Green Climate Fund

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
- The Green Climate Fund (GCF) has approved over USD 120 million to support climate adaptation initiatives in Ghana, the Maldives, and Mauritania, with technical development by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The projects aim to build climate resilience among vulnerable populations through nature-based solutions, climate-resilient agriculture, early warning systems, and water security enhancements.
- These initiatives are critical in delivering adaptation finance to regions like Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and the Sahel, addressing some of the most urgent climate vulnerabilities and are expected to benefit over 3.5 million people.
Project Highlights by Country:
Ghana: Agroecological Resilience in Northern Regions
- Total funding: USD 70 million (USD 63 million GCF grant).
- Objective: Strengthen climate resilience in eight districts across North East, Upper East, and Upper West Ghana.
- Key Interventions:
- Improve access to climate data and early warnings.
- Enable dry-season farming via water storage.
- Restore 28,000 hectares of degraded land to improve water retention and soil health.
- Impact:
- Direct benefits for 619,000 people.
- Early warning systems to reach 2.9 million.
- Improved food security for 120,000 individuals.
- Implementing agencies: Ghana EPA and Ghana Meteorological Agency.
Maldives: Early Warning and Risk Reduction in a SIDS
- Total funding: USD 25 million.
- Project Name: Toward Risk-Aware and Climate-Resilient Communities (TRACT).
- Focus: Expand multi-hazard early warning systems and build national capacity under the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative.
- Risks Addressed: Rising sea levels, storm surges, heatwaves, and coastal erosion threatening agriculture, fisheries, and tourism.
- Impact:
- Coverage for over 500,000 people.
- Special emphasis on remote and marginalized communities, including women and children.
Mauritania: Ecosystem Restoration in the Sahel
- Total funding: USD 33 million (USD 30 million GCF grant).
- Objective: Address desertification, drought, and water scarcity across four vulnerable regions.
- Key Activities:
- Build green-grey infrastructure to stabilize sand dunes.
- Improve water access for farming and land rehabilitation.
- Promote climate-resilient agriculture to reduce food imports.
- Impact:
- 85,000 people to benefit directly; 145,000 indirectly.
- 2,100 hectares of land to be protected.
- Supports the Great Green Wall Initiative—Africa’s flagship response to desertification.
Institutional Roles and Significance:
- The UNEP, as a global leader in environmental governance, has played a key role in contextualizing science-based, locally led climate solutions.
- The GCF, under the Paris Agreement framework, remains the largest international climate fund, supporting countries in implementing their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Chautal

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
During the recent state visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Trinidad and Tobago, a notable cultural highlight was the performance of the traditional Bhojpuri Chautal, reflecting the deep-rooted Indian heritage in the Caribbean diaspora.
Understanding Chautal
- Chautal (also spelled Chartaal or Chowtaal) is a 12-beat rhythmic cycle (taal) integral to Hindustani classical music.
- It is primarily used to accompany vocal forms such as Dhrupad and Dhamar, as well as instrumental music.
- The term “Chautal” can be interpreted as "four claps", hinting at its vibhag (sectional) structure.
Structural Interpretations:
- One tradition describes it as comprising four vibhags of 4, 4, 2, and 2 beats (matras), respectively.
- An alternative view equates its structure with Ektal, dividing the cycle into six segments of 2 beats each.
Musical Characteristics and Cultural Context
- Chautal is closely associated with the pakhawaj, a barrel-shaped percussion instrument, giving it a powerful and resonant character.
- Unlike the subtle and intricate rhythms of the tabla, Chautal emphasizes strength and gravity in performance.
- Beyond classical settings, Chautal holds cultural significance in Bhojpuri folk traditions, especially during festivals and religious gatherings.
Significance in the Indian Diaspora
The inclusion of Chautal in Trinidad and Tobago’s ceremonial welcome reflects the preservation and celebration of Indian classical and folk arts among overseas Indian communities, particularly those with Bhojpuri ancestry.
Gini Index
- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
According to the World Bank’s Spring 2025 Poverty and Equity Brief, India has emerged as the fourth most equal society globally, with a Gini Index of 25.5—outperforming all G7 and G20 nations. Only the Slovak Republic (24.1), Slovenia (24.3), and Belarus (24.4) rank ahead.
This achievement marks a significant improvement from India’s Gini score of 28.8 in 2011 to 25.5 in 2022, reflecting a steady narrowing of income inequality and growing social equity.
Key Highlights:
Gini Index Comparison (2022-2023):
|
Country |
Gini Index |
|
Slovak Republic |
24.1 |
|
Slovenia |
24.3 |
|
Belarus |
24.4 |
|
India |
25.5 |
|
China |
35.7 |
|
United States |
41.8 |
|
Germany (G7) |
~31.4 |
|
United Kingdom (G7) |
~34.4 |
|
France (G7) |
~32.4 |
|
Japan (G7) |
~32.9 |
Poverty Reduction Achievements:
- 171 million people lifted out of extreme poverty (2011–2023).
- Population living under $2.15/day fell from 16.2% (2011–12) to 2.3% (2022–23).
- Under revised poverty line of $3.00/day, poverty fell to 5.3% in 2022–23.
Drivers of Income Equality:
a) Financial Inclusion:
- Jan Dhan Yojana: Over 55.69 crore bank accounts opened (as of June 2025).
- Enabled Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT), reducing leakages and ensuring targeted welfare.
b) Digital Infrastructure:
- Aadhaar: Over 142 crore issued (as of July 2025), enabling real-time, identity-based service delivery.
- DBT savings: Over ?3.48 lakh crore by March 2023.
c) Universal Healthcare Access:
- Ayushman Bharat: Over 41.34 crore health cards issued.
- Covers ?5 lakh per family/year; now extended to all citizens aged 70+ under Ayushman Vay Vandana.
- Over 32,000 empanelled hospitals ensure access to treatment.
d) Empowerment of Marginalized Communities:
- Stand-Up India: Loans worth ?62,807 crore disbursed to SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Nearly 30 lakh artisans registered for credit and marketing support.
Significance for India and the World:
India’s low Gini score demonstrates that economic growth and social equity can be pursued together. The country’s targeted welfare architecture, digital governance tools, and inclusive schemes have created a replicable model for other developing nations.
As global inequality widens, India’s success offers a template for countries seeking to integrate economic reforms with social protection mechanisms to foster inclusive development.
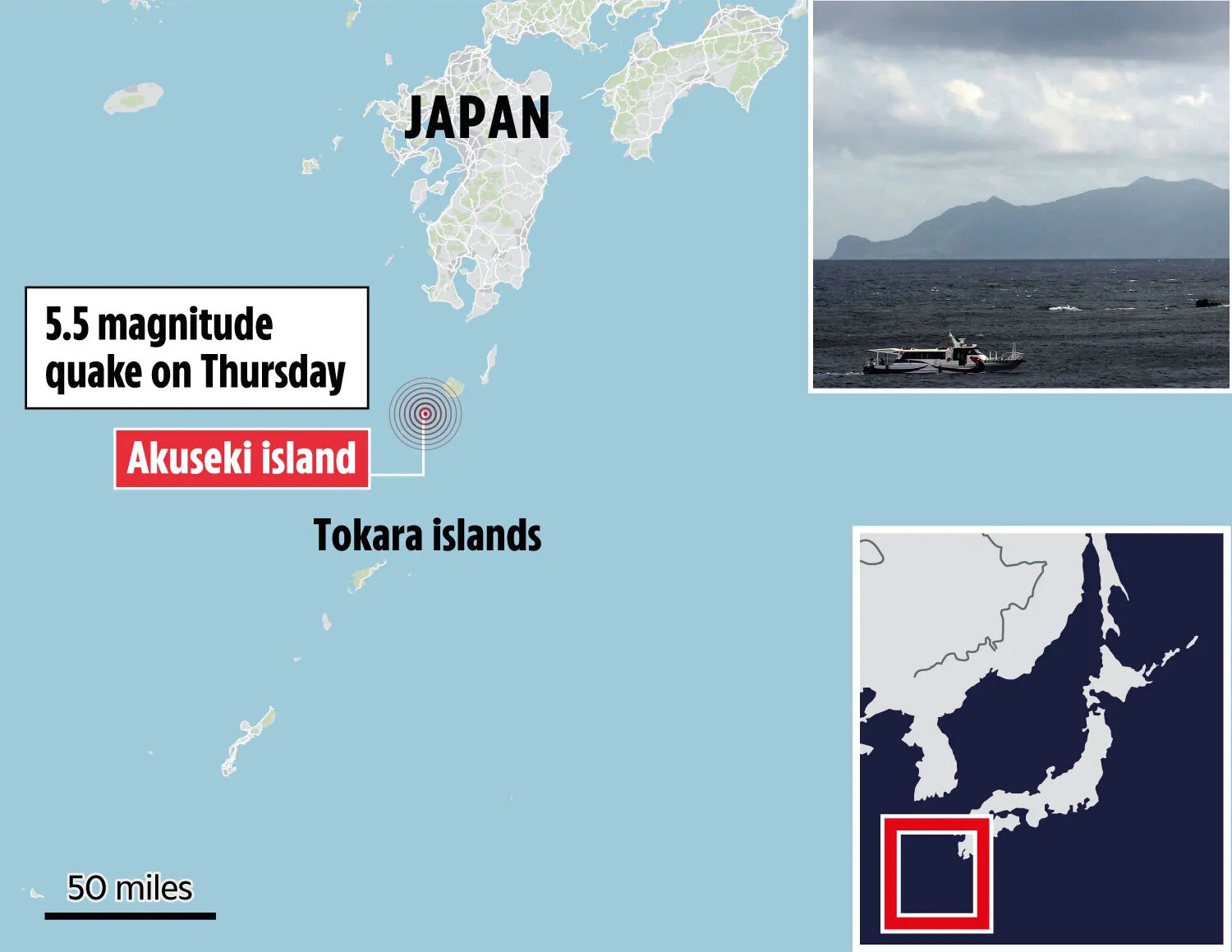
Tokara Islands
- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
In an unusual seismic episode, over 1,000 earthquakes have struck the Tokara Islands in southern Japan since June 1, 2025, triggering panic, evacuation orders, and heightened concerns about a potential larger earthquake. The persistent tremors—several of which registered magnitudes of 5.5 or higher—have had a significant psychological and logistical impact on the island's residents.
About Tokara Islands:
- Located south of Kyushu and north of the Amami Islands, the Tokara archipelago (also called Toshima Islands) consists of seven inhabited and five uninhabited islands.
- The inhabited islands include Kuchinoshima, Nakanoshima, Suwanosejima, Tairajima, Akusekijima, Kodakarajima, and Takarajima.
- Administered by Toshima Village, it is Japan’s longest village, stretching over 160 km.
- Nakanoshima is the largest and most populated island; it is dominated by Mount Otake (979 m).
- The islands lie in a subtropical-temperate climate zone, receiving around 2,700 mm of rainfall annually.
- Geologically, they are situated in one of the most earthquake-prone zones globally.
Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR)

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently carried out a 7-day Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) auction worth ?1 lakh crore. This measure was taken to manage the surplus liquidity in the banking system, which had surged to approximately ?3.75 lakh crore.
What is VRRR?
The Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) is a liquidity management tool employed by the RBI to absorb excess funds from commercial banks for a specified period. Unlike the fixed reverse repo rate, the VRRR rate is determined through an auction mechanism, allowing market forces to decide the interest rate.
Key Characteristics:
- Auction-Based Interest Rate: Interest is not fixed but discovered through competitive bidding.
- Time-Bound Operation: Typically conducted for durations like 7, 14, or 28 days.
- Liquidity Management Tool: Helps the RBI withdraw excess liquidity from the financial system.
- Repo Rate Ceiling: The interest rate in VRRR operations cannot exceed the current repo rate.
- Flexible Tenor: RBI may modify the duration of VRRR auctions based on prevailing liquidity conditions.
Objective of VRRR
- To mop up surplus liquidity from the banking system.
- To help regulate short-term interest rates and support effective transmission of monetary policy.
- To foster a market-driven interest rate environment in the short-term interbank market.
How VRRR Functions
- Auction Announcement: RBI declares the amount and duration of the VRRR operation.
- Bid Submission: Banks submit bids with the amount and the interest rate at which they are willing to park funds with RBI.
- Rate Determination: RBI accepts bids at or above the cut-off rate, determined by the auction.
- Interest Earnings: Banks earn interest at the accepted rate over the auction tenure.
Implications of VRRR Operations
- On the Money Market: Tightens liquidity, leading to an uptick in short-term rates such as the call money rate and TREPS.
- On the Bond Market: May cause short-term government and corporate bond yields to rise, increasing borrowing costs.
- On Banks:
- Offers an avenue to earn returns on idle funds, improving short-term profitability.
- Temporarily locks up funds, which may reduce immediate availability for lending or investment.
This mechanism is a vital part of the RBI's toolkit to maintain financial stability and ensure efficient transmission of monetary policy.
