e-Rakt Kosh

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is set to integrate India’s Rare Donor Registry with e-Rakt Kosh, a centralized national blood bank management platform under the National Health Mission (NHM). This move aims to improve access to rare blood types, enhance donor coordination, and save lives by ensuring timely availability of rare blood groups.
About the Integration
- e-Rakt Kosh: A digital platform developed under NHM for real-time information on blood availability, donation camps, and blood bank locations.
- Rare Donor Registry of India (RDRI): Developed by the ICMR–National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) with four partner institutes. Maintains a database of 4,000 carefully screened rare blood donors, tested for over 300 rare blood markers.
- Objective: To provide a centralized, accessible system for patients needing rare blood and to assist blood banks in managing inventory and donors efficiently.
Key Features and Benefits
- Life-saving Access: Enables patients and hospitals to locate rare blood types like Bombay blood group, Rh-null, and P-null efficiently.
- Safe Transfusions: Helps match blood for patients with multiple antigen deficiencies, common in disorders like thalassemia and sickle cell disease, thus reducing transfusion complications.
- Technological Advancements:
- Use of Multiplex PCR-based DNA testing for rapid identification of rare blood groups.
- Development of a customized blood screening kit tailored for Indian patients.
- Donor Engagement: Aims to ensure a steady, motivated pool of rare blood donors who remain connected to blood banks.
ICMR’s Parallel Work on Hemoglobinopathies and Rare Diseases
- Point-of-Care (POC) Tests Developed For:
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Hemophilia A
- Von Willebrand Disease
- Impact of Innovation:
- Sickle Cell Test Kits cost reduced from ?350 to under ?50 per test through Health Technology Assessment (HTA) led by DHR, ICMR–CRMCH, and NIIH.
- Estimated savings: ?1,857 crore for the government.
- New rapid testing device enables diagnosis even at PHC level.
- International Interest: World Federation for Hemophilia has shown interest in procuring India-developed diagnostic kits for global deployment.
- Commercialization: Technology transferred to Bhat Biotech, which launched the product under the brand Bio-Scan in August 2023.
Significance
- Enhances India’s healthcare infrastructure and emergency response for rare blood groups.
- Aligns with the goals of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and Atmanirbhar Bharat in the field of indigenous diagnostics.
- Showcases India’s growing biotech innovation ecosystem with both national and international relevance.
11th International Day of Yoga (IDY) – 2025

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The 11th International Day of Yoga (IDY) will be observed on June 21, 2025, under the theme “Yoga for One Earth, One Health”. The theme emphasizes the connection between individual well-being and planetary health, aligned with India’s G20 vision of “One Earth, One Family, One Future.”
About the International Day of Yoga
- What it is: An annual global observance promoting yoga as a holistic health practice for physical, mental, and emotional well-being in harmony with nature.
- Adoption: Declared by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) through Resolution 69/131 on December 11, 2014, following India's proposal.
- First Observed: June 21, 2015
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India
Theme for 2025: “Yoga for One Earth, One Health”
- Focuses on the interdependence between human health and environmental sustainability.
- Reinforces yoga’s role in achieving sustainable lifestyles and climate consciousness.
Key Objectives
- Promote mind-body balance, emotional stability, and overall well-being through yoga.
- Raise global awareness on yoga’s health and ecological benefits.
- Encourage adoption of yoga as part of daily life for sustainable living.
- Strengthen India’s soft power and global leadership in wellness traditions.
Highlights and Participation
- Global Reach: Adopted by 175 UN Member States. Global participation has grown from 9 crore in 2018 to 24.53 crore in 2024.
- Mass Events: Celebrated across countries with support from state governments, Indian embassies, UN bodies, and civil society.
- Inclusive Message: Yoga Day’s logo and themes emphasize unity, well-being, and coexistence with nature.
Significance
- Public Health Tool: Promotes a low-cost, accessible, preventive healthcare practice.
- Sustainability Alignment: Advocates for climate-sensitive living and ecological harmony.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Enhances India’s global stature as the birthplace of yoga and a leader in wellness diplomacy.
- Soft Power Projection: Reflects India’s cultural values and promotes its influence through global well-being initiatives.
QS World University Rankings 2026
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
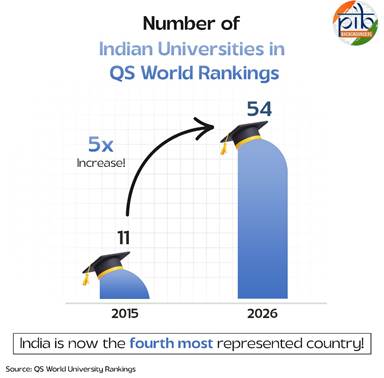
India has recorded its highest representation to date in the QS World University Rankings 2026, with 54 institutions featured—up from 11 in 2015. This marks a five-fold increase in a decade, making India the fourth most represented country, after the US, UK, and China.
Key Highlights
- Total Indian Institutions Ranked (2026): 54
- New Entrants from India: 8
- Top-performing Indian Institution: IIT Delhi (Rank 123)
- Fastest Rising Indian Institution: IIT Madras, up 47 places (from 227 in 2025 to 180 in 2026)
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) Featured: 12
- Debut Institutions in 2026:
- IIT Gandhinagar
- Lovely Professional University (LPU)
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT)
- Ashoka University
- Galgotias University
- Shiv Nadar University
- CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bengaluru
- Manav Rachna International Institute of Research and Studies (MRIIRS)
Significant Trends and Insights
- Global Standing:
- India now ranks 4th globally in terms of number of institutions in the QS Rankings.
- Only the US (192), UK (90), and China (72) rank higher.
- Improvements and Recognition:
- 48% of India’s ranked institutions have improved their positions over last year.
- 6 institutions are in the global top 250.
- 5 Indian universities are among the top 100 globally for Employer Reputation, showing high industry trust.
- 8 institutions rank in the top 100 for Citations per Faculty, with an average score of 43.7—higher than the UK, US, and Germany.
- Diverse Representation:
- Includes central universities, deemed-to-be universities, technical institutions, and private universities, reflecting a balanced and diversified higher education landscape.
QS Ranking Methodology: Key Indicators
Performance Lens Weightage Indicators Weightage
Research & Discovery 50% Academic Reputation 30%
Citations per Faculty 20%
Employability & Outcomes 20% Employer Reputation 15%
Employment Outcomes 5%
Global Engagement 15% International Faculty Ratio 5%
International Research Network 5%
International Student Ratio 5%
Learning Experience 10% Faculty-Student Ratio 10%
Sustainability 5% Sustainability 5%
- New Indicator in 2026: International Student Diversity (tracks number and diversity of international students; non-weighted this cycle)
Significance for India
- The consistent rise highlights the impact of reforms under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, with greater emphasis on research, global collaboration, academic excellence, and employer integration.
- India’s progress makes it the fastest-rising G20 nation in QS rankings.
- Reflects increasing global trust and recognition of India’s higher education system.
Revised Green India Mission (GIM)
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change released the revised roadmap for the National Mission for a Green India (GIM). The updated strategy focuses on restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing forest cover, and addressing climate impacts, especially in vulnerable landscapes like the Aravallis, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangroves.
About Green India Mission (GIM)
- Launched in: 2014
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Core Objectives:
- Increase forest/tree cover by 5 million hectares.
- Improve the quality of forest cover on another 5 million hectares.
- Restore degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Improve the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities.
Achievements So Far
- Afforestation Activities: 11.22 million hectares covered (2015–16 to 2020–21) through central and state schemes.
- Funding: ?624.71 crore released (2019–24) to 18 states; ?575.55 crore utilized.
- Target Areas: Selected based on ecological vulnerability, sequestration potential, and restoration needs.
Key Features of the Revised Roadmap
- Landscape-Specific Restoration:
- Prioritizes Aravalli ranges, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangrove ecosystems.
- Emphasizes regionally adapted best practices for ecosystem restoration.
- Integration with Aravalli Green Wall Project:
- Aims to combat desertification and sandstorm risks in northern India.
- Initial restoration planned across 8 lakh hectares in 29 districts of 4 states.
- Estimated cost: ?16,053 crore.
- Aims to develop a 5 km buffer zone covering 6.45 million hectares around the Aravallis.
- Western Ghats Focus:
- Tackling deforestation, illegal mining, and degradation.
- Measures include afforestation, groundwater recharge, and mining site restoration.
Combating Land Degradation and Climate Change
- Land Degradation (2018–19): Affected 97.85 million hectares (~1/3rd of India’s land), per ISRO data.
- India’s Climate Targets (2030):
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO? equivalent via forest/tree cover.
- Restore 26 million hectares of degraded land.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential (FSI Estimates):
- Restoration of open forests can sequester 1.89 billion tonnes of CO? over 15 million hectares.
- With intensified afforestation and aligned schemes, forest cover could reach 24.7 million hectares—achieving a carbon sink of 3.39 billion tonnes CO? equivalent by 2030.
Significance of the Revised Mission
- Aligns with India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Supports goals under UNCCD and UNFCCC.
- Helps mitigate climate change impacts by creating natural buffers and carbon sinks.
- Promotes ecological sustainability, biodiversity conservation, and community livelihood enhancement.
Bhashini

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Bhashini, the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM), to integrate AI-enabled multilingual tools into rural e-governance platforms.
About Bhashini
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Purpose: Acts as a digital public infrastructure for real-time, AI-powered translation across Indian languages.
Objective of the MoU
- To build an inclusive, multilingual e-governance ecosystem for Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- To bridge language barriers in rural governance and foster participatory democracy.
Key Features of the Initiative
- AI-Driven Language Translation: Offers real-time speech-to-text and text-to-text translation in major Indian languages.
- Platform Integration: Bhashini tools to be integrated with MoPR’s digital platforms like eGramSwaraj, ensuring multilingual access to rural governance services.
- Citizen-Centric Approach: Enables rural citizens to interact with digital governance platforms in their native language, enhancing accessibility and inclusion.
- Promotes Digital Inclusion: Supports rural digital literacy by making digital interfaces linguistically accessible.
- Enhances Transparency and Trust: Facilitates better information dissemination, increasing trust and engagement in local self-governance.
Significance
- Aligns with Digital India goals.
- Empowers Gram Panchayats by ensuring language is not a barrier to governance.
- Sets a precedent for AI-driven, citizen-centric governance reforms.
