. Union of India).
- Notified by MoEFCC: 2017.
- Implementation Authority: CAQM (Commission for Air Quality Management).
Stages of GRAP
GRAP is an incremental system, with measures activated as air quality deteriorates:
- Stage 1: Poor AQI (201-300) – Basic pollution control measures.
- Stage 2: Very Poor AQI (301-400) – Enhanced measures.
- Stage 3: Severe AQI (401-450) – Stricter actions like shutting down industries.
- Stage 4: Severe Plus AQI (Above 450) – Most stringent restrictions, as activated on November 18, 2024.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Introduced: 2014, by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Categories:
- Good: 0-50
- Satisfactory: 51-100
- Moderately Polluted: 101-200
- Poor: 201-300
- Very Poor: 301-400
- Severe: 401-450
- Severe Plus: 451 and above (current status in Delhi).
- Pollutants Considered: PM10, PM2.5, NO?, SO?, CO, O?, NH?, and Pb.
- Measurement: 24-hour average values for PMs, and 8-hour averages for CO and O?.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Established: Under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) Act, 2021.
- Mandate: To coordinate, research, and manage air quality issues in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Composition: Includes government officials, technical experts, and NGO representatives.
- Jurisdiction: Covers Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh has been officially notified as India's 56th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country's conservation efforts. Here's an overview of this new reserve:
Key Details:
- Location: The tiger reserve is located across the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Korea, Surajpur, and Balrampur districts of Chhattisgarh.
- Area: The reserve spans 2,829.38 square kilometers and includes both core and buffer zones.
- Core/critical habitat: 2,049.2 sq. km (includes the Guru Ghasidas National Park and TamorPingla Wildlife Sanctuary).
- Buffer zone: 780.15 sq. km.
- Rank: It is the third largest tiger reserve in India, after the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (Andhra Pradesh) and Manas Tiger Reserve (Assam).
Connectivity:
The reserve forms part of a landscape complex that extends over nearly 4,500 sq. km and is interconnected with other major tiger reserves:
- Sanjay Dubri Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the north.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the west.
- Palamau Tiger Reserve (Jharkhand) to the east.
This connectivity supports greater wildlife movement, reducing the risk of inbreeding and strengthening the overall conservation efforts for the tiger population.
Biodiversity:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve is ecologically rich, harboring a wide array of species:
- 753 species have been documented, including:
- 230 bird species.
- 55 mammal species, including several threatened species such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and wolves.
- A variety of invertebrates, especially insects.
- The reserve's terrain includes dense forests, streams, rivers, and varied elevations, making it an ideal habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
Ecological Importance:
- Situated in the Chota Nagpur and Baghelkhand plateaus, the reserve has varied landscapes that contribute to its ecological diversity. The region's tropical climate and dense forests make it a critical habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- The reserve's core area forms an important critical tiger habitat, providing a sanctuary for tigers to thrive with minimal human disturbance.
Conservation Impact:
With the addition of this tiger reserve, Chhattisgarh now boasts four tiger reserves, complementing the existing Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati reserves. This bolsters the state's and the country's ongoing efforts to protect and conserve tigers, which are a keystone species in maintaining ecological balance.
Procedural Steps for Notification:
- Identification: The state government identifies a significant ecological area with potential for tiger conservation.
- NTCA Approval: After a thorough assessment, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) evaluates and approves the proposal.
- State Notification: The state government officially notifies the area as a tiger reserve under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- Implementation: The state, with NTCA support, begins implementing conservation and management strategies.
Unified Complex Radio Antenna
- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- India and Japan recently signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) to co-develop the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for deployment on Indian Navy ships. This pact marks a significant milestone as it is India's first military technology transfer agreement with Japan.
- The deal follows a 2015 agreement on the transfer of defense equipment and technology, further strengthening defense ties between the two countries.
- The UNICORN mast is a cutting-edge communication and radar system designed to enhance the stealth characteristics of naval vessels. This agreement is seen as an important step towards deepening India-Japan defense cooperation.
What is UNICORN?
The UNICORN mast is an advanced, integrated antenna system that combines several communication and radar components into a single conical structure or radome (a radar-absorbing dome). It is designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of ships, improving their stealth capabilities.
Key features of the UNICORN mast include:
- Integration of multiple antennas: It consolidates various antennas used for tactical data links, communications, and navigation systems (e.g., TACAN - Tactical Air Navigation System).
- Stealth enhancement: By reducing the number of exposed components and consolidating them into a single radome, the mast significantly lowers the ship’s radar signature, making it harder to detect.
- Improved performance: The mast design minimizes mutual interference between antennas, enhances maintainability, and increases lightning resistance.
- Space efficiency: It saves valuable below-deck space and reduces ship-building time by integrating multiple systems into one mast.
The UNICORN system is currently deployed on Mogami-class frigates of the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force.
India-Japan Defense Cooperation
- 2015 Defense Technology Transfer Agreement: This pact established a framework for defense cooperation between India and Japan, paving the way for joint projects like the UNICORN mast.
- Bilateral Military Exercises:
- Veer Guardian 2023: A bilateral exercise conducted between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), which deepened defense interoperability between the two nations.
- Tarang Shakti 2024: The first multilateral air exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force, with Japanese fighter aircraft participating.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Development: Japan has also provided financial aid for infrastructure development in India’s strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands, contributing to enhancing India’s maritime security in the region.
Red-Headed Vulture

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Red-Headed Vulture, a critically endangered species, has been sighted for the first time in Kasaragod, Kerala, marking an important addition to the region’s avian biodiversity. This rare sighting occurred at Manhampothikunnu near Mavungal. Prior to this, the species was predominantly seen in the Wayanad region of Kerala.
- This discovery brings the total number of bird species recorded in Kasaragod to 407, showcasing the district's growing avian diversity.
About the Red-Headed Vulture:
- The Red-Headed Vulture (also known as the Asian King Vulture or Pondicherry Vulture) is one of the rarest and most critically endangered species of vultures in India. It is known for its distinctive scarlet red head and black body with a white patch on the abdomen.
- Physical Features: The bird is medium-sized, weighing around 5 kg, with a wingspan of up to 2.5 meters and a length of 80 cm. It is typically solitary, often found alone or with a mate.
- Distribution: Historically found in Central India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, the Red-Headed Vulture’s numbers have drastically declined in recent decades.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: The Red-Headed Vulture is classified as Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: It is listed under Schedule 1, offering it the highest level of legal protection.
- CITES: The species is also listed in Appendix II, indicating that it requires international conservation efforts to prevent it from becoming endangered.
Threats to Vultures:
- Diclofenac Poisoning: The significant decline in vulture populations in India, including the Red-Headed Vulture, is primarily due to the widespread use of diclofenac (a veterinary drug) to treat livestock. When vultures consume the carcasses of treated animals, they ingest the toxic drug, leading to kidney failure and death.
- Other threats include pesticide contamination, lead poisoning, habitat loss, and collisions with man-made structures like power lines and wind turbines.
Conservation Efforts in India:
- India has undertaken various efforts to protect vultures, including banning diclofenac in 2006 and expanding the ban to other harmful drugs like ketoprofen and aceclofenac in 2023.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres (VCBCs): These centers are focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs for vultures, helping to increase their populations. The Jatayu Conservation and Breeding Centre in Uttar Pradesh is one of the latest initiatives, set up to protect and rehabilitate vultures.
- Vulture Safe Zones have been created across India, providing safe habitats for vulture species to recover.
- Vulture Restaurant Initiative: In some regions, safe feeding centers (such as in Jharkhand) have been established, where vultures are provided uncontaminated carcasses, reducing their exposure to toxic substances.
- Legal Protection: Several species of vultures, including the Red-Headed Vulture, are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring stringent legal measures against poaching and habitat destruction.
Global Conservation Efforts:
- India’s vulture conservation initiatives are part of a broader international effort under the SAVE (Saving Asia’s Vultures from Extinction) programme, which involves multiple regional and global organizations working to protect vulture species in South Asia.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
Europe’s Digital Euro

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The digital euro, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) being developed by the European Central Bank (ECB), aims to revolutionize Europe’s digital payment landscape. However, while the ECB has marketed it as a convenient, free, anonymous, and reliable alternative to existing cashless options like credit cards and mobile payment apps, the true purpose of the digital euro goes beyond these simplified claims.
Key Aspects of the Digital Euro
- Direct Issuance by the ECB: Unlike traditional digital payments that rely on intermediaries like banks or payment service providers, the digital euro is issued directly by the European Central Bank. This allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for third-party banks or payment gateways. It can be used for offline transactions, which is a major technical innovation that sets it apart from other digital currencies.
- A Digital Version of Cash: The digital euro is essentially a digital version of legal tender (cash), providing an alternative to cash in a world increasingly dominated by digital payments. Its key feature is direct payment between users, bypassing the traditional banking system. It aims to offer the same advantages as cash, such as anonymity, but with the convenience of digital transactions.
- Cost Reduction and Micro-Payments: The digital euro promises to lower transaction costs, especially for micro-payments that are currently prohibitively expensive using conventional bank transfers or digital services like PayPal. This cost efficiency is intended to enable new business models by lowering the friction in digital transactions, thus encouraging innovation in commerce.
The ECB’s Claims vs. the Real Motivation
While the ECB portrays the digital euro as a means to make payments easier, faster, and more secure, there is an underlying political and economic agenda that goes beyond improving consumer convenience.
- Sovereignty and Competition: One of the main drivers behind the digital euro is Europe’s desire to assert its digital sovereignty. The ECB positions the digital euro as a tool to strengthen the euro’s competitiveness against non-European payment providers, particularly those from the United States like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. The EU is concerned that foreign companies may dominate the digital payment landscape, thereby reducing Europe's ability to control its own financial systems.
- This is a defensive measure to protect European financial interests. By creating a state-backed alternative to privately controlled digital payment systems, the EU aims to ensure that Europe does not become reliant on foreign corporations for essential services.
- Not About Citizens’ Convenience Alone: While the ECB frames the digital euro as a user-friendly solution for consumers, the real concern is about the control over digital currency. The digital euro offers a more centralized alternative compared to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The ECB aims to harness the power of the state in regulating and controlling digital transactions, thus consolidating private property and ensuring the smooth functioning of Europe’s monetary policies.
- A Tool for Strengthening the Euro: The digital euro is also seen as part of Europe’s broader ambition to establish the euro as a dominant global currency. As the first fully-regulated digital currency issued by a central bank, it could position the euro to compete against other digital currencies, including the digital yuan or the U.S. dollar. The EU sees the digital euro as a way to expand its geopolitical influence by promoting its own currency as a global standard for digital payments.
Commemoration of Birsa Munda’s 150th Birth Anniversary

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
On November 15, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a commemorative stamp and coin to mark the 150th birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, a prominent tribal freedom fighter and leader from Jharkhand.
Key Points about Birsa Munda:
- Iconic Tribal Leader: Birsa Munda, born in 1875, is often referred to as ‘Bhagwan’ (God) and ‘DhartiAaba’ (Father of the Earth) by the tribal communities. He is celebrated for his leadership in the fight against the exploitation of tribal people by both the British and non-tribal settlers.
- Ulgulan Movement: Birsa Munda led the Ulgulan (Great Tumult) against the alienation of land, forced labour, and the illegal appropriation of tribal land in the Chotanagpur Plateau. His efforts were critical in mobilizing tribal communities and challenging the colonial order.
- Religious and Social Reformer: He founded the Birsait faith, focusing on spiritual practices that emphasized prayer, worship of God, and abstaining from alcohol, fostering unity and resilience among tribal communities.
- Death and Legacy: Birsa Munda died in 1900 in British custody at the young age of 25. Despite his early death, his legacy lives on as a symbol of tribal pride and resistance.
- Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas: Since 2021, the Government of India observes November 15 as Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (Tribal Pride Day) in honor of Birsa Munda's birth anniversary, recognizing the contributions of tribal communities and their role in India's history.
- Highlights of the 2024 Commemoration:
- Commemorative Stamp and Coin: To mark the 150th birth anniversary, the Prime Minister unveiled a commemorative stamp and coin in Bihar's Jamui district. This serves as a tribute to Munda's sacrifices for the country.
- Year-Long Celebrations: The 2024 event marks the beginning of year-long celebrations to commemorate Birsa Munda’s legacy, with a focus on tribal welfare and recognition of their historical contributions.
- Welfare Projects and Initiatives:
- Prime Minister Modi inaugurated and laid the foundation for tribal welfare projects worth over ?6,640 crore.
- The PM launched two tribal freedom fighter museums and tribal research institutes.
- 1.16 lakh homes were sanctioned under the Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Yojana.
- 25,000 homes for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) were approved under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) scheme.
- The launch of 50 mobile medical units aims to improve healthcare access in tribal regions.
- 10 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) were inaugurated to promote education for tribal students.
- DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan:
- The DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan aims to address gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood in tribal-majority villages.
- The initiative is being implemented across 63,000 villages with the involvement of 17 ministries and departments.
- PM-JANMAN Scheme for PVTGs:
- Launched in November 2023, the PM-JANMAN initiative aims to uplift Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) through various interventions like safe housing, clean drinking water, healthcare, education, and sustainable livelihoods. The scheme also supports Van Dhan Vikas Kendras for the trade of forest produce and solar-powered systems for households in tribal areas.
World Diabetes Day 2024
- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14th each year to raise awareness about diabetes, its prevention, and management.
- It was created by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Significance: Commemorates the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered insulin in 1922 alongside Charles Best.
- Theme (2024): "Access to Diabetes Care: Empowering Better Health for All".
History:
- Established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and World Health Organization (WHO).
- Recognized as a global observance by the UN in 2006.
- Activities: Awareness campaigns, health check-ups, educational seminars, and lighting of Blue Circle Monuments worldwide as a symbol of unity in the fight against diabetes.
Global Diabetes Data (2022):
- Total Diabetic Adults: 828 million globally.
- India's Share: 212 million (approximately 25% of global cases).
- Other Countries:
-
- China: 148 million.
- USA: 42 million.
- Pakistan: 36 million.
- Indonesia: 25 million.
- Brazil: 22 million.
Risk Factors for Diabetes:
- Global Factors: Obesity and poor diets are key contributors.
- India-Specific Factors: Dietary habits, lack of exercise, and socio-economic disparities contribute significantly to the high prevalence.
Untreated Cases:
- Global untreated cases (2022): 445 million (59% of diabetics globally).
- India untreated cases (2022): 133 million (64 million men, 69 million women).
- Complications: Untreated diabetes leads to severe health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
Types of Diabetes:
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most common type of diabetes, characterized by issues with insulin production or its efficient use.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
- Autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Primarily affects children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
- Insulin resistance combined with reduced insulin production.
- Often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and physical inactivity.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Occurs in pregnant women, leading to high blood sugar.
- Typically resolves after childbirth.
- Diabetes Insipidus:
- Imbalance of water regulation due to inadequate secretion or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- Leads to excessive urination and dehydration.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination.
- Excessive thirst and hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Blurred vision.
- Fatigue.
- Slow-healing wounds.
Role of Insulin in Managing Diabetes:
- Function of Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells.
- In Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin injections or pumps are essential for survival.
- In Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin or oral medications may be prescribed alongside lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
Government Initiatives in India:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Focuses on awareness, early diagnosis, and management of diabetes.
- National Health Policy (2017): Aims to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases by 25% by 2025.
- Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres: Provides free screenings and consultations for diabetes and other non-communicable diseases.
- Eat Right Movement: Promotes healthier dietary habits to combat obesity and reduce diabetes risks.
- School Health Programs: Aims to educate children on healthy lifestyles to prevent the early onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Decline in African Elephant Population

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The population of African elephants has been declining rapidly, with data showing alarming drops across the African continent.
- Survey Period: The study covers population data from 475 sites in 37 countries over 52 years (1964-2016).
- Population Decrease:
- Savannah Elephants: A 70% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Forest Elephants: A 90% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Overall Impact: The study indicates a 77% average decline in elephant populations across both species.
Main Drivers of Decline
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for ivory and other body parts remains a major threat.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and climate change are encroaching on the elephant’s natural habitats.
- Human-Elephant Conflict: Increased human settlements near elephant habitats lead to conflicts, further endangering elephant populations.
Species Overview
- Two Subspecies:
- Savannah Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Larger and more common, found in open savannas.
- Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Smaller and more elusive, found in dense rainforests.
- Conservation Status:
- Savannah Elephant: Endangered (IUCN).
- Forest Elephant: Critically Endangered (IUCN).
- CITES Listing: Both species are listed under CITES Appendix I, which bans international trade in endangered species.
Regional Impact
- Northern and Eastern Africa: These regions have seen drastic declines, particularly in the Sahel (Mali, Chad, Nigeria), where elephants have been extirpated (locally extinct) due to poaching and insufficient protection.
- Southern Africa: Positive Growth in some areas, particularly in Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia, where elephant populations are growing due to strong conservation efforts.
Conservation Success
- Southern Africa: 42% of the surveyed sites showed increasing elephant populations, a testament to successful conservation strategies.
- Government and NGO Efforts: Successful population growth is often attributed to active management, including anti-poaching laws, protected areas, and conservation funding.
Elephant Behavior and Reproduction
- Social Structure: Elephants live in family units led by mature females, with strong social bonds.
- Low Sleep Time: Elephants sleep only 2 hours per day on average.
- Reproduction: They have a long gestation period of up to 2 years, and calves are cared for by mothers and allomothers (non-mother females).
Conservation Challenges
- Sustainability: Continued poaching and habitat destruction threaten to undo gains made in conservation.
- Fragmentation of Populations: With many elephants in isolated pockets, genetic diversity is declining, which could lead to long-term problems for species survival.
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF)

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund to launch ‘Nehru Archive’ next year.
Nehru Archive Initiative
- Launch Date: The Nehru Archive will go online on November 14, 2025, coinciding with Jawaharlal Nehru's birth anniversary.
- Purpose: The archive will showcase less-known published and unpublished works of India’s first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, including his speeches, letters to Chief Ministers, and other writings.
Archive Content
- Key Features:
- 100 volumes of The Selected Works of Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Letters to Chief Ministers (1947-1964), documenting Nehru's communication with state leadership.
- Nehru’s iconic books like:
-
-
- The Discovery of India
- Glimpses of World History
- Letters from a Father to His Daughter
- An Autobiography
- The Unity of India
- A Bunch of Old Letters
-
-
- Speeches from 1917 to 1964.
- Writings on Nehru by his contemporaries.
- Global archival material from international sources.
- Objective: The goal is to provide dynamic, continuously updated, open-ended access to Nehru’s work, making it the most important research source on Nehru.
Significance
- Educational and Intellectual Contribution: The archive will serve as a comprehensive, accessible source of information for students, scholars, and the general public to understand Nehru’s contributions to the making of modern India.
- Preservation of Legacy: It will preserve and promote Nehru’s intellectual legacy and his vision for India's development post-independence.
- Historical Importance: The archive will help contextualize Nehru’s leadership during critical periods of Indian history, including India’s independence, partition, and post-independence challenges.
Governance and Establishment of JNMF
- Founded: The Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF) was established in 1964 through a Deed of Declaration of Trust following a National Committee chaired by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, then President of India.
- Purpose: To preserve and promote Nehru's legacy, especially his role in shaping modern India.
- Governance: The JNMF is governed by 14 trustees and is currently headed by Sonia Gandhi, the Chairperson of the Congress Parliamentary Party.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
Accessibility for Disabled Persons

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India delivered a significant ruling affirming that the right of persons with disabilities (PwDs) to access environments, services, and opportunities is a fundamental human right. The judgment was made in the case of RajiveRaturi vs. Union of India &Ors. and is based on a report submitted by the Centre for Disability Studies (CDS) at NALSAR University of Law.
Key Points of the Judgment:
- Social Model of Disability:
- The Court upheld the social model of disability, which focuses on societal changes to ensure the full inclusion and participation of PwDs.
- The model emphasizes removing social barriers and creating an inclusive environment that accommodates all disabilities.
- Challenges Faced by PwDs: The ruling highlighted various challenges faced by PwDs, as identified in the CDS NALSAR report:
- Accessibility Barriers: Significant gaps exist in accessibility measures across public spaces such as courts, prisons, schools, and public transport.
- Intersectionality & Compounded Discrimination: PwDs often face multiple layers of discrimination, such as caste, gender, and socio-economic status, which compound their marginalization.
- Inconsistent Legal Framework: The RPwD Act (2016) mandates mandatory compliance for accessibility standards, but Rule 15 under RPwD Rules (2017) only offers self-regulatory guidelines, which the Court found insufficient.
- Court's Analysis of Rule 15:
- The Court declared Rule 15(1) of the RPwD Rules, 2017, as ultra vires, meaning it is inconsistent with the mandatory compliance intended by the RPwD Act.
- The Court stressed the need for stronger legal and regulatory enforcement to ensure access for PwDs.
- Principles of Accessibility: The Court outlined several essential principles for achieving accessibility:
- Universal Design: Environments and services should be universally accessible to all, including PwDs.
- Comprehensive Inclusion: All types of disabilities, both visible and invisible, should be addressed.
- Assistive Technology Integration: Using technology to support PwDs in daily activities.
- Stakeholder Consultation: PwDs and disability advocacy groups must be consulted in planning and designing accessible spaces.
- Two-Pronged Approach:
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
- Ensure accessibility in existing infrastructure: Modify and update current institutions and services to become accessible.
- Design future infrastructure with accessibility in mind: Plan and build new spaces and services that are inclusive from the start.
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
Legal and Policy Framework:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016:
- The RPwD Act mandates various accessibility standards and provisions to protect and promote the rights of PwDs, in alignment with India’s obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- The Act defines a person with a benchmark disability as someone with at least 40% of a specified disability.
- International Obligations:
- The ruling reaffirmed the importance of Article 9 of the UNCRPD, which emphasizes the right of PwDs to access the physical environment, transport, and information and communication technologies.
- Government Initiatives: The judgment highlights several initiatives aimed at improving accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): A nationwide effort to make public spaces and services accessible to PwDs.
- Assistance for Aids and Appliances: Government schemes to provide PwDs with necessary aids and appliances.
- Unique Disability Identification Portal: A platform for PwDs to register and obtain a disability certificate.
Notable Judicial Precedents:
The Court referred to several previous rulings that recognized the right to accessibility:
- State of Himachal Pradesh v. Umed Ram Sharma (1986): The Court included the right to accessibility under the Right to Life (Article 21) of the Constitution.
- Disabled Rights Group v. Union of India (2017): The Court directed that educational institutions ensure reserved seats for PwDs.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
Global Education Monitoring Report 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Released at the Global Education Meeting, hosted in Fortaleza by Brazil, the G20 President.
- Highlights progress and challenges in global education, with a focus on leadership, financing, and access.
Key Observations:
Leaders as Agents of Change:
- Education leadership is defined as social influence towards achieving common educational goals.
- Education leaders must:
- Define clear purposes and influence change.
- Balance learning outcomes with equity, quality, and inclusion.
Funding Deficits:
- 4 out of 10 countries spend less than 4% of their GDP on education.
Out-of-School Children:
- 251 million children and youth globally remain out of school, with only a 1% reduction since 2015.
Regional Disparities in Education Access:
- Central and Southern Asia show significant progress, but countries like Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan still have large out-of-school populations.
Recommendations:
- Leadership Development: Empower school principals with the autonomy to manage schools effectively.
- Capacity Building for System Leaders: Strengthen the ability of education officials to act as system leaders.
- Climate Change Education: Introduce climate change topics in early education across subjects, not limited to science.
India’s Educational Initiatives:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on developing school leadership through training and workshops for principals.
- NISHTHA Program: Aims to improve leadership and management competencies of school heads and teachers.
Current Educational Landscape:
- Since 2015, 110 million children have entered school, and 40 million more complete secondary education.
- However, 33% of children in low-income countries remain out of school, compared to only 3% in high-income countries.
- Sub-Saharan Africa houses more than half of the global out-of-school youth.
Challenges in Education Financing:
- UNESCO–World Bank report highlights that 40% of countries allocate less than 15% of their public expenditure to education.
- Countries investing less than 4% of GDP in education face significant resource shortages.
- Low-income countries spend an average of $55 per learner, while high-income countries spend $8,543 per learner.
Need for Innovative Financing Mechanisms:
- Debt-for-Education Swaps: Proposes converting unsustainable debt into funding for education, leveraging past successful initiatives.
- Multilateral Platforms: Suggested to facilitate global negotiations for converting debt into educational investments, involving entities like UNESCO and the G20.
International Cooperation and Solidarity:
- Decline in Education Assistance: Official development assistance for education has decreased from 9.3% in 2019 to 7.6% in 2022.
- Strengthening Partnerships: The need for enhanced global cooperation to fill the educational financing gap and ensure equitable access to quality education.
PM-Vidyalaxmi Scheme
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the PM Vidyalaxmi scheme to provide financial assistance to meritorious students for higher education.
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder students from pursuing quality higher education.
Key Features of the scheme:
- Eligibility:
- Students admitted to top 860 Quality Higher Education Institutions (QHEIs) are eligible.
- Includes both government and private institutions, as per the NIRF (National Institutional Ranking Framework) rankings.
- Loan Provision:
- Collateral-free and guarantor-free education loans for tuition fees and other course-related expenses.
- Loans up to ?7.5 lakhs will have a 75% credit guarantee from the government to encourage banks to offer loans.
- Interest Subvention:
- For students with an annual family income of up to ?8 lakhs (and not eligible for other scholarships or schemes), a 3% interest subvention will be provided on loans up to ?10 lakhs.
- This subvention applies during the moratorium period (when repayment is deferred).
- Preference for interest subvention is given to students in technical/professional courses and those from government institutions.
- Target Beneficiaries:
- Around 22 lakh students are expected to benefit from the scheme annually.
- The government has allocated ?3,600 crore for the period 2024-2025 to 2030-2031, with 7 lakh fresh students anticipated to receive the benefit each year.
- Digital Process:
- A unified “PM-Vidyalaxmi” portal will allow students to apply for loans and interest subvention in a simplified, transparent, and digital manner.
- Payment Method:
- Interest subvention will be paid via E-vouchers or Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) wallets.
Loan Product Features
- Collateral-free & Guarantor-free: Loans will be accessible without the need for collateral or a guarantor.
- Loan Coverage:
- The scheme will cover full tuition fees and other related expenses.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Students enrolled in NIRF top 100 HEIs, state institutions ranked 101-200, and central government institutions are eligible.
- The list of eligible institutions will be updated annually based on the latest NIRF rankings.
Government's Commitment
- The scheme is a part of the National Education Policy 2020’s vision to enhance access to quality education through financial support.
- Additional Support:
- It complements the existing Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS) and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Education Loans (CGFSEL) under PM-USP.
- The CSIS scheme provides full interest subvention for students with an annual family income of up to ?4.5 lakhs, pursuing technical/professional courses.
India-Algeria Strengthen Defence Ties

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of India recently visited Algeria, culminating in the signing of a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defence cooperation.
- Objective: The MoU aims to strengthen the strategic and military ties between India and Algeria.
Recent Developments in India-Algeria Relations
- Important Visit: The CDS’s visit coincided with Algeria’s 70th anniversary of its revolution, celebrated on November 1st, with military parades and ceremonies highlighting Algeria’s historical and political legacy.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India re-established its defence wing in Algeria, and Algeria reciprocated by considering the establishment of its defence wing in India.
- India emphasized its role as a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner) and offered to share defence expertise and experiences with Algeria.
- Strategic Discussion: The MoU aims to enhance mutual understanding, laying the foundation for long-term defence collaboration across multiple sectors, including manufacturing under India’s 'Make in India' and 'Make for the World' initiatives.
- Global Peace Support: CDS reiterated India’s commitment to peaceful conflict resolution and expressed support for Algeria’s defence interests.
Significant Areas of India-Algeria Relationship
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India and Algeria established diplomatic ties in July 1962, the same year Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule.
- India supported Algeria's liberation movement and both countries have maintained close ties as part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade peaked at USD 2.9 billion in 2018 but dropped to USD 1.5 billion by 2021 due to COVID-19 and Algeria’s import restrictions.
- Trade rebounded in 2022, increasing by 24% to USD 2.1 billion.
- Exports from India (2023-24): Rice, pharmaceuticals, granite.
- Imports from Algeria: Petroleum oils, LNG, calcium phosphates.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- 2015 MoU: Between All India Radio (AIR) and Algerian National Radio for cooperation in broadcasting.
- 2018 Space Cooperation Agreement: Focuses on satellite technology for applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Visa Waiver Agreement (2021): Diplomatic and official passport holders are exempt from visa requirements.
- Cultural Engagement:
- International Day of Yoga (2024): Celebrated in Algeria at the Jardin d’Essai du Hamma, attracting over 300 participants.
- Space Cooperation:
- The 2018 India-Algeria Space Cooperation Agreement focuses on joint space science, technology, and applications.
- India has launched four Algerian satellites (2016), and the 2022 Joint Committee Meeting expanded satellite capacity building efforts.
- Algeria’s space agency has engaged with ISRO on satellite applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Indian Community in Algeria:
- Approximately 3,800 Indians live in Algeria, working in various sectors, including technical and semi-skilled roles.
- The community includes 13 Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), 10 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and 15 Indian students.
LignoSat
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
The world's first wooden satellite, LignoSat, is set to launch from the Kennedy Space Center aboard a SpaceX rocket. This pioneering satellite is a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry Co., marking a significant step towards exploring more sustainable materials in space exploration.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:The primary goal of LignoSat is to test the viability of using wood in space technology, with a focus on the eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness of using renewable materials in satellite construction. The satellite will be tested aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assess its durability, strength, and ability to withstand extreme space conditions.
- Material:The satellite is crafted from magnolia wood, chosen for its durability and adaptability. Magnolia was selected for its strength, making it a suitable candidate to endure the harsh conditions of space travel and the intense environmental factors faced in space exploration.
- Mission Details:Once launched, LignoSat will be sent to the ISS, where it will be released from the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo). Researchers will collect data on the satellite’s performance, examining its ability to handle the challenges of space, including temperature fluctuations and physical strain.
- Environmental Benefits:One of the key advantages of wooden satellites is their environmental impact. Traditional metal satellites, when re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, can generate metal particles that contribute to air pollution. In contrast, wooden satellites like LignoSat are designed to be eco-friendly during reentry. Wood is a natural material that burns up more cleanly during reentry, reducing the potential for harmful atmospheric pollution.
Tumaini Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Tumaini Festival is held annually in the Dzaleka Refugee Camp in Malawi, one of the world’s few music festivals hosted within a refugee camp. It brings together refugees and locals for cultural exchange, showcasing music, art, and crafts.
- Dates: The festival runs from Thursday to Saturday each year, typically in November.
- Founded: In 2014 by Congolese poet Menes La Plume.
Festival Highlights:
- The festival features performances from a diverse range of artists, including refugees and local Malawians, as well as artists from South Africa, Zimbabwe, and beyond.
- In 2024, performances included Jetu, a 72-year-old singer, and Vankson Boy V, a Congolese refugee, alongside other acts like Maveriq Mavo from South Africa.
- The festival aims to:
- Celebrate cultural exchange and community solidarity between refugees and locals.
- Humanize the refugee experience by allowing refugees and locals to share common experiences and celebrate cultural diversity.
- Challenge stereotypes by showing refugees as people with the same aspirations, talents, and desires as locals.
Significance of Dzaleka Refugee Camp:
- Location: Situated near Lilongwe, Malawi, Dzaleka was originally a prison before becoming a refugee camp in 1994.
- Capacity: Initially designed for 10,000 refugees, the camp now hosts over 60,000 individuals from countries like Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- Role: Dzaleka has evolved into a hub for humanitarian aid, cultural exchange, and empowerment of its residents.
First Science Result from India's Aditya-L1 Mission

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Aditya-L1 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 2, 2023, is India's first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Primary Payload: The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru, is the spacecraft's main instrument.
Key Highlights:
- First Science Outcome:The first scientific result from the mission, involving VELC, has been released. It successfully estimated the onset time of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred on July 16, 2023.
- CMEs are massive solar eruptions that can disrupt electronics in satellites and communications on Earth.
- Key Findings:
- VELC's Role: The VELC payload was crucial in observing the CME close to the solar surface, providing a detailed understanding of its onset.
- CMEs are typically observed in visible light after they have traveled far from the Sun. However, VELC’s unique spectroscopic observations allowed scientists to study the CME much closer to the Sun's surface.
- Publication:The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Future Significance:
- As the Sun approaches the maximum phase of its current solar cycle (No. 25), CMEs are expected to become more frequent. Continuous monitoring with VELC will provide valuable data for understanding these events.
- Monitoring the thermodynamic properties of CMEs near the Sun is essential to understand their source regions and behavior.
- Mission Details:
- The spacecraft is in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Mission Lifetime: 5 years.
First in the World Challenge
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
ICMR announces ‘First in the World Challenge’ to encourage scientists to find innovative ideas to tackle health issues.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Encourage bold, out-of-the-box ideas for solving difficult health problems.
- Aim to foster novel and groundbreaking biomedical innovations (vaccines, drugs, diagnostics, interventions, etc.).
- Target projects that are “first of their kind” and have never been tried or tested globally.
- Key Features of the Initiative:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Emphasis on high-risk, high-reward ideas with potential for significant global health impact.
- Excludes proposals aiming for incremental knowledge or process innovation.
- Scope of Research:
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Vaccines
- Drugs/Therapeutics
- Diagnostics
- Interventions
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Funding & Support:
- Provides funding for projects at various stages, from proof-of-concept to prototype development and final product.
- Support for projects that have the potential to lead to “first-of-its-kind” biomedical innovations.
- Application Process:
- Open to individual researchers or teams (from single or multiple institutions).
- Teams must designate a Principal Investigator responsible for the project’s technical, administrative, and financial aspects.
- Selection Criteria:
- A selection committee will be formed with:
- Experts, innovators, policymakers, and distinguished scientists with an outstanding research record.
- Proposals evaluated based on originality, impact potential, and innovation.
- A selection committee will be formed with:
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- History:Founded in 1911 as the Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA), renamed ICMR in 1949.
- Role & Mandate:
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- Formulates, coordinates, and promotes biomedical research in India.
- Focus on improving public health and addressing national health challenges.
- Vision:“Translating Research into Action for Improving the Health of the Population.”
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
Melanistic Tigers
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
CRS Mobile App
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union Home Minister Amit Shah launched the Civil Registration System (CRS) mobile app.
- The app aims to integrate technology with governance by making the registration of births and deaths more accessible, seamless, and hassle-free.
Key Features of the App:
- Anytime, Anywhere Registration: Citizens can register births and deaths from anywhere and at any time, in their State’s official language.
- The app is designed to significantly reduce the time required for registration, making it more efficient and convenient for users.
Legal and Policy Background:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act, 2023 mandates that all births and deaths in India, occurring from October 1, 2023, must be digitally registered through the Centre’s portal: dc.crsorgi.gov.in.
- This move is part of the broader effort to digitize civil records and create a centralized database.
Benefits of Digital Registration:
- Digital Birth Certificates: The new system will issue digital birth certificates which will serve as a single document to prove the date of birth for various services, such as:
- Admission to educational institutions
- Applying for government jobs
- Marriage registration
- Centralized Database: The integration of birth and death data into a centralized database will help update critical records such as:
- National Population Register (NPR)
- Ration cards
- Property registration
- Electoral rolls
National Population Register (NPR) Integration:
- The data collected through the CRS app will assist in updating the National Population Register (NPR), which was first collected in 2010 and updated in 2015 through door-to-door enumeration.
- The NPR serves as the first step toward the creation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) under the Citizenship Act, aimed at identifying Indian citizens.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Brazilhas opted not to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), becoming the second BRICS country after India to reject the multi-billion-dollar infrastructure project.
- Brazil prefers to explore alternative ways to collaborate with Chinese investors without signing a formal treaty, aiming to avoid the perceived risks of the BRI.
BRICS and India’s Role:
- Brazil’s decision follows India’s long-standing opposition to the BRI, particularly due to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which India views as a violation of its sovereignty.
- India has consistently argued that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, good governance, and transparency, emphasizing that such initiatives should be financially sustainable and not lead to debt traps.
Brazil’s Broader Economic Strategy:
- Brazil aims to balance its relationship with China, which is a major economic partner, but without being bound by the BRI. This decision reflects broader concerns within Brazil about the long-term financial sustainability of BRI projects, especially after witnessing debt crises in other countries like Sri Lanka.
Global Context and the BRI's Impact:
- The BRI, launched by China in 2013, spans several infrastructure sectors and has expanded globally, but it has faced criticism for its potential to trap smaller nations in unsustainable debt.
- India and Brazil’s resistance to the BRI highlights growing skepticism among emerging economies about the long-term implications of joining China's flagship project.
New Space Missions and Developments

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Space Commission also approved a joint moon mission with Japan called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission. For LUPEX, ISRO is developing a different moon lander than the one it used for Chandrayaan-3
New Space Missions and Developments
- Chandrayaan-4 (Moon Mission):
- Type: Sample-return mission.
- Launch: Expected by 2027.
- Cost: ?2,104 crore.
- Objective: Sample collection of moon soil and rock to return to Earth.
- Mission Details: Two LVM-3 launch vehicles will launch components that will dock in Earth orbit before heading to the moon. The samples will be sent back using a bespoke canister.
- Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX):
- Collaboration: Joint mission with Japan.
- Objective: Exploration of lunar poles with a new lander design, intended for potential crewed missions in future.
- Venus Orbiter Mission:
- Launch Window: March 2028.
- Cost: ?1,236 crore.
- Objective: Study Venus' surface and atmosphere to understand planetary evolution in the Solar System.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):
- Development Budget: ?8,240 crore for first three development flights.
- Objective: A new launcher developed with private sector collaboration for future space missions.
Cabinet Approvals for Space Initiatives
- Human Spaceflight Programme (Gaganyaan):
- Four new missions under Gaganyaan, including an uncrewed Gaganyaan flight.
- Focus on developing technologies for India’s first space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), planned by 2028.
- Space-Based Surveillance (SBS) Missions:
- Phase 3: Approval for building 21 ISRO satellites, with 31 additional satellites by private companies.
- Total Cost: ?26,968 crore.
- Development of a Third Launch Pad:
- To support the NGLV and additional space missions at Sriharikota.
Upcoming Satellite Missions
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar):
- Launch: Early 2025 on a GSAT launch vehicle.
- Purpose: Earth observation using advanced radar technology.
- Issue: Protective coating added due to high temperatures during testing.
- Proba-3 (European Space Agency):
- Launch: November 29, 2024, aboard PSLV-XL.
- Objective: Study the Sun’s corona using two satellites in formation, mimicking an eclipse to capture unique solar data.
Private Sector Involvement
- Manastu Space & Dhruva Space:
- Collaboration: Testing green propulsion technology for the LEAP-3 mission.
- Technology: Hydrogen-peroxide-based green propulsion system.
- Launch: LEAP-3 mission in 2025.
- Bellatrix Aerospace:
- Project: Prototype satellite for ultra-low earth orbit at 200 km altitude.
- Ananth Technologies:
- Achievement: First private company to assemble, integrate, and test Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx) satellites for ISRO.
Space Science and Research Updates
- Chandrayaan-3:
- Findings: The crater where Chandrayaan-3 landed is older than the South Pole-Aitken Basin (4.2-4.3 billion years old).
- Data Source: Optical High-Resolution Camera (Chandrayaan-2) and Pragyaan rover (Chandrayaan-3).
- Astrosat (India’s First Space Observatory):
- Mission Life: Expected to last two more years (originally planned for 5 years).
- Significance: Contributed to over 400 published papers based on multi-wavelength space observatory data.
ISRO-DBT Agreement for Biotechnology Experiments in Space

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to conduct biotechnology experiments on the upcoming Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
- Timeline for BAS:
- The BAS is expected to be operational from 2028-2035, with the initial module launches slated for 2028 and full expansion by 2035.
- It will be located at an altitude of 400 km above Earth and will support 15–20-day missions in space.
Focus Areas of Research
- Health Impact:
- Weightlessness & Muscle Health: Studying the effects of zero-gravity on muscle loss during space missions.
- Radiation Effects: Investigating how space radiation impacts astronaut health over long durations.
- Bio-Manufacturing:
- Algae Studies: Exploring algae for potential use in nutrient-rich, long-lasting food sources and biofuel production.
- Food Preservation: Identifying algae varieties that can help preserve food for longer periods in space.
- Integration with Gaganyaan Mission:
- Experiments may also be conducted during uncrewed test flights for the Gaganyaan mission (India’s first crewed mission to space, scheduled for 2025-2026).
BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Objective: The BioE3 policy aims to boost bio-manufacturing in India, which is projected to contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030.
- Key Focus Areas:
- High-Value Bio-Based Products: Promotes the development of bio-based chemicals, biopolymers, enzymes, and smart proteins.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture & Carbon Capture: Aims to strengthen agricultural practices to withstand climate change and promote carbon capture technologies.
- Healthcare & Nutrition: Focuses on advancements in biotherapeutics, functional foods, and regenerative medicine.
- Marine & Space Biotechnology: Encourages research in space and marine biotechnology for new applications.
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Supports R&D-driven entrepreneurship through the establishment of bio-manufacturing hubs, bio-AI centers, and biofoundries.
- Employment Growth: Aims to create skilled jobs in the growing bioeconomy, promoting green growth and sustainable industries.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) Overview
- Structure: The station will consist of:
- Command Module
- Habitat Module
- Propulsion Systems
- Docking Ports
- Objective: To support long-term research in space life sciences and bio-manufacturing, with a focus on human health, food sustainability, and biotechnology innovations.
National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Ministry of Culture plans to revive and relaunch the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) to enhance the preservation and accessibility of India’s ancient texts.
- The mission’s objective is to document, conserve, digitize, and disseminate India’s rich manuscript heritage, ensuring their protection and public access.
Formation of a New Autonomous Body:
- The National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) is likely to be restructured into an autonomous body called the National Manuscripts Authority, which will be under the Ministry of Tourism and Culture.
- The new body will address the challenges and gaps in manuscript preservation and management, offering more focused and flexible governance.
Background and Achievements:
- Established in 2003, the NMM has been part of the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA).
- Key achievements:
- 52 lakh manuscripts have had metadata prepared.
- Over 3 lakh manuscripts have been digitized, though only one-third have been uploaded for public access.
- Preventive and curative conservation of over 9 crore folios of manuscripts has been undertaken over the last 21 years.
- The NMM has set up 100 Manuscripts Resource Centres and Manuscripts Conservation Centres across India.
Current Challenges and Gaps:
- Data Uploading and Access:
- Of the 130,000 digitized manuscripts, only 70,000 are accessible online due to the absence of a comprehensive access policy.
- A significant portion (around 80%) of manuscripts areprivately owned, restricting public access and usage.
- Digitization Mismatch:
- There have been concerns about discrepancies between the digitized data and the original manuscripts, which requires correction to ensure authenticity and accuracy.
- Lack of Comprehensive Access Policy:
- Limited public access to manuscripts due to policy restrictions hinders further research and public engagement with this rich heritage.
Scope and Future of NMM:
- India's Manuscript Heritage: India is believed to have around 10 million manuscripts, spread across various regions, languages, scripts, and topics.
- Digitization and Accessibility: Moving forward, the key challenge will be ensuring that a larger proportion of the manuscripts are digitized, uploaded, and made publicly available, particularly from private collections.
- The establishment of the National Manuscripts Authority is expected to streamline efforts and enhance coordination between government bodies, private institutions, and scholars.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
Chenchu Tribe

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
The Chenchus of Penukumadugu have lived in the dense Nallamala forests for centuries, their existence intertwined with the wilderness around them. However, their inability to keep up with the relentless pace of modernisation has led to dwindling work opportunities under the MGNREGA.
Chenchu Tribe Overview
- Location: Primarily in the dense Nallamala forests, Andhra Pradesh (AP).
- Tradition: Historically hunter-gatherers, now relying on subsistence farming.
- Vulnerable Status: Classified as one of the 12 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Andhra Pradesh due to low literacy, stagnant population growth, and limited access to development.
- Livelihood: Dependent on forest resources (Non-Timber Forest Produce - NTFP) and agricultural labor.
Impact of MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
- MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project: Launched in 2009 to address specific needs of the Chenchus, such as physical strength, food insecurities, and cultural practices.
- Before Discontinuation: Provided 180 days of work per person annually, which helped Chenchus access regular income, improving food security and living conditions.
- Post-Discontinuation (2022):
- The project was integrated into a nationwide MGNREGS framework, reducing workdays to the standard 100 days per household.
- Consequences: Many Chenchus stopped engaging with MGNREGS due to bureaucratic hurdles (Aadhaar and bank linkage), reduced job days, and irregular wage payments.
- Only 1,500 out of 4,000 enrolled households currently participate in MGNREGS work.
Key Issues Post-MGNREGS Reform
- Aadhaar & Bank Account Challenges:
- Lack of literacy and digital skills makes the Aadhaar-based system intimidating.
- Many Chenchus are excluded from PDS and health benefits due to missing or unlinked Aadhaar cards.
- Absence of mobile phones and access to banks makes wage disbursement difficult.
- Irregular Payments & Trust Issues:
- The shift to bank payments has created trust issues, as many Chenchus are illiterate and cannot verify wage deposits.
- Distance from banks (up to 30 km) adds to the difficulty in accessing payments.
Forest Rights and Wildlife Conservation
- Forest Dependency: The Chenchus continue to depend on the forest for food and livelihood, but increasing restrictions due to wildlife conservation (e.g., Nagarjuna-Srisailam Tiger Reserve) have further curtailed their access to forest produce.
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Many Chenchus have land pattas under the FRA but lack resources or support to utilize their land effectively due to the discontinuation of MGNREGS.
Government and Policy Response
- PVTG Initiatives: Various government initiatives like PM PVTG Mission, Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, and Janjatiya Gaurav Divas aim to uplift PVTGs, but their impact remains limited without proper implementation of specialized support programs like the MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project.
IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
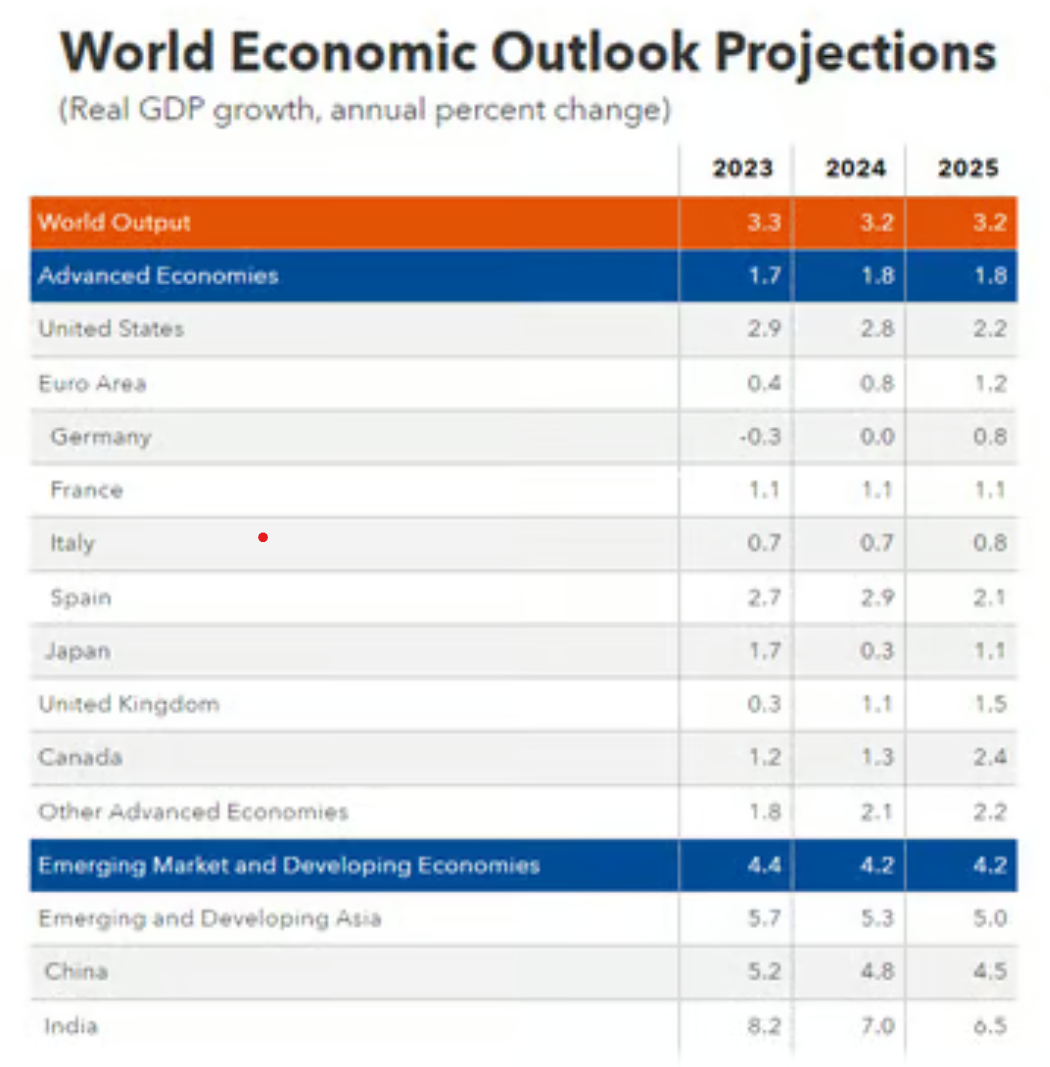
- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has maintained India’s GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY2024, marking a moderation from 8.2% in 2023.
- FY2025 Projection: Growth is expected to slow further to 6.5% in FY2025.
- India’s growth is expected to be stronger than most other large economies, yet the downward revision reflects challenges in the global economy and moderation in domestic economic momentum.
Global Economic Growth Projections:
- Global Growth (2024-2025): Global growth is projected at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, which is stable but modest. This growth rate is largely unchanged from previous IMF forecasts.
- Long-Term Outlook: The IMF's long-term projection for global growth is 3.1%, which is considered subpar compared to pre-pandemic growth rates, signaling a potential era of low growth.
Key Risks and Uncertainties:
- The IMF highlights several downside risks to global growth, including:
-
- Monetary tightening: Central banks' high-interest rate policies to combat inflation could have long-term negative effects on economic growth and financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, could disrupt global supply chains and trade, exacerbating inflation and slowing growth.
- China’s Economic Slowdown: China, the world’s second-largest economy, is facing a slower growth trajectory, especially in its real estate sector, which is dragging down its overall growth.
- Structural Challenges: The aging population and weak productivity are long-term growth inhibitors in many advanced economies, adding uncertainty to future growth prospects.
-
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
- 2023: Global inflation is expected to reach 6.7%.
- 2024: It is forecast to fall to 5.8%, with advanced economies expected to return to inflation targets sooner than emerging markets.
- 2025: A further decline to 4.3%.
- The primary driver of disinflation is not interest rate hikes but the unwinding of pandemic-related shocks, supply chain improvements, and the gradual return of labor supply.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks are likely to ease policies once inflation nears target levels, but risks of further commodity price spikes or geopolitical tensions could delay this.
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
US and Europe Growth:
- Emerging Markets and Developing Economies:
- Growth Outlook: The IMF forecasts growth in emerging markets and developing economies at 4.2% for 2024 and 2025, with a slight moderation to 3.9% by 2026.
- Emerging Asia: Growth in emerging Asia (led by India and China) is expected to slow, from 5.7% in 2023 to 5% in 2025.
- India’s Relative Strength: India’s growth continues to outperform many emerging economies, though the slowdown from 8.2% in 2023 to 7% in 2024 reflects global economic headwinds.
- Income Inequality Risks:
- The IMF warns that low growth over an extended period (4+ years) could exacerbate income inequality within countries, as sluggish growth affects job creation and wage growth.
- Countries with slow economic recovery are likely to see a widening gap between rich and poor, undermining social cohesion and stability.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
Tenkana

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- A team of arachnologists has discovered a new genus of jumping spiders, Tenkana, found across southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The discovery includes two previously known species, Tenkanamanu and Tenkanaarkavathi, and introduces a new species, Tenkanajayamangali, from Karnataka.
Name and Origin:
- The name Tenkana comes from the Kannada word for "south," reflecting the geographical region where all known species of this genus are found—southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The genus belongs to the Plexippina subtribe of jumping spiders, which is distinct from related genera like Hyllus and Telamonia.
Key Findings:
- Tenkanajayamangali was first discovered in Devarayanadurga reserve forest, Tumakuru district, Karnataka, at the origin of the Jayamangali river.
- The new species was identified through genetic analysis and physical examination, showing it did not match any known species.
Physical Characteristics:
- The male and female Tenkanajayamangali exhibit distinct physical differences.
- The male has pale hairs covering most of its carapace, while the female is grey with a pattern.
- The ocular area of T. jayamangali is uniformly covered with white hairs, in contrast to T. arkavathi and T. manu, which have distinctive markings.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Tenkana spiders are typically ground-dwelling and prefer dry, open habitats like short grasses, leaf litter, and rocky outcrops.
- These spiders have been observed in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and some areas in Sri Lanka.
- The male and female spiders of T. jayamangali were discovered in different regions, 2 km apart, at the hilltop and foothills of the same forest.
Ecological and Behavioral Insights:
- The Tenkana genus is considered endemic to India, with species observed in diverse regions such as Bengaluru, Yercaud (Tamil Nadu), and Bannerghatta (Karnataka).
- These spiders are found in complex microhabitats, like shaded short grasses with dry leaf litter or rocky outcrops in relatively dry habitats.
- The movement of Tenkana spiders resembles that of Stenaelurillus, another ground-dwelling spider species.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
