SwavalambiniProgramme

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
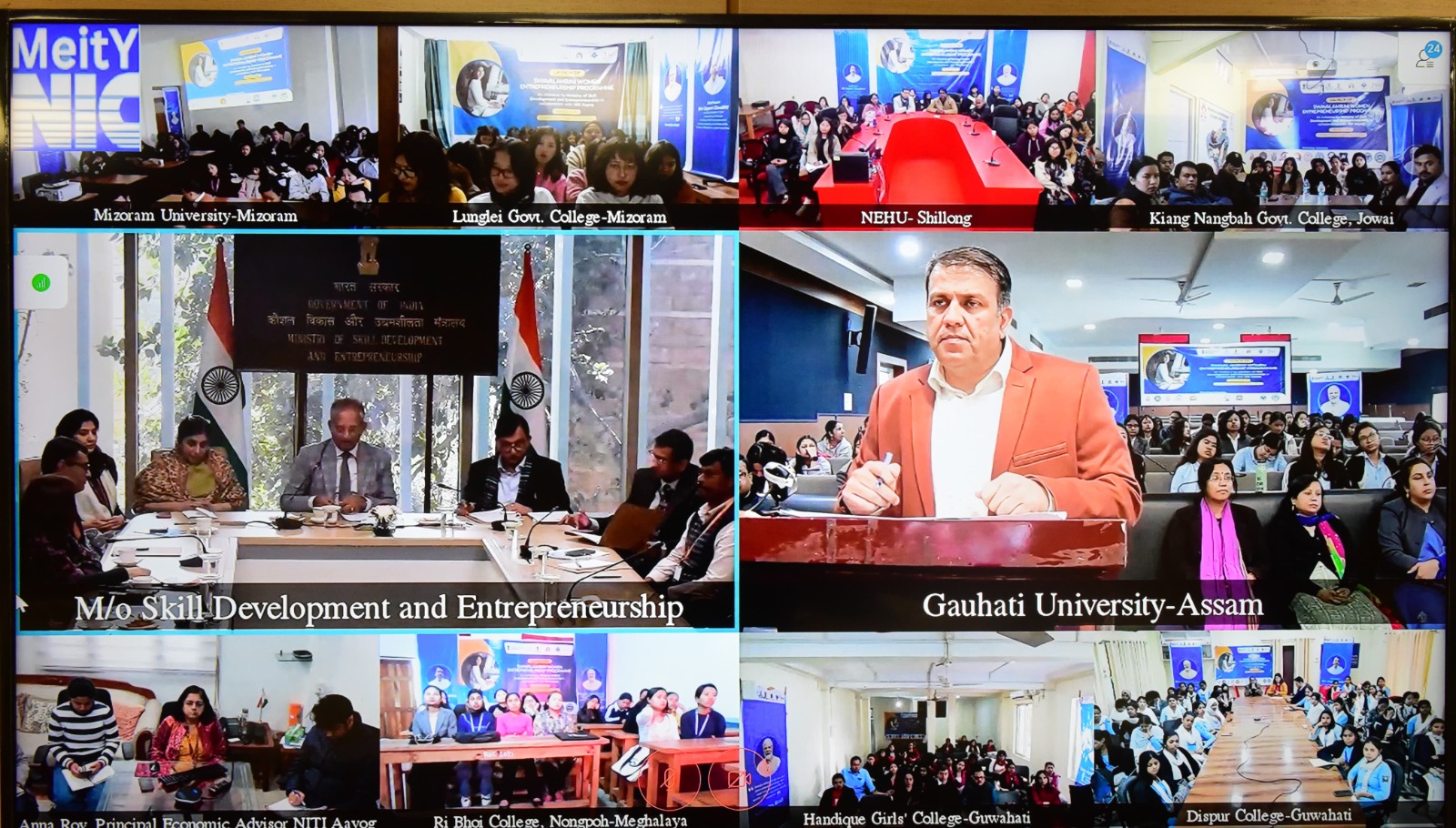
The SwavalambiniProgramme, launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) in collaboration with NITI Aayog, is a pioneering initiative aimed at empowering women in the Northeast.
This programme targets female students in select Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, providing them with an entrepreneurial mindset, essential resources, and ongoing mentorship to ensure their success in entrepreneurial ventures.
Programme Structure and Implementation
The programme follows a structured, stage-wise entrepreneurial process to guide participants through the various phases of business creation, from awareness to development, mentorship, and funding. It includes the following key components:
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP): Introduces 600 female students to entrepreneurship as a viable career option. The programme involves a 2-day session covering foundational entrepreneurial concepts and opportunities.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): This intensive 40-hour training is offered to 300 selected students, covering crucial aspects of business, including:
- Business training and skilling
- Access to finance and market linkages
- Compliance and legal support
- Networking opportunities
- Mentorship: After completing the training, participants receive six months of mentorship to help them translate their ideas into sustainable business ventures.
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP): A 5-day FDP will upskill faculty members in HEIs, enabling them to effectively mentor students in entrepreneurship. The training focuses on industry insights, business incubation strategies, and coaching techniques.
- Award to Rewards Initiative: Successful ventures will be recognized and awarded, inspiring others and fostering a culture of women-led enterprises.
Expected Outcomes and Impact
- The SwavalambiniProgramme aims to promote entrepreneurship among women, with an expectation that 10% of EDP trainees will successfully launch their businesses.
- It strives to establish a clear framework for nurturing and scaling women-led enterprises in India.
- The initiative contributes to economic transformation by making entrepreneurship a viable career path for women, particularly in the Northeast, a region brimming with untapped entrepreneurial potential.
Alignment with National Policies
The SwavalambiniProgramme aligns with several national initiatives and policies aimed at promoting women entrepreneurship:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The programme complements the NEP’s vision by integrating skill development, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-driven education within HEIs.
- Women Entrepreneurship Schemes: It strengthens existing initiatives like Start-Up India, Stand-Up India, PM Mudra Yojana, and the Women Entrepreneurship Platform, providing financial and mentorship support to emerging women entrepreneurs.
- Union Budget 2025: The ?10,000 crore start-up fund and the extension of the 100% tax exemption on start-up profits for five years in the Union Budget 2025 offer crucial financial backing for women-led enterprises.
Launch and Regional Focus
The programme was officially launched across nine colleges and universities in the Northeast, including Gauhati University, North-Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Mizoram University, and others.
GREAT Scheme

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The Grant for Research & Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) scheme, launched in August 2023 under the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM), aims to promote startup-led innovation and entrepreneurship in the rapidly growing sector of technical textiles in India.
As of February 2025, the government has approved four startups under the scheme, providing them with financial assistance to develop commercially viable innovations.
About the GREAT Scheme:
- Objective: To encourage young innovators, scientists, and startups in the technical textiles domain to convert ideas into market-ready products or functional prototypes.
- Implementation: Operated by the Ministry of Textiles under the R&D and Innovation Component of the NTTM.
- Financial Support:
- Grants of up to Rs.50 lakh for a period of up to 18 months.
- 10% upfront contribution from startups (e.g., ?5 lakh for a ?50 lakh grant).
- No royalty or equity required by the government.
- Approved Projects: Focus areas include Medical Textiles, Industrial Textiles, and Protective Textiles.
Complementary Initiatives under NTTM:
Academic and Skill Development:
- Education Institutes:
- ?6.5 crore approved for 3 academic institutes, including IIT Indore and NIT Patna, to introduce new courses in Geotextiles, Sports Textiles, Protective Textiles, and more.
- Skill Training:
- 12 Skill Development Courses launched across application areas such as Medical, Agricultural, Mobile, and Protective Textiles.
- Developed by leading Textile Research Associations: SITRA, NITRA, and SASMIRA.
- Aim to train stakeholders across the technical textile value chain.
National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM): An Overview
- Launched: 2020
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Total Outlay: ?1,480 crore
- Mission Goals:
- Make India a global leader in technical textiles.
- Expand the market size to $40–50 billion with 15–20% annual growth.
- Increase domestic penetration and usage of high-performance technical textiles.
Four Key Components:
- Research, Innovation, and Development
- Promotion and Market Development
- Export Promotion
- Education, Training, and Skill Development
- Sectoral Focus:Agro-textiles, Geotextiles, Medical Textiles, Industrial Textiles, Mobile Textiles, Home Textiles, Sports Textiles, Protective Textiles, and others.
- Policy Support:Includes integration with PLI schemes, PM MITRA Parks, and formulation of quality control regulations to strengthen manufacturing capabilities.
Significance for India’s Development:
- Encourages Atmanirbhar Bharat through self-reliant manufacturing and innovation.
- Strengthens India's competitiveness in high-end technical textiles for defense, healthcare, agriculture, infrastructure, and disaster response.
- Bridges the gap between lab-level R&D and market-ready products, especially by supporting startups in early innovation stages.
India-Japan Steel Dialogue

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
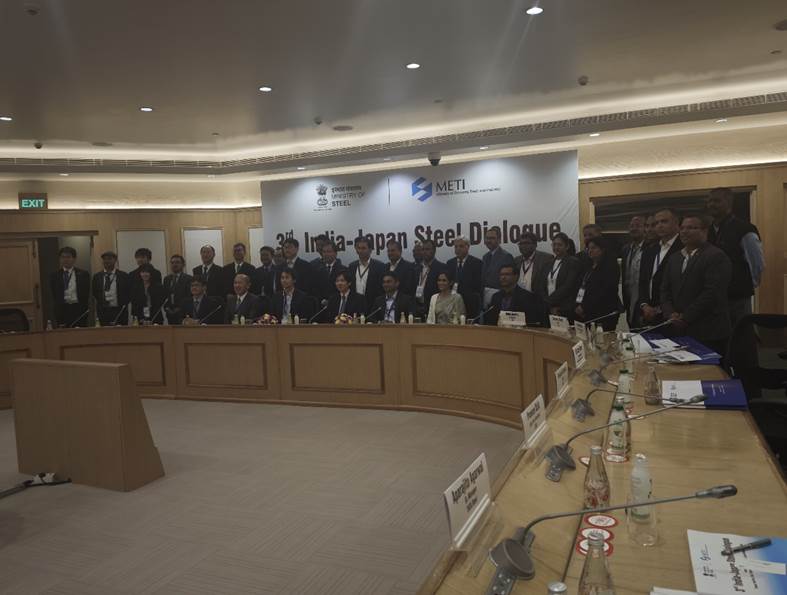
The 3rd India-Japan Steel Dialogue was held on February 4, 2025, at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, as part of the institutional mechanism under the Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) signed between the two nations in December 2020. The dialogue was co-chaired by senior officials from India’s Ministry of Steel and Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
Key Highlights and Strategic Focus Areas:
- Bilateral Steel Cooperation:The dialogue served as a platform to deepen cooperation in areas such as technology exchange, workplace safety, product diversification, and capacity building. Both nations reviewed progress under existing initiatives and reaffirmed commitment to long-term collaboration in the steel sector.
- Ease of Doing Business & Investment Support:India reiterated its commitment to facilitating ease of doing business for Japanese companies, while Japan assured continued technological and financial support for investments in advanced steel technologies in India.
- Sustainable Steel Production:India showcased recent initiatives like the Green Steel Report and the Taxonomy of Green Steel, underlining efforts to align steel production with sustainability goals and climate commitments.
- Demographic & Market Advantages:The Indian delegation highlighted the growing domestic demand driven by infrastructure investments, and the potential of India’s demographic dividend to attract foreign investment in the steel sector.
- Global Regulatory Issues – EU CBAM:Both sides discussed the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (EU CBAM), which seeks to impose carbon pricing on imports in sectors such as iron and steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, electricity, and hydrogen.
- CBAM Phase Timeline:
- Transitional Phase: 2023–2025 (reporting obligations)
- Full Implementation: From 2026 (financial obligations imposed)
- CBAM Phase Timeline:
Relevance:
CBAM has major implications for international steel trade, necessitating cleaner production methods and greater transparency in carbon emissions data.
Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025
- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
MoEFCC Notifies Rules for End-of-Life Vehicles to Minimize Waste and Pollution.
Key Highlights:
Notified by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
Effective from: April 1, 2025
Legal Basis: Environment Protection Act, 1986
Objective: To promote environmentally sound management of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs), enable recycling and reuse of vehicle components, and reduce resource extraction, pollution, and waste generation.
Key Features of the ELV Rules, 2025
1. Scope and Coverage
- Applicable to all vehicle categories including electric vehicles (EVs), e-rickshaws, and e-carts.
- Exempted vehicles: Agricultural tractors, trailers, combine harvesters, and power tillers.
- Exempted waste types: Batteries, plastics, tyres, used oil, and e-waste (governed under separate waste management rules).
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Vehicle producers are mandated to meet annual scrapping targets based on the age of vehicles:
- Transport vehicles: 15 years
- Non-transport vehicles: 20 years
- Producers must fulfill their EPR obligations for all vehicles introduced into the domestic market, including those used internally.
- Annual EPR declarations must be submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) by April 30 each year.
- Producers must promote ELV deposition at designated collection centres or Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs).
3. Responsibilities of Stakeholders
- Registered Owners & Bulk Consumers: Required to deposit ELVs at designated centres or RVSFs within 180 days of becoming unfit.
- Collection Centres:
- Handle ELVs in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Maintain records and ensure safe storage and transfer to RVSFs.
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs):
- Undertake depollution, dismantling, segregation, and recycling.
- Ensure environmentally sound disposal of non-recyclables via authorized TSDFs.
- Issue EPR certificates based on the volume of steel processed; valid for 5 years.
4. Monitoring, Compliance, and Penalties
- CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) are responsible for:
- Registration, inspection, and audit of producers, RVSFs, and bulk consumers.
- Taking action against non-compliance, including suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Levying environmental compensation for violations that cause harm to public health or the environment.
5. Registration & Certification
- Producers register with CPCB; RVSFs and bulk consumers with respective SPCBs.
- Registration certificates are issued within 15 days of application via a centralized online portal.
- EPR certificates are non-transferable and allow adjustment of both current and backlog obligations.
Related Policy and Incentives by MoRTH
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) supports the ELV Rules through:
- Vehicle Scrapping Policy: Targets voluntary phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles.
- Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility) Rules, 2021: Provides operational criteria for RVSFs.
- Central Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Waiver of registration fee for buyers submitting ELV Certificates of Deposit.
- Concession in motor vehicle tax: 25% for non-transport, 15% for transport vehicles.
Electric Mobility Push
- MoRTH has issued several notifications promoting EVs, including:
- Permit exemptions for battery-operated and ethanol/methanol-fueled vehicles.
- Fee exemptions for registration and renewals.
- Tourist permit benefits for EVs and distinct registration marks for visibility.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Launched by Ministry of Heavy Industries on 29th September 2024 with a ?10,900 crore outlay.
- Aims to support electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers, ambulances, trucks, and buses with ?3,679 crore in demand incentives.
- Targets subsidization of over 28 lakh EVs.
Himachal Pradesh: Statehood Day
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister greeted the people of Himachal Pradesh (HP) on the occasion of Statehood Day (25th January).
Key Highlights:
Statehood Day: Celebrated annually on 25th January, marking the day Himachal Pradesh attained full statehood in 1971.
Historical Timeline:
- 15 April 1948: Formation of Chief Commissioner’s Province of Himachal Pradesh through the merger of 30 princely hill states.
- 26 January 1950: Became a Part C State with the commencement of the Indian Constitution. (Part C states comprised former Chief Commissioner’s provinces and some princely states.)
- 1 November 1956: Reconstituted as a Union Territory based on the recommendations of the States Reorganisation Commission.
- 1 November 1966: Kangra district and other hilly areas of Punjab merged into Himachal Pradesh, yet it remained a Union Territory.
- 18 December 1970: The State of Himachal Pradesh Act was passed by Parliament.
- 25 January 1971: Himachal Pradesh became the 18th state of the Indian Union.
10 years of Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Launched on 22nd January 2015 in Panipat, Haryana, BBBP was initiated in response to the declining Child Sex Ratio (CSR), which stood at 918 girls per 1000 boys (Census 2011). It marked a key step towards gender equality, aiming to curb gender-biased sex-selective elimination and improve the status of the girl child.
Key Highlights:
Core Objectives
- Improve Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) by two points annually.
- Sustain institutional delivery rate at ≥95%.
- Increase 1st trimester ANC registration and girls' enrollment in secondary education by 1% annually.
- Reduce dropout rates among girls.
- Promote safe menstrual hygiene management (MHM).
Target Groups
- Primary: Young couples, expecting parents, adolescents, households, communities.
- Secondary: Schools, AWCs, health professionals, PRIs, ULBs, NGOs, SHGs, media, and religious leaders.
Implementation Structure
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with 100% Central funding.
- Ministries Involved:
- Women and Child Development
- Health and Family Welfare
- Education
- Financial Assistance (Per District/Year):
- Rs. 40 lakh (SRB ≤918)
- Rs. 30 lakh (SRB 919–952)
- Rs. 20 lakh (SRB >952)
Integration with Mission Shakti (2021–2026)
BBBP now functions under Mission Shakti, which comprises two verticals:
- Sambal (Safety & Security):
- One Stop Centres (OSCs)
- Women Helpline (181)
- Nari Adalat: Alternative dispute resolution
- Samarthya (Empowerment):
- Sakhi Niwas, Palna Creches
- Shakti Sadans (rehabilitation)
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana: Extended support for a second girl child
- SANKALP-HEW: District-level single-window system for all women-centric schemes
Achievements in 10 Years (2015–2025)
- SRB: Improved from 918 (2014-15) to 930 (2023-24)
- Girls’ GER: Rose from 75.5% (2014-15) to 78% (2023-24) in secondary education
- Institutional Deliveries: Increased from 61% to 97.3%
- Kanya Shiksha Pravesh Utsav: Re-enrolled over 1 lakh out-of-school girls
- Economic Empowerment: Integration with skilling initiatives and 70% of PM Mudra loans disbursed to women
- Awareness Campaigns:
- Selfie with Daughter
- Beti Janmotsav
- Yashaswini Bike Expedition
- "Betiyan Bane Kushal" Skill Conference
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) – A Financial Tool for Empowerment
Launched under BBBP, SSY is a small savings scheme to ensure the financial security of girl children.
Key Features
- Eligibility: Indian girl child below 10 years.
- Account: Max 2 per family (exceptions for twins/triplets).
- Deposit Limit: ?250 to ?1.5 lakh/year (15 years).
- Tenure: Account matures 21 years after opening.
- Withdrawals: Up to 50% for higher education after 18 years.
- Tax Benefits: Exempt under Section 80C (EEE status).
Impact
- Over 4.1 crore accounts opened by Nov 2024.
- Promotes long-term savings and financial inclusion.
- Complements BBBP by addressing economic empowerment of girls.
Mission Vatsalya
- Formerly ICPS (2009), then Child Protection Services (2017).
- Merged into Mission Vatsalya in 2021.
- Focuses on:
- Juvenile justice
- Child protection
- Advocacy and rehabilitation
- Ensures “no child is left behind” principle aligned with SDGs.
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Supports pregnant and lactating mothers:
- ?5,000 in 3 installments + ?1,000 (JSY)
- Now extended to second girl child to promote gender equity.
Targets wage compensation, safe delivery, maternal nutrition, and reduced MMR/IMR.
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
Miyawaki Technique
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
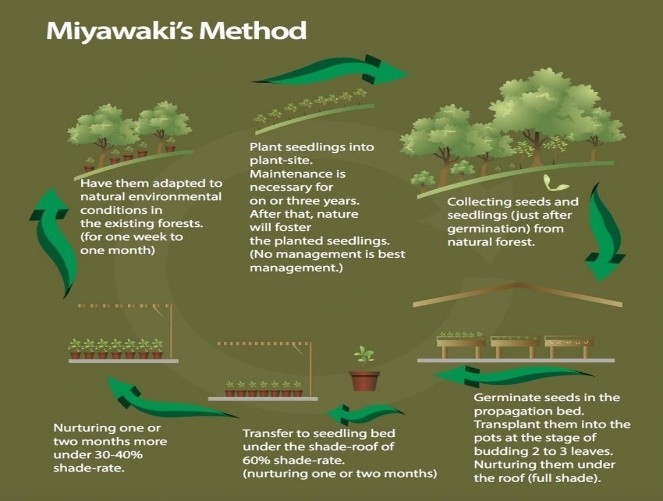
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 celebrated the remarkable contributions of 45 Panchayats from across India for their role in driving sustainable and inclusive development in rural areas. The awards were presented on 11th December 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi, with President Smt. Droupadi Murmu and Union Minister of Panchayati Raj Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh (Lalan Singh) presiding over the event.
Key Highlights:
- Categories of Awards: The awards focus on rural governance, social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP): Recognizes top-performing Gram Panchayats across 9 thematic areas like health, water, sanitation, and governance.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar: Awarded to the best Panchayats based on overall excellence across all LSDG themes.
- Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Honors Panchayats for contributions to renewable energy.
- Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Awarded to Panchayats achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar: Recognizes institutions supporting Panchayats in implementing LSDGs.
- Notable Achievements:
- Women’s Leadership: 42% of the award-winning Panchayats were led by women.
- States with Top Performers: States like Tripura, Odisha, and Maharashtra were prominently recognized for their achievements, especially in sustainability efforts like carbon neutrality and renewable energy adoption.
- Prize Distribution: A total of ?46 crore was awarded to the 45 winners, with funds directly transferred to their accounts.
Objectives:
The National Panchayat Awards aim to:
- Promote rural development through effective Panchayat governance.
- Encourage competition among Panchayats for improving public services and infrastructure.
- Recognize excellence in implementing sustainable development practices.
Key Themes of the Awards:
The awards are aligned with 9 LSDG themes that contribute to achieving 17 SDGs:
- Poverty-Free and Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean and Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just and Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 underscore the significant role of Panchayats in shaping rural India by focusing on inclusive and sustainable development. The awards also promote the importance of localized governance in achieving SDGs, encouraging other Panchayats to adopt best practices and contribute to India's overall development goals.
Development Initiatives for North East Region (NER)

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced as a new Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding in the Union Budget 2022-23 with initial outlay of Rs.1500 crore.
PM-DevINE Scheme:
- Launched in 2022 as a Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay: Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Total outlay: Rs. 6600 crore for the period from FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-2026, approved by the Union Cabinet on 12 October 2022.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure projects in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti.
- Support social development projects tailored to the felt needs of the NER.
- Enable livelihood opportunities for youth and women.
- Address development gaps in various sectors.
- 35 projects worth Rs. 4857.11 crore have been sanctioned under the scheme up to 30 November 2024, including 7 projects from the Union Budget 2022-23.
Industrialization Initiatives:
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched on 1 April 2017, ended on 31 March 2022.
- Aimed at promoting industrialization in the NER.
- UNNATI Scheme:
- Launched on 9 March 2024 for enhancing regional infrastructure and promoting industrial growth.
- Provides specific incentives to industries, including:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development:
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are mandated to allocate at least 10% of their annual Gross Budgetary Allocation towards NER development.
- Between 2019-20 and 2023-24, these Ministries/Departments have incurred Rs. 3,53,412 crore towards the development of NER.
Role of State Governments and Central Support:The Government of India supplements state efforts with various schemes to promote industrialization and infrastructure development in the NER.
The PM-DevINE scheme, along with initiatives like UNNATI and the allocation of substantial funds by the central government, aims to accelerate the holistic development of NER. These efforts focus on infrastructure, social development, and industrialization, with specific emphasis on youth and women empowerment, ensuring long-term growth and prosperity for the region.
‘Anna Chakra’ and SCAN Portal

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and New & Renewable Energy, launched ‘Anna Chakra’, the Public Distribution System (PDS) Supply chain optimisation tool and SCAN (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA) portal a significant step towards modernizing the Public Distribution System and subsidy claim mechanisms of the States.
Anna Chakra: PDS Supply Chain Optimization Tool
- Purpose: A tool developed to enhance the efficiency of PDS logistics across India, optimizing food grain transportation.
- Collaboration: Developed by the Department of Food and Public Distribution, in collaboration with the World Food Programme (WFP) and IIT-Delhi’s Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT).
- Functionality: Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal transportation routes for food grains.
- Key Features:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Achieves annual savings of Rs 250 crores by reducing fuel consumption, time, and logistics costs.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces transportation-related emissions by cutting transportation distance by 15-50%, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Wide Coverage: Impacts 30 states, 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPS), and 6,700 warehouses in the PDS supply chain.
- Technology Integration: Linked with the Freight Operations Information System (FOIS) of Railways and PM Gati Shakti platform, enabling geo-location mapping of FPS and warehouses.
SCAN Portal: Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA
- Objective: To streamline the subsidy claim process under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013, ensuring better utilization of funds.
- Functionality: Provides a unified platform for states to submit food subsidy claims, reducing administrative complexity and delays.
- Key Features:
- Single Window Submission: Simplifies subsidy claim submission for states, enhancing coordination.
- Automated Workflow: End-to-end automation ensures efficiency, transparency, and faster settlements.
- Rule-Based Processing: Claims are scrutinized and approved through a rule-based system, speeding up the approval process.
Public Distribution System (PDS) Overview
- Purpose: Ensures food security by providing subsidized food grains to vulnerable populations under the NFSA, benefitting nearly 80 crore people.
- Management: A joint effort between the Central and State/UT Governments. The Food Corporation of India (FCI) handles procurement and transportation, while state governments manage local distribution.
- Commodities: Primarily wheat, rice, sugar, and kerosene, with some states also distributing pulses and edible oils.
Initiatives to Reform PDS in India
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC):
- Goal: To allow portability of ration cards, benefiting migrant workers and seasonal laborers.
- Features: Biometric authentication, digital payments, and enhanced inclusivity.
- SMART-PDS Scheme (2023-2026):
- Objective: To upgrade technology in PDS, including computerized FPS, point-of-sale (POS) machines, and GPS tracking for transparency and fraud reduction.
- Aadhaar and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- Purpose: Ensures proper beneficiary identification and cash transfers, allowing beneficiaries to purchase grains from the open market.
- Technology and Transparency Enhancements:
- GPS and SMS Monitoring: Ensures the proper delivery of food grains to FPS and provides citizens with updates via SMS.
PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, launched the PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31 dedicated to Indian Sign Language (ISL) on December 6, 2024, in New Delhi.
Channel Purpose and Vision:
- Objective: To bridge the communication gap between the hearing-impaired and hearing populations by promoting ISL.
- Significance: Channel 31 aims to unlock talent and ensure equal opportunities for all, making society more inclusive and progressive.
- ISL's Role: Pradhan emphasized the importance of alternative communication methods like ISL, which ensures that individuals with hearing impairments have equal access to education, employment, and societal participation.
Government's Focus on Inclusivity:
- Legal Framework: Pradhan highlighted the expansion of recognized disabilities from 7 to 21, making the legal framework more comprehensive.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy focuses on inclusive education, with particular attention to Children with Special Needs (CwSN). The NEP promotes the standardization of ISL and its inclusion in educational curricula.
- Employment and Cultural Expression: ISL is not only essential for communication but also contributes to cultural expressions like dance and drama. Pradhan emphasized that learning ISL would open employment opportunities and allow individuals to express themselves fully.
Importance of Channel 31:
- The launch of Channel 31 aligns with India’s commitment to ensuring equal rights and access to education, as enshrined in the Constitution.
- Pradhan urged for widespread adoption of ISL, ensuring that more people learn the language to better support the hearing-impaired community.
PM e-Vidya Initiative:
- Launch Date: PM e-Vidya was launched as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan on May 17, 2020, to bridge the digital divide and ensure inclusive education.
- Key Components:
- DIKSHA: A national platform providing e-content for all grades.
- DTH TV Channels: Initially started with 12 channels, now expanded to 200, offering supplementary education in multiple languages.
- SWAYAM: A platform for online courses and MOOCs for both school and higher education.
- Community Radio & Podcasts: These platforms are used for wider educational outreach, especially in rural and remote areas.
- e-Content for Teachers: Interactive videos and resources aimed at enhancing teacher education.
Channel Content:
- Channel 31 will provide 24x7 educational content for children with hearing impairments, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- The content will include school curricula, career guidance, skill training, mental health support, and promotion of ISL as a subject.
- The content will be available on YouTube, increasing its reach and accessibility.
Hornbill Festival

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The Hornbill Festival, a vibrant celebration of Nagaland's culture and tourism, is an annual event that takes place from December 1 to 10.
About the Hornbill Festival:
- Origin: First held in the year 2000.
- Purpose: The festival aims to foster inter-tribal communication, preserve the cultural heritage of Nagaland, and showcase the harmonious blending of traditional and modern elements.
- Significance: Referred to as the “festival of festivals,” it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural calendar.
- Organizers: It is organized by the Tourism and Art & Culture Departments of the Government of Nagaland.
- Location: The festival takes place annually at the Naga Heritage Village in Kisama, located about 12 kilometers from Kohima.
- Cultural Showcase: Over the years, it has evolved into a significant celebration that highlights the vibrant and diverse cultural traditions of the various tribes in Nagaland.
- Name Origin: The festival is named after the Hornbill bird, which holds cultural importance among the Naga tribes.
- Theme of the 2024 Hornbill Festival:The 2024 edition is themed “Cultural Connect,” celebrating the rich heritage and cultural diversity of Nagaland. The festival continues to merge modernity and tradition through a variety of activities, including Naga wrestling, traditional archery, food stalls, fashion shows, beauty contests, and musical performances. Additionally, the Archives Branch is presenting a special exhibition titled “Naga-Land & People in Archival Mirror” in partnership with the National Archives of India, offering a deeper look at the region's history and cultural practices.
- Recent Milestone:This year marks the 25th anniversary of the Hornbill Festival.
Festival Highlights:
- Annual Event: Held each year since its inception in 2000, it serves as a major cultural event for Nagaland.
- Symbolism: Named after the Hornbill bird, which represents boldness and grandeur in Naga folklore.
- Location: The festival is hosted at Kisama Heritage Village, a cultural center that preserves Naga traditions with 17 indigenous houses (Morungs) that represent each of the tribes.
- Cultural Diversity: Nagaland, known as the “Land of Festivals,” is home to 17 major tribes, each with its distinct festivals and cultural practices. The Hornbill Festival promotes inter-tribal interaction and celebrates the state’s rich heritage.
- National Significance: Reflecting India’s unity in diversity, the festival serves as a platform for different cultural practices to coexist, strengthening the nation’s collective identity.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
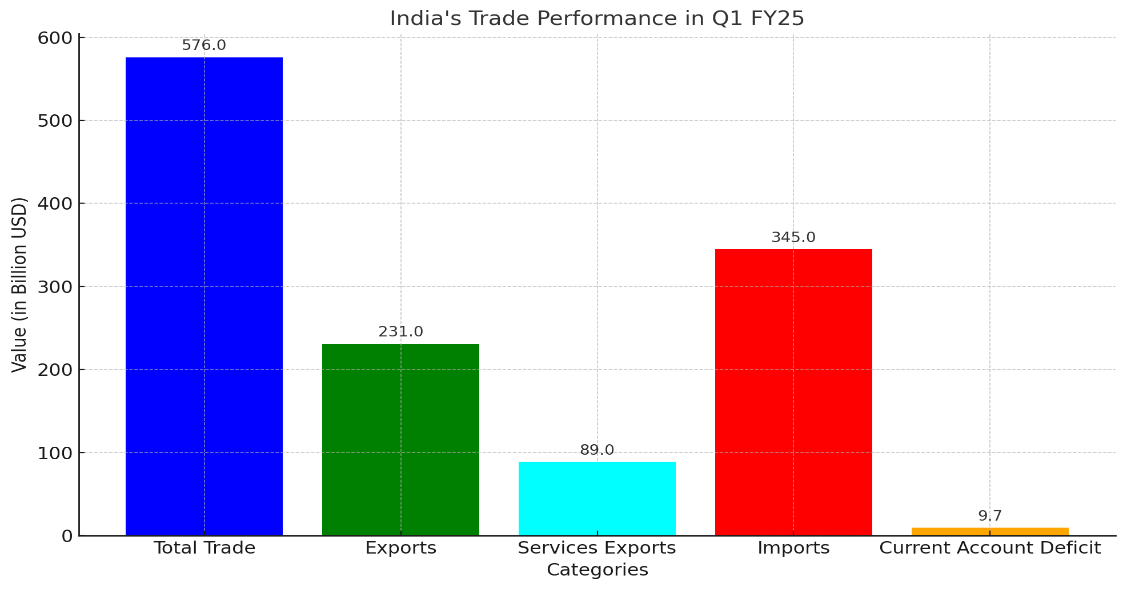
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
SheSTEM 2024

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities (IDPD), observed annually on December 3, celebrates the resilience, contributions, and leadership of persons with disabilities (PwDs) worldwide.
- Theme: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future”
History
- Proclamation: Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1992 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, further advanced the rights and well-being of PwDs and supports the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Initiatives
Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities
- In order to give focused attention to policy issues and meaningful thrust to the activities aimed at the welfare and empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), a separate Department of Disability Affairs was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on May 12, 2012.
- The Department was renamed the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities on December 8, 2014.
- The Department acts as a nodal agency for matters pertaining to disability and persons with disabilities, including effecting closer coordination among different stakeholders: related Central Ministries, State/UT Governments, NGOs, etc., in matters pertaining to disability.
Accessible India Campaign
- The Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan), launched on December 3, 2015 aims to achieve universal accessibility for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) across India.
- The key focus areas include improving Built Environment Accessibility in public spaces, enhancing Transportation Accessibility for independent mobility, creating an accessible Information and Communication ecosystem, and expanding Sign Language Access through interpreter training and better media support.
Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)
- DDRS is a central sector scheme to provide grant-in-aid to non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for projects relating to the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities aimed at enabling persons with disabilities to reach and maintain their optimal, physical, sensory, intellectual, psychiatric, or socio-functional levels.
District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC)
- The District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC) aims to address the needs of persons with disabilities through a multifaceted approach.
- Its objectives include early identification and intervention, raising awareness, and assessing the need for assistive devices along with their provision and fitment, arrangement of loans for self-employment and more. Additionally, it acts as an outreach center for services provided by National Institutes and works to promote a barrier-free environment for individuals with disabilities.
Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/ Appliances (ADIP) Scheme.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to provide grants-in-aid to the various implementing agencies (National Institutes/Composite Regional Centers/Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India.
Schemes For Implementation Of Rights of Persons With Disabilities Act 2016 (SIPDA)
- The Scheme for Implementation of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (SIPDA) is a comprehensive "Central Sector Scheme" that encompasses 10 sub-schemes following its revision during the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) meeting on 11th August 2021.
- This revised scheme, approved by the Hon'ble Finance Minister, is designed to operate from 2021–22 to 2025–26.
Divya Kala Mela
- The Divya Kala Mela is a national-level fair dedicated to Divyangjan and represents a significant milestone in India’s journey toward inclusivity and empowerment of the Divyangjan, or differently-abled individuals.
PM-DAKSH
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri DakshtaAurKushaltaSampannHitgrahi) Yojana is a one-stop destination for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), skill training organizations, and employers across India to be a part of the National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities implemented by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD). Under this portal, there are two modules:
- Divyangjan Kaushal Vikas: Skill training is conducted for PwDs through the portal across the country.
- Divyangjan Rozgar Setu: The platform aims to act as a bridge between PwDs and employers having jobs for PwDs. The platform provides geo-tagged based information on employment/earning opportunities within private companies as well as PwDs across India.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
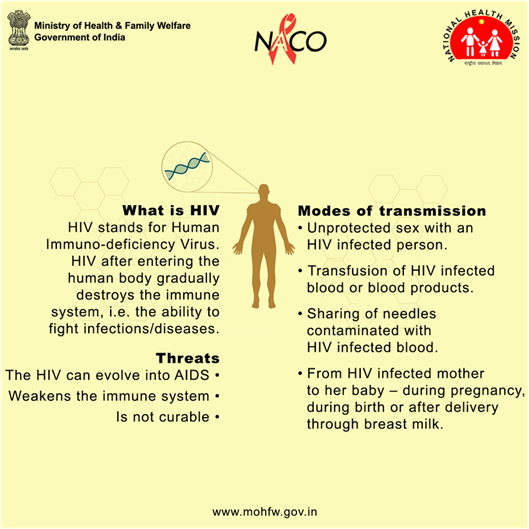
World AIDS Day 2024
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
World AIDS Day is observed annually on December 1 since 1988 to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS and demonstrate solidarity with affected individuals. It commemorates lives lost to AIDS and highlights progress and ongoing challenges in prevention, treatment, and care.
Key Highlights:
- 2024 Theme: "Take the Rights Path: My Health, My Right!"
- Focuses on healthcare access, human rights, and addressing systemic inequalities in HIV prevention and treatment services.
- Aims to empower individuals to manage their health and reduce stigma.
- Advocates for inclusivity and global cooperation to eradicate AIDS.
Global and National Perspective on HIV/AIDS
- Global Progress:
- According to UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023, significant strides have been made globally in reducing new HIV infections and improving treatment access.
- India has been acknowledged for its robust legal framework and financial investments in HIV control.
- India's HIV Statistics:
- Over 2.5 million people live with HIV in India.
- Annual new infections: 66,400, a 44% reduction since 2010.
- HIV prevalence among adults is 0.2%.
- Free lifelong treatment is provided to over 16 lakh people at 725 ART centers (as of 2023).
India’s Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response
- Early Initiatives:
- India’s response to HIV/AIDS began in 1985 with sero-surveillance and blood safety measures.
- The National AIDS and STD Control Programme (NACP) was launched in 1992, evolving into one of the world’s largest HIV/AIDS control programs.
- Evolution of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness and blood safety.
- Phase II (1999-2007): Introduced direct interventions in prevention, detection, and treatment.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Expanded decentralized management at the district level.
- Phase IV (2012-2017): Increased funding and sustainability of interventions.
- Phase IV Extended (2017-2021): Passage of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017; introduction of the ‘Test and Treat’ policy; and response to the COVID-19 pandemic with IT innovations.
- NACP Phase V (2021-2026):
- Central Sector Scheme with an outlay of Rs. 15,471.94 crore.
- Goals: Reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 from 2010 levels.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis, reduce stigma, and ensure universal access to STI/RTI services for vulnerable populations.
- Key strategies include community-centered approaches, technology integration, gender-sensitive responses, and public-private sector partnerships.
Key Objectives of NACP Phase V
- Prevention & Control:
- Ensure 95% of high-risk individuals access prevention services.
- Achieve the 95-95-95 targets: 95% of HIV-positive individuals know their status, are on treatment, and achieve viral suppression.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis.
- Reduce stigma and discrimination to less than 10%.
- STI/RTI Prevention:
- Universal access to high-quality services for at-risk populations.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
India-Cambodia Joint Military Exercise CINBAX

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The first edition of CINBAX (Counter-Terrorism Counter-Bio-Terrorism and Intelligence Operations Exercise) was launched on December 1, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node, Pune.
Key Details:
- Participants: 20 personnel from each side – the Indian Army and the Cambodian Army – focusing on enhancing cooperation for UN peacekeeping operations.
- Objective:
- Enhancing Trust and Interoperability: CINBAX aims to foster mutual trust, build camaraderie, and improve operational efficiency between the two armies in conducting peacekeeping operations under UN guidelines.
- Focus Areas: Joint Counter-Terrorism (CT) operations, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), cyber warfare, logistics, casualty management, and disaster relief operations.
- Phases of the Exercise:
- Phase I: Orientation for Counter-Terrorism operations in the context of UN peacekeeping missions.
- Phase II: Conduct of tabletop exercises to simulate and plan response scenarios.
- Phase III: Finalization of plans and review of lessons learned, focusing on operational strategies and tactical decision-making.
- Key Topics Covered:
- Discussions on setting up a Joint Training Task Force for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
- Exploring cyber warfare, hybrid warfare, and unconventional tactics.
- Strategies for managing logistics, casualties, and coordination during Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- Promotion of Indigenous Defence Equipment:
- The exercise will showcase Indian-made weapons and defence equipment, supporting India’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance in defence production).
- Objective: To highlight India's advanced military technology and indigenous defence capabilities.
- Significance for India-Cambodia Relations:
- The exercise strengthens military ties between India and Cambodia, contributing to improved cooperation in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- CINBAX marks a significant milestone in India-Cambodiadefence collaboration and sets the stage for future joint operations.
India-Cambodia Bilateral Relations
- Historical Context:
- India and Cambodia share strong religious, cultural, and linguistic ties, with Hindu rituals influencing Cambodian culture and Sanskrit and Khmer sharing common words.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1952, even before Cambodia's independence from France.
- Key Developments:
- 1954: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Cambodia, initiating strong diplomatic ties, particularly during the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Post-1970s: India played a pivotal role in Cambodia's recovery from the Khmer Rouge regime. India was the first democratic country to recognize the Heng Samrin regime in 1981 and contributed to Cambodia's political reconciliation.
- 1980s: India facilitated dialogue for the Paris Peace Accord and contributed to the success of UNTAC elections in 1993.
- Strategic and Economic Cooperation:
- Defence: Enhanced cooperation in defence capacity building, military training, and infrastructure development.
- Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, automobiles, and leather products to Cambodia. In return, Cambodia exports organic chemicals, apparel, and footwear to India.
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Established in 2000, MGC includes Cambodia and aims to enhance cooperation in sectors like trade, education, tourism, and cultural exchanges.
- Recent Collaboration:
- India has extended financial assistance for infrastructure projects in Cambodia, especially in restoring and conserving cultural heritage sites like Angkor Wat.
- MoUs signed in bilateral cooperation, cultural exchanges, and development projects highlight the growing India-Cambodia strategic partnership.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
13th National Seed Congress (NSC)

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 13th National Seed Congress (NSC), organized by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, concluded with significant discussions and outcomes focused on advancing India's seed sector.
- The theme for this year's congress, held in Varanasi, was "Innovating for a Sustainable Seed Ecosystem."
Key Highlights:
- Focus Areas:
- Seed Technologies and Biofortification: Emphasis on high-nutrition seeds like iron and zinc-enriched rice and Vitamin A-rich crops to combat malnutrition.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting practices like Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) and the development of stress-tolerant seed varieties to withstand climate change.
- Challenges in India’s Seed Ecosystem:
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): SRR in India is around 15-20%, with 100% for hybrid seeds, pointing to the need for higher adoption of certified seeds.
- Monoculture and Seed Market Monopoly: Issues like over-reliance on Bt cotton and domination by multinational companies (e.g., Bayer) in seed markets.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Seed Corporation (NSC): Produces foundation and certified seeds for over 600 varieties.
- Seed Village Programme (Beej Gram Yojana): Focus on improving the quality of farm-saved seeds.
- National Seed Reserve: Ensures seed availability during climatic disruptions.
- Policy Discussions:
- Proposed Seeds Bill: A new bill to regulate seed quality and promote sustainable practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations to improve seed production, accessibility, and quality.
- Outcomes:
- Biofortified Seeds: Increased development and distribution of nutrient-rich seeds.
- Climate-Resilient Seed Systems: Enhanced focus on developing crops that can withstand climate challenges.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations in seed technology and policy reform.
Global Engagement Scheme
- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Culture plays a pivotal role in promoting India’s rich cultural heritage across the globe through its Global Engagement Scheme.
- The scheme is designed to enhance India's cultural image internationally while fostering people-to-people connections and strengthening bilateral cultural ties with other nations.
- The scheme has three key components: Festival of India, Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies, and Contribution Grants.
Key Components of the Global Engagement Scheme:
- Festival of India (FoI):
- Purpose: The Festival of India is organized abroad to celebrate and promote India's diverse culture. It provides a platform for artists from various cultural fields, including Folk Art (folk music, dance, theatre, puppetry), Classical and Traditional Dance, Classical and Semi-Classical Music, Experimental/Contemporary Dance, and Theatre.
- Impact: Since 2013-14, 62 Festivals of India have been held in different countries, with over 2,348 artists, including folk artists, participating. These festivals serve as a means to promote Indian folk art, culture, and music internationally.
- Artist Participation: Folk artists are remunerated with a performance fee of ?35,000 for the leader/main artist and ?7,000 for accompanying artists per performance.
- Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies:
- Objective: This scheme supports cultural societies abroad that aim to strengthen cultural exchanges and promote Indian art forms. Grants are provided to these societies to organize various cultural programs and activities, fostering closer cultural ties between India and the host countries.
- Support to Folk Artists: This scheme also aids in bringing folk art to the global stage, showcasing India's traditional performances.
- Contribution Grant:
- Objective: The contribution grant is used for India’s membership in international organizations like UNESCO, ICOM, and the World Heritage Fund. This component also facilitates Indian participation in international meetings and helps host global events, further showcasing India’s cultural wealth.
Support for Veteran Artists:
In addition to promoting folk culture globally, the Ministry of Culture supports veteran artists through the Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists scheme. This initiative is aimed at supporting elderly and economically disadvantaged artists (aged 60 and above) who have made significant contributions to their respective art forms, including folk art.
- Financial Support: Artists selected under this scheme receive up to ?6,000 per month, adjusted for any state pension they may already receive.
Regional Contributions:
- The Ministry has empaneled folk artists and groups across India for participation in these international cultural exchanges. For instance, two folk artists/groups and one Kathak artist from Uttarakhand are currently empaneled.
- Notably, a troupe from Uttarakhand participated in the Freedom 70 Cultural Event in Cuba and the Dominican Republic in August 2017, showcasing the diversity of Indian folk art.
- The Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists has also benefitted several artists from Uttarakhand, with four artists from the state receiving support over the past two years.
'Bal VivahMukt Bharat' Campaign

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Minister for Women and Child Development launched the “Bal VivahMukt Bharat” campaign aimed at eradicating child marriage in India.
- Goal: Reduce child marriage rates to below 5% by 2029.
- Focus: Engage multiple stakeholders, raise awareness, and leverage technology for eradication.
Target Areas:
- Target States: West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Tripura, Assam, Andhra Pradesh.
- High-Burden Districts: Nearly 300 districts with higher rates of child marriage.
Child Marriage Free Bharat Portal:
- A digital platform to raise awareness, report cases, and track progress on child marriage prevention.
- Real-time tracking by Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPOs).
Monitoring and Accountability:
- Central nodal officers and CMPOs will oversee the campaign’s implementation at state and district levels.
- The portal facilitates citizens’ participation by allowing complaints and providing information on legal remedies.
Progress and Impact:
- Child marriage rates have reduced from 47.4% (2005-06) to 23.3% (2019-21).
- The goal is to reduce these rates further to below 5% by 2029.
Awareness and Community Engagement:
- Public campaigns and community mobilization to challenge societal norms and change attitudes towards child marriage.
- The campaign will continue through various channels, including the BetiBachaoBetiPadhao initiative.
Legal Framework:
- Strengthening the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, which sets the legal marriage age at 18 for women and 21 for men.
- Penalties for those involved in child marriage include imprisonment and fines.
Key Challenges for Child Marriage:
- Poverty: Families may view early marriage as a financial relief.
- Cultural Norms: Deep-rooted societal beliefs about preserving family honor.
- Gender Inequality: Patriarchal systems view girls as burdens.
- Lack of Education: Limited access to schooling forces early marriages.
- Fear of Sexual Assault: Misguided belief that early marriage protects girls.
- Weak Law Enforcement: Corruption and inadequate resources hinder the law’s implementation.
- Pandemic Impact: Economic hardships during COVID-19 led to an increase in child marriages.
Related Initiatives:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006: Strengthens child marriage laws and establishes CMPOs.
- Success Stories: Individuals like BuchaRamanamma, Durga, and Roshni Perween have inspired others by stopping their own child marriages and advocating for change.
Campaign and National Vision:
- The campaign aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision for a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
- It aims to empower women and girls, providing them with opportunities for education, health, and safety.
- Collective effort from the government, social organizations, and citizens is crucial to eliminating child marriage.
Eklavya Digital Platform
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the “Eklavya” online learning platformnmunder the leadership of General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff (COAS).
- It is part of the Army’s “Decade of Transformation” initiative and aligns with the theme for 2024, “Year of Technology Absorption.”
Platform Development:
- Developed by the Army Training Command (ATC) and sponsored by the Army War College.
- Created at zero cost in collaboration with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), Gandhinagar.
- Hosted on the Army Data Network with scalable architecture to integrate various training establishments.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple courses from 17Category ‘A’ Training Establishments of the Army.
- Allows student officers to register for several courses simultaneously.
- Aims to decongest physical courses and integrate contemporary, application-focused content.
Categories of Courses:
- Pre-Course Preparatory Capsules: Online study material for physical courses, allowing focus on contemporary topics during offline training.
- Appointment-Specific Courses: Online courses for officers appointed to specialized roles (e.g., information warfare, financial planning, etc.), helping them gain domain-specific expertise before posting.
- Professional Development Suite: Includes courses on strategy, leadership, operational art, finance, emerging technologies, etc., focusing on holistic officer development.
Knowledge Highway:
- A searchable database featuring journals, research papers, and articles to support continuous professional education and development.
Impact:
- Promotes continuous professional military education.
- Enhances the efficiency and specialization of officers, particularly in emerging domains.
- Streamlines training processes and integrates modern technology in the Army’s educational system.
E-Daakhil Portal
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- The E-Daakhil portal was launched by the Department of Consumer Affairs to promote consumer rights and ensure timely justice.
- The portal was launched nationwide with its final rollout in Ladakh on 22nd November 2024, making it operational across all states and union territories of India.
Background and Purpose:
- Introduced in September 2020, the portal was developed in response to the Consumer Protection Act 2019, which aims to address emerging consumer concerns.
- Aimed at providing a hassle-free, inexpensive, and speedy mechanism for filing consumer complaints, especially post the COVID-19 pandemic.
- E-Daakhil is an online platform that simplifies the grievance redressal process, allowing consumers to file complaints remotely, without the need for physical presence.
Portal Features:
- User-friendly interface: Simple and intuitive, allowing consumers to file and track complaints online.
- Registration process: Users can register through OTP on their mobile or an activation link via email.
- Paperless and transparent: The entire process, from filing complaints to tracking the case status, is digital and transparent.
- Consumers can file complaints, pay fees, and monitor the progress of their cases from the comfort of their homes.
Success and Impact:
- By the end of 2023, E-Daakhil was available in 35 states and union territories; with Ladakh being the latest addition in November 2024.
- Over 2.81 lakh users have registered, and 1.98 lakh cases have been filed, of which 38,453 cases have been disposed of.
Future Developments:
- E-Jagriti: A new initiative that will further streamline the case filing, tracking, and management process, reducing delays and paperwork.
- E-Jagriti aims to improve communication between parties, ensuring faster dispute resolution.
BioE3 Policy

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The BioE3 Policy outlines guidelines and principles for enabling mechanisms for ‘Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing’ in the country across diverse sectors.
Key Highlights:
Primary Objective:
- Set a framework for the adoption of advanced technologies and innovative research to promote biomanufacturing in India.
- Focus on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality in biomanufacturing.
Alignment with National Goals:
- Supports India’s vision of Green Growth (Union Budget 2023-24) and Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), promoting sustainability.
- Aligns with India’s goal of achieving a Net-Zero carbon economy.
- Supports the Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry initiative announced in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
Key Objectives:
- Revolutionize biomanufacturing for better product quality and environmental sustainability.
- Accelerate the development and commercialization of bio-based, high-value products.
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
Achievements of Indian Bioeconomy (2014-2023):
- Contribution to GDP: Bioeconomy contributes 4.25% to India’s GDP of $3.55 trillion (as of Dec 2023).
- Growth of Bioeconomy: From $10 billion in 2014 to $151 billion in 2023, surpassing 2025 target.
- Increase in Biotech Startups: From 50 startups in 2014 to 8,531 startups in 2023.
Implementation Strategy:
- Establish BioEnablers including Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs, Biofoundries, and Biomanufacturing Hubs across India.
- Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs will support research and innovation using data-driven approaches and AI to develop technologies for bio-based products.
- Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs will provide infrastructure to scale up bio-based technology for commercial applications.
Focus on Human Resource Development:
- Bio-Enablers will offer training and internships to build a skilled workforce with interdisciplinary and technical skills required for biomanufacturing.
Sectoral Focus Areas:
- Based on consultations, six thematic sectors of national importance have been identified for implementation:
- Bio-based chemicals and enzymes
- Functional foods and smart proteins
- Precision biotherapeutics
- Climate-resilient agriculture
- Carbon capture and utilization
- Futuristic marine and space research
- Sectoral Expert Committees are addressing challenges and gaps identified for each of these sectors.
Government Support:
- The DBT-BIRAC (Department of Biotechnology and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) has called for proposals to establish Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs in academia and industry.
- These hubs will support innovation and commercialization of biomanufacturing technologies.
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
One Nation One Subscription (ONOS)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Cabinet approves One Nation One Subscription (ONOS) Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It is a new initiative to provide unified access to international scholarly research articles and journals for all government-managed higher education institutions and research institutions in India.
- Scheme Overview:ONOS aims to make nearly 13,000 scholarly journals accessible to over 1.8 crore students, faculty, researchers, and scientists in more than 6,300 institutions across India. These journals will cover all academic disciplines, promoting both core and interdisciplinary research, including in tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
- Digital Platform:The scheme will be implemented through a fully digital process, coordinated by the Information and Library Network (INFLIBNET), an autonomous center under the University Grants Commission (UGC). The platform will provide easy access to the journals and facilitate a streamlined subscription process.
- Investment and Coverage:A total of ?6,000 crore has been allocated for ONOS for three years (2025-2027). The scheme will cover major international publishers such as Elsevier, Springer, Wiley, and Oxford University Press. It will enable institutions to access 13,000 journals from 30 global publishers.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- Access to Top-Quality Research:ONOS will provide wide access to top-tier scholarly journals, benefiting institutions, researchers, and students across various fields. It will significantly improve the research environment in the country, especially for institutions that previously lacked the resources to access high-impact journals.
- Fostering Research and Development:The initiative aligns with India's vision of becoming an Atmanirbhar and Viksit Bharat by 2047, supporting the government's goals under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF). It will help foster a culture of research and innovation in Indian institutions.
- Inclusivity:The scheme will particularly benefit institutions in smaller towns and rural areas, helping bridge the knowledge gap between urban and rural academic institutions.
- Simplified Access:The scheme eliminates the need for separate subscriptions to individual journals by different institutions, streamlining access to high-quality content through a single platform.
Implementation Details:
- Platform and Process:The ONOS platform will allow institutions to access journals through a unified portal, providing easy and coordinated access. The Department of Higher Education (DHE)will be responsible for conducting awareness campaigns about the initiative, ensuring widespread utilization among students and faculty.
- Review Mechanism:The ANRF will monitor and periodically review the usage of ONOS and track the contributions of Indian authors in the journals, ensuring that the initiative continues to support India’s research landscape.
- Operational Date:The ONOS platform is set to become operational on January 1, 2025, providing comprehensive access to research materials for government-managed higher education and research institutions.
The One Nation One Subscription scheme is a major step towards enhancing India's position in the global research ecosystem. It will provide unparalleled access to scholarly resources, supporting research excellence and innovation across the country.
National Gopal Ratna Award 2024
- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards(NGRA); one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA):
- Purpose:Recognize and encourage individuals, AI technicians, dairy cooperatives, and farmer organizations in the livestock and dairy sector.
- Categories:
- Best Dairy Farmer (Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds)
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT)
- Best Dairy Cooperative/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Addition (2024):Special awards for North Eastern Region (NER) to promote dairy development in the area, with winners in all three categories.
- and Prizes:
- Rs. 5 lakhs for 1st rank, Rs. 3 lakhs for 2nd rank, Rs. 2 lakhs for 3rd rank, and Rs. 2 lakhs for Special NER Award in the categories of Best Dairy Farmer and Best Dairy Cooperative/FPO/MPCs.
- For Best AIT, winners will receive a Certificate of Merit and a memento.
- Process:Winners selected from 2,574 applications via an online portal (https://awards.gov.in).
- The livestock sector is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to agriculture and providing livelihood, especially for small and marginal farmers, women, and landless laborers.
- Indigenous breeds have immense genetic potential, but their population and performance have been declining. To address this, the Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development in 2014 to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
National Milk Day
- It is celebrated annually on November 26 in India to honor the significant contributions of milk and the dairy industry to the country's development.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of Dr VergheseKurien, the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, who played a pivotal role in transforming India into the largest producer of milk globally.
- National Milk Day was first celebrated on November 26, 2014, after the Indian Dairy Association (IDA), along with various dairy institutions across the country.
Nayi Chetna 3.0 – PahalBadlaav Ki

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan launches the third edition of ‘Nayi Chetna – PahalBadlaav Ki’ a month-long national campaign against gender-based violence in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) under the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Led by: DAY-NRLM’s extensive Self-Help Group (SHG) network.
- Aim of the Campaign: Raise awareness and encourage grassroots-level action to combat gender-based violence.
- Campaign Slogan: “EkSaath, EkAwaaz, HinsaKeKhilaaf” (United Voice Against Violence).
- Approach:
- Adopts a "whole-of-government" approach with collaboration from 9 key ministries:
-
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Department of School Education and Literacy
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Department of Justice
- Key Objectives:
- Raise awareness about all forms of gender-based violence.
- Mobilize communities to demand accountability and action.
- Facilitate access to timely intervention and support systems.
- Empower local institutions to take action against violence.
- Goals for Nayi Chetna 3.0:
- Generate widespread awareness about gender-based violence.
- Foster collective action at the grassroots level.
- Drive convergence among government ministries and community stakeholders.
- Create a sustainable and informed movement for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
Project Veer Gatha

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Over 1.76 crore school students from all 36 States and UTs participated in Project Veer Gatha 4.0.
Key Highlights:
- Activities: Students submitted poems, paintings, essays, videos, and other creative works in honor of the bravery and sacrifice of Armed Forces personnel.
- Objective: Instituted in 2021, the project aims to spread the inspiring stories of Gallantry Awardees to foster patriotism among students.
- Platform for Creativity: Students engage in creative projects based on the heroic deeds and sacrifices of Gallantry Award winners.
- Previous Editions:
- Edition 1 (2021): 8 lakh students.
- Edition 2 (2022): 19.5 lakh students.
- Edition 3 (2023): 1.36 crore students.
- School-Level Activities: Schools conducted various activities from 16.09.2024 to 31.10.2024, uploading 4 best entries per school to the MyGov portal.
- Awareness Programs: The Ministry of Defence organized virtual and face-to-face awareness sessions across schools.
- Winner Recognition:
- Past Editions: 25 winners in Editions I and II, and 100 winners in Edition 3.
- Project 4.0: 100 National winners, each receiving Rs. 10,000.
- District & State/UT Winners: 4 District-level and 8 State/UT-level winners will be felicitated by respective authorities.
- Collaborative Initiative: The project is a joint effort of the Ministry of Defence and Ministry of Education.
GQ-RCP Platform
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted better detection of HIV-genome derived G-Quadruplex (GQ).
Key Features of the GQ-RCP Platform
- Technology: GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform developed by Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR).
- Detection Mechanism: Uses a fluorometric test to detect HIV-derived GQ DNA through reverse transcription and amplification.
- Advantage: Increases diagnostic reliability by reducing false positives associated with non-specific DNA probes.
- Process: pH-mediated transition of double-stranded DNA into GQ conformation for targeted detection.
- Flexibility: Initially designed for SARS-CoV-2, now adapted for HIV diagnosis.
About HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, specifically CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections.
- Transmission: Spread through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- AIDS: Without treatment, HIV progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system becomes severely damaged.
- Management: No cure; managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which controls viral replication.
Current HIV Situation in India
- Prevalence: As of 2021, ~2.4 million people living with HIV in India, with a 0.22% adult prevalence rate.
- Demographic Distribution: High prevalence among female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users (5.91%). Women represent 39% of HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: Northeastern states have the highest prevalence (e.g., Mizoram - 2.70%) and southern states (e.g., Andhra Pradesh - 0.67%).
Government Initiatives on HIV
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP): Launched in 1992, aims for prevention, treatment, and care.
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focus on awareness, blood safety, and surveillance.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded interventions for high-risk populations.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Increased targeted interventions and civil society involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Focused on integration of HIV services into public health systems.
- Phase V (2021-2026): Aim to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2026.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) ensures the rights of people living with HIV and access to treatment without discrimination.
- International Support: India receives support from UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and foundations like Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Global Soil Conference 2024
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
- Global Soil Conference (GSC) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- Focused on soil health's importance for food security, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem services.
What is the Global Soil Conference 2024?
- Organizers: Indian Society of Soil Science (ISSS) in collaboration with the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- Objective: Address sustainable soil/resource management challenges and foster global dialogue.
- Theme: "Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services."
Key Highlights of GSC 2024:
- Soil Health Issues:
- Soil degradation threatens productivity and global food security.
- 30% of India's soil is compromised by erosion, salinity, pollution, and organic carbon loss.
- Soil erosion is linked to SDG 15 (Sustainable Development Goal 15), aiming to protect terrestrial ecosystems.
- SDG 15:
- Goals: Promote sustainable land use, combat desertification, halt land degradation, protect biodiversity.
Concerns Regarding Soil Health in India:
- Soil Degradation:One-third of India's land faces degradation due to poor farming practices.
- Soil Erosion & Fertility Loss:
- India loses 15.35 tonnes of soil/hectare annually.
- Results in crop losses, economic damage, and environmental issues like floods and droughts.
- Soil Salinity:Reduces water infiltration, nutrient uptake, and aeration, making land infertile.
- Low Organic Content:
- Organic carbon in Indian soil is 0.54%, which hampers fertility.
- Over 70% of soils are affected by acidity or alkalinity, disrupting nutrient cycles.
- Desertification:Reduces soil fertility, increases erosion, and worsens food insecurity.
- Diversion of Fertile Land:Fertile agricultural land is diverted for non-agricultural purposes.
India's Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme:Provides farmers with soil nutrient information.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:Focuses on efficient water use.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming & Natural Farming Mission:Promotes sustainable farming practices to protect soil health.
Guided Pinaka Weapon System

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully completed the Flight Tests of Guided Pinaka Weapon System.
Key Details of the Flight Tests:
- Conducted as part of Provisional Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) Validation Trials.
- Tests Phases: Flight tests were carried out in three phases at different field firing ranges.
- Parameters Assessed:
- Ranging (the distance the weapon can accurately target).
- Accuracy (precision of hits).
- Consistency (performance over multiple trials).
- Rate of Fire (ability to fire multiple rockets simultaneously in salvo mode).
Guided Pinaka Weapon System:
- Design and Development:
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Research Centre Imarat,
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory,
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
- Proof & Experimental Establishment.
- Production Agencies: Munitions India Limited, Economic Explosives Limited, Tata Advanced Systems Limited, and Larsen & Toubro.
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Key Features:
- Pinaka: A multi-barrel rocket launcher system named after Lord Shiva’s bow.
- Mobility: Highly mobile, providing quick deployment in battlefield scenarios.
- Firepower: Capable of delivering concentrated firepower on enemy targets.
- Upgraded Version (Pinaka Mark II):
- Extended range: 70 to 80 km.
- Future range targets: 120 km and 300 km.
- Salvo Mode: Tested for the ability to launch 12 rockets simultaneously.
- Significance:
- Strategic Importance: The successful trials enhance the artillery firepower of the Indian Armed Forces.
- Completion of Pre-requisite Trials: The system has successfully completed all flight trials before its induction into the Indian Army.
Prasar Bharati’s OTT Platform – WAVES

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, Prasar Bharati launched its OTT platform WAVES, to cater to India’s increasing demand for digital streaming services.
Key Features of WAVES OTT Platform:
- Content Offered: A mix of classic content and contemporary programming, catering to various audiences.
- Target Audience: Aimed at Indians and those abroad wishing to stay connected to their Indian roots.
- Languages: Available in 12+ languages, including Hindi, English, Bengali, Marathi, Kannada, Malayalam, Telugu, Tamil, Gujarati, Punjabi, Assamese.
- Genres: Spanning 10+ genres, including infotainment, games, current affairs, and news.
- Free Access: Most content is available free to download and view, with exceptions for premium content.
- Additional Features:
- Video on demand.
- Free-to-play gaming.
- Radio streaming.
- Live TV streaming with 65 live channels.
- Online shopping via the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) supported e-commerce platform.
Content Highlights:
- Fauji 2.0: A modern adaptation of the iconic 1980s Shahrukh Khan show, focusing on lives of people who serve and protect India.
- Kakbhushandi Ramayana: An original show on DD National now available on WAVES, based on research of over 350 versions of the Ramayana worldwide. The show aims to provide a new portrayal of the epic, appealing to younger audiences.
Vision for WAVES OTT:
- WAVES aims to revive nostalgia while embracing modern digital trends.
- It serves as an inclusive platform that highlights Indian culture with an international outlook.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Daniel Barenboim (Classical Pianist and Conductor) and Ali Abu Awwad (Palestinian Peace Activist) were jointly awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development for 2023.
- Daniel Barenboim was recognized for fostering peace through musical and cultural dialogue initiatives.
- Ali Abu Awwad was honored for his advocacy of peace through dialogue via his organization Roots, which he founded after serving time in Israeli prison.
Significance of the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- The award is given to individuals or organizations who have made outstanding contributions to international peace, disarmament, and development.
- It includes a monetary award of ?25 lakh and a citation.
About the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- Established: 1986 by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust in memory of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- Objective: To honor sustained efforts towards international peace, the development of humanity, and the promotion of disarmament.
- Past recipients: Includes prominent figures and organizations such as Mikhail Gorbachev, UNICEF, Jimmy Carter, Angela Merkel, ISRO, and Sir David Attenborough.
2022 Awardees:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize for 2022 was awarded to the Indian Medical Association and the Trained Nurses Association of India, in recognition of their contribution as COVID-19 warriors.
Key Takeaways:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize is regarded as one of the most prestigious awards for promoting peace, disarmament, and development worldwide.
- Daniel Barenboim's musical initiatives and Ali Abu Awwad's work through dialogue exemplify efforts to bridge divides and promote peaceful resolutions to conflict.
Green World Awards 2024

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Coal India Limited (CIL) under the aegis of the Ministry of Coal, has been conferred with the esteemed Green World Environment Award in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category along with the distinguished tile of Green World Ambassador.
Key Highlights:
- Reason for the Award:
- The award was granted to CIL for its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna, a CSR initiative aimed at providing permanent curative treatment for Thalassemia through Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT).
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?10 lakh for BMT and has helped over 600 Thalassemia patients across India.
- Background of the Award:
- The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group, conferred the award.
- The organization has been recognizing and promoting environmental best practices and CSR initiatives globally since its establishment in 1994.
- CIL’s Role in CSR:
- CIL has been a pioneer in CSR, with its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna being the first of its kind among public sector undertakings in India.
- The initiative partners with 17 prominent hospitals across India to provide stem cell transplants for Thalassemia patients.
- CIL’s Contribution to India's Energy Sector:
- CIL is responsible for producing over 80% of India's coal and contributes to 70% of the total coal-based power generation in the country.
- CIL accounts for 55% of India’s total power generation and meets 40% of the primary commercial energy requirements.
- Environmental Initiatives by CIL:
- CIL has adopted various measures to improve environmental sustainability, including:
- Expanding green cover over mined areas.
- Creating eco-parks and tourism spots.
- Providing mine water for domestic and agricultural use to surrounding villages.
- About Coal India Limited (CIL):
- Established: November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Status: A Maharatna company and the largest coal-producing company in the world.
- Subsidiaries: CIL has seven producing subsidiaries and is a major corporate employer in India.
- About the Green Organization:
- Founded: 1994.
- Nature: Independent, non-political, non-profit organization.
- Objective: To recognize, reward, and promote environmental and CSR best practices worldwide.
- Initiatives: The Green World Awards are part of global efforts to encourage sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Significance of the Award:
- The Green World Environment Award highlights CIL’s commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability while maintaining its core role as an energy provider.
- The recognition underscores CIL’s leadership in integrating CSR initiatives with corporate operations to contribute to national development.
Bhu-Neer Portal
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Minister of Jal Shakti, digitally launched the “Bhu-Neer” portal during the India Water Week 2024.
- Developed by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Portal:
- Centralized platform for managing and regulating groundwater resources across India.
- Aims to ensure transparency, efficiency, and sustainability in groundwater usage, facilitating easier access to groundwater withdrawal permits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplified interface to streamline the application process for groundwater withdrawal.
- PAN-Based Single ID System: Allows seamless user registration, providing a unique identification for all stakeholders.
- NOC with QR Code: Enables verifiable and trackable compliance documents, ensuring authenticity.
- Improved Version: An enhanced version compared to the previous NOCAP system, with improved efficiency and features.
- Streamlined Process Flow: Simplifies the process for obtaining groundwater withdrawal permits.
Goals and Benefits:
- Promotes the sustainable use of groundwater and ensures compliance with legal frameworks at state and national levels.
- Supports Ease of Doing Business: Aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision by making the groundwater regulation process seamless and faceless, reducing bureaucratic delays.
Public Accessibility:
- The portal is now live and accessible to both project proponents and the general public.
- It offers services such as groundwater withdrawal related queries, tracking applications, and payment of statutory charges.
Impact on Groundwater Management:
- The platform is expected to bring improved groundwater regulation by providing centralized access to policies, compliance details, and sustainable practices related to groundwater use.
- It will contribute significantly to monitoring and sustainable management of India’s groundwater resources, crucial in light of increasing water scarcity.
Vision of the Portal:
- In line with the government’s broader goals of digitalization, transparency, and environmental sustainability, the “Bhu-Neer” portal marks a significant step in efficient water resource management.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
India’s Polio Eradication Journey

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's achievement of becoming polio-free in 2014 stands as one of the most remarkable successes in global public health. This milestone, which was celebrated worldwide, represents decades of consistent efforts, collaboration, and innovative strategies, culminating in the elimination of wild poliovirus in the country.
Key Milestones in Polio Eradication
- Pulse Polio Programme Launch (1995):
- The Pulse Polio Immunization Programme was a game-changer, initiating large-scale vaccination campaigns across India, with the first nationwide campaign held on 2nd October 1994 (Gandhi Jayanti) in Delhi.
- The campaign used the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) and reached over 1 million children.
- The slogan "Do BoondZindagi Ki" (Two drops of life) became synonymous with India’s polio eradication efforts.
- Routine Immunization and System Strengthening:
- The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), which launched in 1985, made polio one of the first diseases targeted for elimination. UIP is now one of the world’s largest immunization programs, aiming to provide vaccines against 12 preventable diseases, including polio.
- Cold chain management was improved through systems like the National Cold Chain Training Centre (NCCTE) and Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN), ensuring proper storage and distribution of vaccines.
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) Introduction (2015):
- As part of the Global Polio Endgame Strategy, India introduced the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) in 2015 to provide enhanced protection, particularly against type 2 poliovirus.
- This move followed the global transition from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV (which excludes the type 2 strain) and helped ensure continued protection against all forms of polio.
- Surveillance Systems:
- India implemented Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) Surveillance to track unexplained paralysis in children, a symptom of polio.
- Environmental Surveillance, involving monitoring sewage water for poliovirus strains, played a critical role in identifying potential outbreaks and residual poliovirus transmission.
- Political Will & Community Engagement:
- Strong political commitment from both central and state governments ensured sustained resources and focus on the program.
- Community participation was also vital, with health workers and volunteers working to ensure vaccination coverage in the most remote areas.
The Final Leap: Certification and Maintenance
- 2011 marked the last case of wild poliovirus in Howrah, West Bengal, and India ramped up its surveillance and response efforts to ensure no further cases.
- India achieved polio-free certification from the World Health Organization (WHO) on 27th March 2014, after meeting strict criteria, including three years without wild poliovirus transmission and robust surveillance systems.
Post-Certification Efforts: Keeping Polio at Bay
Even after achieving polio-free status, India remains vigilant to maintain this achievement:
- Annual National Immunization Days (NID) and Sub-National Immunization Days (SNID) are held regularly to boost immunity levels and ensure no child is missed.
- Continuous surveillance and vaccination at international borders help prevent the risk of re-importation of the virus.
- Mission Indradhanush (MI), launched in 2014, aims to increase immunization coverage to 90%, focusing on hard-to-reach areas and improving vaccine coverage.
Ongoing Commitment to Immunization
India’s immunization programs continue to evolve:
- New vaccines like Rotavirus, Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV), and Measles-Rubella (MR) are being added to protect against other vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Mission Indradhanush’s intensified phase has played a crucial role in improving vaccination rates, particularly in underserved areas.
SanyuktVimochan 2024

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Army successfully conducted the Multilateral Annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise, 'SanyuktVimochan 2024' at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
Key Highlights:
- Conducted by: Konark Corps of Southern Command, Indian Army.
- Day 1: Tabletop Exercise (TTX)
- Theme: 'Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat'.
- Focused on simulating a cyclone scenario affecting the Okha-Porbandar coastline.
- Discussed disaster relief strategies and interagency cooperation to improve response readiness.
- Attended by senior officials from NDMA, Armed Forces, State Disaster Management, and industry representatives, including delegates from nine foreign countries.
- Day 2: Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- Held at Chowpatty Beach, Porbandar.
- Simulated Disaster Scenario: Coordinated response to a cyclone, showcasing joint operations by:
- Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, NDRF, SDRF, and other Central and State agencies.
- Key actions demonstrated:
- Requisition and Surveillance: Civil administration’s request for Armed Forces' assistance, followed by area surveillance.
- Rescue Operations: Insertion of personnel to rescue casualties.
- Casualty Evacuation: Use of resources to evacuate and assist victims.
- Resuscitation and Rehabilitation: Restoration efforts for affected citizens.
- Industrial Display &Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative:
- Showcased indigenous HADR equipment from Indian defense industries.
- Highlighted technological advancements and self-reliance in disaster management.
- SanyuktVimochan 2024 enhanced India's disaster response capabilities, ensuring a coordinated and effective approach to humanitarian assistance.
- The exercise also bolstered India’s leadership in global disaster relief, contributing to international best practices and collaborative efforts in humanitarian assistance and disaster response.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Bharat NCX 2024

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024), inaugurated on November 18, 2024, is a key initiative aimed at strengthening India’s cybersecurity resilience. This 12-day exercise is designed to equip cybersecurity professionals and national leadership with the skills to manage complex cyber threats, enhance incident response capabilities, and improve strategic decision-making. The event is organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
Key Details of Bharat NCX 2024:
- Cyber Defense and Incident Response Training
- The exercise focuses on defensive cybersecurity skills, preparing participants to defend against cyberattacks.
- Live-fire simulations will provide hands-on experience with real-time cyberattacks on IT and Operational Technology (OT) systems.
- Strategic Decision-Making Simulations
- A core component is the Strategic Decision-Making Exercise, where senior management from across sectors will simulate decision-making in a national-level cyber crisis.
- This exercise enhances their ability to respond swiftly and strategically in high-pressure scenarios.
- CISO’s Conclave
- The CISO's Conclave brings together Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) from government, public, and private sectors.
- The conclave will feature panel discussions on the latest cybersecurity trends and government initiatives, allowing professionals to exchange knowledge and collaborate.
- Bharat Cybersecurity Startup Exhibition
- An exhibition will highlight innovative cybersecurity solutions developed by Indian startups. This showcases the growing role of the private sector in strengthening India’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Leadership Engagement and Capacity Building
- Leadership engagement is a key feature, ensuring that high-level decision-makers are prepared to lead national cybersecurity efforts.
- The exercise will foster a unified approach to dealing with emerging cyber threats.
Significance for India’s Cybersecurity Strategy
- National Cybersecurity Resilience: Bharat NCX 2024 is a vital step in fortifying India’s cybersecurity defenses, preparing professionals and leadership to address the evolving cyber threat landscape.
- Collaboration and Innovation: The inclusion of industry stakeholders, startups, and leaders from various sectors underscores the importance of collaboration in developing innovative solutions to cybersecurity challenges.
- Capacity Building: The exercise aims to improve decision-making at all levels, helping India build a robust cybersecurity framework to secure its critical infrastructure and respond effectively to potential cyber crises.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Global Maritime Conference
- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
In a bid to enhance India’s clout in the global merchant shipping sector, the government recently hosted a two-day global maritime conference – Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Conference:
- To enhance India's maritime influence and position India as a key player in the global maritime sector, especially in merchant shipping and maritime trade.
- To showcase India's ambitions in expanding its role in global maritime trade, governance, and collaboration.
- India's Maritime Ambitions:
- Despite being the most populous nation and one of the largest global economies, India’s maritime clout has been relatively lower than expected.
- The dialogue aims to shift global attention towards India's growing role and contributions to maritime trade and shipping.
- India's Maritime Growth:
- India contributed to 16% of global maritime growth in 2023 and is on track to become the third-largest global economy within three years.
- As India’s economic and geopolitical influence expands, maritime governance will become increasingly significant, necessitating deeper international collaborations in commerce, connectivity, and trade.
- Focus Areas of the Dialogue:
- Global Maritime Trade: India's expanding role in international shipping, trade routes, and maritime security.
- International Collaborations: Promoting deeper engagement in maritime governance and policy-making ecosystems.
- Human Well-being: Highlighting the role of maritime trade in supporting human welfare, particularly in the context of sustainable development and climate change.
- Significance for India:
- The conference serves as a platform to discuss India’s aspirations, policies, and presence in global maritime affairs.
- It is an opportunity to strengthen maritime relations and address issues of global relevance such as trade routes, shipping governance, and environmental sustainability
1st Bodoland Mohotsav

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 1st Bodoland Mohotsava two-day event focused on language, literature, and culture.
- Objective: Aims to promote peace, unity, and a vibrant Bodo society through cultural integration. The festival celebrates the rich Bodo culture and heritage.
Historical Context and Peace Initiatives:
- End of Violence: The event marks the end of 50 years of violence, following the Bodo Peace Accord (2020), which ended conflict in Bodoland and led to a path of peace and development.
- Peace Agreements: The Bodo Peace Accord served as a catalyst for other peace settlements, such as the KarbiAnglong Accord, Bru-Reang Accord, and NLFT-Tripura Accord.
Development in Bodoland Post-Peace Accord:
- Impact of the Peace Accord:
- Over 10,000 youth in Assam have renounced violence and joined the mainstream of development.
- Increased mutual trust between the people and the government.
- Economic Assistance:
- Rs 1,500 crore special package by the central government.
- Rs 700 crore spent on infrastructure development in education, health, and culture in Bodoland.
- Rs 5 lakh assistance for families affected by the Bodo conflict.
Government Support for Socio-Economic Development:
- Skill Development & SEED Mission:Focus on skilling, entrepreneurship, employment, and development through the SEED Mission for youth empowerment.
- Rehabilitation of Former Cadres:
- Over 4,000 former cadres of the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) have been rehabilitated.
- Many youths have been recruited into Assam Police.
- Tourism & Employment:Growing tourism in Bodoland, with parks like Manas National Park and Raimona National Park, creating employment opportunities for youth.
Cultural Promotion:
- Bodo Culture and GI Tags:Promoting Bodo crafts like Aronnaye, Dokhona, Gamsa, etc., that have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags to preserve cultural identity.
- Bodoland Handloom Mission & Sericulture:Government efforts to promote sericulture and the Bodoland Handloom Mission to sustain Bodo weaving traditions.
- Literary Celebrations:
- Continuous Bodoland Literary Festival in Kokrajhar, enhancing the importance of Bodo literature and language.
- Celebration of Bodo Sahitya Sabha’s 73rd foundation day.
Key Government Initiatives for Development:
- Infrastructure Development:
- Rs 800 crore annually being spent by the Assam government for the development of Bodoland.
- Focus on healthcare, education, and employment.
- Medical Education:Expansion of medical colleges in Assam from 6 to 12, with plans for 12 more new colleges.
Operation Dronagiri

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Operation Dronagiri, launched under the National Geospatial Policy 2022 by the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Objective: It is a pilot project under India’s National Geospatial Policy 2022 aimed at showcasing the potential of geospatial technologies in sectors such as Agriculture, Livelihoods, and Logistics & Transport to improve quality of life and ease of doing business.
- Implementation:
- The first phase will cover five states: Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Sectors Targeted: The focus will be on demonstrating the integration of geospatial data to solve real-world challenges in agriculture, transportation, and livelihoods.
National Geospatial Policy 2022
- Context: The National Geospatial Policy 2022 is aimed at liberalizing geospatial data and enabling widespread access and use of geospatial technologies across various sectors of governance, business, and development.
- Goals:
- Development of Geospatial Infrastructure: Promoting the creation of a robust infrastructure to make spatial data more accessible and usable.
- Geospatial Skill Development: Focus on creating a workforce proficient in geospatial technologies.
- Implementation of Standards: Establishing clear standards for geospatial data to ensure consistency and interoperability.
Role of Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI)
- Launch: Alongside Operation Dronagiri, the Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI) was also unveiled.
- Purpose: GDI is designed to facilitate seamless data sharing, access, and analysis of geospatial data.
- Key Features:
- Data Exchange: Enables smooth sharing of geospatial data for urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
- Privacy and Security: Built with advanced data exchange protocols and privacy-preserving features to ensure secure data sharing.
- Collaboration: It will promote collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, industry, and startups, to unlock actionable insights for decision-making.
- Key Features:
Potential Applications of Geospatial Data
- Urban Planning: Assisting cities in designing efficient infrastructure.
- Disaster Management: Providing real-time data for better disaster response.
- Environmental Monitoring: Supporting initiatives for environmental protection and sustainability.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, crop monitoring, and improving supply chains.
- Logistics & Transport: Streamlining transportation networks, reducing traffic, and improving delivery systems.
Grand Challenge for Startups
- Objective: A Grand Challenge was announced as part of the initiative to support startups in developing Proofs of Concept (POCs) targeting specific problems in the focus sectors.
- Role of Startups: The challenge encourages innovation by early-stage and growth-stage startups in geospatial technology, offering mentorship, resources, and access to datasets.
- Geospatial Innovation Accelerators:
- The Geospatial Innovation Accelerators (GIAs) at prestigious institutions like IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will support this effort.
- Mentorship and Resources: These accelerators will provide the necessary support for startups to turn their innovations into scalable solutions.
Key Stakeholders and Operational Arms
- Geospatial Innovation Cell (DST): Responsible for overseeing the project’s implementation and execution.
- Navavishkar I-Hub Foundation (IITTNiF): Will manage the operational activities of Operation Dronagiri.
- Partnering Institutions: GIAs at IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will be the operational arms.
- Private Sector Involvement: Significant involvement of private sector companies, including startups, is crucial to ensuring the success and scalability of the project.
Impact and Significance
- Socioeconomic Benefits: The integration of geospatial data into agriculture, transport, and logistics will improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost economic activity in critical sectors.
- Geospatial Innovation: The initiative marks a significant step towards making India a global leader in geospatial technology and positioning the country as a hub for innovative solutions using geospatial data.
- Government Engagement: The project will involve various government departments and corporates in a public-private partnership (PPP) model, similar to the successful implementation of the UPI payment system.
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
Nano-Coating Technology for Fertilizer Efficiency

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A mechanically stable, biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating material can enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers by tuning them for slow release, thereby limiting their interaction with the rhizosphere soil, water and microbes.
Development of Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- A biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating has been developed to enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers.
- The nanocoating allows for slow release of nutrients, thus limiting excessive interaction with soil, water, and microbes, and optimizing fertilizer usage.
Coating Composition:
- The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, primarily chitosan (a biopolymer from chitin) and lignin (a plant-based polymer).
- These materials are low-cost, naturally derived, and eco-friendly, ensuring sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Technological Innovation:
- The coating process involves using a drum rotor method to uniformly coat fertilizers, improving their efficiency.
- The tuning of hydrophobicity in the nanocoating alters the release kinetics of fertilizers, ensuring that nutrients are released in accordance with the crop’s nutrient uptake needs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability:
- The nanocoating is biodegradable, which ensures that it does not harm the environment post-application, unlike conventional chemical fertilizers that may lead to soil degradation and water pollution.
- Life cycle assessment confirms the product's long-term sustainability compared to traditional fertilizers.
Enhanced Crop Productivity:
- The slow-release coating enables a reduced fertilizer dose, while maintaining or even increasing crop yields, particularly for staple crops like rice and wheat.
- This technology facilitates higher agricultural output with fewer inputs, contributing to food security.
Industrial Viability:
- The mechanical stability of the coated fertilizers ensures they can withstand transportation and handling, making them suitable for large-scale industrial application.
- The rotary drum system used for coating ensures uniform application and superior mechanical performance, ensuring that the fertilizers are not damaged during the supply chain process.
Economic Benefits:
- The use of slow-release fertilizers can reduce overall fertilizer costs for farmers while enhancing yields, leading to improved socio-economic conditions for farmers.
- The technology holds potential for economic growth by boosting agricultural productivity and reducing the financial burden on farmers for chemical fertilizer inputs.
Global Relevance:
- The research is significant in the context of global sustainable development goals, aiming to reduce the over-reliance on conventional chemical fertilizers that contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Research Collaboration:
- This breakthrough was achieved by scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science: Nano, highlighting its scientific validation.
3rd Indian Space Conclave
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd Indian Space Conclave, held in New Delhi, was a significant event for India's growing role in global space exploration and strategic partnerships.
- Organized by the Indian Space Association (ISPA), the conclave brought together key stakeholders from the government, industry, academia, and space agencies to discuss India’s space ambitions and the transformative role of space technologies.
Key Highlights:
Satcom as a Transformative Force for Digital India
- Emphasis on Satellite Communication (Satcom) is more than a mere tool—it's a transformative force driving Digital India by connecting every household, village, and remote area of the country.
- Satcom has a wide array of applications that extend across essential sectors such as telecommunications, disaster management, healthcare, education, and agriculture, particularly in underserved regions.
Indo-EU Space Collaboration
- The event also showcased India’s growing space partnerships, particularly with the European Union (EU). The EU Ambassador recognized India as a dynamic space power and highlighted shared goals in Earth observation, space security, and human spaceflight.
- Proposed joint initiatives include training programs, collaborative research, and satellite missions, such as the Proba-3 satellite launch by ISRO, focusing on observing the Sun.
- India’s trustworthiness as a partner in space was underscored by its role in the successful launch of the Proba-1 and Proba-2 missions for the EU, with Proba-3 marking India’s third contribution to EU space exploration.
Space Startups and Innovation
- The rise of space-focused startups in India, spurred by the 2020 space sector reforms, was another key highlight. India now has over 300 space startups, contributing to both economic growth and innovation in the space industry.
- These reforms have helped curb brain drain, with many talented Indian professionals returning from global agencies like NASA to join the expanding Indian space ecosystem.
India’s Long-Term Space Goals
- The Indian space program has ambitious long-term goals, including:
- Gaganyaan, India’s human spaceflight mission.
- A crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- The establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040.
- These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technological innovation.
Space Sector Reforms (2020)
- The Space Sector Reforms 2020 were designed to increase the participation of private players in India’s space activities. The creation of agencies like the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) and the strengthening of New Space India Limited (NSIL) have been pivotal in boosting India’s global space market share.
- IN-SPACe serves as an autonomous body fostering industry, academia, and startups, while NSIL handles commercial activities and promotes high-tech space-related ventures.
India's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission
- ISRO's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission was inaugurated in Leh, Ladakh. This mission simulates the conditions of space habitats, specifically focusing on Mars and Moon environments.
- Ladakh's unique climate—high altitude, low oxygen levels, and extreme temperature fluctuations—makes it an ideal location for testing life support systems, space habitat technologies, and sustainable resource utilization.
Key Aspects of the Analog Mission:
- Life support systems like hydroponics (space farming) and standalone solar power systems to support sustainable food production and renewable energy in space habitats.
- Circadian lighting to simulate daylight cycles, maintaining astronaut health and well-being.
- The mission’s goal is to understand the psychological and operational challenges of living in isolation and extreme conditions, preparing India for future interplanetary exploration.
Diclipterapolymorpha

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A new species of Dicliptera, named Diclipterapolymorpha, has been discovered in the Northern Western Ghats of India.
Habitat and Location:
- Diclipterapolymorpha was found in the grasslands of Talegaon-Dabhade, a region known for its grasslands and fodder markets.
- The species thrives in the harsh climatic conditions of the Northern Western Ghats, an area vulnerable to summer droughts and frequent human-induced fires.
Unique Characteristics:
- The species is fire-resilient (pyrophytic), exhibiting a rare dual-blooming pattern:
- First Blooming: Occurs post-monsoon, typically from November to March/April.
- Second Blooming: Triggered by grassland fires in May and June, during which the plant produces dwarf flowering shoots.
- The inflorescence structure is unique in India, with its cymules developing into spicate inflorescences, a feature more commonly found in African species.
Taxonomy:
- The species is named Diclipterapolymorpha to reflect its diverse morphological traits.
- It is taxonomically distinct within the Dicliptera genus, with no known Indian species exhibiting similar characteristics.
Conservation Implications:
- The discovery highlights the need to carefully manage grassland ecosystems, as the species is adapted to fire but still vulnerable to habitat degradation.
- Human-induced fires are essential for the species' blooming cycle but must be managed to avoid overuse and degradation of habitat.
- The species' limited habitat range underscores the need for conservation efforts to protect the delicate ecosystems of the Western Ghats.
Publication:
- A research paper detailing the discovery of Diclipterapolymorpha has been published in the prestigious Kew Bulletin.
AntarikshaAbhyas 2024

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- ‘AntarikshaAbhyas – 2024’ is a three-day space exercise held from November 11-13, 2024, hosted by the Defence Space Agency (DSA), Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff.
- The exercise is the first of its kind and focuses on war-gaming the growing threats to space-based assets and services.
Objective of the Exercise:
- Enhance understanding of space-based assets and their operational dependencies.
- Identify vulnerabilities in military operations in case of denial or disruption of space services.
- Integrate India's space capabilities in military operations to secure national strategic objectives.
Participants:
- Defence Space Agency (DSA) and its allied units.
- Personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Specialist agencies under Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff, including:
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCA)
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Representatives from ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research & Development Organisation).
Focus Areas:
- Space-based asset and service operational dependency.
- Securing national interests in space through technological innovation and development.
- Assessing space service vulnerabilities and impacts on military operations.
Indian Military Heritage Festival 2024

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan inaugurated the 2nd edition of the Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) on November 8, 2024, in New Delhi.
- The two-day festival engages global and Indian experts, corporations, academicians, and non-profits focusing on India’s national security, foreign policy, military history, and military heritage.
Launch of Project Shaurya Gatha:
- Project ‘Shaurya Gatha’ was launched to conserve and promote India’s military heritage.
- The initiative, spearheaded by the Department of Military Affairs and USI of India, focuses on education and tourism to highlight India’s military history and valor.
- Publications Released:
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- "Because of this: A History of the Indo-Pak Air War December 1971" by Air Marshal Vikram Singh (Retd).
- "Valour and Honour", a joint publication by the Indian Army and USI of India.
- "War-wounded, Disabled Soldiers, and Cadets", a joint publication by USI and the War Wounded Federation.
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- Festival's Significance:
- The festival addresses the gap in public awareness regarding India’s military heritage and security concerns.
- It aims to enhance understanding of India’s military traditions, security issues, and the country’s efforts toward self-reliance in military capabilities under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
QS World University Rankings
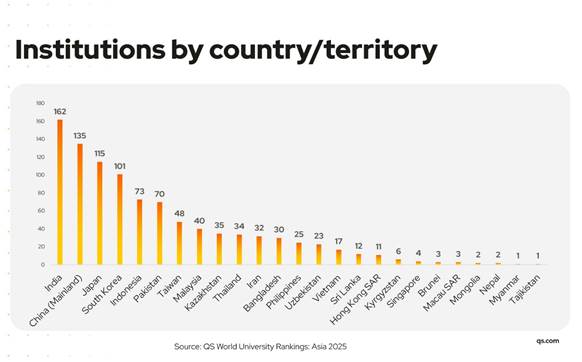
- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
The QS World University Rankings: Asia 2025 spotlights the top institutions in Eastern, Southern, South-Eastern, and Central Asia, emphasizing academic excellence, research, innovation, and internationalization.
India's Performance:
India has shown a remarkable upward trajectory, featuring:
- Two institutions in the Top 50:
- IIT Delhi ranked 44th (up from 46th), with a 99% employer reputation score.
- IIT Bombay ranked 48th, excelling with a 99.5% employer reputation score and 96.6% academic reputation score.
- Top 100 Institutions:
- IIT Madras (56th), IIT Kharagpur (60th), Indian Institute of Science (62nd), IIT Kanpur (67th), and University of Delhi (81st).
- Top 150 Institutions:
- IIT Guwahati, IIT Roorkee, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Chandigarh University (120th), UPES (148th), and VIT (150th).
Key Indicators for India:
- International Research Network and Citations per Paper contribute to India's growing global academic reputation.
- Papers per Faculty and Staff with PhD are India’s strongest indicators, reflecting robust research output and high teaching standards.
- Anna University achieved a perfect score of 100 in the Papers Per Faculty indicator, emphasizing high research output.
- North Eastern Hill University and University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore received a perfect score of 100 in the Faculty-Student Indicator.
Growth of Indian Institutions:
- India now has 46 institutions in the 2025 rankings, up from just 11 in 2015, marking a 318% increase over the past decade.
- India dominates Southern Asia with seven institutions in the top 10, showcasing the country's strengthening educational landscape.
India's Growing Global Influence:
- India's achievements underscore its commitment to academic excellence, competitiveness, and resilience in global higher education.
- Institutions like IIT Delhi and IIT Bombay highlight India’s ability to balance research productivity with high-quality teaching, enhancing its reputation as a global education hub.
AUSTRAHIND 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND started on 8th November 2024 at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra. The exercise will run until 21st November 2024.
Participating Forces:
- Indian Contingent: 140 personnel, primarily from the DOGRA Regiment and Indian Air Force (14 personnel).
- Australian Contingent: 120 personnel from the 13th Light Horse Regiment of the 10th Brigade of the 2nd Division.
Purpose of the Exercise:
- Enhance Military Cooperation between India and Australia.
- Promote Interoperability in conducting joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert terrain.
- Focus on operations under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Key Objectives:
- Joint Tactical Drills and Planning to improve coordination between the forces.
- Training in counter-terrorism operations, special heli-borne operations, and drone countermeasures.
Phases of the Exercise:
Combat Conditioning and Tactical Training Phase:
- Includes drills such as terrorist response, territory capture, and Raid and Search & Destroy Missions.
- Establishment of Joint Operations Centre and securing critical infrastructure like helipads.
- Training on drone operations and counter-drone measures.
Validation Phase: Practical application and testing of skills learned in the previous phase.
Significance:
Best Practices Sharing: Both sides will exchange tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting effective tactical operations.
Camaraderie Building: The exercise will foster a strong bond between soldiers from both countries.
Background: AUSTRAHIND is an annual exercise held alternately in India and Australia. The last edition took place in Australia in December 2023.
PM Vishwakarma Yojana

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The PM Vishwakarma Yojana is a landmark initiative by the Indian government aimed at revitalizing traditional craftsmanship and empowering artisans and craftspeople, often referred to as Vishwakarmas. Launched on September 17, 2023, during Vishwakarma Jayanti, the scheme highlights the government's commitment to preserving India's rich cultural heritage and supporting the unorganized sector.
Key Highlights
- Objective:
- To strengthen the Guru-Shishya tradition and improve the quality, reach, and marketability of products and services by artisans.
- To integrate Vishwakarmas into domestic and global value chains, making them self-reliant.
- To alleviate poverty by supporting rural and urban artisans across India.
- Financial Outlay:,Fully funded by the Union Government with a ?13,000 crore budget spanning five years (2023–2028).
- Eligibility:
- Open to rural and urban artisans and craftspeople involved in 18 traditional crafts, such as blacksmithing, goldsmithing, pottery, boat making, and carpentry.
- Covers 5 lakh families in the first year and aims to reach 30 lakh families over five years.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Support:
- Collateral-free credit of ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) at a concessional 5% interest rate.
- Government provides 8% interest subvention upfront to banks.
- Toolkit Incentive: ?15,000 via e-vouchers for acquiring modern tools.
- Training and Skill Development: Basic and advanced skill training to create industry-ready manpower.
- Digital and Marketing Incentives: Encourages digital transactions and provides marketing support.
- Recognition: Beneficiaries receive a PM Vishwakarma Certificate and ID Card.
- Market Linkage: Facilitates better market access for artisan products.
- Financial Support:
- Achievements (as of Nov 4, 2024):
- 25.8 million applications received.
- 2.37 million artisans registered after verification.
- Over 1 million artisans benefited from toolkit incentives.
Significance
- Promotes inclusive development by supporting an underserved segment of the workforce.
- Recognizes and supports traditional skills passed down through generations, preserving India’s cultural diversity.
- Enhances productivity and competitiveness by integrating artisans into MSME sectors.
- Encourages sustainability through the promotion of handmade, eco-friendly crafts.
Key Institutions Involved
- Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME): Oversees implementation.
- Common Services Centres (CSC): Facilitates registration through biometric-based PM Vishwakarma Portal.
Challenges Addressed
- Lack of access to modern tools and financial support.
- Insufficient market linkages and exposure for traditional crafts.
- Limited opportunities for skill enhancement and product development.
Adoption Awareness Month 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Adoption Awareness Month is an annual event where CARA and all its stakeholders come together to raise awareness about the legal process of adoption.
Context
- Celebrated by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) and the Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA).
- When: November 2024.
- Theme: “Rehabilitation of Older Children through Foster Care and Foster Adoption.”
- Purpose: To raise awareness about legal adoption, foster care, and the rehabilitation of older children in India.
Objectives
- Promote Legal Adoptions:
- Create awareness about the legal framework and processes for adoption.
- Encourage prospective adoptive parents (PAPs) to adopt older children or children with special needs.
- Foster Care Focus:
- Highlight the importance of foster care as a rehabilitative measure for older children.
- Public Engagement:
- Engage various stakeholders, including adoptive families, PAPs, older adoptees, and the general public, to share experiences and insights.
Key Activities
- Nationwide Campaigns:
- Offline events in states like Ladakh, Assam, Mizoram, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and West Bengal.
- Mega event in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, on November 21, 2024.
- Online Initiatives (via MyGov India):
- Storytelling, poster making, slogan writing, pledges, and online surveys.
- Informative content on adoption and foster care shared via social media.
- Interactive Engagements:
- Cultural programs, competitions, Q&A sessions with PAPs, and discussions with stakeholders.
- Sharing of experiences by older adoptees and adoptive parents.
Significance of Adoption Awareness Month
- Focus on Older Children:
- Addresses challenges faced by older children in finding permanent families.
- Promotes inclusive adoption practices for children with special needs or in foster care.
- Stakeholder Involvement:
- Builds trust and awareness by sharing real-life adoption experiences.
- Encourages societal participation in the rehabilitation of vulnerable children.
- Policy Awareness:
- Educates the public about the legal adoption process under CARA.
- Highlights the benefits and responsibilities of foster care and adoption.
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
- Role: Apex body for regulating adoption in India under the MWCD.
- Key Function: Ensures legal, ethical, and transparent adoption processes for orphaned, abandoned, and surrendered children.
Challenges in Adoption and Foster Care
- Limited awareness about adopting older children or children with special needs.
- Cultural and societal barriers.
- Complexities in the legal adoption process.
Way Forward
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify legal procedures to make adoption and foster care accessible.
- Increased Awareness: Continued campaigns to reduce stigma and misinformation about adoption.
- Policy Support: Strengthen programs for foster care and ensure periodic evaluation of their impact.
One Rank One Pension (OROP) Scheme

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
As OROP completes the 10 years in 2024, it is essential to reflect on the immense benefits the scheme has brought to the armed forces community.
Overview:
- Implemented on: November 7, 2015.
- Announced in: Union Budget 2014, allocation of ?1,000 crore.
- Aim: To ensure uniform pension for military personnel retiring at the same rank with equal service duration, irrespective of retirement date.
- Significance: A landmark reform addressing a four-decade-long demand of ex-servicemen.
- Origin: Longstanding demand since the 1970s; first highlighted by the 3rd Central Pay Commission.
- Key Committees: K.P. Singh Dev Committee (1984) and Sharad Pawar Committee (1991) recommended reforms but faced financial and administrative hurdles.
Key Features:
The policy’s primary elements include:
- Re-fixation of Pensions: The pension of all past pensioners is re-fixed based on the pensions of personnel who retired in 2013, starting from July 1, 2014. This created a new benchmark for pensions, with all retirees getting equal benefits for their service.
- Periodic Revision: The pension is to be re-fixed every five years, ensuring that it continues to reflect changes in the pay and pension structure.
- Arrears Payments: Arrears of pension were to be paid in equal half-yearly installments, although the arrears for family pensioners and gallantry awardees were paid in a single installment.
- Safeguarding Above-Average Pension: For personnel drawing pensions higher than the average, their pensions are protected, ensuring that they do not lose out on the benefits of OROP.
- Inclusive of All Ex-Servicemen: The order covered all personnel who retired up to June 30, 2014, and provided a robust framework for revising pensions for all ranks, including family pensioners.
Impact:
- Veterans and Families:
- Benefited over 25 lakh ex-servicemen and families.
- Enhanced financial security, standard of living, and dignity.
- Emotional and Social Value:
- Strengthened trust between veterans and the government.
- Recognized sacrifices of armed forces personnel.
World Cities Report 2024
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
The World Cities Report 2024, released by UN-Habitat, highlights the urgent need for cities to address climate change, both as victims and major contributors.
Key Findings of the Report
- Temperature Increases by 2040: Nearly 2 billion people living in urban areas are projected to face at least a 0.5°C rise in temperature by 2040, exposing them to heatwaves and other climate-related risks.
- Urban Vulnerability and Climate Risk:
- Cities are disproportionately affected by climate change while being major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which exacerbates their vulnerability to events like floods, cyclones, and heatwaves.
- The urban population is facing a dual challenge: increased heat and extreme weather events such as flooding, cyclones, and erratic rainfall.
- Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Risks: Over 2,000 cities in low coastal areas, many located under 5 meters above sea level, are at heightened risk from sea-level rise and storm surges, potentially affecting more than 1.4 billion people by 2040.
- Riverine Flooding: Flood exposure in cities is growing 3.5 times faster than in rural areas, with 517 million people in urban areas projected to be exposed to riverine flooding by 2030.
- Investment Gap: Cities require between USD 4.5 trillion and USD 5.4 trillion annually to build and maintain climate-resilient systems, but current investments stand at only USD 831 billion, highlighting a massive funding shortfall.
- Decline in Urban Green Spaces: The average share of urban green spaces has dropped from 19.5% in 1990 to 13.9% in 2020, reducing cities' ability to absorb carbon, manage heat, and provide essential ecosystem services.
- Vulnerable Communities: Informal settlements and slums, often situated in environmentally sensitive areas, are disproportionately affected by climate impacts. These communities lack adequate infrastructure and are often unable to invest in necessary upgrades due to eviction fears or lack of legal recognition.
- Green Gentrification: While climate interventions like park creation can provide environmental benefits, they can also lead to green gentrification—displacing low-income households or increasing property values and rents, thus pricing vulnerable communities out.
Contributing Factors to Urban Global Warming
- Energy Consumption: Urban areas account for 71-76% of global CO? emissions from energy use, driven by dense populations, industrial activities, transportation, and high-energy demand for buildings.
- Industrial Activities: Urban industries and power plants release a variety of greenhouse gases (GHGs), including CO?, methane (CH?), and nitrous oxide (N?O).
- Land Use Changes: Urban expansion leads to deforestation and reduced carbon absorption, contributing to global warming. Urban land areas are expected to more than triple by 2050, accelerating environmental degradation.
- Waste Generation: Decomposing waste in landfills releases methane, a potent GHG, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) occur when cities absorb and retain more heat due to their dense infrastructure (asphalt, concrete, and buildings), increasing local temperatures and energy consumption.
Impacts of Global Warming on Cities
- Heatwaves: Cities, especially in warmer regions like India, are experiencing more severe heatwaves and rising temperatures.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: UHIs increase the intensity of heatwaves, particularly in high-density cities, where buildings and roads trap heat, exacerbating energy demands and public health risks.
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities with flooding and storm surges, displacing communities and disrupting economies.
- Wildfire Seasons: Warming temperatures and prolonged droughts increase the risk of wildfires in urban areas, particularly in forest-adjacent cities.
India's Climate Initiatives for Urban Areas
- Smart Cities Mission: Focuses on developing sustainable urban infrastructure, promoting smart technologies, and enhancing resilience to climate impacts.
- AMRUT Mission: Aims to provide basic infrastructure and sustainable urban development in cities, including water supply, sewage, and green spaces.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban: Focuses on improving waste management and reducing pollution in urban areas.
- FAME India Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles): Promotes electric vehicles to reduce urban air pollution and carbon emissions.
- Green Energy Corridor (GEC): Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid, encouraging clean energy use in urban centers.
21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) Meeting

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) meeting was held from November 5 to 6, 2024, at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- The meeting focused on strengthening defence ties between India and the US, covering a wide range of topics aimed at improving military cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
- Capacity Building: The meeting discussed initiatives for enhancing defence capacity through training exchanges, joint exercises, and sharing best practices.
- Defence Industrial Cooperation: Both countries explored opportunities for collaborative defence industrial ventures and technology sharing.
- Joint Exercises: The advancement of joint military exercises was highlighted to boost readiness against both conventional and hybrid threats.
- Strategic Objectives: The meeting aimed to enhance interoperability between the two countries' armed forces, enabling more effective joint operations.
Commitment to Strengthen Indo-US Defence Ties
- Strategic Partnership: Both nations reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the Indo-US defence partnership, recognizing the shared challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Focus on Regional Security: The discussions underscored the importance of ensuring regional security and global stability in the face of emerging threats.
The Role of the MCG
- Purpose: The MCG forum serves as a key platform for enhancing strategic and operational defence collaboration between India and the US.
- Long-term Goals: The MCG aims to build mutual defence capabilities, counter emerging threats, and ensure the security of both nations and the wider region.
Maha Kumbh Mela 2025

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025 will be held in Prayagraj from January 13 to February 26.
- The event is a sacred pilgrimage that draws millions of pilgrims to bathe in the holy waters of the Triveni Sangam (the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and Sarasvati rivers) for spiritual purification and liberation.
Significance and Spiritual Importance
- Sacred Rituals:
- The central ritual is the act of bathing in the holy waters of the confluence, believed to cleanse one’s sins and bring spiritual liberation (Moksha).
- Pilgrims also engage in worship, spiritual discourses, and seek blessings from revered sadhus and saints.
- Auspicious Dates:
- The event includes Shahi Snan (Royal Bath), where prominent saints and their followers bathe on specific dates, marking the beginning of the Mela.
- Paush Purnima marks the start of the auspicious bathing period.
- Cultural Ceremonies:
- The Mela features a grand procession (Peshwai) with Akharas (spiritual orders) on elephants, horses, and chariots.
- Cultural performances, traditional music, dance, and art are also part of the festivities, showcasing India’s vibrant cultural diversity.
Mythological and Historical Roots
- Mythology:
- The Kumbh Mela is deeply embedded in Hindu mythology, symbolizing humanity’s quest for spiritual unity and enlightenment.
- The timing of the event is based on astrological positions of celestial bodies, particularly the Sun, Moon, and Jupiter.
- Historical Significance:
- The origins of the Kumbh Mela trace back over 2,000 years, with references found in the Maurya and Gupta periods.
- Royal Patronage: Emperors like Akbar supported the Mela, symbolizing unity among different religions and cultures.
- British Colonial Era: British officials documented the Mela, fascinated by its scale and ritualistic practices.
- Modern Recognition:
- In 2017, the UNESCO recognized the Kumbh Mela as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, underscoring its global significance.
Cultural Celebration and Unity
- Cultural Diversity:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela is a celebration of India's rich cultural heritage, where pilgrims experience traditional crafts, art, music, and dance, alongside spiritual practices.
- International Participation:
- Pilgrims from across the globe attend the Mela, drawn by its message of unity, tolerance, and the universal quest for spiritual growth and peace.
- Message of Unity:
- The Mela serves as a reminder of humanity’s shared desire for self-realization and spiritual fulfillment, transcending national, cultural, and religious boundaries.
PM-Vidyalaxmi Scheme
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the PM Vidyalaxmi scheme to provide financial assistance to meritorious students for higher education.
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder students from pursuing quality higher education.
Key Features of the scheme:
- Eligibility:
- Students admitted to top 860 Quality Higher Education Institutions (QHEIs) are eligible.
- Includes both government and private institutions, as per the NIRF (National Institutional Ranking Framework) rankings.
- Loan Provision:
- Collateral-free and guarantor-free education loans for tuition fees and other course-related expenses.
- Loans up to ?7.5 lakhs will have a 75% credit guarantee from the government to encourage banks to offer loans.
- Interest Subvention:
- For students with an annual family income of up to ?8 lakhs (and not eligible for other scholarships or schemes), a 3% interest subvention will be provided on loans up to ?10 lakhs.
- This subvention applies during the moratorium period (when repayment is deferred).
- Preference for interest subvention is given to students in technical/professional courses and those from government institutions.
- Target Beneficiaries:
- Around 22 lakh students are expected to benefit from the scheme annually.
- The government has allocated ?3,600 crore for the period 2024-2025 to 2030-2031, with 7 lakh fresh students anticipated to receive the benefit each year.
- Digital Process:
- A unified “PM-Vidyalaxmi” portal will allow students to apply for loans and interest subvention in a simplified, transparent, and digital manner.
- Payment Method:
- Interest subvention will be paid via E-vouchers or Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) wallets.
Loan Product Features
- Collateral-free & Guarantor-free: Loans will be accessible without the need for collateral or a guarantor.
- Loan Coverage:
- The scheme will cover full tuition fees and other related expenses.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Students enrolled in NIRF top 100 HEIs, state institutions ranked 101-200, and central government institutions are eligible.
- The list of eligible institutions will be updated annually based on the latest NIRF rankings.
Government's Commitment
- The scheme is a part of the National Education Policy 2020’s vision to enhance access to quality education through financial support.
- Additional Support:
- It complements the existing Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS) and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Education Loans (CGFSEL) under PM-USP.
- The CSIS scheme provides full interest subvention for students with an annual family income of up to ?4.5 lakhs, pursuing technical/professional courses.
VINBAX 2024 Exercise

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The 5th Edition of Vietnam Indian Bilateral Army Exercise “VINBAX 2024” had commenced at Ambala.
Key Participants
- Indian Army: A contingent of 47 personnel from the Corps of Engineers, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Vietnam People's Army: A similar-sized contingent representing Vietnam's military forces.
- Bi-Service Participation: For the first time, personnel from both Army and Air Force of India and Vietnam are participating.
Objectives of VINBAX 2024
- Joint Military Capability Enhancement:
- Focus on enhancing joint military capabilities of both countries, specifically in the deployment of Engineer Companies and Medical Teams.
- Peacekeeping Operations (UN Context):
- The exercise prepares both sides for United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (PKO), under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which deals with peace enforcement actions.
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR):
- The exercise includes a 48-hour validation exercise with demonstrations of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The HADR component will include equipment displays to assess the technical standards of both contingents while executing disaster relief and humanitarian missions in peacekeeping contexts.
Key Activities & Events
- Field Training Exercise: The exercise includes a field training component, with a larger scope than previous editions, focusing on:
- Engineer Tasks.
- Medical Support.
- Disaster Relief Operations.
- Validation Exercise: A critical 48-hour validation exercise to test the preparedness of the two forces in providing HADR, including:
- Demonstrations of disaster relief operations.
- Equipment displays to showcase capabilities in managing and executing peacekeeping and humanitarian operations.
- Cultural Exchange: The exercise will also provide an opportunity for cultural exchange, where the troops will learn about the social and cultural heritage of each other.
Background of VINBAX
- Inception: VINBAX was first conducted in 2018 as part of the growing defense cooperation between India and Vietnam. The inaugural edition took place in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
- Alternating Locations: The exercise alternates between India and Vietnam every year.
- Previous Editions:
- 2023 Edition: Held in Vietnam.
- Current Edition: This is the 5th edition, conducted in India (Ambala and Chandimandir).
Indian Defense Engagements in Southeast Asia
- India-Indonesia Joint Special Forces Exercise (Garud Shakti 2024): Held from November 1-12, 2024, in Cijantung, Jakarta, strengthening ties with Indonesian special forces.
- Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX 2024): Held from October 23-29, 2024, in Visakhapatnam, focusing on maritime security cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
India's Green Leap

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
India's journey toward a sustainable energy future has gained significant momentum with a series of policy reforms designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and accelerate the shift to clean energy. The recent Asia-Pacific Climate Report from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) highlights India's remarkable progress in reforming its fossil fuel subsidy system and its efforts to foster renewable energy, positioning the country as a leader in the region's green transformation.
Key Highlights from the Report:
India's Fossil Fuel Subsidy Reform
- India has successfully reduced fossil fuel subsidies by 85%, from a peak of $25 billion in 2013 to just $3.5 billion by 2023.
- The reform strategy is built on a "remove, target, and shift" approach, which involved phasing out subsidies on petrol and diesel from 2010 to 2014, followed by incremental tax hikes on these fuels through 2017.
- These fiscal changes created space for funding renewable energy projects, such as solar parks, electric vehicle initiatives, and infrastructure improvements.
Role of Taxation in Supporting Clean Energy
- Between 2010 and 2017, India introduced a cess on coal production and imports, which contributed significantly to funding clean energy projects. Approximately 30% of the cess was directed to the National Clean Energy and Environment Fund.
- This funding supported major renewable energy initiatives, including the National Solar Mission and Green Energy Corridor project, helping reduce the cost of utility-scale solar energy and expand off-grid renewable energy solutions.
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 altered the financial landscape, redirecting the cess funds to GST compensation rather than directly to clean energy.
Government Schemes and Initiatives
- India is advancing its clean energy agenda through several key government schemes:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Aimed at establishing India as a leader in green hydrogen production.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme: Focused on promoting solar energy among farmers, allowing them to produce renewable power.
- PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana: A program designed to provide solar energy access to rural communities, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
A Strategic Shift: From Subsidies to Clean Energy
- India’s subsidy reforms are an important part of its strategy to transition from a reliance on fossil fuels to a focus on renewable energy investments.
- These changes reflect India’s long-term goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, as outlined in its climate action plans.
Global Significance of India’s Efforts
- The reduction in fossil fuel subsidies and the surge in clean energy investment serve as a model for other nations seeking to balance economic development with climate action.
- India’s approach demonstrates that policy reforms and innovative financing mechanisms can be used to accelerate the transition to a cleaner, greener economy while creating job opportunities and fostering economic growth.
NAMO DRONE DIDI

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare has released the Operational Guidelines of Central Sector Scheme “NAMO DRONE DIDI”
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Empower women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by providing drones for agricultural rental services.
- Aim to support 14,500 SHGs from 2024 to 2026.
Scheme Overview:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme, under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Target: Women SHGs for providing drone services in agriculture (e.g., nutrient and pesticide spraying).
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance:
- 80% subsidy (up to ?8 lakh) for SHGs to purchase drones.
- Loans for the remaining 20% via the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with 3% interest subvention.
- Drone Package:
- Includes drones, spray assemblies, batteries, cameras, chargers, and measurement tools.
- Additional batteries and propellers allow up to 20 acres of coverage per day.
- Training Program:
- One SHG member will be selected for 15 days of mandatory training.
- Focus on drone operation and agricultural tasks (nutrient and pesticide spraying).
- Implementation & Oversight:
- Central Governance: Empowered Committee comprising secretaries from key ministries (Agriculture, Rural Development, Fertilizers, Civil Aviation, and Women and Child Development).
- State Level: Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs) will implement the scheme in coordination with state departments and SHG federations.
- Monitoring: IT-based Management Information System (MIS) through the Drone Portal for real-time tracking and fund disbursement.
- Financial Flexibility:
- SHGs can access loans through other Ministry of Rural Development schemes if needed.
Implementation Details:
- Governance: Central level oversight by the Empowered Committee and state-level execution by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Ownership: Drones procured by LFCs will be owned by SHGs or their Cluster Level Federations (CLFs).
- Monitoring: The scheme will be tracked and managed through the Drone Portal, ensuring transparency and accountability.
First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi
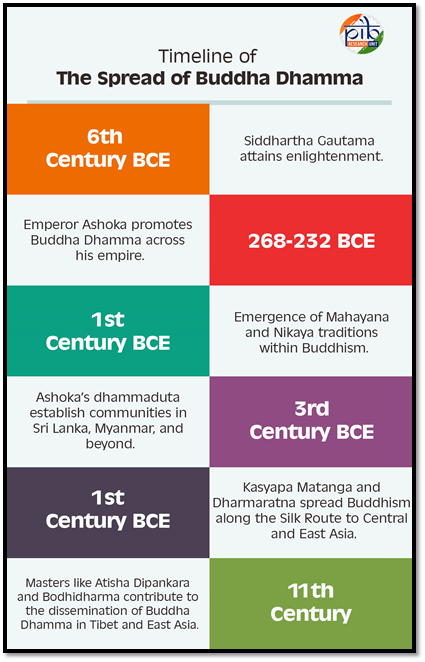
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Government of India, in partnership with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), is hosting the First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi.
- Theme: "Role of Buddha Dhamma in Strengthening Asia."
- Significance: The summit aligns with India’s Act East Policy, focusing on collective, inclusive, and spiritual development across Asia.
- Inauguration: The two-day event will be inaugurated by President Droupadi Murmu on November 5, 2024.
- Participants: Buddhist Sangha leaders, scholars, and practitioners from various Asian Buddhist traditions will gather to promote dialogue, understanding, and address contemporary challenges within the Buddhist community.
Key Themes of the Summit
- Buddhist Art, Architecture, and Heritage
- Focus on preserving and celebrating Buddhist landmarks in India (e.g., Sanchi Stupa, Ajanta Caves).
- Emphasizes the role of Buddhist art in fostering cross-cultural understanding.
- Buddha C?rik? and Dissemination of Buddha Dhamma
- Discusses Buddha’s journeys and how his teachings spread across India and beyond.
- Role of Buddhist Relics in Society
- Relics serve as symbols of Buddha's teachings, promoting devotion, mindfulness, and economic benefits through tourism and pilgrimages.
- Buddha Dhamma in Scientific Research and Well-Being
- Exploration of Buddhist teachings on mindfulness and compassion, and their integration into contemporary scientific practices to enhance well-being.
- Buddhist Literature and Philosophy in the 21st Century
- Delving into timeless Buddhist wisdom that continues to address the human condition, the nature of reality, and paths to enlightenment.
- Exhibition: "India as the Dhamma Setu (Bridge) Connecting Asia," showcasing India's role in the spread of Buddhism and its significance in fostering unity.
India’s Role in Promoting Buddhist Heritage
- Cultural Identity: Buddhism is integral to India's cultural fabric, influencing its national identity and foreign policy.
- Buddhist Tourism Circuit: The Indian government has developed a Buddhist Circuit covering key sites such as Bodh Gaya, Sarnath, and Kapilvastu.
- International Conferences and Symposia: India has hosted several events, including the First Global Buddhist Summit (2023), International Abhidhamma Diwas (2024), and Symposiums on Vipassana Meditation.
- Pali Language Recognition: On October 4, 2024, Pali was granted classical status, recognizing its significance in conveying Buddha’s teachings.
Buddhism’s Influence in Asia
- Historical Context: Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 6th century BCE, spread across Asia with the support of figures like Emperor Ashoka (268-232 BCE), who promoted peace and harmony through Buddhist teachings.
- Spread of Buddhism: From its origins in India, Buddhism spread to Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia, adapting to local cultures and creating diverse schools: Theravada, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
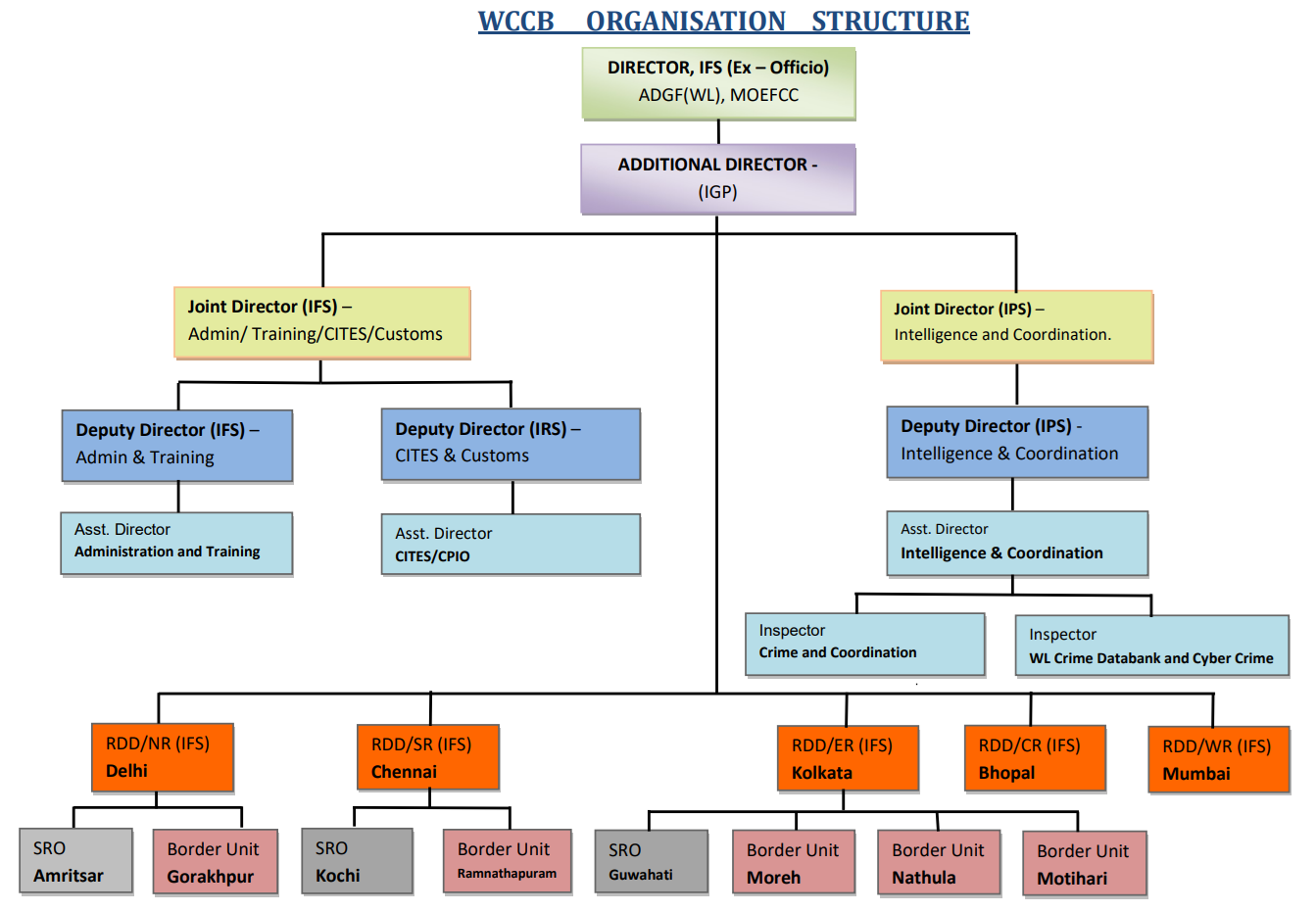
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change has constituted a team to enquire into the death of ten elephants in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh. The team is conducting an independent enquiry in the matter.
- Incident Overview:
- Ten elephants found dead in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh, between October 29-31, 2024.
- Preliminary cause of death suspected to be poisoning; final cause pending postmortem and toxicological analysis.
- Government Actions:
- Union Government:
- The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) has set up a team to conduct an independent investigation into the deaths.
- Madhya Pradesh Government:
- Constituted a five-member State-level inquiry committee, headed by the Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (APCCF, Wildlife).
- Committee includes members from civil society, scientists, and veterinarians.
- The State Tiger Strike Force (STSF) is conducting field investigations, combing surrounding areas for further clues.
- Other Involved Authorities:
- The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (PCCF) and Chief Wildlife Warden of Madhya Pradesh are directly supervising the inquiry in Bandhavgarh.
- Senior officials from the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) have visited the site for discussions and investigation.
- Union Government:
About Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB):
- Mandate:
- Combats organized wildlife crime through intelligence gathering and coordination with enforcement agencies.
- Develops wildlife crime data and assists in prosecutions.
- Provides capacity building for wildlife crime enforcement agencies.
- Operations & Initiatives:
- Conducts operations like SAVE KURMA, THUNDERBIRD, WILDNET, and more to counter wildlife crimes.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
Replicas of Konark Wheels at Rashtrapati Bhavan

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Four replicas of the Konark wheels, made of sandstone, have been installed at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan.
- This initiative is aimed at showcasing India’s rich cultural heritage and promoting traditional historical elements among visitors to Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Significance of the Konark Sun Temple:
- Historical Background: The Konark Sun Temple was built in the 13th century under King Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty in Konark, Odisha.
- Architectural Design: The temple is a colossal stone chariot with twelve pairs of intricately carved wheels, symbolizing the chariot of the Sun God.
- Materials Used: Constructed using Khondalite stones, the temple features detailed carvings that depict mythology and cultural life.
- Astronomical Significance: The temple's orientation is designed to capture the first light of the sun, reflecting ancient Indian knowledge of astronomy.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status: The Konark Sun Temple was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1984, recognizing its architectural and historical importance.
Symbolism of the Konark Wheel:
- Time and Progression: The Konark wheel represents time (Kalachakra), progression, and democracy. Its 24 spokes symbolize ancient Indian wisdom and the passage of time.
- Sundial Function: The wheel was historically used as a sundial in the temple, marking the passage of time and symbolizing India’s commitment to progress and resilience.
- National Emblem: The Konark wheel's design is also reflected in the Ashoka Chakra, the wheel on the national flag of India, symbolizing the nation’s resolve towards progress.
Cultural Heritage at Rashtrapati Bhavan:
- The installation of these replicas is part of a broader effort to introduce and promote traditional cultural and historical elements at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- The Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan serve as platforms to exhibit India’s diverse artistic legacy to visitors, allowing them to experience the grandeur of ancient Indian architecture and its cultural significance.
Ayurveda Day 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
Celebrated on 29th October 2024, marking the 9th Ayurveda Day, with the theme “Ayurveda Innovations for Global Health”.
- Global Participation: Over 150 countries participating, reflecting Ayurveda's growing global influence.
- Venue: Major events held at the All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA), New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Ayurveda and its Global Outreach
- Ancient System: Ayurveda is one of the oldest healthcare systems, focusing on holistic well-being, rooted in Vedic traditions, and dating back over 5,000 years.
- Global Recognition: Recognized in 24 countries and Ayurveda products exported to over 100 countries.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts through forums like BRICS, SCO, BIMSTEC, and WHO to integrate Ayurveda into global health policies.
Role of Dhanvantri in Ayurveda Day
- Dhanvantari Jayanti: Ayurveda Day coincides with Dhanteras, marking the birth anniversary of Lord Dhanvantri, considered the divine physician.
- Cultural & Religious Significance: Worshiped for promoting health and longevity, Dhanvantri symbolizes the healing powers of Ayurveda.
Innovations and Relevance of Ayurveda
- Research and Innovation: The theme emphasizes scientific advancements in Ayurveda to address global health challenges such as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), mental health, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and geriatric care.
- Startup Ecosystem: Focus on fostering innovation through Ayurveda startups, particularly in the North Eastern states and across India.
Ayurveda’s Role in Addressing Global Health Issues
- Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Ayurveda offers preventive and holistic treatment for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
- Mental Health: Ayurveda promotes balance in the mind, body, and spirit, with methods addressing stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Emphasizing traditional medicinal plants and natural remedies to combat resistance to antibiotics.
- Geriatric Health: Ayurveda's role in managing aging and enhancing quality of life through rejuvenation therapies.
Focus Areas for Ayurveda Innovation
- Women’s Health: Developing Ayurvedic solutions tailored for women's health issues, including reproductive health and hormonal balance.
- Workplace Wellness: Integrating Ayurveda in workplace settings to improve mental and physical health.
- School Wellness Programs: Promoting Ayurvedic practices in schools to boost immunity and overall health of children.
- Food Innovation: Modernizing Ayurvedic dietary concepts, focusing on nutritional balance and preventive health.
Government Initiatives and Digital Transformation
- Ayush Digital Platforms: Initiatives like Ayush Grid, Ayurgyan Scheme, Ayush Research Portal, and Namaste Portal are enhancing accessibility to Ayurvedic knowledge.
- WHO Integration: Ayurveda's inclusion in the WHO ICD-11 Traditional Medicine Module facilitates global standardization and recognition.
- I Support Ayurveda Campaign: A public awareness campaign aiming to garner over 250 million votes in support of Ayurveda.
Ayurvedic Education and Research
- Research Centers: Government-supported centers like the Research Centre for Innovation in Ayurveda Biology and WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre advancing Ayurveda's global integration.
- Academic Contributions: Institutes like National Institute of Ayurveda, Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda, and North Eastern Institute of Ayurveda and Homeopathy are leading innovation and education in Ayurveda.
Ayurveda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Ayurveda contributes significantly to public health, with a focus on preventive care and holistic health.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Ayurveda supports affordable, accessible healthcare solutions, complementing the global health agenda.
Launch of 'Abhay'

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, ‘Abhay’, the seventh ship in the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC) series was launched.
Key Details:
Project Background
- Contract Details: The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed a contract with Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in April 2019 for the construction of eight ASW SWC ships.
- Class of Ships: The Arnala-class ships are intended to replace the older Abhay-class ASW Corvettes currently in service with the Indian Navy.
- Purpose: These ships are designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations in coastal waters and to conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and mine-laying activities.
Design and Features of 'Abhay'
- Dimensions:
- Length: 77 meters
- Width: 10 meters
- Speed and Endurance:
- Maximum speed: 25 knots
- Endurance: 1800 nautical miles (NM).
- Propulsion: Waterjet-propelled, offering agility and swift response in tactical situations.
- Indigenous Content: Over 80% indigenous content, supporting India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative in defence manufacturing.
Capabilities of the ASW SWC
- Anti-Submarine Warfare:
- Designed to conduct subsurface surveillance and anti-submarine operations in coastal waters.
- Equipped with advanced sonar systems, including Hull-Mounted Sonar and Low-Frequency Variable Depth Sonar for enhanced underwater surveillance.
- Armament and Equipment:
- Torpedoes and ASW rockets for anti-submarine operations.
- Mines for mine-laying operations.
- Close-in Weapon System (CIWS): 30 mm for close-range defence against aerial and surface threats.
- 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote-Control Guns for additional defensive capability.
Strategic Importance
- Coastal Defence: The ASW SWC ships enhance the Navy’s capability to defend India’s extensive coastline and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) against submarine threats.
- Operational Role:
- In addition to anti-submarine warfare, these ships can conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO), which include operations against non-traditional threats.
- Mine-laying capability to disrupt enemy naval operations.
- Advanced Detection: These ships are equipped to track both surface and underwater targets, enabling them to coordinate operations with aircraft, strengthening maritime security.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Pandemic Fund Project

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying launched the Pandemic Fund Project on "Animal Health Security Strengthening in India for Pandemic Preparedness and Response"in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Pandemic Fund Project
- Objective: Strengthening animal health security in India to enhance pandemic preparedness and response.
- Funding: $25 million initiative funded by the G20 Pandemic Fund.
- Location: New Delhi, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
Context and Importance
- Livestock Sector: Crucial for socio-economic upliftment, contributing to employment and rural development.
- Growth in Livestock Sector: Significant progress in the last 9 years through schemes like the National Animal Disease Control Program (NADCP).
- Key Diseases Targeted:
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Aimed at eradication, with over 90.87 crore vaccines administered.
- Brucellosis: Over 4.23 crore vaccines administered.
Objectives of the Pandemic Fund Project
- Enhanced Disease Surveillance: Includes genomic and environmental monitoring for early warning systems.
- Laboratory Infrastructure Development: Upgradation for better diagnosis and disease management.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships for global monitoring of zoonotic diseases.
- Integrated Monitoring System: Creation of a robust system for managing zoonotic diseases, with a focus on early detection and containment.
Documents Released for Strengthening Animal Health
- Standard Veterinary Treatment Guidelines (SVTG):
- Best practices for veterinary care to improve livestock health and productivity.
- Supports national action plans, especially for combating antimicrobial resistance.
- Crisis Management Plan (CMP) for Animal Diseases:
- Framework for effective response and containment during animal disease outbreaks.
- Ensures timely mitigation of animal disease crises.
One Health Approach
- Integration of Human, Animal, and Environmental Health: Key to preventing and managing future health crises.
- Zoonotic Risks: The project emphasizes reducing zoonotic disease transmission from animals to humans, crucial given the origins of many recent public health emergencies.
Implementation and Collaboration
- The project will be executed in collaboration with global institutions:
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- World Bank
Chanakya Defence Dialogue 2024

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Chanakya Defence Dialogue (CDD) 2024, second edition, was held at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- Theme: "Drivers in Nation Building: Fueling Growth Through Comprehensive Security."
- Focus: Discussions on integrating national security into India's development trajectory and global strategy for a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Objectives:
- The dialogue aimed to explore India’s strategic directions and development priorities by fostering discussions between policymakers, strategic thinkers, defence experts, and academia.
- Highlighted the link between national security and economic growth, stressing how security frameworks are vital for national progress.
Key Sessions and Discussions:
- Session 1: Social Cohesion and Inclusive Growth: Pillars of a Secure Nation:
- Focused on internal security, social unity, and inclusive development.
- Panelists discussed the role of community engagement, countering terrorism, and law enforcement reforms.
- Emphasized the need for integrating social progress and addressing challenges like separatism and terrorist narratives.
- Panelists called for evidence-based policies for equitable growth and stronger security frameworks to protect the country from internal threats.
- Session 2: Blurring Frontiers: The Convergence of Technology & Security:
- Addressed the intersection of technology and national security.
- Topics included AI, quantum computing, IoT, and blockchain for improving cyber resilience and data protection.
- Panelists emphasized the need to balance technological innovation with strong security measures, particularly in cybersecurity and critical infrastructure protection.
- Session 3: Ground-breakers: Shaping Land Warfare, Reflections for the Indian Army:
- Explored the integration of emerging technologies like AI, unmanned systems, and cyber warfare tools in enhancing military readiness.
- Focused on indigenous defense technologies under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, promoting self-reliance and reducing dependency on foreign technologies.
- Emphasized multi-domain operations and the challenges of adapting to evolving security threats, especially from advanced cyber and space warfare.
Strategic Insights:
- Economic Growth & Security: The dialogue highlighted that national security and economic growth are interlinked, with a strong military infrastructure crucial for sustaining development.
- Role of Technology: Technological advancements like AI, space technology, and cybersecurity are pivotal for enhancing India's defense capabilities and strategic posture in a rapidly evolving global security landscape.
- Inclusive Security: Emphasized social cohesion and inclusive growth as key components of national security, acknowledging that a unified society contributes significantly to national resilience.
- Global Diplomacy: India’s global leadership in multilateral forums, its stance on peacekeeping, and its role in promoting sustainable development were discussed as part of the country’s soft power strategy.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Financial Services Secretary stated that Microfinance institutions (MFIs) have played a crucial role in fostering financial inclusion but they should refrain from any reckless lending.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) and Financial Inclusion:
- MFIs provide small loans and financial services to low-income and marginalized groups, particularly those without access to formal banking services.
- Goal: To promote financial inclusion and empower marginalized communities, especially women, by enabling them to become self-sufficient and improve their socio-economic status.
- In India, over 168 MFIs serve around 3 crore clients across 29 states and 563 districts.
- The sector has grown significantly and is crucial for empowering Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) to access credit and other financial services.
Concerns over Reckless Lending:
- The Financial Services Secretary, emphasized that MFIs should avoid reckless lending practices that could harm both borrowers and the sector.
- Poor underwriting and irresponsible lending could lead to unsustainable debt, especially for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) with limited financial literacy.
- Key Advice: Lending practices must be responsible, careful, and should aim to empower borrowers, not exploit their limited understanding.
Government Programs Supporting MFIs:
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme: Over 77 lakh SHGs with a total loan outstanding of ?2.6 lakh crore, benefiting around 10 crore households.
- Lakhpati Didi Yojana: Aimed at empowering women, this scheme helps transform SHG members into women entrepreneurs.
Challenges Facing Microfinance Institutions:
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Many MFIs face scrutiny for high interest rates and non-compliance with borrower assessments. The RBI has urged MFIs to reassess lending practices.
- Over-Indebtedness: Many borrowers take loans from multiple MFIs, leading to unsustainable debt. As of March 2024, over 12% of borrowers had multiple loans, risking defaults.
- Low Financial Literacy: A significant challenge is low financial literacy among borrowers, which increases the risk of defaults and harms the reputation of MFIs.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance (2022):
- Collateral-Free Loans: For households with income up to ?3 lakh, loans should be collateral-free.
- Repayment Cap: Monthly loan repayments should not exceed 50% of the borrower’s monthly income.
- Flexibility in Repayment: MFIs must offer flexible repayment options and ensure proper income assessment.
- Interest Rate Cap: The RBI has implemented guidelines to limit excessive interest rates charged by MFIs.
Government Schemes for Microfinance:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides financial assistance to non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Promotes rural livelihoods through the formation and capacity building of Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Antyodaya Yojana: Focuses on the empowerment of rural poor through skill development and income generation.
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): Provides guarantee cover to micro and small enterprises.
Way Forward for Microfinance Sector:
- Responsible Lending: MFIs must prioritize affordable lending practices, ensuring borrower’s repayment capacity is carefully assessed to avoid over-indebtedness.
- Enhancing Financial Literacy: MFIs should focus on financial education for borrowers, enabling them to make informed choices.
- Adherence to Regulatory Guidelines: MFIs should comply strictly with RBI regulations, including interest rate caps and borrower income assessments, to enhance sector transparency and trust.
- Malegam Committee Recommendations: Implementing suggestions like capping interest rates, tracking multiple loans, and improving transparency to prevent over-indebtedness.
- Diversifying Funding Sources: To reduce vulnerability to economic downturns, MFIs should work on diversifying their funding sources, reducing dependence on external capital.
Environmental Ship Index (ESI)
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Mormugao Port Authority (MPA) has been globally recognized as an incentive provider on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) platform, acknowledged by the International Association of Ports and Harbours (IAPH).
- Mormugao is India's first port to implement Green Ship Incentives through the ESI, contributing to global efforts to reduce maritime air emissions.
‘Harit Shrey’ Scheme:
- Launched in October 2023, the ‘Harit Shrey’ scheme provides discounts on port fees based on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) scores of commercial vessels.
- Ships with higher ESI scores (indicating better environmental performance) are rewarded with incentives to encourage eco-friendly practices in shipping.
ESI and Global Efforts for Emission Reduction:
- The Environmental Ship Index (ESI) is a global system to evaluate and reward ships based on their environmental performance, particularly their emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx).
- The 2023 IMO greenhouse gas strategy aims to reduce the carbon intensity of international shipping by at least 40% by 2030.
Incentives and Benefits:
- The Harit Shrey scheme has already benefitted several vessels, promoting greenhouse gas emission reductions and contributing to sustainable maritime operations.
- The scheme aligns with global sustainability goals, particularly in reducing the carbon footprint of shipping operations.
Sustainability Recognition:
- The Mormugao Port Authority has submitted the Harit Shrey scheme for consideration in the IAPH Sustainability Awards under the World Port Sustainability Programme (WPSP), reflecting its commitment to environmental sustainability.
The Environmental Ship Index (ESI):
- ESI is a system that evaluates and rewards ships for better environmental performance than the standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Ships are assessed based on their emissions of NOx and SOx, with greenhouse gas reporting also included in the evaluation.
Main Features of ESI:
- Port-Centric: Developed as a port-to-port system, where ports can offer incentives based on the ESI score.
- Voluntary Participation: Shipowners participate voluntarily to demonstrate their vessels' environmental performance.
- Automated Calculation: The ESI score is automatically calculated and updated.
- Incentives: Ships with higher ESI scores may receive benefits such as reduced port fees and priority berthing.
National Workshop on SATHI Portal

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Department of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare (DA&FW) organised a National Workshop on the SATHI (Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory) Portal in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Purpose & Focus
- SATHI Portal: Focuses on Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory to enhance seed certification, improve seed traceability, and streamline the seed supply chain.
- Primary Objective: Ensure availability of high-quality seeds to farmers through a transparent and efficient seed management system.
Key Features of the SATHI Portal
- Seed Certification: Aims to streamline seed certification processes across states for faster and more accurate seed certifications.
- Seed Traceability: Enhances transparency and traceability of seeds to ensure quality and authenticity.
- Inventory Management: The portal facilitates seed inventory management, helping farmers and stakeholders access reliable and transparent seed information.
- Technological Integration: Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the portal incorporates technology-driven solutions to minimize transactional time for registrations, approvals, and certifications.
Phase-II Rollout
- Focus on seed inventory management, with the objective of offering farmers reliable access to certified seed varieties.
- It aims to integrate state-specific seed processes into the national framework for greater standardization and efficiency.
Workshops & Technical Sessions
- NIC and ICAR Presentations: Covered the core components of the SATHI Portal, including:
- Seed Law Enforcement
- DNA Fingerprinting for ensuring seed authenticity.
- Seed Laboratory Processes to uphold quality control.
- Review of Phase-I: Discussions on achievements of Phase-I, focusing on improvements in seed certification processes across states.
- State Experiences: 10 state representatives shared insights on their experiences with the portal, discussing both benefits and challenges in the implementation phase.
Role of NIC & Technology
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is the technology partner behind the SATHI Portal, which is designed to enhance the efficiency of seed certification and inventory management.
- The portal contributes to larger digital initiatives like the Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP), which aim to support agricultural development through technology.
PM Young Achievers’ Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM YASASVI)

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
With a vision of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas", the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has implemented the PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM-YASASVI).
- Objective of PM-YASASVI:
- The scheme aims to provide financial support and educational opportunities to students from Other Backward Classes (OBC), Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and Denotified Tribes (DNT).
- The goal is to help these students overcome financial barriers and pursue quality education, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Consolidation of Earlier Schemes:
- PM-YASASVI integrates multiple previous scholarship schemes:
- Dr. Ambedkar Post-Matric Scholarship for EBCs.
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs.
- This consolidation aims to streamline the process and increase the impact on vulnerable groups.
- Key Components of the Scheme:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: For students in Class 9-10 with annual family income below ?2.5 lakh. Provides ?4,000 annually.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: For students pursuing higher education, with academic allowances ranging from ?5,000 to ?20,000 based on course type.
- Top Class School Education: For meritorious students, offering ?1.25 lakh annually for students from OBC, EBC, and DNT categories in Classes 9-12.
- Top Class College Education: Covers tuition, living expenses, and educational materials for students in top institutions.
- Construction of Hostels for OBC Boys and Girls: Provides hostel facilities to socially and educationally backward students near government institutions.
- Scope and Financial Allocation (2023-24):
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: ?32.44 crore allocated to states and UTs for the year 2023-24, benefiting 19.86 lakh students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: ?387.27 crore allocated for the year, benefiting 27.97 lakh students.
- Top Class School Education: ?6.55 crore for 2,602 students.
- Top Class College Education: ?111.18 crore for 4,762 students.
- Hostel Construction: ?14.30 crore allocated for the construction of hostels, accommodating 1,146 students.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Assistance: Reduces the financial burden on students from marginalized communities, enabling them to continue their education without financial stress.
- Inclusive Education: Supports students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they can access quality education from school through to higher education.
- Promotion of Merit: Focuses on meritorious students, ensuring that academic excellence is supported at all levels, from school to top-class institutions.
- Selection Process:
- The YASASVI Entrance Test (YET) is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for candidate selection under the scheme.
- Eligible students must appear for this test, and the results determine scholarship awards.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The scheme is open to OBC, EBC, and DNT students with a family income not exceeding ?2.5 lakh annually.
- Additional specific eligibility criteria may apply for different scholarships under the scheme.
- Application Process:
- Interested students can apply for scholarships via the National Scholarship Portal (scholarships.gov.in), which is the official platform for application submission.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
