Bridging the Gender Gap: Insights from “Women and Men in India 2024”
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) recently released the 26th edition of “Women and Men in India 2024: Selected Indicators and Data”, a flagship publication that offers a gender-disaggregated statistical portrait of India. This comprehensive document provides valuable insights into the progress, challenges, and opportunities in achieving gender equality across various socio-economic spheres.
Purpose and Scope
Drawing from official statistics across Ministries and Departments, the publication covers vital areas such as population dynamics, education, health, economic participation, and political representation, highlighting disparities and gains across gender lines. It also reflects urban-rural divides and regional variations, thus enabling data-driven policymaking for inclusive development.
Education: Moving Towards Gender Parity
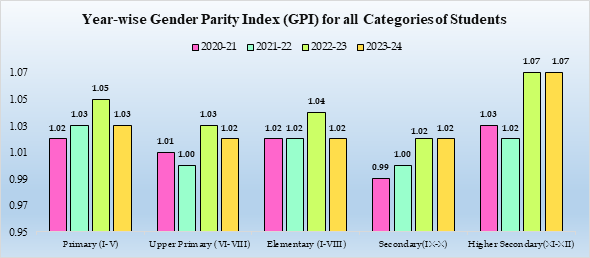
India has shown consistent improvements in Gender Parity Index (GPI) in education. Primary and higher secondary levels have maintained high GPI values, indicating strong female enrolment rates. While upper primary and elementary levels witnessed some fluctuations, they largely remained close to parity, demonstrating the impact of initiatives like Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao and expanding access to girls’ education.
Labour Force and Financial Inclusion
Women’s Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) has seen a marked improvement, rising from 49.8% in 2017-18 to 60.1% in 2023-24 (usual status for ages 15+). This indicates a gradual integration of women into the formal and informal workforce, though structural and cultural barriers persist.
In the financial sector, women now own 39.2% of all bank accounts and contribute 39.7% of total deposits. Their participation is especially prominent in rural India, where they make up 42.2% of account holders, showcasing the success of financial inclusion efforts under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana.
Digital and Entrepreneurial Engagement
A notable trend is the sharp rise in DEMAT accounts, suggesting increased retail participation in capital markets. From March 2021 to November 2024, the total DEMAT accounts quadrupled from 33.26 million to 143.02 million. While men still dominate in terms of numbers, female participation also grew fourfold, rising from 6.67 million to 27.71 million in this period.
Encouragingly, female-led proprietary establishments across sectors such as manufacturing, trade, and services have shown a rising trend over 2021–24, indicating growing entrepreneurial confidence.
Additionally, startups with at least one woman director recognized by DPIIT rose from 1,943 in 2017 to 17,405 in 2024, underscoring the rise of women in innovation and enterprise.
Political Participation and Electoral Empowerment
Electoral data reflects the deepening roots of women’s political empowerment. The number of total electors rose from 173.2 million in 1952 to 978 million in 2024, with increasing female voter registration. Female voter turnout, which was 67.2% in 2019, stood at 65.8% in 2024. Notably, the gender gap in voting has narrowed, with female turnout surpassing male turnout in 2024, signaling a positive shift in political engagement.
Conclusion
The “Women and Men in India 2024” report is more than a statistical compendium—it is a mirror to India’s gender realities. While progress is evident in domains like education, financial inclusion, and entrepreneurship, persistent gaps remain. For India to achieve true gender equity, these insights must inform targeted, data-driven policies that empower women across all sectors, making gender equality central to the nation’s development discourse.
Maternity Leave as a Constitutional and Reproductive Right

- 25 May 2025
Background:
In a landmark ruling in K. Umadevi v. Government of Tamil Nadu (May 2025), the Supreme Court (SC) affirmed that maternity leave is not merely a welfare measure but a constitutional and reproductive right of women. Setting aside the Madras High Court’s judgment, the apex court extended maternity benefits to a government school teacher for her third child, rejecting the Tamil Nadu government's policy that restricts such benefits to only the first two children.
Background of the Case:
The petitioner, a teacher employed in a Tamil Nadu government school, was denied maternity leave for her third biological child, citing Fundamental Rule 101(a) which limits benefits to women with fewer than two surviving children. Notably, the child in question was from her second marriage, while the earlier two children were in the custody of her former husband and born before her employment. The single bench of the High Court had ruled in her favour, finding the state rule inconsistent with the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 and invalid under Article 254 (repugnancy with central law). However, a division bench reversed this decision, prompting an appeal to the SC.
Key Observations by the Supreme Court:
- Maternity leave is integral to a woman’s reproductive autonomy and thus protected under Article 21 of the Constitution, which ensures personal liberty.
- It is also aligned with Directive Principles of State Policy (Article 42) that mandate the state to ensure humane work conditions and maternity relief.
- The SC emphasized that reproductive rights are recognized under international human rights law, including the rights to health, privacy, dignity, equality, and non-discrimination (as per the Universal Declaration of Human Rights).
- The Court clarified that population control, though a valid public policy goal, cannot override the constitutional guarantee of reproductive choice and health.
Reaffirming the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 (Amended 2017):
- The Act applies to workplaces with 10 or more employees, including both public and private sectors.
- Provides 26 weeks of paid maternity leave for women with fewer than two surviving children, and 12 weeks for the third or subsequent child.
- Also covers adoptive and commissioning mothers with 12 weeks of leave.
- Ensures job security, access to crèche facilities in establishments with 50+ employees, and promotes work-from-home options during or after pregnancy.
Significance of the Judgment:
- The verdict ensures gender equity in the workforce by reinforcing women’s right to combine motherhood with professional aspirations.
- It highlights the need to harmonize state policies with central welfare legislation and constitutional mandates.
- It reflects the Court's broader jurisprudence, such as in Suchita Srivastava v. Chandigarh Administration, which had affirmed a woman’s reproductive choices as part of her autonomy.
Implications for Policy and Governance:
This judgment strengthens women’s workforce participation by addressing a key dropout point—childbirth. It serves as a precedent for inclusive, rights-based policy design and calls for reviewing restrictive service rules across states. It aligns with India's commitments under international human rights frameworks and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 5: Gender Equality).
In conclusion, the Supreme Court’s verdict elevates maternity leave to a constitutionally protected right, advancing both social justice and women’s empowerment in India’s democratic framework.
Addressing the Persistent Issue of Gender Pay Disparity

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent World Bank Group report highlighted that women globally earn only 77 cents for every dollar earned by men, underscoring the persistent gender pay gap where women, on average, earn less than men.
Context:
- The World Bank Group's recent report sheds light on the persistent issue of the gender pay gap, revealing that women globally earn only 77 cents for every dollar their male counterparts earn.
- This disparity has been a contention, with critics sometimes questioning its existence.
- However, the International Labour Organisation regards the gender pay gap as a tangible indicator of inequality between men and women.
- While various reports present different figures, it is crucial to acknowledge the underlying factors that contribute to this gap and work towards eradicating them to achieve equitable pay for all individuals, regardless of gender.
How is the Gender Pay Gap Calculated?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines the gender pay gap as the difference between the average wage levels of all working women and men in the labor market, whether they are paid a monthly salary, hourly wage, or daily wage.
- It is crucial to note that this gap does not exclusively represent the wage disparity between men and women with similar qualifications and job responsibilities.
- Rather, it encompasses the overall earnings difference between all working women and men.
- While the concept of "equal pay for equal work" advocates for equitable compensation for men and women with the same qualifications and job duties, the gender pay gap reflects broader income disparities.
- There is no single, universally agreed-upon method for calculating the gender pay gap.
- Different organizations and studies may produce varying figures due to their distinct approaches.
- Understanding the various factors contributing to the gender pay gap and addressing them through appropriate policies and initiatives is vital for achieving gender equality in the workforce and ensuring fair compensation for all workers.
Methodological Differences and the Persistence of the Gender Pay Gap:
- The variation in reported gender pay gaps can be attributed to the distinct methodologies employed by different organizations and studies.
- For instance, Pew Research used hourly wages to calculate the disparity. At the same time, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics utilized weekly wages, considering only full-time workers, defined as those working at least 35 hours per week.
- Such differences in approach can lead to varying estimates of the gender pay gap.
- Despite these discrepancies in methodology, it is essential to recognize that the gender pay gap is a persistent issue in most countries and industries.
- While the extent of the gap may differ across studies, the underlying reality is that income disparities between men and women continue to be a prevalent challenge.
What are the Root Causes of the Gender Pay Disparity?
- The gender pay gap can be attributed to several interconnected factors that perpetuate income inequality between men and women.
- Firstly, women's lower labor force participation rate is influenced by prevailing gender stereotypes and societal expectations about gender roles.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that the global labor force participation rate for women stands at just under 47%, compared to 72% for men.
- In India, the 2011 Census reported a workforce participation rate of 25.51% for women, against 53.26% for men.
- Secondly, even when women join the workforce, they are often concentrated in lower-paying sectors or job roles.
- The ILO's Women in Business and Management report found that fewer women occupy management and leadership positions, particularly at higher levels.
- They are more likely to work in support functions such as human resources and financial administration, leading to a lower average salary compared to male managers.
- A Georgetown University survey in 2013 further highlighted that the top 10 highest-paying professions, primarily in engineering and computer science, were dominated by men, while women were overrepresented in the 10 lowest-paying professions, such as arts and education.
- Additionally, women are more likely to work part-time due to limited full-time employment opportunities and family responsibilities.
- In 73 countries, based on 2018 data, women outnumbered men as part-time workers.
- The ILO explains that part-time work often lacks proportional benefits to full-time positions, impacting women's overall remuneration over time.
- Other institutional and socioeconomic factors, such as the traditional view of men as breadwinners, lower investments in women's education, and concerns over safety in commuting and the workplace, also contribute to the gender pay gap.
- Addressing these underlying issues and promoting gender equity in the workforce is essential to bridging the gender pay gap and achieving fair compensation for all individuals.
Understanding the Implications of the Gender Pay Gap:
- Analyzing the gender pay gap through various demographic factors reveals patterns that provide valuable insights into income disparities between men and women.
- For example, women in their mid-30s and 40s often experience a decline in earnings compared to men in similar positions and professions.
- Critiques of the 77% statistic argue that it overlooks the "motherhood penalty," where unmarried women earn 95 cents or more for every dollar a man makes.
- This penalty suggests that women face career growth setbacks when they take breaks to raise children, highlighting an area requiring attention to promote equal opportunities.
- The 2023 Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences winner, Claudia Goldin, extensively researched pay equality and argued that traditional gender roles force men to "step up" in their careers while women "step back" for family responsibilities.
- This dynamic ultimately disadvantages both genders, as men miss out on family time, and women sacrifice their careers.
- Efforts to close the gender pay gap, such as implementing maternity and paternity leave policies and flexible work arrangements, have shown promise in reducing income disparities.
- However, the pace of progress varies, emphasizing the need for continued attention and innovation in promoting equal opportunities for all workers.
Conclusion
The gender pay gap continues to pose significant challenges across nations and industries. Examining demographics and career stages reveals important patterns that underline disparities between men's and women's earnings. Addressing inequalities, such as the "motherhood penalty," and transforming traditional work structures are vital for achieving equal opportunities. While policies like parental leave and flexible work arrangements have shown promise, sustained commitment to innovation and reform is crucial for fostering lasting progress and a more equitable professional environment.
