Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
The notification of the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025 marks the full operationalisation of India’s DPDP Act, 2023, establishing the country’s first comprehensive data protection regime. This development comes eight years after the Supreme Court’s landmark K.S. Puttaswamy (2017) judgment recognised privacy as a fundamental right under Article 21. The Rules aim to create a structured compliance ecosystem, define stakeholder responsibilities, and institutionalise enforcement through the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI).
Key Features of the Framework
The DPDP architecture follows a citizen-centric and simplified (SARAL) approach, using accessible language and structured compliance obligations.
Rights of Data Principals (citizens) include consent-based processing, correction and erasure of data, and grievance redressal.
Obligations of Data Fiduciaries (entities processing data) include lawful processing, purpose limitation, security safeguards, and breach reporting.
However, implementation is phased. Immediate provisions include operationalisation of the DPBI (four-member body headquartered in New Delhi) and an amendment to the RTI Act, 2005, restricting disclosure of personal information. Core user protectionssuch as informed consent, purpose limitation, breach notification, and appointment of Data Protection Officers (DPOs)will be enforced over the next 12–18 months, with large technology firms expected to achieve full compliance by 2027.
Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs)
Entities will be classified as SDFs based on the volume and sensitivity of data processed and potential risks to sovereignty, democracy, security, and public order. Major technology companies are likely to fall under this category. SDFs face higher obligations, including data protection impact assessments and verifiable parental consent for children’s data.
Data Localisation and Cross-Border Transfers
The Rules introduce conditional data localisation, empowering the government to specify categories of personal and traffic data that must remain within India. A designated committee will determine these categories. While aimed at national security and regulatory oversight, this move has raised industry concerns regarding compliance costs and digital trade implications.
Children’s Data and Safety
Companies must implement mechanisms for verifiable parental consent, though the government has allowed flexibility in designing these systems. Behavioural tracking and targeted advertising directed at children are largely restricted, with limited exceptions to prevent exposure to harmful content.
Breach Notification and Penalties
Data Fiduciaries must inform affected individuals without delay about the nature, scope, consequences, and mitigation steps of a data breach. Penalties for failure to implement adequate safeguards can reach ?250 crore, with enforcement powers vested in the DPBI.
Concerns and Criticisms
Several issues remain contentious:
- RTI Amendment: Removal of the public interest override for personal data of public officials is seen as weakening transparency.
- Government Exemptions: Broad exemptions for state agencies on grounds such as national security may dilute privacy safeguards.
- Delayed Protections: Key user rights becoming operational only after 12–18 months creates a transitional vulnerability.
- Regulatory Capacity: A four-member DPBI may face capacity constraints given India’s digital scale.
- Compliance Burden: Startups and smaller firms may struggle with technical and procedural requirements.
Way Forward
Strengthening institutional capacity and independence of the DPBI is essential. Clearer guidelines on data localisation and parental consent, restoration of the privacy–transparency balance under RTI, and standardised compliance templates can ease implementation. Public awareness and baseline cybersecurity norms will also be crucial.
Conclusion
The DPDP Rules, 2025 represent a landmark step in aligning India’s digital growth with constitutional privacy guarantees. The long-term success of this regime will depend on balanced implementation, regulatory accountability, and continued stakeholder consultation to ensure that innovation, national security, and individual rights evolve together.
Declining Health of Parliamentary Democracy in India

- 01 Dec 2025
In News:
India’s Parliament, constitutionally envisaged as the “grand inquest of the nation”, is increasingly witnessing signs of institutional fatigue. As the Winter Session reconvenes amid controversies such as the Special Intensive Revision (SIR) of electoral rolls, concerns over legislative dysfunction, shrinking deliberation, and executive dominance have resurfaced. This decline is not episodic or partisan, but structural and long-term, threatening the balance of power central to parliamentary democracy.
Empirical Evidence of Decline
Data from PRS Legislative Research reveal a worrying trend. During a recent Monsoon Session, the Lok Sabha functioned for only 29% of its scheduled time and the Rajya Sabha for 34%. Question Hour—the most potent accountability mechanism—was particularly eroded, with the Lok Sabha completing only 23% and the Rajya Sabha merely 6% of its allotted time.
Equally concerning is the rushed passage of legislation. Major Bills such as the Regulation of Online Gaming Bill and the Merchant Shipping Bill were cleared with only minutes of discussion, undermining the deliberative purpose of Parliament under Article 107. Committee scrutiny has weakened sharply: while over 60% of Bills were referred to committees in the 14th and 15th Lok Sabhas, this figure fell to about 20% in the 16th and 17th.
The number of sittings has also declined dramatically. From an average of 121 days per year (1952–1970), Parliament now meets for about 68 days, with the 17th Lok Sabha averaging just 55 days, the lowest in independent India. Notably, it was also the first Lok Sabha without a Deputy Speaker, despite Article 93 mandating the post.
Structural Causes
A key driver of institutional erosion is the Anti-Defection Law. Intended to curb political instability, it has instead suppressed legislative independence, converting MPs into bound agents of party whips. This distorts core parliamentary functions such as:
- Power of the purse, where financial scrutiny becomes ritualistic.
- Impeachment proceedings, where MPs should act as impartial jurors rather than whipped voters.
Simultaneously, executive dominance has grown. Opposition notices, adjournment motions, and demands for discussion are frequently disallowed, forcing protests and disruptions. Presiding officers, constitutionally expected to be neutral, are increasingly perceived as partisan, further weakening trust in parliamentary conventions.
Comparative Perspective
India’s parliamentary system draws from the Westminster model, whose roots lie in the Oxford Parliament of 1258, which subordinated executive power to legislative oversight. In countries like the UK, Prime Minister’s Questions, strong committee systems, and mandatory executive testimony preserve accountability. India, by contrast, has moved in the opposite direction—towards a Parliament that often approves rather than scrutinises.
Way Forward
Reversing this decline requires deliberate reforms:
- Mandating minimum sittings (e.g., 120 days annually) to prevent rushed law-making.
- Compulsory committee referral for all major Bills.
- Reforming the Anti-Defection Law, limiting whips to confidence motions and Money Bills.
- Restoring Question Hour and Zero Hour as non-negotiable accountability tools.
- Institutionalising a Prime Minister’s Question Hour and strengthening executive accountability to committees.
- Upholding neutrality of constitutional offices, including timely election of the Deputy Speaker.
Conclusion
The decline of Parliament is not merely about productivity statistics but about the hollowing out of constitutional spirit. Without urgent corrective measures, India risks reducing Parliament to a symbolic edifice—standing tall, yet silent in its duty to hold power accountable to the people. Reviving parliamentary democracy is thus essential for preserving the republic’s constitutional balance and democratic legitimacy.
Passive Euthanasia in India
- 30 Nov 2025
In News:
In a recent case, the Supreme Court directed the District Hospital, Noida, to constitute a Primary Medical Board to examine whether life-sustaining treatment can be withdrawn for a 32-year-old man in a persistent vegetative state (PVS) for over 12 years. The petition, filed by the patient’s father, sought passive euthanasia, not active intervention. The Court, while acknowledging the patient’s irreversible condition and total disability, reaffirmed that any decision must strictly follow the safeguards laid down in its earlier judgments, and sought a medical report within two weeks before taking a final call.
Understanding Euthanasia and Persistent Vegetative State
A Persistent Vegetative State (PVS) is a condition where higher brain functions such as awareness and cognition are irreversibly lost, while basic functions like breathing, circulation and reflexes continue.
Euthanasia refers to intentionally accelerating death to relieve suffering from an incurable condition and is broadly of two types:
- Active Euthanasia: Direct action to end life (illegal in India).
- Passive Euthanasia: Withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment, allowing natural death.
India permits only passive euthanasia, subject to strict legal and procedural safeguards.
Legal Position in India
Indian law does not recognise an unfettered “right to die” under Article 21, but the Supreme Court has interpreted the right to life to include the right to die with dignity in exceptional circumstances.
- Active euthanasia is prohibited and punishable under the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023, as culpable homicide or murder.
- Passive euthanasia is legally permissible under judicially evolved safeguards.
Key judicial milestones include:
- Aruna Shanbaug case (2011): Allowed withdrawal of life support for incompetent patients under court supervision.
- Common Cause case (2018): Recognised passive euthanasia and validated advance medical directives (living wills) for competent adults.
- 2023 modifications: Simplified procedures by reducing medical board size and experience requirements, and setting clear timelines to make the process workable.
Procedural Safeguards
The Supreme Court mandates a two-tier medical review:
- Primary Medical Board constituted by the hospital.
- Secondary Medical Board at the district level.
These boards assess the medical condition, irreversibility, and best interests of the patient. Judicial oversight ensures protection against misuse while respecting dignity.
Ethical Dimensions
The euthanasia debate reflects a tension between competing ethical principles:
- Arguments in favour emphasise autonomy, compassion, minimisation of suffering, and rational allocation of scarce medical resources.
- Arguments against stress the sanctity of life, the doctor’s duty of non-maleficence, risks of a slippery slope, and erosion of trust in medical ethics.
India’s approach attempts a middle path rejecting active killing while permitting dignified death in narrowly defined circumstances.
Global Perspective
Countries such as the Netherlands and Belgium permit both euthanasia and assisted suicide under strict laws, while others like Switzerland allow assisted suicide but prohibit active euthanasia. These variations show that euthanasia is shaped as much by societal values as by medical capability.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s direction to constitute a medical board reflects India’s cautious, dignity-centric approach to end-of-life decisions. By balancing compassion with safeguards, autonomy with ethics, and medical judgment with judicial oversight, India seeks to ensure that death, when inevitable, is humane rather than mechanical. As medical technology prolongs biological life, evolving jurisprudence on passive euthanasia will remain crucial to uphold constitutional morality, human dignity and ethical restraint.
India’s Four Labour Codes
- 25 Nov 2025
In News:
India has operationalised the four Labour Codes, the Code on Wages (2019), Industrial Relations Code (2020), Code on Social Security (2020), and Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions (OSH) Code (2020) replacing 29 central labour laws.
Enacted on the recommendations of the Second National Commission on Labour (2002), these reforms aim to modernise labour regulation, simplify compliance, extend social security, and align India’s workforce framework with the needs of a dynamic economy and Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
Key Provisions of the Four Labour Codes
1. Code on Wages, 2019
- Universal Coverage: Applies to all employees across sectors, wages, and gender (including transgender persons).
- National Floor Wage: Sets a statutory baseline; States cannot fix wages below it.
- Uniform Wage Definition: Wage includes basic pay, dearness allowance, and retaining allowance; minimum 50% of total remuneration for social security calculations.
- Working Hours & Overtime: Capped at 8 hours/day, 48 hours/week; overtime at twice the normal wage.
- Timely Payment & Documentation: Strict timelines for wage payment; mandatory wage slips (physical/electronic).
- Deductions: Not to exceed 50% of total pay.
2. Code on Social Security, 2020
- Expanded Coverage: Integrates nine laws and extends benefits to organised, unorganised, gig, and platform workers—defined for the first time.
- Social Security Fund: For unorganised, gig, and platform workers; funded by Centre/States, CSR, and aggregator contributions (1–2% of turnover; capped).
- Parity for Fixed-Term Employees: Eligible for gratuity after one year (earlier five years for permanents).
- Wider ESIC & EPF Reach: Nationwide ESIC; mandatory even for a single worker in hazardous occupations; EPF to establishments with 20+ workers irrespective of industry.
- Administrative Reforms: Inspector-cum-facilitators; web-based inspections; time-bound EPF inquiries.
- Worker-Centric Additions: Accidents during commute treated as employment-related; expanded family definition for female employees.
3. Industrial Relations Code, 2020
- Consolidation: Merges laws on trade unions, standing orders, and industrial disputes.
- Fixed-Term Employment (FTE): Permitted with equal benefits; intended for seasonal/short-tenure needs.
- Thresholds: Prior government approval for layoff/retrenchment/closure raised from 100 to 300 workers.
- Strikes & Disputes: Notice requirement extended to all establishments; expanded definition of strike (includes mass casual leave).
- Collective Bargaining: Sole negotiating union with 51% membership; otherwise, a negotiating council with proportional representation.
4. Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions (OSH) Code, 2020
- Consolidation: Integrates 13 laws (Factories, Mines, Plantations, etc.).
- Simplified Compliance: Single registration, common licences, electronic filings; higher thresholds for factory licensing.
- Contract Labour: Threshold raised to 50 workers; conditional use in core activities permitted.
- Women’s Participation: Night work allowed with consent and safety safeguards.
- Migrant Workers: Expanded definition; portability of PDS and social security; annual travel allowance.
- Workplace Safety: Mandatory appointment letters; free annual health check-ups; safety committees for large establishments.
Rationale for Reform
- Fragmentation & Obsolescence: Multiple, overlapping laws unsuited to modern industry and new forms of work.
- High Compliance Costs: Burdensome licensing and reporting, especially for MSMEs.
- Coverage Gaps: Informal and gig workers largely excluded earlier.
- Global Competitiveness: Need for predictable, transparent labour regulation to attract investment.
- Formalisation & Employment: Simplified rules to encourage job creation and transition to formal work.
Key Concerns and Critiques
- MSME Compliance Load: Expanded ESIC/EPF and safety norms may raise costs and require digital capacity.
- Federal Coordination: Labour is on the Concurrent List; divergent State rules risk uneven protections.
- Industrial Relations: Higher thresholds and strike regulations may dilute worker bargaining power; 51% rule may marginalise smaller unions.
- Job Security: Potential overuse of FTE could increase precarity; litigation risk over disguised permanency.
- Awareness Gap: Informal and migrant workers may not fully access new entitlements during transition.
Constitutional Context
- Preamble Values: Justice, equality, dignity guide labour law interpretation.
- Fundamental Rights:
- Articles 14–18: Equality and non-discrimination.
- Articles 19–22: Freedom of association (trade unions).
- Articles 23–24: Prohibition of forced and child labour.
- Article 21: Right to dignified working conditions.
- Judicial Precedents: Bandhua Mukti Morcha, PUDR, Neerja Chaudhary expanded labour rights and rehabilitation.
Way Forward
- Uniform Implementation: Model rules or an intergovernmental labour council to harmonise State regulations.
- Safeguards on FTE: Clear limits, audits, and grievance redress to prevent misuse.
- Gig Worker Security: A dedicated national policy with enforceable aggregator contributions.
- MSME Support: Digital helpdesks, simplified filings, and transitional fiscal support.
- Capacity Building: Worker awareness drives and institutional strengthening for inspectors-facilitators.
Conclusion
The four Labour Codes mark a structural shift toward a simpler, inclusive, and future-ready labour ecosystem balancing worker welfare with business efficiency. Their success hinges on cooperative federalism, robust safeguards against misuse, and effective on-ground implementation to ensure that growth and dignity at work advance together.
Strengthening Regulatory Governance

- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has initiated a major reform process aimed at enhancing transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct within the organisation. In response to concerns over conflicts of interest and allegations involving former SEBI Chairperson Madhabi Puri Buch and offshore financial links—claims denied by the individuals involved—the regulator constituted a High-Level Committee (HLC) in March 2025. This six-member panel, led by former Chief Vigilance Commissioner Pratyush Sinha, has proposed a comprehensive set of ten recommendations intended to overhaul SEBI’s internal governance standards and align them with global best practices followed by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
A key recommendation of the HLC is the establishment of a multi-tier disclosure framework. The Chairperson, Whole-Time Members (WTMs), and senior officials at the level of Chief General Manager (CGM) and above would be required to publicly disclose their assets and liabilities, covering movable and immovable property, investments, and outstanding liabilities. All other employees would file internal disclosures detailing their financial interests, professional relationships, and connections with relatives as defined under the Companies Act, 2013. This framework aims to strengthen public confidence in the regulator’s independence and integrity.
Another critical reform area involves mandatory conflict-of-interest declarations at the time of appointment. Applicants for top SEBI positions must disclose actual, potential, or perceived conflicts of both financial and non-financial nature. Such early disclosures allow the appointing authority to assess ethical suitability and mitigate risks before onboarding senior personnel.
The committee also recommended stringent investment and trading restrictions for SEBI leadership and employees. New investments should be limited to professionally managed pooled funds regulated by Indian financial regulators. For existing investments held at the time of appointment or joining, senior officials must choose among four options: liquidation, freezing, sale through a pre-approved trading plan, or sale with prior SEBI approval. Further, the HLC has advised that the Chairperson and WTMs be classified as “insiders” under the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015, placing them under enhanced scrutiny and disclosure obligations.
To ensure consistency, the committee proposed a broader definition of ‘family’. The revised definition would include spouses, dependent children, individuals for whom officials are legal guardians, and persons related by blood or marriage who are substantially dependent on the employee. This harmonisation between the SEBI Code of Conduct (2008) and the SEBI Employees’ Service Regulations (2001) seeks to remove ambiguities in assessing indirect conflicts of interest.
The HLC also recommended a blanket ban on acceptance of gifts from entities that have or may have official dealings with SEBI. A structured recusal mechanism must be institutionalised, requiring officials to step aside from decision-making roles in matters where conflicts exist. An annual summary of recusals by top officials should be included in SEBI’s Annual Report to enhance transparency.
Finally, the committee proposed post-retirement restrictions, preventing former members and employees from representing parties before SEBI for two years after exit. It also advocated a secure, confidential, anonymous whistle-blower system open not just to employees but also to market intermediaries and the public, ensuring a broad-based mechanism to detect ethical breaches.
Once approved by the SEBI Board and the Ministry of Finance, these recommendations will be incorporated into SEBI’s revised Code of Conduct with prospective applicability. Collectively, these reforms aim to fortify regulatory governance, restore public trust, and uphold the autonomy and integrity of India’s capital markets ecosystem.
Rare Earths, China’s Leverage and Lessons for Global and Indian Strategy

- 14 Nov 2025
In News:
Rare earth elements (REEs) have emerged as a critical geopolitical and economic lever in the 21st century, underpinning technologies central to defence, clean energy, electronics and advanced manufacturing. Recent developments including China’s temporary easing of export controls have highlighted that any relief to global markets is likely to be short-lived. The episode reinforces a deeper structural reality: China’s dominance over rare earth mining, processing and magnet manufacturing gives it enduring strategic leverage.
China’s Rare Earth Dominance
Rare earths comprise 17 chemically similar elements used in high-performance magnets, phosphors, batteries, wind turbines, electric vehicles, missiles and fighter aircraft. While these elements are not geologically rare, economically viable and environmentally manageable deposits are scarce. Over the past three decades, China has systematically built control over the entire value chain from mining to refining to manufacturing.
China’s share in global rare earth mining rose from about 38% in 2020 to nearly 70% in 2023. Its grip is even stronger in processing and refining, where it supplies 85–95% of global demand. Beijing has reinforced this dominance through overseas investments in Africa and Latin America, stakes in processing facilities in Malaysia, and strategic influence in companies such as Australia’s Lynas. Rare earths were formally designated a “strategic mineral” by China in the 1990s, enabling the state to weaponise supply during diplomatic or trade disputes.
Japan’s 2010 Shock: A Strategic Lesson
The clearest early warning came in 2010, when China informally halted rare earth exports to Japan following a maritime dispute. At the time, Japan imported nearly 90% of its rare earths from China, leaving its automobile and electronics industries exposed. Prices surged almost tenfold within a year, revealing the costs of overdependence.
Japan responded with a multi-pronged strategy: stockpiling critical minerals, investing in overseas mines (notably in Australia and Vietnam), expanding recycling, and developing technologies that reduce rare earth intensity. By 2023, Japan had reduced its dependence on China to about 60%. However, the experience also revealed limits partial diversification still leaves room for coercion, while full independence demands sustained, high-cost investment. The fading urgency after crises subside underscores the danger of complacency.
Renewed Global Push: US and EU
China’s recent export restrictions including controls on seven rare earths such as dysprosium, terbium and yttrium have revived concerns in the US and Europe. The US is stockpiling magnets, investing in domestic mining and processing (including Pentagon-backed stakes in firms like MP Materials), and prioritisingdefence supply chains. The European Union has expanded its critical minerals list, pushed for domestic refining, and encouraged recycling and deep-sea mineral research. These efforts reflect a broader “de-risking” approach: reducing vulnerability without severing economic ties.
Implications for India
For India, the immediate impact of China’s controls is limited, but long-term risks are significant. India holds around 6.9 million tonnes of rare earth reserves, mainly in Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan, placing it among the top five globally. Yet production remains minimal about 2,700 tonnes of rare earth oxides in 2023, compared to China’s 2,24,000 tonnes.
Recent policy reforms aim to increase private participation and accelerate exploration. Output has begun to rise, touching nearly 2,900 tonnes in 2023-24 and projected to reach around 5,000 tonnes in coming years. However, slow development, environmental concerns, and limited processing capacity remain constraints. As demand surges from clean energy and defence sectors, India risks strategic vulnerability unless it builds end-to-end capabilities.
Way Forward
The global rare earth challenge underscores three lessons: diversification must be continuous, processing capacity matters as much as mining, and strategic stockpiles are essential. Japan’s experience shows that resilience is built over decades, not crises. For India, aligning mineral policy with industrial strategy, investing in processing and recycling, and forging trusted international partnerships will be critical to safeguarding economic and strategic autonomy in an era of resource geopolitics.
QS Asia University Rankings 2026

- 08 Nov 2025
In News:
The QS World University Rankings: Asia 2026, released by QS Quacquarelli Symonds, highlight a paradox for Indian higher education. While absolute scores of Indian institutions have improved, nine of the top ten Indian universities—including seven IITs—have slipped in rankings, reflecting intensifying competition from East and Southeast Asia.
Key Highlights of QS Asia Rankings 2026
Top Asian Universities
- The University of Hong Kong secured the 1st rank, overtaking Peking University (China).
- National University of Singapore (NUS) and Nanyang Technological University (NTU) shared 3rd position.
- Dominance of Hong Kong, Mainland China, and Singapore in the top 10.
- Universities from South Korea and Malaysia entered the top 20, indicating regional upward mobility.
QS described the trend as a “clear eastward concentration of top performance”, driven by sustained investments in research and internationalisation.
Performance of Indian Institutions
Ranking Trends
- IIT Delhi remained India’s best-ranked institution for the second consecutive year but fell 15 places to rank 59.
- IIT Bombay recorded the steepest decline, dropping 23 places to rank 71.
- IIT Madras, Kanpur, and Kharagpur witnessed their lowest rankings in recent years.
- Chandigarh University emerged as the only Indian institution to improve, rising from 120 to 109.
Overall, 67% of Indian institutions featured in 2025 slipped in 2026 rankings, despite score improvements.
Reasons Behind India’s Relative Decline
1. Intensifying Regional Competition
- Universities in China, Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Malaysia outperformed India in:
- Research impact
- Faculty resources
- Global academic engagement
- Large-scale state-backed R&D investments and strong international collaboration networks boosted regional peers.
2. Expanded Ranking Scope
- 1,529 institutions ranked in 2026, with 552 new entrants.
- China added 261 institutions, India added 137, increasing volatility and competition.
- India now has 294 universities ranked, second only to China.
Decline in Key Performance Metrics for Indian Institutions
Research Impact (Citations per Paper)
- IIT Delhi: 31.5, IIT Bombay: 20.0, IIT Madras: 20.3
- Leading Asian universities score 90+, indicating higher global research visibility.
- Reflects fewer highly cited and internationally co-authored papers.
Faculty–Student Ratio
- IIT scores range from 16.5 (IIT Kharagpur) to 40.9 (IIT Delhi).
- Top Asian universities score in the 80–90 range.
- Indicates large class sizes and faculty shortages.
Internationalisation Indicators
- Poor performance in:
- International Student Ratio (ISR)
- International Faculty presence
- IIT ISR scores range from 2.5 to 12.3, compared to 100 for some global leaders.
- Structural disadvantage due to limited foreign student and faculty inflow.
Areas of Strength for Indian Institutions
Despite rank declines, Indian institutions perform strongly in:
- Academic reputation
- Employer reputation
- Staff with PhD
- Papers per faculty
These metrics consistently fall in the 80–90 score range, reflecting strong domestic credibility and teaching capacity.
Comparative Regional Trends
- China & Hong Kong: Sustained dominance through massive R&D funding and institutional autonomy.
- South Korea: Universities like Yonsei and Korea University show steady upward movement due to global partnerships.
- Malaysia: Institutions such as Universiti Malaya and Universiti Putra Malaysia improved through better faculty-student ratios and internationalisation.
Conclusion
The QS Asia Rankings 2026 underline a critical challenge for India: improving absolutely but falling relatively. As Asian peers surge ahead through research excellence and global engagement, India must bridge gaps in research impact, faculty resources, and internationalisation. Achieving the NEP 2020 vision is essential for transforming Indian universities into globally competitive, innovation-driven institutions.
Strengthening India’s Statistical Ecosystem: MoSPI’s Initiative to Develop a Robust District Domestic Product (DDP) Framework
- 02 Nov 2025
In News:
India’s statistical architecture is undergoing a major transformation as the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) moves toward developing a bottom-up District Domestic Product (DDP) framework.
The initiative seeks to address long-standing limitations in district-level economic measurement by integrating two critical datasets—the Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) and the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS). Beginning January 2025, the combined use of these datasets aims to provide more accurate, granular and timely insights into India’s local economic activity, enabling evidence-based policymaking at the district level.
For decades, most states have relied on top-down allocation methods to estimate DDP, proportionately distributing Gross State Domestic Product based on outdated demographic indicators such as population. This approach produces “near-identical growth rates across districts”, obscuring regional disparities. Recognising this gap, MoSPI has initiated a shift toward a bottom-up estimation model in partnership with state governments. By directly capturing enterprise-level and labour market data from each district, the new framework is expected to radically improve the precision of district economic accounts.
The ASUSE forms the backbone of this strategy. Covering the unincorporated non-agricultural sector—which includes micro, household-based and small enterprises across manufacturing, trade and services—ASUSE produces detailed information on operations, investment patterns, workforce size and value addition. Previously released annually, the survey now offers quarterly data, enhancing frequency and granularity. Given the dominance of the unorganised sector in India’s economy, ASUSE provides an indispensable window into local economic activity.
The PLFS, conducted monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO), complements ASUSE by capturing labour force participation, employment conditions, earnings and occupational structures in both rural and urban areas. Together, the two datasets reflect the dual pillars of district economies—enterprise activity and labour engagement. MoSPI notes that large enterprises are easy to identify, but district-level output is primarily driven by households, nano units and MSMEs, which both surveys cover extensively.
By combining these datasets, MoSPI aims to compute DDP through:
(a) bottom-up aggregation of district-level enterprise and labour data;
(b) integration of informal sector output; and
(c) alignment of statistical systems with decentralised planning structures.
This marks a paradigm shift in India’s economic measurement, aligning with the government’s emphasis on data-driven governance under Viksit Bharat @2047.
The initiative is part of a broader overhaul of the statistical system. Several complementary efforts are underway:
- The Annual Survey of Service Sector Enterprises (ASSSE), launching in January 2026, will map the incorporated services sector.
- The National Household Income Survey (NHIS), beginning February 2026, aims to measure income distribution and inequality—despite traditional challenges of under-reporting.
- A forward-looking capital expenditure survey has been introduced to track investment trends.
- MoSPI is also expanding public access to over 250 datasets, including GST aggregates, e-Vahan registrations and trade statistics, to strengthen national accounts and support research.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Accurate data capture from unincorporated enterprises is difficult, statistical capacity varies across states, and integrating multiple datasets raises risks of double-counting. Yet experts view the reform as a critical step toward improving the granularity, reliability and timeliness of India’s economic statistics. With several states already experimenting with district-level estimation, MoSPI’s framework could soon enable standardised and credible DDP measurement nationwide, transforming local governance and development planning.
Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) 3 Norms

- 03 Oct 2025
In News:
- India has proposed the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) 3 norms, drafted by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), aiming to tighten fuel efficiency standards, reduce vehicular emissions, and promote electric and alternative fuel vehicles.
- First introduced in 2017, CAFE norms regulate fuel consumption and CO? emissions for passenger vehicles weighing up to 3,500 kg, including petrol, diesel, CNG, LPG, hybrid, and electric vehicles.
- The earlier iteration, CAFE 2 (2022-23), capped fuel consumption at 4.78 litres/100 km and CO? emissions at 113 g/km, with penalties for non-compliance.
Need for CAFE 3
Current Indian norms inadvertently favourheavier vehicles like SUVs while imposing stringent targets on smaller cars, unlike international practices in the USA, EU, China, and Japan, where light vehicles enjoy relaxed emission standards. CAFE 3 seeks to align India with global best practices, revive the small car segment, and incentivisegreen mobility, particularly electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids.
Key Features of CAFE 3 Norms
1. Applicability
- Targets M1 category passenger vehicles (seating up to nine people, maximum weight 3,500 kg).
- Non-compliance will attract penalties under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
2. Efficiency Targets
- Efficiency formula: [0.002 × (W – 1170) + c], measured in petrol-equivalent litres/100 km, where W is fleet weight, 1,170 kg is a fixed constant, 0.002 is a multiplier, and ‘c’ decreases yearly from 3.7264 (FY28) to 3.0139 (FY32).
- Lighter vehicles benefit from easier compliance, motivating manufacturers to focus on small cars.
- Additional relaxation: 3.0 g CO?/km (capped at 9 g/km) for compact cars (<909 kg, ≤1200 cc engine, ≤4,000 mm length).
3. Incentives for EVs and Alternative Fuels
- Super credits: Each EV sold counts three times toward fleet compliance; plug-in hybrids 2.5×, strong hybrids 2×, flex-fuel ethanol vehicles 1.5×.
- Carbon Neutrality Factor (CNF): Offers relaxation based on fuel type (e.g., E20–E30 petrol vehicles 8% CNF; strong hybrids 22.3%).
4. Emissions Pooling
- Up to three manufacturers can form a pool, treated as a single entity for compliance.
- Pool managers are legally responsible for penalties, allowing strategic partnerships, cost-sharing, and smoother adherence to targets.
Policy Complementarities
- GST reforms (GST 2.0) reduced taxes on small cars from 28% to 18%, complementing the relaxation measures under CAFE 3.
- By incentivisingEVs, hybrids, and small vehicles, the norms aim to reduce oil import dependency and advance India’s climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Challenges
- Industry adaptation: Transitioning fleets to comply with stricter norms while managing costs.
- Consumer acceptance: Affordability and infrastructure readiness for EVs and hybrids.
- Infrastructure readiness: Charging and fuel infrastructure for alternative vehicles needs significant expansion.
Conclusion
CAFE 3 represents a transformative step in India’s vehicular emission regulation, combining fuel efficiency improvements, emission reductions, and green mobility incentives. By aligning with global practices, reviving the small car segment, and encouraging electric and hybrid vehicles, the norms have the potential to accelerate sustainable transportation while addressing environmental and energy security goals. Successful implementation will require coordinated action between manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers to build a cleaner, efficient, and resilient automotive sector in India.
National Security Act (NSA)

- 01 Oct 2025
Context:
The detention of climate activist Sonam Wangchuk under the National Security Act (NSA), 1980, has reignited a long-standing debate on the balance between national security and civil liberties in India. Wangchuk, who has been leading the movement for Ladakh’s statehood and Sixth Schedule protections, was detained following alleged provocative speeches that, according to the administration, triggered violent protests in Leh leading to four deaths and several injuries. His case illustrates the continuing tension between state power and individual freedoms under India’s preventive detention framework.
Understanding Preventive Detention in India
Preventive detention refers to the practice of detaining an individual not for a crime already committed, but to prevent them from acting in a manner considered prejudicial to public order, security, or essential supplies. Unlike punitive detention, which follows conviction through due process, preventive detention is anticipatory in nature—aimed at averting potential threats before they materialise.
The Constitutional sanction for preventive detention is provided under Article 22 (Clauses 3–7), which permits Parliament and State legislatures to enact laws allowing such detention. A person can be held for up to three months without approval from an Advisory Board of judges, and longer if such approval is obtained. However, detainees are denied the right to legal counsel before the Advisory Board, and authorities may withhold information on grounds of public interest—limiting transparency and accountability.
Evolution of Preventive Detention Laws
Preventive detention has deep colonial roots, beginning with wartime laws such as the Defence of India Acts and the Rowlatt Act (1919). Post-Independence, the Preventive Detention Act, 1950, institutionalised this power, followed by the Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA), 1971, which gained notoriety during the Emergency (1975–77). Although MISA was repealed in 1978, preventive detention returned with the National Security Act (NSA), 1980, reflecting the persistence of this legal mechanism in India’s security architecture.
Provisions and Safeguards under the NSA
The NSA empowers the Central and State governments, as well as authorisedDistrict Magistrates and Police Commissioners, to detain individuals to prevent actions “prejudicial to India’s defence, foreign relations, national security, public order, or essential supplies.”
- Detention orders operate like arrest warrants, allowing transfer across states and detention up to 12 months.
- Grounds for detention must be communicated within 5 to 15 days, and the detainee can submit a representation to the government.
- An Advisory Board of High Court judges must review the case within three weeks and order release if “no sufficient cause” exists.
However, no legal representation is allowed before the Board, and the government may withhold crucial information—leaving wide discretion in official hands.
Use and Misuse: Judicial and Public Concerns
Over the decades, NSA has been used in cases involving separatists, radical preachers, gangsters, and protesters. Notable instances include the detention of Amritpal Singh (2023), Bhim Army chief Chandrashekhar Azad (2017), and Dr. Kafeel Khan (2020). Courts have repeatedly intervened in cases of misuse, emphasising that the Act cannot be a substitute for ordinary criminal law. The Supreme Court’s 2012 ruling striking down detention for kerosene black-marketing underscored this misuse.
Critics argue that preventive detention contradicts the spirit of fundamental rights under Articles 19, 21, and 22, allowing incarceration without trial and enabling governments to suppress dissent under the guise of maintaining order. Scholars contend that Article 22 itself legitimises preventive detention, reflecting what Erich Fromm described as a “fear of freedom”—a societal tendency to trade liberty for perceived security.
Conclusion
The National Security Act remains one of India’s most powerful yet controversial laws. While it provides governments with a vital tool to prevent threats to national security and public order, its frequent and often arbitrary invocation erodes constitutional guarantees of liberty and due process.
The detention of Sonam Wangchuk serves as a stark reminder that preventive detention laws, though constitutionally sanctioned, sit uneasily within a democratic framework. India’s challenge lies in ensuring that security imperatives do not eclipse fundamental freedoms, reaffirming the Constitution’s promise of liberty, justice, and accountability.
Inflation: A Double-Edged Sword for Economic Growth and Fiscal Stability

- 30 Sep 2025
In News:
Inflation, the sustained rise in general price levels, remains one of the most debated macroeconomic phenomena. While high inflation erodes purchasing power and destabilizes economies, moderate and predictable inflation is often considered essential for sustained growth and fiscal stability. Its impact, however, varies depending on the broader economic context and the balance between price stability and growth objectives.
Understanding Inflation and Its Role
Economists typically define inflation as a result of “too much money chasing too few goods.” Moderate inflation signals expanding demand and healthy economic activity, while very high or negative inflation (deflation) indicates structural imbalances. Central banks, such as the U.S. Federal Reserve and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), usually target a low but positive inflation rate — around 2% — to maintain price stability and incentivize investment.
Mild inflation helps prevent deflation, which discourages spending and investment as consumers postpone purchases in anticipation of falling prices. The British economist John Maynard Keynes argued that a small amount of inflation encourages consumption, supports employment, and sustains aggregate demand. This aligns with the concept of the Phillips Curve, which once suggested a trade-off between inflation and unemployment, though the relationship has weakened in recent decades.
Economic Benefits of Moderate Inflation
A modest level of inflation can stimulate economic activity when idle capacity and underutilized labor exist. Rising prices encourage producers to expand output, generating more employment and income. Borrowers, including businesses and households, also benefit since debts can be repaid with “cheaper” money, thus encouraging borrowing and spending. Fixed-rate homeowners and long-term debtors gain, as the real value of their obligations declines over time.
For governments, inflation contributes positively to nominal GDP growth, the key denominator in fiscal ratios such as the debt-to-GDP ratio and fiscal deficit. Higher nominal GDP, driven partly by price growth, increases tax collections and helps meet revenue and deficit targets. Hence, inflation, within manageable limits, supports both macroeconomic stability and fiscal sustainability.
Challenges of High or Low Inflation
Excessive inflation, however, leads to declining real incomes, uncertainty, and reduced investment. Rising input and borrowing costs can trigger stagflation — a combination of stagnant growth and high inflation. On the other hand, very low inflation, as seen in India recently with CPI inflation at 2.07% (August 2025) and WPI at 0.52%, presents a different set of challenges.
While subdued prices benefit consumers, they constrain the government’s fiscal arithmetic. Lower inflation suppresses nominal GDP growth — the sum of real growth and inflation — reducing tax revenue growth and widening fiscal gaps. The Union Budget 2025–26 projected nominal GDP growth at 10.1%, but with low price levels, actual growth has trailed this target, weakening revenue collection and straining fiscal balances.
Moreover, persistently low inflation can reflect weak demand and investment sentiment. Although corporate profits have risen due to falling input costs, private capital expenditure remains sluggish, suggesting that firms are not reinvesting profits into productive capacity — a sign of demand-side weakness rather than efficiency gains.
Conclusion
Inflation’s impact on an economy depends on its source, magnitude, and persistence. Moderate inflation supports economic dynamism, government finances, and debt sustainability. However, extremes on either side — hyperinflation or deflation — can destabilize the macroeconomic framework. For India, the policy challenge lies in maintaining a delicate balance: ensuring that inflation stays within the target range to protect consumers while sustaining enough price growth to support investment, job creation, and fiscal health.
H-1B Visa Overhaul and Its Implications for India–US Tech Relations

- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
The United States government has announced a sweeping change to its H-1B visa programme, introducing a $100,000 annual entry fee per visa effective September 21, 2025. Framed as a measure to protect American workers, this move has significant geopolitical and economic implications, particularly for India, whose citizens constitute over 70% of all H-1B beneficiaries annually.
What the New Rule Entails
Under the new proclamation signed by President Donald Trump, no petition filed for an H-1B worker outside the US will be approved unless the sponsoring employer pays the $100,000 fee upfront. Applications without proof of payment will be denied at consular processing. The rule applies to new entrants or those seeking re-entry after travel, though workers already in the US on valid H-1B status are exempt.
The order, valid for 12 months with scope for review, also directs the Department of Labor to raise wage levels for H-1B jobs and asks the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to prioritise petitions offering higher salaries. A discretionary clause empowers DHS to waive the fee for specific individuals, companies, or entire industries if deemed in the “national interest.” However, the proclamation does not define which sectors qualify—though healthcare, defence, and critical technology are likely candidates.
Rationale and Political Context
Immigration has become a central and polarising issue in US politics. Public concern on immigration rose from 2.1% in 2012 to 14.6% in 2024 as a top voter priority. Trump’s political narrative has long linked immigration—both low-skilled and skilled—to job displacement and wage depression among the American working class. The H-1B programme, originally designed to attract top global talent in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields, is now portrayed by nativist factions as a vehicle for outsourcing and wage suppression.
Data from the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) indicate that nearly 70% of H-1B approvals for Indian workers in FY2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median US IT salary was $104,420.
Economic and Industrial Impact
The fee fundamentally alters the cost structure of hiring global talent. The new surcharge, in addition to existing statutory fees, transforms the H-1B from a skill-mobility programme into a premium channel accessible mainly to top-tier corporations or sectors granted exemptions.
Big Tech firms such as Amazon, Microsoft, Meta, Google, and Apple—already the largest H-1B sponsors—face millions in additional costs. Indian IT service giants like Infosys, TCS, Wipro, and HCL, who rely on the visa for onsite client delivery, are particularly vulnerable. The policy may push more work to offshore hubs in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune, reinforcing India’s role as a global back-office and development centre rather than an onsite service provider.
Startups, universities, and research labs, often operating on tight budgets, may scale back recruitment or face disruption to innovation and research projects if waivers are not granted.
Implications for India
For India, this measure could limit opportunities for young professionals transitioning from student visas (OPT) to H-1Bs, while families already in the US may face travel restrictions and uncertainty. However, it may also spur reshoring of tech investment to India, as multinational firms expand local operations to mitigate costs.
Conclusion
The $100,000 H-1B fee marks a decisive shift in US immigration policy—from selective reform to fiscal deterrence. While it may serve short-term political optics of job protectionism, it risks undermining America’s long-standing advantage in global innovation. For India, the challenge lies in turning this disruption into opportunity—by strengthening domestic tech ecosystems, skilling talent, and positioning itself as a preferred global innovation hub amid shifting international labour dynamics.
State Finances publication 2025 by CAG
- 25 Sep 2025
In News:
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India released the State Finances Publication 2025, providing a comprehensive assessment of revenue, expenditure, debt, and fiscal sustainability across India’s 28 states. The report highlights critical trends in committed expenditure, salary and subsidy bills, and public debt, offering insights for policy planning and fiscal management.
Salary and Subsidy Expenditure
- Over the last decade (2013-14 to 2022-23), states’ salary bills have grown 2.5 times, reaching ?16.6 lakh crore, forming the largest component of committed expenditure.
- Subsidy spending, defined as day-to-day operations that do not create or enhance assets, more than trebled to ?3.09 lakh crore, accounting for 8.61% of total revenue expenditure.
- The distribution of subsidy expenditure is highly uneven. In 2022-23, Punjab, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan spent over 10% of their total expenditure on subsidies, with Punjab at 17%, the highest among states. By contrast, 10 states, including Sikkim, Nagaland, Kerala, and Goa, reported subsidies below 2%, and Arunachal Pradesh recorded no subsidy spending.
Committed Expenditure Patterns
Committed expenditure, comprising salaries, pensions, and interest payments, constituted 43.49% of states’ revenue expenditure in FY 2022-23. The share varied widely across states:
- Nagaland: 74%
- Kerala: 63%
- Tamil Nadu: 51%
- Andhra Pradesh: 42%
- Telangana: 41%
- Karnataka: 33%
- Maharashtra: 32%
In total, 15 states reported committed expenditure exceeding 50% of revenue expenditure, seven between 40–50%, and six below 40%. The report indicates that committed expenditure and subsidies together have frequently exceeded states’ own tax revenues, reaching 102% in 2013-14 and 134% in 2020-21, signaling fiscal pressure and limited flexibility.
Public Debt and Fiscal Risk
Public debt has risen 3.4 times over the last decade, reaching ?59.6 lakh crore, approximately 23% of the combined Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP). This increase in debt, coupled with rising committed expenditure, poses medium-term fiscal risks, necessitating prudent fiscal management and reforms.
Union Tax Devolution and Revenue Sources
States’ major revenue sources include own taxes and non-tax revenues, grants-in-aid, and their share of Union taxes. Between 2013-14 and 2022-23, states’ average share of Union taxes remained around 27% of total revenue receipts, with FY 2022-23 showing the same share.
Distribution of devolved taxes is concentrated:
- Top 5 states (UP, Bihar, MP, West Bengal, Maharashtra) received 50% of devolved taxes.
- Southern states’ shares: Tamil Nadu 4.08%, Andhra Pradesh 4.02%, Karnataka 3.65%, Telangana 2.07%, and Kerala 1.93%.
Policy Implications
The CAG report underscores the rising fiscal pressures on states due to expanding salary bills, high subsidies, and growing debt. With committed expenditure consuming a large portion of revenue, states have limited fiscal space for development and capital investment. The findings highlight the need for targeted reforms in public expenditure management, subsidy rationalisation, and debt sustainability, ensuring that states can maintain service delivery without compromising fiscal health.
Rising State Debt in India: CAG’s Decadal Analysis and Fiscal Implications
- 22 Sep 2025
In News:
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has released a first-of-its-kind decadal report (2013–14 to 2022–23) analysing the fiscal health of Indian states, highlighting a worrying surge in public debt and its implications for fiscal sustainability and cooperative federalism.
Understanding Public Debt
- Public debt arises when government expenditure exceeds revenue from taxes and other receipts, prompting borrowing to bridge the fiscal gap. For states, such debt includes liabilities under the Consolidated Fund of the State, comprising internal debt and loans and advances from the Centre.
- Internal debt consists of marketable securities like government bonds and treasury bills, and non-marketable debt such as loans from financial institutions like LIC and NABARD or the Reserve Bank’s Ways and Means Advances (WMA).
- The Debt-to-GSDP ratio is a key indicator of fiscal sustainability, reflecting a state’s capacity to service its debt. A higher ratio implies greater fiscal stress.
- The NK Singh Committee on FRBM (2016) recommended a combined general government debt ceiling of 60% of GDP — 40% for the Centre and 20% for states.
Key Findings of the CAG Report
- The CAG report reveals that the aggregate public debt of 28 states trebled over the past decade — from ?17.57 lakh crore in 2013–14 to ?59.60 lakh crore in 2022–23.
- As a share of combined GSDP, debt rose from 16.66% to 22.96%, with state debt accounting for 22.17% of India’s GDP in FY 2022–23.
Inter-State Variations
Fiscal vulnerability varies widely:
- Highest debt-to-GSDP ratios: Punjab (40.35%), Nagaland (37.15%), and West Bengal (33.70%).
- Lowest ratios: Odisha (8.45%), Maharashtra (14.64%), and Gujarat (16.37%).
As of March 2023, eight states had debt exceeding 30% of GSDP, while six states maintained it below 20%.
Debt Sustainability and Composition
- The states’ debt-to-revenue receipts ratio ranged from 128% (2014–15) to 191% (2020–21), averaging about 150% of total receipts.
- The debt-to-GSDP ratio oscillated between 17–25%, with a sharp rise during the COVID-19 pandemic year (2020–21) due to falling GSDP and increased borrowing for relief and GST compensation.
- Major sources of debt include open market borrowings, RBI advances, institutional loans, and back-to-back loans from the Centre in lieu of GST shortfall and capital assistance.
Fiscal Management Concerns
- The report flags a violation of the “golden rule of borrowing”, which stipulates that governments should borrow only for capital formation, not to finance revenue expenditure.
- Eleven states, including Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, Kerala, and West Bengal, used borrowings to fund current expenses.
- In Andhra Pradesh, only 17% of borrowings went to capital expenditure; in Punjab, 26%.
Such practices threaten fiscal sustainability, crowd out productive investments, and risk pushing states into a debt trap, thereby undermining macroeconomic stability.
Way Forward
- Fiscal Discipline: States must prioritise borrowing for productive infrastructure and avoid financing recurring expenditure.
- Debt Management Reforms:Operationalising the Public Debt Management Agency (PDMA) could ensure transparency and better coordination in debt operations.
- Revenue Strengthening: Enhancing tax buoyancy, rationalising subsidies, and diversifying revenue bases can reduce dependence on central transfers.
- Adherence to FRBM Targets: States should align fiscal deficit and debt ratios with FRBM norms to ensure long-term sustainability.
- Institutional Oversight: Strengthening State Finance Commissions and CAG monitoring can promote accountable and sustainable fiscal federalism.
Conclusion
The surge in state-level debt underscores the growing strain on subnational fiscal capacity. While borrowing is essential for development, unchecked debt accumulation and non-productive spending threaten fiscal stability. Ensuring fiscal prudence, efficient debt management, and adherence to reform frameworks like FRBM are vital to preserving India’s long-term macroeconomic resilience and cooperative federal balance.
Rising Extreme Rainfall in the Himalayas
- 20 Sep 2025
In News:
The 2025 monsoon season has witnessed intense and destructive rainfall across North India, particularly in the Himalayan states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir. Cloudbursts, landslides, and flash floods have resulted in widespread devastation, exposing the growing vulnerability of India’s mountain ecosystems and urban regions. The intensification of monsoon rainfall can be traced to the complex interplay of global climate change, regional topography, and anthropogenic factors such as urbanisation and deforestation.
Scientific Basis of Intensified Rainfall
Dry regions like northwestern India lie at the confluence of tropical and extratropical systems. Moist monsoon currents from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea increasingly collide with western disturbances, producing strong atmospheric instability and torrential rainfall. This interaction has become more frequent as climate change alters the behaviour of mid-latitude westerlies.
Global warming weakens and destabilises the jet stream, allowing westerly troughs to extend southward and interact with the monsoon more often. A warmer atmosphere holds more moisture, intensifying the hydrological cycle and leading to heavier downpours. These processes have made events like the recent Udhampur (630 mm in 24 hours) and Leh (59 mm in two days) rainfall episodes more common, even in regions historically considered semi-arid.
Why the Himalayas Are More Vulnerable
The Himalayas sit at the convergence of moist tropical monsoon winds and mid-latitude westerlies, creating ideal conditions for orographic uplift and deep convection that trigger extreme precipitation and cloudbursts. When moisture-laden air is forced up steep slopes, it cools rapidly and condenses into intense, localised storms.
Climate change compounds this natural vulnerability. Rapid Arctic warming is weakening the jet stream, causing slower and more meandering weather systems that linger over regions, leading to prolonged heavy rainfall. Similar dynamics have been linked to the Pakistan floods (2010), Germany (2021), and West Asia (2024) events.
In mountainous terrain, rainfall that would be manageable in coastal plains becomes catastrophic — flash floods and landslides occur as water cascades downhill, carrying debris, loose soil, and boulders. Over the last month, such incidents have been recorded in Mandi, Kullu, Dharali, Tharali, and Jammu, destroying homes and cutting off roads.
Challenges in Prediction and Preparedness
Despite technological advances, forecasting cloudbursts remains challenging. Current systems employ Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs), satellites (INSAT-3D/3DR, GPM, Himawari), rain gauges, and high-resolution numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. However, coverage in Himalayan terrain is sparse, satellite resolution is coarse, and models require ultra-fine grid scales (<1 km) with precise initial conditions.
Improved dense observation networks, enhanced process-based models, and integration of AI/ML techniques for real-time data assimilation are critical for reliable nowcasting.
Urban and Developmental Pressures
Rapid urbanisation, deforestation, and construction on unstable slopes have magnified the flood risks in both mountain towns and plains cities. Urban drainage systems, designed for rainfall of only 10–20 mm/hour, are ill-equipped for cloudbursts exceeding 100 mm/hour. Concretised surfaces increase runoff, while encroachments block natural drainage, turning heavy rain into urban deluges.
Mitigation demands a multi-pronged approach—redesigning stormwater systems, enforcing land-use regulations, restoring natural water channels, and incorporating climate risk assessments in infrastructure planning.
Conclusion
The increasing frequency of extreme rainfall and cloudbursts in India’s Himalayan and urban regions reflects the intersection of climate dynamics, fragile topography, and unsustainable development. Strengthening early warning systems, integrating scientific forecasting with local planning, and promoting climate-resilient infrastructure are essential to mitigate future disasters. The Himalayan crisis underscores a broader reality—climate change is no longer a distant threat but an unfolding challenge demanding immediate, coordinated action.
SEBI Announces Major Market Reforms to Enhance Investment and Governance

- 18 Sep 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) recently announced a set of comprehensive reforms aimed at improving foreign investment inflows, easing IPO norms for large issuers, strengthening governance in market infrastructure institutions (MIIs), and promoting financial inclusion. These reforms are introduced amid heightened global uncertainty, with foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) withdrawing over ?63,500 crore from Indian markets since July 2025 due to weak earnings, high valuations, and international trade tensions.
SWAGAT-FI: Single Window Access for Foreign Investors
A cornerstone of SEBI’s reforms is the Single Window Automatic &Generalised Access for Trusted Foreign Investors (SWAGAT-FI) framework, designed to simplify investment access for FPIs and Foreign Venture Capital Investors (FVCIs).
Eligibility and Scope:
- Sovereign wealth funds, central banks, regulated public retail funds (mutual funds, insurance companies, pension funds).
- Existing FPIs meeting criteria can migrate to SWAGAT-FI status.
Features:
- Unified registration and KYC cycle, reducing repeated compliance.
- Exemption from the 50% cap on contributions by NRIs, OCIs, and resident Indians.
- Simplified access through the India Market Access portal, reducing regulatory complexity.
- Implementation over a six-month timeline, aiming to restore investor confidence and enhance India’s global competitiveness.
Relaxed IPO Norms for Large Companies
To encourage large issuers to raise capital efficiently:
- Companies with market capitalization of ?1–5 lakh crore must now offer 2.75–2.8% of post-issue market cap, down from 5%.
- Minimum public offer for mega-IPOs raised to ?6,250 crore.
- Public shareholding timeline relaxed: Firms with <15% float at listing get 10 years to meet 25% minimum, and those with ≥15% float get 5 years.
- Anchor investor quota increased from one-third to 40%, reserving one-third for domestic mutual funds and the rest for life insurers and pension funds.
These measures help promoters reduce immediate dilution while facilitating broad investor participation.
Strengthened Governance in Market Infrastructure Institutions
SEBI has introduced structural reforms to improve transparency and accountability in exchanges and clearing corporations:
- Two executive directors appointed to oversee critical operations (trading, clearing, settlement) and regulatory compliance (risk, investor grievances).
- Defined roles and responsibilities for Managing Directors and Key Managerial Personnel to enhance succession planning.
- Scale-based thresholds introduced for material related-party transactions.
- Separate AIF schemes for accredited investors with flexible compliance norms.
Mutual Fund and Retail Investor Reforms
To promote financial inclusion and investor protection:
- Maximum exit load reduced from 5% to 3%.
- Distributor incentives revised to encourage inflows from B-30 cities and women investors.
- Enhanced transparency in investor reporting and compliance requirements.
Significance and Implications
- For India’s markets: Provides operational flexibility for large issuers, simplifies compliance, and reduces procedural hurdles for trusted foreign investors.
- For global competitiveness: Positions India as a stable, long-term investment hub amid capital volatility.
- For retail investors: Encourages broader participation from smaller cities and underrepresented groups, aligning with inclusive financial growth objectives.
Overall, SEBI’s reforms reflect a balance between market facilitation, investor protection, and governance standards, reinforcing India’s ambition to be an attractive, transparent, and globally competitive capital market.
India-Mauritius Relations
- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
India and Mauritius share deep-rooted historical, cultural, and economic ties, which have been further strengthened through recent diplomatic engagements. In September 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Mauritius PM Navinchandra Ramgoolam in Varanasi, reaffirming the partnership as more than a diplomatic arrangement, describing it as a “family bond” rooted in shared history, values, and strategic interests.
Special Economic Package and Development Cooperation
During the meeting, India announced a special economic package worth $680 million, aimed at supporting Mauritius in infrastructure, healthcare, defence preparedness, and maritime security. Key components of the package include:
- Healthcare: Establishment of a 500-bed Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam National Hospital, an AYUSH Centre of Excellence, and a Veterinary School and Animal Hospital. The first Jan Aushadhi Kendra outside India was also inaugurated.
- Infrastructure: Development of roads, highways, ring roads, and the ATC Tower at SSR International Airport.
- Strategic and Maritime Security: Assistance in Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance, hydrographic surveys, navigation charting, and maritime domain awareness over the next five years.
- Chagos Marine Protected Area: India will support Mauritius in monitoring, developing, and protecting the Chagos EEZ, following Mauritius’ sovereignty agreement with the UK.
These initiatives are positioned as hard and soft power diplomacy, enhancing India’s strategic reach in the Indian Ocean while improving Mauritius’ development and security capabilities.
Economic and Technological Cooperation
Mauritius is one of India’s closest economic partners in Africa, ranking as the second-largest source of FDI into India after Singapore. The two nations signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) in 2021, India’s first trade deal with an African country. Last year, UPI and RuPay services were launched in Mauritius, and both nations are now exploring trade in local currencies.
India also supports academic and civil service capacity building through collaborations between IIT Madras, Indian Institute of Plantation Management, and the University of Mauritius, as well as the launch of Mission Karmayogi training modules.
Geopolitical and Strategic Significance
Mauritius views India as a trusted partner and net security provider in the Indian Ocean, reinforcing a free, open, and secure maritime domain. India’s support aligns with its Neighbourhood First and Vision Mahasagar policies, countering the growing influence of China, Russia, Iran, and Gulf nations in the region. By assisting Mauritius with EEZ surveillance and maritime capacity building, India strengthens its strategic leverage while bolstering Mauritius’ sovereignty, particularly in the Chagos Archipelago.
Cultural and People-to-People Connect
The bond between the two nations is also cultural and historical. Approximately 70% of Mauritius’ 1.3 million population are of Indian descent, and Indian culture, traditions, and languages are deeply embedded in daily life. During the Varanasi visit, the Mauritian Prime Minister participated in the Ganga Aarti and planned prayers at Shri Kashi Vishwanath Dham, highlighting the symbolic spiritual dimension of bilateral relations.
Conclusion
India’s multi-dimensional engagement with Mauritius demonstrates a blend of strategic foresight, development diplomacy, and cultural affinity. Through the special economic package, maritime cooperation, and people-centric initiatives, India not only strengthens Mauritius’ development and security but also consolidates its influence in a geopolitically vital part of the Indian Ocean, fostering mutual prosperity, stability, and strategic partnership.
Land Subsidence in Uttarakhand
- 10 Sep 2025
Introduction
- Uttarakhand, a state already prone to natural calamities such as cloudbursts, flash floods, and landslides, is witnessing a new and alarming hazard—land subsidence.
- The phenomenon has recently surfaced in Chamoli district’s Nanda Nagar, destroying homes, displacing families, and highlighting the fragile ecological balance of the Himalayan region.
Understanding Land Subsidence
Land subsidence is the gradual settling or sudden sinking of the Earth’s surface, caused when the ground loses its ability to support weight. It may occur due to:
- Natural factors: seismic or volcanic activity, collapse of underground cavities, or compaction of fine-grained deposits.
- Anthropogenic factors: excessive groundwater extraction, mining, subsurface energy withdrawal, or unregulated construction.
Globally, nearly 12 million sq. km of land is susceptible to subsidence, with major hotspots in the USA, China, Iran, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Japan. In India, the Himalayas are increasingly vulnerable due to their fragile geology and unplanned development pressures.
The Chamoli Crisis
- In Nanda Nagar, Band Bazar and Lakshmi Market have become epicentres of subsidence. To date, seven buildings have been destroyed and 16 more are at risk, with cracks widening daily. Water seepage from underground fissures has aggravated fears, prompting diversion efforts by Jal Sansthan using pipelines.
- The disaster has displaced several families. While temporary relief camps have been established in wedding halls, many residents have opted for rented houses due to lack of facilities. 18 families have shifted voluntarily, while only a few essential volunteers remain in the camps. Authorities have provided tin sheets, tarpaulins, and fodder for livestock.
- Local administration and police are engaged in evacuation, restricting access to high-risk areas, and issuing rainfall-triggered alerts. Political representatives, including the local MLA, have assured compensation of ?5 lakh per affected family, aligning it with earlier precedents in nearby Thrali.
Causes and Concerns
The Chamoli episode underlines how over-extraction of groundwater and unregulated urbanisation exacerbate subsidence in mountain ecosystems. Groundwater overexploitation reduces pressure in aquifers, compacting porous formations and triggering ground collapse. Additionally, Himalayan terrain, already tectonically active, becomes more unstable with haphazard infrastructure expansion, tunnelling for hydropower, and inadequate drainage systems.
Impacts
- Infrastructure damage: Buildings, roads, and markets are rendered unsafe.
- Displacement: Families lose homes and livelihoods, straining relief systems.
- Water management challenges: Seepage alters drainage gradients and may increase risks of flooding and salinity intrusion.
- Security implications: Frequent disasters weaken borderland resilience in strategically sensitive districts like Chamoli.
Government Response
Authorities have taken short-term measures including relocation, compensation, and infrastructure support. Police and disaster management teams are actively engaged in restricting hazardous zone entry and ensuring safety. Yet, the lack of long-term risk assessment and early warning systems remains a critical gap.
Way Forward
- Scientific mapping of subsidence-prone areas using satellite and ground-based surveys.
- Regulated groundwater extraction and promotion of rainwater harvesting.
- Disaster-resilient urban planning with strict building codes in ecologically fragile zones.
- Community preparedness through awareness, relocation plans, and livelihood diversification.
- Integrated Himalayan policy, balancing development needs with ecological sustainability.
Conclusion
The Nanda Nagar subsidence crisis is not an isolated incident but part of a broader trend of human-induced ecological stress in fragile Himalayan ecosystems. As disasters intensify in frequency and scale, climate-resilient planning and sustainable resource management must become central to India’s mountain development strategy. Addressing land subsidence requires coordinated scientific, administrative, and community-level interventions to safeguard lives, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
Revisiting RTE Exemption for Minority Schools

- 07 Sep 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court has recently reopened the debate on whether minority institutions should be exempt from the Right to Education (RTE) Act, questioning the validity of the 2014 Pramati Educational and Cultural Trust judgment, which granted blanket immunity to minority schools—both aided and unaided—from RTE provisions. This issue lies at the intersection of Article 21A (Right to Education) and Article 30(1) (minority rights to establish and administer institutions), raising questions of inclusivity, equality, and constitutional morality.
The RTE Act and Its Objectives
Enacted in 2009, the RTE Act operationalises Article 21A, guaranteeing free and compulsory education for children aged 6–14 years. Its key mandates include:
- Government schools: Free education for all.
- Aided schools: Free seats proportional to state funding.
- Private unaided schools: Reservation of 25% seats at entry level for disadvantaged children (Section 12(1)(c)), with state reimbursement.
The Act also prescribes standards on infrastructure, pupil-teacher ratios, teacher eligibility, and prohibits corporal punishment and capitation fees. Rooted in child-centric philosophy, RTE aims to build inclusive classrooms as spaces of democracy, equality, and social justice.
The 2014 Pramati Judgment
A five-judge Constitution Bench ruled that applying RTE to minority institutions violated Article 30(1). It held that enforcing quotas and norms could alter their composition, thereby infringing minority rights. Consequently, both aided and unaided minority schools were exempted from RTE obligations.
Fallout
- Many private schools sought minority status to escape compliance.
- Exemption diluted inclusivity, particularly the 25% quota, undermining the spirit of Article 21A.
- Loopholes allowed elite minority institutions to function without admitting disadvantaged children—even from their own communities.
The 2025 Reconsideration
In September 2025, while hearing a case on the applicability of the Teacher Eligibility Test (TET) to minority schools, a two-judge bench led by Justice Dipankar Datta observed that Pramati had gone too far. The Court argued that:
- Articles 21A and 30 must co-exist. Institutional autonomy cannot override children’s rights.
- Standards like qualified teachers and infrastructure do not erode minority character.
- Blanket exemption weakens inclusivity and creates a “regulatory loophole.”
- Compliance with the 25% quota could be interpreted flexibly, e.g., by prioritising disadvantaged children from the same minority group.
Since only a larger bench can overturn Pramati, the matter has been referred to the Chief Justice of India for constitution of a bigger bench.
Challenges Ahead
- Legal Precedent: Overturning a Constitution Bench ruling requires judicial restraint and careful balancing.
- Autonomy vs Inclusivity: Reconciling group rights with universal child rights is constitutionally complex.
- Weak Enforcement: Even where RTE applies, compliance remains patchy.
- Social Resistance: Elite institutions and parents often resist socio-economic mixing in classrooms.
Implications
- For Education: Denial of access to elite minority schools undermines equity and India’s democratic ethos.
- For the Constitution: Current exemption skews the balance, privileging institutional rights over individual rights.
- For Society: Misuse of minority status widens educational inequality, weakening India’s human capital base.
Way Forward
- Judicial Harmonisation: Larger benches must strike a balance, clarifying that autonomy does not equal immunity.
- Policy Realignment: At minimum, teacher qualifications and infrastructure norms should apply to all schools.
- Strengthening Public Schools: Improving government schools can reduce over-reliance on private/minority institutions.
- Social Awareness: Campaigns to highlight inclusive classrooms as spaces of democratic socialisation are vital.
Conclusion
The exemption of minority schools from RTE is not merely a legal question but a test of constitutional morality. Upholding the child’s right to inclusive education must prevail over institutional privileges. The forthcoming larger bench decision offers an opportunity to harmoniseArticles 21A and 30, reaffirming that education is not a privilege of groups but a universal right essential to democracy and nation-building.
Haryana’s New Forest Definition and Its Implications for the Aravallis
- 29 Aug 2025
Introduction
The debate on what constitutes a “forest” in India has resurfaced with the Haryana government’s recent notification defining forests based on “dictionary meaning.” While the state claims its definition aligns with Supreme Court precedents, environmentalists warn that it narrows the scope of protection, particularly threatening the fragile Aravalli ecosystem. The issue reflects the larger legal and ecological contestation over forest governance in India, especially after the 2023 amendment to the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 (FCA).
Haryana’s Definition of Forests
As per the notification (August 18, 2025), a patch of land qualifies as forest if:
- It covers at least 5 hectares in isolation or 2 hectares if contiguous with government-notified forests.
- It has a canopy density of 40% or more.
The definition excludes linear or compact plantations (along roads, canals, railways), agro-forestry plantations, and orchards outside notified forests. Officials argue this provides clarity for surveys mandated by the Supreme Court, but critics fear it sets thresholds too high for naturally sparse ecosystems like the Aravallis.
Supreme Court Directives
In March 2025, the Supreme Court directed all States/UTs to define forests and begin mapping them, in line with the 2011 Lafarge Umiam Mining guidelines. These guidelines mandate:
- A GIS-based decision-support system.
- District-wise mapping of forest-like areas, community lands, eco-sensitive zones, wildlife corridors, and previously diverted forest lands.
- Accountability of Chief Secretaries for non-compliance.
This directive came during hearings on petitions challenging the 2023 FCA amendment (Ashok Kumar Sharma, IFS (Retd) &Ors. vs Union of India).
Godavarman Case and FCA Amendment
The FCA, 1980 originally restricted dereservation and diversion of forest land without Central approval. In the 1996 Godavarman case, the Supreme Court broadened “forest” to its dictionary meaning, bringing all statutorily recognised or naturally forested areas under FCA protection.
However, the 2023 amendment limited FCA applicability to:
- Notified forests, and
- Lands recorded as forests in government records.
The government argued that the Godavarman interpretation hindered developmental projects, even minor ones. Retired IFS officers and NGOs contested this, alleging dilution of forest safeguards. In February 2024, the Court ordered States to continue applying the Godavarman definition until the matter is resolved.
Implications for the Aravallis
The Aravalli range, spread across Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan, and Gujarat, is ecologically critical for groundwater recharge, biodiversity, and as a green buffer against desertification. Its vegetation is naturally stunted, thorny, and scrub-like due to low rainfall (300–600 mm annually) and rocky terrain. Experts argue that imposing a 40% canopy cover threshold would exclude much of the Aravallis, leaving it open to urbanisation, illegal mining, and real estate encroachments.
Furthermore, the minimum area thresholds (2–5 hectares) are considered too high for a dry state like Haryana, where smaller forest patches play a vital ecological role. Analysts call the state’s approach violative of the Godavarman principle, which recognised even small and degraded forests under FCA protection.
Conclusion
Haryana’s restrictive definition exemplifies the ongoing tension between developmental priorities and ecological safeguards. While compliance with the Supreme Court’s directive is necessary, adopting narrow thresholds risks excluding ecologically fragile zones from legal protection. The debate underscores the need for a balanced, scientifically informed, and ecologically sensitive framework, recognising regional variations in vegetation and ensuring long-term sustainability of ecosystems like the Aravallis.
Criminalisation of Politics in India

- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The criminalisation of politics—the entry of individuals facing serious criminal charges into legislative bodies—remains one of the gravest challenges to Indian democracy. Despite repeated judicial observations and public debates, the problem has only deepened over the past decade, threatening the integrity of representative institutions.
Scale of the Problem
Recent data highlights the alarming rise in lawmakers with serious criminal records. In the Lok Sabha, the share of MPs with such cases has increased from 14% in 2009 to 31% in 2024, more than doubling in just 15 years. Certain states reflect extreme cases: Telangana (71% of MPs), Bihar (48%), and Uttar Pradesh (34 MPs, the highest in absolute numbers).
At the state level, the trend is equally stark. In 2024, nearly 29% of MLAs (around 1,200) faced serious criminal charges. Andhra Pradesh (56%), Telangana (50%), and Uttar Pradesh (154 MLAs or 38%) illustrate how deeply entrenched the issue has become.
These figures cover offences punishable by five years or more, including non-bailable crimes such as murder, kidnapping, and corruption, thereby going beyond minor infractions.
Causes of Criminalisation
Several systemic factors perpetuate this trend:
- Electoral Financing – High campaign costs create incentives for parties to field “winnable” candidates, many of whom have criminal clout and access to large financial resources.
- Weak Enforcement of Laws – While conviction leads to disqualification under the Representation of the People Act (RPA), slow judicial processes allow accused legislators to contest multiple elections.
- Patronage Politics – Candidates with criminal backgrounds often command local influence, mobilise voters, and provide muscle power for parties, making them electorally attractive.
- Voter Rationality – In certain constituencies, voters see such candidates as problem-solvers who can deliver despite weak state capacity, reinforcing their acceptability.
Consequences for Democracy
The rising criminalisation of politics undermines the rule of law and corrodes democratic legitimacy. Legislators facing serious charges may prioritise personal or group interests over public welfare. Policy decisions risk being distorted by vested interests, while governance is compromised by declining ethical standards. Over time, this erodes citizen trust in institutions, weakens the credibility of Parliament and Assemblies, and fuels cynicism about democratic accountability.
Judicial and Institutional Responses
The Supreme Court has repeatedly emphasised the need to curb criminalisation. In Lily Thomas v. Union of India (2013), it ruled that convicted legislators would be immediately disqualified. In Public Interest Foundation v. Union of India (2018), it directed parties to publish criminal antecedents of candidates, citing the “urgent need for cleansing politics.”
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has also recommended barring candidates against whom charges have been framed for serious offences. However, political consensus on reforms remains elusive.
Way Forward
Addressing this structural malaise requires a multi-pronged strategy:
- Legal Reforms – Amend the RPA to disqualify candidates at the stage of framing of charges for heinous crimes.
- Judicial Fast-Tracking – Establish special courts for speedy trial of cases against politicians.
- Political Will – Parties must adopt internal reforms, refusing tickets to tainted candidates, with penalties for violations.
- Voter Awareness – Civil society campaigns and public disclosure of candidate records can empower voters to make informed choices.
- State Capacity – Strengthening law enforcement and reducing reliance on “muscle power” will make clean candidates more competitive.
Conclusion
The criminalisation of politics is not merely a legal or electoral issue but a crisis of democratic legitimacy. With nearly one-third of legislators facing serious charges, India risks normalising the presence of alleged criminals in the highest law-making bodies. Urgent institutional, legal, and political reforms are essential to reverse this trend and safeguard the constitutional promise of “purity of elections” and the rule of law.
US–China Trade Truce and the Role of Agricultural Imports in Geoeconomics
- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The United States and China, the world’s two largest economies, have extended their trade truce for another 90 days until November 10, 2025, averting a sharp escalation of tariffs. The pause keeps US duties on Chinese goods at 30% (against a threatened 145%) and Chinese tariffs on US shipments at 10% (down from an earlier 125%). This temporary reprieve reflects the complex mix of economics, politics, and strategic leverage shaping bilateral relations.
Tariffs and Negotiation Dynamics
Since his return to office, US President Donald Trump has pursued aggressive tariff measures to reduce America’s $300 billion trade deficit with China (2024), arguing that higher duties encourage domestic production and investment. Beijing retaliated with counter-tariffs and restrictions, sparking a tit-for-tat escalation that threatened global supply chains.
The extension of the truce provides space for negotiations over trade imbalances, unfair practices, national security concerns, and market access. It also underscores the challenges of balancing protectionism with the risks of inflation, uncertainty for businesses, and potential disruption to global economic stability.
China’s Leverage: Rare Earths and Agriculture
Beijing has strategically wielded two levers of influence. First, it controls the global supply chain of rare-earth elements and magnets, crucial for the US auto, aerospace, defence, and semiconductor industries. Second, it has employed its role as a major importer of agricultural commodities as a “trump card.”
US farm exports to China fell sharply from $13.1 billion (Jan–June 2024) to $6.4 billion (Jan–June 2025), continuing a downward trend from the 2022 peak of $40.7 billion. The steepest decline has been in soybean exports, dropping from $17.9 billion (2022) to just $2.5 billion (Jan–June 2025). China has redirected much of its soybean imports—74.7 million tonnes in 2024—to Brazil, Argentina, and Canada, significantly hurting American “corn belt” states and livestock producers reliant on feed crops.
Beyond soybeans, imports of US corn, sorghum, barley, cotton, beef, pork, poultry, and tree nuts such as almonds and pistachios have also contracted. This has created pressure on Trump from politically influential farm states, prompting him to publicly urge Beijing to expand soybean purchases.
Impact on the US and India
While American agricultural exports to China have fallen by 51.3% (Jan–June 2025 over 2024), those to India have surged 49.1% in the same period. India has emerged as the largest market for US tree nuts, importing over $1.1 billion in 2024, with a 42.8% year-on-year rise in early 2025. At the same time, the US has become India’s largest buyer of seafood, with frozen shrimp exports worth $1.9 billion in 2024–25.
This divergence highlights India’s growing importance in US agricultural trade, even as tariff disputes persist—Washington recently doubled duties on Indian imports to 50%, citing penalties linked to Russian oil purchases.
Broader Strategic Context
The US–China trade confrontation extends beyond tariffs and agriculture. Issues under negotiation include curbs on semiconductor exports, the role of Chinese platforms like TikTok, and energy security linked to Russian oil purchases. Beijing emphasizes “win-win cooperation,” while Washington continues to pursue coercive tools to address trade imbalances and safeguard national security.
Conclusion
The current trade truce reflects a fragile pause rather than resolution. China’s use of agriculture and rare earths as instruments of economic statecraft illustrates the growing intertwining of trade, technology, and geopolitics. For the US, balancing domestic political pressures from farmers and industries with long-term strategic objectives remains a challenge. For India, the shifting trade landscape offers both opportunities for greater market access and risks of tariff retaliation, underlining the complexity of navigating major power rivalries.
Five Years of the National Education Policy 2020

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, India’s third education policy since Independence, was envisioned as a transformative roadmap to make India a “global knowledge superpower.” Five years since its launch, the policy has driven important reforms in both school and higher education. However, progress has been uneven—while curriculum redesign, early childhood education, and digital learning have taken shape, federal tensions, institutional inertia, and funding constraints continue to slow its full realization.
Key Gains in School Education
The NEP replaced the 10+2 structure with a 5+3+3+4 model (foundational, preparatory, middle, secondary). The National Curriculum Framework (2023) set competency-based outcomes, and NCERT released new textbooks for classes 1–8, integrating subjects such as history and geography into a single volume.
Early childhood care and education (ECCE) has gained traction through the JaaduiPitara kits and a national ECCE curriculum. Delhi, Karnataka, and Kerala have enforced the minimum age of six for class 1. However, improving Anganwadi training and infrastructure remains critical.
Under NIPUN Bharat (2021), literacy and numeracy by class 3 became a national focus. Yet, survey data show proficiency levels at 64% (language) and 60% (math)—progressive but below NEP’s universal goals.
Higher Education Reforms
One of NEP’s boldest ideas, the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) and National Credit Framework (NCrF), introduced flexibility with multiple entry-exit options: a certificate after one year, a diploma after two, and a four-year degree. While nearly 90% of HEIs report multidisciplinary curricula, only 36% have implemented multiple entry-exit, and just 64% maintain ABC records, indicating patchy adoption.
The Common University Entrance Test (CUET), introduced in 2022, streamlined admissions by replacing multiple entrance exams. Global outreach expanded, with IIT Madras (Zanzibar), IIT Delhi (Abu Dhabi), and IIM Ahmedabad (Dubai) opening campuses abroad, while foreign universities such as the University of Southampton entered India.
Digital education emerged as a strong adoption area: 96% of HEIs use SWAYAM/DIKSHA, and 94% invested in digital infrastructure. Yet, equitable access and integration of MOOCs into degree programs remain challenges.
Reforms in Progress
- Board exams: From 2026, CBSE will allow class 10 students to appear twice a year to reduce stress.
- Holistic assessment: PARAKH has developed competency-based report cards, though most boards are yet to implement them.
- Four-year undergraduate degrees: Adopted by some central universities and Kerala, but slowed by faculty shortages and weak infrastructure.
- Mother tongue instruction: Encouraged till class 5, with NCERT preparing multilingual textbooks.
Sticking Points and Bottlenecks
Some reforms remain stalled:
- Three-language formula has been rejected by Tamil Nadu as linguistic imposition.
- Teacher education reform lags, with the National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education still pending.
- Higher Education Commission of India (HECI), meant to replace UGC, remains in draft stage.
- Breakfast alongside midday meals, recommended by NEP, was rejected due to financial constraints.
Federalism poses a key hurdle. Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal refused to adopt PM-SHRI schools, citing central overreach, leading to funding freezes under Samagra Shiksha. Karnataka oscillated—adopting and later scrapping the four-year UG model—while pursuing its own state education policy.
Conclusion
Five years on, NEP 2020 has delivered structural reforms in school curricula, foundational learning, higher education flexibility, and digital adoption. Yet, its transformative potential remains unrealized due to limited faculty capacity, uneven state cooperation, and financial bottlenecks. For NEP to succeed, the Union and states must collaborate, ensuring adequate funding, teacher training, and institutional autonomy. Without resolving these foundational issues, the NEP risks remaining a vision more on paper than in classrooms.
Surrogacy Age Cap Debate before the Supreme Court

- 02 Aug 2025
Background – The Legal Framework on Surrogacy in India
India has been a global hub for assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and surrogacy for many years. To address ethical concerns, prevent exploitation, and regulate practices, Parliament enacted two laws in 2021:
- The Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021
- The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021
These Acts, effective from January 2022, prohibit commercial surrogacy and allow only altruistic surrogacy (where a woman volunteers without financial compensation, apart from medical expenses and insurance).
Key Provisions:
- Age limits:
- Married woman (intending mother): 23–50 years
- Married man (intending father): 26–55 years
- Single women: only widows or divorcees aged 35–45 years
- Certificate of essentiality: Proof of infertility, parentage order, and insurance for the surrogate are mandatory.
- Purpose of the law: To prevent commodification of reproduction, ensure surrogacy is used only for genuine medical necessity, and safeguard the health of both surrogate and child.
The Case before the Supreme Court
Recently, the Supreme Court reserved judgment in a set of petitions challenging the age caps under these Acts.
Petitioners’ Concerns:
- Many couples had already begun fertility procedures before January 2022, but became ineligible midway due to the new law.
- Example: A couple aged 62 (husband) and 56 (wife) lost their only child in 2018, started fertility treatment in 2019, but after a failed embryo transfer in 2022, they were barred from further surrogacy attempts due to age restrictions.
- They argue that applying the age limits retrospectively is unfair, as no “grandfather clause” was provided to protect ongoing cases.
Constitutional Arguments:
- Article 14 (Right to Equality): Age-based exclusion is arbitrary.
- Article 21 (Right to Life & Personal Liberty): Reproductive autonomy and the right to family are integral to personal liberty.
- Discrimination against unmarried women: The law only allows widows and divorcees to access surrogacy, excluding single, never-married women.
Government’s Stand
- Age limits reflect natural reproductive timelines and medical safety.
- Advanced parental age poses risks:
- Higher complications for the surrogate.
- Genetic/epigenetic risks for the child.
- Concerns about parents’ ability to provide long-term care.
- Provisions align with international best practices in reproductive health.
Supreme Court’s Observations
The Bench, led by Justices B.V. Nagarathna and K.V. Viswanathan, raised critical questions:
- Why prohibit surrogacy at advanced ages when natural late pregnancies are not barred?
- The intent of the law was to regulate commercial surrogacy, not to deny genuine parenthood.
- The absence of compassionate transitional provisions is problematic: “Stop, no children! Look how harsh it is,” remarked Justice Nagarathna.
Ethical and Social Dimensions
- Balancing Autonomy and State Regulation:Reproductive choice vs. state’s role in safeguarding health and welfare.
- Rights of Single Women:Exclusion of unmarried women raises concerns of gender equality and individual autonomy.
- Best Interests of the Child:Child’s welfare, upbringing, and stability are central concerns in surrogacy regulation.
- Medical Ethics:Need to prevent exploitation of surrogates and maintain ethical standards in ART practices.
Broader Constitutional Questions
- Right to Parenthood as a Fundamental Right? The Court has earlier recognised reproductive rights as part of Article 21.
- Equality vs. Reasonable Classification: Can the state justify different treatment based on age or marital status?
- Legislative Gaps: The lack of a grandfather clause highlights issues in legislative foresight and transitional justice.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s verdict will be pivotal in shaping India’s approach to assisted reproduction. At stake is the balance between medical ethics, legislative intent, and individual reproductive rights.
The outcome may not only determine the fate of couples stuck mid-process but could also set precedents for:
- Expanding reproductive rights,
- Recognising unmarried women’s autonomy
- Ensuring compassionate legal transitions in sensitive health matters.
India’s Early Achievement of Climate Targets
- 25 Jul 2025
In News:
India has achieved a key milestone in its climate commitments under the Paris Agreement by fulfilling one of its core targets five years ahead of schedule. As of June 2025, non-fossil fuel sources contribute over 50% of India’s installed electricity generation capacity — a significant achievement originally set for 2030.
According to the Ministry of Power, India’s installed capacity reached 484.82 GW, of which 242.78 GW is from non-fossil sources like solar, wind, large hydropower, and nuclear energy. This rapid growth, particularly in solar (24 GW added in 2024 alone), underlines India’s leadership in renewable energy deployment. However, it also highlights key structural challenges in decarbonizing the broader energy economy.
India’s updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Climate Agreement (2015) comprise three primary targets for 2030:
- At least 50% of installed electricity capacity from non-fossil fuel sources.
- 45% reduction in emissions intensity (GHG emissions per unit of GDP) from 2005 levels.
- Creation of an additional 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO?-equivalent carbon sink through increased forest and tree cover.
Substantial progress is also evident in the other two targets. By 2020, India had already reduced its emissions intensity by 36%, and given current economic and technological trajectories, the 45% target by 2030 appears achievable. On the forestry front, India added 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink by 2021. Given the annual increase of around 150 million tonnes CO? equivalent reported in the India State of Forest Report (ISFR), the carbon sink target may already be met by 2023, although official confirmation is pending.
Yet, these achievements warrant a closer look. Electricity comprises less than 22% of India’s total energy consumption. Most energy use — particularly in transport, industry, and residential sectors — still relies on direct combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. Furthermore, while non-fossil sources account for over 50% of capacity, they contribute only 28% to actual electricity generation due to intermittency in renewables. Consequently, clean energy forms only around 6% of India’s total energy consumption, which though modest, aligns with the global average.
The road ahead is demanding. India must now focus on decarbonizing non-power sectors through accelerated adoption of electric mobility, green hydrogen, energy-efficient technologies, and clean cooking solutions. Scaling stable power sources like nuclear and hydro is crucial to complement solar and wind. India's Small Modular Reactor (SMR) program remains in the R&D phase and is unlikely to contribute significantly by 2030.
Internationally, India’s climate leadership contrasts with the underperformance of many developed nations, especially regarding climate finance and technology transfer. While India has met and even surpassed its targets, its ability to raise ambition depends on receiving support as promised under the Paris Agreement.
In conclusion, India’s early success in achieving climate targets reflects a commitment to sustainable growth, but true climate leadership will require systemic decarbonization across all sectors, just energy transitions, and global equity in climate action.
Feeding Community Dogs: Balancing Constitutional Compassion with Public Order in India

- 23 Jul 2025
Context:
The issue of feeding stray or community dogs has evolved into a contentious legal and social debate in India. A recent case involving a Noida resident, allegedly harassed for feeding stray dogs in the common areas of her housing society, once again brought this matter to the judicial spotlight. While the Supreme Court refrained from issuing a specific directive, it observed that citizens should consider feeding strays within their own homes—an observation that, while not binding, reignited debate on reconciling individual compassion with community concerns.
Legal Framework: The ABC Rules, 2023
The Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules, 2023, framed under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960, serve as the primary legal instrument governing the care of community animals. These rules replaced the 2001 version and introduced the term “community animals” instead of “stray dogs,” recognizing them as territorial beings who coexist with human residents.
Rule 20 of the ABC Rules mandates that Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs) or local bodies must facilitate the feeding of community dogs if any resident voluntarily chooses to do so. Designated feeding spots must be located away from high-footfall zones like staircases, entrances, and children’s play areas. Cleanliness and fixed feeding times are essential requirements. Additionally, the Rules lay down a dispute resolution mechanism involving veterinary officers, police representatives, and local welfare groups.
Constitutional and Ethical Dimensions
The legal protection of animals finds support in Article 21 of the Constitution. In the 2014 Animal Welfare Board of India vs. A. Nagaraja case, the Supreme Court interpreted the right to life and liberty to include animal life. Further, Article 51A(g) enshrines the fundamental duty of citizens to show compassion to all living beings. Thus, feeding community dogs is not merely an act of personal kindness but a constitutional obligation.
The petitioner in the Noida case was arguably fulfilling this duty. Allegedly harassed by her RWA president—who reportedly destroyed water pots and killed sterilised dogs—she faced institutional apathy when authorities failed to act. Her appeal to the Allahabad High Court was dismissed, citing inconvenience to the "common man," despite the ABC Rules’ clear guidelines.
Judicial Precedents and Clarifications
Contrary to popular media interpretation, the Supreme Court in the current case did not issue an order compelling the petitioner to feed dogs at home. Observations made during hearings are not judicial directions. Notably, the apex court had earlier stayed a 2022 Bombay High Court (Nagpur Bench) order that banned public feeding and required adopters to take dogs home—asserting that such rules violate statutory rights and compassionate duties.
Conclusion
Feeding community dogs intersects with animal rights, public safety, and civic coexistence. The ABC Rules, 2023, strike a legal and ethical balance between compassion and community order. Sterilisation and designated feeding are not only humane solutions but also public health imperatives. Going forward, increased awareness, community dialogue, and strict adherence to legal norms are vital to avoid polarisation and ensure harmonious urban living.
U.S. Designation of The Resistance Front (TRF)

- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s sustained diplomatic campaign against cross-border terrorism received a significant fillip with the United States designating The Resistance Front (TRF) as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) and a Specially Designated Global Terrorist (SDGT). The decision, announced by U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio, marks a strong step in countering global terror networks and reaffirms the deepening Indo-U.S. cooperation in counter-terrorism.
The TRF is widely recognized as a proxy outfit of the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), formed soon after the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019. Projecting itself as an indigenous, secular “resistance” movement, TRF has sought to legitimize militancy under a veneer of local identity while continuing to rely on the operational, logistical, and financial support of LeT and Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI). Its rebranding strategy is aimed at evading scrutiny by international watchdogs such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
TRF has claimed responsibility for several high-profile terror attacks in Jammu and Kashmir, including the Pahalgam attack in April 2025, which killed 26 tourists. Other attacks attributed to it include the Ganderbal killings (October 2024), Reasi bus attack (June 2024), and a 2020 shooting in Lal Chowk, Srinagar. Its leadership, including current chief Sheikh Sajjad Gul and spokesperson Ahmad Khalid, operate largely from Pakistani soil.
The group also runs an elaborate digital propaganda and recruitment ecosystem. Portals like KashmirFight and Jhelum Media House disseminate extremist narratives, claim responsibility for attacks, and operate as fronts for psychological operations and radicalization. These digital tools further complicate counter-terrorism efforts, allowing TRF to recruit and spread misinformation under the guise of human rights advocacy.
India banned TRF under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967, in January 2023, recognizing its existential threat to national security. India has consistently provided evidence of TRF’s linkages with LeT and other Pakistan-backed outfits like Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) in its submissions to the UN 1267 Sanctions Committee, responsible for imposing sanctions on terror-linked entities.
The U.S. designation of TRF as an FTO and SDGT is not just symbolic. It imposes concrete legal and financial restrictions, making it illegal for U.S. individuals or entities to provide support to the group. The move mandates American financial institutions to block any assets tied to TRF and enables further actions through the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC). These actions aim to globally isolate the outfit and can also trigger secondary sanctions against foreign entities that deal with it.
India has welcomed this move, calling it a “strong affirmation” of India-U.S. cooperation in the fight against terrorism. The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) emphasized that such steps are vital to dismantle terror infrastructure and hold proxy actors accountable. The decision also underscores a growing international consensus on the need for zero tolerance towards terrorism.
This development marks a pivotal moment in India’s counter-terror diplomacy and reinforces the need for global synergy in combating the evolving threat of state-sponsored and hybrid terrorism.
Safe Harbour Doctrine
- 21 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant development shaping India’s digital governance framework, the Centre has defended its expanded use of Section 79 of the Information Technology Act and the Sahyog Portal to compel online intermediaries—including social media platforms—to remove or disable unlawful content. The debate, currently before the Karnataka High Court, arises from a challenge by platform X (formerly Twitter), which terms the Sahyog Portal a "censorship portal."
Safe Harbour vs. Government Oversight: The Legal Framework
Section 79 of the IT Act grants “safe harbour” protection to intermediaries from liability over third-party content, provided they act upon government takedown notices. However, failure to comply may lead to the withdrawal of this immunity. By contrast, Section 69A empowers the government to block content under specific grounds such as national security, public order, or foreign relations, in line with Article 19(2) of the Constitution, and backed by procedural safeguards.
Platform X argues that the Centre is bypassing Section 69A’s narrower and more legally constrained provisions by issuing de facto blocking orders under Section 79, without adequate procedural checks. This, it contends, infringes upon digital freedom of expression.
Sahyog Portal and the Government's Rationale
The Sahyog Portal, developed under the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) of the Ministry of Home Affairs, has onboarded 38 intermediaries as of March 2025—including Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Telegram, and YouTube. Meta has allowed API-based integration, while X has refused, citing legal overreach.
Defending its stance, the government argues that algorithmic content curation systems—unlike traditional editorial processes—operate at unprecedented speed and scale, without human oversight or transparency. These systems can amplify harmful or misleading content, targeting users individually in ways that traditional media cannot. Moreover, the anonymity and pseudonymity offered by online platforms, along with encrypted messaging, encourage unaccountable and extreme speech, posing serious risks to public order.
Algorithmic Curation vs. Traditional Editorial Control
The government contends that in traditional media, editors and broadcasters act as gatekeepers, ensuring a degree of content quality and moderation. Social media algorithms, however, lack such discretion, often functioning without clear standards, and thereby require regulatory intervention distinct from that applied to conventional media.
This foundational difference, the government argues, justifies a broader interpretive scope under Section 79 to address a wider class of “unlawful content” that may not directly fall under the remit of Section 69A but still demands intervention.
Balancing Freedom of Speech with Public Interest
At the heart of the issue lies the constitutional balancing of free speech (Article 19(1)(a)) with reasonable restrictions (Article 19(2)). While Section 69A aligns with specific constitutional limitations, the government argues that a broader net under Section 79 is needed to tackle content harmful to national security, social harmony, and public order—even if it doesn’t squarely fall within 19(2).
In its submission, the Centre emphasizes that the matter should be viewed not only from the lens of content creators but also from the rights and safety of content recipients and society at large.
Conclusion
This case marks a crucial intersection of digital freedom, platform responsibility, and state regulation. The government's bid to reinterpret Section 79 reflects the growing challenges of algorithmic governance in the digital era. The Karnataka High Court’s verdict will likely set a precedent in defining the limits of intermediary liability, scope of safe harbour, and the State’s role in regulating online content—all central to India’s evolving digital constitutionalism.
Cybersecurity Threats from Southeast Asia: Rising Cyber Frauds Targeting India

- 19 Jul 2025
Introduction
Cybersecurity has emerged as a critical component of national security in the digital era. India, with its expanding digital footprint, is increasingly facing threats from transnational cybercrime syndicates. A recent analysis by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) reveals a staggering Rs 1,000 crore loss per month due to cyber frauds originating from Southeast Asian countries, posing a serious threat to the Indian economy and internal security.
Magnitude of the Threat
- According to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under MHA: In the first five months of 2025, cyber frauds caused a total loss of around Rs 7,000 crore.
- Over 50% of the losses were attributed to networks operating from Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Modus Operandi
- Fraud Centers: Operate from high-security scam compounds, primarily in Cambodia (45 identified), Laos (5), and Myanmar (1), allegedly run by Chinese operators.
- Forced Labor: Trafficked individuals, including more than 5,000 Indians, were reportedly forced to carry out cyber frauds under coercion.
- Types of Scams:
- Stock trading/investment scams
- Digital arrest scams
- Task-based/investment-based scams
Recruitment Networks and Source States
- Recruitment agents operate largely from:
- Maharashtra (59 agents)
- Tamil Nadu (51)
- Jammu & Kashmir (46)
- Uttar Pradesh (41)
- Delhi (38)
- Travel Routes Tracked:
- Routes include India to Cambodia via Dubai, China, Thailand, Vietnam, Singapore, etc.
- Cities involved include Mumbai, Chennai, Delhi, Jaipur, Lucknow, Kochi, and Kolkata.
Government Response
- Diplomatic Engagement:
- Cambodian officials met Indian authorities (MEA and Central agencies) in Delhi.
- Requested geographical coordinates of scam centers for local enforcement action.
- Inter-Ministerial Committee: Formed to identify systemic loopholes in banking, telecom, and immigration sectors.
- CBI Investigation: Registered FIRs against PoS agents involved in issuing ghost SIM cards aiding cybercrime.
Wider Implications
- Global Human Trafficking Concern: Victims from Africa, East Asia, South Asia, Central Asia, Europe, and the Americas have been found in these compounds.
- Transnational Organized Crime: The scams highlight growing cooperation between international criminal networks, using digital tools to exploit vulnerabilities across borders.
Conclusion
The scale and transnational nature of cyber frauds targeting India from Southeast Asia require a coordinated national and international response. Strengthening cyber intelligence, cross-border cooperation, digital infrastructure resilience, and public awareness are vital to securing India's cyberspace. Proactive steps such as bilateral cooperation, inter-agency coordination, and targeted enforcement are crucial to mitigate this growing internal security threat.
AI 171 Crash
- 16 Jul 2025
In News:
On June 12, 2025, Air India flight AI 171, a Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner en route from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick, tragically crashed shortly after takeoff, killing 260 people—including 19 on the ground—in what is now the deadliest aviation disaster involving an Indian airline in four decades. A preliminary report by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) has placed the aircraft’s fuel control switches at the centre of the crash investigation.
Fuel Control Switches: Function and Design
Fuel control switches are critical safety components that regulate the flow of fuel to aircraft engines. On a Boeing 787, equipped in this case with two GE engines, these switches are located below the thrust levers and are spring-loaded and bracket-protected to prevent accidental activation. They require a deliberate two-step manual action—lifting the switch and moving it between two positions:
- RUN: Allows fuel flow for engine operation.
- CUTOFF: Cuts fuel flow, effectively shutting down the engine.
These switches are typically used on the ground for engine startup and shutdown, and only in-flight during an engine failure or critical damage. Modern twin-engine aircraft like the 787 are capable of continuing flight on a single engine, making the simultaneous use of both switches highly unusual and dangerous.
Sequence of Events: Preliminary Findings
According to flight data from the Flight Data Recorder (FDR) and Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR), both engine fuel control switches were moved from ‘RUN’ to ‘CUTOFF’ within seconds of each other, shortly after takeoff. This led to simultaneous loss of thrust in both engines. Moments later, both switches were returned to the ‘RUN’ position, but by then the aircraft had lost critical altitude and control.
The cockpit recording captured one pilot asking the other why the fuel was cut off. The other responded that he had not done so. The pilots—Captain Sumeet Sabharwal with over 8,600 flying hours on the 787, and Co-pilot Clive Kundar with 1,100 hours—were both adequately experienced.
Technical and Human Factors under scrutiny
Aviation experts argue that accidental activation of both switches is nearly impossible due to the stop-lock mechanism and protective brackets. However, speculation persists over a possible technical malfunction, human error, or incorrect engine identification. A theory suggests that one engine may have failed and the pilots mistakenly shut down the working engine, though this remains unconfirmed.
Attention has also turned to the switches themselves, manufactured by Honeywell (Part No. 4TL837-3D). A 2018 FAA advisory had flagged potential issues with their locking mechanisms but did not mandate corrective action. Air India reportedly did not conduct voluntary checks, raising questions about maintenance protocols.
Conclusion:
The AI 171 crash highlights critical lapses in cockpit procedures, technical maintenance, and possibly design flaws. It underscores the need for stringent implementation of safety advisories, thorough crew training, and the use of redundant safety mechanisms. As investigations continue, the incident may prompt global regulatory reviews on cockpit ergonomics and fuel system safety protocols, reinforcing the imperative of fail-safe systems in civil aviation.
Maharashtra’s Special Public Security Bill, 2024
- 15 Jul 2025
In News:
The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, passed by the Legislative Assembly, aims to combat “urban Maoism” and left-wing extremism (LWE). Modeled on the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), the Bill introduces stringent provisions to identify and dismantle urban support networks aiding insurgents. However, it has generated significant legal and civil liberty concerns due to its vague definitions, broad executive powers, and pre-trial punitive measures.
Understanding Urban Maoism
Urban Maoism refers to the strategy of the banned CPI (Maoist) to infiltrate cities and mobilise intellectuals, students, professionals, and minorities through NGOs, protests, and media campaigns. This ideology, outlined in the 2004 document Strategies and Tactics of Indian Revolution (STIR), aims to build urban logistical support for rural armed struggles while operating under the legal guise of activism, journalism, or civil society work. Notable examples include the Elgar Parishad case (2018), where activists were arrested for alleged Maoist links following Bhima Koregaon violence.
Key Provisions of the Bill
The Bill allows the government to declare an organisation “unlawful” and penalises individuals associated with it—whether through membership, fundraising, or aiding operations. It defines “unlawful activity” as interference with public order, use of criminal force against officials, incitement to disobedience of the law, or even disrupting communication systems. Punishments range from 2 to 7 years of imprisonment along with fines. All offences are cognizable and non-bailable.
A major provision allows pre-trial forfeiture of property belonging to accused persons or organisations, with only 15 days’ notice. While the affected party can appeal to the High Court within 30 days, the initial declaration is confirmed only by an Advisory Board comprising High Court-qualified persons.
Constitutional and Legal Concerns
Civil society and legal experts argue that the Bill risks criminalising legitimate dissent and peaceful protest, given its ambiguous phrasing like “practising disobedience” or “generating apprehension in the public.” Unlike the UAPA, which requires a higher threshold for proving threat to national integrity, Maharashtra’s Bill introduces lower benchmarks that could conflate dissent with sedition.
The pre-trial forfeiture of property mirrors provisions in the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), yet lacks equivalent safeguards like adjudication by a quasi-judicial body. Moreover, principles of natural justice, such as presumption of innocence and burden of proof on the state, appear diluted.
Broader Implications
While the state’s intent to counter urban LWE influence is valid—especially given the shift of Maoist strategies from forested hinterlands to urban centres—the means adopted pose risks to constitutional rights and federal norms. The legislation exemplifies a growing trend where extraordinary laws designed for national threats are adapted at the state level, potentially disrupting the balance between security imperatives and civil liberties.
Conclusion
The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill reflects the complex challenge of safeguarding national security while upholding democratic freedoms. Any future enactment must incorporate judicial oversight, clearer definitions, and proportionate safeguards to ensure that the fight against extremism does not erode the fundamental rights enshrined in the Constitution.
India’s Reinvigorated Outreach to the Global South

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s foreign policy has witnessed a dynamic recalibration with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s expansive visit to Brazil, Ghana, Trinidad & Tobago, Argentina, and Namibia. While participation in the BRICS Summit in Rio de Janeiro was central, the broader aim was to deepen India’s leadership role within the Global South — a diverse group of developing nations in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania.
Reclaiming Leadership in the Global South
India has long championed the cause of the Global South, grounded in its non-aligned foreign policy legacy and postcolonial solidarity. This identity was rejuvenated through:
- Hosting two Voice of the Global South Summits (2023, 2024), giving a platform to over 125 developing countries.
- Advocating for and securing African Union’s permanent membership in the G20 during its presidency, symbolizing India’s commitment to an inclusive global governance architecture.
These initiatives portray India as a bridge between the Global North and South, positioning itself as a leader that represents the interests of the voiceless in multilateral forums.
Diplomatic Course Correction: The Gaza Challenge
India’s explicit support for Israel during the Gaza conflict (post-October 7, 2023) triggered discomfort among many Global South countries, especially in the Arab and African regions that strongly support the Palestinian cause. Consequences included:
- India’s defeat to Pakistan in the UNESCO Executive Board Vice-Chair election.
- Limited engagement from key Global South nations in the Second Voice of the Global South Summit.
Recognizing these diplomatic setbacks, India recalibrated its stance. At the BRICS Foreign Ministers’ Meeting (2024) and the 2025 Rio BRICS Summit, India joined in expressing grave concern over Israeli military operations in Gaza and condemned strikes on Iran, signaling a return to its balanced, multivector diplomacy.
Strategic Gains at BRICS: Securing Core Interests
India also used the BRICS platform to secure vital national interests. The BRICS Leaders’ Declaration condemned the Pahalgam terror attack in Kashmir and called for combating terrorism, including cross-border terror financing. This was diplomatically significant, given:
- China’s prior reluctance to name Pakistan-based terror actors.
- BRICS’ growing relevance in shaping global narratives.
India’s success in inserting its security concerns into multilateral dialogue marks a maturing assertiveness in diplomacy.
Countering China, Offering Alternatives
India’s proactive outreach also serves to counter China’s rising influence in the Global South. Unlike Beijing’s Belt and Road Initiative, India emphasizes:
- Transparent, demand-driven development assistance.
- Capacity-building and digital partnerships.
- Ethical, sustainable models of cooperation.
Through initiatives like International Solar Alliance, Digital Public Infrastructure partnerships, and humanitarian aid, India offers a democratic, credible alternative to Chinese financing and infrastructure diplomacy.
Conclusion:
India’s current foreign policy trajectory reflects a delicate balancing act—protecting strategic partnerships with global powers while retaining the trust of fellow developing nations. As global multipolarity deepens, India’s role as a consensus builder, ethical voice, and pragmatic actor will shape its success in becoming the leading voice of the Global South.
Conserving the Western Ghats

- 03 Jul 2025
Context:
The Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the world’s eight hottest biodiversity hotspots, stretch across six Indian states—Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. Rich in endemic flora and fauna, they play a critical role in influencing the Indian monsoon, regulating climate, and sustaining major river systems like the Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. However, this ecologically sensitive region faces growing environmental and governance challenges.
Renowned ecologist Madhav Gadgil has strongly advocated for a community-led conservation model, citing the failures of top-down forest bureaucracy and the neglect of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006. He argues that without empowering local communities, conservation efforts will remain ineffective.
Geological and Ecological Background
The Western Ghats are ancient, formed through Precambrian cratonic uplift and Deccan Traps volcanism over 600 million years ago. The western edge of the Deccan Plateau subsided post-Gondwana breakup, forming the escarpments we see today. Over time, monsoon-fed rivers carved deep valleys, resulting in the current terrain of lateritic plateaus and ridges.
With over 7,400 species—many of them endemic—the region is home to unique ecosystems. Yet, despite its ecological importance, conservation has suffered due to flawed governance, industrial exploitation, and neglect of community rights.
Challenges in Western Ghats Conservation
- Flawed Forest Governance:Government agencies often rely on outdated and inflated forest data. For instance, Gadgil's 1975 study in Uttara Kannada revealed bamboo stocks were overestimated tenfold to justify resource extraction.
- Industrial Pollution:Unregulated industries operate in fragile zones. The Grasim Rayon Factory in Kerala discharged mercury into the Chaliyar River, decimating fisheries and affecting tribal livelihoods.
- Non-implementation of FRA (2006):Despite legal entitlements, Community Forest Rights (CFR) remain unimplemented in most districts, particularly in Kerala and Karnataka.
- Monoculture Plantations:Replacement of native forests with eucalyptus and acacia has led to biodiversity loss, declining soil health, and reduced pollinator populations, as seen in Wayanad.
- Forest Fires from Unsustainable Practices:Fire-based tendu leaf collection methods degrade forest cover. For instance, Gadchiroli and Karnataka have witnessed increased fire incidents.
- Inaccessible Ecological Data:Forest data remains aggregated and delayed. Studies using NRSC and Global Forest Watch have exposed discrepancies in official forest cover claims.
Committee Recommendations
- WGEEP (2011), led by Gadgil, advocated for Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA) zoning, Gram Sabha-led conservation, and strict implementation of CFR.
- The Kasturirangan Committee (2013) diluted these recommendations by reducing ESA coverage and favouring development-centric governance.
Way Forward
- Implement CFR Provisions: E.g., Pachgaon in Maharashtra demonstrates how CFR-based governance can lead to sustainable bamboo harvesting and fire prevention.
- Promote Democratic Decentralisation: Empowering Gram Sabhas, as in Kerala’s VSS model, ensures accountability and local participation.
- Modernise Ecological Monitoring: Tools like Google Earth and Bhuvan offer real-time forest tracking, countering manipulated datasets.
- Ban Unsustainable Industries in ESA: SC orders on mining bans in wildlife corridors must be enforced, especially in states like Goa and Kerala.
- Support Biodiversity-Friendly Livelihoods: NTFP-based enterprises, eco-tourism, and agroforestry, like Wayanad tribal co-operatives selling organic turmeric and wild honey, can align conservation with income.
Conclusion
The Western Ghats are central to India’s ecological, hydrological, and cultural stability. Conservation rooted in community empowerment, transparent governance, and ecological integrity is essential. Only a democratic, decentralized, and data-driven model, as envisioned by Gadgil, can secure the future of this ecological treasure.
Strait of Hormuz Blockade
- 29 Jun 2025
Context:
The recent approval by Iran’s Parliament to potentially close the Strait of Hormuz, pending a final decision by its Supreme National Security Council, has intensified global concerns about energy security and geopolitical stability. This comes in response to U.S. strikes on Iranian military sites, marking a serious escalation in the Gulf region.
Strategic Significance of the Strait of Hormuz
- The Strait of Hormuz is a 33 km-wide maritime chokepoint linking the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and, subsequently, the Arabian Sea. It handles over 25% of global seaborne oil trade, 20% of global oil consumption, and 20% of LNG trade, primarily from Qatar.
- The geographical location of the strait—falling within Iranian and Omani territorial waters—makes it one of the most sensitive energy corridors globally.
- The strait’s vulnerability is compounded by its narrow 3 km-wide navigational channels, making it susceptible to blockades, naval mines, missile strikes, or cyberattacks.
- Historically, Iran has issued such threats without actual closure, even during periods of conflict, largely due to its own dependency on the strait for oil exports, especially to China.
Implications of a Blockade
A complete or even partial blockade could have catastrophic global impacts:
- Disruption of Global Energy Supply: With no alternative sea route, any disruption would curtaildaily movement of 20 million barrels of oil, causingsharp price spikes.
- Limited Overland Alternatives: Saudi Arabia’s East-West pipeline (5 million bpd) and the UAE’s Fujairah pipeline (1.8 million bpd) cannot compensate for the loss of Hormuz transit.
- Higher Shipping and Insurance Costs: Perceived risk increases freight rates, insurance premiums, and logistical expenses globally.
Impact on India
India, the third-largest crude oil consumer, imports over 85% of its oil and 50% of its natural gas. In May 2025 alone, 47% of India’s crude imports passed through the Strait of Hormuz. Disruption would result in:
- Price Volatility: Even if supplies are not entirely blocked, oil and gas prices will spike, stressing the economy.
- Macroeconomic Stress: A surge in energy prices could widen the trade deficit, weaken the rupee, reduce forex reserves, and raise inflation.
- Competitive Pressure: If Iran’s exports to China are blocked, Beijing may seek oil from other producers, increasing global demand and costs, impacting India’s energy budget.
India’s Resilience and Strategic Measures
Despite the vulnerabilities, India has certain buffers:
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Imports from Russia, the U.S., Africa, and Latin America are not dependent on Hormuz. Russian oil arrives via the Suez Canal or Cape of Good Hope, while Qatar’s LNG also uses alternate maritime routes.
- Strategic Reserves: India maintains 9–10 days’ worth of strategic oil reserves for emergencies.
- Government Policy Levers: In case of a prolonged crisis, the government may offer price subsidies for diesel and LPG to contain inflation.
Conclusion
The Strait of Hormuz remains a vital artery of global energy supply and a flashpoint of geopolitical tensions. While India has taken commendable steps toward energy diversification and crisis preparedness, continued diplomatic engagement in West Asia, investments in energy alternatives, and strengthening strategic reserves will be key to mitigating the fallout from any potential blockade.
Fossil Fuel Financing in 2024

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
In a stark contradiction to global climate goals, the world’s 65 largest banks increased their fossil fuel financing by $162 billion in 2024, reaching a total of $869 billion, up from $707 billion in 2023, according to the Fossil Fuel Finance Report 2025. This trend threatens to derail global commitments under the Paris Agreement and undermines the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) roadmap to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
India’s Position:
Among global lenders, the State Bank of India (SBI) was the only Indian bank featured in the top 65, rising from the 49th to 47th position. SBI’s fossil fuel financing increased modestly by $65 million, taking its 2024 total to $2.62 billion. Cumulatively, between 2021 and 2024, SBI extended $10.6 billion to fossil fuel projects. In contrast, JPMorgan Chase topped the global list with $53.5 billion in 2024 alone.
Despite this, SBI has also signalled intent to transition. It has pledged to become net zero by 2055, and aims to ensure that 7.5% of its domestic advances are green by 2030. As of March 2024, SBI had sanctioned ?20,558 crore in sustainable finance. However, this dual-track financing model raises questions about the coherence of India's green finance agenda.
Global Setbacks and Policy Rollbacks
2024 witnessed a rollback in climate-related financial commitments, particularly in the United States. The withdrawal of the US from the Paris Agreement, scheduled to take effect in 2026, was accompanied by policy shifts like exiting the Net Zero Banking Alliance and the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS). Major banks such as Wells Fargo abandoned their net-zero commitments, signaling a broader retreat from climate-aligned finance.
This global trend is no longer confined to North America. European banks, traditionally viewed as progressive, also weakened fossil fuel exclusion policies. The result: a global rise in fossil fuel merger and acquisition financing, which reached $82.9 billion in 2024, up by $19.2 billion from 2023. Although M&As do not directly add infrastructure, they consolidate fossil fuel power at a time when the world urgently needs to pivot to renewables.
Indian Banks and the Coal Dilemma
Indian financial institutions, barring a few exceptions like Federal Bank and RBL Bank, lack explicit coal exclusion policies. According to Climate Risk Horizons, this constitutes a major blind spot. The economics of energy is shifting — renewables and storage are now often cheaper than coal, making continued fossil fuel investments financially and environmentally risky.
Conclusion
The rise in fossil fuel financing reflects a disconnect between climate rhetoric and financial action, threatening the global transition to clean energy. For India, this highlights the need for a coherent climate finance strategy, integrating environmental, financial, and developmental priorities. As a signatory to the Paris Agreement and a G20 economy, India must not only align public finance with green goals but also push for global financial reforms that discourage fossil fuel dependencies and reward sustainable investments.
Why Governments Revise GDP Base Year and Why India’s 2026 Revision Matters

- 20 Jun 2025
Context:
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the most critical metric used to measure the size and performance of a country’s economy. The "base year" is the reference year against which future GDP growth is calculated. India’s current GDP base year is 2011–12. The government, through the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), is now preparing to revise it to 2022–23, with the updated series to be released in February 2026.
Why GDP Base Years are Revised
Base year revisions are necessary to reflect structural changes in the economy, incorporate improved and updated data sources, and align with global statistical standards. GDP calculation, by its definition—the market value of all final goods and services produced in an economy—requires accurate, timely, and sectorally-relevant data. However, India’s economy evolves rapidly, particularly with the expansion of the services sector and changes in consumption, production, and labour patterns.
Past revisions (seven since 1948-49) reflect efforts to modernize methodology and include newer data sources, such as the shift from decennial Census-based workforce estimates to five-yearly Employment-Unemployment Surveys by the NSSO. This aligns with the National Statistical Commission’s recommendation of rebasing economic indices every five years.
The last revision occurred in 2015 (base year changed to 2011–12), following which methodological changes attracted controversy. Experts, including former Chief Economic Advisor Arvind Subramanian, argued that the revised methodology overestimated India’s GDP growth, especially in manufacturing, due to reliance on corporate database MCA-21 over the traditional Annual Survey of Industries.
Why the 2026 Revision Is Crucial
The 2026 revision comes after India missed a base year update in 2017–18 due to data-related concerns. Two key surveys—the Consumer Expenditure Survey (CES) and the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)—faced credibility and methodological challenges. The 2017-18 CES suggested rising poverty, while the PLFS showed a 45-year high in unemployment—trends contrary to government narratives. These issues led to scrapping the proposed 2017–18 base year.
Additionally, disruptive policy changes like demonetisation (2016) and the rollout of GST (2017), followed by the COVID-19 pandemic, meant the following years were not "normal" reference points. The 2022–23 base year is likely to mark the first post-pandemic stable year suitable for a revised series.
This revision is especially significant as India is poised to become the world’s third-largest economy by nominal GDP. At such a juncture, the quality, accuracy, and global credibility of GDP data will directly influence investor confidence, credit ratings, and policymaking.
The base year revision will also extend to other indicators: the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) will be revised to 2022–23, and the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to 2023–24. These changes ensure that inflation and industrial output metrics remain reflective of present-day consumption and production structures.
Conclusion
Revising the GDP base year is not merely a technical exercise—it is central to economic governance. The upcoming 2026 revision must restore faith in India's statistical systems, offer a transparent methodology, and align with international best practices. Its credibility will shape India’s economic narrative for the decade to come, both domestically and on the global stage.
Israel–Iran Strike 2025

- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
On June 13, 2025, Israel launched a large-scale military strike on Iran, targeting nuclear and military sites in Tehran. The attack resulted in the deaths of Iran’s Revolutionary Guard chief and two top nuclear scientists, marking a sharp escalation in the long-running shadow conflict between Israel and Iran.
Backdrop: Iran’s Nuclear Programme and Global Concerns
Iran claims its nuclear programme is peaceful, aimed at energy production and medical research. However, international skepticism remains high. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) recently declared Iran in breach of its non-proliferation obligations for the first time in two decades, citing a lack of transparency, failure to account for undeclared nuclear material, and enrichment of uranium up to 60% purity, dangerously close to weapons-grade (90%). According to reports, Iran possesses enough stockpiled uranium to build up to nine nuclear weapons, raising alarm globally.
Israel’s Strategic Calculus and the Execution of the Strike
Israel has long opposed Iran’s nuclear ambitions and the 2015 nuclear deal (JCPOA). The June 2025 assault was the culmination of years of covert operations, including the 2020 assassination of Mohsen Fakhrizadeh and earlier strikes on Iran-linked targets. The latest strike, targeting nuclear and missile facilities as well as residences of top scientists and generals, is seen as the most severe blow to Iran since the 1979 revolution.
The collapse of Iran’s regional deterrence network—its so-called “axis of resistance”—following the fall of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad in December 2024 played a critical role. With Syria no longer serving as a strategic corridor between Tehran and Hezbollah, Israel perceived an opportune moment to act.
US Foreign Policy Shift and Trump’s Role
The re-election of President Donald Trump in 2024 introduced a more confrontational posture toward Iran. Although the U.S. initially delayed the planned May strike to explore diplomacy, the failure of talks led to U.S. backing for the June operation, using military pressure as leverage for a new nuclear deal demanding Iran's full disarmament.
Regional Fallout and Global Economic Implications
The strike triggered an immediate 8% rise in global oil prices, exposing energy vulnerabilities across oil-importing nations. Particularly affected is India, which imports over 80% of its crude oil. Though India imports little directly from Iran, it depends heavily on Gulf producers like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, whose exports transit through the Strait of Hormuz—a vital chokepoint now under threat.
Further, disruptions in Red Sea and Suez Canal shipping routes may force Indian exporters to reroute via the Cape of Good Hope, increasing transit times by 15–20 days and pushing shipping costs up by 40–50%.
Market Response and Strategic Concerns
While oil prices are expected to stabilise due to global reserves and supply diversification, gold prices surged above ?1 lakh per 10g as investors moved to safer assets. The broader geopolitical uncertainty may stoke inflationary pressures, affecting global and Indian economic stability.
Conclusion
The Israel–Iran conflict, while regionally contained for now, holds serious global implications—challenging non-proliferation efforts, disrupting energy security, and threatening global economic stability. For India, the crisis underscores the need for diversified energy sourcing, geopolitical agility, and resilient export infrastructure to mitigate such strategic shocks.
Iran’s Non-Compliance with IAEA Safeguards

- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
In a pivotal move, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Board of Governors, recently passed a resolution declaring Iran in breach of its 1974 Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement. This marks the first formal non-compliance declaration since 2006 and signals a possible escalation of Iran’s nuclear issue to the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). The resolution was passed with 19 votes in favour, 3 against (China, Russia, Venezuela), and 11 abstentions.
What led to the resolution?
The IAEA expressed grave concern over Iran’s failure to explain uranium traces found at three undeclared sites—Lavisan-Shian, Varamin, and Turquzabad. These sites, suspected to be part of an undeclared nuclear program until the early 2000s, reflect Iran’s longstanding reluctance to grant the IAEA full access and credible information.
The IAEA resolution cited Iran’s “many failures” since 2019 to provide timely cooperation. This includes Iran’s inability to account for undeclared nuclear material and activities, in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and its 1974 Safeguards Agreement.
IAEA Safeguards and Article XII.C
Under the 1974 Safeguards Agreement, Iran is legally required to:
- Declare all nuclear materials and maintain detailed inventories.
- Notify the IAEA about any new nuclear facilities.
- Allow routine and special inspections and surveillance.
The IAEA’s inability to verify the absence of nuclear material diversion for weaponisation constitutes a major safeguard failure.
The resolution was passed under Article XII.C of the IAEA Statute, which grants the Board powers to:
- Demand corrective actions.
- Suspend technical assistance.
- Notify all member states.
- Refer the case to the UNSC.
This rare Article has only been invoked six times before—against Iraq, North Korea, Iran (2006), Libya, Romania, and Syria.
Iran’s Response and Regional Tensions
Iran denounced the resolution as “political” and retaliated by:
- Announcing plans for a new underground uranium enrichment facility.
- Upgrading centrifuges at Fordow.
- Placing air defence systems on alert.
- Threatening “proportional measures” in response to Israeli and Western pressure.
A day after the IAEA resolution, Israel launched preliminary airstrikes on Iranian nuclear sites and declared a state of emergency. Iran reportedly mobilised drones in response, escalating military tensions in the region.
Broader Geopolitical Implications
This development coincides with the October 2025 deadline for the expiration of U.N. sanctions relief under the 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal (JCPOA). The U.S., which exited the JCPOA in 2018, has signaled support for “special inspections” of Iranian sites. Meanwhile, back-channel talks in Oman remain stalled, and the threat of sanctions “snapback” looms large.
The IAEA also maintains $1.5 million worth of peaceful nuclear projects in Iran, including in radiopharmaceuticals and desalination—now potentially at risk.
What lies ahead?
Iran now has a limited window to respond. If it fails to provide adequate clarifications, the Board may escalate the issue to the UNSC, which could result in renewed sanctions or binding resolutions. A follow-up Board meeting and vote is expected in September 2025.
Conclusion
The IAEA’s resolution represents a critical juncture in global non-proliferation diplomacy. It underscores the challenges of verification in the absence of cooperation and the rising tensions in the Middle East nuclear landscape. For India and the world, this raises important questions on nuclear governance, energy diplomacy, and regional stability.
Scaling India's Apparel Sector for Export Growth

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
India’s textiles and apparel (T&A) sector is one of its oldest and most employment-intensive industries, contributing 2.3% to GDP and employing over 45 million people, making it the second-largest employer after agriculture. Despite this, India’s share in global apparel trade has remained stagnant at around 3% for two decades—far below its potential. With global apparel trade at $529.3 billion, India’s contribution stands at just $15.7 billion, and the ambitious target of $40 billion in exports by 2030 remains distant unless bold structural reforms are initiated.
Structural Challenges
The fragmentation of the industry is a major bottleneck. Over 80% of apparel units are MSMEs, operating with limited scale, informal labour, and poor integration. In contrast, countries like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh have achieved scale by setting up large, export-oriented factories or coordinated "buying houses" to pool capacity.
India’s cost of capital (≈9%) also hampers competitiveness, compared to 3–4.5% in China and Vietnam. Further, rigid labour laws, such as mandatory 2x overtime pay, discourage formal employment. Supply chains are dispersed, increasing delivery timelines and logistics costs. These issues are compounded by low female labour force participation, despite women comprising 70% of the workforce in leading apparel hubs.
Success Story: Shahi Exports
The example of Shahi Exports illustrates what is achievable with scale, professionalism, and inclusive practices. From a 15-member unit in 1974, it has evolved into India’s largest apparel exporter, employing over 100,000 workers (70% women) across 50+ factories in 8 states, with over $1 billion in revenue. It shows that Indian firms can scale and compete globally, but organic growth alone is too slow to meet national export goals.
Policy Reforms: A Way Forward
To unlock the sector’s full potential, transformative policy measures are required:
- Capital Access for Scale: A 25–30% capital subsidy and a 5–7 year tax holiday for units with 1,000+ machines would help achieve viable scale. Linking incentives to size, as proposed under PLI 2.0, is essential.
- Flexible Labour Norms: Labour reforms, such as rationalising overtime pay to 1.25x (ILO standard), and easing compliance can encourage formal hiring. Linking MGNREGA funds (25–30%) to wage subsidies in garment units can promote productive, formal employment.
- Skilling for Demand: Schemes like SAMARTH should be expanded for short-cycle, demand-driven training, especially for women and youth, to bridge the skills gap in the sector.
- Cluster-Based Development: At least two PM MITRA Parks should be designated as garment hubs in labour-abundant, low-cost states like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh to reduce migration, cut costs, and promote inclusive industrialisation.
- Export-Linked Incentives (ELI): Shift from production-linked to export-linked schemes that reward global competitiveness, not just output.
Conclusion
The apparel sector offers a rare opportunity to generate mass employment, promote inclusive growth, and boost exports. But without scale, reforms, and a strategic policy shift, the $40 billion export dream will remain elusive. India must act swiftly to replicate success stories like Shahi Exports, not over decades, but within years. The time for bold policy innovation is now.
Revisiting NREGA Wage Rates: A Case for Urgent Reform

- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) is the world’s largest public employment programme, aimed at ensuring livelihood security through guaranteed rural employment. However, a recent report by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (April 2025) underscores a critical challenge: the wage rates under MGNREGA are increasingly inadequate, failing to provide even subsistence-level income.
With over 25 crore registered workers, the scheme is central to rural welfare. Yet, its effectiveness is diluted due to systemic underpayment. For FY 2025–26, MGNREGA wages vary from ?241 in Nagaland to ?400 in Haryana, averaging only ?294 nationally—a meagre 5% increase from the previous year. In many states, this rate is significantly lower than the prevailing minimum wage, in some cases by over ?200, raising serious questions about wage fairness and constitutional obligations.
Legal and Policy Background
Section 6 of the MGNREGA Act permits the Centre to fix wage rates independently of the Minimum Wages Act, 1948, though the wage cannot be below ?60. Historically, from 2005 to 2009, NREGA wages matched each state’s minimum agricultural wage. However, the Centre capped NREGA wages at ?100 in 2009 due to financial concerns, leading to payments falling below statutory minimum wages—a move that the Karnataka High Court (2011) and Supreme Court (2012) found violative of labour rights.
In response to mounting concerns, wage indexation to the Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL) began in FY 2011–12, with 2009 as the base year. Nevertheless, CPI-AL is narrow in scope compared to CPI-Rural (CPI-R), which better reflects the cost of living for rural workers across sectors.
Ignored Recommendations and Institutional Apathy
Several expert bodies have urged wage revisions. The Jean Dreze Committee (2010) advocated aligning NREGA wages with state minimum wages or, at the very least, indexing them effectively. The Mahendra Dev Committee (2014) recommended CPI-R-based indexing with an updated base year, while the Anoop Satpathy Committee (2019) proposed a national floor wage of ?375 (at July 2018 prices). However, the Centre has largely disregarded these suggestions, citing fiscal constraints.
Only a few states, including Odisha and Himachal Pradesh, have supplemented NREGA wages from their own budgets. Most continue with the Centre’s insufficient rates, causing regional disparities and undermining the constitutional promise of equal pay for equal work (Article 39).
Need for Course Correction
The current wage structure risks violating Article 23 of the Constitution, as flagged in the Supreme Court’s 1983 Sanjit Roy vs State of Rajasthan verdict, which held that paying less than the minimum wage constitutes “forced labour.”
Moreover, stagnant wages have contributed to declining worker participation. The Standing Committee rightly argues that current wages do not meet basic daily expenses and recommends a minimum daily wage of ?400. Without wage parity and realistic indexation, the scheme fails to uphold its foundational promise of dignified rural employment.
Conclusion
MGNREGA is more than a welfare scheme—it is a statutory right. To realize its full potential in promoting rural livelihoods and inclusive growth, wage reforms are imperative. Revising NREGA wages to reflect minimum wage laws, inflation trends, and regional parity is not just an economic necessity—it is a constitutional obligation.
Kashmir Rail Link: A Strategic and Developmental Milestone
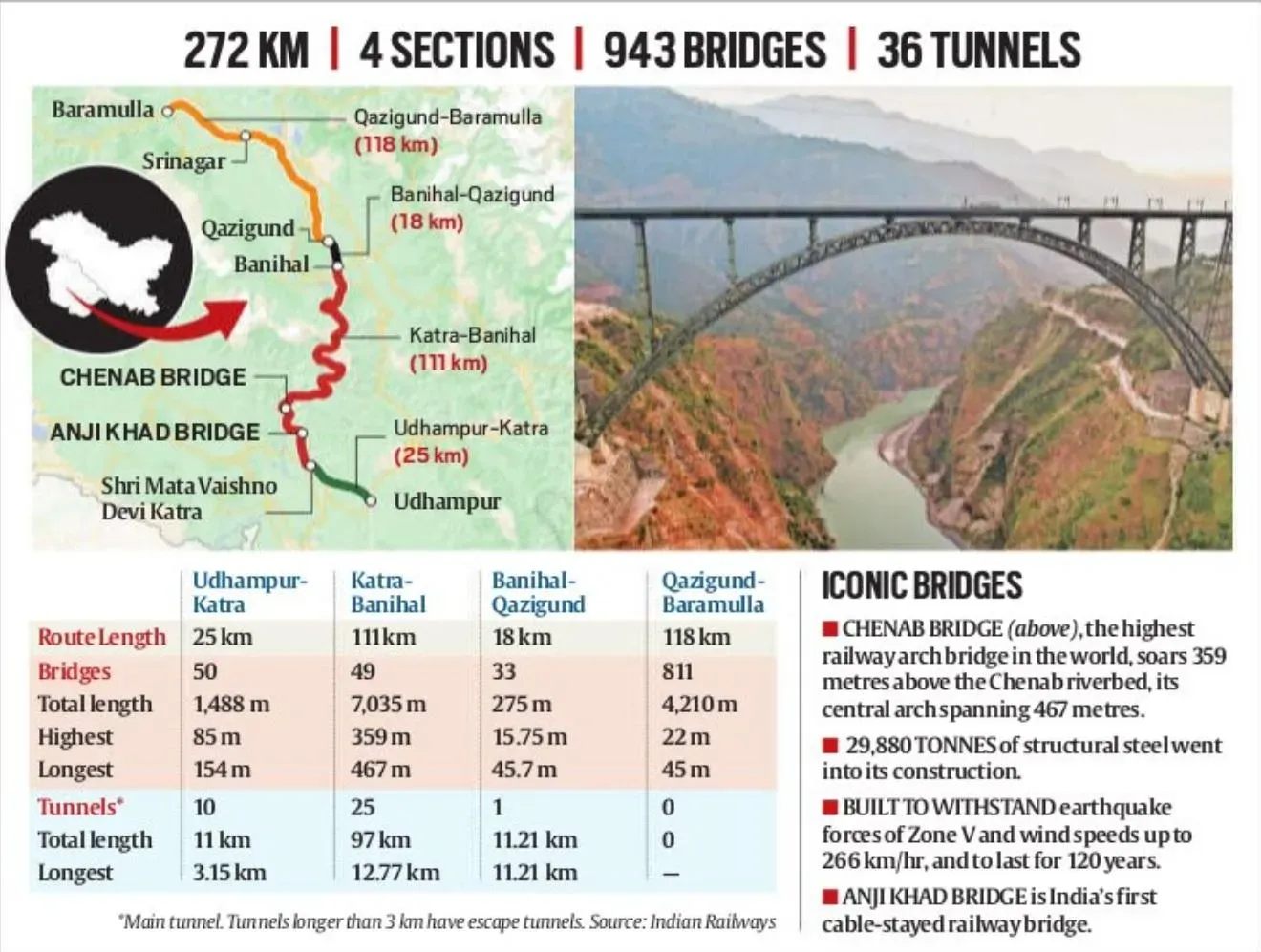
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The launch of the Vande Bharat Express between Katra and Srinagar by Prime Minister Narendra Modi marks a transformative chapter in Jammu and Kashmir’s infrastructural journey. The long-awaited completion of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) is not merely a technological feat, but a symbol of national integration, economic upliftment, and inclusive development in the Kashmir Valley.
Historical Background
The evolution of rail connectivity in Jammu and Kashmir dates back to the colonial era when, in 1897, a 40–45 km rail line linked Jammu to Sialkot (now in Pakistan). Subsequent plans to extend railways to Srinagar in the early 20th century were shelved. After the 1947 Partition, Jammu was cut off from the rail grid as Sialkot became part of Pakistan. The region had to wait until 1975 for the inauguration of the Pathankot–Jammu line. The Jammu–Udhampur line, started in 1983, was completed only in 2004.
In 1994, the rail project was further extended to include Srinagar and Baramulla, and the USBRL was declared a national project in 2002, with the initial estimated cost of ?2,500 crore.
USBRL: Engineering Triumph
The fully operational 272 km USBRL has been completed at a revised cost of ?43,780 crore. It includes 36 tunnels, 943 bridges, and several record-setting engineering marvels in the seismically active, snow-covered terrain of the Shivalik and Pir Panjal ranges.
- Chenab Bridge: The world’s tallest railway arch bridge, 359 meters above the riverbed, surpassing even the Eiffel Tower. Designed to withstand wind speeds of 260 km/h and extreme temperatures, it spans 1,315 meters and has a life expectancy of 120 years.
- Anji Khad Bridge: India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Reasi, towers 331 meters above the river and stretches 725 meters. Its iconic inverted Y-shaped pylon is supported by 96 high-tensile cables.
- Tunnel T-49: At 12.77 km, it is India’s longest transport tunnel, located in Ramban district, designed to ensure seamless all-weather connectivity.
Strategic and Socio-Economic Significance
This rail link is a game-changer for the region. By reducing Katra–Srinagar travel time to just 3 hours, it ensures year-round, all-weather accessibility, even during harsh Himalayan winters. The connectivity is critical not only for civilians but also for the rapid movement of security personnel in this strategically sensitive region.
Economically, the rail link is poised to boost trade and tourism. It will facilitate the quicker and more cost-effective transport of local produce such as apples, walnuts, saffron, pashmina, and handicrafts, thereby integrating the Valley with national markets. Reduced logistics costs will also lower the prices of essential goods imported into Kashmir.
Way Forward
The upcoming extension to Jammu Tawi aims to further enhance nationwide connectivity to Srinagar. This project stands as a testament to India’s commitment to inclusive development, national unity, and strategic infrastructure in border regions. With its blend of engineering excellence and socio-political impact, the USBRL reinforces the vision of a Viksit Bharat that leaves no region behind.
Tiger Conservation in India
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India, which hosts over 70% of the world’s wild tiger population, holds a dual responsibility of pride and stewardship. The near-collapse of tiger numbers in 2006, with populations falling to around 1,400 and local extinctions in Sariska and Panna, prompted a national awakening. Strengthened interventions such as the formation of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and Project Tiger rejuvenation efforts helped India register over 3,600 tigers in the 2023 census, reflecting significant progress.
From Crisis to Recovery: Institutional Response
The disappearance of tigers due to poaching, habitat degradation, and poor monitoring led to structural reforms post-2006. The NTCA (established in 2005) ensured stricter protocols, better surveillance, and habitat restoration. India now boasts 53 Tiger Reserves, with central and southern states like Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Uttarakhand emerging as conservation success stories.
Emerging Challenge: Prey Base Decline
Despite rising tiger numbers nationally, several reserves in eastern and central India—such as Guru Ghasidas, Indravati, Udanti-Sitanadi (Chhattisgarh), Palamau (Jharkhand), and Simlipal and Satkosia (Odisha)—have shown worrying trends of tiger decline. The core issue is not direct poaching but the fall in prey density, especially species like chital, sambar, and gaur. Scientific evidence indicates that tiger viability is closely tied to prey abundance, with a threshold of at least 10–15 prey animals per sq km required for stable populations.
Socioeconomic Roots of Ecological Depletion
Many affected reserves lie in poverty-stricken tribal regions. In the absence of alternative protein sources and sustainable livelihoods, communities turn to bushmeat hunting using traditional snares and traps. This not only reduces herbivore populations but also threatens predator survival. Palamau Reserve is a stark example where both large herbivores and tigers have nearly vanished under such pressures.
Institutional Recommendations and Ecological Restoration
The NTCA-WII 2023 report recommends short-term herbivore breeding enclosures but recognizes their limitations in rewilding success. A sustainable solution lies in habitat quality enhancement and involving communities in conservation. Some reserves still retain dense forests, providing an ecological foundation for revival. The decline of left-wing extremism in many areas also opens avenues for focused conservation interventions.
Towards Inclusive Conservation: Eco-Tourism and Livelihoods
Prosperous reserves like Bandhavgarh and Ranthambore benefit from conservation-linked tourism and community participation. In contrast, remote and underdeveloped areas lack such economic linkages. Promoting inclusive eco-tourism, skill development, and income-generation activities—such as SHGs, poultry farming, and forest produce marketing—can transform local attitudes.
Way Forward: Integrated, People-Centric Approaches
India must adopt multidimensional strategies combining ecological, institutional, and social measures:
- Implement prey recovery plans in Tiger Conservation Plans (TCPs).
- Provide targeted funding and technical support to underperforming states.
- Restore grasslands, ensure wildlife corridors, and adopt technology (drones, AI) for monitoring.
- Recognize community forest rights, promote Gram Sabha governance, and expand MGNREGA to conservation-linked jobs.
Conclusion
India’s tiger conservation success is laudable but remains precarious if prey depletion continues unchecked. The path ahead demands a shift from protectionism to participatory conservation—rooted in equity, ecological integrity, and community empowerment. The survival of the tiger is not merely a wildlife concern, but a test of India’s commitment to sustainable development and inclusive environmental governance.
India’s Green Economy: A Catalyst for Employment and Sustainable Development
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
India’s transition to a green economy is not only central to achieving its environmental and climate goals but is also emerging as a powerful engine for economic growth and employment generation.
According to a recent report by NLB Services, India’s green sector is expected to generate approximately 7.29 million new jobs by FY2027–28, with the figure projected to rise to 35 million by 2047, aligning with India’s long-term net-zero commitments.
Understanding the Green Economy
A green economy encompasses sectors and activities that contribute to ecological sustainability, low-carbon development, and resource efficiency, while also promoting inclusive employment. It integrates environmental goals with economic planning, thus creating green jobs in areas such as renewable energy, electric mobility, sustainable construction, waste management, and green agriculture.
Sectoral and Regional Dynamics
The most significant employment potential lies in industries such as renewable energy, electric vehicles (EVs), green infrastructure, sustainable textiles, and waste-to-energy solutions. These sectors have witnessed rising investments and policy focus under national missions such as PM-KUSUM, Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME), and the National Hydrogen Mission.
While metropolitan areas like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Delhi remain hubs for green employment, tier II and III cities are poised to play a crucial role in the decentralisation of the green economy. Cities such as Jaipur, Coimbatore, Bhubaneswar, Visakhapatnam, and Indore are projected to account for 35–40% of the green job creation by FY28, primarily in logistics, warehousing, sustainable agriculture, and urban waste management.
Evolving Skill Demands
The transition towards green employment is redefining workforce skill requirements. Modern green jobs demand a blend of environmental sustainability expertise and technological proficiency, particularly in AI, IoT, GIS, blockchain, and data analytics. This digital integration is reshaping job profiles and creating pathways for future-ready employment.
In response, industries are shifting hiring strategies to focus more on skill-based recruitment rather than conventional degrees. There is also a growing emphasis on industry-academia collaborations to align curricula with the evolving demands of the green economy, thus fostering climate-literate and digitally equipped professionals.
Gender Inclusion and Equity Challenges
Despite the promising employment potential, women currently constitute only 11–12% of the green workforce in India. Barriers include limited access to STEM education, workplace safety concerns, and socio-cultural constraints. However, progressive employers are increasingly adopting inclusive hiring practices, promoting women-centric skill development programmes, and partnering with training agencies to build a more diverse and equitable green talent pipeline. These efforts are expected to improve female participation by 12–15% in the next 5–6 years.
Economic Significance
India’s green economy is expected to contribute significantly to national GDP. Its valuation is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2030, and expand to $15 trillion by 2070, supporting India’s target of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070. Thus, it offers a dual dividend—economic prosperity and environmental security.
Conclusion:
India’s green transition presents a transformative opportunity to simultaneously address climate change, unemployment, and regional disparities. With appropriate policy support, capacity building, and inclusivity, the green economy can become the bedrock of sustainable and equitable growth.
Structural Shift in India’s Remittance Landscape

- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
According to the RBI’s latest Remittances Survey (2023–24), there has been a significant structural transformation in India's inward remittance patterns. Advanced Economies (AEs) — led by the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Singapore, and Australia — have overtaken the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations as the primary sources of remittances. This shift holds major implications for India’s migration, financial inflows, and socio-economic planning.
Changing Source Geography of Remittances
India’s total remittance inflow touched USD 118.7 billion in 2023–24, doubling since 2011. The United States alone accounted for 27.7%, followed by the UAE (19.2%), the UK (10.8%), Saudi Arabia (6.7%), and Singapore (6.6%). This marks a departure from the earlier dominance of the Gulf region, whose collective share has dropped to 38%, while Advanced Economies now contribute over 50%.
The top recipient states of these remittances in India are Maharashtra (20.5%), Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
Factors Behind the Shift
1. Evolving Migration Trends:There has been a surge in professional, high-skilled Indian migrants heading to AEs, particularly in sectors like STEM, finance, and healthcare. These migrants tend to earn higher wages, have stronger job security, and remit more per capita compared to their low-skilled counterparts in the Gulf.
2. Declining Opportunities in the GCC:Several Gulf countries have implemented nationalisation policies like Saudi Arabia’s “Nitaqat,” which prioritise local hiring. Moreover, automation and economic diversification have reduced demand for foreign low-skilled workers. This, combined with COVID-19-induced job losses and return migration, has contributed to the decline in remittances from the region.
3. Education-Driven Migration:Countries like the UK, Australia, and Canada have emerged as popular education destinations. For instance, Indian migration to the UK tripled from 76,000 in 2020 to 250,000 in 2023. Post-study work opportunities and migration partnerships like the India-UK “Migration and Mobility Partnership” (2021) have bolstered this trend.
4. Cost and Mode of Transfers:Digitalisation has reduced remittance costs to India below the global average, although it still exceeds the SDG target of 3% for a US$200 transfer. Nonetheless, cash-based transactions remain significant for smaller amounts.
Economic and Policy Implications
1. Macroeconomic Importance:Remittances contribute about 3–3.5% of India’s GDP, consistently surpassing FDI and Official Development Assistance (ODA). They help finance nearly half of the merchandise trade deficit and act as buffers against external economic shocks.
2. Household-Level Impact:Remittances are pivotal for improving living standards, enabling expenditure on food, healthcare, and education. In Kerala, for instance, remittances account for over 36% of the state's domestic product.
3. Policy Challenges and Recommendations:
- Skill Alignment: Training systems must align with global job markets to prevent ‘wilful deskilling’ — where highly educated migrants take up low-skilled jobs.
- Migration Diplomacy: India must proactively negotiate bilateral/multilateral mobility agreements to secure rights, fair wages, and career progression for migrants.
- Diaspora Engagement: Policies should encourage productive use of remittances (e.g., investments, health, education) and tap diaspora networks for technology and knowledge transfer.
Conclusion
India’s remittance ecosystem is transitioning from Gulf-led low-skilled flows to knowledge-intensive, high-value contributions from Advanced Economies. Sustaining this trend will require strategic migration governance, skill reforms, and deepened engagement with the global Indian diaspora.
India’s Employment Challenge: Bridging the Gap Between Labour& Capital in the Era of Technological Transformation

- 06 Apr 2025
Context:
India is experiencing a paradoxical trend — despite a rapidly expanding working-age population and rising production capacity, the generation of formal employment opportunities remains insufficient. Since 2017–18, while the working-age population has increased by approximately 9 crore, formal sector jobs have grown by only 6 crore, indicating an annual shortfall of around 50 lakh jobs. This mismatch is further compounded by the dominance of self-employment and informal sector jobs, especially in rural areas, raising concerns about both the quality and sustainability of employment.
Structural Shift Towards Capital-Intensive Growth
The country’s production systems are increasingly exhibiting capital-intensive tendencies — even in traditionally labour-intensive sectors such as textiles and food processing. This phenomenon, often referred to as "skill-biased technological change," is driven by two broad factors:
- Demand-Side Factors: The pressure to enhance productivity and reduce costs incentivises adoption of automated and capital-intensive technologies, especially in high-value manufacturing and services.
- Supply-Side Constraints: A shortage of skilled and technically trained labour impedes the effective utilisation of labour resources. Less than 10% of India’s workforce has received formal vocational or technical training, and most youth entering the labour market lack industry-relevant skills.
The declining cost of technology, coupled with stagnant real wages and rigid labour laws in some states, further tilts the balance in favour of machines over human labour.
Policy Interventions and Challenges
The Government of India has initiated schemes such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme and the Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) Scheme to address the employment deficit.
- PLI Scheme: While it aims to boost manufacturing output, the scheme is heavily focused on high-tech sectors like electronics, drones, and IT hardware — which are capital- and skill-intensive. Despite this, the highest job creation under the PLI has been observed in food processing and pharmaceuticals, suggesting a disconnect between investment focus and employment potential.
- ELI Scheme: Designed to subsidise the cost of hiring untrained workers in labour-intensive sectors, the ELI provides short-term financial support via EPFO contributions. However, its long-term efficacy in ensuring sustainable skilling and employment remains uncertain due to lack of outcome data and short subsidy duration (2–3 years).
Need for a Cohesive Labour-Capital Policy Framework
India’s employment challenge cannot be addressed through fragmented policies. A cohesive framework is required that integrates:
- Industrial Policy with Skilling Policy: Ministries responsible for industrial production, labour, and skilling must work in tandem to ensure the availability of a workforce with skills that are aligned with the demands of emerging sectors.
- Incentive Structuring: The current flat subsidies under ELI could be modified into a graded structure, where higher transfers are provided for higher levels of certified skill acquisition, encouraging continuous skill upgrading.
- Skill Supply Chain Reform: Skill development institutions like ITIs and vocational centres should be incentivised based on placement rates and wage outcomes, not just enrolments or certifications.
- Labour Law Flexibility: State-level reforms in labour regulations are essential to reduce the cost of employing formal workers and to encourage job creation, especially in micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs).
Way Forward for a Viksit Bharat (Developed India)
As India transitions towards becoming a high-value production economy, it must simultaneously invest in its human capital. This requires:
- Dynamic Skill Development Programs: Adaptive skilling strategies must be designed to align with evolving technological trends such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, and green energy.
- Data-Driven Employment Policies: Regular labour market surveys and outcome tracking of employment schemes are critical for evidence-based policymaking.
- Support for Labour-Intensive Sectors: Focused support to industries with high employment elasticity, such as textiles, leather, food processing, tourism, and construction, can yield substantial job creation.
In conclusion, advancing the agenda of Viksit Bharat demands equal emphasis on capital and labour. Without a strong and skilled workforce, India's demographic dividend risks turning into a demographic burden. Therefore, employment generation must be at the core of India’s development policy, with a strategic vision that links skilling, production, and structural transformation.
India–US Civil Nuclear Deal

- 01 Apr 2025
Context:
Nearly two decades after the landmark India–US Civil Nuclear Agreement (123 Agreement) was signed in 2007, a major operational milestone has been achieved. In March 2025, the US Department of Energy (DoE) granted regulatory clearance under “10CFR810” of the US Atomic Energy Act (1954), allowing Holtec International, a US-based nuclear engineering firm, to transfer unclassified Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology to three Indian private entities: Holtec Asia (its subsidiary), Tata Consulting Engineers (TCE), and Larsen & Toubro (L&T).
Key Regulatory and Safeguard Provisions
- Authorization Duration: 10 years, subject to a five-year review.
- Safeguards: Technology to be used only for peaceful nuclear activities under IAEA safeguards.
- Restrictions:
- No retransfer to other Indian or foreign entities without US approval.
- Prohibited for military/naval propulsion or enrichment purposes.
- No access to Sensitive Nuclear Technology.
- Compliance: Holtec is required to file quarterly progress reports to the US DoE.
Strategic and Technological Significance for India
- Modernizing India's Nuclear Fleet: India's nuclear program has traditionally relied on Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) using natural uranium. The transfer of SMR technology based on Pressurised Water Reactors (PWRs) represents a shift towards the global mainstream of nuclear reactor technology.
- Boost to Domestic Manufacturing: Collaboration with Indian firms like L&T and TCE can localize manufacturing and engineering, promoting Make in India and self-reliance in nuclear energy technology.
- Entry into Global SMR Supply Chain: This development aligns India with an emerging global trend, as SMRs (30–300 MWe) are increasingly viewed as crucial for decarbonization and energy security.
- Strategic Counterbalance to China: As China advances its SMR technology for energy diplomacy in the Global South, this India–US initiative presents a geopolitical counterweight, especially as both nations face challenges in independently competing with China’s scale and state-led investments.
Legal and Policy Bottlenecks
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010: Cited by foreign companies as a barrier due to concerns about supplier liability in case of accidents.
- Atomic Energy Act, 1962: Needs amendments to permit private sector participation in nuclear generation, currently reserved for public sector undertakings like NPCIL and NTPC.
- Despite Holtec's request, these PSUs were not included in the initial authorization due to pending non-proliferation assurances from the Indian government. However, they may be added later, contingent on further diplomatic progress.
Way Forward and Future Prospects
- Holtec’s Expansion Plans: Its non-nuclear manufacturing unit in Dahej, Gujarat is poised for expansion, with a potential doubling of its workforce once SMR manufacturing begins.
- Partnership Pipeline:
- TCE for engineering design.
- L&T for high-precision nuclear component manufacturing.
- Future engagement with NPCIL and NTPC as operators of Holtec’s SMR-300 reactors.
- Clean Energy Strategy: SMRs are positioned as a key component of India's low-carbon energy transition, addressing both rising power demands and global climate commitments.
Conclusion
The US’s clearance for technology transfer to Indian private firms marks a pivotal operational step in the long-stalled India–US civil nuclear partnership. It opens the door for India to enter the global SMR market, boosts its domestic nuclear industry, and strengthens strategic cooperation with the US. However, legal reforms and institutional readiness remain critical for realizing the full potential of this deal.
Judicial Independence vs Accountability
- 22 May 2025
Context:
The recent controversy surrounding Justice Yashwant Varma and the subsequent remarks by Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar have reignited a crucial debate in Indian constitutional discourse: How can the judiciary remain independent while also being held accountable? At the heart of this debate lies the tension between institutional autonomy and the growing demand for transparency in judicial conduct.
The Varma Case: Catalyst for a Larger Debate
In March 2024, unaccounted cash was reportedly found at the residence of Justice Yashwant Varma, then serving on the Delhi High Court. Following the discovery, he was transferred to the Allahabad High Court. An in-house inquiry conducted by the Supreme Court found him culpable, yet it dismissed a petition seeking criminal investigation, forwarding the report instead to the President and Prime Minister.
Vice President Dhankhar questioned the constitutional basis of the in-house mechanism and called for a re-examination of the K Veeraswami judgment (1991), suggesting that the current legal framework grants excessive immunity to judges and hampers accountability.
Constitutional Safeguards and In-House Procedures
The Indian Constitution protects judicial independence through Article 124, which stipulates that judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts can only be removed through impeachment—a process that requires a special majority in Parliament. However, this safeguard has made judicial removal politically difficult. Despite several attempts, no judge has ever been successfully impeached since independence.
To address ethical complaints, the judiciary devised the in-house inquiry mechanism, wherein a panel headed by senior judges examines allegations against fellow judges. While this preserves the judiciary’s autonomy, the mechanism lacks statutory backing and has no power to impose penalties or recommend criminal prosecution.
The Veeraswami Judgment: Balancing Act or Bottleneck?
In the K Veeraswami case, the Supreme Court ruled that a judge could be treated as a public servant under the Prevention of Corruption Act. However, it mandated that any criminal case against a judge could proceed only with the approval of the Chief Justice of India (CJI), not the executive. This was intended to prevent misuse of prosecutorial powers and ensure judicial independence.
Critics argue that this judgment has created a judicial monopoly over sanctioning investigations, undermining public accountability. In practice, criminal prosecution against judges remains extremely rare. Notably, in 2019, then CJI Ranjan Gogoi sanctioned an FIR against Justice S.N. Shukla of the Allahabad High Court—one of the few instances of such approval.
Towards a Transparent and Accountable Judiciary
The current episode underscores a critical gap in India’s judicial accountability mechanisms. While independence is essential to prevent executive interference, absolute immunity risks eroding public confidence in the judiciary. The lack of transparency and enforceability in in-house inquiries has further exacerbated this perception.
There is a growing case for revisiting the Veeraswami judgment, possibly through constitutional or legislative reform, to allow limited and well-regulated avenues for criminal investigation into judicial misconduct—without compromising judicial independence.
Conclusion
A nuanced balance must be struck between judicial independence and accountability. India’s democracy cannot afford a judiciary that is either vulnerable to political manipulation or immune from public scrutiny. Strengthening internal accountability frameworks, reinforcing institutional checks, and ensuring transparency in disciplinary processes are essential to uphold both the dignity and integrity of the judiciary.
Live Baiting and the Conservation Dilemma

- 20 May 2025
Context:
In recent years, India's tiger conservation practices have come under scrutiny due to the continued use of live baiting, particularly for feeding injured or aging tigers. While originally a hunting tactic used by British colonialists—placing prey like buffalo or goats to lure tigers for easy shooting—live baiting found new life in post-independence India as a tourism tool in reserves like Sariska. This practice was officially banned in 1982 by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, yet it persists in conflict scenarios and as a means of care for ailing tigers.
National Policy and Ecological Concerns
According to the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), live baiting for tourism is prohibited, and its use for injured or old tigers is “not advisable.” The SOP emphasizes minimal human intervention, underscoring that wildlife conservation must adhere to the principle of survival of the fittest. Artificial feeding undermines this, fostering dependency, disrupting natural selection, and increasing the risk of human-wildlife conflict.
Despite these guidelines, many reserves continue the practice under humanitarian or public pressure. Feeding wild tigers, even as an emergency measure, is permitted only in exceptional cases—such as when an injured tigress with dependent cubs cannot hunt. Experts like Valmik Thapar recommend baiting no more than once every two weeks and only for a short duration of up to three months.
Case Studies Highlighting Consequences
The tragic case of Kankati, a 23-month-old tigress in Ranthambore, illustrates the dangers of early habituation. Raised on live bait after her mother, Arrowhead, fell ill, Kankati and her siblings lost their fear of humans. She has since killed two people, raising alarms about human safety in reserves.
Similar outcomes have been observed in the cases of T36, T37, and Simba—young tigers raised on bait following the deaths of their mothers. Without learning essential hunting skills, these tigers either perished prematurely or became threats to others. Even aging icons like Machhli and T2 were kept alive unnaturally with bait; while Machhli survived on human-provided food for seven years, T2 died too weak to kill.
The Cultural Shift Toward Over-Intervention
A growing culture of emotional overreach is increasingly shaping wildlife management. Tourists now demand treatment for limping or injured tigers, triggering unnecessary tranquilizations and medical interventions. From transporting prey animals to creating artificial water sources during dry spells, reserves like Corbett, Kanha, Bandipur, and Pench are altering ecosystems to sustain tigers artificially.
This overmanagement leads to unnatural survival of weaker individuals, overcrowding, and territorial conflicts—not just between tigers but also between tigers and humans. Experts caution that such interference only weakens the ecological integrity of tiger populations.
Conclusion: Let Nature Lead
Veteran conservationists argue that wild tigers do not require pet-like care. The most effective conservation strategy remains the preservation of natural habitats and prey bases, with minimal human interference. Misplaced kindness, though emotionally compelling, endangers both tiger and human populations by disrupting nature’s balance.
For India to achieve sustainable tiger conservation, it must resist populist interventions and re-anchor policies in ecological wisdom—protect, don’t pamper.
Kolkata-Northeast Sea Route and the Strategic Highway Project
- 19 May 2025
In News:
India’s northeast has long faced logistical isolation due to its geographical constraints and overdependence on the narrow Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken’s Neck. A recent strategic initiative aims to transform this scenario through the creation of a multi-modal connectivity route that bypasses Bangladesh and directly links the Northeast to the sea via Myanmar and Kolkata. This development gains added relevance in light of recent remarks by Bangladesh’s interim leader Muhammad Yunus, who described Northeast India as “landlocked” and dependent solely on Dhaka for maritime access—a claim that India seeks to counter through tangible connectivity upgrades.
Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP)
At the heart of this initiative lies the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP), a flagship project under India’s Act East Policy, designed to connect the eastern seaport of Kolkata to the landlocked Northeast through Myanmar. The project includes:
- Sea Leg: Kolkata Port to Sittwe Port in Myanmar (~539 km).
- Inland Waterway: From Sittwe to Paletwa via the Kaladan River (~158 km).
- Road Leg in Myanmar: Paletwa to Zorinpui on the India-Myanmar border (~110 km).
- Indian Extension: Zorinpui to Lawngtlai and Aizawl in Mizoram, connecting to the national highway network.
This corridor not only reduces reliance on routes through Bangladesh but also serves as a strategic counterbalance in India’s regional geopolitics, particularly in strengthening ties with Southeast Asia and enhancing its maritime influence in the Bay of Bengal.
Strategic Shillong-Silchar Highway
Complementing the KMTTP is the construction of a 166.8 km four-lane high-speed highway from Mawlyngkhung (near Shillong) to Panchgram (near Silchar) along NH-6. This is the first high-speed corridor in the North-East and the first in a hilly terrain, and is slated for completion by 2030. The project is being developed under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) at a cost of ?22,864 crore, with implementation by NHIDCL for the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
The highway will include:
- 19 major bridges, 153 minor bridges, 326 culverts
- 22 underpasses, 26 overpasses, 8 subways, and 34 viaducts
It will reduce travel time between Shillong and Silchar from 8.5 to 5 hours and act as a crucial link to states like Mizoram, Tripura, and Manipur. More significantly, it will integrate with the Kaladan route, offering a direct link to Kolkata via Myanmar and the Bay of Bengal.
Strategic and Economic Significance
This integrated connectivity initiative holds multi-dimensional importance:
- Reduces dependency on Bangladesh and the Siliguri Corridor
- Enhances trade and people-to-people ties with ASEAN nations
- Strengthens regional integration under the Act East Policy
- Boosts economic development in the North-East through improved logistics
- Improves India’s strategic posture in the Indo-Pacific and Bay of Bengal
In conclusion, the Kolkata-Northeast sea route and supporting infrastructure like the Shillong-Silchar highway represent a decisive step towards bridging geographical constraints, boosting regional development, and reinforcing India’s strategic autonomy in the eastern frontier.
Operation Sindoor

- 18 May 2025
In News:
Operation Sindoor marked a significant leap in India's military and technological prowess, not only achieving its strategic objectives but also demonstrating the operational maturity of Made-in-Indiadefence systems. The operation was characterised by a multi-layered approach involving precision strikes, air defence, unmanned systems, and advanced surveillance tools—most of which were indigenously developed.
Precision and Navigation Capabilities
One of the defining features of Operation Sindoor was the pinpoint accuracy of strikes deep inside Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir. Specific terrorist camps and infrastructure were destroyed with minimal collateral damage, underlining India’s commitment to responsible military engagement. This precision was enabled by a combination of advanced guidance systems and real-time data from space-based and ground-based assets.
India's indigenous Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) system, offering positional accuracy of 10–20 cm, played a pivotal role. High-resolution satellites such as Cartosat, RISAT, and EOS provided real-time imagery, allowing sub-metre targeting. These capabilities are a result of sustained investments by DRDO and ISRO and reflect the prioritisation of guidance and navigation as a critical technology domain in DRDO’s 2023 R&D roadmap.
Lethality and Advanced Weapon Systems
The destruction caused during Operation Sindoor also demonstrated the high lethality of Indian weapon systems. Deep penetration warheads, advanced fusing mechanisms, and powerful propulsion systems—developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme—were central to the operation’s success. The likely use of the BrahMos missile, equipped with state-of-the-art guidance and propulsion, underscores the maturity of indigenous missile technology.
Emerging technologies such as Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs), including laser-based systems, were reportedly deployed to neutralise incoming drones. DEWs have been a priority sector for the Defence Ministry since 2022, and DRDO showcased them during the 2025 Republic Day Parade.
Integrated Air Defence and Radar Systems
A critical success factor in Operation Sindoor was India’s ability to neutralise almost every aerial threat, including drones and missiles. This was achieved through a combination of imported and indigenous systems. The S-400 Triumph, along with DRDO-developed radars like Rajendra, Rohini, LLTR, and low-level 3D radars, formed a robust air defence network. These systems enabled accurate detection, tracking, and interception of aerial threats.
Cutting-edge R&D continues in radar technologies, including AI-powered signal processing, stealth detection, and foliage-penetrating radars, which will further enhance India’s battlefield awareness and response capability.
Role of Unmanned Systems
For the first time in an India-Pakistan conflict, drones played a decisive role. Indian UAVs executed deep strikes into Pakistani territory, while enemy drone swarms were largely neutralised. India also deployed upgraded Bofors guns and SAMAR systems to counter low-flying threats. The success of unmanned platforms indicates a paradigm shift towards hybrid warfare, with manned-unmanned teaming becoming a future norm.
However, to sustain this capability, India must strengthen its domestic manufacturing base, ensure secure raw material supply chains, and foster collaboration between industry, academia, and the armed forces.
Conclusion:
Operation Sindoor represents a watershed moment in India’s defence preparedness. It validated years of indigenous R&D and affirmed India’s self-reliant defence posture. As warfare evolves, India’s ability to synergise space, cyber, and kinetic capabilities with unmanned platforms will be critical in ensuring strategic deterrence and national security.
Voter ID Rules in India
- 15 May 2025
Context:
Recent developments surrounding the deportation of Pakistani nationals from India, many of whom reportedly held Indian identity documents such as Voter IDs, Aadhaar, and ration cards, have sparked concern over the integrity of the electoral rolls and the effectiveness of the voter verification process. This issue holds significant implications for the sanctity of India’s democratic system, particularly with regard to voter eligibility and the legal safeguards against electoral fraud.
Constitutional and Legal Provisions
Under Article 326 of the Indian Constitution, the right to vote is granted to every citizen of India aged 18 years and above, provided they are not disqualified under any law. The Representation of the People Act, 1950, particularly Section 16, lays down conditions for disqualification from voter registration, including non-citizenship, unsound mind (as declared by a competent court), and legal disqualification due to corrupt practices.
To register as a new elector, applicants must fill out Form 6 of the Election Commission of India (ECI). While proof of age and address are mandatory, no separate citizenship document is required. Instead, a self-declared statement affirming Indian citizenship is submitted. However, under Section 31 of the RP Act, submitting false information, particularly with respect to citizenship, can attract legal penalties including imprisonment of up to one year, a fine, or both.
Verification and Role of Electoral Authorities
The onus of verifying the eligibility of voters lies primarily with the Electoral Registration Officer (ERO), assisted by Booth Level Officers (BLOs). These authorities are empowered to conduct investigations, hold hearings, and scrutinize documents before accepting applications. In cases of doubt or objections, the ERO must assess all evidence independently and ensure that non-citizens are not included in the electoral roll.
Citizenship is typically assumed unless there is a reason to believe otherwise. However, in instances of objection, the applicant bears the initial burden of proof to establish citizenship. For internal migrants or married women lacking documentation, alternative proofs such as prior voter registration or certificates from local authorities may be accepted.
Issues of Non-Citizens Holding Voter IDs
Instances of non-citizens obtaining Indian voter IDs have occurred in the past and are not isolated. The ECI has previously identified and removed such names from the electoral roll following investigations. In such cases, legal proceedings are initiated against individuals who fraudulently secured voter registration.
The current incident involving deported Pakistani nationals allegedly holding Indian Voter IDs brings this issue back into focus. It highlights systemic lapses in identity verification and raises concerns over the use of forged or easily obtainable documents to exploit electoral loopholes.
Current Measures and Challenges
To curb such malpractices, the ECI has initiated a linkage between Aadhaar and Voter ID cards to detect and eliminate duplicates and ineligible entries. However, this initiative has limitations, as Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship. Non-citizens can still possess Aadhaar cards, making this linkage an insufficient standalone measure for verifying voter eligibility.
Conclusion
The integrity of India’s electoral system is foundational to its democracy. While the legal framework governing voter registration is robust, implementation gaps, documentation loopholes, and lax verification processes expose vulnerabilities. Strengthening the verification mechanisms, enhancing accountability of electoral officers, and exploring alternative digital authentication methods are imperative to safeguard the electoral roll from misuse and to uphold the principle of “one citizen, one vote.”
Delhi’s unprecedented Pre-Monsoon Rainfall
- 14 May 2025
In News:
On May 2, 2024, Delhi witnessed one of its most intense pre-monsoon weather events in over a century, recording the second-highest single-day rainfall for May since 1901, surpassed only by 119.3 mm in 2021. This extreme event, though meteorologically significant, also underscores critical vulnerabilities in urban disaster preparedness and climate resilience.
Meteorological Dynamics behind the event
This rare weather event was driven by a complex interplay of meteorological phenomena. Delhi became the focal point for two moisture-laden wind systems: easterlies from the Bay of Bengal and southerlies from the Arabian Sea. Their collision over the National Capital Region created a low-level convergence zone, which forced moisture-rich air upward, initiating intense convective activity.
Compounding this situation was the presence of troughs—elongated low-pressure systems—that enhanced instability and facilitated vertical atmospheric lifting. As the moist air ascended, it cooled rapidly, forming towering cumulonimbus clouds reaching altitudes of over 13 km. These clouds, commonly associated with thunderstorms and intense rainfall, released torrential downpours over the city.
Additionally, the region was under the influence of a Western Disturbance, coupled with upper-air cyclonic circulations over Rajasthan and Punjab. These systems altered wind patterns, induced powerful vertical lifts, and further fed moisture into the storm system through an active monsoon trough extending from Madhya Pradesh to Kerala.
Timing and Transitional Weather
The event occurred during May, a transitional month for northern India as it shifts from spring to the monsoon phase. This seasonal flux often leads to volatile weather, but the scale and intensity observed this year were unusual and alarming. Factors such as strong westerly surface winds (up to 54 kmph) and cool descending winds from the Himalayas further enhanced convection, creating a perfect storm scenario.
Impacts on Urban Infrastructure
The heavy rainfall overwhelmed Delhi’s urban infrastructure. Several parts of the city faced severe waterlogging, power outages, flight disruptions, and, tragically, five deaths due to weather-related accidents. The lack of adequate stormwater drainage systems, combined with high urban density and poor land-use planning, exacerbated the crisis.
Broader Implications for Policy and Planning
This event serves as a wake-up call for urban disaster management and climate adaptation. With climate variability increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, Indian cities—especially megacities like Delhi—must invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.
Policymakers must:
- Strengthen early warning systems and inter-agency coordination.
- Enhance urban planning with a focus on green infrastructure and permeable surfaces.
- Improve data integration across meteorological and civic bodies for real-time response.
- Mainstream climate risk assessments in city development plans.
Conclusion
Delhi’s record-breaking rainfall is not just a weather anomaly but a symptom of deeper systemic vulnerabilities. It emphasizes the urgent need for holistic, science-backed urban resilience strategies to safeguard lives, infrastructure, and ecological balance in a rapidly urbanizing and warming world.
Operation Sindoor and the Emerging Imperative of Digital Warfare in India’s National Security

- 12 May 2025
In News:
On May 7, India launched Operation Sindoor, targeting terrorist bases in Pakistan in response to the Pahalgam terrorist attack on April 22. This military action quickly became a case study in how modern warfare extends beyond physical battlegrounds to include digital and information domains.
Managing Information During Conflict
Following the operation, India’s Ministry of Defence issued an advisory on May 9 urging media, digital platforms, and individuals to avoid live or real-time reporting of military movements. The Press Information Bureau (PIB) also stressed sharing only official updates to counter the spread of misinformation. This advisory was crucial after fake news, including false claims that the INS Vikrant aircraft carrier attacked Pakistani ports, spread rapidly on social media and TV channels. The misinformation originated from a fraudulent social media account pretending to be the INS Vikrant, causing panic and confusion, which was then amplified by Pakistani sources.
Hybrid Nature of Modern Conflicts
Modern conflicts have evolved into “hybrid wars” that combine traditional military operations with sophisticated information warfare. Research from King’s College London highlights how states use both traditional and social media platforms for “perception management”—influencing public opinion to strengthen domestic support or destabilise opponents. In such environments, misinformation spreads rapidly due to media pressure to break news first, public anxiety seeking instant updates, and social media algorithms that prioritise sensational content regardless of accuracy.
Cyber Warfare: The Invisible Battlefield
Digital warfare also includes cyberattacks on critical infrastructure and military networks. Since the Pahalgam attack, India has faced several cyber intrusions originating from Pakistani and spoofed networks. Cyber operations now run parallel to physical conflicts, forming a multi-domain battlespace where controlling information flow and disrupting enemy networks are as vital as territorial gains.
Recent global examples include Russia’s cyberattacks on Ukraine during the 2022 invasion and retaliatory cyber operations by Ukrainian hackers. Similarly, after Hamas’s October 2023 attack, Israel faced massive cyber assaults and widespread disinformation campaigns on social media using AI-generated content.
Challenges in Cyber Conflict
Cyber warfare is especially challenging because attacks are remote, anonymous, and difficult to attribute. Attackers hide behind proxies and compromised systems, complicating diplomatic responses and exposing gaps in international laws governing cyber conflicts. As tensions rise, India may encounter more frequent and sophisticated cyberattacks targeting its infrastructure, military communications, and financial systems, alongside conventional military threats.
India’s Preparedness Strategy
To tackle these challenges, India must adopt a comprehensive strategy combining legal, diplomatic, and technological measures:
- Legal: Strengthen cybersecurity laws under the Information Technology Act and push for international agreements to regulate state-sponsored cyberattacks.
- Diplomatic: Enhance cooperation in global forums like the UN Group of Governmental Experts (GGE) and partner with technologically advanced nations to identify and counter hostile cyber activities.
- Technological: Invest heavily in cyber defence and offence capabilities. Critical infrastructure must be fortified through security audits, network segmentation, and resilient backups. Agencies such as the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) and CERT-In need enhanced capacities to detect and respond to threats. Regulators should promote continuous network monitoring and public awareness on cybersecurity, exemplified by the Reserve Bank of India’s directives to banks.
Conclusion
The digital battlefield—comprising misinformation and cyberattacks—demands a coordinated government response and active citizen engagement. As conventional and digital warfare increasingly overlap, India’s national security depends on not only military preparedness but also information resilience and cybersecurity. With well-planned, multi-dimensional strategies, India can effectively confront emerging digital threats and secure its sovereignty in an increasingly complex geopolitical environment.
Child Labour in India
- 10 May 2025
In News:
Despite a comprehensive constitutional and legal framework designed to prohibit child labour, India continues to face the persistent challenge of millions of children engaged in hazardous and exploitative work. The prevalence of child labour in sectors such as matchstick factories, brick kilns, leather processing units, and construction sites highlights the gap between legal intent and ground realities.
Defining Child Labour
Child labour involves employing children in work that deprives them of their childhood, interferes with education, and is harmful mentally, physically, socially, or morally. It constitutes a violation of basic child rights and hampers the child’s overall development.
Legal and Constitutional Framework
India’s fight against child labour is backed by strong constitutional provisions and statutes:
- Constitutional Safeguards:
- Article 24 prohibits the employment of children below 14 years in factories, mines, and hazardous occupations.
- Directive Principles (Articles 39(e) and 39(f)) direct the State to protect children from exploitation and ensure their development.
- Statutory Measures:
- The Child and Adolescent Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, 1986 (amended in 2016) prohibits employment of children under 14 and restricts adolescents (14–18 years) from hazardous work. However, it permits work in family enterprises after school hours, a provision often misused.
- The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection) Act, 2015 treats child labour victims as children in need of care and protection.
- The Right to Education Act, 2009 mandates free and compulsory education for children aged 6–14, indirectly aiming to reduce child labour by keeping children in schools.
- Judicial Interventions:
- The Supreme Court has reinforced child rights under Article 21 (Right to Life with dignity), with landmark rulings emphasizing the state’s duty to eradicate child labour(e.g., M.C. Mehta v. State of Tamil Nadu, 1996).
Magnitude and Ground Realities
According to UNICEF’s analysis of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (2018-19), approximately 18 to 33 lakh children are engaged in labour in India. Nearly half of these children work within their families, making detection and intervention difficult. The worst-affected sectors include agriculture, fireworks, glass-making, leather tanning, mining, and construction.
Children working in these sectors face hazardous conditions involving exposure to toxic substances, long working hours, and physical and verbal abuse. This leads to long-term damage to their physical health, mental well-being, and education prospects. The lack of access to sanitation and healthcare further exacerbates their vulnerability.
Enforcement Challenges
Despite the severity of the problem, enforcement remains weak. In 2021, only 613 cases under the Child Labour Act were registered, indicating a large enforcement gap. Additionally, data on child labour is outdated and fragmented, with the last Census conducted in 2011 and poor disaggregation of data by gender and rural-urban divide. Coordination between labour departments, police, and child welfare agencies is inadequate.
Instances like the 2024 Madhya Pradesh distillery case, where 58 children were rescued after working long hours in hazardous conditions, expose the failures in inspection and enforcement at the state level.
Root Causes
Poverty remains the primary driver of child labour. The International Labour Organization highlights that child labour is both a cause and consequence of poverty. Families often push children into work due to economic necessity, especially when adult unemployment is high (estimated 6 million unemployed adults). Malnutrition and deprivation perpetuate this cycle, with India accounting for half of the world's wasted children.
Way Forward
To effectively combat child labour, India must focus on:
- Strengthening Enforcement:Establishing a National Child Labour Enforcement Grid integrating labour inspectors, district magistrates, Juvenile Justice Boards, NGOs, and Child Welfare Committees to ensure coordinated action.
- Closing Legal Gaps:Revisiting the “family enterprise” exemption and mandating compulsory reporting and rehabilitation of child labourers under the Juvenile Justice Act.
- Improving Data Systems:Fast-tracking the 2021 Census and including child labour modules in PLFS and NFHS, leveraging technology like geo-tagging and mobile apps for real-time monitoring.
- Linking Education and Welfare:Strengthening schemes like Samagra Shiksha, PM POSHAN, and Anganwadi services, alongside conditional cash transfers to incentivize withdrawal of children from labour.
- Raising Awareness:Scaling up mass communication campaigns to change societal attitudes toward child labour.
Conclusion
While India’s legal framework against child labour is among the strongest globally, enforcement weaknesses and socio-economic realities hinder progress. Addressing poverty, improving governance, and ensuring children’s right to education and protection are imperative to break the cycle of child labour and promote a just and equitable society.
16th Finance Commission

- 06 May 2025
In News:
The 16th Finance Commission (FC), constituted under Article 280 of the Constitution in December 2023, and chaired by Arvind Panagariya, faces a formidable task: redefining the contours of fiscal federalism for the period 2026–2031 amidst growing demands for fiscal autonomy by states and mounting fiscal pressures on the Union government.
The central concern is the shrinking divisible tax pool. Though the 15th Finance Commission recommended a 41% share of the divisible pool for states (reduced from 42% due to the reorganization of Jammu & Kashmir), the effective share received by states has hovered around 32%, owing to the increasing use of cesses and surcharges, which are not shared. According to RBI data, the divisible pool has shrunk from 88.6% in 2011–12 to 78.9% in 2021–22 of the Centre’s gross tax revenue. Consequently, many states are demanding that their share be increased to 50%, and a cap be placed on cesses and surcharges.
However, expanding transfers is fiscally challenging. The Union government is already borrowing to fund grants to states, raising concerns over sustainability and fiscal priorities. States account for nearly 60% of general government expenditure, and their argument for greater fiscal autonomy is not unfounded. A possible resolution lies not in increasing total transfers, but in restructuring the composition—shifting from tied to untied transfers.
The overreliance on Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS), which dictate how funds must be spent, has constrained state-level innovation and discretion. Rationalizing CSS and expanding untied transfers would empower states to prioritize their unique developmental needs. However, this is politically sensitive, as CSS often serve national priorities and electoral interests.
Yet, more untied funds come with trade-offs. Several states, including Karnataka and Punjab, are grappling with rising revenue deficits, indicating growing expenditure on salaries, interest payments, and subsidies rather than capital investment. This raises the risk that untied funds may be diverted to populist schemes, such as non-merit subsidies or quasi-universal cash transfers. A report by Axis Bank notes that 14 states have launched income transfer schemes, amounting to 0.6% of GDP, raising concerns about the long-term fiscal discipline.
A key question is whether increased untied transfers will improve inter-state equity in public service delivery. Low-income states like Bihar have far lower per capita spending on health, education, and infrastructure. Without accountability frameworks, there is a risk that increased autonomy may not translate into equitable development outcomes.
Moreover, the third tier of governance—local bodies—remains underfunded. Greater untied transfers could incentivize states to empower panchayats and municipalities, aligning with the principle of subsidiarity and deepening democratic decentralization.
Conclusion
The 16th Finance Commission must strike a delicate balance—ensuring fiscal autonomy for states without jeopardizing national fiscal stability. It must consider capping non-divisible levies, reforming transfer mechanisms, and introducing performance-linked incentives to strengthen accountability. Only a recalibrated, transparent, and equitable devolution framework can advance India’s cooperative federalism in both spirit and practice.
Caste Data in India: The SECC 2011 and the Road Ahead

- 05 May 2025
Context:
India has not released detailed caste-based population data since the 1931 Census, leaving a significant void in understanding the country’s socio-economic and caste demographics. The Socio Economic and Caste Census (SECC) 2011 attempted to fill this gap, but while socio-economic data was released in 2016, caste-wise data—except for total Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs)—was withheld.
Historically, the 1941 Census did collect caste data, but findings were not released due to World War II. Post-independence, Indian Censuses have only collected data on SCs and STs, without disaggregating by specific caste or including Other Backward Classes (OBCs). As a result, the 1931 Census remains the last comprehensive source of caste-wise demographic data, and now serves as the baseline for any future caste enumeration, including the pandemic-delayed Census 2021.
SECC 2011: Objectives and Scope
Launched by the Ministry of Rural Development on June 29, 2011, SECC was a comprehensive door-to-door survey aimed at assessing the socio-economic status of rural and urban households across the country. Conducted in approximately 24 lakh enumeration blocks, each covering about 125 households, the SECC aimed to support evidence-based policy formulation and targeted implementation of welfare schemes. While the socio-economic part of the SECC was managed by the Rural Development Ministry, the caste data was overseen by the Ministry of Home Affairs under the Registrar General of India (RGI).
Unlike Census 2011, which is legally bound to maintain confidentiality under the Census Act, SECC data is accessible to government departments for the identification of scheme beneficiaries.
SECC vs Census 2011: Key Differences
While both exercises shared some common demographic questions—such as age, gender, literacy, and marital status—the SECC collected more granular data. For example:
- Caste and Tribe Details: Census 2011 asked only whether a respondent belonged to SC or ST. SECC 2011 went further, asking for the exact name of the caste/tribe under categories like SC (Code 1), ST (Code 2), Other (Code 3), or No Caste/Tribe (Code 4).
- Religion-based Caste Restrictions: In line with a 1990 government order, SECC noted that only Hindus, Sikhs, and Buddhists can be listed as SCs, while STs can belong to any religion.
- Economic and Health Indicators: SECC asked about household assets (mobile phones, refrigerators, vehicles), housing conditions, source of lighting, water access, latrine availability, and kitchen facilities. It also collected details on disabilities (mental and physical) and chronic illnesses like TB and leprosy.
- Employment Data: SECC captured diverse income sources in both urban (e.g., rag-picking, street vending) and rural areas (e.g., cultivation, casual labour, manual scavenging). It also recorded landholding patterns and mechanisation levels in agriculture.
Conclusion
The absence of updated, disaggregated caste data has hindered the effective formulation of policies aimed at social justice and economic equity. The SECC 2011 highlighted the possibilities of comprehensive caste enumeration but fell short in data disclosure. The upcoming Census 2021, if it includes detailed caste data, could significantly reshape India’s welfare landscape by ensuring more targeted and inclusive governance through data-driven policymaking.
Myanmar-Thailand Earthquake 2025
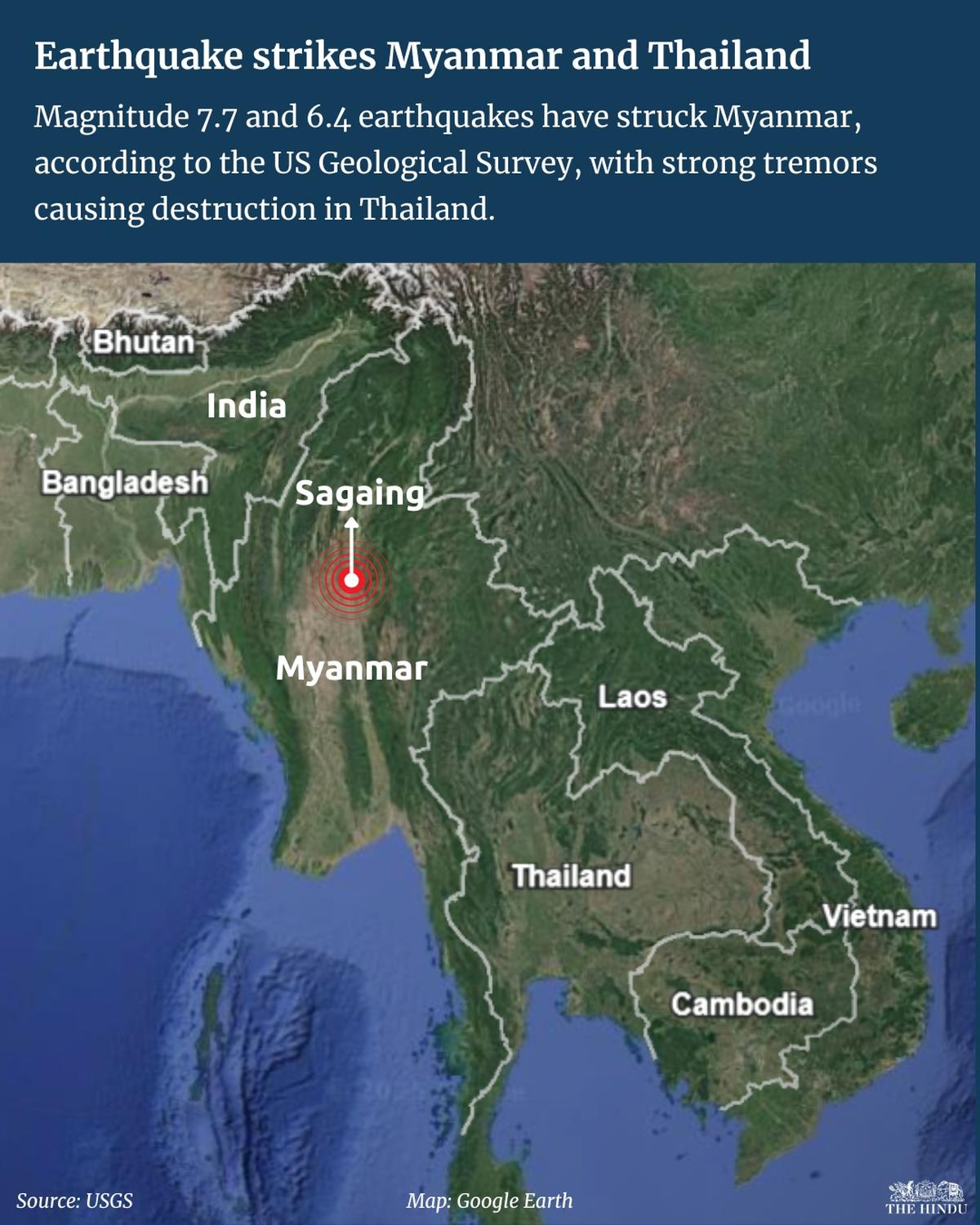
- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, a devastating 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck central Myanmar near Mandalay, resulting in catastrophic destruction across Myanmar and Thailand. The tremor, the strongest in the region in 75 years and globally the most powerful in two years, occurred at a shallow depth of 10 km, amplifying its destructive impact.
Human and Structural Impact
In Myanmar, at least 144 people were killed and 730 injured, while in Thailand, particularly Bangkok, eight deaths were confirmed, including three from a 33-storey building collapse. The death toll is expected to rise as search and rescue operations continue. Infrastructure damage was widespread—residential buildings, pagodas, a dam, and a 90-year-old bridge in Myanmar collapsed. In Bangkok, high-rises swayed dangerously, rapid transit systems shut down, and panic gripped the city. Over 90 people were reported missing in Bangkok’s construction site collapse.
The quake severely impacted regions already suffering from ongoing humanitarian crises, particularly Myanmar, where a civil war has displaced over 3 million people, and 20 million are in need of assistance, according to the UN. Emergency services were hindered by damaged roads and downed power lines.
Geological Context and Causes
The earthquake was caused by strike-slip faulting along the Sagaing Fault, a major tectonic boundary between the Indian and Eurasian plates. This north-south fault is highly seismically active and has been responsible for several past quakes, including those in 1839 (M 8.3), 1912 (M 7.9), and 2016 (M 6.9).
Shallow-focus earthquakes like this one, occurring at just 10 km depth, tend to cause significant surface damage due to minimal energy dissipation before the seismic waves reach the surface. Additionally, seismic waves radiate along the entire fault line, affecting regions far beyond the epicenter, including China’s Yunnan and Sichuan provinces, where structural damage and injuries were also reported.
Preparedness and Vulnerabilities
Myanmar's infrastructure is ill-prepared for high-magnitude earthquakes, especially in the Mandalay region where modern seismic-resistant construction is limited. The USGS estimated potential fatalities between 10,000 and 100,000, and economic losses up to 70% of Myanmar’s GDP, underscoring the country’s vulnerability. The affected area lies in the central region of the country, less accustomed to high-magnitude tremors than the traditionally more seismically active western regions.
International and Regional Response
Myanmar declared a state of emergency in six regions, including Naypyidaw and Mandalay. Thailand’s city hall declared Bangkok a disaster zone to mobilize emergency responses. Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi offered immediate support, stating that Indian authorities and the Ministry of External Affairs are in touch with both governments. The disaster also holds diplomatic relevance, with Bangkok set to host the BIMSTEC Summit, highlighting the importance of regional disaster cooperation.
Conclusion
The 2025 Myanmar-Thailand earthquake exposes the urgent need for seismic resilience, urban preparedness, and regional disaster response cooperation in South and Southeast Asia. With climate change and tectonic vulnerabilities intersecting, India and neighboring nations must integrate robust disaster management frameworks into developmental planning and regional diplomacy.
Judges’ Asset Disclosure in India

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
The recent recovery of large sums of cash from the residence of Delhi High Court judge Justice Yashwant Varma has reignited the debate over transparency and accountability in India’s higher judiciary. This incident underscores the pressing need for a legal framework mandating the public disclosure of assets by judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts—currently one of the few segments of public office bearers exempt from such transparency norms.
Current Norms and Judicial Practice
In 1997, the Supreme Court under then Chief Justice J.S. Verma adopted a resolution requiring judges to declare their assets (including those of spouses and dependents) to the Chief Justice. However, this was an internal exercise, with no provision for public disclosure.
In 2009, responding to public pressure and a Right to Information (RTI) application, the Supreme Court resolved to allow voluntary disclosures on its website. While asset declarations were briefly published starting November 2009, the practice faded. Since 2018, the SC website has not been updated, and declarations by current or former judges are no longer publicly available.
In a landmark judgment in 2019, the Supreme Court ruled that judges' assets and liabilities are not “personal information” and hence fall within the scope of RTI. Despite this, judicial compliance with voluntary disclosures remains minimal.
High Court Practices and Resistance
As of March 1, 2024, only 97 of the 770 sitting High Court judges (less than 13%) across seven High Courts (Delhi, Punjab & Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Madras, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, and Karnataka) have publicly declared their assets. Many High Courts have outright rejected RTI applications or passed resolutions opposing the idea of asset disclosure. For example, in 2012, the Uttarakhand High Court strongly objected to bringing judges’ assets under RTI. The Allahabad High Court, and several others including Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Bombay, have also denied such information under RTI citing exemptions.
Comparison with Other Public Servants
In stark contrast, civil servants, ministers, and elected representatives in India are bound by law or convention to publicly disclose their assets:
- Civil Servants: Must annually declare assets to their cadre-controlling authority; many states such as Gujarat and Kerala make this information accessible via RTI.
- Union Ministers and MPs: Since 2009, ministers submit asset declarations to the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO), which are available on its website. MPs submit declarations to the Speaker or Chairperson, which can be accessed through RTI.
- Election Candidates: A 2002 Supreme Court judgment mandates detailed public asset disclosure as part of the nomination process. Even minor errors can disqualify a candidate.
Legislative Recommendations and the Way Forward
Recognizing the gap, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice recommended in 2023 that legislation be introduced to mandate asset disclosures by judges. However, no progress has been made on this front.
In a democratic setup, the judiciary must not only be impartial but also seen as such. Mandatory public asset disclosure is a vital step toward strengthening judicial accountability and restoring public trust in the institution. Balancing judicial independence with transparency is essential for good governance and ethical public administration.
India’s E-Retail Landscape

- 28 Mar 2025
Context:
India’s e-retail sector has emerged as a global frontrunner, surpassing the United States in terms of online shopper base and attaining a Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of $60 billion in 2024. Despite this milestone, the sector’s growth rate halved from historical averages of 20% to 10–12% in 2024. This deceleration is attributed primarily to macroeconomic headwinds—particularly high inflation and stagnation in real wages, which have also slowed private consumption growth from 11% (2017–19) to 8% (2022–24).
Structural Drivers and Government Support
Notwithstanding short-term sluggishness, India’s long-term e-retail outlook remains promising. Key government initiatives—such as Digital India, Make in India, Startup India, and Skill India—have laid a strong digital foundation. The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) crossed ?4 lakh crore GMV in FY24, reflecting growing public sector adoption of digital commerce.
Policy reforms have facilitated e-commerce expansion:
- 100% FDI in B2B e-commerce
- Implementation of Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules, 2020
- Strengthening digital infrastructure through 5G rollout
- The CSC-ONDC partnership aims to democratize access to digital markets in rural areas.
Key Growth Trends Shaping the Sector
The Flipkart–Bain & Company report identifies three transformative trends:
- Quick Commerce:Quick commerce now commands over two-thirds of e-grocery orders and constitutes 10% of total e-retail spending. It is projected to grow at over 40% CAGR until 2030, driven by faster deliveries, increasing product categories, and geographic expansion into Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
- Trend-First Commerce:Particularly dominant in fashion, this segment caters to consumers who prioritize latest trends and styles. Trend-first fashion alone is forecasted to grow fourfold to $8–10 billion by 2028, with more than half of the sales occurring online.
- Hyper-Value Commerce:This model emphasizes ultra-low-priced assortments aimed at lower-middle-income consumers. Its share of e-retail GMV has increased from 5% in 2021 to over 12% in 2024, gaining momentum in smaller towns and cities.
Demographic and Regional Shifts
The e-retail customer and seller base is witnessing increasing diversification:
- Since 2020, 60% of new shoppers have emerged from Tier-3 or smaller cities.
- The Northeastern states show 1.2 times higher e-retail penetration compared to the national average.
- Similarly, 60% of new sellers since 2021 are from Tier-2 or smaller towns, indicating broad-based entrepreneurial participation.
Future Outlook
E-retail is expected to reach a GMV of $170–190 billion by 2030, growing at over 18% annually. A key inflection point will be when India’s GDP per capita crosses the $3,500–4,000 threshold, historically associated with significant upticks in discretionary digital spending. By 2030, one in ten retail dollars is projected to be spent online, with high-frequency categories such as grocery, lifestyle, and general merchandise accounting for two-thirds of e-retail expenditure.
Conclusion
India’s e-retail sector reflects the dynamic interplay of technology, policy, and socio-economic shifts. While macroeconomic challenges have tempered short-term growth, strong structural fundamentals and strategic disruptions position the sector for robust expansion. The transformation of digital commerce, particularly through inclusivity and value-driven models, is not only reshaping consumer behavior but also holds significant implications for employment, urbanization, and digital governance in India’s developmental journey.
India’s Deep Tech Ecosystem & the Government’s ?20,000 Crore Funding Initiative
- 27 Mar 2025
Context:
India’s deep technology (deep tech) sector is emerging as a key driver of transformative innovation, leveraging advanced scientific breakthroughs to address complex challenges across sectors such as defence, healthcare, artificial intelligence (AI), biotechnology, aerospace, and renewable energy. Deep tech encompasses disruptive technologies including AI and machine learning, quantum computing, biotechnology, advanced materials, robotics, and aerospace systems.
Growth and Potential of India’s Deep Tech Sector
India’s deep tech ecosystem has seen rapid expansion in recent years. According to NASSCOM’s 2024 report, over 3,600 deep tech startups operate in India, with 480 new startups launched in 2023 alone, doubling the number from the previous year. While India ranks as the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, its deep tech sector ranks sixth worldwide. This growth reflects a rising blend of entrepreneurial ambition, government support, and increasing collaboration between academic institutions, research organisations, and industry.
Government initiatives such as the Draft National DeepTech Start-up Policy, the National Quantum Mission, India AI Mission, and substantial venture capital funds (e.g., ?1,000 crore for space tech startups) underscore India’s commitment to strengthening this ecosystem. Programmes like the Atal Innovation Mission, NITI Aayog’s innovation initiatives, and Start-up India provide critical support through incubators, accelerators, and funding mechanisms.
The ?20,000 Crore Deep Tech Fund
In the Union Budget 2024-25, Finance Minister announced a ?20,000 crore allocation as a 50-year interest-free loan to private sector-driven deep tech research and innovation. The fund aims to catalyse cutting-edge R&D and position India as a global leader in disruptive technologies.
However, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Science and Technology, Environment, Forests and Climate Change has raised significant concerns about this scheme. While acknowledging the boldness of the initiative, the Committee warned of risks including potential misallocation of funds, national security implications, and low return on investment for the government. It expressed doubts over the competence of fund managers in selecting impactful projects, cautioning that private entities might benefit disproportionately at public expense.
The Committee suggested that directing such substantial funding toward government research institutions might yield more measurable impact. It emphasized the need for transparency, accountability, and a robust framework to guide the implementation of the fund.
Underutilisation of Scientific Research Funds and Reviving Public Sector Units
The Committee also flagged suboptimal utilisation of allocated funds by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, with over half of the budget remaining unused late into the financial year. A significant portion (62%) is consumed by salaries and pensions, leaving limited funds for actual research and infrastructure development.
Further, the Committee highlighted concerns over the poor condition of two public sector undertakings under the Department of Biotechnology—BIBCOL and IVCOL. It recommended their revival to ensure affordable vaccine availability domestically and improve India’s position in the global vaccine market, especially for exports.
Policy Recommendations and Future Outlook
To unlock the full potential of deep tech innovation, the Committee and experts suggest multiple policy measures for Budget 2025 and beyond:
- Ensuring long-term, patient capital through government grants and venture capital funds to meet the high risk and capital-intensive nature of deep tech ventures.
- Strengthening intellectual property rights and establishing commercialisation hubs for startups.
- Enhancing public-private partnerships and specialised talent development through tailored skilling and certifications in AI, robotics, and quantum computing.
- Modernising infrastructure by establishing research hubs, technology parks, and national facilities such as wind tunnels.
- Streamlining regulatory frameworks for faster deployment of emerging technologies like autonomous vehicles and drones.
- Promoting sustainability by incentivising green and climate tech innovations.
Conclusion:
India’s deep tech sector is poised for a transformative leap, but its success hinges on addressing governance, funding utilisation, and ecosystem-building challenges. The government’s strategic interventions and sound policy frameworks will be crucial in translating India’s scientific prowess into global technological leadership.
Tracking Migration in India
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
The Covid-19 pandemic significantly altered migration patterns in India, with a massive reverse migration from urban areas to rural regions. The first lockdown saw 44.13 million people migrating, followed by 26.3 million during the second lockdown. These migrants, mostly low-wage workers, faced hardships like wage theft, food insecurity, and a lack of healthcare. Many, reliant on remittances, were economically strained.
Rebound of Rural-to-Urban Migration
Five years post-pandemic, migration trends have largely reverted to pre-Covid patterns. The rural economy struggled to accommodate returning migrants, offering limited job opportunities and low wages, leading many to return to urban centers. Rural distress and urban aspirations, supported by schemes like the Smart Cities Mission, continue to drive migration. Projections suggest that by 2026, 40% of India’s population will reside in urban areas. Additionally, climate change is intensifying migration, especially in agrarian states like Odisha, where disrupted agriculture forces people to migrate.
Shifts in International Migration
International migration also experienced changes post-Covid. While Indian emigrants faced challenges like job losses and poor living conditions abroad, remittances remained resilient, reaching $83.15 billion in 2020. Migration patterns shifted, with increasing numbers moving to Europe, particularly skilled professionals benefiting from the EU Blue Card program. Migration to Africa has also risen, driven by growth in sectors like IT and healthcare. The pandemic also fueled a rise in student migration, with the number of student emigrants from Kerala nearly doubling from 1.29 lakh in 2018 to 2.5 lakh in 2023.
Governance Challenges in Migration
Despite changes in migration patterns, several governance challenges persist. The lack of up-to-date migration data, compounded by delays in the 2021 Census and outdated figures from the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), hampers effective policy-making. The Ministry of External Affairs' data underrepresents seasonal and temporary migrants, while illegal migration remains largely untracked.
Moreover, social security schemes remain inadequately implemented. The e-Shram portal, designed for unorganised workers, faces limited uptake due to digital exclusion and awareness gaps. Similarly, the One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC) scheme only covers part of the migrant population. Legal protections for migrant workers, like those under the Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, 1979, remain weak, and the implementation of new Labour Codes introduced in 2020 is still incomplete.
Vulnerabilities and Gaps in Support
Certain vulnerable groups, such as migrant women and children, are often neglected in migration policies. Women face risks of trafficking and exploitation, while children suffer from disrupted education and inadequate healthcare. Climate-induced migration, resulting from floods and droughts, is also under-addressed in disaster management and climate adaptation policies, leaving communities unsupported during distress-induced mobility.
Recommendations for Strengthening Migration Governance
To address these challenges, India must strengthen migration governance:
- Robust Migration Data Systems: Expand Kerala’s migration surveys to other states for better national data systems.
- National Migration Policy: Expedite the NITI Aayog’s draft policy to ensure inter-ministerial coordination and gender-sensitive provisions.
- International Migration Frameworks: Enhance labour mobility agreements with emerging destinations like Europe and Africa, along with skill-building initiatives.
- Improved Social Security Access: Implement the Code on Social Security, 2020, and ensure portability of benefits across states.
- One-Stop Migrant Facilitation Centers: Establish urban centers to assist migrants with registration, legal aid, and grievance redressal.
- Address Vulnerable Groups: Develop policies protecting migrant women and children, ensuring education and healthcare access.
- Climate-Induced Migration: Integrate climate migration in national policies for adequate community support.
Conclusion
Migration in India has largely returned to urban centers, but governance remains a challenge. Strengthening migration data, enhancing social security systems, and improving coordination at all levels of government will ensure that migration serves as a tool for development and the welfare of millions of migrants across India.
India–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Negotiations
- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
India and New Zealand have officially resumed negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) after a prolonged hiatus since 2015. This strategic move aims to enhance bilateral trade, deepen economic interdependence, and strengthen regional cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
Background and Significance
The FTA talks, first initiated in 2010, were stalled due to differences, particularly over India’s high tariffs on New Zealand’s dairy and agricultural exports. The revival of discussions during New Zealand Prime Minister Christopher Luxon's official visit to India in 2025 signals a renewed commitment towards building a balanced, ambitious, and mutually beneficial trade framework.
The bilateral trade relationship, though modest, has shown robust growth. In 2023–24, India exported goods worth $538 million to New Zealand and imported $335 million, generating a trade surplus of $203 million. By December 2024, exports rose by 21.49%, and imports surged by 78.72%, narrowing the trade surplus to $33 million.
Key Objectives of the India–New Zealand FTA
- Enhance supply chain integration.
- Improve market access for goods, services, and investments.
- Strengthen economic resilience and bilateral commercial ties.
- Facilitate trade through the Authorized Economic Operators Mutual Recognition Arrangement (AEO-MRA).
India’s major exports to New Zealand include pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, and precious stones, while imports largely consist of wool, aluminum, fruits, and steel products.
Strategic and Geopolitical Dimensions
Beyond economics, the agreement holds strategic significance:
- A defense cooperation MoU was signed to institutionalize military engagements and promote maritime collaboration.
- New Zealand expressed intent to join India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Both nations pledged support for a free, open, inclusive Indo-Pacific, aligning with the UNCLOS-based rules-based international order.
- New Zealand reiterated support for India’s permanent membership in the reformed UNSC and entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
Sectoral Cooperation and Emerging Areas
- Climate Change and Sustainability:
- New Zealand joined India-led initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Both countries committed to joint action under the Paris Agreement and Sendai Framework.
- Education and Skill Development:
- A renewed Education Cooperation Arrangement was signed to boost academic partnerships, student mobility, and vocational training.
- Plans are underway to commemorate 100 years of sports relations in 2026, coupled with a new MoU on sports cooperation.
- Diaspora and People-to-People Ties:
- The Indian diaspora forms 6% of New Zealand’s population, playing a pivotal role in cultural and economic relations.
- India raised concerns regarding pro-Khalistan activities, and New Zealand assured cooperation in addressing such issues.
Opportunities and Complementarities
India’s Strategic Importance to New Zealand:
- Large market with a growing middle class and rising demand for dairy, meat, and high-value agricultural exports.
- Largest source of skilled migrants and second-largest source of international students.
- Booming digital economy offers collaboration potential in fintech, AI, and digital services.
New Zealand’s Relevance to India:
- Expertise in sustainable farming and dairy technology supports India’s agricultural reforms.
- Recognized climate tech sector aligns with India’s clean energy transition.
- Potential buyer of India’s defense equipment and surveillance systems, enhancing maritime security amid Indo-Pacific tensions.
Challenges in Bilateral Relations
- Stalled FTA negotiations due to tariff sensitivities, particularly in the dairy sector.
- Non-tariff barriers (NTBs) affecting Indian exports like fruits and vegetables.
- Low trade volumes and limited awareness of New Zealand’s economic strengths among Indian businesses.
- Divergences in geopolitical alignments, with New Zealand’s reliance on China creating potential strategic friction.
Way Forward
- Conclude FTA negotiations through dialogue and sectoral agreements in pharmaceuticals, technology, and horticulture.
- Consider an interim Early Harvest Agreement, akin to India–Australia ECTA, to fast-track gains.
- Enhance market access by reducing NTBs, fast-tracking Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MRAs), and organizing trade expos and B2B interactions.
- Leverage climate and renewable energy cooperation, strengthen defense collaboration, and institutionalize maritime security mechanisms.
Conclusion
The renewed India–New Zealand FTA negotiations mark a pivotal step in recalibrating bilateral economic and strategic relations. Anchored in democratic values and shared Indo-Pacific interests, the partnership is poised to evolve into a multi-dimensional engagement encompassing trade, technology, climate resilience, and defense cooperation. The agreement, if concluded, could serve as a model for equitable North–South economic partnerships in a multipolar world order.
Battling India’s Infodemic

- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
India, with over 95.04 crore internet users, faces a growing crisis of misinformation and disinformation. The spread of fake news has surged, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, where misinformation increased by 214%, making India responsible for one in six pieces of global fake news related to the pandemic. This infodemic is fueled by unregulated social media platforms, AI-driven disinformation, and weak legal frameworks. As digital platforms become the primary source of news, addressing the spread of fake news is critical for maintaining public trust and democratic integrity.
Factors Driving the Infodemic
1. Unregulated Social Media: Platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook, and YouTube are major conduits for misinformation. The viral nature of content on these platforms often leads to false information reaching millions before fact-checking can occur. For instance, during the COVID-19 crisis, false cures and misleading health information spread rapidly on WhatsApp, creating public panic.
2. AI and Deepfakes: AI-powered tools have enabled the creation of deepfake content, including videos, audio, and images that mimic real people. During the 2024 Lok Sabha elections, deepfakes reinforced political biases, influencing voter sentiment. Similarly, AI-generated propaganda has played a role in amplifying social divides, as seen in global elections.
3. Political Manipulation: Fake news has become a political weapon, particularly during election cycles. In India’s 2024 elections, AI-generated speeches and content contributed to voter polarization. The use of algorithmic echo chambers exacerbates this by curating content that reinforces biases, thereby fostering ideological divides.
4. Weak Legal and Fact-Checking Mechanisms: India lacks a comprehensive legal framework to counter fake news. Existing laws, such as the Information Technology Act, 2000 and the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, address certain aspects of disinformation but fail to tackle the broader, evolving issue. The Election Commission of India (ECI) is under-resourced to handle the volume of misinformation during elections, further complicating efforts.
Challenges in Countering the Infodemic
1. Legal Gaps: Current laws are insufficient to address the modern challenges posed by fake news, particularly with the rise of AI-generated content. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP), 2023, while a step forward, faces implementation challenges, and ad hoc measures like internet shutdowns only offer temporary solutions.
2. Sluggish Response by Tech Platforms: Social media giants like Meta, X, and YouTube have been criticized for their slow response in removing fake news. For instance, X’s "Community Notes" program has struggled to counter misinformation in real-time, allowing malicious actors to exploit the system before action is taken.
3. Lack of Awareness and Digital Literacy: Many users in India struggle to distinguish between credible and fake news, especially in rural areas where digital literacy is limited. This lack of awareness has led to tragic consequences, such as mob lynchings triggered by fake news spread on platforms like WhatsApp.
International Models and the Way Forward
1. Strong Legal Framework: Countries like Singapore and Germany have enacted robust laws to combat fake news. Singapore’s Protection from Online Falsehoods and Manipulation Act imposes severe penalties for spreading deliberate misinformation. Similarly, Germany’s NetzDG Law mandates that social media platforms remove fake news within 24 hours or face heavy fines. India could draw lessons from these models, ensuring any new law balances freedom of speech with the need to curb harmful misinformation.
2. AI Regulation and Transparency: India must enforce strict regulations on AI-generated content, including mandatory labeling of deepfakes and AI-driven media. The EU's AI Act and Finland's digital literacy initiatives provide useful frameworks for promoting transparency and user awareness.
3. Strengthening the Election Commission: The ECI needs enhanced resources and clear guidelines for countering misinformation, particularly during elections. Collaborating with fact-checkers and media outlets can improve response times and effectiveness.
4. Digital Literacy Campaigns: A nationwide initiative, similar to Finland’s digital literacy program, is essential to educate the public on identifying fake news. Empowering citizens with the tools to critically evaluate information will reduce the spread and impact of misinformation.
Conclusion
India’s battle against fake news requires urgent legal intervention, especially as deepfakes and AI-driven misinformation continue to evolve. A comprehensive framework—one that protects free speech while holding platforms accountable for the spread of disinformation—is essential to preserve the integrity of democratic processes. The introduction of strict regulations, coupled with initiatives to boost digital literacy, will help safeguard public trust and social harmony in the digital age.
UN Women’s Report 2025

- 12 Mar 2025
Context:
Marking the 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995)—a landmark global framework for achieving gender equality—the UN Women’s Report 2025 presents a sobering assessment of the status of women’s rights worldwide. Released ahead of International Women’s Day 2025, the report reflects a disturbing pattern: while there has been measurable progress, recent years have witnessed an alarming backlash against gender equality in many parts of the world.
Key Findings
- Backsliding of Women’s Rights: Nearly one in four countries reported a backlash against women’s rights, often linked to democratic erosion and rise of authoritarian or conservative forces. The report warns of "anti-rights actors" systematically working to undermine legal and policy gains made over decades.
- Escalation in Gender-Based Violence
The world continues to grapple with high levels of violence against women:
-
- A woman or girl is killed every 10 minutes by an intimate partner or family member.
- Conflict-related sexual violence has risen 50% since 2022, with 95% of victims being women and girls.
These trends point to both persistent patriarchal norms and the failure of protective systems, especially in conflict and humanitarian settings.
- Legal and Political Disempowerment
Despite notable legislative progress:
- Women globally have only 64% of the legal rights enjoyed by men.
- Only 87 countries have ever had a female head of state.
- Women occupy just 26% of parliamentary seats, even though this figure has doubled since 1995.
These gaps reflect the structural barriers and gender biases embedded in political systems and governance.
- Economic and Health Inequities
- 10% of women and girls live in extreme poverty.
- Young women (ages 15–24) face limited access to family planning, impacting health and autonomy.
- Maternal mortality has remained stagnant since 2015, reflecting uneven healthcare access.
Positive Developments
Despite the challenges, there are signs of progress:
- 88% of countries now have laws against violence towards women.
- Most countries have banned workplace discrimination.
- 44% of countries are working to improve education and training for women.
- Female legislative representation has more than doubled since 1995.
UN Women’s Roadmap for Gender Equality (2030)
To address setbacks and accelerate progress, the report outlines a five-pronged strategy:
- Digital Inclusion – Ensure equitable access to digital technologies.
- Social Protection – Invest in universal healthcare, education, and safety nets.
- Zero Gender-Based Violence – Strengthen laws, services, and public awareness.
- Equal Decision-Making – Promote women's leadership in all sectors.
- Gender-Sensitive Crisis Response – Integrate gender priorities in humanitarian aid.
Conclusion
The UN Women’s Report 2025 underscores a critical paradox: legal and policy advancements coexist with deep-rooted inequalities and growing resistance to gender justice. As UN Secretary-General António Guterres aptly noted, “Instead of mainstreaming equal rights, we’re seeing the mainstreaming of misogyny.” Achieving SDG 5 (Gender Equality) by 2030 demands sustained political will, democratic resilience, and transformative reforms. For India and the global community, this is both a warning and an opportunity—to reaffirm their commitment to gender justice and inclusive development.
USAID Funding in India

- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has been a major development partner for India, contributing over $2.8 billion in Official Development Assistance (ODA) since 2001. While initial assistance focused on food aid, recent decades saw a shift toward public health, environmental sustainability, digital infrastructure, and institutional capacity building.
Between 2022 and 2024, India received substantial aid from USAID — $228 million in 2022, $175 million in 2023, and $151 million in 2024 (as of December). A significant portion of this funding targeted health and population programs, including polio eradication, maternal and child health, tuberculosis (TB), HIV/AIDS, and Covid-19 response.
In 2022 alone, $120 million was allocated to Covid-19 control, alongside support for healthcare infrastructure and awareness campaigns.
USAID also supported India’s environmental goals, providing funds for air pollution control, clean water initiatives, and climate resilience, with $17.12 million allocated in 2024. Additionally, USAID backed India's technological advancement by exploring secure 5G Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) systems, aligning with the U.S. Indo-Pacific strategy aimed at countering China’s influence.
However, the January 20, 2025 Executive Order by the U.S. administration directed a halt to foreign aid and restructuring of USAID. Although initially stayed by a U.S. Federal Court in February, the Supreme Court’s March 5 verdict upheld the aid cuts, jeopardizing thousands of ongoing development projects globally, including in India.
This decision critically affects India’s public health landscape. For instance, the ‘Breaking the Barriers’ TB awareness program in Karnataka, Bihar, Telangana, and Assam — funded with $7 million between 2022–23 — is being discontinued. The President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), another major source of HIV/AIDS support, also faces disruption, risking higher infection and mortality rates. The cuts particularly threaten NGOs like Karnataka Health Promotion Trust (KHPT), which relied on USAID for operational continuity.
Beyond health, the withdrawal of USAID support may create a strategic vacuum in South Asia, enabling greater Chinese geopolitical and economic influence. Legal uncertainty around development aid has also raised concerns about the stability of global health and environmental partnerships.
Way Forward for India
- Diversify donor engagement: India must strengthen development ties with consistent partners like Japan ($2.97B in 2022), the EU ($383.5M), and Germany ($235M).
- Increase domestic investments in public health, sanitation, and clean energy to reduce dependence on external aid.
- Boost private sector and philanthropic partnerships to ensure continuity of key health and environmental programs.
- Strengthen indigenous R&D capacity, especially in digital infrastructure and vaccine development.
- Diplomatic dialogue with U.S. policymakers can explore possibilities for reinstating targeted support.
Conclusion
The scaling back of USAID poses significant challenges to India's public health, environmental sustainability, and strategic autonomy. However, it also presents an opportunity for India to reinforce its developmental sovereignty through diversified funding, innovation, and international cooperation.
Over-Centralisation and Federal Health Governance in India

- 10 Mar 2025
Introduction
India’s health governance follows a quasi-federal structure where health is constitutionally a State subject. However, increasing centralisation, particularly in medical education and national health schemes, is raising concerns over States’ autonomy and the effectiveness of federal health policies.
Judicial Push Towards Centralisation
The recent Supreme Court ruling in Dr. Tanvi Behl vs Shrey Goyal (2025) declared domicile-based reservations in post-graduate (PG) medical admissions unconstitutional, citing Article 14 and the principle of meritocracy. This decision, however, overlooks the critical link between State investments in medical education and their ability to retain specialists within local health systems. Domicile quotas served as a strategic tool to ensure a stable, locally adapted healthcare workforce, especially amid chronic specialist shortages.
Striking down such quotas may discourage States from investing in medical institutions if their graduates are siphoned off to other regions. Unlike central institutions like AIIMS or PGIMER, which enjoy selection autonomy, State medical colleges now face limited control over admissions, weakening their role as pillars of regional health systems.
Centralisation Through Policy and Institutions
Beyond judiciary-led centralisation, several national initiatives have expanded the Centre's role:
- National Health Mission (NHM): While implemented by States, funding and guidelines remain Centre-dominated.
- Ayushman Bharat (2018) and AB Digital Mission: These schemes shifted healthcare financing and data control towards the Centre, reducing the relevance of State-run insurance programs.
- National Medical Commission Act (2019): Replacing the MCI, this law enhanced the Centre's control over medical education regulation.
- Epidemic and Disaster Management Acts: Empower the Centre during health emergencies, as witnessed during COVID-19.
Consequences of Over-Centralisation
Excessive centralisation undermines India’s diverse health needs and local governance:
- Limited Responsiveness to Local Needs: Uniform policies ignore State-specific demographics. For instance, Kerala requires elderly care, while Bihar and UP demand maternal and child health focus.
- Reduced Decision-Making Power: States lose flexibility in tailoring central schemes, as seen with Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY.
- Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Delays in fund disbursal under centrally sponsored schemes hinder timely execution.
- Weakening of Local Health Systems: Panchayats and municipal bodies—crucial to grassroots delivery—are often bypassed in favour of top-down mechanisms.
Meritocracy vs Social Equity
The rigid focus on merit in PG admissions disregards structural inequalities. As seen in recent NEET-PG cutoffs being lowered to zero percentile to fill seats, the current meritocratic model is flawed. Regional representation and public service outcomes should be considered in defining ‘merit’, aligning medical education with societal needs.
Way Forward
- Restore State Autonomy in Admissions: States should be empowered to design admissions aligned with local healthcare priorities.
- Fiscal and Functional Decentralisation: Grant flexibility in using central funds and reduce bureaucratic controls.
- Strengthen Cooperative Federalism: Institutionalise Centre-State coordination in health planning and policy-making.
- Invest in Local Systems: Enhance capacities of State health departments and grassroots governance bodies.
Conclusion
While central guidance is essential for national health objectives, excessive centralisation risks weakening India’s federal health architecture. A balanced approach rooted in cooperative federalism is vital to create an inclusive, efficient, and resilient healthcare system for all.
AI and the Justice System: A Tool for Reform in India

- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping governance globally, with nations like the United States and China making significant investments in AI-led legal and policing reforms. The U.S. government’s $100 billion Stargate AI Initiative and China’s development of cost-effective large language models (LLMs) like QWQ and DeepSeek highlight the competitive race for technological dominance. For India, grappling with over 50 million pending cases, AI offers a transformative opportunity to enhance efficiency, transparency, and trust in its criminal justice system.
AI in Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention
India’s SMART policing initiative—Strategic, Meticulous, Adaptable, Reliable, Transparent—can be significantly enhanced through AI integration. AI tools such as Automated FIR registration (e.g., Mumbai Police’s AI-assisted e-FIR system) reduce administrative burdens and accelerate complaint processing. Predictive policing, using crime mapping and data analysis like that piloted by Delhi Police, helps identify crime hotspots. AI-enabled facial recognition systems, like the Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS) of NCRB, assist in criminal identification.
Cybersecurity also benefits from AI. Organizations like CERT-In deploy AI to counter phishing, ransomware, and deepfake threats. Banks and law enforcement utilize AI-based fraud detection systems, such as those powered by RBI’s CRILC, to flag suspicious transactions. AI tools are increasingly used to detect deepfakes and synthetic media, enhancing digital forensics.
Moreover, AI can assist in real-time crime analysis. Field-level policing data—such as offender patterns and patrol routes—can feed AI models to guide proactive interventions. Supervisory efficiency improves through AI-powered collation and analysis of data at the district level, allowing redeployment of personnel from administrative roles to core policing duties.
AI in the Judicial System
In courts, AI supports the e-Courts Project by digitizing case files, reducing delays in documentation and improving record management. Tools like SUPACE (Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court Efficiency) assist judges in legal research, precedent identification, and judgment writing. AI-driven real-time transcription systems, being piloted in the U.S., can improve transparency and reduce dependence on manual record-keeping.
AI also plays a role in bail and sentencing decisions. For instance, the Delhi High Court is exploring AI-based risk assessment tools to promote consistency. Additionally, AI tools can detect anomalies in legal documents, preventing delays due to forged or inaccurate filings.
Challenges and the Way Forward
The integration of AI into justice faces several challenges. AI models trained on biased data, as seen in the U.S. tool COMPAS, can perpetuate systemic inequities. Privacy concerns are also paramount and must align with India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023. Implementation gaps include the lack of AI literacy among legal and police personnel and the absence of a comprehensive regulatory framework, as highlighted by the B.N. Srikrishna Committee.
To overcome these, India must establish a central AI Justice Task Force, expand AI usage in high courts, formulate ethical AI standards aligned with NITI Aayog’s AI strategy, and invest in AI training programs for judicial and law enforcement staff.
Conclusion
AI offers a critical path to revitalizing India’s overstretched justice system. If implemented responsibly, it can streamline policing, reduce judicial delays, and enhance public trust. A technology-first approach, combined with ethical safeguards, will be key to ensuring that justice in India becomes not only swift but also fair and inclusive.
India’s Textile Industry

- 08 Mar 2025
Context:
India’s textile and apparel industry is one of the largest globally, contributing significantly to the economy through employment, exports, and industrial output. It accounts for 2.3% of India’s GDP (projected to rise to 5% by 2030), 13% of industrial production, and 12% of total exports. Employing over 4.5 crore people, it is second only to agriculture in job creation. Yet, despite its scale, India lags behind competitors like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh in global exports.
Current Status and Strengths
India is the world’s second-largest producer of cotton and man-made fibres (MMFs) such as polyester and viscose. Cotton alone engages over 60 lakh farmers, mainly in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Telangana. The country is also a global leader in jute and technical textiles. The textile and apparel market is projected to reach USD 350 billion by 2030.
FY24 exports stood at USD 35.9 billion, a marginal increase from USD 33.4 billion in FY20. Key destinations include the US, EU, and UAE. Yet, apparel exports have declined from USD 15.5 billion in FY20 to USD 14.5 billion in FY24. While cotton textile exports rose to USD 12.3 billion, growth has remained modest.
Challenges Holding Back the Sector
- Fragmented Supply Chains: India’s textile value chain is highly fragmented, concentrated in MSME clusters with regional specializations (e.g., Tiruppur for knitwear, Surat for polyester). This hampers integration and increases logistics costs. In contrast, competitors operate vertically integrated “fibre-to-fashion” hubs.
- High Raw Material Costs: Quality Control Orders (QCOs) on polyester and viscose restrict cheaper imports. As a result, domestic fibres are significantly costlier—polyester by 33–36% and viscose by 14–16% compared to China.
- Lack of FTAs: Unlike Vietnam and Bangladesh, India lacks preferential trade agreements with major markets like the EU and the US. This undermines price competitiveness and limits market access.
- Regulatory Burden: Complex customs and compliance procedures increase operational costs, particularly for small exporters. In contrast, simplified systems in competing nations reduce red tape.
- Sustainability Pressures: Global markets now demand higher environmental compliance—renewable energy use, water recycling, and traceability. EU regulations (2021–2024) affect 20% of India’s textile exports. MSMEs find it difficult to adapt without financial support.
- Low Per Capita Fibre Consumption: Despite being a major producer, India’s fibre consumption is just 5.5 kg per capita—half the global average.
Way Forward
- Supply Chain Integration: Develop MITRA textile parks and “fibre-to-fashion” hubs to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Raw Material Reforms: Reassess QCOs to allow controlled imports and reduce input prices.
- Trade Policy: Secure FTAs with key markets to enhance export competitiveness.
- Labour Productivity: Set up housing near textile clusters (as in China) to improve worker efficiency and reduce attrition.
- Boost MMF Usage: Promote domestic MMF consumption through targeted incentives.
- Green Transition: Provide financial and technical support to MSMEs to adopt sustainable practices and enter the recycled textile market, projected to reach USD 400 million in India.
With structural reforms and global alignment, India’s textile industry holds immense potential to emerge as a global leader while promoting sustainable, inclusive growth.
India-Qatar Relations
- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
India and Qatar have significantly deepened their bilateral relationship, particularly with the recent state visit of Qatar’s Amir, Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al-Thani, to India. This visit marked a pivotal moment, as both countries elevated their ties to a "strategic partnership," exploring avenues for collaboration in energy, trade, and diplomacy.
Evolution of India-Qatar Relations
India's relationship with the Gulf region is multifaceted, encompassing economic, cultural, and people-to-people ties. Qatar holds a special place in India’s foreign policy due to its strategic position in the Middle East, its influence in the LNG market, and its robust ties with both Western powers and regional players such as Israel and Afghanistan. As one of the largest suppliers of LNG to India, Qatar’s energy significance is paramount.
India has consistently prioritized relations with the Gulf, with the Prime Minister placing special emphasis on strengthening ties. The recent visits by India’s External Affairs Minister to Qatar underscore the diplomatic importance of this relationship.
Key Outcomes of the Amir’s Visit
The visit of Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al-Thani resulted in several key agreements and developments:
- Strategic Partnership:India and Qatar upgraded their relationship to a "strategic partnership," signaling enhanced cooperation across various domains such as energy security, trade, and investment. This move aligns Qatar with India’s other strategic Gulf partners like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman, reinforcing regional cooperation under the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
- Economic and Trade Cooperation:The two countries committed to doubling bilateral trade from $14 billion to $28 billion over the next five years. Qatar also pledged $10 billion in new investments in India, particularly in the infrastructure, energy, and technology sectors. Several agreements on economic cooperation, youth affairs, and double taxation avoidance were also signed, aimed at facilitating business activities.
- Energy Cooperation:A landmark agreement between QatarEnergy and India’s Petronet LNG extended their LNG supply deal for 20 years, marking the largest-ever LNG agreement. This deal secures India’s long-term energy needs and diversifies its energy sources, ensuring stable pricing for LNG imports.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Possibilities:Discussions were held on a potential India-Qatar Free Trade Agreement (FTA) to boost trade relations. While Qatar has existing FTAs with countries like China, a similar agreement with India could further enhance trade and investment flows. However, India must ensure safeguards to prevent the dumping of third-party goods through Qatar.
- Resolution of Diplomatic Setback:Bilateral relations were strained in 2022 following the arrest of eight Indian Navy personnel in Qatar on espionage charges. The Amir’s decision to pardon these individuals removed a significant diplomatic roadblock, improving goodwill between the two countries.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the positive developments, challenges persist:
- Economic and Trade Barriers:Non-tariff barriers and bureaucratic hurdles remain significant obstacles to smoother business transactions. Moreover, Qatar’s investments in India are still limited compared to other Gulf nations, despite its substantial sovereign wealth fund. India must encourage greater Qatari participation in sectors like infrastructure, startups, and energy exploration.
- Political and Security Risks:The volatile security situation in the Middle East, particularly tensions between Iran and Israel, poses risks to India’s energy supply chains. Any diplomatic tensions between Qatar and its Gulf neighbors could indirectly affect India’s trade interests.
- Labor and Migration Issues:India must continue to advocate for better working conditions and legal protections for Indian workers in Qatar. Ensuring the welfare of Indian expatriates, including seamless remittance flows and social security benefits, is essential for strengthening bilateral ties.
Conclusion
The elevation of India-Qatar relations to a strategic partnership marks a new chapter in their ties, positioning Qatar as a critical partner in India’s energy security and trade. As India’s influence in the Middle East and global energy markets grows, its relationship with Qatar will play an increasingly important role in shaping the region’s geopolitical landscape. The continued focus on economic cooperation, energy security, and labor welfare will be vital to sustaining and expanding this crucial partnership.
India Philanthropy Report 2025

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
The India Philanthropy Report 2025, a joint publication by Bain & Company and Dasra, presents an insightful overview of the evolving landscape of philanthropic giving in India. With private philanthropic funding projected to grow annually by 10–12% over the next five years, the report underlines the increasing role of family philanthropy and corporate social responsibility (CSR) in complementing public sector expenditure on social development.
Growth of Social Sector Funding
India's total social sector funding reached approximately ?25 lakh crore ($300 billion) in FY24, accounting for 8.3% of the GDP. Public funding continues to dominate, constituting 95% of the total with allocations towards flagship welfare schemes like MGNREGS and the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana. Private philanthropy, however, is steadily gaining ground, contributing ?1.3 lakh crore ($16 billion) in FY24, and is expected to grow significantly by FY29.
Despite this growth, a considerable funding gap persists—estimated at ?14 lakh crore in FY24 and projected to widen to ?16 lakh crore by FY29. Bridging this deficit is critical for meeting India's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the vision of Viksit Bharat@2047.
Rise of Family Philanthropy
Family philanthropy has emerged as a key driver of private social funding, accounting for around 40% of total private contributions. It spans diverse sectors including education, healthcare, gender equity, diversity and inclusion (GEDI), climate action, and social justice. Notably, 55% of family philanthropic initiatives are women-led, and around one-third involve next-generation leadership, indicating a shift towards more inclusive and innovative giving.
Structured philanthropy is becoming more prominent, with nearly 65% of family-run initiatives now managed by professional teams. The report projects that by building robust advisory infrastructure and tapping into family offices, India can unlock an additional ?50,000–55,000 crore ($6–$7 billion) in family philanthropy over the next five years.
Corporate Social Responsibility: Compliance and Concentration
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) spending, mandated under the Companies Act, is another critical pillar. CSR expenditure is growing at a projected 10–12% per annum, driven by increased compliance and strategic integration into corporate goals. The number of CSR-compliant firms rose from 12,000 in FY22 to around 15,000 in FY23.
Family-owned businesses contribute nearly 65%–70% of total private CSR spending, with major conglomerates like Tata, Adani, Birla, and Ambani alone accounting for ?800–1,000 crore each annually. However, the sector remains top-heavy: just 2% of family-owned firms are responsible for over half of all CSR contributions.
HNIs, UHNIs, and the Philanthropic Disparity
Despite the promising trends, Indian High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNIs) and Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals (UHNIs) still contribute a relatively small fraction of their wealth towards philanthropy. Indian UHNIs donate only 0.1%–0.15% of their wealth, compared to 1.2%–2.5% in the US, 0.5%–1.8% in the UK, and 0.5%–1.4% in China.
In FY24, average annual philanthropic contributions from UHNIs (net worth ?1,000 crore and above) hovered around ?5 crore, while HNIs (?200–1,000 crore) contributed ?0.4–?5 crore. This indicates a large untapped potential that can significantly bolster India's development financing.
Institutionalization and Diaspora Potential
The number of family offices—dedicated institutions managing family wealth and philanthropy—has increased from 45 in 2018 to 300 in 2024, with projections to cross 500 by 2029. Institutions like Dasra, Sattva, and Bridgespan have been instrumental in supporting structured and high-impact philanthropy.
India’s diaspora, growing from 18 million in 2019 to 35 million in 2024, also presents a significant but underutilized opportunity. While diaspora philanthropy is estimated at $130 billion currently, better awareness, simplified compliance norms, and digital platforms could enhance its impact and push the potential closer to $200 billion.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the optimistic outlook, several challenges hinder the full realization of philanthropic potential in India:
- Persistent funding gaps in critical sectors like healthcare, education, and climate change.
- Regulatory and compliance barriers, especially affecting foreign and diaspora contributions.
- Fragmented infrastructure, with limited advisory services and high transaction costs.
- Short-term funding models, with only 23% of family philanthropies combining grants with direct program implementation, undermining sustainable impact.
To address these, the report suggests:
- Promoting long-term funding mechanisms, including multi-year grants.
- Professionalizing philanthropy through structured advisory services and capacity building.
- Unlocking diaspora contributions via simplified regulations and dedicated philanthropic platforms.
- Enhancing collaboration across stakeholders to amplify social impact and innovation.
Conclusion
The India Philanthropy Report 2025 underscores the transformative potential of private giving, particularly through family philanthropy and CSR. While public funding remains the bedrock of India’s social development agenda, strengthening the philanthropic ecosystem—by leveraging wealth, institutions, and global networks—is vital to achieving equitable growth and meeting national development goals.
Farmers’ Share in Consumer Prices for Rabi Crops

- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) conducted a comprehensive pan-India survey during May–July 2024 to assess the farmers’ share in consumer prices for 12 major rabi crops. The survey spanned mandis and villages across 86 centres in 18 states, and included detailed inputs from farmers, traders, and retailers, with over 10,699 respondents.
Key Findings:
- Farmers’ Share in Consumer Prices:
- Ranged between 40% and 67% across rabi crops.
- Wheat farmers received the highest share (67%), attributed to its status as a notified commodity under the public procurement system; about 25% of wheat farmers sold at Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- Rice farmers received 52%, a figure consistent over previous surveys (49% in 2018, 45% in 2022), indicating stability.
- In pulses, lentil (masoor) farmers earned 66%, and gram (chana) farmers earned 60% of the retail price.
- In oilseeds, mustard farmers received 52%, slightly lower than the 55% found in a 2021 study.
- Perishables vs Non-Perishables:
- Fruits and vegetables showed lower farmer share (40–63%), due to their perishability, seasonal production, and logistical challenges.
- The combined markup of traders and retailers exceeded 50% in most perishable crops (except tomatoes).
- Perishables face higher post-harvest losses, quality variation, and price volatility due to climate dependency and demand-supply fluctuations.
Supply Chain and Payments:
- The agriculture supply chain remains unorganized, especially for fruits and vegetables, with multiple intermediaries reducing transparency in pricing, logistics, and fund flows.
- Retailer markups were typically higher than those of traders. An empirical analysis showed that:
- Higher transaction costs (e.g., transport, labour) reduce retailer markups.
- High post-harvest losses in perishables allow markups to be passed on to consumers.
Digital Transactions:Though cash transactions still dominate, the adoption of electronic payments saw a significant rise in 2024 across all stakeholders compared to previous surveys in 2018 and 2022.
Policy Implications:
- A higher farmers’ share is essential to:
- Enhance farm incomes
- Incentivise crop diversification, particularly from cereals to pulses and oilseeds
- Improve transparency in the agri-supply chain
- Strengthening public procurement, digital infrastructure, and organised logistics are vital for ensuring fair price realisation by farmers.
India-EU Strategic Partnership

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
The recent visit of European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen to India, marked a significant recalibration in India-EU relations. Amid global geopolitical flux—characterized by U.S.-Europe divergences, China’s assertiveness, and disrupted supply chains—India and the EU are deepening cooperation in trade, technology, climate, and security. This partnership is crucial for regional stability and shaping a multipolar, rules-based global order.
Strategic and Economic Dimensions
- Trade and Investment:The EU is India’s largest trading partner, accounting for 12.2% of India’s total trade in 2023. Bilateral goods trade reached $135 billion (FY 2023–24), and services trade stood at $53 billion. The EU is the second-largest source of FDI into India ($117.4 billion since 2000), while Indian FDI to the EU was $40 billion. Free Trade Agreement (FTA) talks, revived in 2021, aim to resolve tariff and regulatory barriers in sectors like automobiles, dairy, pharma, and IT services.
- Technology and Digital Cooperation:The India-EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC), launched in 2022, promotes collaboration in semiconductors, AI, clean energy, and resilient supply chains. Key developments include MoUs on semiconductor R&D and high-performance computing. Challenges remain, particularly around EU data adequacy under GDPR, which affects Indian digital exporters.
- Green Transition and Energy Security:The EU-India Clean Energy and Climate Partnership focuses on renewable energy, smart grids, and sustainable cities. A €1 billion European Investment Bank fund supports green hydrogen projects. India’s participation in European Hydrogen Week 2024 signals growing collaboration in clean energy. Initiatives like SWITCH-Asia promote sustainable consumption and circular economy practices.
- Maritime and Defense Cooperation:Under the ESIWA framework, India and the EU are expanding maritime security ties. The EU has stationed a liaison officer at India’s Information Fusion Centre (Gurugram), and the first joint naval exercise in the Gulf of Guinea (2023) emphasized Indo-Pacific cooperation. However, defense ties remain limited due to India's stronger military relationships with Russia and the U.S.
Institutional and Societal Ties
India-EU relations date back to 1962 and were elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2004. The Roadmap to 2025, adopted in 2020, prioritizes digital transformation, climate action, and multilateralism. The TTC’s recent meetings reaffirm commitment to tech and trade collaboration.
People-to-people ties are strengthening. Indians received over 20% of EU Blue Cards (2023–24). Over 6,000 Indian students have benefitted from Erasmus scholarships, and 2,700 researchers from Marie Sk?odowska-Curie Actions.
Key Challenges
- Stalled FTA Talks over tariffs and market access.
- Regulatory barriers under SPS and TBT norms.
- Data governance divergence due to lack of EU data adequacy for India.
- Foreign policy misalignments, especially over Russia-Ukraine.
- Fragmented defense engagement due to EU’s limited commitment.
Way Forward
India and the EU must resolve FTA hurdles, negotiate a data-sharing framework, align Indo-Pacific strategies, and invest in alternative supply chains via IMEC. Enhanced cooperation in green tech, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure is key. India must also reform its regulatory landscape to attract EU tech and manufacturing investments.
Conclusion
India-EU ties are entering a transformative phase. Anchored in shared democratic values and strategic interests, the partnership can promote multipolarity, sustainable development, and a resilient global governance architecture.
Reducing India's Dependence on Imported Fertilisers

- 27 Feb 2025
Context
The Indian government is strategizing to cap or reduce the consumption of high-analysis fertilizers—Urea, Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP), and Muriate of Potash (MOP)—due to their heavy import dependence, rising economic burden, and adverse environmental impacts. This shift is crucial for ensuring nutrient balance, reducing foreign exchange outflows, and promoting sustainable agriculture.
India’s Dependence on Imported Fertilisers
- MOP: India is fully dependent on imports from countries like Canada, Russia, Jordan, Israel, Turkmenistan, and Belarus, as it has no mineable potash reserves.
- Urea: While over 85% of urea demand is met domestically, production relies on imported liquefied natural gas (LNG) from Qatar, the US, UAE, and Angola.
- DAP: Imported both as finished fertiliser and raw materials (rock phosphate, sulphur, phosphoric acid, ammonia) mainly from Saudi Arabia, Morocco, Jordan, China, and others.
The Need to Limit High-Analysis Fertiliser Usage
Economic Concerns
- The rupee's depreciation increases fertiliser import costs.
- India spent ?1.75 lakh crore on fertiliser subsidies in 2023-24.
- Subsidised urea is sold at rates far below cost, draining government resources and encouraging overuse.
- DAP's landed price stands at ?55,150 per tonne, with production costs exceeding ?65,000 per tonne, while the government-fixed retail price remains ?27,000 per tonne, necessitating large subsidies.
Environmental Concerns
- Excessive application of urea and DAP depletes organic carbon in soils, reduces microbial diversity, and causes groundwater contamination through nitrate leaching.
- Soil health degradation ultimately reduces crop productivity and ecological resilience.
Governance Challenges
- High subsidies encourage black marketing and non-agricultural diversion.
- Lack of strict nutrient management regulations leads to soil nutrient imbalances.
The Shift Towards Balanced Fertilisation
High-analysis fertilisers like urea (46% nitrogen), DAP (46% phosphorus + 18% nitrogen), and MOP (60% potash) often lead to over-application and inefficiency. Crops instead require a balanced supply of:
- Macronutrients (N, P, K),
- Secondary nutrients (sulphur, calcium, magnesium),
- Micronutrients (zinc, iron, copper, boron, manganese, molybdenum).
Balanced fertilisation ensures efficient nutrient uptake, enhances yields, preserves soil health, and optimises resource use.
Emerging Alternatives
Ammonium Phosphate Sulphate (APS – 20:20:0:13)
- Contains 20% N, 20% P, and 13% S, but no K.
- Sulphur-rich, making it ideal for oilseeds, pulses, maize, cotton, onion, and chilli.
- APS manufacturing is more economical, requiring less costly phosphoric acid compared to DAP.
- Sales surged 32.4%, from 4.9 million tonnes (2022-23) to 6.5 million tonnes (2023-24), making APS the third-most consumed fertiliser after urea and DAP.
- Leading APS producers include Coromandel International, Paradeep Phosphates, and Mangalore Chemicals & Fertilizers.
Single Super Phosphate (SSP – 16% P, 11% S)
- A low-cost, sulphur-rich fertiliser ideal for oilseeds and vegetable cultivation.
Nano Urea and Nano DAP
- Developed by Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO).
- Enhance nutrient use efficiency by 15–20%, require lower application rates, and reduce overall fertiliser consumption.
NPKS Complex Fertilisers
- Formulations like 10:26:26:0, 12:32:16:0, 15:15:15:0, and 14:35:14:0 provide balanced nutrients.
- Help integrate potash application into complexes, reducing direct MOP use.
- NPKS fertiliser sales are projected to reach 14 million tonnes in 2024-25, up from 7.3 million tonnes in 2013-14.
Biofertilisers and Organic Manure
- Promote sustainable farming by improving soil health and reducing chemical fertiliser dependence.
- Supported by government initiatives like the PM-PRANAM scheme.
Effectiveness of Substitutes
- Reduces Import Costs: APS and Nano Urea reduce foreign exchange outflows.
- Enhances Soil Health: Balanced fertilisers prevent soil degradation and restore fertility.
- Improves Crop Yields: Trials demonstrate better nutrient absorption and yield improvements.
- Promotes Sustainability: Encourages ecological farming practices.
Policy Support and The Way Forward
Government Initiatives
- PM-PRANAM Scheme: Promotes alternative fertilisers.
- Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS): Encourages balanced fertiliser use.
- Soil Health Card Campaign: Educates farmers about soil-specific nutrient needs.
Strategic Recommendations
- Subsidy Reforms: Focus subsidies on APS, Nano Urea, and complex fertilisers rather than high-analysis fertilisers.
- Technology Adoption: Use AI-based tools like Microsoft FarmVibes AI for precision fertiliser application.
- Domestic R&D Investment: Strengthen indigenous production of fertilisers and biofertilisers.
- Policy Alignment: Integrate fertiliser policy with climate change and agricultural sustainability strategies.
Conclusion
India’s high dependence on imported urea, DAP, and MOP is economically unsustainable and environmentally detrimental. Transitioning towards balanced fertilisers like APS, Nano Urea, and organic alternatives is critical for ensuring long-term agricultural sustainability, reducing subsidy burdens, conserving foreign exchange, and preserving soil health. This shift requires concerted efforts through government policy, farmer education, and technological innovation.
'Rarest of Rare' Doctrine
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
The application of the death penalty in India continues to evoke debate, particularly in light of contrasting verdicts such as those in the 2024 R.G. Kar Medical College case and the Sharon Raj murder case. These cases highlighted the inconsistent application of the 'rarest of rare' doctrine, a judicial principle guiding capital punishment in the country.
Evolution of the 'Rarest of Rare' Doctrine
The debate surrounding the constitutionality and application of the death penalty began with Jagmohan Singh vs. State of Uttar Pradesh (1972). The Supreme Court upheld the death penalty’s constitutionality under Article 21 (Right to Life), ruling that it did not violate Articles 14 (equality before law) or 19 (freedom of speech and expression), despite concerns over lack of sentencing guidelines.
A definitive framework emerged in Bachan Singh vs. State of Punjab (1980), where the apex court held that the death penalty should only be awarded in the 'rarest of rare' cases. However, the Court did not precisely define what constituted "rarest of rare," leaving the interpretation to judicial discretion.
To bring clarity, the Supreme Court in Machhi Singh vs. State of Punjab (1983) outlined five guiding criteria to determine such cases:
- Manner of the Crime – Exceptionally brutal, grotesque, or shocking to the community.
- Motive of the Crime – Exhibiting extreme depravity or sadistic intent.
- Socially Abhorrent Nature – Offenses targeting marginalized individuals or groups.
- Magnitude of Crime – Cases involving multiple murders or large-scale violence.
- Victim’s Vulnerability – When victims are children, women, elderly, or otherwise helpless.
Further, in Mithu vs. State of Punjab (1983), the Court struck down Section 303 of the IPC, which mandated the death penalty for life convicts committing murder. The judgment reaffirmed that capital punishment must remain discretionary, emphasizing judicial evaluation of aggravating and mitigating circumstances.
Case Studies: A Reflection of Judicial Discretion
- In the R.G. Kar Medical College case, a female medical trainee was raped and murdered. Despite the brutality, the court ruled that the case did not meet the threshold of 'rarest of rare' and awarded life imprisonment to the convict.
- Conversely, in the Sharon Raj case, a young man was poisoned by his partner in a premeditated act. The court termed it one of the 'rarest of rare' cases and awarded the death penalty, citing the calculated nature and moral depravity of the crime.
These differing verdicts underscore the subjective application of the doctrine, with considerable weight placed on judicial interpretation.
Contemporary Concerns and Legal Developments
While the doctrine aims to preserve the sanctity of life by making the death penalty an exception, its lack of statutory definition and variability in interpretation has invited criticism. In 2022, the Supreme Court referred the issue to a Constitution Bench to explore how sentencing procedures could better accommodate mitigating factors and ensure a "meaningful, real and effective" hearing before sentencing.
Conclusion
The 'rarest of rare' doctrine represents a critical balancing act between justice and retribution in India's legal system. Although it seeks to restrict capital punishment to the most egregious crimes, its ambiguous parameters and judicial discretion often lead to inconsistent outcomes. Going forward, a more standardized and transparent sentencing framework could strengthen judicial credibility and uphold constitutional morality.
Sovereign Green Bonds in India

- 20 Feb 2025
Context:
India has adopted sovereign green bonds (SGrBs) as a key strategy to finance its transition to a low-carbon economy. However, these bonds have faced muted demand from investors, limiting the effectiveness of this funding source. Despite efforts to ease participation rules and attract foreign investors, the expected "greenium" (lower borrowing costs) remains weak, leading to funding shortfalls for vital green projects.
What are Sovereign Green Bonds?
Sovereign Green Bonds are issued by the government to raise capital for environmentally sustainable projects such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate resilience. In India, the government established a framework for issuing these bonds in 2022. Since their introduction, India has raised nearly Rs 53,000 crore through eight issuances, with funds primarily allocated to projects like energy-efficient locomotives and metro developments.
Weak Investor Demand
Despite the government's efforts, India's SGrBs have struggled to attract investor interest. A significant issue is the limited greenium, which in India has only reached 2–3 basis points, far below the global average of 7–8 basis points. This lack of financial incentive makes these bonds less attractive compared to regular bonds. Additionally, small issue sizes and limited secondary market trading further discourage investors. Many bonds are held to maturity, stifling liquidity and market participation.
Impact on Green Initiatives
The weak demand for SGrBs has directly impacted the funding for critical green projects. Initially, India planned to raise Rs 32,061 crore from SGrB proceeds in 2024-25. However, after weak investor response, the revised estimate was reduced to Rs 25,298 crore, resulting in significant cuts to funding for projects such as grid-scale solar energy. The budget for grid-scale solar projects was slashed from Rs 10,000 crore to just Rs 1,300 crore. As a result, India is increasingly relying on general revenue to fill the funding gap.
Key Areas Affected by Funding Cuts
- Electric Locomotive Manufacturing: Rs 12,600 crore
- Metro Projects: Rs 8,000 crore
- Renewable Energy (including National Green Hydrogen Mission): Rs 4,607 crore
- Afforestation (National Mission for a Green India): Rs 124 crore
Challenges Contributing to Weak Demand
- Lack of Social Impact Funds: India lacks a robust ecosystem of social impact funds and responsible investment mandates, which are present in other markets and drive demand for green bonds.
- Liquidity Issues: Small bond issues and a lack of secondary market trading have made SGrBs less liquid and attractive to investors.
- Higher Yields in Other Investment Avenues: Investors are reluctant to accept the relatively low yields of SGrBs, as they offer little financial advantage over regular bonds.
Way Forward
To improve the attractiveness of SGrBs, India could explore the issuance of sustainability bonds, which fund both green and social projects, attracting a broader base of investors. Additionally, post-issuance transparency is crucial, with detailed allocation and impact reports needed to build investor confidence. The government can also collaborate with multilateral development banks like the World Bank to back its green bonds, enhancing their credibility and attracting investment.
Furthermore, enhancing liquidity and developing a more robust market for green finance are essential steps to ensure that India can achieve its climate goals. With proper strategy and structural changes, India can enhance investor confidence and ensure sustainable funding for its green initiatives.
India’s Sovereign Green Bonds: Challenges and Prospects

- 18 Feb 2025
Context:
India’s Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs) are a key instrument to mobilize resources for climate-resilient infrastructure and sustainable development. However, despite their potential, the bonds have struggled to attract robust investor interest, thereby limiting the government’s ability to secure a meaningful greenium—a lower cost of borrowing that typically incentivizes green finance globally.
What are Sovereign Green Bonds?
SGrBs are debt instruments issued by the Government of India to raise capital for projects that contribute to environmental sustainability and low-carbon development. They are part of India’s broader green financing strategy to meet its Net Zero target by 2070. These bonds are issued by the Ministry of Finance, under the oversight of the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), and are guided by India’s Green Finance Framework, aligned with global green bond principles.
Application of Funds:
The proceeds from SGrBs are earmarked exclusively for green projects, ensuring transparency and impact-based investment. Key sectors financed include:
- Electric Locomotive Manufacturing (largest beneficiary through the Ministry of Railways)
- Urban Mobility: Metro rail and public transport systems
- Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and the National Green Hydrogen Mission
- Afforestation: Under the National Mission for a Green India
- Grid-Scale Solar Projects, though allocations here have been curtailed due to fiscal constraints
Performance and Allocation Trends:
India raised ?16,000 crore through SGrBs in FY 2022–23 and ?20,000 crore in FY 2023–24. For FY 2024–25, ?16,697 crore has been raised so far. However, due to muted investor demand, the revised fundraising estimate has been reduced from ?32,061 crore to ?25,298 crore. A fiscal gap of ?3,600 crore will be met through general revenue, reflecting limited success in expanding green finance.
Challenges:
- Weak Greenium: Indian SGrBs offer little to no financial advantage over conventional bonds, with greenium as low as 2–3 basis points. Globally, it averages 7–8 basis points, still modest but relatively attractive.
- Low Investor Demand: Several bond auctions witnessed under-subscription. For instance, ?7,443 crore worth of bonds were devolved to primary dealers in recent auctions due to high yield expectations from investors.
- Illiquid Secondary Market: Small issuance sizes and a trend of holding bonds till maturity restrict active trading, deterring market participants.
- Underdeveloped Sustainable Finance Ecosystem: India lacks dedicated ESG funds, responsible investment mandates, or regulatory incentives for green bond investments.
Recommendations:
- Enhance Credit Guarantees: Collaborate with multilateral institutions like the World Bank or IFC to back green bonds, enhancing their creditworthiness.
- Expand Domestic Green Investment Base: Promote ESG-focused mutual funds, offer tax incentives, and establish a regulatory framework to attract long-term green capital.
- Improve Market Liquidity: Increase bond issuance sizes and introduce market-making mechanisms to deepen secondary market activity.
- Leverage Public-Private Partnerships: Engage private players in project implementation to diversify and scale up green investment opportunities.
Conclusion:
India’s Sovereign Green Bonds symbolize a strategic shift toward sustainable development financing. While challenges persist, especially in market participation and pricing incentives, strengthening domestic financial ecosystems and leveraging global support can make green bonds a cornerstone of India’s climate financing roadmap.
Passive Euthanasia for Rabies Patients: SC to Hear Plea

- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has recently agreed to hear a plea seeking the right to passive euthanasia for rabies patients, citing the exceptional nature of the disease and the absence of a cure. The matter, listed for hearing after two weeks, is poised to test the scope and application of the 2018 passive euthanasia ruling under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Background of the Case
- The petition was filed by the NGO All Creatures Great and Small in 2019, challenging a Delhi High Court order (July 2019) which refused to classify rabies as an exceptional case warranting "death with dignity".
- The Supreme Court issued notice in January 2020 to the Centre and other stakeholders, seeking their response.
- On February 10, 2025, a bench of Justices B.R. Gavai and K. Vinod Chandran agreed to hear the matter after two weeks.
Grounds for the Plea
The NGO has urged the Court to lay down a specific protocol enabling terminally ill rabies patients or their guardians to opt for passive euthanasia under medical supervision. Key arguments include:
- Rabies has a 100% fatality rate once symptoms appear.
- The disease often leads to violent neurological symptoms, requiring patients to be tied or shackled to beds, stripping them of dignity and personal freedom.
- The intense suffering and irreversible nature of rabies, coupled with the lack of any effective treatment, makes it distinct from other terminal conditions.
- The plea seeks the creation of an exceptional legal category for rabies within the framework of the 2018 Supreme Court judgment.
Understanding Euthanasia in India
Definitions:
- Euthanasia literally means “good death” and refers to hastening death to relieve pain and suffering.
- Active Euthanasia involves deliberate acts to cause death (e.g., lethal injection) and remains illegal in India.
- Passive Euthanasia involves withholding or withdrawing life support from terminally ill patients and was legalised in 2018.
Legal Milestone:
- In the Common Cause v. Union of India (2018) case, a five-judge Constitution Bench ruled that the right to die with dignity is a part of the fundamental right to life under Article 21.
- The verdict permitted passive euthanasia and the creation of a “living will”—a legal document allowing patients to refuse life support if in a terminal or vegetative state.
Ethical and Constitutional Dimensions
- The plea raises significant questions about human dignity, bodily autonomy, and the limits of state intervention in end-of-life decisions.
- It also brings focus to judicial responsibility in expanding fundamental rights, especially in the context of terminal, untreatable illnesses.
Conclusion
The outcome of this case could have far-reaching implications on medical jurisprudence and the ethics of end-of-life care in India. If the Court recognizes rabies as an exception, it may set a precedent for disease-specific passive euthanasia protocols, expanding the practical application of the 2018 ruling.
La Niña 2024–25

- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
Despite the expected cooling influence of La Niña, January 2025 became the hottest January on record, with global average surface air temperatures 1.75°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900), according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). This marked the 18th out of the last 19 months that global temperatures exceeded the 1.5°C threshold. The inability of La Niña to curb this warming trend underscores the intensifying impact of anthropogenic climate change.
Understanding La Niña and the ENSO Cycle
La Niña, meaning "The Little Girl" in Spanish, is the cool phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)—a recurring climate phenomenon involving variations in oceanic and atmospheric conditions in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- Phases of ENSO:
- El Niño (warm phase): Warmer ocean temperatures in the eastern Pacific, weakening trade winds and reducing rainfall in the western Pacific.
- La Niña (cool phase): Colder sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific, strengthening trade winds and enhancing rainfall in the western Pacific.
- Neutral phase: Sea surface temperatures are near average with no dominant anomalies.
- Mechanism: During La Niña, strengthened trade winds push warm surface waters westward, causing cold waters to upwell in the eastern Pacific. This typically results in global cooling.
- ENSO Cycle: These phases occur every 2 to 7 years and influence weather patterns globally. The ENSO cycle leads to sea surface temperature variations between ±1°C to ±3°C from the long-term average.
The 2024–25 La Niña: A Weakened Climate Driver
- Emergence: The current La Niña phase began in December 2024, later than anticipated. Forecasts had expected it around September 2024, giving it insufficient time to strengthen before its typical peak in the Northern Hemisphere winter.
- Intensity: It is projected to be a mild La Niña, reducing its capacity to significantly influence global temperatures.
- Past Events: The most recent La Niña cycle lasted from 2020 to 2023, followed by a strong El Niño through mid-2023.
- Delayed Cooling Effect: The weaker-than-usual La Niña failed to produce the anticipated cooling, surprising scientists. As Julien Nicolas from Copernicus observed, the expected “temporary brake” on global temperatures did not materialize.
Why January 2025 Remained Hot Despite La Niña
- Global Ocean Warming: Oceans have retained higher-than-usual warmth due to long-term climate change, diluting La Niña’s cooling influence.
- Weak La Niña Onset: A late and weak phase meant less disruption to the prevailing warming trend. According to NOAA, La Niña events need more time and intensity to impact temperatures effectively.
- Persistent GHG Emissions: The concentration of greenhouse gases reached record highs in 2024, adding to the Earth's heat burden. Typically, La Niña-induced rains spur vegetation growth and carbon absorption, but weaker rains in this cycle limited that effect.
- Reduced Aerosols: Declines in atmospheric aerosols—due to cleaner air policies—lessened their usual cooling impact. Aerosols scatter solar radiation and influence cloud dynamics, contributing to temperature moderation.
Global and Regional Climatic Impacts of La Niña
Despite its weak intensity, La Niña still shaped regional weather in varied ways:
Asia
- India: Higher monsoon rainfall (July–September) is expected. This boosts rice production but may reduce pulse output in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- Southeast Asia: Nations like Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines face increased rainfall—raising flood risks but aiding rice and palm oil yields.
South America
- Southern Brazil, Uruguay, northern Argentina, and southern Bolivia face drought due to reduced rainfall, affecting soybean and maize crops.
- Northern Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and parts of Ecuador and Peru receive excess rain, risking floods.
Africa
- East Africa: Experiences dry conditions in December–January, hampering harvests in February–March.
- Southern Africa: Receives above-average rainfall, benefitting crops like maize, wheat, sorghum, and soybeans.
Oceania
- Australia: Faces heavy rain and possible flooding in its northern and eastern regions.
North America
- Southern US: Experiences dry conditions.
- Northern US, Canada, and Alaska face wetter, stormier weather.
Significance for India
- Agriculture: Enhanced monsoon rains improve farm productivity, especially rice.
- Water Resources: Better reservoir levels alleviate water stress.
- Energy: Increases hydropower potential.
- Heat Mitigation: Reduces severity of heatwaves compared to El Niño years.
Monitoring & Prediction
- Oceanic Niño Index (ONI): Tracks 3-month average SST anomalies. Values below –0.5°C indicate La Niña.
- Nino-3.4 Index: Confirms ENSO thresholds. Anomalies of ±0.5°C signal event onset; ±1.5°C indicates strong events.
- Tools Used: Satellite data, trade wind strength, and ocean buoys support forecasts. La Niña can be predicted up to two years in advance if preceded by a strong El Niño.
Conclusion:
The 2024–25 La Niña's inability to cool global temperatures highlights a worrisome trend—the diminishing moderating influence of natural climate phenomena. With greenhouse gas emissions continuing to rise and natural cooling cycles weakening, urgent global action is needed to reduce emissions and mitigate climate change impacts.
Article 22 of the Indian Constitution

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
Article 22 of the Indian Constitution, enshrined in Part III under Fundamental Rights, provides critical safeguards to individuals against arbitrary arrest and detention. It ensures that liberty is not curtailed without adherence to due process. These rights are applicable to all individuals—citizens and non-citizens—except enemy aliens and those under preventive detention laws.
Key Provisions of Article 22:
- Article 22(1): No person who is arrested shall be detained without being informed of the grounds for such arrest. The arrestee has the right to consult and be defended by a legal practitioner of their choice.
- Article 22(2): The arrested person must be produced before the nearest magistrate within 24 hours of arrest (excluding travel time). Further detention without magistrate’s approval is unconstitutional.
- Article 22(3): The above protections do not apply to:
- Enemy aliens.
- Persons detained under preventive detention laws.
- Article 22(4): Preventive detention cannot exceed three months unless approved by an Advisory Board comprising judges of a High Court.
- Article 22(5): The detained individual must be informed of the grounds of detention and given a chance to make a representation against it.
- Article 22(6): Authorities may withhold facts if disclosure is deemed against public interest.
- Article 22(7): Parliament may prescribe:
- Circumstances under which detention can extend beyond three months without Advisory Board opinion.
- Maximum period of detention.
- Advisory Board procedure.
Supreme Court Ruling: Mandatory Compliance with Article 22(1)
In a recent landmark judgment, the Supreme Court reaffirmed that non-disclosure of grounds of arrest violates Articles 22(1) and 21, rendering such arrests illegal.
A bench comprising Justices A.S. Oka and N.K. Singh ruled that the obligation to inform an arrested person of the grounds of arrest is not a mere formality but a constitutional mandate. Failure to do so deprives the individual of liberty without due process, violating the fundamental rights under Article 21 (Right to Life and Liberty) as well.
Key observations of the Court:
- Communication of Arrest Grounds: The arrested individual must be informed “as soon as may be” after arrest in a language and manner understandable to them. Merely mentioning grounds in the remand report or charge sheet does not satisfy Article 22(1).
- Written Communication Preferred: While not mandatory, providing the grounds of arrest in writing is encouraged to avoid controversy and ensure clarity (as suggested earlier in Pankaj Bansal v. Union of India).
- Duty of Magistrate: At the time of remand, the magistrate must verify if Article 22(1) compliance has occurred. If not, remand is unconstitutional, and the arrest stands vitiated.
- Burden of Proof: If the accused alleges non-compliance, the Investigating Officer bears the burden to prove that Article 22(1) was followed.
- Ground for Bail: Violation of Article 22(1) can itself be a ground for granting bail, even in cases where statutory restrictions exist.
- Communication to Relatives (CrPC Section 50A): Justice Singh emphasized that the grounds of arrest should also be conveyed to friends, relatives, or nominated persons of the arrestee. This facilitates immediate legal recourse to secure release, reinforcing the right to liberty under Article 21.
Conclusion:
The Supreme Court’s judgment marks a crucial reaffirmation of constitutional liberties. It ensures that procedural safeguards under Articles 21 and 22 are not diluted by executive convenience and establishes a higher standard of accountability in the process of arrest and detention in India.
M23 Rebellion
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has once again become the epicenter of a severe humanitarian and geopolitical crisis. In early 2025, the M23 militia, a Tutsi-led rebel group allegedly backed by Rwanda, captured Goma, the capital of North Kivu province.
This strategic and mineral-rich city lies on the eastern border with Rwanda and has historically been a flashpoint in the region. The recent offensive has escalated the violence, displacing over 7,00,000 people, killing more than 2,900, and risking a wider regional conflict.
Historical Roots of the Conflict
The current instability can be traced back to colonial and post-independence ethnic tensions in the Great Lakes region. Under German and Belgian colonial rule, power structures in Rwanda favored the minority Tutsi population, generating long-standing resentment among the Hutus. Following Rwanda’s independence in 1962, a Hutu-majority government took power, culminating in the 1994 Rwandan Genocide, where nearly 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus were killed.
Post-genocide, around 2 million Hutus, including militia members responsible for the killings, fled into eastern Congo (then Zaire), leading to the formation of over 120 armed groups, including the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR), a Hutu militia. Rwanda intervened in Congo in 1996 and 1998, triggering the First and Second Congo Wars, which resulted in millions of deaths and regional destabilization.
Emergence and Role of M23
The M23 (March 23 Movement) was formed in 2012 by former fighters of the Tutsi-led National Congress for the Defence of the People (CNDP), who rebelled after accusing the DRC government of violating a 2009 peace deal meant to integrate them into the national army. Led by SultaniMakenga, M23 initially captured Goma in 2012 but retreated after international pressure.
Resurfacing in 2022, M23 cited non-implementation of the agreement and vowed to protect Tutsi interests against groups like the FDLR. Since then, they have gained control of key mining regions, particularly Rubaya, rich in coltan, a critical mineral used in electronic devices. The UN estimates that M23 earns $800,000 per month from coltan production taxes, indicating that economic motives are as significant as ethnic ones.
The 2025 Escalation
On January 27, 2025, M23 rebels entered Goma and seized control of the airport by the following evening. By January 30, they had captured the city despite sporadic resistance from government forces and allied militias. The group then began advancing southward towards Bukavu, the capital of South Kivu province. The UN has confirmed reports of Rwandan troop incursions into South Kivu, while Burundian forces have joined Congolese troops in resisting the offensive.
Regional Dynamics and Rwanda’s Involvement
The Congolese government, along with the UN and Western powers, accuses Rwanda of backing M23 militarily and logistically. A 2022 UN expert report provided "solid evidence" of Rwandan troops fighting alongside M23, though Rwanda continues to deny these allegations. President Paul Kagame justifies his government's position as defensive, blaming the DRC for its alliance with the FDLR, which threatens Tutsis across the region.
Neighboring Burundi, led by President ÉvaristeNdayishimiye, has warned that Rwanda’s ambitions could spark a wider war, even threatening Burundi’s sovereignty. Uganda, meanwhile, plays a balancing role—supporting Congolese efforts against Islamic State-linked militants, while allegedly allowing M23 safe haven, as per UN reports.
Strategic and Economic Importance of Goma
Goma is not just a city; it is a strategic trade and transport hub at the heart of the DRC’s mineral wealth, particularly coltan, of which the DRC supplies nearly 40% of the world’s demand. The region is crucial for smartphone and electronics manufacturing due to coltan’s utility in capacitors.
Thus, the control of Goma and surrounding territories represents not only a military advantage but also a significant economic resource for M23 and its alleged sponsors.
Humanitarian Impact and Global Concerns
The humanitarian toll of the conflict is staggering. With over a million people displaced since M23’s resurgence, the DRC’s fragile state apparatus is further strained. Corpses reportedly lay unburied in Goma after the assault, reflecting a deep crisis of governance, security, and human rights.
Given the ethnic complexities, resource conflicts, and regional rivalries, there are growing fears of the conflict escalating into a full-fledged regional war, drawing in Rwanda, Burundi, and Uganda.
RBI Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) cuts Repo Rate

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
In a landmark decision during its February 2025 meeting, the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) reduced the repo rate by 25 basis points, from 6.5% to 6.25%, marking the first rate cut in five years (since May 2020). This move follows the Union Government’s recent cut in personal income tax, aimed at boosting consumption.
What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
The MPC is a six-member statutory body responsible for setting India’s monetary policy. Its primary objective is price stability while ensuring economic growth. It meets bi-monthly to assess economic indicators and modify key policy rates like the repo rate, which influences overall borrowing and lending costs in the economy.
Key Highlights from the MPC Decision:
Repo Rate Cut:
- Reduced to 6.25% from 6.5%.
- Objective: Stimulate credit growth, investment, and consumer demand.
- Expected Impact: Lower EMIs for borrowers, reduced interest rates on EBLR and MCLR-linked loans.
GDP Growth Outlook (FY26):
- RBI projects 6.7% GDP growth for FY26.
- This is slightly higher than the FY25 estimate of 6.4%, and in line with the Economic Survey’s projection of 6.3–6.8%.
- Growth recovery is attributed to calibrated fiscal consolidation and stable private consumption.
Inflation Projections (CPI-based):
- FY26 Inflation Estimate: 4.2%
- Q1: 4.5%
- Q2: 4.0%
- Q3: 3.8%
- Q4: 4.2%
- CPI inflation had already dropped to 5.22% in December 2024, aided by easing food prices.
- RBI emphasized continued transmission of past policy measures and food price moderation as drivers of disinflation.
Broader Monetary Policy Context
- RBI will maintain a “neutral” policy stance to remain flexible amid evolving macroeconomic conditions.
- RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra stressed that the inflation-targeting framework has helped stabilize prices, especially post-pandemic.
- The policy space was created by the simultaneous drop in inflation and moderate growth, allowing support for the economy without derailing price stability.
Cybersecurity & Digital Measures
- Additional Factor Authentication (AFA) introduced for international digital payments.
- Launch of exclusive domains:
- "bank.in" for Indian banks
- "fin.in" for the wider financial sector
These aim to bolster digital transaction security amid rising cyber fraud.
Forex & External Sector Outlook
- RBI reiterated that it does not target exchange rate levels, intervening only to curb excessive volatility.
- Ongoing global challenges include:
- Strengthening of the US dollar
- Higher bond yields
- Geopolitical tensions
- Threat of trade wars
- These have led to capital outflows, currency depreciation, and increased financial market volatility.
Conclusion
The RBI’s rate cut signals a strategic shift towards supporting economic growth amid global uncertainties. With a moderate inflation outlook and improving macroeconomic indicators, the decision is expected to boost domestic demand and investment, while reinforcing RBI’s commitment to price and financial stability.
India’s Pursuit of a Sovereign Foundational AI Model

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
As artificial intelligence (AI) reshapes global economic, strategic, and technological landscapes, the question of whether India should build its own sovereign foundational AI model has gained prominence. Sovereign AI models—developed, trained, and deployed using domestic infrastructure, datasets, and expertise—are now seen as strategic assets, with countries like the US and China already establishing their own. India, however, remains dependent on foreign AI giants such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Meta.
Why India Needs a Sovereign AI Model
1. Data Sovereignty and Security: India generates one of the world’s largest data pools, including sensitive data from healthcare, finance, and governance. Using foreign-built AI models risks privacy breaches and potential misuse. A homegrown model would ensure control over data and ethical AI deployment.
2. Reducing Foreign Dependence: Sovereign AI is crucial for applications in defense, cybersecurity, and governance, where reliance on foreign technology may undermine strategic autonomy. Sanctions or export controls could otherwise disrupt access to essential technologies like GPUs or software updates.
3. Cultural and Linguistic Alignment: Current global AI models are largely English-centric. A sovereign model trained on Indian languages and datasets would bridge the digital divide and make AI more inclusive. Projects like AI4Bharat’s IndicTrans2 and Sarvam AI’s Sarvam-1, a multilingual model built with Nvidia, exemplify this direction.
4. National Security and Innovation: Sovereign AI is essential in military intelligence, predictive security, and surveillance. It also fosters an innovation ecosystem, generating high-skilled jobs and encouraging academic-industry collaboration.
Challenges in Building Foundational AI Models
1. Infrastructure Gaps: India lacks cutting-edge chip manufacturing capabilities. With no agreements with firms like TSMC, India relies on imports of GPUs and processors, unlike countries developing supercomputers (e.g., Denmark’s Gefion, Japan’s AI Grid).
2. High Development Costs: Training a large AI model can cost millions. DeepSeek V3, for instance, cost $5.6 million for a single run, while India’s annual AI R&D budget remains modest compared to Big Tech’s $80 billion.
3. Fragmented Resources: Subsidized GPUs are spread thin across institutions, diluting their impact. Meta’s Llama 4, for example, used large dedicated clusters—unfeasible under current Indian frameworks.
4. Public R&D Inefficiencies: Bureaucratic red tape discourages risk-taking needed in AI research. Unlike flexible spending in firms like OpenAI, Indian R&D lacks autonomy and long-term funding.
Policy Recommendations and Way Forward
- Invest in IndiaAI Mission: Develop a national AI infrastructure with over 10,000 GPUs, secure cloud systems, and supercomputing clusters to train and deploy large-scale models.
- Build DPI for AI Builders: Create datasets, APIs, and platforms to support data annotation, fine-tuning, and delivery in Indian contexts.
- Adopt a Phased Approach: Focus on sovereign models in sensitive sectors (defense, healthcare) while using global open models for non-critical applications.
- Promote Public-Private Collaboration: Forge partnerships with companies like Nvidia or OpenAI for technology transfer and joint ventures.
- Encourage Innovation Under Constraints: India must emulate models like Alibaba or DeepSeek, which succeeded with limited resources and targeted innovations.
Conclusion
Building a sovereign foundational AI model is not merely a technological ambition but a strategic necessity. With coordinated efforts between government, industry, and academia, India can achieve AI self-reliance—ensuring data sovereignty, inclusive growth, and a strong global presence in the AI-driven future.
MSMEs in India’s Economic Growth
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Finance Minister proposed a significant policy shift by increasing the investment and turnover limits for MSME classification by 2.5 and 2 times respectively. This move is expected to enhance the growth prospects and scalability of India’s micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs).
Economic Significance:
The MSME sector forms the backbone of the Indian economy, contributing 30% to the GDP and nearly 45% to manufacturing output. With over 1 crore registered units employing 7.5 crore people, it is the largest source of non-agricultural employment in the country. It plays a pivotal role in inclusive development, offering livelihood opportunities to the rural, urban poor, and semi-skilled workforce.
The formalization drive has been significant, with over 4 crore MSMEs registered on the Udyam portal by March 2024. Key schemes like PM Vishwakarma Yojana (?13,000 crore) and Mudra Yojana (?5.41 lakh crore disbursed in FY24) have supported artisans and first-time entrepreneurs, particularly women and marginalized communities.
Boost to Trade and Innovation:
MSMEs account for 45.73% of India’s total exports in sectors like textiles, leather, and engineering goods. Their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs) is being facilitated by reforms in trade logistics, the GeM portal, and PLI schemes. Digital transformation is advancing rapidly, with 72% MSME transactions now digital, supported by platforms like ONDC and the RBI’s Public Tech Platform.
Women and Rural Empowerment:
Women entrepreneurs constitute 20.5% of Udyam registrations, and 68% of Mudra loans benefit them. MSMEs are also catalyzing rural industrialization by promoting agro-processing and curbing rural-urban migration through schemes like the SRI Fund and Animal Husbandry Credit Guarantee Scheme.
Key Challenges:
Despite their potential, MSMEs face critical bottlenecks:
- Credit access remains limited; only 20% of units access formal finance. Payment delays amounting to ?10.7 lakh crore (2022) hinder working capital.
- Regulatory burdens, inadequate infrastructure, and poor digital skills further constrain productivity.
- Low awareness of schemes and limited integration into global ESG standards affect competitiveness.
- The sector remains largely informal, weakening labor rights and policy outreach.
Recent Reforms & Recommendations:
To unlock MSMEs’ potential, a multi-pronged reform strategy is underway:
- Credit Measures: Promotion of cash-flow based lending, expansion of CGTMSE, Vyapar Credit Cards, and enhanced TReDS-GeM integration.
- Ease of Doing Business: Single-window clearances, self-certification, and stronger MSME facilitation councils.
- Digital & Skill Upgradation: Launch of Digital MSME 2.0, apprenticeship hubs, and innovation incubators.
- Market Access: Expansion of cluster-based models, branding support, and ONDC-GeM integration.
- Green MSMEs: ESG-linked credit, circular economy incentives, and green certifications.
- Formalization Push: Linking benefits to Udyam registration, backed by SIDBI-led equity support.
Conclusion:
MSMEs are central to India’s vision of a $5 trillion economy and Viksit Bharat by 2047. With increased investment thresholds, focused policy interventions, and digital empowerment, India can build a resilient, inclusive, and globally competitive MSME ecosystem.
Geo-Economic Fragmentation (GEF)

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
Geo-economic fragmentation refers to a policy-driven reversal of global economic integration, increasingly shaped by geopolitical alignments. It signifies a shift from globalization to strategically-driven economic blocs, where nations prioritize political alliances over market efficiency.
Key Characteristics
- Emergence of friend-shoring, re-shoring, and economic nationalism.
- Fragmentation of trade, capital flows, FDI, and migration.
- Retreat from multilateralism, with institutions like the WTO and IMF under stress.
- Strategic use of environmental, labor, and social standards by developed countries to impose uniform regulations, causing tensions.
Globalization to Fragmentation: Statistical Evidence
- Trade-to-GDP Ratio: Increased from 39% (1980) to 60% (2012); now threatened by rising protectionism.
- FDI Inflows: Rose from $54 billion (1980) to $1.5 trillion (2019); now increasingly concentrated among like-minded countries.
- Global Economy: Expanded from $11 trillion (1980) to over $100 trillion (2022).
- Trade Restrictions (WTO Report):
- 2023–24: 169 new measures covering $887.7 billion in trade.
- 2022–23: Covered $337.1 billion — shows a dramatic rise in protectionism.
- Over 24,000 new trade and investment restrictions imposed globally between 2020–24.
IMF on Costs of GEF
- Trade fragmentation could cause 0.2% to 7% GDP losses, especially for developing countries.
- Current fragmentation is more costly than Cold War era, as trade now constitutes 45% of global GDP (vs. 16% then).
- Less trade = less knowledge diffusion, innovation, and productivity gains.
Strategic Impacts: Global Supply Chains
China’s Dominance
- 80% of global battery manufacturing.
- 80% of solar panel components.
- 60% of wind turbine capacity.
- 70% of global rare earth mineral processing.
- Dominates EV supply chains, critical mineral refining, and clean energy manufacturing.
FDI Realignment
- FDI is increasingly relocating from China to India, Vietnam, Mexico, etc.
- Friend-shoring reduces capital access for emerging markets.
- Emerging economies face reduced FDI, slower growth, and technological decoupling.
India’s Strategic Response: Deregulation and Internal Growth
Policy Recommendations (Economic Survey 2024–25)
- Amplify deregulation to lower compliance costs and boost entrepreneurship.
- Empower SMEs to withstand global shocks and strengthen domestic manufacturing.
- Encourage inter-state learning for best practices in economic governance.
- Redouble efforts to boost exports and foreign investment amidst global volatility.
Rationale
- With the decline of global cooperation, internal engines of growth become crucial.
- Deregulation can unleash innovation, enhance productivity, and ensure resilient growth.
- India's response must be strategic, systematic, and state-inclusive to capitalize on this global transition.
Addressing Environmental Challenges and Strengthening Regulations in India

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
India's recent coal mining tragedy in Dima Hasao, Assam, underscores the nation's ongoing struggle with illegal and hazardous rat-hole mining, despite the National Green Tribunal's 2014 ban. This persistent exploitation, driven by industrial demand for coal, highlights the gap between environmental regulations and their enforcement, revealing a broader issue of balancing economic growth with environmental protection. As India strives to meet ambitious climate goals and sustain economic development, strengthening environmental regulations becomes critical.
Current Environmental Regulations in India
India has established a strong legal framework to protect its environment, grounded in the Indian Constitution. Articles 48A and 51A(g) direct the state and citizens to safeguard the environment, while Article 21 ensures the right to a clean and healthy environment, as interpreted by the Supreme Court. Key pollution control laws include:
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: Regulates water pollution and establishes pollution control boards at the national and state levels.
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981: Controls air pollution from industrial emissions and vehicles.
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986: Provides overarching powers for environmental protection.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016: Regulates plastic waste disposal and bans single-use plastics.
Other significant laws focus on forest and wildlife protection, including the Indian Forest Act, 1927, and the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, along with the National Green Tribunal (NGT) Act, 2010, which ensures quick resolution of environmental disputes.
Key Issues with Enforcement
- Despite these stringent regulations, enforcement remains weak due to institutional limitations. Many industrial units fail to meet environmental standards, with regulatory bodies underfunded and understaffed. For example, pollution control boards in states like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are plagued by staffing shortages, hampering their ability to monitor pollution effectively.
- Inadequate public participation and insufficient technology adoption further exacerbate these challenges.
- The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process, often bypassed or diluted, leads to development projects being approved without full consideration of their environmental impacts, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas.
Weak Enforcement and Conflict between Development and Conservation
The tension between development and conservation is evident in policies that relax environmental regulations for economic growth. The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, prioritizes infrastructure projects over forest preservation, undermining ecological conservation. Moreover, the rapid urbanization of cities like Gurugram and Faridabad has led to large-scale deforestation and a reduction in natural conservation zones, worsening air and water quality.
Strengthening Environmental Regulations
To address these challenges, India needs to strengthen its environmental regulatory mechanisms:
- Enhance Enforcement: Adequate funding, skilled personnel, and advanced technology, such as AI-based pollution monitoring and drone surveillance, are essential to improve compliance.
- EIA Reforms: The EIA process should be made more transparent and participatory, ensuring that marginalized communities are included in decision-making.
- Promote Clean Energy: Expanding subsidies for renewable energy and encouraging industries to adopt green technologies will help reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Circular Economy: Encouraging industries to adopt recycling and upcycling practices can minimize waste and reduce resource extraction.
- Strengthen Local Involvement: Empowering local communities through decentralization under the Forest Rights Act will ensure more inclusive environmental governance.
Conclusion
India’s environmental challenges require a balanced approach, integrating sustainable development with robust environmental protections. Strengthening regulatory enforcement, reforming the EIA process, and fostering community-led conservation are essential to aligning economic growth with environmental sustainability. By addressing these gaps, India can better navigate its path toward achieving both its development goals and climate commitments.
India-Indonesia Relations

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of Indonesia, visited India as the Chief Guest for the 76th Republic Day in January 2025. This marked the 75th anniversary of diplomatic ties, reaffirming the commitment to deepen cooperation in economic, strategic, cultural, and defense domains.
Historical Foundations
- Ancient Civilizational Links: Trade and cultural exchanges date back to the 2nd century BCE, reflected in the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism on Indonesian society (e.g., Ramayana, Mahabharata, Borobudur, Prambanan).
- Modern Diplomatic Ties:
- Formalized in 1950, with a Treaty of Friendship in 1951.
- Collaborated in the 1955 Bandung Conference and co-founded the Non-Aligned Movement (1961).
- Indonesia’s first President Sukarno was the Guest of Honour at India’s first Republic Day in 1950.
- Cold War and Beyond:
- Relations cooled in the 1960s but revived in the 1980s.
- The 1991 'Look East' Policy and the 2014 'Act East' Policy revitalized ties.
- Strategic Partnership in 2005; upgraded to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2018.
Key Pillars of Cooperation
- Economic and Trade Relations
- Trade Volume: Reached USD 38.8 billion (2022–23), targeted to increase to USD 50 billion by 2025.
- Key Imports: India imports coal, palm oil, and nickel.
- Investment: Indian investments in Indonesia total USD 1.56 billion in infrastructure, textiles, and energy.
- New Developments:
- MoU on Local Currency Settlement Systems to reduce dependency on USD.
- Focus on resolving trade barriers via forums like WGTI and BMTF.
- Cooperation in critical minerals like nickel and bauxite.
- BPCL to invest USD 121 million in the Nunukan gas block.
- Military Exercises: Garuda Shakti (Army), Samudra Shakti (Navy), and participation in Milan, Komodo, Super Garuda Shield, etc.
- Key Agreements:
- 2018 Defense Cooperation Agreement.
- White Shipping Information Exchange (WSIE).
- Proposal for Bilateral Maritime Dialogue and Cyber Security Dialogue.
- Joint vision on maritime cooperation under SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- BrahMos Deal: Talks underway for Indonesia’s acquisition of BrahMos missiles (~USD 450 million).
- Cultural Diplomacy: Shared heritage of Hindu-Buddhist traditions; India assisting in restoring Prambanan temple.
- Tourism & Connectivity: Direct flights since 2023; India is the second-largest source of tourists to Bali.
- New Initiatives:
- Cultural Exchange Programme (2025–2028).
- India reaffirmed the Kashi Cultural Pathway for heritage restoration and repatriation of artifacts.
- Science, Technology, and Space
- ISRO supports Indonesia’s satellite ambitions; agreement on Biak Tracking Station.
- Renewed MoU on STEM cooperation.
- Areas of collaboration: Quantum tech, high-performance computing, and digital public infrastructure.
- Energy and Health Security
- Collaboration on biofuels under the Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Joint initiatives on mid-day meals and public distribution systems.
- MoUs on digital health, capacity building, and traditional medicine.
Multilateral and Regional Cooperation
- ASEAN & Indo-Pacific: Commitment to ASEAN centrality and cooperation through IPOI, India-Indonesia-Australia Trilateral, and ASEAN-India outlook.
- Global Platforms: Collaboration in BRICS, G20, IORA, and advocacy for the Global South.
- Climate & Disaster Resilience:
- Joint efforts under CDRI.
- Indonesia invited to the International Solar Alliance and Big Cat Alliance.
Key Challenges
- Trade Imbalance: Heavy reliance on limited imports (coal, palm oil); imbalance persists as Indonesia’s trade with China is far greater (~USD 139 billion).
- Bureaucratic & Regulatory Barriers: Slow progress on infrastructure and investment due to permit and regulatory issues.
- Geopolitical Pressures: Indo-Pacific instability and China's expanding influence pose strategic challenges.
- Logistical Constraints: Inadequate connectivity infrastructure hinders deeper integration.
Way Forward
- Trade Diversification: Include sectors like tech, agriculture, and green energy.
- Defense Deepening: Expand joint exercises, maritime patrols, and intelligence-sharing.
- Enhance Connectivity: Boost air, sea, and digital linkages for trade and tourism.
- Green Collaboration: Advance renewable energy and sustainable mining ventures.
- Cultural & Educational Engagement: Promote student exchanges, scholarships (e.g., ITEC), and diaspora involvement.
Conclusion
India and Indonesia share deep-rooted civilizational links and are strategically aligned in the Indo-Pacific. Their evolving Comprehensive Strategic Partnership encompasses trade, defense, technology, and cultural diplomacy. Strengthening this partnership will not only boost bilateral growth but also ensure a stable, multipolar, and cooperative regional order.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
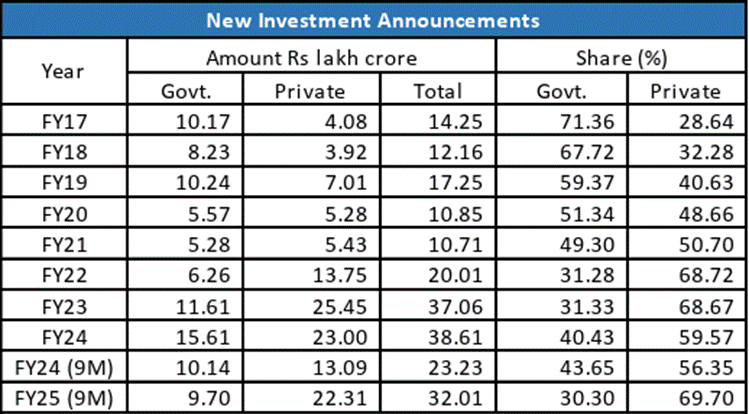
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent State Bank of India (SBI) report highlights the evolving trends in investment activity and the increasing importance of External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) in financing India's economic growth. It also reflects rising private sector participation and a robust capital formation trend.
Investment Trends in India:
- Total Investment Announcements reached ?32.01 lakh crore during April–December 2024 (9MFY25), up 39% from the same period in FY24.
- The private sector accounted for 70% of investments in 9MFY25, up from 56% in FY24, indicating rising business confidence.
- Gross block of Indian corporates rose to ?106.5 lakh crore (March 2024), from ?73.94 lakh crore in March 2020—an addition of over ?8 lakh crore annually.
- Capital Work in Progress stood at ?13.63 lakh crore, reflecting ongoing infrastructure and industrial projects.
- Household Net Financial Savings (HNFS) improved to 5.3% of GDP in FY24 from 5.0% in FY23.
- Investment-to-GDP ratio improved, with:
- Government investment at 4.1% of GDP (FY23) — highest since FY12.
- Private corporate investment rising to 11.9% in FY23, projected to reach 12.5% in FY24.
What are External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)?
ECBs refer to loans raised by Indian entities from foreign lenders, including commercial banks, export credit agencies, and institutional investors. These borrowings are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and used for purposes like capital expansion, modernization, and infrastructure development.
Current Status of ECBs (as of Sept–Nov 2024):
- Outstanding ECBs stood at $190.4 billion (Sept 2024).
- Private sector share: 63% (~$97.6 billion).
- Public sector share: 37% (~$55.5 billion).
- Of the total, non-Rupee and non-FDI ECBs accounted for $154.9 billion.
- ECBs registered (April–Nov 2024): $33.8 billion, mainly for capital goods import, local capex, and new projects.
- Cost of ECBs declined to:
- 6.6% average during April–November 2024.
- 5.8% in November 2024, down by 71 basis points from the previous month.
- Hedging practices: Private companies hedge about 74% of their ECB exposure, essential for managing currency risk.
Why Are ECBs Important for India?
- Bridging Capital Gaps: Domestic markets may not meet the capital needs of large projects.
- Lower Interest Rates: ECBs often offer cheaper financing than domestic loans.
- Infrastructure Financing: Key source of funds for sectors needing long-term investment.
- Foreign Exchange Access: Supports imports, modernization, and technology adoption.
- Private Sector Expansion: Enables firms to grow, diversify, and remain globally competitive.
Challenges and Risks:
- Currency Risk: Rupee depreciation can raise repayment costs.
- Interest Rate Risk: Linked to global rates (e.g., LIBOR/SOFR), which can rise unpredictably.
- Hedging Costs: Though necessary, hedging adds to borrowing costs.
- Global Dependency: Exposure to international financial volatility.
- Regulatory Constraints: RBI norms on end-use, maturity, and cost ceilings can reduce flexibility.
- Over-Borrowing Risk: Mismanagement can lead to unsustainable debt levels and strain forex reserves.
Clarification on ECB Liability Data:
- Some media reports mistakenly cited India’s ECB stock as $273 billion.
- The actual ECBs, as per RBI (Sept 2024), stand at $190.4 billion.
- The inflated figure includes $72 billion in FPI (Debt), which should not be classified as ECBs.
Way Forward:
- Regulatory Refinement: Simplify ECB rules for strategic sectors and long-term projects.
- Encourage Hedging: Make risk management more affordable and accessible.
- Prudent Borrowing: Promote ECBs for infrastructure, exports, and modernization rather than working capital.
- Monitoring and Oversight: Ensure transparency and prevent over-leverage.
- Strengthen Domestic Financing: To reduce overdependence on foreign borrowing.
Judiciary in Crisis and the Digital Transformation of India

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian judiciary is grappling with an unprecedented backlog of cases, while India’s digital economy is witnessing exponential growth, promising to be a key driver of future economic expansion. Simultaneously, India's strides in the space sector and emerging technologies signal its increasing role as a global innovator.
The Crisis of Judicial Pendency in India
- Background: The Supreme Court recently permitted High Courts to appoint ad-hoc retired judges under Article 224A to address the mounting pendency of cases. This move revives a constitutional provision that had remained dormant, with only three recorded instances of its use.
- Scale of Backlog:
- As of January 2025, over 62 lakh cases are pending in High Courts.
- Nearly 4 crore cases are pending in subordinate courts.
- 30% of High Court judicial positions remain vacant.
- Reasons for Pendency
- Insufficient Judicial Strength: Low judge-to-population ratio.
- Infrastructure Deficit: Poor court facilities, especially in rural areas.
- Administrative Delays: Outdated systems and slow bureaucratic processing.
- Rising Litigation: Increase in public awareness and socio-economic issues.
- Adjournments & Procedural Delays: Inefficient court practices.
- Vacancies in Appointments: Delay in filling judicial posts due to the standoff between executive and judiciary.
Constitutional Provision: Article 224A
- Enables High Courts to appoint retired judges temporarily with the President’s consent.
- Judges appointed under this article have full powers and jurisdiction of a regular High Court judge.
- Supreme Court in Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021) provided guidelines for such appointments, including limiting it to instances where judicial vacancies are not more than 20%.
Judicial Appointments Debate: Collegium vs. NJAC
- Collegium System
- CJI + Four senior-most judges decide appointments.
- Criticized for lack of transparency, nepotism, and non-accountability.
- National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC)
- Proposed inclusion of judiciary, executive, and civil society (2 eminent persons).
- Struck down by SC in 2015 to preserve judicial independence.
- Current Debate: Rising demands for a reformed NJAC to bring in accountability while retaining independence.
Global Models of Judicial Appointments
Country System Key Feature
UK Judicial Appointments Commission Transparent, includes laypersons
South Africa Judicial Service Commission Diverse representation: judiciary, politicians, academics
France High Council of Judiciary Balanced approach with civil society input
Impacts of Judicial Delay
- Delayed Justice: Undermines public trust.
- Overcrowded Prisons: Over 70% of inmates are undertrials; prisons operate at 114% capacity.
- Economic Costs: Delays in dispute resolution hamper business environment and economic efficiency.
- Judicial Burnout: Overburdened judges impact quality of judgments.
Addressing Judicial Pendency
- Short-Term Measures
- Appointment of Ad-Hoc Judges under Article 224A.
- Fast Track Courts for specific offenses (e.g., crimes against women, corruption).
- Long-Term Reforms
- Reforming Judicial Appointments: Transparent and accountable system through restructured NJAC.
- Enhancing Collegium Transparency: Clear criteria and public disclosure.
- Promoting ADR Mechanisms: Arbitration, mediation, and conciliation to reduce court burden.
- Judicial Infrastructure Development: More courtrooms, modern facilities, and digitalization.
Way Forward
Judicial Reform
- Strengthen judicial accountability while maintaining independence.
- Incorporate global best practices in appointment systems.
- Promote Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) and digitization of court processes
Why Indian cities need Behavioral Change Officers

- 21 Jan 2025
Urban India at a Crossroads
India's urban population is projected to reach 40% by 2030, up from 30% in 2011. While this urban surge brings opportunities for economic and social progress, it also amplifies challenges such as:
- Infrastructure strain
- Environmental degradation
- Social inequality
- Climate impacts—including increased frequency of floods, heatwaves, and climate-driven migration
Traditionally, governments have relied on a combination of policy reforms, infrastructure investment, and technological advancements. However, a crucial component is often overlooked: behavioral change.
The Case for Behavioral Change in Urban Governance
Urban planning and service delivery frequently overlook how citizen and provider behavior shapes outcomes. Sustained, meaningful change requires more than just awareness campaigns—it demands behaviorally-informed governance. Here's why:
- Enhancing Service Delivery: Cities like Indore showcase how behavior change can revolutionize urban systems. Once struggling with waste management, Indore became India’s cleanest city through:
- Door-to-door campaigns
- Strict enforcement of segregation rules
- Viral initiatives like the ‘Kachra Gadi’ song to shift mindsets
- Driving Sustainability: In cities like Delhi, the odd-even vehicle rule led to a 30% reduction in traffic congestion by using simple default behavioral triggers. When people opt for public transport or energy conservation, it reduces emissions and eases city operations.
- Improving Public Safety: Behavioral strategies also improve law enforcement and community trust. For instance, Kerala’s ‘Janamaithri Suraksha’ program emphasizes empathetic policing, resulting in stronger police-citizen relations.
- Boosting Institutional Efficiency: Embedding behavioral insights can improve the efficiency of government schemes. The NITI Aayog’s Behavioral Insights Unit and initiatives in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar demonstrate success in using nudges to improve outcomes in areas like maternal health and welfare delivery.
Why Cities need Chief Behavioral Officers (CBOs)
To embed these insights systematically, Indian cities must institutionalize behavioral science through dedicated roles like Chief Behavioral Officers (CBOs) within Urban Local Bodies.
CBO Functions:
- Integrate behavioral strategies into urban planning
- Design evidence-backed nudges and campaigns
- Collaborate with stakeholders, municipal officers, and researchers
- Guide data-driven policy experimentation
Support Structure:
- A small team of behavioral fellows
- Annual Behavioral Plans aligned with city goals
- Investment in citizen engagement platforms
- Use of big data and surveys to uncover behavioral bottlenecks
Examples from global cities like New Orleans (via What Works Cities) show that CBOs can drive change quickly and cost-effectively.
Challenges to Behaviorally-Informed Urbanism
Despite its promise, this approach faces several roadblocks:
- Cultural inertia and resistance to change (e.g., reluctance in waste segregation)
- Lack of training in behavioral science among officials
- Resource constraints in smaller municipalities
- Fragmented coordination between departments (e.g., transport, sanitation)
Way Forward
To overcome these challenges, cities must:
- Institutionalize behavioral roles in governance structures
- Partner with behavioral scientists and think tanks
- Leverage technology (e.g., mobile apps for citizen feedback)
- Scale successful pilots (e.g., Indore’s waste model) across regions
This structured approach not only improves efficiency and citizen satisfaction, but also reduces the costs of service delivery, allowing long-term savings.
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
After 15 months of war triggered by Hamas' October 2023 attack on Israel, a ceasefire agreement has been brokered by Qatar, Egypt, and the US, marking a fragile but significant pause in one of the most destructive phases of the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Key Features of the Ceasefire Agreement
The agreement is based on a three-phase framework proposed by US President Joe Biden in June 2024 and endorsed by the UN Security Council:
Phase I (42 days)
- Complete ceasefire and withdrawal of Israeli forces from all populated areas in Gaza.
- Release of 33 Israeli hostages (women, elderly, injured) by Hamas.
- Release of 900–1,650 Palestinian prisoners, including minors and those detained since October 7, 2023.
- Daily entry of 600 humanitarian aid trucks into Gaza.
- Partial Israeli withdrawal from key corridors like Netzarim (splitting Gaza) and parts of the Philadelphi Corridor (Gaza-Egypt border).
Phase II
- Release of remaining hostages, primarily male soldiers.
- Complete Israeli military withdrawal from Gaza.
- Details to be negotiated during Phase I; no written guarantees for its execution.
Phase III
- Return of the remains of deceased hostages.
- Initiation of a multi-year reconstruction plan for Gaza under international supervision.
Challenges to Implementation
Fragile Political Consensus in Israel
- Far-right ministers (e.g., Itamar Ben-Gvir) oppose the deal, threatening to quit the government.
- Prime Minister Netanyahu faces pressure from both hawks demanding a full military victory and moderates seeking peace.
Hamas' Demands
- Seeks permanent ceasefire and complete Israeli withdrawal, making it unwilling to release all hostages without guarantees.
- Israel, in contrast, insists on neutralizing Hamas militarily.
Unclear Future Governance of Gaza
- Israel rejects both Hamas and the Palestinian Authority (PA) as future administrators.
- Global consensus supports Palestinian-led governance, but viable alternatives remain elusive.
Wider Geopolitical Impact
Reshaping West Asia
- Conflict escalated tensions with Hezbollah (Lebanon) and drew Israel into direct conflict with Iran.
- Iran’s influence weakened due to losses in Hezbollah and Syria.
- Assad regime in Syria collapsed, altering regional power dynamics.
Diplomatic Repercussions for Israel
- Despite military dominance, Israel faces global condemnation over civilian casualties.
- PM Netanyahu is under scrutiny at the ICC (war crimes) and ICJ (genocide allegations).
- Israel is now diplomatically isolated, particularly after the humanitarian toll in Gaza.
Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza
- Over 64,000 Palestinians killed (The Lancet, 2024), including large numbers of civilians.
- Massive destruction of infrastructure—schools, hospitals, homes—rendering Gaza nearly uninhabitable.
- Reconstruction hinges on sustained peace and international aid.
Conclusion
The ceasefire presents a rare opportunity for de-escalation in a deeply entrenched conflict. However, distrust between parties, domestic political constraints, and regional rivalries pose significant risks to its sustainability. A durable peace can only emerge through inclusive political dialogue, humanitarian prioritization, and movement toward a two-state solution.
River Interlinking in India

- 18 Jan 2025
Context:
India, with 17% of the world’s population but only 4% of its freshwater resources, faces significant water distribution challenges. The ambitious river interlinking project aims to mitigate regional water imbalances by transferring water from surplus areas to water-deficient regions, addressing irrigation, drinking water supply, flood control, and overall development.
Background and Evolution
The idea of interlinking rivers dates back to 1858 when British engineer Captain Arthur Cotton proposed linking rivers for inland navigation. Post-independence, Dr. K.L. Rao (1972) suggested the ‘Ganga-Cauvery Link Canal,’ followed by Captain Dinshaw J. Dastur’s ‘National Garland Canal’ proposal in 1977. However, these were deemed infeasible. In 1980, the Ministry of Water Resources formulated the National Perspective Plan (NPP), identifying 30 river link projects—14 under the Himalayan component and 16 under the Peninsular component.
The National Water Development Agency (NWDA) was established in 1982 to study and implement these projects. The Supreme Court, in response to a PIL in 2002, directed the government to expedite the completion of interlinking projects.
Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)
The first project under the NPP, the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP), was inaugurated on December 25, 2024. It aims to provide irrigation to Bundelkhand, one of India’s most drought-prone regions, by transferring surplus water from the Ken River in Madhya Pradesh to the Betwa River in Uttar Pradesh. Covering 10.62 lakh hectares of land (8.11 lakh ha in MP and 2.51 lakh ha in UP), the project will supply drinking water to 62 lakh people and generate 103 MW of hydropower along with 27 MW of solar power. However, environmental concerns persist as it passes through the Panna Tiger Reserve.
Significance of River Interlinking
- Water Redistribution: The scheme will transfer about 200 billion cubic meters (BCM) of water annually to water-scarce regions, ensuring equitable distribution.
- Agricultural Benefits: It will irrigate approximately 34 million hectares of farmland, enhancing food security and increasing agricultural productivity.
- Hydropower Generation: An estimated 34,000 MW of hydropower will be generated, supporting renewable energy expansion.
- Flood and Drought Mitigation: Excess water will be stored in reservoirs, reducing flood risks while ensuring availability during droughts.
- Economic Growth: Improved water availability will boost industries, generate employment, and aid in rural development.
Environmental and Social Concerns
- Ecological Disruptions: Altering river morphology can impact sediment transport, water quality, and aquatic ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Loss: Dams and canals may disrupt fish migration patterns and submerge forests, leading to biodiversity depletion.
- Climate Impact: Water transfer may affect regional climate attributes, altering temperature, precipitation, and humidity levels.
- Displacement and Social Issues: Large-scale projects often lead to displacement of communities, causing resettlement challenges and conflicts over compensation.
- Economic Viability: High project costs and potential delays raise concerns about financial feasibility compared to alternative solutions like rainwater harvesting and local water conservation.
Conclusion
While river interlinking presents a potential solution to India’s water crisis, it must be carefully assessed against environmental and social impacts. Sustainable water management strategies, such as efficient irrigation techniques and localized conservation methods, should complement large-scale projects to ensure a balanced approach to water security and development.
Digital Governance in India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
India is making significant strides toward digital governance, an initiative aimed at enhancing both citizen services and the capabilities of government employees. This transition to a digitally-driven framework is designed to improve the efficiency, transparency, and accountability of government operations, positioning India as a global leader in modern governance practices.
What is Digital Governance?
Digital governance refers to the application of technology to enhance the functioning of government processes. By integrating digital tools and platforms, it aims to streamline administrative operations, reduce inefficiencies, and improve public service delivery. This approach also extends to ensuring greater transparency and accountability in government dealings.
Key Initiatives in Digital Governance
India has launched several critical initiatives to modernize governance through digital means. Some of the key programs include:
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform: The iGOT Karmayogi platform is a government initiative to provide online training to public employees. It aims to enhance public administration skills, foster expertise in data analytics, and equip employees with the necessary tools in digital technologies. This initiative aims to prepare government personnel to handle the challenges of a digitally evolving governance landscape.
- e-Office Initiative: The e-Office program is designed to reduce paper-based work by digitizing workflows within government departments. This initiative facilitates real-time communication among offices and ensures more efficient and transparent management of tasks. It also helps streamline decision-making processes and improves the speed of governance operations.
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM): The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is an online platform developed to optimize procurement processes. It allows government agencies to procure goods and services efficiently, transparently, and with accountability. This platform has contributed to reducing corruption and ensuring that government purchases represent the best value for public money.
- Cybersecurity Training for Employees: As digital operations increase, ensuring the safety of sensitive data is paramount. The cybersecurity training program for government employees is designed to enhance their ability to recognize and respond to potential cyber threats. This initiative ensures data protection, safe online practices, and cyber resilience across digital governance platforms.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Governance
Despite its benefits, India faces several challenges in the successful implementation of digital governance. These obstacles must be addressed to unlock the full potential of technology-driven governance.
- Resistance to Technological Change: One of the key barriers to digital transformation in government is the resistance among employees to adopt new technologies. Many government officials remain accustomed to traditional, paper-based processes and are reluctant to transition to digital systems due to concerns about complexity and job security.
- Digital Divide in Rural Areas: While urban regions in India have better access to high-speed internet and digital infrastructure, many rural areas face significant digital divide challenges. Limited access to technology hampers the successful implementation of digital governance in these regions, restricting equitable service delivery across the country.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The rise of digital operations in governance increases the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. With government data being digitized, the threat of cybercrimes becomes more pronounced, making it critical to implement robust cybersecurity measures and data protection strategies to safeguard sensitive information.
- Lack of Incentives for Training Outcomes: Although government employees are encouraged to take part in training programs such as iGOT Karmayogi, the absence of clear incentives to complete these programs can undermine their effectiveness. Establishing tangible rewards or career progression linked to the successful completion of training would encourage employees to fully engage in capacity-building initiatives.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
To ensure the success of digital governance, several strategies must be put in place to address the challenges identified.
- Foster Innovation-Friendly Environments: Promoting an innovation-friendly culture within government offices can help reduce resistance to new technologies. Encouraging employees to engage with digital tools, offering regular training, and providing ongoing support will facilitate a smoother transition to a technology-driven governance system.
- Invest in Digital Infrastructure for Rural Areas: Addressing the digital divide requires significant investment in digital infrastructure in rural and remote areas. Ensuring that these regions have reliable internet access and the necessary technological resources will empower citizens across India to benefit from digital governance.
- Continuous Capacity-Building Programs: Establishing continuous training programs for government employees will ensure that they remain up-to-date with the latest technological trends. Regular updates to training content will help employees stay prepared to handle emerging challenges in digital governance.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity Protocols: To mitigate cybersecurity risks, it is essential to implement stringent cybersecurity measures across all levels of government operations. This includes regular cybersecurity awareness programs, proactive threat management systems, and rigorous data protection protocols to safeguard both government data and citizens’ personal information.
Conclusion
India’s shift towards digital governance represents a significant step toward modernizing administrative systems, enhancing transparency, and improving service delivery to citizens. However, challenges such as resistance to change, the digital divide, cybersecurity risks, and the lack of clear incentives for training must be addressed. By investing in digital infrastructure, offering continuous training programs, and reinforcing cybersecurity measures, India can create an effective and secure framework for digital governance that benefits both its citizens and the government workforce.
India’s Startup Revolution

- 15 Jan 2025
Context
India has solidified its position as one of the most dynamic startup ecosystems globally, emerging as a hub for innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological progress. However, realizing its ambition of becoming the top startup ecosystem requires addressing critical challenges and leveraging available opportunities.
Current Landscape of Indian Startups
Growth and Innovation
India ranks as the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world, following the U.S. and China. As of January 15, 2025, over 1.59 lakh startups have been officially recognized by DPIIT, with more than 120 attaining unicorn status (valuation exceeding $1 billion).
Investment Trends
Despite economic fluctuations, India's startups continue to attract significant investments. In 2022, venture capitalists infused $25 billion into the ecosystem, reaffirming India’s position as a preferred destination for global investors. Although there was a slowdown in 2023, domains like Software as a Service (SaaS) and climate tech continue to secure substantial funding.
Government Support
India’s startup-friendly policies, including Startup India, Digital India, and Atmanirbhar Bharat, have created an enabling environment. Notable initiatives include:
- Tax incentives, faster patent approvals, and regulatory relaxations.
- The launch of a ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) in 2023 to improve capital accessibility.
- The Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR) to streamline collaboration among startups and investors.
Regional Growth
- Tier II and III Expansion: Nearly 50% of startups are now based in emerging hubs such as Indore, Jaipur, and Ahmedabad.
- Tamil Nadu: The state boasts a $28 billion startup ecosystem, growing at 23%. Chennai alone houses around 5,000 startups, significantly contributing to employment generation.
- Kerala: With a $1.7 billion startup ecosystem, Kerala exhibits a compound annual growth rate of 254%, emphasizing cost-effective tech talent hiring.
Key Challenges Faced by Startups
1. Funding Constraints
The global economic downturn, coupled with rising interest rates, has limited venture capital inflows, resulting in layoffs and operational cutbacks.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Barriers
Despite government support, startups grapple with complex tax structures, evolving data protection laws, and stringent compliance requirements, including ESOP taxation policies.
3. Scaling and Market Adaptability
Many startups struggle with operational inefficiencies, limited market penetration, and inadequate infrastructure, hampering growth potential.
4. High Failure Rate
Approximately 90% of Indian startups fail within five years due to poor product-market fit, lack of financial planning, and insufficient adaptation to market needs.
5. Talent Shortages
India faces stiff competition in acquiring skilled professionals in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and machine learning, making retention increasingly difficult amid economic uncertainties.
Strategic Measures to Strengthen India’s Startup Ecosystem
1. Enhancing Policy Frameworks
- Simplified Regulations: Streamline startup registration, funding approvals, and international business operations.
- IP Protection: Strengthen intellectual property laws to boost R&D investment.
- Sector-Specific Initiatives: Develop targeted policies for AI, deep tech, healthcare, and green technologies.
2. Expanding Funding Access
- Encouraging Domestic Investment: Leverage pension and sovereign wealth funds to invest in startups.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster large-scale government-industry collaboration to finance emerging ventures.
- Decentralized Funding: Expand angel investor networks and micro-investment opportunities, particularly in Tier II and III cities.
3. Building Robust Infrastructure
- Tech Parks and Incubation Centers: Establish state-of-the-art facilities with mentorship programs.
- Improved Digital Connectivity: Ensure high-speed internet access in underserved regions.
- Enhanced Logistics and Supply Chains: Strengthen infrastructure to support startup scalability.
4. Developing a Skilled Workforce
- STEM and Entrepreneurial Education: Introduce curriculum enhancements in technical and business disciplines.
- Upskilling Programs: Collaborate with industry leaders to train professionals in high-demand skills.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promote initiatives encouraging women and marginalized communities in entrepreneurship.
5. Fostering Innovation and Risk-Taking
- Strengthened R&D Funding: Increase allocations to universities and private research sectors.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Reduce societal stigma surrounding startup failures to promote risk-taking.
- Leveraging Domestic Challenges: Address local issues like climate change and urbanization through innovation.
6. Expanding Global Reach
- International Collaborations: Partner with foreign accelerators and governments.
- Ease of Cross-Border Trade: Simplify export and import regulations for startups.
- Engaging the Indian Diaspora: Encourage successful overseas entrepreneurs to mentor and invest in Indian startups.
7. Advancing Sustainability Goals
- Green Tech Promotion: Support startups focusing on renewable energy and circular economy initiatives.
- Eco-Friendly Incentives: Offer financial support to ventures aligning with sustainability targets.
- Inclusive Growth Strategies: Expand agritech, edtech, and health-tech startups in rural areas, supporting platforms like the Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) by NITI Aayog.
Building a Resilient Digital Economy
To fortify India's digital economy, startups should leverage existing infrastructure like UPI and Aadhaar while capitalizing on emerging technologies such as AI, 5G, and blockchain. A robust cybersecurity framework and data protection policies will be essential to ensure investor confidence.
Genome India Project

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Genome India Project is an ambitious national initiative aimed at decoding the genetic diversity of India’s population. Launched in January 2020 by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), the project seeks to create a comprehensive map of India’s genetic variations, offering insights that can revolutionize public health, medicine, and our understanding of human genetics.
What is Genome Sequencing?
Genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome. The human genome, composed of about 3 billion base pairs of DNA, contains all the genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, and functioning of the human body. The process involves extracting DNA from a sample (often blood), breaking it into smaller fragments, and using a sequencer to decode these fragments. The data is then reassembled to reconstruct the full genome.
Key Aims and Objectives
The Genome India Project aims to address several crucial scientific and healthcare challenges:
- Create an Exhaustive Catalog of Genetic Variations: This includes common, low-frequency, rare, and structural variations (such as Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs).
- Establish a Reference Haplotype Structure: This reference panel will be used for imputing missing genetic variations in future genetic studies.
- Design Affordable Genome-wide Arrays: These arrays will be useful for research and diagnostics at a lower cost, making genetic analysis accessible.
- Create a Biobank for Future Research: The collected DNA and plasma will be preserved for future studies to facilitate ongoing genetic research.
Genome India Project: Phase 1 and Key Findings
The project’s Phase 1 focused on sequencing the genomes of 10,074 individuals from 99 ethnic groups across India. This initiative provides a critical baseline for studying the country’s genetic diversity. Some of the key findings include:
- 459 plant species have been identified as part of genetic diversity studies.
- 135 million genetic variations have been uncovered, including 7 million that are unique to India, not found in global databases.
- The project has revealed several genetic risks specific to Indian populations, such as the MYBPC3 mutation (linked to cardiac arrest) and the LAMB3 mutation (associated with a lethal skin condition), which are not commonly seen in global datasets.
This database will serve as a vital resource for researchers, contributing to the development of precision medicine, better disease diagnosis, and more personalized treatments.
Second Phase: Expanding the Scope
The second phase of the Genome India Project will focus on sequencing the genomes of individuals suffering from specific diseases. This will enable researchers to:
- Compare the genomes of healthy individuals with those having diseases, helping identify genetic mutations responsible for conditions like cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Investigate rare diseases specific to Indian populations and develop therapies tailored to these conditions.
By sequencing the genomes of individuals with various conditions, the project aims to pinpoint genetic factors that contribute to the pre-disposition or causation of diseases.
Data Sharing and Security
To ensure data security and privacy, the genetic information will be made available only through managed access. Researchers interested in using the data will need to submit a proposal and collaborate with the Department of Biotechnology. The data will be stored securely at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad, Haryana, and anonymized to maintain confidentiality.
Why Does India Need Its Own Genetic Database?
India is home to a highly diverse population, with over 4,600 distinct ethnic groups and varying genetic backgrounds. The country’s genetic diversity, shaped by its geographical, cultural, and historical context, cannot be fully understood through datasets derived from other countries. The Genome India Project helps:
- Identify Genetic Risk Factors: For various diseases, paving the way for developing targeted diagnostic tools and therapies.
- Uncover Unique Variants: Some genetic mutations found in India, such as the Vaishya community’s resistance to anaesthetics, are absent in global databases.
- Address Population-specific Health Issues: Genetic mapping enables the identification of prevalent diseases and health conditions specific to Indian populations.
Global Context and Comparison
India’s genome sequencing effort is part of a larger global movement in genomics:
- Human Genome Project (2003): The first international effort to decode the human genome.
- 1,000 Genome Project (2012): Published 1,092 human genome sequences.
- UK 100,000 Genome Project (2018): Sequenced 100,000 genomes for health research.
- European Genome Project: Aims to sequence over 1 million genomes across 24 countries.
The Genome India Project fills a crucial gap by focusing on the genetic diversity of Indian populations, which differs significantly from the genetic profiles studied in Western or European genomes.
Applications of Genome India Project
The Genome India Project has the potential to impact multiple areas:
- Advancements in Medicine: Understanding genetic variations can lead to the development of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Genetic and Infectious Disease Control: The project helps identify genetic resistance to diseases, and aids in understanding how certain populations may respond differently to drugs or vaccines.
- Public Health Policies: Data from the project can inform health policies, especially in tackling diseases prevalent in specific regions or communities.
- International Research Collaboration: The project aims to foster collaboration with global research communities, enhancing India’s presence in the field of genomics.
Conclusion:
The Genome India Project is a landmark initiative for India’s scientific community, enabling better understanding of the country’s genetic diversity and paving the way for breakthroughs in medicine, healthcare, and disease prevention. The ability to analyze genetic variations on such a large scale provides immense opportunities for precision medicine and personalized treatments.
Why Farmers Deserve Price Security
- 11 Jan 2025
Introduction:
The future of Indian agriculture is at a crossroads. With the shrinking of the agricultural workforce and the diversion of fertile farmlands for urbanization, ensuring the sustainability of farming is a strategic imperative. Among the various support mechanisms for farmers, the Minimum Support Price (MSP) remains a central point of debate. Should there be a legal guarantee for MSP? This question has gained prominence, especially with the rising challenges in agriculture, from unpredictable climate patterns to volatile market prices.
The Decline of Agriculture and Its Impact
India’s agricultural sector faces a dual crisis: loss of both land and human resources. Prime agricultural lands across river basins, such as the Ganga-Yamuna Doab or the Krishna-Godavari delta, are being repurposed for real estate, infrastructure, and industrial projects. Additionally, the number of "serious farmers" – those deriving at least half of their income from agriculture – is dwindling. The number of operational holdings may be 146.5 million, but only a small fraction of these farmers remains committed to agriculture.
This decline threatens the future of India’s food security, as the country will need to feed a population of 1.7 billion by the 2060s. To sustain farming and ensure long-term food security, we must secure farmers' livelihoods. Price security, particularly through MSP, plays a crucial role in this context.
The Role of MSP in Securing Farmers
MSP is the government-mandated price at which it guarantees the purchase of crops if market prices fall below a certain threshold. It provides a safety net for farmers against price volatility. The process of fixing MSP involves recommendations by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which takes into account factors such as the cost of production and market trends. Once approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), MSP is set for various crops, including rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
For farmers to stay in business, there must be a balance between production costs and returns. Farming is a risky business – yield losses can occur due to weather anomalies, pest attacks, or other natural factors. However, price risks can be mitigated with a guaranteed MSP. This would encourage farmers to invest in their land and adopt modern farming technologies, which would boost productivity and reduce costs.
Arguments for and Against Legal MSP Guarantee
Supporters of a legal MSP guarantee argue that it would provide financial security to farmers, protecting them from unpredictable market conditions. It would also promote crop diversification, encourage farmers to shift from water-intensive crops to those less dependent on irrigation, and inject resources into rural economies, thus addressing distress in rural areas.
However, critics highlight several challenges with a legal guarantee for MSP. The most significant concern is the fiscal burden it would impose on the government, potentially reaching Rs. 5 trillion. Furthermore, such a system could distort market dynamics, discouraging private traders and leading to a situation where the government becomes the primary buyer of agricultural produce. This could be economically unsustainable, especially for crops with low yields. Additionally, legal MSP guarantees could violate World Trade Organization (WTO) subsidy principles, adversely impacting India’s agricultural exports.
The Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
Given the challenges associated with a legal MSP guarantee, alternative measures should be explored. Price Deficiency Payment (PDP) schemes, such as those implemented in Madhya Pradesh and Haryana, could be expanded at the national level. These schemes compensate farmers for the difference between market prices and MSP, ensuring price security without the fiscal burden of procurement.
Additionally, the government can focus on improving agricultural infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities, to help farmers better access markets and increase price realization. Supporting Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) could also help farmers by enhancing collective bargaining power and ensuring better prices for their produce. Moreover, gradual expansion of MSP coverage to include a wider range of crops would encourage diversification, reducing the dominance of rice and wheat.
River Interlinking: Environmental Disaster or Solution?
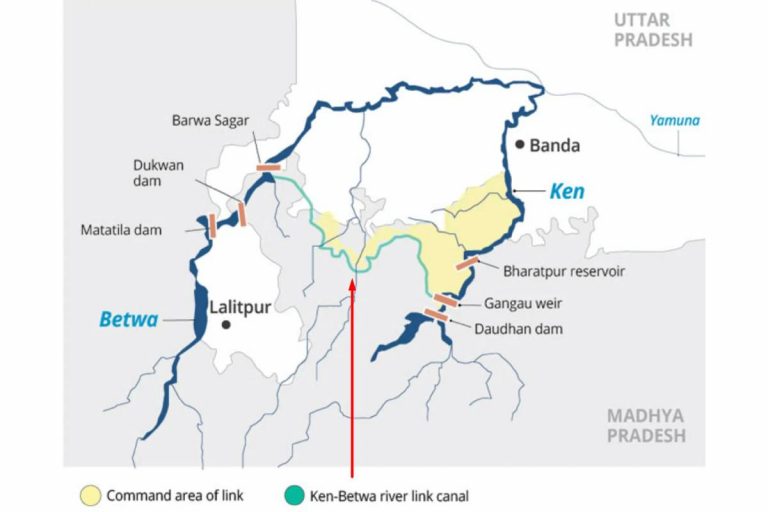
- 09 Jan 2025
Overview of the River Interlinking Concept
The concept of river interlinking in India traces its origins to the 19th century, when Sir Arthur Cotton first proposed inter-basin water transfer to address irrigation issues. Over time, this idea was refined by other experts. It evolved into the National Water Grid and, later, the River-Interlinking Project (ILR) under the Ministry of Water Resources. The goal is to transfer surplus water from rivers to drought-prone areas, aiming for water security, irrigation, and power generation.
Key Projects and Initiatives
- Ken-Betwa River Link Project (KBLP): Launched in December 2024, the KBLP will link the water-surplus Ken River with the drought-stricken Betwa River. It aims to irrigate over 10 lakh hectares, supply drinking water to 62 lakh people, and generate hydropower and solar power. However, concerns over the environmental impact of building a dam within the Panna Tiger Reserve have been raised.
- National River Linking Project (NRLP): The NRLP, formally known as the National Perspective Plan, is an ambitious proposal that includes 30 river links—14 Himalayan and 16 Peninsular—to connect India's rivers and create a giant South Asian Water Grid.
Benefits of Interlinking Rivers
- Flood and Drought Mitigation: Redistributing water from surplus areas to drought-prone regions, such as Bundelkhand, will reduce the severity of floods and droughts.
- Agriculture and Irrigation: Expanding irrigation systems across 35 million hectares of land could significantly boost agricultural productivity and food security.
- Hydropower Generation: The interlinking project has the potential to generate up to 34 GW of hydropower, contributing to India's renewable energy targets.
- Economic Growth: Improving water availability can boost industries, provide drinking water, and support economic development in underdeveloped regions.
- Inland Waterways: The project will also contribute to the expansion of inland waterways, benefiting trade and reducing transportation costs.
Challenges and Concerns
- Environmental Impact:
- Biodiversity Loss: Projects like the Ken-Betwa project raise alarms about the destruction of ecologically sensitive areas, such as the Panna Tiger Reserve.
- River Ecosystem Disruption: Altering natural river courses can harm aquatic life, disrupt deltaic ecosystems, and degrade water quality. For instance, the Sardar Sarovar Dam's impact on the Narmada river system shows the long-term consequences of such projects.
- Pollution: The mixing of cleaner and more polluted rivers could exacerbate water contamination issues.
- Social and Financial Costs:
- Displacement: Large-scale interlinking projects will displace millions, especially marginalized communities and indigenous people, and disturb local livelihoods.
- High Financial Burden: The total estimated cost of the NRLP is ?5.5 lakh crore, which does not include environmental rehabilitation costs or the long-term maintenance of the infrastructure.
- Climate Change: Predictions suggest that climate change could affect river flows and the availability of surplus water. This might render the interlinking project ineffective in the long term.
- Inter-State Conflicts: Water-sharing disputes, like the long-standing issues over the Cauvery and Krishna rivers, could intensify with more interlinking projects.
- Infrastructural Challenges: Maintaining vast canal networks and reservoirs, managing sedimentation, and acquiring land for construction are logistical hurdles.
Alternative Approaches and Solutions
- Efficient Water Management:
- Integrated Watershed Management: Implementing a comprehensive approach to manage existing water resources can reduce the need for large-scale river transfers.
- Groundwater Recharge: Focusing on efficient groundwater management by identifying recharge mechanisms and regulating water use is crucial for sustainability.
- Modern Irrigation Techniques:
- Drip Irrigation: Israel’s success with drip irrigation, which reduces water use by 25%-75%, provides an example of how modern technologies can save significant amounts of water.
- Virtual Water: Emphasizing the import of water-intensive goods (like wheat) could save local water resources, which would otherwise be used for domestic agriculture.
- National Waterways Project (NWP): An alternative to the interlinking project, NWP aims to improve water management by creating navigation channels that double as water distribution networks with a fraction of the land use.
Way Forward
- Comprehensive Impact Assessments: The need for multidisciplinary studies to evaluate the environmental, social, and economic impacts of river interlinking projects cannot be overstated. Stakeholder engagement is crucial for equitable decision-making.
- Sustainable Water Policies: A national water policy should prioritize sustainable water practices, focusing on local solutions, such as water harvesting, watershed management, and smart irrigation.
- Focus on Regional Solutions: Smaller, state-specific projects should be prioritized to address water scarcity issues without triggering large-scale environmental degradation.
The Impact of Climate Change on Earth’s Water Cycle

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Climate change is significantly affecting Earth's water cycle, leading to extreme weather events such as intense floods and prolonged droughts. According to the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report, this disruption is increasingly evident, as seen in the devastating weather patterns experienced worldwide in 2024. The report, based on data from international researchers, highlights how these changes are directly linked to rising global temperatures and the resulting shifts in precipitation patterns.
Understanding the Water Cycle
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water in various forms—solid, liquid, and gas—throughout the Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. This cycle involves processes such as:
- Evaporation: Water from the surface of oceans, lakes, and rivers turns into vapor.
- Transpiration: Water is absorbed by plants from the soil and released as vapor.
- Precipitation: Water vapor condenses into clouds and falls as rain or snow, replenishing the Earth's surface.
- Runoff and Infiltration: Precipitation either flows into rivers or infiltrates the soil, contributing to groundwater.
The water cycle is vital for maintaining the planet’s ecosystems, regulating weather patterns, and providing water for all living organisms. However, climate change is intensifying these natural processes, with far-reaching consequences.
Impact of Climate Change on the Water Cycle
As global temperatures rise, climate change is having a profound impact on the water cycle. Warmer temperatures lead to:
- Increased evaporation: As air temperatures soar, more water evaporates into the atmosphere. For every 1°C rise in temperature, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more moisture, which exacerbates storms and increases the intensity of rainfall.
- More intense precipitation: With more moisture in the atmosphere, storms have become more intense, leading to severe flooding in various regions.
- Increased droughts: Warmer air also dries out the soil. This reduces the amount of water available for crops and plants, while also increasing the evaporation rate from soil, leading to longer and more intense droughts.
This disruption of the water cycle is already causing erratic weather patterns, as some regions face severe droughts, while others are experiencing extreme rainfall and floods.
Key Findings from the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report
The 2024 report presents several alarming statistics that highlight the growing impact of climate change on the water cycle:
- Water-related disasters: In 2024, these disasters caused over 8,700 fatalities, displaced 40 million people, and resulted in economic losses exceeding $550 billion globally.
- Dry months: There were 38% more record-dry months in 2024 than the baseline period (1995-2005), underlining the growing frequency of droughts.
- Intense rainfall: Record-breaking rainfall occurred 27% more frequently in 2024 compared to 2000, with daily rainfall records set 52% more often. This shows the growing intensity of precipitation events.
- Terrestrial water storage (TWS): Many dry regions faced ongoing low TWS levels, reflecting the scarcity of water in these areas, while some regions, such as parts of Africa, saw an increase in water storage.
- Future predictions: Droughts may worsen in regions like northern South America, southern Africa, and parts of Asia, while areas like the Sahel and Europe could experience increased flood risks in the coming years.
Conclusion
The findings of the 2024 report underscore the alarming impact of climate change on the global water cycle. As temperatures continue to rise, we can expect more frequent and severe weather events, including extreme flooding and devastating droughts. These changes will affect billions of people worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for action to mitigate climate change and adapt to its consequences. Addressing this challenge requires global cooperation to reduce emissions, enhance water management systems, and protect vulnerable regions from the intensifying effects of climate change.
India-Sri Lanka Diplomatic Engagement

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD) to India marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, as it was his first foreign trip since assuming office. The visit underscored key diplomatic exchanges and collaborations between the two countries, showcasing both areas of agreement and divergence.
Key Takeaways from AKD's Visit
Assurance on Anti-India Activities: One of the primary concerns for India was the use of Sri Lankan territory for activities detrimental to its security, particularly the presence of Chinese “research vessels” at Sri Lankan ports. President AKD assured Prime Minister Narendra Modi that Sri Lanka would not allow its territory to be used in ways that threaten India’s interests. This assurance is crucial, as it signals Sri Lanka's stance on maintaining regional stability, despite AKD’s perceived pro-China inclinations.
Tamil Minority Issue: Divergent Views: A notable divergence in their discussions was the issue of the Tamil minority in Sri Lanka. India has long advocated for the full implementation of the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, which would grant greater autonomy to the Tamil minority. However, AKD resisted this, reaffirming his opposition to the amendment’s full implementation. While India emphasized the importance of reconciliation and holding provincial elections, AKD focused on unity, sustainable development, and social protection, sidestepping any definitive commitments on the Tamil issue.
Sri Lanka's Assertive Diplomatic Posture: AKD’s strong parliamentary mandate has allowed him to adopt a more assertive diplomatic stance. This is evident not only in his handling of the Tamil issue but also in his approach to dealing with major powers like India and China. His administration appears to be prioritizing a more independent foreign policy, signaling a shift from previous administrations.
Bilateral Cooperation and Development Initiatives
The visit saw significant agreements on bilateral cooperation, particularly in development and connectivity. Both nations acknowledged the positive impact of India’s assistance in Sri Lanka’s socio-economic growth. Key projects discussed include:
- Indian Housing Project: Phases III and IV.
- Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects across three islands.
- High-Impact Community Development Projects.
- Digital collaborations, such as the implementation of Aadhaar and UPI systems in Sri Lanka.
Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing energy cooperation, including the supply of LNG, development of offshore wind power in the Palk Strait, and the high-capacity power grid interconnection. The resumption of passenger ferry services between key Indian and Sri Lankan ports was also a priority.
Defence and Security Cooperation
The two leaders agreed to explore a Defence Cooperation Framework and intensify collaboration on maritime surveillance, cyber security, and counter-terrorism. This aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region, as it seeks to ensure stability in the Indian Ocean and strengthen its defense ties with Sri Lanka.
Strategic Continuity Amid Leadership Change
Despite a change in leadership, the core strategic interests between India and Sri Lanka remain aligned. India views Sri Lanka’s stability as crucial to regional security, and both countries are focused on a mutually beneficial partnership. AKD’s emphasis on economic recovery and tackling corruption within Sri Lanka, as seen in his actions against political figures like Speaker Asoka Ranwala, further signals his determination to build a strong foundation for his government’s future.
Conclusion
President AKD’s visit highlighted the evolving dynamics of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy, marked by a more confident and independent approach in engaging with India. While challenges remain, especially regarding the Tamil issue, both countries have reaffirmed their commitment to deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on development, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
Bank Credit to Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs)

- 21 Dec 2024
Introduction
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) is a flagship program by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) that aims to reduce poverty by empowering women, especially through Self-Help Groups (SHGs). These SHGs have been instrumental in improving financial inclusion, providing access to credit, and enhancing the economic and social status of women across India. The program has made significant strides in mobilizing women, improving their access to financial services, and facilitating entrepreneurial ventures in rural areas.
Key Features and Initiatives of DAY-NRLM
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs):
- Formation: DAY-NRLM supports the creation and strengthening of SHGs, primarily focusing on rural women from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Mobilization: As of 2024, over 10.05 crore women have been mobilized into 90.87 lakh SHGs across India.
- Objective: The main goal is to reduce poverty through empowerment by providing access to financial services and sustainable livelihoods.
- Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP):
- Support for Rural Enterprises: SVEP, a sub-scheme under DAY-NRLM, encourages SHG women and their families to set up small-scale businesses.
- Impact: As of October 2024, 3.13 lakh rural enterprises have been supported under this initiative.
- State-wise Distribution: The program has supported enterprises across various states, with notable contributions from Andhra Pradesh (27,651 enterprises), Kerala (34,569), and Uttar Pradesh (28,904).
- Banking Correspondent Sakhis:
- Role: Women in SHGs are trained as Banking Correspondent Sakhis to enhance access to banking services such as deposits, credit, remittances, pensions, and insurance in rural areas.
- Current Deployment: 1,35,127 Sakhis have been deployed under DAY-NRLM, empowering women to be financial intermediaries in their communities.
- Financial Support for SHGs:
- Revolving Fund: SHGs receive funds ranging from Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 30,000 to boost their operations and financial stability.
- Community Investment Fund: SHGs can avail of up to Rs. 2.50 lakh under the Community Investment Fund to strengthen their financial position.
- Interest Subvention: To make bank loans more affordable, DAY-NRLM provides interest subvention to SHGs, reducing their overall credit costs.
- Online Marketing Platform:
- www.esaras.in: This online platform allows SHGs to market their products, improving their access to broader markets and enhancing their income-generating potential.
Impact of DAY-NRLM and SHGs
- Financial Inclusion: SHGs play a vital role in financial inclusion by providing access to banking services, loans, and insurance to women, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Credit Mobilization: As of November 2024, SHGs have leveraged Rs. 9.71 lakh crore in bank credit, thanks to the capitalization support provided by DAY-NRLM, including Revolving Funds and Community Investment Funds.
- Empowerment of Women: SHGs have significantly contributed to the empowerment of women, providing them with financial independence, social support, and the ability to make decisions in their households and communities.
Challenges Faced by SHGs
- Beneficiary Identification: Ensuring that the most marginalized individuals are included in SHGs can be challenging.
- Training Gaps: There is a lack of quality training programs and expert trainers to build the capacity of SHG members.
- Financial Literacy: Many SHG members have limited knowledge of formal financial services, hindering effective financial management.
- Market Linkages: Poor integration with markets limits the growth potential of SHGs, especially in terms of product sales and business expansion.
- Community Support: Insufficient business environment support and value chain linkages pose challenges to SHG sustainability and growth.
Government Initiatives Supporting SHGs
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP): Launched by NABARD in 1992, this initiative aims to link SHGs with formal banking institutions, facilitating financial inclusion.
- Mission for Financial Inclusion (MFI): A broader initiative to ensure that rural populations have access to affordable financial services such as savings, credit, insurance, and pensions.
- Lakhpati Didi Initiative: Launched in 2023, this initiative empowers SHG women to adopt sustainable livelihood practices and aim for an annual household income exceeding Rs. 1 lakh.
Role of SHGs in Rural Development
- Women Empowerment: SHGs have emerged as a powerful tool for empowering women through financial independence, social security, and the ability to make informed decisions.
- Economic Growth: SHGs foster small-scale entrepreneurship, thereby creating local businesses that contribute to rural economic growth.
- Social Cohesion: By promoting collective action, SHGs provide a social support system that helps in addressing common issues faced by their members, such as health, education, and safety.
Future Prospects and Way Forward
- Technological Integration: SHGs should leverage advanced digital platforms for transaction management, record-keeping, and communication, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Reducing Informal Borrowing: Linking SHGs with formal financial institutions will reduce reliance on informal lenders, promoting financial inclusion.
- Inclusive Approach: SHGs should adopt an inclusive model to ensure that members from diverse socio-economic backgrounds are fairly represented and benefit equally.
- Training and Capacity Building: There is a need for more Community Resource Persons (CRPs) who can guide SHGs in beneficiary identification, financial management, and scaling their activities.
The Costly Push for 100% Electrification of Indian Railways

- 19 Dec 2024
Introduction
RITES Ltd., the consultancy arm of the Indian Railways, has secured two contracts to repurpose six broad gauge diesel-electric locomotives for export to African railways. These locomotives, originally designed for India’s broad gauge of 1,676 mm, will be modified for use on railways with the narrower Cape Gauge of 1,067 mm. While this is a commendable re-engineering effort, it also highlights a larger issue within Indian Railways: the unnecessary redundancy of functional diesel locomotives, leading to significant wastage of resources.
The Growing Problem of Idle Diesel Locomotives
As of March 2023, there were 585 diesel locomotives idling across the Indian Railways network due to electrification. This number has now reportedly grown to 760 locomotives, many of which still have more than 15 years of serviceable life. The root cause of this redundancy lies in the government’s mission to electrify the entire broad gauge network at an accelerated pace. This electrification push has resulted in the premature retirement of locomotives that could still serve the network for years, raising questions about the economic and environmental logic behind this decision.
The Justification for Electrification: Foreign Exchange and Environmental Concerns
The Indian government’s electrification drive is often justified on two primary grounds: saving foreign exchange by reducing the import of crude oil and reducing environmental pollution. Additionally, electrification is framed as a step toward a “green railway” powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. However, the reality of these claims is more complicated.
Foreign Exchange Savings: A Small Impact on National Diesel Consumption
While electrification may reduce India’s diesel consumption, the impact on national fuel use is minimal. Railways account for just 2% of the country’s total diesel consumption. A report by AC Nielsen in 2014 indicated that the transport sector consumed 70% of the total diesel, with railways accounting for only 3.24%. Even with 100% electrification, the savings in foreign exchange would have little impact on the country’s overall diesel consumption, leaving other sectors like trucking and agriculture as the main contributors.
Environmental Concerns: Shifting Pollution, Not Reducing It
The environmental argument for electrification is also flawed. Electricity in India is still largely generated from coal-fired power plants, with nearly 50% of the country’s electricity coming from coal. Since the Indian Railways is heavily involved in transporting coal, switching from diesel to electric locomotives simply shifts pollution from the tracks to the power plants. This means that the transition to electric traction will not result in a cleaner environment unless the country significantly reduces its reliance on coal. Without a substantial increase in renewable energy generation, the push for a “green railway” remains unrealistic.
The Dilemma of Retaining Diesel Locomotives for Strategic Purposes
Despite the goal of 100% electrification, a significant number of diesel locomotives will remain in service. Reports indicate that 2,500 locomotives will be kept for “disaster management” and “strategic purposes,” although it is unclear why such a large fleet is necessary for these purposes. Additionally, about 1,000 locomotives will continue to operate for several more years to meet traffic commitments. This suggests that even with a fully electrified network, Indian Railways will continue to rely on thousands of diesel locomotives, many of which have substantial residual service life left.
Financial Sustainability and Coal Dependency
The financial sustainability of this transition remains a concern. Currently, the Indian Railways generates a significant portion of its freight revenue from transporting coal—40% of its total freight earnings in 2023-24. If the railways become fully electrified, it will need to find alternative revenue sources, as coal is a primary contributor. Until non-coal freight options can replace this income, the financial health of the railways may be at risk.
Conclusion: Wasted Resources and Unmet Goals
The mission to electrify the Indian Railways, while ambitious, is an example of how vanity projects can lead to colossal waste. Thousands of diesel locomotives are being discarded prematurely, despite their potential to continue serving the network. The environmental and financial justifications for 100% electrification, while appealing in theory, fail to account for the complexities of India’s energy landscape. As a result, the drive to create a “green railway” is likely to fall short, leaving behind a legacy of wasted taxpayer money and unfinished goals.
Arctic Tundra: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Arctic tundra, a frozen, treeless biome, has historically been a vital carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO?) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). However, recent findings suggest that, for the first time in millennia, this ecosystem is emitting more carbon than it absorbs, a change that could have significant global consequences. This alarming shift was highlighted in the 2024 Arctic Report Card published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The Arctic Tundra’s Role as a Carbon Sink
The Arctic tundra plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. In typical ecosystems, plants absorb CO? through photosynthesis, and when they die, carbon is either consumed by decomposers or released back into the atmosphere. In contrast, the tundra’s cold environment significantly slows the decomposition process, trapping organic carbon in permafrost—the permanently frozen ground that underpins much of the region.
Over thousands of years, this accumulation of organic matter has resulted in the Arctic storing an estimated 1.6 trillion metric tonnes of carbon. This figure is roughly double the amount of carbon in the entire atmosphere. As such, the tundra has served as a critical carbon sink, helping to mitigate global warming by trapping vast quantities of CO?.
Shifting Dynamics: Emission of Greenhouse Gases
Recent reports indicate a dramatic shift in the Arctic tundra’s role in the carbon cycle. Rising temperatures and increasing wildfire activity have disrupted the tundra’s balance, leading it to transition from a carbon sink to a carbon source.
Impact of Rising Temperatures
The Arctic region is warming at a rate approximately four times faster than the global average. In 2024, Arctic surface air temperatures were recorded as the second-warmest on record since 1900. This rapid warming is causing permafrost to thaw, which in turn activates microbes that break down trapped organic material. As this decomposition accelerates, carbon in the form of CO? and methane (CH?)—a more potent greenhouse gas—are released into the atmosphere.
The experts, explained the process by comparing thawing permafrost to meat left out of the freezer. Similarly, thawing permafrost accelerates the breakdown of trapped carbon.
The Role of Wildfires
In addition to warming temperatures, the Arctic has experienced a surge in wildfires in recent years. 2024 marked the second-highest wildfire season on record in the region, releasing significant amounts of GHGs into the atmosphere. Wildfires exacerbate the thawing of permafrost, creating a feedback loop where increased carbon emissions contribute further to warming, which, in turn, leads to more emissions.
Between 2001 and 2020, these combined factors caused the Arctic tundra to release more carbon than it absorbed, likely for the first time in millennia.
The Global Consequences of Emission
The transition of the Arctic tundra from a carbon sink to a carbon source is alarming, as it represents a significant amplification of global climate change. The release of additional CO? and CH? into the atmosphere further accelerates the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures. This warming is already having visible consequences around the world, from extreme weather events to rising sea levels.
If the Arctic tundra continues to emit more carbon than it absorbs, it could significantly exacerbate the climate crisis. The report underscores the urgency of addressing global emissions, as reducing greenhouse gases remains the most effective way to prevent further destabilization of this sensitive ecosystem.
Mitigating the Impact: The Path Forward
Despite the alarming trends, the Arctic Report Card suggests that it is still possible to reverse this process. By reducing global GHG emissions, it may be possible to slow the thawing of permafrost and allow the Arctic tundra to regain its role as a carbon sink. Scientists emphasize that mitigating climate change on a global scale is essential to prevent further emissions from the Arctic ecosystem.
Scientists, stressed the importance of emission reductions, stating, “With lower levels of climate change, you get lower levels of emissions from permafrost… That should motivate us all to work towards more aggressive emissions reductions.”
However, current trends suggest that achieving this goal may be challenging. A recent report from the Global Carbon Project indicates that fossil fuel emissions are likely to rise in 2024, with total CO? emissions projected to reach 41.6 billion tonnes, up from 40.6 billion tonnes in 2023.
Artificial Solar Eclipse: Why Are Satellites Trying to Block the Sun?
- 14 Dec 2024
Introduction
The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched Proba-3, a mission that will create an artificial solar eclipse to study the Sun's atmosphere, known as the corona. This mission aims to demonstrate new technology and address unresolved questions about the Sun's outer layers.
What is an Artificial Solar Eclipse?
- Definition: An artificial solar eclipse mimics the natural phenomenon where the moon blocks sunlight, allowing detailed observation of the Sun’s corona.
- Created By: The eclipse is created by two satellites, which align to block the Sun's light and generate a controlled shadow for scientific study.
- Purpose: The goal is to study the Sun’s corona, particularly to understand why it is significantly hotter than the Sun’s surface.
How Does the Proba-3 Create an Eclipse?
Launch and Spacecraft
Proba-3 was launched on December 5 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India. The mission uses two satellites:
- Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC): This spacecraft guides the other satellite.
- Occulter Spacecraft (OSC): This satellite has a disk that creates a controlled shadow onto the CSC.
Formation Flying
Using Precise Formation Flying (PFF) technology, the two spacecraft maintain a precise distance of 150 meters (492 feet) apart, aligning perfectly with the Sun. This alignment mimics the effect of a solar eclipse.
Precision Requirements
The eclipse will need to maintain millimetre-level accuracy for up to six hours per orbit to provide scientists with stable observational conditions.
Mission Goals
- Demonstrating PFF Technology: One of the primary objectives of the Proba-3 mission is to demonstrate PFF technology. This involves using GPS and inter-satellite radio links for positioning, as well as maintaining a precise distance between the two spacecraft.
- Studying the Sun’s Corona: Another goal is to understand why the corona is hotter than the Sun's surface. The onboard instruments, including a coronagraph, will help with this research. The coronagraph will block out the Sun’s bright light, enabling clearer observations of the corona.
- ASPICCS Coronagraph: The Proba-3 coronagraph, named the Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun (ASPICCS), is designed to observe the corona in high detail, mimicking the observational conditions of a total solar eclipse.
Why Is This Such a Big Deal?
- Revealing the Sun’s Corona: The Sun’s corona is typically invisible because it is much less bright than the Sun’s surface. It can only be seen during a solar eclipse when the Moon blocks the Sun's light.
- Predicting Space Weather: Studying the corona helps scientists predict space weather and geomagnetic storms, which can disrupt satellites and other systems on Earth.
- Extended Observations: Unlike natural solar eclipses, which last only a few minutes, Proba-3 can provide six hours of observation time in each orbit (approximately 19 hours and 36 minutes), allowing for continuous study of the corona.
What is Precise Formation Flying (PFF) Technology?
- Definition: PFF technology allows satellites to maintain exact positions and orientations relative to each other in orbit.
- Mechanism: The technology uses GPS, inter-satellite radio links, and automated control systems to ensure alignment.
- Implementation in Proba-3: In the Proba-3 mission, the Coronagraph and Occulter spacecraft stay 150 meters apart, using PFF to maintain millimetre-level precision, which is crucial for simulating a solar eclipse.
- Benefits: PFF enhances mission accuracy and provides a platform for advanced observational techniques that will enable more detailed studies of the Sun's corona.
Conclusion
Proba-3 is a groundbreaking mission that will offer unprecedented insights into the Sun’s corona by simulating solar eclipses using advanced satellite technology. By studying the Sun’s outer layers, scientists aim to improve our understanding of space weather and the mysterious temperature anomaly of the corona.
Impeachment of Judges
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent controversy surrounding remarks made by Justice Shekhar Kumar Yadav of the Allahabad High Court has prompted calls for his impeachment. During an event organized by the Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP), Justice Yadav made statements that were perceived as communal, leading to concerns over judicial impartiality. This incident has reignited discussions about the impeachment process for judges in India, highlighting the delicate balance between judicial independence and accountability.
Impeachment Process for Judges in India
In India, the impeachment process for judges, although not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, serves as a mechanism to ensure judicial accountability while safeguarding judicial independence. The process is outlined under Articles 124 and 218 of the Indian Constitution, which govern the removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges, respectively.
Grounds for Impeachment
Judges in India can be removed on two grounds:
- Proved Misbehavior: Conduct that breaches the ethical standards of the judiciary.
- Incapacity: A judge’s inability to perform judicial duties due to physical or mental infirmity.
These grounds are clearly specified to prevent arbitrary removal, ensuring that the process remains fair and just.
Steps in the Impeachment Process
- Initiation of Motion: The process begins when a motion for impeachment is introduced in Parliament, either in the Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha. The motion must be supported by at least 100 members of the Lok Sabha or 50 members of the Rajya Sabha. This ensures significant parliamentary backing before the motion proceeds.
- Formation of an Inquiry Committee: If the motion is admitted, a three-member inquiry committee is constituted. This includes a Supreme Court judge, the Chief Justice of a High Court, and a distinguished jurist. The committee conducts a thorough investigation into the allegations.
- Committee Report and Parliamentary Debate: Following the investigation, the committee submits its findings. If the judge is found guilty, the report is debated in Parliament. Both Houses must approve the motion by a special majority, which requires a two-thirds majority of members present and voting, as well as a majority of the total membership.
- Final Removal by the President: Once the motion is passed in both Houses, it is presented to the President, who issues the removal order.
Safeguards Against Misuse
The impeachment process includes several safeguards to prevent misuse:
- High Threshold for Initiation: The requirement for significant support from Parliament ensures that the process cannot be initiated frivolously.
- Objective Inquiry: The inquiry committee, comprising legal experts, guarantees an impartial investigation.
- Parliamentary Scrutiny: Both Houses of Parliament are involved, ensuring that the process undergoes democratic scrutiny.
Challenges and Precedents
Despite the rigorous process, no Supreme Court judge has been successfully impeached to date. Past attempts, such as those against Justice V. Ramaswami (1993) and Chief Justice Dipak Misra (2018), were unsuccessful. These instances demonstrate the complexities involved in the impeachment process.
Guidelines for Judges’ Public Statements
Judges in India are entitled to freedom of speech, but they are expected to exercise caution in public statements to maintain the dignity of their office. The Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct (2002) and the Restatement of Values of Judicial Life (1997) outline key principles for judicial conduct, including:
- Non-Interference in Political Matters: Judges should refrain from commenting on political issues to avoid any perception of bias.
- Impartiality: Judges must avoid statements that could prejudice ongoing cases or align them with specific ideologies.
Upholding Judicial Impartiality in a Diverse Society
To maintain impartiality, judges must interpret laws based on constitutional values of justice, equality, and secularism. Furthermore, the judiciary must ensure representation from diverse backgrounds to foster inclusivity and reduce systemic biases. Training programs focused on cultural competence and social diversity are essential to ensure that judges are sensitive to the needs of marginalized communities.
Conclusion
The impeachment process, while stringent, plays a critical role in maintaining judicial accountability in India. As seen in the case of Justice Yadav, judicial conduct, particularly public statements, must be carefully scrutinized to preserve the integrity of the judiciary. Upholding impartiality and adhering to constitutional values are paramount in ensuring that the judiciary continues to function as a neutral arbiter in India’s democracy.
Analysis of Female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) Trends in India: 2017-2023
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) recently released a working paper revealing critical insights into the trends of female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India from 2017-18 to 2022-23. The report highlights an overall increase in female LFPR, with rural areas experiencing more significant growth compared to urban areas. This article delves into the key findings, regional disparities, influencing factors, and government initiatives aimed at promoting female workforce participation.
Key Findings on Female LFPR
The period between 2017-18 and 2022-23 witnessed a notable rise in female LFPR, both in rural and urban regions, though rural areas saw higher gains.
Rural female LFPR surged by approximately 69%, from 24.6% to 41.5%, while urban female LFPR increased from 20.4% to 25.4%. This consistent growth was observed even after excluding unpaid family workers or household helpers, reinforcing the long-term trend of increased female workforce participation across India.
However, a significant point of discussion in the report was the regional variations in female LFPR. States like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana have consistently reported low female LFPR, which is noteworthy considering that Punjab and Haryana are among India's wealthiest states, while Bihar is the poorest. This regional disparity suggests that economic prosperity does not automatically translate into higher female labour force participation, highlighting deeper socio-cultural and structural barriers.
Regional Disparities in Female LFPR
The report emphasizes the persistent challenges in northern and eastern India. Punjab and Haryana, despite their affluence, have struggled with low female LFPR. Cultural and societal norms in these regions may contribute to the underrepresentation of women in the workforce, particularly in rural areas where traditional gender roles are more entrenched.
On the other hand, Bihar, the poorest state in India, had the lowest female LFPR in the country, particularly in rural areas. However, there has been a significant improvement in recent years, especially among rural married women. This indicates a slow but positive shift in attitudes towards female employment in these states.
In contrast, northeastern states such as Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh have shown significant improvements in female LFPR, particularly in rural areas. These states have demonstrated that regional and cultural factors can also create conducive environments for female workforce participation.
Demographic Factors Affecting Female LFPR
Several demographic patterns influence female LFPR, including marital status and age. The report notes that married men consistently exhibit higher LFPR compared to women. Marriage, however, has a detrimental impact on female LFPR, particularly in urban areas, where women often face greater familial and societal pressures to prioritize domestic responsibilities over formal employment.
Age dynamics also play a crucial role in female LFPR trends. The data reveals a bell-shaped curve for female participation, peaking around the age of 30-40 years and sharply declining thereafter. This is in stark contrast to male LFPR, which remains almost universally high between the ages of 30-50 before gradually declining. These trends underscore the challenges women face in sustaining their participation in the workforce due to familial responsibilities, especially after marriage and childbirth.
Government Initiatives and the Rise in Female LFPR
The government's focus on women-led development is evident through various schemes aimed at increasing female workforce participation. Programs like Mudra Loans, the Drone Didi Scheme, and the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana have been particularly instrumental in empowering women, especially in rural areas. These initiatives provide women with access to financial resources, skill development opportunities, and avenues for entrepreneurship, all of which contribute to the rise in female LFPR.
The EAC-PM's analysis acknowledges the positive impact of these government schemes, but it also stresses the need for further research to evaluate their long-term effectiveness. While the descriptive analysis highlights a substantial increase in female LFPR between 2017-18 and 2022-23, especially in rural areas, there remains a need for continuous monitoring and assessment of these schemes to ensure their sustained impact.
Conclusion: A Positive Shift, but Challenges Remain
The increase in female LFPR across India from 2017-18 to 2022-23 signals a positive shift in employment trends, particularly in rural areas. However, regional disparities, societal norms, and demographic factors continue to pose challenges. The rise in female LFPR is encouraging, but it is essential to understand the deeper socio-economic factors that shape women's participation in the workforce.
Government schemes have contributed to this growth, but future research is necessary to gauge their long-term effects and ensure that women’s participation in the workforce is not just a short-term trend. It is crucial that the government continues to refine policies that support women in overcoming socio-cultural and economic barriers, especially in less prosperous states like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana. Sustained efforts, including education, skill development, and gender-sensitive policies, will be key to ensuring that the rise in female LFPR is both inclusive and long-lasting.
The analysis by the EAC-PM provides an essential framework for policymakers to design more targeted interventions to address regional disparities and create a more inclusive labor market for women in India.
No-Confidence Motion Against Rajya Sabha Chairman

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
In December 2024, around 60 opposition MPs from the INDIA (Indian National Developmental, Inclusive Alliance) bloc submitted a notice to the Rajya Sabha Secretariat, seeking the removal of Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. This unprecedented move has sparked significant political debate, with the opposition accusing Dhankhar of partisanship and bias in the conduct of parliamentary proceedings.
The Charges Against Jagdeep Dhankhar
Allegations of Bias and Partisanship
The opposition has raised several allegations against Dhankhar since his appointment as the Rajya Sabha Chairman in August 2022. These include:
- Partiality towards the ruling government: The opposition claims that Dhankhar has shown bias in favor of the BJP, with accusations of repeatedly denying the Leader of the Opposition, Mallikarjun Kharge, the opportunity to respond to statements made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and BJP President J.P. Nadda.
- Interference in Parliamentary Debates: Opposition MPs have accused Dhankhar of disrupting their speeches and allowing ruling party members to dominate parliamentary discussions.
- Unbecoming Remarks: The notice also refers to comments made by Dhankhar, including praising the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) and recalling his association with "so-called cultural organizations." These actions, according to the opposition, violate the non-partisan nature expected of the Chairman.
The Constitutional Framework for Removal of the Vice-President
Legal Provisions for Impeachment
The Vice-President of India, who also serves as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, is elected for a five-year term. Article 67 of the Indian Constitution outlines the procedure for his removal:
- Notice Requirement: A motion for the removal of the Vice-President must be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with a prior 14-day notice.
- Approval Process: The resolution must be passed by a majority in the Rajya Sabha and then approved by the Lok Sabha.
- Grounds for Removal: The Vice-President can only be removed through a resolution that is supported by a majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Opposition’s Plan and Challenges
Despite lacking the necessary numbers in the Rajya Sabha to succeed in the impeachment motion, the opposition's move is aimed at sending a political message to the BJP, expressing dissatisfaction with the functioning of the Parliament under Dhankhar’s leadership.
The current session of Parliament is scheduled to end on December 20, 2024, leaving little time for the motion to gain traction. The opposition also does not have the numbers needed for a majority in the Rajya Sabha, which complicates the chances of success for the motion.
Historical Precedents for Similar Resolutions
The last notable attempt to remove a parliamentary officer occurred in 2020 when the opposition moved a no-confidence motion against Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman Harivansh. This motion was prompted by his decision to extend the session during the contentious farm Bills debate. Although the motion was discussed, it did not result in any significant change.
Similarly, there have been instances where motions to remove Lok Sabha Speakers have been moved but not passed, such as against G.V. Mavalankar in 1951, Sardar Hukam Singh in 1966, and Balram Jakhar in 1987.
Role and Significance of the Vice-President in India
Constitutional Role
The Vice-President of India holds the second-highest constitutional office, primarily functioning as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. His duties include:
- Presiding over Rajya Sabha Sessions: The Vice-President ensures the smooth functioning of the Rajya Sabha and maintains order during debates. He does not typically vote except in the case of a tie.
- Acting President: In the absence, resignation, or death of the President, the Vice-President assumes the role of the Acting President.
Removal Process Under Article 67
- Article 67(b) of the Constitution specifies the process for the removal of the Vice-President, requiring a 14-day notice and approval from both Houses of Parliament. This provision ensures that any such resolution receives due consideration and is not moved hastily.
Implications for Parliamentary Democracy
- Risks to Parliamentary Integrity: Opposition leaders have expressed concern that the current political environment is eroding the integrity of India’s parliamentary system. They argue that by misusing constitutional offices for partisan ends, the ruling government risks undermining the democratic foundations of the country.
Significance of the Move
- Although the opposition may not succeed in removing Dhankhar, the notice serves as a powerful symbol of resistance. The move underscores the opposition’s commitment to defending the principles of parliamentary democracy and the need for impartiality in the conduct of parliamentary affairs.
Conclusion
The opposition’s push to remove Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha highlights the growing political tensions in India’s Parliament. While the move may not succeed due to the lack of numerical support, it brings to the forefront critical issues regarding the independence of constitutional offices and the functioning of parliamentary democracy in India. The developments around this notice will continue to be a significant point of discussion as the winter session of Parliament draws to a close.
Scrapping of Windfall Gains Tax

- 05 Dec 2024
Introduction
On December 2, 2024, the Indian government withdrew the windfall gains tax on domestic crude oil production and fuel exports (diesel, petrol, and aviation turbine fuel - ATF). This tax, initially imposed in July 2022, was introduced in response to the surge in global oil prices following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Its removal reflects the current global oil market stability and the improved fuel supply situation in India.
What is Windfall Gains Tax?
Definition
A windfall tax is a levy imposed on unexpected profits that result from extraordinary events, such as geopolitical crises or market disruptions. In the case of India, the tax was applied to the super-normal profits of oil producers and fuel exporters due to the global energy turmoil.
Key Features
- Domestic Crude Oil: The Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) was imposed on domestic crude oil production.
- Fuel Exports: A combination of SAED and Road and Infrastructure Cess (RIC) was levied on diesel, petrol, and ATF exports.
Rationale Behind the Windfall Gains Tax
Immediate Context
The tax was introduced during a period of soaring global crude oil prices, driven by the Russia-Ukraine conflict. India, which imports over 85% of its oil, faced concerns about the availability of fuels and the impact of rising prices on domestic consumption. The tax was seen as a way to:
- Ensure Domestic Fuel Supply: By discouraging excessive fuel exports during a period of global supply chain disruptions.
- Increase Government Revenue: The tax aimed to capture windfall profits and offset the duty cuts on domestic fuel sales.
Global Context
Other countries also implemented similar windfall taxes during this period, as energy companies saw record profits due to the price surge.
Decline in Windfall Gains Tax Revenue
Revenue Collection
The windfall gains tax initially raised significant revenue, but the amount has decreased over time due to falling global oil prices:
- FY 2022-23: Rs 25,000 crore
- FY 2023-24: Rs 13,000 crore
- FY 2024-25 (so far): Rs 6,000 crore
This decline, combined with reduced oil prices, led to the tax being effectively inactive before its formal withdrawal.
Withdrawal of the Windfall Gains Tax
Reasons for the Withdrawal
- Global Stabilization: Crude oil prices, which had exceeded $100 per barrel, have now stabilized under $75 per barrel, with no immediate signs of a significant price surge.
- Domestic Fuel Availability: There is now a robust fuel supply in the domestic market, making the tax less necessary.
- Declining Revenues: With the tax generating diminishing returns, it was no longer economically viable for the government to maintain it.
Impact of the Scrapping
The government's move to scrap the windfall gains tax is seen as a signal of stability and predictability in the taxation regime. It assures the oil industry that the government is confident in the stability of global oil prices and supply chains.
Criticism of the Windfall Tax
Industry Opposition
The windfall tax faced opposition from the oil industry, which argued that it:
- Reduced Profitability: The tax limited the profits of publicly listed companies like ONGC and Reliance Industries.
- Discouraged Oil Production: By making the taxation environment unpredictable, it deterred investment in oil exploration and production in a country that is heavily dependent on oil imports.
- Created Uncertainty: Frequent revisions of the tax led to an unstable business environment.
Conclusion
The scrapping of the windfall gains tax is a significant policy shift. It not only provides relief to oil companies but also signals a more predictable and stable taxation regime. By withdrawing the tax, the government is fostering a conducive environment for future investments in domestic oil production and signaling its confidence in the stability of global oil prices. This move is a crucial step in ensuring that India’s energy policies remain adaptable and aligned with the evolving global market conditions.
Current Representation of Women in CAPFs

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) of India, comprising forces like CRPF, BSF, CISF, and others, play a crucial role in maintaining internal security. Women’s participation in these forces has been historically limited, but recent efforts have focused on increasing their representation. As of 2024, women constitute only 4.4% of the total personnel in CAPFs, highlighting the slow progress despite various initiatives.
Current Representation and Changes Over Time
- Overall Representation: Women make up 4.4% of the 9.48 lakh-strong CAPFs. Within this, the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has the highest representation at 7.02%, followed by the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) at 4.43%, Border Security Force (BSF) at 4.41%, Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) at 4.05%, Assam Rifles at 4.01%, and Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) at 3.38%.
- Growth of Women Personnel: From 15,499 women in 2014, the number has tripled to 42,190 in 2024, reflecting a steady increase in recruitment. However, the percentage remains low despite these gains.
- Recruitment Trends: In 2024, 835 women were recruited, with 5,469 more in the process. In 2025, 4,138 women are expected to be recruited.
Government Efforts and Parliamentary Committee Recommendations
- Policy Measures: The government has introduced several steps to encourage women’s participation in CAPFs, such as reservations in constable-level positions: one-third for CRPF and CISF, and 14-15% for border forces like BSF, SSB, and ITBP.
- Challenges in Recruitment: Despite these policies, recruitment has not kept pace with the targets. The 2022 Parliamentary Committee on Home Affairs expressed disappointment over the “abysmally low” number of women in CAPFs, noting that women made up only 3.68% of the forces at that time.
- Recommendations by Parliamentary Committees:
- The Home Affairs Committee recommended fast-tracking phase-wise recruitment of women, particularly in CISF and CRPF.
- The Standing Committee on Personnel (2023) suggested “soft postings” for women to avoid difficult working conditions, especially in remote or strenuous terrains. It also called for reservations for transgender individuals.
- In 2024, further steps like fee waivers, relaxed physical standards, and provisions for maternity and child care leave were introduced to make the work environment more inclusive.
Reasons Behind Low Representation
- Cultural Barriers: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations deter many women from pursuing careers in security forces.
- Work Environment: The demanding nature of the job, which includes postings in remote areas and high-risk operations, makes it less appealing, especially for women with family responsibilities.
- Infrastructure Issues: Lack of adequate accommodation, sanitation facilities, and safety measures for women are deterrents to joining and retaining female personnel.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Although the representation of women in CAPFs has seen improvement, it remains below expectations due to persistent challenges. The government’s continuous focus on recruitment reforms, better working conditions, and policy incentives will be crucial to achieve gender parity in these forces. As societal attitudes evolve and the infrastructure improves, more women may be encouraged to serve in these vital security roles. Future efforts must include targeted recruitment drives and creating a more inclusive and supportive environment to enhance women’s participation in CAPFs.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved the launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF), marking a significant shift in the government's approach to agriculture. This initiative, a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, aims to promote natural farming across India, focusing on reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and promoting environmentally sustainable practices.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming, as defined by the Ministry of Agriculture, is a chemical-free agricultural method that relies on inputs derived from livestock and plant resources. The goal is to encourage farmers to adopt practices that rejuvenate soil health, improve water use efficiency, and enhance biodiversity, while reducing the harmful effects of fertilizers and pesticides on human health and the environment. The NMNF will initially target regions with high fertilizer consumption, focusing on areas where the need for sustainable farming practices is most urgent.
Evolution of Natural Farming Initiatives
The NMNF is not an entirely new concept but a scaled-up version of the Bhartiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhti (BPKP) introduced during the NDA government's second term (2019-24). The BPKP was part of the larger Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna (PKVY) umbrella scheme, and natural farming was also promoted along the Ganga River under the NamamiGange initiative in 2022-23. With the renewed focus on natural farming following the 2024 elections, the government aims to extend the lessons learned from BPKP into a comprehensive mission mode, setting a clear direction for sustainable agriculture.
In Budget speech for 2024-25, it was announced a plan to initiate one crore farmers into natural farming over the next two years. The mission will be implemented through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats, with the establishment of 10,000 bio-input resource centers (BRCs) to ensure easy access to the necessary inputs for natural farming.
Key Objectives
The NMNF aims to bring about a paradigm shift in agricultural practices by:
- Expanding Coverage: The mission plans to bring an additional 7.5 lakh hectares of land under natural farming within the next two years. This will be achieved through the establishment of 15,000 clusters in gram panchayats, benefiting 1 crore farmers.
- Training and Awareness: The mission will establish around 2,000 model demonstration farms at Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Agricultural Universities (AUs), and farmers' fields. These farms will serve as hubs for training farmers in natural farming techniques and input preparation, such as Jeevamrit and Beejamrit, using locally available resources.
- Incentivizing Local Inputs: The creation of 10,000 bio-input resource centers will provide farmers with easy access to bio-fertilizers and other natural farming inputs. The mission emphasizes the use of locally sourced inputs to reduce costs and improve the sustainability of farming practices.
- Farmer Empowerment: 30,000 Krishi Sakhis (community resource persons) will be deployed to assist in mobilizing and guiding farmers. These trained individuals will play a key role in generating awareness and providing on-ground support to the farmers practicing natural farming.
- Certifications and Branding: A major aspect of the mission is to establish scientific standards for natural farming produce, along with a national certification system. This will help in creating a market for organically grown produce and encourage more farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Targeting High Fertilizer Consumption Areas
The Ministry of Agriculture has identified 228 districts in 16 states, including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Maharashtra, and West Bengal, where fertilizer consumption is above the national average. These districts will be prioritized for the NMNF rollout, as they have high fertilizer usage but low adoption of natural farming practices. By focusing on these areas, the mission seeks to reduce the over-dependence on chemical fertilizers and foster a transition to more sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of Natural Farming
The NMNF aims to deliver multiple benefits to farmers and the environment:
- Cost Reduction: Natural farming practices can significantly reduce input costs by decreasing the need for costly chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Soil Health and Fertility: By rejuvenating the soil through organic inputs, natural farming improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity, leading to long-term agricultural sustainability.
- Climate Resilience: Natural farming enhances resilience to climate-induced challenges such as drought, floods, and waterlogging.
- Healthier Produce: Reduced use of chemicals results in safer, healthier food, benefitting both farmers and consumers.
- Environmental Conservation: The promotion of biodiversity, water conservation, and carbon sequestration in soil leads to a healthier environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming represents a critical step toward transforming India's agricultural practices into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly model. By targeting regions with high fertilizer usage, providing farmers with the tools and knowledge for natural farming, and creating a system for certification and branding, the government hopes to make natural farming a mainstream practice. As India continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, soil degradation, and health risks from chemical inputs, the NMNF provides a promising framework for sustainable agriculture that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
The Controversy around the Sambhal Mosque

- 27 Nov 2024
Introduction
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has become a flashpoint in a larger religious and legal dispute after a petition was filed questioning its historical origins. Alleging that the mosque was built on the site of an ancient Hindu temple, the case has triggered both legal challenges and violent clashes, raising concerns about communal harmony and the protection of religious sites.
Background of the Dispute
On November 19, 2024, a petition was filed in the Sambhal district court, claiming that the 16th-century Jama Masjid was constructed over the site of an ancient Hari Har Mandir. This claim mirrors similar petitions filed in other parts of India, including Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have sought to alter the religious character of mosques they believe were built on temple sites. The petitioners in the Sambhal case include advocate Hari Shanker Jain, a key figure in the Gyanvapi and Mathura disputes.
Survey and Clashes
The Sambhal court ordered a survey of the mosque on November 19, 2024, to investigate the historical claims. The initial phase of the survey, conducted peacefully, involved mosque authorities and local police. However, a second survey on November 24 escalated tensions, as it was accompanied by a procession led by a local priest chanting Hindu slogans. Protests soon turned violent, leading to stone-pelting, police firing, and at least five deaths, including two teenagers. Locals accused the police of excessive force, while the police denied allegations of shooting.
The Mosque’s Historical Context
The Shahi Jama Masjid was built by Mughal Emperor Babur's general, Mir Hindu Beg, around 1528. It is one of the three mosques constructed during Babur's reign, the other two being in Panipat and Ayodhya. Architectural studies suggest it was constructed using stone masonry with plaster, and while some historians believe it was built on a pre-existing structure, the mosque’s historical context is complex. Local Hindu tradition holds that the site was originally a Vishnu temple, with the belief that Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu, will arrive there.
Legal Implications: The Places of Worship Act, 1991
The dispute touches upon the Places of Worship Act, 1991, which mandates the preservation of the religious character of all places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947. The Act was designed to prevent further disputes over religious sites, except for the Babri Masjid case, which was already under litigation at the time. The petitioners in the Sambhal case argue that the religious character of the mosque should be altered, contradicting the Act’s provisions.
Challenges to the Places of Worship Act
The Places of Worship Act has been criticized for barring judicial review and preventing any changes to the religious status of sites that existed before India’s independence. Some legal experts suggest that while an inquiry into the religious nature of a place might be permissible, changing that character would violate the Act. The ongoing legal challenges in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, and now Sambhal, highlight the complexities of reconciling India’s legal framework with communal sensitivities.
Conclusion
The Sambhal mosque dispute underscores the challenges in balancing India’s legal framework with religious and communal dynamics. While the Places of Worship Act aims to preserve the status quo, petitions challenging it have revived contentious debates over historical monuments and their religious significance. As the legal proceedings continue, the case will likely have far-reaching implications for India’s secular fabric and the preservation of communal harmony.
29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29), held in Baku, Azerbaijan, focused on enhancing climate finance, adaptation measures, and global cooperation.
Key Outcomes of COP29:
- Climate Finance: A new goal was set to triple climate finance for developing countries to USD 300 billion annually by 2035. The total climate finance target aims for USD 1.3 trillion annually by 2035.
- Carbon Markets: The conference operationalized Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which establishes frameworks for carbon credit trading between countries. It also launched the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism, ensuring safeguards for human rights and the environment.
- Transparency and Adaptation: COP29 saw 13 countries submit their Biennial Transparency Reports, promoting greater accountability. The Baku Adaptation Roadmap was launched to speed up National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) in Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Gender and Inclusivity: A new Gender Action Plan was developed, and the Lima Work Programme on Gender was extended for another 10 years. Over 55,000 people, including civil society, Indigenous peoples, and youth, participated.
- Global Climate Action: The 2024 Yearbook of Global Climate Action highlighted the role of non-Party stakeholders like businesses and sub-national actors in combating climate change.
India’s Role at COP29: India played an active role in highlighting resilient infrastructure initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and advocated for financial resources to support Small Island Developing States (SIDS). India also pushed for solar energy adoption through the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and promoted gender-inclusive climate policies. India co-hosted the LeadIT summit with Sweden, focusing on industrial decarbonization.
Challenges at COP29:
- Inadequate Finance: Despite ambitious targets, many countries felt the financial commitments were insufficient and distant.
- Private Sector Dependency: The reliance on private sector contributions raised concerns about the reliability of funding.
- Emission Reduction Gaps: There was a lack of sufficient pledges to meet the 1.5°C global warming target, with rising emissions.
- Geopolitical Conflicts: Disputes over issues like the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) hindered progress.
India’s Carbon Credit Framework:
India introduced the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022, establishing a domestic carbon market and setting a legislative framework for carbon credit trading. This aligns with India’s NDCs and aims to support sustainable growth while reducing emissions. However, concerns about the integrity of carbon credits and potential "greenwashing" need to be addressed through rigorous verification systems.
Conclusion:
COP29 marked progress in scaling up climate finance, carbon markets, and adaptation efforts, but significant challenges remain, especially in finance, emission reductions, and geopolitical cooperation. India's initiatives in carbon credit frameworks and resilience are steps toward a sustainable future. Moving forward, a collaborative, transparent, and adaptive approach is crucial to meet global climate goals.
Challenges in Municipal Financing

- 25 Nov 2024
Introduction
Municipal corporations (MCs) in India are essential service providers in urban areas, but they face severe financial constraints, which hinder their ability to provide quality services. While urban India contributes almost 60% of the nation's economic output, MCs are heavily reliant on state and central government transfers, limiting their financial autonomy and operational capacity.
Key Issues in Municipal Financing
- Limited Revenue Generation
- Low Property Tax Revenues: Property tax, the main source of municipal revenue, contributes only 0.12% of GDP, a figure that reflects poor tax collection mechanisms and outdated property valuation systems.
- Revenue Concentration: Over 58% of municipal revenue comes from the top 10 cities, highlighting fiscal disparity between urban areas.
- Dependence on Government Transfers: Municipalities rely significantly on state and central transfers, constituting a large portion of their revenue. This reduces their ability to plan and execute long-term projects independently.
- Inefficiency in Tax and Fee Collection
- Ineffective Property Tax Systems: Existing tax formulas do not reflect actual property valuations, leading to under-taxation and revenue loss.
- Inadequate User Charges: Fees for essential services like water supply, sanitation, and waste management are not regularly adjusted, impacting cost recovery and service quality.
Strategies for Strengthening Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
- Enhancing Revenue Sources
- Property Tax Reforms: Implementing GIS-based property tax mapping and linking tax rates to actual property valuations can improve tax compliance and revenue generation.
- Rationalising User Charges: Regular adjustments to service fees for water, sanitation, and waste management can ensure cost recovery and better service delivery.
- Reducing Dependence on Transfers
- State and Central Transfers: A rule-based framework for government transfers, accounting for inflation and city growth, can ensure predictability and adequate compensation for MCs.
- Boosting Non-Tax Revenues: MCs can increase income from user fees (e.g., for urban transport and waste management) and explore public-private partnerships (PPPs) to enhance service delivery.
- Leveraging Technology for Efficiency
- Digitalisation and Automation: Streamlining processes through technology can reduce inefficiencies, cut down on waste, and free up resources for capital expenditure.
- Monitoring Systems: Improved monitoring and reporting can reduce pilferage, enhance revenue collection, and ensure accountability.
Fiscal Management and Innovative Financing
- Municipal Bonds and Innovative Financing
- Larger MCs are already using municipal bonds to fund infrastructure projects. Smaller cities can adopt similar financing instruments to diversify funding sources and attract private investment.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Fostering partnerships in sectors like urban transport and waste management can attract private investment and reduce the financial burden on MCs.
- Resource Pooling for Infrastructure Projects
- MCs can collaborate to pool resources for large-scale projects, such as renewable energy or urban transport initiatives, overcoming fiscal constraints that individual corporations face.
Government Initiatives for Urban Governance
- Citizen-Centric Programs
- Swachh Sarvekshan (2017) promotes citizen participation to improve urban cleanliness.
- Swachh Bharat Idea Book empowers citizens to propose innovative solutions to urban challenges.
- Performance-Based Indices
- Ease of Living Index (2017) and the Municipal Performance Index (2019) assess urban quality of life, service delivery, and governance, encouraging better performance in ULBs.
Conclusion
Empowering urban local bodies is crucial for effective urban governance and development. By improving revenue generation through reforms, reducing dependence on transfers, and adopting innovative financing mechanisms, municipal corporations can enhance their capacity to meet the growing demands of urbanization. Collaborative efforts between the government, civil society, and academia are essential to ensure sustainable urban development and better living conditions for urban residents.
Reimagining Governance with AI: The Promise of GovAI

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's rapid digital transformation, coupled with the advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), presents a unique opportunity to reimagine governance. The concept of GovAI—using AI to enhance public administration—holds the potential to revolutionize governance, improve efficiency, and create more responsive and inclusive public systems.
Digital Transformation in Governance
- Evolution of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- Over the past decade, India has made significant strides in digital governance through the development of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). DPI has reduced inefficiencies, enhanced transparency, and improved service delivery, transforming India's governance landscape.
- Impact of AI on Governance
- As AI becomes a critical enabler in various sectors, its application to governance promises to deliver more efficient, inclusive, and responsive government services. The potential of AI lies in its ability to provide more with less, driving innovation across key public services.
Key Trends Driving GovAI
- Rapid Digitalization of India
- Currently, 90 crore Indians are connected to the Internet, with projections indicating 120 crore by 2026, positioning India as the most connected country globally.
- Digitalization serves as the backbone for AI-driven governance, enabling efficient data collection, analysis, and informed policy-making.
- Data as a Valuable Resource
- The rapid digitalization of India has led to the generation of vast amounts of data. This data serves as the fuel for AI models, which can be used to enhance governance.
- Programs like the IndiaDatasetsProgramme aim to harness government datasets for AI development while safeguarding data privacy through legislation.
- Demand for Efficient Governance
- The post-COVID world has underscored the need for governments to deliver better outcomes with fewer resources. AI has the potential to optimize the use of public resources, enabling more efficient and targeted governance.
India’s Leadership in AI-Driven Governance
- Positioning India as a Global Leader
- India’s digital governance initiatives have placed it at the forefront of AI adoption in the public sector. Through GovAI, India can solidify its position as a global leader in using technology for public good.
- As the Chair of the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), India is advocating for the inclusive development of AI to ensure that it benefits all nations, not just a select few.
- Role of Innovation Ecosystem
- India’s innovation ecosystem, comprising startups, entrepreneurs, and tech hubs, can play a crucial role in driving the development of AI models, platforms, and apps for governance.
- A strong partnership between the government and private sector is essential to successfully deploy AI solutions across various sectors of governance.
Potential Benefits of GovAI
- Enhanced Efficiency and Service Delivery
- AI-powered tools, such as chatbots, can provide citizens with 24/7 assistance, streamlining public service delivery and reducing waiting times.
- AI can help in automating processes and improving the overall efficiency of government operations.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
- AI can analyze large datasets to make informed policy decisions and design targeted interventions in sectors like healthcare, education, and social welfare.
- Data-driven insights can enhance the effectiveness of welfare schemes, improving outcomes for marginalized communities.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability
- AI can enhance transparency in governance by minimizing human intervention in processes, thus reducing corruption and ensuring efficient use of public resources.
- Predictive analytics and real-time data monitoring can enable proactive governance, preventing issues before they escalate.
Challenges and Drawbacks of GovAI
- Privacy Concerns
- The use of AI in governance requires the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and surveillance.
- Robust data protection laws must be enforced to ensure citizens' data is handled responsibly.
- Accountability and Bias
- AI systems may produce biased outcomes depending on the data they are trained on. Ensuring accountability for decisions made by AI systems remains a challenge, particularly when errors or biases occur.
- Transparent mechanisms must be established to hold AI systems accountable for their actions.
- Increased State Control and Surveillance
- The integration of AI in governance could lead to increased state control, potentially compromising individual freedoms. Ensuring that AI is used responsibly to balance power between the government and citizens is critical.
- Digital Divide
- The benefits of AI in governance may not be evenly distributed across the population, exacerbating the digital divide.
- Efforts must be made to ensure that marginalized communities, without access to digital technologies or skills, are not left behind.
Conclusion
- Balancing Benefits and Risks
- The integration of AI into governance systems presents significant benefits, including enhanced efficiency, transparency, and proactive governance. However, there are challenges related to privacy, accountability, and state control.
- To ensure AI serves the public good, India must implement strong regulatory frameworks, promote transparency, and develop ethical AI systems that respect citizens’ rights and freedoms.
- Moving Toward Maximum Governance
- AI can help realize the vision of maximum governance, enabling more effective and targeted interventions across sectors like healthcare, security, education, and disaster management.
- The success of GovAI will depend on a trusted partnership between the government, private sector, and innovation ecosystem, ensuring that AI technology serves the larger public interest.
Khap Panchayats: Evolving Towards Modern Governance and Justice

- 17 Nov 2024
Why in the News?
Khap Panchayats have attracted attention due to their evolving role in addressing key socio-economic issues like unemployment, education, and rural development. Modernization efforts are underway to regulate these traditional councils, integrating them into formal Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) systems for better governance, accountability, and social justice.
What are Khap Panchayats?
Definition and Origin:
Khap Panchayats are community-based councils primarily found in North India, particularly in Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan. These informal bodies, composed of elders from kinship groups (Khaps), have historically served as local governance bodies that resolve disputes within their communities. Their origins trace back centuries and they function alongside formal legal systems, often prioritizing customary norms over constitutional law.
Historical Role:
Historically, Khap Panchayats have maintained social order in rural areas, acting as forums for dispute resolution related to marriage, property, and community matters. While their decisions were respected within their communities, they operated parallel to formal courts, and their influence was often seen as a stabilizing force in rural society. However, their structure has also contributed to the perpetuation of patriarchal practices and social exclusion.
Issues with Khap Panchayats
- Patriarchal Practices:Khap Panchayats have often been associated with gender inequality. They enforce rigid social norms that limit women's autonomy, particularly in matrimonial matters, inheritance rights, and personal freedoms. This has led to criticism for their role in suppressing women's rights.
- Honor Killings and Social Conservatism:Khap Panchayats are notorious for opposing inter-caste and same-gotra marriages, at times even endorsing honor killings to preserve social order. Such practices are violations of fundamental rights and personal freedoms guaranteed by the Indian Constitution.
- Legality Concerns:The decisions of Khap Panchayats often clash with constitutional values such as equality, personal liberty, and dignity. Their informal judgments lack legal validity and frequently violate the rule of law, raising significant concerns about their adherence to India’s legal framework.
- Caste-based Discrimination:Khap Panchayats have been criticized for reinforcing caste hierarchies, which leads to discrimination and exclusion of marginalized communities. Their focus on preserving traditional caste structures often results in the oppression of the vulnerable, particularly lower-caste groups.
Gender Dynamics and Evolving Roles of Khap Panchayats
In recent years, some Khap Panchayats have started to show more progressive and inclusive stances, particularly in promoting gender justice:
- Support for Women Athletes:Khap Panchayats have begun to recognize and celebrate the achievements of women, particularly in sports. Several Khap bodies have felicitated women sportspersons, contributing to a growing culture of sports among rural women. This marks a shift from their traditionally patriarchal stance.
- Promoting Gender Justice:Notably, the MehamChaubisiKhap in Haryana has played a significant role in advocating for women’s rights and gender equality. It was involved in supporting the 2023 wrestlers' protest against sexual harassment, demonstrating a shift towards gender-related activism and social reform.
Supreme Court Ruling on Khap Panchayats:
In the landmark Shakti Vahini v. Union of India case (2018), the Supreme Court of India addressed the issue of honor killings and inter-caste marriages. The Court emphasized that honor killings violate fundamental rights and called for strict measures to prevent such crimes. The Court further directed state governments to establish special protection cells for couples facing threats from their families and communities. This ruling underscored the importance of personal liberty and freedom of choice, regardless of community or caste.
What is Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)?
Definition and Importance:
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) refers to methods of resolving disputes without resorting to formal litigation. These methods include mediation, arbitration, and conciliation, all of which encourage cooperative problem-solving and mutually agreeable solutions. ADR is particularly important in India due to the overburdened judicial system, which faces a backlog of cases and delays.
ADR offers several advantages, including:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Confidentiality
- Flexibility
- Improved relationships between parties involved
Types of ADR Mechanisms:
- Arbitration: A formal process where an arbitrator resolves disputes and their decision is legally binding.
- Conciliation: A third-party neutral assists the parties in reaching an agreement, and the recommendations can be accepted or rejected.
- Mediation: A mediator facilitates communication between disputing parties, helping them reach a voluntary and mutually agreeable resolution.
- Negotiation: A direct negotiation between the parties without third-party involvement, aiming for a mutually acceptable settlement.
Integrating Khap Panchayats into the Formal ADR System
Given the potential of Khap Panchayats as community-based governance bodies, integrating them into the formal ADR framework can significantly enhance their role in dispute resolution. Here are some strategies for modernizing Khap Panchayats:
- Legal Recognition of ADR Role:Khap Panchayats can be legally recognized within the ADR framework, formalizing their role in mediation and dispute resolution, ensuring their decisions align with constitutional norms and human rights.
- Training and Capacity Building:Khap leaders can undergo training in ADR techniques such as mediation and arbitration, equipping them with skills to resolve conflicts impartially and in line with legal standards. This would help transition Khaps from informal bodies to more structured and legally compliant dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Legal Regulation and Oversight:Regulations can be put in place to define the scope and limitations of Khap Panchayats' authority, ensuring their decisions do not violate human rights or the constitution. Oversight mechanisms should be established to monitor their actions and prevent practices like honor killings or forced marriages.
- Shift Towards Developmental Roles:Some Khap Panchayats are already advocating for progressive reforms in areas like unemployment, education, and rural development. By focusing on these issues, Khap Panchayats can serve as agents of social change and contribute to community development.
- Awareness and Accountability:Awareness campaigns can educate rural communities about constitutional rights and the legal system, emphasizing the importance of formal legal frameworks and human rights. At the same time, Khap Panchayats should be held accountable for actions that undermine justice or equality.
- Collaboration with Formal Institutions:Khap Panchayats can collaborate with local governance bodies and judicial institutions, ensuring that their decisions align with the rule of law and contribute to social justice. This would enhance their role in inclusive decision-making and legally sound governance.
Conclusion
Khap Panchayats, with their deep-rooted history and influence, have the potential to evolve into modern governance institutions. By integrating them into the formal ADR framework, aligning their practices with constitutional values, and focusing on community development, they can contribute positively to dispute resolution and social reform in rural India. This transformation will require legal regulation, training, oversight, and awareness to ensure that Khap Panchayats function as effective, equitable bodies that respect the fundamental rights of all individuals.
The Need for More Women in Politics
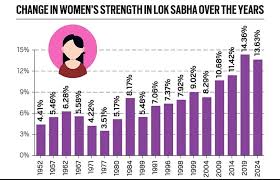
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
India, the world's largest democracy, is at a crucial juncture where women’s active political participation is essential for holistic development and true democratic engagement. The year 2024 demands increased involvement of women in politics to address issues of gender inequality and ensure comprehensive policy representation.
Current Status of Women’s Political Representation in India
Women in Parliament
- Initial Representation: In 1952, women accounted for only 4.41% of the Lok Sabha. This gradually rose to around 14.36% in the 2019 elections.
- Recent Trends: In the 2024 elections, women made up approximately 16% of the Lok Sabha, with 74 women MPs, 43 of whom are first-time representatives.
Women in State Legislatures
- Representation in state legislative assemblies remains low, with the highest percentages in Chhattisgarh (14.4%), West Bengal (13.7%), and Jharkhand (12.4%).
Global Comparison
- According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), India ranks lower than many countries in terms of female representation in parliament, with global averages standing at 26.1%. India lags behind several African and South Asian nations.
Importance of Women’s Political Empowerment
- Enhancing Governance and Accountability: Political empowerment of women ensures better representation of gender-sensitive issues, promoting accountability in governance.
- Breaking Patriarchal Norms: Increasing women’s participation helps challenge the patriarchal structure that dominates Indian politics and promotes inclusive governance.
- Policy and Social Impact: Women in politics are more likely to advocate for policies that address issues like health, education, and gender equality, leading to improved societal welfare.
- Economic Benefits: Studies suggest that women in political leadership tend to improve economic outcomes for their constituencies by prioritizing social infrastructure.
Barriers to Women’s Political Participation
- Gender Gaps in Political Ambition: Women are less likely to pursue political careers due to gender conditioning, family pressures, and stereotypes about leadership abilities.
- Patriarchal Culture: A deeply ingrained patriarchal society hampers women’s political involvement, with male-dominated party structures and social norms limiting opportunities.
- High Election Costs: The financial burden of running for office often discourages women from contesting elections due to unequal access to resources.
- Male Gatekeepers in Politics: Political parties often show a preference for male candidates, especially for higher-profile positions, hindering the rise of women leaders.
- Criminalisation and Corruption in Politics: Growing criminalisation in politics and lack of political education further alienates women from the political process.
Key Legislative and Constitutional Measures for Women’s Political Empowerment
Legislative Measures
- Nari Shakti VandanAdhiniyam (2023): Provides 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
- 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992): Introduced 33% reservation for women in Panchayats and Municipalities.
- Gender-Neutral Rules: Lok Sabha adopted gender-neutral rules in 2014, promoting inclusivity in legislative procedures.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 14 and 15: Ensure equality and non-discrimination, fundamental to women’s political participation.
- Article 243D: Mandates 33% reservation for women in Panchayats.
International Commitments
- CEDAW (1979): Advocates for women’s participation in political and public life.
- Beijing Platform (1995) and SDGs (2015): Call for removing barriers to women’s participation in politics.
Measures for Promoting Women’s Political Participation
- Quotas and Reservations: Ensuring mandatory quotas for women candidates in party tickets and legislative bodies can help bridge gender gaps.
- Capacity Building and Training: Offering political training programs for women can empower them with the skills and resources necessary for effective political participation.
- Strengthening Grassroots Movements: Support for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) can build leadership among women at the local level.
- Supportive Political Ecosystem: Political parties should be encouraged to nominate women for higher office positions, such as the Rajya Sabha or state legislative councils.
- Raising Public Awareness: Public awareness campaigns focusing on the importance of women in politics can shift societal attitudes and garner wider public support.
Conclusion:
As India moves forward, the active participation of women in politics is not merely a matter of equity but an essential building block for a vibrant, inclusive, and effective democracy. Through structural reforms, public awareness, and the promotion of female leadership, India can strengthen its democratic framework, ensuring that all citizens, regardless of gender, have an equal stake in shaping the nation's future.
Significance of LignoSat
- 12 Nov 2024
Introduction
- LignoSat is the world's first satellite constructed with wood, developed to test the viability of using timber as a sustainable material in space exploration.
- Launched on November 5, 2024, the satellite was sent to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard a SpaceX Dragon cargo capsule and will be released into orbit after a month for a six-month test.
What is LignoSat?
- Dimensions: LignoSat measures 4 inches (10 cm) on each side and weighs 900 grams.
- Material Composition: The satellite features panels made from magnolia wood using traditional Japanese craftsmanship, without screws or glue.
- Development Collaboration: LignoSat was developed by Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry, in collaboration with various researchers and space organizations.
Purpose and Objectives of the Mission
- Testing Timber in Space:
- The primary goal is to study how wood performs in the extreme conditions of space, where temperatures fluctuate dramatically between -100°C to 100°C.
- The satellite will also assess how wood interacts with space radiation and its potential to reduce the impact of radiation on sensitive electronics, such as semiconductors.
- Space Sustainability:
- LignoSat aims to demonstrate that wood can be a sustainable, renewable alternative to metals (like aluminium) traditionally used in spacecraft construction.
- The satellite will help determine if wood can be used in future space missions, potentially reducing reliance on non-renewable materials.
Testing the Durability of Wood in Space
- Challenges of Space Environment:
- Space is an extremely harsh environment with extreme temperature variations, exposure to radiation, and the lack of water and oxygen, all of which affect material durability.
- Unlike Earth, where wood decomposes due to moisture and oxygen, space's vacuum conditions could potentially preserve the wood's integrity, providing valuable insights into its durability.
- Previous Use of Wood in Space:
- Wood has already been tested in space applications: cork has been used on spacecraft to withstand re-entry conditions.
- The LignoSat mission builds on this knowledge, aiming to test wood's performance in space's high-radiation and vacuum environment.
Potential Advantages of Using Wood in Space Exploration
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits:
- Unlike conventional aluminium satellites, which generate harmful pollutants upon re-entry (e.g., aluminium oxides), LignoSat's wooden components will degrade in a more environmentally friendly manner, minimizing atmospheric pollution.
- As space exploration increases, particularly with mega-constellations (e.g., SpaceX’s Starlink), space debris management becomes critical. Using wood could reduce the environmental impact of satellite disposal.
- Renewable Resource:
- Wood is a renewable resource, which offers a potential solution to the growing demand for materials used in space technology.
- Kyoto University researchers have long been exploring the idea of building habitats on the Moon and Mars using timber, with LignoSat seen as a stepping stone to proving the material's space-grade capabilities.
LignoSat's Design and Construction
- Hybrid Construction:
- While the outer panels of LignoSat are made from magnolia wood, the satellite still incorporates traditional aluminium structures and electronic components inside.
- The hybrid construction allows researchers to compare the performance of wood against conventional materials used in spacecraft.
- Testing Methods:
- LignoSat will orbit Earth for six months and monitor the wood’s reaction to space conditions, providing valuable data for future space missions.
- Sensors embedded in the satellite will track various environmental factors, such as radiation exposure, temperature fluctuations, and the structural integrity of the wood.
The Long-Term Vision: Building Timber Habitats in Space
- The research team, led by Takao Doi (astronaut and Kyoto University professor), envisions a future where timber is used for constructing space habitats on the Moon and Mars.
- The team’s ultimate goal is to plant trees in space and develop timber houses on extraterrestrial bodies, providing a sustainable, self-sufficient environment for humans in space.
Broader Implications for Space Exploration
- Sustainability in Space Missions:
- LignoSat represents an innovative step toward more sustainable space technologies by investigating eco-friendly materials that can minimize the environmental impact of space missions.
- It aligns with global efforts to make space exploration more sustainable, especially as space tourism and colonization plans grow.
- Future Prospects:
- If successful, LignoSat could pave the way for wood-based materials being used in spacecraft construction, not only for satellites but also for space stations and future human habitats in space.
Conclusion
- LignoSat’s mission marks a significant milestone in space exploration by exploring wood as a sustainable material in space technology.
- As the first wooden satellite, its results could pave the way for more eco-friendly, renewable materials in future space missions, aligning with global goals for sustainability and reducing space-related pollution.
Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court recently upheld the constitutional validity of the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004 (also called the Madarsa Act), while striking down certain provisions related to the granting of higher education degrees. The Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's previous decision, which had deemed the Act unconstitutional on the grounds that it violated the principle of secularism.
What is the Madarsa Act?
The Madarsa Act provides a legal framework for regulating madrasas (Islamic educational institutions) in Uttar Pradesh. The Act:
- Establishes the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education, which oversees the curriculum and examinations for madrasas.
- Ensures that madrasas follow the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) curriculum for mainstream secular education alongside religious instruction.
- Empowers the state government to create rules for regulating madrasa education.
Allahabad High Court's Ruling
In March 2024, the Allahabad High Court declared the Madarsa Act unconstitutional, citing:
- Violation of secularism: The Court argued that the Act's emphasis on compulsory Islamic education, with modern subjects being optional, discriminated on religious grounds, violating the secular nature of the Constitution.
- Right to Education: The Court also claimed that the Act denied quality education under Article 21A, which guarantees free and compulsory education to children.
- Higher Education Degrees: The Act's provisions allowing the granting of Fazil and Kamil degrees were found to conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, 1956, which regulates higher education.
Supreme Court's Ruling
The Supreme Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's decision on several grounds:
- Basic Structure Doctrine: The Court clarified that the basic structure doctrine, which applies to constitutional amendments, does not apply to ordinary legislation like the Madarsa Act. Therefore, a law cannot be struck down simply for violating secularism unless explicitly prohibited by the Constitution.
- State's Authority to Regulate Education: The Court held that the state has the right to regulate education in minority institutions, as long as the regulation is reasonable and rational. It emphasized that the Madarsa Act does not deprive these institutions of their minority character.
- Right to Education for Minority Institutions: Referring to a 2014 decision, the Court ruled that the Right to Education Act (RTE) does not apply to minority institutions, as it would undermine their right to impart religious education and self-administer.
Striking Down Higher Education Provisions
While upholding most of the Act, the Supreme Court struck down the provisions related to higher education degrees (Fazil and Kamil). It ruled that:
- Section 9 of the Act, which allowed the Board to grant these degrees, is in conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, which only permits degrees to be awarded by universities recognized by the UGC.
Implications of the Ruling
- Regulation of Madrasa Education: The ruling affirms the state's authority to ensure quality education in madrasas, balancing religious instruction with secular subjects.
- Protection of Minority Rights: By upholding the Madarsa Act, the Court protected the rights of religious minorities to run educational institutions while ensuring they meet educational standards.
- Focus on Inclusivity: The judgment emphasizes the integration of madrasas within the broader educational framework, ensuring that madrasa students receive quality education.
In conclusion, the Supreme Court's decision supports the regulation of madrasa education while safeguarding the rights of minority institutions, except in areas related to the granting of higher education degrees, which remain under the jurisdiction of the UGC Act.
RBI brings back 102 tonnes gold from BoE; 60 per cent reserves in India

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
England over the past two-and-a-half years, reflecting a strategic shift in its approach to safeguarding gold reserves. This move marks a significant increase in the RBI's domestic gold holdings.
Rise in the RBI's Domestic Gold Holdings
- Current Status (September 2024):The RBI's domestic gold reserves have grown to 510.46 metric tonnes, up from 295.82 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Reduction in Gold Held Abroad:The gold held under the custodianship of the Bank of England has decreased to 324 metric tonnes from 453.52 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Gold as a Share of Foreign Exchange Reserves:The proportion of gold in India's total foreign exchange reserves increased from 8.15% in March 2024 to 9.32% in September 2024.
Gold Kept in the Bank of England
- Overview of the Bank of England's Gold Vault:The Bank of England is home to one of the largest gold vaults in the world, second only to the New York Federal Reserve, housing around 400,000 bars of gold.
- India’s Gold Held Abroad:The RBI continues to retain 324 metric tonnes of its gold with the Bank of England and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
- Additional Gold Management:Around 20 tonnes of gold are managed through gold deposit schemes.
- Strategic Role of London’s Gold Market:Storing gold in London provides immediate access to the global London bullion market, enhancing liquidity for India’s gold assets.
Historical Context of India’s Gold Holdings
- 1991 Balance of Payments Crisis:During a financial crisis in 1991, India had to send 47 tonnes of gold to the Bank of England to secure loans for repaying international creditors.
RBI’s Strategy to Bring Gold Back to India
- Global Trend of Central Banks Buying Gold:Since the imposition of U.S. sanctions on Russia in 2022, central banks globally have been increasing their gold reserves as a hedge against inflation and to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar. India has outpaced other G20 nations in this trend, surpassing Russia and China in gold purchases.
- De-dollarisation:This shift is part of a broader strategy of de-dollarisation, aiming to diversify away from the U.S. dollar amidst rising gold prices and growing geopolitical tensions.
Significance of Repatriating Gold to India
- Sign of Economic Strength
- Recovery from the 1991 Crisis:The decision to repatriate gold reflects a significant improvement in India's economic position, a stark contrast to the 1991 economic crisis when India had to pledge gold for financial survival.
- Optimizing Financial Resources
- Reducing Storage Costs:Storing gold domestically allows the RBI to save on storage fees paid to foreign custodians, such as the Bank of England.
- Strategic Significance
- Enhanced Resilience Amid Global Instability:By repatriating its gold, India enhances its strategic autonomy and strengthens its economic position in a world of rising uncertainties and currency volatility.
RBI's Capacity to Safeguard Gold Domestically
- Increasing Domestic Storage Capacity:The RBI has been increasing its domestic capacity for gold storage to accommodate rising reserves and reduce dependence on foreign gold safekeeping facilities.
- Current Foreign Exchange Reserves:As of October 2024, India’s total foreign exchange reserves stand at $684.8 billion, sufficient to cover over 11.2 months of imports.
Diversification of Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Mitigating Currency Risks:By increasing gold reserves, India diversifies its foreign exchange holdings, reducing reliance on any single currency and shielding itself from global currency fluctuations and economic volatility.
- Gold as a Stable Asset:Gold serves as a stable asset, providing a safeguard against global economic shocks, and balances India’s reserves portfolio.
Gold as a Hedge against Inflation
- Preserving Wealth amid Inflation:Gold is traditionally viewed as a hedge against inflation, maintaining or appreciating in value when other currencies weaken. By increasing its gold reserves, India positions itself to better withstand the adverse effects of inflation and ensure long-term financial stability.
Conclusion
The repatriation of gold by the RBI reflects a strategic move to bolster India's economic strength and diversify its financial assets. The decision to bring gold back to India not only signifies an improvement in India's economic fundamentals but also aligns with global trends of central banks increasing their gold reserves to ensure long-term stability and reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar.
The right to die with dignity

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's draft guidelines (October 2024) aim to implement the Supreme Court's 2018 and 2023 orders on the right to die with dignity.
Legal Context: Supreme Court Rulings and Constitutional Rights
- Right to Refuse Treatment:
- Common Law & Article 21: The right to refuse medical treatment is grounded in common law and is now recognized as a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, following the 2018 Supreme Court judgment in Common Cause v. Union of India.
- Supreme Court Rulings: The court's rulings in 2018 and 2023 affirmed that individuals have the constitutional right to refuse life-sustaining treatment and to die with dignity.
Withholding and Withdrawing Life-Sustaining Treatment
- Definition and Meaning:
- What Is Life-Sustaining Treatment? Life-sustaining treatments, such as ventilators and feeding tubes, artificially replace vital bodily functions to sustain life.
- Withholding/Withdrawal: This refers to discontinuing these treatments when they no longer improve the patient's condition or merely prolong suffering.
- When Is It Done?
- End-of-Life Care: Withholding or withdrawing treatment is considered when further medical intervention is futile and would only artificially prolong the dying process.
- Focus on Comfort: After withdrawing life-sustaining measures, the focus shifts to palliative care to alleviate pain and suffering.
Understanding Euthanasia and Misconceptions
- What Is Euthanasia?
- Definition: Euthanasia refers to the intentional ending of a terminally ill patient’s life by medical professionals to relieve suffering.
- Passive Euthanasia Misconception: In India, the term "passive euthanasia" is often mistakenly used to describe withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment, but this does not involve the active killing of the patient.
- Legal Framework: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) clarified in 2018 that "passive euthanasia" is not a legally accepted practice in the country.
The Role of Doctors: Ethical Dilemmas and Shared Decision-Making
- Is Withdrawing Treatment "Giving Up" on the Patient?
- Not Abandonment: Withdrawing life-sustaining treatment is not about abandoning the patient but recognizing when further interventions would cause unnecessary suffering.
- Palliative Care: The patient’s comfort and dignity are prioritized through palliative care, which focuses on pain management and emotional support for both the patient and family.
- Doctors' Ethical Responsibility:
- Shared Decision-Making: The process encourages a collaborative approach between doctors and the patient’s family or surrogate decision-makers. This joint decision-making ensures that the wishes of the patient are respected and relieves the doctor from bearing sole responsibility for life-and-death decisions.
Living Wills and Advance Medical Directives
- What Is a Living Will?
- Definition: A living will is a legal document where a person outlines their medical preferences in the event they lose decision-making capacity.
- Eligibility and Process: Individuals aged 18 or older, who are capable of making decisions, can draft a living will, naming at least two trusted surrogate decision-makers.
- Legal Requirements: The document must be signed in the presence of an executor, two witnesses, and notarized to be legally binding.
- 2023 Supreme Court Guidelines: The Court simplified the procedure for making living wills to ensure that the right to die with dignity is upheld.
Medical Procedure for Withholding or Withdrawing Treatment
- Supreme Court Guidelines
- The Supreme Court laid out a clear procedure for withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment, emphasizing patient autonomy, expert assessments, and family consent.
- Primary and Secondary Medical Boards:
- Primary Medical Board: The treating hospital sets up a Primary Medical Board, consisting of the treating doctor and two subject-matter experts, to assess the patient's condition and determine if life-sustaining treatment is appropriate.
- Secondary Medical Board: A Secondary Medical Board, comprising independent experts, reviews the Primary Board's decision for added oversight.
- Consent from Family/Surrogate Decision-Makers:
- The patient’s wishes, as outlined in an advance directive or by a surrogate, must be respected, and their consent is essential for proceeding with treatment withdrawal.
- Judicial Oversight:
- Once the decision to withdraw treatment is made, the hospital is required to notify the local judicial magistrate, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Conclusion: Legal and Ethical Clarity in End-of-Life Care
- Shared Decision-Making: The process ensures that medical teams, families, and surrogate decision-makers collaborate, preventing any medical professional from facing moral or legal dilemmas alone.
- Protection of Autonomy: These frameworks and guidelines uphold patient autonomy, offering a legal and ethical pathway for terminally ill patients to exercise their right to die with dignity.
Biodiversity COP16

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), while historically overshadowed by climate change discussions, is now gaining increasing attention due to the growing recognition of the global biodiversity crisis. This evolving prominence highlights the need for urgent action to preserve ecosystems and halt biodiversity loss, which is intimately linked with the climate crisis.
Overview of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Origins and Objectives:
- The CBD emerged from the 1992 Rio Earth Summit, alongside the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Main Goals:
- Protect global biodiversity.
- Restore ecosystems.
- Ensure equitable distribution of the benefits derived from biological resources.
- COP16 and the Kunming-Montreal Framework:
- The 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) marks the first meeting following the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework adopted at COP15 in 2022.
- The framework sets out four key goals and 23 targets to be achieved by 2030, including:
- Protect 30% of global lands and oceans by 2030.
- Restore 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030.
The Growing Convergence Between Climate Change and Biodiversity
- Interlinkages Between Climate Change and Biodiversity:
- Mutual Impact:
- Climate change accelerates biodiversity loss by altering habitats and threatening species.
- In turn, ecosystem degradation contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases (GHGs) from deforestation and soil degradation.
- Shared Drivers:
- Both crises are driven by unsustainable human activities, including over-exploitation of natural resources, deforestation, over-consumption, and pollution.
- Increasing Synergy:
- There is a growing realization of the need for integrated solutions that address both climate change and biodiversity loss simultaneously.
- Momentum for 30 x 30 Targets
- The 30 x 30 Commitment:
- The 30 x 30 targets are central to the Kunming-Montreal Framework, which includes:
- Conservation of 30% of the world's lands and oceans.
- Restoration of 30% of degraded ecosystems.
- These targets aim to ensure the preservation of biodiversity-rich areas and the restoration of degraded ecosystems globally by 2030.
- National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs):
- Countries are required to develop and submit their NBSAPs (akin to Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for climate change).
- As of now, only 32 countries have submitted their NBSAPs, with more expected during COP16.
- High Seas Treaty:
- A crucial agreement for achieving 30 x 30 targets is the High Seas Treaty (also called Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdictions (BBNJ)), which focuses on:
- Establishing protected marine areas in biodiversity-rich regions beyond national jurisdictions.
- Ensuring regulation of human activities in these areas.
Access and Benefit Sharing: The Case of Genetic Resources
- Genetic Resources and Their Exploitation:
- The oceans, along with terrestrial ecosystems, harbor a wide variety of genetic resources that can be exploited for medical, commercial, and scientific purposes.
- Advances in biotechnology and digital sequencing of genetic material have raised issues about the equitable sharing of benefits from these resources.
- Nagoya Protocol and Benefit Sharing:
- The Nagoya Protocol (2010) set out guidelines for the access and fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources.
- At COP16, discussions will center on how genetic sequences (used in products such as medicines, crops, etc.) can be used fairly, ensuring that indigenous communities, who may be the original custodians of these resources, benefit equitably.
Finance Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Financial Targets:
- One of the key goals of the Kunming-Montreal Framework is to mobilize $200 billion per year by 2030 for biodiversity conservation globally.
- Developed countries are expected to contribute $20 billion annually to developing nations, increasing to $30 billion by 2030.
- Phasing Out Harmful Subsidies:
- Countries are urged to eliminate perverse incentives that harm biodiversity, such as subsidies for:
- Over-fishing.
- Deforestation.
- Fossil fuel consumption.
- The goal is to repurpose such incentives to support sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
- New Financial Mechanisms:
- COP16 discussions will also focus on creating innovative financial mechanisms, such as:
- A biodiversity fund.
- Biodiversity credits, similar to carbon credits, which would allow countries or organizations to offset their biodiversity loss by investing in conservation projects elsewhere.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Implementation of 30 x 30 Targets:
- The main challenge lies in translating ambitious goals into actionable plans at the national and local levels. Countries must not only submit action plans but also implement and monitor them effectively.
- Increased Global Cooperation:
- Addressing biodiversity loss requires collaboration between countries, industries, and local communities to ensure that efforts are comprehensive and inclusive.
- Public Awareness and Engagement:
- It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation and the urgent need for collective action to mitigate the combined threats of biodiversity loss and climate change.
Conclusion: The Need for Urgent Action
The discussions at COP16 signal an important shift in how the world addresses biodiversity and its links to climate change. As countries continue to recognize the interconnectedness of these two crises, the outcome of the CBD negotiations could play a pivotal role in shaping global environmental policy. However, meeting the ambitious goals set forth by the Kunming-Montreal Framework requires strong political will, adequate financing, and effective global cooperation.
