Pax Silica initiative
- 23 Feb 2026
In News:
India has joined the U.S.-led Pax Silica initiative (2025) to strengthen resilient supply chains in critical minerals, semiconductors, electronics, and AI technologies.
India Joins Pax Silica
India has signed the Pax Silica Declaration and joined the U.S.-led global initiative aimed at building secure and diversified supply chains for emerging technologies and critical minerals.
The initiative is spearheaded by the United States Department of State.
What is Pax Silica?
Pax Silica is a strategic international framework designed to promote:
- Resilient supply chains for critical minerals
- Secure semiconductor and electronics ecosystems
- Collaboration in Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies
- Trusted and diversified global technology networks
It emerged in response to rising concerns over supply chain concentration, particularly in rare-earth processing and advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
Background
- Conceptualised amid growing geopolitical tensions over critical technology supply chains
- Inaugural Summit: December 2025
- Venue: Washington D.C.
Objectives
- Diversify and secure global supply chains for:
- Critical minerals
- Semiconductors
- AI-related technologies
- Reduce dependence on concentrated or monopolistic supply sources
- Deepen strategic and economic partnerships among like-minded countries
- Strengthen technology governance and economic security frameworks
Key Features
1. Supply Chain Security
- Diversification of sourcing and processing
- Reduced vulnerability to coercive economic practices
2. Critical Minerals Cooperation
- Coordinated refining and processing networks
- Access to rare-earth and strategic minerals essential for electronics and AI
3. AI & Semiconductor Collaboration
- Cooperation in AI systems and data infrastructure
- Development of advanced manufacturing ecosystems
4. Investment & Infrastructure
- Shared investments in trusted industrial ecosystems
- Incentives for innovation and supply chain resilience
5. Fair Market & Security Framework
- Address non-market practices and unfair dumping
- Protect critical infrastructure and sensitive technologies
6. Private Sector Participation
- Mobilises industry and innovation ecosystems
- Encourages entrepreneurship in advanced technology sectors
Participating Countries
- Signatories: Australia, Greece, Israel, Japan, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Singapore, UAE, United Kingdom and India.
- Non-signatory Participants: Canada, European Union, Netherlands, OECD, and Taiwan
Significance for India
- Enhances India’s role in trusted technology supply chains
- Supports India’s ambitions in semiconductor manufacturing and AI development
- Strengthens cooperation in critical mineral sourcing and processing
- Aligns with India’s push for resilient and diversified global economic architecture
Guru Ravidas

- 02 Feb 2026
In News:
The recent inauguration and renaming of Adampur Airport in Punjab after Sri Sant Guru Ravidas Ji highlights the continued relevance of medieval Bhakti saints in India’s socio-cultural landscape. Such recognition goes beyond symbolic tribute and reflects the enduring influence of Guru Ravidas’s teachings on equality, dignity, and spiritual freedom.
Guru Ravidas
- Guru Ravidas (c. 1377–1527 CE) was a prominent saint-poet of the Bhakti Movement, born in Sir Gobardhanpur near Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh). His life coincided with other major Bhakti figures such as Kabir, and he is traditionally regarded as a disciple of Ramananda.
- Guru Ravidas composed devotional poetry in local dialects, making spiritual ideas accessible to common people. His verses emphasised direct devotion to the divine without ritualism or priestly mediation.
Teachings and Philosophy
Guru Ravidas’s philosophy was deeply egalitarian and reformist:
- Rejected the caste hierarchy and social discrimination
- Advocated human dignity and equality
- Promoted spiritual freedom over ritual orthodoxy
- Emphasised Nirguna Bhakti (devotion to a formless divine)
A central idea in his teachings is “Beghumpura” — an ideal city without sorrow, fear, or discrimination, symbolising a just and casteless society. This vision makes him a powerful voice in India’s historical struggle against untouchability and social exclusion.
Literary and Religious Legacy
Guru Ravidas’s influence transcended religious boundaries:
- 41 hymns attributed to him are included in the Guru Granth Sahib, the holy scripture of Sikhism
- His verses also appear in the Panch Vani of the Dadu Panthi tradition
- The Bhakti saint Meera Bai is believed to have regarded him as her spiritual guide
Over time, his teachings became the foundation of the Ravidassia religion, whose followers revere him as their central spiritual authority. The community follows the Amrit Bani Guru Ravidass as its holy book and has developed distinct religious symbols and practices.
Sickle Cell Disease
- 18 Nov 2025
In News:
Recent medical findings from a decade-long study conducted at Fortis Memorial Research Institute (FMRI), Gurugram, have demonstrated significant success in curing Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in children through bone marrow (stem cell) transplantation. The study, published in the journal Haemoglobin,analysed100 paediatric cases treated between 2015–2024, reporting an overall survival rate of 87%, with 96% success in matched sibling donor transplants and 78% success in half-matched (haploidentical) family donor transplants. These outcomes place India among the leading countries in advanced paediatric transplant care, particularly notable because SCD disproportionately affects India and sub-Saharan Africa, which together account for nearly half of global cases.
About Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease is a genetic blood disorder caused by the inheritance of two defective genes encoding hemoglobin S—one from each parent. It affects hemoglobin’s structure and function. Normally, red blood cells (RBCs) are round, flexible, and able to move smoothly through blood vessels. In SCD, RBCs distort into a sickle or crescent shape, become rigid and sticky, and obstruct blood flow. This blockage reduces oxygen delivery to tissues and leads to severe pain episodes, organ damage, stroke risk, and a shortened lifespan. The most severe form is Sickle Cell Anemia.
Symptoms
- Early childhood: Persistent tiredness, anemia, painful swelling of hands and feet, jaundice
- Later stages: Recurrent pain crises, infections, stroke, liver and kidney damage, chronic anemia
Causes
- Inherited autosomal recessive disorder
- A child must inherit two copies of the defective sickle cell gene
- Carriers (with one defective gene) do not have the disease but may pass it on
Treatment Approaches
1. Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant
- Currently the only curative treatment for SCD
- Involves replacing defective bone marrow with healthy stem cells
- FMRI study shows high success rates, comparable to global standards
- Early diagnosis and timely transplant significantly improve survival
2. Supportive Medical Care
- Pain management
- Blood transfusions
- Infection control
- Prevention of complications
3. Gene Therapy (Emerging)
- UK became the first country to approve a gene therapy cure
- Targets and corrects the defective gene producing hemoglobin S
Significance of India’s Transplant Success
The FMRI study demonstrates that developing countries can achieve outcomes similar to the most advanced clinical centres worldwide when equipped with appropriate medical infrastructure and protocols. The success is attributed to:
- Use of reduced-toxicity conditioning regimens
- Adoption of post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) to reduce graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
- Expansion of haploidentical (half-matched) donor options when full sibling matches are unavailable
- Strengthened donor registries, early diagnosis, and improved infection control
The findings indicate that cost-effective and safe transplant strategies can be scaled in India and Africa, improving access for children in low-resource settings.
Public Health Relevance
Sickle Cell Disease is a major public health challenge in India, especially among tribal populations in central and western India. Improving outcomes requires:
- Early screening
- Increased awareness
- Strengthening transplant facilities
- Improved donor availability
- Supportive state and national programs
The success of bone marrow transplantation offers a model for scalable, curative intervention for millions living with SCD, demonstrating India’s growing capability in advanced paediatric care.
ESCAPEDE Mission
- 16 Nov 2025
In News:
Blue Origin successfully launched NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) mission to Mars aboard the New Glenn heavy-lift rocket from Cape Canaveral.
The launch marks a major milestone for both interplanetary science and commercial reusable rocket technology.
About ESCAPADE Mission
ESCAPADE is NASA’s first coordinated dual-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars.
Key Components
- Twin spacecraft named Blue and Gold.
- Designed for simultaneous observations from different regions of Martian space.
- Developed under NASA’s SIMPLEx (Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration) program.
- Utilises a “launch and loiter” flight strategy:
- Spacecraft first travel toward the Sun–Earth Lagrange Point 2 (L2).
- They remain at L2 until the optimal Mars-transfer window opens.
- Cruise toward Mars in late 2026, with arrival expected by 2027.
Mission Objectives
- Study the interaction between the solar wind and the Martian magnetosphere.
- Investigate how space weather affects Mars’ atmospheric dynamics.
- Understand the process of atmospheric escape, a key factor behind:
- Mars losing its thick ancient atmosphere
- Decline in surface habitability
- Generate real-time data on:
- Magnetic field variations
- Plasma environment
- Solar wind–atmosphere coupling
These insights support future human exploration and long-term Mars climate modelling.
Scientific Rationale
- The solar wind continually erodes Mars’ upper atmosphere.
- By observing from dual vantage points, ESCAPADE will map:
- Plasma flow patterns
- Energy transfer from solar particles
- Changes in the induced magnetosphere over time
- Understanding these processes helps reconstruct the planet’s evolution and potential for past habitability.
Launch Details and Timeline
- Launched using Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket.
- Mission timeline:
- Up to one year in Earth orbit (loiter phase)
- Mars transit: 2026–2027
- Science operations: 2027–2029
Significance of Blue Origin’s Role
- Advancement in Heavy-Lift Commercial Launches
- This was the second flight of the 321-foot New Glenn rocket.
- Demonstrates Blue Origin’s readiness for planetary missions.
- Breakthrough in Reusability
- Rocket’s first stage successfully landed on the recovery ship “Jacklyn” in the Atlantic.
- Places Blue Origin alongside SpaceX in recovering large boosters.
- Enhances competitiveness in:
- NASA contracts
- Deep-space mission launches
- Commercial satellite markets
- Expansion of Infrastructure
- Over $1 billion invested in Florida launch facilities.
- Signals Blue Origin’s long-term commitment to reusable, cost-efficient spaceflight.
LVM3-M5 Launch Vehicle

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
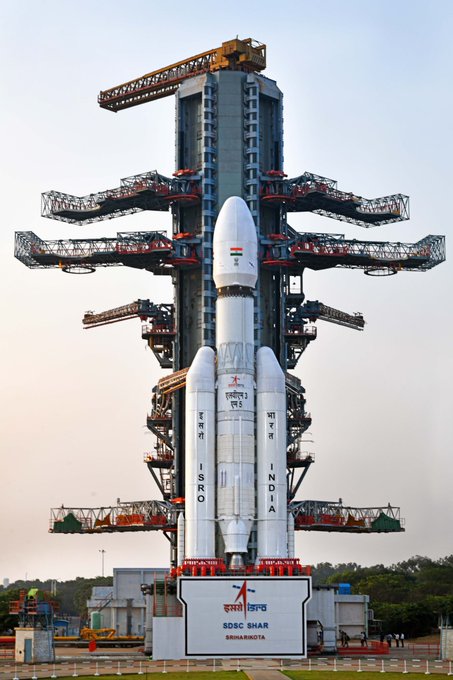
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched CMS-03 (GSAT-7R), India’s heaviest communication satellite, aboard the LVM3-M5 launch vehicle from Sriharikota. The mission strengthens India’s strategic communication architecture, particularly maritime and defence networks, while reinforcing self-reliance in heavy satellite launch capability.
CMS-03 (GSAT-7R)
- CMS-03, also known as GSAT-7R, is an advanced multi-band communication satellite designed to enhance secure, high-capacity communication links across land and oceanic regions.
- It replaces the ageing GSAT-7 “Rukmini” and significantly expands India’s maritime communication footprint.
- Developed by: ISRO under the Department of Space, with all stages, subsystems, and payloads built using indigenous technology.
- Key Objectives:
- To provide secure, high-bandwidth communication for defence, especially the Indian Navy.
- To enhance network-centric warfare, fleet coordination, and maritime domain awareness.
- To strengthen India’s digital, strategic, and disaster management communication infrastructure.
- To expand India’s oceanic communication footprint under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Major Features
- Mass: 4,410 kg — heaviest Indian satellite launched from Indian soil.
- Bands & Payloads: Multi-band communication including C, extended-C, Ku, Ka, and support for UHF & S bands for strategic defence applications.
- High-throughput transponders supporting broadband, satellite internet, and real-time secure data flow.
- Coverage: Entire Indian mainland and wide Indian Ocean Region (IOR), including remote and contested waters.
- Mission Life: ~15 years.
- Role in Naval Operations:
- Backbone of the Navy’s communication grid.
- Supports secure voice, video, and data links between warships, submarines, aircraft, and command centres.
- Enhances situational awareness, joint operations, and maritime security.
LVM3-M5
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM3), known as the “Baahubali” of Indian rockets, is ISRO’s most powerful three-stage heavy-lift launcher capable of placing 4-tonne class satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- Key Objectives:
- To ensure self-reliance in launching heavy communication and strategic satellites.
- To reduce dependence on foreign launch services.
- To support future deep-space, high-mass, and crewed platforms.
- Key Features
- Three-stage configuration:
- Two S200 solid boosters
- One L110 liquid core stage
- C25 cryogenic upper stage with an indigenously developed engine
- Three-stage configuration:
- Capabilities:
- 4,000 kg to GTO
- 8,000 kg to Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Mass & Size: 641 tonnes; 43.5 metres tall.
- Cryogenic re-ignition test conducted for future multi-satellite deployment.
- Developed by Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) with enhanced payload efficiency (~10%).
- Proven reliability in eight consecutive missions, including Chandrayaan-3 and now CMS-03.
- Candidate launcher for future Gaganyaan crewed missions.
Snow Leopard
- 07 Oct 2025
In News:
- A recent survey by the Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department has revealed that the state now hosts 83 adult snow leopards, a notable increase from the 51 recorded in 2021.
- Conducted over one year with strong community participation, the assessment marks Himachal Pradesh as the first state in India to carry out a second state-wide snow leopard survey, providing a robust baseline for future conservation efforts.
About Snow Leopards (Panthera uncia):
- Known as the “ghost of the mountains”, snow leopards are large, elusive wild cats and serve as important indicator species for fragile high-altitude ecosystems.
- State Animal: Himachal Pradesh
- Distribution: Native to high mountains across 12 countries in Central and South Asia, including Afghanistan, China, India, Nepal, and Mongolia. In India, found in Western Himalayas (J&K, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand) and Eastern Himalayas (Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh).
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable (VU)
Key Characteristics:
- Physical Traits: Thick white-grey fur with dark rosettes for camouflage; powerful hind legs for leaping across rugged terrain.
- Diet: Carnivorous—feeds on blue sheep, Himalayan ibex, marmots, pikas, hares, and other high-altitude prey.
- Habitat & Territory: Prefers cold deserts and rocky slopes above 3,000 m, sometimes reaching 5,500 m; requires large territories (5–190 sq miles) due to low prey density.
- Behavior: Solitary and territorial, mostly nocturnal and elusive.
Survey Highlights:
- Conducted across six sites covering Himachal’s 26,000 sq km snow leopard habitat using camera traps.
- Snow leopards recorded in core areas such as Lahaul-Spiti, Kinnaur, and Pangi Valley, and also beyond protected areas like Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary, Great Himalayan National Park, Sechu Tuan Nala, and Asrang Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Prey and Biodiversity: Updated distribution maps for blue sheep, Himalayan ibex, musk deer, Himalayan wolves, brown bears, red foxes, leopards, and martens. First official sighting of Pallas’s cat in Kinnaur and rediscovery of the woolly flying squirrel in Lahaul.
Exercise Pacific Angel 2025
- 20 Sep 2025
In News:
India has joined the United States and Sri Lanka in Exercise Pacific Angel 2025, the largest multilateral disaster response and humanitarian assistance drill in the Indo-Pacific. The exercise signifies growing regional collaboration in humanitarian aid, disaster relief (HADR), and emergency preparedness amid increasing natural and geopolitical challenges in the Indian Ocean region.
About Exercise Pacific Angel 2025
- Host: Sri Lanka (Katunayake Air Base)
- Participants: United States, Sri Lanka, India, Australia, Bangladesh, Japan, and Maldives.
- Troop Strength: Nearly 90 U.S. and 120 Sri Lankan Air Force personnel, along with contingents and observers from partner nations.
- Assets Deployed:
- U.S.: Two C-130J aircraft
- Sri Lanka: Bell 412, B-212 helicopters, and a King Air 350 aircraft
Key Focus Areas
- Search and Rescue (SAR) operations
- Medical readiness and mass casualty response
- Aviation safety and engineering support
- Aeromedical evacuation drills and air mobility exercises
Linked Regional Drills and Strategic Context
The Pacific Angel series forms part of a broader network of U.S.-led multilateral exercises in South Asia aimed at improving interoperability, crisis response, and regional security.
1. Exercise Tiger Lightning 2025
- Host: Bangladesh
- Participants: Bangladesh Army and U.S. Army Pacific
- Objective: Strengthen counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, jungle warfare, and medical evacuation capabilities.
- Highlights: Simulation-based drills, rescue operations, and counterinsurgency coordination.
2. Exercise Tiger Shark 2025 (Flash Bengal Series)
- Host: Bangladesh
- Participants: Bangladesh Navy’s Special Warfare Diving & Salvage Unit, Para Commando Brigade, and U.S. Special Forces.
- Aim: Enhance maritime security, small-unit tactics, and special operations readiness.
- Training Components: Patrol boat handling, small-arms marksmanship, and maritime interdiction.
3. RQ-21 Blackjack UAS Program
- Location: Bangladesh
- Partnership: U.S. Army & Navy with Bangladesh Army and Navy.
- Purpose: Develop indigenous unmanned aerial surveillance capabilities for border monitoring, maritime domain awareness, and UN peacekeeping missions.
- Structure: Establishment of a joint Army-Navy UAS regiment.
Strategic and Geopolitical Significance
- Enhancing Humanitarian Preparedness:Pacific Angel 25 reinforces the ability of Indo-Pacific nations to jointly respond to natural disasters such as cyclones, tsunamis, and earthquakes, ensuring rapid humanitarian assistance and coordination.
- Building Regional Trust and Interoperability:Joint training fosters mutual understanding, operational coordination, and shared standard operating procedures (SOPs) among participating air forces and disaster response agencies.
- Geostrategic Balancing:The U.S. engagement through multilateral drills in Sri Lanka and Bangladesh, both immediate neighbours of India, signals Washington’s intent to expand its strategic presence in South Asia. This move is viewed within the broader Indo-Pacific strategy aimed at maintaining a “free, open, and resilient region” while counterbalancing China’s growing influence.
- India’s Role:India’s participation aligns with its Neighbourhood First, Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), and Act East policies. It also strengthens HADR diplomacy, reinforcing India’s image as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean.
Rajendra Chola I
- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
India is commemorating 1,000 years of Rajendra Chola I’s Southeast Asian expedition through cultural events and heritage projects.
Key Highlights:
Rajendra I Chola (r. 1014–1044 CE), son of Rajaraja I, was one of India’s most formidable monarchs, remembered for transforming the Chola Empire into a powerful naval and commercial force that extended influence far beyond the Indian subcontinent.
Background: Rise of the Chola Empire
- Imperial Cholas, based in Thanjavur, rose to prominence after Vijayalaya Chola captured the region around 850 CE.
- Successive rulers like Aditya I and Rajaraja I expanded the empire by defeating the Pallavas, Pandyas, and Rashtrakutas.
- Rajaraja I built the Brihadeeswarar Temple (1010 CE) and initiated overseas campaigns, laying the foundation for maritime expansion.
Rajendra I Chola’s Expansionist Vision
- Ascended the throne in 1014 CE, though anointed in 1012 CE.
- Sought to establish Chola supremacy across land and sea.
- Completed the conquest of Sri Lanka, capturing King Mahinda V and consolidating the southern frontier.
- Defeated the Western Chalukyas, Pandyas, Cheras, and Palas, earning the title Gangaikonda Chola (“the Chola who conquered the Ganges”).
New Capital – Gangaikondacholapuram
- To commemorate northern victories, Rajendra founded Gangaikondacholapuram, an imperial capital that served as a political, administrative, and cultural hub.
Naval Expeditions to Southeast Asia
Motivation:
- Establish maritime supremacy, protect trade routes, and forge strategic alliances.
- Respond to shifting alliances in Southeast Asia (Khmer Empire vs Srivijaya).
The Campaign (c. 1025 CE):
- Launched a massive naval expedition targeting the Srivijaya Empire (modern-day Indonesia, Malaysia).
- Conquered strategic regions like:
- Kadaram (Kedah)
- Pannai (Sumatra)
- Malaiyur (Malay Peninsula)
- Tambralinga, Pegu, and Kalingga
Significance:
- Asserted dominance over key trade routes to Song China.
- Cemented Chola-Khmer alliance.
- Extended Tamil commercial and cultural influence across Southeast Asia.
Commercial and Cultural Legacy
- Promoted merchant guilds such as Manigramam, Ayyavole, and Ainnurruvar, which flourished in overseas ports.
- Tamil inscriptions, artifacts, and temple architecture found across Indonesia, Malaysia, Cambodia, and China.
- Tamil loanwords persist in the Karo language of Sumatra.
- Contributed to a Tamil diaspora that influenced art, architecture, trade, and religion in Southeast Asia.
Military and Administrative Excellence
- Maintained a vast army and navy.
- Efficient administrative system with support from Krishnadeva Kendras (early research and extension centers).
- Built upon the model of divine kingship with Nataraja (Shiva as cosmic dancer) symbolizing spiritual legitimacy.
Global Recognition and Commemoration
- India’s training ship TS Rajendra, commissioned in 1972, honours his naval prowess.
- Chinese accounts from the 11th century describe the Chola court’s wealth, discipline, and grandeur.
- The Coromandel Coast derives its name from Cholamandala ("realm of the Cholas").
Conclusion
Rajendra I Chola stands out in Indian history as a maritime emperor, who not only expanded territorial frontiers but also projected Indian influence across Southeast Asia. His legacy lies in blending military conquests with trade diplomacy, and establishing cultural ties that endured for centuries. His reign marks one of the earliest and most successful examples of Indian soft power abroad.
Maglev Technology
- 18 Jul 2025
In News:
China has successfully tested magnetic levitation (Maglev) technology, potentially enabling trains to travel faster than aircraft.
What is Maglev Technology?
Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) is an advanced transportation technology that uses electromagnetic forces to levitate and propel trains without physical contact with the track. The train is lifted off the track using opposing magnetic fields, eliminating friction and enabling extremely smooth, silent, and high-speed travel.
Origin and Development
- Inventors: Robert Goddard (USA) and Emile Bachelet (French-American) first conceptualized maglevs in the early 1900s.
- Commercial Use: Maglev systems have been operational since 1984.
How Maglev Works
Maglev trains operate on three core principles:
- Levitation: Magnets lift the train above the guideway.
- Guidance: Electromagnets maintain lateral stability.
- Propulsion: Linear motors create magnetic fields that push/pull the train forward.
- The system involves superconducting magnets or electromagnets embedded in both the train and the track (guideway).
- Recent advancements include the use of high-temperature superconducting levitation and vacuum tubes, reducing air resistance and energy loss.
Recent Breakthrough: China's Supersonic Maglev
- Developed by: China Railway Rolling Stock Corporation (CRRC)
- Top Speed Achieved: 620+ mph (998+ km/h), faster than commercial aircraft (547–575 mph).
- Latest Test Site: Donghu Laboratory, Hubei Province, June 2024.
- A 1.1-ton train accelerated to 404 mph in under 7 seconds on a 1,968-foot track inside a vacuum tube.
- Design:
- Sleek, aerodynamic nose to reduce drag.
- Spacious interior with digital displays for passenger comfort.
Future Potential
- Travel Time Reduction:
- Beijing–Shanghai: From 5.5 hours (current high-speed rail) to 2.5 hours.
- Delhi–Kolkata (if implemented in India): Estimated to take under 2.5 hours for ~1,200 km.
- Ongoing Projects: Full-scale high-speed maglev tracks expected to be completed in China by end of 2025.
Key advantages of Maglev
|
Feature |
Benefits |
|
Speed |
Exceeds 600 km/h; faster than short-haul flights |
|
Efficiency |
Lower energy loss; high acceleration/deceleration capacity |
|
Eco-Friendliness |
Zero direct emissions; compatible with renewable energy |
|
Low Maintenance |
No physical contact = minimal wear & tear |
|
Passenger Comfort |
Silent ride with negligible vibration |
Chautal

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
During the recent state visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Trinidad and Tobago, a notable cultural highlight was the performance of the traditional Bhojpuri Chautal, reflecting the deep-rooted Indian heritage in the Caribbean diaspora.
Understanding Chautal
- Chautal (also spelled Chartaal or Chowtaal) is a 12-beat rhythmic cycle (taal) integral to Hindustani classical music.
- It is primarily used to accompany vocal forms such as Dhrupad and Dhamar, as well as instrumental music.
- The term “Chautal” can be interpreted as "four claps", hinting at its vibhag (sectional) structure.
Structural Interpretations:
- One tradition describes it as comprising four vibhags of 4, 4, 2, and 2 beats (matras), respectively.
- An alternative view equates its structure with Ektal, dividing the cycle into six segments of 2 beats each.
Musical Characteristics and Cultural Context
- Chautal is closely associated with the pakhawaj, a barrel-shaped percussion instrument, giving it a powerful and resonant character.
- Unlike the subtle and intricate rhythms of the tabla, Chautal emphasizes strength and gravity in performance.
- Beyond classical settings, Chautal holds cultural significance in Bhojpuri folk traditions, especially during festivals and religious gatherings.
Significance in the Indian Diaspora
The inclusion of Chautal in Trinidad and Tobago’s ceremonial welcome reflects the preservation and celebration of Indian classical and folk arts among overseas Indian communities, particularly those with Bhojpuri ancestry.
India’s Burden of Zero-Dose Children in 2023
- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
According to a recent Lancet study based on Global Burden of Disease data, India ranked second globally in terms of the number of unvaccinated or “zero-dose” children in 2023, trailing only Nigeria.
What Are Zero-Dose Children?
- The term “zero-dose children” refers to those who have not received even a single dose of any routine childhood vaccine.
- In 2023, 1.44 million children in India were identified as zero-dose, highlighting significant immunisation gaps.
Global and National Trends:
- Nigeria topped the list with approximately 2.5 million zero-dose children.
- Eight countries, including India and Nigeria, together accounted for over 50% of the global zero-dose burden.
- Globally, the number of zero-dose children dropped from 58.8 million in 1980 to 14.7 million in 2019, reflecting long-term progress.
Challenges in India:
- Despite the Universal ImmunisationProgramme (UIP) covering 12 vaccine-preventable diseases, several challenges persist:
- COVID-19 pandemic led to significant disruptions in routine immunisation.
- Vaccine hesitancy continues to undermine public health efforts.
- Geographical and socio-economic inequalities limit access to health services in certain regions.
- Between 2010 and 2019, measles vaccine coverage declined in over 100 countries, including India, further exacerbating public health risks.
Fattah Hypersonic Missile

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In light of intensifying hostilities between Iran and Israel, Iran has deployed its advanced Fattah hypersonic ballistic missile, marking a significant shift in regional military capabilities and raising concerns over existing air defence systems such as Israel’s Iron Dome.
About Fattah Hypersonic Missile
- Developed by: Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Iran
- Unveiled: November 2022 (on the 11th death anniversary of missile scientist Hassan Tehrani Moghaddam)
- Inducted: 2023
- Name Meaning: “Fattah” translates to “victor” or “conqueror”
Key Capabilities:
Feature Specification
Speed Mach 13–15 (approx. 15,000 km/h)
Range 1,400 km (planned upgrade to 2,000 km)
Mobility Capable of mid-air directional changes
Stealth Forms a plasma shield that blinds radar & blocks radio signals
Deployment Used in attacks against Israeli territory
- A more advanced version, Fattah-2, with a range of 1,500 km, is reportedly under development.
Strategic Significance
- The missile’s ability to evade modern air defence systems—such as Iron Dome and David’s Sling—makes it a potential game-changer.
- Iran claims Fattah is capable of operating within the upper atmosphere with unpredictable trajectory, making interception extremely difficult.
- This hypersonic manoeuvrability marks a leap over traditional ballistic missiles that follow a predictable parabolic trajectory.
Comparative Global Context
Iran claims to be the fourth country globally to possess operational hypersonic missiles, after:
- Russia
- China
- India
Other nations like the USA and North Korea are developing or testing hypersonic systems but have not fielded them in combat as Iran reportedly has.
Operational History
- October 2024: Fattah missiles were reportedly used by Iran in a prior attack on Israeli targets.
- 2025 Escalation: The missile was deployed during “Operation Honest Promise 3,” marking the 11th wave of retaliatory attacks by Iran on Israeli territory.
Iran’s Broader Ballistic Missile Arsenal
In addition to Fattah, Iran possesses a wide range of short-to-long range missiles, including:
- Fateh Series: Short-range solid-fuel missiles (Fateh-110, Fateh-313)
- Zolfaghar and Qasem: Extended versions of Fateh series
- Emad: Long-range liquid-fuel missile with 1,700 km range
- Sejjil: Solid-fuel missile with 2,500 km range, speeds up to 17,000 km/h
- Others: Kheibar, Ghadr-110, Fajr-3, Shahab-3, Ashoura, Haj Qasem, Basir
Implications for India and the Region
- Regional Arms Race: Iran’s hypersonic capability may trigger further military build-up in the Middle East.
- India’s Position: As one of the few nations with hypersonic R&D, India must monitor evolving doctrines and maintain strategic balance.
- Global Security: The usage of such missiles in conflict zones raises concerns over escalation, proliferation, and undermining of existing missile defence systems.
Cyprus & India-EU FTA
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi began his five-day, three-nation tour with a historic visit to Cyprus—the first by an Indian PM in over 20 years. His visit focused on strengthening economic ties and pushing forward the India–European Union Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
Key Highlights of the Visit
- India-EU FTA Commitment: PM Modi announced that India and the EU are committed to concluding a Free Trade Agreement by the end of 2025. Negotiations have gained momentum.
- India–Cyprus Economic Engagement:
- Addressed the India-Cyprus CEO Forum in Limassol, pitching India as a hub for digital innovation and infrastructure.
- Highlighted India’s digital growth: Over 50% of global digital transactions via UPI originate from India. Talks are ongoing to onboard Cyprus into UPI.
- Announced a new shipbuilding policy and noted an annual investment of USD 100 billion in infrastructure.
- Supported the launch of the India–Cyprus–Greece Business and Investment Council, promoting trilateral cooperation.
- Welcomed the NSE–Cyprus Stock Exchange partnership in GIFT City, Gujarat.
- Startup and Innovation Focus: Emphasised India's vibrant startup ecosystem with over 1 lakh startups offering innovative, scalable solutions.
About Cyprus – Key Facts for Prelims
- Location: Eurasian island in the northeastern Mediterranean Sea, south of Turkey and southeast of Greece.
- Capital: Nicosia
- Area: 9,251 sq. km (3rd largest island in the Mediterranean after Sicily and Sardinia)
- Climate: Mediterranean – dry summers and wet winters
- Highest Point: Mount Olympus (1,952 m)
Geopolitical Context
- Divided Island:
- Since 1974, Cyprus has been partitioned between a Turkish-controlled north and a Greek-Cypriot-controlled south.
- Only Turkey recognises Northern Cyprus as an independent state.
- A UN-patrolled Green Line separates the two regions.
- Political System: Presidential republic – the President is both head of state and government.
- Official Languages: Greek and Turkish
- EU Membership: Joined the European Union on May 1, 2004
- Major Cities: Limassol, Larnaca, Famagusta, Paphos
Kerala Establish Senior Citizens Commission
- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
In a landmark move, Kerala has become the first state in India to pass legislation creating a Senior Citizens Commission, with the passing of the Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission Bill, 2025.
Background: Rising Elderly Population in Kerala
- Kerala is witnessing rapid population ageing, outpacing national trends.
- Elderly (60+) as % of total population:
- 1961: 5.1% (Kerala) vs. 5.6% (India)
- 2001: 10.5% (Kerala) vs. 7.5% (India)
- 2015: 13.1% (Kerala) vs. 8.3% (India)
- Current elderly population: Approximately 4.8 million, expected to rise to 8.4 million by 2036.
- Key issues: neglect, abuse, financial insecurity, and loneliness.
Senior Citizens Commission: Key Highlights
- Statutory body under the Kerala State Senior Citizens Commission Act, 2025.
- Objective: Protection, welfare, rehabilitation, and empowerment of senior citizens.
- Will act as an independent authority with powers similar to a civil court.
Structure:
- Chairperson (status of Govt. Secretary) and three members (all senior citizens).
- Composition includes at least one woman and one member from SC/ST communities.
- Term: 3 years.
- Experts may be invited as special invitees (no voting rights).
Core Functions and Responsibilities:
- Policy Advisory:
- Recommends policies for elderly welfare.
- Aligns with national goals, such as the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007.
- Legal and Grievance Redressal:
- Investigates complaints of abuse, neglect, or exploitation.
- Can summon individuals, record evidence, and recommend protective actions.
- Healthcare and Mental Well-being:
- Promotes geriatric care, regular health check-ups, and mental health support.
- Addresses loneliness, depression, and social isolation.
- Social Inclusion and Engagement:
- Encourages intergenerational bonding and community programs.
- Utilizes skills and experience of the elderly for social and community development.
- Financial Security Support:Aids in accessing pensions, social security schemes, and financial counselling.
- Monitoring and Reporting:
- Submits periodic reports to the state government.
- Makes recommendations for policy improvement and conflict resolution.
- Custodial Oversight:Addresses issues related to elderly detainees in prisons and lock-ups.
Budget and Administrative Details:
- Annual expenditure: Approx. ?1 crore (salaries, allowances, operations).
- One-time setup cost: ?9 lakh from the Consolidated Fund of the State of Kerala.
Significance:
- First such commission in India, fulfilling recommendations under the National Policy on Senior Citizens, 2011.
- Aims to serve as a model for other Indian states facing similar demographic shifts.
- Reinforces Kerala’s leadership in elderly welfare policies.
Huajiang Grand Canyon Bridge
- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
China is set to unveil the Huajiang Grand Canyon Bridge, a record-breaking steel truss suspension bridge that will become the world’s highest bridge. The bridge, located in Zhenfeng County, Guizhou Province, is part of the Shantou–Kunming Expressway, connecting the coastal city of Shantou with Kunming, the capital of Yunnan Province.
Key Facts about the Bridge:
- Height: The bridge will stand 625 meters (2,051 feet) above the Beipan River, 200 meters taller than the Eiffel Tower (at 330 meters).
- Length: Spanning 2,890 meters (9,482 feet) in total.
- Construction Period: Started on January 18, 2022, and took 3.5 years to complete.
- Cost: Estimated at £216 million (?2,200 crore).
- Travel Time Reduction: It will reduce the travel time across the canyon from 60 minutes to just 2 minutes.
Design and Engineering:
- Steel Framework: The steel trusses of the bridge weigh approximately 22,000 tons, about three times the weight of the Eiffel Tower.
- Engineering Feat: The bridge is a significant engineering achievement, showcasing China’s capabilities in bridge construction. The structure’s design and dramatic location are expected to attract tourists, bolstering the region’s economy.
Strategic and Economic Impact:
- The bridge is a major transportation infrastructure project aimed at improving connectivity in the remote Guizhou Province, a mountainous region that already hosts many of the world’s tallest bridges.
- Tourism and Regional Growth: Besides serving as a crucial transportation link, the bridge is expected to boost tourism and contribute to economic development in the region.
China’s Engineering Milestones:
- The Huajiang Grand Canyon Bridge surpasses the Millau Viaduct in France (343 meters), which previously held the record for the tallest bridge.
- China has been a leader in the construction of the world’s tallest bridges, further solidified by this record-breaking structure.
Blue Ghost Mission

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
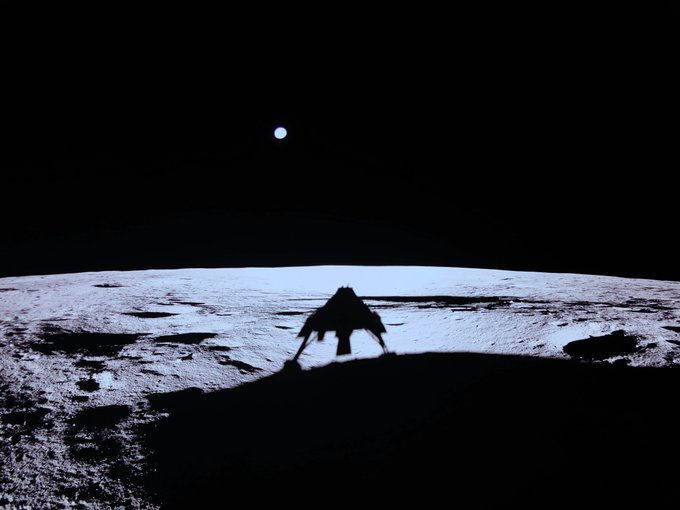
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander successfully achieved a stable, upright landing on the Moon's Mare Crisium region on March 2, 2025, marking it as the second private spacecraft to land on the Moon and the first to do so upright. This mission is a part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative.
Key Details of the Blue Ghost Mission
- Developer: Firefly Aerospace, Texas-based private aerospace firm
- Launch Date: January 15, 2025
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon 9
- Landing Site: Near Mons Latreille, a volcanic formation in the Mare Crisium
- Descent & Duration: 16-day lunar orbit followed by powered descent; operates for one lunar day (14 Earth days)
Mission Objectives
- Scientific Research:
- Study heat flow from the Moon’s interior to understand its thermal history
- Analyze plume-surface interactions to refine lunar landing techniques
- Collect data on magnetic and electric fields to infer geological evolution
- Conduct X-ray imaging of Earth's magnetosphere
- Examine lunar dust dynamics, particularly its levitation due to solar radiation
- Investigate soil adhesion for improved lunar hardware design
- Technology Demonstration:
- Test radiation-hardened systems
- Evaluate the use of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals on the Moon
Payload and Instruments
- Number of Payloads: 10 NASA scientific payloads
- Notable Tools:
- Vacuum device for soil collection
- Subsurface drill measuring temperature up to 3 meters deep
Significant Observations
- Eclipse Imaging: Scheduled to capture a total lunar eclipse (March 14)
- Lunar Sunset: Will image lunar horizon glow during sunset (March 16), a phenomenon first noted during Apollo 17
- Firsts Achieved:
- First commercial lander to land upright on the Moon
- First of three major private lunar missions scheduled in 2025
Relevance for India and the World
- Demonstrates the viability of public-private partnerships in deep space missions
- Advances NASA’s Artemis program by developing cost-effective lunar logistics
- Paves the way for international lunar commerce and exploration
National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Patient advocacy groups across India have raised serious concerns over delays in implementing the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021, which has left many rare disease patients — especially children — in life-threatening situations. They have urged the government for immediate intervention to resume life-saving treatments and release stalled funds under the policy.
Rare Diseases:
- Rare diseases are severe, often genetic, life-threatening disorders that impact a small percentage of the population.
- They disproportionately affect children, with 30% of diagnosed patients not surviving beyond age five without timely treatment.
- Examples include Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs) such as Gaucher, Pompe, Fabry, and MPS I & II.
About NPRD 2021
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the National Policy for Rare Diseases in March 2021 to streamline the diagnosis, research, and treatment of rare diseases in India.
Key Features of NPRD 2021:
- 63 rare diseases currently included under the policy (as recommended by the Central Technical Committee for Rare Diseases (CTCRD)).
- Categorization of diseases into three groups:
- Group 1: Diseases amenable to one-time curative treatment.
- Group 2: Diseases requiring long-term/lifelong treatment with relatively lower cost.
- Group 3: Diseases requiring very high-cost lifelong therapy where patient selection is critical.
Institutional Support:
- 12 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) identified at premier government hospitals to provide diagnosis and treatment.
- Nidan Kendras established to provide genetic testing and counselling services.
- National Consortium for Research and Development on Therapeutics for Rare Diseases (NCRDTRD) set up to coordinate R&D and promote indigenous drug manufacturing.
- Tax exemptions (on GST and Customs Duty) granted for imported drugs for individual and institutional use.
Financial Provisions:
- Financial assistance of up to ?50 lakh per patient for treatment at CoEs.
- Patients must register at CoEs to receive diagnosis and initiate treatment.
Challenges and Crisis
Despite policy provisions, implementation has been stalled, leading to a healthcare emergency for rare disease patients.
Key Issues Raised:
- Insufficient funding: The ?50 lakh cap is inadequate for chronic and ultra-rare diseases that need lifelong therapy.
- Administrative delays: Fund disbursement to CoEs has been slow, disrupting continuity of treatment.
- Impact on Patients:
- Patients like Alishba Khan, Ashok Kumar, Imran Ghoshi, and Adrija Mudy with Gaucher or MPS I have exhausted their funding.
- Patients who had previously stabilized are now regressing due to interrupted therapy at leading hospitals like AIIMS Delhi, IGICH Bangalore, and IPGMER Kolkata.
Legal Developments:
- On October 4, 2024, the Delhi High Court directed the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to:
- Release additional funds beyond the ?50 lakh limit.
- Create a ?974 crore National Fund for FY 2024–25 and 2025–26.
- Months later, no concrete action has been taken, further eroding trust in the policy's effectiveness.
Demands by Advocacy Groups
- Sustainable, long-term funding model for lifelong treatment of rare and ultra-rare diseases.
- Immediate fund release to CoEs and simplification of administrative processes.
- Ensure uninterrupted access to essential therapies and expand the scope of financial support.
National Geospatial Mission
- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the launch of a National Geospatial Mission in the Budget 2025-26.
Key Highlights:
Objective: To modernize land records, enhance urban planning, and create a robust geospatial infrastructure to support India’s broader development goals, including sustainable growth, efficient governance, and improved public service delivery.
Key Features of the Mission:
- Modernization of Land Records:
- Digitization and updation of land records using geospatial technology.
- Aim to reduce land disputes and promote efficient and transparent land use.
- Urban and Infrastructure Planning:
- Provides high-resolution geospatial data for informed urban planning.
- Supports better design and execution of infrastructure through integration with the PM Gati Shakti framework.
- Development of National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (NGDI):
- Integrates geospatial data from multiple departments and ministries.
- Enables seamless access and interoperability for users across sectors.
- Open Geospatial Data Policy:
- Encourages private sector participation by allowing access to non-sensitive, high-resolution data.
- Reduces reliance on foreign geospatial data providers.
- Sectoral Impact:
- Agriculture: Precision farming, resource mapping, and yield optimization.
- Disaster Management: Enhances early warning systems and response planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Facilitates conservation, deforestation tracking, and ecosystem health analysis.
- Transportation: Improves logistics, routing, and infrastructure placement.
- Climate Monitoring: Aids in data-driven climate action and adaptation planning.
- Technological Integration:
- Utilizes emerging technologies such as AI, drones, and quantum computing for spatial data collection and analysis.
- Promotes research and development in geospatial science to drive innovation.
- Support to Private Sector:
- Anticipated growth in demand for services from geospatial startups, drone companies, and mapping enterprises.
- Strengthens India’s indigenous geospatial capability aligned with the booming global geospatial market (projected to reach $1,064 million by 2030).
Significance and Alignment with National Goals:
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in land governance.
- Contributes to sustainable urban development.
- Aligns with Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing data dependency on foreign sources.
- Acts as a foundational enabler for India’s development agenda, particularly in areas of resource management, climate resilience, and national security.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
