USAID Freeze and Its Global Implications
- 17 Feb 2025
Context:
On January 20, U.S. President Donald Trump, upon beginning his second term, issued an executive order imposing a 90-day freeze on foreign assistance. The directive aimed to reassess the efficiency and alignment of U.S. foreign development programs with its foreign policy priorities. This decision led to an immediate halt in operations of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), with the majority of its 10,000 personnel placed on administrative leave and project funding suspended worldwide.
What is USAID?
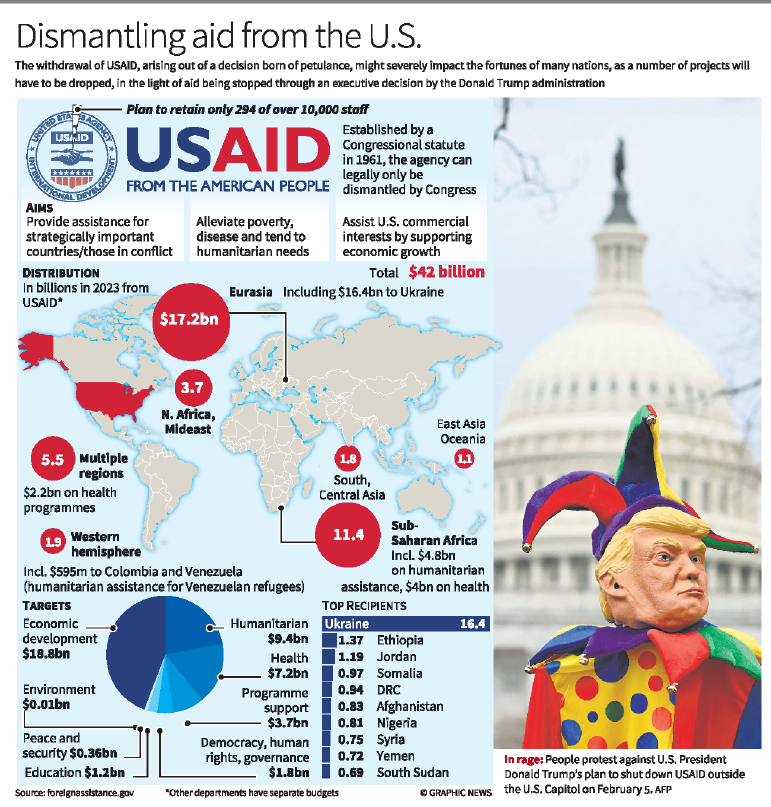
- Established in 1961 under President John F. Kennedy through an Act of Congress, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) functions as an independent agency responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance.
- Its core mission is to promote democratic values, global peace, and prosperity while advancing American national security and economic interests.
- USAID operates in over 100 countries, partnering with governments, NGOs, private firms, and international organizations.
- It offers financial support, technical assistance, and capacity-building across key sectors such as health, education, food security, economic development, humanitarian relief, environmental sustainability, and governance.
- Prominent initiatives include:
- PEPFAR: A flagship HIV/AIDS prevention and treatment program.
- Feed the Future: Focused on combating hunger and improving food security.
- Power Africa: Aimed at expanding electricity access across Africa.
- Water for the World Act: Enhancing water, sanitation, and hygiene infrastructure.
- In 2024, USAID disbursed $44.2 billion globally, which accounted for approximately 0.4% of the U.S. federal budget. Notably, the agency contributed to around 42% of all humanitarian aid tracked by the United Nations that year.
Rationale and Political Overtones
The Trump administration justified the freeze as a review for improving programmatic efficiency and ensuring alignment with U.S. strategic interests. However, critics argue the move is politically motivated, targeting Biden-era programs. Elon Musk, heading the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), labeled USAID a "criminal organization," while Secretary of State Marco Rubio indicated a broader plan for restructuring.
Global Impact of the Freeze
The abrupt suspension of USAID operations threatens development and humanitarian efforts across numerous vulnerable regions. Top recipients like Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen face the sudden withdrawal of critical support in health, food security, disaster relief, and infrastructure.
The United Nations has warned that halting support for HIV/AIDS programs alone could result in over six million deaths within four years. In several African and Middle Eastern nations, the absence of aid could derail long-term projects aimed at poverty alleviation, maternal and child health, vaccination drives, and crisis response mechanisms.
Moreover, the withdrawal risks diminishing the U.S.’s diplomatic influence in the Global South, potentially creating a vacuum for geopolitical competitors such as China, which may expand its presence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Impact on India
USAID's involvement in India dates back to 1951, when President Truman signed the India Emergency Food Aid Act. Over the decades, it evolved from providing food aid to supporting economic reforms, infrastructure, and public health initiatives. However, India’s dependency on USAID has significantly declined in recent years.
In 2024, USAID allocated approximately $79.3 million to India, primarily focused on healthcare, including HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, maternal and child health, and immunization programs. This constituted only about 0.2% to 0.4% of USAID’s global disbursement.
While the immediate impact on India may be limited due to reduced reliance and growing self-sufficiency, some ongoing health and sanitation projects could face temporary disruptions. The Indian government and implementing agencies have been directed to suspend USAID-funded operations, raising concerns about the continuity of services for vulnerable populations.
Conclusion and the Way Forward
The freeze on USAID funding reflects a shift in U.S. foreign aid philosophy and signals potential isolationist tendencies. While India may be resilient, many developing nations in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia could witness significant humanitarian and developmental setbacks.
To mitigate the impact, affected countries must:
- Enhance domestic resource mobilization to sustain critical development programs.
- Deepen partnerships with multilateral institutions like the UN, World Bank, and WHO.
- Encourage private sector participation through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
- Foster South-South cooperation to promote shared growth models.
The episode underscores the urgent need for the Global South to diversify funding sources and build internal capacities to safeguard developmental progress from geopolitical uncertainties.
