India’s Renewable Energy Transition: From Expansion to System Strength

- 27 Oct 2025
In News:
India’s renewable energy journey has evolved from an era of rapid capacity expansion to one focused on creating a stable, resilient, and system-integrated clean energy ecosystem. With a target of 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030, the country is moving from quantity to quality—shifting from mere capacity addition to building institutional, technical, and infrastructural strength capable of sustaining long-term decarbonisation.
Progress and Current Landscape
Over the past decade, India’s renewable energy capacity (excluding large hydro) has grown from around 35 GW in 2014 to over 197 GW in 2025, making it one of the world’s fastest-growing clean energy markets. The country continues to add 15–25 GW annually, driven by solar, wind, and hybrid installations. However, this phase of “rapid expansion” has revealed structural challenges — inadequate grid capacity, financing gaps, and the need for skilled manpower — necessitating a pivot toward “capacity absorption” and system integration.
From Speed to System Strength
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has emphasized that India’s renewable growth story is entering a new phase centered on system reliability, grid integration, and financial discipline. The focus now lies in synchronising renewable generation with transmission infrastructure, market mechanisms, and energy storage.
India’s grid is being reimagined through a ?2.4 lakh crore Transmission Plan for 500 GW, connecting renewable-rich states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Ladakh with industrial and urban demand centers. The Green Energy Corridors and planned High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission lines are expected to unlock over 200 GW of new capacity. The CERC’s 2025 General Network Access (GNA) regulations, introducing dynamic “solar-hour” and “non-solar-hour” access, will further optimise grid use and reduce congestion.
Building Institutional and Human Capacity
Capacity building in renewable energy involves strengthening human, institutional, and technical systems to manage grid variability, storage integration, and emerging technologies like offshore wind and green hydrogen. Institutions such as the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) and State Nodal Agencies (SNAs) are training engineers and regulators, while international collaborations with IRENA and GIZ are enhancing India’s technical knowledge base.
At the policy level, reforms such as Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for solar modules, domestic content requirements, and duties on imported cells are deepening India’s manufacturing ecosystem, reducing import dependence, and enhancing competitiveness.
Innovation and Market Mechanisms
India’s renewable transition is increasingly driven by hybrid projects, Round-the-Clock (RTC) renewable energy, battery energy storage systems (BESS), and Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPAs). These innovations ensure dispatchable power, attract private capital, and strengthen market-based renewable trading. Additionally, the National Green Hydrogen Mission is linking renewables to industrial decarbonisation, while distributed solar and agrovoltaic projects under PM Suryaghar and PM KUSUM are expanding rural participation in the clean energy transition.
Challenges and the Way Forward
India faces challenges including skill shortages, limited training infrastructure, financing constraints, and coordination gaps among multiple agencies. Rapid technological evolution demands continuous upskilling and institutional flexibility. Financial reforms, transmission readiness, and greater private sector participation will be key to sustaining the current momentum.
Conclusion
India’s renewable energy story is maturing—from a race for capacity to a strategy for endurance. Policy focus has shifted from expansion to integration, ensuring that the next growth phase is more stable, dispatchable, and sustainable. By aligning infrastructure, innovation, and institutions, India is laying the foundation for a resilient 500 GW clean energy system by 2030, driving its march toward Viksit Bharat and global climate leadership.
India’s Reinvigorated Outreach to the Global South

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s foreign policy has witnessed a dynamic recalibration with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s expansive visit to Brazil, Ghana, Trinidad & Tobago, Argentina, and Namibia. While participation in the BRICS Summit in Rio de Janeiro was central, the broader aim was to deepen India’s leadership role within the Global South — a diverse group of developing nations in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania.
Reclaiming Leadership in the Global South
India has long championed the cause of the Global South, grounded in its non-aligned foreign policy legacy and postcolonial solidarity. This identity was rejuvenated through:
- Hosting two Voice of the Global South Summits (2023, 2024), giving a platform to over 125 developing countries.
- Advocating for and securing African Union’s permanent membership in the G20 during its presidency, symbolizing India’s commitment to an inclusive global governance architecture.
These initiatives portray India as a bridge between the Global North and South, positioning itself as a leader that represents the interests of the voiceless in multilateral forums.
Diplomatic Course Correction: The Gaza Challenge
India’s explicit support for Israel during the Gaza conflict (post-October 7, 2023) triggered discomfort among many Global South countries, especially in the Arab and African regions that strongly support the Palestinian cause. Consequences included:
- India’s defeat to Pakistan in the UNESCO Executive Board Vice-Chair election.
- Limited engagement from key Global South nations in the Second Voice of the Global South Summit.
Recognizing these diplomatic setbacks, India recalibrated its stance. At the BRICS Foreign Ministers’ Meeting (2024) and the 2025 Rio BRICS Summit, India joined in expressing grave concern over Israeli military operations in Gaza and condemned strikes on Iran, signaling a return to its balanced, multivector diplomacy.
Strategic Gains at BRICS: Securing Core Interests
India also used the BRICS platform to secure vital national interests. The BRICS Leaders’ Declaration condemned the Pahalgam terror attack in Kashmir and called for combating terrorism, including cross-border terror financing. This was diplomatically significant, given:
- China’s prior reluctance to name Pakistan-based terror actors.
- BRICS’ growing relevance in shaping global narratives.
India’s success in inserting its security concerns into multilateral dialogue marks a maturing assertiveness in diplomacy.
Countering China, Offering Alternatives
India’s proactive outreach also serves to counter China’s rising influence in the Global South. Unlike Beijing’s Belt and Road Initiative, India emphasizes:
- Transparent, demand-driven development assistance.
- Capacity-building and digital partnerships.
- Ethical, sustainable models of cooperation.
Through initiatives like International Solar Alliance, Digital Public Infrastructure partnerships, and humanitarian aid, India offers a democratic, credible alternative to Chinese financing and infrastructure diplomacy.
Conclusion:
India’s current foreign policy trajectory reflects a delicate balancing act—protecting strategic partnerships with global powers while retaining the trust of fellow developing nations. As global multipolarity deepens, India’s role as a consensus builder, ethical voice, and pragmatic actor will shape its success in becoming the leading voice of the Global South.
Structural Shift in India’s Remittance Landscape

- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
According to the RBI’s latest Remittances Survey (2023–24), there has been a significant structural transformation in India's inward remittance patterns. Advanced Economies (AEs) — led by the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Singapore, and Australia — have overtaken the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations as the primary sources of remittances. This shift holds major implications for India’s migration, financial inflows, and socio-economic planning.
Changing Source Geography of Remittances
India’s total remittance inflow touched USD 118.7 billion in 2023–24, doubling since 2011. The United States alone accounted for 27.7%, followed by the UAE (19.2%), the UK (10.8%), Saudi Arabia (6.7%), and Singapore (6.6%). This marks a departure from the earlier dominance of the Gulf region, whose collective share has dropped to 38%, while Advanced Economies now contribute over 50%.
The top recipient states of these remittances in India are Maharashtra (20.5%), Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
Factors Behind the Shift
1. Evolving Migration Trends:There has been a surge in professional, high-skilled Indian migrants heading to AEs, particularly in sectors like STEM, finance, and healthcare. These migrants tend to earn higher wages, have stronger job security, and remit more per capita compared to their low-skilled counterparts in the Gulf.
2. Declining Opportunities in the GCC:Several Gulf countries have implemented nationalisation policies like Saudi Arabia’s “Nitaqat,” which prioritise local hiring. Moreover, automation and economic diversification have reduced demand for foreign low-skilled workers. This, combined with COVID-19-induced job losses and return migration, has contributed to the decline in remittances from the region.
3. Education-Driven Migration:Countries like the UK, Australia, and Canada have emerged as popular education destinations. For instance, Indian migration to the UK tripled from 76,000 in 2020 to 250,000 in 2023. Post-study work opportunities and migration partnerships like the India-UK “Migration and Mobility Partnership” (2021) have bolstered this trend.
4. Cost and Mode of Transfers:Digitalisation has reduced remittance costs to India below the global average, although it still exceeds the SDG target of 3% for a US$200 transfer. Nonetheless, cash-based transactions remain significant for smaller amounts.
Economic and Policy Implications
1. Macroeconomic Importance:Remittances contribute about 3–3.5% of India’s GDP, consistently surpassing FDI and Official Development Assistance (ODA). They help finance nearly half of the merchandise trade deficit and act as buffers against external economic shocks.
2. Household-Level Impact:Remittances are pivotal for improving living standards, enabling expenditure on food, healthcare, and education. In Kerala, for instance, remittances account for over 36% of the state's domestic product.
3. Policy Challenges and Recommendations:
- Skill Alignment: Training systems must align with global job markets to prevent ‘wilful deskilling’ — where highly educated migrants take up low-skilled jobs.
- Migration Diplomacy: India must proactively negotiate bilateral/multilateral mobility agreements to secure rights, fair wages, and career progression for migrants.
- Diaspora Engagement: Policies should encourage productive use of remittances (e.g., investments, health, education) and tap diaspora networks for technology and knowledge transfer.
Conclusion
India’s remittance ecosystem is transitioning from Gulf-led low-skilled flows to knowledge-intensive, high-value contributions from Advanced Economies. Sustaining this trend will require strategic migration governance, skill reforms, and deepened engagement with the global Indian diaspora.
India’s Roadmap to High-Income Status by 2047
- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
India, currently classified as a lower-middle-income economy with a Gross National Income (GNI) per capita of USD 2,540 (2023), aspires to achieve high-income status by 2047, coinciding with the centenary of its independence. A recent World Bank report titled “Becoming a High-Income Economy in a Generation” outlines the necessary reforms, challenges, and growth scenarios India must navigate to meet this ambitious target.
Growth Imperatives and Economic Targets
To transition into a high-income economy, India must sustain an average real GDP growth rate of 7.8% annually until 2047, raising its GNI per capita nearly eightfold. Historically, India grew at 6.3% (2000–2024) and has become the world’s fifth-largest economy, doubling its global share to 3.4%. However, "business-as-usual" growth (6.6%) will fall short, and only accelerated reforms can enable a successful transition—something achieved by few countries like Chile and Poland.
Key Policy Areas for Reform
- Boosting Investment and Capital Formation:
- Increase total investment from 33.5% to 40% of GDP by 2035 through public-private synergy.
- Address infrastructure deficits, streamline land acquisition, and liberalize FDI norms.
- Improve financial markets to support long-term infrastructure and SME financing.
- Enhancing Labor Force Participation:
- Raise overall labor force participation from 56.4% to 65%.
- Increase female workforce participation from 35.6% to 50% by addressing socio-economic barriers and improving childcare and safety infrastructure.
- Target job-rich sectors like manufacturing, logistics, hospitality, and care economy to generate employment.
- Structural Transformation and Trade Integration:
- Shift labor from agriculture (currently employing 45% of workforce) towards manufacturing and services.
- Boost India's Global Value Chain (GVC) participation by reducing high tariffs and non-tariff barriers, particularly on intermediate and capital goods.
- Simplify customs, improve regulatory clarity, and promote technological adoption across sectors.
- Promoting Balanced Regional Growth:
- Support low-income states in developing healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- Deepen industrial reforms and trade competitiveness in developed states through federal programs like the Urban Challenge Fund.
- Strengthening Human Capital and Innovation:
- Expand vocational training and R&D investments in emerging areas such as AI, biotechnology, and clean energy.
- Encourage entrepreneurship and formalization to reduce the high informal employment rate (73%).
Challenges on the Path
India faces slowing investment rates (down from 35.8% in 2008 to 27.5% in 2024), low FDI inflows (just 1.6% of GDP), and declining trade openness (exports and imports fell from 56% of GDP in 2012 to 46% in 2023). Regulatory unpredictability and complex business processes hinder private investment.
Conclusion
India’s vision to become a high-income economy by 2047 is ambitious yet attainable, contingent on sustained growth, robust reforms, and inclusive development. Strategic policy execution in trade, labor, investment, and federal cooperation will be critical to transforming India's economic trajectory and positioning it as a global leader by its centenary year.
India’s Renewable Energy Revolution
- 22 Jan 2025
Introduction
India's transition towards clean energy has accelerated, with 2024 witnessing record-breaking renewable energy (RE) installations and policy innovation. With a vision to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030 and net-zero emissions by 2070, India is shaping itself as a global leader in sustainable development.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is derived from naturally replenishing sources like solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass. It plays a vital role in:
- Reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Ensuring long-term energy security.
India’s RE Targets and Progress
Parameter Target/Status
2030 Target 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity
Net Zero by 2070
Current Status (Jan 2025) 217.62 GW of non-fossil fuel-based capacity
Short-term Goal 50% energy capacity from renewable sources
2024: Year of Renewable Milestones
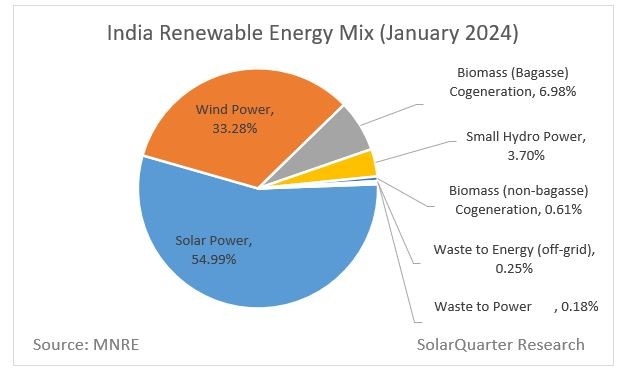
Solar Energy
- 24.5 GW added in 2024 — a 2.8x increase over 2023.
- 18.5 GW utility-scale solar: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu contributed 71%.
- Rooftop Solar:
- 4.59 GW added (↑53%)
- 7 lakh installations under PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana.
- Off-grid Solar:
- 1.48 GW added (↑182%), promoting rural energy access.
Wind Energy
- 3.4 GW added: Gujarat (1,250 MW), Karnataka (1,135 MW), Tamil Nadu (980 MW) = 98% of new capacity.
Hydropower & Others
- Existing hydropower plants modernized to improve efficiency.
Government Initiatives Driving Growth
Scheme/Initiative Purpose
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana Rooftop solar subsidies for households
Green Energy Corridor (GEC) Transmission infra for RE-rich states
Hydrogen Energy Mission Promote green hydrogen production
National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM) Integration of variable RE sources into the grid
FAME Scheme Promote EV adoption, indirectly supporting RE usage
International Solar Alliance (ISA) Strengthen global cooperation in solar energy
Challenges in RE Expansion
- Land Acquisition: Resistance from locals, especially in solar park areas.
- Grid Stability: Intermittency of solar/wind leads to voltage and frequency issues.
- Storage Gaps: Lack of large-scale battery storage limits surplus utilization.
- E-Waste Concerns: Rising disposal of solar panels and batteries.
- Mineral Dependency: Import reliance on lithium, cobalt, etc.
- Regulatory Bottlenecks: Delay in approvals and lack of inter-state coordination.
Way Forward: Strategic Interventions
Technological Innovation
- Floating Solar Projects: Utilize reservoirs to save land and reduce evaporation.
- Decentralized Systems: Peer-to-peer trading via blockchain for energy democratization.
- Green Hydrogen: Use surplus RE for hydrogen fuel, develop hydrogen corridors.
Infrastructure & Manufacturing
- Renewable Energy SEZs: Promote local manufacturing and innovation.
- Smart Grid Development: Improve grid flexibility and real-time balancing.
Environmental Management
- Circular Economy for RE Waste: Design policies for solar panel and battery recycling.
- Urban Integration: Incentivize rooftop installations in urban centers.
Conclusion
India’s renewable energy revolution is at a crucial juncture. With 2024 setting a strong precedent through record installations and policy progress, the path to 2030 and beyond will require addressing infrastructural, financial, and regulatory challenges. A multi-pronged, inclusive, and technology-driven approach will help India lead the global clean energy transition.
India’s R&D Funding, Breaking Down the Numbers
- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The announcement in the interim Budget for 2024-25, of a corpus of ?1 lakh crore to bolster the research and innovation ecosystem within the country, has sparked enthusiasm within the scientific and research communities.
Context:
- In the current scenario, the recent allocation of a substantial ?1 lakh crore in India's Interim Budget for 2024-25 to enhance the research and innovation ecosystem underscores the nation's dedication to advancing scientific pursuits.
- Additionally, the decision to expand the iconic slogan 'Jai Jawan Jai Kisan' to 'Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan, Jai Vigyan, Jai Anusandhan' signifies a renewed focus on research and innovation as essential elements of development.
- Evaluating the present state of India's research and development (R&D) landscape, including its funding, output, and the potential impact of recent initiatives on nurturing a conducive environment for research and innovation, is imperative.
Current Outlook of India's R&D Landscape:
- Gross Expenditure on Research and Development: India's R&D sector has witnessed substantial growth, with Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) increasing from ?6,01,968 million in 2010-11 to ?12,73,810 million in 2020-21.
- Despite this growth, India's research investment as a percentage of GDP remains at 0.64%, lagging behind major developed and emerging economies like China (2.4%), Germany (3.1%), South Korea (4.8%), and the United States (3.5%).
- Academic Talent: Despite the relatively lower GDP allocation for R&D, India has emerged as a key producer of academic talent, annually producing an impressive 40,813 PhDs, ranking third globally after the United States and China.
- Research Output: India's research output remains substantial, ranking third globally with over 3,00,000 publications in 2022, showcasing the nation's robust research ecosystem and its dedication to advancing knowledge across various fields.
- Innovation: India demonstrates commendable performance in patent grants, securing the sixth position globally with 30,490 patents granted in 2022.
- While this number is lower compared to the U.S. and China, it reflects India's evolving innovation landscape and its potential for further growth in intellectual property creation.
- Major Sponsors: In India, GERD is primarily driven by the government sector, including the central government (43.7%), State governments (6.7%), Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) (8.8%), and the public sector industry (4.4%), with the private sector industry contributing only 36.4% during 2020–21.
- Investment in R&D: According to R&D statistics (2022-23) from the Department of Science and Technology, India's total investment in R&D reached $17.2 billion in 2020-21.
- Within this sum, 54% ($9.4 billion) is allocated to the government sector, predominantly utilized by four key scientific agencies — the DRDO (30.7%), the Department of Space (18.4%), ICAR (12.4%), and the Department of Atomic Energy (11.4%).
Major Challenges Facing R&D:
- Private Sector Inertia: Despite India's significant Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD), private industries contribute only 37% of the country's R&D funding, reflecting a discrepancy compared to the global trend where business enterprises typically contribute over 65%.
- Low Participation by Higher Education Institutions (HEIs): HEIs play a minor role in R&D investment, contributing only 8.8% ($1.5 billion), limiting their potential contribution to research and innovation.
- Brain Drain: Talented researchers often migrate to countries with better research infrastructure and funding opportunities, leading to a loss of skilled manpower and hindering R&D progress.
- Inadequate Education and Training: The education system may fail to adequately equip students with the requisite skills and knowledge needed to excel in R&D, posing a challenge to innovation and scientific advancement.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Complex procedures and bureaucratic red tape can impede research initiatives, delaying progress and discouraging potential investors from engaging in R&D activities.
- Limited Collaboration with Academia: A gap exists between academic research and industry needs, hampering the effective transfer of knowledge and technology, and inhibiting the development of innovative solutions to real-world problems.
Proposed Measures:
- Embrace a Collaborative Approach: Fostering collaboration among the government, business enterprises, and Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) is imperative to harness the full potential of science, technology, and innovation for driving economic growth and technological progress.
- Promote Public-Private Partnerships: Encouraging collaboration between academia and industry can facilitate the translation of research findings into commercial applications, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Directing resources towards safeguarding intellectual property rights and addressing technical challenges can unlock new markets and spur innovation.
- Provide Government Subsidies to Stimulate Private Sector Investment: Implementing government initiatives such as tax incentives and grants can incentivize increased private sector investment in Research and Development (R&D), bolstering India's R&D ecosystem and fostering stronger industry-academia partnerships for knowledge exchange and innovation.
- Prioritize Skill Development: Reforms in education that prioritize the development of critical thinking, problem-solving, and research skills are essential to nurture a workforce capable of driving innovation and scientific advancement.
- Streamline Bureaucratic Processes: Simplifying regulatory procedures and regulations can expedite research projects, attract investments, and create a conducive environment for R&D activities.
- Incentivize Innovation: Introducing government schemes and awards to recognize and reward innovative research endeavors can incentivize scientists, researchers, and businesses to pursue groundbreaking innovations that contribute to societal progress and economic development.
Government Initiatives:
- National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP): Recent initiatives, such as the National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) Act, signal a strong commitment to fostering research and innovation.
- The NDTSP aims to incentivize private sector engagement in R&D, while the ANRF Act seeks to bridge the R&D investment gap and nurture a robust research culture within HEIs.
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) Act: Enacted to address India's persistent R&D investment gap, this legislation aims to cultivate a thriving research culture within Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and drive innovation across various sectors.
- UchhatarAvishkarYojana (UAY): Geared towards promoting innovation that addresses industry needs and enhances India's manufacturing competitiveness, UAY fosters collaboration between academia and industry, both domestically and internationally, to drive advancements in research and technology.
- Impacting Research Innovation & Technology (IMPRINT): This initiative endeavors to tackle pressing engineering challenges by facilitating interdisciplinary research collaborations and translating knowledge into practical solutions across ten designated technology domains.
- Establishment of Research Parks: Research parks established at premier institutes such as IIT Delhi, IIT Guwahati, and IIT Kharagpur serve as platforms for fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and entrepreneurial ventures, facilitating the establishment of R&D units, and promoting innovation.
- Impact of Recent Initiatives: These initiatives, coupled with the allocation in the interim Budget, are poised to drive India's research and innovation agenda forward, particularly in burgeoning industries.
Way Forward:
- India's technological and manufacturing ambitions rely on a pivotal transformation within its R&D domain, necessitating a dual-pronged strategy:
- Encouraging active participation from the private sector, alongside
- Strengthening the research infrastructure within academia.
- Embracing a multifaceted approach that engages a spectrum of stakeholders is imperative to confront the challenges and unlock the full potential of R&D, fostering India's economic expansion and global competitiveness.
- Drawing insights from the R&D frameworks of developed nations while leveraging India's inherent strengths in agile decision-making and strategic alignment could catalyze a formidable evolution within its R&D landscape.
Conclusion
While significant strides have been made, there is a need for increased funding, stronger industry-academia collaboration, and policy measures to incentivize private sector involvement. Recent initiatives such as the NDTSP and the ANRF Act represent positive steps towards realizing India's potential as a powerhouse of research and innovation. By creating a conducive environment for research and innovation, India can pave the way for sustainable development and prosperity in the years to come.
